4bit,6.5GHz Flash ADC for High Speed Application in 130nm
|
|
|
- Herbert McKenzie
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(10): , 2011 ISSN bit,6.5GHz Flash ADC for High Speed Application in 130nm 1 M.J. Taghizadeh.Marvast, 2 M.A. Mohd.Ali, 3 H. Sanusi Department of Electrical Electronic and Systems Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, National University of Malaysia, UKM Bang, Selangor Darul Ehsan, Malaysia. Abstract: A 6.5-GS/s4-bit flash ADC for high speed and ultra wide band application is designed in130 nanometer CMOS process. Several techniques are used to improve performance of flash ADC. High-speed ADC needs a fast comparator, a high-speed encoder, and a suitable reference ladder. Anew comparator used to improve sampling rate of flash ADC. This fully differential comparator consists of three stages using a new structure (domino CMOS logic) to improve its performance. In this paper, used of ballast capacitance to reduce reference voltage deviation at each tap and its effective technique to reduce thermal noise in ladder network. Moreover, the ADC also achieves lower power consumption compared to the earlier design. The flash ADC is able to operate with2v peak-topeak input ranges and consume design. The flash ADC is able to operate with2v peak-to-peak input ranges and consume only19.83mw. The measured ENOB is 5.42Bits at 6.5GS/s with a 2.2GHz sine wave input signal. The predicted performance is verified by analyses and simulations using HSPICE tool. Key words: Analog-to-digital converter, Comparator, High speed, Low power, Preamplifier, Decoder. INTRODUCTION Flash Flash analog-to-digital converters (ADC) with ultra wide-band (UWB) frequency sampling rates are critical components for applications such as radar, signal capture, satellite, digital oscilloscopes, disk drive read channels, wireless communication, UWB receivers and waveform recorders (Poutlon, 1995). UWB is an emerging technology for short range high data rate communications. The approval of UWB for unlicensed operation in the GHz band under a power emission level of dbm/mhz by the Federal Communications Commission (FCC), opened for the public to issue a standard for this communication. Today researchers and the industry have extended the requirement for higher frequency and higher sampling rate. On the other hand, flash ADC has many drawbacks. The first drawback is the hardware complexity. The flash ADC hardware complexity increases exponentially with the resolutions because it needs 2 N -1 comparator circuits. As a result the power dissipation and the chip area also increase exponentially with the resolution. However, the flash ADC is a suitable choice when high speed and low to moderate resolution are required. Flash ADCs published in recent years (Khalilzadeh, 2007; Park, 2006) still have relatively high power consumption and operate with sampling rate lower than the expected future requirement. Hence a new flash ADC structure using an improved comparator is proposed to be used for UWB technology that offer capabilities for the design of communications devices requiring very high performance and low power consumption. In this paper a new CMOS positive feedback and output logic is proposed to increase the speed of track and hold (T/H) of the comparator. The comparator design incorporates various techniques to lower its power consumption and improve its overall performance. II. Flash ADC Architecture: Fig.1 illustrates the role of flash ADC in a UWB system. For an "N"-bit converter, the circuit employs 2 N -1 comparators. A 4-bit flash ADC architecture are that consists of sample and hold, differential ladder network, comparators and digital back end is proposed. A resistive ladder with 2 N resistors provides the reference voltage. Here two independent resistive ladders are used as a differential reference ladder network. Ballast capacitance is used to reduce the reference voltage deviation, being an effective technique to reduce thermal noise (in high frequency) in the ladder network. Corresponding Author: M.J. Taghizadeh.Marvast, Department of Electrical Electronic and Systems Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, National University of Malaysia, UKM Bang, Selangor Darul Ehsan, Malaysia. Taghizad@eng.ukm.my 99
2 Aust. J. Basic & Appl. Sci., 5(10): , 2011 Fig.2 illustrates the proposed flash ADC block diagram.figure 2. Block diagram of 4bit flash ADC. The fully differential comparators form a new structure to achieve the overall high speed for the comparators. For the digital design stage MOS Common Mode Logic (MCML) is used with some dynamic logic and buffers. The encoder first converts the thermometer-code into Gray-code, and then generates the respective binary code. Gray-code encoding can also greatly improve metastability. Flash ADCs can generally achieve the higher sampling rates, with the comparator limiting the maximum achievable. Techniques to improve the performance of the ADC are proposed at each of its stages. Fig. 1: UWB system. Fig. 2: Block diagram of 4bit flash ADC. III. Reference Ladder: There are two design methods for the reference ladder network. Each method has particular advantages and disadvantages. The single structure is preferred when low power consumption and small die area are important, but in the single structure design kickback noise and crosstalk create a big problem for reference voltage at high frequency. In this paper we used two independent resistive ladders as differential reference ladder network, because the flash ADC is used at high frequency.figure 3. (a) single structure (b) two ladder network. As shown in Fig.3 the reference voltages are generated by a resistive ladder. This ladder is for 4-bit ADC and has 15 resistors with two redundant resistors on each ladder and generates 16 differential reference voltages for the comparators. All reference voltages for each pre-amplifier, which should be constant under all conditions. The voltage at each tap of the ladder network may change substantially from its nominal DC value and that is a big problem. Therefore, one important source of errors in flash A/D converter is affected by the capacitive feedthrough of the high frequency input signal to the resistive reference ladde r. In other words, the signal feedthrough causes variations of the reference voltages. The middle reference net output V mid is affected the most by the input signal feedthrough. The capacitance feedthrough is simulated by the model of Fig.4 that also shows ladder with capacitance feedthrough effect. Meanwhile, the feedthrough to the midpoint of the ladder as a worst case follows the equation: 100
3 V V mid in (4 ). f. RC. Aust. J. Basic & Appl. Sci., C(): CC-CC, 2011 (1) After expanding the model to the general case of 2 N 1 comparators, R and C are given by: R R tot N (2 1) (2) C C tot 2 N (3) where R tot is the total reference net resistance, N is number of bits and C tot is the total input. A good estimate of the maximum value of the ladder resistance is given by: R ( V V ) ( f C ) 4 (2 f C ) n Ladder max mid in in in. tot in in. tot (4) where Ф is the acceptable deviation value of central reference voltage and C in.tot is total input capacitance and f in is input frequency (Venes, 1996). In addition, resistance is scaled down to achieve a small feedthrough but considerable power-consumption in the reference ladder network (for high input frequencies). Therefore, there is a tradeoff between power consumption and feedthrough. The matching of the different resistors in the ladder network has directly influence on the differential and integral non-linearity of the converter. In this paper is used of ballast capacitance to reduce reference voltage deviation at each tap. This technique play important role to solve charge injection in front of preamplifier, the ballast capacitance is also effective technique to reduce thermal noise (in high frequency) in ladder network. Fig. 3: (a) single structure (b) two ladder network. Fig. 4: Model of capacitance feedthrough from input ladder. IV. Comparator: A. Comparator Architecture: The architecture of the comparator is shown in Fig. 5. The comparator structure is fully differential and consists of preamplifier, T/H and output circuits. The first stage is a low gain classical differential amplifier with resistive loads (Rd), which isolates the latches from reference voltages. 101
