(54) BUFFER INTERFACE ARCHITECTURE Publication Classification. An up to 3x breakdown voltage tristate capable integrated
|
|
|
- Camilla Mills
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 (19) United States us Al (12) Patent Applicatin Publicatin (10) Pub..: US 2002/ Al Prdanv (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 12, 2002 (54) BUFFER TERFAE ARHTETURE Publicatin lassificatin (76) nventr: Vladimir. Prdanv, ew (51) nt.? H03B 1/00 (52) U.S.. 327/108 Prvidence, J (US) rrespndence Address: (57) ABSTRAT DUAE MORRS, LLP An up t 3x breakdwn vltage tristate capable integrated ATT: WLLAM H. MURRAY OE LBERTY PLAE circuit MOS buffer includes a level shifter circuit and a 1650 MARKET STREET driver circuit. The driver stage includes a series cnnected PHLADELPHA, PA (US) n-channel and p-channel cascde stacks, each including at least three transistrs. Dynamic gate biasing is prvided fr (21) Appl..: 10/128,140 the third n-channel and p-channel cascde transistrs t (22) Filed: Apr. 23, 2002 prevent vltage verstress f the cascde transistrs. The level shifter circuit includes at least ne pseud -MOS Related U.S. Applicatin Data inverter including an input transistr, a prtective cascde stack including at least ne n-channel cascde transistr, and (60) Prvisinal applicatin. 60/287,674, filed n May a lad transistr. The level shifter prvides at least ne 1,2001. vltage shifted input signal t the driver. 3V max 2V max.jl 2Vmax """'g9 52 3Vmax (VH1GH) V max U (VGROUD)
2 Patent Applicatin Publicatin Dec. 12, 2002 Sheet 1 f 12 US 2002/ Al r c L_ ""'- J --, -c r- c <.,:) r- --, 1 > a:::: - """'" J , t- 1 1 <:r:: 1 e:::: 0 l b a:::: _J a - L J L_ > a:::: l.lj<":) - --:::Z _- l.l.., :;co:::: (/')L..a... 1> c --.J:::Z L.&.J. <:..:) ::>:::z c L.&.J --.J:::Z , - :::z :::z L..a...
3 Patent Applicatin Publicatin Dec. 12, 2002 Sheet 2 f 12 US 2002/ Al (/) U«) - - «:z:: :::::::E D «L >-..J ) :::> D r Q f0 """"" e:::: ::c «c..::> c.b -e:::: -::c 0 > e:::: a.. r j r ---j L _ --, _...J J- ) :z:: c..::> -:z:: :z:: L.a..J
4 Patent Applicatin Publicatin Dec. 12, 2002 Sheet 3 f 12 US 2002/ Al FG. 2A 30 V 34 OE 32 LEVEL SHFTER OUT FG. 2B ATVE MODE Vmax FG. 2 TRSTATE MODE V --j V p V n
5 FG. 3A FG. 3B 100 't:l 't:l "" > -"l 3Vmax (VH1GH) 3Vmax (VH1GH) 0 3V maxl -"l 2Vmax Vp Pl 2V max q, _d 2V max P2 S2 \ "' ! 51 ) Vmax- al V max V max L 0'1 V n -::- (VGROUD) 3V max 'JJ. U , P L----i, "" 0 0!"l '""'" 8 '""'" d 'JJ. --- '""'" QO Ul QO > '""'"
6 FG. 3 FG. 3D -"l 0 3Vmax (VHGH ) 3Vmax (V HGH ) 0 -"l P1 0-41_ P1 0 ZV Pz ZV max T 9LPz max 9 Vmax 4 l1 104 VU i + D. '.J P4 l L Z P L. 4[ '-106 V max 11-? d 'JJ. c P3 3 e> (VGROUD) -- (VGROUD) c 10Z "" 't:l> 't:l ""!"l '""'" c 'JJ. Ul 0, '""'" --- '""'" QO 0'1 Ul QO > '""'"
7 Patent Applicatin Publicatin Dec. 12, 2002 Sheet 6 f 12 US 2002/ Al FG. 3E 3Vmax (VHGH ) 2V max ----t d 108 Ps S Vmax
8 Patent Applicatin Publicatin Dec. 12, 2002 Sheet 7 f 12 US 2002/ Al FG. 3F 3Vmax (V HGH ) Pl 2Vmax Ps P2 P3 104 P6 6 V pad 102 Vmax J S
9 FG. 4 2Vmax (VHGH) 200 't:l "" FG. SA > 300 't:l "l, 206 3Vmax (V HGH ) "" 2Vmaxn r s ,, g. e>-41 Pl "l V max : Gn P2 i s Ps d V V max 2Vmax Gl pad 1 max V [ t + d S s Vman l G 1-_ P : e> VGROUD U VmaxGl g '""'" S r ' ) G ll S D D S S!"l '""'" 8 'JJ. QO ọ..., d 'JJ. QO '""'" 0'1 -- VGROUD Ul QO > '""'"
10 V max rr-l 2 JL.l-J -' n ljl l " '" " La FG. --V, 5B,, '" 3000 J - GROUD 300b J - GROUD 304 )J 1_, Vmax (VHGH),!lJ J, lsl 310, 2V max "" 't:l> 't:l "l "" g. "l!"l '""'" 8 - V Ul QO 'JJ. '0 ọ..., '""'" d 'JJ. QO '""'" 0'1 > '""'"
11 V mx-,. V 314 L maxjls r ) --- D :;r; r:d-f> : 2 i : L... _ FG. 5 J E1 l J ; _ p,i JlS 3V max _ , 3V max : 2Vmax max J 1Jl2v 3V 2Vmax max "" 't:l> 't:l "l "" g. "l!"l '""'" V max 'JJ. JlS 318 1Jl: max c '""'" ọ..., '""'" d 'JJ. QO '""'" 0'1 Ul QO > '""'"
12 Patent Applicatin Publicatin Dec. 12, 2002 Sheet 11 f 12 US 2002/ Al - > L.L.J -
13 U Vmax FG Vmax \, , 3V max "" 't:l "l 0 "l 4 S,, : 20B Y 6 : 0-1 L 'JJ. \ TO V TO 2V max max '""'", P6!"l :102 0 TO 3V '""'" max 8 : n3vmax J2 '""'"! d 'JJ max OUT _--rj-' : : v - QO '""'" i L... VGROUD -': Ul 0'1 QO > '""'"
14 US 2002/ A1 Dec. 12, BUFFER TERFAE ARHTETURE ROSS-REFEREE TO RELATED APPLATOS [0001] This applicatin claims pririty frm U.S. prvisinal applicatin serial. 60/287,674, filed May 1,2001 and entitled "Buffer nterface Architecture." FELD OF THE VETO [0002] The present inventin relates t integrated circuits, generally, and mre specifically t a buffer fr interfacing a lw-vltage technlgy with a relatively high-vltage technlgy. DESRPTO OF THE RELATED ART [0003] Advances in the semicnductr arts have driven devices t decreasing sizes perating at increasing speeds. This cntinuus effrt t maximize the perfrmance f integrated circuits ("s") has prduced several additinal benefits, including decreased perating vltages and reductins in pwer cnsumptin. [0004] As MOS technlgy scales belw 0.2,um, acceptable supply vltages have lwered belw the previus 3.3V and 5V standards. As lwer and lwer perating vltage technlgy is develped and cmmercialized, hwever, a distinct prblem has arisen. Mstly because f ecnmic reasns, electrnic systems ften use s that span several technlgy generatins, each generatin having different supply vltage requirements. The ability t interface newer lw pwer s with their predecessrs where each has a different range f perating vltages is f cncern, particulady as it relates t metal xide semicnductrs ("MOS"). nterfacing an lder higher perating vltage with a lwer perating vltage technlgy may cause reliability issues and/r temprary r even permanent damage. Fr example, the buffer circuits f a l.5v can neither prvide nr sustain (when in a high impedance state) a 3.3V drive. [0005] T vercme this interface prblem, several slutins have been prpsed. One apprach entails the develpment f MOS devices capable f handling bth lw and high vltages n the same semicnductr substrate. While this "dual supply" apprach is simple in circuit implementatin, presently, it is substantially mre expensive than the traditinally knwn MOS technlgy because f the additinal prcessing steps required t fabricate the high-vltage devices. urrently, many 0.2,um technlgies utilize this "dual supply" apprach. [0006] Alternatively, several buffer interface architectures are als knwn in the art fr prviding high vltage drive capability using lw vltage MOS technlgy. Using this methdlgy, the incremental csts assciated with the additinal circuitry required t realize an interface having high vltage drive capability while implemented in lw vltage MOS technlgy are negligible. [0007] Prir appraches t high-vltage drive buffers with lw-vltage transistrs (HVBLVT) can be classified int tw basic grups. FG. 1A illustrates a circuit with bth high-vltage tlerance and high-vltage drive. Such a circuit is prpsed in U.S. Pat.. 5,663,917 t Oka et a., the entirety f which is hereby incrprated by reference herein. FG. 1B illustrates a circuit with high-vltage tlerance and lw-vltage drive, such as may be fund in M. Pelgrm and E. Dijkmans, "A 3/sV cmpatible /O Buffer," EEE J. f Slid-State ircuits, vl. 30,.7, p.p , July, 1995, the entirety f which is hereby incrprated by reference herein. [0008] Fr purpses f circuit 10 f FG. la, it is assumed that the breakdwn vltage f the transistrs used in the circuit is nly slightly higher than 'h VHGH-the vltage swing f the input signal. The circuit 10 f FG. 1A includes a pad driver 12 which includes p-channel and n-channel cascde stacks, which include MOS devices Pl' P2 and l' 2' respectively. The cascde transistrs P2 and 2 allw the utput at pad nde 14 t traverse between OV and VHGH while the VGS's (vltage gate t surce) and VGO's (vltage gate t drain) f all fur transistrs P 1, P 2, 1, 2 remain lwer than 'h VHGH' and thus lwer than the breakdwn vltage f the transistrs. The vltage capability f the pad driver 12, therefre, is tw times larger than the vltage capability f the MOSFETs used in the driver. Such a circuit may be referred t as a "2x driver." [0009] Fr prper peratin, the cascde pad driver 12 requires tw in-phase input signals at ndes 18 and 20. Bth signals must have a vltage swing that des nt exceed 'h V in rder t avid exceeding the vltage capability f the tr;;'istrs used therein. These signals are prvided frm the level shifter 16 t the driver 12 thrugh tw cnventinal inverter chains. The level shifter 16 takes a 0 t 'h VHGH swing input data signal and prduces a data signal that swings between 'h VHGH and VHGH at nde 18. aturally, the level shifter 16 shuld be implemented in such a way that nne f its transistrs experience vltage verstress. [0010] Unlike the circuit 10 f FG. la, the circuit 20 f FG. 1B is a high vltage buffer with lw vltage transistrs that is biased frm a lwer supply vltage 'h VHGH and is characterized by high vltage tlerance but lw vltage drive. As a result, its utput drive is nly between 0 and 'h VHGH' The structure, hwever, allws the pad vltage t exceed the supply vltage when the buffer is in the tristate mde, i.e., the circuit can be driven by a vltage f apprximately VHGH withut damaging the cmpnents. The circuit, therefre, may be characterized as having a "2x tlerance." The circuit 10 f FG. 1A may als be characterized as a "2x tlerance" circuit. [0011] Three prblems are eliminated t achieve the 2x tlerance f the circuit 20: (a) VOG (vltage drain t gate) verstress f the n-channel transistr 1; (b) cnductin f the p-channel transistr P1 in tristate mde when the utput nde exceeds the supply vltage by apprximately a threshld vltage; and (c) frward biasing f the drain-bulk p-n junctin f the p-channel transistr P1 when the utput sufficiently exceeds the supply vltage. The first prblem is reslved by using an n-channel cascde- 2 -while the secnd and the third prblems are eliminated by using dynamic gate and bulk biasing (cnceptually illustrated using tw pairs f switches). [0012] Recently, tw HVB/LVT's with beynd-2x vltage capabilities have been reprted. A first circuit has a 3.3V drive and 5V tlerance using 2V transistrs and is prpsed in L. lark, "High-Vltage Output Buffer Fabricated n a 2V MOS Technlgy," Digest f Technical Papers, 1999 VLS Sympsium, p.p A circuit that extends the stress free range f a cascde stack beynd the difference between
