EE 40. Midterm 3. November 14, 2002
|
|
|
- Owen Dawson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lab TA: Dan Bart Nir Konrad Yu Ching EE 40 Midterm 3 November 14, 2002 PLEASE WRITE YOUR NAME ON EACH ATTACHED PAGE PLEASE SHOW YOUR WORK TO RECEIVE PARTIAL CREDIT Problem 1: 10 Points Possible Problem 2: 20 Points Possible Problem 3: 10 Points Possible Problem 4: 20 Points Possible Problem 5: 20 Points Possible Problem 6: 20 Points Possible TOTAL: 100 Points Possible
2 Page 1 Problem 1: 10 Points Fill in the blanks to correctly complete the sentences. To improve conduction in silicon, atoms from other elements are incorporated into the lattice. The addition of Group III elements creates p - type material. For example, boron is a Group III element that might be added to the silicon. The addition of Group V elements creates n - type material. For example, phosphorus is a Group V element that might be added to the silicon. The Group III elements need one more electron in the outer shell to complete all four lattice bonds. This lack of an electron is called a hole. When the two types of material are joined together, electrons cross the junction between the two materials to complete lattice bonds where needed. The movement of free electrons from an area of greater concentration to lesser concentration, motivated by the need to complete lattice bonds, is called diffusion This creates a layer without free charge carriers, called the depletion layer. The movement of electrons creates positive charge in the atoms the electrons have left behind, and negative charge in the atoms which the electrons have joined. This creates a potential difference across the junction; the n - type material is at higher potential. This causes electrons to move across the junction towards the higher electric potential. This movement, due to attraction by positive potential, is called drift.
3 Page 2 Problem 2: 20 Points Determine the logical operation performed by the circuit below (copied 4 times for convenience):
4 Page 3 Problem 3: 10 Points Consider the following circuit, with the input voltage just below V DD V T. Here, the NMOS threshold voltage is V T and the PMOS threshold voltage is V T. V T is positive, and much smaller than V DD. Assume that the transistors have matched I D /V DS characteristics. Determine the most likely mode of operation for each transistor. V GS(P) = V DD V T ε V DD = -V T - ε V GS(P) is near threshold, so transistor is barely turned on => shallow curve => small I D V GS(N) = V DD V T ε V GS(N) is well above threshold, so transistor is fully turned on => steep curve small I D (from PMOS) and steep curve => V DS(N) small => NMOS in triode V DS(N) small => V DS(P) not small => PMOS in saturation
5 Page 4 Problem 4: 20 Points Consider the following circuit. Find V OUT when V IN is 3.7 V. V T(N) = 1 V λ = 0 I DSAT(N) = 10-3 (V GS(N) -V T(N) ) 2 A V T(P) = -1 V λ = 0 I DSAT(P) = (V GS(P) -V T(P) ) 2 A I D(P) + I D(N) = 0 V DS(N) V DS(P) = 5 V Guess that PMOS is in saturation and NMOS is in triode (basically situation from Problem 3). I D(P) = I DSAT(P) (1+λV DS(P) ) = (V GS(P) -V T(P) ) 2 = ( ) 2 = -9 x 10-5 A I D(N) = 2 I DSAT(P) (V GS(N) -V T(N) -V DS(N) /2)V DS(N) / (V GS(N) V T(N) ) 2 = 2 x 10-3 (3.7 1 V DS(N) /2)V DS(N) = V DS(N) x 10-3 V DS(N) = -I D(P) = 9 x 10-5 Roots of V DS(N) x 10-3 V DS(N) - 9 x 10-5 : V DS(N) = V and V V DS(N) = V impossible, so V DS(N) = V = V OUT V DS(N) = V agrees with triode mode & V DS(P) = = V agrees with saturation
6 Page 5 Problem 5: 20 Points Consider the following circuit. Find V OUT when V IN is 3.7 V. V T(N) = 1 V λ = 0 I DSAT(N) = 10-3 (V GS(N) -V T(N) ) 2 A V T(P) = -1 V λ = 0 I DSAT(P) = (V GS(P) -V T(P) ) 2 A I D(P) + I D(N) + V DS(N) /1000 = 0 V DS(N) V DS(P) = 5 V Guess that PMOS is in saturation and NMOS is in triode (keep guess from Problem 4). I D(P) = I DSAT(P) (1+λV DS(P) ) = (V GS(P) -V T(P) ) 2 = ( ) 2 = -9 x 10-5 A I D(N) = 2 I DSAT(P) (V GS(N) -V T(N) -V DS(N) /2)V DS(N) / (V GS(N) V T(N) ) 2 = 2 x 10-3 (3.7 1 V DS(N) /2)V DS(N) = V DS(N) x 10-3 V DS(N) = -I D(P) -V DS(N) /1000 = 9 x V DS(N) Roots of V DS(N) x 10-3 V DS(N) - 9 x 10-5 : V DS(N) = V and V V DS(N) = V impossible, so V DS(N) = V = V OUT V DS(N) = V agrees with triode mode & V DS(P) = = V agrees with saturation
7 Page 6 Problem 6: 20 Points Sketch V OUT (t) for the diode circuit a) using the ideal model b) using the large-signal model c) using the small-signal model. Provide enough detail to completely indicate the effect created by the circuit. Ideal model: neither diode can accept positive forward voltage Vin Vout V t Large-signal model: each diode can accept any forward voltage up to 0.7 V, acting like open circuit. Above 0.7, a diode conducts current and resistor takes rest of input voltage Vin Vout V t
8 Page 7 Problem 6 Workspace Small signal model: each diode acts as open circuit for forward voltage up to 0.6 V. Above 0.6, a diode conducts current through the 20 Ω resistor and its own 20 Ω resistance (part of its model). The difference between the input and 0.6 V is distributed across the 20 Ω resistors; thus the diode gets 0.6 V plus half the difference between 0.6 and the input voltage Vin Vout V t
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527 VLSI Design I CMOS Inverter. CMOS Inverter: A First Look
 CPE/EE 427, CPE 527 VLSI Design I CMOS Inverter Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alabama in Huntsville Aleksandar Milenkovic CMOS Inverter: A First Look C L 9/11/26 VLSI
CPE/EE 427, CPE 527 VLSI Design I CMOS Inverter Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Alabama in Huntsville Aleksandar Milenkovic CMOS Inverter: A First Look C L 9/11/26 VLSI
Learning Outcomes. Spiral 2-6. Current, Voltage, & Resistors DIODES
 26.1 26.2 Learning Outcomes Spiral 26 Semiconductor Material MOS Theory I underst why a diode conducts current under forward bias but does not under reverse bias I underst the three modes of operation
26.1 26.2 Learning Outcomes Spiral 26 Semiconductor Material MOS Theory I underst why a diode conducts current under forward bias but does not under reverse bias I underst the three modes of operation
Session 10: Solid State Physics MOSFET
 Session 10: Solid State Physics MOSFET 1 Outline A B C D E F G H I J 2 MOSCap MOSFET Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor: Al (metal) SiO2 (oxide) High k ~0.1 ~5 A SiO2 A n+ n+ p-type Si (bulk)
