pss InGaAs channel MOSFET with self-aligned source/drain MBE regrowth technology solidi status physica
|
|
|
- Valentine Burke
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
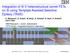
1 Phys. Status Solidi C 6, No. 6, (2009) / DOI /pss physia pss InGaAs hannel MOSFET with self-aligned soure/drain MBE regrowth tehnology urrent topis in solid state physis Uttam Singisetti *1, Mark A. istey 1,2, Gregory J. Burek 1, Erdem Arkun 2, Ashish K. Baraskar 1, Yanning Sun 3, Edward. Kiewra 3, Brian J. Thibeault 1, Arthur C. Gossard 1,2, Chris J. Palmstrøm 1,2, and Mark J.. Rod 1 1 ECE University of California, Santa Barbara, CA, USA 2 Materials Departments, University of California, Santa Barbara, CA, USA 3 IBM T.J. atson Researh Center, Yorktown Heights, NY, USA Reeived 13 September 2008, aepted 2 January 2009 Published online 20 April 2009 PACS Kp, Ea, Hi, Tv * Corresponding author: uttam@ee.usb.edu, Phone: , Fax: InGaAs is a promising alternative hannel material to Si for sub-22 nm node tehnology beause of its low eletron effetive mass (m * ) hene high eletron veloities. e report a gate-first MOSFET proess with self-aligned soure/drain formation using non-seletive MBE re-growth, suitable for realizing high performane saled III-V MOSFETs. A // gate stak was defined on thin (4 nm/2.5 nm) In- GaAs/InP hannel by an alternating seletive dry eth tehnique. A 5 nm Al 2 O 3 layer was used as gate dieletri. An InAlAs bottom provided vertial onfinement of the hannel. An in-situ H leaning of the wafer leaves an epiready surfae suitable for MBE or MOCVD regrowth. Soure/Drain region were defined by non-seletive MBE regrowth and in situ molybdenum ontats. First generation of devies fabriated using this proess showed extremely low drive urrent of 2 µa/µm. The drive urrent was limited by an extremely high soure resistane. A regrowth gap between soure/drain and gate was the ause for high soure resistane. The gap in the regrowth was beause of low growth temperature (400 ºC). A modified high temperature growth tehnique resolved the problem. Si is expeted to reah the saling limit beyond 22 nm gate node mainly due to the inability to ahieve low leakage sub-0.5 nm equivalent oxide thikness (EOT) gate dieletris. Also, sub-22 nm gate length and sub-1 nm EOT Si devies annot realize omplete ballisti transport, hene not ahieving the full potential drive urrents [1]. High eletron veloity III-V materials are investigated as an alternative hannel to Si in N-MOSFETs. In x Ga 1-x As (x 0.53) is a leading andidate as a hannel material beause of its low eletron effetive mass (m * ) and high saturation veloities (v). Also the large inter-valley separation in In 0.53 Ga 0.47 As (InGaAs) redues inter-valley sattering, blanket metal oxide InGaAs hannel InP subhannel SI substrate (starting material) Ti/ gate blanket gate deposition Figure 1 Overall proess flow. eth gate, eth dieletri eth upper hannel sidewall formation S/D regrowth S/D ontats sidewall mesa isolate S/D
2 Contributed Artile Phys. Status Solidi C 6, No. 6 (2009) 1395 so eletron veloities remain high even at high eletri fields. The main obstale of unpinned interfaes to high-k dieletri on InGaAs have been addressed by several groups with various high-k dieletris [2-4]. However these devies either have long gate lengths or were not saled vertially. The full potential of InGaAs hannel devies an only be realized in MOSFETs whih are saled both horizontally and vertially. e report the design and proess flow development of a self-aligned InGaAs MOSFET using MBE regrown soure/drain (S/D) regions. Detailed MOSFET saling laws and sub-22 nm III-V FET design are disussed in referenes [1, 5, 6]. Lateral saling of the gate length to 22 nm ditates a vertial saling of the devie. At sub-22 nm gate lengths, a maximum of 1 nm EOT dieletri and 5 nm thik hannel with strong vertial onfinement are required for maximum transondutane (g m ) and aeptably low drain indued lowering (DIBL). e use In 0.52 Al 0.48 As (InAlAs) heterojuntion to ahieve this onfinement. An alternative approah using eletrostati onfinement would need high p + doping in the InGaAs hannel, whih would redue the hannel mobility beause of impurity sattering and will also degrade the short hannel effets due to disrete dopant flutuations. In sub-22 nm devies, the devie parasiti apaitanes dominate and limit the iruit delay [1, 5]. The IC delay (τ) an be redued only through high drive urrent (I d ) and high g m. InGaAs MOSFETs are expeted to ahieve very high drive urrents (5 ma/μm) and transondutanes (7 ms/μm) beause of high thermal veloities (J = qnv) [1, 5, 6]. These urrent levels are ahieved at a sheet onentration of ~ m -2. Large intervalley separation (E Γ L, E Γ X = 0.5 ev) in InGaAs makes it possible to ahieve these densities without populating the slower satellite valleys. Furthermore, soure aess resistane plays an important role in saled devies beause it degrades the available I d and g m from the devie. Even a very low soure aess resistane of 15 Ω-μm would degrade I d by 10% [5]. This value is an order of magnitude smaller than the ITRS roadmap listed soure aess resistane of 180 Ω-μm [7]. IC layout density requirement would onstrain L = L g = 22 nm, whih means a speifi ontat resistivity ρ = 0.25 Ω- μm 2 orresponding to 10 Ω-μm resistane. A 4 Ω-μm S/D extension aess resistane translates into a high m -3 ative doping in these regions. Besides soure resistane, high doping onentrations is required in S/D to avoid soure starvation [6]. Unlike Si, ion implantation is not a viable tehnique for InGaAs due to various diffiulties. There is no data showing the apability of implantation realizing these high ative onentrations and ontat resistane values. Instead we are using MBE to regrow S/D regions after gate formation. Ative Si doping ~ m -3 and low ontat resistane of 0.5 Ω-μm 2 have Poly-InGaAs Gate Figure 2 SEM of Poly-InGaAs regrowth. been demonstrated by MBE and in-situ molybdenum (Mo) ontats [8]. Saled sub 50 nm Shottky FETs (HEMTs) with 1 nm EOT have been reported but have not been able to ahieve the high simulated drive urrents [9]. HEMTs have non-salable soure resistane beause of the high bandgap under the S/D ontats [10]. The Shottky gate also has a higher gate leakage urrent than dieletris do, making it unsuitable for VLSI appliations. The details of the proess flow are provided below, but the general flow is as follows. As shown in Fig. 1, the gate was defined first by a salable dry eth proess rather than by traditional III-V lifoff tehniques. The high-k dieletri was wet ethed and gate was enapsulated in a SiN sidewall, followed by InGaAs soure/drain regrowth by moleular beam epitaxy (MBE). Self-aligned ontats were defined by a blanket metal deposition and a heightseletive eth, then the devies were mesa isolated. e shall now disuss these steps in greater detail. First, a omposite InGaAs (4 nm)/inp (2.5 nm) hannel and 100 nm of InAlAs bak was grown by MBE on semi-insulating InP. Then the wafer was ooled to 50 ºC and apped with 100 nm of As. The wafer was unloaded and transferred to an Atomi Layer Deposition (ALD) hamber, then the As ap was desorbed, and 5 nm of Al 2 O 3 dieletri was grown immediately. Next, the blanket gate stak (50nm)/(50nm)/ (300nm)/(50nm) was deposited. For these devies, the gate dieletri is diretly on top of the thin hannel, without any intentional intermediate layers. This imparts a onsiderable proessing hallenge as thin layers are prone to damage during dry ethes. A damaged hannel layer would result in imperfet S/D regrowth, whih leads to high soure resistanes. Also, any pinhole introdued in the hannel beause of the dry eth would expose and oxidize the underlying InAlAs layer. This would again ause defet ridden S/D regrowth and high resistanes. Figure 2 shows the faeted and resistive poly-ingaas whih results from regrowth on a damaged hannel.
