TLC3704, TLC3704Q QUAD MICROPOWER LinCMOS VOLTAGE COMPARATORS
|
|
|
- Lucas Carr
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
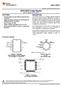
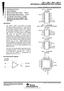
1 Push-Pull CMOS Output Drives Capacitive Loads Without Pullup Resistor, I O = ± 8 ma Very Low Power µw Typ at V Fast Response Time...t PLH = 2.7 µs Typ With -mv Overdrive Single Supply Operation...3 V to 16 V TLC3704M...4 V to 16 V On-Chip ESD Protection D, J, OR N PACKAGE (TOP VIEW) 1OUT 2OUT V DD 2IN 2IN 1IN 1IN OUT 4OUT GND 4IN 4IN 3IN 3IN description The TLC3704 consists of four independent micropower voltage comparators designed to operate from a single supply and be compatible with modern HCMOS logic systems. They are functionally similar to the LM339 but use 1/20th the power for similar response times. The push-pull CMOS output stage drives capacitive loads directly without a power-consuming pullup resistor to achieve the stated response time. Eliminating the pullup resistor not only reduces power dissipation, but also saves board space and component cost. The output stage is also fully compatible with TTL requirements. Texas Instruments LinCMOS process offers superior analog performance to standard CMOS processes. Along with the standard CMOS advantages of low power without sacrificing speed, high input impedance, and low bias currents, the LinCMOS process offers extremely stable input offset voltages with large differential input voltages. This characteristic makes it possible to build reliable CMOS comparators. The TLC3704C is characterized for operation over the commercial temperature range of 0 C to 70 C. The TLC3704I is characterized for operation over the extended industrial temperature range of 40 C to 8 C. The TLC3704M is characterized for operation over the full military temperature range of C to 12 C. The TLC3704Q is characterized for operation from 40 C to 12 C. 1OUT 2OUT V DD 2IN 2IN 1IN 1IN V DD NC 2IN NC 2IN FK PACKAGE (TOP VIEW) 2OUT 1OUT NC 3OUT 4OUT IN 1IN NC 3IN 3IN NC No internal connection symbol (each comparator) IN IN PW PACKAGE (TOP VIEW) GND NC 4IN NC 4IN OUT 3OUT 4OUT GND 4IN 4IN 3IN 3IN
2 TA VIOmax at 2 C SMALL OUTLINE (D) AVAILABLE OPTIONS CERAMIC (FK) PACKAGE CERAMIC DIP (J) PLASTIC DIP (N) TSSOP (PW) 0 C to 70 C mv TLC3704CD TLC3704CN TLC3704CPW 40 C to 8 C mv TLC3704ID TLC3704IN TLC3704IPW C to 12 C mv TLC3704MFK TLC3704MJ 40 C to 12 C mv TLC3704QJ The D and PW packages are available taped and reeled. Add R suffix to the device type (e.g., TLC3704CDR). functional block diagram (each comparator) VDD IN IN Differential Input Circuits OUT absolute maximum ratings over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted) Supply voltage range, V DD (see Note 1) V to 18 V Differential input voltage, V ID (see Note 2) ± 18 V Input voltage range, V I to V DD Output voltage range, V O to V DD Input current, I I ± ma Output current, I O (each output) ± 20 ma Total supply current into V DD ma Total current out of GND ma Continuous total power dissipation See Dissipation Rating Table Operating free-air temperature range, T A : TLC3704C to 70 C TLC3704I C to 8 C TLC3704M C to 12 C TLC3704Q C to 12 C Storage temperature range C to 10 C Case temperature for 60 seconds: FK package C Lead temperature 1,6 mm (1/16 inch) from case for 10 seconds: D or N package C Lead temperature 1,6 mm (1/16 inch) from case for 60 seconds: J package C Stresses beyond those listed under absolute maximum ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under recommended operating conditions is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. NOTES: 1. All voltage values, except differential voltages, are with respect to network ground. 2. Differential voltages are at IN with respect to IN. GND 2
3 DISSIPATION RATING TABLE PACKAGE TA 2 C POWER RATING DERATING FACTOR ABOVE TA = 2 C TA = 70 C POWER RATING TA = 8 C POWER RATING TA = 12 C POWER RATING D FK J N PW 90 mw 137 mw 137 mw 110 mw 67 mw 7.6 mw/ C 11.0 mw/ C 11.0 mw/ C 9.2 mw/ C.4 mw/ C 608 mw 880 mw 880 mw 736 mw 432 mw 494 mw 71 mw 71 mw 98 mw 31 mw N/A 27 mw 27 mw N/A N/A recommended operating conditions TLC3704C MIN NOM MAX UNIT Supply voltage, VDD 3 16 V Common-mode input voltage, VIC 0.2 VDD 1. V High-level output current, IOH 20 ma Low-level output current, IOL 20 ma Operating free-air temperature, TA 0 70 C electrical characteristics at specified operating free-air temperature, V DD = V (unless otherwise noted) VIO PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS TA Input offset voltage IIO Input offset current VIC = 2. V IIB Input bias current VIC = 2. V VICR Common-mode mode input voltage range TLC3704C MIN TYP MAX VDD = V to 10 V, 2 C 1.2 VIC = VICRmin, See Note 3 0 C to 70 C 6. UNIT mv 2 C 1 pa 70 C 0.3 na 2 C pa 70 C 0.6 na 2 C 0 C to 70 C 0 to VDD 1 0 to VDD 1. 2 C 84 CMRR Common-mode rejection ratio VIC = VICRmin 70 C 84 db 0 C 84 2 C 8 ksvr Supply-voltage rejection ratio VDD = V to 10 V 70 C 8 db VOH High-level output voltage VID =1V V, IOH = 4mA VOL Low-level output voltage VID = 1V, IOH =4mA IDD Supply current (all four comparators) Outputs low, No load 0 C 8 2 C C C C 37 2 C C to 70 C 100 All characteristics are measured with zero common-mode voltage unless otherwise noted. NOTE 3: The offset voltage limits given are the maximum values required to drive the output up to 4. V or down to 0.3 V. V V mv µa 3
4 recommended operating conditions TLC3704I MIN NOM MAX UNIT Supply voltage, VDD 3 16 V Common-mode input voltage, VIC 0.2 VDD 1. V High-level output current, IOH 20 ma Low-level output current, IOL 20 ma Operating free-air temperature, TA 40 8 C electrical characteristics at specified operating free-air temperature, V DD = V, V IC = 0 (unless otherwise noted) VIO PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS TA Input offset voltage IIO Input offset current VIC = 2. V IIB Input bias current VIC = 2. V VICR Common-mode mode input voltage range TLC3704I MIN TYP MAX VDD = V to 10 V, 2 C 1.2 VIC = VICRmin, See Note 3 40 C to 8 C 7 UNIT mv 2 C 1 pa 8 C 1 na 2 C pa 8 C 2 na 2 C 40 C to 8 C 0 to VDD 1 0 to VDD 1. 2 C 84 CMRR Common-mode rejection ratio VIC = VICRmin 8 C 84 db 40 C 83 2 C 8 ksvr Supply-voltage rejection ratio VDD = V to 10 V 8 C 8 db VOH High-level output voltage VID =1V V, IOH = 4mA VOL Low-level output voltage VID = 1V, IOH =4mA IDD Supply current (all four comparators) Outputs low, No load 40 C 83 2 C C C C C C to 8 C 12 NOTE 3: The offset voltage limits given are the maximum values required to drive the output up to 4. V or down to 0.3 V. V V mv µa 4
5 recommended operating conditions TLC3704M UNIT MIN NOM MAX Supply voltage, VDD 4 16 V Common-mode input voltage, VIC 0 VDD 1. V High-level output current, IOH 20 ma Low-level output current, IOL 20 ma Operating free-air temperature, TA 12 C electrical characteristics at specified operating free-air temperature, V DD = V, V IC = 0 (unless otherwise noted) VIO PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS TA Input offset voltage IIO Input offset current VIC = 2. V IIB Input bias current VIC = 2. V VICR Common-mode mode input voltage range TLC3704M MIN TYP MAX VDD = V to 10 V, 2 C 1.2 VIC = VICRmin, See Note 3 C to 12 C 10 UNIT mv 2 C 1 pa 12 C 1 na 2 C pa 12 C 30 na 2 C C to 12 C 0 to VDD 1 0 to VDD 1. 2 C 84 CMRR Common-mode rejection ratio VIC = VICRmin 12 C 83 db C 82 2 C 8 ksvr Supply-voltage rejection ratio VDD = V to 10 V 12 C 8 db VOH High-level output voltage VID =1V V, IOH = 4mA VOL Low-level output voltage VID = 1V, IOH =4mA IDD Supply current (all four comparators) Outputs low, No load C 82 2 C C C C 00 2 C 3 80 C to 12 C 17 NOTE 3: The offset voltage limits given are the maximum values required to drive the output up to 4. V or down to 0.3 V. V V mv µa
6 recommended operating conditions TLC3704Q MIN NOM MAX UNIT Supply voltage, VDD 3 16 V Common-mode input voltage, VIC 0.2 VDD 1. V High-level output current, IOH 20 ma Low-level output current, IOL 20 ma Operating free-air temperature, TA C electrical characteristics at specified operating free-air temperature, V DD = V, V IC = 0 (unless otherwise noted) VIO PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS TA Input offset voltage IIO Input offset current VIC = 2. V IIB Input bias current VIC = 2. V VICR TLC3704Q MIN TYP MAX VDD = V to 10 V, 2 C 1.2 VIC = VICRmin, See Note 3 40 C to 12 C 7 UNIT mv 2 C 1 pa 12 C 1 na 2 C pa 12 C 30 na Common-mode input voltage 2 C 0 to VDD 1 range 40 C to 12 C 0 to VDD 1. 2 C 84 CMRR Common-mode rejection ratio VIC = VICRmin 12 C 83 db 40 C 83 2 C 8 ksvr Supply-voltage rejection ratio VDD = V to 10 V 12 C 8 db VOH High-level output voltage VID =1V V, IOH = 4mA VOL Low-level output voltage VID = 1V, IOH =4mA IDD Supply current (all four comparators) Outputs low, No load 40 C 83 2 C C C C 00 2 C C to 12 C 17 NOTE 3: The offset voltage limits given are the maximum values required to drive the output up to 4. V or down to 0.3 V. V V mv µa 6
7 switching characteristics, V DD = V, T A = 2 C PARAMETER f = 10 khz, tplh Propagation delay time, low-to-high-level level output CL =0pF f = 10 khz, tphl Propagation delay time, high-to-low-level level output CL =0pF tf tr Fall time Rise time TEST CONDITIONS TLC3704C, TLC3704I TLC3704M, TLC3704Q MIN TYP MAX Overdrive = 2 mv 4. Overdrive = mv 2.7 Overdrive = 10 mv 1.9 Overdrive = 20 mv 1.4 Overdrive = 40 mv 1.1 VI = 1.4-V step at IN 1.1 Overdrive = 2 mv 4 Overdrive = mv 2.3 Overdrive = 10 mv 1. Overdrive = 20 mv 0.9 Overdrive = 40 mv 0.6 VI = 1.4-V step at IN 0.1 f = 10 khz, CL = 0 pf f = 10 khz, CL = 0 pf Simultaneous switching of inputs causes degradation in output response. UNIT µs µs Overdrive = 0 mv 0 ns Overdrive = 0 mv 12 ns 7