Session 10: Solid State Physics MOSFET 1 Outline A B C D E F G H I J 2 MOSCap MOSFET Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor: Al (metal) SiO2 (oxide) High k ~0.1 ~5 A SiO2 A n+ n+ p-type Si (bulk)
Lecture 13 - Digital Circuits (II) MOS Inverter Circuits. October 25, 2005
 6.12 - Microelectronic Devices and Circuits - Fall 25 Lecture 13-1 Lecture 13 - Digital Circuits (II) MOS Inverter Circuits October 25, 25 Contents: 1. NMOS inverter with resistor pull-up (cont.) 2. NMOS
6.12 - Microelectronic Devices and Circuits - Fall 25 Lecture 13-1 Lecture 13 - Digital Circuits (II) MOS Inverter Circuits October 25, 25 Contents: 1. NMOS inverter with resistor pull-up (cont.) 2. NMOS
EE70 - Intro. Electronics
 EE70 - Intro. Electronics Course website: ~/classes/ee70/fall05 Today s class agenda (November 28, 2005) review Serial/parallel resonant circuits Diode Field Effect Transistor (FET) f 0 = Qs = Qs = 1 2π
EE70 - Intro. Electronics Course website: ~/classes/ee70/fall05 Today s class agenda (November 28, 2005) review Serial/parallel resonant circuits Diode Field Effect Transistor (FET) f 0 = Qs = Qs = 1 2π
Georgia Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Midterm Exam
 Georgia Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Midterm Exam ECE-3400 Fall 2013 Tue, September 24, 2013 Duration: 80min First name Solutions Last name Solutions ID number
Georgia Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Midterm Exam ECE-3400 Fall 2013 Tue, September 24, 2013 Duration: 80min First name Solutions Last name Solutions ID number
EEC 118 Lecture #11: CMOS Design Guidelines Alternative Static Logic Families
 EEC 118 Lecture #11: CMOS Design Guidelines Alternative Static Logic Families Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation Announcements Homework 5 this week Lab
EEC 118 Lecture #11: CMOS Design Guidelines Alternative Static Logic Families Rajeevan Amirtharajah University of California, Davis Jeff Parkhurst Intel Corporation Announcements Homework 5 this week Lab
Lecture 16. Complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) CMOS 1-1
 Lecture 16 Complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) CMOS 1-1 Outline Complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) Inverting circuit Properties Operating points Propagation delay Power dissipation
Lecture 16 Complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) CMOS 1-1 Outline Complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) Inverting circuit Properties Operating points Propagation delay Power dissipation
Electronics I. Midterm #1
 The University of Toledo s6ms_elct7.fm - Electronics I Midterm # Problems Points. 4 2. 5 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo s6ms_elct7.fm - 2 Problem 4 points For full credit,
The University of Toledo s6ms_elct7.fm - Electronics I Midterm # Problems Points. 4 2. 5 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo s6ms_elct7.fm - 2 Problem 4 points For full credit,
ELEC 350L Electronics I Laboratory Fall 2012
 ELEC 350L Electronics I Laboratory Fall 2012 Lab #9: NMOS and CMOS Inverter Circuits Introduction The inverter, or NOT gate, is the fundamental building block of most digital devices. The circuits used
ELEC 350L Electronics I Laboratory Fall 2012 Lab #9: NMOS and CMOS Inverter Circuits Introduction The inverter, or NOT gate, is the fundamental building block of most digital devices. The circuits used
Basic Fabrication Steps
 Basic Fabrication Steps and Layout Somayyeh Koohi Department of Computer Engineering Adapted with modifications from lecture notes prepared by author Outline Fabrication steps Transistor structures Transistor
Basic Fabrication Steps and Layout Somayyeh Koohi Department of Computer Engineering Adapted with modifications from lecture notes prepared by author Outline Fabrication steps Transistor structures Transistor
Microelectronics Circuit Analysis and Design. MOS Capacitor Under Bias: Electric Field and Charge. Basic Structure of MOS Capacitor 9/25/2013
 Microelectronics Circuit Analysis and Design Donald A. Neamen Chapter 3 The Field Effect Transistor In this chapter, we will: Study and understand the operation and characteristics of the various types
Microelectronics Circuit Analysis and Design Donald A. Neamen Chapter 3 The Field Effect Transistor In this chapter, we will: Study and understand the operation and characteristics of the various types
EECE 481. MOS Basics Lecture 2
 EECE 481 MOS Basics Lecture 2 Reza Molavi Dept. of ECE University of British Columbia reza@ece.ubc.ca Slides Courtesy : Dr. Res Saleh (UBC), Dr. D. Sengupta (AMD), Dr. B. Razavi (UCLA) 1 PN Junction and
EECE 481 MOS Basics Lecture 2 Reza Molavi Dept. of ECE University of British Columbia reza@ece.ubc.ca Slides Courtesy : Dr. Res Saleh (UBC), Dr. D. Sengupta (AMD), Dr. B. Razavi (UCLA) 1 PN Junction and
Ch5 Diodes and Diodes Circuits
 Circuits and Analog Electronics Ch5 Diodes and Diodes Circuits 5.1 The Physical Principles of Semiconductor 5.2 Diodes 5.3 Diode Circuits 5.4 Zener Diode References: Floyd-Ch2; Gao-Ch6; 5.1 The Physical
Circuits and Analog Electronics Ch5 Diodes and Diodes Circuits 5.1 The Physical Principles of Semiconductor 5.2 Diodes 5.3 Diode Circuits 5.4 Zener Diode References: Floyd-Ch2; Gao-Ch6; 5.1 The Physical
ELEC 2210 EXPERIMENT 12 NMOS Logic
 ELEC 2210 EXPERIMENT 12 NMOS Logic Objectives: The experiments in this laboratory exercise will provide an introduction to NMOS logic. You will use the Bit Bucket breadboarding system to build and test
ELEC 2210 EXPERIMENT 12 NMOS Logic Objectives: The experiments in this laboratory exercise will provide an introduction to NMOS logic. You will use the Bit Bucket breadboarding system to build and test
Electronics I. Midterm #1
 EECS:3400 Electronics I s5ms_elct7.fm - Section Electronics I Midterm # Problems Points. 4 2. 5 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no EECS:3400 Electronics I s5ms_elct7.fm - 2 Problem 4 points For full
EECS:3400 Electronics I s5ms_elct7.fm - Section Electronics I Midterm # Problems Points. 4 2. 5 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no EECS:3400 Electronics I s5ms_elct7.fm - 2 Problem 4 points For full
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences.
