Narrowband Data Transmission ASK/FSK
|
|
|
- Poppy May
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Objectives Communication Systems II - Laboratory Experiment 9 Narrowband Data Transmission ASK/FSK To generate amplitude-shift keyed (ASK) and frequency-shift keyed (FSK) signals, study their properties, and to recover the data sequence back from them. Apparatus 1. MCM31 board of the Elettronica Veneta (EV) training kits. 2. DC power supply. 3. Oscilloscope. 4. Connecting wires. Theory 1. Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) The simplest digital modulation technique is amplitude-shift keying (ASK), where a binary information signal directly modulates the amplitude of an analog carrier. ASK is similar to standard amplitude modulation except there are only two output amplitudes possible. Amplitude-shift keying is sometimes called digital amplitude modulation (DAM). Mathematically, amplitude-shift keying could be described as (1) where, ( )( ) = amplitude-shift keying wave ( ) = digital information (modulating) signal (volts) A/2 = unmodulated carrier amplitude (volts) = analog carrier radian frequency (radians per second, 2 ) The modulated wave ( )( ), is either cos( ) or 0. Hence, the carrier is either ON. or OFF, which is why amplitude-shift keying is sometimes referred to as on-off keying (OOK). Figure 1 clarify the signal waveforms of Digital amplitude modulation. The demodulation can be coherent or non-coherent. In the first case, more complex as concerns the circuits but more effective as against the noise effect, a product demodulator multiplies the ASK signal by locally regenerated carriers. In both cases the detector is followed a low pass filter, which removes the residual carrier components, and a threshold circuit which squares the data signal. Figure 2 clarifies coherent ASK demodulator. Figure 3 describes a non-coherent ASK demodulator. The minimum bandwidth requirement of ASK modulation scheme is equal to the bit rate, which is equal to 1/, where is the bit duration. 1 5
2 Figure 1 Digital amplitude modulation: (a) input binary; (b) output OOK waveform. Figure 2 Coherent ASK demodulator. 2. Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) Figure 3 Non-coherent ASK demodulator. Frequency-shift keying (FSK) is another relatively simple, low-performance type of digital modulation. FSK is a form of constant-amplitude angle modulation similar to standard frequency modulation (FM) except the modulating signal is a binary signal that varies between two discrete voltage levels rather than a continuously changing analog waveform. Consequently, FSK is sometimes called binary FSK (BFSK). The general expression for FSK is where, ( ) = binary FSK waveform = peak analog carrier amplitude (volts) = analog carrier center frequency (hertz) = peak change (shift) in the analog carrier frequency (hertz) ( ) = binary input (modulating) signal (volts) (2) From Equation 2, it can be seen that the peak shift in the carrier frequency,, is proportional to the amplitude of the binary input signal ( ). Figure 4 confirms the idea. 2 5
3 Figure 4 FSK in the frequency domain. The minimum bandwidth can be approximated as = 2( + ), where is the input bit rate (bps). Figure 5 shows FSK modulator. ( ) must be NRZ unipolar format for this type of FSK modulator. Figure 5 FSK modulator. FSK demodulation is quite simple with a circuit such as the one shown in Figure 6. The FSK input signal is simultaneously applied to the inputs of both bandpass filters (BPFs) through a power splitter. The respective filter passes only the mark or only the space frequency on to its respective envelope detector. The envelope detectors, in turn, indicate the total power in each passband, and the comparator responds to the largest of the two powers. This type of FSK detection is referred to as noncoherent detection; there is no frequency involved in the demodulation process that is synchronized either in phase, frequency, or both with the incoming FSK signal. Figure 7 shows the block diagram for a coherent FSK receiver. The incoming FSK signal is multiplied by a recovered carrier signal that has the exact same frequency and phase as the transmitter reference. However, the two transmitted frequencies (the mark and space 3 5
4 frequencies) are not generally continuous; it is not practical to reproduce a local reference that is coherent with both of them. Consequently, coherent FSK detection is seldom used. Figure 6 Noncoherent FSK demodulator. Figure 7 Coherent FSK demodulator. The most common circuit used for demodulating binary FSK signals is the phase locked loop (PLL), which is shown in block diagram form in Figure 8. A PLL-FSK demodulator works similarly to a PLL-FM demodulator. As the input to the PLL shifts between the mark and space frequencies, the dc error voltage at the output of the phase comparator follows the frequency shift. Because there are only two input frequencies (mark and space), there are also only two output error voltages. One represents a logic 1 and the other a logic 0. Therefore, the output is a two-level (binary) representation of the FSK input. Generally, the natural frequency of the PLL is made equal to the center frequency of the FSK modulator. As a result, the changes in the dc error voltage follow the changes in the analog input frequency and are symmetrical around 0 V. Figure 8 PLL-FSK demodulator 4 5
5 Procedure Part I: OOK Modulation and Demodulation 1. Set the circuit in ASK mode, with 24-bit data source and without data coding (connect J1c-J3d-J4-J5-J6a; set SW2=Normal, SW3=24-bit, SW4=1200, SW6=ASK, SW8=Bit, ATT=min, Noise=min). 2. Set an alternated data sequence 00/11 and push START. 3. Display and sketch the input binary sequence along with the ASK modulated signal. 4. Adjust the phase of the carrier to make the zero of the sine wave corresponds to the starting of the bit interval. 5. Display and sketch the signals before and after the communication channel. 6. Note the effect of the communication channel on the ASK signal. 7. Display and sketch the signals at TP23, TP24 and TP29. Map those signals to Figure 3 in theory. Part II: FSK Modulation and Demodulation 1. Set the circuit in FSK mode, with 24-bit data source and without data coding (connect J1c-J3a-J4-J5-J6b; set SW2=Normal, SW3=24-bit, SW4=1800, SW5=1200/0 o, SW6=FSK, SW8=Bit, ATT=min, Noise=min). 2. Set an alternated data sequence 00/11 and push START. 3. Display and sketch the input binary sequence along with the FSK modulated signal. 4. Adjust the phase of the 1200 Hz carrier to get continuity of FSK signal in the passage between the two frequencies (this kind of modulation is known as Minimum Frequency Shift Keying). 5. Display and sketch the signals before and after the communication channel. 6. Not the effect of the communication channel on the FSK signal. 7. Display and sketch the signals at TP23, TP24 and TP29. Describe those signals. Discussion 1. With a unipolar NRZ baseband data format of 1 Mbps transmission rate, determine the minimum required ASK and FSK transmission bandwidth. 2. Describe continuous-phase FSK (CP-FSK) and compare it to ordinary FSK. References [1] W. Tomasi, Advanced Electronic Communications Systems, Pearson Education Limited, Sixth Edition, [2] EV-MCM31 Training Kit Manual, Elettronica Veneta & Inel Spa, Treviso, Italy. Prepared by: Yaseen A. Mohammed (Communications Lab. Instructor) Dr. Lubab A. Salman (Communications Lab. Supervisor) 5 5
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECOM 4101 (ECE 4203) COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING LAB II SEMESTER 2, 2016/2017 EXPERIMENT NO.
