LSM 5 EXCITER Laser Scanning Microscope
|
|
|
- Octavia Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Microscopy from Carl Zeiss LSM 5 EXCITER Laser Scanning Microscope Tracking of Cellular Processes We make it visible.
2 The LSM 5 EXCITER from Carl Zeiss is a confocal laser scanning microscope for fundamental research in medicine and biology. Equipped with optimized, user-friendly hardware and software, this system delivers excellent confocal images and image stacks, especially in fluorescence applications. It is optimally designed for the acquisition of time series for the analysis of molecule mobilities by bleaching or photoconversion. Cultured rat ovary cells. ß-Actin labelled with Alexa Phalloidin (green), Mitochondria with Mitotracker - red (red), Nucleus with DAPI (blue).
3 Contents Confocality 4 Components 6 Configurations 8 MultiTracking 10 Colocalization 12 3D Image Stacks 14 FRAP 16 Photoconversion 17 FRET 18 Physiology 20 Visualization 22 Archiving 23 Specification 24 System Overview 26 Glossary 29
4 2
5 Efficient Navigation With the new software ZEN we have made it possible to concentrate completely on the essentials. Discover a new era in laser scanning microscopy. 3
6 Experience Confocality Fascinating Contrast The LSM 5 EXCITER is a confocal microscope system that scans a specimen with laser light, point by point and line by line, in order to acquire an optical section. Many optical sections collected from different Z planes form a 3D image stack. Confocal image stacks acquired with fluorescent light provide information on selectively labelled functional regions of cells, tissues and organisms. Confocal... The special advantage of confocal laser scanning microscopy results from the use of a pinhole diaphragm located conjugate to the focal plane. The pinhole only admits light coming from the focal plane, while emissions from planes above or below it are rejected.... laser... Intensity (I) Excitation Emission A fluorochrome can be excited by different wavelengths within its excitation spectrum. Light is then emitted with a characteristic emission spectra. The emission intensity is a function of the radiation intensity and excitation efficiency of the light. For the LSM 5 EXCITER, lasers with several lines ranging from 405 to 633 nm are available for excitation. The lasers are coupled to the scanning module reliably and efficiently via separate optical fibers. Laser intensities can be adjusted with a software-controlled acousto-optical tunable filter (AOTF).... scanning I 0 Wavelength (λ) Detector Point-by-point and line-by-line scanning of the specimen with a focused laser beam produces twodimensional images free from scattered light. Scanning at different levels as the laser focus is shifted along the Z axis generates a series of optical sections (slices), which can then be combined into a three-dimensional image stack. I Dichroic beamsplitter I Detector In case of a multiple-stained specimen, the various emission signals are separated by highquality dichroic filters, which can be selected and changed to suit the application. 1 Fiber (from laser source) 2 Collimator 3 Main dichroic beamsplitter* 4 Objective* 5 Specimen 6 Pinhole 7 Emission filter* 8 Detector 9 Scanning mirror 10 Scanning optics 11 Focal plane *user-exchangeable components 4
7 xy
8 Components Matched for Efficient Operation A Perfect Team Carl Zeiss configures every LSM 5 EXCITER to suit the user s scope of applications. For that purpose, a great number of well-matched, high-quality system components are available. The heart of the system The scanning module includes collimators, the scanner, and a freely positionable and adjustable pinhole. Detection is by highly sensitive photomultipliers. Advanced scanning control allows the precise positioning of the two scanning mirrors, and continuous laser attenuation to permit the user to apply many different scanning strategies. Fluorescence signals can for example, be detected along a straight line or a freely defined curve, or at a diffraction-limited spot. Pixel resolutions of confocal images can be freely selected between 4 x 1 and 2,048 x 2,048 pixels. The two independent scanning mirrors allow the scanning field to be rotated to any angle between 0 and 360. The scanning speed can be precisely varied in 26 steps, with line frequencies ranging from 4 to 2,600 Hz. LSM 5 EXCITER with Axio Observer, Axioskop 2 FS MOT and Axio Imager 6
9 C-Apochromats: Optimized for confocal microscopy. The intelligent control center The electronics module houses the main component of scanner control and image acquisition. A trigger interface allows synchronization of external devices (TriggerOut), e.g., a micromanipulator, as well as remote-controlled triggering of confocal image acquisition (TriggerIn) by external devices such as a breath sensor. EC Plan-Neofluars: High contrast for general use. The stable basis Depending on the user s application, several high-end research microscopes are available as platforms for the LSM 5 EXCITER system: Axio Imager, Axio Observer and Axioskop 2 FS MOT. All of them are equipped with IC 2 S optics, which guarantee unrivalled image quality, brilliant contrast, and perfect color correction. The LSM software automatically detects all objectives in use, reproduces saved microscope settings at the touch of a button, and accurately controls the system s image acquisition process. Plan-Apochromats and Fluars: High-aperture photon collectors. The keen eyes High-grade objectives from Carl Zeiss allow you to set just the right combination of resolving power, speed, working distance, the refractive index of the immersion liquid, etc., as required for your application. C-Apochromat objectives provide the ultimate in confocal microscopy: diffraction-limited resolution and perfect chromatic correction from the UV to the NIR range. The flare-reduced EC Plan-Neofluar objectives deliver enhanced contrast, and the slender LCI Objectives provide extra space for convenient manipulation and temperature control of live cell specimens. Achroplans: Water-immersed objectives for electrophysiological specimens. LCI Plan-Neofluars: With temperature compensation for living specimens. 7
10 Configuration with just a Mouse Click Proper Settings The success of a microscopic experiment is a matter of correct settings. All parameters of the fully motordriven LSM 5 EXCITER can be selected quickly and correctly, via its intuitive software ZEN. The parameters of the experiment from laser setting to image acquisition can be precisely restored whenever they are needed again. So rather than having to care too much about the microscope, you can fully concentrate on your research. (2+1) detection channels up to 4 dyes simoultaneously! In the LSM 5 EXCITER, one or two channels are available for fluorescence and reflection measurements, each featuring a highly sensitive, low-noise photomultiplier. XY adjustment of the pinhole is effected through a software-controlled motor; the pinhole diameter can be controlled continuously, as can the intensity of the laser. In some experiments it is helpful to superimpose transmitted-light and fluorescence images to get the whole picture. Especially with differential interference contrast (DIC), the optional transmitted-light channel supplies important information about the topology of your specimen. New double-bandpass emission filters allow the detection of up to 4 dyes using fast simultaneous imaging. Cultured cells. Fluorescence image superimposed with differential interference contrast in the transmitted-light channel. HeLa cells, mitochondria labeled with DsRed. Specimen: Prof. S. Yamamoto, Hamamatsu Medical University, Japan Clear and easy to use: The software of the LSM 5 EXCITER. 8
11 Complex functionality under control Use the Light Path tool to select the main and secondary dichroic beamsplitters and emission filters in the confocal beam path, and to optimize the detection parameters. Alternatively, the system falls back on settings made in earlier experiments: the triedand-approved ReUse function not only speeds up procedures in the lab but also exactly reproduces experimental conditions. Use the Aquisition Mode tool to define all scanning parameters, such as frame size (up to 2,048 x 2,048 pixels), scanning speed, data resolution, and scanning direction (uni- or bidirectional). Use the Find function to have the system find the optimum contrast and brightness settings within seconds of clicking the mouse. The Crop function allows a new scanning area to be selected and rotated with speed and ease. Cultured ovary cells: ß-actin labeled with Alexa phalloidin (green), mitochondria with Mitotracker (red), Nucleus with DAPI (blue). The images can be displayed individually or superimposed. Cell division of HEp-2 cells. Microtubules labeled with rhodamine (red), centromeres with FITC (green), PML nuclear bodies with Alexa 633 (blue). Specimen: S. Weidtkamp-Peters, Fritz-Lipmann-Institute Jena, Germany 9
12 Sequential Imaging for Clear Signal Separation No Crosstalk Sequential Imaging is an elegant and reliable solution which efficiently prevents interchannel crosstalk between several fluorochromes. Colocalization studies, in particular, benefit from the increase in reliability gained from Sequential Imaging. Unique capabilities The LSM 5 EXCITER allows the user to optimize excitation parameters and detection settings for a single dye signal, and to define and save it as a track. A list of such tracks for independently optimized dye signals can then be run automatically as an Experiment in Channel Mode. Unblanking and blanking of the laser lines between the tracks is accomplished by acoustooptical devices. Up to eight fluorescent signals can thus be imaged sequentially in a single run, section by section or line by line. Due to the selective excitation and detection of the dyes, signal crosstalk is reliably prevented. Isolated salivary gland of a cockroach. Cell nuclei are labeled with DAPI (blue), Na + /K + ATPase with Cy2 (green), and F-actin with Alexa 568 phalloidin (red). Specimen: Dr. D. Malun, Free University of Berlin, Germany The simultaneous recording of either DAPI and Cy2, or Cy2 and Alexa 568 shows strong bleedthrough of the DAPI signal into the Cy2 channel (middle), or of the Cy2 signal into the Alexa 568 channel (right). The same specimen recorded by Sequential Imaging (with the same laser intensity). The channels are clearly separated. Sequential Imaging is as easy as pie: Select the laser lines, main dichroic beamsplitters and emission filters for each channel in the Light Path tool. Once compiled, a list of tracks can be saved and activated later whenever needed. 10