8 LinCMOS process PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION The LinCMOS process is a linear polysilicon-gate CMOS process. Primarily designed for single-supply applications, LinCMOS products facilitate the design of a wide range of high-performance analog functions from operational amplifiers to complex mixed-mode converters. This short guide is intended to answer the most frequently asked questions related to the quality and reliability of LinCMOS products. Direct further questions to the nearest TI field sales office. electrostatic discharge CMOS circuits are prone to gate oxide breakdown when exposed to high voltages even if the exposure is only for very short periods of time. Electrostatic discharge (ESD) is one of the most common causes of damage to CMOS devices. It can occur when a device is handled without proper consideration for environmental electrostatic charges, e.g., during board assembly. If a circuit in which one amplifier from a dual op amp is being used and the unused pins are left open, high voltages tends to develop. If there is no provision for ESD protection, these voltages may eventually punch through the gate oxide and cause the device to fail. To prevent voltage buildup, each pin is protected by internal circuitry. Standard ESD-protection circuits safely shunt the ESD current by providing a mechanism whereby one or more transistors break down at voltages higher than the normal operating voltages but lower than the breakdown voltage of the input gate. This type of protection scheme is limited by leakage currents which flow through the shunting transistors during normal operation after an ESD voltage has occurred. Although these currents are small, on the order of tens of nanoamps, CMOS amplifiers are often specified to draw input currents as low as tens of picoamps. To overcome this limitation, TI design engineers developed the patented ESD-protection circuit shown in Figure 1. This circuit can withstand several successive 2-kV ESD pulses, while reducing or eliminating leakage currents that may be drawn through the input pins. A more detailed discussion of the operation of the TI ESD-protection circuit is presented on the next page. All input and output pins on LinCMOS and Advanced LinCMOS products have associated ESD-protection circuitry that undergoes qualification testing to withstand 2000 V discharged from a 100-pF capacitor through a 100-Ω resistor (human body model) and 200 V from a 100-pF capacitor with no current-limiting resistor (charged device model). These tests simulate both operator and machine handling of devices during normal test and assembly operations. Input R1 VDD To Protected Circuit Q1 Q2 R2 D1 D2 D3 GND Figure 1. LinCMOS ESD-Protection Schematic 8
9 input protection circuit operation PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION Texas Instruments patented protection circuitry allows for both positive- and negative-going ESD transients. These transients are characterized by extremely fast rise times and usually low energies, and can occur both when the device has all pins open and when it is installed in a circuit. positive ESD transients Initial positive charged energy is shunted through Q1 to V SS. Q1 turns on when the voltage at the input rises above the voltage on the V DD pin by a value equal to the V BE of Q1. The base current increases through R2 with input current as Q1 saturates. The base current through R2 forces the voltage at the drain and gate of Q2 to exceed its threshold level (V T 22 to 26 V) and turn Q2 on. The shunted input current through Q1 to V SS is now shunted through the n-channel enhancement-type MOSFET Q2 to V SS. If the voltage on the input pin continues to rise, the breakdown voltage of the zener diode D3 is exceeded, and all remaining energy is dissipated in R1 and D3. The breakdown voltage of D3 is designed to be 24 to 27 V, which is well below the gateoxide voltage of the circuit to be protected. negative ESD transients The negative charged ESD transients are shunted directly through D1. Additional energy is dissipated in R1 and D2 as D2 becomes forward biased. The voltage seen by the protected circuit is 0.3 V to 1 V (the forward voltage of D1 and D2). circuit-design considerations LinCMOS products are being used in actual circuit environments that have input voltages that exceed the recommended common-mode input voltage range and activate the input protection circuit. Even under normal operation, these conditions occur during circuit power up or power down, and in many cases, when the device is being used for a signal conditioning function. The input voltages can exceed V ICR and not damage the device only if the inputs are current limited. The recommended current limit shown on most product data sheets is ± ma. Figures 2 and 3 show typical characteristics for input voltage versus input current. Normal operation and correct output state can be expected even when the input voltage exceeds the positive supply voltage. Again, the input current should be externally limited even though internal positive current limiting is achieved in the input protection circuit by the action of Q1. When Q1 is on, it saturates and limits the current to approximately -ma collector current by design. When saturated, Q1 base current increases with input current. This base current is forced into the V DD pin and into the device I DD or the V DD supply through R2 producing the current limiting effects shown in Figure 2. This internal limiting lasts only as long as the input voltage is below the V T of Q2. When the input voltage exceeds the negative supply voltage, normal operation is affected and output voltage states may not be correct. Also, the isolation between channels of multiple devices (duals and quads) can be severely affected. External current limiting must be used since this current is directly shunted by D1 and D2 and no internal limiting is achieved. If normal output voltage states are required, an external input voltage clamp is required (see Figure 4). 9
10 circuit-design considerations (continued) PRINCIPLES OF OPERATION INPUT CURRENT INPUT VOLTAGE INPUT CURRENT INPUT VOLTAGE 8 7 TA = 2 C 10 9 TA = 2 C Input Current ma II Input Current ma II VDD VDD 4 VDD 8 VDD 12 VI Input Voltage V Figure 2 VDD 0 VDD 0.3 VDD 0. VDD 0.7 VDD 0.9 VI Input Voltage V Figure 3 VI RI See Note A Vref 1/2 TLC3704 Positive Voltage Input Current Limit : R I V I V DD 0.3 V ma Negative Voltage Input Current Limit : R I V I V DD ( 0.3 V) ma NOTE A: If the correct input state is required when the negative input exceeds GND, a Schottky clamp is required. Figure 4. Typical Input Current-Limiting Configuration for a LinCMOS Comparator 10
11 PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION The TLC3704 contains a digital output stage which, if held in the linear region of the transfer curve, can cause damage to the device. Conventional operational amplifier/comparator testing incorporates the use of a servo loop which is designed to force the device output to a level within this linear region. Since the servo-loop method of testing cannot be used, we offer the following alternatives for measuring parameters such as input offset voltage, common-mode rejection, etc. To verify that the input offset voltage falls within the limits specified, the limit value is applied to the input as shown in Figure (a). With the noninverting input positive with respect to the inverting input, the output should be high. With the input polarity reversed, the output should be low. A similar test can be made to verify the input offset voltage at the common-mode extremes. The supply voltages can be slewed as shown in Figure (b) for the V ICR test, rather than changing the input voltages, to provide greater accuracy. V 1 V Applied VIO Limit VO Applied VIO Limit VO 4 V (a) VIO WITH VIC = 0 V (b) VIO WITH VIC = 4 V Figure. Method for Verifying That Input Offset Voltage Is Within Specified Limits A close approximation of the input offset voltage can be obtained by using a binary search method to vary the differential input voltage while monitoring the output state. When the applied input voltage differential is equal, but opposite in polarity, to the input offset voltage, the output changes states. Figure 6 illustrates a practical circuit for direct dc measurement of input offset voltage that does not bias the comparator in the linear region. The circuit consists of a switching mode servo loop in which IC1a generates a triangular waveform of approximately 20-mV amplitude. IC1b acts as a buffer, with C2 and R4 removing any residual d.c. offset. The signal is then applied to the inverting input of the comparator under test, while the noninverting input is driven by the output of the integrator formed by IC1c through the voltage divider formed by R8 and R9. The loop reaches a stable operating point when the output of the comparator under test has a duty cycle of exactly 0%, which can only occur when the incoming triangle wave is sliced symmetrically or when the voltage at the noninverting input exactly equals the input offset voltage. Voltage divider R8 and R9 provides an increase in the input offset voltage by a factor of 100 to make measurement easier. The values of R, R7, R8, and R9 can significantly influence the accuracy of the reading; therefore, it is suggested that their tolerance level be one percent or lower. Measuring the extremely low values of input current requires isolation from all other sources of leakage current and compensation for the leakage of the test socket and board. With a good picoammeter, the socket and board leakage can be measured with no device in the socket. Subsequently, this open socket leakage value can be subtracted from the measurement obtained with a device in the socket to obtain the actual input current of the device. 11
12 PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION IC1a 1/4 TLC274CN VDD R 1.8 kω 1% C µf Buffer R1 240 kω C2 1 µf R4 47 kω DUT R6 1 MΩ R7 1.8 kω 1% IC1c 1/4 TLC274CN Integrator VIO (X100) C1 0.1 µf IC1b 1/4 TLC274CN Triangle Generator R9 100 Ω 1% R8 10 kω 1% C4 0.1 µf R3 100 Ω R2 10 kω Figure 6. Circuit for Input Offset Voltage Measurement Response time is defined as the interval between the application of an input step function and the instant when the output reaches 0% of its maximum value. Response time for the low-to-high-level output is measured from the leading edge of the input pulse, while response time for the high-to-low-level output is measured from the trailing edge of the input pulse. Response time measurement at low input signal levels can be greatly affected by the input offset voltage. The offset voltage should be balanced by the adjustment at the inverting input as shown in Figure 7, so that the circuit is just at the transition point. A low signal, for example 10-mV or -mv overdrive, causes the output to change state. 12
13 PARAMETER MEASUREMENT INFORMATION VDD Pulse Generator 1 µf 1 V 10 Ω 10-Turn Potentiometer 1 V 0 Ω 1 kω 0.1 µf DUT CL (see Note A) TEST CIRCUIT Overdrive Overdrive Input 100 mv Input 100 mv Low-to-High Level Output 0% 90% High-to-Low Level Output 90% 0% 10% 10% tr tf tplh tphl NOTE A: CL includes probe and jig capacitance. VOLTAGE WAVEFORMS Figure 7. Response, Rise, and Fall Times Circuit and Voltage Waveforms 13