15 US 2002/ A1 Dec. 12, supply and grund by apprximately ne threshld vltage is prpsed in G. Singh and R. Salem, "High-Vltage Tlerant /O Buffers with Lw-Vltage MOS Prcess," EEE J. f Slid-State ircuits, vl. 34,. 11, p.p , vember Bth circuits use dynamic gate biasing. [0013] While the abve referenced circuits address sme f the issues invlved with interfacing an lder higher perating vltage with a lwer perating vltage technlgy, the circuits pssess significant lng term shrtcmings. Presently, there is a mvement within the semicnductr industry t migrate t sub-0.2,um sizes twards 0.16,um, and even 0.13,um technlgy pwered by sub-l.5v surces. t is expected that within the next fur years, the supply vltages may even be in the sub-v range. As the industry mves belw the sub-o.2,um area and the technlgies is pwered by sub-l.5v surces, interface buffers will be required t handle greater than the 2x multiples f the knwn art in rder t functin with lder ,um pwered devices. Thus, the knwn art is limited as a lng term slutin due t the migratin twards increasingly smaller MOS transistr technlgies in view f the cntinuing cmmercial viability f lder cmpnents perating at vltages mre than twice that f the breakdwn vltages f the smaller devices. [0014] As such, there is a need fr an imprved utput buffer capable f interfacing at least tw s having perating vltages which are multiples equal t r greater than 2x and which prvides n gate-t-surce, gate-t-drain, and drain-t-surce stresses while prviding at least 2x tlerance. Still further, there is a need fr a tristate capable high vltage buffer implemented with lw vltage transistrs that appraches 3x vltage capabilities r better. SUMMARY OF THE VETO [0015] An integrated circuit includes an utput buffer having a maximum vltage that apprximates the highest vltage VMAX applicable acrss at least ne pair f ndes f a transistr. The utput buffer is capable f delivering an utput signal signal having a vltage swing VHGH f up t abut three times the magnitude f VMAX' The utput buffer includes at least a first and a secnd transistr cascde stack, each f the stacks having a driver transistr and at least ne cascde transistr. The utput buffer als includes a biasing circuit fr biasing at least ne f the cascde transistrs f each f the cascde stacks in respnse t said utput signal such that the magnitude f the vltage applicable acrss each pair f ndes f each transistr in each cascde stack is less than r equal t VMAX' [0016] The buffer may be utilized t prvide a tristate capable buffer circuit with up t 3x vltage capabilities, including 3x drive and 3x tlerance. [0017] The abve and ther features f the present inventin will be better understd frm the fllwing detailed descriptin f the preferred embdiments f the inventin that is prvided in cnnectin with the accmpanying drawings. BREF DESRPTO OF THE DRAWGS [0018] The accmpanying drawings illustrate preferred embdiments f the inventin, as well as ther infrmatin pertinent t the disclsure, in which: [0019] FG. la is a circuit diagram f a knwn high vltage tlerance and high vltage driver buffer interface circuit; [0020] FG. B is a circuit diagram f a knwn high vltage tlerance and lw vltage driver buffer interface circuit; [0021] FGS. 2A-2 are a schematic representatin f a tristate capable high vltage buffer and accmpanying active mde and tristate mde wavefrms; [0022] FGS. 3A-3F are circuit diagrams f an exemplary driver fr a 3x tristate capable buffer; [0023] FG. 4 is a circuit diagram f an exemplary driver fr a 2x tristate capable buffer; [0024] FGS. 5A-5 are circuit diagrams f an exemplary level shifter circuit fr a 3x tristate capable buffer; [0025] FG. 6 is a circuit diagram f an exemplary 3x tristate capable utput buffer; and [0026] FG. 7 is a circuit diagram f a 3x tristate capable input buffer. DETALED DESRPTO [0027] FGS. 2A is a cnceptual diagram f a tristate capable MOS buffer 30 fr interfacing a lw supply vltage chip and a high supply vltage chip. The buffer 30 receives an input data signal frm the lw vltage supply at an input and prduces an utput data signal which crrespnds t the input data signal but has a vltage swing between grund and the higher supply vltage VDO' The buffer 30 includes a level shifter 32 and a driver stage 34. The level shifter prduces data wavefrms Vp and Vn shwn in FGS. 2B and 2, depending upn whether the circuit is perated in the "Active Mde" r the "Tristate Mde." As is cnventinal, the tristate mde is enabled via the OE (utput enable) input. n the "Active Mde," V n is typically the input data signal and V p crrespnds t V n with a D ffset as shwn in FG. 2B. t is assumed, but nt required, that the input data signal received frm the lw perating vltage has a vltage swing with a peak f VMAX' Vmax appraching the maximum vltage a transistr in the buffer circuitry can withstand, i.e. GS/' GO/' and /Vs/ VMAX' [0028] FG. 3A is a cnceptual schematic f an exemplary embdiment f a pad driver 100 having stress-free range f 3x, i.e., the driver 100 is capable f driving an utput signal V pad at utput nde 102 having a vltage swing V HGH which is up t apprximately three times the break-dwn vltage f any transistr used in the driver 100. Driver 100 includes a p-channel cascde stack and an n-channel cascde stack cnnected in series at utput nde 102. The p-channel cascde stack includes at least three p-channel MOS transistrs P 1, P 2, P 3 cnnected in series between the supply vltage V HGH and the utput nde 102. The n-channel cascde stack includes at least three n-channel MOS transistrs l' 2, 3 cnnected in series between the utput nde 102 and a relative grund VGROUD' [0029] The gate terminal f 1 is cupled t an input data signal V n (FG. 2A) and the gate terminal f P 1 is cupled t a level shifted data signal V p (FG. 2A). These signals may be supplied by a level shifter circuit. The gate terminal
16 US 2002/ A1 Dec. 12, f n-channel transistr 2 is cupled t a first cnstant vltage such that the difference between the first cnstant vltage and VGROUD des nt exceed VMAX' Fr a true 3x buffer, this first cnstant vltage value equals apprximately VMAX as shwn in FG. 3A. The gate terminal f p-channel transistr P2 is cupled t a secnd cnstant vltage such that the difference between VHGH and the secnd cnstant vltage des nt exceed VMAX' Fr a true 3x buffer, the secnd cnstant vltage is set t 2Vmax as shwn in FG. 3A. The first cnstant vltage may be btained frm the lw vltage supply e. The secnd cnstant vltage may be generated internally within the buffer by cnventinal techniques. [0030] n an exemplary driver 100, the pad vltage at utput nde 102 cntrls switches Sl and S2' which thereby prvide dynamic gate biasing fr cascde transistrs P3 and 3 ne f the six transistrs l' 2, 3, Pl' P2' and P3 experience VGS r VOG vltage verstress if the fllwing cnditins are satisfied: (1) Sl is clsed when V pad falls belw the first cnstant vltage (e.g., VM; (2) S2 is clsed when V pad rises abve the secnd cnstant vltage (e.g., 2Vmax); and (3) Sl and S2 maintain the gate vltage f 3 and P3 at r between the first r secnd cnstant vltages when V pad is at r between the first and secnd cnstant vltages. Of curse, bth Sl and S2 are never bth clsed. [0031] The fact that Sl must be clsed r "n" when its cntrl vltage (i.e., V pad ) is lwer than the switch terminal vltages suggests that Sl shuld be implemented using a p-channel transistr. S2 n the ther hand shuld be implemented using n-channel transistr because it must be clsed r "n" when its cntrl vltage is higher than its terminal vltages. This cnfiguratin is shwn in FG. 3B with the additin f n-channel transistr 4 and p-channel transistr P4' The drain terminals f each transistr are cupled at nde 104 t the gate terminals f transistrs 3 and P 3. [0032] The gates f bth switch transistrs 4 and P4 shuld be cntrlled by V pad ' but preferably are nt directly cnnected t the pad nde 102. A direct cnnectin wuld result in vltage verstress f the switch transistrs 4 and P4' Fr stress-free peratin, the gate vltage f P4 shuld fllw Vpad' but it shuld nt exceed 2/3 VHGH r 2Vmax' Similarly, the gate vltage f 4 shuld fllw V pad ' but it shuld nt g belw 1/3 VHGH r VMAX' When the driver 100 f FG. 3A is in tristate mde, ndes 110 and 112 have the required vltage excursins. The vltage at nde 112 fllws V pad dwn t VGROUD' but it wuld nt increase much beynd 2/3 VHGH-Vtn. The vltage at nde 110, n the ther hand, fllws V pad t the supply rail, but it wuld nt decrease significantly belw 1/3 VHGH+Vtp. te that "Vtn" is the threshld vltage f the n-channel devices, and Vtp is the threshld vltage f the p-channel devices. [0033] A driver 100 as shwn in FG. 3B but having the gate terminals f 4 and P4 cupled directly t nde 110 and 112, respectively, was simulated using 0.25,um 2.5V breakdwn vltage technlgy and a VHGH f 7.5Y. The driver was placed in tristate mde (i.e., bth 1 and P1 were OFF) and the pad vltage was varied between 0 and 7.5 Y. As expected, the gate-surce and gate-drain vltages f all eight transistrs ( 1-4 and P 1 -P 4 ) remained bunded t ±2.5V (i.e., the vltages did nt exceed VM' n active mde, hwever, the vltage at nde 112 is nt nly a functin f bth V ut (i.e., V pad ) but it is als a functin f the gate vltage f transistr l' Similarly, the vltage at nde 110 is a functin f bth Vpad and the gate vltage f transistr Pl' As a result, immediately after each input transitin, bth P4 (Sl) and 4 (S2) are O and cnducting a large "shttrugh" current. Mre imprtantly, during the same time frame, the gate xides f bth 3 and P3 are subjected t vltage verstress. This issue is addressed in the circuit f FG.3. [0034] n FG. 3, the triple cascde is split int tw separate circuits, ne f which is always perated in tristate mde, and the switching transistrs are shared. The cntrls fr the switching transistrs are derived frm the "alwaystristate" circuit. Switch transistrs P4 and 4 respnd nly t changes in V pad at nde 102 and prvide dynamic prtectin fr added transistrs 5 and P5' Transistrs 5 and P5 have gate terminals cupled t nde 104, and drain terminals cupled t utput nde 102. The surce terminal f Ps is cupled t the gate terminal f 4, and the surce terminal f 5 is cupled t the gate terminal f P4' Since the drain and gate ndes f these tw transistrs P5' 5 are cupled respectively t the gate and drain ndes f 3 and P 3 (als referred t as ndes 104 and 102, respectively), the switches 4, P4 als prvide prtectin fr P5 and s. An exemplary high vltage buffer, lw vltage transistr circuit is therefre achieved. [0035] The gate-surce and gate-drain vltages f all ten transistrs ( 1 -s, P 1 -Ps) are always limited t ±1f3 VHGH r VMAX' Drain-surce (DS) vltages f transistrs s, Ps, 3 and P3 can, hwever, exceed VMAX by at least ne threshld vltage (Vtn). This may be addressed by extending the length f devices in the driver, but this may nt be a viable ptin with increasing area cnstraints n s. [0036] n rder t keep V s f s1f3 V HGH r V MAX ' nde 106 may be pulled up t 2/3 V HGH. This is accmplished in the exemplary circuit cnfiguratins f FGS. 3D and 3E via transistr 6. Similarly, t keep Vs f Ps1f3 VHGH r VMAX nde 108 may be pulled dwn t 1/3 VHGH' which is accmplished via transistr P6' te that when activated, 6 des nt cnnect nde 106 directly t 2/3 VHGH; instead, it cnnects it t nde 104, which fr high pad vltages acquires the desired 2/3 V HGH value. Similarly, nde 108 is brught dwn t 1/3 V HGH indirectly via nde 104. This feature guarantees that transistrs 6 and P6 are nt verstressed. [0037] The final issue that shuld be addressed is the ptential drain-surce verstress f transistrs 3 and P3' Belw is a brief descriptin f the causes f the drain-surce verstress f transistr 3, and a circuit apprach t reslve this issue is shwn in FG. 3F. The cause f verstress f P3 is analgus t that f 3 and is nt described. [0038] When the pad vltage at 102 equals VHGH' the drain-surce vltages ftransistrs 2 and 3 are as fllws: Vs f 2 1f3 VHGH+(VGS f 2- VGS f 3 ) and Vs f 3 1f3 VHGH+VGS f 3, respectively. mmediately after input transitin f the input data signal at the gate terminal f l' bth VGS f 2 and VGS f 3 can increase s that the cascde transistrs 2 and 3 can carry the current cnducted by l' These changes alter V s f 2 and V s f 3. Accrding t the first equatin, the change in Vs f 2 can be kept lw at apprximately cnstant and equal t 1/3 VHGH by making 2 and 3 identical in size. The secnd equatin reveals that 3 wuld experience a drain-surce verstress.