13 Increased efficiency Sequential Imaging is a distinct benefit especially when signals are very faint. Here, you can now use longpass emission filters to obtain the entire emission spectrum of the dyes. The pinhole diameter can be set individually for each track to help balance the signal intensity for the respective dye type or dye concentration. This allows either optimum balance between greatly differing dye intensities, or to perfectly match the optical slice thicknesses in critical colocalization studies. Superposition of the images obtained from three channels clearly illustrates the difference: Simultaneous recording results in massive signal crosstalk, which wrongly suggests a colocalization (shown in orange and turquoise). With Sequential Imaging, the signals from the various channels are clearly separated, and optimum signal yield is guaranteed. The Imaging Setup Tool displays the detection bands and the selected laser lines for a clear overview of the experiment. Example of a configuration for detecting DAPI (blue), GFP (green) and Alexa 568 (red). 11
14 3D Colocalization Quantified Perfect Coincidence With the LSM 5 EXCITER, quantitative colocalization analyses can be made with unprecedented reliability and precision. Image presentation, scatter plot and data table are interactively linked to the region-ofinterest (ROI) and thresholding tools. The colocalization of labeled cell structures is often considered a first indicator of a potential functional interaction. Through Sequential Imaging with the LSM 5 EXCITER, genuine colocalization can readily be distinguished from emission channel crosstalk. Therefore, a region of interest can be selected immediately in the scatter plot, whereupon the system immediately indicates the occurrence of these colocalized fluorophores in the image. In the same way, the data table is interlinked with the scatter plot and the image. There is no more intuitive and precise way of analyzing your data. Visualization and analysis of colocalization experiments Interactive linking of images, scatter plots and data tables Interactive or automatic threshold determination Results of the colocalization analysis superimposed on image channels Quantitative colocalization analysis for up to 99 ROIs, including area and mean gray level intensity degree of colocalization coefficient of colocalization Pearson s correlation coefficient Manders overlap coefficient Export of analysis results Artery of a rat's lung. Endothelin B labeled with Alexa 555 (red), α-actin (SMA) with Alexa 647 (blue), autofluorescent elastic fibers (green). Specimen: L. Villeneuve, Heart Montreal Institute Research Center, Montreal, Quebec, Canada 12
15 First-rate tools properly applied: Image presentation, scatter plots and data table are interactively linked with the ROI and thresholding tools. Analysis of the colocalized area in a double tagged HEK 293 cell (green GFP, red YFP). Coloc view with scattergram and quantitative parameters. Presentation of single-tagged (red and green) and colocalized image areas (white). Extracted colocalized areas, according to regions 1, 2 and 3 in the scattergram. 13
16 Analyzing 3D Image Stacks to µm Accuracy Governed Space Confocal microscopy is distinguished from conventional microscopy mainly by its capability to precisely analyze a specimen in three dimensions. From 3D image stacks, the researcher can gain new insights into the complex structures and interrelations on the cellular level. The LSM 5 EXCITER can turn such image stacks into projections of infinite depth of field, even from thick tissue sections. Slice by slice Thanks to the use of the confocal pinhole, which only admits light from the focal plane while rejecting emission from planes lying above or below it, the system produces a confocal optical section, which is free from out-of-focus scattered light. The thickness of the slice depends on the pinhole diameter and the wavelength of the laser light. Digitally stacked one above the other, many of such sections made at equidistant intervals along the Z axis assemble into a 3D representation of quasi-infinite depth of field. This stack of images is the basis for an analysis of the specimen s spatial structure. Guard cells, transfected with AtVAM3-GFP (green), and autofluorescence in chloroplasts (red). The gallery view of the image stack shows the in-focus information in different Z positions. Specimen: Dr. M. Sato, Kyoto University, Japan Indication of optical slice thicknesses (intervals) for various wavelengths. All relevant parameters are automatically used to calculate the resultant slice thickness, displayed as a graph, and equalized at the click of a button. 14
17 Rendering the section planes Using the LSM 5 EXCITER, you can generate virtual optical sections of any orientation inside the image stack. These virtual sections show you the spatial arrangements inside the specimen, even with structures that are only faintly fluorescent. Integrated measurement functions furnish geometric measurements such as length, angles, circumference or area, as well as densitometric parameters. The Profile function measures signal intensities along freely defined curves. The gray level data are presented in a clearly arranged table. Orthogonal presentation of a stack of 15 images. Simultaneous view of XY, XZ and YZ planes. Intensity measurement of the various channels along a freely defined curve by means of the Profile function. The Cut function allows virtual section planes of any orientation to be visualized. 15
18 FRAP Dynamic Processes Observed with Single-Pixel Accuracy Using acousto-optical attenuation (AOTF) of the laser beam, and the FRAP tool of the LSM software, you can conveniently study the distribution dynamics of biomolecules. The LSM 5 EXCITER delivers quantitative results within a few minutes. In addition to the mere imaging of cellular structures, it is also possible to irreversibly quench the fluorescence of many dyes or fusion proteins from defined regions. Non-bleached dye molecules from the surrounding regions will diffuse into this bleached region, therefore causing a signal increase within the bleached region. Fast, precise light flashes The AOTF technology allows the laser output to be maximized within microseconds to efficiently bleach a region defined with single-pixel accuracy. Therefore, the LSM 5 EXCITER is capable of running many photobleaching techniques such as FRAP (Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching) or FLIP (Fluorescence Loss In Photobleaching), which have become established as standard experiments in biomedical analysis. The FRAP tool The LSM 5 EXCITER readily supports other designs of bleaching experiments as well. Various kinetic models (single- and bi-exponential fits) are provided for the reliable determination of regeneration times and mobile or immobile molecule fractions all with simple menu prompts. FRAP In a FRAP experiment, a defined region in a cell expressing, e.g., a GFP fusion protein is bleached by brief but intense laser irradiation. The recovery of fluorescence is documented by time-lapse images and measured. FLIP In a FLIP experiment, the same region within a cell is bleached repeatedly, and the loss in fluorescence outside that region is measured. 16
19 The Use of Photoconvertible Fluorescent Proteins Telling Changes The fluorescence of organelles or tissue cells expressing PA-GFP, Kaede or Dronpa can be selectively activated, deactivated or spectrally changed by local irradiation with violet light. With the proper light, the LSM 5 EXCITER visualizes your photoactivable proteins by fluorescence. Single-molecule activation Compared to bleaching experiments, photoactivation has the advantage that individual molecules can be activated selectively and their movements analyzed directly. With fast AOTF laser switching and the 405 nm laser diode of the LSM 5 EXCITER, you have everything you need to directly follow the journey of a protein inside a living cell. Tracking the green-to-red ratio The Time Series functionality and the unmixing of spectrally overlapping emission signals allow you to observe the changing ratio of photoconverted (red) to non-converted (green) Kaede. Labeled molecules taking part in transport processes in cells can thus be precisely identified and localized at any time. The blinker protein The photoswitchable protein Dronpa can be turned on with a dose of 405 nm light, and turned off again with 488 nm, repeatedly. Using the Visual Macro Editor of the LSM software, you can thus repeat experiments with the same cell several times. This facilitates optimization of the ambient conditions (including stimulants), and it increases the certainty of your assessment of the result. PA-GFP + Dronpa Dronpa is a fluorescent protein which can be optically stimulated to switch between a fluorescent and a non-fluorescent state. PA-GFP Dronpa Kaede is a fluorescent protein which changes from green to red color when irradiated with ultraviolet light. 17
20 FRET Visualize Molecular Interactions FRET (Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer) is a radiationless energy transfer between two fluorophores located close to each other. Its intensity change can be harnessed for the investigation of intramolecular protein-protein interactions, enzyme activities, ion concentrations, and interactions between messenger substances in cells. FRET-sensitive emission Regions of arbitrary shape can be selected precisely thanks to fast, pixel-accurate switching of the laser intensity by the AOTF. With the linewise or framewise Sequential Imaging capability of the LSM 5 EXCITER, donor, acceptor and FRET signal portions and their overlaps can be clearly identified. Proper excitation The intensive bleaching program With its wide range of suitable laser lines, dichroic beamsplitters and emission filters, the LSM 5 EXCITER is optimally suited to excite selected dye combinations known as FRET fluorophore pairs such as CFP/YFP, GFP/mRFP or GFP/Rhodamine. Alternatively, the FRET effect can be detected elegantly and quickly by the bleaching of the acceptor fluorophore. An increase in donor intensity in a Region of Interest (ROI) immediately after bleaching can be unambiguously proven by means of the Time Series function of the LSM 5 EXCITER. Example beam path configuration for the simultaneous acquisition of CFP and YFP for FRET studies. Continuous variation of laser intensities with AOTF. One or two ratio channels can be defined in addition and the result displayed during the measurement. 18
21 With the Visual Macro Editor of the LSM 5 EXCITER complete experiments for unmistakable detection of the FRET signal can be configured in a convenient and reproducible way. If needed, also in combination with Sequential Imaging. A number of bio-sensors have been designed recently that permit ion concentrations to be changed via a variation of FRET intensity. One of these bio-sensors used to detect changes in intracellular calcium concentration is Yellow Cameleon 2. Time series of the CFP and YFP fluorescences of Yellow Cameleon 2 (in hepatocytes) after stimulation with ATP and ionomycin. Specimen: Prof. T. Kawanishi, National Institute of Health Science, Tokyo, Japan Intensity (I) The intensities of the CFP and YFP fluorescences and the YFP/CFP signal ratio in the ROI marked above. ATP Ionomycin Ratio YFP CFP Time (s) Spectral configuration for FRET on the LSM 5 EXCITER using CFP/YFP 19