14 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS Table of Graphs FIGURE VIO Input offset voltage Distribution 8 IIB Input bias current Free-air temperature 9 CMRR Common-mode rejection ratio Free-air temperature 10 ksvr Supply-voltage rejection ratio Free-air temperature 11 VOH High-level output current Free-air temperature 12 High-level output current 13 VOL Low-level output voltage Low-level output current 14 Free-air temperature 1 tt Output transition time Load capacitance 16 Supply current response to an output voltage transition 17 Low-to-high-level output response for various input overdrives 18 High-to-low-level output response for various input overdrives 19 tplh Low-to-high-level output response time Supply voltage 20 tphl High-to-low-level output response time Supply voltage 21 Frequency 22 IDD Supply current Supply voltage 23 Free-air temperature 24 Number of Units DISTRIBUTION OF INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE VDD = V VIC = 2. V TA = 2 C 698 Units Tested From 4 Wafer Lots É É ÉÇÇ ÉÇÇ ÉÇÇ ÉÇÇ ÇÇÉ ÇÇ ÇÇÉ ÇÇ ÇÇÇ ÉÉÇÇÉ ÇÇÇ ÉÉÇÇÉ ÇÉÉ ÇÉÉÇ ÉÉÇÇÉ ÇÉÉÇ VIO Input Offset Voltage mv Figure 8 Input Bias Current na IB I INPUT BIAS CURRENT FREE-AIR TEMPERATURE VDD = V VIC = 2. V TA Free-Air Temperature C Figure 9 Data at high and low temperatures are applicable only within the rated operating free-air temperature ranges of the various devices. 14
15 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS COMMON-MODE REJECTION RATIO FREE-AIR TEMPERATURE SUPPLY VOLTAGE REJECTION RATIO FREE-AIR TEMPERATURE CMRR Common-Mode Rejection Ratio db VDD = V ksvr Supply Voltage Rejection Ratio db VDD = V to 10 V TA Free-Air Temperature C Figure TA Free-Air Temperature C Figure 11 HIGH-LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE FREE-AIR TEMPERATURE HIGH-LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE HIGH-LEVEL OUTPUT CURRENT V OH High-Level Outout Voltage V VDD = V IOH = 4 ma High-Input Level Output Voltage V V OH VDD TA = 2 C 3 V VDD = 16 V 10 V 4 V V TA Free-Air Temperature C Figure IOH High-Level Output Current ma Figure 13 Data at high and low temperatures are applicable only within the rated operating free-air temperature ranges of the various devices. 1
16 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS LOW-LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE LOW-LEVEL OUTPUT CURRENT LOW-LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE FREE-AIR TEMPERATURE VOL Low-Level Output Voltage V TA = 2 C 3 V 4 V 10 V V VDD = 16 V V OL Low-Level Output Voltage mv VDD = V IOL = 4 ma IOL Low-Level Output Current ma Figure TA Free-Air Temperature C Figure 1 tt Transition Time ns VDD = V TA = 2 C OUTPUT TRANSITION TIME LOAD CAPACITANCE Rise Time Fall Time I DD Supply Current ma Output Voltage V SUPPLY CURRENT RESPONSE TO AN OUTPUT VOLTAGE TRANSITION VDD = V CL = 0 pf f = 10 khz CL Load Capacitance pf Figure 16 t Time Figure 17 Data at high and low temperatures are applicable only within the rated operating free-air temperature ranges of the various devices. 16
17 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS LOW-TO-HIGH-LEVEL OUTPUT RESPONSE FOR VARIOUS INPUT OVERDRIVES HIGH-TO-LOW-LEVEL OUTPUT RESPONSE FOR VARIOUS INPUT OVERDRIVES V O Output Voltage V 0 40 mv 20 mv 10 mv mv 2 mv VO Output Voltage V 0 40 mv 20 mv 10 mv mv 2 mv Differential Input Voltage mv VDD = V TA = 2 C CL = 0 pf Differential Input Voltage mv VDD = V TA = 2 C CL = 0 pf tplh Low-to-High-Level Output Response Time µs tphl High-to-Low-Level Output Response Time µs Figure 18 Figure 19 LOW-TO-HIGH-LEVEL OUTPUT RESPONSE TIME SUPPLY VOLTAGE HIGH-TO-LOW-LEVEL OUTPUT RESPONSE TIME SUPPLY VOLTAGE 6 CL = 0 pf TA = 2 C Overdrive = 2 mv 6 CL = 0 pf TA = 2 C t PLH Low-to-High-Level Output Response µs mv mv 10 mv 40 mv t PHL High-to-Low-Level Output Response µs mv 10 mv 20 mv 40 mv Overdrive = 2 mv VDD Supply Voltage V Figure 20 VDD Supply Voltage V Figure 21 17
18 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS AVERAGE SUPPLY CURRENT (PER COMPARATOR) FREQUENCY SUPPLY CURRENT SUPPLY VOLTAGE V DD Average Supply Current µ A TA = 2 C CL = 0 pf VDD = 16 V 4 V 10 V V 3 V V DD Supply Current µ A Outputs Low No Loads TA = 40 C TA = C TA = 8 C TA = 2 C TA = 12 C f Frequency khz VDD Supply Voltage V Figure 22 Figure 23 SUPPLY CURRENT FREE-AIR TEMPERATURE IDD Supply Current µa VDD = V No Load Outputs Low Outputs High TA Free-Air Temperature C Figure 24 Data at high and low temperatures are applicable only within the rated operating free-air temperature ranges of the various devices. 18
19 APPLICATION INFORMATION The inputs should always remain within the supply rails in order to avoid forward biasing the diodes in the electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection structure. If either input exceeds this range, the device is not damaged as long as the input is limited to less than ma. To maintain the expected output state, the inputs must remain within the common-mode range. For example, at 2 C with V DD = V, both inputs must remain between 0.2 V and 4 V to ensure proper device operation. To ensure reliable operation, the supply should be decoupled with a capacitor (0.1 µf) that is positioned as close to the device as possible. Output and supply current limitations should be watched carefully since the TLC3704 does not provide current protection. For example, each output can source or sink a maximum of 20 ma; however, the total current to ground can only be an absolute maximum of 60 ma. This prohibits sinking 20 ma from each of the four outputs simultaneously since the total current to ground would be 80 ma. The TLC3704 has internal ESD-protection circuits that prevents functional failures at voltages up to 2000 V as tested under MIL-STD-883C, Method 301.2; however, care should be exercised in handling these devices as exposure to ESD may result in the degradation of the device parametric performance. Table of Applications FIGURE Pulse-width-modulated motor speed controller 2 Enhanced supply supervisor 26 Two-phase nonoverlapping clock generator 27 Micropower switching regulator 28 19
20 APPLICATION INFORMATION 12 V V DIR SN7603 Half-H Driver 1/2 TLC kω See Note A EN 10 kω V 10 kω C µf (see Note B) 1/2 TLC V Motor 10 kω DIR SN7604 Half-H Driver V 10 kω Motor Speed Control Potentiometer EN V Direction Control S1 SPDT NOTES: A. The recommended minimum capacitance is 10 µf to eliminate common ground switching noise. B. Adjust C1 for change in oscillator frequency Figure 2. Pulse-Width-Modulated Motor Speed Controller 20
21 APPLICATION INFORMATION V 12 V VCC SENSE V 12-V Sense 3.3 kω 1 kω 1/2 TLC kω RESIN TL770A RESET To µp Reset REF CT GND 2. V 1 µf CT (see Note B) V(UNREG) (see Note A) R1 R2 1/2 TLC3704 To µp Interrupt Early Power Fail Monitors VDC Rail Monitors 12 VDC Rail Early Power Fail Warning NOTES: A. (R1 R2) V (UNREG) 2. R2 B. The value of CT determines the time delay of reset. Figure 26. Enhanced Supply Supervisor 21
22 APPLICATION INFORMATION 12 V 12 V R1 100 kω (see Note B) 12 V 1/2 TLC3704 1/2 TLC kω R2 kω (see Note C) OUT1 22 kω 100 kω 100 kω C µf (see Note A) R3 100 kω (see Note B) 1/2 TLC3704 OUT2 12 V OUT1 OUT2 NOTES: A. Adjust C1 for a change in oscillator frequency where: 1/f = 1.8(100 kω)c1 B. Adjust R1 and R3 to change duty cycle C. Adjust R2 to change deadtime Figure 27. Two-Phase Nonoverlapping Clock Generator 22
23 APPLICATION INFORMATION V I 6 V to 16 V I L 0.01 ma to 0.2 ma (R1 V O R2) 2. R2 VI 100 kω 1/2 TLC kω 100 kω C1 180 µf (see Note A) 1/2 TLC3704 VI SK904 (see Note C) G S D IN818 VI 47 µf Tantalum 100 kω TLC271 (see Note B) VI R1 100 kω 470 µf R = 6 Ω L = 1 mh (see Note D) RL VO R2 100 kω C2 100 pf 100 kω 270 kω VI LM38 2. V NOTES: A. Adjust C1 for a change in oscillator frequency B. TLC271 Tie pin 8 to pin 7 for low bias operation C. SK904 VDS = 40 V IDS = 1 Awill D. To achieve microampere current drive, the inductance of the circuit must be increased. Figure 28. Micropower Switching Regulator 23
24 D (R-PDSO-G**) 8 PINS SHOWN MECHANICAL DATA PLASTIC SMALL-OUTLINE PACKAGE 0.00 (1,27) (0,1) (0,3) (0,2) (6,20) (,80) (0,20) NOM 0.17 (4,00) 0.10 (3,81) Gage Plane 1 4 A (0,2) (1,12) (0,40) Seating Plane (1,7) MAX (0,2) (0,10) (0,10) DIM PINS ** A MAX (,00) (8,7) (10,00) A MIN (4,80) (8,) (9,80) /E 09/01 NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in inches (millimeters). B. This drawing is subject to change without notice. C. Body dimensions do not include mold flash or protrusion, not to exceed (0,1). D. Falls within JEDEC MS
25 FK (S-CQCC-N**) 28 TERMINALS SHOWN MECHANICAL DATA LEADLESS CERAMIC CHIP CARRIER NO. OF TERMINALS ** MIN A MAX MIN B MAX (8,69) 0.38 (9,09) (7,80) 0.38 (9,09) A SQ B SQ (11,23) (16,26) (18,78) (23,83) (28,99) 0.48 (11,63) (16,76) (19,32) (24,43) 1.16 (29,9) (10,31) 0.49 (12,8) 0.49 (12,8) 0.80 (21,6) (26,6) 0.48 (11,63) 0.60 (14,22) 0.60 (14,22) 0.88 (21,8) (27,0) (0,1) (0,2) (2,03) (1,63) (0,1) (0,2) 0.0 (1,40) 0.04 (1,14) 0.04 (1,14) 0.03 (0,89) (0,71) (0,4) 0.00 (1,27) 0.04 (1,14) 0.03 (0,89) / C 11/9 NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in inches (millimeters). B. This drawing is subject to change without notice. C. This package can be hermetically sealed with a metal lid. D. The terminals are gold-plated. E. Falls within JEDEC MS-004 2
26 J (R-GDIP-T**) 14 LEADS SHOWN MECHANICAL DATA CERAMIC DUAL-IN-LINE DIM PINS ** B A MAX (7,87) (7,87) (7,87) 14 8 A MIN (7,37) (7,37) (7,37) C B MAX B MIN 0.78 (19,94) 0.7 (19,18) 0.78 (19,94) 0.7 (19,18) 0.97 (24,77) (23,62) (1,6) 0.04 (1,14) 7 C MAX C MIN (7,62) 0.24 (6,22) (7,62) 0.24 (6,22) (7,62) 0.24 (6,22) (2,4) (1,78) (0,1) MIN A (,08) MAX Seating Plane (3,30) MIN (0,8) 0.01 (0,38) (2,4) (0,36) (0,20) /E 03/99 NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in inches (millimeters). B. This drawing is subject to change without notice. C. This package is hermetically sealed with a ceramic lid using glass frit. D. Index point is provided on cap for terminal identification. E. Falls within MIL STD 183 GDIP1-T14, GDIP1-T16, and GDIP1-T20 26