4 The comparator with resistive loads shows better linearity, offset and gain response in comparison with amplifiers with active or diode loads. Low noise amplifier is utilized to reduce the input referred offset of the comparator. The second stage is a CMOS T/H with positive feedback, inductor and current source are used to reduce regenerative time and consists of preamplifier, T/H and output circuits. Fig. 5: Schematic of comparator. There is a question that what aspects of the performance of comparator are important? In addition to power dissipation and speed, such parameters as supply voltage, gain, voltage swings, band width, distortion, input offset, linearity and overdrive recovery may be important. In practice, most of these parameter trade with each other, making the design a multi-dimensional optimization problem. Illustrated in Fig.6 such trade-off present many challenges in the design of high quality comparator for flash ADC, requiring intuition and experience to arrive at an acceptable compromise. Fig. 6: Relationship between comparator design parameters. B. Resistive Averaging: Averaging is a well known method to reduce the input offset of the comparators. Resistive averaging uses some resistors between the outputs of adjacent preamplifiers. This technique has been used in most of the flash ADCs. Fig.7 shows the structure of preamplifier with resistive averaging. In this method signal-to-noise is improved without extra power consumption. In addition, this is an effective technique to reduce the mismatch impact in comparator arrays. Furthermore, this technique has been used to improve static errors induced due to amplifiers offset error. The main drawback with this method is that we need over-range comparators to maintain the linearity at the edges. 102
5 Fig. 7: Resistive averaging in the comparator. Fig. 8: Comparator core (Track/Hold). C. Comparator Core (T/H) and Output Circuit: The comparator core is shown in Fig.8. The load is formed by the series combination of a resistor and an inductor. V p and V m are the differential analog inputs signal from the preamplifier. It has input differential pairs (MI and M2) that turn on when the clock is low and track the input from the previous stage. When the clock is high, the comparator goes into hold mode. In this paper CMOS positive feedback is used to improve speed of comparator and reduce the regenerative time in latching mode. The passive inductor peaking technique is also employed in the T/H circuit to enhance the bandwidth (Taghizadeh.,; Mohan, 2000). The domino output circuit as shown in Fig.5 is used instead of SR Latch to support the comparator in high sampling rate operation. The combination of T/H and output circuit (domino CMOS logic) creates a fast structure for the comparator. V. Encoder Circuit: The encoder in a flash ADC is very critical and one of the bottlenecks in high-speed operation. Furthermore, the encoder should be able to properly handle comparator metastability and bubble errors in the thermometer code. The schematic of encoder is shown in Fig.9. The encoder is designed using MOS Common Mode Logic (MCML). This type of design is the most efficient in terms of speed and very low swing signal operation. In other words, MCML circuits allow for operating on low-swing signals of the comparator outputs without converting them full-swing digital signals, therefore its reduced output swing and hence low-power dissipation. The encoder first converts the thermometer-code into gray-code, and then generates the respective binary code. The gray code stage provides only a 1-bit transition between consecutive states and thereby reduces the effects of code skipping and bubble errors at the output of the encoder. 103
6 A set of equations (5) shows the conversion from thermometer to gray code and then gray to 4-bit binary code. G1 C1C3. C5C7. C9C11. C13C15 G2 C2C6. C10C14 G3 C4C12 G4 C8 B1 G1 B2 B2 G2 B3 B3 G3 B4 B4 G4 (5) where C is thermometer code, B is bit binary code and G is gray code. Fig. 9: The schematic of a proposed encoder. VI. Simulation Results: The proposed flash ADC structure was designed using 130 nm CMOS technology. Simulation result was obtained by using HSPICE tool. Fig.10 shows the output wave of comparator with 0.5 GHz analog input signal and clock frequency of 6.5 Gs/s. Table I shows the summary of flash ADC, in comparison with the designs in (Khalilzadeh, 2007) and (Park, 2006). Performance Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) is performed to observe the dynamic characteristics of the comparator such as the effective number of bits (ENOB). Fig.11 illustrates FFT of flash ADC at input frequency of 2.2 GHz and sampling rate of 6.5 Gs/s. The new flash ADC dissipates only mw at 6.5 GS/s. Fig. 10: Output wave of comparator at Fin = 500 MGHz, F clk = 6.5 Gs/s. 104
7 Fig. 11: FFT at input frequency of 2200MHz and sampling rate of 6.5Gs/s Table I: ADC Performance Comparison. Item (Park, 2006) (Khalilzadeh, 2007) This work VDD 1.8 V 1.8 V 2 V Clock frequency 4 GS/s 4 GS/s 6.5 GS/s Resolution 4 bit 4bit 4bit DNL LSB 0.25LSB INL LSB 0.39 LSB SFDR 30 db dB Power consumption 89 mw 68 mw mw ENOB @ fin=1.5g 5.42@ fin=2.2g Process 0.18 μm 0.18 μm 0.13 μm years Conclusion: In this paper, a 0.13 μm CMOS flash ADC for high speed, low power and UWB application is proposed. The maximum sampling speed is 6.5 GS/s and the SFDR at 2.2 GHz is 26.4 db. The analog supply voltage is only 2 V. Several design issues have been discussed and used in the optimization. CMOS positive feedback and a new structure based on domino CMOS logic as output circuit are used to improve sampling rate and performance of comparator. The measured ENOB is 5.42 Bits at 6.5 GS/s with a 2.2 GHz sine wave input signal. ACKNOWLEDGMENT The authors would like to acknowledge Dr. Abdolreza Nabavi for his useful suggestion and Microelectronic Laboratory of Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran for software facilities REFERENCES Khalilzadeh, M., A. Nabavi, A Low-Power High-Speed 4-Bit ADC for DS-UWB Communications, IEEE Computer Society Annual Symposium on VLSI. ISVLSI'07, Porto Alege, Brazil. Mohan, S.S., M.D.M. Hershenson, S.P. Boyd and T.H. Lee, Bandwidth extension in CMOS with optimized on-chip inductors, IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits, 35(3): Mohan, A., A. Zayegh, A. Stojcevski, R. Veljanovski, High Speed Ultra Wide Band Comparator in Deep Sub-Micron CMOS, IEEE International Symposium on Integrated Circuits. ISIC07, Singapore. Oliveira, S.P., J. Goes, N. Paulino, J. Fernandes,2007. Improve low power low voltage CMOS comparator for 4-bit FLASH ADCS for UWB applications 14th International Conference. MIXDES07, Poland, Mohan, A., A. Zayegh and A. Stojcevski, A High Speed Analog to Digital Converter for Ultra Wide Band Applications, IFIP International Federation for Information Processing. Victoria, Australia, pp:
8 Poutlon, K., K.L. Knudsen, J.J. Corcoran, K. Wang, R.B. Nubling, R.L. Pierson, M.F. Chang, P.M. Asbeck, and R.T. Huang, A 6-b 4GSa/s GaAs HBT ADC, IEEE J. Solid- State Circuits, 30(10): Park, S., Y. Palaskas, and M.P. Flynn, A 4GS/s 4b Flash ADC in 0.18 CMOS, IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Input Frequency (GHz) Conference. ISSCC, San Francisco, USA, pp: Razavi, B.,1995. Principles of Data Conversion System Design, IEEE Pres. Venes A.G.W. and R.J. van de Plassche, "An 80-MHz, 80-mW, 8-b CMOS folding A/D converter with distributed track-and-hold preprocessing, IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, vol. 31, no. 12, pp Taghizadeh., M.J., M.A. Marvast, Mohd. Ali, High Speed Comparator for Flash ADC and UWB Application in 130 nm CMOS Technology IEEE International Conferenc. 106
The Caspian Sea Journal ISSN: Design of a New Flash ADC in 65 Nm CMOS Process
 Available online at http://www.csjonline.org/ The Caspian Sea Journal ISSN: 1578-7899 Volume 10, Issue 1, Supplement 4 (2016) 515-524 Design of a New Flash ADC in 65 Nm CMOS Process Mohammad Jafar Taghizadeh
Available online at http://www.csjonline.org/ The Caspian Sea Journal ISSN: 1578-7899 Volume 10, Issue 1, Supplement 4 (2016) 515-524 Design of a New Flash ADC in 65 Nm CMOS Process Mohammad Jafar Taghizadeh
A 42 fj 8-bit 1.0-GS/s folding and interpolating ADC with 1 GHz signal bandwidth
 LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.11, No.2, 1 9 A 42 fj 8-bit 1.0-GS/s folding and interpolating ADC with 1 GHz signal bandwidth Mingshuo Wang a), Fan Ye, Wei Li, and Junyan Ren b) State Key Laboratory
LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.11, No.2, 1 9 A 42 fj 8-bit 1.0-GS/s folding and interpolating ADC with 1 GHz signal bandwidth Mingshuo Wang a), Fan Ye, Wei Li, and Junyan Ren b) State Key Laboratory
A High Speed Analog to Digital Converter for Ultra Wide Band Applications
 A High Speed Analog to Digital Converter for Ultra Wide and Applications Anand Mohan, Aladin Zayegh, and Alex Stojcevski Centre for Telecommunications and Microelectronics School of Electrical Engineering
A High Speed Analog to Digital Converter for Ultra Wide and Applications Anand Mohan, Aladin Zayegh, and Alex Stojcevski Centre for Telecommunications and Microelectronics School of Electrical Engineering
A 2-bit/step SAR ADC structure with one radix-4 DAC
 A 2-bit/step SAR ADC structure with one radix-4 DAC M. H. M. Larijani and M. B. Ghaznavi-Ghoushchi a) School of Engineering, Shahed University, Tehran, Iran a) ghaznavi@shahed.ac.ir Abstract: In this letter,
A 2-bit/step SAR ADC structure with one radix-4 DAC M. H. M. Larijani and M. B. Ghaznavi-Ghoushchi a) School of Engineering, Shahed University, Tehran, Iran a) ghaznavi@shahed.ac.ir Abstract: In this letter,
