By Christopher Henderson This article is a continuation of last month s article on leadframes.
|
|
|
- Marlene Poole
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
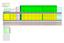
1 Leadframes Part II By Christopher Henderson This article is a continuation of last month s article on leadframes. Today, we mainly use plated leadframes. Plated leadframes can help improve adhesion of the die attach, wire bonds, and mold compound, and improve the solderability of the leadframe. The plating materials need to meet environmental regulations associated with the Removal of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) (pronounced rowhos ), and they need to be inexpensive. RoHS requirements eliminate the possibility of lead, so that means we must use other plating materials. Figure 1 (below) shows an example of a leadframe plating system. In order to reduce costs, some companies plate the leadrame prior to stamping. This is called a pre-plated leadframe. Page 1 Page 5 Page 7 Page 8 Leadframes Part II Technical Tidbit Ask the Experts Spotlight Page 11 Upcoming Courses Figure 1. Leadframe plating system.
2 Many companies use tin as a leadframe plating. The leadframe supplier deposits a plating layer between 7 and 20 microns thick. This improves solderability. However, copper-tin intermetallics can form and interfere with the reliability of the solder joint, and can aid in the growth of tin whiskers, another reliability problem. Some companies will anneal or fuse the tin plating to reduce this problem. Some companies will also use silver plating. The silver plating is on the order of 2.5 to 8 microns thick, and the assembly site deposits this after mold on the exposed portion of the leads. Some companies use a nickelpalladium-gold plating to prevent the intermetallic growth. The nickel-palladium-gold layer is quite thin, with the nickel between 0.5 and 2 microns thick, the palladium between 10 and 100 nanometers thick, and the gold only 3 to 9 nanometers thick, to reduce costs. This process is done by the leadframe supplier. Figure 2. Drawing showing various leadframes and plating options. One technique to improve adhesion is to change the plating finish. One can roughen the nickel layer through a chemical etch before depositing the palladium. This improves adhesion, and is particularly effective with downbonds. This is also important with copper wire since it has lower fatigue strength. However, a rough leadframe costs 15 30% more. 2
3 Figure 3. Standard and rough nickel-palladium-gold (NiPdAu) plating. Rough leadframes help control mold and die attach delamination. The rough leadframe keeps the stress low on the ball and stitch bonds to prevent lifted ball and broken stitch bonds. It also protects the thermal path. Figure 4 below helps to illustrate this. The upper drawing shows a schematic cross section of the nickel-palladium-gold pre-plated leadframe, and the lower figures show scanning electron microscope (SEM) images of the standard and rough leadframes. Figure 4. Drawing showing cross-section (top) and SEM images of standard and rough leadframe platings (bottom). The scanning acoustic microscope images in Fig. 5 show how a rough leadframe can improve adhesion. The samples on the left show significant areas of red after undergoing the JEDEC Level 3 Moisture Sensitivity Stress Test. The red indicates delamination has occurred. The samples on the right show very 3
4 little delamination. The red mark on each package in the lower right corner is an artifact of the mold release process, and is not associated with leadframe delamination. Figure 5. Scanning acoustic microscope images after moisture sensitivity stress on standard plating (left) and rough plating (right). In conclusion, we briefly discussed the different types of leadframes used in packaging semiconductor devices. We learned that the industry primarily uses copper and copper alloys because of their lower resistance. We also discussed several types of platings, including tin, silver, and nickel-palladium-gold coatings, and their advantages and disadvantages. Leadframe technology is an older technology that is mature, but it is still widely used in the industry. We still make billions of devices per year with leadframes, and will continue to do so for the foreseeable future. 4
5 Technical Tidbit IDDQ Behavior and the Curve Tracer Quiescent Power Supply Current ( IDDQ) is a powerful way to examine a component during a failure analysis effort. Many types of defects can be identified from the IDDQ signature. We won t go into why this is so here, as there is more information on this topic on our Online Training site. However, we will discuss the nature of the IDDQ measurement and what it tells us. First, let s discuss how to make a Quiescent Power Supply Current (IDDQ) measurement on a bench setup. To perform this test, one needs a curve tracer or a parameter analyzer, a switchbox capable of connecting to the curve tracer and the device, and the device to be tested. The analyst should then place the IC in a non-contention state. A non-contention state is one where there are no transistor outputs trying to drive a logical high and a low at the same time on the same node. In order to remove the contention, it may be necessary to clock the IC or input a few vectors to the appropriate inputs. The analyst should tie all of the inputs to either VDD or VSS, float all of the outputs, and sweep the voltage on the V DD side from the maximum rated supply voltage down to zero. This will yield a curve similar to the curve shown in the lower left portion of this slide. Figure 1. Basic setup for IDDQ on a curve tracer. Figure 2 shows some actual examples of IDD-VDD curves. These are all taken from microprocessor analysis work done several years ago. The microprocessors are 0.5µm CMOS circuits with approximately 800,000 transistors. The curve on the upper left has an obvious parabolic shape to it. Subsequent failure analysis localized the problem to a gate oxide short in an n-channel transistor within the random logic. The curve on the upper right shows a linear shape. In this case, the defect was localized to a high 5
6 resistance short between VDD and VSS In the example in the lower left, the IDD-VDD curve exhibits an exponential characteristic. The current is well within the specified limits at 3.3 volts and 5.0 volts, but it increases rapidly at about 5.5 volts, somewhat sooner than a defect-free circuit. This leakage is due to a soft pn junction, and possibly attributable to electrostatic discharge damage. The I DD -VDD curve on the lower right has an erratic shape to it. We created the IDD-VDD curve by sweeping from the supply voltage down to zero. Notice that the current starts at a low value, then jumps high. It then meanders erratically downward until about 1 volt, where it then drops to a low value. An erratic, time-varying current is indicative of an open circuit defect. Figure 2. IDD-VDD curves associated with various defects. Gate oxide short (upper left), VDD-VSS bridging short (upper right), ESD damage causing soft breakdown (lower left), and open vias (lower right). 6
7 Ask the Experts Q: How accurate is an IDDQ vs. VDD curve trace in determining the actual defect on an IC? A: We actually discuss this test and defects in this month's Technical Tidbit. IDDQ vs. VDD can help the analyst separate opens from shorts, and identify various types of shorts, but the accuracy level is only around 85% or so. Although IDDQ is a great test for establishing the direction of an analysis, it is even less accurate by itself in determining what the actual defect will be. One will need further analysis to identify the actual defect. 7
8 Spotlight: Process Integration Short Course OVERVIEW Semiconductor and integrated circuit developments continue to proceed at an incredible pace. For example, today s microprocessor chips have one thousand times the processing power of those a decade ago. These challenges have been accomplished because of the integrated circuit industry s ability to track something known as Moore s Law. Moore s Law states that an integrated circuit s processing power will double every two years. This has been accomplished by making devices smaller and smaller. The question looming in everyone s mind is How far into the future can this continue? CMOS and BiCMOS Process Integration is a five-day course that offers detailed instruction on the physics behind the operation of a modern integrated circuit, and the processing technologies required to make them. We place special emphasis on current issues related to designing and manufacturing the next generation devices. This course is a must for every manager, engineer and technician working in the semiconductor industry, using semiconductor components or supplying tools to the industry. By focusing on the fundamentals of transistor operation and interconnect performance, participants will learn why advances in the industry are occurring along certain lines and not others. Our instructors work hard to explain how semiconductor devices work without delving heavily into the complex physics and mathematical expressions that normally accompany this discipline. Participants learn basic but powerful aspects about the semiconductor industry. This skill-building series is divided into four segments: 1. Basic Device Operation. Participants learn the fundamentals of transistor operation. They learn why CMOS (Complimentary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) devices dominate the industry today 2. Fabrication Technologies. Participants learn the fundamental manufacturing technologies that are used to make modern integrated circuits. They learn the typical CMOS and BiCMOS process flows used in integrated circuit fabrication. 