27 N (R-PDIP-T**) 16 PINS SHOWN MECHANICAL DATA PLASTIC DUAL-IN-LINE PACKAGE DIM PINS ** A A MAX 0.77 (19,69) 0.77 (19,69) (23,37) 0.97 (24,77) 16 9 A MIN 0.74 (18,92) 0.74 (18,92) 0.80 (21,9) (23,88) (6,60) (6,10) (1,78) MAX (0,89) MAX (0,1) MIN 0.32 (8,26) (7,62) (,08) MAX 0.01 (0,38) Gauge Plane Seating Plane 0.12 (3,18) MIN (0,2) NOM (2,4) (10,92) MAX (0,3) 0.01 (0,38) (0,2) M 14/18 PIN ONLY /D 02/00 NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in inches (millimeters). B. This drawing is subject to change without notice. C. Falls within JEDEC MS-001 (20-pin package is shorter than MS-001). 27
28 PW (R-PDSO-G**) 14 PINS SHOWN MECHANICAL DATA PLASTIC SMALL-OUTLINE PACKAGE 0,30 0,6 0,10 M 0, ,0 4,30 6,60 6,20 0,1 NOM Gage Plane 1 A ,2 0,7 0,0 1,20 MAX 0,1 0,0 Seating Plane 0,10 DIM PINS ** A MAX 3,10,10,10 6,60 7,90 9,80 A MIN 2,90 4,90 4,90 6,40 7,70 9, /F 01/97 NOTES: A. All linear dimensions are in millimeters. B. This drawing is subject to change without notice. C. Body dimensions do not include mold flash or protrusion not to exceed 0,1. D. Falls within JEDEC MO-13 28
29 PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM 22-Feb-200 PACKAGING INFORMATION Orderable Device Status (1) Package Type Package Drawing Pins Package Qty Eco Plan (2) Lead/Ball Finish MSL Peak Temp (3) M2A ACTIVE LCCC FK 20 1 None POST-PLATE Level-NC-NC-NC MCA ACTIVE CDIP J 14 1 None A42 SNPB Level-NC-NC-NC TLC3704CD ACTIVE SOIC D 14 0 Pb-Free (RoHS) TLC3704CDR ACTIVE SOIC D Pb-Free (RoHS) TLC3704CN ACTIVE PDIP N 14 2 Pb-Free (RoHS) TLC3704CNSR ACTIVE SO NS Pb-Free (RoHS) CU NIPDAU CU NIPDAU CU NIPDAU CU NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1YEAR/ Level-1-220C-UNLIM Level-2-260C-1YEAR/ Level-1-220C-UNLIM Level-NC-NC-NC Level-2-260C-1YEAR/ Level-1-220C-UNLIM TLC3704CPW ACTIVE TSSOP PW None CU NIPDAU Level-1-220C-UNLIM TLC3704CPWLE OBSOLETE TSSOP PW 14 None Call TI Call TI TLC3704CPWR ACTIVE TSSOP PW None CU NIPDAU Level-1-220C-UNLIM TLC3704ID ACTIVE SOIC D 14 0 Pb-Free (RoHS) TLC3704IDR ACTIVE SOIC D Pb-Free (RoHS) TLC3704IN ACTIVE PDIP N 14 2 Pb-Free (RoHS) CU NIPDAU CU NIPDAU CU NIPDAU Level-2-260C-1YEAR/ Level-1-220C-UNLIM Level-2-260C-1YEAR/ Level-1-220C-UNLIM Level-NC-NC-NC TLC3704IPW ACTIVE TSSOP PW None CU NIPDAU Level-1-220C-UNLIM TLC3704IPWR ACTIVE TSSOP PW None CU NIPDAU Level-1-220C-UNLIM TLC3704MD ACTIVE SOIC D 14 0 None CU NIPDAU Level-1-220C-UNLIM TLC3704MDR ACTIVE SOIC D None CU NIPDAU Level-1-220C-UNLIM TLC3704MFKB ACTIVE LCCC FK 20 1 None POST-PLATE Level-NC-NC-NC TLC3704MJ ACTIVE CDIP J 14 1 None A42 SNPB Level-NC-NC-NC TLC3704MJB ACTIVE CDIP J 14 1 None A42 SNPB Level-NC-NC-NC (1) The marketing status values are defined as follows: ACTIVE: Product device recommended for new designs. LIFEBUY: TI has announced that the device will be discontinued, and a lifetime-buy period is in effect. NRND: Not recommended for new designs. Device is in production to support existing customers, but TI does not recommend using this part in a new design. PREVIEW: Device has been announced but is not in production. Samples may or may not be available. OBSOLETE: TI has discontinued the production of the device. None: Not yet available Lead (Pb-Free). Pb-Free (RoHS): TI's terms "Lead-Free" or "Pb-Free" mean semiconductor products that are compatible with the current RoHS requirements for all 6 substances, including the requirement that lead not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous materials. Where designed to be soldered at high temperatures, TI Pb-Free products are suitable for use in specified lead-free processes. Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br): TI defines "Green" to mean "Pb-Free" and in addition, uses package materials that do not contain halogens, including bromine (Br) or antimony (Sb) above 0.1% of total product weight. (3) MSL, Peak Temp. -- The Moisture Sensitivity Level rating according to the JEDECindustry standard classifications, and peak solder temperature. Addendum-Page 1
TLC3704, TLC3704Q QUAD MICROPOWER LinCMOS VOLTAGE COMPARATORS
 Push-Pull CMOS Output Drives Capacitive Loads Without Pullup Resistor, I O = ± 8 ma Very Low Power...200 µw Typ at V Fast Response Time...t PLH = 2.7 µs Typ With -mv Overdrive Single Supply Operation...3
Push-Pull CMOS Output Drives Capacitive Loads Without Pullup Resistor, I O = ± 8 ma Very Low Power...200 µw Typ at V Fast Response Time...t PLH = 2.7 µs Typ With -mv Overdrive Single Supply Operation...3
TLC3704, TLC3704Q QUAD MICROPOWER LinCMOS VOLTAGE COMPARATORS
 Push-Pull CMOS Output Drives Capacitive Loads Without Pullup Resistor, I O = ± 8 ma Very Low Power... 200 µw Typ at V Fast Response Time...t PLH = 2.7 µs Typ With -mv Overdrive Single Supply Operation...3
Push-Pull CMOS Output Drives Capacitive Loads Without Pullup Resistor, I O = ± 8 ma Very Low Power... 200 µw Typ at V Fast Response Time...t PLH = 2.7 µs Typ With -mv Overdrive Single Supply Operation...3
TLC3702, TLC3702Q DUAL MICROPOWER LinCMOS VOLTAGE COMPARATORS
 Push-Pull CMOS Output Drives Capacitive Loads Without Pullup Resistor, I O = ± 8 ma Very Low Power...1 µw Typ at V Fast Response Time...t PLH = 2.7 µs Typ With -mv Overdrive Single-Supply Operation...3
Push-Pull CMOS Output Drives Capacitive Loads Without Pullup Resistor, I O = ± 8 ma Very Low Power...1 µw Typ at V Fast Response Time...t PLH = 2.7 µs Typ With -mv Overdrive Single-Supply Operation...3
TLC3702 DUAL MICROPOWER LinCMOS VOLTAGE COMPARATORS
 Push-Pull CMOS Output Drives Capacitive Loads Without Pullup Resistor, I O = ± 8 ma Very Low Power...100 µw Typ at V Fast Response Time...t PLH = 2.7 µs Typ With -mv Overdrive Single-Supply Operation...3
Push-Pull CMOS Output Drives Capacitive Loads Without Pullup Resistor, I O = ± 8 ma Very Low Power...100 µw Typ at V Fast Response Time...t PLH = 2.7 µs Typ With -mv Overdrive Single-Supply Operation...3
TLC3702-EP DUAL MICROPOWER LinCMOS VOLTAGE COMPARATOR
 Controlled Baseline One Assembly/Test Site, One Fabrication Site Extended Temperature Performance of C to 12 C Enhanced Diminishing Manufacturing Sources (DMS) Support Enhanced Product Change Notification
Controlled Baseline One Assembly/Test Site, One Fabrication Site Extended Temperature Performance of C to 12 C Enhanced Diminishing Manufacturing Sources (DMS) Support Enhanced Product Change Notification
TLC3702 DUAL MICROPOWER LinCMOS VOLTAGE COMPARATORS
 Push-Pull CMOS Output Drives Capacitive Loads Without Pullup Resistor, I O = ± 8 ma Very Low Power... 100 μw Typ at 5 V Fast Response Time...t PLH = 2.7 μs Typ With 5-mV Overdrive Single-Supply Operation...3
Push-Pull CMOS Output Drives Capacitive Loads Without Pullup Resistor, I O = ± 8 ma Very Low Power... 100 μw Typ at 5 V Fast Response Time...t PLH = 2.7 μs Typ With 5-mV Overdrive Single-Supply Operation...3
TLC3704, TLC3704M QUAD MICROPOWER LinCMOS VOLTAGE COMPARATORS
 Push-Pull CMOS Output Drives Capacitive Loads Without Pullup Resistor, I O = ± 8 ma Very Low Power... 200 µw Typ at 5 V Fast Response Time...t PLH = 2.7 µs Typ With 5-mV Overdrive Single Supply Operation...3
Push-Pull CMOS Output Drives Capacitive Loads Without Pullup Resistor, I O = ± 8 ma Very Low Power... 200 µw Typ at 5 V Fast Response Time...t PLH = 2.7 µs Typ With 5-mV Overdrive Single Supply Operation...3
TLC3704, TLC3704M QUAD MICROPOWER LinCMOS VOLTAGE COMPARATORS
 Push-Pull CMOS Output Drives Capacitive Loads Without Pullup Resistor, I O = ± 8 ma Very Low Power... 200 µw Typ at 5 V Fast Response Time...t PLH = 2.7 µs Typ With 5-mV Overdrive Single Supply Operation...3
Push-Pull CMOS Output Drives Capacitive Loads Without Pullup Resistor, I O = ± 8 ma Very Low Power... 200 µw Typ at 5 V Fast Response Time...t PLH = 2.7 µs Typ With 5-mV Overdrive Single Supply Operation...3
LinCMOS is a trademark of Texas Instruments Incorporated. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
 Single or Dual-Supply Operation Wide Range of Supply Voltages 2 V to 18 V Low Supply Current Drain 150 µa Typ at 5 V Fast Response Time... 200 ns Typ for TTL-Level Input Step Built-in ESD Protection High
Single or Dual-Supply Operation Wide Range of Supply Voltages 2 V to 18 V Low Supply Current Drain 150 µa Typ at 5 V Fast Response Time... 200 ns Typ for TTL-Level Input Step Built-in ESD Protection High
TLC555, TLC555Y LinCMOS TIMERS
 ery Low Power Consumption mw Typ at DD = 5 Capable of Operation in Astable Mode CMOS Output Capable of Swinging Rail to Rail High Output-Current Capability Sink 00 ma Typ Source 0 ma Typ Output Fully Compatible
ery Low Power Consumption mw Typ at DD = 5 Capable of Operation in Astable Mode CMOS Output Capable of Swinging Rail to Rail High Output-Current Capability Sink 00 ma Typ Source 0 ma Typ Output Fully Compatible
LinCMOS is a trademark of Texas Instruments Incorporated. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
 SLCS115E DECEMBER 1986 REVISED JULY 2003 Very Low Power...110 µw Typ at 5 V Fast Response Time...t PLH = 2.5 µs Typ With 5-mV Overdrive Single Supply Operation: TLC393C...3 V to 16 V TLC393I...3 V to 16
SLCS115E DECEMBER 1986 REVISED JULY 2003 Very Low Power...110 µw Typ at 5 V Fast Response Time...t PLH = 2.5 µs Typ With 5-mV Overdrive Single Supply Operation: TLC393C...3 V to 16 V TLC393I...3 V to 16
TLC3702 DUAL MICROPOWER LinCMOS VOLTAGE COMPARATORS
 Push-Pull CMOS Output Drives Capacitive Loads Without Pullup Resistor, I O = ± 8 ma Very Low Power... 100 μw Typ at 5 V Fast Response Time...t PLH = 2.7 μs Typ With 5-mV Overdrive Single-Supply Operation...3
Push-Pull CMOS Output Drives Capacitive Loads Without Pullup Resistor, I O = ± 8 ma Very Low Power... 100 μw Typ at 5 V Fast Response Time...t PLH = 2.7 μs Typ With 5-mV Overdrive Single-Supply Operation...3
TLC3702 DUAL MICROPOWER LinCMOS VOLTAGE COMPARATORS
 Push-Pull CMOS Output Drives Capacitive Loads Without Pullup Resistor, I O = ± 8 ma Very Low Power...100 µw Typ at 5 V Fast Response Time...t PLH = 2.7 µs Typ With 5-mV Overdrive Single-Supply Operation...3
Push-Pull CMOS Output Drives Capacitive Loads Without Pullup Resistor, I O = ± 8 ma Very Low Power...100 µw Typ at 5 V Fast Response Time...t PLH = 2.7 µs Typ With 5-mV Overdrive Single-Supply Operation...3
TLC226x, TLC226xA Advanced LinCMOS RAIL-TO-RAIL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 Output Swing includes Both Supply Rails Low Noise... 2 nv/ Hz Typ at f = khz Low Input Bias Current... pa Typ Fully Specified for Both Single-Supply and Split-Supply Operation Low Power... µa Max Common-Mode
Output Swing includes Both Supply Rails Low Noise... 2 nv/ Hz Typ at f = khz Low Input Bias Current... pa Typ Fully Specified for Both Single-Supply and Split-Supply Operation Low Power... µa Max Common-Mode
