International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering
|
|
|
- Lionel Morris
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Volume 3, Issue 1, January 2013 ISSN: X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: Low Power High Speed 4 Bit Resolution Pipeline ADC Design in Submicron CMOS Technology Ms. Rita M. Shende Dept of E.X.T.C. Sipna C.O.E.T.Amravati University, Maharashtra, India Prof. P. R. Gumble Dept of E.X.T.C. Sipna C.O.E.T.Amravati University, Maharashtra, India Abstract- Analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) are key design blocks and are currently adopted in many application fields to improve digital systems, which achieve superior performances with respect to analog solutions. With the fast advancement of CMOS fabrication technology, more and more signal-processing functions are implemented in the digital domain for a lower cost, lower power consumption, higher yield, and higher re-configurability. Wide spread usage confers great importance to the design activities, which nowadays largely contributes to the production cost in integrated circuit devices (ICs). This has recently generated a great demand for low-power, low-voltage ADCs that can be realized in a mainstream deep-submicron CMOS technology. Various examples of ADC applications can be found in data acquisition systems, measurement systems and digital communication systems also imaging, instrumentation systems. Hence, we have to considered all the parameters and improving the associated performance may significantly reduce the industrial cost of an ADC manufacturing process and improved the resolution and design specially power consumption. This paper presents a 4 bit Pipeline ADC with low power dissipation implemented in <0.18μm CMOS technology with a power supply of 1.2V. Keywords: Analog-to-digital converter (ADC), CMOS circuits I. INTRODUCTION As IC fabrication technology has advanced, more analog signal processing functions have been replaced by digital blocks,analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) retain an important role in most modern electronic systems because most signals of interest are analog in nature and must to be converted to digital signals for further signal processing in the digital domain. There is wide variety of different ADC architectures available depending on the requirements of the application. Pipeline ADCs are one of the best examples. Pipeline analog to-digital converters (Pipeline ADC) have recently become very attractive in energy efficient moderate-resolution/moderate-speed applications due to their minimal active analog circuit requirements. It typically generate one bit per clock cycle, the benefits are the low area needed for the implementation. ADCs of this type have good resolutions and quite wide ranges. By combining the merits of the successive approximation and flash ADCs this type is fast, has a high resolution, and only requires a small die size. The pipeline analog-to-digital converter (ADC) is a promising topology for high-speed data conversion with compact area and efficient power dissipation. Its speed of operation far surpasses that of serial-based structures, such as successive approximation or cyclic converters, while its die area and power dissipation favorably compare to that of flash and other more parallelized architectures. Pipelined ADCs are widely used in the areas of wireless communications, digital subscriber line analog front ends, CCD imaging digitizers, studio cameras, ultrasound monitors, and many other high speed applications. Pipeline analog-to-digital converters (ADC S ) represent the majority of the ADC market for medium-to highresolution ADC S. Pipeline ADC S provide up to 5Msps sampling rates with resolutions from 8 to 18 bits. The Pipeline ADC architecture allows for high performance, low power ADC S to be packaged in small form factors for today s applications. With ADC we have designed 4 bit low power high speed Pipeline ADC with 0.18μm technology. II. REWIEW OF WORK The first documented example of an ADC was a 5-bit, electro-optical and mechanical flash-type converter patented by Paul Rainey in 1921, used to transmit facsimile over telegraph lines with 5-bit pulse-coded modulation (PCM). The first all-electrical implementation came in 1937 by Alec Harvey Reeves, this also had a 5-bit resolution and the ADC was implemented by converting the input signal to a train of pulses which was counted to generate the binary output at a sample rate of 6 ks/s. Following this the successive approximation ADC was developed in 1948 by Black, Edson Goodall to digitize voice to 5-bits at 8 ks/s. Also in 1948, a 96 ks/s, 7-bit ADC was developed and it was developed and it was implemented using an electron beam with a sensor placed on the other side of a mask. The mask had holes patterned according to the binary weights so that all bits were simultaneously detected, the pattern also employed Gray coding of the output in order to reduce the effect of errors in the most significant bit (MSB) transition, much as is done in modern high-speed flash ADC S [12]. 2013, IJARCSSE All Rights Reserved Page 189
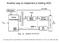
2 Following the development of the transistor in 1947 and the integrated circuit in 1958, the ADC development continued in the 1960 s with for example an 8-bit, 10 MS/s converter that was used in missile-defence programs in the United States. During the same decade, all the currently used high-speed architectures were developed including Pipeline ADC S with error correction. Commercial flash converters appeared in instruments and modules of the 1960 S and 1970 S and quickly migrated to integrated circuits during the 1980 S. The monolithic 8-bit flash ADC became an industry standard in digital video applications of the 1980 S. Today, the flash converter is primarily used as a building block within subranging pipeline [9]. Using Partial amplifier sharing topology, a 6-bit pipeline ADC, developed in 0.35μm CMOS process. A 6-bit, 2.5 V flash ADC design has been reported new flash topology and this new topology has only 2(N-2) + 2 comparators required. Here area of the chip is large and its required to minimize it [10]. The AD7880 is a high speed, low power, 12-bit A/D converter which operates from a single +5V supply. First commercial converter, 1954 "DATRAC" 11-Bit, 50-kSPS SAR ADC Designed by Bernard M. Gordon at EPSCO. In the recent years there has been a trend in ADC research to use low accuracy analog components which are compensated for through the use of digital error correction. Because of their popularity, successive approximation ADCs are available in a wide variety of resolutions, sampling rates, input and output options, package styles, and costs. Many SAR ADCs now offer on-chip input multiplexers, making them the ideal choice for multichannel data acquisition system. An example of modern charge redistribution successive approximation ADCs is Analog Devices' PulSAR series. TheAD7641 is a 18-bit, 2-MSPS, fully differential, ADC that operates from a single 2.5 V power supply. The part contains a high-speed 18-bit sampling ADC, an internal conversion clock, error correction circuits, internal reference, and both serial and parallel system interface ports. The AD7641 is hardware factory calibrated and comprehensively tested to ensure such ac parameters as signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and total harmonic distortion (THD), in addition to the more traditional dc parameters of gain, offset, and linearity. The motivation behind this is that analog design have not been able to benefit from process scaling in the same way as digital logic and therefore the relatively area cheap digital logic is used to compensate for the shortcomings of expensive analog circuits. For device reliability reasons, the supply voltage needs to be reduced to ensure gate oxide integrity over time and prevent p-n junction from breakdown. Present-day CMOS processes are making the transition from 3.3 V to 1.8 V supplies. The converter should operate with high sampling rate from an operating supply as low as possible, to facilitate integration with low-voltage, power efficient digital circuits. III. PIPELINE ADC DESIGN The pipeline ADC architecture combines the benefits of high throughput and an input capacitance bound by noise constraints. Typical pipeline architecture is illustrated in Figure 1. Each stage has the four elements of Comparator, a summer, multiplier, mux and transmission gate. Fig 1 pipeline A/D converter The pipeline ADC is an N-step converter, with 1 bit being converted per stage. Able to achieve high resolution (10-13 bits) at relatively fast speeds, the pipeline ADC consists of N stages connected in series (Fig.). Each stage contains a 1-bit ADC (a comparator), a sample-and-hold, a summer, and a gain of two amplifiers. Each stage of the converter performs the following operation: 1. After the input signal has been sampled, compare it to vref/2. The output of each comparator is the bit conversion for that stage. 2. If vm > vref/2 (comparator output is 1), vref/2 is subtracted from the held signal and pass the result to the amplifier. If vin < vref/2 (comparator output is 0), then pass the original input signal to the amplifier. The output of each stage in the converter is referred to as the residue. 3. Multiply the result of the summation by 2 and pass the result to the sample and- hold of the next stage. 2013, IJARCSSE All Rights Reserved Page 190