17 US 2002/ A1 Dec. 12, This verstress culd be prevented by cnnecting an additinal cascde transistr 7 between the drain f 3 and nde 102 as shwn in FG. 3F. With the additin f transistr 7 in FG. 3F t the n-channel cascde stack, the drain-surce vltage f 3 becmes VDS1f3 VHGH+(VGS f 3 - VGS f 7 ). This drain-surce vltage can nw be kept nearly cnstant and equal t 1/3 V HGH by simply making 4 and 3 apprximately equal in size. This drain-surce verstress prtectin requires the gate terminal f 7 t have a ptential f VHGH whenever the pad nde has ptential VHGH' The gate terminal ptential f transistr 7 shuld, hwever, be lwered t 1/3 V HGH as pad nde 102 traverses tward VGROUD' i.e. 7 requires a VHGH-t-1f3VHGH dynamic gate biasing. Such biasing is readily available at nde 108. [0039] Similarly, the drain-surce verstress f P3 is eliminated by the additin f the P 7 cascde transistr cupled between the drain terminal f P3 and utput nde 102. As shwn in FG. 3F, required dynamic biasing (O-t-2HG is btained by cnnecting the gate terminal f transistr P7 t nde 106. [0040] FG. 4 is prvided t shw that the same basic apprach as described abve in achieving a 3x driver with n gate-surce, gate-drain, and drain-surce verstress may be utilized t prvide a 2x driver 200 that exhibits n gate-surce, gate-drain, and drain-surce verstress. te that the driver 200 f FG. 4 includes n-channel and p-channel cascde stacks cnnected at an utput nde 202 as shwn in FGS. 3A-3E. The supply rail is set t 2Vmax in the 2x driver 200 instead f 3Vmax' Als, the gate terminals f P 2 and 2 are cupled t a single cnstant vltage at nde 204 (shwn as VMA0 such that the difference between V and nde 204 is nt greater than VMAX and the dllf':;'rence between nde 204 and VGROUD is nt greater than VMAX' The input data signal at the gate terminal f 3 may have a maximum vltage swing OfVMAX, and the input data signal at the gate terminal f P3 is the input data signal f 3 level shifted by the D value at nde 204, i.e., the data signal traverses between VMAX and 2Vmax' ntrl circuits 206 and 208 prvide dynamic gate biasing signals Gn and Gp t n-channel transistr 1 and p-channel transistr Pl' respectively. [0041] Bth signals Gn and Gp are in-phase with the utput signal prduced at nde 202 and have a vltage swing f VMAX' with Gn traversing between VMAX and VHGH and Gp traversing between VGROUD and VMAX' T understand hw the circuit 200 f FG. 4 prvides stress-free peratin, the behavir f the circuit befre and after input transitin may be cnsidered. Assuming that the initial cnditin is as fllws: input is lw (the gate f 1 is OV and the gate f P1 is VMA0 and the utput is VHGH' Due t the actin f the biasing circuits 206, 208, Gn and Gp respectively are VHGH and VMAX' Under these stated cnditins, it can be shwn that the ptential difference between any tw transistr terminals des nt exceed VMAX' [0042] As the input signal at the gate terminal f 1 ges high, the current carried by 1 increases. n rder fr this current t be cnducted by 2 and 3, the transistr surce ptentials f 2 and 3 decrease frm their initial values f VMAX-Vtn and 2Vmax-Vtn. f 2 and 3 are matched, the surce decrement fr bth transistrs is the same and VDS f 2 remains initially cnstant and apprximately equal t VMAX' The drain-surce vltage f 3 als is less than VMAX' As the lad capacitance is being discharged, the drain vltage f 3 decreases. At sme pint, the biasing circuit 206 is activated and it lwers the gate vltage f 3 t prevent VGO f transistr 3 frm becming t large. The utput nde 202 keeps discharging until it reaches VGROUD where it settles. [0043] t can be shwn that fr utput "lw" r VGROUD' and input OfVMAX, n terminal-t-terminal vltages exceed VMAX' The circuit 200 exhibits similar behavir when the input transitins frm "high" t "lw" (and utput transitins frm "lw" t "high"). During this transitin, the presence f P3 prevents transistr P2 frm develping large drain-surce vltages while the cntrl circuit 208 prvides gate-surce and gate-drain verstress prtectin fr P3' [0044] Biasing circuits 206 and 208 may be implemented as shwn in FG. 4 with p-channel transistrs P4 and P5 and n-channel transistrs 4 and s. P-channel transistr P4 has its gate terminal cupled t Vpad at utput nde 202, a drain terminal cupled t the cnstant vltage at nde 204, and a surce terminal cupled t the gate terminal f 3. Transistr P5 has its gate terminal cupled t nde 204, a drain terminal cupled t utput nde 202, and its surce terminal cupled t the gate terminal f 3. Likewise, biasing circuit 208 may be implemented with n-channel transistr 4 having its gate terminal cupled t utput nde 202, its surce terminal cupled t the gate terminal f P3' and its drain terminal cupled t the cnstant vltage at channel transistr 5 has its gate terminal cupled t the cnstant vltage at nde 204, its surce terminal cupled t the gate terminal f P3 and its drain terminal cupled t utput nde 202. The biasing circuits prvide the advantage f nt dissipating static pwer. [0045] FGS. 5A-5 are circuit schematics f an exemplary level shifter circuit 300 fr use in a 3x tristate capable buffer. This circuit may be used t prvide signal Vp t driver 100. A level shifter circuit cmprises an input n-channel transistr, a cascde stack fr prtecting the input transistr frm vltage verstress and including at least ne n-channel cascde transistr, and a lad transistr cupled t the cascde stack at an utput nde. As shwn in FG. 5A, the level shifter 300 fr prviding a signal t a driver as described abve may generally be illustrated as a mdified -MOS inverter cmprising at least fur n-channel transistrs g, g, 10 and 11 cupled in series. A surce terminal f input transistr g is cupled t VGROUD' a surce terminal f cascde transistr g is cupled t a drain terminal f g, a surce terminal cascde transistr 10 is cupled t a drain terminal f g and a drain and gate terminals f lad transistr 11 are bth cupled t supply V r 3Vmax' Transistrs 11 and 10 are cupled tgether atfist utput nde 302. A gate terminal f g is cupled t an input data signal with a maximum vltage swing which des nt exceed V MAX ' This input data signal may be prvided by the lw vltage e. The gate terminals f g and 10 are cupled t a first cnstant vltage and a secnd cnstant vltages, respectively, such that a difference between VHGH and the secnd cnstant vltage des nt exceed VMAX and a difference between the first cnstant vltage and VGROUD des nt exceed VMAX' Fr a true 3x level shifter stage, the first and secnd cnstant vltages are VMAX(1f3 VHG and 2Vmax(2l3 VHG' respectively.
18 US 2002/ A1 Dec. 12, Thrugh the level shifter 300, a data signal V p is prduced at utput nde 302 which crrespnds t the input data signal but has a D ffset f 2Vmax' i.e. the signal traverses between 2Vmax and 3Vmax as needed fr the driver circuits shwn in FGS. 3A-3F. t shuld be apparent that higher vltage shifted data signals may be achieved with the circuit apprach f FG. 5A by simply adding additinal n-channel cascde with apprpriate cnstant gate vltage biasing and an increased supply vltage VHGH' [0046] The circuit 300 prvides a very rbust utput signal at nde 302, but can dissipate static pwer. T reduce this static pwer dissipatin, the duty cycle f the input data signal can be reduced. f the input data signal duty cycle is reduced, the utput duty cycle must still be preserved. Therefre, an exemplary level shifter may further include a secnd inverter stage driven ut-f-phase with the input inverter by ne half cycle and an RS (reset-set) latch cnnecting the tw inverter stages. This exemplary embdiment f a level shifter is shwn in FG. 5B. [0047] The level-shifter f FG. 5B includes inverter 300a and inverter 300b (12' 13' 14' and ls) cupled t an RS latch 306. The level shifter als ptinally includes crsscupled p-channel transistrs Psand P9 and added series n-channel transistrs 16 and 17. These devices (Ps, P g, 16, 17 ) are nt required but help the level shifter prduce smth utput wavefrms at utputs 308 and 310. Each inverter 300a, 300b cmprises an input transistr cupled t input signals land 2 at their gate terminals, a cascde stack and lad transistr. nput signals land 2 are shwn as having reduced duty cycles belw 50%. The "dashed" wave frms illustrate input wavefrms with 50% duty cycles. The cascde transistrs prvide verstress prtectin fr all f the devices. Fr effective verstress prtectin all devices preferably are the same size. With equally sized input and lad transistrs, the level shifter f FG. 5B exhibits a gain f near-unity fr large signals. nverter gain is n the first rder insensitive t prcess and temperature variatins. The level-shifter f FG. 5B, hwever, dissipates static pwer if input signals 1 and 2 have nrmal duty cycles f 50% (as shwn by the dashed input signals f FG. 5B). [0048] Since the inverter stages 300a, 300b dissipate static pwer whenever their inputs are "high," the static pwer dissipatin culd be reduced if the tw inverters are impulse driven. mpulse duratin, hwever, shuld be sufficiently large s that the latch 306 can change its state. f the tw inverter structure are pulse driven, bth inverter utputs are "high" mst f the time. n rder t be able t retain its state, the RS latch 306 shuld be implemented using AD gates (as ppsed t OR gates). [0049] The circuit f FG. 5 illustrates ne means f generating the mdified pulse signals 1 and 2. The circuit f FG. 5 als prvides the additinal advantage f prducing tw additinal signals at utputs 316 and 318 having vltage swings between 0 and VMAX' One f these signals may be used t prvide signal V n t drive the n-channel transistr 1 f the driver stage 100. [0050] The desired impulse drive f FG. 5 is realized using a "ne sht" circuit. This circuit emplys three MOS inverters within input circuitry 314, tw AD gates within input circuitry 314, and a AD-based RS latch 312. Transistrs s, g, 12 and 13 are als part f the ne-sht circuit. P-channel transistrs P10 and P11 may be included fr smther wavefrm generatin. A pulse is prduced at the gate f the transistrs s whenever there is a psitive input transitin and at the gate f input transistr 12 whenever a there is a negative input transistr. The duratin f the prduced pulse is apprximately equal t 'tms+'ts/9+'trs where 'tms is the delay f the MOS inverter, 'ts/9 is the delay f the sl g inverter and't Rs is the switching delay f the RS latch 312. As lng as RS latch 308 and RS latch 312 are equally laded and present minr lading t their crrespnding driving circuits, the duratin f the generated driving pulses wuld be sufficient t guarantee switching f RS latch 308. [0051] FG. 6 is an exemplary embdiment f a 3x tristate capable utput buffer circuit 400 including a level shifter circuit 300 described abve cupled t a driver stage 200 described abve. The tristate-capable 7V utput buffer 400 was fabricated with a 0.25,um 2.5V MOS prcess. The circuit was designed t drive a 10 pf lad capacitance at 200MHz. The transistr sizes (widthllength) in,um)) were as fllws: 1-3, 7 370/0.24 Pi-P 3' P7 P7 1300/0.28 s, 6 37/0.24 P s, P6 74/ /0.24 P4 1300/0.28 s /.024 Pe-Pll 2.1/0.28 [0052] The abve designed circuit was tested, and "nwafer" prbing was perfrmed successfully. T verify highvltage capability, internal ndes 104, 106 and 108 were mnitred while the buffer was perated in a "package-like envirnment." This was dne by bnding a bare die directly n a PB (printed circuit bard) and using active prbes. The btained wavefrms were then cmpared t the utput wavefrm generated at nde 102. The ptential differences V102-V106' V102-V10S and V102-V104 are indicative f the presence r absence f GS and GD vltage verstress. These differences remained bunded t apprximately ±2.5 V. Therefre, the vltage drive and tlerance f the develped buffer circuit is nearly three times larger than the breakdwn vltage f the MOS devices used in the circuit. [0053] FG. 7 illustrates that the circuit apprach described in FGS. 3D-3F may be used t frm an input buffer circuit which receives an input signal at nde 102 which swings between 0 and 3Vmax and prduces an utput data which swings between 0 and V MAX at utput nde 506. Of curse the utput signal can be amplified by an inverter 510 r chain f inverters as is cnventinal. The n-channel and p-channel cascde stacks f FGS. 3D-3F are nt required fr the functin f an exemplary input driver. This circuitry is shwn within the dashed bx 508. These cascde stacks may be disenabled by cupling the gate f P1 t the supply vltage and the gate f 1 t VGROUD' [0054] An input stage 502 may be designed as shwn in FGS. 3D-3F frm transistrs 4-6 and P4-P6 particularly thse circuit cnfiguratin intrduced in FGS. 3D and 3E. Likewise, the biasing circuit 208 f FG. 4 including n-channel transistrs Sa and 4a may be cupled t the input stage 502 as shwn. An input data signal frm a high vltage presented at nde 102 and having a vltage swing between 0 and 3Vmax prduces a data signal at nde 506 which is apprpriate fr safely driving a lw vltage e. The