3 physia p s s 1396 U. Singisetti et al.: InGaAs hannel MOSFET with self-aligned soure/drain MBE regrowth tehnology SF 6 / Ar eth 50 SF 6 / Ar resist Cl 2 / O 2 eth mask Cl 2 / O 2 eth stop gate metal dieletri KOH wet eth Al 2 O 3 ( ) InGaAs InP SI substrate FIB oss-setion Damage free hannel Dry eth sheme Figure 3 Dry eth sheme and FIB rosssetion SEM image of a gate. Therefore a multiple layer gate stak and alternating seletive dry eth sheme was developed (Fig. 3). The top layer was used as a dry eth mask after patterning it with photoresist and i-line photolithography, followed by a Cl 2 /O 2 dry eth. The was removed before the hannel was exposed. Next, before the was ethed, the photoresist was stripped and O 2 plasma ethed; the proteted the hannel from damage, and the aggressive O 2 eth prevented organi ontamination of the MBE hamber. The alternating seletive dry eth sheme (Fig. 3) allows a final low power dry eth of the layer without damaging the hannel. The Al 2 O 3 dieletri was wet ethed in dilute KOH solution. As a result, 300 nm long and 400 nm thik gate staks were fabriated on 4 nm InGaAs hannel. The proess an be easily used to fabriate sub-50 nm features by using eletron beam lithography. A 45 nm, onformal layer of SiN x was deposited over the gates by PECVD, and a low power anisotropi eth was performed to remove the SiN x from the far field, leaving defined sidewalls. The final // struture with SiN x sidewalls leaves the metals unexposed in the MBE hamber during regrowth avoiding any possible metal ontamination. The InGaAs hannel was seletively wet ethed, stopping on the InP sub-hannel, and an overeth was done to eth a small amount InGaAs under the SiN x sidewall. Next the wafer was treated with 30 minute UV-Ozone forming a 1 nm sarifiial oxide. It was followed by 1 minute 1:10 HCl:DI treatment to remove the oxide, 1 minute DI rinse, and blown dry in N 2. Then it was immediately loaded into MBE hamber and baked overnight at 200 ºC. The wafer was atomi hydrogen leaned at 400 ºC for 30 minutes. A (2 4) surfae reonstrution was seen in refletion high energy eletron diffration (RHEED) before regrowth, indiating an epi-ready surfae. Using this leaning proedure, defet free epitaxial InGaAs films were regrown on InGaAs and showed low sheet and ontat resistanes [11]. A 25 nm/ 5 nm InGaAs/ InAs with m -3 ative Si doping was grown non-seletively at 400 C. Then the wafer was then transferred to an eletron beam evaporator attahed to the MBE under ultra high vauum, and 20 nm of Mo was deposited. Both the InGaAs regrowth and Mo are deposited over the top of the gate, shorting the soure to the drain. To remove the undesired material, the wafer was planarized by spinning photo-resist and ashed bak in an indutively oupled O 2 plasma (ICP) until the tops of the gates were exposed. Then the Mo was dry ethed in a SF 6 /Ar plasma, and the InGaAs layers were wet ethed [11, 12]. The PR was stripped to give a self-aligned S/D MOSFET. Next S/D pads were lifted-off, and devies were mesa isolated and measured by needle probe. A shemati of the saled InGaAs MOSFET is given in Fig. 4. The self-aligned S/D regrowth ensures the soure resistane does not degrade from surfae state indued depletion [13]. The RHEED was spotty during the regrowth on the MOSFET wafer, whih indiated a rough surfae. e attribute this to InP to InAs onversion during the initial N + soure InP N + drain Mo Figure 4 oss-setion shemati of final devie. stage of regrowth. [14] The highly strained InAs layer relaxed, and the subsequent InGaAs growth beame rough. This phenomenon was onfirmed by the failure of the seletive Arsenide wet eth to stop on the InP layer after regrowth. Spotty RHEED and rough InGaAs regrowth were
4 Contributed Artile Phys. Status Solidi C 6, No. 6 (2009) 1397 Drain Current (µa) L =10µm, =50µm g g V =0 to 2 V, V step = 0.25 V gs gs Vds (Volts) Figure 5 Measured I d -V d of the MOSFET. also observed on unproessed wafers with thin InP but with no gates. A similar rough surfae was observed even in hemial beam epitaxy (CBE) growth. This onfirmed A sanning eletron mirosope (SEM) image of the devie showed a nm gap between the n + regrowth regions and the gate. Similar gaps in regrowth were observed on o-proessed wafers with gates but without highk (Fig. 6). The gap is most likely due to shadowing by the gate during MBE regrowth and/or by a thin (nm) layer of SiN x remaining on the surfae near the gate even after the sidewall eth. The gap was also observed in proess monitor wafers on whih no sidewall was deposited. e attribute this to shadowing by the tall gate features as as redued surfae mobility of group III adatoms at the growth temperature (400 ºC). As a result, the hannel surfae next to gate is starved of group III elements, resulting in a gap. ithout the high doping from regrowth, the hannel in the gap region is depleted of all eletrons beause of the pinning of Fermi-level below the ondution band edge due to surfae states. Furthermore a large underut in Al 2 O 3 dieletri an introdue an additional depleted region between the hannel and the soure. Figure 7 shows // gate N + regrowth Gap Gap in regrowth InGaAs regrowth InP Figure 6 SEM and shemati image showing a gap in regrowth. that the problem was a growth related issue, rather than proess related ontamination. Transmission line measurements (TLM) on the regrowth layer gave a high sheet resistane of 310 Ω μm and a ontat resistane of 130 Ω μm 2. A soure resistane of 300 Ω μm was expeted from the TLM data. A low sheet resistane of 28 Ω μm and ontat resistane of 9 Ω μm 2 were measured on a oproessed wafer with no high-k and no InP, onfirming the possibility of high quality regrowth on a proessed wafer. e attribute the higher resistane observed in the MOS- FET wafer to relaxation and rough growth on the thin InP layer. Figure 5 shows the output harateristis of a 10 µm gate length devie. The maximum drive urrent is ~ 2 μa/μm at V gs = 2.0 V and V ds = 2.0 V. Similar low drive urrents were observed for the shorter gate length devies. The I d -V g haraterstis showed an extremely high soure resistane limited linear behavior with R s ~ kω. The on resistane is orders of magnitude higher than the value alulated from the TLM strutures. I d -V ds of a devie where the InGaAs hannel was not ethed. The breakdown voltage is 8 V onsistent with an InGaAs breakdown of 20 V/μm [15] for total S/D to gate gap of 400 nm as seen in SEM. Thus we believe the low drive urrents resulted from the undoped gaps in regrowth. The two main reasons for the high soure resistane are the inability to re-grow low resistane epitaxial InGaAs on thin InP sub-hannel, and a gap region with no regrowth next to the gate. Instead of the thin InP layer, introduing a 2 nm strained In 0.88 Ga 0.12 P (InGaP) sub-hannel eth stop layer allowed suessful regrowth of low resistane In- GaAs [11]. A high temperature migration enhaned epitaxy (MEE) regrowth tehnique showed no gaps next to the gate [16]. Furthermore, a 5-10 nm thik SiN x sidewall tehnology is being developed. This would mean a 5-10 nm lateral extension under sidewall, so the MBE regrowth would only need to fill in a horizontal void with a 1:1 or 1:2 aspet ratio. In summary, we developed a salable, self-aligned, III- V MOSFET proess with MBE S/D regrowth. The gate
5 physia p s s 1398 U. Singisetti et al.: InGaAs hannel MOSFET with self-aligned soure/drain MBE regrowth tehnology I d (µa) 1200 L = 10 µm =10 µm V =0.0 V g V (V) ds Figure 7 Breakdown haraterstis of the MOSFET. proess and H leaning leave a 5 nm thik, lean, undamaged, epi-ready hannel surfae suitable for MBE or MOCVD regrowth. orking devies were fabriated with this proess. The devies show low drive urrent beause of undoped gaps between the S/D and the gate in the early devies. Improved high temperature S/D growth tehniques have been developed and will be used in the next generation of devies. Aknowledgements e gratefully aknowledge Semiondutor Researh Corporation (SRC) for supporting this work. Referenes [1] P.M. Solomon and S. Laux, IEEE IEDM Teh. Dig. 2001, pp [2] Y. Sun et al., 66th DRC, Santa Barbara, 2008, pp [3] S. Koveshnikov et al., 66th DRC, Santa Barbara, 2008, pp [4] Y. Xuan et al., 66th DRC, Santa Barbara, 2008, pp [5] M. J. Rod, M. istey, U. Singisetti, G. Burek et al., 20th IEEE IPRM, [6] M.V. Fishetti et al., IEEE IEDM Teh. Dig., 2007, pp [7] International Tehnology Roadmap of Semiondutor, Front End Proesses, 2007, p. 21. [8] U. Singisetti et al., 65th DRC, Notre Dame, 2007, pp [9] D.-H. Kim et al., IEEE IEDM Teh. Dig., 2005, pp [10] T. Takahashi et al., 19th IEEE IPRM, 2007, pp [11] M. A. istey et al., Eletroni Materials Conferene, 2008, p. Z4. [12] G.J. Burek et al., J. yst. Growth, 2008, submitted for publiation. [13] T. Suemitsu et al., Jpn. J. Appl. Phy. 37, (1998). [14] M.A.istey et al., in preparation. [15] Yu.A. Goldberg and N. M. Shmidt, Handbook Series on Semiondutor Parameters, Vol. 2 (orld Sientifi, London, 1999), pp [16] M. A. istey et al., 15th Int. Conf. on Moleular Beam Epitaxy, Vanouver, Canada, Aug. 2008, p 199.