3 A main advantage of the pipeline converter is its high throughput. After an initial latency of N clock cycles, one conversion will be completed per clock cycle. While the residue of the first stage is being operated on by the second stage, the first stage is free to operate on the next samples. Each stage operates on the residue passed down from the previous stage, thereby allowing for fast conversions. The disadvantage is having the initial N clock cycle delay before the first digital output appears. The severity of this disadvantage depends, of course, on the application. One interesting aspect of this converter is its dependency on the most significant stages for accuracy. A slight error in the first stage propagates through the converter and results in a much larger error at the end of the conversion. Each succeeding stage requires less accuracy than the one before, so special care must be taken when considering the first several stages. The Pipelined ADC can be thought of as an amplitude- interleaved topology where errors from one stage are correlated with errors from previous stage. The basic block diagram implementation of an N-bit Pipelined ADC using the cyclic stages is as shown in Figure 2. Instead of cycling the analog output of the 1 bit/stage section back to its input, we feed the output into next stage. The stages are clocked with opposite phases of the master clock signal. The comparator outputs are labelled digital in figure. Fig 2. Pipeline ADC based on cyclic stages The digital comparator outputs are delayed through latches so that the final digital output word corresponds to the input signal sampled N clock cycles earlier. The first stage in figure must be N-bit accurate. It must amplify its analog output voltage, VN-1 to within 1 LSB of the ideal value. The second stage output, VN-2 must be an analog voltage within 2 LSB of its ideal value. The third stage output, VN-3 must be an analog voltage within 4 LSB of its ideal value. Power dissipation in ADC Power dissipation in CMOS logic arises from following 1) Switching current from charging and discharging parasitic capacitance. 2) Short circuit current when both N & P channel transistors are momentarily on at the same time. 3) Leakage current & subthreshold current. Average dynamic power dissipated is given by :- Pavg =Ctot * VDD 2 *Fclk Notice that power dissipation is a function of clock frequency. A great deal of effort is put into reducing the Power dissipation in CMOS circuits. Together with the scaling of process geometry, the supply voltage (squared term) is reduced in order to both reduce the digital Power dissipation and the rate of device degradation. Also we have to reduce short circuit current, subthreshold current, leakage current. The basic problems coupled to SC, such as clock feedthrough from digital part through the switches, capacitor mismatch and op-amp non-idealities, have been taken into account during the design of the ADC. AS we are using 0.18μm technology, supply voltage is 1.2 V. Also due to clock redundancy Power dissipation is reduced. IV. CIRCUIT IMPLEMENTATION With ADS and various designed components we have designed complete Pipeline Architecture shown in fig 3. And we got the simulation results shown in fig 4. And table 1 shows digital values for given analog voltage. 2013, IJARCSSE All Rights Reserved Page 191
4 Fig 3 Pipeline Architecture For our Design of 4 bit resolution ADC digital code we are getting is as follows Table 1 Digital Codes Input analog Q3 Q2 Q1 Q0 voltage , IJARCSSE All Rights Reserved Page 192
5 tv, V a3, V a2, V a1, V as0, V bin3, V bin2, V bin1, V bin0, V Rita et al., International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering 3(1), Simulation Results time, nsec time, nsec Fig 4 Simulation Results for Pipeline ADC The ADC is fabricated in 0.18μm standard CMOS process with 4 bit rsolution. The value of the unit capacitor is 100fF. The static performance of the ADC is shown in Fig. 3. ADC operats at 1.2v. The DNL and INL of the ADC are a measurement factor of linearity.. Pipeline ADC vs other ADCs Power dissipation of Pipeline ADCs varies with the sampling rate unlike Flash and SAR architectures. Hence find applications in PDAs. The SAR ADC's are low power consumption, high resolution, and accuracy. In a SAR ADC, increased resolution comes with the increased cost of more-accurate internal components. Flash ADC is much faster, less accurate and takes more silicon area due to the number of comparators 2N for N bit 2013, IJARCSSE All Rights Reserved Page 193
6 resolution. Oversampled/Σ-J ADCs have low conversion rates, high precision, averaging noise and no requirement for trimming or calibration even up to 16 bits of resolution. V. CONCLUSION ADC is the key design Block in modern microelectronics digital communication system. With the fast advancement of CMOS fabrication technology and continued proliferation of mixed analog and digital VLSI systems, the need for small sized, low-power and high-speed analog-to-digital converters has increased. With an increasing trend to a system-on-chip, an ADC has to be implemented in a low-voltage submicron CMOS technology in order to achieve low manufacturing cost while being able to integrate with other digital circuits. So we have proposed low power ADC. From different ADC architectures available Flash ADC is having the drawback of large chip area n high power dissipation and Pipeline ADC has complex circuit. The Pipeline ADC is best suitable for low power application. For designing purpose we have used Advanced Designing System. The Pipeline ADC core is composed by comparator, Transmission Gate, and pipeline control logic; these components have been designed targeting to fulfill several constraints on requirements such as low power dissipation, the offsets due to mismatch. From the results presented we could conclude that conversion is performed without missing codes and a low-power high speed 4-bit Pipeline ADC in a 0.18μm CMOS process with a 1.2 V supply voltage is designed. REFERENCES [1] Baker, R. Jacob, Li, Harry W., Boyce, David E., CMOS Circuit Design, Layout, and Simulation, 1st on edition (IEEE Press Series on Microelectronic Systems) [2] Stephen H. Lewis and Paul. Gray, A Pipelined 5-Msample/s 9-bit Analog-to-Digital Converter, IEEE J. Solid- State Circuits, vol. 22, issue.12,pp , Dec [3] Razavi, Behzad; Principles of Data Conversion System Design; IEEE Press, [4] A. M. Abo and P. R. Gray, A -V, 10-bit, 14.3-MS/s CMOS pipeline analog-to-digital converter, IEEE J. Solid- State Circuits, vol. 34, no. 5, pp , May [5] T. Stockstad and H. Yoshizawa, "A 0.9-V ma Rail-to-Rail CMOS Operational Amplifier," IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, vol. 37, pp , [6] N. Verma and A. P. chandrakasan, A 25uW 100kS/s 12b ADC for wireless micro-sensor applications, IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC) Dig. Tech. Papers, pp , [7] Circuit Design Techniques for low-voltage high-speed A/D converters, by Mikko Waltari; Distributed by Helsinki University of Technology,2002. [8] Dwight U. Thomson and Bruce A. Wooley, A 15-b pipelined CMOS floating point A/D converter, Journal of IEEE Solid State Circuit,vol. 36, no. 2, February [9]R. Samer and Jan Van der Speigel and K. Nagaraj, Background digital error correction technique for pipeline ADC, IEEE, [10] A. Shabra and Hae-Seung Lee, Oversampled pipelined A/D converter with mismatch shaping, Journal of IEEE Solid State Circuit, vol. 37, no. 5, May2002.Makalah /1937/5/methodology.pdf,may2007 Edition, Oxford University Press, Oxford, ISBN , (2002). [11] S H Lewis, P. H. Gray A pipelined 5-Msampled/s 9-bit Analog-to digital converter.", JSSC, December 1987 [12] Timmy Sundstrom, Design of high-speed, Low-Power, Nyquist Analog-to-Digital Converters, Thesis No. 1423, ISBN ISSN [13]Van De Plassche, Rudy; Integrated Analog-to-Digital and Digital-to-Analog Converters; Kluwer Academic Publishers, [14] Siddharth Devarajan and Larry Singer, A 16-bit, 125 MS/s, 385 mw, 78.7 db SNR CMOS Pipeline ADC, IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits, vol. 44, No.12, pp , Dec [15] A Crash Course on using Agilent Advanced Design System (ADS) By Chris sanabria, sanabria@ece.ucsb.edu [16] Chang-Hyuk Cho, A POWER OPTIMIZED PIPELINED ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTER DESIGN IN SUB-MICRON CMOS TECHNOLOGY A Thesis Presented, Dec [17] Y. Chiu, P. R. Gray, and B. Nikolic, A 14-b 12-MS/s CMOS pipeline ADC with over 100-dB SFDR, IEEE J.Solid-State Circuits, vol. 39, No. 12, pp , Dec , IJARCSSE All Rights Reserved Page 194
ISSCC 2004 / SESSION 25 / HIGH-RESOLUTION NYQUIST ADCs / 25.4
 ISSCC 2004 / SESSION 25 / HIGH-RESOLUTION NYQUIST ADCs / 25.4 25.4 A 1.8V 14b 10MS/s Pipelined ADC in 0.18µm CMOS with 99dB SFDR Yun Chiu, Paul R. Gray, Borivoje Nikolic University of California, Berkeley,
ISSCC 2004 / SESSION 25 / HIGH-RESOLUTION NYQUIST ADCs / 25.4 25.4 A 1.8V 14b 10MS/s Pipelined ADC in 0.18µm CMOS with 99dB SFDR Yun Chiu, Paul R. Gray, Borivoje Nikolic University of California, Berkeley,
A Low-Power 6-b Integrating-Pipeline Hybrid Analog-to-Digital Converter
 A Low-Power 6-b Integrating-Pipeline Hybrid Analog-to-Digital Converter Quentin Diduck, Martin Margala * Electrical and Computer Engineering Department 526 Computer Studies Bldg., PO Box 270231 University
A Low-Power 6-b Integrating-Pipeline Hybrid Analog-to-Digital Converter Quentin Diduck, Martin Margala * Electrical and Computer Engineering Department 526 Computer Studies Bldg., PO Box 270231 University
2008 IEEE ASIA PACIFIC CONFERENCE ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS
 2008 IEEE ASIA PACIFIC CONFERENCE ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS November 30 - December 3, 2008 Venetian Macao Resort-Hotel Macao, China IEEE Catalog Number: CFP08APC-USB ISBN: 978-1-4244-2342-2 Library of Congress:
2008 IEEE ASIA PACIFIC CONFERENCE ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS November 30 - December 3, 2008 Venetian Macao Resort-Hotel Macao, China IEEE Catalog Number: CFP08APC-USB ISBN: 978-1-4244-2342-2 Library of Congress:
Power Optimization in 3 Bit Pipelined ADC Structure
 Global Journal of researches in engineering Electrical and Electronics engineering Volume 11 Issue 7 Version 1.0 December 2011 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher:
Global Journal of researches in engineering Electrical and Electronics engineering Volume 11 Issue 7 Version 1.0 December 2011 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher:
ISSN:
 1391 DESIGN OF 9 BIT SAR ADC USING HIGH SPEED AND HIGH RESOLUTION OPEN LOOP CMOS COMPARATOR IN 180NM TECHNOLOGY WITH R-2R DAC TOPOLOGY AKHIL A 1, SUNIL JACOB 2 1 M.Tech Student, 2 Associate Professor,
1391 DESIGN OF 9 BIT SAR ADC USING HIGH SPEED AND HIGH RESOLUTION OPEN LOOP CMOS COMPARATOR IN 180NM TECHNOLOGY WITH R-2R DAC TOPOLOGY AKHIL A 1, SUNIL JACOB 2 1 M.Tech Student, 2 Associate Professor,
Index terms: Analog to Digital conversion, capacitor sharing, high speed OPAMP-sharing pipelined analog to digital convertor, Low power.