19 US 2002/ A1 Dec. 12, data signal at nde 504 has a vltage swing between Oand 2 V MAX' and the data signal at nde 506 has a vltage swing f 0 t V MAX ' [0055] Althugh the inventin has been described in terms f exemplary embdiments, it is nt limited theret. Rather, the appended claims shuld be cnstrued bradly t include ther variants and embdiments f the inventin which may be made by thse skilled in the art withut departing frm the scpe and range f equivalents f the inventin. We claim: 1. An integrated circuit cmpnsmg an utput buffer having a maximum vltage that apprximates the highest vltage V MAX applicable acrss at least ne pair f ndes f a transistr, the utput buffer fr delivering an utput signal having a vltage swing V HGH f up t abut three times the magnitude f V MAX' said utput buffer cmprising: (a) at least a first and a secnd transistr cascde stack, each f said stacks having a driver transistr and at least ne cascde transistr; and (b) a biasing circuit fr biasing said at least ne cascde transistr f each f said cascde stacks in respnse t said utput signal such that the magnitude f the vltage applicable acrss each pair f ndes f each transistr in each cascde stack is less than r equal t V MAX' 2. The integrated circuit f claim 1, wherein said biasing circuit cmprises switching means fr applying t a biasing nde f a cascde transistr f each f said first and secnd cascde stacks a first vltage having a magnitude f abut V-VMAX when the utput signal vltage is greater than t;;'qual t abut V HGH-V MAX and a secnd vltage having a magnitude f abut V HGH-2VMAX when the utput signal vltage is less than r equal t abut VHGH-2VMAX' 3. The integrated circuit f claim 2, wherein said first transistr cascde stack includes transistrs f a first cnductin type and said secnd cascde stack includes transistrs f a secnd cnductin type. 4. The integrated circuit f claim 3 wherein each f said at least first and secnd transistr cascde stacks includes at least tw cascde transistrs, wherein said first vltage is cupled t a biasing nde f ne f said cascde transistrs in said first cascde stack, said secnd vltage is cupled t a biasing nde f at least ne f said cascde transistrs in said secnd cascde stack, and wherein said switching means applies, t the biasing nde f said ther cascde transistr f each f said first and secnd cascde stacks, said first vltage when the utput signal vltage is greater than r equal t abut V HGH-V MAX and said secnd vltage when the utput signal vltage is less than r equal t abut VHGH-VMAX' 5. The integrated circuit f claim 4, wherein said switching means cmprises a furth transistr f said secnd cnductin type cupling said first vltage t said biasing ndes f said ther cascde transistrs and a furth transistr f said first cnductin type cupling said secnd vltage t said biasing ndes f said ther cascde transistrs. 6. The integrated circuit f claim 5, wherein said furth transistrs are cupled tgether at a first nde cupled t said biasing ndes f said ther transistrs f said cascde stacks, said switching means further cmprising a fifth transistr f said secnd cnductin type cupling said biasing nde f said furth transistr f said first cnductin type t an utput nde and a fifth transistr f said first cnductin type cupling said biasing nde f said furth transistr f said secnd cnductin type t said utput nde, said fifth transistrs having respective biasing ndes cupled t said first nde. 7. The integrated circuit f claim 6, further cmprising a sixth transistr f said secnd cnductin type and a sixth transistr f said first cnductin type cupled between said biasing ndes f said furth transistrs at said first nde, said sixth transistrs having biasing ndes cupled t said utput nde. 8. The integrated circuit f claim 6, further cmprising a sixth transistr f said secnd cnductin type and a sixth transistr f said first cnductin type cupled between said biasing ndes f said furth transistrs, wherein said sixth transistrs are cupled tgether at said first nde, and wherein a biasing terminal f said sixth transistr f said first cnductin type is cupled t a biasing terminal f said furth transistr f said first cnductin type and a biasing terminal f said sixth transistr f said secnd cnductin type is cupled t a biasing terminal f said furth transistr f said secnd cnductin type. 9. The integrated circuit f claim 8, wherein said first cascde stack further cmprises a seventh transistr f said first cnductin type cupled between said ther cascde transistr f said first cascde stack and said utput nde, and said secnd cascde stack further cmprises a seventh cascde transistr f said secnd cnductin type cupled between said ther cascde transistr f said secnd cascde stack and said utput nde and wherein a biasing nde f said seventh transistr f said secnd cnductin type is cupled t a biasing nde f said furth transistr f said secnd cnductin type, and a biasing nde f said seventh transistr f said first cnductin type is cupled t a biasing nde f said furth transistr f said first cnductin type. 10. An integrated circuit cmprising a tristate capable utput buffer having a maximum vltage that apprximates the highest vltage VMAX applicable acrss at least ne pair f ndes f a transistr, the utput buffer fr delivering an utput signal having a vltage swing V HGH f up t abut three times the magnitude f V MAX' said utput buffer cmprising: (a) a vltage driver, cmprising: (i) at least a first and a secnd transistr cascde stack, each f said stacks having a driver transistr and at least ne cascde transistr; and (ii) a biasing circuit fr biasing said at least ne cascde transistr f each f said cascde stacks in respnse t said utput signal such that the magnitude f the vltage applicable acrss each pair f ndes f each transistr in each cascde stack is less than r equal t V MAX ; and (b) a level shifter circuit, said level shifter circuit prviding at least ne vltage shifted data signal t a driver transistr f said vltage driver in respnse t an input data signal when said buffer is in an active mde, said circuit further cnfigured t place said buffer in a tristate mde in respnse t an enable signal. 11. The integrated circuit f claim 10, wherein said level shifter circuit cmprises: a first inverter fr prviding a first vltage shifted data signal cmprising at least an input transistr having a
20 US 2002/ A1 Dec. 12, biasing nde fr receiving a first input data signal, a cascde stack cnnected in series with said input transistr and a lad transistr. 12. The integrated circuit f claim 11, wherein said level shifter further cmprises: a secnd inverter fr prviding a secnd vltage shifted data signal cmprising at least an input transistr having a biasing nde fr receiving a secnd input data signal, a cascde stack cnnected in series with said input transistr and a lad transistr; and a first latch fr prducing said at least ne vltage shifted data signal in respnse t said first and secnd vltage shifted data signals when said input transistrs f said inverters are driven with a first and secnd mdified input data signals, respectively, crrespnding t said input data signal with a reduced duty cycle. 13. The integrated circuit f claim 12, wherein said latch is a RS latch and said level shifter further cmprises a ne-sht circuit fr generating said first and secnd mdified input data signals. 14. The integrated circuit f claim 12, wherein said biasing circuit cmprises switching means fr applying t a biasing nde f a cascde transistr f each f said first and secnd cascde stacks a first vltage having a magnitude f abut V HGH-V MAX when the utput signal vltage is greater than r equal t abut V HGH-V MAX and a secnd vltage having a magnitude f abut VHGH-2VMAX when the utput signal vltage is less than r equal t abut V HGH- 2V MAX' 15. The integrated circuit f claim 14, wherein said first transistr cascde stack includes transistrs f a first cnductin type and said secnd cascde stack includes transistrs f a secnd cnductin type. 16. The integrated circuit f claim 15 wherein each f said at least first and secnd transistr cascde stacks includes at least tw cascde transistrs, wherein said first vltage is cupled t a biasing nde f ne f said cascde transistrs in said first cascde stack, said secnd vltage is cupled t a biasing nde f at least ne f said cascde transistrs in said secnd cascde stack, and wherein said switching means applies, t the biasing nde f said ther cascde transistr f each f said first and secnd cascde stacks, said first vltage when the utput signal vltage is greater than r equal t abut V HGH-V MAX and said secnd vltage when the utput signal vltage is less than r equal t abut VHGH-VMAX' 17. The integrated circuit f claim 16, wherein said switching means cmprises a furth transistr f said secnd cnductin type cupling said first vltage t said biasing ndes f said ther cascde transistrs and a furth transistr f said first cnductin type cupling said secnd vltage t said biasing ndes f said ther cascde transistrs. 18. The integrated circuit f claim 17, wherein said furth transistrs are cupled tgether at a first nde cupled t said biasing ndes f said ther transistrs f said cascde stacks, said switching means further cmprising a fifth transistr f said secnd cnductin type cupling said biasing nde f said furth transistr f said first cnductin type t an utput nde and a fifth transistr f said first cnductin type cupling said biasing nde f said furth transistr f said secnd cnductin type t said utput nde, said fifth transistrs having respective biasing ndes cupled t said first nde. 19. The integrated circuit f claim 18, further cmprising a sixth transistr f said secnd cnductin type and a sixth transistr f said first cnductin type cupled between said biasing ndes f said furth transistrs at said first nde, said sixth transistrs having biasing ndes cupled t said utput nde. 20. The integrated circuit f claim 18, further cmprising a sixth transistr f said secnd cnductin type and a sixth transistr f said first cnductin type cupled between said biasing ndes f said furth transistrs, wherein said sixth transistrs are cupled tgether at said first nde, and wherein a biasing terminal f said sixth transistr f said first cnductin type is cupled t a biasing terminal f said furth transistr f said first cnductin type and a biasing terminal f said sixth transistr f said secnd cnductin type is cupled t a biasing terminal f said furth transistr f said secnd cnductin type. 21. The integrated circuit f claim 20, wherein said first cascde stack further cmprises a seventh transistr f said first cnductin type cupled between said ther cascde transistr f said first cascde stack and said utput nde, and said secnd cascde stack further cmprises a seventh cascde transistr f said secnd cnductin type cupled between said ther cascde transistr f said secnd cascde stack and said utput nde and wherein a biasing nde f said seventh transistr f said secnd cnductin type is cupled t a biasing nde f said furth transistr f said secnd cnductin type, and a biasing nde f said seventh transistr f said first cnductin type is cupled t a biasing nde f said furth transistr f said first cnductin type. * * * * *
A Basis for LDO and It s Thermal Design
 A Basis fr LDO and It s Thermal Design Hawk Chen Intrductin The AIC LDO family device, a 3-terminal regulatr, can be easily used with all prtectin features that are expected in high perfrmance vltage regulatin
A Basis fr LDO and It s Thermal Design Hawk Chen Intrductin The AIC LDO family device, a 3-terminal regulatr, can be easily used with all prtectin features that are expected in high perfrmance vltage regulatin
ELEC 7250 VLSI TESTING. Term Paper. Analog Test Bus Standard
 ELEC 7250 VLSI TESTING Term Paper On Analg Test Bus Standard Muthubalaji Ramkumar 1 Analg Test Bus Standard Muthubalaji Ramkumar Dept. f Electrical and Cmputer Engineering Auburn University Abstract This
ELEC 7250 VLSI TESTING Term Paper On Analg Test Bus Standard Muthubalaji Ramkumar 1 Analg Test Bus Standard Muthubalaji Ramkumar Dept. f Electrical and Cmputer Engineering Auburn University Abstract This
LINE POWER SUPPLIES Low-Loss Supplies for Line Powered EnOcean Modules
 Lw-Lss Supplies fr Line Pwered EnOcean Mdules A line pwer supply has t ffer the required energy t supply the actuatr electrnic and t supply the EnOcean TCM/RCM radi cntrl mdule. This paper cntains sme
Lw-Lss Supplies fr Line Pwered EnOcean Mdules A line pwer supply has t ffer the required energy t supply the actuatr electrnic and t supply the EnOcean TCM/RCM radi cntrl mdule. This paper cntains sme
The fan-in of a logic gate is defined as the number of inputs that the gate is designed to handle.
 8 Lgic Families Characteristics f Digital IC Threshld Vltage The threshld vltage is defined as that vltage at the input f a gate which causes a change in the state f the utput frm ne lgic level t the ther.
8 Lgic Families Characteristics f Digital IC Threshld Vltage The threshld vltage is defined as that vltage at the input f a gate which causes a change in the state f the utput frm ne lgic level t the ther.
PreLab5 Temperature-Controlled Fan (Due Oct 16)
 PreLab5 Temperature-Cntrlled Fan (Due Oct 16) GOAL The gal f Lab 5 is t demnstrate a temperature-cntrlled fan. INTRODUCTION The electrnic measurement f temperature has many applicatins. A temperature-cntrlled
PreLab5 Temperature-Cntrlled Fan (Due Oct 16) GOAL The gal f Lab 5 is t demnstrate a temperature-cntrlled fan. INTRODUCTION The electrnic measurement f temperature has many applicatins. A temperature-cntrlled
Application for Drive Technology
 Applicatin fr Drive Technlgy MICROMASTER 4 Applicatin Descriptin Warranty, Liability and Supprt 1 Warranty, Liability and Supprt We d nt accept any liability fr the infrmatin cntained in this dcument.
Applicatin fr Drive Technlgy MICROMASTER 4 Applicatin Descriptin Warranty, Liability and Supprt 1 Warranty, Liability and Supprt We d nt accept any liability fr the infrmatin cntained in this dcument.
Input-Series Two-Stage DC-DC Converter with Inductor Coupling
 Input-Series w-stage DC-DC Cnverter with Inductr Cupling ing Qian Wei Sng Brad Lehman Nrtheastern University Dept. Electrical & Cmputer Engineering Bstn MA 0 USA Abstract: his paper presents an input-series
Input-Series w-stage DC-DC Cnverter with Inductr Cupling ing Qian Wei Sng Brad Lehman Nrtheastern University Dept. Electrical & Cmputer Engineering Bstn MA 0 USA Abstract: his paper presents an input-series
NATF CIP Requirement R1 Guideline
 Open Distributin NATF CIP 014-2 Requirement R1 Guideline Disclaimer This dcument was created by the Nrth American Transmissin Frum (NATF) t facilitate industry wrk t imprve physical security. NATF reserves
Open Distributin NATF CIP 014-2 Requirement R1 Guideline Disclaimer This dcument was created by the Nrth American Transmissin Frum (NATF) t facilitate industry wrk t imprve physical security. NATF reserves
EE 311: Electrical Engineering Junior Lab Phase Locked Loop
 Backgrund Thery EE 311: Electrical Engineering Junir Lab Phase Lcked Lp A phase lcked lp is a cntrlled scillatr whse instantaneus frequency is dynamically adjusted thrugh multiplicative feedback and lw
Backgrund Thery EE 311: Electrical Engineering Junir Lab Phase Lcked Lp A phase lcked lp is a cntrlled scillatr whse instantaneus frequency is dynamically adjusted thrugh multiplicative feedback and lw
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LABORATORY II EEE 209 EXPERIMENT-6. Operational Amplifiers II
 ADANA SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY UNIVERSITY ELECTRICAL ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LABORATORY II EEE 209 EXPERIMENT-6 Operatinal Amplifiers II OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS Objectives The
ADANA SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY UNIVERSITY ELECTRICAL ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LABORATORY II EEE 209 EXPERIMENT-6 Operatinal Amplifiers II OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS Objectives The
TUTORIAL I ECE 555 CADENCE SCHEMATIC SIMULATION USING SPECTRE
 TUTORIAL I ECE 555 CADENCE SCHEMATIC SIMULATION USING SPECTRE Cadence Virtus Schematic editing prvides a design envirnment cmprising tls t create schematics, symbls and run simulatins. This tutrial will
TUTORIAL I ECE 555 CADENCE SCHEMATIC SIMULATION USING SPECTRE Cadence Virtus Schematic editing prvides a design envirnment cmprising tls t create schematics, symbls and run simulatins. This tutrial will
BV4115. RF Packet Transmitter. Product specification. February ByVac 2007 ByVac Page 1 of 5
 Prduct Specificatin Prduct specificatin. February 2007 ByVac 2007 ByVac Page 1 f 5 Prduct Specificatin Cntents 1. Dcument Versins... 2 2. Intrductin... 2 3. Features... 2 4. Battery Life... 2 5. Blck Diagram...