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECOM 4101 (ECE 4203) COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING LAB II SEMESTER 2, 2016/2017 EXPERIMENT NO. 2 ASK MODULATION NAME: MATRIC NO: DATE: SECTION: Objectives To
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECOM 4101 (ECE 4203) COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING LAB II SEMESTER 2, 2016/2017 EXPERIMENT NO. 2 ASK MODULATION NAME: MATRIC NO: DATE: SECTION: Objectives To
EXPERIMENT NO. 3 FSK Modulation
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 4203: COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING LAB II SEMESTER 2, 2017/2018 EXPERIMENT NO. 3 FSK Modulation NAME: MATRIC NO: DATE: SECTION: FSK MODULATION Objective
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 4203: COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING LAB II SEMESTER 2, 2017/2018 EXPERIMENT NO. 3 FSK Modulation NAME: MATRIC NO: DATE: SECTION: FSK MODULATION Objective
CHAPTER 2 DIGITAL MODULATION
 2.1 INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 2 DIGITAL MODULATION Referring to Equation (2.1), if the information signal is digital and the amplitude (lv of the carrier is varied proportional to the information signal, a
2.1 INTRODUCTION CHAPTER 2 DIGITAL MODULATION Referring to Equation (2.1), if the information signal is digital and the amplitude (lv of the carrier is varied proportional to the information signal, a
Digital Communication
 Digital Communication Laboratories bako@ieee.org DigiCom Labs There are 5 labs related to the digital communication. Study of the parameters of metal cables including: characteristic impendance, attenuation
Digital Communication Laboratories bako@ieee.org DigiCom Labs There are 5 labs related to the digital communication. Study of the parameters of metal cables including: characteristic impendance, attenuation
EXPERIMENT NO. 5 4-PSK Modulation
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 4203: COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING LAB II SEMESTER 2, 2017/2018 EXPERIMENT NO. 5 4-PSK Modulation NAME: MATRIC NO: DATE: SECTION: 4-PSK MODULATION Objectives
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 4203: COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING LAB II SEMESTER 2, 2017/2018 EXPERIMENT NO. 5 4-PSK Modulation NAME: MATRIC NO: DATE: SECTION: 4-PSK MODULATION Objectives
EXPERIMENT NO. 4 PSK Modulation
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECOM 4101 (ECE 4203) COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING LAB II SEMESTER 2, 2016/2017 EXPERIMENT NO. 4 PSK Modulation NAME: MATRIC NO: DATE: SECTION: PSK MODULATION
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECOM 4101 (ECE 4203) COMMUNICATIONS ENGINEERING LAB II SEMESTER 2, 2016/2017 EXPERIMENT NO. 4 PSK Modulation NAME: MATRIC NO: DATE: SECTION: PSK MODULATION
EE 460L University of Nevada, Las Vegas ECE Department
 EE 460L PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in the context of digital communications is a modulation process which imparts to a sinusoid two or more discrete amplitude levels. These are related
EE 460L PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in the context of digital communications is a modulation process which imparts to a sinusoid two or more discrete amplitude levels. These are related
ECE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications
 ECE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Advanced Digital Communications, Spring-2015, Week-8 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation Any bandpass
ECE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Advanced Digital Communications, Spring-2015, Week-8 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation Any bandpass
EE3723 : Digital Communications
 EE3723 : Digital Communications Week 8-9: Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad - Digital Communications - EE3723 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation
EE3723 : Digital Communications Week 8-9: Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad - Digital Communications - EE3723 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation
Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engg. LAB MANUAL. B.Tech V Semester [ ] (Branch: ETE)
![Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engg. LAB MANUAL. B.Tech V Semester [ ] (Branch: ETE) Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engg. LAB MANUAL. B.Tech V Semester [ ] (Branch: ETE)](/thumbs/86/93078052.jpg) Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engg. LAB MANUAL SUBJECT:-DIGITAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEM [BTEC-501] B.Tech V Semester [2013-14] (Branch: ETE) KCT COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH., FATEHGARH PUNJAB TECHNICAL
Department of Electronics & Telecommunication Engg. LAB MANUAL SUBJECT:-DIGITAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEM [BTEC-501] B.Tech V Semester [2013-14] (Branch: ETE) KCT COLLEGE OF ENGG & TECH., FATEHGARH PUNJAB TECHNICAL
Thus there are three basic modulation techniques: 1) AMPLITUDE SHIFT KEYING 2) FREQUENCY SHIFT KEYING 3) PHASE SHIFT KEYING
 CHAPTER 5 Syllabus 1) Digital modulation formats 2) Coherent binary modulation techniques 3) Coherent Quadrature modulation techniques 4) Non coherent binary modulation techniques. Digital modulation formats:
CHAPTER 5 Syllabus 1) Digital modulation formats 2) Coherent binary modulation techniques 3) Coherent Quadrature modulation techniques 4) Non coherent binary modulation techniques. Digital modulation formats:
EXPERIMENT 2: Frequency Shift Keying (FSK)
 EXPERIMENT 2: Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) 1) OBJECTIVE Generation and demodulation of a frequency shift keyed (FSK) signal 2) PRELIMINARY DISCUSSION In FSK, the frequency of a carrier signal is modified
EXPERIMENT 2: Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) 1) OBJECTIVE Generation and demodulation of a frequency shift keyed (FSK) signal 2) PRELIMINARY DISCUSSION In FSK, the frequency of a carrier signal is modified
College of information Technology Department of Information Networks Telecommunication & Networking I Chapter 5. Analog Transmission
 Analog Transmission 5.1 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERSION Digital-to-analog conversion is the process of changing one of the characteristics of an analog signal based on the information in digital data. The
Analog Transmission 5.1 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERSION Digital-to-analog conversion is the process of changing one of the characteristics of an analog signal based on the information in digital data. The
EE 400L Communications. Laboratory Exercise #7 Digital Modulation
 EE 400L Communications Laboratory Exercise #7 Digital Modulation Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, at Las Vegas PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in
EE 400L Communications Laboratory Exercise #7 Digital Modulation Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, at Las Vegas PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in
CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY NH-67, TRICHY MAIN ROAD, PULIYUR, C.F , KARUR DT.
 CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY NH-67, TRICHY MAIN ROAD, PULIYUR, C.F. 639 114, KARUR DT. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING COURSE MATERIAL Subject Name: Analog & Digital
CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY NH-67, TRICHY MAIN ROAD, PULIYUR, C.F. 639 114, KARUR DT. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING COURSE MATERIAL Subject Name: Analog & Digital
Universitas Sumatera Utara
 Amplitude Shift Keying & Frequency Shift Keying Aim: To generate and demodulate an amplitude shift keyed (ASK) signal and a binary FSK signal. Intro to Generation of ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK -
Amplitude Shift Keying & Frequency Shift Keying Aim: To generate and demodulate an amplitude shift keyed (ASK) signal and a binary FSK signal. Intro to Generation of ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK -
Communication Systems Lab
 LAB MANUAL Communication Systems Lab (EE-226-F) Prepared by: Varun Sharma (Lab In-charge) Dayal C. Sati (Faculty In-charge) B R C M CET BAHAL DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Page
LAB MANUAL Communication Systems Lab (EE-226-F) Prepared by: Varun Sharma (Lab In-charge) Dayal C. Sati (Faculty In-charge) B R C M CET BAHAL DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Page
German Jordanian University. Department of Communication Engineering. Digital Communication Systems Lab. CME 313-Lab. Experiment 8
 German Jordanian University Department of Communication Engineering Digital Communication Systems Lab CME 313-Lab Experiment 8 Binary Frequency-shift keying (BPSK) Eng. Anas Al-ashqar Dr. Ala' Khalifeh
German Jordanian University Department of Communication Engineering Digital Communication Systems Lab CME 313-Lab Experiment 8 Binary Frequency-shift keying (BPSK) Eng. Anas Al-ashqar Dr. Ala' Khalifeh
QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION (15EC61)
 QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION (15EC61) Module 1 1. Explain Digital communication system with a neat block diagram. 2. What are the differences between digital and analog communication systems?
QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION (15EC61) Module 1 1. Explain Digital communication system with a neat block diagram. 2. What are the differences between digital and analog communication systems?
On-off keying, which consists of keying a sinusoidal carrier on and off with a unipolar binary signal
 Bandpass signalling Thus far only baseband signalling has been considered: an information source is usually a baseband signal. Some communication channels have a bandpass characteristic, and will not propagate
Bandpass signalling Thus far only baseband signalling has been considered: an information source is usually a baseband signal. Some communication channels have a bandpass characteristic, and will not propagate
Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering LAB MANUAL SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION LABORATORY [ECE324] (Branch: ECE)
![Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering LAB MANUAL SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION LABORATORY [ECE324] (Branch: ECE) Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering LAB MANUAL SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION LABORATORY [ECE324] (Branch: ECE)](/thumbs/96/127341232.jpg) Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering LAB MANUAL SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION LABORATORY [ECE324] B.Tech Year 3 rd, Semester - 5 th (Branch: ECE) Version: 01 st August 2018 The LNM Institute
Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering LAB MANUAL SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION LABORATORY [ECE324] B.Tech Year 3 rd, Semester - 5 th (Branch: ECE) Version: 01 st August 2018 The LNM Institute
German Jordanian University Department of Communication Engineering Digital Communication Systems Lab. CME 313-Lab
 German Jordanian University Department of Communication Engineering Digital Communication Systems Lab CME 313-Lab Experiment 7 Binary Frequency-shift keying (BPSK) Eng. Anas Al-ashqar Dr. Ala' Khalifeh
German Jordanian University Department of Communication Engineering Digital Communication Systems Lab CME 313-Lab Experiment 7 Binary Frequency-shift keying (BPSK) Eng. Anas Al-ashqar Dr. Ala' Khalifeh
Class 4 ((Communication and Computer Networks))
 Class 4 ((Communication and Computer Networks)) Lesson 5... SIGNAL ENCODING TECHNIQUES Abstract Both analog and digital information can be encoded as either analog or digital signals. The particular encoding
Class 4 ((Communication and Computer Networks)) Lesson 5... SIGNAL ENCODING TECHNIQUES Abstract Both analog and digital information can be encoded as either analog or digital signals. The particular encoding
DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS. MSc in Electronic Technologies and Communications
 DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS MSc in Electronic Technologies and Communications Bandpass binary signalling The common techniques of bandpass binary signalling are: - On-off keying (OOK), also known as
DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS MSc in Electronic Technologies and Communications Bandpass binary signalling The common techniques of bandpass binary signalling are: - On-off keying (OOK), also known as
Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM)
 Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM) April 11, 2008 Today s Topics 1. Frequency-division multiplexing 2. Frequency modulation
Signals and Systems Lecture 9 Communication Systems Frequency-Division Multiplexing and Frequency Modulation (FM) April 11, 2008 Today s Topics 1. Frequency-division multiplexing 2. Frequency modulation
UNIT TEST I Digital Communication
 Time: 1 Hour Class: T.E. I & II Max. Marks: 30 Q.1) (a) A compact disc (CD) records audio signals digitally by using PCM. Assume the audio signal B.W. to be 15 khz. (I) Find Nyquist rate. (II) If the Nyquist
Time: 1 Hour Class: T.E. I & II Max. Marks: 30 Q.1) (a) A compact disc (CD) records audio signals digitally by using PCM. Assume the audio signal B.W. to be 15 khz. (I) Find Nyquist rate. (II) If the Nyquist
B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering)
 Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
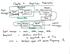 Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
CARRIER ACQUISITION AND THE PLL
 CARRIER ACQUISITION AND THE PLL PREPARATION... 22 carrier acquisition methods... 22 bandpass filter...22 the phase locked loop (PLL)....23 squaring...24 squarer plus PLL...26 the Costas loop...26 EXPERIMENT...
