FullFlex Synchronous SDR Dual-Port SRAM
|
|
|
- Aubrey Jacobs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Synchronous SD Dual-Port SAM Features True dual-ported memory allows simultaneous access to the shared array from each port Synchronous pipelined operation with Single Data ate (SD) operation on each port SD interface at 250 MHz Up to 36-Gb/s bandwidth (250 MHz * 72 bit * 2 ports) Selectable pipelined or flow-through mode 1.5V or 1.8V core power supply ommercial and Industrial temperature IEEE JTAG boundary scan Available in 484-ball PBGA Packages and 256-ball FBGA packages 72 family 36-Mbit: 512K x 72 (YD36S72V18) 18-Mbit: 256K x 72 (YD18S72V18) 9-Mbit: 128K x 72 (YD09S72V18) 4-Mbit: 64K x 72 (YD04S72V18) 36 family 36-Mbit: 1M x 36 (YD36S36V18) 18-Mbit: 512K x 36 (YD18S36V18) 9-Mbit: 256K x 36 (YD09S36V18) 4-Mbit: 128K x 36 (YD04S36V18) 18 family 36-Mbit: 2M x 18 (YD36S18V18) 18-Mbit: 1M x 18 (YD18S18V18) 9-Mbit: 512K x 18 (YD09S18V18) 4-Mbit: 256K x 18 (YD04S18V18) Built-in deterministic access control to manage address collisions Deterministic flag output upon collision detection ollision detection on back-to-back clock cycles First Busy Address readback Advanced features for improved high-speed data transfer and flexibility Variable Impedance Matching (VIM) Echo clocks Selectable VTT (3.3V), Extended HST (1.4V 1.9V), 1.8V VMOS, or 2.5V VMOS I/O on each port Burst counters for sequential memory access Mailbox with interrupt flags for message passing Dual hip Enables for easy depth expansion Functional Description The Dual-Port SAM families consist of 4-Mbit, 9-Mbit, 18-Mbit, and 36-Mbit synchronous, true dual-port static AMs that are high-speed, low-power 1.8V/1.5V MOS. Two ports are provided, allowing the array to be accessed simultaneously. Simultaneous access to a location triggers deterministic access control. For 72 these ports can operate independently with 72-bit bus widths and each port can be independently configured for two pipelined stages. Each port can also be configured to operate in pipelined or flow-through mode. Advanced features include built-in deterministic access control to manage address collisions during simultaneous access to the same memory location, Variable Impedance Matching (VIM) to improve data transmission by matching the output driver impedance to the line impedance, and echo clocks to improve data transfer. To reduce the static power consumption, chip enables can be used to power down the internal circuitry. The number of cycles of latency before a change in E0 or E1 will enable or disable the databus matches the number of cycles of read latency selected for the device. In order for a valid write or read to occur, both chip enable inputs on a port must be active. Each port contains an optional burst counter on the input address register. After externally loading the counter with the initial address, the counter will increment the address internally. Additional features of this device include a mask register and a mirror register to control counter increments and wrap-around. The counter-interrupt (NTINT) flags notify the host that the counter will reach maximum count value on the next clock cycle. The host can read the burst-counter internal address, mask register address, and busy address on the address lines. The host can also load the counter with the address stored in the mirror register by utilizing the retransmit functionality. Mailbox interrupt flags can be used for message passing, and JTAG boundary scan and asynchronous Master eset (MST) are also available. The logic block diagram in Figure 1 displays these features. The 72 is offered in a 484-ball plastic BGA package. The 36 and 18 are offered in both 484-ball and 256-ball fine pitch BGA packages. ypress Semiconductor orporation 198 hampion ourt San Jose, A Document #: ev. *F evised September 6, 2006
2 FTSE FTSE QEN POTSTD[1:0] ONFIG Block ONFIG Block QEN POTSTD[1:0] DQ[71:0] BE [7:0] E0 E1 OE IO ontrol IO ontrol DQ [71:0] BE [7:0] E0 E1 OE /W /W Q1 Q1 Q0 Q0 Q1 Q1 Q0 Q0 Dual Ported Array BUSY ollision Detection ogic BUSY A [20:0] NT/MSK ADS NTEN NTST ET NTINT Address & ounter ogic Address & ounter ogic A [20:0] NT/MSK ADS NTEN NTST ET NTINT WP WP INT Mailboxes INT JTAG TST TMS TDI TDO TK ZQ0 ZQ1 EADY owspd ESET OGI ZQ0 ZQ1 MST EADY owspd Figure Mbit (YD18S72V18) Block Diagram [1, 2, 3] Notes: 1. The YD36S18V18 device has 21 address bits. The YD36S36V18 and the YD18S18V18 devices have 20 address bits. The YD36S72V18, YD18S36V18, and the YD09S18V18 devices have 19 address bits. The YD18S72V18, YD09S36V18, and the YD04S18V18 devices have 18 address bits. The YD09S72V18 and the YD04S36V18 devices have 17 address bits. The YD04S72V18 has 16 address bits. 2. The 72 family of devices has 72 data lines. The 36 family of devices has 36 data lines. The 18 family of devices has 18 data lines. 3. The 72 family of devices has eight byte enables. The 36 family of devices has four byte enables. The 18 family of devices has two byte enables. Document #: ev. *F Page 2 of 52
3 A B D E F G H J K M N P T U V W Y AA AB 72 SD 484-ball BGA Pinout (Top View) N DQ63 DQ65 DQ67 DQ69 DQ71 DQ61 DQ62 DQ64 DQ66 DQ68 DQ70 DQ59 DQ60 DQ57 DQ58 DQ54 DQ55 VSS VSS DQ56 DQ51 DQ52 DQ53 DQ48 DQ49 DQ50 DQ45 DQ46 DQ47 DQ42 DQ43 DQ44 DQ39 DQ40 DQ41 DQ36 DQ37 DQ38 DQ36 DQ37 DQ38 DQ39 DQ40 DQ41 VSS VSS VSS Q1 Q1 VSS OW POT ZQ0 BUSY NTI [4] SPD STD0 NT O VSS VSS O E1 E0 O A0 A1 ET BE4 O A2 A3 WP A4 A5 EAD Y A6 A7 ZQ1 [4] BE5 O BE6 O BE7 VTT O O O O VO E A8 A9 OE VTT VO E A10 A11 VSS BE3 VTT VO E A12 A13 ADS BE2 O A14 A15 NT/ BE1 MSK O A16 [7] A18 [5] DQ35 DQ33 DQ31 DQ29 DQ27 N A17 [6] N DQ34 DQ32 DQ30 DQ28 DQ26 DQ25 NTE N NT ST /W FTSE BE0 O INT QE N O O O N VO E O O O O O O O VEF O O O O O VO E DQ42 DQ43 DQ44 POT STD1 VTT VTT VTT O VO E VO E VO E O DQ45 DQ46 DQ47 DQ48 DQ49 DQ50 DQ51 DQ52 DQ53 DQ54 DQ55 DQ56 DQ57 DQ58 DQ59 DQ60 DQ61 DQ62 VSS VSS DQ64 N Q1 Q1 VSS VSS VSS DQ66 O O O O VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VEF O O O VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS O VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS O VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VO E VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VO E VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VO E VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VO E VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS O VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS O VEF O O VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VEF O O O O VSS MST VSS Q0 Q0 N POT STD1 VSS VSS DQ20 DQ24 DQ23 DQ22 DQ21 DQ19 DQ18 DQ17 DQ16 DQ15 DQ14 DQ13 DQ12 DQ11 DQ10 VO E VO E VO E VO E VTT VTT VTT O NTI NT BUSY ZQ0 [4] POT STD0 O O OW SPD O O DQ8 DQ5 DQ2 DQ2 DQ5 DQ8 DQ11 DQ7 DQ4 DQ1 DQ1 DQ4 DQ7 DQ10 O O O O O N VSS O O O O O O DQ68 E0 E1 DQ70 N DQ63 DQ65 DQ67 DQ69 DQ71 BE4 ET A1 A0 BE5 WP BE6 EAD Y BE7 ZQ1 [4] A3 A5 A7 A2 A4 A6 VTT OE A9 A8 VTT BE3 VSS A11 A10 VTT BE2 ADS A13 A12 O O O O BE1 NT/ MSK BE0 NTE N INT NT ST QE N TST O A15 A14 A17 [6] /W DQ34 FTSE A16 [7] N A18 [5] DQ32 VSS Q0 Q0 VSS TDI TDO DQ30 DQ14 DQ13 DQ9 DQ6 DQ3 DQ0 DQ0 DQ3 DQ6 DQ9 DQ12 DQ17 DQ16 DQ15 DQ20 DQ19 DQ18 TMS TK DQ28 DQ22 DQ21 DQ24 DQ23 DQ26 DQ25 DQ35 DQ33 DQ31 DQ29 DQ27 N Notes: 4. eaving this pin N disables VIM. 5. eave this ball unconnected for YD18S72V18, YD09S72V18 and YD04S72V eave this ball unconnected for YD09S72V18 and YD04S72V eave this ball unconnected for YD04S72V18. Document #: ev. *F Page 3 of 52
4 A B D E F G H J K M N P T U V W Y AA AB 36 SD 484-ball BGA Pinout (Top View) [8] N N N N N DQ33 N N N N N DQ34 N N VSS VSS N DQ35 DQ30 DQ31 DQ32 DQ27 DQ28 DQ29 DQ24 DQ25 DQ26 DQ21 DQ22 DQ23 DQ18 DQ19 DQ20 DQ18 DQ19 DQ20 DQ21 DQ22 DQ23 N N VSS VSS VSS Q1 Q1 VSS OW POT ZQ0 BUSY NTI [4] SPD STD0 NT N N O VSS VSS O N N E1 E0 O A0 A1 ET BE2 O A2 A3 WP A4 A5 EAD Y A6 A7 ZQ1 [4] BE3 O N O O O O O N VTT VO E A8 A9 OE VTT VO E A10 A11 VSS N VTT VO E A12 A13 ADS N O A14 A15 NT/ BE1 MSK O A16 A17 NTE N A18 A19 NT ST BE0 O INT N N /W QE N N N FTSE O O O N VO E O O O O O O O VEF O O O O O VO E DQ24 DQ25 DQ26 POT STD1 VTT VTT VTT O VO E VO E VO E O DQ27 DQ28 DQ29 DQ30 DQ31 DQ32 DQ33 DQ34 DQ35 N N N N N N N N N N N VSS VSS N N N Q1 Q1 VSS VSS VSS N N O O O O VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VEF O O O VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS O VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS O VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VO E VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VO E VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VO E VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VO E VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS O VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS O VEF O O VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VEF O O O O N N VSS MST VSS Q0 Q0 N POT STD1 N N VSS VSS N DQ17 N N N N N DQ16 N N N N N DQ15 DQ14 DQ13 DQ12 DQ11 DQ10 VO E VO E VO E VO E VTT VTT VTT O NTI NT BUSY ZQ0 [4] POT STD0 O O OW SPD O O DQ8 DQ5 DQ2 DQ2 DQ5 DQ8 DQ11 DQ7 DQ4 DQ1 DQ1 DQ4 DQ7 DQ10 O O O O O N VSS O O O O O O N N E0 E1 N N BE2 ET A1 A0 BE3 WP N N EAD Y ZQ1 [4] A3 A5 A7 A2 A4 A6 VTT OE A9 A8 VTT N VSS A11 A10 VTT N ADS A13 A12 O O O O BE1 NT/ MSK BE0 NTE N A15 A14 A17 A16 INT NT A19 A18 ST QE N TST O /W N N FTSE N N VSS Q0 Q0 VSS TDI TDO N N DQ14 DQ13 DQ9 DQ6 DQ3 DQ0 DQ0 DQ3 DQ6 DQ9 DQ12 DQ17 DQ16 DQ15 N TMS TK N N N N N N N N N N N N Note: 8. Use this pinout only for device YD36S36V18 of the 36 family. Document #: ev. *F Page 4 of 52