TLC271, TLC271A, TLC271B LinCMOS PROGRAMMABLE LOW-POWER OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 Input Offset Voltage Drift...Typically. µv/month, Including the First 3 Days Wide Range of Supply Voltages Over Specified Temperature Range: C 7 C...3 V 6 V 4 C 85 C...4 V 6 V 55 C 25 C...5 V 6 V Single-Supply
Input Offset Voltage Drift...Typically. µv/month, Including the First 3 Days Wide Range of Supply Voltages Over Specified Temperature Range: C 7 C...3 V 6 V 4 C 85 C...4 V 6 V 55 C 25 C...5 V 6 V Single-Supply
LM139, LM139A, LM239, LM239A, LM339, LM339A, LM339Y, LM2901 QUAD DIFFERENTIAL COMPARATORS
 Single Supply or Dual Supplies Wide Range of Supply Voltage...2 V to 36 V Low Supply-Current Drain Independent of Supply Voltage... 0.8 ma Typ Low Input Bias Current... 25 Typ Low Input Offset Current...3
Single Supply or Dual Supplies Wide Range of Supply Voltage...2 V to 36 V Low Supply-Current Drain Independent of Supply Voltage... 0.8 ma Typ Low Input Bias Current... 25 Typ Low Input Offset Current...3
TLC556, TLC556Y DUAL LinCMOS TIMERS
 ery Low Power Consumption...2 mw Typ at DD = 5 Capable of Operation in Astable Mode CMOS Output Capable of Swinging Rail to Rail High Output-Current Capability Sink 100 ma Typ Source 10 ma Typ Output Fully
ery Low Power Consumption...2 mw Typ at DD = 5 Capable of Operation in Astable Mode CMOS Output Capable of Swinging Rail to Rail High Output-Current Capability Sink 100 ma Typ Source 10 ma Typ Output Fully
TLC227x, TLC227xA, TLC227xY Advanced LinCMOS RAIL-TO-RAIL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS SLOS190 FEBRUARY 1997
 SLOS19 FEBRUARY 1997 Output Swing Includes Both Supply Rails Low Noise...9 nv/ Hz Typ at f = 1 khz Low Input Bias Current...1 pa Typ Fully Specified for Both Single-Supply and Split-Supply Operation Common-Mode
SLOS19 FEBRUARY 1997 Output Swing Includes Both Supply Rails Low Noise...9 nv/ Hz Typ at f = 1 khz Low Input Bias Current...1 pa Typ Fully Specified for Both Single-Supply and Split-Supply Operation Common-Mode
LinCMOS is a trademark of Texas Instruments Incorporated. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
 Single or Dual-Supply Operation Wide Range of Supply Voltages 2 V to 18 V Low Supply Current Drain 150 µa Typ at 5 V Fast Response Time... 200 ns Typ for TTL-Level Input Step Built-in ESD Protection High
Single or Dual-Supply Operation Wide Range of Supply Voltages 2 V to 18 V Low Supply Current Drain 150 µa Typ at 5 V Fast Response Time... 200 ns Typ for TTL-Level Input Step Built-in ESD Protection High
TLC3702 DUAL MICROPOWER LinCMOS VOLTAGE COMPARATORS
 Push-Pull CMOS Output Drives Capacitive Loads Without Pullup Resistor, I O = ± 8 ma Very Low Power... 100 μw Typ at 5 V Fast Response Time...t PLH = 2.7 μs Typ With 5-mV Overdrive Single-Supply Operation...3
Push-Pull CMOS Output Drives Capacitive Loads Without Pullup Resistor, I O = ± 8 ma Very Low Power... 100 μw Typ at 5 V Fast Response Time...t PLH = 2.7 μs Typ With 5-mV Overdrive Single-Supply Operation...3
SN5406, SN5416, SN7406, SN7416 HEX INVERTER BUFFERS/DRIVERS WITH OPEN-COLLECTOR HIGH-VOLTAGE OUTPUTS SDLS031A DECEMBER 1983 REVISED DECEMBER 2001
 SN5406, SN5416, SN7406, SN7416 HEX INVERTER BUFFERS/DRIVERS WITH OPEN-COLLECTOR HIGH-VOLTAGE OUTPUTS SDLS031A DECEMBER 1983 REVISED DECEMBER 2001 Convert TTL Voltage Levels to MOS Levels High Sink-Current
SN5406, SN5416, SN7406, SN7416 HEX INVERTER BUFFERS/DRIVERS WITH OPEN-COLLECTOR HIGH-VOLTAGE OUTPUTS SDLS031A DECEMBER 1983 REVISED DECEMBER 2001 Convert TTL Voltage Levels to MOS Levels High Sink-Current
NE556, SA556, SE556, SE556C DUAL PRECISION TIMERS
 Two Precision Timing Circuits per Package Astable or Monostable Operation TTL-Compatible Output Can Sink or Source Up to 50 ma Active Pullup or Pulldown Designed to be Interchangeable With Signetics SE556,
Two Precision Timing Circuits per Package Astable or Monostable Operation TTL-Compatible Output Can Sink or Source Up to 50 ma Active Pullup or Pulldown Designed to be Interchangeable With Signetics SE556,
SN54ALS05A, SN74ALS05A HEX INVERTERS WITH OPEN-COLLECTOR OUTPUTS
 SN54ALS05A, SN74ALS05A HEX INVERTERS WITH OPEN-COLLECTOR OUTPUTS SDAS190A APRIL 1982 REVISED DECEMBER 1994 Package Options Include Plastic Small-Outline (D) Packages, Ceramic Chip Carriers (FK), and Standard
SN54ALS05A, SN74ALS05A HEX INVERTERS WITH OPEN-COLLECTOR OUTPUTS SDAS190A APRIL 1982 REVISED DECEMBER 1994 Package Options Include Plastic Small-Outline (D) Packages, Ceramic Chip Carriers (FK), and Standard
LM139, LM139A, LM239, LM239A, LM339 LM339A, LM339Y, LM2901, LM2901Q QUAD DIFFERENTIAL COMPARATORS SLCS006C OCTOBER 1979 REVISED NOVEMBER 1996
 Single Supply or Dual Supplies Wide Range of Supply Voltage 2 V to 36 V Low Supply-Current Drain Independent of Supply Voltage... 0.8 ma Typ Low Input Bias Current...25 na Typ Low Input Offset Current...3
Single Supply or Dual Supplies Wide Range of Supply Voltage 2 V to 36 V Low Supply-Current Drain Independent of Supply Voltage... 0.8 ma Typ Low Input Bias Current...25 na Typ Low Input Offset Current...3
CD4066B CMOS QUAD BILATERAL SWITCH
 15-V Digital or ±7.5-V Peak-to-Peak Switching 125-Ω Typical On-State Resistance for 15-V Operation Switch On-State Resistance Matched to Within 5 Ω Over 15-V Signal-Input Range On-State Resistance Flat
15-V Digital or ±7.5-V Peak-to-Peak Switching 125-Ω Typical On-State Resistance for 15-V Operation Switch On-State Resistance Matched to Within 5 Ω Over 15-V Signal-Input Range On-State Resistance Flat
LM723/LM723C Voltage Regulator
 1 LM723, LM723C LM723/LM723C Voltage Regulator Check for Samples: LM723, LM723C 1FEATURES DESCRIPTION 2 150 ma Output Current Without External Pass The LM723/LM723C is a voltage regulator designed Transistor
1 LM723, LM723C LM723/LM723C Voltage Regulator Check for Samples: LM723, LM723C 1FEATURES DESCRIPTION 2 150 ma Output Current Without External Pass The LM723/LM723C is a voltage regulator designed Transistor
SN54ALS32, SN54AS32, SN74ALS32, SN74AS32 QUADRUPLE 2-INPUT POSITIVE-OR GATES
 SN54ALS32, SN54AS32, SN74ALS32, SN74AS32 QUADRUPLE 2-INPUT POSITIVE-OR GATES SDAS113B APRIL 1982 REVISED DECEMBER 1994 Package Options Include Plastic Small-Outline (D) Packages, Ceramic Chip Carriers
SN54ALS32, SN54AS32, SN74ALS32, SN74AS32 QUADRUPLE 2-INPUT POSITIVE-OR GATES SDAS113B APRIL 1982 REVISED DECEMBER 1994 Package Options Include Plastic Small-Outline (D) Packages, Ceramic Chip Carriers
SN75C185 LOW-POWER MULTIPLE DRIVERS AND RECEIVERS
 Meets or Exceeds the Requirements of ANSI EIA/TIA-232-E and ITU Recommendation V.28 Single Chip With Easy Interface Between UART and Serial Port Connector Less Than 9-mW Power Consumption Wide Driver Supply
Meets or Exceeds the Requirements of ANSI EIA/TIA-232-E and ITU Recommendation V.28 Single Chip With Easy Interface Between UART and Serial Port Connector Less Than 9-mW Power Consumption Wide Driver Supply
TL494C, TL494I, TL494M, TL494Y PULSE-WIDTH-MODULATION CONTROL CIRCUITS
 Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for 00-mA Sink or Source Current Output Control Selects Single-Ended or Push-Pull Operation Internal Circuitry Prohibits Double Pulse at Either
Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for 00-mA Sink or Source Current Output Control Selects Single-Ended or Push-Pull Operation Internal Circuitry Prohibits Double Pulse at Either
Related Synchronous MOSFET Drivers DEVICE NAME ADDITIONAL FEATURES INPUTS TPS2830. Noninverted TPS2831. Inverted TPS2834. Noninverted TPS2835
 Floating Bootstrap or Ground-Reference High-Side Driver Adaptive Dead-Time Control 50-ns Max Rise/Fall Times and 00-ns Max Propagation Delay 3.3-nF Load Ideal for High-Current Single or Multiphase Power
Floating Bootstrap or Ground-Reference High-Side Driver Adaptive Dead-Time Control 50-ns Max Rise/Fall Times and 00-ns Max Propagation Delay 3.3-nF Load Ideal for High-Current Single or Multiphase Power
The ULN2003AI has a 2.7-kΩ series base resistor for each Darlington pair for operation directly with TTL or 5-V CMOS devices. ORDERING INFORMATION
 查询 ULN23AI 供应商 www.ti.com FEATURES 5-mA-Rated Collector Current (Single Output) High-Voltage Outputs... 5 V Output Clamp Diodes Inputs Compatible With Various Types of Logic Relay-Driver Applications DESCRIPTION/ORDERING
查询 ULN23AI 供应商 www.ti.com FEATURES 5-mA-Rated Collector Current (Single Output) High-Voltage Outputs... 5 V Output Clamp Diodes Inputs Compatible With Various Types of Logic Relay-Driver Applications DESCRIPTION/ORDERING
TLC272, TLC272A, TLC272B, TLC272Y, TLC277 LinCMOS PRECISION DUAL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 SLOS91E OCTOBER 1987 REVISED FEBRUARY 22 Trimmed Offset Voltage: TLC277... 5 µv Max at 25 C, V DD = 5 V Input Offset Voltage Drift...Typically.1 µv/month, Including the First 3 Days Wide Range of Supply
SLOS91E OCTOBER 1987 REVISED FEBRUARY 22 Trimmed Offset Voltage: TLC277... 5 µv Max at 25 C, V DD = 5 V Input Offset Voltage Drift...Typically.1 µv/month, Including the First 3 Days Wide Range of Supply
MC1489, MC1489A, SN55189, SN55189A, SN75189, SN75189A QUADRUPLE LINE RECEIVERS
 MC489, MC489A, SN5589, SN5589A, SN7589, SN7589A QUADRUPLE LINE RECEIVERS SLLS095D SEPTEMBER 973 REVISED OCTOBER 998 Input Resistance...3 kω to 7 kω Input Signal Range...±30 V Operate From Single 5-V Supply
MC489, MC489A, SN5589, SN5589A, SN7589, SN7589A QUADRUPLE LINE RECEIVERS SLLS095D SEPTEMBER 973 REVISED OCTOBER 998 Input Resistance...3 kω to 7 kω Input Signal Range...±30 V Operate From Single 5-V Supply
LM148, LM248, LM348 QUADRUPLE OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 µa741 Operating Characteristics Low Supply Current Drain...0.6 ma Typ (per amplifier) Low Input Offset Voltage Low Input Offset Current Class AB Output Stage Input/Output Overload Protection Designed to
µa741 Operating Characteristics Low Supply Current Drain...0.6 ma Typ (per amplifier) Low Input Offset Voltage Low Input Offset Current Class AB Output Stage Input/Output Overload Protection Designed to
SN55451B, SN55452B, SN55453B, SN55454B SN75451B, SN75452B, SN75453B, SN75454B DUAL PERIPHERAL DRIVERS
 PERIPHERAL DRIVERS FOR HIGH-CURRENT SWITCHING AT VERY HIGH SPEEDS Characterized for Use to 00 ma High-Voltage Outputs No Output Latch-Up at 0 V (After Conducting 00 ma) High-Speed Switching Circuit Flexibility
PERIPHERAL DRIVERS FOR HIGH-CURRENT SWITCHING AT VERY HIGH SPEEDS Characterized for Use to 00 ma High-Voltage Outputs No Output Latch-Up at 0 V (After Conducting 00 ma) High-Speed Switching Circuit Flexibility