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Discussion #9 EE 05 Spring 2008 Prof. u MOSFETs The standard MOSFET structure is shown
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA AT BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Discussion #9 EE 05 Spring 2008 Prof. u MOSFETs The standard MOSFET structure is shown
The CMOS Inverter. Lecture 3a Static properties (VTC and noise margins)
 The CMOS Inverter Lecture 3a Static properties (VTC and noise margins) Why so much about inverters? The current that any CMOS logic gate can deliver or sink can be calculated from equivalent inverter!
The CMOS Inverter Lecture 3a Static properties (VTC and noise margins) Why so much about inverters? The current that any CMOS logic gate can deliver or sink can be calculated from equivalent inverter!
ENG2410 Digital Design CMOS Technology. Fall 2017 S. Areibi School of Engineering University of Guelph
 ENG2410 Digital Design CMOS Technology Fall 2017 S. reibi School of Engineering University of Guelph The Transistor Revolution First transistor Bell Labs, 1948 Bipolar logic 1960 s Intel 4004 processor
ENG2410 Digital Design CMOS Technology Fall 2017 S. reibi School of Engineering University of Guelph The Transistor Revolution First transistor Bell Labs, 1948 Bipolar logic 1960 s Intel 4004 processor
Mechatronics and Measurement. Lecturer:Dung-An Wang Lecture 2
 Mechatronics and Measurement Lecturer:Dung-An Wang Lecture 2 Lecture outline Reading:Ch3 of text Today s lecture Semiconductor 2 Diode 3 4 Zener diode Voltage-regulator diodes. This family of diodes exhibits
Mechatronics and Measurement Lecturer:Dung-An Wang Lecture 2 Lecture outline Reading:Ch3 of text Today s lecture Semiconductor 2 Diode 3 4 Zener diode Voltage-regulator diodes. This family of diodes exhibits
5. CMOS Gates: DC and Transient Behavior
 5. CMOS Gates: DC and Transient Behavior Jacob Abraham Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin VLSI Design Fall 2017 September 18, 2017 ECE Department, University
5. CMOS Gates: DC and Transient Behavior Jacob Abraham Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Texas at Austin VLSI Design Fall 2017 September 18, 2017 ECE Department, University
EE5320: Analog IC Design
 EE5320: Analog IC Design Handout 3: MOSFETs Saurabh Saxena & Qadeer Khan Indian Institute of Technology Madras Copyright 2018 by EE6:Integrated Circuits & Systems roup @ IIT Madras Overview Transistors
EE5320: Analog IC Design Handout 3: MOSFETs Saurabh Saxena & Qadeer Khan Indian Institute of Technology Madras Copyright 2018 by EE6:Integrated Circuits & Systems roup @ IIT Madras Overview Transistors
Digital Integrated Circuits EECS 312
 14 12 10 8 6 Fujitsu VP2000 IBM 3090S Pulsar 4 IBM 3090 IBM RY6 CDC Cyber 205 IBM 4381 IBM RY4 2 IBM 3081 Apache Fujitsu M380 IBM 370 Merced IBM 360 IBM 3033 Vacuum Pentium II(DSIP) 0 1950 1960 1970 1980
14 12 10 8 6 Fujitsu VP2000 IBM 3090S Pulsar 4 IBM 3090 IBM RY6 CDC Cyber 205 IBM 4381 IBM RY4 2 IBM 3081 Apache Fujitsu M380 IBM 370 Merced IBM 360 IBM 3033 Vacuum Pentium II(DSIP) 0 1950 1960 1970 1980
Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors (MOSFETs)
 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors (MOSFETs) Device Structure N-Channel MOSFET Providing electrons Pulling electrons (makes current flow) + + + Apply positive voltage to gate: Drives away
Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors (MOSFETs) Device Structure N-Channel MOSFET Providing electrons Pulling electrons (makes current flow) + + + Apply positive voltage to gate: Drives away
ECE520 VLSI Design. Lecture 2: Basic MOS Physics. Payman Zarkesh-Ha
 ECE520 VLSI Design Lecture 2: Basic MOS Physics Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Wednesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: pzarkesh@unm.edu Slide: 1 Review of Last Lecture Semiconductor
ECE520 VLSI Design Lecture 2: Basic MOS Physics Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Wednesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: pzarkesh@unm.edu Slide: 1 Review of Last Lecture Semiconductor
MOSFET Terminals. The voltage applied to the GATE terminal determines whether current can flow between the SOURCE & DRAIN terminals.