22 Close Monitoring of Physiological Processes Fast Action Physiological experiments are another field in which the LSM 5 EXCITER can show its strengths. Its image acquisition and processing functions are ideally suited to the investigation of fast processes in live cells and tissues. Capture processes with correct timing Whether you study a fast process or a long-time change: the LSM 5 EXCITER covers a wide range of biologically relevant time intervals between 0.1 ms and 10 hours. Highly frequent, linear scanner movements ensure reliable image data. All parameters can be optimized on-line during image acquisition. Release pulses on time Outgoing trigger signals provide precise control of external equipment, e.g., microinjectors. Incoming trigger signals can be used, e.g., for synchronization with electrophysiological experiments in order to start confocal image acquisition. Intensity (I) Ratio Selection of Regions of Interest (ROIs) within a specimen. ROI1: Cytosol ROI2: Cell membrane Time (min) Time (min) Individual intensities (left), and the ratio of intensities (right) of the two ROIs boxed in the picture (far left). Colors are assigned accordingly. 20
23 Results available at any time With freely defined regions of interest (ROIs) you can investigate precisely those structures of a specimen you are looking for. During image acquisition, either the series of images or the intensity curves inside the ROIs or both can be displayed. In ratiometric measurements, rather than waiting until the end of the time series, you can keep track of the results in a separate channel in real time. Dialog window for the interactive calibration of ion-sensitive dyes. On-line ratio calculations allow the data to be presented live during image acquisition. The system utilizes preset calculation formulas with user-defined parameters. Various calibration routines and display modes are available for calibrating fluorophores to be used in concentration analysis. Equipped with these process features, the LSM 5 EXCITER can do justice to any fluorescent dye. Vary experimental setups from time to time The optional Visual Macro Editor can be used to create complex time series experiments. This allows you to automatically switch between complete configurations, e.g., capture of an XY image in one configuration (GFP), and recording of a Z stack in another. Investigation of protein movements Time series experiment in HeLa cells transfected with PKC-GFP. Stimulation of the cells with PMA at the time t =1 min causes redistribution of PKC from the cytosol to the cell membrane. Specimen: Dr. S. Yamamoto, Hamamatsu Medical University, Japan 21
24 Fast Visualization and Archiving Spectacular Views Lucid presentation The optional Image VisArt plus software package provides a broad range of functions for 3D and 4D visualizations of image stacks and time series, e.g., as shadow and/or transparency projection in combination with up to three different cutting planes. Image VisArt plus not only delivers added information but also helps you to present and publish your findings in the most perfect way. Thanks to fast algorithms, such visualizations are generated at an amazing speed. Handling this tool is extremely easy: To create an animation, simply specify the desired viewing angles. The system then automatically computes a virtual camera flight around, into or through the specimen. 3D reconstruction of a Daphnia. On the 3 Clipping Planes, the fluorescence signals are displayed in false colors. 22
25 Convenient management Transparency and lucidity were prime concerns in the development of an archiving system for the LSM. The ZEN File Browser not only saves all settings (laser lines, pinhole sizes, scanning mode, objective, etc.) but allows them to be retrieved and reproduced with a mouse click, thanks to the approved ReUse function. To integrate the documents into other programs, the system offers many export formats. The same applies to measured data and tables. As a genuine multiuser system, the LSM 5 EXCITER allows every user to save configurations in their preferred way. This way, the system is optimized to match the special application of every investigator in its user team. The ZEN File Browser in Gallery-View. Each image represents the entire acquisition method. 3 different views (Table-View, Gallery-View and Form-View) make image browsing easy and fast. 23
26 Specification LSM 5 EXCITER Microscopes Models Z drive XY stage (option) Accessories Upright: Axio Imager.Z1, M1, Axioskop 2 FS MOT; Inverted: Axio Observer.Z1 BP (BasePort) or SP (SidePort) Upright: Stepper motor, smallest increment 25 nm or 50 nm Inverted: DC motor with optoelectronic coding; smallest increment 25 nm Motorized XY scanning stage with Mark & Find (XYZ) and Tile Scan (mosaic scan) functions; smallest increment approx. 1 μm High-resolution digital AxioCam microscope camera; incubation chambers, micromanipulators, etc. Scanning module Scanner Scanning resolution 2 independent galvanometric scanning mirrors for rotation, zoom, offset 4 x1 to 2048x2048 pixels, user-definable Scanning speed Standard mode: scalable imaging of up to 4 dyes, e.g fps with 1024x768 pixels Fast mode: scalable imaging of up to 2 dyes, e.g. 27 fps with 512x96 pixels, 5 fps with 512x512 pixels Step mode: scalable imaging of up to 2 dyes, e.g. 154 fps with 512x32 (binned) pixels Line scan mode: scalable in 13 speeds from 4 to 2600 lines/s with 512x1 pixels Scanning zoom 0.5x to 30x, variable in steps of 0.1 Scanning rotation Free rotation through 360, variable in steps of 1 Scanning field Field diagonal 18 mm (max.) in the intermediate image plane, homogeneous field illumination Pinhole 1 confocal pinhole, continuously variable diameter, preadjusted Detection 1 or 2 confocal channels (R/FL), 1 optional external transmitted-light channel (DIC-capable); each channel equipped with high-sensitivity PMT detectors Data depth Selectable between 8 and 12 bit Laser Modules Lasers Fiber optics Attenuation Ar laser (458, 488, 514 nm) 25 mw; HeNe laser (543 nm) 1 mw; HeNe laser (633 nm) 5 mw; diode laser (405 nm) 25 mw (specification valid to the end of life time) Polarization-preserving single-mode fibers Individual and variable intensity setting of all laser lines by means of AOTF Electronics Module LSM 5 Control Computer Controls the microscope, the laser modules, the scanning module and other accessories. Controls and synchronizes data acquisition through real-time electronics; data exchange with user PC through Gigabit Ethernet Interface High-end PC with ample RAM and hard disk storage capacity; with ergonomic high-resolution TFT flat panel display, Windows XP operating system with multi-user capability Image Browser Free software package for the display, editing, sorting, printing and export/import of LSM 5 images 24
27 Standard Software System configuration ReUse function Acquisition modes Crop function ROI scan Spline scan Sequential Imaging Image processing Convenient control and configuration of all motor-driven microscope functions, the laser modules and the scanning module; saving and retrieval of application-specific configurations Restoration of acquisition parameters with just a single mouse click Spot, line/spline, frame, Z stack, time series and combinations: xy, xyz, xyt, xyzt, xz, xt, xzt, spot-t. On-line computation and presentation of ratio images; averaging and summation (linewise or framewise, configurable); Step Scan (for higher frame rates, configurable) Convenient selection of scanning ranges (simultaneous zoom, offset and rotation) Scanning of up to 99 regions of interest (ROIs) of any shape, and blanking of the lasers by means of AOTF Scanning along a freehand defined line Signal crosstalk in multifluorescence acquisition minimized by fast change between excitation lines Image processing options for any kind of mathematical procedures, such as crosstalk correction by selective channel subtraction Visualization Orthogonal view (xy, xz, yz in one view), cut view (3D section made under a freely definable spatial angle), 2.5D view for time series of line scans, projections (stereo, maximum, transparent) for single frames and series (animations), depth coding (pseudo-color presentation of height information), brightness and contrast variation, off-line interpolation for Z stacks, selection and modification of color lookup tables (LUTs), drawing functions for documentation Analysis, measurement Advanced tools for colocalization and scatter plot analysis with individual parameters and options, profile measurement on straight lines and curves of any shape, measurement of lengths, angles, areas, intensities, and many other capabilities Image operations Data archiving, export, import Addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, ratioing, shift, filters (low pass, median, high pass, etc., or user-definable) LSM image database with comfortable functions for managing images together with the associated acquisition parameters; Multiprint function for creating assembled image-plus-data views; more than 20 file formats (TIF, BMP, JPG, PSD, PCX, GIF, AVI, Quicktime,...) for compatibility with all common image processing programs Software Options Physiology FRAP FRET Comprehensive software for the analysis of time series, graphic mean-of-roi analyses, on-line and off-line calibration of ion concentrations Menu prompting for recording FRAP experiments (Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching) Acquisition of FRET image data (Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer) with subsequent analysis and computation of FRET efficiency. Methods supported: Acceptor Photobleaching and Sensitized Emission Visual Macro Editor Creation and editing of macros using representative icons for programming routine procedures LSM Image VisArt plus Fast 3D and 4D reconstruction and animation (shadow and transparency projection, surface and mixed rendering modes, cutting planes, fly-through mode, distance measurement in 3D) Multiple Time Series Topography Package Stitch Art plus 3D Deconvolution 3D for LSM Complex time series with varied application-specific configurations Visualization of 3D surfaces (fast rendering modes), plus many measurement functions (roughness, surface areas, volumes) MXZ and MXYZ stitching software for reflection (motor-driven XY scanning stage required) Image restoration based on computed point spread functions (modes: nearest neighbor, maximum likelihood, constraint iterative) 3D presentation and 3D measurement of volume data records 25
28 26 System Overview LSM 5 EXCITER
29
30 28