5 A B D E F G H J K M N P T U V W 18 SD 484-ball BGA Pinout (Top View) [9] N N N N N N N N DQ15 N N N N N N N N DQ16 N N VSS VSS N N N N DQ17 DQ12 DQ13 DQ14 DQ9 DQ9 DQ12 DQ10 DQ11 DQ10 DQ11 DQ13 DQ14 N N VSS VSS VSS Q1 Q1 VSS OW POT ZQ0 BUSY NTI SPD STD0 [4] NT N N O VSS VSS O N N E1 E0 O A0 A1 ET BE1 O A2 A3 WP A4 A5 EAD Y A6 A7 ZQ1 [4] N N O O O O O O N VTT VO E A8 A9 OE VTT VO E A10 A11 VSS N VTT VO E A12 A13 ADS N O A14 A15 NT/ MSK A16 A17 NTE N A18 A19 NT ST N O BE0 O INT A20 N /W QE N N N FTSE O O O N VO E O O O O O O O VEF O O O O O VO E DQ15 DQ16 DQ17 POT STD1 VTT VTT VTT O VO E VO E VO E O N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N VSS VSS N N N Q1 Q1 VSS VSS VSS N N O O O O VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VEF O O O VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS O VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS O VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VO E VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VO E VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VO E VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VO E VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS O VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS O VEF O O VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VEF O O O O N N VSS MST VSS Q0 Q0 N POT STD1 VO E VO E VO E VO E VTT VTT VTT O NTI NT BUSY ZQ0 [4] POT STD0 O O OW SPD O O O O O O O N VSS O O O O O O N N E0 E1 N N BE1 ET A1 A0 N N N WP EAD Y ZQ1 [4] A3 A5 A7 A2 A4 A6 VTT OE A9 A8 VTT N VSS A11 A10 VTT N ADS A13 A12 O O O O N NT/ MSK A15 A14 BE0 NTE A17 A16 N INT NT ST QE N TST O A19 A18 /W N A20 FTSE N N VSS Q0 Q0 VSS TDI TDO N N Y N N VSS VSS N N N N DQ8 DQ5 DQ2 DQ2 DQ5 DQ8 N N N N TMS TK N N AA N N N N N N N N DQ7 DQ4 DQ1 DQ1 DQ4 DQ7 N N N N N N N N AB N N N N N N N N DQ6 DQ3 DQ0 DQ0 DQ3 DQ6 N N N N N N N N Note: 9. Use this pinout only for device YD36S18V18 of the 18 family. Document #: ev. *F Page 5 of 52
6 36 SD 256-Ball BGA (Top View) A DQ32 DQ30 DQ28 DQ26 DQ24 DQ22 DQ20 DQ18 DQ18 DQ20 DQ22 DQ24 DQ26 DQ28 DQ30 DQ32 B DQ33 DQ31 DQ29 DQ27 DQ25 DQ23 DQ21 DQ19 DQ19 DQ21 DQ23 DQ25 DQ27 DQ29 DQ31 DQ33 DQ34 DQ35 ET INT Q1 Q1 N TST MST ZQ0 [4] Q1 Q1 INT ET DQ35 DQ34 D A0 A1 WP VEF FTSE OWSP D VSS VTT VTT VSS OWSP D FTSE VEF WP A1 A0 E A2 A3 E0 E1 O O O VOE VOE O O O E1 E0 A3 A2 F A4 A5 NTINT BE3 O VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS O BE3 NTINT A5 A4 G A6 A7 BUSY BE2 ZQ0 [4] VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS O BE2 BUSY A7 A6 H A8 A9 VTT VOE VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VOE VTT A9 A8 J A10 A11 VSS POTST D1 VOE VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VOE POTST D1 VSS A11 A10 K A12 A13 OE BE1 O VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS O BE1 OE A13 A12 A14 A15 ADS BE0 O VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS O BE0 ADS A15 A14 M A16 A17 [11] /W QEN O O O VOE VOE O O O QEN /W A17 [11] A16 N A18 [10] N NT/MS K VEF P DQ16 DQ17 NTEN NTST POTST D0 EADY ZQ1 [4] VTT VTT ZQ1 [4] EADY POTST D0 VEF Q0 Q0 TK TMS TDO TDI Q0 Q0 NTST NT/MS K NTEN DQ17 N A18 [10] DQ15 DQ13 DQ11 DQ9 DQ7 DQ5 DQ3 DQ1 DQ1 DQ3 DQ5 DQ7 DQ9 DQ11 DQ13 DQ15 T DQ14 DQ12 DQ10 DQ8 DQ6 DQ4 DQ2 DQ0 DQ0 DQ2 DQ4 DQ6 DQ8 DQ10 DQ12 DQ14 DQ16 Notes: 10. eave this ball unconnected for YD09S36V18 and YD04S36V eave this ball unconnected for YD04S36V18. Document #: ev. *F Page 6 of 52
7 18 SD 256-Ball BGA (Top View) A N N N DQ17 DQ16 DQ13 DQ12 DQ9 DQ9 DQ12 DQ13 DQ16 DQ17 N N N B N N N N DQ15 DQ14 DQ11 DQ10 DQ10 DQ11 DQ14 DQ15 N N N N N N ET INT Q1 Q1 N TST MST ZQ0 [4] Q1 Q1 INT ET N N D A0 A1 WP VEF FTSE OWSP D VSS VTT VTT VSS OWSP D FTSE VEF WP A1 A0 E A2 A3 E0 E1 O O O VOE VOE O O O E1 E0 A3 A2 F A4 A5 NTINT N O VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS O N NTINT A5 A4 G A6 A7 BUSY N ZQ0 [4] VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS O N BUSY A7 A6 H A8 A9 VTT VOE VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VOE VTT A9 A8 J A10 A11 VSS POTST D1 VOE VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VOE POTST D1 VSS A11 A10 K A12 A13 OE BE1 O VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS O BE1 OE A13 A12 A14 A15 ADS BE0 O VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS VSS O BE0 ADS A15 A14 M A16 A17 /W QEN O O O VOE VOE O O O QEN /W A17 A16 N A18 [13] A19 [12] NT/MS K VEF P N N NTEN NTST POTST D0 EADY ZQ1 [4] VTT VTT ZQ1 [4] EADY POTST D0 VEF Q0 Q0 TK TMS TDO TDI Q0 Q0 NTST NT/MS K A19 [12] A18 [13] NTEN N N N N N N DQ6 DQ5 DQ2 DQ1 DQ1 DQ2 DQ5 DQ6 N N N N T N N N DQ8 DQ7 DQ4 DQ3 DQ0 DQ0 DQ3 DQ4 DQ7 DQ8 N N N Notes: 12. eave this ball unconnected for YD09S18V18 and YD04S18V eave this ball unconnected for YD04S18V18. Document #: ev. *F Page 7 of 52
8 Table 1. Selection Guide Unit f [15] MAX MHz Max. Access Time (lock to Data) ns Typical Operating urrent I 930 [14] 800 [14] 700 [14] ma Typical Standby urrent for I SB3 (Both Ports MOS evel) 210 [14] 210 [14] 210 [14] ma Pin Definitions eft Port ight Port Description A[20:0] A[20:0] Address Inputs. [1] DQ[71:0] DQ[71:0] Data Bus Input/Output. [2] BE[7:0] BE[7:0] Byte Select Inputs. [3] Asserting these signals enables ead and Write operations to the corresponding bytes of the memory array. BUSY BUSY Port Busy Output. When there is an address match and both chip enables are active for both ports, an external BUSY signal is asserted on the fifth clock cycles from when the collision occurs. lock Signal. Maximum clock input rate is f MAX. E0 E0 Active OW hip Enable Input. E1 E1 Active HIGH hip Enable Input. QEN QEN Echo lock Enable Input. Assert HIGH to enable echo clocking on respective port. Q0 Q0 Echo lock Signal Output for DQ[35:0] for 72 devices. Echo lock Signal Output for DQ[17:0] for 36 devices. Echo lock Signal Output for DQ[8:0] for 18 devices. Q0 Q0 Inverted Echo lock Signal Output for DQ[35:0] for 72 devices. Inverted Echo lock Signal Output for DQ[17:0] for 36 devices. Inverted Echo lock Signal Output for DQ[8:0] for 18 devices. Q1 Q1 Echo lock Signal Output for DQ[71:36] for 72 devices. Echo lock Signal Output for DQ[35:18] for 36 devices. Echo lock Signal Output for DQ[17:9] for 18 devices. Q1 Q1 Inverted Echo lock Signal Output for DQ[71:36] for 72 devices. Inverted Echo lock Signal Output for DQ[35:18] for 36 devices. Inverted Echo lock Signal Output for DQ[17:9] for18 devices. ZQ[1:0] ZQ[1:0] VIM Output Impedance Matching Input. To use, connect a calibrating resistor between ZQ and ground. The resistor must be five times larger than the intended line impedance driven by the dual-port. Assert HIGH or leave N to disable Variable Impedance Matching. OE OE Output Enable Input. This asynchronous signal must be asserted OW to enable the DQ data pins during ead operations. INT INT Mailbox Interrupt Flag Output. The mailbox permits communications between ports. The upper two memory locations can be used for message passing. INT is asserted OW when the right port writes to the mailbox location of the left port, and vice versa. An interrupt to a port is deasserted HIGH when it reads the contents of its mailbox. owspd owspd Port ow Speed Select Input. Assert this pin OW to disable the D. For operation at less than 100 MHz, assert this pin OW. [16] [16] POTSTD[1:0] POTSTD[1:0] Port lock/address/ontrol/data/echo lock/i/o Standard Select Input. Assert these pins OW/OW for VTT, OW/HIGH for HST, HIGH/OW for 2.5V VMOS, and HIGH/HIGH for 1.8V VMOS, respectively. These pins must be driven by VTT referenced levels. Notes: 14. For 18-Mbit x72 commercial configuration only, please refer to the electrical characteristics section for complete information. 15. SD mode with two pipelined stages. 16. POTSTD[1:0] and POTSTD[1:0] have internal pull-down resistors. Document #: ev. *F Page 8 of 52
9 Pin Definitions (continued) eft Port ight Port Description /W /W ead/write Enable Input. Assert this pin OW to Write to, or HIGH to ead from the dual-port memory array. EADY EADY Port D eady Output. This signal will be asserted OW when the D and Variable Impedance Matching circuits have completed calibration. This is a wired O capable output. NT/MSK NT/MSK Port ounter/mask Select Input. ounter control input. ADS ADS Port ounter Address oad Strobe Input. ounter control input. NTEN NTEN Port ounter Enable Input. ounter control input. NTST NTST Port ounter eset Input. ounter control input. NTINT NTINT Port ounter Interrupt Output. This pin is asserted OW one cycle before the unmasked portion of the counter is incremented to all 1s. WP WP Port ounter Wrap Input. When the burst counter reaches the maximum count, on the next counter increment WP can be set OW to load the unmasked counter bits to 0 or set HIGH to load the counter with the value stored in the mirror register. ET ET Port ounter etransmit Input. Assert this pin OW to reload the initial address for repeated access to the same segment of memory. VEF VEF Port External HST I/O eference Input. This pin is left N when HST is not used. O O Port Data I/O Power Supply. FTSE FTSE Port Flow-through Mode Select Input. Assert this pin OW to select Flow-through mode. Assert this pin HIGH to select Pipelined mode. MST Master eset Input. MST is an asynchronous input signal and affects both ports. Asserting MST OW performs all of the reset functions as described in the text. A MST operation is required at power-up. This pin must be driven by a O referenced signal. TMS TDI TST TK TDO VSS VOE VTT JTAG Test Mode Select Input. It controls the advance of JTAG TAP state machine. State machine transitions occur on the rising edge of TK. Operation for VTT or 2.5V VMOS. JTAG Test Data Input. Data on the TDI input will be shifted serially into selected registers. Operation for VTT or 2.5V VMOS. JTAG eset Input. Operation for VTT or 2.5V VMOS. JTAG Test lock Input. Operation for VTT or 2.5V VMOS. JTAG Test Data Output. TDO transitions occur on the falling edge of TK. TDO is normally three-stated except when captured data is shifted out of the JTAG TAP. Operation for VTT or 2.5V VMOS. Ground Inputs. Device ore Power Supply. VTT Power Supply. Selectable I/O Standard The device families also offer the option of choosing one of four port standards for the device. Each port can independently select standards from single-ended HST class I, single-ended VTT, 2.5V VMOS, or 1.8V VMOS. The selection of the standard is determined by the POTSTD pins for each port. These pins should be connected to either an VTT or 2.5V VMOS power suppy. This will determine the input clock, address, control, data, and Echo clock standard for each port as shown in Table 2. Please note that only 1.8V VMOS and HST are supported for 4-Mbit, 9-Mbit, 18-Mbit devices running at 250 MHz, and for 36-Mbit devices running at 200 MHz. Table 2. Port Standard Selection POTSTD1 POTSTD0 I/O Standard VSS VSS VTT VSS VTT HST VTT VSS 2.5V VMOS VTT VTT 1.8V VMOS locking Separate clocks synchronize the operations on each port. Each port has one clock input. In this mode, all the transactions on the address, control, and data will be on the rising Document #: ev. *F Page 9 of 52