 MOSFET Terminals The voltage applied to the GATE terminal determines whether current can flow between the SOURCE & DRAIN terminals. For an n-channel MOSFET, the SOURCE is biased at a lower potential (often
MOSFET Terminals The voltage applied to the GATE terminal determines whether current can flow between the SOURCE & DRAIN terminals. For an n-channel MOSFET, the SOURCE is biased at a lower potential (often
Lecture 13 - Digital Circuits (II) MOS Inverter Circuits. March 22, 2001
 6.12 - Microelectronic Devices and Circuits - Spring 21 Lecture 13-1 Lecture 13 - Digital Circuits (II) MOS Inverter Circuits March 22, 21 Contents: 1. NMOS inverter with resistor pull-up (cont.) 2. NMOS
6.12 - Microelectronic Devices and Circuits - Spring 21 Lecture 13-1 Lecture 13 - Digital Circuits (II) MOS Inverter Circuits March 22, 21 Contents: 1. NMOS inverter with resistor pull-up (cont.) 2. NMOS
Reading. Lecture 17: MOS transistors digital. Context. Digital techniques:
 Reading Lecture 17: MOS transistors digital Today we are going to look at the analog characteristics of simple digital devices, 5. 5.4 And following the midterm, we will cover PN diodes again in forward
Reading Lecture 17: MOS transistors digital Today we are going to look at the analog characteristics of simple digital devices, 5. 5.4 And following the midterm, we will cover PN diodes again in forward
Power dissipation in CMOS
 DC Current in For V IN < V TN, N O is cut off and I DD = 0. For V TN < V IN < V DD /2, N O is saturated. For V DD /2 < V IN < V DD +V TP, P O is saturated. For V IN > V DD + V TP, P O is cut off and I
DC Current in For V IN < V TN, N O is cut off and I DD = 0. For V TN < V IN < V DD /2, N O is saturated. For V DD /2 < V IN < V DD +V TP, P O is saturated. For V IN > V DD + V TP, P O is cut off and I
Electronic Circuits for Mechatronics ELCT 609 Lecture 6: MOS-FET Transistor
 Electronic Circuits for Mechatronics ELCT 609 Lecture 6: MOS-FET Transistor Assistant Professor Office: C3.315 E-mail: eman.azab@guc.edu.eg 1 Introduction Why we call it Transistor? The name came as an
Electronic Circuits for Mechatronics ELCT 609 Lecture 6: MOS-FET Transistor Assistant Professor Office: C3.315 E-mail: eman.azab@guc.edu.eg 1 Introduction Why we call it Transistor? The name came as an
Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras
 Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Sample Questions on Semiconductor Devices EE3 applicants who are interested to pursue their research in microelectronics devices area (fabrication and/or
Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Sample Questions on Semiconductor Devices EE3 applicants who are interested to pursue their research in microelectronics devices area (fabrication and/or
PHYS 3050 Electronics I
 PHYS 3050 Electronics I Chapter 4. Semiconductor Diodes and Transistors Earth, Moon, Mars, and Beyond Dr. Jinjun Shan, Associate Professor of Space Engineering Department of Earth and Space Science and
PHYS 3050 Electronics I Chapter 4. Semiconductor Diodes and Transistors Earth, Moon, Mars, and Beyond Dr. Jinjun Shan, Associate Professor of Space Engineering Department of Earth and Space Science and
Field Effect Transistors (FET s) University of Connecticut 136
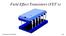 Field Effect Transistors (FET s) University of Connecticut 136 Field Effect Transistors (FET s) FET s are classified three ways: by conduction type n-channel - conduction by electrons p-channel - conduction
Field Effect Transistors (FET s) University of Connecticut 136 Field Effect Transistors (FET s) FET s are classified three ways: by conduction type n-channel - conduction by electrons p-channel - conduction
NAME: Last First Signature
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE 130: IC Devices Spring 2003 FINAL EXAMINATION NAME: Last First Signature STUDENT
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE 130: IC Devices Spring 2003 FINAL EXAMINATION NAME: Last First Signature STUDENT
MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY
 MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY Introduction A MOS transistor is a majority-carrier device, in which the current in a conducting channel between the source and the drain is modulated by a voltage applied to the
MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY Introduction A MOS transistor is a majority-carrier device, in which the current in a conducting channel between the source and the drain is modulated by a voltage applied to the
ENGR4300 Fall 2005 Test 4A. Name. Section. Question 1 (25 points) Question 2 (25 points) Question 3 (25 points) Question 4 (25 points)
 ENGR4300 Fall 2005 Test 4A Name Section Question 1 (25 points) Question 2 (25 points) Question 3 (25 points) Question 4 (25 points) Total (100 points): Please do not write on the crib sheets. On all questions:
ENGR4300 Fall 2005 Test 4A Name Section Question 1 (25 points) Question 2 (25 points) Question 3 (25 points) Question 4 (25 points) Total (100 points): Please do not write on the crib sheets. On all questions:
6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 Page 1 of 13 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Final Eam Closed Book: Formula sheet provided;
Page 1 of 13 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Final Eam Closed Book: Formula sheet provided;
D n ox GS THN DS GS THN DS GS THN. D n ox GS THN DS GS THN DS GS THN
 Name: EXAM #3 Closed book, closed notes. Calculators may be used for numeric computations only. All work is to be your own - show your work for maximum partial credit. Data: Use the following data in all
Name: EXAM #3 Closed book, closed notes. Calculators may be used for numeric computations only. All work is to be your own - show your work for maximum partial credit. Data: Use the following data in all
Review Sheet for Midterm #2
 Review Sheet for Midterm #2 Brian Bircumshaw brianb@eecs.berkeley.edu 1 Miterm #1 Review See Table 1 on the following page for a list of the most important equations you should know from Midterm #1. 2
Review Sheet for Midterm #2 Brian Bircumshaw brianb@eecs.berkeley.edu 1 Miterm #1 Review See Table 1 on the following page for a list of the most important equations you should know from Midterm #1. 2
Laboratory No. 01: Small & Large Signal Diode Circuits. Electrical Enginnering Departement. By: Dr. Awad Al-Zaben. Instructor: Eng.
 Laboratory No. 01: Small & Large Signal Diode Circuits Electrical Enginnering Departement By: Dr. Awad Al-Zaben Instructor: Eng. Tamer Shahta Electronics Laboratory EE 3191 February 23, 2014 I. OBJECTIVES
Laboratory No. 01: Small & Large Signal Diode Circuits Electrical Enginnering Departement By: Dr. Awad Al-Zaben Instructor: Eng. Tamer Shahta Electronics Laboratory EE 3191 February 23, 2014 I. OBJECTIVES
General Structure of MOS Inverter
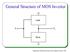 General Structure of MOS Inverter Load V i Drive Department of Microelectronics and omputer Science, TUL Digital MOS ircuits Families Digital MOS ircuits PMOS NMOS MOS BiMOS Depletion mode load Enhancement
General Structure of MOS Inverter Load V i Drive Department of Microelectronics and omputer Science, TUL Digital MOS ircuits Families Digital MOS ircuits PMOS NMOS MOS BiMOS Depletion mode load Enhancement
The Design and Realization of Basic nmos Digital Devices
 Proceedings of The National Conference On Undergraduate Research (NCUR) 2004 Indiana University Purdue University Indianapolis, Indiana April 15-17, 2004 The Design and Realization of Basic nmos Digital