31 Functions of the LSM 5 EXCITER from Carl Zeiss Glossary Sequential Imaging Scanning mode in the LSM, generates multifluorescence images without crosstalk of emission signals by means of fast switching between excitation and detection. Spline Scan Scanning along a freehand-defined line for capturing fast (physiological) processes, e.g., along neuronal appendices. Spot Scan Scanning mode in which the signal intensity in a confocal spot can be monitored with extremely high time resolution. Step Scan Fast overview scan, in which intermediate lines are supplemented by interpolation. Tile Scan Acquisition of a mosaic of partial images of a large object, to improve resolution. AOTF CFP DDS DSP EC FP FLIP FRAP FRET GFP IC 2 S LCI NIR PA ROI YFP Acousto-Optical Tunable Filter Cyan Fluorescent Protein Dual Direction Scan Digital Signal Processor Enhanced Contrast Fluorescent Protein Fluorescence Loss in Photobleaching Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching Fluorescence (or Förster) Resonance Energy Transfer Green Fluorescent Protein Infinity Contrast and Color Corrected System Live Cell Imaging Near InfraRed PhotoActivation Region of Interest Yellow Fluorescent Protein US Patents: , , , , German Patents: C2, T2 29
32 Reliable service is part of our tradition To ensure smooth operation of your LSM 510 EXCITER, we offer you the following services: Our competent regional consultants and technicians will provide technical support to assist you in your research. After every system installation your LSM users are given comprehensive training. Carl Zeiss also offers training courses and workshops, which provide in-depth know-how about practical topics and applications in laser scanning microscopy. For further information, please contact: Carl Zeiss MicroImaging GmbH Jena, Germany Phone: Fax: Subject to change. Printed on environment-friendly paper, bleached without the use of chlorine e/08.07
Multifluorescence The Crosstalk Problem and Its Solution
 Multifluorescence The Crosstalk Problem and Its Solution If a specimen is labeled with more than one fluorochrome, each image channel should only show the emission signal of one of them. If, in a specimen
Multifluorescence The Crosstalk Problem and Its Solution If a specimen is labeled with more than one fluorochrome, each image channel should only show the emission signal of one of them. If, in a specimen
LSM 510 META in Chang Gung University
 Content LSM 510 META in Chang ung University LSM 510 META 路 理 The features and applications of LSM 510 META 01-09 Introduction of the hardware 10-12 Fluorescence observation in conventional microscope
Content LSM 510 META in Chang ung University LSM 510 META 路 理 The features and applications of LSM 510 META 01-09 Introduction of the hardware 10-12 Fluorescence observation in conventional microscope
Zeiss 780 Training Notes
 Zeiss 780 Training Notes Turn on Main Switch, System PC and Components Switches 780 Start up sequence Do you need the argon laser (458, 488, 514 nm lines)? Yes Turn on the laser s main power switch and
Zeiss 780 Training Notes Turn on Main Switch, System PC and Components Switches 780 Start up sequence Do you need the argon laser (458, 488, 514 nm lines)? Yes Turn on the laser s main power switch and
Microscopy from Carl Zeiss LSM 700. Laser Scanning Microscope. High-End for All Uncompromised Quality and Operating Convenience
 Microscopy from Carl Zeiss LSM 700 Laser Scanning Microscope High-End for All Uncompromised Quality and Operating Convenience 2 3 The New LSM 700 from Carl Zeiss From a specialists system to the high-end
Microscopy from Carl Zeiss LSM 700 Laser Scanning Microscope High-End for All Uncompromised Quality and Operating Convenience 2 3 The New LSM 700 from Carl Zeiss From a specialists system to the high-end
ADVANCED METHODS FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY II. Jean-Yves Chatton Sept. 2006
 ADVANCED METHODS FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY II Jean-Yves Chatton Sept. 2006 Workshop outline Confocal microscopy of living cells and tissues X-Z scanning Time series Bleach: FRAP, photoactivation Emission
ADVANCED METHODS FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY II Jean-Yves Chatton Sept. 2006 Workshop outline Confocal microscopy of living cells and tissues X-Z scanning Time series Bleach: FRAP, photoactivation Emission
Zeiss 880 Training Notes Zen 2.3
 Zeiss 880 Training Notes Zen 2.3 1 Turn on the HXP 120V Lamp 2 Turn on Main Power Switch Turn on the Systems PC Switch Turn on the Components Switch. 3 4 5 Turn on the PC and log into your account. Start
Zeiss 880 Training Notes Zen 2.3 1 Turn on the HXP 120V Lamp 2 Turn on Main Power Switch Turn on the Systems PC Switch Turn on the Components Switch. 3 4 5 Turn on the PC and log into your account. Start
Quick Guide. LSM 5 MP, LSM 510 and LSM 510 META. Laser Scanning Microscopes. We make it visible. M i c r o s c o p y f r o m C a r l Z e i s s
 LSM 5 MP, LSM 510 and LSM 510 META M i c r o s c o p y f r o m C a r l Z e i s s Quick Guide Laser Scanning Microscopes LSM Software ZEN 2007 August 2007 We make it visible. Contents Page Contents... 1
LSM 5 MP, LSM 510 and LSM 510 META M i c r o s c o p y f r o m C a r l Z e i s s Quick Guide Laser Scanning Microscopes LSM Software ZEN 2007 August 2007 We make it visible. Contents Page Contents... 1
長庚大學共軛焦顯微鏡課程 長庚大學共軛焦顯微鏡課程. Spot light 長庚大學
 長庚大學共軛焦顯微鏡課程 Spot light 長庚大學共軛焦顯微鏡課程 20071030 長庚大學 Basic principle of Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy The application of LSM 510 META detector Multiphoton microscopy basic principle and introduction
長庚大學共軛焦顯微鏡課程 Spot light 長庚大學共軛焦顯微鏡課程 20071030 長庚大學 Basic principle of Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy The application of LSM 510 META detector Multiphoton microscopy basic principle and introduction
Microscopy from Carl Zeiss
 Microscopy from Carl Zeiss Contents Page Contents... 1 Introduction... 1 Starting the System... 2 Introduction to ZEN Efficient Navigation... 5 Setting up the microscope... 10 Configuring the beam path
Microscopy from Carl Zeiss Contents Page Contents... 1 Introduction... 1 Starting the System... 2 Introduction to ZEN Efficient Navigation... 5 Setting up the microscope... 10 Configuring the beam path
Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev. Microscopy course, Michmoret Dec 2005
 Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Why use confocal microscopy? Principles of the laser scanning confocal microscope. Image resolution. Manipulating the
Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Why use confocal microscopy? Principles of the laser scanning confocal microscope. Image resolution. Manipulating the
Confocal Microscopy. Kristin Jensen
 Confocal Microscopy Kristin Jensen 17.11.05 References Cell Biological Applications of Confocal Microscopy, Brian Matsumoto, chapter 1 Studying protein dynamics in living cells,, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz
Confocal Microscopy Kristin Jensen 17.11.05 References Cell Biological Applications of Confocal Microscopy, Brian Matsumoto, chapter 1 Studying protein dynamics in living cells,, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz
Microscopy from Carl Zeiss LSM 710. The Power of Sensitivity. A New Dimension in Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
 Microscopy from Carl Zeiss LSM 710 The Power of Sensitivity A New Dimension in Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Sensitivity Is the Key Whether it is in live cell imaging, single molecule analysis or
Microscopy from Carl Zeiss LSM 710 The Power of Sensitivity A New Dimension in Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Sensitivity Is the Key Whether it is in live cell imaging, single molecule analysis or
ZEISS LSM510META confocal manual
 ZEISS LSM510META confocal manual Switching on the system 1) Switch on the Remote Control button located on the table to the right of the microscope. This is the main switch for the whole system including
ZEISS LSM510META confocal manual Switching on the system 1) Switch on the Remote Control button located on the table to the right of the microscope. This is the main switch for the whole system including
Shreyash Tandon M.S. III Year
 Shreyash Tandon M.S. III Year 20091015 Confocal microscopy is a powerful tool for generating high-resolution images and 3-D reconstructions of a specimen by using point illumination and a spatial pinhole
Shreyash Tandon M.S. III Year 20091015 Confocal microscopy is a powerful tool for generating high-resolution images and 3-D reconstructions of a specimen by using point illumination and a spatial pinhole
Leica TCS SP8 Quick Start Guide
 Leica TCS SP8 Quick Start Guide Leica TCS SP8 System Overview Start-Up Procedure 1. Turn on the CTR Control Box, EL6000 fluorescent light source for the microscope stand. 2. Turn on the Scanner Power
Leica TCS SP8 Quick Start Guide Leica TCS SP8 System Overview Start-Up Procedure 1. Turn on the CTR Control Box, EL6000 fluorescent light source for the microscope stand. 2. Turn on the Scanner Power
Practical work no. 3: Confocal Live Cell Microscopy
 Practical work no. 3: Confocal Live Cell Microscopy Course Instructor: Mikko Liljeström (MIU) 1 Background Confocal microscopy: The main idea behind confocality is that it suppresses the signal outside
Practical work no. 3: Confocal Live Cell Microscopy Course Instructor: Mikko Liljeström (MIU) 1 Background Confocal microscopy: The main idea behind confocality is that it suppresses the signal outside
LSM 510 NLO and LSM 510 META NLO Multiphoton Laser Scanning Microscopes Deep Insights Carefully Gained
 Microscopy from Carl Zeiss LSM 510 NLO and LSM 510 META NLO Multiphoton Laser Scanning Microscopes Deep Insights Carefully Gained LSM 510 NLO and LSM 510 META NLO Deep Insights Carefully Gained In multiphoton
Microscopy from Carl Zeiss LSM 510 NLO and LSM 510 META NLO Multiphoton Laser Scanning Microscopes Deep Insights Carefully Gained LSM 510 NLO and LSM 510 META NLO Deep Insights Carefully Gained In multiphoton
1 Co Localization and Working flow with the lsm700
 1 Co Localization and Working flow with the lsm700 Samples -1 slide = mousse intestine, Dapi / Ki 67 with Cy3/ BrDU with alexa 488. -1 slide = mousse intestine, Dapi / Ki 67 with Cy3/ no BrDU (but with
1 Co Localization and Working flow with the lsm700 Samples -1 slide = mousse intestine, Dapi / Ki 67 with Cy3/ BrDU with alexa 488. -1 slide = mousse intestine, Dapi / Ki 67 with Cy3/ no BrDU (but with
Leica TCS SP8 Quick Start Guide
 Leica TCS SP8 Quick Start Guide Leica TCS SP8 System Overview Start-Up Procedure 1. Turn on the CTR Control Box, Fluorescent Light for the microscope stand. 2. Turn on the Scanner Power (1) on the front
Leica TCS SP8 Quick Start Guide Leica TCS SP8 System Overview Start-Up Procedure 1. Turn on the CTR Control Box, Fluorescent Light for the microscope stand. 2. Turn on the Scanner Power (1) on the front
Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 510 META Confocal Microscope
 Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 510 META Confocal Microscope AIM 4.2 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON Components and System/PC switches
Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 510 META Confocal Microscope AIM 4.2 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON Components and System/PC switches
LSM 710 Confocal Microscope Standard Operation Protocol
 LSM 710 Confocal Microscope Standard Operation Protocol Basic Operation Turning on the system 1. Switch on Main power switch 2. Switch on System / PC power button 3. Switch on Components power button 4.