3. Current Issues in Process Integration. Participants learn how device operation is increasingly constrained by three parameters. They also learn about the impact of using new materials in the fabrication process and how those materials may create problems for the manufacturers in the future. 4. An Overview of Issues Related to Process Integration. Participants learn about the image of new materials, yield, reliability and scaling on technology and process integration. They receive an overview of the major reliability mechanisms that affect silicon ICs today. COURSE OBJECTIVES 1. The seminar will provide participants with an in-depth understanding of the semiconductor industry and its technical issues. 2. Participants will understand the basic concepts behind transistor operation and performance. 3. The seminar will identify the key issues related to the continued growth of the semiconductor industry. 8
9 4. The seminar offers a wide variety of sample problems that participants work to help them gain knowledge of the fundamentals of device operation and manufacturing. 5. Participants will be able to identify basic and advanced technology features on semiconductor devices. This includes features like silicon-germanium, strained silicon, copper, and low-k dielectrics. 6. Participants will understand how reliability, power consumption and device performance are interrelated. 7. Participants will be able to make decisions about how to construct and evaluate new CMOS, BiCMOS, and bipolar technologies. INSTRUCTIONAL STRATEGY By using a combination of instruction by lecture, classroom exercises, and question/answer sessions, participants will learn practical information on semiconductor devices and the operation of this industry. From the very first moments of the seminar until the last sentence of the training, the driving instructional factor is application. We use instructors who are internationally recognized experts in their fields that have years of experience (both current and relevant) in this field. The handbook offers hundreds of pages of additional reference material the participants can use back at their daily activities. COURSE OUTLINE 1. Introduction 2. Conventional CMOS a. Key Components and Parameters b. Process Overview and Integration Issues c. Scaling and Limitations 3. Mobility Enhancement Techniques a. Strained Silicon b. Crystal Orientation 4. Gate Stacks, High-k Dielectrics a. Gate Conductor Materials and Properties b. High-k Materials and Properties c. Gate Stack Integration 5. Options for Source-Drain, Extensions a. Elevated Source/Drain b. Co-Implantation of Inactive Species c. Schottky-Barrier Source-Drain 9
10 6. Three-Dimensional Structures a. FinFETs, Multi-Gates 7. Interconnects a. Aluminum Interconnects, Issues b. Copper Interconnects, Issues c. Low-k Dielectrics 8. Conventional BiCMOS a. Bipolar Transistor Fundamentals b. BiCMOS Process Overview c. Scaling and Limitations 9. Bipolar Enhancement Techniques a. SiGe b. SiGe:C 10. CMOS/BiCMOS Reliability Considerations a. Electrostatic Discharge b. Electromigration and Stress Migration c. Soft Errors, Plasma Damage d. Dielectric Reliability e. Bias Temperature Instabilities f. Hot Carrier Reliability g. Burn-In 11. Yield Considerations a. Yield Detractors b. Models c. Monitors 10
11 Upcoming Courses (Click on each item for details) ESD Design and Technology February 11 13, 2014 (Tue Thur) San Jose, California, USA Semiconductor Reliability February 11 13, 2014 (Tues Thur) San Jose, California, USA Failure and Yield Analysis February 17 20, 2014 (Mon Thur) San Jose, California, USA Wafer Fab Processing February 18, 2014 (Tue) San Jose, California, USA Feedback If you have a suggestion or a comment regarding our courses, online training, discussion forums, or reference materials, or if you wish to suggest a new course or location, please call us at or us (info@semitracks.com). To submit questions to the Q&A section, inquire about an article, or suggest a topic you would like to see covered in the next newsletter, please contact Jeremy Henderson by (jeremy.henderson@semitracks.com). We are always looking for ways to enhance our courses and educational materials. ~ For more information on Semitracks online training or public courses, visit our web site! Microelectronic Defect, Fault Isolation and Failure Analysis February 19 21, 2014 (Wed Fri) Malaysia Microelectronic Defect, Fault Isolation and Failure Analysis February 24 26, 2014 (Mon Wed) Singapore CMOS, BICMOS and Bipolar Process Integraion March 25 26, 2014 (Tue Wed) Austin, Texas, USA To post, read, or answer a question, visit our forums. We look forward to hearing from you! 11
Decapsulation Overview
 Decapsulation Overview By Christopher Henderson This month we will cover an overview of decapsulation. For standard plastic packages, there are two basic methods for exposing the die surface a standard
Decapsulation Overview By Christopher Henderson This month we will cover an overview of decapsulation. For standard plastic packages, there are two basic methods for exposing the die surface a standard
Test Structures Basics Part 1
 Test Structures Basics Part 1 By Christopher Henderson In this document we will provide an overview of test structures as they pertain to reliability. Test structures can provide critical insight into
Test Structures Basics Part 1 By Christopher Henderson In this document we will provide an overview of test structures as they pertain to reliability. Test structures can provide critical insight into
Fault Diagnosis Algorithms Part 2
 Fault Diagnosis Algorithms Part 2 By Christopher Henderson Page 1 Fault Diagnosis Algorithms Part 2 Page 5 Technical Tidbit Page 8 Ask the Experts Figure 4. Circuit schematic. This is an example of a circuit
Fault Diagnosis Algorithms Part 2 By Christopher Henderson Page 1 Fault Diagnosis Algorithms Part 2 Page 5 Technical Tidbit Page 8 Ask the Experts Figure 4. Circuit schematic. This is an example of a circuit
Die Attach 1. Page 1 Die Attach 1. Page Technical Tidbit. Page Ask the Experts
 Die Attach 1 By Christopher Henderson In this section we will cover die attach materials. There are several major classes of materials, including liquid-dispensed materials and adhesive films. Stay tuned
Die Attach 1 By Christopher Henderson In this section we will cover die attach materials. There are several major classes of materials, including liquid-dispensed materials and adhesive films. Stay tuned
Issue 112 October 2018
 Latch-Up Overview Part 2 By Christopher Henderson In this section, we will continue to discuss the topic of latchup. We will discuss latch-up testing. We perform latch-up testing to determine the robustness
Latch-Up Overview Part 2 By Christopher Henderson In this section, we will continue to discuss the topic of latchup. We will discuss latch-up testing. We perform latch-up testing to determine the robustness
Quartz Disc Storage Systems
 Quartz Disc Storage Systems By Christopher Henderson In this short section we will cover a recently developed technology for storing data on a quartz disc. Researchers demonstrate a high-density five dimensional
Quartz Disc Storage Systems By Christopher Henderson In this short section we will cover a recently developed technology for storing data on a quartz disc. Researchers demonstrate a high-density five dimensional
Figure 1. Wafer redistribution process flow.
 Bump Processes Part III By Christopher Henderson In Part III this month, we will discuss the redistribution layer process. The drawing on the left shows a standard RDL process flow. We begin by depositing
Bump Processes Part III By Christopher Henderson In Part III this month, we will discuss the redistribution layer process. The drawing on the left shows a standard RDL process flow. We begin by depositing
Lead Free Solders General Issues
 Lead Free Solders General Issues By Christopher Henderson In this section we will discuss some of the technical challenges associated with the use of lead-free solders. Lead-free solders are now in widespread
Lead Free Solders General Issues By Christopher Henderson In this section we will discuss some of the technical challenges associated with the use of lead-free solders. Lead-free solders are now in widespread
Issue 89 November 2016
 Voltage Contrast Part 1 By Christopher Henderson In this presentation, we discuss voltage contrast, one of a number of techniques that use scanning electron microscopy to aid in fault isolation. Voltage
Voltage Contrast Part 1 By Christopher Henderson In this presentation, we discuss voltage contrast, one of a number of techniques that use scanning electron microscopy to aid in fault isolation. Voltage
Figure 7. Hot Carrier Damage Tracks the P-well Current.
