Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
|
|
|
- Daisy Conley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Politecnico di Torino Electronic Eng. Master Degree Analog and Telecommunication Electronics C5 - Synchronous demodulation» AM and FM demodulation» Coherent demodulation» Tone decoders AY /03/ ATLCE - C5 -
2 Lesson C5: synchronous demodulation FM demodulators AM demodulators Envelope and Synchronous demodulators Digital modulations FSK, PSK, ASK and others Tone decoders NE 567 block diagram and parameters References: D. Del Corso: Elettronica per Telecomunicazioni: 3.7 S. Franco: Design with OA and Analog IC: /03/ ATLCE - C5 -
3 FM mo-demodulation Carrier frequency Fp, modulating signal M(t) Fp= Fpo+ K M(t) Actual spectrum related with K Demodulation: Techniques derived from AM» Change FM into AM» Use AM demodulator PLL-based technique» Fp must be in the lock range» M(t) proportional to Vc(t) 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
4 Analog FM example Red: modulating signal White: FM signal Add spectrum 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
5 FM AM demodulation Exploit the transition region of a steep filter Frequency changes become amplitude changes V1/V2 AM f FM 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
6 FM PLL demodulation Fp= Fpo+ K M(t) PLL locked Full Fp spectrum in the lock range Vc(t) proportional to M(t) 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
7 Lesson C5: synchronous demod. FM demodulators AM demodulators Envelope demodulators Synchronous demodulators Digital modulations FSK, PSK, ASK and others Tone decoders NE 567 block diagram and parameters 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
8 AM signals Modulation: Multiplication of carrier P(Fp) by modulating signal M» S = Fp x M» Time domain: M is the envelope of S(t)» Frequency domain: M spectrum M(0) translated to M(Fp ) Demodulation Obtain envelope:» Half- or full-wave rectifier + LPF Move S to baseband (spectral translation)» Coherent demodulation» Needs reference signal: PLL 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
9 Examples of AM signals AM modulation Modulating signal: A sin t + B» max: A+B, min: B-A» Modulation index m m = (max-min)/(max+min) = A/B» m = 1: A = B (DC = Vp) Examples with simulator» AM 25% (m = 0,25)» AM 50% (m = 0,5)» AM 100% (m = 1)» AM 200% (PSK-180, DSB suppressed carrier) 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
10 AM modulation: m = 0,25 A = 2,5V, B = 10 V, m = 0,25 (25%) 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
11 AM modulation; m = 1 A = 10V, B = 10V, m = 1 (100%) the spectrum shows the carrier Modulation signal envelope (red) 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
12 AM modulation - PSK A = 10V, B = 0V (suppressed carrier, PSK/180 ) the carrier does not appear in the spectrum Modulation signal envelope (red) 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
13 Envelope demodulator Peak detector with loss C charged to + peaks, discharged through R Problems: Diode threshold Noise sensitivity Not for M > 1 Improvements Active diode Full wave rectifier 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
14 Coherent demodulation B1 cuts outband noise The PLL generates the reference signal The multiplier M moves Vi to baseband B3 isolates baseband signal π/2 phase shift M 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
15 Effect of frequency drift Changes in Fi cause phase error in the PLL To move the VCO: Vc 0 To get Vc 0: θe 0 Output error cos θe Effect of amplitude change with phase shift: Cross-demodulation (FM causes output from AM detectoor) To reduce the error Increase loop gain I/Q demodulator or 0 i θ e 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
16 AM demodulator output vs frequency AM demod output VCO control (Vc) or i, o 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
17 I-Q demodulation V V C S V V cos t sin t Q (cos) V 2 V C V 2 S Vc (Q comp.) V Vs (I component) I (sin) 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
18 Analog I-Q demodulation Independent I-Q amplitude demodulation Va independent from Ve Vo phase relation 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
19 IF Digital I-Q demodulation A/D conversion after the multiplier (baseband) Digital processing ADC DSP ADC 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
20 RF digital I-Q demodulation Direct A/D conversion of RF signal Digital I/Q demodulation Digital processing X Anti-alias filter (lowpass or bandpass) A/D X sin cos Digital processing 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
21 Lesson C5: synchronous demod. FM demodulators AM demodulators Envelope demodulators Synchronous demodulators Digital modulations FSK, PSK, ASK and others Tone decoders NE 567 block diagram Tone decoder parameters Lab experiment 5: tone decoder behavior 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
22 Digital modulations ASK, PAM FSK PSK Amplitude Shift Keyed: AM to discrete levels (also called Pulse Amplitude Modulation) Frequency Shift Keyed: FM to 2, N frequencies Phase Shift Keyed: PM to 2, N phases Mixed QAM QPSK. 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
23 Digital FM FSK signal FSK frequency shift keyed Q ω2 ω1 I Same techniques as analog FM The transient response depends on loop parameters Separate AM channels for each carrier Tone decoders with WTA 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
24 FSK Demodulators Frequency Shift Keyed: FM to 2, N frequencies Demodulation techniques Single PLL, always locked output = Vc Multiple coherent AM detector» For each frequency PLL + AM coherent demodulators + output comparison (Winner Take All) Multiple envelope detector» Passband filter bank + envelope demodulators + output comparison (Winner Take All) Tradeoff for all circuits (symbol passband filters) Wideband: fast response, noise-sensitive Narrowband: slow response (good if Bitrate < carrier/10) 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
25 PAM/ASK demodulators Pulse Amplitude Modulation (PAM) or Amplitude Shift Keyed (ASK) Discrete AM (2, N levels) Demodulation techniques Envelope detector Coherent demodulation (PLL) Tradeoff for all circuits: post-detection filter Wideband : fast response, noise-sensitive Narrowband: slow response 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
26 ASK signal ASK (PAM) discrete amplitude change Q S1 S2 2-level ASK I 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
27 PSK signal PSK phase shift Q Q S1 S2 I I 2-phase (rotation π) 8-phase (rotation π/4) 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
28 Complex signals demodulation Example 2 Phase shift: п/2 (4 states) Amplitude levels 2 3 bit/symbol Q In both cases: I I/Q demodulation The I/Q components are obtained by coherent demodulation 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
29 Complex signal (ASK+PSK) Amplitude and phase discrete changes QAM (Quadrature AM) Signal constellation Q Example with 16 symbols In the I/Q plane can be seen as combinations of 4 possible I values 4 possible Q values 2+2 = 4 bit/symbol I 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