LSM 710 Confocal Microscope Standard Operation Protocol Basic Operation Turning on the system 1. Switch on Main power switch 2. Switch on System / PC power button 3. Switch on Components power button 4.
Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 5 LIVE Confocal Microscope
 Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 5 LIVE Confocal Microscope AIM 4.2 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Verify that main power switches on the
Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 5 LIVE Confocal Microscope AIM 4.2 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Verify that main power switches on the
Quick Start Guide. Leica SP5 X
 Quick Start Guide Leica SP5 X Please note: Some of the information in this guide was taken from Leica Microsystems Leica TCS SP5 LAS AF Guide for New Users. This work is licensed under the Creative Commons
Quick Start Guide Leica SP5 X Please note: Some of the information in this guide was taken from Leica Microsystems Leica TCS SP5 LAS AF Guide for New Users. This work is licensed under the Creative Commons
Opterra II Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope. Innovation with Integrity
 Opterra II Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Enabling 4D Live-Cell Fluorescence Imaging through Speed, Sensitivity, Viability and Simplicity Innovation with Integrity Fluorescence Microscopy The
Opterra II Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Enabling 4D Live-Cell Fluorescence Imaging through Speed, Sensitivity, Viability and Simplicity Innovation with Integrity Fluorescence Microscopy The
Training Guide for Leica SP8 Confocal/Multiphoton Microscope
 Training Guide for Leica SP8 Confocal/Multiphoton Microscope LAS AF v3.3 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON power switch for epifluorescence
Training Guide for Leica SP8 Confocal/Multiphoton Microscope LAS AF v3.3 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON power switch for epifluorescence
Things to check before start-up.
 Byeong Cha Page 1 11/24/2009 Manual for Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Enter you name, the date, the time, and the account number in the user log book. Things to check before start-up. Make sure that your
Byeong Cha Page 1 11/24/2009 Manual for Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Enter you name, the date, the time, and the account number in the user log book. Things to check before start-up. Make sure that your
ZEN 2012 SP5 black edition Hotfix 12
 Information about the software ZEN 2012 SP5 black edition Hotfix 12 Software name: ZEN 2012 Service Pack 5 black edition Hotfix 12 Software version: The software version in ZEN Help About changes to 14.0.12.201
Information about the software ZEN 2012 SP5 black edition Hotfix 12 Software name: ZEN 2012 Service Pack 5 black edition Hotfix 12 Software version: The software version in ZEN Help About changes to 14.0.12.201
Contents. Introduction
 Contents Page Contents... 1 Introduction... 1 Starting the System... 2 Introduction to ZEN Efficient Navigation... 5 Setting up the microscope... 10 Configuring the beam path and lasers... 12 Scanning
Contents Page Contents... 1 Introduction... 1 Starting the System... 2 Introduction to ZEN Efficient Navigation... 5 Setting up the microscope... 10 Configuring the beam path and lasers... 12 Scanning
TRAINING MANUAL. Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO
 TRAINING MANUAL Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO September 2010 Multiphoton Microscopy Training Manual Multiphoton microscopy is only available on the LSM 510 META-NLO system. This system is equipped
TRAINING MANUAL Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO September 2010 Multiphoton Microscopy Training Manual Multiphoton microscopy is only available on the LSM 510 META-NLO system. This system is equipped
Operation Guide for the Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Bio-Imaging Facility Hunter College October 2009
 Operation Guide for the Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Bio-Imaging Facility Hunter College October 2009 Introduction of Fluoresence Confocal Microscopy The first confocal microscope was invented by Princeton
Operation Guide for the Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Bio-Imaging Facility Hunter College October 2009 Introduction of Fluoresence Confocal Microscopy The first confocal microscope was invented by Princeton
Opterra. Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope. Innovation with Integrity. Cell-Friendly, High-Speed, High-Resolution Imaging
 Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Cell-Friendly, High-Speed, High-Resolution Imaging Innovation with Integrity Fluorescence Microscopy Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Superior
Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Cell-Friendly, High-Speed, High-Resolution Imaging Innovation with Integrity Fluorescence Microscopy Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Superior
LSM 510 META Laser Scanning Microscope Fluorescence Signals Reliably Separated
 Microscopy from Carl Zeiss LSM 510 META Laser Scanning Microscope Fluorescence Signals Reliably Separated Highlights of Laser Scanning Microscopy 1982 The first Laser Scanning Microscope from Carl Zeiss.
Microscopy from Carl Zeiss LSM 510 META Laser Scanning Microscope Fluorescence Signals Reliably Separated Highlights of Laser Scanning Microscopy 1982 The first Laser Scanning Microscope from Carl Zeiss.
Zeiss LSM 510 Confocor III Training Notes. Center for Cell Analysis & Modeling
 Zeiss LSM 510 Confocor III Training Notes Center for Cell Analysis & Modeling Confocor 3 Start Up Go to System Module Turn on Main Switch, System/ PC, and Components Switches Do you need the arc lamp?
Zeiss LSM 510 Confocor III Training Notes Center for Cell Analysis & Modeling Confocor 3 Start Up Go to System Module Turn on Main Switch, System/ PC, and Components Switches Do you need the arc lamp?
Confocal imaging on the Leica TCS SP8. 1) Turn the system on. 2) Use TCS user account. 3) Start LAS X software:
 Confocal imaging on the Leica TCS SP8 1) Turn the system on. 2) Use TCS user account. 3) Start LAS X software: 4) Do not touch the microscope while the software is initializing. Choose your options: Turn
Confocal imaging on the Leica TCS SP8 1) Turn the system on. 2) Use TCS user account. 3) Start LAS X software: 4) Do not touch the microscope while the software is initializing. Choose your options: Turn
Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement
 Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY BioVis Uppsala, 2017 Jeremy Adler Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Widefield & Confocal Microscopy
Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY BioVis Uppsala, 2017 Jeremy Adler Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Widefield & Confocal Microscopy
Supplemental Figure 1: Histogram of 63x Objective Lens z axis Calculated Resolutions. Results from the MetroloJ z axis fits for 5 beads from each
 Supplemental Figure 1: Histogram of 63x Objective Lens z axis Calculated Resolutions. Results from the MetroloJ z axis fits for 5 beads from each lens with a 1 Airy unit pinhole setting. Many water lenses
Supplemental Figure 1: Histogram of 63x Objective Lens z axis Calculated Resolutions. Results from the MetroloJ z axis fits for 5 beads from each lens with a 1 Airy unit pinhole setting. Many water lenses
Travel to New Dimensions- LSM 880. The Resolution of a Microscope is limited. The Resolution of a Microscope is limited. Image. Image. Object.
 Travel to New Dimensions- LSM 880 LSM 880: The Power of Sensitivity Our Latest Member of the LSM 880 with GaAsP Detectors Sensitivity, and Ease of Use Innovative High-End Laser Scanning Microscopes from
Travel to New Dimensions- LSM 880 LSM 880: The Power of Sensitivity Our Latest Member of the LSM 880 with GaAsP Detectors Sensitivity, and Ease of Use Innovative High-End Laser Scanning Microscopes from
Guide to Confocal 5. Starting session
 Guide to Confocal 5 Remember that when booking and before starting session you can check for any problems at https://www.bris.ac.uk/biochemistry/uobonly/cif/index.html Starting session Switch on microscope
Guide to Confocal 5 Remember that when booking and before starting session you can check for any problems at https://www.bris.ac.uk/biochemistry/uobonly/cif/index.html Starting session Switch on microscope
ANSWER KEY Lab 2 (IGB): Bright Field and Fluorescence Optical Microscopy and Sectioning
 Phys598BP Spring 2016 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign ANSWER KEY Lab 2 (IGB): Bright Field and Fluorescence Optical Microscopy and Sectioning Location: IGB Core Microscopy Facility Microscope:
Phys598BP Spring 2016 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign ANSWER KEY Lab 2 (IGB): Bright Field and Fluorescence Optical Microscopy and Sectioning Location: IGB Core Microscopy Facility Microscope:
Basics of confocal imaging (part I)
 Basics of confocal imaging (part I) Swiss Institute of Technology (EPFL) Faculty of Life Sciences Head of BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS BIOP arne.seitz@epfl.ch Lateral resolution BioImaging &Optics Platform Light
Basics of confocal imaging (part I) Swiss Institute of Technology (EPFL) Faculty of Life Sciences Head of BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS BIOP arne.seitz@epfl.ch Lateral resolution BioImaging &Optics Platform Light
Leica_Dye_Finder :53 Uhr Seite 6 Dye Finder LAS AF
 Dye Finder LAS AF Dye Finder Multicolor live cell fluorescence microscopy is limited by the availability of spectrally separable fluorescent dyes. Fluorescent dyes (or spectral GFP variants) with incongruent
Dye Finder LAS AF Dye Finder Multicolor live cell fluorescence microscopy is limited by the availability of spectrally separable fluorescent dyes. Fluorescent dyes (or spectral GFP variants) with incongruent
LSM 780 Confocal Microscope Standard Operation Protocol
 LSM 780 Confocal Microscope Standard Operation Protocol Basic Operation Turning on the system 1. Sign on log sheet according to Actual start time 2. Check Compressed Air supply for the air table 3. Switch
LSM 780 Confocal Microscope Standard Operation Protocol Basic Operation Turning on the system 1. Sign on log sheet according to Actual start time 2. Check Compressed Air supply for the air table 3. Switch
Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 7 MP Multiphoton Microscope
 Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 7 MP Multiphoton Microscope ZEN 2009 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn Chameleon TiS laser key from Standby
Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 7 MP Multiphoton Microscope ZEN 2009 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn Chameleon TiS laser key from Standby
 07 Setting Place a specimen, and select a fluorescence dye. The FV10i automatically selects the most suitable imaging conditions based on the fluorescence dye selection. Set Image mapping menu Just click
07 Setting Place a specimen, and select a fluorescence dye. The FV10i automatically selects the most suitable imaging conditions based on the fluorescence dye selection. Set Image mapping menu Just click
TRAINING MANUAL. Olympus FV1000
 TRAINING MANUAL Olympus FV1000 September 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS A. Start-Up Procedure... 1 B. Visual Observation under the Microscope... 1 C. Image Acquisition... 4 A brief Overview of the Settings...