Proceedings of The National Conference On Undergraduate Research (NCUR) 2004 Indiana University Purdue University Indianapolis, Indiana April 15-17, 2004 The Design and Realization of Basic nmos Digital
Digital circuits. Bởi: Sy Hien Dinh
 Digital circuits Bởi: Sy Hien Dinh This module presents the basic concepts of MOSFET digital logic circuits. We will examine NMOS logic circuits, which contain only n-channel transistors, and complementary
Digital circuits Bởi: Sy Hien Dinh This module presents the basic concepts of MOSFET digital logic circuits. We will examine NMOS logic circuits, which contain only n-channel transistors, and complementary
Lecture 4. MOS transistor theory
 Lecture 4 MOS transistor theory 1.7 Introduction: A MOS transistor is a majority-carrier device, in which the current in a conducting channel between the source and the drain is modulated by a voltage
Lecture 4 MOS transistor theory 1.7 Introduction: A MOS transistor is a majority-carrier device, in which the current in a conducting channel between the source and the drain is modulated by a voltage
12/01/2009. Practice with past exams
 EE40 Final Exam Review Prof. Nathan Cheung 12/01/2009 Practice with past exams http://hkn.eecs.berkeley.edu/exam/list/?examcourse=ee%2040 Slide 1 Overview of Course Circuit components: R, C, L, sources
EE40 Final Exam Review Prof. Nathan Cheung 12/01/2009 Practice with past exams http://hkn.eecs.berkeley.edu/exam/list/?examcourse=ee%2040 Slide 1 Overview of Course Circuit components: R, C, L, sources
Written Examination on. Wednesday October 17, 2007,
 Written Examination on Wednesday October 17, 2007, 08.00-12.00 The textbook and a calculator are allowed on the examination 1. The following logical function is given Q= AB( CD+ CE) + F a. Draw the schematic
Written Examination on Wednesday October 17, 2007, 08.00-12.00 The textbook and a calculator are allowed on the examination 1. The following logical function is given Q= AB( CD+ CE) + F a. Draw the schematic
Lecture 4. The CMOS Inverter. DC Transfer Curve: Load line. DC Operation: Voltage Transfer Characteristic. Noise in Digital Integrated Circuits
 Noise in Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 4 The CMOS Inverter i(t) v(t) V DD Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail:
Noise in Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 4 The CMOS Inverter i(t) v(t) V DD Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail:
problem grade total
 Fall 2005 6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. J. A. del Alamo Name: Recitation: November 16, 2005 Quiz #2 problem grade 1 2 3 4 total General guidelines (please read carefully before starting):
Fall 2005 6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. J. A. del Alamo Name: Recitation: November 16, 2005 Quiz #2 problem grade 1 2 3 4 total General guidelines (please read carefully before starting):
Laboratory #5 BJT Basics and MOSFET Basics
 Laboratory #5 BJT Basics and MOSFET Basics I. Objectives 1. Understand the physical structure of BJTs and MOSFETs. 2. Learn to measure I-V characteristics of BJTs and MOSFETs. II. Components and Instruments
Laboratory #5 BJT Basics and MOSFET Basics I. Objectives 1. Understand the physical structure of BJTs and MOSFETs. 2. Learn to measure I-V characteristics of BJTs and MOSFETs. II. Components and Instruments
Intrinsic Semiconductor
 Semiconductors Crystalline solid materials whose resistivities are values between those of conductors and insulators. Good electrical characteristics and feasible fabrication technology are some reasons
Semiconductors Crystalline solid materials whose resistivities are values between those of conductors and insulators. Good electrical characteristics and feasible fabrication technology are some reasons
DIGITAL VLSI LAB ASSIGNMENT 1
 DIGITAL VLSI LAB ASSIGNMENT 1 Problem 1: NMOS and PMOS plots using Cadence. In this exercise, you are required to generate both NMOS and PMOS I-V device characteristics (I/P and O/P) using Cadence (Use
DIGITAL VLSI LAB ASSIGNMENT 1 Problem 1: NMOS and PMOS plots using Cadence. In this exercise, you are required to generate both NMOS and PMOS I-V device characteristics (I/P and O/P) using Cadence (Use
Field-Effect Transistor (FET) is one of the two major transistors; FET derives its name from its working mechanism;
 Chapter 3 Field-Effect Transistors (FETs) 3.1 Introduction Field-Effect Transistor (FET) is one of the two major transistors; FET derives its name from its working mechanism; The concept has been known
Chapter 3 Field-Effect Transistors (FETs) 3.1 Introduction Field-Effect Transistor (FET) is one of the two major transistors; FET derives its name from its working mechanism; The concept has been known
Experiment 5 Single-Stage MOS Amplifiers
 Experiment 5 Single-Stage MOS Amplifiers B. Cagdaser, H. Chong, R. Lu, and R. T. Howe UC Berkeley EE 105 Fall 2005 1 Objective This is the first lab dealing with the use of transistors in amplifiers. We
Experiment 5 Single-Stage MOS Amplifiers B. Cagdaser, H. Chong, R. Lu, and R. T. Howe UC Berkeley EE 105 Fall 2005 1 Objective This is the first lab dealing with the use of transistors in amplifiers. We
EE301 Electronics I , Fall
 EE301 Electronics I 2018-2019, Fall 1. Introduction to Microelectronics (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Introduction, Historical Background, Basic Consepts 2. Rewiev of Semiconductors (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Semiconductor materials
EE301 Electronics I 2018-2019, Fall 1. Introduction to Microelectronics (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Introduction, Historical Background, Basic Consepts 2. Rewiev of Semiconductors (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Semiconductor materials
EECE2412 Final Exam. with Solutions
 EECE2412 Final Exam with Solutions Prof. Charles A. DiMarzio Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Northeastern University Fall Semester 2010 My file 11480/exams/final General Instructions:
EECE2412 Final Exam with Solutions Prof. Charles A. DiMarzio Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Northeastern University Fall Semester 2010 My file 11480/exams/final General Instructions:
CMOS VLSI Design M.Tech. First semester VTU
 CMOS VLSI Design M.Tech. First semester VTU Introduction The present chapter first develops the fundamental physical characteristics of the MOS transistor, in which the electrical currents and voltages
CMOS VLSI Design M.Tech. First semester VTU Introduction The present chapter first develops the fundamental physical characteristics of the MOS transistor, in which the electrical currents and voltages
BJT Amplifier. Superposition principle (linear amplifier)
 BJT Amplifier Two types analysis DC analysis Applied DC voltage source AC analysis Time varying signal source Superposition principle (linear amplifier) The response of a linear amplifier circuit excited
BJT Amplifier Two types analysis DC analysis Applied DC voltage source AC analysis Time varying signal source Superposition principle (linear amplifier) The response of a linear amplifier circuit excited
Improved Inverter: Current-Source Pull-Up. MOS Inverter with Current-Source Pull-Up. What else could be connected between the drain and V DD?
 Improved Inverter: Current-Source Pull-Up MOS Inverter with Current-Source Pull-Up What else could be connected between the drain and? Replace resistor with current source I SUP roc i D v IN v OUT Find
Improved Inverter: Current-Source Pull-Up MOS Inverter with Current-Source Pull-Up What else could be connected between the drain and? Replace resistor with current source I SUP roc i D v IN v OUT Find
Lecture 3: Diodes. Amplitude Modulation. Diode Detection.