10 edge. All transactions on the address, control, data input, output, and byte enables will occur on the rising edge. Table 3. Data Pin Assignment BE Pin Name BE[7] BE[6] BE[5] BE[4] BE[3] BE[2] BE[1] BE[0] Data Pin Name DQ[71:63] DQ[62:54] DQ[53:45] DQ[44:36] DQ[35:27] DQ[26:18] DQ[17:9] DQ[8:0] Selectable Pipelined/Flow-through Mode To meet data rate and throughput requirements, the families offer selectable pipelined or flow-through mode. Echo clocks are not supported in flow-through mode and the D must be disabled. Flow-through mode is selected by the FTSE pin. Strapping this pin HIGH selects pipelined mode. Strapping this pin OW selects flow-through mode. D The familes of devices have an on-chip D. Enabling the D reduces the clock to data valid (t D ) time allowing more set-up time for the receiving device. For operation below 100 MHz, the D must be disabled. This is selectable by strapping owspd low. Whenever the operating frequency is altered beyond the lock Input ycle to ycle Jitter spec, the D is required to be reset followed by 1024 clocks before any valid operation. owspd pins can be used to reset the D(s) for a single port independent of all other circuitry. MST can be used to reset all Ds on the chip, for information on D lock and reset time, please see the Master eset section below. Echo locking As the speed of data increases, on-board delays caused by parasitics make providing accurate clock trees extremely difficult. To counter this problem, the families incorporate Echo locks. Echo locks are enabled on a per port basis. The dual-port receives input clocks that are used to clock in the address and control signals for a read operation. The dual-port retransmits the input clocks relative to the data output. The buffered clocks are provided on the Q1/Q1 and Q0/Q0 outputs. Each port has a pair of Echo clocks. Each clock is associated with half the data bits. The output clock will match the corresponding ports I/O configuration. To enable Echo clock outputs, tie QEN HIGH. To disable Echo clock outputs, tie QEN OW. Input lock Data Out Echo lock Echo lock Figure 2. SD Echo lock Delay Deterministic Access ontrol Deterministic Access ontrol is provided for ease of design. The circuitry detects when both ports are accessing the same location and provides an external BUSY flag to the port on which data may be corrupted. The collision detection logic saves the address in conflict (Busy Address) to a readable register. In the case of multiple collisions, the first Busy address will be written to the Busy Address register. If both ports are accessing the same location at the same time and only one port is doing a write, if t S is met, then the data being written to and read from the address is valid data. For example, if the right port is reading and the left port is writing and the left ports clock meets t S, then the data being read from the address by the right port will be the old data. In the same case, if the right ports clock meets t S, then the data being read out of the address from the right port will be the new data. In the above case, if t S is violated by the either ports clock with respect to the other port and the right port gets the external BUSY flag, the data from the right port is corrupted. Table 4 shows the t S timing that must be met to guarantee the data. Table 5 shows that, in the case of the left port writing and the right port reading, when an external BUSY flag is asserted on the right port, the data read out of the device will not be guaranteed. The value in the busy address register can be read back to the address lines. The required input control signals for this function are shown in Table 8. The value in the busy address register will be read out to the address lines t A after the same amount of latency as a data read operation. After an initial address match, the BUSY flag is asserted and the address under contention is saved in the busy address register. All following address matches cause the BUSY flag to be generated, however, none of the addresses are saved into the busy address register. Once a busy readback is performed, the address of the first match that happens at least two clocks cycles after the busy readback is saved into the busy address register. Table 4. t S Timing for All Operating Modes Port A Early Arriving Port Port B ate Arriving Port t S Mode Active Edge Mode Active Edge ise to Opposite ise Set-up Time for Non-corrupt Data Unit SD SD t Y(min) 0.5 ns Document #: ev. *F Page 10 of 52
11 Table 5. Deterministic Access ontrol ogic eft Port ight Port eft lock ight lock BUSY BUSY Description ead ead X X H H No ollision Write ead >t S 0 H H ead OD Data 0 >t S H H ead NEW Data <t S 0 H H ead OD Data H Data Not Guaranteed 0 <t S H H ead NEW Data H Data Not Guaranteed ead Write >t S 0 H H ead NEW Data 0 >t S H H ead OD Data <t S 0 H H ead NEW Data H Data Not Guaranteed 0 <t S H H ead OD Data H Data Not Guaranteed Write Write 0 > t S & <t S Array Data orrupted 0 >t S H Array Stores ight Port Data >t S 0 H Array Stores eft Port Data Variable Impedance Matching (VIM) Each port contains a Variable Impedance Matching circuit to set the impedance of the I/O driver to match the impedance of the on-board traces. The impedance is set for all outputs except JTAG and is done on a per port basis. To take advantage of the VIM feature, connect a calibrating resistor (Q) that is five times the value of the intended line impedance from the ZQ pin to VSS. The output impedance is then adjusted to account for drifts in supply voltage and temperature every 1024 clock cycles. If a port s clock is suspended, the VIM circuit will retain its last setting until the clock is restarted. On restart, it will then resume periodic adjustment. In the case of a significant change in device temperature or supply voltage, recalibration will happen every 1024 clock cycles. A Master eset will initialize the VIM circuitry. Table 6 shows the VIM parameters and Table 7 describes the VIM operation modes. In order to disable VIM, the ZQ pin must be connected to O of the relative supply for the I/Os before a Master eset. Table 6. Variable Impedance Matching Parameters Parameter Min. Max. Unit Tolerance Q Value Ω ± 2% Output Impedance Ω ± 15% eset Time N/A 1024 ycles N/A Update Time N/A 1024 ycles N/A Table 7. Variable Impedance Matching Operation Q onnection Output onfiguration 100Ω - 275Ω to VSS Output Driver Impedance = Q/5 ± 15% at Vout = O/2 ZQ to O VIM Disabled. out < 20Ω at Vout = O/2 Address ounter and Mask egister Operations [1] Each port of the family contains a programmable burst address counter. The burst counter contains four registers: a counter register, a mask register, a mirror register, and a busy address register. The counter register contains the address used to access the AM array. It is changed only by the master reset (MST), ounter eset, ounter oad, etransmit, and ounter Increment operations. The mask register value affects the ounter Increment and ounter eset operations by preventing the corresponding bits of the counter register from changing. It also affects the counter interrupt output (NTINT). The mask register is only changed by Mask eset, Mask oad, and MST. The Mask oad operation loads the value of the address bus into the mask register. The mask register defines the counting range of the counter register. The mask register is divided into two or three consecutive regions. Zero or more 0s define the masked region and one or more 1s define the unmasked portion of the counter register. The counter register may only be divided into up to three regions. The region containing the least significant bits must be no more than two 0s. Bits one and zero may be 10 respectively, masking the least significant counter bit and causing the counter to increment by two instead of one. If bits one and zero are 00, the two least significant bits are masked and the counter will increment by four instead of one. For example, in the case of a 256Kx72 Document #: ev. *F Page 11 of 52