TL494 PULSE-WIDTH-MODULATION CONTROL CIRCUITS
 FEATURES Complete PWM Power-Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for 200-mA Sink or Source Current Output Control Selects Single-Ended or Push-Pull Operation Internal Circuitry Prohibits Double Pulse
FEATURES Complete PWM Power-Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for 200-mA Sink or Source Current Output Control Selects Single-Ended or Push-Pull Operation Internal Circuitry Prohibits Double Pulse
LM111, LM211, LM311, LM311Y DIFFERENTIAL COMPARATORS WITH STROBES
 Fast Response Times Strobe Capability Maximum Input Bias Current...3 na Maximum Input Offset Current...7 na Can Operate From Single -V Supply Designed Be Interchangeable With National Semiconducr LM, LM,
Fast Response Times Strobe Capability Maximum Input Bias Current...3 na Maximum Input Offset Current...7 na Can Operate From Single -V Supply Designed Be Interchangeable With National Semiconducr LM, LM,
SN54ABT125, SN74ABT125 QUADRUPLE BUS BUFFER GATES WITH 3-STATE OUTPUTS
 Typical V OLP (Output Ground Bounce)
Typical V OLP (Output Ground Bounce)
UNISONIC TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD ULC3702 Advance CMOS IC
 UNISONIC TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD ULC3702 Advance CMOS IC DUAL MICROPOWER CMOS VOLTAGE COMPARATORS DESCRIPTION The UTC ULC3702 consists of two independent micropower voltage comparators designed to operate
UNISONIC TECHNOLOGIES CO., LTD ULC3702 Advance CMOS IC DUAL MICROPOWER CMOS VOLTAGE COMPARATORS DESCRIPTION The UTC ULC3702 consists of two independent micropower voltage comparators designed to operate
TLC2654, TLC2654A Advanced LinCMOS LOW-NOISE CHOPPER-STABILIZED OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 Input Noise Voltage.5 µv (Peak-to-Peak) Typ, f = to 1 Hz 1.5 µv (Peak-to-Peak) Typ, f = to 1 Hz 7 nv/ Hz Typ, f = 1 Hz 13 nv/ Hz Typ, f = 1 khz High Chopping Frequency... 1 khz Typ No Clock Noise Below
Input Noise Voltage.5 µv (Peak-to-Peak) Typ, f = to 1 Hz 1.5 µv (Peak-to-Peak) Typ, f = to 1 Hz 7 nv/ Hz Typ, f = 1 Hz 13 nv/ Hz Typ, f = 1 khz High Chopping Frequency... 1 khz Typ No Clock Noise Below
TLC27L2, TLC27L2A, TLC27L2B, TLC27L7 LinCMOS PRECISION DUAL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 SLOS52B OCTOBER 987 REVISED AUGUST 994 Trimmed Offset Voltage: TLC27L7... 5 µv Max at 25 C, V DD = 5 V Input Offset Voltage Drift... Typically. µv/month, including the First 3 Days Wide Range of Supply
SLOS52B OCTOBER 987 REVISED AUGUST 994 Trimmed Offset Voltage: TLC27L7... 5 µv Max at 25 C, V DD = 5 V Input Offset Voltage Drift... Typically. µv/month, including the First 3 Days Wide Range of Supply
SN54HCT14, SN74HCT14 HEX SCHMITT-TRIGGER INVERTERS
 SN54HCT14, SN74HCT14 HEX SCHMITT-TRIGGER INVERTERS SCLS225E JULY 1995 REVISED JULY 2003 Operating Voltage Range of 4.5 V to 5.5 V Outputs Can Drive Up To 10 LSTTL Loads Low Power Consumption, 20-µA Max
SN54HCT14, SN74HCT14 HEX SCHMITT-TRIGGER INVERTERS SCLS225E JULY 1995 REVISED JULY 2003 Operating Voltage Range of 4.5 V to 5.5 V Outputs Can Drive Up To 10 LSTTL Loads Low Power Consumption, 20-µA Max
TLC27M4, TLC27M4A, TLC27M4B, TLC27M4Y, TLC27M9 LinCMOS PRECISION QUAD OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 SLOS93C OCTOBER 1987 REVISED MAY 1999 Trimmed Offset Voltage: TLC27M9...9 µv Max at T A = 25 C, V DD = 5 V Input Offset Voltage Drift...Typically.1 µv/month, Including the First 3 Days Wide Range of Supply
SLOS93C OCTOBER 1987 REVISED MAY 1999 Trimmed Offset Voltage: TLC27M9...9 µv Max at T A = 25 C, V DD = 5 V Input Offset Voltage Drift...Typically.1 µv/month, Including the First 3 Days Wide Range of Supply
TL494M PULSE-WIDTH-MODULATION CONTROL CIRCUIT
 Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for 00-mA Sink or Source Current Output Control Selects Single-Ended or Push-Pull Operation Internal Circuitry Prohibits Double Pulse at Either
Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for 00-mA Sink or Source Current Output Control Selects Single-Ended or Push-Pull Operation Internal Circuitry Prohibits Double Pulse at Either
TLC272, TLC272A, TLC272B, TLC272Y, TLC277 LinCMOS PRECISION DUAL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 Trimmed Offset Voltage: TLC277... 5 µv Max at 25 C, V DD = 5 V Input Offset Voltage Drift...Typically.1 µv/month, Including the First 3 Days Wide Range of Supply Voltages Over Specified Temperature Range:
Trimmed Offset Voltage: TLC277... 5 µv Max at 25 C, V DD = 5 V Input Offset Voltage Drift...Typically.1 µv/month, Including the First 3 Days Wide Range of Supply Voltages Over Specified Temperature Range:
NE555,SA555,SE555 PRECISION TIMERS
 Timing From Microseconds to Hours Astable or Monostable Operation Adjustable Duty Cycle TTL-Compatible Output Can Sink or Source Up To 200 ma Description/ordering information These devices are precision
Timing From Microseconds to Hours Astable or Monostable Operation Adjustable Duty Cycle TTL-Compatible Output Can Sink or Source Up To 200 ma Description/ordering information These devices are precision
TL594C, TL594I, TL594Y PULSE-WIDTH-MODULATION CONTROL CIRCUITS
 Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for 200-mA Sink or Source Current Output Control Selects Single-Ended or Push-Pull Operation Internal Circuitry Prohibits Double Pulse at Either
Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for 200-mA Sink or Source Current Output Control Selects Single-Ended or Push-Pull Operation Internal Circuitry Prohibits Double Pulse at Either
description/ordering information
 SCLS087E DECEMBER 1982 REVISED AUGUST 2003 Wide Operating Voltage Range of 2 V to 6 V Outputs Can Drive Up To 10 LSTTL Loads Low Power Consumption, 20-µA Max I CC Typical t pd = 11 ns ±4-mA Output Drive
SCLS087E DECEMBER 1982 REVISED AUGUST 2003 Wide Operating Voltage Range of 2 V to 6 V Outputs Can Drive Up To 10 LSTTL Loads Low Power Consumption, 20-µA Max I CC Typical t pd = 11 ns ±4-mA Output Drive
SN75150 DUAL LINE DRIVER
 Meets or Exceeds the Requirement of ANSI EIA/TIA-232-E and ITU Recommendation V.28 Withstands Sustained Output Short Circuit to Any Low-Impedance Voltage Between 25 V and 25 V 2-µs Max Transition Time
Meets or Exceeds the Requirement of ANSI EIA/TIA-232-E and ITU Recommendation V.28 Withstands Sustained Output Short Circuit to Any Low-Impedance Voltage Between 25 V and 25 V 2-µs Max Transition Time
TL070 JFET-INPUT OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
 Low Power Consumption Wide Common-Mode and Differential Voltage Ranges Low Input Bias and Offset Currents Output Short-Circuit Protection Low Total Harmonic Distortion.3% Typ Low Noise V n = 8 nv/ Hz Typ
Low Power Consumption Wide Common-Mode and Differential Voltage Ranges Low Input Bias and Offset Currents Output Short-Circuit Protection Low Total Harmonic Distortion.3% Typ Low Noise V n = 8 nv/ Hz Typ
TL594 PULSE-WIDTH-MODULATION CONTROL CIRCUITS
 Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for 200-mA Sink or Source Current Output Control Selects Single-Ended or Push-Pull Operation Internal Circuitry Prohibits Double Pulse at Either
Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for 200-mA Sink or Source Current Output Control Selects Single-Ended or Push-Pull Operation Internal Circuitry Prohibits Double Pulse at Either
GENERAL-PURPOSE OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 µa71, µa71y Short-Circuit Protection Offset-Voltage Null Capability Large Common-Mode and Differential Voltage Ranges No Frequency Compensation Required Low Power Consumption No Latch-Up Designed to Be
µa71, µa71y Short-Circuit Protection Offset-Voltage Null Capability Large Common-Mode and Differential Voltage Ranges No Frequency Compensation Required Low Power Consumption No Latch-Up Designed to Be
ua9636ac DUAL LINE DRIVER WITH ADJUSTABLE SLEW RATE
 SLLSB OCTOBER 9 REVISED MAY 995 Meets or Exceeds the Requirements of ANSI Standards EIA/TIA-3-B and -3-E and ITU Recommendations V. and V. Output Slew Rate Control Output Short-Circuit-Current Limiting
SLLSB OCTOBER 9 REVISED MAY 995 Meets or Exceeds the Requirements of ANSI Standards EIA/TIA-3-B and -3-E and ITU Recommendations V. and V. Output Slew Rate Control Output Short-Circuit-Current Limiting
6N135, 6N136, HCPL4502 OPTOCOUPLERS/OPTOISOLATORS
 Compatible with TTL Inputs High-Speed Switching... Mbit/s Typ Bandwidth...2 MHz Typ High Common-Mode Transient Immunity... 000 V/µs Typ High-Voltage Electrical Insulation... 3000 Vdc Min Open-Collector
Compatible with TTL Inputs High-Speed Switching... Mbit/s Typ Bandwidth...2 MHz Typ High Common-Mode Transient Immunity... 000 V/µs Typ High-Voltage Electrical Insulation... 3000 Vdc Min Open-Collector
TL494 PULSE-WIDTH-MODULATION CONTROL CIRCUITS
 Complete PWM Power-Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for 200-mA Sink or Source Current Output Control Selects Single-Ended or Push-Pull Operation Internal Circuitry Prohibits Double Pulse at Either
Complete PWM Power-Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for 200-mA Sink or Source Current Output Control Selects Single-Ended or Push-Pull Operation Internal Circuitry Prohibits Double Pulse at Either
THS MHz HIGH-SPEED AMPLIFIER
 THS41 27-MHz HIGH-SPEED AMPLIFIER Very High Speed 27 MHz Bandwidth (Gain = 1, 3 db) 4 V/µsec Slew Rate 4-ns Settling Time (.1%) High Output Drive, I O = 1 ma Excellent Video Performance 6 MHz Bandwidth
THS41 27-MHz HIGH-SPEED AMPLIFIER Very High Speed 27 MHz Bandwidth (Gain = 1, 3 db) 4 V/µsec Slew Rate 4-ns Settling Time (.1%) High Output Drive, I O = 1 ma Excellent Video Performance 6 MHz Bandwidth
SN54ALS1035, SN74ALS1035 HEX NONINVERTING BUFFERS WITH OPEN-COLLECTOR OUTPUTS
 Noninverting Buffers With Open-Collector Outputs description These devices contain six independent noninverting buffers. They perform the Boolean function Y = A. The open-collector outputs require pullup
Noninverting Buffers With Open-Collector Outputs description These devices contain six independent noninverting buffers. They perform the Boolean function Y = A. The open-collector outputs require pullup
ua9637ac DUAL DIFFERENTIAL LINE RECEIVER
 ua967ac Meets or Exceeds the Requirements of ANSI Standards EIA/TIA--B and EIA/TIA--B and ITU Recommendations V. and V. Operates From Single -V Power Supply Wide Common-Mode Voltage Range High Input Impedance