A 4 GSample/s 8-bit ADC in. Ken Poulton, Robert Neff, Art Muto, Wei Liu, Andrew Burstein*, Mehrdad Heshami* Agilent Laboratories Palo Alto, California
 A 4 GSample/s 8-bit ADC in 0.35 µm CMOS Ken Poulton, Robert Neff, Art Muto, Wei Liu, Andrew Burstein*, Mehrdad Heshami* Agilent Laboratories Palo Alto, California 1 Outline Background Chip Architecture
A 4 GSample/s 8-bit ADC in 0.35 µm CMOS Ken Poulton, Robert Neff, Art Muto, Wei Liu, Andrew Burstein*, Mehrdad Heshami* Agilent Laboratories Palo Alto, California 1 Outline Background Chip Architecture
DESIGN OF A 500MHZ, 4-BIT LOW POWER ADC FOR UWB APPLICATION
 DESIGN OF A 500MHZ, 4-BIT LOW POWER ADC FOR UWB APPLICATION SANTOSH KUMAR PATNAIK 1, DR. SWAPNA BANERJEE 2 1,2 E & ECE Department, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur, Kharagpur, India Abstract-This
DESIGN OF A 500MHZ, 4-BIT LOW POWER ADC FOR UWB APPLICATION SANTOSH KUMAR PATNAIK 1, DR. SWAPNA BANERJEE 2 1,2 E & ECE Department, Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur, Kharagpur, India Abstract-This
Analog-to-Digital i Converters
 CSE 577 Spring 2011 Analog-to-Digital i Converters Jaehyun Lim, Kyusun Choi Department t of Computer Science and Engineering i The Pennsylvania State University ADC Glossary DNL (differential nonlinearity)
CSE 577 Spring 2011 Analog-to-Digital i Converters Jaehyun Lim, Kyusun Choi Department t of Computer Science and Engineering i The Pennsylvania State University ADC Glossary DNL (differential nonlinearity)
A High Speed Encoder for a 5GS/s 5 Bit Flash ADC
 A High Speed Encoder for a 5GS/s 5 Bit Flash ADC George Tom Varghese and K. K. Mahapatra Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, India E-mail:
A High Speed Encoder for a 5GS/s 5 Bit Flash ADC George Tom Varghese and K. K. Mahapatra Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, India E-mail:
10.1: A 4 GSample/s 8b ADC in 0.35-um CMOS
 10.1: A 4 GSample/s 8b ADC in 0.35-um CMOS Ken Poulton, Robert Neff, Art Muto, Wei Liu*, Andy Burstein**, Mehrdad Heshami*** Agilent Technologies, Palo Alto, CA *Agilent Technologies, Colorado Springs,
10.1: A 4 GSample/s 8b ADC in 0.35-um CMOS Ken Poulton, Robert Neff, Art Muto, Wei Liu*, Andy Burstein**, Mehrdad Heshami*** Agilent Technologies, Palo Alto, CA *Agilent Technologies, Colorado Springs,
A 14-bit 2.5 GS/s DAC based on Multi-Clock Synchronization. Hegang Hou*, Zongmin Wang, Ying Kong, Xinmang Peng, Haitao Guan, Jinhao Wang, Yan Ren
 Joint International Mechanical, Electronic and Information Technology Conference (JIMET 2015) A 14-bit 2.5 GS/s based on Multi-Clock Synchronization Hegang Hou*, Zongmin Wang, Ying Kong, Xinmang Peng,
Joint International Mechanical, Electronic and Information Technology Conference (JIMET 2015) A 14-bit 2.5 GS/s based on Multi-Clock Synchronization Hegang Hou*, Zongmin Wang, Ying Kong, Xinmang Peng,
High Speed Flash Analog to Digital Converters
 ECE 551, Analog Integrated Circuit Design, High Speed Flash ADCs, Dec 2005 1 High Speed Flash Analog to Digital Converters Alireza Mahmoodi Abstract Flash analog-to-digital converters, also known as parallel
ECE 551, Analog Integrated Circuit Design, High Speed Flash ADCs, Dec 2005 1 High Speed Flash Analog to Digital Converters Alireza Mahmoodi Abstract Flash analog-to-digital converters, also known as parallel
Cmos Full Adder and Multiplexer Based Encoder for Low Resolution Flash Adc
 IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 2278-2834,p- ISSN: 2278-8735.Volume 12, Issue 2, Ver. II (Mar.-Apr. 2017), PP 20-27 www.iosrjournals.org Cmos Full Adder and
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 2278-2834,p- ISSN: 2278-8735.Volume 12, Issue 2, Ver. II (Mar.-Apr. 2017), PP 20-27 www.iosrjournals.org Cmos Full Adder and
Deep-Submicron CMOS Design Methodology for High-Performance Low- Power Analog-to-Digital Converters
 Deep-Submicron CMOS Design Methodology for High-Performance Low- Power Analog-to-Digital Converters Abstract In this paper, we present a complete design methodology for high-performance low-power Analog-to-Digital
Deep-Submicron CMOS Design Methodology for High-Performance Low- Power Analog-to-Digital Converters Abstract In this paper, we present a complete design methodology for high-performance low-power Analog-to-Digital
A Novel ROM Architecture for Reducing Bubble and Metastability Errors in High Speed Flash ADCs
 1 A Novel ROM Architecture for Reducing Bubble and Metastability Errors in High Speed Flash ADCs Mustafijur Rahman, Member, IEEE, K. L. Baishnab, F. A. Talukdar, Member, IEEE Dept. of Electronics & Communication
1 A Novel ROM Architecture for Reducing Bubble and Metastability Errors in High Speed Flash ADCs Mustafijur Rahman, Member, IEEE, K. L. Baishnab, F. A. Talukdar, Member, IEEE Dept. of Electronics & Communication
Investigation of Comparator Topologies and their Usage in a Technology Independent Flash-ADC Testbed
 Investigation of Comparator Topologies and their Usage in a Technology Independent Flash-ADC Testbed Cand.-Ing. Öner B. Ergin Prof. Dr.-Ing. Klaus Solbach Department of Microwave and RF-Technology University
Investigation of Comparator Topologies and their Usage in a Technology Independent Flash-ADC Testbed Cand.-Ing. Öner B. Ergin Prof. Dr.-Ing. Klaus Solbach Department of Microwave and RF-Technology University
A 4-bit High Speed, Low Power Flash ADC by Employing Binary Search Algorithm 1 Brahmaiah Throvagunta, 2 Prashant K Shah
 A 4-bit High Speed, Low Power Flash ADC by Employing Binary Search Algorithm 1 Brahmaiah Throvagunta, 2 Prashant K Shah 1 Master of Technology,Dept. of VLSI &Embedded Systems,Sardar Vallabhbhai National
A 4-bit High Speed, Low Power Flash ADC by Employing Binary Search Algorithm 1 Brahmaiah Throvagunta, 2 Prashant K Shah 1 Master of Technology,Dept. of VLSI &Embedded Systems,Sardar Vallabhbhai National
A Successive Approximation ADC based on a new Segmented DAC
 A Successive Approximation ADC based on a new Segmented DAC segmented current-mode DAC successive approximation ADC bi-direction segmented current-mode DAC DAC INL 0.47 LSB DNL 0.154 LSB DAC 3V 8 2MS/s
A Successive Approximation ADC based on a new Segmented DAC segmented current-mode DAC successive approximation ADC bi-direction segmented current-mode DAC DAC INL 0.47 LSB DNL 0.154 LSB DAC 3V 8 2MS/s
10 GHz Voltage Controlled Ring Oscillator for High Speed Application in 130nm CMOS Technology
 Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 6(8): 17-22, 2012 ISSN 1991-8178 10 GHz Voltage Controlled Ring Oscillator for High Speed Application in 130nm CMOS Technology FatemehTaghizadeh-Marvast,
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 6(8): 17-22, 2012 ISSN 1991-8178 10 GHz Voltage Controlled Ring Oscillator for High Speed Application in 130nm CMOS Technology FatemehTaghizadeh-Marvast,
A Comparative Study of Dynamic Latch Comparator
 A Comparative Study of Dynamic Latch Comparator Sandeep K. Arya, Neelkamal Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering Guru Jambheshwar University of Science & Technology, Hisar, India (125001)
A Comparative Study of Dynamic Latch Comparator Sandeep K. Arya, Neelkamal Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering Guru Jambheshwar University of Science & Technology, Hisar, India (125001)
Index terms: Analog to digital converter, Flash ADC, Pseudo NMOS logic, Pseudo Dynamic CMOS logic multi threshold voltage CMOS inverters.
 Low Power CMOS Flash ADC C Mohan, T Ravisekhar Abstract The present investigation proposes an efficient low power encoding scheme intended for a flash analog to digital converter. The designing of a thermometer
Low Power CMOS Flash ADC C Mohan, T Ravisekhar Abstract The present investigation proposes an efficient low power encoding scheme intended for a flash analog to digital converter. The designing of a thermometer
A Low-Noise Self-Calibrating Dynamic Comparator for High-Speed ADCs
 1 A Low-Noise Self-Calibrating Dynamic Comparator for High-Speed ADCs Masaya Miyahara, Yusuke Asada, Daehwa Paik and Akira Matsuzawa Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan Outline 2 Motivation The Calibration
1 A Low-Noise Self-Calibrating Dynamic Comparator for High-Speed ADCs Masaya Miyahara, Yusuke Asada, Daehwa Paik and Akira Matsuzawa Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan Outline 2 Motivation The Calibration
Low-Power Pipelined ADC Design for Wireless LANs
 Low-Power Pipelined ADC Design for Wireless LANs J. Arias, D. Bisbal, J. San Pablo, L. Quintanilla, L. Enriquez, J. Vicente, J. Barbolla Dept. de Electricidad y Electrónica, E.T.S.I. de Telecomunicación,
Low-Power Pipelined ADC Design for Wireless LANs J. Arias, D. Bisbal, J. San Pablo, L. Quintanilla, L. Enriquez, J. Vicente, J. Barbolla Dept. de Electricidad y Electrónica, E.T.S.I. de Telecomunicación,
Fig. 2. Schematic of the THA. M1 M2 M3 M4 Vbias Vdd. Fig. 1. Simple 3-Bit Flash ADC. Table1. THA Design Values ( with 0.