CARRIER ACQUISITION AND THE PLL PREPARATION... 22 carrier acquisition methods... 22 bandpass filter...22 the phase locked loop (PLL)....23 squaring...24 squarer plus PLL...26 the Costas loop...26 EXPERIMENT...
EE-4022 Experiment 3 Frequency Modulation (FM)
 EE-4022 MILWAUKEE SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING 2015 Page 3-1 Student Objectives: EE-4022 Experiment 3 Frequency Modulation (FM) In this experiment the student will use laboratory modules including a Voltage-Controlled
EE-4022 MILWAUKEE SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING 2015 Page 3-1 Student Objectives: EE-4022 Experiment 3 Frequency Modulation (FM) In this experiment the student will use laboratory modules including a Voltage-Controlled
Exercise 2: FM Detection With a PLL
 Phase-Locked Loop Analog Communications Exercise 2: FM Detection With a PLL EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to explain how the phase detector s input frequencies
Phase-Locked Loop Analog Communications Exercise 2: FM Detection With a PLL EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to explain how the phase detector s input frequencies
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal
 Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
Department of Electronic and Information Engineering. Communication Laboratory. Phase Shift Keying (PSK) & Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK)
 Department of Electronic and Information Engineering Communication Laboratory Phase Shift Keying (PSK) & Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK) Objectives To familiar with the concept of describing phase
Department of Electronic and Information Engineering Communication Laboratory Phase Shift Keying (PSK) & Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK) Objectives To familiar with the concept of describing phase
ECE 4600 Communication Systems
 ECE 4600 Communication Systems Dr. Bradley J. Bazuin Associate Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering College of Engineering and Applied Sciences Course Topics Course Introduction
ECE 4600 Communication Systems Dr. Bradley J. Bazuin Associate Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering College of Engineering and Applied Sciences Course Topics Course Introduction
Experiment No. 3 Pre-Lab Phase Locked Loops and Frequency Modulation
 Experiment No. 3 Pre-Lab Phase Locked Loops and Frequency Modulation The Pre-Labs are informational and although they follow the procedures in the experiment, they are to be completed outside of the laboratory.
Experiment No. 3 Pre-Lab Phase Locked Loops and Frequency Modulation The Pre-Labs are informational and although they follow the procedures in the experiment, they are to be completed outside of the laboratory.
6. has units of bits/second. a. Throughput b. Propagation speed c. Propagation time d. (b)or(c)
 King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Information Technology Department First Semester 1436/1437 IT224: Networks 1 Sheet# 10 (chapter 3-4-5) Multiple-Choice Questions 1. Before
King Saud University College of Computer and Information Sciences Information Technology Department First Semester 1436/1437 IT224: Networks 1 Sheet# 10 (chapter 3-4-5) Multiple-Choice Questions 1. Before
5.1 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERSION
 CHAPTERS Analog Transmission n Chapter 3, we discussed the advantages and disadvantages of digital and analog transmission. We saw that while digital transmission is very desirable, a low-pass channel
CHAPTERS Analog Transmission n Chapter 3, we discussed the advantages and disadvantages of digital and analog transmission. We saw that while digital transmission is very desirable, a low-pass channel
ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory Amplitude Modulation (AM)
 ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory 1 ---- Amplitude Modulation (AM) 1. Objectives 1.1 Through this the laboratory experiment, you will investigate demodulation of an amplitude modulated (AM)
ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory 1 ---- Amplitude Modulation (AM) 1. Objectives 1.1 Through this the laboratory experiment, you will investigate demodulation of an amplitude modulated (AM)
Amplitude Modulation Chapter 2. Modulation process
 Question 1 Modulation process Modulation is the process of translation the baseband message signal to bandpass (modulated carrier) signal at frequencies that are very high compared to the baseband frequencies.
Question 1 Modulation process Modulation is the process of translation the baseband message signal to bandpass (modulated carrier) signal at frequencies that are very high compared to the baseband frequencies.