 Hot Carrier Degradation Physics By Christopher Henderson One useful technique to indirectly observe the damage created by hot carriers is to measure the p-well current. The p-well current closely tracks
Hot Carrier Degradation Physics By Christopher Henderson One useful technique to indirectly observe the damage created by hot carriers is to measure the p-well current. The p-well current closely tracks
Issue 111 September 2018
 Latch-Up Overview Part 1 By Christopher Henderson In this section, we will discuss the topic of latch-up. Latch-up is a form of electrical overstress that results in malfunction of the circuit, but may
Latch-Up Overview Part 1 By Christopher Henderson In this section, we will discuss the topic of latch-up. Latch-up is a form of electrical overstress that results in malfunction of the circuit, but may
Chapter 3 Basics Semiconductor Devices and Processing
 Chapter 3 Basics Semiconductor Devices and Processing 1 Objectives Identify at least two semiconductor materials from the periodic table of elements List n-type and p-type dopants Describe a diode and
Chapter 3 Basics Semiconductor Devices and Processing 1 Objectives Identify at least two semiconductor materials from the periodic table of elements List n-type and p-type dopants Describe a diode and
Chapter 3: Basics Semiconductor Devices and Processing 2006/9/27 1. Topics
 Chapter 3: Basics Semiconductor Devices and Processing 2006/9/27 1 Topics What is semiconductor Basic semiconductor devices Basics of IC processing CMOS technologies 2006/9/27 2 1 What is Semiconductor
Chapter 3: Basics Semiconductor Devices and Processing 2006/9/27 1 Topics What is semiconductor Basic semiconductor devices Basics of IC processing CMOS technologies 2006/9/27 2 1 What is Semiconductor
MICROPROCESSOR TECHNOLOGY
 MICROPROCESSOR TECHNOLOGY Assis. Prof. Hossam El-Din Moustafa Lecture 3 Ch.1 The Evolution of The Microprocessor 17-Feb-15 1 Chapter Objectives Introduce the microprocessor evolution from transistors to
MICROPROCESSOR TECHNOLOGY Assis. Prof. Hossam El-Din Moustafa Lecture 3 Ch.1 The Evolution of The Microprocessor 17-Feb-15 1 Chapter Objectives Introduce the microprocessor evolution from transistors to
Lecture #29. Moore s Law
 Lecture #29 ANNOUNCEMENTS HW#15 will be for extra credit Quiz #6 (Thursday 5/8) will include MOSFET C-V No late Projects will be accepted after Thursday 5/8 The last Coffee Hour will be held this Thursday
Lecture #29 ANNOUNCEMENTS HW#15 will be for extra credit Quiz #6 (Thursday 5/8) will include MOSFET C-V No late Projects will be accepted after Thursday 5/8 The last Coffee Hour will be held this Thursday
420 Intro to VLSI Design
 Dept of Electrical and Computer Engineering 420 Intro to VLSI Design Lecture 0: Course Introduction and Overview Valencia M. Joyner Spring 2005 Getting Started Syllabus About the Instructor Labs, Problem
Dept of Electrical and Computer Engineering 420 Intro to VLSI Design Lecture 0: Course Introduction and Overview Valencia M. Joyner Spring 2005 Getting Started Syllabus About the Instructor Labs, Problem
2.8 - CMOS TECHNOLOGY
 CMOS Technology (6/7/00) Page 1 2.8 - CMOS TECHNOLOGY INTRODUCTION Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Illustrate the fabrication sequence for a typical MOS transistor 2.) Show the physical
CMOS Technology (6/7/00) Page 1 2.8 - CMOS TECHNOLOGY INTRODUCTION Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Illustrate the fabrication sequence for a typical MOS transistor 2.) Show the physical
In this lecture we will begin a new topic namely the Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor.
 Solid State Devices Dr. S. Karmalkar Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 38 MOS Field Effect Transistor In this lecture we will begin
Solid State Devices Dr. S. Karmalkar Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 38 MOS Field Effect Transistor In this lecture we will begin
ECE 5745 Complex Digital ASIC Design Topic 2: CMOS Devices
 ECE 5745 Complex Digital ASIC Design Topic 2: CMOS Devices Christopher Batten School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cornell University http://www.csl.cornell.edu/courses/ece5950 Simple Transistor
ECE 5745 Complex Digital ASIC Design Topic 2: CMOS Devices Christopher Batten School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cornell University http://www.csl.cornell.edu/courses/ece5950 Simple Transistor
Gallium nitride (GaN)
 80 Technology focus: GaN power electronics Vertical, CMOS and dual-gate approaches to gallium nitride power electronics US research company HRL Laboratories has published a number of papers concerning
80 Technology focus: GaN power electronics Vertical, CMOS and dual-gate approaches to gallium nitride power electronics US research company HRL Laboratories has published a number of papers concerning
Thermal Management in the 3D-SiP World of the Future
 Thermal Management in the 3D-SiP World of the Future Presented by W. R. Bottoms March 181 th, 2013 Smaller, More Powerful Portable Devices Are Driving Up Power Density Power (both power delivery and power
Thermal Management in the 3D-SiP World of the Future Presented by W. R. Bottoms March 181 th, 2013 Smaller, More Powerful Portable Devices Are Driving Up Power Density Power (both power delivery and power
SAMPLE SLIDES & COURSE OUTLINE. Core Competency In Semiconductor Technology: 2. FABRICATION. Dr. Theodore (Ted) Dellin
 & Digging Deeper Devices, Fabrication & Reliability For More Info:.com or email Dellin@ieee.org SAMPLE SLIDES & COURSE OUTLINE In : 2. A Easy, Effective, of How Devices Are.. Recommended for everyone who
& Digging Deeper Devices, Fabrication & Reliability For More Info:.com or email Dellin@ieee.org SAMPLE SLIDES & COURSE OUTLINE In : 2. A Easy, Effective, of How Devices Are.. Recommended for everyone who
Integrated diodes. The forward voltage drop only slightly depends on the forward current. ELEKTRONIKOS ĮTAISAI
 1 Integrated diodes pn junctions of transistor structures can be used as integrated diodes. The choice of the junction is limited by the considerations of switching speed and breakdown voltage. The forward
1 Integrated diodes pn junctions of transistor structures can be used as integrated diodes. The choice of the junction is limited by the considerations of switching speed and breakdown voltage. The forward
Issue 90 December 2016
 Voltage Contrast Part 2 By Christopher Henderson The next variation of voltage contrast is biased voltage contrast. Biased voltage contrast is the imaging of voltages on a device with a bias applied to
Voltage Contrast Part 2 By Christopher Henderson The next variation of voltage contrast is biased voltage contrast. Biased voltage contrast is the imaging of voltages on a device with a bias applied to
EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis. Lecture 1 Introduction Zhuo Feng
 EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Lecture 1 Introduction Zhuo Feng 1.1 Prof. Zhuo Feng Office: EERC 730 Phone: 487-3116 Email: zhuofeng@mtu.edu Class Website http://www.ece.mtu.edu/~zhuofeng/ee4800fall2010.html
EE4800 CMOS Digital IC Design & Analysis Lecture 1 Introduction Zhuo Feng 1.1 Prof. Zhuo Feng Office: EERC 730 Phone: 487-3116 Email: zhuofeng@mtu.edu Class Website http://www.ece.mtu.edu/~zhuofeng/ee4800fall2010.html
Ridgetop Group, Inc.