 A 2-GSPS 4-Bit Flash A/D Converter Using Multiple Track/Hold Amplifiers By Dr. Mahmoud Fawzy Wagdy, Professor And Chun-Shou (Charlie) Huang, MSEE Department of Electrical Engineering, California State
A 2-GSPS 4-Bit Flash A/D Converter Using Multiple Track/Hold Amplifiers By Dr. Mahmoud Fawzy Wagdy, Professor And Chun-Shou (Charlie) Huang, MSEE Department of Electrical Engineering, California State
Chapter 3 Novel Digital-to-Analog Converter with Gamma Correction for On-Panel Data Driver
 Chapter 3 Novel Digital-to-Analog Converter with Gamma Correction for On-Panel Data Driver 3.1 INTRODUCTION As last chapter description, we know that there is a nonlinearity relationship between luminance
Chapter 3 Novel Digital-to-Analog Converter with Gamma Correction for On-Panel Data Driver 3.1 INTRODUCTION As last chapter description, we know that there is a nonlinearity relationship between luminance
@IJMTER-2016, All rights Reserved 333
 Design of High Performance CMOS Comparator using 90nm Technology Shankar 1, Vasudeva G 2, Girish J R 3 1 Alpha college of Engineering, 2 Knowx Innovations, 3 sjbit Abstract- In many digital circuits the
Design of High Performance CMOS Comparator using 90nm Technology Shankar 1, Vasudeva G 2, Girish J R 3 1 Alpha college of Engineering, 2 Knowx Innovations, 3 sjbit Abstract- In many digital circuits the
A NEW APPROACH TO DESIGN LOW POWER CMOS FLASH A/D CONVERTER
 A NEW APPROACH TO DESIGN LOW POWER CMOS FLASH A/D CONVERTER C Mohan¹ and T Ravisekhar 2 ¹M. Tech (VLSI) Student, Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering College (Autonomous), Tirupati, India 2 Assistant Professor,
A NEW APPROACH TO DESIGN LOW POWER CMOS FLASH A/D CONVERTER C Mohan¹ and T Ravisekhar 2 ¹M. Tech (VLSI) Student, Sree Vidyanikethan Engineering College (Autonomous), Tirupati, India 2 Assistant Professor,
Design and Implementation of Low Power Dynamic Thermometer Encoder For Flash ADC
 Design and Implementation of Low Power Dynamic Thermometer Encoder For Flash ADC Abstract: In the design of a low power Flash ADC, a major challenge lies in designing a high speed thermometer code to binary
Design and Implementation of Low Power Dynamic Thermometer Encoder For Flash ADC Abstract: In the design of a low power Flash ADC, a major challenge lies in designing a high speed thermometer code to binary
EE247 Lecture 20. Comparator architecture examples Flash ADC sources of error Sparkle code Meta-stability
 EE247 Lecture 2 ADC Converters ADC architectures (continued) Comparator architectures Latched comparators Latched comparators incorporating preamplifier Sample-data comparators Offset cancellation Comparator
EE247 Lecture 2 ADC Converters ADC architectures (continued) Comparator architectures Latched comparators Latched comparators incorporating preamplifier Sample-data comparators Offset cancellation Comparator
DAT175: Topics in Electronic System Design
 DAT175: Topics in Electronic System Design Analog Readout Circuitry for Hearing Aid in STM90nm 21 February 2010 Remzi Yagiz Mungan v1.10 1. Introduction In this project, the aim is to design an adjustable
DAT175: Topics in Electronic System Design Analog Readout Circuitry for Hearing Aid in STM90nm 21 February 2010 Remzi Yagiz Mungan v1.10 1. Introduction In this project, the aim is to design an adjustable
Asynchronous SAR ADC: Past, Present and Beyond. Mike Shuo-Wei Chen University of Southern California MWSCAS 2014
 Asynchronous SAR ADC: Past, Present and Beyond Mike Shuo-Wei Chen University of Southern California MWSCAS 2014 1 Roles of ADCs Responsibility of ADC is increasing more BW, more dynamic range Potentially
Asynchronous SAR ADC: Past, Present and Beyond Mike Shuo-Wei Chen University of Southern California MWSCAS 2014 1 Roles of ADCs Responsibility of ADC is increasing more BW, more dynamic range Potentially
ISSCC 2004 / SESSION 25 / HIGH-RESOLUTION NYQUIST ADCs / 25.4
 ISSCC 2004 / SESSION 25 / HIGH-RESOLUTION NYQUIST ADCs / 25.4 25.4 A 1.8V 14b 10MS/s Pipelined ADC in 0.18µm CMOS with 99dB SFDR Yun Chiu, Paul R. Gray, Borivoje Nikolic University of California, Berkeley,
ISSCC 2004 / SESSION 25 / HIGH-RESOLUTION NYQUIST ADCs / 25.4 25.4 A 1.8V 14b 10MS/s Pipelined ADC in 0.18µm CMOS with 99dB SFDR Yun Chiu, Paul R. Gray, Borivoje Nikolic University of California, Berkeley,
Another way to implement a folding ADC
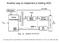 Another way to implement a folding ADC J. Van Valburg and R. van de Plassche, An 8-b 650 MHz Folding ADC, IEEE JSSC, vol 27, #12, pp. 1662-6, Dec 1992 Coupled Differential Pair J. Van Valburg and R. van
Another way to implement a folding ADC J. Van Valburg and R. van de Plassche, An 8-b 650 MHz Folding ADC, IEEE JSSC, vol 27, #12, pp. 1662-6, Dec 1992 Coupled Differential Pair J. Van Valburg and R. van
DESIGN OF FOLDING CIRCUIT AND SAMPLE AND HOLD FOR 6 BIT ADC
 DESIGN OF FOLDING CIRCUIT AND SAMPLE AND HOLD FOR 6 BIT ADC Prajeesh R 1, Manukrishna V R 2, Bellamkonda Saidilu 3 1 Assistant Professor, ECE Department, SVNCE, Mavelikara, Kerala, (India) 2,3 PhD Research
DESIGN OF FOLDING CIRCUIT AND SAMPLE AND HOLD FOR 6 BIT ADC Prajeesh R 1, Manukrishna V R 2, Bellamkonda Saidilu 3 1 Assistant Professor, ECE Department, SVNCE, Mavelikara, Kerala, (India) 2,3 PhD Research
An Ultra Low Power Successive Approximation ADC for Wireless Sensor Network
 Internatıonal Journal of Natural and Engineering Sciences 7 (2): 38-42, 213 ISSN: 137-1149, E-ISSN: 2146-86, www.nobel.gen.tr An Ultra Low Power Successive Approximation ADC for Wireless Sensor Network
Internatıonal Journal of Natural and Engineering Sciences 7 (2): 38-42, 213 ISSN: 137-1149, E-ISSN: 2146-86, www.nobel.gen.tr An Ultra Low Power Successive Approximation ADC for Wireless Sensor Network
DESIGN AND PERFORMANCE VERIFICATION OF CURRENT CONVEYOR BASED PIPELINE A/D CONVERTER USING 180 NM TECHNOLOGY
 DESIGN AND PERFORMANCE VERIFICATION OF CURRENT CONVEYOR BASED PIPELINE A/D CONVERTER USING 180 NM TECHNOLOGY Neha Bakawale Departmentof Electronics & Instrumentation Engineering, Shri G. S. Institute of
DESIGN AND PERFORMANCE VERIFICATION OF CURRENT CONVEYOR BASED PIPELINE A/D CONVERTER USING 180 NM TECHNOLOGY Neha Bakawale Departmentof Electronics & Instrumentation Engineering, Shri G. S. Institute of
Low Power Folding and Interpolating Analog to Digital Converter using 180nm Technology
 Low Power Folding and Interpolating Analog to Digital Converter using 180nm Technology Jayesh L. Prajapati 1, Prof. Priyesh P. Gandhi 2 1 M.E. Student, Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering,Laljibhai
Low Power Folding and Interpolating Analog to Digital Converter using 180nm Technology Jayesh L. Prajapati 1, Prof. Priyesh P. Gandhi 2 1 M.E. Student, Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering,Laljibhai
A 45nm Flash Analog to Digital Converter for Low Voltage High Speed System-on-Chips
 A 45nm Flash Analog to Digital Converter for Low Voltage High Speed System-on-Chips Dhruva Ghai Saraju P. Mohanty Elias Kougianos dvg0010@unt.edu smohanty@cse.unt.edu eliask@unt.edu VLSI Design and CAD
A 45nm Flash Analog to Digital Converter for Low Voltage High Speed System-on-Chips Dhruva Ghai Saraju P. Mohanty Elias Kougianos dvg0010@unt.edu smohanty@cse.unt.edu eliask@unt.edu VLSI Design and CAD
Design of an Assembly Line Structure ADC
 Design of an Assembly Line Structure ADC Chen Hu 1, Feng Xie 1,Ming Yin 1 1 Department of Electronic Engineering, Naval University of Engineering, Wuhan, China Abstract This paper presents a circuit design
Design of an Assembly Line Structure ADC Chen Hu 1, Feng Xie 1,Ming Yin 1 1 Department of Electronic Engineering, Naval University of Engineering, Wuhan, China Abstract This paper presents a circuit design
LAYOUT IMPLEMENTATION OF A 10-BIT 1.2 GS/s DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER IN 90nm CMOS
 LAYOUT IMPLEMENTATION OF A 10-BIT 1.2 GS/s DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER IN 90nm CMOS A thesis submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Electrical Engineering
LAYOUT IMPLEMENTATION OF A 10-BIT 1.2 GS/s DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTER IN 90nm CMOS A thesis submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Electrical Engineering
THE QUANTIZED DIFFERENTIAL COMPARATOR IN FLASH ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER DESIGN