UNIT-2 Angle Modulation System
 UNIT-2 Angle Modulation System Introduction There are three parameters of a carrier that may carry information: Amplitude Frequency Phase Frequency Modulation Power in an FM signal does not vary with modulation
UNIT-2 Angle Modulation System Introduction There are three parameters of a carrier that may carry information: Amplitude Frequency Phase Frequency Modulation Power in an FM signal does not vary with modulation
Amplitude Frequency Phase
 Chapter 4 (part 2) Digital Modulation Techniques Chapter 4 (part 2) Overview Digital Modulation techniques (part 2) Bandpass data transmission Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) Phase Shift Keying (PSK) Frequency
Chapter 4 (part 2) Digital Modulation Techniques Chapter 4 (part 2) Overview Digital Modulation techniques (part 2) Bandpass data transmission Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) Phase Shift Keying (PSK) Frequency
BINARY AMPLITUDE SHIFT KEYING
 BINARY AMPLITUDE SHIFT KEYING AIM: To set up a circuit to generate Binary Amplitude Shift keying and to plot the output waveforms. COMPONENTS AND EQUIPMENTS REQUIRED: IC CD4016, IC 7474, Resistors, Zener
BINARY AMPLITUDE SHIFT KEYING AIM: To set up a circuit to generate Binary Amplitude Shift keying and to plot the output waveforms. COMPONENTS AND EQUIPMENTS REQUIRED: IC CD4016, IC 7474, Resistors, Zener
Analog Transmission CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 5 Analog Transmission n Chapter 3, we discussed the advantages and disadvantages of digital and analog transmission. We saw that while digital transmission is very desirable, a low-pass channel
CHAPTER 5 Analog Transmission n Chapter 3, we discussed the advantages and disadvantages of digital and analog transmission. We saw that while digital transmission is very desirable, a low-pass channel
Chapter 14 FSK Demodulator
 Chapter 14 FSK Demodulator 14-1 : Curriculum Objectives 1. To understand the operation theory of FSK demodulator. 2. To implement the FSK detector circuit by using PLL. 3. To understand the operation theory
Chapter 14 FSK Demodulator 14-1 : Curriculum Objectives 1. To understand the operation theory of FSK demodulator. 2. To implement the FSK detector circuit by using PLL. 3. To understand the operation theory
(b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3]
![(b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3] (b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3]](/thumbs/85/91561193.jpg) Code No: RR220401 Set No. 1 1. (a) The antenna current of an AM Broadcast transmitter is 10A, if modulated to a depth of 50% by an audio sine wave. It increases to 12A as a result of simultaneous modulation
Code No: RR220401 Set No. 1 1. (a) The antenna current of an AM Broadcast transmitter is 10A, if modulated to a depth of 50% by an audio sine wave. It increases to 12A as a result of simultaneous modulation
Downloaded from 1
 VII SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2004 Attempt ALL questions. Q. [1] How does Digital communication System differ from Analog systems? Draw functional block diagram of DCS and explain the significance of
VII SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION-2004 Attempt ALL questions. Q. [1] How does Digital communication System differ from Analog systems? Draw functional block diagram of DCS and explain the significance of
Signal Characteristics
 Data Transmission The successful transmission of data depends upon two factors:» The quality of the transmission signal» The characteristics of the transmission medium Some type of transmission medium
Data Transmission The successful transmission of data depends upon two factors:» The quality of the transmission signal» The characteristics of the transmission medium Some type of transmission medium
COSC 3213: Computer Networks I: Chapter 3 Handout #4. Instructor: Dr. Marvin Mandelbaum Department of Computer Science York University Section A
 COSC 3213: Computer Networks I: Chapter 3 Handout #4 Instructor: Dr. Marvin Mandelbaum Department of Computer Science York University Section A Topics: 1. Line Coding: Unipolar, Polar,and Inverted ; Bipolar;
COSC 3213: Computer Networks I: Chapter 3 Handout #4 Instructor: Dr. Marvin Mandelbaum Department of Computer Science York University Section A Topics: 1. Line Coding: Unipolar, Polar,and Inverted ; Bipolar;
Synchronization. EE442 Lecture 17. All digital receivers must be synchronized to the incoming signal s(t).
 Synchronization EE442 Lecture 17 All digital receivers must be synchronized to the incoming signal s(t). This means we must have a way to perform (1) Bit or symbol synchronization (2) Frame synchronization
Synchronization EE442 Lecture 17 All digital receivers must be synchronized to the incoming signal s(t). This means we must have a way to perform (1) Bit or symbol synchronization (2) Frame synchronization
CME 312-Lab Communication Systems Laboratory
 Objective: By the end of this experiment, the student should be able to: 1. Demonstrate the Modulation and Demodulation of the AM. 2. Observe the relation between modulation index and AM signal envelope.
Objective: By the end of this experiment, the student should be able to: 1. Demonstrate the Modulation and Demodulation of the AM. 2. Observe the relation between modulation index and AM signal envelope.
CSE4214 Digital Communications. Bandpass Modulation and Demodulation/Detection. Bandpass Modulation. Page 1
 CSE414 Digital Communications Chapter 4 Bandpass Modulation and Demodulation/Detection Bandpass Modulation Page 1 1 Bandpass Modulation n Baseband transmission is conducted at low frequencies n Passband
CSE414 Digital Communications Chapter 4 Bandpass Modulation and Demodulation/Detection Bandpass Modulation Page 1 1 Bandpass Modulation n Baseband transmission is conducted at low frequencies n Passband
CME312- LAB Manual DSB-SC Modulation and Demodulation Experiment 6. Experiment 6. Experiment. DSB-SC Modulation and Demodulation
 Experiment 6 Experiment DSB-SC Modulation and Demodulation Objectives : By the end of this experiment, the student should be able to: 1. Demonstrate the modulation and demodulation process of DSB-SC. 2.
Experiment 6 Experiment DSB-SC Modulation and Demodulation Objectives : By the end of this experiment, the student should be able to: 1. Demonstrate the modulation and demodulation process of DSB-SC. 2.