 Pipeline ADC using Switched Capacitor Sharing Technique with 2.5 V, 10-bit Ankit Jain Dept. of Electronics and Communication, Indore Institute of Science & Technology, Indore, India Abstract: This paper
Pipeline ADC using Switched Capacitor Sharing Technique with 2.5 V, 10-bit Ankit Jain Dept. of Electronics and Communication, Indore Institute of Science & Technology, Indore, India Abstract: This paper
DESIGN OF A 500MHZ, 4-BIT LOW POWER ADC FOR UWB APPLICATION
 DESIGN OF A 500MHZ, 4-BIT LOW POWER ADC FOR UWB APPLICATION SANTOSH KUMAR PATNAIK 1, DR. SWAPNA BANERJEE 2 1,2 E & ECE Department, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur, Kharagpur, India Abstract-This
DESIGN OF A 500MHZ, 4-BIT LOW POWER ADC FOR UWB APPLICATION SANTOSH KUMAR PATNAIK 1, DR. SWAPNA BANERJEE 2 1,2 E & ECE Department, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur, Kharagpur, India Abstract-This
Summary Last Lecture
 EE247 Lecture 23 Converters Techniques to reduce flash complexity Interpolating (continued) Folding Multi-Step s Two-Step flash Pipelined s EECS 247 Lecture 23: Data Converters 26 H.K. Page Summary Last
EE247 Lecture 23 Converters Techniques to reduce flash complexity Interpolating (continued) Folding Multi-Step s Two-Step flash Pipelined s EECS 247 Lecture 23: Data Converters 26 H.K. Page Summary Last
RECENTLY, low-voltage and low-power circuit design
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 55, NO. 4, APRIL 2008 319 A Programmable 0.8-V 10-bit 60-MS/s 19.2-mW 0.13-m CMOS ADC Operating Down to 0.5 V Hee-Cheol Choi, Young-Ju
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 55, NO. 4, APRIL 2008 319 A Programmable 0.8-V 10-bit 60-MS/s 19.2-mW 0.13-m CMOS ADC Operating Down to 0.5 V Hee-Cheol Choi, Young-Ju
EE247 Lecture 23. EECS 247 Lecture 23 Pipelined ADCs 2008 H.K. Page 1. Pipeline ADC Block Diagram DAC ADC. V res2. Stage 2 B 2.
 EE247 Lecture 23 Pipelined ADCs (continued) Effect gain stage, sub-dac non-idealities on overall ADC performance Digital calibration (continued) Correction for inter-stage gain nonlinearity Implementation
EE247 Lecture 23 Pipelined ADCs (continued) Effect gain stage, sub-dac non-idealities on overall ADC performance Digital calibration (continued) Correction for inter-stage gain nonlinearity Implementation
A Rail-to-Rail Input 12b 2 MS/s 0.18 µm CMOS Cyclic ADC for Touch Screen Applications
 160 HEE-CHEOL CHOI et al : A RAIL-TO-RAIL INPUT 12B 2 MS/S 0.18 µm CMOS CYCLIC ADC FOR TOUCH SCREEN APPLICATIONS A Rail-to-Rail Input 12b 2 MS/s 0.18 µm CMOS Cyclic ADC for Touch Screen Applications Hee-Cheol
160 HEE-CHEOL CHOI et al : A RAIL-TO-RAIL INPUT 12B 2 MS/S 0.18 µm CMOS CYCLIC ADC FOR TOUCH SCREEN APPLICATIONS A Rail-to-Rail Input 12b 2 MS/s 0.18 µm CMOS Cyclic ADC for Touch Screen Applications Hee-Cheol
A Multichannel Pipeline Analog-to-Digital Converter for an Integrated 3-D Ultrasound Imaging System
 1266 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 38, NO. 7, JULY 2003 A Multichannel Pipeline Analog-to-Digital Converter for an Integrated 3-D Ultrasound Imaging System Kambiz Kaviani, Student Member,
1266 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 38, NO. 7, JULY 2003 A Multichannel Pipeline Analog-to-Digital Converter for an Integrated 3-D Ultrasound Imaging System Kambiz Kaviani, Student Member,
A 12-bit 100kS/s SAR ADC for Biomedical Applications. Sung-Chan Rho 1 and Shin-Il Lim 2. Seoul, Korea. Abstract
 , pp.17-22 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijunesst.2016.9.8.02 A 12-bit 100kS/s SAR ADC for Biomedical Applications Sung-Chan Rho 1 and Shin-Il Lim 2 1 Department of Electronics and Computer Engineering, Seokyeong
, pp.17-22 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijunesst.2016.9.8.02 A 12-bit 100kS/s SAR ADC for Biomedical Applications Sung-Chan Rho 1 and Shin-Il Lim 2 1 Department of Electronics and Computer Engineering, Seokyeong
A Two- Bit- per- Cycle Successive- Approximation ADC with Background Offset Calibration
 M. Casubolo, M. Grassi, A. Lombardi, F. Maloberti, P. Malcovati: "A Two-Bit-per- Cycle Successive-Approximation ADC with Background Calibration"; 15th IEEE Int. Conf. on Electronics, Circuits and Systems,
M. Casubolo, M. Grassi, A. Lombardi, F. Maloberti, P. Malcovati: "A Two-Bit-per- Cycle Successive-Approximation ADC with Background Calibration"; 15th IEEE Int. Conf. on Electronics, Circuits and Systems,
Design of Pipeline Analog to Digital Converter
 Design of Pipeline Analog to Digital Converter Vivek Tripathi, Chandrajit Debnath, Rakesh Malik STMicroelectronics The pipeline analog-to-digital converter (ADC) architecture is the most popular topology
Design of Pipeline Analog to Digital Converter Vivek Tripathi, Chandrajit Debnath, Rakesh Malik STMicroelectronics The pipeline analog-to-digital converter (ADC) architecture is the most popular topology
Another way to implement a folding ADC
 Another way to implement a folding ADC J. Van Valburg and R. van de Plassche, An 8-b 650 MHz Folding ADC, IEEE JSSC, vol 27, #12, pp. 1662-6, Dec 1992 Coupled Differential Pair J. Van Valburg and R. van
Another way to implement a folding ADC J. Van Valburg and R. van de Plassche, An 8-b 650 MHz Folding ADC, IEEE JSSC, vol 27, #12, pp. 1662-6, Dec 1992 Coupled Differential Pair J. Van Valburg and R. van
CMOS High Speed A/D Converter Architectures
 CHAPTER 3 CMOS High Speed A/D Converter Architectures 3.1 Introduction In the previous chapter, basic key functions are examined with special emphasis on the power dissipation associated with its implementation.
CHAPTER 3 CMOS High Speed A/D Converter Architectures 3.1 Introduction In the previous chapter, basic key functions are examined with special emphasis on the power dissipation associated with its implementation.