30 : ATLCE - C5 19/03/2016 I/Q demodulation: A/P components Artg(Ve) - X/Y V V C S V cos t V sin t V V V 2 C arctg V V V 2 S S C 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
31 The ADPLL PLL based on digital circuits Wired logic Programmable logic Processor + SW DSPLL Programmable parameters, with better control Digital Vi ADC on Vd Digital loop filter + Numeric Controlled Oscillator Analog Vi ADC on Vi Digital PD + Digital loop filter + NCO 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
32 Example of DSP-PLL: Si550 Variable frequency clock generator Analog PD, then ADC 10 MHz 1,4 GHz range (Si550) From 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
33 Lesson C5: synchronous demod. FM demodulators AM demodulators Envelope demodulators Synchronous demodulators Digital modulations FSK, PSK, ASK and others Tone decoder Synchronous AM demodulator NE 567 block diagram and parameters 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
34 Integrated Tone Decoder NE567, LM576, : bipolar / LMC567: CMOS Synchronous AM Detector, slightly different structures Tone decoder operation: Recognize a carrier (tone) within a frequency interval, even with strong interferences by noise and other signals Used to recognize commands, numbers (phone), signalling overlapped with other signals Structure PLL for analog signals + AM synchronous demodulator Features Very narrow bandwidth ON/OFF output + intermediate analog output 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
35 Tone decoder: block diagram PLL loop: generates the reference signal Synchronous AM detector Filters: input, loop, output π/2 phase shift M 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
36 Tone decoder: specs Frequency range Allowed values for the tone to be recognized Bandwidth Frequency window for deconding of the tone Input amplitude range Maximum in-band input signal which is not recognized Minimum in-band input signal which is recognized Noise and interferers Tolerated wideband noise Tolerated narrowband interferers (other tones) 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
37 Tone decoder: bandwidth The device is designed to recognize a specific frequency, with minimum change The PLL can lock only to a narrow frequency range The possible shift of the VCO is minimum Detection bandwidth: about 15% of central frequency 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
38 Tone decoder: input range Amplitude range for tone recognition Guaranteed minimum input level which is definitely recognized by the tone decoder (max of the min levels among several devices) Guaranteed maximum input level which is NOT recognized by the tone decoder (min of max levels) Same kind of specs as Vih/Vil for logic circuits 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
39 Tone decoder: noise and interferers Noise immunity Tone detection capability with noise or interferer stronger than the tone itself (Outband signal)/(inband tone): + 6 db signal(tone)/(wideband noise): - 6 db 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
40 Tone decoder: bandwidth and F(s) The next diagram plots the capture range vs VI and filter parameters Detection bandwidth (capture range) depends on: Input level Loop filter F(s) Linear area Vi < 100 mv Capture range depends on Vi Saturation area Vi > 200 mv Capture range does not depend on Vi 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
41 Linear and saturating input levels saturation Linear operation 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
42 Tone decoder A: block diagram /03/ ATLCE - C5 -
43 Tone decoder functional units 1. Phase detector 2. Amplitude demodulator Gilbert cell multiplier 3. Loop filter 4. AM filter Single pole (RC), Internal R, external capacitor 5. VCO and I/Q outputs C charge/discharge, threshold control Third comparator or double frequency VCO 6. Output stage open collector, high current capability (150 ma) 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
44 PD and AM demodulators Gilbert cell multipliers Output Iz (current) Input Vx Input Vy 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
45 Linearization of differential stage output Iz (current) Vx input (Vo from VCO) Input bias network Vy input (Vi signal) R26, R27: emitter feedback Vy input to AM demodulator 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
46 I-C fixed τ VCO Unique time constant (τ = RC) Frequency control by variable thresholds (Vs1, Vs2) Limited frequency change Vs1 Vs2 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
47 I/Q VCO outputs Additional comparator on the capacitor voltage Almost triangular waveform on C Intermediate threshold Vs3 Vs3 Vo Va 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
48 VCO waveforms Additional comparator on the capacitor voltage Almost triangular waveform Vs1 Vs2 Vs3 Vo Va 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
49 Tone decoder: VCO circuit C charge/discharge switches RC timing group VCO Vs1 comparator Q-oputput Comparator (Vs3) VCO Vs2 comparator 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
50 Tone decoder B: block diagram CMOS features Higher R/Z Lower current Better I/Q VCO 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
51 Double VCO frequency to get I/Q VCO operates at double frequency I/Q signals by Mod2 dividers on complementary edges Vo Va 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
52 Lab experiment 4 Design a circuit using the NE567 IC, to obtain a tone decoder with detection range centered on 25 khz, and the maximum bandwidth allowed by the device. Build the circuit Verify the tone decoder parameters Measure capture and lock ranges Find the amplitude threshold (at central frequency) Plot the VCO characteristic: Fo(Vc) Plot the Va(Fi) and Va(Vi) characteristic Verify the behaviour with noise and interferers at the input 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
53 NE 576 PD and AM demodulator PD and AM demodulator outputs vs input signal frequency. VCO control voltage (butterfly plot) Coherent AM demodulator output (cosine shape) 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
54 Lesson C5 Describe the techniques for FM demodulation, with and without PLL. Define the criteria to select R and C in the AM envelope detector. Which are the benefits of coherent AM demodulation vs envelope demodulation? How to reduce the FM sensitivity of an AM coherent demodulator? List the parameters which describe the performance of a tone decoder. Propose some circuits to generate I/Q signals from a single VCO. 19/03/ ATLCE - C5 -
Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics C1 - PLL linear analysis» PLL basics» Application examples» Linear analysis» Phase error 08/04/2011-1 ATLCE - C1-2010 DDC Lesson
Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics C1 - PLL linear analysis» PLL basics» Application examples» Linear analysis» Phase error 08/04/2011-1 ATLCE - C1-2010 DDC Lesson
Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics B5 - Multipliers/mixer circuits» Error taxonomy» Basic multiplier circuits» Gilbert cell» Bridge MOS and diode circuits» Balanced
Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics B5 - Multipliers/mixer circuits» Error taxonomy» Basic multiplier circuits» Gilbert cell» Bridge MOS and diode circuits» Balanced
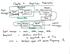 Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS
 EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS Pulse Code Modulation: 1. Draw the block diagram of basic digital communication system. How it is different from analog communication system. 2. What are the advantages of
EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS Pulse Code Modulation: 1. Draw the block diagram of basic digital communication system. How it is different from analog communication system. 2. What are the advantages of
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering)
 Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
TLCE - A3 08/09/ /09/ TLCE - A DDC. IF channel Zc. - Low noise, wide dynamic Ie Vo 08/09/ TLCE - A DDC
 Politecnico di Torino ICT School Telecommunication Electronics A3 Amplifiers nonlinearity» Reference circuit» Nonlinear models» Effects of nonlinearity» Applications of nonlinearity Large signal amplifiers
Politecnico di Torino ICT School Telecommunication Electronics A3 Amplifiers nonlinearity» Reference circuit» Nonlinear models» Effects of nonlinearity» Applications of nonlinearity Large signal amplifiers
RF/IF Terminology and Specs
 RF/IF Terminology and Specs Contributors: Brad Brannon John Greichen Leo McHugh Eamon Nash Eberhard Brunner 1 Terminology LNA - Low-Noise Amplifier. A specialized amplifier to boost the very small received
RF/IF Terminology and Specs Contributors: Brad Brannon John Greichen Leo McHugh Eamon Nash Eberhard Brunner 1 Terminology LNA - Low-Noise Amplifier. A specialized amplifier to boost the very small received
Master Degree in Electronic Engineering
 Master Degree in Electronic Engineering Analog and telecommunication electronic course (ATLCE-01NWM) Miniproject: Baseband signal transmission techniques Name: LI. XINRUI E-mail: s219989@studenti.polito.it
Master Degree in Electronic Engineering Analog and telecommunication electronic course (ATLCE-01NWM) Miniproject: Baseband signal transmission techniques Name: LI. XINRUI E-mail: s219989@studenti.polito.it
ATLCE - B5 07/03/2016. Analog and Telecommunication Electronics 2016 DDC 1. Politecnico di Torino - ICT School. Lesson B5: multipliers and mixers
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Lesson B5: multipliers and mixers Analog and Telecommunication Electronics B5 - Multipliers/mixer circuits» Error taxonomy» Basic multiplier circuits» Gilbert cell» Bridge
Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Lesson B5: multipliers and mixers Analog and Telecommunication Electronics B5 - Multipliers/mixer circuits» Error taxonomy» Basic multiplier circuits» Gilbert cell» Bridge
Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics E1 - Filters type and design» Filter taxonomy and parameters» Design flow and tools» FilterCAD example» Basic II order cells
Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics E1 - Filters type and design» Filter taxonomy and parameters» Design flow and tools» FilterCAD example» Basic II order cells
Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics E1 - Filters type and design» Filter taxonomy and parameters» Design flow and tools» FilterCAD example» Basic II order cells
Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics E1 - Filters type and design» Filter taxonomy and parameters» Design flow and tools» FilterCAD example» Basic II order cells
Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engg. LAB MANUAL. B.Tech V Semester [ ] (Branch: ETE)
![Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engg. LAB MANUAL. B.Tech V Semester [ ] (Branch: ETE) Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engg. LAB MANUAL. B.Tech V Semester [ ] (Branch: ETE)](/thumbs/86/93078052.jpg) Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engg. LAB MANUAL SUBJECT:-DIGITAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEM [BTEC-501] B.Tech V Semester [2013-14] (Branch: ETE) KCT COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH., FATEHGARH PUNJAB TECHNICAL
Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engg. LAB MANUAL SUBJECT:-DIGITAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEM [BTEC-501] B.Tech V Semester [2013-14] (Branch: ETE) KCT COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH., FATEHGARH PUNJAB TECHNICAL
Recap of Last 2 Classes
 Recap of Last 2 Classes Transmission Media Analog versus Digital Signals Bandwidth Considerations Attentuation, Delay Distortion and Noise Nyquist and Shannon Analog Modulation Digital Modulation What
Recap of Last 2 Classes Transmission Media Analog versus Digital Signals Bandwidth Considerations Attentuation, Delay Distortion and Noise Nyquist and Shannon Analog Modulation Digital Modulation What
Telecommunication Electronics
 Test 1 In the circuit shown in the diagram C1, C2 and C3 have negligible impedance at the operating frequency R1 = 120kΩ R2 = 220kΩ Rc = 6,8kΩ Val = 15 V hfe > 500 Vi C1 R1 R2 I1 Rc Ve Re1 Re2 C3 C2 V
Test 1 In the circuit shown in the diagram C1, C2 and C3 have negligible impedance at the operating frequency R1 = 120kΩ R2 = 220kΩ Rc = 6,8kΩ Val = 15 V hfe > 500 Vi C1 R1 R2 I1 Rc Ve Re1 Re2 C3 C2 V
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II
 EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
ECE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications
 ECE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Advanced Digital Communications, Spring-2015, Week-8 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation Any bandpass
ECE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Advanced Digital Communications, Spring-2015, Week-8 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation Any bandpass
Digital Communication
 Digital Communication Laboratories bako@ieee.org DigiCom Labs There are 5 labs related to the digital communication. Study of the parameters of metal cables including: characteristic impendance, attenuation
Digital Communication Laboratories bako@ieee.org DigiCom Labs There are 5 labs related to the digital communication. Study of the parameters of metal cables including: characteristic impendance, attenuation
UNIT III ANALOG MULTIPLIER AND PLL
 UNIT III ANALOG MULTIPLIER AND PLL PART A (2 MARKS) 1. What are the advantages of variable transconductance technique? [AUC MAY 2012] Good Accuracy Economical Simple to integrate Reduced error Higher bandwidth
UNIT III ANALOG MULTIPLIER AND PLL PART A (2 MARKS) 1. What are the advantages of variable transconductance technique? [AUC MAY 2012] Good Accuracy Economical Simple to integrate Reduced error Higher bandwidth
EE3723 : Digital Communications
 EE3723 : Digital Communications Week 8-9: Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad - Digital Communications - EE3723 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation
EE3723 : Digital Communications Week 8-9: Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad - Digital Communications - EE3723 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation
Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier
 Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier and the first channel. The modulation of the main carrier
Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier and the first channel. The modulation of the main carrier
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal
 Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
cosω t Y AD 532 Analog Multiplier Board EE18.xx Fig. 1 Amplitude modulation of a sine wave message signal
 University of Saskatchewan EE 9 Electrical Engineering Laboratory III Amplitude and Frequency Modulation Objectives: To observe the time domain waveforms and spectra of amplitude modulated (AM) waveforms
University of Saskatchewan EE 9 Electrical Engineering Laboratory III Amplitude and Frequency Modulation Objectives: To observe the time domain waveforms and spectra of amplitude modulated (AM) waveforms
Telecommunication Electronics
 Test 1 In this amplifier C1, C2 and C3 have negligible impedance at the operating frequency. R1 = 82k R2 = 27k RL = 22 k Re =?? Rc =?? Val = 15 V hfe > 500 Vi C1 R1 R2 I1 Rc Re Ve C3 C2 RL V AL Vu a) Find
Test 1 In this amplifier C1, C2 and C3 have negligible impedance at the operating frequency. R1 = 82k R2 = 27k RL = 22 k Re =?? Rc =?? Val = 15 V hfe > 500 Vi C1 R1 R2 I1 Rc Re Ve C3 C2 RL V AL Vu a) Find
Problems from the 3 rd edition
 (2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
(2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
FSK DEMODULATOR / TONE DECODER
 FSK DEMODULATOR / TONE DECODER GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a monolithic phase-locked loop (PLL) system especially designed for data communications. It is particularly well suited for FSK modem applications,
FSK DEMODULATOR / TONE DECODER GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a monolithic phase-locked loop (PLL) system especially designed for data communications. It is particularly well suited for FSK modem applications,
Emona Telecoms-Trainer ETT-101
 EXPERIMENTS IN MODERN COMMUNICATIONS Emona Telecoms-Trainer ETT-101 Multi-Experiment Single Board Telecommunications Trainer for Technical College and Technical High School Students EMONA INSTRUMENTS www.ett101.com
EXPERIMENTS IN MODERN COMMUNICATIONS Emona Telecoms-Trainer ETT-101 Multi-Experiment Single Board Telecommunications Trainer for Technical College and Technical High School Students EMONA INSTRUMENTS www.ett101.com
LINEAR IC APPLICATIONS
 1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
CSE4214 Digital Communications. Bandpass Modulation and Demodulation/Detection. Bandpass Modulation. Page 1
 CSE414 Digital Communications Chapter 4 Bandpass Modulation and Demodulation/Detection Bandpass Modulation Page 1 1 Bandpass Modulation n Baseband transmission is conducted at low frequencies n Passband
CSE414 Digital Communications Chapter 4 Bandpass Modulation and Demodulation/Detection Bandpass Modulation Page 1 1 Bandpass Modulation n Baseband transmission is conducted at low frequencies n Passband
DMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
 DMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING EC8453 - LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Question Bank (II-ECE) UNIT I BASICS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS PART A 1.Mention the
DMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING EC8453 - LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUITS Question Bank (II-ECE) UNIT I BASICS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS PART A 1.Mention the
Lecture 2 Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 2, Slide 1
 Lecture 2 General concepts Digital modulation in general Optical modulation Direct modulation External modulation Modulation formats Differential detection Coherent detection Fiber Optical Communication
Lecture 2 General concepts Digital modulation in general Optical modulation Direct modulation External modulation Modulation formats Differential detection Coherent detection Fiber Optical Communication
ECEN620: Network Theory Broadband Circuit Design Fall 2014
 ECEN60: Network Theory Broadband Circuit Design Fall 014 Lecture 13: Frequency Synthesizer Examples Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Agenda Frequency Synthesizer Examples Design
ECEN60: Network Theory Broadband Circuit Design Fall 014 Lecture 13: Frequency Synthesizer Examples Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Agenda Frequency Synthesizer Examples Design
f o Fig ECE 6440 Frequency Synthesizers P.E. Allen Frequency Magnitude Spectral impurity Frequency Fig010-03
 Lecture 010 Introduction to Synthesizers (5/5/03) Page 010-1 LECTURE 010 INTRODUCTION TO FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZERS (References: [1,5,9,10]) What is a Synthesizer? A frequency synthesizer is the means by which
Lecture 010 Introduction to Synthesizers (5/5/03) Page 010-1 LECTURE 010 INTRODUCTION TO FREQUENCY SYNTHESIZERS (References: [1,5,9,10]) What is a Synthesizer? A frequency synthesizer is the means by which
Part I - Amplitude Modulation
 EE/CME 392 Laboratory 1-1 Part I - Amplitude Modulation Safety: In this lab, voltages are less than 15 volts and this is not normally dangerous to humans. However, you should assemble or modify a circuit
EE/CME 392 Laboratory 1-1 Part I - Amplitude Modulation Safety: In this lab, voltages are less than 15 volts and this is not normally dangerous to humans. However, you should assemble or modify a circuit
Outline. Communications Engineering 1
 Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino Electronic Eng. Master Degree Analog and Telecommunication Electronics D4 - Signal conditioning» Protection circuits» Amplifiers» Anti-aliasing filter» Multiplexer» Sample/Hold AY
Politecnico di Torino Electronic Eng. Master Degree Analog and Telecommunication Electronics D4 - Signal conditioning» Protection circuits» Amplifiers» Anti-aliasing filter» Multiplexer» Sample/Hold AY
Amplitude Modulated Systems
 Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
A Complete Set of Experiments for Communication Classes
 A Complete Set of Experiments for Communication Classes Firas Hassan Ohio Northern University, Ada, OH 45810 f-hassan@onu.edu Abstract In this paper, a set of module based hands-on experiments that cover
A Complete Set of Experiments for Communication Classes Firas Hassan Ohio Northern University, Ada, OH 45810 f-hassan@onu.edu Abstract In this paper, a set of module based hands-on experiments that cover
ADVANCED EXPERIMENTS IN MODERN COMMUNICATIONS
 ADVANCED EXPERIMENTS IN MODERN COMMUNICATIONS NEW FIBER OPTICS KIT New Generation Single-Board Telecoms Experimenter for Advanced Experiments Emona ETT-101 BiSKIT Multi-Experiment Telecommunications &
ADVANCED EXPERIMENTS IN MODERN COMMUNICATIONS NEW FIBER OPTICS KIT New Generation Single-Board Telecoms Experimenter for Advanced Experiments Emona ETT-101 BiSKIT Multi-Experiment Telecommunications &
Analog Communication.