 Whites, EE 322 Lecture 3 Page 1 of 10 Lecture 3: Diodes. Amplitude Modulation. Diode Detection. Diodes are the fourth basic discrete component listed in Lecture 2. These and transistors are both nonlinear
Whites, EE 322 Lecture 3 Page 1 of 10 Lecture 3: Diodes. Amplitude Modulation. Diode Detection. Diodes are the fourth basic discrete component listed in Lecture 2. These and transistors are both nonlinear
Exam 1 ECE 410 Fall 2002
 NAME: Exa 1 ECE 410 Fall 2002 During this exa you are allowed to use a calculator and the equations sheet provided. You are not allowed to speak to or exchange books, papers, calculators, etc. with other
NAME: Exa 1 ECE 410 Fall 2002 During this exa you are allowed to use a calculator and the equations sheet provided. You are not allowed to speak to or exchange books, papers, calculators, etc. with other
Lecture 16: MOS Transistor models: Linear models, SPICE models. Context. In the last lecture, we discussed the MOS transistor, and
 Lecture 16: MOS Transistor models: Linear models, SPICE models Context In the last lecture, we discussed the MOS transistor, and added a correction due to the changing depletion region, called the body
Lecture 16: MOS Transistor models: Linear models, SPICE models Context In the last lecture, we discussed the MOS transistor, and added a correction due to the changing depletion region, called the body
Microelectronics Circuit Analysis and Design
 Microelectronics Circuit Analysis and Design Donald A. Neamen Chapter 3 The Field Effect Transistor Neamen Microelectronics, 4e Chapter 3-1 In this chapter, we will: Study and understand the operation
Microelectronics Circuit Analysis and Design Donald A. Neamen Chapter 3 The Field Effect Transistor Neamen Microelectronics, 4e Chapter 3-1 In this chapter, we will: Study and understand the operation
f14m1s_elct7.fm - 1 The University of Toledo EECS:3400 Electronocs I Electronics I Problems Points Total 15 Was the exam fair?
 f4ms_elct7.fm - Electronics I Midterm I Examination Problems Points. 4 2. 5 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no f4ms_elct7.fm - 2 Problem 4 points For full credit, mark your answers yes, no, or not
f4ms_elct7.fm - Electronics I Midterm I Examination Problems Points. 4 2. 5 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no f4ms_elct7.fm - 2 Problem 4 points For full credit, mark your answers yes, no, or not
PAPER SOLUTION_DECEMBER_2014_VLSI_DESIGN_ETRX_SEM_VII Prepared by Girish Gidaye
 Q1a) The MOS System under External Bias Depending on the polarity and the magnitude of V G, three different operating regions can be observed for the MOS system: 1) Accumulation 2) Depletion 3) Inversion
Q1a) The MOS System under External Bias Depending on the polarity and the magnitude of V G, three different operating regions can be observed for the MOS system: 1) Accumulation 2) Depletion 3) Inversion
Week 7: Common-Collector Amplifier, MOS Field Effect Transistor
 EE 2110A Electronic Circuits Week 7: Common-Collector Amplifier, MOS Field Effect Transistor ecture 07-1 Topics to coer Common-Collector Amplifier MOS Field Effect Transistor Physical Operation and I-V
EE 2110A Electronic Circuits Week 7: Common-Collector Amplifier, MOS Field Effect Transistor ecture 07-1 Topics to coer Common-Collector Amplifier MOS Field Effect Transistor Physical Operation and I-V
! PN Junction. ! MOS Transistor Topology. ! Threshold. ! Operating Regions. " Resistive. " Saturation. " Subthreshold (next class)
 ESE370: ircuit-level Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems Today! PN Junction! MOS Transistor Topology! Threshold Lec 7: September 16, 2015 MOS Transistor Operating Regions Part 1! Operating
ESE370: ircuit-level Modeling, Design, and Optimization for Digital Systems Today! PN Junction! MOS Transistor Topology! Threshold Lec 7: September 16, 2015 MOS Transistor Operating Regions Part 1! Operating
EE 330 Laboratory 8 Discrete Semiconductor Amplifiers
 EE 330 Laboratory 8 Discrete Semiconductor Amplifiers Fall 2017 Contents Objective:... 2 Discussion:... 2 Components Needed:... 2 Part 1 Voltage Controlled Amplifier... 2 Part 2 Common Source Amplifier...
EE 330 Laboratory 8 Discrete Semiconductor Amplifiers Fall 2017 Contents Objective:... 2 Discussion:... 2 Components Needed:... 2 Part 1 Voltage Controlled Amplifier... 2 Part 2 Common Source Amplifier...
Chapter 2 : Semiconductor Materials & Devices (II) Feb
 Chapter 2 : Semiconductor Materials & Devices (II) 1 Reference 1. SemiconductorManufacturing Technology: Michael Quirk and Julian Serda (2001) 3. Microelectronic Circuits (5/e): Sedra & Smith (2004) 4.
Chapter 2 : Semiconductor Materials & Devices (II) 1 Reference 1. SemiconductorManufacturing Technology: Michael Quirk and Julian Serda (2001) 3. Microelectronic Circuits (5/e): Sedra & Smith (2004) 4.