 THE QUANTIZED DIFFERENTIAL COMPARATOR IN FLASH ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER DESIGN Meghana Kulkarni 1, V. Sridhar 2, G.H.Kulkarni 3 1 Asst.Prof., E & C Dept, Gogte Institute of Technology, Bgm, Karnataka,
THE QUANTIZED DIFFERENTIAL COMPARATOR IN FLASH ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER DESIGN Meghana Kulkarni 1, V. Sridhar 2, G.H.Kulkarni 3 1 Asst.Prof., E & C Dept, Gogte Institute of Technology, Bgm, Karnataka,
RECENTLY, low-voltage and low-power circuit design
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 55, NO. 4, APRIL 2008 319 A Programmable 0.8-V 10-bit 60-MS/s 19.2-mW 0.13-m CMOS ADC Operating Down to 0.5 V Hee-Cheol Choi, Young-Ju
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 55, NO. 4, APRIL 2008 319 A Programmable 0.8-V 10-bit 60-MS/s 19.2-mW 0.13-m CMOS ADC Operating Down to 0.5 V Hee-Cheol Choi, Young-Ju
ISSN:
 1391 DESIGN OF 9 BIT SAR ADC USING HIGH SPEED AND HIGH RESOLUTION OPEN LOOP CMOS COMPARATOR IN 180NM TECHNOLOGY WITH R-2R DAC TOPOLOGY AKHIL A 1, SUNIL JACOB 2 1 M.Tech Student, 2 Associate Professor,
1391 DESIGN OF 9 BIT SAR ADC USING HIGH SPEED AND HIGH RESOLUTION OPEN LOOP CMOS COMPARATOR IN 180NM TECHNOLOGY WITH R-2R DAC TOPOLOGY AKHIL A 1, SUNIL JACOB 2 1 M.Tech Student, 2 Associate Professor,
Systematic Design of a 200 MS/s 8-bit Interpolating A/D Converter
 Systematic Design of a MS/s 8-bit Interpolating A/D Converter J. Vandenbussche, E. Lauwers, K. Uyttenhove, G. Gielen and M. Steyaert Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Dept. of Electrical Engineering, ESAT-MICAS
Systematic Design of a MS/s 8-bit Interpolating A/D Converter J. Vandenbussche, E. Lauwers, K. Uyttenhove, G. Gielen and M. Steyaert Katholieke Universiteit Leuven, Dept. of Electrical Engineering, ESAT-MICAS
CDK bit, 1 GSPS, Flash A/D Converter
 CDK1303 8-bit, 1 GSPS, Flash A/D Converter FEATURES n 1:2 Demuxed ECL compatible outputs n Wide input bandwidth 900MHz n Low input capacitance 15pF n Metastable errors reduced to 1 LSB n Gray code output
CDK1303 8-bit, 1 GSPS, Flash A/D Converter FEATURES n 1:2 Demuxed ECL compatible outputs n Wide input bandwidth 900MHz n Low input capacitance 15pF n Metastable errors reduced to 1 LSB n Gray code output
IMPLEMENTING THE 10-BIT, 50MS/SEC PIPELINED ADC
 98 CHAPTER 5 IMPLEMENTING THE 0-BIT, 50MS/SEC PIPELINED ADC 99 5.0 INTRODUCTION This chapter is devoted to describe the implementation of a 0-bit, 50MS/sec pipelined ADC with different stage resolutions
98 CHAPTER 5 IMPLEMENTING THE 0-BIT, 50MS/SEC PIPELINED ADC 99 5.0 INTRODUCTION This chapter is devoted to describe the implementation of a 0-bit, 50MS/sec pipelined ADC with different stage resolutions
Chapter 2 Basics of Digital-to-Analog Conversion
 Chapter 2 Basics of Digital-to-Analog Conversion This chapter discusses basic concepts of modern Digital-to-Analog Converters (DACs). The basic generic DAC functionality and specifications are discussed,
Chapter 2 Basics of Digital-to-Analog Conversion This chapter discusses basic concepts of modern Digital-to-Analog Converters (DACs). The basic generic DAC functionality and specifications are discussed,
VLSI DESIGN OF 12-BIT ADC WITH 1GSPS IN 180NM CMOS INTEGRATING WITH SAR AND TWO-STEP FLASH ADC
 VLSI DESIGN OF 12-BIT ADC WITH 1GSPS IN 180NM CMOS INTEGRATING WITH SAR AND TWO-STEP FLASH ADC 1 K.LOKESH KRISHNA, 2 T.RAMASHRI 1 Associate Professor, Department of ECE, Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering
VLSI DESIGN OF 12-BIT ADC WITH 1GSPS IN 180NM CMOS INTEGRATING WITH SAR AND TWO-STEP FLASH ADC 1 K.LOKESH KRISHNA, 2 T.RAMASHRI 1 Associate Professor, Department of ECE, Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering
Design of Low Power High Speed Fully Dynamic CMOS Latched Comparator
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 10, Issue 4 (April 2014), PP.01-06 Design of Low Power High Speed Fully Dynamic
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 10, Issue 4 (April 2014), PP.01-06 Design of Low Power High Speed Fully Dynamic
International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering & Technology (IJECET), INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRONICS AND
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJECET) ISSN 0976 6464(Print) ISSN 0976 6472(Online) Volume 4, Issue 3, May June, 2013, pp. 24-32 IAEME: www.iaeme.com/ijecet.asp
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY (IJECET) ISSN 0976 6464(Print) ISSN 0976 6472(Online) Volume 4, Issue 3, May June, 2013, pp. 24-32 IAEME: www.iaeme.com/ijecet.asp
High-Speed Analog to Digital Converters. ELCT 1003:High Speed ADCs
 High-Speed Analog to Digital Converters Ann Kotkat Barbara Georgy Mahmoud Tantawi Ayman Sakr Heidi El-Feky Nourane Gamal 1 Outline Introduction. Process of ADC. ADC Specifications. Flash ADC. Pipelined
High-Speed Analog to Digital Converters Ann Kotkat Barbara Georgy Mahmoud Tantawi Ayman Sakr Heidi El-Feky Nourane Gamal 1 Outline Introduction. Process of ADC. ADC Specifications. Flash ADC. Pipelined
Design of a Low Power Current Steering Digital to Analog Converter in CMOS
 Design of a Low Power Current Steering Digital to Analog Converter in CMOS Ranjan Kumar Mahapatro M. Tech, Dept. of ECE Centurion University of Technology & Management Paralakhemundi, India Sandipan Pine
Design of a Low Power Current Steering Digital to Analog Converter in CMOS Ranjan Kumar Mahapatro M. Tech, Dept. of ECE Centurion University of Technology & Management Paralakhemundi, India Sandipan Pine
DIGITAL wireless communication applications such as
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 57, NO. 8, AUGUST 2010 1829 An Asynchronous Binary-Search ADC Architecture With a Reduced Comparator Count Ying-Zu Lin, Student Member,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 57, NO. 8, AUGUST 2010 1829 An Asynchronous Binary-Search ADC Architecture With a Reduced Comparator Count Ying-Zu Lin, Student Member,
THE comparison is the basic operation in an analog-to-digital
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 53, NO. 7, JULY 2006 541 Kickback Noise Reduction Techniques for CMOS Latched Comparators Pedro M. Figueiredo, Member, IEEE, and João
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 53, NO. 7, JULY 2006 541 Kickback Noise Reduction Techniques for CMOS Latched Comparators Pedro M. Figueiredo, Member, IEEE, and João
CMOS ADC & DAC Principles
 CMOS ADC & DAC Principles Willy Sansen KULeuven, ESAT-MICAS Leuven, Belgium willy.sansen@esat.kuleuven.be Willy Sansen 10-05 201 Table of contents Definitions Digital-to-analog converters Resistive Capacitive
CMOS ADC & DAC Principles Willy Sansen KULeuven, ESAT-MICAS Leuven, Belgium willy.sansen@esat.kuleuven.be Willy Sansen 10-05 201 Table of contents Definitions Digital-to-analog converters Resistive Capacitive
A 12b 50MS/s 2.1mW SAR ADC with redundancy and digital background calibration
 A b 5MS/s.mW SAR ADC with redundancy and digital background calibration The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As
A b 5MS/s.mW SAR ADC with redundancy and digital background calibration The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As
CHAPTER 3 DESIGN OF PIPELINED ADC USING SCS-CDS AND OP-AMP SHARING TECHNIQUE
 CHAPTER 3 DESIGN OF PIPELINED ADC USING SCS-CDS AND OP-AMP SHARING TECHNIQUE 3.1 INTRODUCTION An ADC is a device which converts a continuous quantity into discrete digital signal. Among its types, pipelined
CHAPTER 3 DESIGN OF PIPELINED ADC USING SCS-CDS AND OP-AMP SHARING TECHNIQUE 3.1 INTRODUCTION An ADC is a device which converts a continuous quantity into discrete digital signal. Among its types, pipelined
A low-variation on-resistance CMOS sampling switch for high-speed high-performance applications
 A low-variation on-resistance CMOS sampling switch for high-speed high-performance applications MohammadReza Asgari 1 and Omid Hashemipour 2a) 1 Microelectronic Lab, Shahid Beheshti University, G. C. Tehran,
A low-variation on-resistance CMOS sampling switch for high-speed high-performance applications MohammadReza Asgari 1 and Omid Hashemipour 2a) 1 Microelectronic Lab, Shahid Beheshti University, G. C. Tehran,
Modulator with Op- Amp Gain Compensation for Nanometer CMOS Technologies
 A. Pena Perez, V.R. Gonzalez- Diaz, and F. Maloberti, ΣΔ Modulator with Op- Amp Gain Compensation for Nanometer CMOS Technologies, IEEE Proceeding of Latin American Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Feb.