InGaAs channel MOSFET with self-aligned source/drain MBE regrowth technology
 pss-header will be provided by the publisher Review copy not for distribution 0 0 (pss-logo will be inserted here by the publisher) InGaAs channel MOSFET with self-aligned source/drain MBE regrowth technology
pss-header will be provided by the publisher Review copy not for distribution 0 0 (pss-logo will be inserted here by the publisher) InGaAs channel MOSFET with self-aligned source/drain MBE regrowth technology
Planarization and Regrowth of Self-Aligned Ohmic Contacts on InGaAs
 MBE 2008, Vancouver, B.C. Planarization and Regrowth of Self-Aligned Ohmic Contacts on InGaAs Mark Wistey, Greg Burek, Uttam Singisetti, Austin Nelson, Brian Thibeault, Joël Cagnon, Susanne Stemmer, Arthur
MBE 2008, Vancouver, B.C. Planarization and Regrowth of Self-Aligned Ohmic Contacts on InGaAs Mark Wistey, Greg Burek, Uttam Singisetti, Austin Nelson, Brian Thibeault, Joël Cagnon, Susanne Stemmer, Arthur
THERMAL STABILITY AND IV CHARACTERISTICS OF IN-SITU EPITAXIAL AL ON GaAs P-HEMT GROWN BY SOLID SOURCE MBE.
 THERMAL STABILITY AND IV CHARACTERISTICS OF IN-SITU EPITAXIAL AL ON GaAs P-HEMT GROWN BY SOLID SOURCE MBE. Azlan Abdul Aziz Solid State Semiondutor Group, Shool ofphysis, Universiti Sains Malaysia, 11800
THERMAL STABILITY AND IV CHARACTERISTICS OF IN-SITU EPITAXIAL AL ON GaAs P-HEMT GROWN BY SOLID SOURCE MBE. Azlan Abdul Aziz Solid State Semiondutor Group, Shool ofphysis, Universiti Sains Malaysia, 11800
Record Extrinsic Transconductance (2.45 ms/μm at V DS = 0.5 V) InAs/In 0.53 Ga 0.47 As Channel MOSFETs Using MOCVD Source-Drain Regrowth
 Record Extrinsic Transconductance (2.45 ms/μm at = 0.5 V) InAs/In 0.53 Ga 7 As Channel MOSFETs Using MOCVD Source-Drain Regrowth Sanghoon Lee 1*, C.-Y. Huang 1, A. D. Carter 1, D. C. Elias 1, J. J. M.
Record Extrinsic Transconductance (2.45 ms/μm at = 0.5 V) InAs/In 0.53 Ga 7 As Channel MOSFETs Using MOCVD Source-Drain Regrowth Sanghoon Lee 1*, C.-Y. Huang 1, A. D. Carter 1, D. C. Elias 1, J. J. M.
Record I on (0.50 ma/μm at V DD = 0.5 V and I off = 100 na/μm) 25 nm-gate-length ZrO 2 /InAs/InAlAs MOSFETs
 Record I on (0.50 ma/μm at V DD = 0.5 V and I off = 100 na/μm) 25 nm-gate-length ZrO 2 /InAs/InAlAs MOSFETs Sanghoon Lee 1*, V. Chobpattana 2,C.-Y. Huang 1, B. J. Thibeault 1, W. Mitchell 1, S. Stemmer
Record I on (0.50 ma/μm at V DD = 0.5 V and I off = 100 na/μm) 25 nm-gate-length ZrO 2 /InAs/InAlAs MOSFETs Sanghoon Lee 1*, V. Chobpattana 2,C.-Y. Huang 1, B. J. Thibeault 1, W. Mitchell 1, S. Stemmer
Device Research Conference 2007
 Devie Researh Conerene 2007 560 GHz t, max InGaAs/InP DHBT in a novel dry-ethed emitter proess Erik Lind, Adam M. Crook, Zah Griith, and Mark J.W. Rodwell Department o Eletrial and Computer Engineering
Devie Researh Conerene 2007 560 GHz t, max InGaAs/InP DHBT in a novel dry-ethed emitter proess Erik Lind, Adam M. Crook, Zah Griith, and Mark J.W. Rodwell Department o Eletrial and Computer Engineering
Scaling of InGaAs MOSFETs into deep-submicron regime (invited)
 Scaling of InGaAs MOSFETs into deep-submicron regime (invited) Y.Q. Wu, J.J. Gu, and P.D. Ye * School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN 47906 * Tel: 765-494-7611,
Scaling of InGaAs MOSFETs into deep-submicron regime (invited) Y.Q. Wu, J.J. Gu, and P.D. Ye * School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN 47906 * Tel: 765-494-7611,
InGaAs MOSFETs for CMOS:
 InGaAs MOSFETs for CMOS: Recent Advances in Process Technology J. A. del Alamo, D. Antoniadis, A. Guo, D.-H. Kim 1, T.-W. Kim 2, J. Lin, W. Lu, A. Vardi and X. Zhao Microsystems Technology Laboratories,
InGaAs MOSFETs for CMOS: Recent Advances in Process Technology J. A. del Alamo, D. Antoniadis, A. Guo, D.-H. Kim 1, T.-W. Kim 2, J. Lin, W. Lu, A. Vardi and X. Zhao Microsystems Technology Laboratories,
A New Broadband Microstrip-to-SIW Transition Using Parallel HMSIW
 JOURNAL OF ELECTROMAGNETIC ENGINEERING AND SCIENCE, VOL. 12, NO. 2, 171~175, JUN. 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.5515/jkiees.2012.12.2.171 ISSN 2234-8395 (Online) ISSN 2234-8409 (Print) A New Broadband Mirostrip-to-
JOURNAL OF ELECTROMAGNETIC ENGINEERING AND SCIENCE, VOL. 12, NO. 2, 171~175, JUN. 2012 http://dx.doi.org/10.5515/jkiees.2012.12.2.171 ISSN 2234-8395 (Online) ISSN 2234-8409 (Print) A New Broadband Mirostrip-to-
Fin-Shaped Field Effect Transistor (FinFET) Min Ku Kim 03/07/2018
 Fin-Shaped Field Effect Transistor (FinFET) Min Ku Kim 03/07/2018 ECE 658 Sp 2018 Semiconductor Materials and Device Characterizations OUTLINE Background FinFET Future Roadmap Keeping up w/ Moore s Law
Fin-Shaped Field Effect Transistor (FinFET) Min Ku Kim 03/07/2018 ECE 658 Sp 2018 Semiconductor Materials and Device Characterizations OUTLINE Background FinFET Future Roadmap Keeping up w/ Moore s Law
A Digitally Controlled Oscillator for ADPLL Application. Wu Xiulong, Wang Faniu, Lin Zhiting, and Chen Junning
 pplied Mehanis and Materials Online: 22--29 ISSN: 662-7482, Vols. 229-23, pp 55-58 doi:.428/www.sientifi.net/mm.229-23.55 22 Trans Teh ubliations, Switzerland Digitally Controlled Osillator for DLL ppliation
pplied Mehanis and Materials Online: 22--29 ISSN: 662-7482, Vols. 229-23, pp 55-58 doi:.428/www.sientifi.net/mm.229-23.55 22 Trans Teh ubliations, Switzerland Digitally Controlled Osillator for DLL ppliation
Zota, Cezar B.; Lindelow, Fredrik; Wernersson, Lars Erik; Lind, Erik
 InGaAs tri-gate MOSFETs with record on-current Zota, Cezar B.; Lindelow, Fredrik; Wernersson, Lars Erik; Lind, Erik Published in: 6 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, IEDM 6 DOI:.9/IEDM.6.7886
InGaAs tri-gate MOSFETs with record on-current Zota, Cezar B.; Lindelow, Fredrik; Wernersson, Lars Erik; Lind, Erik Published in: 6 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting, IEDM 6 DOI:.9/IEDM.6.7886
Sub-30 nm InAs Quantum-Well MOSFETs with Self-Aligned Metal Contacts and Sub-1 nm EOT HfO 2 Insulator
 Sub-30 nm InAs Quantum-Well MOSFETs with Self-Aligned Metal Contacts and Sub-1 nm EOT HfO 2 Insulator Jianqiang Lin, Dimitri A. Antoniadis, and Jesús A. del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories,
Sub-30 nm InAs Quantum-Well MOSFETs with Self-Aligned Metal Contacts and Sub-1 nm EOT HfO 2 Insulator Jianqiang Lin, Dimitri A. Antoniadis, and Jesús A. del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories,
III-V CMOS: the key to sub-10 nm electronics?
 III-V CMOS: the key to sub-10 nm electronics? J. A. del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT 2011 MRS Spring Meeting and Exhibition Symposium P: Interface Engineering for Post-CMOS Emerging
III-V CMOS: the key to sub-10 nm electronics? J. A. del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT 2011 MRS Spring Meeting and Exhibition Symposium P: Interface Engineering for Post-CMOS Emerging
InGaAs MOSFET Electronics
 InGaAs MOSFET Electronics J. A. del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT The 17 th International Symposium Physics of Semiconductors and Applications Jeju, Korea, December 7-11, 2014 Acknowledgements:
InGaAs MOSFET Electronics J. A. del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT The 17 th International Symposium Physics of Semiconductors and Applications Jeju, Korea, December 7-11, 2014 Acknowledgements:
In0.53Ga0.47As MOSFETs with 5 nm channel and self-aligned source/drain by MBE regrowth
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA Santa Barbara In0.53Ga0.47As MOSFETs with 5 nm channel and self-aligned source/drain by MBE regrowth A Dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA Santa Barbara In0.53Ga0.47As MOSFETs with 5 nm channel and self-aligned source/drain by MBE regrowth A Dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the
Nanometer-Scale InGaAs Field-Effect Transistors for THz and CMOS Technologies
 Nanometer-Scale InGaAs Field-Effect Transistors for THz and CMOS Technologies J. A. del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT ESSDERC-ESSCIRC 2013 Bucharest, Romania, September 16-20, 2013 Acknowledgements:
Nanometer-Scale InGaAs Field-Effect Transistors for THz and CMOS Technologies J. A. del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT ESSDERC-ESSCIRC 2013 Bucharest, Romania, September 16-20, 2013 Acknowledgements:
Nanoscale III-V CMOS
 Nanoscale III-V CMOS J. A. del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories Massachusetts Institute of Technology SEMI Advanced Semiconductor Manufacturing Conference Saratoga Springs, NY; May 16-19, 2016
Nanoscale III-V CMOS J. A. del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories Massachusetts Institute of Technology SEMI Advanced Semiconductor Manufacturing Conference Saratoga Springs, NY; May 16-19, 2016
ADVANCE MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CONTENTS. High Frequency and Optical Devices. Technical Reports. Sep / Vol Overview...