 Ridgetop Group, Inc. Ridgetop Group Facilities in Tucson, AZ Arizona-based firm, founded in 2000, with focus on electronics for critical applications Two divisions: Semiconductor & Precision Instruments
Ridgetop Group, Inc. Ridgetop Group Facilities in Tucson, AZ Arizona-based firm, founded in 2000, with focus on electronics for critical applications Two divisions: Semiconductor & Precision Instruments
Lecture 0: Introduction
 Lecture 0: Introduction Introduction Integrated circuits: many transistors on one chip. Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI): bucketloads! Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor Fast, cheap, low power
Lecture 0: Introduction Introduction Integrated circuits: many transistors on one chip. Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI): bucketloads! Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor Fast, cheap, low power
UNIT-VI FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR. 1. Explain about the Field Effect Transistor and also mention types of FET s.
 UNIT-I FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR 1. Explain about the Field Effect Transistor and also mention types of FET s. The Field Effect Transistor, or simply FET however, uses the voltage that is applied to their
UNIT-I FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR 1. Explain about the Field Effect Transistor and also mention types of FET s. The Field Effect Transistor, or simply FET however, uses the voltage that is applied to their
Newer process technology (since 1999) includes :
 Newer process technology (since 1999) includes : copper metalization hi-k dielectrics for gate insulators si on insulator strained silicon lo-k dielectrics for interconnects Immersion lithography for masks
Newer process technology (since 1999) includes : copper metalization hi-k dielectrics for gate insulators si on insulator strained silicon lo-k dielectrics for interconnects Immersion lithography for masks
A NEW TECHNIQUE TO RAPIDLY IDENTIFY LOW LEVEL GATE OXIDE LEAKAGE IN FIELD EFFECT SEMICONDUCTORS USING A SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE.
 A NEW TECHNIQUE TO RAPIDLY IDENTIFY LOW LEVEL GATE OXIDE LEAKAGE IN FIELD EFFECT SEMICONDUCTORS USING A SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE. Jim Colvin Waferscale Integration Inc. 47280 Kato Rd. Fremont, CA 94538
A NEW TECHNIQUE TO RAPIDLY IDENTIFY LOW LEVEL GATE OXIDE LEAKAGE IN FIELD EFFECT SEMICONDUCTORS USING A SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPE. Jim Colvin Waferscale Integration Inc. 47280 Kato Rd. Fremont, CA 94538
ECE520 VLSI Design. Lecture 2: Basic MOS Physics. Payman Zarkesh-Ha
 ECE520 VLSI Design Lecture 2: Basic MOS Physics Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Wednesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: pzarkesh@unm.edu Slide: 1 Review of Last Lecture Semiconductor
ECE520 VLSI Design Lecture 2: Basic MOS Physics Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: ECE Bldg. 230B Office hours: Wednesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: pzarkesh@unm.edu Slide: 1 Review of Last Lecture Semiconductor
The Art of ANALOG LAYOUT Second Edition
 The Art of ANALOG LAYOUT Second Edition Alan Hastings 3 EARSON Pearson Education International Contents Preface to the Second Edition xvii Preface to the First Edition xix Acknowledgments xxi 1 Device
The Art of ANALOG LAYOUT Second Edition Alan Hastings 3 EARSON Pearson Education International Contents Preface to the Second Edition xvii Preface to the First Edition xix Acknowledgments xxi 1 Device
Source: IC Layout Basics. Diodes
 Source: IC Layout Basics C HAPTER 7 Diodes Chapter Preview Here s what you re going to see in this chapter: A diode is a PN junction How several types of diodes are built A look at some different uses
Source: IC Layout Basics C HAPTER 7 Diodes Chapter Preview Here s what you re going to see in this chapter: A diode is a PN junction How several types of diodes are built A look at some different uses
Basic Fabrication Steps
 Basic Fabrication Steps and Layout Somayyeh Koohi Department of Computer Engineering Adapted with modifications from lecture notes prepared by author Outline Fabrication steps Transistor structures Transistor
Basic Fabrication Steps and Layout Somayyeh Koohi Department of Computer Engineering Adapted with modifications from lecture notes prepared by author Outline Fabrication steps Transistor structures Transistor
FinFET vs. FD-SOI Key Advantages & Disadvantages
 FinFET vs. FD-SOI Key Advantages & Disadvantages Amiad Conley Technical Marketing Manager Process Diagnostics & Control, Applied Materials ChipEx-2014, Apr 2014 1 Moore s Law The number of transistors
FinFET vs. FD-SOI Key Advantages & Disadvantages Amiad Conley Technical Marketing Manager Process Diagnostics & Control, Applied Materials ChipEx-2014, Apr 2014 1 Moore s Law The number of transistors
INTRODUCTION TO MOS TECHNOLOGY
 INTRODUCTION TO MOS TECHNOLOGY 1. The MOS transistor The most basic element in the design of a large scale integrated circuit is the transistor. For the processes we will discuss, the type of transistor
INTRODUCTION TO MOS TECHNOLOGY 1. The MOS transistor The most basic element in the design of a large scale integrated circuit is the transistor. For the processes we will discuss, the type of transistor
TDDB Time Depending Dielectric Breakdown. NBTI Negative Bias Temperature Instability. Human Body Model / Machine Model
 For integrated circuits or discrete semiconductors select Amkor-Kr to ASECL Assembly Transfer with Cu wire bonds ID Type of change No Yes AC TC SD Headings ANY A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 B1 B2 B3 C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6
For integrated circuits or discrete semiconductors select Amkor-Kr to ASECL Assembly Transfer with Cu wire bonds ID Type of change No Yes AC TC SD Headings ANY A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 B1 B2 B3 C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6
EMT 251 Introduction to IC Design
 EMT 251 Introduction to IC Design (Pengantar Rekabentuk Litar Terkamir) Semester II 2011/2012 Introduction to IC design and Transistor Fundamental Some Keywords! Very-large-scale-integration (VLSI) is
EMT 251 Introduction to IC Design (Pengantar Rekabentuk Litar Terkamir) Semester II 2011/2012 Introduction to IC design and Transistor Fundamental Some Keywords! Very-large-scale-integration (VLSI) is
Chapter 1, Introduction
 Introduction to Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology Chapter 1, Introduction hxiao89@hotmail.com 1 Objective After taking this course, you will able to Use common semiconductor terminology Describe a
Introduction to Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology Chapter 1, Introduction hxiao89@hotmail.com 1 Objective After taking this course, you will able to Use common semiconductor terminology Describe a
Integrated Circuit Technology (Course Code: EE662) Lecture 1: Introduction
 Indian Institute of Technology Jodhpur, Year 2015 2016 Integrated Circuit Technology (Course Code: EE662) Lecture 1: Introduction Course Instructor: Shree Prakash Tiwari, Ph.D. Email: sptiwari@iitj.ac.in
Indian Institute of Technology Jodhpur, Year 2015 2016 Integrated Circuit Technology (Course Code: EE662) Lecture 1: Introduction Course Instructor: Shree Prakash Tiwari, Ph.D. Email: sptiwari@iitj.ac.in
Transistor was first invented by William.B.Shockley, Walter Brattain and John Bardeen of Bell Labratories. In 1961, first IC was introduced.