12 configuration, a mask register value of 003F divides the mask register into three regions. With bit 0 being the least significant bit and bit 17 being the most significant bit, the two least significant bits are masked, the next eight bits are unmasked, and the remaining bits are masked. The mirror register is used to reload the counter register on retransmit operations (see retransmit below) and wrap functions (see counter increment below). The last value loaded into the counter register is stored in the mirror register. The mirror register is only changed by master reset (MST), ounter eset, and ounter oad. Table 8 summarizes the operations of these registers and the required input control signals. All signals except MST are synchronized to the ports clock. ounter oad Operation [1] The address counter and mirror registers are both loaded with the address value presented on the address lines. This value ranges from 0 to 1FFFFF. Mask oad Operation [1] The mask register is loaded with the address value presented on the address bus. This value ranges from 0 to 1FFFFF though not all values permit correct increment operations. Permitted values are in the form of 2 n 1, 2 n 2, or 2 n 4. The counter register can only be segmented in up to three regions. From the most significant bit to the least significant bit, permitted values have zero or more 0s, one or more 1s, and the least significant two bits can be 11, 10, or 00. Thus 1FFFFE, 07FFFF, and 003FF are permitted values but 02FFFF, 003FFA, and 07FFE4 are not. ounter eadback Operation The internal value of the counter register can be read out on the address lines. The address will be valid t A after the selected number of latency cycles configured by FTSE. The data bus (DQ) is tri-stated on the cycle that the address is presented on the address lines. Figure 3 shows a block diagram of this logic. Mask eadback Operation The internal value of the mask register can be read out on the address lines. The address will be valid t A after the selected number of latency cycles configured by FTSE. The data bus (DQ) is tri-stated on the cycle that the address is presented on the address lines. Figure 3 shows a block diagram of the operation. ounter eset Operation All unmasked bits of the counter and mirror registers are reset to 0. All masked bits remain unchanged. A mask reset followed by a counter reset will reset the counter and mirror registers to Mask eset Operation The mask register is reset to all 1s, which unmasks every bit of the burst counter. Document #: ev. *F Page 12 of 52
13 Table 8. Burst ounter and Mask egister ontrol Operation (Any Port) [17, 18] MST NTST NT/MSK NTEN ADS ET Operation Description X X X X X X Master eset eset address counter to all 0s, mask register to all 1s, and busy address to all 0 s. H H X X X ounter eset eset counter and mirror unmasked portion to all 0s. H X X X Mask eset eset mask register to all 1s. H H H X ounter oad oad burst counter and mirror with external address value presented on address lines. H H X Mask oad oad mask register with value presented on the address lines. H H H H etransmit oad counter with value in the mirror register H H H H H ounter Internally increment address counter value. Increment H H H H H H ounter Hold onstantly hold the address value for multiple clock cycles. H H H H H ounter eadback H H H H Mask eadback H H H H Busy Address eadback H H H X eserved H H H eserved H H H H H eserved H H H H eserved H H H H H eserved ead out counter internal value on address lines. ead out mask register value on address lines. ead out first busy address after last busy address readback Notes: 17. X = Don t are, H = HIGH, = OW. 18. ounter operation and mask register operation is independent of chip enables. Document #: ev. *F Page 13 of 52
14 Increment Operation [1] Once the address counter is initially loaded with an external address, the counter can internally increment the address value and address the entire memory array. Only the unmasked bits of the counter register are incremented. In order for a counter bit to change, the corresponding bit in the mask register must be 1. If the two least significant bits of the mask register are 11, the burst counter will increment by one. If the two least significant bits are 10, the burst counter will increment by two, and if they are 00, the burst counter will increment by four. If all unmasked counter bits are incremented to 1 and WP is deasserted, the next increment will wrap the counter back to the initially loaded value. The cycle before the increment that results in all unmasked counter bits to become 1s, a counter interrupt flag (NTINT) is asserted if the counter is incremented again. This increment will cause the counter to reach its maximum value and the next increment will return the counter register to its initial value that was stored in the mirror register if WP is deasserted. If WP is asserted, the unmasked portion of the counter is filled with 0 instead. The example shown in Figure 4 shows an example of the YDD36S18V18 device with the mask register loaded with a mask value of 00007F unmasking the seven least significant bits. Setting the mask register to this value allows the counter to access the entire memory space. The address counter is then loaded with an initial value of assuming WP is deasserted. The masked bits, the seventh address through the twenty-first address, do not increment in an increment operation. The counter address will start at address and will increment its internal address value until it reaches the mask register value of 00007F. The counter wraps around the memory block to location at the next count. NTINT is issued when the counter reaches the maximum 1 count. Hold Operation The value of all three registers can be constantly maintained unchanged for an unlimited number of clock cycles. Such operation is useful in applications where wait states are needed, or when address is available a few cycles ahead of data in a shared bus interface. etransmit etransmit allows repeated access to the same block of memory without the need to reload the initial address. An internal mirror register stores the address counter value last loaded. While ET is asserted low, the counter will continue to wrap back to the value in the mirror register independent of the state of WP. ounter Interrupt The counter interrupt (NTINT) is asserted OW one clock cycle before an increment operation that results in the unmasked portion of the counter register being all 1s. It is deasserted by counter reset, counter load, mask reset, mask load, and MST. ounting by Two When the two least significant bits of the mask register are 10, the counter increments by two. ounting by Four When the two least significant bits of the mask register are 00, the counter increments by four. Mailbox Interrupts The upper two memory locations can be used for message passing and permit communications between ports. Table 9 shows the interrupt operation for both ports. The highest memory location is the mailbox for the right port and the maximum address 1 is the mailbox for the left port. When one port Writes to the other port s mailbox, the INT flag of the port that the mailbox belongs to is asserted OW. The INT flag remains asserted until the mailbox location is read by the other port. When a port reads its mailbox, the INT flag is deasserted high after one cycle of latency with respect to the input clock of the port to which the mailbox belongs and is independent of OE. Table 9 shows that in order to set the INT flag, a Write operation by the left port to address 1FFFFF will assert INT OW. A valid ead of the 1FFFFF location by the right port will reset INT HIGH after one cycle of latency with respect to the right port s clock. At least one byte enable has to be activated to set or reset the mailbox interrupt. Document #: ev. *F Page 14 of 52
15 NT/MSK NTEN A NTST Decode ogic ET MST A Mask egister ounter/ Address egister Address Decode AM Array From Address ines From Mask egister Mirror Increment ogic Wrap oad/increment ounter 20 To eadback and Address Decode From Mask From ounter Bit 0 +1 and 1 1 Wrap Detect Wrap To ounter Figure 3. ounter, Mask, and Mirror ogic Block Diagram [1] Document #: ev. *F Page 15 of 52
16 NTINT Example: oad ounter-mask H egister = 00007F oad Address ounter = Max Address Value Max + 1 Address Value Master eset The family of Dual-Ports undergo a complete reset when MST is asserted. The MST can be asserted asynchronously to the clocks and must remain asserted for at least t S. Once asserted MST deasserts EADY, initializes the internal burst counters, internal mirror registers, and internal Busy Addresses to zero, and initializes the internal mask register to all 1s. All mailbox interrupts (INT), Busy Address Outputs (BUSY), and burst counter interrupts (NTINT) are deasserted upon master reset. eleasing MST also signifies that the power supplies and all port clocks are stable. This begins calibration of the D and VIM circuits. EADY will be asserted within 1024 clock cycles. EADY is a wired O capable output with a strong pull-up and weak H H 0 0 0s Masked Address Unmasked Address X X Xs X X X Xs X X X Xs X Figure 4. Programmable ounter-mask egister Operation with WP [1, 22] deasserted Mask egister SB Address ounter SB Table 9. Interrupt Operation Example [1, 17, 19, 20, 21] eft Port ight Port Function /W E A 0 20 INT /W E A 0 20 INT Set ight INT Flag Max. Address X X X X eset ight INT Flag X X X X H Max. Address H Set eft INT Flag X X X Max. Address 1 X eset eft INT Flag H Max. Address 1 H X X X X pull-down. Up to four outputs may be connected together. For faster pull-down of the signal, connect a 250 Ohm resistor to VSS. If the D and VIM circuits are disabled for a port, the port will be operational within five clock cycles. However, the EADY will be asserted within 160 clock cycles. IEEE Serial Boundary Scan (JTAG) The families incorporate an IEEE serial boundary scan test access port (TAP). The TAP operates using JEDE-standard 3.3V or 2.5V I/O logic levels depending on the VTT power supply. It is composed of four input connections and one output connection required by the test logic defined by the standard. Notes: 19. E is internal signal. E = OW if E 0 = OW and E 1 = HIGH. For a single ead operation, E only needs to be asserted once at the rising edge of the and can be deasserted after that. Data will be out after the following edge and will be tri-stated after the next edge. 20. OE is Don t are for mailbox operation. 21. At least one of BE0, BE1, BE2, BE3, BE4, BE5, BE6, or BE7 must be OW. 22. The X in this diagram represents the counter s upper bits. Document #: ev. *F Page 16 of 52