Deep-Submicron CMOS Design Methodology for High-Performance Low- Power Analog-to-Digital Converters
 Deep-Submicron CMOS Design Methodology for High-Performance Low- Power Analog-to-Digital Converters Abstract In this paper, we present a complete design methodology for high-performance low-power Analog-to-Digital
Deep-Submicron CMOS Design Methodology for High-Performance Low- Power Analog-to-Digital Converters Abstract In this paper, we present a complete design methodology for high-performance low-power Analog-to-Digital
CMOS ADC & DAC Principles
 CMOS ADC & DAC Principles Willy Sansen KULeuven, ESAT-MICAS Leuven, Belgium willy.sansen@esat.kuleuven.be Willy Sansen 10-05 201 Table of contents Definitions Digital-to-analog converters Resistive Capacitive
CMOS ADC & DAC Principles Willy Sansen KULeuven, ESAT-MICAS Leuven, Belgium willy.sansen@esat.kuleuven.be Willy Sansen 10-05 201 Table of contents Definitions Digital-to-analog converters Resistive Capacitive
A 14-bit 2.5 GS/s DAC based on Multi-Clock Synchronization. Hegang Hou*, Zongmin Wang, Ying Kong, Xinmang Peng, Haitao Guan, Jinhao Wang, Yan Ren
 Joint International Mechanical, Electronic and Information Technology Conference (JIMET 2015) A 14-bit 2.5 GS/s based on Multi-Clock Synchronization Hegang Hou*, Zongmin Wang, Ying Kong, Xinmang Peng,
Joint International Mechanical, Electronic and Information Technology Conference (JIMET 2015) A 14-bit 2.5 GS/s based on Multi-Clock Synchronization Hegang Hou*, Zongmin Wang, Ying Kong, Xinmang Peng,
DESIGN OF A NOVEL CURRENT MIRROR BASED DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER DESIGN WITH LATCH NETWORK. Thota Keerthi* 1, Ch. Anil Kumar 2
 ISSN 2277-2685 IJESR/October 2014/ Vol-4/Issue-10/682-687 Thota Keerthi et al./ International Journal of Engineering & Science Research DESIGN OF A NOVEL CURRENT MIRROR BASED DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER DESIGN
ISSN 2277-2685 IJESR/October 2014/ Vol-4/Issue-10/682-687 Thota Keerthi et al./ International Journal of Engineering & Science Research DESIGN OF A NOVEL CURRENT MIRROR BASED DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER DESIGN
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (IJARET)
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (IJARET) International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN ISSN 0976-6480 (Print) ISSN 0976-6499
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY (IJARET) International Journal of Advanced Research in Engineering and Technology (IJARET), ISSN ISSN 0976-6480 (Print) ISSN 0976-6499
6-Bit Charge Scaling DAC and SAR ADC
 6-Bit Charge Scaling DAC and SAR ADC Meghana Kulkarni 1, Muttappa Shingadi 2, G.H. Kulkarni 3 Associate Professor, Department of PG Studies, VLSI Design and Embedded Systems, VTU, Belgavi, India 1. M.Tech.
6-Bit Charge Scaling DAC and SAR ADC Meghana Kulkarni 1, Muttappa Shingadi 2, G.H. Kulkarni 3 Associate Professor, Department of PG Studies, VLSI Design and Embedded Systems, VTU, Belgavi, India 1. M.Tech.
Design of 1.8V, 72MS/s 12 Bit Pipeline ADC in 0.18µm Technology
 Design of 1.8V, 72MS/s 12 Bit Pipeline ADC in 0.18µm Technology Ravi Kumar 1, Seema Kanathe 2 ¹PG Scholar, Department of Electronics and Communication, Suresh GyanVihar University, Jaipur, India ²Assistant
Design of 1.8V, 72MS/s 12 Bit Pipeline ADC in 0.18µm Technology Ravi Kumar 1, Seema Kanathe 2 ¹PG Scholar, Department of Electronics and Communication, Suresh GyanVihar University, Jaipur, India ²Assistant
A low power 12-bit and 25-MS/s pipelined ADC for the ILC/Ecal integrated readout
 A low power 12-bit and 25-MS/s pipelined ADC for the ILC/Ecal integrated readout F. Rarbi, D. Dzahini, L. Gallin-Martel To cite this version: F. Rarbi, D. Dzahini, L. Gallin-Martel. A low power 12-bit
A low power 12-bit and 25-MS/s pipelined ADC for the ILC/Ecal integrated readout F. Rarbi, D. Dzahini, L. Gallin-Martel To cite this version: F. Rarbi, D. Dzahini, L. Gallin-Martel. A low power 12-bit
DESIGN AND PERFORMANCE VERIFICATION OF CURRENT CONVEYOR BASED PIPELINE A/D CONVERTER USING 180 NM TECHNOLOGY
 DESIGN AND PERFORMANCE VERIFICATION OF CURRENT CONVEYOR BASED PIPELINE A/D CONVERTER USING 180 NM TECHNOLOGY Neha Bakawale Departmentof Electronics & Instrumentation Engineering, Shri G. S. Institute of
DESIGN AND PERFORMANCE VERIFICATION OF CURRENT CONVEYOR BASED PIPELINE A/D CONVERTER USING 180 NM TECHNOLOGY Neha Bakawale Departmentof Electronics & Instrumentation Engineering, Shri G. S. Institute of
MT-025: ADC Architectures VI: Folding ADCs
 MT-025: ADC Architectures VI: Folding ADCs by Walt Kester REV. 0, 02-13-06 INTRODUCTION The "folding" architecture is one of a number of possible serial or bit-per-stage architectures. Various architectures
MT-025: ADC Architectures VI: Folding ADCs by Walt Kester REV. 0, 02-13-06 INTRODUCTION The "folding" architecture is one of a number of possible serial or bit-per-stage architectures. Various architectures
A Design of 8-bit Pipelined ADC for High Speed Applications Using Cadence Virtuoso
 A Design of 8-bit Pipelined ADC for High Speed Applications Using Cadence Virtuoso C Ashwini 1, Prof Naveen I G 2, Bhanuteja G 3 P.G. Student, Department of Electronics Engineering, Sir MVIT College, Bangalore,
A Design of 8-bit Pipelined ADC for High Speed Applications Using Cadence Virtuoso C Ashwini 1, Prof Naveen I G 2, Bhanuteja G 3 P.G. Student, Department of Electronics Engineering, Sir MVIT College, Bangalore,
A 2-bit/step SAR ADC structure with one radix-4 DAC
 A 2-bit/step SAR ADC structure with one radix-4 DAC M. H. M. Larijani and M. B. Ghaznavi-Ghoushchi a) School of Engineering, Shahed University, Tehran, Iran a) ghaznavi@shahed.ac.ir Abstract: In this letter,
A 2-bit/step SAR ADC structure with one radix-4 DAC M. H. M. Larijani and M. B. Ghaznavi-Ghoushchi a) School of Engineering, Shahed University, Tehran, Iran a) ghaznavi@shahed.ac.ir Abstract: In this letter,
International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development. Design of Pipelined ADC for High Speed Application
 g Scientific Journal of Impact Factor(SJIF): 3.134 e-issn(o): 2348-4470 p-issn(p): 2348-6406 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 2,Issue 4, April -2015 Design of
g Scientific Journal of Impact Factor(SJIF): 3.134 e-issn(o): 2348-4470 p-issn(p): 2348-6406 International Journal of Advance Engineering and Research Development Volume 2,Issue 4, April -2015 Design of
Proposing. An Interpolated Pipeline ADC
 Proposing An Interpolated Pipeline ADC Akira Matsuzawa Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan Matsuzawa & Okada Lab. Background 38GHz long range mm-wave system Role of long range mm-wave Current Optical
Proposing An Interpolated Pipeline ADC Akira Matsuzawa Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan Matsuzawa & Okada Lab. Background 38GHz long range mm-wave system Role of long range mm-wave Current Optical
DESIGN OF MULTI-BIT DELTA-SIGMA A/D CONVERTERS
 DESIGN OF MULTI-BIT DELTA-SIGMA A/D CONVERTERS DESIGN OF MULTI-BIT DELTA-SIGMA A/D CONVERTERS by Yves Geerts Alcatel Microelectronics, Belgium Michiel Steyaert KU Leuven, Belgium and Willy Sansen KU Leuven,
DESIGN OF MULTI-BIT DELTA-SIGMA A/D CONVERTERS DESIGN OF MULTI-BIT DELTA-SIGMA A/D CONVERTERS by Yves Geerts Alcatel Microelectronics, Belgium Michiel Steyaert KU Leuven, Belgium and Willy Sansen KU Leuven,
Analysis of the system level design of a 1.5 bit/stage pipeline ADC 1 Amit Kumar Tripathi, 2 Rishi Singhal, 3 Anurag Verma
 014 Fourth International Conference on Advanced Computing & Communication Technologies Analysis of the system level design of a 1.5 bit/stage pipeline ADC 1 Amit Kumar Tripathi, Rishi Singhal, 3 Anurag
014 Fourth International Conference on Advanced Computing & Communication Technologies Analysis of the system level design of a 1.5 bit/stage pipeline ADC 1 Amit Kumar Tripathi, Rishi Singhal, 3 Anurag
High Voltage Operational Amplifiers in SOI Technology
 High Voltage Operational Amplifiers in SOI Technology Kishore Penmetsa, Kenneth V. Noren, Herbert L. Hess and Kevin M. Buck Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Idaho Abstract This paper