 Sep. 29 / Vol. 127 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC ADVANCE High Frequeny and Optial Devies Editorial-Chief Kiyoshi Takakuwa Editorial Advisors Chisato Kobayashi Kanae Ishida Makoto Egashira Koji Yasui Hiroaki Kawahi
Sep. 29 / Vol. 127 MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC ADVANCE High Frequeny and Optial Devies Editorial-Chief Kiyoshi Takakuwa Editorial Advisors Chisato Kobayashi Kanae Ishida Makoto Egashira Koji Yasui Hiroaki Kawahi
A New Self-aligned Quantum-Well MOSFET Architecture Fabricated by a Scalable Tight-Pitch Process
 A New Self-aligned Quantum-Well MOSFET Architecture Fabricated by a Scalable Tight-Pitch Process Jianqiang Lin, Xin Zhao, Tao Yu, Dimitri A. Antoniadis, and Jesús A. del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories,
A New Self-aligned Quantum-Well MOSFET Architecture Fabricated by a Scalable Tight-Pitch Process Jianqiang Lin, Xin Zhao, Tao Yu, Dimitri A. Antoniadis, and Jesús A. del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories,
General look back at MESFET processing. General principles of heterostructure use in FETs
 SMA5111 - Compound Semiconductors Lecture 11 - Heterojunction FETs - General HJFETs, HFETs Last items from Lec. 10 Depletion mode vs enhancement mode logic Complementary FET logic (none exists, or is likely
SMA5111 - Compound Semiconductors Lecture 11 - Heterojunction FETs - General HJFETs, HFETs Last items from Lec. 10 Depletion mode vs enhancement mode logic Complementary FET logic (none exists, or is likely
InGaAs Nanoelectronics: from THz to CMOS
 InGaAs Nanoelectronics: from THz to CMOS J. A. del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT IEEE International Conference on Electron Devices and Solid-State Circuits Hong Kong, June 3, 2013 Acknowledgements:
InGaAs Nanoelectronics: from THz to CMOS J. A. del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT IEEE International Conference on Electron Devices and Solid-State Circuits Hong Kong, June 3, 2013 Acknowledgements:
A Novel Switched-Turn Continuously-Tunable Liquid RF MEMS Solenoid Inductor
 A Novel Swithed-Turn Continuously-Tunable Liquid RF MEMS Solenoid Indutor Fatemeh Banitorfian, Farshad Eshghabadi, Asrulnizam Abd Manaf, Norlaili Mohd Noh, Mohd Tafir Mustaffa, Othman Sidek Shool of Eletrial
A Novel Swithed-Turn Continuously-Tunable Liquid RF MEMS Solenoid Indutor Fatemeh Banitorfian, Farshad Eshghabadi, Asrulnizam Abd Manaf, Norlaili Mohd Noh, Mohd Tafir Mustaffa, Othman Sidek Shool of Eletrial
A compact dual-band bandpass filter using triple-mode stub-loaded resonators and outer-folding open-loop resonators
 Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sienes Vol. 24, February 2017, pp. 13-17 A ompat dual-band bandpass filter using triple-mode stub-loaded resonators and outer-folding open-loop resonators Ming-Qing
Indian Journal of Engineering & Materials Sienes Vol. 24, February 2017, pp. 13-17 A ompat dual-band bandpass filter using triple-mode stub-loaded resonators and outer-folding open-loop resonators Ming-Qing
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11293 1. Formation of (111)B polar surface on Si(111) for selective-area growth of InGaAs nanowires on Si. Conventional III-V nanowires (NWs) tend to grow in
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11293 1. Formation of (111)B polar surface on Si(111) for selective-area growth of InGaAs nanowires on Si. Conventional III-V nanowires (NWs) tend to grow in
Compact Band-Pass and Band-Reject Microwave Filters Using Partial H-Plane Waveguide and Dielectric Layers
 Compat Band-Pass and Band-Rejet Mirowave Filters Using ial H-Plane Waveguide and Dieletri ayers A. Ghajar Department of Eletrial Engineering University of Guilan Rasht, Iran alighajar199@gmail.om H. Ghorbaninejad-Foumani
Compat Band-Pass and Band-Rejet Mirowave Filters Using ial H-Plane Waveguide and Dieletri ayers A. Ghajar Department of Eletrial Engineering University of Guilan Rasht, Iran alighajar199@gmail.om H. Ghorbaninejad-Foumani
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices
 EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 11/01/2007 MOSFETs Lecture 5 Announcements HW7 set is due now HW8 is assigned, but will not be collected/graded. MOSFET Technology Scaling Technology
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 11/01/2007 MOSFETs Lecture 5 Announcements HW7 set is due now HW8 is assigned, but will not be collected/graded. MOSFET Technology Scaling Technology
FinFET Devices and Technologies
 FinFET Devices and Technologies Jack C. Lee The University of Texas at Austin NCCAVS PAG Seminar 9/25/14 Material Opportunities for Semiconductors 1 Why FinFETs? Planar MOSFETs cannot scale beyond 22nm
FinFET Devices and Technologies Jack C. Lee The University of Texas at Austin NCCAVS PAG Seminar 9/25/14 Material Opportunities for Semiconductors 1 Why FinFETs? Planar MOSFETs cannot scale beyond 22nm
III. DESIGN OF CIRCUIT COMPONENTS
 ISSN: 77-3754 ISO 900:008 ertified Volume, Issue 5, November 0 Design and Analysis of a MOS 0.7V ow Noise Amplifier for GPS Band Najeemulla Baig, handu DS, 3 Satyanarayana hanagala, 4 B.Satish,3 Assoiate
ISSN: 77-3754 ISO 900:008 ertified Volume, Issue 5, November 0 Design and Analysis of a MOS 0.7V ow Noise Amplifier for GPS Band Najeemulla Baig, handu DS, 3 Satyanarayana hanagala, 4 B.Satish,3 Assoiate
Vertical InAs/GaAsSb/GaSb tunneling field-effect transistor on Si with S = 48 mv/decade and Ion = 10 A/m for Ioff = 1 na/m at VDS = 0.
 Vertical InAs/GaAsSb/GaSb tunneling field-effect transistor on Si with S = 48 mv/decade and Ion = 10 A/m for Ioff = 1 na/m at VDS = 0.3 V Memisevic, E.; Svensson, Johannes; Hellenbrand, Markus; Lind, Erik;
Vertical InAs/GaAsSb/GaSb tunneling field-effect transistor on Si with S = 48 mv/decade and Ion = 10 A/m for Ioff = 1 na/m at VDS = 0.3 V Memisevic, E.; Svensson, Johannes; Hellenbrand, Markus; Lind, Erik;
Hierarchical Extreme-Voltage Stress Test of Analog CMOS ICs for Gate-Oxide Reliability Enhancement*
 Hierarhial Extreme-Voltage Stress Test of Analog MOS Is for Gate-Oxide Reliability Enhanement* hin-long Wey Department of Eletrial Engineering National entral University hung-li, Taiwan lway@ee.nu.edu.tw
Hierarhial Extreme-Voltage Stress Test of Analog MOS Is for Gate-Oxide Reliability Enhanement* hin-long Wey Department of Eletrial Engineering National entral University hung-li, Taiwan lway@ee.nu.edu.tw
Final Report. Contract Number Title of Research Principal Investigator
 Final Report Contract Number Title of Research Principal Investigator Organization N00014-05-1-0135 AIGaN/GaN HEMTs on semi-insulating GaN substrates by MOCVD and MBE Dr Umesh Mishra University of California,
Final Report Contract Number Title of Research Principal Investigator Organization N00014-05-1-0135 AIGaN/GaN HEMTs on semi-insulating GaN substrates by MOCVD and MBE Dr Umesh Mishra University of California,
Hydrogenated Amorphous Silicon Sensors based on Thin Film on ASIC technology
 Hydrogenated Amorphous Silion Sensors based on Thin Film on ASIC tehnology M. Despeisse, D. Moraes, G. Anelli, P. Jarron, J. Kaplon, R. Rusak, S. Saramad and N. Wyrsh Abstrat The performane and limitations
Hydrogenated Amorphous Silion Sensors based on Thin Film on ASIC tehnology M. Despeisse, D. Moraes, G. Anelli, P. Jarron, J. Kaplon, R. Rusak, S. Saramad and N. Wyrsh Abstrat The performane and limitations
TRANSISTORS: DYNAMIC CIRCUITS. Introduction
 TRANSISTORS: DYNAMIC CIRCUITS Introdution The point of biasing a iruit orretly is that the iruit operate in a desirable fashion on signals that enter the iruit. These signals are perturbations about the
TRANSISTORS: DYNAMIC CIRCUITS Introdution The point of biasing a iruit orretly is that the iruit operate in a desirable fashion on signals that enter the iruit. These signals are perturbations about the
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTRON DEVICES, VOL. 51, NO. 2, FEBRUARY
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTRON DEVICES, VOL. 51, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2004 195 A Global Interonnet Optimization Sheme for Nanometer Sale VLSI With Impliations for Lateny, Bandwidth, and Power Dissipation Man
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTRON DEVICES, VOL. 51, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2004 195 A Global Interonnet Optimization Sheme for Nanometer Sale VLSI With Impliations for Lateny, Bandwidth, and Power Dissipation Man
Acknowledgements. Curriculum Vitæ. List of Figures. List of Tables. 1 Introduction Si MOSFET Scaling... 2
 Contents Acknowledgements Curriculum Vitæ Abstract List of Figures List of Tables v vi viii xii xviii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Si MOSFET Scaling......................... 2 2 General MOSFET Scaling Theory 7
Contents Acknowledgements Curriculum Vitæ Abstract List of Figures List of Tables v vi viii xii xviii 1 Introduction 1 1.1 Si MOSFET Scaling......................... 2 2 General MOSFET Scaling Theory 7
III-V CMOS: Quo Vadis?