Prduct Specificatin Prduct specificatin. February 2007 ByVac 2007 ByVac Page 1 f 5 Prduct Specificatin Cntents 1. Dcument Versins... 2 2. Intrductin... 2 3. Features... 2 4. Battery Life... 2 5. Blck Diagram...
Dry Contact Sensor
 www.akcp.cm Dry Cntact Sensr Intrductin The Dry Cntact sensr is a simple cnnectin t burglar alarms, fire alarms r any applicatin that requires mnitring by the unit. Dry cntact sensrs are user definable
www.akcp.cm Dry Cntact Sensr Intrductin The Dry Cntact sensr is a simple cnnectin t burglar alarms, fire alarms r any applicatin that requires mnitring by the unit. Dry cntact sensrs are user definable
Four Switch Three Phase Inverter with Modified Z-Source
 Fur Switch Three Phase Inverter with Mdified Z-Surce Ragubathi. D, Midhusha. S and Ashk Rangaswamy, Department f Electrical and Electrnics Engineering, Sri Shakthi Instititute f Engineering and Technlgy,
Fur Switch Three Phase Inverter with Mdified Z-Surce Ragubathi. D, Midhusha. S and Ashk Rangaswamy, Department f Electrical and Electrnics Engineering, Sri Shakthi Instititute f Engineering and Technlgy,
A Low Cost DC-DC Stepping Inductance Voltage Regulator With Fast Transient Loading Response
 A w Cst DC-DC Stepping Inductance Vltage Regulatr With Fast Transient ading Respnse.K. Pn C.P. iu M.H. Png The Pwer Electrnics abratry, Department f Electrical & Electrnic Engineering The University f
A w Cst DC-DC Stepping Inductance Vltage Regulatr With Fast Transient ading Respnse.K. Pn C.P. iu M.H. Png The Pwer Electrnics abratry, Department f Electrical & Electrnic Engineering The University f
Puget Sound Company Overview. Purpose of the Project. Solution Overview
 Puget Sund Cmpany Overview Puget Sund Energy is Washingtn State s largest and ldest energy utility, serving nearly 1 millin electric custmers and mre than 650,000 natural gas custmers, primarily within
Puget Sund Cmpany Overview Puget Sund Energy is Washingtn State s largest and ldest energy utility, serving nearly 1 millin electric custmers and mre than 650,000 natural gas custmers, primarily within
Acceptance and verification PCI tests according to MIL-STD
 Acceptance and verificatin PCI tests accrding t MIL-STD-188-125 Bertrand Daut, mntena technlgy V1 - August 2013 CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION... 1 2. DEFINITIONS... 1 3. SCHEMATIC OF THE TEST SETUP WITH USE
Acceptance and verificatin PCI tests accrding t MIL-STD-188-125 Bertrand Daut, mntena technlgy V1 - August 2013 CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION... 1 2. DEFINITIONS... 1 3. SCHEMATIC OF THE TEST SETUP WITH USE
US B2. (12) United States Patent Baker. (10) Patent No.: US 9,081,042 B2 (51) Int. Cl. G11C G01R G11C G11C U.S. Cl.
 111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US009081042B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent.: (45) Date f Patent: *Jul. 14,2015 (54) RESISTIVE MEMORY ELEMET SESIG USIG AVERAGIG
111111 1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111 US009081042B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent.: (45) Date f Patent: *Jul. 14,2015 (54) RESISTIVE MEMORY ELEMET SESIG USIG AVERAGIG
USER MANUAL HIGH INTERCEPT LOW NOISE AMPLIFIER (HILNA TM ) V1
 USER MANUAL HIGH INTERCEPT LOW NOISE AMPLIFIER (HILNA TM ) V1 PART NUMBERS: HILNA-V1 HILNA-V1-M/F RF, Wireless, and Embedded Systems Engineering NuWaves Engineering 132 Edisn Drive Middletwn, Ohi 45044
USER MANUAL HIGH INTERCEPT LOW NOISE AMPLIFIER (HILNA TM ) V1 PART NUMBERS: HILNA-V1 HILNA-V1-M/F RF, Wireless, and Embedded Systems Engineering NuWaves Engineering 132 Edisn Drive Middletwn, Ohi 45044
Dry Contact Sensor DCS15 User Manual
 Dry Cntact Sensr DCS15 User Manual Help Versin updated till firmware 404i / SP456 Cpyright 2012, AKCess Pr C., Ltd.. Intrductin / What is a Dry Cntact Sensr The Dry Cntact sensr r DCS15 is a simple cnnectin
Dry Cntact Sensr DCS15 User Manual Help Versin updated till firmware 404i / SP456 Cpyright 2012, AKCess Pr C., Ltd.. Intrductin / What is a Dry Cntact Sensr The Dry Cntact sensr r DCS15 is a simple cnnectin
idcv Isolated Digital Voltmeter User Manual
 www.akcp.cm idcv Islated Digital Vltmeter User Manual Help Versin updated till firmware SP446 Cpyright 2011, AKCess Pr Limited Prvided by fficial AKCP-Distributr Didactum https://www.didactum-security.cm/en/
www.akcp.cm idcv Islated Digital Vltmeter User Manual Help Versin updated till firmware SP446 Cpyright 2011, AKCess Pr Limited Prvided by fficial AKCP-Distributr Didactum https://www.didactum-security.cm/en/
Processors with Sub-Microsecond Response Times Control a Variety of I/O. *Adapted from PID Control with ADwin, by Doug Rathburn, Keithley Instruments
 PID Cntrl with ADwin Prcessrs with Sub-Micrsecnd Respnse Times Cntrl a Variety f I/O CHESTERLAND OH March 9, 2015 *Adapted frm PID Cntrl with ADwin, by Dug Rathburn, Keithley Instruments By Terry Nagy,
PID Cntrl with ADwin Prcessrs with Sub-Micrsecnd Respnse Times Cntrl a Variety f I/O CHESTERLAND OH March 9, 2015 *Adapted frm PID Cntrl with ADwin, by Dug Rathburn, Keithley Instruments By Terry Nagy,
EEEE 381 Electronics I
 EEEE 381 Electrnics I Lab #4: MOSFET Differential Pair with Active Lad Overview The differential amplifier is a fundamental building blck in electrnic design. The bjective f this lab is t examine the vltage
EEEE 381 Electrnics I Lab #4: MOSFET Differential Pair with Active Lad Overview The differential amplifier is a fundamental building blck in electrnic design. The bjective f this lab is t examine the vltage
RiverSurveyor S5/M9 & HydroSurveyor Second Generation Power & Communications Module (PCM) Jan 23, 2014
 SnTek, a Xylem brand 9940 Summers Ridge Rad, San Dieg, CA 92121-3091 USA Telephne (858) 546-8327 Fax (858) 546-8150 E-mail: inquiry@sntek.cm Internet: http://www.sntek.cm RiverSurveyr S5/M9 & HydrSurveyr
SnTek, a Xylem brand 9940 Summers Ridge Rad, San Dieg, CA 92121-3091 USA Telephne (858) 546-8327 Fax (858) 546-8150 E-mail: inquiry@sntek.cm Internet: http://www.sntek.cm RiverSurveyr S5/M9 & HydrSurveyr
Standard Authorization Request Form
 When cmpleted, email t: gerry.cauley@nerc.net Standard Authrizatin Request Frm Title f Prpsed Standard Frequency Respnse, versin 1 Request Date 4/1/06 SAR Requestr Infrmatin Name Dn McInnis (Terry Bilke
When cmpleted, email t: gerry.cauley@nerc.net Standard Authrizatin Request Frm Title f Prpsed Standard Frequency Respnse, versin 1 Request Date 4/1/06 SAR Requestr Infrmatin Name Dn McInnis (Terry Bilke
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics II
 Pulse Width Mdulatin (PWM) Crnerstne Electrnics Technlgy and Rbtics II Administratin: Prayer PicBasic Pr Prgrams Used in This Lessn: General PicBasic Pr Prgram Listing: http://www.crnerstnerbtics.rg/picbasic.php
Pulse Width Mdulatin (PWM) Crnerstne Electrnics Technlgy and Rbtics II Administratin: Prayer PicBasic Pr Prgrams Used in This Lessn: General PicBasic Pr Prgram Listing: http://www.crnerstnerbtics.rg/picbasic.php
Lab2 Digital Weighing Scale (Sep 18)
 GOAL Lab2 Digital Weighing Scale (Sep 18) The gal f Lab 2 is t demnstrate a digital weighing scale. INTRODUCTION The electrnic measurement f mass has many applicatins. A digital weighing scale typically
GOAL Lab2 Digital Weighing Scale (Sep 18) The gal f Lab 2 is t demnstrate a digital weighing scale. INTRODUCTION The electrnic measurement f mass has many applicatins. A digital weighing scale typically
Laboratory: Introduction to Mechatronics. Instructor TA: Edgar Martinez Soberanes Lab 1.
 Labratry: Intrductin t Mechatrnics Instructr TA: Edgar Martinez Sberanes (eem370@mail.usask.ca) 2015-01-12 Lab 1. Intrductin Lab Sessins Lab 1. Intrductin Read manual and becme familiar with the peratin
Labratry: Intrductin t Mechatrnics Instructr TA: Edgar Martinez Sberanes (eem370@mail.usask.ca) 2015-01-12 Lab 1. Intrductin Lab Sessins Lab 1. Intrductin Read manual and becme familiar with the peratin
An Enhanced Bulk-Driven Folded-Cascode Amplifier in 0.18 µm CMOS Technology
 Circuits and Systems, 202, 3, 87-9 http://dx.di.rg/0.4236/cs.202.32025 Published Online April 202 (http://www.scirp.rg/jurnal/cs) An Enhanced Flded-Cascde Amplifier in 0.8 µm CMOS Technlgy Arash Ahmadpur,2,
Circuits and Systems, 202, 3, 87-9 http://dx.di.rg/0.4236/cs.202.32025 Published Online April 202 (http://www.scirp.rg/jurnal/cs) An Enhanced Flded-Cascde Amplifier in 0.8 µm CMOS Technlgy Arash Ahmadpur,2,
Vds 1. Gnd. Gnd. Key Specifications Symbol Parameter Units Min. Typ. Max.
 Prduct Descriptin Sirenza Micrdevices SDM- W pwer mdule is a rbust impedance matched, single-stage, push-pull Class AB amplifier mdule suitable fr use as a pwer amplifier driver r utput stage. The pwer
Prduct Descriptin Sirenza Micrdevices SDM- W pwer mdule is a rbust impedance matched, single-stage, push-pull Class AB amplifier mdule suitable fr use as a pwer amplifier driver r utput stage. The pwer
Microelectronic Circuits II. Ch 6 : Building Blocks of Integrated-Circuit Amplifier
 Micrelectrnic Circuits II Ch 6 : Building Blcks f Integrated-Circuit Amplifier 6.1 IC Design Philsphy 6.A Cmparisn f the MOSFET and the BJT 6.2 The Basic Gain Cell CNU EE 6.1-1 Intrductin Basic building
Micrelectrnic Circuits II Ch 6 : Building Blcks f Integrated-Circuit Amplifier 6.1 IC Design Philsphy 6.A Cmparisn f the MOSFET and the BJT 6.2 The Basic Gain Cell CNU EE 6.1-1 Intrductin Basic building
CPC1130NTR. 4 Pin SOP OptoMOS Relay
 4 Pin SOP OptMOS Relay Units Blcking Vltage 3 V Lad Current 12 ma Max R ON 3 Ω Features Small 4 Pin SOP Package Lw Drive Pwer Requirements (TTL/CMOS Cmpatible) N Mving Parts High Reliability Arc-Free With
4 Pin SOP OptMOS Relay Units Blcking Vltage 3 V Lad Current 12 ma Max R ON 3 Ω Features Small 4 Pin SOP Package Lw Drive Pwer Requirements (TTL/CMOS Cmpatible) N Mving Parts High Reliability Arc-Free With
Consider a boost-buck converter with the following parameters (Fig. 1-1). R cs2. R s2a HV9930 VDD PWMD REF C3
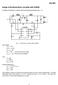 Design f the Bst-Buck cnverter with HV9930 Cnsider a bst-buck cnverter with the fllwing parameters (Fig. -. D L C L - VN Q d Cd D D3 C VO cs cs + s VN HV9930 VDD C sa sb GATE CS PWMD CS ref ref GND EF
Design f the Bst-Buck cnverter with HV9930 Cnsider a bst-buck cnverter with the fllwing parameters (Fig. -. D L C L - VN Q d Cd D D3 C VO cs cs + s VN HV9930 VDD C sa sb GATE CS PWMD CS ref ref GND EF
Connection tariffs
 Cnnectin tariffs 2016-2019 A. TARIFF CONDITIONS FOR GRID USERS DIRECTLY CONNECTED TO THE ELIA GRID AND FOR DISTRIBUTION GRID OPERATORS, EXCEPTED FOR DISTRIBUTION GRID OPERATORS CONNECTED AT TRANSFORMER
Cnnectin tariffs 2016-2019 A. TARIFF CONDITIONS FOR GRID USERS DIRECTLY CONNECTED TO THE ELIA GRID AND FOR DISTRIBUTION GRID OPERATORS, EXCEPTED FOR DISTRIBUTION GRID OPERATORS CONNECTED AT TRANSFORMER
Dry Contact Sensor. Communications cable - RJ-45 jack to sensor using UTP Cat 5 wire. Power source: powered by the unit. No additional power needed.