 Analog Communication Vishnu N V Tele is Greek for at a distance, and Communicare is latin for to make common. Telecommunication is the process of long distance communications. Early telecommunications
Analog Communication Vishnu N V Tele is Greek for at a distance, and Communicare is latin for to make common. Telecommunication is the process of long distance communications. Early telecommunications
Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino ICT School Telecommunication Electronics C4 Signal conditioning» Protection circuits» Amplifiers» Anti-aliasing filter» Multiplexer» Sample/Hold Lesson C4: signal conditioning Protection
Politecnico di Torino ICT School Telecommunication Electronics C4 Signal conditioning» Protection circuits» Amplifiers» Anti-aliasing filter» Multiplexer» Sample/Hold Lesson C4: signal conditioning Protection
Internal Examination I Answer Key DEPARTMENT OF CSE & IT. Semester: III Max.Marks: 100
 NH 67, Karur Trichy Highways, Puliyur C.F, 639 114 Karur District Internal Examination I Answer Key DEPARTMENT OF CSE & IT Branch & Section: II CSE & IT Date & Time: 06.08.15 & 3 Hours Semester: III Max.Marks:
NH 67, Karur Trichy Highways, Puliyur C.F, 639 114 Karur District Internal Examination I Answer Key DEPARTMENT OF CSE & IT Branch & Section: II CSE & IT Date & Time: 06.08.15 & 3 Hours Semester: III Max.Marks:
AM Limitations. Amplitude Modulation II. DSB-SC Modulation. AM Modifications
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
4 FSK Demodulators. 4.1 FSK Demodulation Zero-crossing Detector. FSK Demodulator Architectures Page 23
 FSK Demodulator Architectures Page 23 4 FSK Demodulators T he previous chapter dealt with the theoretical aspect of Frequency Shift Keying demodulation. The conclusion from this analysis was that coherent
FSK Demodulator Architectures Page 23 4 FSK Demodulators T he previous chapter dealt with the theoretical aspect of Frequency Shift Keying demodulation. The conclusion from this analysis was that coherent
Lecture 12. Carrier Phase Synchronization. EE4900/EE6720 Digital Communications
 EE49/EE6720: Digital Communications 1 Lecture 12 Carrier Phase Synchronization Block Diagrams of Communication System Digital Communication System 2 Informatio n (sound, video, text, data, ) Transducer
EE49/EE6720: Digital Communications 1 Lecture 12 Carrier Phase Synchronization Block Diagrams of Communication System Digital Communication System 2 Informatio n (sound, video, text, data, ) Transducer
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY 2 Basic Definitions Time and Frequency db conversion Power and dbm Filter Basics 3 Filter Filter is a component with frequency
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY 2 Basic Definitions Time and Frequency db conversion Power and dbm Filter Basics 3 Filter Filter is a component with frequency
Amplitude Modulation II
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
Analog & Telecommunication Electronics
 Test 1 In this amplifier C1, C2 and C3 have negligible impedance at the operating frequency. R1 = 18k R2 =??? Re = 10 k Rc = 8,2 k RL = 22 k Val = 15 V hfe > 400 Vbe = 0,6 V; Vcesat = 0,2 V Vi C1 R1 C2
Test 1 In this amplifier C1, C2 and C3 have negligible impedance at the operating frequency. R1 = 18k R2 =??? Re = 10 k Rc = 8,2 k RL = 22 k Val = 15 V hfe > 400 Vbe = 0,6 V; Vcesat = 0,2 V Vi C1 R1 C2
EE4512 Analog and Digital Communications Chapter 6. Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation
 Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Amplitude Modulation Pages 306-309 309 The analytical signal for double sideband, large carrier amplitude modulation
Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Amplitude Modulation Pages 306-309 309 The analytical signal for double sideband, large carrier amplitude modulation
Lecture 6. Angle Modulation and Demodulation
 Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics D5 - Special A/D converters» Differential converters» Oversampling, noise shaping» Logarithmic conversion» Approximation, A and
Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics D5 - Special A/D converters» Differential converters» Oversampling, noise shaping» Logarithmic conversion» Approximation, A and
 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER GCE@Bodi_ SCIENCE GCE@Bodi_ AND ENIGNEERING GCE@Bodi_ GCE@Bodi_ GCE@Bodi_ Analog and Digital Communication GCE@Bodi_ DEPARTMENT OF CsE Subject Name: Analog and Digital Communication
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER GCE@Bodi_ SCIENCE GCE@Bodi_ AND ENIGNEERING GCE@Bodi_ GCE@Bodi_ GCE@Bodi_ Analog and Digital Communication GCE@Bodi_ DEPARTMENT OF CsE Subject Name: Analog and Digital Communication
Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino ICT School Telecommunication Electronics C5 - Special A/D converters» Logarithmic conversion» Approximation, A and µ laws» Differential converters» Oversampling, noise shaping Logarithmic
Politecnico di Torino ICT School Telecommunication Electronics C5 - Special A/D converters» Logarithmic conversion» Approximation, A and µ laws» Differential converters» Oversampling, noise shaping Logarithmic
Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino Electronic Eng. Master Degree Analog and Telecommunication Electronics D6 - High speed A/D converters» Spectral performance analysis» Undersampling techniques» Sampling jitter» Interleaving
Politecnico di Torino Electronic Eng. Master Degree Analog and Telecommunication Electronics D6 - High speed A/D converters» Spectral performance analysis» Undersampling techniques» Sampling jitter» Interleaving
PHASELOCK TECHNIQUES INTERSCIENCE. Third Edition. FLOYD M. GARDNER Consulting Engineer Palo Alto, California A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC.