TRAINING MANUAL Olympus FV1000 September 2014 TABLE OF CONTENTS A. Start-Up Procedure... 1 B. Visual Observation under the Microscope... 1 C. Image Acquisition... 4 A brief Overview of the Settings...
Bi Imaging. Multicolor Imaging: The Important Question of Co-Localization. Anna Smallcombe Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hemel Hempstead, UK
 Multicolor Imaging: The Important Question of Co-Localization Anna Smallcombe Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hemel Hempstead, UK The use of specific fluorescent probes, combined with confocal or multiphoton microscopy
Multicolor Imaging: The Important Question of Co-Localization Anna Smallcombe Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hemel Hempstead, UK The use of specific fluorescent probes, combined with confocal or multiphoton microscopy
Non-Descanned FLIM Detection in Multiphoton Microscopes
 Non-Descanned FLIM Detection in Multiphoton Microscopes Abstract. Multiphoton microscopes use a femtosecond NIR laser to excite fluorescence in the sample. Excitation is performed via a multi-photon absorption
Non-Descanned FLIM Detection in Multiphoton Microscopes Abstract. Multiphoton microscopes use a femtosecond NIR laser to excite fluorescence in the sample. Excitation is performed via a multi-photon absorption
Fundamentals of Light Microscopy II: Fluorescence, Deconvolution, Confocal, Multiphoton, Spectral microscopy. Integrated Microscopy Course
 Fundamentals of Light Microscopy II: Fluorescence, Deconvolution, Confocal, Multiphoton, Spectral microscopy Integrated Microscopy Course Review Lecture 1: Microscopy Basics Light train Kohler illumination*
Fundamentals of Light Microscopy II: Fluorescence, Deconvolution, Confocal, Multiphoton, Spectral microscopy Integrated Microscopy Course Review Lecture 1: Microscopy Basics Light train Kohler illumination*
LEICA TCS SP5 AOBS TANDEM USER MANUAL
 LEICA TCS SP5 AOBS TANDEM USER MANUAL STARTING THE SYSTEM...2 THE LAS AF SOFTWARE...3 THE «ACQUIRE» MENU...5 CHOOSE AND CREATE A SETTING...6 THE CONTROL PANEL...8 THE DMI6000B MICROSCOPE...10 ACQUIRE ONE
LEICA TCS SP5 AOBS TANDEM USER MANUAL STARTING THE SYSTEM...2 THE LAS AF SOFTWARE...3 THE «ACQUIRE» MENU...5 CHOOSE AND CREATE A SETTING...6 THE CONTROL PANEL...8 THE DMI6000B MICROSCOPE...10 ACQUIRE ONE
IC 2 S High Performance Objectives
 M i c r o s c o p y f r o m C a r l Z e i s s IC 2 S igh Performance Objectives for Biomedical Applications with Laser Based Imaging Systems LSM,, ConfoCor, TIRF and ELYRA Carl Zeiss offers a large range
M i c r o s c o p y f r o m C a r l Z e i s s IC 2 S igh Performance Objectives for Biomedical Applications with Laser Based Imaging Systems LSM,, ConfoCor, TIRF and ELYRA Carl Zeiss offers a large range
Last updated: May 2014 Y.DeGraaf
 FLINDERS MICROSCOPY BIOMEDICAL SERVICES AVAILABLE MICROSCOPES AND SPECIFICATIONS & INFORMATION REGARDING TRAINING FOR NEW USERS Last updated: May 2014 Y.DeGraaf If you have new staff or students (Honours/Masters
FLINDERS MICROSCOPY BIOMEDICAL SERVICES AVAILABLE MICROSCOPES AND SPECIFICATIONS & INFORMATION REGARDING TRAINING FOR NEW USERS Last updated: May 2014 Y.DeGraaf If you have new staff or students (Honours/Masters
Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
 Name of the Core Facility: Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy CORE Forschungszentrum Immunologie Mainz Welcome to the CSLM Core Facility: The CLSM Core Facility enables working groups to incorporate high
Name of the Core Facility: Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy CORE Forschungszentrum Immunologie Mainz Welcome to the CSLM Core Facility: The CLSM Core Facility enables working groups to incorporate high
Light Microscopy. Upon completion of this lecture, the student should be able to:
 Light Light microscopy is based on the interaction of light and tissue components and can be used to study tissue features. Upon completion of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1- Explain the
Light Light microscopy is based on the interaction of light and tissue components and can be used to study tissue features. Upon completion of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1- Explain the
BASICS OF CONFOCAL IMAGING (PART I)
 BASICS OF CONFOCAL IMAGING (PART I) INTERNAL COURSE 2012 LIGHT MICROSCOPY Lateral resolution Transmission Fluorescence d min 1.22 NA obj NA cond 0 0 rairy 0.61 NAobj Ernst Abbe Lord Rayleigh Depth of field
BASICS OF CONFOCAL IMAGING (PART I) INTERNAL COURSE 2012 LIGHT MICROSCOPY Lateral resolution Transmission Fluorescence d min 1.22 NA obj NA cond 0 0 rairy 0.61 NAobj Ernst Abbe Lord Rayleigh Depth of field
Microscopy from Carl Zeiss LSM 710 NLO. Information in Depth. Innovative Systems for Multiphoton Microscopy
 Microscopy from Carl Zeiss LSM 710 NLO Information in Depth Innovative Systems for Multiphoton Microscopy Providing Support for Progress and Innovation Biomedical sciences represent one of the most important
Microscopy from Carl Zeiss LSM 710 NLO Information in Depth Innovative Systems for Multiphoton Microscopy Providing Support for Progress and Innovation Biomedical sciences represent one of the most important
Leica Sp5 II Confocal User Guide
 Leica Sp5 II Confocal User Guide Turning on the Confocal System (instructions are posted in the room) 1. Turn on Laser Power Button 2. Turn Key to On position 3. Turn on Scanner Power Button 4. Turn on
Leica Sp5 II Confocal User Guide Turning on the Confocal System (instructions are posted in the room) 1. Turn on Laser Power Button 2. Turn Key to On position 3. Turn on Scanner Power Button 4. Turn on
Bi/BE 227 Winter Assignment #3. Adding the third dimension: 3D Confocal Imaging
 Bi/BE 227 Winter 2016 Assignment #3 Adding the third dimension: 3D Confocal Imaging Schedule: Jan 20: Assignment Jan 20-Feb 8: Work on assignment Feb 10: Student PowerPoint presentations. Goals for this
Bi/BE 227 Winter 2016 Assignment #3 Adding the third dimension: 3D Confocal Imaging Schedule: Jan 20: Assignment Jan 20-Feb 8: Work on assignment Feb 10: Student PowerPoint presentations. Goals for this
ZEISS LSM 710 CONFOCAL MICROSCOPE USER MANUAL
 ZEISS LSM 710 CONFOCAL MICROSCOPE USER MANUAL START THE SYSTEM... 2 START ZEN SOFTWARE... 3 SET THE TEMPERATURE AND THE CO2 CONTROLLERS... OBSERVATION AT OCULARS... 5 STATIF PRESENTATION... 6 ACQUIRE ONE
ZEISS LSM 710 CONFOCAL MICROSCOPE USER MANUAL START THE SYSTEM... 2 START ZEN SOFTWARE... 3 SET THE TEMPERATURE AND THE CO2 CONTROLLERS... OBSERVATION AT OCULARS... 5 STATIF PRESENTATION... 6 ACQUIRE ONE
Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 880 with AiryScan FAST
 Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 880 with AiryScan FAST ZEN 2.3 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2018) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON Main Switch from the remote control
Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 880 with AiryScan FAST ZEN 2.3 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2018) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON Main Switch from the remote control
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
 Zeiss LSM 510 M eta Confocal M icroscope OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS Starting the System: 1. Turn the black knob on the laser box one-quarter turn from Off to On. You will hear the laser cooling mechanisms
Zeiss LSM 510 M eta Confocal M icroscope OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS Starting the System: 1. Turn the black knob on the laser box one-quarter turn from Off to On. You will hear the laser cooling mechanisms
Quick Guide for Zeiss 710 Laser Scanning Confocal MGH Cancer Center
 Quick Guide for Zeiss 710 Laser Scanning Confocal MGH Cancer Center For any questions or concerns, please contact: Linda Nieman lnieman@mgh.harvard.edu Office: (617) 643-9684 Cell: (512) 565-8076 Chenyue
Quick Guide for Zeiss 710 Laser Scanning Confocal MGH Cancer Center For any questions or concerns, please contact: Linda Nieman lnieman@mgh.harvard.edu Office: (617) 643-9684 Cell: (512) 565-8076 Chenyue
LSM 710 NLO and LSM 780 NLO
 M i c r o s c o p y f r o m C a r l Z e i s s LSM 710 NLO and LSM 780 NLO Information in Depth Innovative Systems for Multiphoton Microscopy Providing Support for Progress and Innovation Biomedical sciences
M i c r o s c o p y f r o m C a r l Z e i s s LSM 710 NLO and LSM 780 NLO Information in Depth Innovative Systems for Multiphoton Microscopy Providing Support for Progress and Innovation Biomedical sciences
Bio 407. Applied microscopy. Introduction into light microscopy. José María Mateos. Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis
 Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Bio 407 Applied Introduction into light José María Mateos Fundamentals of light Compound microscope Microscope composed of an objective and an additional lens (eyepiece,
Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Bio 407 Applied Introduction into light José María Mateos Fundamentals of light Compound microscope Microscope composed of an objective and an additional lens (eyepiece,
Megapixel FLIM with bh TCSPC Modules
 Megapixel FLIM with bh TCSPC Modules The New SPCM 64-bit Software Abstract: Becker & Hickl have recently introduced version 9.60 of their SPCM TCSPC data acquisition software. SPCM version 9.60 not only
Megapixel FLIM with bh TCSPC Modules The New SPCM 64-bit Software Abstract: Becker & Hickl have recently introduced version 9.60 of their SPCM TCSPC data acquisition software. SPCM version 9.60 not only
Nikon AZ100. Laser Scanning Macro Confocal Microscope. Jordan Briscoe Adam Fries Kyle Marchuk Kaitlin Corbin. May 2017.