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering 1
 UNIT I SAMPLING AND QUANTIZATION Pulse Modulation 1. Explain in detail the generation of PWM and PPM signals (16) (M/J 2011) 2. Explain in detail the concept of PWM and PAM (16) (N/D 2012) 3. What is the
UNIT I SAMPLING AND QUANTIZATION Pulse Modulation 1. Explain in detail the generation of PWM and PPM signals (16) (M/J 2011) 2. Explain in detail the concept of PWM and PAM (16) (N/D 2012) 3. What is the
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II
 EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
9.4. Synchronization:
 9.4. Synchronization: It is the process of timing the serial transmission to properly identify the data being sent. There are two most common modes: Synchronous transmission: Synchronous transmission relies
9.4. Synchronization: It is the process of timing the serial transmission to properly identify the data being sent. There are two most common modes: Synchronous transmission: Synchronous transmission relies
Department of Electronic and Information Engineering. Communication Laboratory
 Department of Electronic and Information Engineering Communication Laboratory Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) & Differential Phase Shift Keying (DPSK) & Differential Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (DQPSK)
Department of Electronic and Information Engineering Communication Laboratory Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) & Differential Phase Shift Keying (DPSK) & Differential Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (DQPSK)
Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino Electronic Eng. Master Degree Analog and Telecommunication Electronics C5 - Synchronous demodulation» AM and FM demodulation» Coherent demodulation» Tone decoders AY 2015-16 19/03/2016-1
Politecnico di Torino Electronic Eng. Master Degree Analog and Telecommunication Electronics C5 - Synchronous demodulation» AM and FM demodulation» Coherent demodulation» Tone decoders AY 2015-16 19/03/2016-1
The quality of the transmission signal The characteristics of the transmission medium. Some type of transmission medium is required for transmission:
 Data Transmission The successful transmission of data depends upon two factors: The quality of the transmission signal The characteristics of the transmission medium Some type of transmission medium is
Data Transmission The successful transmission of data depends upon two factors: The quality of the transmission signal The characteristics of the transmission medium Some type of transmission medium is
EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS
 EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS Pulse Code Modulation: 1. Draw the block diagram of basic digital communication system. How it is different from analog communication system. 2. What are the advantages of
EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS Pulse Code Modulation: 1. Draw the block diagram of basic digital communication system. How it is different from analog communication system. 2. What are the advantages of
Amplitude Modulation. Ahmad Bilal
 Amplitude Modulation Ahmad Bilal 5-2 ANALOG AND DIGITAL Analog-to-analog conversion is the representation of analog information by an analog signal. Topics discussed in this section: Amplitude Modulation
Amplitude Modulation Ahmad Bilal 5-2 ANALOG AND DIGITAL Analog-to-analog conversion is the representation of analog information by an analog signal. Topics discussed in this section: Amplitude Modulation
Digital Modulation Schemes
 Digital Modulation Schemes 1. In binary data transmission DPSK is preferred to PSK because (a) a coherent carrier is not required to be generated at the receiver (b) for a given energy per bit, the probability
Digital Modulation Schemes 1. In binary data transmission DPSK is preferred to PSK because (a) a coherent carrier is not required to be generated at the receiver (b) for a given energy per bit, the probability
Computer Networks and Internets
 GLOBAL EDITION Computer Networks and Internets SIXTH EDITION Douglas E. Comer This page is intentionally left blank. 200 Modulation And Modems Chap. 10 10.3 Analog Modulation Schemes We use the term modulation
GLOBAL EDITION Computer Networks and Internets SIXTH EDITION Douglas E. Comer This page is intentionally left blank. 200 Modulation And Modems Chap. 10 10.3 Analog Modulation Schemes We use the term modulation
Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM)
 Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM) Modules: Integrate & Dump, Digital Utilities, Wideband True RMS Meter, Tuneable LPF, Audio Oscillator, Multiplier, Utilities, Noise Generator, Speech, Headphones. 0 Pre-Laboratory
Pulse-Width Modulation (PWM) Modules: Integrate & Dump, Digital Utilities, Wideband True RMS Meter, Tuneable LPF, Audio Oscillator, Multiplier, Utilities, Noise Generator, Speech, Headphones. 0 Pre-Laboratory
Analog Communication.
 Analog Communication Vishnu N V Tele is Greek for at a distance, and Communicare is latin for to make common. Telecommunication is the process of long distance communications. Early telecommunications
Analog Communication Vishnu N V Tele is Greek for at a distance, and Communicare is latin for to make common. Telecommunication is the process of long distance communications. Early telecommunications
Digital Transceiver using H-Ternary Line Coding Technique
 Digital Transceiver using H-Ternary Line Coding Technique Abstract In this paper Digital Transceiver using Hybrid Ternary Technique gives the details about digital transmitter and receiver with the design
Digital Transceiver using H-Ternary Line Coding Technique Abstract In this paper Digital Transceiver using Hybrid Ternary Technique gives the details about digital transmitter and receiver with the design
COMPUTER COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKS ENCODING TECHNIQUES
 COMPUTER COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKS ENCODING TECHNIQUES Encoding Coding is the process of embedding clocks into a given data stream and producing a signal that can be transmitted over a selected medium.
COMPUTER COMMUNICATION AND NETWORKS ENCODING TECHNIQUES Encoding Coding is the process of embedding clocks into a given data stream and producing a signal that can be transmitted over a selected medium.
LAB 4 GENERATION OF ASK MODULATION SIGNAL
 Total Marks: / LAB 4 GENERATION OF ASK MODULATION SIGNAL Student Name:... Metrics Num:... Date:... Instructor Name:... Faculty of Engineering Technology (BTECH), Universiti Malaysia Perlis SUBMITTED Signature
Total Marks: / LAB 4 GENERATION OF ASK MODULATION SIGNAL Student Name:... Metrics Num:... Date:... Instructor Name:... Faculty of Engineering Technology (BTECH), Universiti Malaysia Perlis SUBMITTED Signature
 Sixth Semester B.E. Degree Examination, May/June 2010 Digital Communication Note: Answer any FIVEfull questions, selecting at least TWO questionsfrom each part. PART-A a. With a block diagram, explain
Sixth Semester B.E. Degree Examination, May/June 2010 Digital Communication Note: Answer any FIVEfull questions, selecting at least TWO questionsfrom each part. PART-A a. With a block diagram, explain
Problem Sheet 1 Probability, random processes, and noise
 Problem Sheet 1 Probability, random processes, and noise 1. If F X (x) is the distribution function of a random variable X and x 1 x 2, show that F X (x 1 ) F X (x 2 ). 2. Use the definition of the cumulative
Problem Sheet 1 Probability, random processes, and noise 1. If F X (x) is the distribution function of a random variable X and x 1 x 2, show that F X (x 1 ) F X (x 2 ). 2. Use the definition of the cumulative
2011 PSW American Society for Engineering Education Conference
 Communications Laboratory with Commercial Test and Training Instrument Peter Kinman and Daniel Murdock California State University Fresno Abstract A communications laboratory course has been designed around
Communications Laboratory with Commercial Test and Training Instrument Peter Kinman and Daniel Murdock California State University Fresno Abstract A communications laboratory course has been designed around
17 - Binary phase shift keying
 Name: Class: 17 - Binary phase shift keying Experiment 17 Binary Phase Shift Keying Preliminary discussion Experiments 15 and 16 show that the AM and FM modulation schemes can be used to transmit digital
Name: Class: 17 - Binary phase shift keying Experiment 17 Binary Phase Shift Keying Preliminary discussion Experiments 15 and 16 show that the AM and FM modulation schemes can be used to transmit digital
Carrier Phase Recovery. EE3723 : Digital Communications. Synchronization. Carrier Phase Recovery. Carrier Phase Synchronization Techniques.