 PHASELOCK TECHNIQUES Third Edition FLOYD M. GARDNER Consulting Engineer Palo Alto, California INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION CONTENTS PREFACE NOTATION xvii xix 1 INTRODUCTION 1 1.1
PHASELOCK TECHNIQUES Third Edition FLOYD M. GARDNER Consulting Engineer Palo Alto, California INTERSCIENCE A JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC., PUBLICATION CONTENTS PREFACE NOTATION xvii xix 1 INTRODUCTION 1 1.1
Real and Complex Modulation
 Real and Complex Modulation TIPL 4708 Presented by Matt Guibord Prepared by Matt Guibord 1 What is modulation? Modulation is the act of changing a carrier signal s properties (amplitude, phase, frequency)
Real and Complex Modulation TIPL 4708 Presented by Matt Guibord Prepared by Matt Guibord 1 What is modulation? Modulation is the act of changing a carrier signal s properties (amplitude, phase, frequency)
Radio Technology and Architectures. 1 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless L#1
 Radio Technology and Architectures 1 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless L#1 Radio (Architectures) Spectrum plan and legal issues Radio Architectures and components 2 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless
Radio Technology and Architectures 1 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless L#1 Radio (Architectures) Spectrum plan and legal issues Radio Architectures and components 2 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless
EE 460L University of Nevada, Las Vegas ECE Department
 EE 460L PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in the context of digital communications is a modulation process which imparts to a sinusoid two or more discrete amplitude levels. These are related
EE 460L PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in the context of digital communications is a modulation process which imparts to a sinusoid two or more discrete amplitude levels. These are related
Outline. Communications Engineering 1
 Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Experiment 7: Frequency Modulation and Phase Locked Loops
 Experiment 7: Frequency Modulation and Phase Locked Loops Frequency Modulation Background Normally, we consider a voltage wave form with a fixed frequency of the form v(t) = V sin( ct + ), (1) where c
Experiment 7: Frequency Modulation and Phase Locked Loops Frequency Modulation Background Normally, we consider a voltage wave form with a fixed frequency of the form v(t) = V sin( ct + ), (1) where c
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY An Overview of Modulation Techniques: chapter 3.1 3.3.1 2 Introduction (3.1) Analog Modulation Amplitude Modulation Phase and
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY An Overview of Modulation Techniques: chapter 3.1 3.3.1 2 Introduction (3.1) Analog Modulation Amplitude Modulation Phase and
Universitas Sumatera Utara
 Amplitude Shift Keying & Frequency Shift Keying Aim: To generate and demodulate an amplitude shift keyed (ASK) signal and a binary FSK signal. Intro to Generation of ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK -
Amplitude Shift Keying & Frequency Shift Keying Aim: To generate and demodulate an amplitude shift keyed (ASK) signal and a binary FSK signal. Intro to Generation of ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK -
DEPARTMENT OF E.C.E.
 PVP SIDDHARTHA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, KANURU, VIJAYAWADA-7 DEPARTMENT OF E.C.E. ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS LAB MANUAL Department of Electronics & Communication engineering Prasad V.Potluri Siddhartha Institute
PVP SIDDHARTHA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, KANURU, VIJAYAWADA-7 DEPARTMENT OF E.C.E. ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS LAB MANUAL Department of Electronics & Communication engineering Prasad V.Potluri Siddhartha Institute
CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY NH-67, TRICHY MAIN ROAD, PULIYUR, C.F , KARUR DT.
 CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY NH-67, TRICHY MAIN ROAD, PULIYUR, C.F. 639 114, KARUR DT. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING COURSE MATERIAL Subject Name: Analog & Digital
CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY NH-67, TRICHY MAIN ROAD, PULIYUR, C.F. 639 114, KARUR DT. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING COURSE MATERIAL Subject Name: Analog & Digital
Tender Notice No- COEP/ /01. Tender Quotation for Electronics & Telecommunication Laboratory Material
 SHRI VITHAL EDUCATION & RESEARCH INSTITUTE S COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, PANDHARPUR ISO 90-2008 Certified Institute & Accredited by Institute of Engineers,India, Gopalpur -Ranjani Road, Gopalpur, P.B. No.
SHRI VITHAL EDUCATION & RESEARCH INSTITUTE S COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING, PANDHARPUR ISO 90-2008 Certified Institute & Accredited by Institute of Engineers,India, Gopalpur -Ranjani Road, Gopalpur, P.B. No.
Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino Electronic Eng. Master Degree Analog and Telecommunication Electronics D1 - A/D/A conversion systems» Sampling, spectrum aliasing» Quantization error» SNRq vs signal type and level»
Politecnico di Torino Electronic Eng. Master Degree Analog and Telecommunication Electronics D1 - A/D/A conversion systems» Sampling, spectrum aliasing» Quantization error» SNRq vs signal type and level»
Carrier Phase Recovery. EE3723 : Digital Communications. Synchronization. Carrier Phase Recovery. Carrier Phase Synchronization Techniques.