A. Pena Perez, V.R. Gonzalez- Diaz, and F. Maloberti, ΣΔ Modulator with Op- Amp Gain Compensation for Nanometer CMOS Technologies, IEEE Proceeding of Latin American Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Feb.
High-speed ADC techniques - overview and scaling issues - Vladimir Stojanovic
 High-speed ADC techniques - overview and scaling issues - Vladimir Stojanovic Outline High-Speed ADC applications Basic ADC performance metrics Architectures overview ADCs in 90s Limiting factors Conclusion
High-speed ADC techniques - overview and scaling issues - Vladimir Stojanovic Outline High-Speed ADC applications Basic ADC performance metrics Architectures overview ADCs in 90s Limiting factors Conclusion
Summary of Last Lecture
 EE247 Lecture 2 ADC Converters (continued) Successive approximation ADCs (continued) Flash ADC Flash ADC sources of error Sparkle code Meta-stability Comparator design EECS 247 Lecture 2: Data Converters
EE247 Lecture 2 ADC Converters (continued) Successive approximation ADCs (continued) Flash ADC Flash ADC sources of error Sparkle code Meta-stability Comparator design EECS 247 Lecture 2: Data Converters
A High Speed and Low Voltage Dynamic Comparator for ADCs
 A High Speed and Low Voltage Dynamic Comparator for ADCs M.Balaji 1, G.Karthikeyan 2, R.Baskar 3, R.Jayaprakash 4 1,2,3,4 ECE, Muthayammal College of Engineering Abstract A new dynamic comparator is proposed
A High Speed and Low Voltage Dynamic Comparator for ADCs M.Balaji 1, G.Karthikeyan 2, R.Baskar 3, R.Jayaprakash 4 1,2,3,4 ECE, Muthayammal College of Engineering Abstract A new dynamic comparator is proposed
A 35 fj 10b 160 MS/s Pipelined- SAR ADC with Decoupled Flip- Around MDAC and Self- Embedded Offset Cancellation
 Y. Zu, C.- H. Chan, S.- W. Sin, S.- P. U, R.P. Martins, F. Maloberti: "A 35 fj 10b 160 MS/s Pipelined-SAR ADC with Decoupled Flip-Around MDAC and Self- Embedded Offset Cancellation"; IEEE Asian Solid-
Y. Zu, C.- H. Chan, S.- W. Sin, S.- P. U, R.P. Martins, F. Maloberti: "A 35 fj 10b 160 MS/s Pipelined-SAR ADC with Decoupled Flip-Around MDAC and Self- Embedded Offset Cancellation"; IEEE Asian Solid-
A Serial Link Transceiver Based on 8 GSa/s A/D and D/A Converters
 A Serial Link Transceiver Based on 8 GSa/s A/D and D/A Converters in 0.25µm m CMOS William Ellersick 1,3, Chih-Kong Ken Yang 2 Vladimir Stojanovic 1, Siamak Modjtahedi 2, Mark A. Horowitz 1 1 Stanford
A Serial Link Transceiver Based on 8 GSa/s A/D and D/A Converters in 0.25µm m CMOS William Ellersick 1,3, Chih-Kong Ken Yang 2 Vladimir Stojanovic 1, Siamak Modjtahedi 2, Mark A. Horowitz 1 1 Stanford
A 16-GHz Ultra-High-Speed Si SiGe HBT Comparator
 1584 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 38, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2003 A 16-GHz Ultra-High-Speed Si SiGe HBT Comparator Jonathan C. Jensen, Student Member, IEEE, and Lawrence E. Larson, Fellow, IEEE
1584 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 38, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2003 A 16-GHz Ultra-High-Speed Si SiGe HBT Comparator Jonathan C. Jensen, Student Member, IEEE, and Lawrence E. Larson, Fellow, IEEE
A 12-bit 100kS/s SAR ADC for Biomedical Applications. Sung-Chan Rho 1 and Shin-Il Lim 2. Seoul, Korea. Abstract
 , pp.17-22 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijunesst.2016.9.8.02 A 12-bit 100kS/s SAR ADC for Biomedical Applications Sung-Chan Rho 1 and Shin-Il Lim 2 1 Department of Electronics and Computer Engineering, Seokyeong
, pp.17-22 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/ijunesst.2016.9.8.02 A 12-bit 100kS/s SAR ADC for Biomedical Applications Sung-Chan Rho 1 and Shin-Il Lim 2 1 Department of Electronics and Computer Engineering, Seokyeong
A 130-NM CMOS 400 MHZ 8-BIT LOW POWER BINARY WEIGHTED CURRENT STEERING DAC
 A 130-NM CMOS 400 MHZ 8-BIT LOW POWER BINARY WEIGHTED CURRENT STEERING DAC Ashok Kumar Adepu and Kiran Kumar Kolupuri Department of Electronics and communication Engineering,MVGR College of Engineering,
A 130-NM CMOS 400 MHZ 8-BIT LOW POWER BINARY WEIGHTED CURRENT STEERING DAC Ashok Kumar Adepu and Kiran Kumar Kolupuri Department of Electronics and communication Engineering,MVGR College of Engineering,
Design and Implementation of a Low Power Successive Approximation ADC. Xin HUANG, Xiao-ning XIN, Jian REN* and Xin-lei CHEN
 2018 International Conference on Mechanical, Electronic and Information Technology (ICMEIT 2018) ISBN: 978-1-60595-548-3 Design and Implementation of a Low Power Successive Approximation ADC Xin HUANG,
2018 International Conference on Mechanical, Electronic and Information Technology (ICMEIT 2018) ISBN: 978-1-60595-548-3 Design and Implementation of a Low Power Successive Approximation ADC Xin HUANG,
Architectures and circuits for timeinterleaved. Sandeep Gupta Teranetics, Santa Clara, CA
 Architectures and circuits for timeinterleaved ADC s Sandeep Gupta Teranetics, Santa Clara, CA Outline Introduction to time-interleaved architectures. Conventional Sampling architectures and their application
Architectures and circuits for timeinterleaved ADC s Sandeep Gupta Teranetics, Santa Clara, CA Outline Introduction to time-interleaved architectures. Conventional Sampling architectures and their application
Optimizing the Stage Resolution of a 10-Bit, 50 Ms/Sec Pipelined A/D Converter & Its Impact on Speed, Power, Area, and Linearity
 Circuits and Systems, 202, 3, 66-75 http://dx.doi.org/0.4236/cs.202.32022 Published Online April 202 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/cs) Optimizing the Stage Resolution of a 0-Bit, 50 Ms/Sec Pipelined A/D
Circuits and Systems, 202, 3, 66-75 http://dx.doi.org/0.4236/cs.202.32022 Published Online April 202 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/cs) Optimizing the Stage Resolution of a 0-Bit, 50 Ms/Sec Pipelined A/D
Design And Implementation of Pulse-Based Low Power 5-Bit Flash Adc In Time-Domain
 IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 2278-2834,p- ISSN: 2278-8735.Volume 13, Issue 3, Ver. I (May. - June. 2018), PP 55-60 www.iosrjournals.org Design And Implementation
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE) e-issn: 2278-2834,p- ISSN: 2278-8735.Volume 13, Issue 3, Ver. I (May. - June. 2018), PP 55-60 www.iosrjournals.org Design And Implementation
Flash ADC (Part-I) Architecture & Challenges
 project synopsis In The Name of Almighty Lec. 4: Flash ADC (PartI) Architecture & Challenges Lecturer: Samaneh Babayan Integrated Circuit Lab. Department of Computer Science & Engineering ImamReza University
project synopsis In The Name of Almighty Lec. 4: Flash ADC (PartI) Architecture & Challenges Lecturer: Samaneh Babayan Integrated Circuit Lab. Department of Computer Science & Engineering ImamReza University
Find Those Elusive ADC Sparkle Codes and Metastable States. by Walt Kester
 TUTORIAL Find Those Elusive ADC Sparkle Codes and Metastable States INTRODUCTION by Walt Kester A major concern in the design of digital communications systems is the bit error rate (BER). The effect of