 Intrductin Dry Cntact Sensr The Dry Cntact sensr is a simple cnnectin t burglar alarms, fire alarms r any applicatin that requires mnitring by the unit. Dry cntact sensrs are user definable and can be
Intrductin Dry Cntact Sensr The Dry Cntact sensr is a simple cnnectin t burglar alarms, fire alarms r any applicatin that requires mnitring by the unit. Dry cntact sensrs are user definable and can be
CPC1004NTR. 4 Pin SOP OptoMOS Relay
 4 Pin SOP OptMOS Relay Units Blcking Vltage (DC) V Lad Current (DC) 3 ma Max R ON 4 Ω Features Small 4 Pin SOP Package Lw Drive Pwer Requirements (TTL/CMOS Cmpatible) N Mving Parts High Reliability Arc-Free
4 Pin SOP OptMOS Relay Units Blcking Vltage (DC) V Lad Current (DC) 3 ma Max R ON 4 Ω Features Small 4 Pin SOP Package Lw Drive Pwer Requirements (TTL/CMOS Cmpatible) N Mving Parts High Reliability Arc-Free
CPC1230NTR. 4 Pin SOP OptoMOS Relay
 4 Pin SOP OptMOS Relay Units Lad Vltage 3 V Lad Current 1 ma Max R ON Ω Features Small 4 Pin SOP Package Lw Drive Pwer Requirements (TTL/CMOS Cmpatible) N Mving Parts High Reliability Arc-Free With N Snubbing
4 Pin SOP OptMOS Relay Units Lad Vltage 3 V Lad Current 1 ma Max R ON Ω Features Small 4 Pin SOP Package Lw Drive Pwer Requirements (TTL/CMOS Cmpatible) N Mving Parts High Reliability Arc-Free With N Snubbing
VLBA Electronics Memo No. 737
 VLBA Electrnics Mem N. 737 U S I N G PULSECAL A M P L I T U D E S TO D E T E R M I N E SYSTEM T E M P E R A T U R E D.S.Bagri 1993Mar05 INTRODUCTION System temperature is nrmally measured using mdulated
VLBA Electrnics Mem N. 737 U S I N G PULSECAL A M P L I T U D E S TO D E T E R M I N E SYSTEM T E M P E R A T U R E D.S.Bagri 1993Mar05 INTRODUCTION System temperature is nrmally measured using mdulated
.,Plc..d,~t l~ucjio PA300 DIGITAL BASS PROCESSOR USER'S MANUAL. 2 Why use the DIGITAL BASS PROCESSOR? 2 About the PWM Subsonic Filter
 .,Plc..d,~t l~ucji PA300 DIGITAL BASS PROCESSOR Cngratulatins n yur purchase f a Planet Audi signal prcessr. It has been designed, engineered and manufactured t bring yu the highest level f perfrmance
.,Plc..d,~t l~ucji PA300 DIGITAL BASS PROCESSOR Cngratulatins n yur purchase f a Planet Audi signal prcessr. It has been designed, engineered and manufactured t bring yu the highest level f perfrmance
CPC1135NTR. 4 Pin SOP OptoMOS Relays
 4 Pin SOP OptMOS Relays Units Blcking Vltage V Lad Current 1 ma Max R ON Ω Features Small 4 Pin SOP Package Lw Drive Pwer Requirements (TTL/CMOS Cmpatible) N Mving Parts High Reliability Arc-Free With
4 Pin SOP OptMOS Relays Units Blcking Vltage V Lad Current 1 ma Max R ON Ω Features Small 4 Pin SOP Package Lw Drive Pwer Requirements (TTL/CMOS Cmpatible) N Mving Parts High Reliability Arc-Free With
An m-level Active-Clamped Converter Topology Operating Principle
 An m-level Active-lamped nverter Tplgy Operating Principle S. Busquets-Mnge and J. Niclás-Apruzzese Department f Electrnic Engineering, Technical University f atalnia, Barcelna, Spain sergi.busquets@upc.edu,
An m-level Active-lamped nverter Tplgy Operating Principle S. Busquets-Mnge and J. Niclás-Apruzzese Department f Electrnic Engineering, Technical University f atalnia, Barcelna, Spain sergi.busquets@upc.edu,
DEI 1028 Voltage Clamping Circuit
 Device Engineering Incrprated 385 East Alam Drive handler, AZ 85225 Phne: (48) 33-822 Fax: (48) 33-824 E-mail: admin@deiaz.cm DEI 128 ltage lamping ircuit Features Prtectin fr pwer electrnics n 28D avinics
Device Engineering Incrprated 385 East Alam Drive handler, AZ 85225 Phne: (48) 33-822 Fax: (48) 33-824 E-mail: admin@deiaz.cm DEI 128 ltage lamping ircuit Features Prtectin fr pwer electrnics n 28D avinics
CPC1030NTR. 4 Pin SOP OptoMOS Relay
 4 Pin SOP OptMOS Relay Units Lad Vltage 3 V Lad Current 1 ma Max R ON Ω Features Small 4 Pin SOP Package Lw Drive Pwer Requirements (TTL/CMOS Cmpatible) N Mving Parts High Reliability Arc-Free With N Snubbing
4 Pin SOP OptMOS Relay Units Lad Vltage 3 V Lad Current 1 ma Max R ON Ω Features Small 4 Pin SOP Package Lw Drive Pwer Requirements (TTL/CMOS Cmpatible) N Mving Parts High Reliability Arc-Free With N Snubbing
LED wdali MC Switch Input Modul Set - User Manual
 LED wli MC Switch Input Mdul Set - User Manual Buttn mdul (Transmitter) 1. Prduct Descriptin Item N.: LC-004-302 Receive mdul (Receiver) The wli MC Switch Input Mdul Set is a cmpact wireless Multi Cntrl
LED wli MC Switch Input Mdul Set - User Manual Buttn mdul (Transmitter) 1. Prduct Descriptin Item N.: LC-004-302 Receive mdul (Receiver) The wli MC Switch Input Mdul Set is a cmpact wireless Multi Cntrl
Experiment 4 Op-Amp Circuits
 Experiment 4 Op-Amp Circuits Purpse: In this experiment, yu will learn abut peratinal amplifiers (r p-amps). Simple circuits cntaining peratinal amplifiers can be used t perfrm mathematical peratins, such
Experiment 4 Op-Amp Circuits Purpse: In this experiment, yu will learn abut peratinal amplifiers (r p-amps). Simple circuits cntaining peratinal amplifiers can be used t perfrm mathematical peratins, such
Operating Instructions
 TC 60/8 THERMOCOMPUTER TC 60/8 temp / time s s temp / time k start stp Operating Instructins Cntents General Infrmatin...1 Security Advice...1 Firing Curves...1 Typical Firing Curves...2 Entering a Firing
TC 60/8 THERMOCOMPUTER TC 60/8 temp / time s s temp / time k start stp Operating Instructins Cntents General Infrmatin...1 Security Advice...1 Firing Curves...1 Typical Firing Curves...2 Entering a Firing
EE 3323 Electromagnetics Laboratory
 EE 3323 Electrmagnetics Labratry Experiment #1 Waveguides and Waveguide Measurements 1. Objective The bjective f Experiment #1 is t investigate waveguides and their use in micrwave systems. Yu will use
EE 3323 Electrmagnetics Labratry Experiment #1 Waveguides and Waveguide Measurements 1. Objective The bjective f Experiment #1 is t investigate waveguides and their use in micrwave systems. Yu will use
Maxon Motor & Motor Controller Manual
 Maxn Mtr & Mtr Cntrller Manual Nte: This manual is nly fr use fr the Maxn mtr and cntrller utlined belw. This infrmatin is based upn the tutrial vides fund nline and thrugh testing. NOTE: Maximum Permitted
Maxn Mtr & Mtr Cntrller Manual Nte: This manual is nly fr use fr the Maxn mtr and cntrller utlined belw. This infrmatin is based upn the tutrial vides fund nline and thrugh testing. NOTE: Maximum Permitted
CPC1025NTR. 4 Pin SOP OptoMOS Relay
 4 Pin SOP OptMOS Relay Units Lad Vltage 4 V Lad Current 12 ma Typ. R ON 2 Ω Features Small 4 Pin SOP Package Lw Drive Pwer Requirements (TTL/CMOS Cmpatible) N Mving Parts High Reliability Arc-Free With
4 Pin SOP OptMOS Relay Units Lad Vltage 4 V Lad Current 12 ma Typ. R ON 2 Ω Features Small 4 Pin SOP Package Lw Drive Pwer Requirements (TTL/CMOS Cmpatible) N Mving Parts High Reliability Arc-Free With
Operational Amplifiers High Speed Operational Amplifiers
 F Electrnics: Operatinal Amplifiers Page 11.1 Operatinal Amplifiers High Speed Operatinal Amplifiers Operatinal amplifiers with 3 db bandwidths f up t 1.5 GHz are nw available, such peratinal amplifiers
F Electrnics: Operatinal Amplifiers Page 11.1 Operatinal Amplifiers High Speed Operatinal Amplifiers Operatinal amplifiers with 3 db bandwidths f up t 1.5 GHz are nw available, such peratinal amplifiers
Exclusive Technology Feature. A Practical Primer On Motor Drives (Part 8): Power Semiconductors. Drives And Other Power Converters
 A Practical Primer On Mtr Drives (Part 8): Pwer Semicnductrs by Ken Jhnsn, Teledyne LeCry, Chestnut Ridge, N.Y. ISSUE: September 2016 The preceding parts f this article series have discussed the varius
A Practical Primer On Mtr Drives (Part 8): Pwer Semicnductrs by Ken Jhnsn, Teledyne LeCry, Chestnut Ridge, N.Y. ISSUE: September 2016 The preceding parts f this article series have discussed the varius
Hospital Task Scheduling using Constraint Programming
 Hspital Task Scheduling using Cnstraint Prgramming Authr: Chaman Chahal Supervisr: Dr. P. Bse, Schl f Cmputer Science Organizatin: Carletn University Curse: COMP4905 Date: Dec. 11, 2012 1 Abstract Hspitals
Hspital Task Scheduling using Cnstraint Prgramming Authr: Chaman Chahal Supervisr: Dr. P. Bse, Schl f Cmputer Science Organizatin: Carletn University Curse: COMP4905 Date: Dec. 11, 2012 1 Abstract Hspitals
Output Stages. Microelectronic Circuits. Ching-Yuan Yang. National Chung-Hsing University Department of Electrical Engineering.