17 Table 10.JTAG IDODE egister Definitions Part Number onfiguration Value YD36S72V18 512Kx h (x2) YD36S36V Kx h YD36S18V Kx h YD18S72V18 256Kx h YD18S36V18 512Kx h YD18S18V Kx h YD09S72V18 128Kx h YD09S36V18 256Kx h YD09S18V18 512Kx18 002A069h YD04S72V18 64Kx72 002B069h YD04S36V18 128Kx h YD04S18V18 256Kx18 002D069h Table 11.Scan egisters Sizes egister Name Bit Size Instruction 4 Bypass 1 Identification 32 Boundary Scan n [23] Table 12.Instruction Identification odes Instruction ode Description EXTEST 0000 aptures the Input/Output ring contents. Places the BS between the TDI and TDO. BYPASS 1111 Places the BY between TDI and TDO. IDODE 1011 oads the ID with the vendor ID code and places the register between TDI and TDO. HIGHZ 0111 Places BY between TDI and TDO. Forces all 72 and 36 output drivers to a High-Z state. AMP 0100 ontrols boundary to 1/0. Places BY between TDI and TDO. SAMPE/PEOAD 1000 aptures the input/output ring contents. Places BS between TDI and TDO. ESEVED All other codes Other combinations are reserved. Do not use other than the above. Note: 23. Details of the boundary scan length can be found in the BSD file for the device. Document #: ev. *F Page 17 of 52
18 Maximum atings (Above which the useful life may be impaired. For user guidelines, not tested.) Storage Temperature to Ambient Temperature with Power Applied to Supply Voltage to Ground Potential V to + 4.1V D Voltage Applied to Outputs in High-Z State V to V DDIO + 0.5V D Input Voltage V to V DDIO + 0.5V Output urrent into Outputs (OW) ma Static Discharge Voltage...> 2200V (JEDE JESD8-6, JESD8-B) atch-up urrent...> 200 ma Operating ange ange Ambient Temperature VOE ommercial 0 to V ± 100 mv 1.5V ± 80 mv Industrial 40 to V ± 100 mv 1.5V ± 80 mv Power Supply equirements Min. Typ. Max. VTT O 3.0V 3.3V 3.6V 2.5V VMOS O 2.3V 2.5V 2.7V HST O 1.4V 1.5V 1.9V 1.8V VMOS O 1.7V 1.8V 1.9V 3.3V VTT 3.0V 3.3V 3.6V 2.5V VTT 2.3V 2.5V 2.7V HST VEF 0.68V 0.75V 0.95V Electrical haracteristics Over the Operating ange All Speed Bins [24] Parameter Description onfiguration Min. Typ. Max. V OH Output HIGH Voltage VTT 2.4 [25] V (V DDIO = Min., I OH = 8 ma) (V DDIO = Min., I OH = 4 ma) HST (D) [26] O 0.4 [25] V (V DDIO = Min., I OH = 4 ma) HST (A) [26] O 0.5 [25] V (V DDIO = Min., I OH = 6 ma) 2.5V VMOS 1.7 [25] V (V DDIO = Min., I OH = 4 ma) 1.8V VMOS O 0.45 [25] V V O Output HIGH Voltage VTT 0.4 [25] V (V DDIO = Min., I O = 8 ma) (V DDIO = Min., I O = 4 ma) HST(D) [26] 0.4 [25] V (V DDIO = Min., I O = 4 ma) HST (A) [26] 0.5 [25] V (V DDIO = Min., I O = 6 ma) 2.5V VMOS 0.7 [25] V (V DDIO = Min., I O = 4 ma) 1.8V VMOS 0.45 [25] V V IH Input HIGH Voltage VTT 2 O V HST(D) [26] VEF O V 2.5V VMOS 1.7 V 1.8V VMOS 1.26 V V I Input OW Voltage VTT V HST(D) [26] 0.3 VEF 0.1 V 2.5V VMOS 0.7 V 1.8V VMOS 0.36 V Unit Notes: 24. VTT and 2.5V VMOS are not available for 4-Mbit, 9-Mbit, 18-Mbit devices running at 250 MHz and 36-Mbit devices running at 200 MHz. 25. These parameters are met with VIM disabled. 26. The (D) specifications are measured under steady state conditions. The (A) specifications are measured while switching at speed. Document #: ev. *F Page 18 of 52
19 Electrical haracteristics Over the Operating ange (continued) All Speed Bins [24] Unit Parameter Description onfiguration Min. Typ. Max. EADY Output HIGH Voltage VTT 2.7 [25] V V OH (V DDIO = Min., I OH = 24 ma) (V DDIO = Min., I OH = 12 ma) HST(D) [26] O 0.4 [25] V (V DDIO = Min., I OH = 12 ma) HST (A) [26] O 0.5 [25] V (V DDIO = Min., I OH = 15 ma) 2.5V VMOS 2.0 [25] V (V DDIO = Min., I OH = 12 ma) 1.8V VMOS O 0.45 [25] V EADY Output HIGH Voltage VTT 0.4 [25] V V O (V DDIO = Min., I O = 0.12 ma) (V DDIO = Min., I O = 0.12 ma) HST(D) [26] 0.4 [25] V (V DDIO = Min., I O = 0.12 ma) HST (A) [26] 0.5 [25] V (V DDIO = Min., I O = 0.15 ma) 2.5V VMOS 0.7 [25] V (V DDIO = Min., I O = 0.08 ma) 1.8V VMOS 0.45 [25] V I OZ Output eakage urrent µa I IX1 Input eakage urrent Except µa TDI, TMS, MST I IX2 Input eakage urrent TDI, µa TMS, MST I IX3 Input eakage urrent POTSTD, DDON µa Document #: ev. *F Page 19 of 52
20 Electrical haracteristics Over the Operating ange 250 [24] 200 [24] Parameter Description onfiguration Typ. Max. Typ. Max. Typ. Max. Typ. Max. Unit I Operating urrent 512Kx72 om. N/A N/A ma (V OE = Max.,I OUT = 0 ma) Outputs Disabled Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 1024Kx36 om. N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 2048Kx18 om. N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 256Kx72 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 512Kx36 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 1024Kx18 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 128Kx72 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 256Kx36 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 512Kx18 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 64Kx72 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 128Kx36 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 256Kx18 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma Document #: ev. *F Page 20 of 52
21 Electrical haracteristics Over the Operating ange (continued) Parameter Description onfiguration I SB1 Standby urrent (Both Ports TT evel) E and E V IH, f = f MAX 250 [24] 200 [24] Typ. Max. Typ. Max. Typ. Max. Typ. Max. Unit 512Kx72 om. N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 1024Kx36 om. N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 2048Kx18 om. N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 256Kx72 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 512Kx36 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 1024Kx18 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 128Kx72 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 256Kx36 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 512Kx18 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 64Kx72 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 128Kx36 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 256Kx18 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma Document #: ev. *F Page 21 of 52
22 Electrical haracteristics Over the Operating ange (continued) Parameter Description onfiguration I SB2 Standby urrent (One Port TT or MOS evel) E E V IH, f = f MAX 250 [24] 200 [24] Typ. Max. Typ. Max. Typ. Max. Typ. Max. Unit 512Kx72 om. N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 1024Kx36 om. N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 2048Kx18 om. N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 256Kx72 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 512Kx36 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 1024Kx18 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 128Kx72 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 256Kx36 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 512Kx18 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 64Kx72 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 128Kx36 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma 256Kx18 om N/A N/A ma Ind. N/A N/A N/A N/A ma Document #: ev. *F Page 22 of 52
23 Electrical haracteristics Over the Operating ange All Speed Bins [24] Parameter Description onfiguration Typ. Max. Unit I SB3 Standby urrent 512Kx72 om ma (Both Ports MOS evel) Ind ma E and E V OE 0.2V, f = Kx36 om ma Ind ma 2048Kx18 om ma Ind ma 256Kx72 om ma Ind ma 512Kx36 om ma Ind ma 1024Kx18 om ma Ind ma 128Kx72 om ma Ind ma 256Kx36 om ma Ind ma 512Kx18 om ma Ind ma 64Kx72 om ma Ind ma 128Kx36 om ma Ind ma 256Kx18 om ma Ind ma Table 13.apacitance Signals YDD18S72V18 YDD09S72V18 YDD04S72V18 YDD18S36V18 YDD09S36V18 YDD04S36V18 YDD18S18V18 YDD09S18V18 YDD04S18V18 Packages YDD36S72V18 YDD36S36V18 YDD36S18V18 OE 12 pf 12 pf 20 pf 20 pf BE, DQ 10 pf 18 pf 16 pf 30 pf All other signals 10 pf 10 pf 16 pf 16 pf Document #: ev. *F Page 23 of 52
24 A Test oad and Waveforms VTH = 1.5V for VTT VTH = 50% O for 2.5V M OS VTH = 50% O for 1.8V M OS V EF = N V EF 50 Ohm 50 Ohm Output =250 Ohm Test Point VTH EADY ZQ Device under te s t Q=250 Ohm = 10pF =250 O hm Figure 5. Output Test oad for VTT/MOS V T H = 5 0 % V D D IO V E F = 0.75V V E F 50 O hm 50 O hm O u tp u t Test Point E A D Y ZQ V T H D evice under te s t Q = O h m = 10pF for SD Figure 6. Output Test oad for HST Figure 7. HST Input Waveform Document #: ev. *F Page 24 of 52