 EE3723 : Digital Communications Carrier Phase Recovery Week 10: Synchronization (Frequency, Phase, Symbol and Frame Synchronization) Carrier and Phase Recovery Phase-Locked Loop 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali
EE3723 : Digital Communications Carrier Phase Recovery Week 10: Synchronization (Frequency, Phase, Symbol and Frame Synchronization) Carrier and Phase Recovery Phase-Locked Loop 20-May-15 Muhammad Ali
CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall Lecture 5 Physical Layer Continued
 CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall 2016 Lecture 5 Physical Layer Continued 1 Topics Definitions Analog Transmission of Digital Data Digital Transmission of Analog Data Multiplexing 2 Different Types of
CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall 2016 Lecture 5 Physical Layer Continued 1 Topics Definitions Analog Transmission of Digital Data Digital Transmission of Analog Data Multiplexing 2 Different Types of
Digital Modulation Lecture 01. Review of Analogue Modulation Introduction to Digital Modulation Techniques Richard Harris
 Digital Modulation Lecture 01 Review of Analogue Modulation Introduction to Digital Modulation Techniques Richard Harris Objectives You will be able to: Classify the various approaches to Analogue Modulation
Digital Modulation Lecture 01 Review of Analogue Modulation Introduction to Digital Modulation Techniques Richard Harris Objectives You will be able to: Classify the various approaches to Analogue Modulation
Spread Spectrum Communications and Jamming Prof. Debarati Sen G S Sanyal School of Telecommunications Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Spread Spectrum Communications and Jamming Prof. Debarati Sen G S Sanyal School of Telecommunications Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 07 Slow and Fast Frequency Hopping Hello students,
Spread Spectrum Communications and Jamming Prof. Debarati Sen G S Sanyal School of Telecommunications Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 07 Slow and Fast Frequency Hopping Hello students,
Chapter 6 Passband Data Transmission
 Chapter 6 Passband Data Transmission Passband Data Transmission concerns the Transmission of the Digital Data over the real Passband channel. 6.1 Introduction Categories of digital communications (ASK/PSK/FSK)
Chapter 6 Passband Data Transmission Passband Data Transmission concerns the Transmission of the Digital Data over the real Passband channel. 6.1 Introduction Categories of digital communications (ASK/PSK/FSK)
Objectives. Presentation Outline. Digital Modulation Lecture 01
 Digital Modulation Lecture 01 Review of Analogue Modulation Introduction to Digital Modulation Techniques Richard Harris Objectives You will be able to: Classify the various approaches to Analogue Modulation
Digital Modulation Lecture 01 Review of Analogue Modulation Introduction to Digital Modulation Techniques Richard Harris Objectives You will be able to: Classify the various approaches to Analogue Modulation
Experiment 02: Amplitude Modulation
 ECE316, Experiment 02, 2017 Communications Lab, University of Toronto Experiment 02: Amplitude Modulation Bruno Korst - bkf@comm.utoronto.ca Abstract In this second laboratory experiment, you will see
ECE316, Experiment 02, 2017 Communications Lab, University of Toronto Experiment 02: Amplitude Modulation Bruno Korst - bkf@comm.utoronto.ca Abstract In this second laboratory experiment, you will see
CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall Lecture 5 Physical Layer Continued
 CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall 2016 Lecture 5 Physical Layer Continued 1 Topics Definitions Analog Transmission of Digital Data Digital Transmission of Analog Data Multiplexing 2 Different Types of
CSCD 433 Network Programming Fall 2016 Lecture 5 Physical Layer Continued 1 Topics Definitions Analog Transmission of Digital Data Digital Transmission of Analog Data Multiplexing 2 Different Types of
Charan Langton, Editor
 Charan Langton, Editor SIGNAL PROCESSING & SIMULATION NEWSLETTER Baseband, Passband Signals and Amplitude Modulation The most salient feature of information signals is that they are generally low frequency.
Charan Langton, Editor SIGNAL PROCESSING & SIMULATION NEWSLETTER Baseband, Passband Signals and Amplitude Modulation The most salient feature of information signals is that they are generally low frequency.
ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory Frequency Shift Keying (FSK)
 ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory 1 ---- Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) 1) Frequency Shift Keying Objectives To appreciate the principle of frequency shift keying and its relationship to analogue
ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory 1 ---- Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) 1) Frequency Shift Keying Objectives To appreciate the principle of frequency shift keying and its relationship to analogue
Time division multiplexing The block diagram for TDM is illustrated as shown in the figure
 CHAPTER 2 Syllabus: 1) Pulse amplitude modulation 2) TDM 3) Wave form coding techniques 4) PCM 5) Quantization noise and SNR 6) Robust quantization Pulse amplitude modulation In pulse amplitude modulation,
CHAPTER 2 Syllabus: 1) Pulse amplitude modulation 2) TDM 3) Wave form coding techniques 4) PCM 5) Quantization noise and SNR 6) Robust quantization Pulse amplitude modulation In pulse amplitude modulation,
MSK has three important properties. However, the PSD of the MSK only drops by 10log 10 9 = 9.54 db below its midband value at ft b = 0.