High Voltage Operational Amplifiers in SOI Technology Kishore Penmetsa, Kenneth V. Noren, Herbert L. Hess and Kevin M. Buck Department of Electrical Engineering, University of Idaho Abstract This paper
620 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 45, NO. 3, MARCH /$ IEEE
 620 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 45, NO. 3, MARCH 2010 A 12 bit 50 MS/s CMOS Nyquist A/D Converter With a Fully Differential Class-AB Switched Op-Amp Young-Ju Kim, Hee-Cheol Choi, Gil-Cho
620 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 45, NO. 3, MARCH 2010 A 12 bit 50 MS/s CMOS Nyquist A/D Converter With a Fully Differential Class-AB Switched Op-Amp Young-Ju Kim, Hee-Cheol Choi, Gil-Cho
A Design of Sigma-Delta ADC Using OTA
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS A Design of Sigma-Delta ADC Using OTA Miss. Niveditha Yadav M 1, Mr. Yaseen Basha 2, Dr. Venkatesh kumar H 3 1 Department of ECE, PG Student, NCET/VTU, and Bengaluru, India
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS A Design of Sigma-Delta ADC Using OTA Miss. Niveditha Yadav M 1, Mr. Yaseen Basha 2, Dr. Venkatesh kumar H 3 1 Department of ECE, PG Student, NCET/VTU, and Bengaluru, India
Design of Successive Approximation Analog to Digital Converter with Modified DAC
 Design of Successive Approximation Analog to Digital Converter with Modified DAC Nikhil A. Bobade Dr. Mahendra A. Gaikwad Prof. Jayshri D. Dhande Dept. of Electronics Professor Assistant Professor Nagpur
Design of Successive Approximation Analog to Digital Converter with Modified DAC Nikhil A. Bobade Dr. Mahendra A. Gaikwad Prof. Jayshri D. Dhande Dept. of Electronics Professor Assistant Professor Nagpur
CAPACITOR mismatch is a major source of missing codes
 1626 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 43, NO. 7, JULY 2008 An 11-Bit 45 MS/s Pipelined ADC With Rapid Calibration of DAC Errors in a Multibit Pipeline Stage Imran Ahmed, Student Member, IEEE,
1626 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 43, NO. 7, JULY 2008 An 11-Bit 45 MS/s Pipelined ADC With Rapid Calibration of DAC Errors in a Multibit Pipeline Stage Imran Ahmed, Student Member, IEEE,
EE247 Lecture 23. Advanced calibration techniques. Compensating inter-stage amplifier non-linearity Calibration via parallel & slow ADC
 EE247 Lecture 23 Pipelined ADCs Combining the bits Stage implementation Circuits Noise budgeting Advanced calibration techniques Compensating inter-stage amplifier non-linearity Calibration via parallel
EE247 Lecture 23 Pipelined ADCs Combining the bits Stage implementation Circuits Noise budgeting Advanced calibration techniques Compensating inter-stage amplifier non-linearity Calibration via parallel
High-Speed Analog to Digital Converters. ELCT 1003:High Speed ADCs
 High-Speed Analog to Digital Converters Ann Kotkat Barbara Georgy Mahmoud Tantawi Ayman Sakr Heidi El-Feky Nourane Gamal 1 Outline Introduction. Process of ADC. ADC Specifications. Flash ADC. Pipelined
High-Speed Analog to Digital Converters Ann Kotkat Barbara Georgy Mahmoud Tantawi Ayman Sakr Heidi El-Feky Nourane Gamal 1 Outline Introduction. Process of ADC. ADC Specifications. Flash ADC. Pipelined
A Low Power, 8-Bit, 5MS/s Digital to Analog Converter for Successive Approximation ADC
 IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP) ISSN: 2319 4200, ISBN No. : 2319 4197 Volume 1, Issue 4 (Nov. - Dec. 2012), PP 42-46 A Low Power, 8-Bit, 5MS/s Digital to Analog Converter for Successive
IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP) ISSN: 2319 4200, ISBN No. : 2319 4197 Volume 1, Issue 4 (Nov. - Dec. 2012), PP 42-46 A Low Power, 8-Bit, 5MS/s Digital to Analog Converter for Successive
Simulation of High Performance Pipelined ADC Based on Optical Component Using VHDL
 Simulation of High Performance Pipelined ADC Based on Optical Component Using VHDL Kavita chourasia, Abhishek Choubey, Sudhir kumar Abstract This thesis explores the high performance ADC based on optical
Simulation of High Performance Pipelined ADC Based on Optical Component Using VHDL Kavita chourasia, Abhishek Choubey, Sudhir kumar Abstract This thesis explores the high performance ADC based on optical
DESIGN OF LOW POWER SAR ADC FOR ECG USING 45nm CMOS TECHNOLOGY
 DESIGN OF LOW POWER SAR ADC FOR ECG USING 45nm CMOS TECHNOLOGY Silpa Kesav 1, K.S.Nayanathara 2 and B.K. Madhavi 3 1,2 (ECE, CVR College of Engineering, Hyderabad, India) 3 (ECE, Sridevi Women s Engineering
DESIGN OF LOW POWER SAR ADC FOR ECG USING 45nm CMOS TECHNOLOGY Silpa Kesav 1, K.S.Nayanathara 2 and B.K. Madhavi 3 1,2 (ECE, CVR College of Engineering, Hyderabad, India) 3 (ECE, Sridevi Women s Engineering
Design of a Low Power Current Steering Digital to Analog Converter in CMOS
 Design of a Low Power Current Steering Digital to Analog Converter in CMOS Ranjan Kumar Mahapatro M. Tech, Dept. of ECE Centurion University of Technology & Management Paralakhemundi, India Sandipan Pine
Design of a Low Power Current Steering Digital to Analog Converter in CMOS Ranjan Kumar Mahapatro M. Tech, Dept. of ECE Centurion University of Technology & Management Paralakhemundi, India Sandipan Pine
Design Strategy for a Pipelined ADC Employing Digital Post-Correction
 Design Strategy for a Pipelined ADC Employing Digital Post-Correction Pieter Harpe, Athon Zanikopoulos, Hans Hegt and Arthur van Roermund Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, Mixed-signal Microelectronics
Design Strategy for a Pipelined ADC Employing Digital Post-Correction Pieter Harpe, Athon Zanikopoulos, Hans Hegt and Arthur van Roermund Technische Universiteit Eindhoven, Mixed-signal Microelectronics
A low-variation on-resistance CMOS sampling switch for high-speed high-performance applications
 A low-variation on-resistance CMOS sampling switch for high-speed high-performance applications MohammadReza Asgari 1 and Omid Hashemipour 2a) 1 Microelectronic Lab, Shahid Beheshti University, G. C. Tehran,
A low-variation on-resistance CMOS sampling switch for high-speed high-performance applications MohammadReza Asgari 1 and Omid Hashemipour 2a) 1 Microelectronic Lab, Shahid Beheshti University, G. C. Tehran,
A Digitally Enhanced 1.8-V 15-b 40- Msample/s CMOS Pipelined ADC
 A Digitally Enhanced.8-V 5-b 4- Msample/s CMOS d ADC Eric Siragusa and Ian Galton University of California San Diego Now with Analog Devices San Diego California Outline Conventional PADC Example Digitally
A Digitally Enhanced.8-V 5-b 4- Msample/s CMOS d ADC Eric Siragusa and Ian Galton University of California San Diego Now with Analog Devices San Diego California Outline Conventional PADC Example Digitally
SUCCESSIVE approximation register (SAR) analog-todigital
 426 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 62, NO. 5, MAY 2015 A Novel Hybrid Radix-/Radix-2 SAR ADC With Fast Convergence and Low Hardware Complexity Manzur Rahman, Arindam
426 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 62, NO. 5, MAY 2015 A Novel Hybrid Radix-/Radix-2 SAR ADC With Fast Convergence and Low Hardware Complexity Manzur Rahman, Arindam
MT-024: ADC Architectures V: Pipelined Subranging ADCs
 MT-024: ADC Architectures V: Pipelined Subranging ADCs by Walt Kester Rev. 0, 02-13-06 INTRODUCTION The pipelined subranging ADC architecture dominates today's applications where sampling rates of greater
MT-024: ADC Architectures V: Pipelined Subranging ADCs by Walt Kester Rev. 0, 02-13-06 INTRODUCTION The pipelined subranging ADC architecture dominates today's applications where sampling rates of greater
EE247 Lecture 20. Comparator architecture examples Flash ADC sources of error Sparkle code Meta-stability
 EE247 Lecture 2 ADC Converters ADC architectures (continued) Comparator architectures Latched comparators Latched comparators incorporating preamplifier Sample-data comparators Offset cancellation Comparator
EE247 Lecture 2 ADC Converters ADC architectures (continued) Comparator architectures Latched comparators Latched comparators incorporating preamplifier Sample-data comparators Offset cancellation Comparator