 Nikon AZ100 Laser Scanning Macro Confocal Microscope Jordan Briscoe Adam Fries Kyle Marchuk Kaitlin Corbin May 2017 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Hardware - Startup 2 3 Software/Operation 4 3.1 Multidimensional
Nikon AZ100 Laser Scanning Macro Confocal Microscope Jordan Briscoe Adam Fries Kyle Marchuk Kaitlin Corbin May 2017 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 Hardware - Startup 2 3 Software/Operation 4 3.1 Multidimensional
Leica TCS SL Confocal Training. Neuroscience Imaging Core Staff. Core Director. Facility Manager
 Leica TCS SL Confocal Training Neuroscience Imaging Facility The Ohio State University Rightmire Hall 614-292-1367 Staff Core Director Anthony Brown, Ph. D. 060 Rightmire Hall 614-292-1205 brown.2302@osu.edu
Leica TCS SL Confocal Training Neuroscience Imaging Facility The Ohio State University Rightmire Hall 614-292-1367 Staff Core Director Anthony Brown, Ph. D. 060 Rightmire Hall 614-292-1205 brown.2302@osu.edu
Leica SP8 TCS Users Manual
 Leica SP8 TCS Users Manual Follow the procedure for start up and log on as posted in the lab. Please log on with your account only and do not share your password with anyone. We track and confirm usage
Leica SP8 TCS Users Manual Follow the procedure for start up and log on as posted in the lab. Please log on with your account only and do not share your password with anyone. We track and confirm usage
LSM 510 Meta Training Notes
 LSM 510 Meta Training Notes Turning on the system Turn on X-Cite power supply. This supplies light for epifluorescence for viewing your samples through the microscope. Turn on the remote control switch.
LSM 510 Meta Training Notes Turning on the system Turn on X-Cite power supply. This supplies light for epifluorescence for viewing your samples through the microscope. Turn on the remote control switch.
Supplemental Method Information Zeiss LSM710
 Supplemental Method Information Zeiss LSM710 1 Under the Light Path window set up the confocal for imaging a green dye (Alexa488-EGFP). For example, set up the light path as shown here using the 488 nm
Supplemental Method Information Zeiss LSM710 1 Under the Light Path window set up the confocal for imaging a green dye (Alexa488-EGFP). For example, set up the light path as shown here using the 488 nm
Cell Biology and Bioimaging Core
 Cell Biology and Bioimaging Core Leica TCS SP5 Operating Instructions Starting up the instrument 1. First, log in the log book located on the confocal desk. Include your name, your lab s PI, an account
Cell Biology and Bioimaging Core Leica TCS SP5 Operating Instructions Starting up the instrument 1. First, log in the log book located on the confocal desk. Include your name, your lab s PI, an account
Leica SP8 TCS Users Manual
 Version : 07/08/0 Leica SP8 TCS Users Manual Start up:. Turn the PC Microscope, Scanner Power, Laser Power, and the Laser Emission key to on (bottom right of desk).. Turn on the fluorescent lamp (top left
Version : 07/08/0 Leica SP8 TCS Users Manual Start up:. Turn the PC Microscope, Scanner Power, Laser Power, and the Laser Emission key to on (bottom right of desk).. Turn on the fluorescent lamp (top left
LSM 510 Training Notes
 LSM 510 Training Notes Turning on the system Turn on the arc lamp, found on the bench top left of the microscope. This supplies light for epifluorescence for viewing your samples through the microscope.
LSM 510 Training Notes Turning on the system Turn on the arc lamp, found on the bench top left of the microscope. This supplies light for epifluorescence for viewing your samples through the microscope.
CONFOCAL MICROSCOPE (Zeiss LSM 510 META v4.2)
 Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics Molecular Cytogenetics and Microscopy Core CONFOCAL MICROSCOPE (Zeiss LSM 510 META v4.2) 1) STARTING THE SYSTEM Abridged INSTRUCTIONS Switch on the mercury bulb
Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics Molecular Cytogenetics and Microscopy Core CONFOCAL MICROSCOPE (Zeiss LSM 510 META v4.2) 1) STARTING THE SYSTEM Abridged INSTRUCTIONS Switch on the mercury bulb
Microscope Confocal Sp2 Upright.
 Microscope Confocal Sp2 Upright. Welcome to the Leica Sp2 Confocal Upright tutorial. Before using the Sp2 Invert, You will need to put down your name on the reservation system = http://svintranet.epfl.ch/index.php?optio
Microscope Confocal Sp2 Upright. Welcome to the Leica Sp2 Confocal Upright tutorial. Before using the Sp2 Invert, You will need to put down your name on the reservation system = http://svintranet.epfl.ch/index.php?optio
Maria Smedh, Centre for Cellular Imaging. Maria Smedh, Centre for Cellular Imaging
 Nonlinear microscopy I: Two-photon fluorescence microscopy Multiphoton Microscopy What is multiphoton imaging? Applications Different imaging modes Advantages/disadvantages Scattering of light in thick
Nonlinear microscopy I: Two-photon fluorescence microscopy Multiphoton Microscopy What is multiphoton imaging? Applications Different imaging modes Advantages/disadvantages Scattering of light in thick
Nikon C1si Spectral Laser Scanning Confocal Microscope. User Guide
 Nikon C1si Spectral Laser Scanning Confocal Microscope User Guide Contents: C1Si Turn-On/ShutDown Procedures... 2 Overview... 4 Setup for epi-illumination to view through the eyepieces:... 5 Setup for
Nikon C1si Spectral Laser Scanning Confocal Microscope User Guide Contents: C1Si Turn-On/ShutDown Procedures... 2 Overview... 4 Setup for epi-illumination to view through the eyepieces:... 5 Setup for
ZEISS LSM 710 NLO Multiphoton microscope Manual/Quick guide
 ZEISS LSM 710 NLO Multiphoton microscope Manual/Quick guide Matyas Molnar, Biovis 2016 Starting the microscpe 1. Check the microscope if everything looks clean and normal. If not, report it in the logbook.
ZEISS LSM 710 NLO Multiphoton microscope Manual/Quick guide Matyas Molnar, Biovis 2016 Starting the microscpe 1. Check the microscope if everything looks clean and normal. If not, report it in the logbook.
Life Science Instrumentation. New Generation. Light Sheet Fluorescence Microscope. Alph
 Life Science Instrumentation Light Sheet Fluorescence Microscope New Generation Alph Modular Light Sheet Microscope Alpha 3 is a new generation of light sheet fluorescence microscope addressing the needs
Life Science Instrumentation Light Sheet Fluorescence Microscope New Generation Alph Modular Light Sheet Microscope Alpha 3 is a new generation of light sheet fluorescence microscope addressing the needs
Final Exam, 150 points PMB 185: Techniques in Light Microscopy
 Final Exam, 150 points Name PMB 185: Techniques in Light Microscopy Point value is in parentheses at the end of each question. Note: GFP = green fluorescent protein ; CFP = cyan fluorescent protein ; YFP
Final Exam, 150 points Name PMB 185: Techniques in Light Microscopy Point value is in parentheses at the end of each question. Note: GFP = green fluorescent protein ; CFP = cyan fluorescent protein ; YFP
FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY. Matyas Molnar and Dirk Pacholsky
 FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY Matyas Molnar and Dirk Pacholsky 1 The human eye perceives app. 400-700 nm; best at around 500 nm (green) Has a general resolution down to150-300 μm (human hair: 40-250 μm) We need
FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY Matyas Molnar and Dirk Pacholsky 1 The human eye perceives app. 400-700 nm; best at around 500 nm (green) Has a general resolution down to150-300 μm (human hair: 40-250 μm) We need
VivaTome. Discover the Dynamics of Life. The Entry-level System that Captures Dynamic Processes with Outstanding Image Quality.