 Unit 1 Basic MOS Technology Transistor was first invented by William.B.Shockley, Walter Brattain and John Bardeen of Bell Labratories. In 1961, first IC was introduced. Levels of Integration:- i) SSI:-
Unit 1 Basic MOS Technology Transistor was first invented by William.B.Shockley, Walter Brattain and John Bardeen of Bell Labratories. In 1961, first IC was introduced. Levels of Integration:- i) SSI:-
EFFECTS OF USG CURRENT AND BONDING LOAD ON BONDING FORMATION IN QFN STACKED DIE PACKAGE. A. Jalar, S.A. Radzi and M.A.A. Hamid
 Solid State Science and Technology, Vol. 16, No 2 (2008) 65-71 EFFECTS OF USG CURRENT AND BONDING LOAD ON BONDING FORMATION IN QFN STACKED DIE PACKAGE A. Jalar, S.A. Radzi and M.A.A. Hamid School of Applied
Solid State Science and Technology, Vol. 16, No 2 (2008) 65-71 EFFECTS OF USG CURRENT AND BONDING LOAD ON BONDING FORMATION IN QFN STACKED DIE PACKAGE A. Jalar, S.A. Radzi and M.A.A. Hamid School of Applied
VLSI Design. Introduction
 VLSI Design Introduction Outline Introduction Silicon, pn-junctions and transistors A Brief History Operation of MOS Transistors CMOS circuits Fabrication steps for CMOS circuits Introduction Integrated
VLSI Design Introduction Outline Introduction Silicon, pn-junctions and transistors A Brief History Operation of MOS Transistors CMOS circuits Fabrication steps for CMOS circuits Introduction Integrated
Digital Integrated Circuits EECS 312
 14 12 10 8 6 Fujitsu VP2000 IBM 3090S Pulsar 4 IBM 3090 IBM RY6 CDC Cyber 205 IBM 4381 IBM RY4 2 IBM 3081 Apache Fujitsu M380 IBM 370 Merced IBM 360 IBM 3033 Vacuum Pentium II(DSIP) 0 1950 1960 1970 1980
14 12 10 8 6 Fujitsu VP2000 IBM 3090S Pulsar 4 IBM 3090 IBM RY6 CDC Cyber 205 IBM 4381 IBM RY4 2 IBM 3081 Apache Fujitsu M380 IBM 370 Merced IBM 360 IBM 3033 Vacuum Pentium II(DSIP) 0 1950 1960 1970 1980
Semiconductor Process Reliability SVTW 2012 Esko Mikkola, Ph.D. & Andrew Levy
 Semiconductor Process Reliability SVTW 2012 Esko Mikkola, Ph.D. & Andrew Levy 1 IC Failure Modes Affecting Reliability Via/metallization failure mechanisms Electro migration Stress migration Transistor
Semiconductor Process Reliability SVTW 2012 Esko Mikkola, Ph.D. & Andrew Levy 1 IC Failure Modes Affecting Reliability Via/metallization failure mechanisms Electro migration Stress migration Transistor
Session 3: Solid State Devices. Silicon on Insulator
 Session 3: Solid State Devices Silicon on Insulator 1 Outline A B C D E F G H I J 2 Outline Ref: Taurand Ning 3 SOI Technology SOl materials: SIMOX, BESOl, and Smart Cut SIMOX : Synthesis by IMplanted
Session 3: Solid State Devices Silicon on Insulator 1 Outline A B C D E F G H I J 2 Outline Ref: Taurand Ning 3 SOI Technology SOl materials: SIMOX, BESOl, and Smart Cut SIMOX : Synthesis by IMplanted
CMOS Digital Integrated Circuits Lec 2 Fabrication of MOSFETs
 CMOS Digital Integrated Circuits Lec 2 Fabrication of MOSFETs 1 CMOS Digital Integrated Circuits 3 rd Edition Categories of Materials Materials can be categorized into three main groups regarding their
CMOS Digital Integrated Circuits Lec 2 Fabrication of MOSFETs 1 CMOS Digital Integrated Circuits 3 rd Edition Categories of Materials Materials can be categorized into three main groups regarding their
+1 (479)
 Introduction to VLSI Design http://csce.uark.edu +1 (479) 575-6043 yrpeng@uark.edu Invention of the Transistor Vacuum tubes ruled in first half of 20th century Large, expensive, power-hungry, unreliable
Introduction to VLSI Design http://csce.uark.edu +1 (479) 575-6043 yrpeng@uark.edu Invention of the Transistor Vacuum tubes ruled in first half of 20th century Large, expensive, power-hungry, unreliable
LSI Logic LSI53C1030 PCI-X to Dual Channel Ultra320 SCSI Controller 0.18 µm CMOS Process
 LSI Logic LSI53C13 PCI-X to Dual Channel Ultra32 SCSI Controller.18 µm CMOS Process Structural Analysis For comments, questions, or more information about this report, or for any additional technical needs
LSI Logic LSI53C13 PCI-X to Dual Channel Ultra32 SCSI Controller.18 µm CMOS Process Structural Analysis For comments, questions, or more information about this report, or for any additional technical needs
ECE 340 Lecture 37 : Metal- Insulator-Semiconductor FET Class Outline:
 ECE 340 Lecture 37 : Metal- Insulator-Semiconductor FET Class Outline: Metal-Semiconductor Junctions MOSFET Basic Operation MOS Capacitor Things you should know when you leave Key Questions What is the
ECE 340 Lecture 37 : Metal- Insulator-Semiconductor FET Class Outline: Metal-Semiconductor Junctions MOSFET Basic Operation MOS Capacitor Things you should know when you leave Key Questions What is the
Sub-micron technology IC fabrication process trends SOI technology. Development of CMOS technology. Technology problems due to scaling
 Goodbye Microelectronics Welcome Nanoelectronics Sub-micron technology IC fabrication process trends SOI technology SiGe Tranzistor in 50nm process Virus The thickness of gate oxide= 1.2 nm!!! Today we
Goodbye Microelectronics Welcome Nanoelectronics Sub-micron technology IC fabrication process trends SOI technology SiGe Tranzistor in 50nm process Virus The thickness of gate oxide= 1.2 nm!!! Today we
Alternatives to standard MOSFETs. What problems are we really trying to solve?