IMPLEMENTING THE 10-BIT, 50MS/SEC PIPELINED ADC
 98 CHAPTER 5 IMPLEMENTING THE 0-BIT, 50MS/SEC PIPELINED ADC 99 5.0 INTRODUCTION This chapter is devoted to describe the implementation of a 0-bit, 50MS/sec pipelined ADC with different stage resolutions
98 CHAPTER 5 IMPLEMENTING THE 0-BIT, 50MS/SEC PIPELINED ADC 99 5.0 INTRODUCTION This chapter is devoted to describe the implementation of a 0-bit, 50MS/sec pipelined ADC with different stage resolutions
Pipelined Analog-to-Digital Converters
 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Pipelined Analog-to-Digital Converters Vishal Saxena Vishal Saxena -1- Multi-Step A/D Conversion Basics Vishal Saxena -2-2 Motivation for Multi-Step Converters
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Pipelined Analog-to-Digital Converters Vishal Saxena Vishal Saxena -1- Multi-Step A/D Conversion Basics Vishal Saxena -2-2 Motivation for Multi-Step Converters
Scalable and Synthesizable. Analog IPs
 Scalable and Synthesizable Analog IPs Akira Matsuzawa Tokyo Institute of Technology Background and Motivation 1 Issues It becomes more difficult to obtain good analog IPs Insufficient design resources
Scalable and Synthesizable Analog IPs Akira Matsuzawa Tokyo Institute of Technology Background and Motivation 1 Issues It becomes more difficult to obtain good analog IPs Insufficient design resources
A 12b 50MS/s 2.1mW SAR ADC with redundancy and digital background calibration
 A b 5MS/s.mW SAR ADC with redundancy and digital background calibration The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As
A b 5MS/s.mW SAR ADC with redundancy and digital background calibration The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As
BICMOS Technology and Fabrication
 12-1 BICMOS Technology and Fabrication 12-2 Combines Bipolar and CMOS transistors in a single integrated circuit By retaining benefits of bipolar and CMOS, BiCMOS is able to achieve VLSI circuits with
12-1 BICMOS Technology and Fabrication 12-2 Combines Bipolar and CMOS transistors in a single integrated circuit By retaining benefits of bipolar and CMOS, BiCMOS is able to achieve VLSI circuits with
Mrs. C.Mageswari. [1] Mr. M.Ashok [2]
![Mrs. C.Mageswari. [1] Mr. M.Ashok [2] Mrs. C.Mageswari. [1] Mr. M.Ashok [2]](/thumbs/82/85891871.jpg) DESIGN OF HIGH SPEED SPLIT SAR ADC WITH IMPROVED LINEARITY Mrs. C.Mageswari. [1] Mr. M.Ashok [2] Abstract--Recently low power Analog to Digital Converters (ADCs) have been developed for many energy constrained
DESIGN OF HIGH SPEED SPLIT SAR ADC WITH IMPROVED LINEARITY Mrs. C.Mageswari. [1] Mr. M.Ashok [2] Abstract--Recently low power Analog to Digital Converters (ADCs) have been developed for many energy constrained
A 4 GSample/s 8-bit ADC in. Ken Poulton, Robert Neff, Art Muto, Wei Liu, Andrew Burstein*, Mehrdad Heshami* Agilent Laboratories Palo Alto, California
 A 4 GSample/s 8-bit ADC in 0.35 µm CMOS Ken Poulton, Robert Neff, Art Muto, Wei Liu, Andrew Burstein*, Mehrdad Heshami* Agilent Laboratories Palo Alto, California 1 Outline Background Chip Architecture
A 4 GSample/s 8-bit ADC in 0.35 µm CMOS Ken Poulton, Robert Neff, Art Muto, Wei Liu, Andrew Burstein*, Mehrdad Heshami* Agilent Laboratories Palo Alto, California 1 Outline Background Chip Architecture
Optimizing the Stage Resolution of a 10-Bit, 50 Ms/Sec Pipelined A/D Converter & Its Impact on Speed, Power, Area, and Linearity
 Circuits and Systems, 202, 3, 66-75 http://dx.doi.org/0.4236/cs.202.32022 Published Online April 202 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/cs) Optimizing the Stage Resolution of a 0-Bit, 50 Ms/Sec Pipelined A/D
Circuits and Systems, 202, 3, 66-75 http://dx.doi.org/0.4236/cs.202.32022 Published Online April 202 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/cs) Optimizing the Stage Resolution of a 0-Bit, 50 Ms/Sec Pipelined A/D
Design of Analog Integrated Systems (ECE 615) Outline
 Design of Analog Integrated Systems (ECE 615) Lecture 9 SAR and Cyclic (Algorithmic) Analog-to-Digital Converters Ayman H. Ismail Integrated Circuits Laboratory Ain Shams University Cairo, Egypt ayman.hassan@eng.asu.edu.eg
Design of Analog Integrated Systems (ECE 615) Lecture 9 SAR and Cyclic (Algorithmic) Analog-to-Digital Converters Ayman H. Ismail Integrated Circuits Laboratory Ain Shams University Cairo, Egypt ayman.hassan@eng.asu.edu.eg
AD9772A - Functional Block Diagram
 F FEATURES single 3.0 V to 3.6 V supply 14-Bit DAC Resolution 160 MPS Input Data Rate 67.5 MHz Reconstruction Passband @ 160 MPS 74 dbc FDR @ 25 MHz 2 Interpolation Filter with High- or Low-Pass Response
F FEATURES single 3.0 V to 3.6 V supply 14-Bit DAC Resolution 160 MPS Input Data Rate 67.5 MHz Reconstruction Passband @ 160 MPS 74 dbc FDR @ 25 MHz 2 Interpolation Filter with High- or Low-Pass Response
Summary Last Lecture
 EE247 Lecture 23 Converters Techniques to reduce flash complexity Interpolating (continued) Folding Multi-Step s Two-Step flash Pipelined s EECS 247 Lecture 23: Data Converters 26 H.K. Page 1 Summary Last
EE247 Lecture 23 Converters Techniques to reduce flash complexity Interpolating (continued) Folding Multi-Step s Two-Step flash Pipelined s EECS 247 Lecture 23: Data Converters 26 H.K. Page 1 Summary Last
MSP430 Teaching Materials
 MSP430 Teaching Materials Chapter 9 Data Acquisition A/D Conversion Introduction Texas Instruments t Incorporated University of Beira Interior (PT) Pedro Dinis Gaspar, António Espírito Santo, Bruno Ribeiro,
MSP430 Teaching Materials Chapter 9 Data Acquisition A/D Conversion Introduction Texas Instruments t Incorporated University of Beira Interior (PT) Pedro Dinis Gaspar, António Espírito Santo, Bruno Ribeiro,
High-speed ADC techniques - overview and scaling issues - Vladimir Stojanovic
 High-speed ADC techniques - overview and scaling issues - Vladimir Stojanovic Outline High-Speed ADC applications Basic ADC performance metrics Architectures overview ADCs in 90s Limiting factors Conclusion
High-speed ADC techniques - overview and scaling issues - Vladimir Stojanovic Outline High-Speed ADC applications Basic ADC performance metrics Architectures overview ADCs in 90s Limiting factors Conclusion
A Successive Approximation ADC based on a new Segmented DAC
 A Successive Approximation ADC based on a new Segmented DAC segmented current-mode DAC successive approximation ADC bi-direction segmented current-mode DAC DAC INL 0.47 LSB DNL 0.154 LSB DAC 3V 8 2MS/s
A Successive Approximation ADC based on a new Segmented DAC segmented current-mode DAC successive approximation ADC bi-direction segmented current-mode DAC DAC INL 0.47 LSB DNL 0.154 LSB DAC 3V 8 2MS/s
Analog to Digital Conversion
 Analog to Digital Conversion Florian Erdinger Lehrstuhl für Schaltungstechnik und Simulation Technische Informatik der Uni Heidelberg VLSI Design - Mixed Mode Simulation F. Erdinger, ZITI, Uni Heidelberg
Analog to Digital Conversion Florian Erdinger Lehrstuhl für Schaltungstechnik und Simulation Technische Informatik der Uni Heidelberg VLSI Design - Mixed Mode Simulation F. Erdinger, ZITI, Uni Heidelberg
DESIGN OF FOLDING CIRCUIT AND SAMPLE AND HOLD FOR 6 BIT ADC
 DESIGN OF FOLDING CIRCUIT AND SAMPLE AND HOLD FOR 6 BIT ADC Prajeesh R 1, Manukrishna V R 2, Bellamkonda Saidilu 3 1 Assistant Professor, ECE Department, SVNCE, Mavelikara, Kerala, (India) 2,3 PhD Research
DESIGN OF FOLDING CIRCUIT AND SAMPLE AND HOLD FOR 6 BIT ADC Prajeesh R 1, Manukrishna V R 2, Bellamkonda Saidilu 3 1 Assistant Professor, ECE Department, SVNCE, Mavelikara, Kerala, (India) 2,3 PhD Research
A Low-Noise Self-Calibrating Dynamic Comparator for High-Speed ADCs
 1 A Low-Noise Self-Calibrating Dynamic Comparator for High-Speed ADCs Masaya Miyahara, Yusuke Asada, Daehwa Paik and Akira Matsuzawa Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan Outline 2 Motivation The Calibration
1 A Low-Noise Self-Calibrating Dynamic Comparator for High-Speed ADCs Masaya Miyahara, Yusuke Asada, Daehwa Paik and Akira Matsuzawa Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan Outline 2 Motivation The Calibration
A Low-power Area-efficient Switching Scheme for Chargesharing