Week 9a OUTLINE. MOSFET I D vs. V GS characteristic Circuit models for the MOSFET. Reading. resistive switch model small-signal model
 Week 9a OUTLINE MOSFET I vs. V GS characteristic Circuit models for the MOSFET resistive switch model small-signal model Reading Rabaey et al.: Chapter 3.3.2 Hambley: Chapter 12 (through 12.5); Section
Week 9a OUTLINE MOSFET I vs. V GS characteristic Circuit models for the MOSFET resistive switch model small-signal model Reading Rabaey et al.: Chapter 3.3.2 Hambley: Chapter 12 (through 12.5); Section
Solution HW4 Dr. Parker EE477
 Solution HW4 Dr. Parker EE477 Assume for the problems below that V dd = 1.8 v, V tp0 is -.7 v. and V tn0 is.7 V. V tpbodyeffect is -.9 v. and V tnbodyeffect is.9 V. Assume ß n (k n )= 219.4 W/L µ A(microamps)/V
Solution HW4 Dr. Parker EE477 Assume for the problems below that V dd = 1.8 v, V tp0 is -.7 v. and V tn0 is.7 V. V tpbodyeffect is -.9 v. and V tnbodyeffect is.9 V. Assume ß n (k n )= 219.4 W/L µ A(microamps)/V
Design cycle for MEMS
 Design cycle for MEMS Design cycle for ICs IC Process Selection nmos CMOS BiCMOS ECL for logic for I/O and driver circuit for critical high speed parts of the system The Real Estate of a Wafer MOS Transistor
Design cycle for MEMS Design cycle for ICs IC Process Selection nmos CMOS BiCMOS ECL for logic for I/O and driver circuit for critical high speed parts of the system The Real Estate of a Wafer MOS Transistor
5.1 BJT Device Structure and Physical Operation
 11/28/2004 section 5_1 BJT Device Structure and Physical Operation blank 1/2 5.1 BJT Device Structure and Physical Operation Reading Assignment: pp. 377-392 Another kind of transistor is the Bipolar Junction
11/28/2004 section 5_1 BJT Device Structure and Physical Operation blank 1/2 5.1 BJT Device Structure and Physical Operation Reading Assignment: pp. 377-392 Another kind of transistor is the Bipolar Junction
Physics 160 Lecture 5. R. Johnson April 13, 2015
 Physics 160 Lecture 5 R. Johnson April 13, 2015 Half Wave Diode Rectifiers Full Wave April 13, 2015 Physics 160 2 Note that there is no ground connection on this side of the rectifier! Output Smoothing
Physics 160 Lecture 5 R. Johnson April 13, 2015 Half Wave Diode Rectifiers Full Wave April 13, 2015 Physics 160 2 Note that there is no ground connection on this side of the rectifier! Output Smoothing
HW#3 Solution. Dr. Parker. Fall 2014
 HW#3 Solution Dr. Parker Fall 2014 Assume for the problems below that V dd = 1.8 V, V tp0 is -.7 V. and V tn0 is.7 V. V tpbodyeffect is -.9 V. and V tnbodyeffect is.9 V. lambda=100 nm. Assume ß n (k n
HW#3 Solution Dr. Parker Fall 2014 Assume for the problems below that V dd = 1.8 V, V tp0 is -.7 V. and V tn0 is.7 V. V tpbodyeffect is -.9 V. and V tnbodyeffect is.9 V. lambda=100 nm. Assume ß n (k n
Conduction Characteristics of MOS Transistors (for fixed Vds)! Topic 2. Basic MOS theory & SPICE simulation. MOS Transistor
 Conduction Characteristics of MOS Transistors (for fixed Vds)! Topic 2 Basic MOS theory & SPICE simulation Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London (Weste&Harris,
Conduction Characteristics of MOS Transistors (for fixed Vds)! Topic 2 Basic MOS theory & SPICE simulation Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London (Weste&Harris,
Topic 2. Basic MOS theory & SPICE simulation
 Topic 2 Basic MOS theory & SPICE simulation Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London (Weste&Harris, Ch 2 & 5.1-5.3 Rabaey, Ch 3) URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/
Topic 2 Basic MOS theory & SPICE simulation Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London (Weste&Harris, Ch 2 & 5.1-5.3 Rabaey, Ch 3) URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/
Conduction Characteristics of MOS Transistors (for fixed Vds) Topic 2. Basic MOS theory & SPICE simulation. MOS Transistor
 Conduction Characteristics of MOS Transistors (for fixed Vds) Topic 2 Basic MOS theory & SPICE simulation Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London (Weste&Harris,
Conduction Characteristics of MOS Transistors (for fixed Vds) Topic 2 Basic MOS theory & SPICE simulation Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London (Weste&Harris,
4.1 Device Structure and Physical Operation
 10/12/2004 4_1 Device Structure and Physical Operation blank.doc 1/2 4.1 Device Structure and Physical Operation Reading Assignment: pp. 235-248 Chapter 4 covers Field Effect Transistors ( ) Specifically,
10/12/2004 4_1 Device Structure and Physical Operation blank.doc 1/2 4.1 Device Structure and Physical Operation Reading Assignment: pp. 235-248 Chapter 4 covers Field Effect Transistors ( ) Specifically,
Electronics The basics of semiconductor physics
 Electronics The basics of semiconductor physics Prof. Márta Rencz, Gábor Takács BME DED 17/09/2015 1 / 37 The basic properties of semiconductors Range of conductivity [Source: http://www.britannica.com]
Electronics The basics of semiconductor physics Prof. Márta Rencz, Gábor Takács BME DED 17/09/2015 1 / 37 The basic properties of semiconductors Range of conductivity [Source: http://www.britannica.com]
MOS Field-Effect Transistors (MOSFETs)
 6 MOS Field-Effect Transistors (MOSFETs) A three-terminal device that uses the voltages of the two terminals to control the current flowing in the third terminal. The basis for amplifier design. The basis
6 MOS Field-Effect Transistors (MOSFETs) A three-terminal device that uses the voltages of the two terminals to control the current flowing in the third terminal. The basis for amplifier design. The basis
EEC 118 Spring 2010 Lab #1: NMOS and PMOS Transistor Parameters
 EEC 118 Spring 2010 Lab #1: NMOS and PMOS Transistor Parameters Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Davis March 18, 2010 Reading: Rabaey Chapter 3 [1]. Reference: Kang
EEC 118 Spring 2010 Lab #1: NMOS and PMOS Transistor Parameters Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Davis March 18, 2010 Reading: Rabaey Chapter 3 [1]. Reference: Kang
INTRODUCTION: Basic operating principle of a MOSFET:
 INTRODUCTION: Along with the Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET), there is another type of Field Effect Transistor available whose Gate input is electrically insulated from the main current carrying
INTRODUCTION: Along with the Junction Field Effect Transistor (JFET), there is another type of Field Effect Transistor available whose Gate input is electrically insulated from the main current carrying
EE 5611 Introduction to Microelectronic Technologies Fall Thursday, September 04, 2014 Lecture 02
 EE 5611 Introduction to Microelectronic Technologies Fall 2014 Thursday, September 04, 2014 Lecture 02 1 Lecture Outline Review on semiconductor materials Review on microelectronic devices Example of microelectronic
EE 5611 Introduction to Microelectronic Technologies Fall 2014 Thursday, September 04, 2014 Lecture 02 1 Lecture Outline Review on semiconductor materials Review on microelectronic devices Example of microelectronic
8. Characteristics of Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)
 1 8. Characteristics of Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) 8.1. Objectives The purpose of this experiment is to measure input and output characteristics of n-channel and p- channel field effect transistors