 Microscopy from Carl Zeiss VivaTome Discover the Dynamics of Life The Entry-level System that Captures Dynamic Processes with Outstanding Image Quality. Innovative Technology Captures Dynamic Processes
Microscopy from Carl Zeiss VivaTome Discover the Dynamics of Life The Entry-level System that Captures Dynamic Processes with Outstanding Image Quality. Innovative Technology Captures Dynamic Processes
Microscopy from Carl Zeiss LSM 710. The Power of Sensitivity. A New Dimension in Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
 Microscopy from Carl Zeiss LSM 710 The Power of Sensitivity A New Dimension in Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Providing Support for Progress and Innovation The biomedical sciences are considered some
Microscopy from Carl Zeiss LSM 710 The Power of Sensitivity A New Dimension in Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Providing Support for Progress and Innovation The biomedical sciences are considered some
Nikon. King s College London. Imaging Centre. N-SIM guide NIKON IMAGING KING S COLLEGE LONDON
 N-SIM guide NIKON IMAGING CENTRE @ KING S COLLEGE LONDON Starting-up / Shut-down The NSIM hardware is calibrated after system warm-up occurs. It is recommended that you turn-on the system for at least
N-SIM guide NIKON IMAGING CENTRE @ KING S COLLEGE LONDON Starting-up / Shut-down The NSIM hardware is calibrated after system warm-up occurs. It is recommended that you turn-on the system for at least
Axio Zoom.V16 The Fluorescence Zoom Microscope for Large Fields
 Product Information Interactive PDF internet-link video/animation Release 1.0 It s About Brilliance. Because Only the Best Is Good Enough In Brief The Advantages The Applications In 1994, the molecular
Product Information Interactive PDF internet-link video/animation Release 1.0 It s About Brilliance. Because Only the Best Is Good Enough In Brief The Advantages The Applications In 1994, the molecular
Confocal Microscope. Confocal Microscope C2
 Confocal Microscope Confocal Microscope C2 Confocal Microscope An essential microscopy laboratory instrument The C2 confocal microscope system comprises a new generation of Nikon confocal instruments designed
Confocal Microscope Confocal Microscope C2 Confocal Microscope An essential microscopy laboratory instrument The C2 confocal microscope system comprises a new generation of Nikon confocal instruments designed
START-UP PROCEDURE 1 THE MICROSCOPE STAND 3 OBJECTIVES 5 STARTING WITH LAS (SOFTWARE) AND SETTING UP THE MICROSCOPE STAND 7
 Leica DMI AF6000LX Table of contents START-UP PROCEDURE 1 THE MICROSCOPE STAND 3 OBJECTIVES 5 STARTING WITH LAS (SOFTWARE) AND SETTING UP THE MICROSCOPE STAND 7 ACQUIRE MODULE 6 SETTING THE LIGHTPATH 6
Leica DMI AF6000LX Table of contents START-UP PROCEDURE 1 THE MICROSCOPE STAND 3 OBJECTIVES 5 STARTING WITH LAS (SOFTWARE) AND SETTING UP THE MICROSCOPE STAND 7 ACQUIRE MODULE 6 SETTING THE LIGHTPATH 6
Confocal Microscope. Confocal Microscope C2
 Confocal Microscope Confocal Microscope C2 Confocal Microscope An essential microscopy laboratory insturument The C2 confocal microscope system comprises a new generation of Nikon confocal instruments
Confocal Microscope Confocal Microscope C2 Confocal Microscope An essential microscopy laboratory insturument The C2 confocal microscope system comprises a new generation of Nikon confocal instruments
Title: Leica SP5 Confocal User Manual
 Title: Leica SP5 Confocal User Manual Date of first issue: 23/10/2015 Date of review: Version: Admin For assistance or to report an issue Office: CG07 or 05 Email: Igmm-imaginghelpdesk@igmm.ed.ac.uk Website:
Title: Leica SP5 Confocal User Manual Date of first issue: 23/10/2015 Date of review: Version: Admin For assistance or to report an issue Office: CG07 or 05 Email: Igmm-imaginghelpdesk@igmm.ed.ac.uk Website:
Advanced Live Cell Imaging
 FRET Analysis in Laser Scanning Microscopy What is FRET? FRET (fluorescence resonance energy transfer) is the non-radiative transfer of photon energy from an excited fluorophore (the donor) to another
FRET Analysis in Laser Scanning Microscopy What is FRET? FRET (fluorescence resonance energy transfer) is the non-radiative transfer of photon energy from an excited fluorophore (the donor) to another
microscopy A great online resource Molecular Expressions, a Microscope Primer Partha Roy
 Fundamentals of optical microscopy A great online resource Molecular Expressions, a Microscope Primer http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/index.html Partha Roy 1 Why microscopy Topics Functions of a microscope
Fundamentals of optical microscopy A great online resource Molecular Expressions, a Microscope Primer http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/index.html Partha Roy 1 Why microscopy Topics Functions of a microscope
Components of confocal and two-photon microscopes
 Components of confocal and two-photon microscopes Internal training 07/04/2016 A. GRICHINE Platform Optical microscopy Cell imaging, IAB, ISdV Plan Confocal laser scanning microscope o o o Principle Main
Components of confocal and two-photon microscopes Internal training 07/04/2016 A. GRICHINE Platform Optical microscopy Cell imaging, IAB, ISdV Plan Confocal laser scanning microscope o o o Principle Main
Operating Instructions for Zeiss LSM 510
 Operating Instructions for Zeiss LSM 510 Location: GNL 6.312q (BSL3) Questions? Contact: Maxim Ivannikov, maivanni@utmb.edu 1 Attend A Complementary Training Before Using The Microscope All future users
Operating Instructions for Zeiss LSM 510 Location: GNL 6.312q (BSL3) Questions? Contact: Maxim Ivannikov, maivanni@utmb.edu 1 Attend A Complementary Training Before Using The Microscope All future users
DCS-120. Confocal Scanning FLIM Systems. Based on bh s Multidimensional Megapixel FLIM Technology
 Based on bh s Multidimensional Megapixel FLIM Technology Complete Laser Scanning FLIM Microscopes FLIM Upgrades for Existing Conventional Microscopes Multidimensional TCSPC technique High throughput dual-channel
Based on bh s Multidimensional Megapixel FLIM Technology Complete Laser Scanning FLIM Microscopes FLIM Upgrades for Existing Conventional Microscopes Multidimensional TCSPC technique High throughput dual-channel
The DCS-120 Confocal Scanning FLIM System
 he DCS-120 Confocal Scanning FLIM System he bh DCS-120 confocal scanning FLIM system converts a conventional microscope into a high-performance fluorescence lifetime imaging system. he system is based
he DCS-120 Confocal Scanning FLIM System he bh DCS-120 confocal scanning FLIM system converts a conventional microscope into a high-performance fluorescence lifetime imaging system. he system is based
Fast Laser Raman Microscope RAMAN
 Fast Laser Raman Microscope RAMAN - 11 www.nanophoton.jp Fast Raman Imaging A New Generation of Raman Microscope RAMAN-11 developed by Nanophoton was created by combining confocal laser microscope technology
Fast Laser Raman Microscope RAMAN - 11 www.nanophoton.jp Fast Raman Imaging A New Generation of Raman Microscope RAMAN-11 developed by Nanophoton was created by combining confocal laser microscope technology
Quality Performance, Innovative Design
 Dimensions Confocal Laser Scanning Biological Microscope Table size (mm): 1400(W) 800(D) * Table is not available from Olympus. Avoid placing the controller directly on the floor. Dimensions / Weight /
Dimensions Confocal Laser Scanning Biological Microscope Table size (mm): 1400(W) 800(D) * Table is not available from Olympus. Avoid placing the controller directly on the floor. Dimensions / Weight /
SHORT INSTRUCTIONS FOR OPERATING LSM1/2 (Zeiss LSM510) AT CIAN Version 1.4, September 2014
 CIAN LSM1 or LSM2 short instructions, version 1.4, September 2014 page 1 of 6 SHORT INSTRUCTIONS FOR OPERATING LSM1/2 (Zeiss LSM510) AT CIAN Version 1.4, September 2014 Before starting To work with LSM1
CIAN LSM1 or LSM2 short instructions, version 1.4, September 2014 page 1 of 6 SHORT INSTRUCTIONS FOR OPERATING LSM1/2 (Zeiss LSM510) AT CIAN Version 1.4, September 2014 Before starting To work with LSM1
AxioCam HR Success Through Performance
 Microscopy from Carl Zeiss AxioCam HR Success Through Performance The high-resolution camera for digital documentation Superior performance for research and routine work brilliant quality documentation
Microscopy from Carl Zeiss AxioCam HR Success Through Performance The high-resolution camera for digital documentation Superior performance for research and routine work brilliant quality documentation
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup.
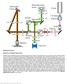 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup. Excitation from a femtosecond laser is passed through intensity control and shuttering optics (1/2 λ wave plate, polarizing beam splitting
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup. Excitation from a femtosecond laser is passed through intensity control and shuttering optics (1/2 λ wave plate, polarizing beam splitting
Nasmyth Ultraview Vox User Protocol
 Nasmyth Ultraview Vox User Protocol Switch on all wall sockets labelled Nasmyth, switch camera on (power supply located on table behind monitor), switch on laser switch in laser rack, switch computer on
Nasmyth Ultraview Vox User Protocol Switch on all wall sockets labelled Nasmyth, switch camera on (power supply located on table behind monitor), switch on laser switch in laser rack, switch computer on