 A Low-power Area-efficient Switching Scheme for Chargesharing DACs in SAR ADCs The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
A Low-power Area-efficient Switching Scheme for Chargesharing DACs in SAR ADCs The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
A 1.2V 8 BIT SAR ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER IN 90NM CMOS
 A 1.2V 8 BIT SAR ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER IN 90NM CMOS Shruti Gatade 1, M. Nagabhushan 2, Manjunath.R 3 1,3 Student, Department of ECE, M S Ramaiah Institute of Technology, Bangalore (India) 2 Assistant
A 1.2V 8 BIT SAR ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER IN 90NM CMOS Shruti Gatade 1, M. Nagabhushan 2, Manjunath.R 3 1,3 Student, Department of ECE, M S Ramaiah Institute of Technology, Bangalore (India) 2 Assistant
EFFICIENT LOW POWER DYNAMIC COMPARATOR FOR HIGH SPEED ADC s
 EFFICIENT LOW POWER DYNAMIC COMPARATOR FOR HIGH SPEED ADC s B.Padmavathi, ME (VLSI Design), Anand Institute of Higher Technology, Chennai, India krishypadma@gmail.com Abstract In electronics, a comparator
EFFICIENT LOW POWER DYNAMIC COMPARATOR FOR HIGH SPEED ADC s B.Padmavathi, ME (VLSI Design), Anand Institute of Higher Technology, Chennai, India krishypadma@gmail.com Abstract In electronics, a comparator
A 4b/cycle Flash-assisted SAR ADC with Comparator Speed-boosting Technique
 JOURNAL OF SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, VOL.18, NO.2, APRIL, 2018 ISSN(Print) 1598-1657 https://doi.org/10.5573/jsts.2018.18.2.281 ISSN(Online) 2233-4866 A 4b/cycle Flash-assisted SAR ADC with
JOURNAL OF SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, VOL.18, NO.2, APRIL, 2018 ISSN(Print) 1598-1657 https://doi.org/10.5573/jsts.2018.18.2.281 ISSN(Online) 2233-4866 A 4b/cycle Flash-assisted SAR ADC with
Design And Simulation Of First Order Sigma Delta ADC In 0.13um CMOS Technology Jaydip H. Chaudhari PG Student L. C. Institute of Technology, Bhandu
 Design And Simulation Of First Order Sigma Delta ADC In 0.13um CMOS Technology Jaydip H. Chaudhari PG Student L. C. Institute of Technology, Bhandu Gireeja D. Amin Assistant Professor L. C. Institute of
Design And Simulation Of First Order Sigma Delta ADC In 0.13um CMOS Technology Jaydip H. Chaudhari PG Student L. C. Institute of Technology, Bhandu Gireeja D. Amin Assistant Professor L. C. Institute of
Low Power Design of Successive Approximation Registers
 Low Power Design of Successive Approximation Registers Rabeeh Majidi ECE Department, Worcester Polytechnic Institute, Worcester MA USA rabeehm@ece.wpi.edu Abstract: This paper presents low power design
Low Power Design of Successive Approximation Registers Rabeeh Majidi ECE Department, Worcester Polytechnic Institute, Worcester MA USA rabeehm@ece.wpi.edu Abstract: This paper presents low power design
A 35 fj 10b 160 MS/s Pipelined- SAR ADC with Decoupled Flip- Around MDAC and Self- Embedded Offset Cancellation
 Y. Zu, C.- H. Chan, S.- W. Sin, S.- P. U, R.P. Martins, F. Maloberti: "A 35 fj 10b 160 MS/s Pipelined-SAR ADC with Decoupled Flip-Around MDAC and Self- Embedded Offset Cancellation"; IEEE Asian Solid-
Y. Zu, C.- H. Chan, S.- W. Sin, S.- P. U, R.P. Martins, F. Maloberti: "A 35 fj 10b 160 MS/s Pipelined-SAR ADC with Decoupled Flip-Around MDAC and Self- Embedded Offset Cancellation"; IEEE Asian Solid-
A 4-bit High Speed, Low Power Flash ADC by Employing Binary Search Algorithm 1 Brahmaiah Throvagunta, 2 Prashant K Shah
 A 4-bit High Speed, Low Power Flash ADC by Employing Binary Search Algorithm 1 Brahmaiah Throvagunta, 2 Prashant K Shah 1 Master of Technology,Dept. of VLSI &Embedded Systems,Sardar Vallabhbhai National
A 4-bit High Speed, Low Power Flash ADC by Employing Binary Search Algorithm 1 Brahmaiah Throvagunta, 2 Prashant K Shah 1 Master of Technology,Dept. of VLSI &Embedded Systems,Sardar Vallabhbhai National
An 11 Bit Sub- Ranging SAR ADC with Input Signal Range of Twice Supply Voltage
 D. Aksin, M.A. Al- Shyoukh, F. Maloberti: "An 11 Bit Sub-Ranging SAR ADC with Input Signal Range of Twice Supply Voltage"; IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, ISCAS 2007, New Orleans,
D. Aksin, M.A. Al- Shyoukh, F. Maloberti: "An 11 Bit Sub-Ranging SAR ADC with Input Signal Range of Twice Supply Voltage"; IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, ISCAS 2007, New Orleans,
A SAR-Assisted Two-Stage Pipeline ADC Chun C. Lee, Member, IEEE, and Michael P. Flynn, Senior Member, IEEE
 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 46, NO. 4, APRIL 2011 859 A SAR-Assisted Two-Stage Pipeline ADC Chun C. Lee, Member, IEEE, and Michael P. Flynn, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract Successive approximation
IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 46, NO. 4, APRIL 2011 859 A SAR-Assisted Two-Stage Pipeline ADC Chun C. Lee, Member, IEEE, and Michael P. Flynn, Senior Member, IEEE Abstract Successive approximation
High Speed CMOS Comparator Design with 5mV Resolution
 High Speed CMOS Comparator Design with 5mV Resolution Raghava Garipelly Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Sree Chaitanya College of Engineering, Karimnagar, A.P, INDIA. Abstract: A high speed CMOS comparator
High Speed CMOS Comparator Design with 5mV Resolution Raghava Garipelly Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Sree Chaitanya College of Engineering, Karimnagar, A.P, INDIA. Abstract: A high speed CMOS comparator
PG Scholar, Electronics (VLSI Design), PEC University of Technology, Chandigarh, India
 A Low Power 4 Bit Successive Approximation Analog-To-Digital Converter Using 180nm Technology Jasbir Kaur 1, Praveen Kumar 2 1 Assistant Professor, ECE Department, PEC University of Technology, Chandigarh,
A Low Power 4 Bit Successive Approximation Analog-To-Digital Converter Using 180nm Technology Jasbir Kaur 1, Praveen Kumar 2 1 Assistant Professor, ECE Department, PEC University of Technology, Chandigarh,
A Novel Architecture For An Energy Efficient And High Speed Sar Adc
 A Novel Architecture For An Energy Efficient And High Speed Sar Adc Ms.Vishnupriya Iv 1, Ms. Prathibha Varghese 2 1 (Electronics And Communication dept. Sree Narayana Gurukulam College of Engineering,
A Novel Architecture For An Energy Efficient And High Speed Sar Adc Ms.Vishnupriya Iv 1, Ms. Prathibha Varghese 2 1 (Electronics And Communication dept. Sree Narayana Gurukulam College of Engineering,
SAR ADC USING SINGLE-CAPACITOR PULSE WIDTH TO ANALOG CONVERTER BASED DAC. A Thesis. Presented to. The Graduate Faculty of the University of Akron
 SAR ADC USING SINGLE-CAPACITOR PULSE WIDTH TO ANALOG CONVERTER BASED DAC A Thesis Presented to The Graduate Faculty of the University of Akron In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree
SAR ADC USING SINGLE-CAPACITOR PULSE WIDTH TO ANALOG CONVERTER BASED DAC A Thesis Presented to The Graduate Faculty of the University of Akron In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree
2. ADC Architectures and CMOS Circuits
 /58 2. Architectures and CMOS Circuits Francesc Serra Graells francesc.serra.graells@uab.cat Departament de Microelectrònica i Sistemes Electrònics Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona paco.serra@imb-cnm.csic.es
/58 2. Architectures and CMOS Circuits Francesc Serra Graells francesc.serra.graells@uab.cat Departament de Microelectrònica i Sistemes Electrònics Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona paco.serra@imb-cnm.csic.es
Optimizing the Number of Bits/Stage in 10-Bit, 50Ms/Sec Pipelined A/D Converter Considering Area, Speed, Power and Linearity
 Optimizing the Number of Bits/Stage in 10-Bit, 50Ms/Sec Pipelined /D Converter Considering rea, Speed, Power and Linearity P. Prasad Rao, K. Lal Kishore bstract Pipeline DCs are becoming popular at high
Optimizing the Number of Bits/Stage in 10-Bit, 50Ms/Sec Pipelined /D Converter Considering rea, Speed, Power and Linearity P. Prasad Rao, K. Lal Kishore bstract Pipeline DCs are becoming popular at high
Optimizing the Number of Bits/Stage in 10-Bit, 50Ms/Sec Pipelined A/D Converter Considering Area, Speed, Power and Linearity