 Alternatives to standard MOSFETs A number of alternative FET schemes have been proposed, with an eye toward scaling up to the 10 nm node. Modifications to the standard MOSFET include: Silicon-in-insulator
Alternatives to standard MOSFETs A number of alternative FET schemes have been proposed, with an eye toward scaling up to the 10 nm node. Modifications to the standard MOSFET include: Silicon-in-insulator
LOW-POWER SOFTWARE-DEFINED RADIO DESIGN USING FPGAS
 LOW-POWER SOFTWARE-DEFINED RADIO DESIGN USING FPGAS Charlie Jenkins, (Altera Corporation San Jose, California, USA; chjenkin@altera.com) Paul Ekas, (Altera Corporation San Jose, California, USA; pekas@altera.com)
LOW-POWER SOFTWARE-DEFINED RADIO DESIGN USING FPGAS Charlie Jenkins, (Altera Corporation San Jose, California, USA; chjenkin@altera.com) Paul Ekas, (Altera Corporation San Jose, California, USA; pekas@altera.com)
INCREASING PACKAGE ROBUSTNESS WITH PALLADIUM COATED COPPER WIRE
 INCREASING PACKAGE ROBUSTNESS WITH PALLADIUM COATED COPPER WIRE Rodan A. Melanio Regine B. Cervantes Sonny E. Dipasupil New Package Development ON Semiconductor Philippines Incorporated Golden Mile Business
INCREASING PACKAGE ROBUSTNESS WITH PALLADIUM COATED COPPER WIRE Rodan A. Melanio Regine B. Cervantes Sonny E. Dipasupil New Package Development ON Semiconductor Philippines Incorporated Golden Mile Business
ATV 2011: Computer Engineering
 ATV 2011: Technology Trends in Computer Engineering Professor Per Larsson-Edefors ATV 2011, L1, Per Larsson-Edefors Page 1 Solid-State Devices www.cse.chalmers.se/~perla/ugrad/ SemTech/Lectures_2000.pdf
ATV 2011: Technology Trends in Computer Engineering Professor Per Larsson-Edefors ATV 2011, L1, Per Larsson-Edefors Page 1 Solid-State Devices www.cse.chalmers.se/~perla/ugrad/ SemTech/Lectures_2000.pdf
VLSI Design. Introduction
 Tassadaq Hussain VLSI Design Introduction Outcome of this course Problem Aims Objectives Outcomes Data Collection Theoretical Model Mathematical Model Validate Development Analysis and Observation Pseudo
Tassadaq Hussain VLSI Design Introduction Outcome of this course Problem Aims Objectives Outcomes Data Collection Theoretical Model Mathematical Model Validate Development Analysis and Observation Pseudo
Tape Automated Bonding
 Tape Automated Bonding Introduction TAB evolved from the minimod project begun at General Electric in 1965, and the term Tape Automated Bonding was coined by Gerard Dehaine of Honeywell Bull in 1971. The
Tape Automated Bonding Introduction TAB evolved from the minimod project begun at General Electric in 1965, and the term Tape Automated Bonding was coined by Gerard Dehaine of Honeywell Bull in 1971. The
Yield, Reliability and Testing. Technical University of Lodz - Department of Microelectronics and Computer Science
 Yield, Reliability and Testing The Progressive Trend of IC Technology Integration level Year Number of transistors DRAM integration SSI 1950s less than 10 2 MSI 1960s 10 2-10 3 LSI 1970s 10 3-10 5 4K,
Yield, Reliability and Testing The Progressive Trend of IC Technology Integration level Year Number of transistors DRAM integration SSI 1950s less than 10 2 MSI 1960s 10 2-10 3 LSI 1970s 10 3-10 5 4K,
CREATING RELIABLE AND MANUFACTURABLE RF DESIGNS
 CREATING RELIABLE AND MANUFACTURABLE RF DESIGNS Chandra Gupta, Ph.D., MBA CPI, BMD, Beverly, MA IEEE Boston Reliability Chapter, Lexington, MA Sept 13, 2017 IEEE Boston Reliability Boston Chapter Sept
CREATING RELIABLE AND MANUFACTURABLE RF DESIGNS Chandra Gupta, Ph.D., MBA CPI, BMD, Beverly, MA IEEE Boston Reliability Chapter, Lexington, MA Sept 13, 2017 IEEE Boston Reliability Boston Chapter Sept
Body-Biased Complementary Logic Implemented Using AlN Piezoelectric MEMS Switches
 University of Pennsylvania From the SelectedWorks of Nipun Sinha 29 Body-Biased Complementary Logic Implemented Using AlN Piezoelectric MEMS Switches Nipun Sinha, University of Pennsylvania Timothy S.
University of Pennsylvania From the SelectedWorks of Nipun Sinha 29 Body-Biased Complementary Logic Implemented Using AlN Piezoelectric MEMS Switches Nipun Sinha, University of Pennsylvania Timothy S.
Gold plating, 140 Gases compressed, 393 liquid,393 Grounding, safety, 403
 INDEX Acids, safety, 394 Activities, 1 Adhesives, 349 Allowances manufacturing, 77 rework,82 Aluminum Plating, 139 Analysis work distribution, 20, 29 processes, 32 Analyzing job details, 19 Assemblers
INDEX Acids, safety, 394 Activities, 1 Adhesives, 349 Allowances manufacturing, 77 rework,82 Aluminum Plating, 139 Analysis work distribution, 20, 29 processes, 32 Analyzing job details, 19 Assemblers
Advanced PDK and Technologies accessible through ASCENT
 Advanced PDK and Technologies accessible through ASCENT MOS-AK Dresden, Sept. 3, 2018 L. Perniola*, O. Rozeau*, O. Faynot*, T. Poiroux*, P. Roseingrave^ olivier.faynot@cea.fr *Cea-Leti, Grenoble France;
Advanced PDK and Technologies accessible through ASCENT MOS-AK Dresden, Sept. 3, 2018 L. Perniola*, O. Rozeau*, O. Faynot*, T. Poiroux*, P. Roseingrave^ olivier.faynot@cea.fr *Cea-Leti, Grenoble France;
CMOS Technology. 1. Why CMOS 2. Qualitative MOSFET model 3. Building a MOSFET 4. CMOS logic gates. Handouts: Lecture Slides. metal ndiff.
 CMOS Technology 1. Why CMOS 2. Qualitative MOSFET model 3. Building a MOSFET 4. CMOS logic gates poly pdiff metal ndiff Handouts: Lecture Slides L03 - CMOS Technology 1 Building Bits from Atoms V in V
CMOS Technology 1. Why CMOS 2. Qualitative MOSFET model 3. Building a MOSFET 4. CMOS logic gates poly pdiff metal ndiff Handouts: Lecture Slides L03 - CMOS Technology 1 Building Bits from Atoms V in V
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 19 CMOS Implementation Technologies. Recap and Outline
 EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 19 CMOS Implementation Technologies Oct. 31, 2013 Prof. Ronald Fearing Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley (slides courtesy
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 19 CMOS Implementation Technologies Oct. 31, 2013 Prof. Ronald Fearing Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley (slides courtesy
6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 MIT, Spring 2003 6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Jesús del Alamo Dimitri Antoniadis, Judy Hoyt, Charles Sodini Pablo Acosta, Susan Luschas, Jorg Scholvin, Niamh Waldron Lecture 1 6.012 overview
MIT, Spring 2003 6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Jesús del Alamo Dimitri Antoniadis, Judy Hoyt, Charles Sodini Pablo Acosta, Susan Luschas, Jorg Scholvin, Niamh Waldron Lecture 1 6.012 overview
EE 410: Integrated Circuit Fabrication Laboratory
 EE 410: Integrated Circuit Fabrication Laboratory 1 EE 410: Integrated Circuit Fabrication Laboratory Web Site: Instructor: http://www.stanford.edu/class/ee410 https://ccnet.stanford.edu/ee410/ (on CCNET)
EE 410: Integrated Circuit Fabrication Laboratory 1 EE 410: Integrated Circuit Fabrication Laboratory Web Site: Instructor: http://www.stanford.edu/class/ee410 https://ccnet.stanford.edu/ee410/ (on CCNET)
Semiconductor Devices
 Semiconductor Devices - 2014 Lecture Course Part of SS Module PY4P03 Dr. P. Stamenov School of Physics and CRANN, Trinity College, Dublin 2, Ireland Hilary Term, TCD 3 th of Feb 14 MOSFET Unmodified Channel
Semiconductor Devices - 2014 Lecture Course Part of SS Module PY4P03 Dr. P. Stamenov School of Physics and CRANN, Trinity College, Dublin 2, Ireland Hilary Term, TCD 3 th of Feb 14 MOSFET Unmodified Channel
SURFACE FINISH FOR ELECTRONIC PACKAGING WITH LEAD-FREE SOLDERS. Abstract
 ~ ~ SURFACE FINISH FOR ELECTRONIC PACKAGING WITH LEAD-FREE SOLDERS PDF- I. V. Kadija J. A. Abys AT&T Bell Laboratories 600 Mountain Avenue Murray Hill, NJ 07974 Abstract Current trends in the preservation
~ ~ SURFACE FINISH FOR ELECTRONIC PACKAGING WITH LEAD-FREE SOLDERS PDF- I. V. Kadija J. A. Abys AT&T Bell Laboratories 600 Mountain Avenue Murray Hill, NJ 07974 Abstract Current trends in the preservation
Lecture Introduction
 Lecture 1 6.012 Introduction 1. Overview of 6.012 Outline 2. Key conclusions of 6.012 Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini, Chapter 1 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits-Fall 200 Lecture 1 1 Overview