 III-V CMOS: Quo Vadis? J. A. del Alamo, X. Cai, W. Lu, A. Vardi, and X. Zhao Microsystems Technology Laboratories Massachusetts Institute of Technology Compound Semiconductor Week 2018 Cambridge, MA, May
III-V CMOS: Quo Vadis? J. A. del Alamo, X. Cai, W. Lu, A. Vardi, and X. Zhao Microsystems Technology Laboratories Massachusetts Institute of Technology Compound Semiconductor Week 2018 Cambridge, MA, May
Application of TEM horn antenna in radiating NEMP simulator
 Journal of Physis: Conferene Series Appliation of TEM horn antenna in radiating NEMP simulator To ite this artile: Yun Wang et al 013 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 418 010 View the artile online for updates and
Journal of Physis: Conferene Series Appliation of TEM horn antenna in radiating NEMP simulator To ite this artile: Yun Wang et al 013 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 418 010 View the artile online for updates and
Chapter 3: Basics Semiconductor Devices and Processing 2006/9/27 1. Topics
 Chapter 3: Basics Semiconductor Devices and Processing 2006/9/27 1 Topics What is semiconductor Basic semiconductor devices Basics of IC processing CMOS technologies 2006/9/27 2 1 What is Semiconductor
Chapter 3: Basics Semiconductor Devices and Processing 2006/9/27 1 Topics What is semiconductor Basic semiconductor devices Basics of IC processing CMOS technologies 2006/9/27 2 1 What is Semiconductor
Topic 3. CMOS Fabrication Process
 Topic 3 CMOS Fabrication Process Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: p.cheung@ic.ac.uk Lecture 3-1 Layout of a Inverter
Topic 3 CMOS Fabrication Process Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: p.cheung@ic.ac.uk Lecture 3-1 Layout of a Inverter
Ultra High-Speed InGaAs Nano-HEMTs
 Ultra High-Speed InGaAs Nano-HEMTs 2003. 10. 14 Kwang-Seok Seo School of Electrical Eng. and Computer Sci. Seoul National Univ., Korea Contents Introduction to InGaAsNano-HEMTs Nano Patterning Process
Ultra High-Speed InGaAs Nano-HEMTs 2003. 10. 14 Kwang-Seok Seo School of Electrical Eng. and Computer Sci. Seoul National Univ., Korea Contents Introduction to InGaAsNano-HEMTs Nano Patterning Process
Nanoscale III-V Electronics: from Quantum-Well Planar MOSFETs to Vertical Nanowire MOSFETs
 Nanoscale III-V Electronics: from Quantum-Well Planar MOSFETs to Vertical Nanowire MOSFETs J. A. del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN; September 29,
Nanoscale III-V Electronics: from Quantum-Well Planar MOSFETs to Vertical Nanowire MOSFETs J. A. del Alamo Microsystems Technology Laboratories, MIT Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN; September 29,
CMOS Digital Integrated Circuits Lec 2 Fabrication of MOSFETs
 CMOS Digital Integrated Circuits Lec 2 Fabrication of MOSFETs 1 CMOS Digital Integrated Circuits 3 rd Edition Categories of Materials Materials can be categorized into three main groups regarding their
CMOS Digital Integrated Circuits Lec 2 Fabrication of MOSFETs 1 CMOS Digital Integrated Circuits 3 rd Edition Categories of Materials Materials can be categorized into three main groups regarding their
Micro-Piezoelectric Head Technology of Color Inkjet Printer
 DPP2: International Conferene on Digital Prodution Printing and Industrial Appliations Miro-Piezoeletri Head Tehnology of Color Inkjet Printer Takao Mimura & Shinri Sakai SEIKO EPSON Corporation Shiojiri-shi,
DPP2: International Conferene on Digital Prodution Printing and Industrial Appliations Miro-Piezoeletri Head Tehnology of Color Inkjet Printer Takao Mimura & Shinri Sakai SEIKO EPSON Corporation Shiojiri-shi,
Enhancing System-Wide Power Integrity in 3D ICs with Power Gating
 Enhaning System-Wide Power Integrity in 3D ICs with Power Gating Hailang Wang and Emre Salman Department of Eletrial and Computer Engineering, Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, NY 794 USA E-mail: {hailang.wang,
Enhaning System-Wide Power Integrity in 3D ICs with Power Gating Hailang Wang and Emre Salman Department of Eletrial and Computer Engineering, Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, NY 794 USA E-mail: {hailang.wang,
EE 5611 Introduction to Microelectronic Technologies Fall Thursday, September 04, 2014 Lecture 02
 EE 5611 Introduction to Microelectronic Technologies Fall 2014 Thursday, September 04, 2014 Lecture 02 1 Lecture Outline Review on semiconductor materials Review on microelectronic devices Example of microelectronic
EE 5611 Introduction to Microelectronic Technologies Fall 2014 Thursday, September 04, 2014 Lecture 02 1 Lecture Outline Review on semiconductor materials Review on microelectronic devices Example of microelectronic
Analysis and Design of an UWB Band pass Filter with Improved Upper Stop band Performances
 Analysis and Design of an UWB Band pass Filter with Improved Upper Stop band Performanes Nadia Benabdallah, 1 Nasreddine Benahmed, 2 Fethi Tari Bendimerad 3 1 Department of Physis, Preparatory Shool of
Analysis and Design of an UWB Band pass Filter with Improved Upper Stop band Performanes Nadia Benabdallah, 1 Nasreddine Benahmed, 2 Fethi Tari Bendimerad 3 1 Department of Physis, Preparatory Shool of
Transistor was first invented by William.B.Shockley, Walter Brattain and John Bardeen of Bell Labratories. In 1961, first IC was introduced.
 Unit 1 Basic MOS Technology Transistor was first invented by William.B.Shockley, Walter Brattain and John Bardeen of Bell Labratories. In 1961, first IC was introduced. Levels of Integration:- i) SSI:-
Unit 1 Basic MOS Technology Transistor was first invented by William.B.Shockley, Walter Brattain and John Bardeen of Bell Labratories. In 1961, first IC was introduced. Levels of Integration:- i) SSI:-
Layout of a Inverter. Topic 3. CMOS Fabrication Process. The CMOS Process - photolithography (2) The CMOS Process - photolithography (1) v o.