 Micrelectrnic Circuits Output Stages Ching-Yuan Yang Natinal Chung-Hsing University Department f Electrical Engineering Outline Classificatin f Output Stages Class A Output Stage Class B Output Stage Class
Micrelectrnic Circuits Output Stages Ching-Yuan Yang Natinal Chung-Hsing University Department f Electrical Engineering Outline Classificatin f Output Stages Class A Output Stage Class B Output Stage Class
Process Gain and Loop Gain
 Prcess Gain and Lp Gain By nw, it is evident that ne can calculate the sensitivity fr each cmpnent in a cntrlled prcess. Smetimes, this sensitivity is referred t as a gain. The cnfusin is understandable
Prcess Gain and Lp Gain By nw, it is evident that ne can calculate the sensitivity fr each cmpnent in a cntrlled prcess. Smetimes, this sensitivity is referred t as a gain. The cnfusin is understandable
Review of Electronic I. Lesson #2 Solid State Circuitry Diodes & Transistors Chapter 3. BME Electronics II J.Schesser
 Review f Electrnic I Lessn #2 Slid State Circuitry Dides & Transistrs Chapter 3 ME 498008 Electrnics II 55 Dides Typical Dide VI Characteristics Frward ias Regin Reverse ias Regin Reverse reakdwn Regin
Review f Electrnic I Lessn #2 Slid State Circuitry Dides & Transistrs Chapter 3 ME 498008 Electrnics II 55 Dides Typical Dide VI Characteristics Frward ias Regin Reverse ias Regin Reverse reakdwn Regin
DC-DC Double PWM Converter for Dimmable LED Lighting
 I J C T A, 9(16), 216, pp. 8333-8339 Internatinal Science Press DC-DC Duble PWM Cnverter fr Dimmable LED Lighting Pavankumar, Rhit Shinde and R. Gunabalan* ABSTRACT A simplebuck-bst cnverter tplgywith
I J C T A, 9(16), 216, pp. 8333-8339 Internatinal Science Press DC-DC Duble PWM Cnverter fr Dimmable LED Lighting Pavankumar, Rhit Shinde and R. Gunabalan* ABSTRACT A simplebuck-bst cnverter tplgywith
Experiment 7 Digital Logic Devices and the 555-Timer
 Experiment 7 Digital Lgic Devices and the 555-Timer Purpse: In this experiment we address the cncepts f digital electrnics and lk at the 555-timer, a device that uses digital devices and ther electrnic
Experiment 7 Digital Lgic Devices and the 555-Timer Purpse: In this experiment we address the cncepts f digital electrnics and lk at the 555-timer, a device that uses digital devices and ther electrnic
TC 60 THERMOCOMPUTER TC 60. prog. start stop. Operating Instructions
 TC 60 prg start stp THERMOCOMPUTER TC 60 h C/h C Operating Instructins Cntents General Infrmatin...1 Security Advice...1 Firing Curves...1 Typical Firing Curves...2 Entering a Firing Curve...2 Checing
TC 60 prg start stp THERMOCOMPUTER TC 60 h C/h C Operating Instructins Cntents General Infrmatin...1 Security Advice...1 Firing Curves...1 Typical Firing Curves...2 Entering a Firing Curve...2 Checing
Compound Semiconductors; GaN and SiC, Separating Fact from Fiction in both Research and Business
 6/25/2013 Cmpund Semicnductrs; and, Separating Fact frm Fictin in bth Research and Business Prfessr Umesh Mishra, Ph.D. Redefining Energy Efficiency Cmpund semicnductrs separating Fact frm Fictin Why d
6/25/2013 Cmpund Semicnductrs; and, Separating Fact frm Fictin in bth Research and Business Prfessr Umesh Mishra, Ph.D. Redefining Energy Efficiency Cmpund semicnductrs separating Fact frm Fictin Why d
CPC1035NTR. 4 Pin SOP OptoMOS Relay
 4 Pin SOP OptMOS Relay Units Lad Vltage 3 V Lad Current 12 ma Max R ON 3 Ω Features Small 4 Pin SOP Package Lw Drive Pwer Requirements (TTL/CMOS Cmpatible) N Mving Parts High Reliability Arc-Free With
4 Pin SOP OptMOS Relay Units Lad Vltage 3 V Lad Current 12 ma Max R ON 3 Ω Features Small 4 Pin SOP Package Lw Drive Pwer Requirements (TTL/CMOS Cmpatible) N Mving Parts High Reliability Arc-Free With
Rectifiers convert DC to AC. Inverters convert AC to DC.
 DT23-3 Inverter Ntes 3 January 23. The difference between Rectifiers and Inverters Rectifiers cnvert DC t AC. Inverters cnvert AC t DC. 2. Uses f Inverters Battery Backup. Batteries stre DC. Many appliances
DT23-3 Inverter Ntes 3 January 23. The difference between Rectifiers and Inverters Rectifiers cnvert DC t AC. Inverters cnvert AC t DC. 2. Uses f Inverters Battery Backup. Batteries stre DC. Many appliances
P ^ DETERMINATION OF. Part I. Doner, W3FAL. maximum ratings and typical operating conditions. service are given below. This procedure may
 1 AT P ^ -, r A PUBLICATION OF THE RCA ELECTRON TUBE DIVISION VOL., NO. 1, RADIO CORPORATION OF AMERICA DECEMBER, 1 DETERMINATION OF TYPICAL OPERATING CONDITIONS Fr RCA Tubes Used as Linear RF Pwer Amplifiers
1 AT P ^ -, r A PUBLICATION OF THE RCA ELECTRON TUBE DIVISION VOL., NO. 1, RADIO CORPORATION OF AMERICA DECEMBER, 1 DETERMINATION OF TYPICAL OPERATING CONDITIONS Fr RCA Tubes Used as Linear RF Pwer Amplifiers
HIGH POWER UPS SELECTION METHODOLOGY AND INSTALLATION GUIDELINE FOR HIGH RELIABILITY POWER SUPPLY
 HIGH POWER UPS SELECTION METHODOLOGY AND INSTALLATION GUIDELINE FOR HIGH RELIABILITY POWER SUPPLY A. Sudrià 1, E. Jaureguialz 2, A. Sumper 1, R. Villafáfila 1 and J. Rull 1 1 Centre fr Technlgical Innvatin
HIGH POWER UPS SELECTION METHODOLOGY AND INSTALLATION GUIDELINE FOR HIGH RELIABILITY POWER SUPPLY A. Sudrià 1, E. Jaureguialz 2, A. Sumper 1, R. Villafáfila 1 and J. Rull 1 1 Centre fr Technlgical Innvatin
Project Information o Simulating Cumulus Entrainment: A Resolution Problem, or Conceptual? o Sonia Lasher-Trapp, UIUC o
 Annual Reprt fr Blue Waters Allcatin: Snia Lasher-Trapp, Oct 2016 Prject Infrmatin Simulating Cumulus Entrainment: A Reslutin Prblem, r Cnceptual? Snia Lasher-Trapp, UIUC slasher@illinis.edu Executive
Annual Reprt fr Blue Waters Allcatin: Snia Lasher-Trapp, Oct 2016 Prject Infrmatin Simulating Cumulus Entrainment: A Reslutin Prblem, r Cnceptual? Snia Lasher-Trapp, UIUC slasher@illinis.edu Executive
High Level Design Circuit CitEE. Irere Kwihangana Lauren Mahle Jaclyn Nord
 High Level Design Circuit CitEE Irere Kwihangana Lauren Mahle Jaclyn Nrd 12/16/2013 Table f Cntents 1 Intrductin. 3 2 Prblem Statement and Prpsed Slutin. 3 3 Requirements. 3 4 System Blck Diagram 4.1 Overall
High Level Design Circuit CitEE Irere Kwihangana Lauren Mahle Jaclyn Nrd 12/16/2013 Table f Cntents 1 Intrductin. 3 2 Prblem Statement and Prpsed Slutin. 3 3 Requirements. 3 4 System Blck Diagram 4.1 Overall
Experiment 6 Electronic Switching
 Experiment 6 Electrnic Switching Purpse: In this experiment we will discuss ways in which analg devices can be used t create binary signals. Binary signals can take n nly tw states: high and lw. The activities
Experiment 6 Electrnic Switching Purpse: In this experiment we will discuss ways in which analg devices can be used t create binary signals. Binary signals can take n nly tw states: high and lw. The activities
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL (ADC) & DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG (DAC) CONVERTERS
 ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL (ADC) & DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG (DAC) CONVERTERS 37 Many events mnitred and cntrlled by the micrprcessr are analg events. ADC & DAC CONVERTERS These range frm mnitring all frms f events, even
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL (ADC) & DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG (DAC) CONVERTERS 37 Many events mnitred and cntrlled by the micrprcessr are analg events. ADC & DAC CONVERTERS These range frm mnitring all frms f events, even
CM5530 GENERAL DESCRIPTION APPLICATIONS TYPICAL APPLICATION CIRCU. Rev.1.0 0
 FEATURES Quasi-Resnant Primary Side Regulatin (QR-PSR) Cntrl with High Efficiency Multi-Mde PSR Cntrl Fast Dynamic Respnse Built-in Dynamic Base Drive Audi Nise Free Operatin ±4% CC and C Regulatin Lw
FEATURES Quasi-Resnant Primary Side Regulatin (QR-PSR) Cntrl with High Efficiency Multi-Mde PSR Cntrl Fast Dynamic Respnse Built-in Dynamic Base Drive Audi Nise Free Operatin ±4% CC and C Regulatin Lw
Experiment 4 Op-Amp Circuits
 Experiment 4 Op-Amp Circuits Purpse: In this experiment, yu will learn abut peratinal amplifiers (r p-amps). Simple circuits cntaining peratinal amplifiers can be used t perfrm mathematical peratins, such
Experiment 4 Op-Amp Circuits Purpse: In this experiment, yu will learn abut peratinal amplifiers (r p-amps). Simple circuits cntaining peratinal amplifiers can be used t perfrm mathematical peratins, such
Experiment 7 Digital Logic Devices and the 555-Timer
 Experiment 7 Digital Lgic Devices and the 555-Timer Purpse: In this experiment we address the cncepts f digital electrnics and lk at the 555-timer, a device that uses digital devices and ther electrnic
Experiment 7 Digital Lgic Devices and the 555-Timer Purpse: In this experiment we address the cncepts f digital electrnics and lk at the 555-timer, a device that uses digital devices and ther electrnic
M. Darwish Brunel University/School of Engineering and Design, London, C. C. Marouchos Cyprus University of Technology/Electrical
 An nvestigatin f the Switched-apacitr ircuit as a Slid-State Fault urrent imiting and nterrupting Device (FD) with Pwer Factr rrectin Suitable fr w-vltage Distributin Netwrks.. Maruchs yprus University
An nvestigatin f the Switched-apacitr ircuit as a Slid-State Fault urrent imiting and nterrupting Device (FD) with Pwer Factr rrectin Suitable fr w-vltage Distributin Netwrks.. Maruchs yprus University
High Step up Switched Capacitor Inductor DCDC Converter for UPS System with Renewable. Energy Source
 nternatinal Jurnal f Electrnics and Electrical Engineering Vl. 3, N. 2, April, 25 High Step up Switched Capacitr nductr DCDC fr UPS System with Renewable Energy Surce Maheshkumar. K and S. Ravivarman K.S.
nternatinal Jurnal f Electrnics and Electrical Engineering Vl. 3, N. 2, April, 25 High Step up Switched Capacitr nductr DCDC fr UPS System with Renewable Energy Surce Maheshkumar. K and S. Ravivarman K.S.
The demand for a successful flaw analysis is that the test equipment produces no distortion on the echos no noise. I _... I i.j J...
 SYSTEM ANALYSIS FOR WIDE BAND ULTRASONIC TEST SET-UPS Ulrich Opara Krautkramer GmbH Clgne, West Germany INTRODUCTION In the last years, the discussins abut ultrasnic test equipment fcussed n amplifier
SYSTEM ANALYSIS FOR WIDE BAND ULTRASONIC TEST SET-UPS Ulrich Opara Krautkramer GmbH Clgne, West Germany INTRODUCTION In the last years, the discussins abut ultrasnic test equipment fcussed n amplifier
Hands-Free Music Tablet
 Hands-Free Music Tablet Steven Tmer Nate Decker Grup Website: steve@wasatch.cm milamberftheassembly@yah.cm http://www.cs.utah.edu/~ndecker/ce3992/ Abstract The typical musician handles a great deal f sheet
Hands-Free Music Tablet Steven Tmer Nate Decker Grup Website: steve@wasatch.cm milamberftheassembly@yah.cm http://www.cs.utah.edu/~ndecker/ce3992/ Abstract The typical musician handles a great deal f sheet
VIP-200. Point to Point Extension Configuration Quick Start Guide. Video over IP Extender and Matrix System
 VIP-200 Vide ver IP Extender and Matrix System Pint t Pint Extensin Cnfiguratin Quick Start Guide PureLink TM 535 East Crescent Avenue Ramsey, NJ 07446 USA Cntents What is in the bx... 3 Transmitter kit
VIP-200 Vide ver IP Extender and Matrix System Pint t Pint Extensin Cnfiguratin Quick Start Guide PureLink TM 535 East Crescent Avenue Ramsey, NJ 07446 USA Cntents What is in the bx... 3 Transmitter kit
ENGR-2300 ELCTRONIC INSTRUMENTATION Experiment 8. Experiment 8 Diodes
 Experiment 8 Dides Purpse: The bjective f this experiment is t becme familiar with the prperties and uses f dides. We will first cnsider the i-v characteristic curve f a standard dide that we can use in
Experiment 8 Dides Purpse: The bjective f this experiment is t becme familiar with the prperties and uses f dides. We will first cnsider the i-v characteristic curve f a standard dide that we can use in
Summary of High Energy Particle Detector Elements
 1 Summary f High Energy Particle Detectr Elements Cntents Abstract... 1 Phtmultipliers vs. Phtdides... 2 Phtmultiplier tube... 2 Phtdides... 3 Preamplifier... 4 Amplifier... 5 Multi-Channel Analyser (MCA)...
1 Summary f High Energy Particle Detectr Elements Cntents Abstract... 1 Phtmultipliers vs. Phtdides... 2 Phtmultiplier tube... 2 Phtdides... 3 Preamplifier... 4 Amplifier... 5 Multi-Channel Analyser (MCA)...