 EE3723 : Digital Communications Carrier Phase Recovery Week 10: Synchronization (Frequency, Phase, Symbol and Frame Synchronization) Carrier and Phase Recovery Phase-Locked Loop 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali
EE3723 : Digital Communications Carrier Phase Recovery Week 10: Synchronization (Frequency, Phase, Symbol and Frame Synchronization) Carrier and Phase Recovery Phase-Locked Loop 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali
Communication Systems Lab
 LAB MANUAL Communication Systems Lab (EE-226-F) Prepared by: Varun Sharma (Lab In-charge) Dayal C. Sati (Faculty In-charge) B R C M CET BAHAL DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Page
LAB MANUAL Communication Systems Lab (EE-226-F) Prepared by: Varun Sharma (Lab In-charge) Dayal C. Sati (Faculty In-charge) B R C M CET BAHAL DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Page
Communication Channels
 Communication Channels wires (PCB trace or conductor on IC) optical fiber (attenuation 4dB/km) broadcast TV (50 kw transmit) voice telephone line (under -9 dbm or 110 µw) walkie-talkie: 500 mw, 467 MHz
Communication Channels wires (PCB trace or conductor on IC) optical fiber (attenuation 4dB/km) broadcast TV (50 kw transmit) voice telephone line (under -9 dbm or 110 µw) walkie-talkie: 500 mw, 467 MHz
Chapter 3 Communication Concepts
 Chapter 3 Communication Concepts 1 Sections to be covered 3.1 General Considerations 3.2 Analog Modulation 3.3 Digital Modulation 3.4 Spectral Regrowth 3.7 Wireless Standards 2 Chapter Outline Modulation
Chapter 3 Communication Concepts 1 Sections to be covered 3.1 General Considerations 3.2 Analog Modulation 3.3 Digital Modulation 3.4 Spectral Regrowth 3.7 Wireless Standards 2 Chapter Outline Modulation
ATLCE - A3 01/03/2016. Analog and Telecommunication Electronics 2016 DDC 1. Politecnico di Torino - ICT School. Lesson A3: BJT Amplifiers
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics A3 BJT Amplifiers»Biasing» Output dynamic range» Small signal analysis» ltage gain» Frequency response AY 2015-16 Biasing Output
Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics A3 BJT Amplifiers»Biasing» Output dynamic range» Small signal analysis» ltage gain» Frequency response AY 2015-16 Biasing Output
Antenna Measurements using Modulated Signals
 Antenna Measurements using Modulated Signals Roger Dygert MI Technologies, 1125 Satellite Boulevard, Suite 100 Suwanee, GA 30024-4629 Abstract Antenna test engineers are faced with testing increasingly
Antenna Measurements using Modulated Signals Roger Dygert MI Technologies, 1125 Satellite Boulevard, Suite 100 Suwanee, GA 30024-4629 Abstract Antenna test engineers are faced with testing increasingly
Digital Modulation Schemes
 Digital Modulation Schemes 1. In binary data transmission DPSK is preferred to PSK because (a) a coherent carrier is not required to be generated at the receiver (b) for a given energy per bit, the probability
Digital Modulation Schemes 1. In binary data transmission DPSK is preferred to PSK because (a) a coherent carrier is not required to be generated at the receiver (b) for a given energy per bit, the probability
Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics A3 BJT Amplifiers»Biasing» Output dynamic range» Small signal analysis» Voltage gain» Frequency response 12/03/2012-1 ATLCE -
Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics A3 BJT Amplifiers»Biasing» Output dynamic range» Small signal analysis» Voltage gain» Frequency response 12/03/2012-1 ATLCE -
EXPERIMENT 2: Frequency Shift Keying (FSK)
 EXPERIMENT 2: Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) 1) OBJECTIVE Generation and demodulation of a frequency shift keyed (FSK) signal 2) PRELIMINARY DISCUSSION In FSK, the frequency of a carrier signal is modified
EXPERIMENT 2: Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) 1) OBJECTIVE Generation and demodulation of a frequency shift keyed (FSK) signal 2) PRELIMINARY DISCUSSION In FSK, the frequency of a carrier signal is modified
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the
 Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
Parallel Programming Design of BPSK Signal Demodulation Based on CUDA
 Int. J. Communications, Network and System Sciences, 216, 9, 126-134 Published Online May 216 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijcns http://dx.doi.org/1.4236/ijcns.216.9511 Parallel Programming
Int. J. Communications, Network and System Sciences, 216, 9, 126-134 Published Online May 216 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ijcns http://dx.doi.org/1.4236/ijcns.216.9511 Parallel Programming
ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I. Review. ELEC 350 Fall
 ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I Review ELEC 350 Fall 007 1 Final Examination Saturday, December 15-3 hours Two pages of notes allowed Calculator Tables provided Fourier transforms Table.1
ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I Review ELEC 350 Fall 007 1 Final Examination Saturday, December 15-3 hours Two pages of notes allowed Calculator Tables provided Fourier transforms Table.1
Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics F3 - Actuator driving» Driving BJT switches» Driving MOS-FET» SOA and protection» Smart switches 29/06/2011-1 ATLCE - F3-2011
Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics F3 - Actuator driving» Driving BJT switches» Driving MOS-FET» SOA and protection» Smart switches 29/06/2011-1 ATLCE - F3-2011
ECE 6560 Multirate Signal Processing Chapter 13
 Multirate Signal Processing Chapter 13 Dr. Bradley J. Bazuin Western Michigan University College of Engineering and Applied Sciences Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 1903 W. Michigan Ave.
Multirate Signal Processing Chapter 13 Dr. Bradley J. Bazuin Western Michigan University College of Engineering and Applied Sciences Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 1903 W. Michigan Ave.