 Layout of a Inverter Topic 3 CMOS Fabrication Process V DD Q p Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London v i v o Q n URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: p.cheung@ic.ac.uk
Layout of a Inverter Topic 3 CMOS Fabrication Process V DD Q p Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London v i v o Q n URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: p.cheung@ic.ac.uk
III-V on Si for VLSI. 200 mm III-V on Si. Accelerating the next technology revolution. III-V nfet on 200 mm Si
 III-V on Si for VLSI Accelerating the next technology revolution 200 mm III-V on Si III-V nfet on 200 mm Si R. Hill, C. Park, J. Barnett, J. Huang, N. Goel, J. Oh, W.Y. Loh, J. Price, P. Kirsch, P, Majhi,
III-V on Si for VLSI Accelerating the next technology revolution 200 mm III-V on Si III-V nfet on 200 mm Si R. Hill, C. Park, J. Barnett, J. Huang, N. Goel, J. Oh, W.Y. Loh, J. Price, P. Kirsch, P, Majhi,
ECE 5745 Complex Digital ASIC Design Topic 2: CMOS Devices
 ECE 5745 Complex Digital ASIC Design Topic 2: CMOS Devices Christopher Batten School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cornell University http://www.csl.cornell.edu/courses/ece5950 Simple Transistor
ECE 5745 Complex Digital ASIC Design Topic 2: CMOS Devices Christopher Batten School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cornell University http://www.csl.cornell.edu/courses/ece5950 Simple Transistor
Integration of III-V heterostructure tunnel FETs on Si using Template Assisted Selective Epitaxy (TASE)
 Integration of III-V heterostructure tunnel FETs on Si using Template Assisted Selective Epitaxy (TASE) K. Moselund 1, D. Cutaia 1. M. Borg 1, H. Schmid 1, S. Sant 2, A. Schenk 2 and H. Riel 1 1 IBM Research
Integration of III-V heterostructure tunnel FETs on Si using Template Assisted Selective Epitaxy (TASE) K. Moselund 1, D. Cutaia 1. M. Borg 1, H. Schmid 1, S. Sant 2, A. Schenk 2 and H. Riel 1 1 IBM Research
Chapter 3 Basics Semiconductor Devices and Processing
 Chapter 3 Basics Semiconductor Devices and Processing 1 Objectives Identify at least two semiconductor materials from the periodic table of elements List n-type and p-type dopants Describe a diode and
Chapter 3 Basics Semiconductor Devices and Processing 1 Objectives Identify at least two semiconductor materials from the periodic table of elements List n-type and p-type dopants Describe a diode and
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices
 EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 11/6/2007 MOSFETs Lecture 6 BJTs- Lecture 1 Reading Assignment: Chapter 10 More Scalable Device Structures Vertical Scaling is important. For example,
EECS130 Integrated Circuit Devices Professor Ali Javey 11/6/2007 MOSFETs Lecture 6 BJTs- Lecture 1 Reading Assignment: Chapter 10 More Scalable Device Structures Vertical Scaling is important. For example,
Major Fabrication Steps in MOS Process Flow
 Major Fabrication Steps in MOS Process Flow UV light Mask oxygen Silicon dioxide photoresist exposed photoresist oxide Silicon substrate Oxidation (Field oxide) Photoresist Coating Mask-Wafer Alignment
Major Fabrication Steps in MOS Process Flow UV light Mask oxygen Silicon dioxide photoresist exposed photoresist oxide Silicon substrate Oxidation (Field oxide) Photoresist Coating Mask-Wafer Alignment
45nm Bulk CMOS Within-Die Variations. Courtesy of C. Spanos (UC Berkeley) Lecture 11. Process-induced Variability I: Random
 45nm Bulk CMOS Within-Die Variations. Courtesy of C. Spanos (UC Berkeley) Lecture 11 Process-induced Variability I: Random Random Variability Sources and Characterization Comparisons of Different MOSFET
45nm Bulk CMOS Within-Die Variations. Courtesy of C. Spanos (UC Berkeley) Lecture 11 Process-induced Variability I: Random Random Variability Sources and Characterization Comparisons of Different MOSFET
MOSFET & IC Basics - GATE Problems (Part - I)
 MOSFET & IC Basics - GATE Problems (Part - I) 1. Channel current is reduced on application of a more positive voltage to the GATE of the depletion mode n channel MOSFET. (True/False) [GATE 1994: 1 Mark]
MOSFET & IC Basics - GATE Problems (Part - I) 1. Channel current is reduced on application of a more positive voltage to the GATE of the depletion mode n channel MOSFET. (True/False) [GATE 1994: 1 Mark]
Helicon Resonator based Strong Magnetic Field Sensor
 1.48/v148-11-9- MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 11, No., 11 Helion Resonator based Strong Magneti Field Sensor. aurinavičius Department of Eletrial Engineering Vilnius Gediminas Tehnial University,
1.48/v148-11-9- MEASUREMENT SCIENCE REVIEW, Volume 11, No., 11 Helion Resonator based Strong Magneti Field Sensor. aurinavičius Department of Eletrial Engineering Vilnius Gediminas Tehnial University,
Finite-States Model Predictive Control with Increased Prediction Horizon for a 7-Level Cascade H-Bridge Multilevel STATCOM
 Proeedings of The 2th World Multi-Conferene on Systemis, Cybernetis and Informatis (WMSCI 216) Finite-States Model Preditive Control with Inreased Predition Horizon for a 7-Level Casade H-Bridge Multilevel
Proeedings of The 2th World Multi-Conferene on Systemis, Cybernetis and Informatis (WMSCI 216) Finite-States Model Preditive Control with Inreased Predition Horizon for a 7-Level Casade H-Bridge Multilevel
CA8120 Georgia Institute of Technology Office -of Contract Administration PROJECT CLOSEOUT - NOTICE. Page: 1 20-JUL :41
 CA8120 Georgia Institute of Tehnology Offie -of Contrat Administration PROJECT CLOSEOUT - OTICE Page: 1 20-JUL-1998 13:41 Closeout otie Date 20-JUL-199I Projet umber E-21-J66 Doh Id 47324 Center umber
CA8120 Georgia Institute of Tehnology Offie -of Contrat Administration PROJECT CLOSEOUT - OTICE Page: 1 20-JUL-1998 13:41 Closeout otie Date 20-JUL-199I Projet umber E-21-J66 Doh Id 47324 Center umber
Silicon-on-insulator polarization splitting and rotating device for polarization diversity circuits
 Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Ot 19, 2018 Silion-on-insulator polarization splitting and rotating devie for polarization diversity iruits Liu, Liu; Ding, Yunhong; Yvind, Kresten; Hvam, Jørn Marher Published
Downloaded from orbit.dtu.dk on: Ot 19, 2018 Silion-on-insulator polarization splitting and rotating devie for polarization diversity iruits Liu, Liu; Ding, Yunhong; Yvind, Kresten; Hvam, Jørn Marher Published
Time scale of the excitation of electrons at the breakdown of the quantum Hall effect
 Time sale of the exitation of eletrons at the breakdown of the quantum Hall effet B. E. Saǧol, 1 G. Nahtwei, 1 K. von Klitzing, 2 G. Hein, 3 and K. Eberl 2 1 Tehnishe Universität Braunshweig, Mendelssohnstrasse
Time sale of the exitation of eletrons at the breakdown of the quantum Hall effet B. E. Saǧol, 1 G. Nahtwei, 1 K. von Klitzing, 2 G. Hein, 3 and K. Eberl 2 1 Tehnishe Universität Braunshweig, Mendelssohnstrasse
Monolithically integrated InGaAs nanowires on 3D. structured silicon-on-insulator as a new platform for. full optical links
 Monolithically integrated InGaAs nanowires on 3D structured silicon-on-insulator as a new platform for full optical links Hyunseok Kim 1, Alan C. Farrell 1, Pradeep Senanayake 1, Wook-Jae Lee 1,* & Diana.
Monolithically integrated InGaAs nanowires on 3D structured silicon-on-insulator as a new platform for full optical links Hyunseok Kim 1, Alan C. Farrell 1, Pradeep Senanayake 1, Wook-Jae Lee 1,* & Diana.