ua967ac Meets or Exceeds the Requirements of ANSI Standards EIA/TIA--B and EIA/TIA--B and ITU Recommendations V. and V. Operates From Single -V Power Supply Wide Common-Mode Voltage Range High Input Impedance
SN54221, SN54LS221, SN74221, SN74LS221 DUAL MONOSTABLE MULTIVIBRATORS WITH SCHMITT-TRIGGER INPUTS
 Dual Versions of Highly Stable SN542 and SN742 One Shots SN5422 and SN7422 Demonstrate Electrical and Switching Characteristics That Are Virtually Identical to the SN542 and SN742 One Shots Pinout Is Identical
Dual Versions of Highly Stable SN542 and SN742 One Shots SN5422 and SN7422 Demonstrate Electrical and Switching Characteristics That Are Virtually Identical to the SN542 and SN742 One Shots Pinout Is Identical
AVAILABLE OPTIONS PACKAGED DEVICES CHIP CARRIER (FK) 100 µv TLC4502IDR. 50 µv TLC4502AIDR
 Power On Calibration of Input Offset Voltage Low Input Offset Voltage...< 5 µv Max (TLC5A) Low Input Offset Voltage Drift...< µv/ C Low Input Bias Current High Output Drive Capability C L < nf and R L
Power On Calibration of Input Offset Voltage Low Input Offset Voltage...< 5 µv Max (TLC5A) Low Input Offset Voltage Drift...< µv/ C Low Input Bias Current High Output Drive Capability C L < nf and R L
LT1014, LT1014A, LT1014D QUAD PRECISION OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 LT, LTA, LTD SLOS39D JULY 989 REVISED AUGUST 29 Single-Supply Operation: Input Voltage Range Extends to Ground, and Output Swings to Ground While Sinking Current Input Offset Voltage 3 µv Max at 2 C for
LT, LTA, LTD SLOS39D JULY 989 REVISED AUGUST 29 Single-Supply Operation: Input Voltage Range Extends to Ground, and Output Swings to Ground While Sinking Current Input Offset Voltage 3 µv Max at 2 C for
TLC274, TLC274A, TLC274B, TLC274Y, TLC279 LinCMOS PRECISION QUAD OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 SLOS92B SEPTEMBER 987 REVISED AUGUST 994 Trimmed Offset Voltage: TLC279... 9 µv Max at 25 C, V DD = 5 V Input Offset Voltage Drift...Typically. µv/month, Including the First 3 Days Wide Range of Supply
SLOS92B SEPTEMBER 987 REVISED AUGUST 994 Trimmed Offset Voltage: TLC279... 9 µv Max at 25 C, V DD = 5 V Input Offset Voltage Drift...Typically. µv/month, Including the First 3 Days Wide Range of Supply
TSX3702. Micropower dual CMOS voltage comparators. Related products. Applications. Description. Features
 Micropower dual CMOS voltage comparators Datasheet - production data Input common-mode voltage range includes ground Push-pull output High input impedance: 10 12 Ω typ Fast response time: 2.7 µs typ. for
Micropower dual CMOS voltage comparators Datasheet - production data Input common-mode voltage range includes ground Push-pull output High input impedance: 10 12 Ω typ Fast response time: 2.7 µs typ. for
TSX339. Micropower quad CMOS voltage comparators. Related products. Applications. Description. Features
 Micropower quad CMOS voltage comparators Datasheet - production data Related products Pin-to-pin and functionally compatible with the quad CMOS TS339 comparators See TSX3704 for push-pull output Applications
Micropower quad CMOS voltage comparators Datasheet - production data Related products Pin-to-pin and functionally compatible with the quad CMOS TS339 comparators See TSX3704 for push-pull output Applications
AVAILABLE OPTIONS CERAMIC DIP (J) CERAMIC DIP (JG) TL071CPWLE 6 mv TL071ACD TL071ACP 3 mv TL071BCD TL071BCP TL072CP
 Low Power Consumption Wide Common-Mode and Differential Voltage Ranges Low Input Bias and Offset Currents Output Short-Circuit Protection Low Total Harmonic Distortion.3% Typ TL7, TL7A, TL7B, TL72 Low
Low Power Consumption Wide Common-Mode and Differential Voltage Ranges Low Input Bias and Offset Currents Output Short-Circuit Protection Low Total Harmonic Distortion.3% Typ TL7, TL7A, TL7B, TL72 Low
TLC2652, TLC2652A, TLC2652Y Advanced LinCMOS PRECISION CHOPPER-STABILIZED OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 Extremely Low Offset Voltage...1 µv Max Extremely Low Change on Offset Voltage With Temperature....3 µv/ C Typ Low Input Offset Current 5 pa Max at T A = 55 C to 125 C A VD... 135 db Min CMRR and k SVR...
Extremely Low Offset Voltage...1 µv Max Extremely Low Change on Offset Voltage With Temperature....3 µv/ C Typ Low Input Offset Current 5 pa Max at T A = 55 C to 125 C A VD... 135 db Min CMRR and k SVR...
SN74LVC138A-Q1 3-LINE TO 8-LINE DECODER/DEMULTIPLEXER SCAS708B SEPTEMBER 2003 REVISED FEBRUARY 2008
 1 1FEATURES Qualified for Automotive Applications ESD Protection Exceeds 2000 V Per MIL-STD-883, Method 3015; Exceeds 200 V Using Machine Model (C = 200 pf, R = 0) Operates From 2 V to 3.6 V Inputs Accept
1 1FEATURES Qualified for Automotive Applications ESD Protection Exceeds 2000 V Per MIL-STD-883, Method 3015; Exceeds 200 V Using Machine Model (C = 200 pf, R = 0) Operates From 2 V to 3.6 V Inputs Accept
SN54LS373, SN54LS374, SN54S373, SN54S374, SN74LS373, SN74LS374, SN74S373, SN74S374 OCTAL D-TYPE TRANSPARENT LATCHES AND EDGE-TRIGGERED FLIP-FLOPS
 Choice of Eight Latches or Eight D-Type Flip-Flops in a Single Package 3-State Bus-Driving Outputs Full Parallel Access for Loading Buffered Control Inputs Clock-Enable Input Has Hysteresis to Improve
Choice of Eight Latches or Eight D-Type Flip-Flops in a Single Package 3-State Bus-Driving Outputs Full Parallel Access for Loading Buffered Control Inputs Clock-Enable Input Has Hysteresis to Improve
TLC556, TLC556Y DUAL LinCMOS TIMERS
 TLC556, TLC556Y DUAL LinCMOS TIMERS ery Low Power Consumption...2 mw Typ at DD = 5 Capable of Operation in Astable Mode CMOS Output Capable of Swinging Rail to Rail High Output-Current Capability Sink
TLC556, TLC556Y DUAL LinCMOS TIMERS ery Low Power Consumption...2 mw Typ at DD = 5 Capable of Operation in Astable Mode CMOS Output Capable of Swinging Rail to Rail High Output-Current Capability Sink
TPS2816, TPS2817, TPS2818, TPS2819, TPS2828, TPS2829 SINGLE-CHANNEL HIGH-SPEED MOSFET DRIVER
 Low-Cost Single-Channel High-Speed MOSFET Driver I CC...-µA Max (TPS88, TPS89) -ns Max Rise/Fall Times and 0-ns Max Propagation Delay...-nF Load -A Peak Output Current -V to -V Driver Supply Voltage Range;
Low-Cost Single-Channel High-Speed MOSFET Driver I CC...-µA Max (TPS88, TPS89) -ns Max Rise/Fall Times and 0-ns Max Propagation Delay...-nF Load -A Peak Output Current -V to -V Driver Supply Voltage Range;
 SLOS070C JULY 979 REVISED SEPTEMBER 2004 Equivalent Input Noise Voltage... 3.5 nv/ Hz Typ Unity-Gain Bandwidth... 0 MHz Typ Common-Mode Rejection Ratio... 00 db Typ High DC Voltage Gain... 00 V/mV Typ
SLOS070C JULY 979 REVISED SEPTEMBER 2004 Equivalent Input Noise Voltage... 3.5 nv/ Hz Typ Unity-Gain Bandwidth... 0 MHz Typ Common-Mode Rejection Ratio... 00 db Typ High DC Voltage Gain... 00 V/mV Typ
SN54ACT573, SN74ACT573 OCTAL D-TYPE TRANSPARENT LATCHES WITH 3-STATE OUTPUTS
 4.5-V to 5.5-V V CC Operation Inputs Accept Voltages to 5.5 V Max t pd of 9.5 ns at 5 V Inputs Are TTL-Voltage Compatible description/ordering information These 8-bit latches feature 3-state outputs designed
4.5-V to 5.5-V V CC Operation Inputs Accept Voltages to 5.5 V Max t pd of 9.5 ns at 5 V Inputs Are TTL-Voltage Compatible description/ordering information These 8-bit latches feature 3-state outputs designed
HIGH SPEED-10 MBit/s LOGIC GATE OPTOCOUPLERS
 HIGH SPEED- MBit/s DESCRIPTION The, /6 single-channel and /6 dual-channel optocouplers consist of a 5 nm AlGaAS LED, optically coupled to a very high speed integrated photodetector logic gate with a strobable
HIGH SPEED- MBit/s DESCRIPTION The, /6 single-channel and /6 dual-channel optocouplers consist of a 5 nm AlGaAS LED, optically coupled to a very high speed integrated photodetector logic gate with a strobable
TL494 PULSE-WIDTH-MODULATION CONTROL CIRCUITS
 Complete PWM Power-Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for 200-mA Sink or Source Current Output Control Selects Single-Ended or Push-Pull Operation Internal Circuitry Prohibits Double Pulse at Either
Complete PWM Power-Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for 200-mA Sink or Source Current Output Control Selects Single-Ended or Push-Pull Operation Internal Circuitry Prohibits Double Pulse at Either
TLC227x, TLC227xA Advanced LinCMOS RAIL-TO-RAIL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 TLC7x, TLC7xA SLOS9E FEBRUARY 997 REVISED MARCH Output Swing Includes Both Supply Rails Low Noise...9 nv/ Hz Typ at f = khz Low Input Bias Current... pa Typ Fully Specified for Both Single-Supply and Split-Supply
TLC7x, TLC7xA SLOS9E FEBRUARY 997 REVISED MARCH Output Swing Includes Both Supply Rails Low Noise...9 nv/ Hz Typ at f = khz Low Input Bias Current... pa Typ Fully Specified for Both Single-Supply and Split-Supply
TLC5620C, TLC5620I QUADRUPLE 8-BIT DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERTERS
 Four -Bit Voltage Output DACs 5-V Single-Supply Operation Serial Interface High-Impedance Reference Inputs Programmable or 2 Times Output Range Simultaneous-Update Facility Internal Power-On Reset Low
Four -Bit Voltage Output DACs 5-V Single-Supply Operation Serial Interface High-Impedance Reference Inputs Programmable or 2 Times Output Range Simultaneous-Update Facility Internal Power-On Reset Low
description V DD GND DISCH THRES CONT TRIG OUT RESET GND NC TRIG NC OUT NC DISCH THRES CONT RESET GND TRIG DISCH THRES OUT RESET CONT
 ery Low Power Consumption mw Typ at DD = 5 Capable of Operation in Astable Mode CMOS Output Capable of Swinging Rail to Rail High Output-Current Capability Sink 00 ma Typ Source 0 ma Typ Output Fully Compatible
ery Low Power Consumption mw Typ at DD = 5 Capable of Operation in Astable Mode CMOS Output Capable of Swinging Rail to Rail High Output-Current Capability Sink 00 ma Typ Source 0 ma Typ Output Fully Compatible
TLV226x, TLV226xA Advanced LinCMOS RAIL-TO-RAIL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 Output Swing Includes Both Supply Rails Low Noise... 2 nv/ Hz Typ at f = khz Low Input Bias Current... pa Typ Fully Specified for Both Single-Supply and Split-Supply Operation Low Power... 5 µa Max Common-Mode
Output Swing Includes Both Supply Rails Low Noise... 2 nv/ Hz Typ at f = khz Low Input Bias Current... pa Typ Fully Specified for Both Single-Supply and Split-Supply Operation Low Power... 5 µa Max Common-Mode
GENERAL-PURPOSE OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 Short-Circuit Protection Offset-Voltage Null Capability Large Common-Mode and Differential Voltage Ranges No Frequency Compensation Required Low Power Consumption No Latch-Up Designed to Be Interchangeable