25 Switching haracteristics Over the Operating ange Table 14.SD Mode with D Enabled (OWSPD-HIGH) [29] Parameter Description f MAX Maximum Operating (PIPEINED) Frequency for Pipelined Mode f MAX (FOW- THOUGH) Maximum Operating Frequency for Flow-through Mode t Y lock ycle Time for (PIPEINED) Pipelined Mode t Y (FOW- THOUGH) lock ycle Time for Flow-through Mode 250 [24] 200 [24] Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max MH z Unit MH z 4.00 [30] [30] [30] [30] ns [30] [30] [30] [30] ns t KD lock Duty Time % t SD Data Input HST 1.20 [28,30] 1.50 [28,30] 1.70 [28,30] 1.80 [28, ns Set-up Time 1.8V VMOS 30] to ise t HD t SA 2.5V VMOS 3.3V VTT Data Input Hold Time after ise Address & ontrol Input Setup Time to ise HST 1.8V VMOS 2.5V VMOS 3.3V VTT t HA Address & ontrol Input Hold Time after ise t OE Output Enable to Data Valid 3.40 [28, 30] [27] t OZ t [27] OHZ OE to High Z [28, 30] t D1 t D2 [31] t A1 t A [28,30] 1.75 [28,30] 1.95 [28,30] 2.05 [28, 30] ns 1.20 [28,30] 1.50 [28,30] 1.70 [28,30] 1.80 [28,30] 1.45 [28,30] 1.75 [28,30] 1.95 [28,30] 2.05 [28, 30] ns 4.40 [28, 30] 5.00 [28, 30] 5.50 [28, 30] OE to ow Z ns [28, [28, [28, ns 30] 30] 30] ise to DQ Valid for Flow-through Mode (owspd = 1) ise to DQ Valid for Pipelined Mode (owspd = 1) ise to Address eadback Valid for Flow-through Mode ise to Address eadback Valid for Pipelined Mode 7.20 [28, 30] 2.64 [28, 30] 9.00 [28, 30] 3.30 [28, 30] [28,30] 4.00 [28, 30] 7.20 [30] 9.00 [30] [30] [28,30] 4.50 [28, 30] [30] 4.00 [30] 5.00 [30] 6.00 [30] 7.50 [30] ns t [31] D DQ Output Hold after ise ns [31] t Q ise to Q ise [30] [30] [30] [30] ns t JIT lock Input ycle to ycle Jitter +/ / / /- 200 ps Notes: 27. Parameters specified with the load capacitance in Figure 5 and Figure For the x18 devices, add 200 ps to this parameter in the table above. 29. Test conditions assume a signal transition time of 2 V/ns. 30. Add 15% to this parameter if a VOE of 1.5V is used. 31. This parameter assumes input clock cycle to cycle jitter of +/- 0ps. ns ns ns ns ns ns ns Document #: ev. *F Page 25 of 52
26 Table 14.SD Mode with D Enabled (OWSPD-HIGH) [29] (continued) Parameter [31] t QHQV t QHQX [31] t KHZ1 [27] t KZ1 [27] t [27, KHZ2 31] t [27, KZ2 31] t A t KHZA1 [27] Echo lock (Q) High to Output Valid Echo lock (Q) High to Output Hold Description HST 1.8V VMOS 2.5V VMOS 3.3V VTT HST 1.8V VMOS 2.5V VMOS 3.3V VTT ise to DQ Output High Z in Flow-through Mode ise to DQ Output ow Z in Flow-through Mode ise to DQ Output High Z in Pipelined Mode ise to DQ Output ow Z in Pipelined Mode Address Output Hold after ise ise to Address Output High Z for Flow-through Mode 250 [24] 200 [24] Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max [28] 0.70 [28] 0.80 [28] 0.90 [28] ns 0.70 [28] 0.80 [28] 0.90 [28] 1.00 [28] ns ns ns [28, 30] [28, 30] [28,30] [28,30] ns [28, 30] [28, 30] [28, 30] [28, 30] ns ns [30] [30] [30] [30] t [27] KHZA2 ise to Address Output [30] [30] [30] [30] ns High Z for Pipelined Mode [27] t KZA ise to Address Output ns ow Z t SINT ise to NTINT ow [30] [30] [30] [30] ns t INT ise to NTINT High [30] [30] [30] [30] ns t SINT ise to INT ow [30] [30] [30] [30] ns t INT ise to INT High [30] [30] [30] [30] ns t BSY ise to BUSY Valid [30] [30] [30] [30] ns Table 15.SD Mode with D Disabled (OWSPD-OW) [29] All Speed Bins Parameter Description Min. Max. Unit f MAX (PIPEINED) Maximum Operating Frequency for Pipelined Mode 100 MHz f MAX (FOW-THOUGH) Maximum Operating Frequency for Flow-through Mode 55.6 MHz t Y (PIPEINED) lock ycle Time for Pipelined Mode [30] ns t Y (FOW-THOUGH) lock ycle Time for Flow-through Mode [30] ns t KD lock Duty Time % t SD Data Input Set-up Time to ise HST/1.8V VMOS 1.80 [28,30] ns 2.5V VMOS/3.3V VTT 2.05 [28,30] ns t HD Data Input Hold Time after ise 0.50 ns t SA Address & ontrol Input Setup HST/1.8V VMOS 1.80 [28,30] ns Time to ise 2.5V VMOS/3.3V VTT 2.05 [28,30] ns t HA Address & ontrol Input Hold Time after ise 0.70 ns t OE Output Enable to Data Valid 5.50 [28,30] ns t [27] OZ OE to ow Z 1.00 ns Unit ns ns ns Document #: ev. *F Page 26 of 52
27 Table 15.SD Mode with D Disabled (OWSPD-OW) [29] All Speed Bins Parameter Description Min. Max. Unit [27] t OHZ OE to High Z [28,30] ns t D1 ise to DQ Valid for Flow-through Mode (owspd = 0) [28, 30] ns t [31] D2 ise to DQ Valid for Pipelined Mode (owspd = 0) 6.00 [28,30] ns t A1 ise to Address eadback Valid for Flow-through Mode [30] ns t A2 ise to Address eadback Valid for Pipelined Mode 7.50 [30] ns t [31] D DQ Output Hold after ise 1.00 ns t [31] Q ise to Q ise [30] ns t [31] QHQV Echo lock (Q) High to Output HST/1.8V VMOS 0.90 [28] ns Valid 2.5V VMOS/3.3V VTT 1.00 [28] ns t [31] QHQX Echo lock (Q) High to Output HST/1.8V VMOS 0.90 ns Hold 2.5V VMOS/3.3V VTT 1.05 ns t [27] KHZ1 ise to DQ Output High Z in Flow-through Mode [28, 30] ns [27] t KZ1 ise to DQ Output ow Z in Flow-through Mode 1.00 ns t [27,31] KHZ2 ise to DQ Output High Z in Pipelined Mode [28,30] ns t [27,31] KZ2 ise to DQ Output ow Z in Pipelined Mode 1.00 ns t A Address Output Hold after ise 1.00 ns t [27] KHZA1 ise to Address Output High Z for Flow-through mode [30] ns t [27] KHZA2 ise to Address Output High Z for Pipelined Mode [30] ns t [27] KZA ise to Address Output ow Z 1.00 ns t SINT ise to NTINT ow [30] ns t INT ise to NTINT High [30] ns t SINT ise to INT ow [30] ns t INT ise to INT High [30] ns t BSY ise to BUSY Valid [30] ns Table 16.Master eset Timing 250 [24] 200 [24] Parameter Description Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Unit t PUP Power-Up Time ms t S Master eset Pulse Width cycles t S Master eset ecovery Time cycles t SF Master eset to Outputs Inactive/Hi Z ns [32] t DY Master eset elease to Port eady cycles t [33] ODY ise to Port eady 8 [30] 9.5 [30] 11 [30] 13 [30] ns Table 17.JTAG Timing 250 [24] 200 [24] Parameter Description Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Unit f JTAG JTAG TAP ontroller Frequency MHz Notes: 32. EADY is a wired O capable output with a weak pull-down. For a decreased falling delay, connect a 250-Ω resistor to VSS. 33. Add this propagation delay after t DY for all Master eset Operations. Document #: ev. *F Page 27 of 52
28 Table 17.JTAG Timing 250 [24] 200 [24] Parameter Description Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max. Unit t TY TK ycle Time ns t TH TK High Time ns t T TK ow Time ns t TMSS TMS Set-up to TK ise ns t TMSH TMS Hold to TK ise ns t TDIS TDI Set-up to TK ise ns t TDIH TDI Hold to TK ise ns t TDOV TK ow to TDO Valid ns t TDOX TK ow to TDO Invalid ns t JXZ TK ow to TDO High Z ns t JZX TK ow to TDO Active ns t JZX TK ow to TDO Active ns Switching Waveforms JTAG Timing t TH t T Test lock TK Test Mode Select TMS t TMSS t TMSH t TY t TDIS t TDIH Test Data-In TDI Test Data-Out TDO t TDOX t TDOV Document #: ev. *F Page 28 of 52
29 Switching Waveforms (continued) Master eset [32] V OE ~ t PUP t S MST ~ ~ t DY t ODY EADY t SF ~ All Address & Data ~ t S All Other Inputs ~ EAD ycle for Pipelined Mode t Y E OE t SA t HA /W A A n A n+1 A n+2 A n+3 A n+4 A n+5 A n+6 2 Pipelined stages DQ DQ x-1 DQ x DQ n DQ n+1 DQ n+2 DQ n+3 DQ n+4 t D td2 Document #: ev. *F Page 29 of 52
30 Switching Waveforms (continued) WITE ycle for Pipelined and Flow-through Modes t Y E /W A A n A n+1 A n+2 A n+3 A n+4 A n+5 A n+6 2 Pipelined stages DQ DQ n DQ n+1 DQ n+2 DQ n+3 DQ n+4 DQ n+5 DQ n+6 t SD t HD EAD with Address ounter Advance for Pipelined Mode t Y A A n Internal Address A n A n+1 A n+2 A n+3 ADS NTEN DQ DQ x-1 DQ x DQ n DQ n+1 DQn+2 DQ n+3 Document #: ev. *F Page 30 of 52
31 Switching Waveforms (continued) EAD with Address ounter Advance for Flow-through Mode ty tsa tha A An ADS tsa tha NTEN td1 DQ DQx DQn DQn + 1 DQn + 2 DQn + 3 DQn + 4 td EAD EXTENA ADDESS EAD WITH OUNTE OUNTE HOD EAD WITH OUNTE Document #: ev. *F Page 31 of 52
32 Switching Waveforms (continued) Port-to-Port WITE EAD for Pipelined Mode eft Port t Y A A n /W DQ DQ n ight Port t Y t S A A n /W t SA t HA DQ DQ n hip Enable EAD for Pipelined Mode t Y t D2 t D E0 E1 /W t SA t HA A A n A n+1 A n+2 A n+3 A n+4 A n+5 A n+6 DQ DQ n DQ n+3 t D2 t D tkz2 Document #: ev. *F Page 32 of 52
33 Switching Waveforms (continued) OE ontrolled WITE for Pipelined Mode t Y A A x+1 A x+2 A x+3 A n A n+1 A n+2 A n+3 /W OE t OHZ DQ DQ x-1 DQ x DQ x+1 DQ n DQ n+1 DQ n+2 DQ n+3 OE ontrolled WITE for Flow-through Mode t Y A A x+1 A x+2 A x+3 A n A n+1 A n+2 A n+3 /W OE t OHZ DQ DQ x DQ x+1 DQ x+2 DQ n DQ n+1 DQ n+2 DQ n+3 Document #: ev. *F Page 33 of 52
34 Switching Waveforms (continued) Byte-Enable EAD for Pipelined Mode t Y A A n A n+1 A n+2 A n+3 /W BE7 BE6 BE5 BE4 BE3 BE2 BE1 BE0 DQ 63:71 DQ 54:62 t KZ2 t DQ KHZ2 n+1(63:71) DQ n+1(54:62) DQ 45:53 DQ n+2(45:53) DQ 36:44 DQ n+2(36:44) DQ 27:35 DQ 18:26 DQ n+1(27:35) DQ n+2(18:26) DQ 9:17 DQ 0:8 DQ n+3(9:17) DQ n+3(0:8) Document #: ev. *F Page 34 of 52
35 Switching Waveforms (continued) Port-to-Port WITE-to-EAD for Flow-through Mode /W tsa tha A MATH NO MATH tsd thd DQ VAID ts td1 /W tsa tha A MATH NO MATH td1 DQ VAID VAID td td Busy Address eadback for Pipelined and Flow-through Modes, DDON = NT/MSK = ET = OW [34] t Y ~ Internal Address BUSY ~ A match+2 A match+3 A match+4 ~ NTEN ~ ADS ~ External Address Pipelined External Address Flow-through ~ ~ Note: 34. A match is the matching address which will be reported on the address bus of the losing port. The counter operation selected for reporting the address is Busy Address eadback. t A1 A match t A2 t A A match t A Document #: ev. *F Page 35 of 52
36 Switching Waveforms (continued) ead ycle for Flow-through Mode ty E0 tsa tha E1 BEn /W A tsa An tha An + 1 An + 2 An + 3 td1 td tkhz1 DQ DQn DQn + 1 DQn + 2 tkz1 tohz toz td OE EAD-to-WITE for Pipelined Mode (OE = V I ) [35,36,37] toe t H t Y t A A x A n A n+1 A n+2 t SA t HA t SA t HA /W t KZ2 DQ DQ x-2 DQ x-1 DQ x DQn DQ n+1 DQ n+2 t D2 t D t KHZ2 tsd t HD Notes: 35. When OE = V I, the last read operation is allowed to complete before the DQ bus is tri-stated and the user is allowed to drive write data. 36. Two dummy writes should be issued to accomplish bus turnaround. The 3rd instruction is the first valid write. 37. hip enable or all byte enables should be held inactive during the two dummy writes to avoid data corruption. Document #: ev. *F Page 36 of 52