Universal input/output controller
 Embedded autmatin equipment (Shanghai) Limited Rm 305. Twer B.NO.18Talin rad Pudng District, Shanghai Phne: +86-21-51090839/50750355, fax: +86-21-50758598, e-mail: sales@stammkn.cm Universal input/utput
Embedded autmatin equipment (Shanghai) Limited Rm 305. Twer B.NO.18Talin rad Pudng District, Shanghai Phne: +86-21-51090839/50750355, fax: +86-21-50758598, e-mail: sales@stammkn.cm Universal input/utput
INLINE TE 01δ MODE DIELECTRIC-RESONATOR FIL- TERS WITH CONTROLLABLE TRANSMISSION ZERO FOR WIRELESS BASE STATIONS
 Prgress In Electrmagnetics Research Letters, Vl. 38, 11 11, 213 INLINE TE 1δ MODE DIELECTRIC-RESONATOR FIL- TERS WITH CONTROLLABLE TRANSMISSION ZERO FOR WIRELESS BASE STATIONS Xia Ouyang * and B-Yng Wang
Prgress In Electrmagnetics Research Letters, Vl. 38, 11 11, 213 INLINE TE 1δ MODE DIELECTRIC-RESONATOR FIL- TERS WITH CONTROLLABLE TRANSMISSION ZERO FOR WIRELESS BASE STATIONS Xia Ouyang * and B-Yng Wang
Upgrading to PlanetPress Suite Version 5
 Upgrading t PlanetPress Suite Versin 5 Creatin date: September 2, 2005 Revisin date: June 14, 2006 Table f Cntents System Requirements... 4 Imprtant Cnsideratins... 4 Knwn Issues... 6 Prcedure t imprt
Upgrading t PlanetPress Suite Versin 5 Creatin date: September 2, 2005 Revisin date: June 14, 2006 Table f Cntents System Requirements... 4 Imprtant Cnsideratins... 4 Knwn Issues... 6 Prcedure t imprt
Simplified Control Technique for Three-Phase Rectifier PFC Based on the Scott Transformer
 Simplified Cntrl Technique fr ThreePhase Rectifier PFC Based n the Sctt Transfrmer A.A. Badin * and. Barbi ** Federal University f Santa Catarina Pwer Electrnics nstitute P.O.Bx 5119 CEP:88040970 Flrianplis,
Simplified Cntrl Technique fr ThreePhase Rectifier PFC Based n the Sctt Transfrmer A.A. Badin * and. Barbi ** Federal University f Santa Catarina Pwer Electrnics nstitute P.O.Bx 5119 CEP:88040970 Flrianplis,
Figure 1: View, connection compartment closed
 Radi Management Art. N. : 2700AP Operating instructins 1 Safety instructins Electrical equipment may nly be installed and fitted by electrically skilled persns. Serius injuries, fire r prperty damage pssible.
Radi Management Art. N. : 2700AP Operating instructins 1 Safety instructins Electrical equipment may nly be installed and fitted by electrically skilled persns. Serius injuries, fire r prperty damage pssible.
The UNIVERSITY of NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL
 Yu will learn the fllwing in this lab: The UNIVERSITY f NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL Cmp 541 Digital Lgic and Cmputer Design Prf. Mntek Singh Fall 2016 Lab Prject (PART A): Attaching a Display t the Prcessr
Yu will learn the fllwing in this lab: The UNIVERSITY f NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL Cmp 541 Digital Lgic and Cmputer Design Prf. Mntek Singh Fall 2016 Lab Prject (PART A): Attaching a Display t the Prcessr
A Novel Matrix Converter Topology With Simple Commutation
 A Nvel Matrix Cnverter Tplgy With Simple Cmmutatin Abstract-Matrix cnverter is very simple in structure and has pwerful cntrllability. Hwever, cmmutatin prblem and cmplicated PWM methd keep it frm being
A Nvel Matrix Cnverter Tplgy With Simple Cmmutatin Abstract-Matrix cnverter is very simple in structure and has pwerful cntrllability. Hwever, cmmutatin prblem and cmplicated PWM methd keep it frm being
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
 Lad with min. 5 kg 405000090 405070090 INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS CONTENT: 1. Imprtant safety instructins. 2. Specificatins and main dimensins. 3. Parts included. 4. Installatin. 5. Adjusting the strke
Lad with min. 5 kg 405000090 405070090 INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS CONTENT: 1. Imprtant safety instructins. 2. Specificatins and main dimensins. 3. Parts included. 4. Installatin. 5. Adjusting the strke
High Efficiency Frequency Tunable Inverse Class-E Amplifier in VHF Band
 High Efficiency Frequency Tunable Inverse Class-E Amplifier in VHF Band Kumh Natinal Institute f Technlgy, 1 Yangh-Dng, Gumi, Gyungbuk, 730-701, Krea yungk@kumh.ac.kr Abstract This paper prpses the use
High Efficiency Frequency Tunable Inverse Class-E Amplifier in VHF Band Kumh Natinal Institute f Technlgy, 1 Yangh-Dng, Gumi, Gyungbuk, 730-701, Krea yungk@kumh.ac.kr Abstract This paper prpses the use
Composite Materials with Self-Contained Wireless Sensing Networks
 Cmpsite Materials with Self-Cntained Wireless Sensing Netwrks Kristin Schaaf, Rbert Kim, and Sia Nemat-Nasser Department f Mechanical and Aerspace Engineering, Center f Excellence fr Advanced Materials,
Cmpsite Materials with Self-Cntained Wireless Sensing Netwrks Kristin Schaaf, Rbert Kim, and Sia Nemat-Nasser Department f Mechanical and Aerspace Engineering, Center f Excellence fr Advanced Materials,
CB-030S Circuit Board
 CB-030S Circuit Bard Designed fr use with the high trque PM486FH (up t 7A) Adjustable acceleratin and deceleratin time (0 t 2.5s) Stable speed peratin Switch fr manual r autmatic recvery f the thermal
CB-030S Circuit Bard Designed fr use with the high trque PM486FH (up t 7A) Adjustable acceleratin and deceleratin time (0 t 2.5s) Stable speed peratin Switch fr manual r autmatic recvery f the thermal
Implementation of a Sixth Order Active Band-pass R-Filter. Igwue,G.A,Amah,A.N,Atsuwe,B.A
 Internatinal Jurnal f Scientific & Engineering Research, lume 5, Issue, April-0 ISSN 9-558 Implementatin f a Sixth Order Active Band-pass R-Filter 598 Igwue,G.A,Amah,A.N,Atsuwe,B.A Abstract In this paper,
Internatinal Jurnal f Scientific & Engineering Research, lume 5, Issue, April-0 ISSN 9-558 Implementatin f a Sixth Order Active Band-pass R-Filter 598 Igwue,G.A,Amah,A.N,Atsuwe,B.A Abstract In this paper,
CUSTOMER PORTAL. Floorplan Management
 CUSTOMER PORTAL Flrplan Management FLOORPLAN ANALYTICS The flrplan analytics area displays flrplans yu have uplad t the prtal (if yu haven t yet upladed a flrplan please cntact ur supprt department). Frm
CUSTOMER PORTAL Flrplan Management FLOORPLAN ANALYTICS The flrplan analytics area displays flrplans yu have uplad t the prtal (if yu haven t yet upladed a flrplan please cntact ur supprt department). Frm
PROBABILITY OF DETECTION OF FLAWS IN A GAS TURBINE ENGINE. Gary L. Burkhardt and R.E. Beissner
 PROBABILITY OF DETECTION OF FLAWS IN A GAS TURBINE ENGINE COMPONENT USING ELECTRIC CURRENT PERTURBATION Gary L. Burkhardt and R.E. Beissner Suthwest Research Institute 6220 CUlebra Rad San Antni, Texas
PROBABILITY OF DETECTION OF FLAWS IN A GAS TURBINE ENGINE COMPONENT USING ELECTRIC CURRENT PERTURBATION Gary L. Burkhardt and R.E. Beissner Suthwest Research Institute 6220 CUlebra Rad San Antni, Texas
ACPL-8x7. Data Sheet. Multi-Channel Full-Pitch Phototransistor Optocoupler. Description. Features. Applications
 Data Sheet ACPL-8x7 Multi-Channel Full-Pitch Phttransistr Optcupler Descriptin The ACPL-827 is a DC-input dual-channel, full-pitch phttransistr ptcupler that cntains tw light emitting dides ptically cupled
Data Sheet ACPL-8x7 Multi-Channel Full-Pitch Phttransistr Optcupler Descriptin The ACPL-827 is a DC-input dual-channel, full-pitch phttransistr ptcupler that cntains tw light emitting dides ptically cupled
FIRMWARE RELEASE NOTES. Versions V2.0.0 to V Model HDL-32E. High Definition LiDAR Sensor
 FIRMWARE RELEASE NOTES Versins V2.0.0 t V2.2.21.0 Mdel HDL-32E High Definitin LiDAR Sensr HDL-32E Firmware Release Ntes Page 2 Fr all new features and changes, refer t the dcumentatin that accmpanies the
FIRMWARE RELEASE NOTES Versins V2.0.0 t V2.2.21.0 Mdel HDL-32E High Definitin LiDAR Sensr HDL-32E Firmware Release Ntes Page 2 Fr all new features and changes, refer t the dcumentatin that accmpanies the
SENSOR AND MEASUREMENT TECHNOLOGY
 SENSOR AND MEASUREMENT TECHNOLOGY FOR SENSOR MANUFACTURERS The perfect wireless system FOR MACHINE MANUFACTURERS Transferring sensr data directly int the cntrl unit Using the Wireless Sensr Gateway DATAEAGLE
SENSOR AND MEASUREMENT TECHNOLOGY FOR SENSOR MANUFACTURERS The perfect wireless system FOR MACHINE MANUFACTURERS Transferring sensr data directly int the cntrl unit Using the Wireless Sensr Gateway DATAEAGLE
integrated circuits design, which are widely utilized in portable-system applications [1-3].
![integrated circuits design, which are widely utilized in portable-system applications [1-3]. integrated circuits design, which are widely utilized in portable-system applications [1-3].](/thumbs/89/98632971.jpg) CHAPTER 1 LOW POWER VLSI DESIGN A REVIEW Intrductry aspects and need f Lw Pwer design are discussed, VM, CM and ther circuit methds are reviewed in the perspective f Lw Pwer design. Sme imprtant cnsideratins
CHAPTER 1 LOW POWER VLSI DESIGN A REVIEW Intrductry aspects and need f Lw Pwer design are discussed, VM, CM and ther circuit methds are reviewed in the perspective f Lw Pwer design. Sme imprtant cnsideratins
Specification for a communicating Panelboard system to monitor, control and maintain LV electrical installations
 Specificatin fr a cmmunicating Panelbard system t mnitr, cntrl and maintain LV electrical installatins A system fr: - Mnitring the prtectin and cntrl devices in an electrical installatin and prviding the
Specificatin fr a cmmunicating Panelbard system t mnitr, cntrl and maintain LV electrical installatins A system fr: - Mnitring the prtectin and cntrl devices in an electrical installatin and prviding the
ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS
 Physics Department Electricity and Magnetism Labratry ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS 1. Aim. Learn t use measuring instruments: Digital multimeter. Analg scillscpe. Assembly f simple elementary circuit. Cllectin
Physics Department Electricity and Magnetism Labratry ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS 1. Aim. Learn t use measuring instruments: Digital multimeter. Analg scillscpe. Assembly f simple elementary circuit. Cllectin
Lab 6 Spirometer System (Feb 20/21)
 GOAL Lab 6 Spirmeter System (Feb 20/21) Demnstrate a spirmeter system incrprating a (1) Lilly-type flw tube (2) piezresistive differential pressure sensr (3) instrumentatin amplifier and lw-pass filter
GOAL Lab 6 Spirmeter System (Feb 20/21) Demnstrate a spirmeter system incrprating a (1) Lilly-type flw tube (2) piezresistive differential pressure sensr (3) instrumentatin amplifier and lw-pass filter
Implementation Of 12V To 330V Boost Converter With Closed Loop Control Using Push Pull Topology
 Implementatin Of 12V T 330V Bst Cnverter With Clsed Lp Cntrl Using Push Pull Tplgy Anande J.T 1, Odinya J.O.. 2, Yilwatda M.M. 3 1,2,3 Department f Electrical and Electrnics Engineering, Federal University
Implementatin Of 12V T 330V Bst Cnverter With Clsed Lp Cntrl Using Push Pull Tplgy Anande J.T 1, Odinya J.O.. 2, Yilwatda M.M. 3 1,2,3 Department f Electrical and Electrnics Engineering, Federal University
INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS
 Lad: Min. 5 kg Max. 100 kg TS1000A TS700A INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS CONTENT: 1. Imprtant safety instructins. 2. Specificatins and main measures. 3. Parts included. 4. Installatin. 5. Adjusting the strke
Lad: Min. 5 kg Max. 100 kg TS1000A TS700A INSTALLATION INSTRUCTIONS CONTENT: 1. Imprtant safety instructins. 2. Specificatins and main measures. 3. Parts included. 4. Installatin. 5. Adjusting the strke