TUTORIAL Find Those Elusive ADC Sparkle Codes and Metastable States INTRODUCTION by Walt Kester A major concern in the design of digital communications systems is the bit error rate (BER). The effect of
Performance Analysis of 4-bit Flash ADC with Different Comparators Designed in 0.18um Technology
 Performance Analysis of 4-bit Flash with Different Comparators Designed in 0.18um Technology A.Nandhini PG Scholar, Dept of ECE Kumaraguru College of Technology Coimbatore -641 049 M.Shanthi Associate
Performance Analysis of 4-bit Flash with Different Comparators Designed in 0.18um Technology A.Nandhini PG Scholar, Dept of ECE Kumaraguru College of Technology Coimbatore -641 049 M.Shanthi Associate
A Two- Bit- per- Cycle Successive- Approximation ADC with Background Offset Calibration
 M. Casubolo, M. Grassi, A. Lombardi, F. Maloberti, P. Malcovati: "A Two-Bit-per- Cycle Successive-Approximation ADC with Background Calibration"; 15th IEEE Int. Conf. on Electronics, Circuits and Systems,
M. Casubolo, M. Grassi, A. Lombardi, F. Maloberti, P. Malcovati: "A Two-Bit-per- Cycle Successive-Approximation ADC with Background Calibration"; 15th IEEE Int. Conf. on Electronics, Circuits and Systems,
Tuesday, March 1st, 9:15 11:00. Snorre Aunet Nanoelectronics group Department of Informatics University of Oslo.
 Nyquist Analog to Digital it Converters Tuesday, March 1st, 9:15 11:00 Snorre Aunet (sa@ifi.uio.no) Nanoelectronics group Department of Informatics University of Oslo 3.1 Introduction 3.1.1 DAC applications
Nyquist Analog to Digital it Converters Tuesday, March 1st, 9:15 11:00 Snorre Aunet (sa@ifi.uio.no) Nanoelectronics group Department of Informatics University of Oslo 3.1 Introduction 3.1.1 DAC applications
Design and Analysis of High Gain Differential Amplifier Using Various Topologies
 Design and Analysis of High Gain Amplifier Using Various Topologies SAMARLA.SHILPA 1, J SRILATHA 2 1Assistant Professor, Dept of Electronics and Communication Engineering, NNRG, Ghatkesar, Hyderabad, India.
Design and Analysis of High Gain Amplifier Using Various Topologies SAMARLA.SHILPA 1, J SRILATHA 2 1Assistant Professor, Dept of Electronics and Communication Engineering, NNRG, Ghatkesar, Hyderabad, India.
A Serial Link Transceiver Based on 8 GSa/s A/D and D/A Converters
 A Serial Link Transceiver Based on 8 GSa/s A/D and D/A Converters in 0.25µm m CMOS William Ellersick 1,3, Chih-Kong Ken Yang 2 Vladimir Stojanovic 1, Siamak Modjtahedi 2, Mark A. Horowitz 1 1 Stanford
A Serial Link Transceiver Based on 8 GSa/s A/D and D/A Converters in 0.25µm m CMOS William Ellersick 1,3, Chih-Kong Ken Yang 2 Vladimir Stojanovic 1, Siamak Modjtahedi 2, Mark A. Horowitz 1 1 Stanford
Design of Analog Integrated Systems (ECE 615) Outline
 Design of Analog Integrated Systems (ECE 615) Lecture 9 SAR and Cyclic (Algorithmic) Analog-to-Digital Converters Ayman H. Ismail Integrated Circuits Laboratory Ain Shams University Cairo, Egypt ayman.hassan@eng.asu.edu.eg
Design of Analog Integrated Systems (ECE 615) Lecture 9 SAR and Cyclic (Algorithmic) Analog-to-Digital Converters Ayman H. Ismail Integrated Circuits Laboratory Ain Shams University Cairo, Egypt ayman.hassan@eng.asu.edu.eg
ADC1002S General description. 2. Features. 3. Applications. Single 10 bits ADC, up to 20 MHz
 Rev. 03 2 July 2012 Product data sheet 1. General description The is a 10-bit high-speed Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) for professional video and other applications. It converts with 3.0 V to 5.25
Rev. 03 2 July 2012 Product data sheet 1. General description The is a 10-bit high-speed Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) for professional video and other applications. It converts with 3.0 V to 5.25
A 6-bit Subranging ADC using Single CDAC Interpolation
 A 6-bit Subranging ADC using Single CDAC Interpolation Hyunui Lee, Masaya Miyahara, and Akira Matsuzawa Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan Outline Background Interpolation techniques 6-bit, 500 MS/s
A 6-bit Subranging ADC using Single CDAC Interpolation Hyunui Lee, Masaya Miyahara, and Akira Matsuzawa Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan Outline Background Interpolation techniques 6-bit, 500 MS/s
DESIGN OF A NOVEL CURRENT MIRROR BASED DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER DESIGN WITH LATCH NETWORK. Thota Keerthi* 1, Ch. Anil Kumar 2
 ISSN 2277-2685 IJESR/October 2014/ Vol-4/Issue-10/682-687 Thota Keerthi et al./ International Journal of Engineering & Science Research DESIGN OF A NOVEL CURRENT MIRROR BASED DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER DESIGN
ISSN 2277-2685 IJESR/October 2014/ Vol-4/Issue-10/682-687 Thota Keerthi et al./ International Journal of Engineering & Science Research DESIGN OF A NOVEL CURRENT MIRROR BASED DIFFERENTIAL AMPLIFIER DESIGN
Design of 10-bit current steering DAC with binary and segmented architecture
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. III (May. June. 2018), PP 62-66 www.iosrjournals.org Design of 10-bit current
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 2320-3331, Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. III (May. June. 2018), PP 62-66 www.iosrjournals.org Design of 10-bit current
A Low-Offset Latched Comparator Using Zero-Static Power Dynamic Offset Cancellation Technique
 1 A Low-Offset Latched Comparator Using Zero-Static Power Dynamic Offset Cancellation Technique Masaya Miyahara and Akira Matsuzawa Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan 2 Outline Motivation Design Concept
1 A Low-Offset Latched Comparator Using Zero-Static Power Dynamic Offset Cancellation Technique Masaya Miyahara and Akira Matsuzawa Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan 2 Outline Motivation Design Concept
SPT BIT, 30 MSPS, TTL, A/D CONVERTER
 12-BIT, MSPS, TTL, A/D CONVERTER FEATURES Monolithic 12-Bit MSPS Converter 6 db SNR @ 3.58 MHz Input On-Chip Track/Hold Bipolar ±2.0 V Analog Input Low Power (1.1 W Typical) 5 pf Input Capacitance TTL
12-BIT, MSPS, TTL, A/D CONVERTER FEATURES Monolithic 12-Bit MSPS Converter 6 db SNR @ 3.58 MHz Input On-Chip Track/Hold Bipolar ±2.0 V Analog Input Low Power (1.1 W Typical) 5 pf Input Capacitance TTL
Design of Low Voltage and High Speed Double-Tail Dynamic Comparator for Low Power Applications
 International Journal of Engineering Inventions e-issn: 2278-7461, p-issn: 2319-6491 Volume 3, Issue 11 (June 2014) PP: 1-7 Design of Low Voltage and High Speed Double-Tail Dynamic Comparator for Low Power
International Journal of Engineering Inventions e-issn: 2278-7461, p-issn: 2319-6491 Volume 3, Issue 11 (June 2014) PP: 1-7 Design of Low Voltage and High Speed Double-Tail Dynamic Comparator for Low Power
A 8-Bit Hybrid Architecture Current-Steering DAC
 A 8-Bit Hybrid Architecture Current-Steering DAC Mr. Ganesha H.S. 1, Dr. Rekha Bhandarkar 2, Ms. Vijayalatha Devadiga 3 1 Student, Electronics and communication, N.M.A.M. Institute of Technology, Karnataka,
A 8-Bit Hybrid Architecture Current-Steering DAC Mr. Ganesha H.S. 1, Dr. Rekha Bhandarkar 2, Ms. Vijayalatha Devadiga 3 1 Student, Electronics and communication, N.M.A.M. Institute of Technology, Karnataka,