37 Switching Waveforms (continued) EAD-to-WITE for Pipelined Mode (OE ontrolled) [38,39] t Y A A x A x+1 A x+2 A n A n+1 A n+2 A n+3 t SA t HA /W OE t OHZ t SD t HD DQ DQ x-2 DQ x-1 DQ x DQ n DQ n+1 DQ n+2 DQ n+3 Notes: 38. OE should be deasserted and t OHZ allowed to elapse before the first write operation is issued. 39. Any write scheduled to complete after OE is deasserted will be preempted. Document #: ev. *F Page 37 of 52
38 Switching Waveforms (continued) ead-to-write-to-ead for Flow-through Mode (OE = OW) ty tsa tha E0 E1 BEn tsa tha /W A An An + 1 An + 2 An + 2 An + 3 An + 4 tsd thd DQIN DQn + 2 td1 td1 td1 td1 DQOUT DQn DQn + 1 DQn + 3 tkhz1 tkz1 td td EAD NOP WITE EAD Document #: ev. *F Page 38 of 52
39 Switching Waveforms (continued) ead-to-write-to-ead for Flow-through Mode (OE ontrolled) ty tsa tha E0 E1 BEn tsa tha /W A An An + 1 An + 2 An + 3 An + 4 An + 5 tsd thd DQIN td1 td DQn + 2 DQn + 3 toe td1 td1 DQOUT DQn DQn + 4 tohz tkz1 td OE EAD WITE EAD Document #: ev. *F Page 39 of 52
40 Switching Waveforms (continued) BUSY Timing, WITE-WITE ollision for Pipelined and Flow-through Modes, lock Timing Violates t S. (Flag Both Ports) Port A A /W BUSY < t S t BSY t BSY Port B A /W BUSY t BSY t BSY BUSY Timing, WITE-WITE ollision for Pipelined and Flow-through Modes, lock Timing Meets t S. (Flag osing Port) osing Port A /W BUSY t ccs t BSY t BSY Winning Port A Match /W BUSY Document #: ev. *F Page 40 of 52
41 Switching Waveforms (continued) ead with Echo lock for Pipelined and Flow-through Modes (QEN = HIGH) t SA t HA /W A A n A n+1 A n+2 A n+3 A n+4 A n+5 A n+6 Q0 Q0 t Q Q1 Q1 t QHQV t QHQX DQ DQ x-1 DQ x DQ n DQ n+1 DQ n+2 DQ n+3 DQ n+4 Document #: ev. *F Page 41 of 52
42 Switching Waveforms (continued) Mailbox Interrupt Output t Y A A MAX /W DQ INT t SINT tint A A MAX /W DQ DQ MAX Document #: ev. *F Page 42 of 52
43 Ordering Information 512K 72 (36 Mbit) 1.8V/1.5V Synchronous YD36S72V18 Dual-Port SAM Speed (MHz) Ordering ode Package Name Package Type Operating ange 200 YD36S72V18-200BGX BY484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD36S72V18-200BG BG484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial 167 YD36S72V18-167BGX BY484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD36S72V18-167BG BG484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial YD36S72V18-167BGXI BY484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) Industrial YD36S72V18-167BGI BG484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) Industrial 133 YD36S72V18-133BGX BY484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD36S72V18-133BG BG484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial YD36S72V18-133BGXI BY484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) Industrial YD36S72V18-133BGI BG484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) Industrial 256K 72 (18 Mbit) 1.8V/1.5V Synchronous YD18S72V18 Dual-Port SAM Speed (MHz) Ordering ode Package Name Package Type Operating ange 250 YD18S72V18-250BGX BY ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD18S72V18-250BG BG ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial 200 YD18S72V18-200BGX BY ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD18S72V18-200BG BG ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial YD18S72V18-200BGXI BY ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) Industrial YD18S72V18-200BGI BG ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) Industrial 167 YD18S72V18-167BGX BY ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD18S72V18-167BG BG ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial YD18S72V18-167BGXI BY ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) Industrial YD18S72V18-167BGI BG ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) Industrial 128K 72 (9 Mbit) 1.8V/1.5V Synchronous YD09S72V18 Dual-Port SAM Speed (MHz) Ordering ode Package Name Package Type Operating ange 250 YD09S72V18-250BGX BY ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD09S72V18-250BG BG ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial 200 YD09S72V18-200BGX BY ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD09S72V18-200BG BG ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial YD09S72V18-200BGXI BY ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) Industrial YD09S72V18-200BGI BG ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) Industrial 167 YD09S72V18-167BGX BY ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD09S72V18-167BG BG ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial YD09S72V18-167BGXI BY ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) Industrial YD09S72V18-167BGI BG ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) Industrial Document #: ev. *F Page 43 of 52
44 Ordering Information (continued) 64K 72 (4 Mbit) 1.8V/1.5V Synchronous YD04S72V18 Dual-Port SAM Speed (MHz) Ordering ode Package Name Package Type Operating ange 250 YD04S72V18-250BGX BY ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD04S72V18-250BG BG ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial 200 YD04S72V18-200BGX BY ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD04S72V18-200BG BG ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial YD04S72V18-200BGXI BY ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) Industrial YD04S72V18-200BGI BG ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) Industrial 167 YD04S72V18-167BGX BY ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD04S72V18-167BG BG ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial YD04S72V18-167BGXI BY ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) Industrial YD04S72V18-167BGI BG ball Grid Array 23 mm x 23 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) Industrial 1024K 36 (36 Mbit) 1.8V/1.5V Synchronous YD36S36V18 Dual-Port SAM Speed (MHz) Ordering ode Package Name Package Type Operating ange 200 YD36S36V18-200BGX BY484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD36S36V18-200BG BG484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial 167 YD36S36V18-167BGX BY484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD36S36V18-167BG BG484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial YD36S36V18-167BGXI BY484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) Industrial YD36S36V18-167BGI BG484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) Industrial 133 YD36S36V18-133BGX BY484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD36S36V18-133BG BG484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial YD36S36V18-133BGXI BY484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) Industrial YD36S36V18-133BGI BG484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) Industrial 512K 36 (18 Mbit) 1.8V/1.5V Synchronous YD18S36V18 Dual-Port SAM Speed (MHz) Ordering ode Package Name Package Type Operating ange 250 YD18S36V18-250BBX BW ball Grid Array 19 mm x 19 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD18S36V18-250BB BB ball Grid Array 19 mm x 19 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial 200 YD18S36V18-200BBX BW ball Grid Array 19 mm x 19 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD18S36V18-200BB BB ball Grid Array 19 mm x 19 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial YD18S36V18-200BBXI BW ball Grid Array 19 mm x 19 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) Industrial YD18S36V18-200BBI BB ball Grid Array 19 mm x 19 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) Industrial 167 YD18S36V18-167BBX BW ball Grid Array 19 mm x 19 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD18S36V18-167BB BB ball Grid Array 19 mm x 19 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial YD18S36V18-167BBXI BW ball Grid Array 19 mm x 19 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) Industrial YD18S36V18-167BBI BB ball Grid Array 19 mm x 19 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) Industrial Document #: ev. *F Page 44 of 52
45 Ordering Information (continued) 256K 36 (9 Mbit) 1.8V/1.5V Synchronous YD09S36V18 Dual-Port SAM Speed (MHz) Ordering ode Package Name Package Type Operating ange 250 YD09S36V18-250BBX BW ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD09S36V18-250BB BB ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial 200 YD09S36V18-200BBX BW ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD09S36V18-200BB BB ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial YD09S36V18-200BBXI BW ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) Industrial YD09S36V18-200BBI BB ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) Industrial 167 YD09S36V18-167BBX BW ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD09S36V18-167BB BB ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial YD09S36V18-167BBXI BW ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) Industrial YD09S36V18-167BBI BB ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) Industrial 128K 36 (4 Mbit) 1.8V/1.5V Synchronous YD04S36V18 Dual-Port SAM Speed (MHz) Ordering ode Package Name Package Type Operating ange 250 YD04S36V18-250BBX BW ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD04S36V18-250BB BB ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial 200 YD04S36V18-200BBX BW ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD04S36V18-200BB BB ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial YD04S36V18-200BBXI BW ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) Industrial YD04S36V18-200BBI BB ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) Industrial 167 YD04S36V18-167BBX BW ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD04S36V18-167BB BB ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial YD04S36V18-167BBXI BW ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) Industrial YD04S36V18-167BBI BB ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) Industrial 2048K 18 (36 Mbit) 1.8V/1.5V Synchronous YD36S18V18 Dual-Port SAM Speed (MHz) Ordering ode Package Name Package Type Operating ange 200 YD36S18V18-200BGX BY484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD36S18V18-200BG BG484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial 167 YD36S18V18-167BGX BY484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD36S18V18-167BG BG484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial YD36S18V18-167BGXI BY484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) Industrial YD36S18V18-167BGI BG484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) Industrial 133 YD36S18V18-133BGX BY484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD36S18V18-133BG BG484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial YD36S18V18-133BGXI BY484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) Industrial YD36S18V18-133BGI BG484S 484-ball Grid Array 27 mm x 27 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) Industrial Document #: ev. *F Page 45 of 52