Short-Circuit Protection Offset-Voltage Null Capability Large Common-Mode and Differential Voltage Ranges No Frequency Compensation Required Low Power Consumption No Latch-Up Designed to Be Interchangeable
TSX393. Micropower dual CMOS voltage comparators
 Micropower dual CMOS voltage comparators Datasheet - production data D SO8 (plastic micropackage) Input common-mode voltage range includes ground Open drain output High input impedance: 10 12 Ω typ Fast
Micropower dual CMOS voltage comparators Datasheet - production data D SO8 (plastic micropackage) Input common-mode voltage range includes ground Open drain output High input impedance: 10 12 Ω typ Fast
SN55451B, SN55452B, SN55453B, SN55454B SN75451B, SN75452B, SN75453B, SN75454B DUAL PERIPHERAL DRIVERS
 PERIPHERAL DRIVERS FOR HIGH-CURRENT SWITCHING AT VERY HIGH SPEEDS Characterized for Use to 00 ma High-Voltage Outputs No Output Latch-Up at 0 V (After Conducting 00 ma) High-Speed Switching Circuit Flexibility
PERIPHERAL DRIVERS FOR HIGH-CURRENT SWITCHING AT VERY HIGH SPEEDS Characterized for Use to 00 ma High-Voltage Outputs No Output Latch-Up at 0 V (After Conducting 00 ma) High-Speed Switching Circuit Flexibility
SN55115, SN75115 DUAL DIFFERENTIAL RECEIVERS
 SN, SN7 Choice of Open-Collector or Active Pullup (Totem-Pole) Outputs Single -V Supply Differential Line Operation Dual-Channel Operation TTL Compatible ± -V Common-Mode Input Voltage Range Optional-Use
SN, SN7 Choice of Open-Collector or Active Pullup (Totem-Pole) Outputs Single -V Supply Differential Line Operation Dual-Channel Operation TTL Compatible ± -V Common-Mode Input Voltage Range Optional-Use
description TPS3836, TPS3838 DBV PACKAGE (TOP VIEW) V DD GND RESET TPS3837 DBV PACKAGE (TOP VIEW)
 М TPS3836E18-Q1 / J25-Q1 / H30-Q1 / L30-Q1 / K33-Q1 Qualified for Automotive Applications Customer-Specific Configuration Control Can Be Supported Along With Major-Change Approval ESD Protection Exceeds
М TPS3836E18-Q1 / J25-Q1 / H30-Q1 / L30-Q1 / K33-Q1 Qualified for Automotive Applications Customer-Specific Configuration Control Can Be Supported Along With Major-Change Approval ESD Protection Exceeds
SN75C185 LOW-POWER MULTIPLE DRIVERS AND RECEIVERS
 Meets or Exceeds the Requirements of TIA/EIA-232-F and ITU Recommendation V.28 Single Chip With Easy Interface Between UART and Serial-Port Connector Less Than 9-mW Power Consumption Wide Driver Supply
Meets or Exceeds the Requirements of TIA/EIA-232-F and ITU Recommendation V.28 Single Chip With Easy Interface Between UART and Serial-Port Connector Less Than 9-mW Power Consumption Wide Driver Supply
AVAILABLE OPTIONS CERAMIC DIP (J) CERAMIC DIP (JG) TL071CPWLE 6 mv TL071ACD TL071ACP 3 mv TL071BCD TL071BCP TL072CP
 Low Power Consumption Wide Common-Mode and Differential Voltage Ranges Low Input Bias and Offset Currents Output Short-Circuit Protection Low Total Harmonic Distortion.3% Typ TL7, TL7A, TL7B, TL72 Low
Low Power Consumption Wide Common-Mode and Differential Voltage Ranges Low Input Bias and Offset Currents Output Short-Circuit Protection Low Total Harmonic Distortion.3% Typ TL7, TL7A, TL7B, TL72 Low
LM101A, LM201A, LM301A HIGH-PERFORMANCE OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 HIGH-PERFORMAE OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS D9, OCTOBER 979 REVISED SEPTEMBER 990 Low Input Currents Low Input Offset Parameters Frequency and Transient Response Characteristics Adjustable Short-Circuit Protection
HIGH-PERFORMAE OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS D9, OCTOBER 979 REVISED SEPTEMBER 990 Low Input Currents Low Input Offset Parameters Frequency and Transient Response Characteristics Adjustable Short-Circuit Protection
TL594 PULSE-WIDTH-MODULATION CONTROL CIRCUIT
 Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for 200-mA Sink or Source Current Output Control Selects Single-Ended or Push-Pull Operation Internal Circuitry Prohibits Double Pulse at Either
Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for 200-mA Sink or Source Current Output Control Selects Single-Ended or Push-Pull Operation Internal Circuitry Prohibits Double Pulse at Either
LMV331TP / LMV393TP. General Purpose, 1.8V, RRI, Open-Drain Output Comparators. Features. Description. Applications. Pin Configuration (Top View)
 Features 3PEAK LMV331TP / LMV393TP Description Down to 1.8V Supply Voltage: 1.8V to 5.5V Low Supply Current: 40 μa per Channel High-to-Low Propagation Delay: 10 ns Internal Hysteresis Ensures Clean Switching
Features 3PEAK LMV331TP / LMV393TP Description Down to 1.8V Supply Voltage: 1.8V to 5.5V Low Supply Current: 40 μa per Channel High-to-Low Propagation Delay: 10 ns Internal Hysteresis Ensures Clean Switching
ua733c, ua733m DIFFERENTIAL VIDEO AMPLIFIERS
 -MHz Bandwidth -kω Input Resistance Selectable Nominal Amplification of,, or No Frequency Compensation Required Designed to be Interchangeable With Fairchild ua7c and ua7m description The ua7 is a monolithic
-MHz Bandwidth -kω Input Resistance Selectable Nominal Amplification of,, or No Frequency Compensation Required Designed to be Interchangeable With Fairchild ua7c and ua7m description The ua7 is a monolithic
LM101A, LM201A, LM301A HIGH-PERFORMANCE OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 HIGH-PERFORMAE OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS D9, OCTOBER 99 REVISED SEPTEMBER 99 Low Input Currents Low Input Offset Parameters Frequency and Transient Response Characteristics Adjustable Short-Circuit Protection
HIGH-PERFORMAE OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS D9, OCTOBER 99 REVISED SEPTEMBER 99 Low Input Currents Low Input Offset Parameters Frequency and Transient Response Characteristics Adjustable Short-Circuit Protection
MC3486 QUADRUPLE DIFFERENTIAL LINE RECEIVER WITH 3-STATE OUTPUTS
 Meets or Exceeds the Requirements of ANSI Standards EIA/TIA-422-B and EIA/TIA-423-B and ITU Recommendations V.10 and V.11 3-State, TTL-Compatible s Fast Transition Times Operates From Single 5-V Supply
Meets or Exceeds the Requirements of ANSI Standards EIA/TIA-422-B and EIA/TIA-423-B and ITU Recommendations V.10 and V.11 3-State, TTL-Compatible s Fast Transition Times Operates From Single 5-V Supply
description/ordering information
 SCLS107E DECEMBER 1982 REVISED SEPTEMBER 2003 Targeted Specifically for High-Speed Memory Decoders and Data-Transmission Systems Wide Operating Voltage Range of 2 V to 6 V Outputs Can Drive Up To 10 LSTTL
SCLS107E DECEMBER 1982 REVISED SEPTEMBER 2003 Targeted Specifically for High-Speed Memory Decoders and Data-Transmission Systems Wide Operating Voltage Range of 2 V to 6 V Outputs Can Drive Up To 10 LSTTL
GENERAL-PURPOSE OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 查询 UA71 供应商 捷多邦, 专业 PCB 打样工厂, 小时加急出货 µa71, µa71y Short-Circuit Protection Offset-Voltage Null Capability Large Common-Mode and Differential Voltage Ranges No Frequency Compensation Required Low Power Consumption
查询 UA71 供应商 捷多邦, 专业 PCB 打样工厂, 小时加急出货 µa71, µa71y Short-Circuit Protection Offset-Voltage Null Capability Large Common-Mode and Differential Voltage Ranges No Frequency Compensation Required Low Power Consumption
TL5001, TL5001A PULSE-WIDTH-MODULATION CONTROL CIRCUITS
 Complete PWM Power Control 3.6-V to 4-V Operation Internal Undervoltage-Lockout Circuit Internal Short-Circuit Protection Oscillator Frequency... 2 khz to 5 khz Variable Dead Time Provides Control Over
Complete PWM Power Control 3.6-V to 4-V Operation Internal Undervoltage-Lockout Circuit Internal Short-Circuit Protection Oscillator Frequency... 2 khz to 5 khz Variable Dead Time Provides Control Over
description/ordering information
 Low Power Consumption Wide Common-Mode and Differential Voltage Ranges Low Input Bias and Offset Currents Output Short-Circuit Protection Low Total Harmonic Distortion....3% Typ SLOS8G FEBRUARY 977 REVISED
Low Power Consumption Wide Common-Mode and Differential Voltage Ranges Low Input Bias and Offset Currents Output Short-Circuit Protection Low Total Harmonic Distortion....3% Typ SLOS8G FEBRUARY 977 REVISED
CDC337 CLOCK DRIVER WITH 3-STATE OUTPUTS
 Low Output Skew, Low Pulse Skew for Clock-Distribution and Clock-Generation Applications TTL-Compatible Inputs and CMOS-Compatible Outputs Distributes One Clock Input to Eight Outputs Four Same-Frequency
Low Output Skew, Low Pulse Skew for Clock-Distribution and Clock-Generation Applications TTL-Compatible Inputs and CMOS-Compatible Outputs Distributes One Clock Input to Eight Outputs Four Same-Frequency
LM124, LM124A, LM224, LM224A LM324, LM324A, LM2902 QUADRUPLE OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
 Wide Range of Supply Voltages: Single Supply...3 V to 30 V (LM2902 3 V to 26 V) or Dual Supplies Low Supply Drain Independent of Supply Voltage... 0.8 Typ Common-Mode Input Voltage Range Includes Ground
Wide Range of Supply Voltages: Single Supply...3 V to 30 V (LM2902 3 V to 26 V) or Dual Supplies Low Supply Drain Independent of Supply Voltage... 0.8 Typ Common-Mode Input Voltage Range Includes Ground
SN75C1406 TRIPLE LOW-POWER DRIVERS/RECEIVERS
 Meet or Exceed the Requirements of TIA/EIA-232-F and ITU Recommendation V.28 Very Low Power Consumption... 5 mw Typ Wide Driver Supply Voltage Range... ±4.5 V to ±15 V Driver Output Slew Rate Limited to
Meet or Exceed the Requirements of TIA/EIA-232-F and ITU Recommendation V.28 Very Low Power Consumption... 5 mw Typ Wide Driver Supply Voltage Range... ±4.5 V to ±15 V Driver Output Slew Rate Limited to
15 DEVICES COVER COMMERCIAL, INDUSTRIAL, AND MILITARY TEMPERATURE RANGES AVAILABLE OPTIONS CERAMIC DIP (J) CERAMIC DIP (JG)
 TL7, TL7A, TL7B, TL72 SLOS8D SEPTERMBER 978 REVISED AUGUST 996 Low Power Consumption Wide Common-Mode and Differential Voltage Ranges Low Input Bias and Offset Currents Output Short-Circuit Protection
TL7, TL7A, TL7B, TL72 SLOS8D SEPTERMBER 978 REVISED AUGUST 996 Low Power Consumption Wide Common-Mode and Differential Voltage Ranges Low Input Bias and Offset Currents Output Short-Circuit Protection
TC4421/TC A High-Speed MOSFET Drivers. General Description. Features. Applications. Package Types (1)
 9A High-Speed MOSFET Drivers Features High Peak Output Current: 9A Wide Input Supply Voltage Operating Range: - 4.5V to 18V High Continuous Output Current: 2A Max Fast Rise and Fall Times: - 3 ns with
9A High-Speed MOSFET Drivers Features High Peak Output Current: 9A Wide Input Supply Voltage Operating Range: - 4.5V to 18V High Continuous Output Current: 2A Max Fast Rise and Fall Times: - 3 ns with