Fall 2004; E6316: Analog Systems in VLSI; 4 bit Flash A/D converter
 Fall 2004; E6316: Analog Systems in VLSI; 4 bit Flash A/D converter Nagendra Krishnapura (nkrishna@vitesse.com) due on 21 Dec. 2004 You are required to design a 4bit Flash A/D converter at 500 MS/s. The
Fall 2004; E6316: Analog Systems in VLSI; 4 bit Flash A/D converter Nagendra Krishnapura (nkrishna@vitesse.com) due on 21 Dec. 2004 You are required to design a 4bit Flash A/D converter at 500 MS/s. The
Highly linear common-gate mixer employing intrinsic second and third order distortion cancellation
 Highly linear common-gate mixer employing intrinsic second and third order distortion cancellation Mahdi Parvizi a), and Abdolreza Nabavi b) Microelectronics Laboratory, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran
Highly linear common-gate mixer employing intrinsic second and third order distortion cancellation Mahdi Parvizi a), and Abdolreza Nabavi b) Microelectronics Laboratory, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran
Proposing. An Interpolated Pipeline ADC
 Proposing An Interpolated Pipeline ADC Akira Matsuzawa Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan Matsuzawa & Okada Lab. Background 38GHz long range mm-wave system Role of long range mm-wave Current Optical
Proposing An Interpolated Pipeline ADC Akira Matsuzawa Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan Matsuzawa & Okada Lab. Background 38GHz long range mm-wave system Role of long range mm-wave Current Optical
A Unity Gain Fully-Differential 10bit and 40MSps Sample-And-Hold Amplifier in 0.18μm CMOS
 A Unity Gain Fully-Differential 0bit and 40MSps Sample-And-Hold Amplifier in 0.8μm CMOS Sanaz Haddadian, and Rahele Hedayati Abstract A 0bit, 40 MSps, sample and hold, implemented in 0.8-μm CMOS technology
A Unity Gain Fully-Differential 0bit and 40MSps Sample-And-Hold Amplifier in 0.8μm CMOS Sanaz Haddadian, and Rahele Hedayati Abstract A 0bit, 40 MSps, sample and hold, implemented in 0.8-μm CMOS technology
SUCCESSIVE approximation register (SAR) analog-todigital
 426 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 62, NO. 5, MAY 2015 A Novel Hybrid Radix-/Radix-2 SAR ADC With Fast Convergence and Low Hardware Complexity Manzur Rahman, Arindam
426 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 62, NO. 5, MAY 2015 A Novel Hybrid Radix-/Radix-2 SAR ADC With Fast Convergence and Low Hardware Complexity Manzur Rahman, Arindam
DATASHEET HI5805. Features. Applications. Ordering Information. Pinout. 12-Bit, 5MSPS A/D Converter. FN3984 Rev 7.00 Page 1 of 12.
 12-Bit, 5MSPS A/D Converter NOT RECOMMENDED FOR NEW DESIGNS NO RECOMMENDED REPLACEMENT contact our Technical Support Center at 1-888-INTERSIL or www.intersil.com/tsc DATASHEET FN3984 Rev 7.00 The HI5805
12-Bit, 5MSPS A/D Converter NOT RECOMMENDED FOR NEW DESIGNS NO RECOMMENDED REPLACEMENT contact our Technical Support Center at 1-888-INTERSIL or www.intersil.com/tsc DATASHEET FN3984 Rev 7.00 The HI5805
IN the design of the fine comparator for a CMOS two-step flash A/D converter, the main design issues are offset cancelation
 JOURNAL OF STELLAR EE315 CIRCUITS 1 A 60-MHz 150-µV Fully-Differential Comparator Erik P. Anderson and Jonathan S. Daniels (Invited Paper) Abstract The overall performance of two-step flash A/D converters
JOURNAL OF STELLAR EE315 CIRCUITS 1 A 60-MHz 150-µV Fully-Differential Comparator Erik P. Anderson and Jonathan S. Daniels (Invited Paper) Abstract The overall performance of two-step flash A/D converters
Ultra Low Power High Speed Comparator for Analog to Digital Converters
 Ultra Low Power High Speed Comparator for Analog to Digital Converters Suman Biswas Department Of Electronics Kiit University Bhubaneswar,Odisha Dr. J. K DAS Rajendra Prasad Abstract --Dynamic comparators
Ultra Low Power High Speed Comparator for Analog to Digital Converters Suman Biswas Department Of Electronics Kiit University Bhubaneswar,Odisha Dr. J. K DAS Rajendra Prasad Abstract --Dynamic comparators
A 1.2V 8 BIT SAR ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER IN 90NM CMOS
 A 1.2V 8 BIT SAR ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER IN 90NM CMOS Shruti Gatade 1, M. Nagabhushan 2, Manjunath.R 3 1,3 Student, Department of ECE, M S Ramaiah Institute of Technology, Bangalore (India) 2 Assistant
A 1.2V 8 BIT SAR ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER IN 90NM CMOS Shruti Gatade 1, M. Nagabhushan 2, Manjunath.R 3 1,3 Student, Department of ECE, M S Ramaiah Institute of Technology, Bangalore (India) 2 Assistant
DESIGN OF ULTRA HIGH SPEED FLASH ADC, LOW POWER FOLDING AND. INTERPOLATING ADC IN CMOS 90nm TECHNOLOGY
 DESIGN OF ULTRA HIGH SPEED FLASH ADC, LOW POWER FOLDING AND INTERPOLATING ADC IN CMOS 90nm TECHNOLOGY A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in
DESIGN OF ULTRA HIGH SPEED FLASH ADC, LOW POWER FOLDING AND INTERPOLATING ADC IN CMOS 90nm TECHNOLOGY A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in
Design Of A Comparator For Pipelined A/D Converter
 Design Of A Comparator For Pipelined A/D Converter Ms. Supriya Ganvir, Mr. Sheetesh Sad ABSTRACT`- This project reveals the design of a comparator for pipeline ADC. These comparator is designed using preamplifier
Design Of A Comparator For Pipelined A/D Converter Ms. Supriya Ganvir, Mr. Sheetesh Sad ABSTRACT`- This project reveals the design of a comparator for pipeline ADC. These comparator is designed using preamplifier
A 19-bit column-parallel folding-integration/cyclic cascaded ADC with a pre-charging technique for CMOS image sensors
 LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.14, No.2, 1 12 A 19-bit column-parallel folding-integration/cyclic cascaded ADC with a pre-charging technique for CMOS image sensors Tongxi Wang a), Min-Woong Seo
LETTER IEICE Electronics Express, Vol.14, No.2, 1 12 A 19-bit column-parallel folding-integration/cyclic cascaded ADC with a pre-charging technique for CMOS image sensors Tongxi Wang a), Min-Woong Seo
Low Power and High Speed CMOS Comparator for A/D Converter Applications - A Review Sweta Kumari 1 Prof. Sampath KumarV 2
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 2, Issue 10, 2014 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Low Power and High Speed CMOS Comparator for A/D Converter Applications - A Review Sweta
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 2, Issue 10, 2014 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 Low Power and High Speed CMOS Comparator for A/D Converter Applications - A Review Sweta
Workshop ESSCIRC. Low-Power Data Acquisition System For Very Small Signals At Low Frequencies With12-Bit- SAR-ADC. 17. September 2010.
 Workshop ESSCIRC Low-Power Data Acquisition System For Very Small Signals At Low Frequencies With12-Bit- SAR-ADC 17. September 2010 Christof Dohmen Outline System Overview Analog-Front-End Chopper-Amplifier
Workshop ESSCIRC Low-Power Data Acquisition System For Very Small Signals At Low Frequencies With12-Bit- SAR-ADC 17. September 2010 Christof Dohmen Outline System Overview Analog-Front-End Chopper-Amplifier