 Optimizing the Number of Bits/Stage in 10-Bit, 50Ms/Sec Pipelined /D Converter Considering rea, Speed, Power and Linearity P. Prasad Rao, K. Lal Kishore bstract Pipeline DCs are becoming popular at high
Optimizing the Number of Bits/Stage in 10-Bit, 50Ms/Sec Pipelined /D Converter Considering rea, Speed, Power and Linearity P. Prasad Rao, K. Lal Kishore bstract Pipeline DCs are becoming popular at high
CHAPTER 3 DESIGN OF PIPELINED ADC USING SCS-CDS AND OP-AMP SHARING TECHNIQUE
 CHAPTER 3 DESIGN OF PIPELINED ADC USING SCS-CDS AND OP-AMP SHARING TECHNIQUE 3.1 INTRODUCTION An ADC is a device which converts a continuous quantity into discrete digital signal. Among its types, pipelined
CHAPTER 3 DESIGN OF PIPELINED ADC USING SCS-CDS AND OP-AMP SHARING TECHNIQUE 3.1 INTRODUCTION An ADC is a device which converts a continuous quantity into discrete digital signal. Among its types, pipelined
International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering & Technology (IJECET), INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRONICS AND
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJECET) ISSN 0976 6464(Print) ISSN 0976 6472(Online) Volume 4, Issue 3, May June, 2013, pp. 24-32 IAEME: www.iaeme.com/ijecet.asp
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJECET) ISSN 0976 6464(Print) ISSN 0976 6472(Online) Volume 4, Issue 3, May June, 2013, pp. 24-32 IAEME: www.iaeme.com/ijecet.asp
A PSEUDO-CLASS-AB TELESCOPIC-CASCODE OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
 A PSEUDO-CLASS-AB TELESCOPIC-CASCODE OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER M. Taherzadeh-Sani, R. Lotfi, and O. Shoaei ABSTRACT A novel class-ab architecture for single-stage operational amplifiers is presented. The structure
A PSEUDO-CLASS-AB TELESCOPIC-CASCODE OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER M. Taherzadeh-Sani, R. Lotfi, and O. Shoaei ABSTRACT A novel class-ab architecture for single-stage operational amplifiers is presented. The structure
THE pipelined ADC architecture has been adopted into
 1468 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 39, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2004 A 1.8-V 67-mW 10-bit 100-MS/s Pipelined ADC Using Time-Shifted CDS Technique Jipeng Li, Member, IEEE, and Un-Ku Moon, Senior Member,
1468 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 39, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2004 A 1.8-V 67-mW 10-bit 100-MS/s Pipelined ADC Using Time-Shifted CDS Technique Jipeng Li, Member, IEEE, and Un-Ku Moon, Senior Member,
ISSCC 2004 / SESSION 25 / HIGH-RESOLUTION NYQUIST ADCs / 25.3
 ISSCC 2004 / SESSION 25 / HIGH-RESOLUTION NYQUIST ADCs / 25.3 25.3 A 96dB SFDR 50MS/s Digitally Enhanced CMOS Pipeline A/D Converter K. Nair, R. Harjani University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN Analog-to-digital
ISSCC 2004 / SESSION 25 / HIGH-RESOLUTION NYQUIST ADCs / 25.3 25.3 A 96dB SFDR 50MS/s Digitally Enhanced CMOS Pipeline A/D Converter K. Nair, R. Harjani University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN Analog-to-digital
A 130mW 100MS/s Pipelined ADC with 69dB SNDR Enabled by Digital Harmonic Distortion Correction. Andrea Panigada, Ian Galton
 A 130mW 100MS/s Pipelined ADC with 69dB SNDR Enabled by Digital Harmonic Distortion Correction Andrea Panigada, Ian Galton University of California at San Diego, La Jolla, CA INTEGRATED SIGNAL PROCESSING
A 130mW 100MS/s Pipelined ADC with 69dB SNDR Enabled by Digital Harmonic Distortion Correction Andrea Panigada, Ian Galton University of California at San Diego, La Jolla, CA INTEGRATED SIGNAL PROCESSING
/$ IEEE
 894 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 56, NO. 5, MAY 2009 A 1.2-V 12-b 120-MS/s SHA-Free Dual-Channel Nyquist ADC Based on Midcode Calibration Hee-Cheol Choi, Young-Ju Kim,
894 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 56, NO. 5, MAY 2009 A 1.2-V 12-b 120-MS/s SHA-Free Dual-Channel Nyquist ADC Based on Midcode Calibration Hee-Cheol Choi, Young-Ju Kim,
Mixed-Signal-Electronics
 1 Mixed-Signal-Electronics PD Dr.-Ing. Stephan Henzler 2 Chapter 6 Nyquist Rate Analog-to-Digital Converters 3 Pipelined ADC 2 4 High-Speed ADC: Pipeline Processing Stephan Henzler Advanced Integrated
1 Mixed-Signal-Electronics PD Dr.-Ing. Stephan Henzler 2 Chapter 6 Nyquist Rate Analog-to-Digital Converters 3 Pipelined ADC 2 4 High-Speed ADC: Pipeline Processing Stephan Henzler Advanced Integrated
Design of 10-bit current steering DAC with binary and segmented architecture
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. III (May. June. 2018), PP 62-66 www.iosrjournals.org Design of 10-bit current
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. III (May. June. 2018), PP 62-66 www.iosrjournals.org Design of 10-bit current
Electronics A/D and D/A converters
 Electronics A/D and D/A converters Prof. Márta Rencz, Gábor Takács, Dr. György Bognár, Dr. Péter G. Szabó BME DED December 1, 2014 1 / 26 Introduction The world is analog, signal processing nowadays is
Electronics A/D and D/A converters Prof. Márta Rencz, Gábor Takács, Dr. György Bognár, Dr. Péter G. Szabó BME DED December 1, 2014 1 / 26 Introduction The world is analog, signal processing nowadays is
Test Results of the HTADC12 12 Bit Analog to Digital Converter at 250 O C
 Test Results of the HTADC12 12 Bit Analog to Digital Converter at 250 O C Thomas J. Romanko and Mark R. Larson Honeywell International Inc. Honeywell Aerospace, Defense & Space 12001 State Highway 55,
Test Results of the HTADC12 12 Bit Analog to Digital Converter at 250 O C Thomas J. Romanko and Mark R. Larson Honeywell International Inc. Honeywell Aerospace, Defense & Space 12001 State Highway 55,
Performance Evaluation of Different Types of CMOS Operational Transconductance Amplifier
 Performance Evaluation of Different Types of CMOS Operational Transconductance Amplifier Kalpesh B. Pandya 1, Kehul A. shah 2 1 Gujarat Technological University, Department of Electronics & Communication,
Performance Evaluation of Different Types of CMOS Operational Transconductance Amplifier Kalpesh B. Pandya 1, Kehul A. shah 2 1 Gujarat Technological University, Department of Electronics & Communication,
Low-Power Pipelined ADC Design for Wireless LANs
 Low-Power Pipelined ADC Design for Wireless LANs J. Arias, D. Bisbal, J. San Pablo, L. Quintanilla, L. Enriquez, J. Vicente, J. Barbolla Dept. de Electricidad y Electrónica, E.T.S.I. de Telecomunicación,
Low-Power Pipelined ADC Design for Wireless LANs J. Arias, D. Bisbal, J. San Pablo, L. Quintanilla, L. Enriquez, J. Vicente, J. Barbolla Dept. de Electricidad y Electrónica, E.T.S.I. de Telecomunicación,
Implementation of High Performance Carry Save Adder Using Domino Logic
 Page 136 Implementation of High Performance Carry Save Adder Using Domino Logic T.Jayasimha 1, Daka Lakshmi 2, M.Gokula Lakshmi 3, S.Kiruthiga 4 and K.Kaviya 5 1 Assistant Professor, Department of ECE,
Page 136 Implementation of High Performance Carry Save Adder Using Domino Logic T.Jayasimha 1, Daka Lakshmi 2, M.Gokula Lakshmi 3, S.Kiruthiga 4 and K.Kaviya 5 1 Assistant Professor, Department of ECE,
10.1: A 4 GSample/s 8b ADC in 0.35-um CMOS
 10.1: A 4 GSample/s 8b ADC in 0.35-um CMOS Ken Poulton, Robert Neff, Art Muto, Wei Liu*, Andy Burstein**, Mehrdad Heshami*** Agilent Technologies, Palo Alto, CA *Agilent Technologies, Colorado Springs,
10.1: A 4 GSample/s 8b ADC in 0.35-um CMOS Ken Poulton, Robert Neff, Art Muto, Wei Liu*, Andy Burstein**, Mehrdad Heshami*** Agilent Technologies, Palo Alto, CA *Agilent Technologies, Colorado Springs,
Asynchronous SAR ADC: Past, Present and Beyond. Mike Shuo-Wei Chen University of Southern California MWSCAS 2014
 Asynchronous SAR ADC: Past, Present and Beyond Mike Shuo-Wei Chen University of Southern California MWSCAS 2014 1 Roles of ADCs Responsibility of ADC is increasing more BW, more dynamic range Potentially
Asynchronous SAR ADC: Past, Present and Beyond Mike Shuo-Wei Chen University of Southern California MWSCAS 2014 1 Roles of ADCs Responsibility of ADC is increasing more BW, more dynamic range Potentially