Voltage Scalable Switched Capacitor DC-DC Converter for Ultra-Low-Power On-Chip Applications
 Voltage Salable Swithed Capaitor DC-DC Converter for Ultra-ow-Power On-Chip Appliations Yogesh K. amadass and Anantha P. Chandrakasan Mirosystems Tehnology aboratory Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology
Voltage Salable Swithed Capaitor DC-DC Converter for Ultra-ow-Power On-Chip Appliations Yogesh K. amadass and Anantha P. Chandrakasan Mirosystems Tehnology aboratory Massahusetts Institute of Tehnology
Performance of Random Contention PRMA: A Protocol for Fixed Wireless Access
 Int. J. Communiations, Network and System Sienes, 2011, 4, 417-423 doi:10.4236/ijns.2011.47049 Published Online July 2011 (http://www.sirp.org/journal/ijns) Performane of Random Contention PRMA: A Protool
Int. J. Communiations, Network and System Sienes, 2011, 4, 417-423 doi:10.4236/ijns.2011.47049 Published Online July 2011 (http://www.sirp.org/journal/ijns) Performane of Random Contention PRMA: A Protool
High-efficiency, high-speed VCSELs with deep oxidation layers
 Manuscript for Review High-efficiency, high-speed VCSELs with deep oxidation layers Journal: Manuscript ID: Manuscript Type: Date Submitted by the Author: Complete List of Authors: Keywords: Electronics
Manuscript for Review High-efficiency, high-speed VCSELs with deep oxidation layers Journal: Manuscript ID: Manuscript Type: Date Submitted by the Author: Complete List of Authors: Keywords: Electronics
Proton Damage in LEDs with Wavelengths Above the Silicon Wavelength Cutoff
 Proton Damage in EDs with Wavelengths Above the Silion Wavelength Cutoff Heidi N. Beker and Allan H. Johnston Jet Propulsion aboratory California Institute of Tehnology Pasadena, Califomia Abstrat Proton
Proton Damage in EDs with Wavelengths Above the Silion Wavelength Cutoff Heidi N. Beker and Allan H. Johnston Jet Propulsion aboratory California Institute of Tehnology Pasadena, Califomia Abstrat Proton
Atomic-layer deposition of ultrathin gate dielectrics and Si new functional devices
 Atomic-layer deposition of ultrathin gate dielectrics and Si new functional devices Anri Nakajima Research Center for Nanodevices and Systems, Hiroshima University 1-4-2 Kagamiyama, Higashi-Hiroshima,
Atomic-layer deposition of ultrathin gate dielectrics and Si new functional devices Anri Nakajima Research Center for Nanodevices and Systems, Hiroshima University 1-4-2 Kagamiyama, Higashi-Hiroshima,
Alternative Channel Materials for MOSFET Scaling Below 10nm
 Alternative Channel Materials for MOSFET Scaling Below 10nm Doug Barlage Electrical Requirements of Channel Mark Johnson Challenges With Material Synthesis Introduction Outline Challenges with scaling
Alternative Channel Materials for MOSFET Scaling Below 10nm Doug Barlage Electrical Requirements of Channel Mark Johnson Challenges With Material Synthesis Introduction Outline Challenges with scaling
High-Performance Si Nanowire FET with a Semi Gate-Around Structure Suitable for Integration
 High-Performance Si Nanowire FET with a Semi Gate-Around Structure Suitable for Integration Soshi Sato 1, Hideyuki Kamimura 1, Hideaki Arai 1, Kuniyuki Kakushima 2, Parhat Ahmet 1, Kenji Ohmori 3, Keisaku
High-Performance Si Nanowire FET with a Semi Gate-Around Structure Suitable for Integration Soshi Sato 1, Hideyuki Kamimura 1, Hideaki Arai 1, Kuniyuki Kakushima 2, Parhat Ahmet 1, Kenji Ohmori 3, Keisaku
Portable Marx Generator for Microplasma Applications
 J. Plasma Fusion Res. SERIES, Vol. 8 (2009) Portable Marx Generator for Miroplasma Appliations T. UENO*, T. SAKUGAWA**, M. AKIYAMA**, T. NAMIHIRA**, S. KATSUKI** and H. AKIYAMA** *Department of Eletrial
J. Plasma Fusion Res. SERIES, Vol. 8 (2009) Portable Marx Generator for Miroplasma Appliations T. UENO*, T. SAKUGAWA**, M. AKIYAMA**, T. NAMIHIRA**, S. KATSUKI** and H. AKIYAMA** *Department of Eletrial
Semiconductor Materials for Power Electronics (SEMPEL) GaN power electronics materials
 Semiconductor Materials for Power Electronics (SEMPEL) GaN power electronics materials Kjeld Pedersen Department of Physics and Nanotechnology, AAU SEMPEL Semiconductor Materials for Power Electronics
Semiconductor Materials for Power Electronics (SEMPEL) GaN power electronics materials Kjeld Pedersen Department of Physics and Nanotechnology, AAU SEMPEL Semiconductor Materials for Power Electronics
Self-Aligned-Gate GaN-HEMTs with Heavily-Doped n + -GaN Ohmic Contacts to 2DEG
 Self-Aligned-Gate GaN-HEMTs with Heavily-Doped n + -GaN Ohmic Contacts to 2DEG K. Shinohara, D. Regan, A. Corrion, D. Brown, Y. Tang, J. Wong, G. Candia, A. Schmitz, H. Fung, S. Kim, and M. Micovic HRL
Self-Aligned-Gate GaN-HEMTs with Heavily-Doped n + -GaN Ohmic Contacts to 2DEG K. Shinohara, D. Regan, A. Corrion, D. Brown, Y. Tang, J. Wong, G. Candia, A. Schmitz, H. Fung, S. Kim, and M. Micovic HRL
Parameter Optimization Of GAA Nano Wire FET Using Taguchi Method
 Parameter Optimization Of GAA Nano Wire FET Using Taguchi Method S.P. Venu Madhava Rao E.V.L.N Rangacharyulu K.Lal Kishore Professor, SNIST Professor, PSMCET Registrar, JNTUH Abstract As the process technology
Parameter Optimization Of GAA Nano Wire FET Using Taguchi Method S.P. Venu Madhava Rao E.V.L.N Rangacharyulu K.Lal Kishore Professor, SNIST Professor, PSMCET Registrar, JNTUH Abstract As the process technology
Electro-acoustic transducers with cellular polymer electrets
 Proeedings of 20 th International Congress on Aoustis, ICA 2010 23-27 August 2010, Sydney, Australia Eletro-aousti transduers with ellular polymer eletrets Yoshinobu Yasuno, Hidekazu Kodama, Munehiro Date
Proeedings of 20 th International Congress on Aoustis, ICA 2010 23-27 August 2010, Sydney, Australia Eletro-aousti transduers with ellular polymer eletrets Yoshinobu Yasuno, Hidekazu Kodama, Munehiro Date
In the system, however, after the 350 ~s risetime of the pulse to ~10 MA, either cables or cable adaptors experience failures at approximately 10C kv.
 PERFORMANCE OF THE LAGUNA PULSED POWER SYSTEM* J. H. Goforth, R. S. Caird, C. M. Fowler, A. E. Greene, H. W. Kruse, I. R. Lindemuth, H. Oona, and R. E. Reinovsky Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos,
PERFORMANCE OF THE LAGUNA PULSED POWER SYSTEM* J. H. Goforth, R. S. Caird, C. M. Fowler, A. E. Greene, H. W. Kruse, I. R. Lindemuth, H. Oona, and R. E. Reinovsky Los Alamos National Laboratory Los Alamos,
Numerical modeling of DPSK pressure signals and their transmission characteristics in mud channels
 66 Pet.Si.(9)6:66-7 DOI.7/s8-9-4-8 Numerial modeling of DPSK pressure signals and their transmission harateristis in mud hannels Shen Yue, Su Yinao, Li Gensheng 3, Li Lin and Tian Shoueng 3 College of
66 Pet.Si.(9)6:66-7 DOI.7/s8-9-4-8 Numerial modeling of DPSK pressure signals and their transmission harateristis in mud hannels Shen Yue, Su Yinao, Li Gensheng 3, Li Lin and Tian Shoueng 3 College of
Analysis of As 2 S 3 -Ti: LiNbO 3 Taper Couplers Using Supermode Theory
 Optis and Photonis Journal, 2012, 2, 344-351 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/opj.2012.24043 Published Online Deember 2012 (http://www.sirp.org/journal/opj) Analysis of As 2 S 3 -Ti: LiNbO 3 Taper Couplers Using
Optis and Photonis Journal, 2012, 2, 344-351 http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/opj.2012.24043 Published Online Deember 2012 (http://www.sirp.org/journal/opj) Analysis of As 2 S 3 -Ti: LiNbO 3 Taper Couplers Using
III-V Channel Transistors
 III-V Channel Transistors Jesús A. del Alamo Professor Microsystems Technology Laboratories MIT Acknowledgements: Students and collaborators: D. Antoniadis, J. Lin, W. Lu, A. Vardi, X. Zhao Sponsors: Applied
III-V Channel Transistors Jesús A. del Alamo Professor Microsystems Technology Laboratories MIT Acknowledgements: Students and collaborators: D. Antoniadis, J. Lin, W. Lu, A. Vardi, X. Zhao Sponsors: Applied
FOUNDRY SERVICE. SEI's FEATURE. Wireless Devices FOUNDRY SERVICE. SRD-800DD, SRD-500DD D-FET Process Lg=0.8, 0.5µm. Ion Implanted MESFETs SRD-301ED
 FOUNDRY SERVICE 01.04. Foundry services have been one of the core businesses at SEI, providing sophisticated GaAs IC technology for all customers. SEI offers very flexible service to support the customers
FOUNDRY SERVICE 01.04. Foundry services have been one of the core businesses at SEI, providing sophisticated GaAs IC technology for all customers. SEI offers very flexible service to support the customers
ACTIVE VIBRATION CONTROL OF AN INTERMEDIATE MASS: VIBRATION ISOLATION IN SHIPS
 ACTIVE VIBRATION CONTROL OF AN INTERMEDIATE MASS: VIBRATION ISOLATION IN SHIPS Xun Li, Ben S. Cazzolato and Colin H. Hansen Shool of Mehanial Engineering, University of Adelaide Adelaide SA 5005, Australia.
ACTIVE VIBRATION CONTROL OF AN INTERMEDIATE MASS: VIBRATION ISOLATION IN SHIPS Xun Li, Ben S. Cazzolato and Colin H. Hansen Shool of Mehanial Engineering, University of Adelaide Adelaide SA 5005, Australia.
NATIONAL RADIO ASTRONOMY OBSERVATORY
 NATIONAL RADIO ASTRONOMY OBSERVATORY CHARLOTTESVILLE VIRGINIA ELECTRONICS DIVISION INTERNAL REPORT No 186 A PROGRESS REPORT ON JOSEPHSON JUNCTION MIXERS FOR MILLIMETER WAVE RADIO ASTRONOMY D R DECKER FEBRUARY
NATIONAL RADIO ASTRONOMY OBSERVATORY CHARLOTTESVILLE VIRGINIA ELECTRONICS DIVISION INTERNAL REPORT No 186 A PROGRESS REPORT ON JOSEPHSON JUNCTION MIXERS FOR MILLIMETER WAVE RADIO ASTRONOMY D R DECKER FEBRUARY
Chapter 1. Introduction
 Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Introduction of Device Technology Digital wireless communication system has become more and more popular in recent years due to its capability for both voice and data communication.