 Gaussian MSK MSK has three important properties Constant envelope (why?) Relatively narrow bandwidth Coherent detection performance equivalent to that of QPSK However, the PSD of the MSK only drops by
Gaussian MSK MSK has three important properties Constant envelope (why?) Relatively narrow bandwidth Coherent detection performance equivalent to that of QPSK However, the PSD of the MSK only drops by
The figures and the logic used for the MATLAB are given below.
 MATLAB FIGURES & PROGRAM LOGIC: Transmitter: The figures and the logic used for the MATLAB are given below. Binary Data Sequence: For our project we assume that we have the digital binary data stream.
MATLAB FIGURES & PROGRAM LOGIC: Transmitter: The figures and the logic used for the MATLAB are given below. Binary Data Sequence: For our project we assume that we have the digital binary data stream.
Problems from the 3 rd edition
 (2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
(2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
Analog Transmission 5.1 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERSION
 Analog Transmission In Chapter 3, we discussed the advantages and disadvantages of digital and analog transmission. We saw that while digital transmission is very desirable, a low-pass channel is needed.
Analog Transmission In Chapter 3, we discussed the advantages and disadvantages of digital and analog transmission. We saw that while digital transmission is very desirable, a low-pass channel is needed.
Lecture 6. Angle Modulation and Demodulation
 Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
Outline. Communications Engineering 1
 Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
Digital Communication
 Digital Communication (ECE4058) Electronics and Communication Engineering Hanyang University Haewoon Nam Lecture 1 1 Digital Band Pass Modulation echnique Digital and-pass modulation techniques Amplitude-shift
Digital Communication (ECE4058) Electronics and Communication Engineering Hanyang University Haewoon Nam Lecture 1 1 Digital Band Pass Modulation echnique Digital and-pass modulation techniques Amplitude-shift
 UNIT 2 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION DIGITAL COMMUNICATION-Introduction The techniques used to modulate digital information so that it can be transmitted via microwave, satellite or down a cable pair is different
UNIT 2 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION DIGITAL COMMUNICATION-Introduction The techniques used to modulate digital information so that it can be transmitted via microwave, satellite or down a cable pair is different
RF Basics 15/11/2013
 27 RF Basics 15/11/2013 Basic Terminology 1/2 dbm is a measure of RF Power referred to 1 mw (0 dbm) 10mW(10dBm), 500 mw (27dBm) PER Packet Error Rate [%] percentage of the packets not successfully received
27 RF Basics 15/11/2013 Basic Terminology 1/2 dbm is a measure of RF Power referred to 1 mw (0 dbm) 10mW(10dBm), 500 mw (27dBm) PER Packet Error Rate [%] percentage of the packets not successfully received
Electrical signal types
 Electrical signal types With BogusBus, our signals were very simple and straightforward: each signal wire (1 through 5) carried a single bit of digital data, 0 Volts representing "off" and 24 Volts DC
Electrical signal types With BogusBus, our signals were very simple and straightforward: each signal wire (1 through 5) carried a single bit of digital data, 0 Volts representing "off" and 24 Volts DC
Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier
 Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier and the first channel. The modulation of the main carrier
Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier and the first channel. The modulation of the main carrier
EXPERIMENT 1: Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK)
 EXPERIMENT 1: Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) 1) OBJECTIVE Generation and demodulation of an amplitude shift keyed (ASK) signal 2) PRELIMINARY DISCUSSION In ASK, the amplitude of a carrier signal is modified
EXPERIMENT 1: Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) 1) OBJECTIVE Generation and demodulation of an amplitude shift keyed (ASK) signal 2) PRELIMINARY DISCUSSION In ASK, the amplitude of a carrier signal is modified
CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY NH-67, TRICHY MAIN ROAD, PULIYUR, C.F , KARUR DT.
 CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY NH-67, TRICHY MAIN ROAD, PULIYUR, C.F. 639 114, KARUR DT. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING COURSE MATERIAL Subject Name: Digital Communication
CHETTINAD COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY NH-67, TRICHY MAIN ROAD, PULIYUR, C.F. 639 114, KARUR DT. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING COURSE MATERIAL Subject Name: Digital Communication
COMM 601: Modulation I
 Prof. Ahmed El-Mahdy, Communications Department The German University in Cairo Text Books [1] Couch, Digital and Analog Communication Systems, 7 th edition, Prentice Hall, 2007. [2] Simon Haykin, Communication
Prof. Ahmed El-Mahdy, Communications Department The German University in Cairo Text Books [1] Couch, Digital and Analog Communication Systems, 7 th edition, Prentice Hall, 2007. [2] Simon Haykin, Communication
EEE 309 Communication Theory
 EEE 309 Communication Theory Semester: January 2017 Dr. Md. Farhad Hossain Associate Professor Department of EEE, BUET Email: mfarhadhossain@eee.buet.ac.bd Office: ECE 331, ECE Building Types of Modulation
EEE 309 Communication Theory Semester: January 2017 Dr. Md. Farhad Hossain Associate Professor Department of EEE, BUET Email: mfarhadhossain@eee.buet.ac.bd Office: ECE 331, ECE Building Types of Modulation
Digital modulation techniques
 Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Lecture Topics. Doppler CW Radar System, FM-CW Radar System, Moving Target Indication Radar System, and Pulsed Doppler Radar System
 Lecture Topics Doppler CW Radar System, FM-CW Radar System, Moving Target Indication Radar System, and Pulsed Doppler Radar System 1 Remember that: An EM wave is a function of both space and time e.g.
Lecture Topics Doppler CW Radar System, FM-CW Radar System, Moving Target Indication Radar System, and Pulsed Doppler Radar System 1 Remember that: An EM wave is a function of both space and time e.g.