1 8. Characteristics of Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) 8.1. Objectives The purpose of this experiment is to measure input and output characteristics of n-channel and p- channel field effect transistors
Electronics I. Midterm #1
 The University of Toledo Section s7ms_elct7.fm - Electronics I Midterm # Problems Points. 4 2. 5 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo s7ms_elct7.fm - 2 Problem 4 points For full
The University of Toledo Section s7ms_elct7.fm - Electronics I Midterm # Problems Points. 4 2. 5 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo s7ms_elct7.fm - 2 Problem 4 points For full
Microelectronics, BSc course
 Microelectronics, BSc course MOS circuits: CMOS circuits, construction http://www.eet.bme.hu/~poppe/miel/en/14-cmos.pptx http://www.eet.bme.hu The abstraction level of our study: SYSTEM + MODULE GATE CIRCUIT
Microelectronics, BSc course MOS circuits: CMOS circuits, construction http://www.eet.bme.hu/~poppe/miel/en/14-cmos.pptx http://www.eet.bme.hu The abstraction level of our study: SYSTEM + MODULE GATE CIRCUIT
ELEC 2210 EXPERIMENT 8 MOSFETs
 ELEC 10 EXPERIMENT 8 MOSFETs Objectives: The experiments in this laboratory exercise will provide an introduction to the MOSFET. You will use the Bit Bucket breadboarding system to build and test several
ELEC 10 EXPERIMENT 8 MOSFETs Objectives: The experiments in this laboratory exercise will provide an introduction to the MOSFET. You will use the Bit Bucket breadboarding system to build and test several
Lesson 5. Electronics: Semiconductors Doping p-n Junction Diode Half Wave and Full Wave Rectification Introduction to Transistors-
 Lesson 5 Electronics: Semiconductors Doping p-n Junction Diode Half Wave and Full Wave Rectification Introduction to Transistors- Types and Connections Semiconductors Semiconductors If there are many free
Lesson 5 Electronics: Semiconductors Doping p-n Junction Diode Half Wave and Full Wave Rectification Introduction to Transistors- Types and Connections Semiconductors Semiconductors If there are many free
 Electronic Devices 1. Current flowing in each of the following circuits A and respectively are: (Circuit 1) (Circuit 2) 1) 1A, 2A 2) 2A, 1A 3) 4A, 2A 4) 2A, 4A 2. Among the following one statement is not
Electronic Devices 1. Current flowing in each of the following circuits A and respectively are: (Circuit 1) (Circuit 2) 1) 1A, 2A 2) 2A, 1A 3) 4A, 2A 4) 2A, 4A 2. Among the following one statement is not
The Discussion of this exercise covers the following points:
 Exercise 1 The Diode EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the operation of a diode. DISCUSSION OUTLINE The Discussion of this exercise covers the following
Exercise 1 The Diode EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the operation of a diode. DISCUSSION OUTLINE The Discussion of this exercise covers the following
Transistor was first invented by William.B.Shockley, Walter Brattain and John Bardeen of Bell Labratories. In 1961, first IC was introduced.
 Unit 1 Basic MOS Technology Transistor was first invented by William.B.Shockley, Walter Brattain and John Bardeen of Bell Labratories. In 1961, first IC was introduced. Levels of Integration:- i) SSI:-
Unit 1 Basic MOS Technology Transistor was first invented by William.B.Shockley, Walter Brattain and John Bardeen of Bell Labratories. In 1961, first IC was introduced. Levels of Integration:- i) SSI:-
(Refer Slide Time: 02:05)
 Electronics for Analog Signal Processing - I Prof. K. Radhakrishna Rao Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Lecture 27 Construction of a MOSFET (Refer Slide Time:
Electronics for Analog Signal Processing - I Prof. K. Radhakrishna Rao Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Madras Lecture 27 Construction of a MOSFET (Refer Slide Time:
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University. ECE 3150: Microelectronics. Spring 2017
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University ECE 3150: Microelectronics Spring 017 Final Exam ` May, 017 INSTRUCTIONS: Every problem must be done in the separate booklet Only work
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Cornell University ECE 3150: Microelectronics Spring 017 Final Exam ` May, 017 INSTRUCTIONS: Every problem must be done in the separate booklet Only work
Downloaded from
 Question 14.1: In an n-type silicon, which of the following statement is true: (a) Electrons are majority carriers and trivalent atoms are the dopants. (b) Electrons are minority carriers and pentavalent
Question 14.1: In an n-type silicon, which of the following statement is true: (a) Electrons are majority carriers and trivalent atoms are the dopants. (b) Electrons are minority carriers and pentavalent
Student Lecture by: Giangiacomo Groppi Joel Cassell Pierre Berthelot September 28 th 2004
 Student Lecture by: Giangiacomo Groppi Joel Cassell Pierre Berthelot September 28 th 2004 Lecture outline Historical introduction Semiconductor devices overview Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Field
Student Lecture by: Giangiacomo Groppi Joel Cassell Pierre Berthelot September 28 th 2004 Lecture outline Historical introduction Semiconductor devices overview Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Field
ECE315 / ECE515 Lecture 8 Date:
 ECE35 / ECE55 Lecture 8 Date: 05.09.06 CS Amplifier with Constant Current Source Current Steering Circuits CS Stage Followed by CG Stage Cascode as Current Source Cascode as Amplifier ECE35 / ECE55 CS
ECE35 / ECE55 Lecture 8 Date: 05.09.06 CS Amplifier with Constant Current Source Current Steering Circuits CS Stage Followed by CG Stage Cascode as Current Source Cascode as Amplifier ECE35 / ECE55 CS
Transistors, Gates and Busses 3/21/01 Lecture #
 Transistors, Gates and Busses 3/2/ Lecture #8 6.7 The goal for today is to understand a bit about how a computer actually works: how it stores, adds, and communicates internally! How transistors make gates!
Transistors, Gates and Busses 3/2/ Lecture #8 6.7 The goal for today is to understand a bit about how a computer actually works: how it stores, adds, and communicates internally! How transistors make gates!
Microelectronics, BSc course
 Microelectronics, BSc course MOS inverters http://www.eet.bme.hu/~poppe/miel/en/13-mosfet2.pptx http://www.eet.bme.hu Overview of MSOFET types 13-11-2014 Microelectronics BSc course, MOS inverters András
Microelectronics, BSc course MOS inverters http://www.eet.bme.hu/~poppe/miel/en/13-mosfet2.pptx http://www.eet.bme.hu Overview of MSOFET types 13-11-2014 Microelectronics BSc course, MOS inverters András
Electronics I. Midterm #1
 The University of Toledo Section f6ms_elct7.fm - Electronics I Midterm # Problems Points. 4 2. 5 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo f6ms_elct7.fm - 2 Problem 4 points For full
The University of Toledo Section f6ms_elct7.fm - Electronics I Midterm # Problems Points. 4 2. 5 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo f6ms_elct7.fm - 2 Problem 4 points For full
Today's Goals. Finish MOS transistor Finish NMOS logic Start CMOS logic
 Bi Today's Goals Finish MOS transistor Finish Start Bi MOS Capacitor Equations Threshold voltage Gate capacitance V T = ms Q i C i Q II C i Q d C i 2 F n-channel - - p-channel ± ± + + - - Contributions
Bi Today's Goals Finish MOS transistor Finish Start Bi MOS Capacitor Equations Threshold voltage Gate capacitance V T = ms Q i C i Q II C i Q d C i 2 F n-channel - - p-channel ± ± + + - - Contributions