Chapter 1 Introduction 1.1 Introduction of Device Technology Digital wireless communication system has become more and more popular in recent years due to its capability for both voice and data communication.
Wu Lu Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering and Microelectronics Laboratory, University of Illinois, Urbana, Illinois 61801
 Comparative study of self-aligned and nonself-aligned SiGe p-metal oxide semiconductor modulation-doped field effect transistors with nanometer gate lengths Wu Lu Department of Electrical and Computer
Comparative study of self-aligned and nonself-aligned SiGe p-metal oxide semiconductor modulation-doped field effect transistors with nanometer gate lengths Wu Lu Department of Electrical and Computer
Single suspended InGaAs nanowire MOSFETs
 Single suspended InGaAs nanowire MOSFETs Zota, Cezar B.; Wernersson, Lars-Erik; Lind, Erik Published in: Technical Digest - International Electron Devices Meeting, IEDM DOI:.9/IEDM.5.7988 Published: 6--6
Single suspended InGaAs nanowire MOSFETs Zota, Cezar B.; Wernersson, Lars-Erik; Lind, Erik Published in: Technical Digest - International Electron Devices Meeting, IEDM DOI:.9/IEDM.5.7988 Published: 6--6
Effect of orientation and size of silicon single crystal to Electro-Ultrasonic Spectroscopy
 Effet of orientation and size of silion single rystal to Eletro-Ultrasoni Spetrosopy Mingu KANG 1, Byeong-Eog JUN 1, Young H. KIM 1 1 Korea Siene Aademy of KAIST, Korea Phone: +8 51 606 19, Fax: +8 51
Effet of orientation and size of silion single rystal to Eletro-Ultrasoni Spetrosopy Mingu KANG 1, Byeong-Eog JUN 1, Young H. KIM 1 1 Korea Siene Aademy of KAIST, Korea Phone: +8 51 606 19, Fax: +8 51
Characterization of the dielectric properties of various fiberglass/epoxy composite layups
 Charaterization of the dieletri properties of various fiberglass/epoxy omposite layups Marotte, Laurissa (University of Kansas); Arnold, Emily Center for Remote Sensing of Ie Sheets, University of Kansas
Charaterization of the dieletri properties of various fiberglass/epoxy omposite layups Marotte, Laurissa (University of Kansas); Arnold, Emily Center for Remote Sensing of Ie Sheets, University of Kansas
1020 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTRON DEVICES, VOL. 63, NO. 3, MARCH 2016
 1020 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTRON DEVICES, VOL. 63, NO. 3, MARCH 2016 InGaAs Quantum-Well MOSFET Arrays for Nanometer-Scale Ohmic Contact Characterization J. Lin, Student Member, IEEE, D. A. Antoniadis,
1020 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON ELECTRON DEVICES, VOL. 63, NO. 3, MARCH 2016 InGaAs Quantum-Well MOSFET Arrays for Nanometer-Scale Ohmic Contact Characterization J. Lin, Student Member, IEEE, D. A. Antoniadis,
Acoustic Transmissions for Wireless Communications and Power Supply in Biomedical Devices
 roeedings of th International ongress on Aoustis, IA 1 3-7 August 1, Sydney, Australia Aousti Transmissions for Wireless ommuniations and ower Supply in Biomedial Devies Graham Wild and Steven Hinkley
roeedings of th International ongress on Aoustis, IA 1 3-7 August 1, Sydney, Australia Aousti Transmissions for Wireless ommuniations and ower Supply in Biomedial Devies Graham Wild and Steven Hinkley
value of W max for the device. The at band voltage is -0.9 V. Problem 5: An Al-gate n-channel MOS capacitor has a doping of N a = cm ;3. The oxi
 Prof. Jasprit Singh Fall 2001 EECS 320 Homework 10 This homework is due on December 6 Problem 1: An n-type In 0:53 Ga 0:47 As epitaxial layer doped at 10 16 cm ;3 is to be used as a channel in a FET. A
Prof. Jasprit Singh Fall 2001 EECS 320 Homework 10 This homework is due on December 6 Problem 1: An n-type In 0:53 Ga 0:47 As epitaxial layer doped at 10 16 cm ;3 is to be used as a channel in a FET. A
A Study on The Performance of Multiple-beam Antenna Satellite Receiving System Dezhi Li, Bo Zeng, Qun Wu*
 16 nd International Conferene on Mehanial, Eletroni and Information Tehnology Engineering (ICMITE 16) ISBN: 978-1-6595-34-3 A Study on The Performane of Multiple-beam Antenna Satellite Reeiving System
16 nd International Conferene on Mehanial, Eletroni and Information Tehnology Engineering (ICMITE 16) ISBN: 978-1-6595-34-3 A Study on The Performane of Multiple-beam Antenna Satellite Reeiving System
This Week s Subject. DRAM & Flexible RRAM. p-channel MOSFET (PMOS) CMOS: Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor
 DRAM & Flexible RRAM This Week s Subject p-channel MOSFET (PMOS) CMOS: Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor CMOS Logic Inverter NAND gate NOR gate CMOS Integration & Layout GaAs MESFET (JFET) 1 Flexible
DRAM & Flexible RRAM This Week s Subject p-channel MOSFET (PMOS) CMOS: Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor CMOS Logic Inverter NAND gate NOR gate CMOS Integration & Layout GaAs MESFET (JFET) 1 Flexible
Newer process technology (since 1999) includes :
 Newer process technology (since 1999) includes : copper metalization hi-k dielectrics for gate insulators si on insulator strained silicon lo-k dielectrics for interconnects Immersion lithography for masks
Newer process technology (since 1999) includes : copper metalization hi-k dielectrics for gate insulators si on insulator strained silicon lo-k dielectrics for interconnects Immersion lithography for masks
Design cycle for MEMS
 Design cycle for MEMS Design cycle for ICs IC Process Selection nmos CMOS BiCMOS ECL for logic for I/O and driver circuit for critical high speed parts of the system The Real Estate of a Wafer MOS Transistor
Design cycle for MEMS Design cycle for ICs IC Process Selection nmos CMOS BiCMOS ECL for logic for I/O and driver circuit for critical high speed parts of the system The Real Estate of a Wafer MOS Transistor
FABRICATION OF CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. Dr. Mohammed M. Farag
 FABRICATION OF CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Dr. Mohammed M. Farag Outline Overview of CMOS Fabrication Processes The CMOS Fabrication Process Flow Design Rules Reference: Uyemura, John P. "Introduction to
FABRICATION OF CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Dr. Mohammed M. Farag Outline Overview of CMOS Fabrication Processes The CMOS Fabrication Process Flow Design Rules Reference: Uyemura, John P. "Introduction to
State-of-the-art device fabrication techniques
 State-of-the-art device fabrication techniques! Standard Photo-lithography and e-beam lithography! Advanced lithography techniques used in semiconductor industry Deposition: Thermal evaporation, e-gun
State-of-the-art device fabrication techniques! Standard Photo-lithography and e-beam lithography! Advanced lithography techniques used in semiconductor industry Deposition: Thermal evaporation, e-gun
High Power Performance InP/InGaAs Single HBTs
 High Power Performance InP/InGaAs Single HBTs D Sawdai, K Hong, A Samelis, and D Pavlidis Solid-State Electronics Laboratory, Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, The University of
High Power Performance InP/InGaAs Single HBTs D Sawdai, K Hong, A Samelis, and D Pavlidis Solid-State Electronics Laboratory, Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, The University of
Multilevel Modular Converter for VSC-HVDC Transmission Applications: Control and Operational Aspects
 6th ATIOAL POWER SYSTEMS OFEREE, 5th-7th DEEMBER, 2 45 Multilevel Modular onverter for VS-HVD Transmission Appliations: ontrol and Operational Aspets dana. Gnanarathna, Aniruddha M. Gole Dept. of Eletrial
6th ATIOAL POWER SYSTEMS OFEREE, 5th-7th DEEMBER, 2 45 Multilevel Modular onverter for VS-HVD Transmission Appliations: ontrol and Operational Aspets dana. Gnanarathna, Aniruddha M. Gole Dept. of Eletrial
Indium Phosphide and Related Materials Selectively implanted subcollector DHBTs
 Indium Phosphide and Related Materials - 2006 Selectively implanted subcollector DHBTs Navin Parthasarathy, Z. Griffith, C. Kadow, U. Singisetti, and M.J.W. Rodwell Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
Indium Phosphide and Related Materials - 2006 Selectively implanted subcollector DHBTs Navin Parthasarathy, Z. Griffith, C. Kadow, U. Singisetti, and M.J.W. Rodwell Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering,
Research Title: High dielectrics on InGaAs and GaN Growth, interfacial structural studies, and surface Fermi level unpinning Date: April 18, 2011
 Final Report for FA2386-10-1-4058 AOARD Grant 104058 Research Title: High dielectrics on InGaAs and GaN - Growth, interfacial structural studies, and surface Fermi level unpinning Date: April 18, 2011
Final Report for FA2386-10-1-4058 AOARD Grant 104058 Research Title: High dielectrics on InGaAs and GaN - Growth, interfacial structural studies, and surface Fermi level unpinning Date: April 18, 2011