Lecture 1 6.012 Introduction 1. Overview of 6.012 Outline 2. Key conclusions of 6.012 Reading Assignment: Howe and Sodini, Chapter 1 6.012 Electronic Devices and Circuits-Fall 200 Lecture 1 1 Overview
Wirebond challenges in QFN. Engineering Team - Wire bond section SPEL Semiconductor Limited
 Introduction: Wirebond challenges in QFN by Engineering Team - Wire bond section SPEL Semiconductor Limited The market for the portable & handheld consumer electronic goods is growing rapidly and technological
Introduction: Wirebond challenges in QFN by Engineering Team - Wire bond section SPEL Semiconductor Limited The market for the portable & handheld consumer electronic goods is growing rapidly and technological
CGHV1J070D. 70 W, 18.0 GHz, GaN HEMT Die
 Rev 1.0 May 2017 CGHV1J070D 70 W, 18.0 GHz, GaN HEMT Die Cree s CGHV1J070D is a high voltage gallium nitride (GaN) High Electron Mobility Transistor (HEMT) on a silicon carbide substrate, using a 0.25
Rev 1.0 May 2017 CGHV1J070D 70 W, 18.0 GHz, GaN HEMT Die Cree s CGHV1J070D is a high voltage gallium nitride (GaN) High Electron Mobility Transistor (HEMT) on a silicon carbide substrate, using a 0.25
Reliability Qualification Report
 Reliability Qualification Report SGA-5263Z Products Qualified by Similarity SGA-4563Z/4463Z/4363Z/4263Z/4163Z SGA-3563Z/3463Z/3363Z/3263Z SGA-2463Z/2363Z/2263Z/2163Z SGA-1263Z/1163Z SGA-0363Z/0163Z SGA-8343Z/8543Z
Reliability Qualification Report SGA-5263Z Products Qualified by Similarity SGA-4563Z/4463Z/4363Z/4263Z/4163Z SGA-3563Z/3463Z/3363Z/3263Z SGA-2463Z/2363Z/2263Z/2163Z SGA-1263Z/1163Z SGA-0363Z/0163Z SGA-8343Z/8543Z
Application Note 5012
 MGA-61563 High Performance GaAs MMIC Amplifier Application Note 5012 Application Information The MGA-61563 is a high performance GaAs MMIC amplifier fabricated with Avago Technologies E-pHEMT process and
MGA-61563 High Performance GaAs MMIC Amplifier Application Note 5012 Application Information The MGA-61563 is a high performance GaAs MMIC amplifier fabricated with Avago Technologies E-pHEMT process and
Altera APEX EP20K600CB652C8ES Programmable Logic Device Structural Analysis
 April 27, 2006 Altera APEX EP20K600CB652C8ES Programmable Logic Device Structural Analysis Table of Contents List of Figures...Page 1 Introduction...Page 4 Device Summary...Page 5 Device Identification
April 27, 2006 Altera APEX EP20K600CB652C8ES Programmable Logic Device Structural Analysis Table of Contents List of Figures...Page 1 Introduction...Page 4 Device Summary...Page 5 Device Identification
Practical 2P12 Semiconductor Devices
 Practical 2P12 Semiconductor Devices What you should learn from this practical Science This practical illustrates some points from the lecture courses on Semiconductor Materials and Semiconductor Devices
Practical 2P12 Semiconductor Devices What you should learn from this practical Science This practical illustrates some points from the lecture courses on Semiconductor Materials and Semiconductor Devices
Lecture Notes 5 CMOS Image Sensor Device and Fabrication
 Lecture Notes 5 CMOS Image Sensor Device and Fabrication CMOS image sensor fabrication technologies Pixel design and layout Imaging performance enhancement techniques Technology scaling, industry trends
Lecture Notes 5 CMOS Image Sensor Device and Fabrication CMOS image sensor fabrication technologies Pixel design and layout Imaging performance enhancement techniques Technology scaling, industry trends
Powerchip Semiconductor Corporation A3R12E3GEF G6E 635BLC4M 512 Megabit DDR2 SDRAM Structural Analysis
 February 23, 2007 Powerchip Semiconductor Corporation A3R12E3GEF G6E 635BLC4M Structural Analysis For comments, questions, or more information about this report, or for any additional technical needs concerning
February 23, 2007 Powerchip Semiconductor Corporation A3R12E3GEF G6E 635BLC4M Structural Analysis For comments, questions, or more information about this report, or for any additional technical needs concerning
Student Lecture by: Giangiacomo Groppi Joel Cassell Pierre Berthelot September 28 th 2004
 Student Lecture by: Giangiacomo Groppi Joel Cassell Pierre Berthelot September 28 th 2004 Lecture outline Historical introduction Semiconductor devices overview Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Field
Student Lecture by: Giangiacomo Groppi Joel Cassell Pierre Berthelot September 28 th 2004 Lecture outline Historical introduction Semiconductor devices overview Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Field
Digital Design and System Implementation. Overview of Physical Implementations
 Digital Design and System Implementation Overview of Physical Implementations CMOS devices CMOS transistor circuit functional behavior Basic logic gates Transmission gates Tri-state buffers Flip-flops
Digital Design and System Implementation Overview of Physical Implementations CMOS devices CMOS transistor circuit functional behavior Basic logic gates Transmission gates Tri-state buffers Flip-flops
High Temperature Mixed Signal Capabilities
 High Temperature Mixed Signal Capabilities June 29, 2017 Product Overview Features o Up to 300 o C Operation o Will support most analog functions. o Easily combined with up to 30K digital gates. o 1.0u
High Temperature Mixed Signal Capabilities June 29, 2017 Product Overview Features o Up to 300 o C Operation o Will support most analog functions. o Easily combined with up to 30K digital gates. o 1.0u
6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 MIT, Spring 2009 6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Charles G. Sodini Jing Kong Shaya Famini, Stephanie Hsu, Ming Tang Lecture 1 6.012 Overview Contents: Overview of 6.012 Reading Assignment: Howe
MIT, Spring 2009 6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Charles G. Sodini Jing Kong Shaya Famini, Stephanie Hsu, Ming Tang Lecture 1 6.012 Overview Contents: Overview of 6.012 Reading Assignment: Howe
ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 1 / PLENARY / 1.1
 ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 1 / PLENARY / 1.1 1.1 No Exponential is Forever: But Forever Can Be Delayed! Gordon E. Moore Intel Corporation Over the last fifty years, the solid-state-circuits industry has grown
ISSCC 2003 / SESSION 1 / PLENARY / 1.1 1.1 No Exponential is Forever: But Forever Can Be Delayed! Gordon E. Moore Intel Corporation Over the last fifty years, the solid-state-circuits industry has grown
FABRICATION OF CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. Dr. Mohammed M. Farag
 FABRICATION OF CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Dr. Mohammed M. Farag Outline Overview of CMOS Fabrication Processes The CMOS Fabrication Process Flow Design Rules Reference: Uyemura, John P. "Introduction to
FABRICATION OF CMOS INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Dr. Mohammed M. Farag Outline Overview of CMOS Fabrication Processes The CMOS Fabrication Process Flow Design Rules Reference: Uyemura, John P. "Introduction to
Lecture 020 ECE4430 Review II (1/5/04) Page 020-1
 Lecture 020 ECE4430 Review II (1/5/04) Page 020-1 LECTURE 020 ECE 4430 REVIEW II (READING: GHLM - Chap. 2) Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Identify the prerequisite material as taught
Lecture 020 ECE4430 Review II (1/5/04) Page 020-1 LECTURE 020 ECE 4430 REVIEW II (READING: GHLM - Chap. 2) Objective The objective of this presentation is: 1.) Identify the prerequisite material as taught
Introduction to Electronic Devices
 (Course Number 300331) Fall 2006 Instructor: Dr. Dietmar Knipp Assistant Professor of Electrical Engineering Information: http://www.faculty.iubremen.de/dknipp/ Source: Apple Ref.: Apple Ref.: IBM Critical
(Course Number 300331) Fall 2006 Instructor: Dr. Dietmar Knipp Assistant Professor of Electrical Engineering Information: http://www.faculty.iubremen.de/dknipp/ Source: Apple Ref.: Apple Ref.: IBM Critical
The Advantages of Integrated MEMS to Enable the Internet of Moving Things
 The Advantages of Integrated MEMS to Enable the Internet of Moving Things January 2018 The availability of contextual information regarding motion is transforming several consumer device applications.