The steeper the phase shift as a function of frequency φ(ω) the more stable the frequency of oscillation
 It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
CHAPTER 2 DIGITAL MODULATION
 2.1 INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 2 DIGITAL MODULATION Referring to Equation (2.1), if the information signal is digital and the amplitude (lv of the carrier is varied proportional to the information signal, a
2.1 INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 2 DIGITAL MODULATION Referring to Equation (2.1), if the information signal is digital and the amplitude (lv of the carrier is varied proportional to the information signal, a
EE452 Senior Capstone Project: Integration of Matlab Tools for DSP Code Generation. Kwadwo Boateng Charles Badu. May 8, 2006
 EE452 Senior Capstone Project: Integration of Matlab Tools for DSP Code Generation Kwadwo Boateng Charles Badu May 8, 2006 Bradley University College of Engineering and Technology Electrical and Computer
EE452 Senior Capstone Project: Integration of Matlab Tools for DSP Code Generation Kwadwo Boateng Charles Badu May 8, 2006 Bradley University College of Engineering and Technology Electrical and Computer
 UNIT 2 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION DIGITAL COMMUNICATION-Introduction The techniques used to modulate digital information so that it can be transmitted via microwave, satellite or down a cable pair is different
UNIT 2 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION DIGITAL COMMUNICATION-Introduction The techniques used to modulate digital information so that it can be transmitted via microwave, satellite or down a cable pair is different
Page 1. Telecommunication Electronics TLCE - C4 27/10/ DDC 1. Politecnico di Torino ICT School. Lesson C4: signal conditioning
 Politecnico di Torino ICT School Telecommunication Electronics C4 Signal conditioning» Protection circuits» Amplifiers» Antialiasing filter» Multiplexer» Sample/Hold Lesson C4: signal conditioning Protection
Politecnico di Torino ICT School Telecommunication Electronics C4 Signal conditioning» Protection circuits» Amplifiers» Antialiasing filter» Multiplexer» Sample/Hold Lesson C4: signal conditioning Protection
Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics B1 - Radio systems architecture» Basic radio systems» Image rejection» Digital and SW radio» Functional units 19/03/2012-1 ATLCE
Politecnico di Torino - ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics B1 - Radio systems architecture» Basic radio systems» Image rejection» Digital and SW radio» Functional units 19/03/2012-1 ATLCE
Mobile Communication An overview Lesson 03 Introduction to Modulation Methods
 Mobile Communication An overview Lesson 03 Introduction to Modulation Methods Oxford University Press 2007. All rights reserved. 1 Modulation The process of varying one signal, called carrier, according
Mobile Communication An overview Lesson 03 Introduction to Modulation Methods Oxford University Press 2007. All rights reserved. 1 Modulation The process of varying one signal, called carrier, according
Wireless Communication Fading Modulation
 EC744 Wireless Communication Fall 2008 Mohamed Essam Khedr Department of Electronics and Communications Wireless Communication Fading Modulation Syllabus Tentatively Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5
EC744 Wireless Communication Fall 2008 Mohamed Essam Khedr Department of Electronics and Communications Wireless Communication Fading Modulation Syllabus Tentatively Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5
COMPUTER COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKS ENCODING TECHNIQUES
 COMPUTER COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKS ENCODING TECHNIQUES Encoding Coding is the process of embedding clocks into a given data stream and producing a signal that can be transmitted over a selected medium.
COMPUTER COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKS ENCODING TECHNIQUES Encoding Coding is the process of embedding clocks into a given data stream and producing a signal that can be transmitted over a selected medium.
ECE 4600 Communication Systems
 ECE 4600 Communication Systems Dr. Bradley J. Bazuin Associate Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering College of Engineering and Applied Sciences Course Topics Course Introduction
ECE 4600 Communication Systems Dr. Bradley J. Bazuin Associate Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering College of Engineering and Applied Sciences Course Topics Course Introduction
Digital Communication System
 Digital Communication System Purpose: communicate information at certain rate between geographically separated locations reliably (quality) Important point: rate, quality spectral bandwidth requirement
Digital Communication System Purpose: communicate information at certain rate between geographically separated locations reliably (quality) Important point: rate, quality spectral bandwidth requirement
ISHIK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Science Department of Information Technology Fall Course Name: Wireless Networks
 ISHIK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Science Department of Information Technology 2017-2018 Fall Course Name: Wireless Networks Agenda Lecture 4 Multiple Access Techniques: FDMA, TDMA, SDMA and CDMA 1. Frequency
ISHIK UNIVERSITY Faculty of Science Department of Information Technology 2017-2018 Fall Course Name: Wireless Networks Agenda Lecture 4 Multiple Access Techniques: FDMA, TDMA, SDMA and CDMA 1. Frequency
Narrowband Data Transmission ASK/FSK
 Objectives Communication Systems II - Laboratory Experiment 9 Narrowband Data Transmission ASK/FSK To generate amplitude-shift keyed (ASK) and frequency-shift keyed (FSK) signals, study their properties,
Objectives Communication Systems II - Laboratory Experiment 9 Narrowband Data Transmission ASK/FSK To generate amplitude-shift keyed (ASK) and frequency-shift keyed (FSK) signals, study their properties,
QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION (15EC61)
 QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION (15EC61) Module 1 1. Explain Digital communication system with a neat block diagram. 2. What are the differences between digital and analog communication systems?
QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION (15EC61) Module 1 1. Explain Digital communication system with a neat block diagram. 2. What are the differences between digital and analog communication systems?
Phase-locked loop PIN CONFIGURATIONS
 NE/SE DESCRIPTION The NE/SE is a versatile, high guaranteed frequency phase-locked loop designed for operation up to 0MHz. As shown in the Block Diagram, the NE/SE consists of a VCO, limiter, phase comparator,
NE/SE DESCRIPTION The NE/SE is a versatile, high guaranteed frequency phase-locked loop designed for operation up to 0MHz. As shown in the Block Diagram, the NE/SE consists of a VCO, limiter, phase comparator,
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 8 AMPLITUDE MODULATION AND DEMODULATION OBJECTIVES The focus of this lab is to familiarize the student
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 8 AMPLITUDE MODULATION AND DEMODULATION OBJECTIVES The focus of this lab is to familiarize the student
EE 400L Communications. Laboratory Exercise #7 Digital Modulation
 EE 400L Communications Laboratory Exercise #7 Digital Modulation Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, at Las Vegas PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in
EE 400L Communications Laboratory Exercise #7 Digital Modulation Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, at Las Vegas PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in
RFIC Design ELEN 351 Lecture 2: RFIC Architectures
 RFIC Design ELEN 351 Lecture 2: RFIC Architectures Instructor: Dr. Allen Sweet Copy right 2003 ELEN 351 1 RFIC Architectures Modulation Choices Receiver Architectures Transmitter Architectures VCOs, Phase
RFIC Design ELEN 351 Lecture 2: RFIC Architectures Instructor: Dr. Allen Sweet Copy right 2003 ELEN 351 1 RFIC Architectures Modulation Choices Receiver Architectures Transmitter Architectures VCOs, Phase
Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics A0 Course Introduction» Goals and contents» Course organization» Learning material» Reference system 15/03/2011-1 ATLCE - A0-2010
Politecnico di Torino ICT School Analog and Telecommunication Electronics A0 Course Introduction» Goals and contents» Course organization» Learning material» Reference system 15/03/2011-1 ATLCE - A0-2010
Digital Communication System
 Digital Communication System Purpose: communicate information at required rate between geographically separated locations reliably (quality) Important point: rate, quality spectral bandwidth, power requirements
Digital Communication System Purpose: communicate information at required rate between geographically separated locations reliably (quality) Important point: rate, quality spectral bandwidth, power requirements