The Advantages of Integrated MEMS to Enable the Internet of Moving Things January 2018 The availability of contextual information regarding motion is transforming several consumer device applications.
I DDQ Current Testing
 I DDQ Current Testing Motivation Early 99 s Fabrication Line had 5 to defects per million (dpm) chips IBM wanted to get 3.4 defects per million (dpm) chips Conventional way to reduce defects: Increasing
I DDQ Current Testing Motivation Early 99 s Fabrication Line had 5 to defects per million (dpm) chips IBM wanted to get 3.4 defects per million (dpm) chips Conventional way to reduce defects: Increasing
EECS 151/251A Spring 2019 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits. Instructors: Wawrzynek. Lecture 8 EE141
 EECS 151/251A Spring 2019 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits Instructors: Wawrzynek Lecture 8 EE141 From the Bottom Up IC processing CMOS Circuits (next lecture) EE141 2 Overview of Physical Implementations
EECS 151/251A Spring 2019 Digital Design and Integrated Circuits Instructors: Wawrzynek Lecture 8 EE141 From the Bottom Up IC processing CMOS Circuits (next lecture) EE141 2 Overview of Physical Implementations
Some Key Researches on SiC Device Technologies and their Predicted Advantages
 18 POWER SEMICONDUCTORS www.mitsubishichips.com Some Key Researches on SiC Device Technologies and their Predicted Advantages SiC has proven to be a good candidate as a material for next generation power
18 POWER SEMICONDUCTORS www.mitsubishichips.com Some Key Researches on SiC Device Technologies and their Predicted Advantages SiC has proven to be a good candidate as a material for next generation power
EE 330 Lecture 7. Design Rules. IC Fabrication Technology Part 1
 EE 330 Lecture 7 Design Rules IC Fabrication Technology Part 1 Review from Last Time Technology Files Provide Information About Process Process Flow (Fabrication Technology) Model Parameters Design Rules
EE 330 Lecture 7 Design Rules IC Fabrication Technology Part 1 Review from Last Time Technology Files Provide Information About Process Process Flow (Fabrication Technology) Model Parameters Design Rules
providing current-voltage signatures and temporal characteristics. Identifying defects in deep-submicron CMOS ICs
 Identifying defects in deep-submicron CMOS ICs Jerry M. Soden Sandia National Laboratories Charles F. Hawkins University of New Mexico Anthony C. Miller Intel Corp. Given the oft-cited difficulty of testing
Identifying defects in deep-submicron CMOS ICs Jerry M. Soden Sandia National Laboratories Charles F. Hawkins University of New Mexico Anthony C. Miller Intel Corp. Given the oft-cited difficulty of testing
CGHV1J025D. 25 W, 18.0 GHz, GaN HEMT Die
 Rev 2.0 May 2017 CGHV1J025D 25 W, 18.0 GHz, GaN HEMT Die Cree s CGHV1J025D is a high voltage gallium nitride (GaN) High Electron Mobility Transistor (HEMT) on a silicon carbide substrate, using a 0.25
Rev 2.0 May 2017 CGHV1J025D 25 W, 18.0 GHz, GaN HEMT Die Cree s CGHV1J025D is a high voltage gallium nitride (GaN) High Electron Mobility Transistor (HEMT) on a silicon carbide substrate, using a 0.25
Mobile Electrostatic Carrier (MEC) evaluation for a GaAs wafer backside manufacturing process
 Mobile Electrostatic Carrier (MEC) evaluation for a GaAs wafer backside manufacturing process H.Stieglauer 1, J.Nösser 1, A.Miller 1, M.Lanz 1, D.Öttlin 1, G.Jonsson 1, D.Behammer 1, C.Landesberger 2,
Mobile Electrostatic Carrier (MEC) evaluation for a GaAs wafer backside manufacturing process H.Stieglauer 1, J.Nösser 1, A.Miller 1, M.Lanz 1, D.Öttlin 1, G.Jonsson 1, D.Behammer 1, C.Landesberger 2,
Lecture: Integration of silicon photonics with electronics. Prepared by Jean-Marc FEDELI CEA-LETI
 Lecture: Integration of silicon photonics with electronics Prepared by Jean-Marc FEDELI CEA-LETI Context The goal is to give optical functionalities to electronics integrated circuit (EIC) The objectives
Lecture: Integration of silicon photonics with electronics Prepared by Jean-Marc FEDELI CEA-LETI Context The goal is to give optical functionalities to electronics integrated circuit (EIC) The objectives
Samsung K4B1G0846F-HCF8 1 Gbit DDR3 SDRAM 48 nm CMOS DRAM Process
 Samsung K4B1G0846F-HCF8 48 nm CMOS DRAM Process Structural Analysis For comments, questions, or more information about this report, or for any additional technical needs concerning semiconductor and electronics
Samsung K4B1G0846F-HCF8 48 nm CMOS DRAM Process Structural Analysis For comments, questions, or more information about this report, or for any additional technical needs concerning semiconductor and electronics
Ultra Low Power VLSI Design: A Review
 International Journal of Emerging Engineering Research and Technology Volume 4, Issue 3, March 2016, PP 11-18 ISSN 2349-4395 (Print) & ISSN 2349-4409 (Online) Ultra Low Power VLSI Design: A Review G.Bharathi
International Journal of Emerging Engineering Research and Technology Volume 4, Issue 3, March 2016, PP 11-18 ISSN 2349-4395 (Print) & ISSN 2349-4409 (Online) Ultra Low Power VLSI Design: A Review G.Bharathi
3D TSV Micro Cu Column Chip-to-Substrate/Chip Assmbly/Packaging Technology
 3D TSV Micro Cu Column Chip-to-Substrate/Chip Assmbly/Packaging Technology by Seung Wook Yoon, *K. T. Kang, W. K. Choi, * H. T. Lee, Andy C. B. Yong and Pandi C. Marimuthu STATS ChipPAC LTD, 5 Yishun Street
3D TSV Micro Cu Column Chip-to-Substrate/Chip Assmbly/Packaging Technology by Seung Wook Yoon, *K. T. Kang, W. K. Choi, * H. T. Lee, Andy C. B. Yong and Pandi C. Marimuthu STATS ChipPAC LTD, 5 Yishun Street
Pramoda N V Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, MCE Hassan Karnataka India
 Advanced Low Power CMOS Design to Reduce Power Consumption in CMOS Circuit for VLSI Design Pramoda N V Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, MCE Hassan Karnataka India Abstract: Low
Advanced Low Power CMOS Design to Reduce Power Consumption in CMOS Circuit for VLSI Design Pramoda N V Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, MCE Hassan Karnataka India Abstract: Low
Module-3: Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) & Emitter coupled logic (ECL) families
 1 Module-3: Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) & Emitter coupled logic (ECL) families 1. Introduction 2. Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) logic 2.1. Enhancement and depletion mode 2.2. NMOS and PMOS inverter
1 Module-3: Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) & Emitter coupled logic (ECL) families 1. Introduction 2. Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) logic 2.1. Enhancement and depletion mode 2.2. NMOS and PMOS inverter
Topic 3. CMOS Fabrication Process
 Topic 3 CMOS Fabrication Process Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: p.cheung@ic.ac.uk Lecture 3-1 Layout of a Inverter
Topic 3 CMOS Fabrication Process Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London URL: www.ee.ic.ac.uk/pcheung/ E-mail: p.cheung@ic.ac.uk Lecture 3-1 Layout of a Inverter