46 Ordering Information (continued) 1024K 18 (18 Mbit) 1.8V/1.5V Synchronous YD18S18V18 Dual-Port SAM Speed MHz) Ordering ode Package Name Package Type Operating ange 250 YD18S18V18-250BBX BW ball Grid Array 19 mm x 19 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD18S18V18-250BB BB ball Grid Array 19 mm x 19 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial 200 YD18S18V18-200BBX BW ball Grid Array 19 mm x 19 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD18S18V18-200BB BB ball Grid Array 19 mm x 19 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial YD18S18V18-200BBXI BW ball Grid Array 19 mm x 19 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) Industrial YD18S18V18-200BBI BB ball Grid Array 19 mm x 19 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) Industrial 167 YD18S18V18-167BBX BW ball Grid Array 19 mm x 19 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD18S18V18-167BB BB ball Grid Array 19 mm x 19 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial YD18S18V18-167BBXI BW ball Grid Array 19 mm x 19 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) Industrial YD18S18V18-167BBI BB ball Grid Array 19 mm x 19 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) Industrial 512K 18 (9 Mbit) 1.8V/1.5V Synchronous YD09S18V18 Dual-Port SAM Speed (MHz) Ordering ode Package Name Package Type Operating ange 250 YD09S18V18-250BBX BW ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD09S18V18-250BB BB ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial 200 YD09S18V18-200BBX BW ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD09S18V18-200BB BB ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial YD09S18V18-200BBXI BW ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) Industrial YD09S18V18-200BBI BB ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) Industrial 167 YD09S18V18-167BBX BW ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD09S18V18-167BB BB ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial YD09S18V18-167BBXI BW ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) Industrial YD09S18V18-167BBI BB ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) Industrial 256K 18 (4 Mbit) 1.8V/1.5V Synchronous YD04S18V18 Dual-Port SAM Speed (MHz) Ordering ode Package Name Package Type Operating ange 250 YD04S18V18-250BBX BW ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD04S18V18-250BB BB ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial 200 YD04S18V18-200BBX BW ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD04S18V18-200BB BB ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial YD04S18V18-200BBXI BW ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) Industrial YD04S18V18-200BBI BB ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) Industrial 167 YD04S18V18-167BBX BW ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) ommercial YD04S18V18-167BB BB ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) ommercial YD04S18V18-167BBXI BW ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (ead-free) Industrial YD04S18V18-167BBI BB ball Grid Array 17 mm x 17 mm with 1.0 mm pitch (eaded) Industrial Document #: ev. *F Page 46 of 52
47 Package Diagrams TOP VIEW 256-ball ead-free FBGA (17 x 17 mm) BW ball eaded FBGA (17 x 17 mm) BB256 Ø0.05 M Ø0.25MAB BOTTOM VIEW PIN 1 ONE Ø0.45±0.05(256X)-PD DEVIES (37K & 39K) PIN 1 ONE Ø0.50 (256X)-A OTHE DEVIES A B D E F G 1.00 A B D E F G H J K 17.00± H J K M N P T 7.50 M N P T ± B A 17.00±0.10 A A1 SEATING PANE (4X) EFEENE JEDE MO *F A A 1.40 MAX MAX. Document #: ev. *F Page 47 of 52
48 Package Diagrams (continued) 256-ball ead-free FBGA (19 x 19 x 1.7 mm) BW ball eaded FBGA (19 x 19 x 1.7 mm) BB256 BOTTOM VIEW TOP VIEW Ø0.05 M A1 ONE Ø0.25 M A B PIN A1 ONE Ø0.50 (256 X) A A B B D D E E F F G G H J K M N P T T -A- -B (EF) (EF) / (4X) 0.70 (EF) 0.15 Package Weight grams SEATING PANE 0.56 (EF) / MAX / (EF) 1.00 (EF) H J K M N P 0.25 Jedec Outline - Design Guide *A Document #: ev. *F Page 48 of 52
49 f f Package Diagrams (continued) 484-ball ead-free PBGA (23 mm x 23 mm x 2.03 mm) BY ball eaded PBGA (23 mm x 23 mm x 2.03 mm) BG484 PIN #1 ONE Ø0.50~Ø0.70(484X) Ø1.00(3X) EF A B D E F G H J K M N P T U V W Y AA AB EF ± A B D E F G H J K M N P T U V W Y AA AB 3.20*45 (4x) -B EF. -A ± (4X) 0.97 EF TYP Package Weight grams Jedec Outline - Design Guide EF. -- SEATING PANE 0.40~ ± ** Document #: ev. *F Page 49 of 52
50 Package Diagrams (continued) 484-ball ead-free PBGA (27 mm x 27 mm x 2.33 mm) BY484S 484-ball eaded PBGA (27 mm x 27 mm x 2.33 mm) BG484S ** is a trademark of ypress Semiconductor orporation. All product and company names mentioned in this document are trademarks of their respective holders. Document #: ev. *F Page 50 of 52 ypress Semiconductor orporation, The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. ypress Semiconductor orporation assumes no responsibility for the use of any circuitry other than circuitry embodied in a ypress product. Nor does it convey or imply any license under patent or other rights. ypress products are not warranted nor intended to be used for medical, life support, life saving, critical control or safety applications, unless pursuant to an express written agreement with ypress. Furthermore, ypress does not authorize its products for use as critical components in life-support systems where a malfunction or failure may reasonably be expected to result in significant injury to the user. The inclusion of ypress products in life-support systems application implies that the manufacturer assumes all risk of such use and in doing so indemnifies ypress against all charges.
FullFlex Synchronous SDR Dual Port SRAM
 FullFlex Synchronous SDR Dual Port SRAM FullFlex Synchronous SDR Dual Port SRAM Features True dual port memory enables simultaneous access the shared array from each port Synchronous pipelined operation
FullFlex Synchronous SDR Dual Port SRAM FullFlex Synchronous SDR Dual Port SRAM Features True dual port memory enables simultaneous access the shared array from each port Synchronous pipelined operation
18-Mbit DDR-II SRAM 2-Word Burst Architecture
 Y736AV8 Y732AV8 Features 8-Mb density (2M x 8, M x 8, 52 x 36) 25-MHz clock for high bandwidth 2-Word burst for reducing address bus frequency Double Data Rate (DDR) interfaces (data transferred at 5 MHz)
Y736AV8 Y732AV8 Features 8-Mb density (2M x 8, M x 8, 52 x 36) 25-MHz clock for high bandwidth 2-Word burst for reducing address bus frequency Double Data Rate (DDR) interfaces (data transferred at 5 MHz)
18-Mbit DDR-II SRAM 2-Word Burst Architecture
 8-Mbit DDR-II SRAM 2-Word Burst Architecture Features Functional Description 8-Mbit density (2M x 8, 2M x 9, M x 8, 52 x 36) 3-MHz clock for high bandwidth 2-Word burst for reducing address bus frequency
8-Mbit DDR-II SRAM 2-Word Burst Architecture Features Functional Description 8-Mbit density (2M x 8, 2M x 9, M x 8, 52 x 36) 3-MHz clock for high bandwidth 2-Word burst for reducing address bus frequency
18-Mbit QDR -II SRAM 4-Word Burst Architecture
 Y73BV8 8-Mbit QDR -II SRAM 4-Word Burst Architecture Features Functional Description Separate Independent Read and data ports Supports concurrent transactions 3-MHz clock for high bandwidth 4-Word Burst
Y73BV8 8-Mbit QDR -II SRAM 4-Word Burst Architecture Features Functional Description Separate Independent Read and data ports Supports concurrent transactions 3-MHz clock for high bandwidth 4-Word Burst
36-Mbit QDR -II SRAM 4-Word Burst Architecture
 36-Mbit QDR -II SRAM 4-Word Burst Architecture Features Separate Independent Read and data ports Supports concurrent transactions 3-MHz clock for high bandwidth 4-Word Burst for reducing address bus frequency
36-Mbit QDR -II SRAM 4-Word Burst Architecture Features Separate Independent Read and data ports Supports concurrent transactions 3-MHz clock for high bandwidth 4-Word Burst for reducing address bus frequency
36-Mbit QDR-II SRAM 2-Word Burst Architecture
 36-Mbit QDR-II SRAM 2-Word Burst Architecture Features Functional Description Separate Independent Read and Write data ports Supports concurrent transactions 2-MHz clock for high bandwidth 2-Word Burst
36-Mbit QDR-II SRAM 2-Word Burst Architecture Features Functional Description Separate Independent Read and Write data ports Supports concurrent transactions 2-MHz clock for high bandwidth 2-Word Burst
FLEx18 3.3V 64K/128K/256K/512K x 18 Synchronous Dual-Port RAM
 FLEx18 3.3V 64K/128K/256K/512K x 18 Synchronous Dual-Port RAM Features Functional Description True dual-ported memory cells that allow simultaneous access of the same memory location Synchronous pipelined
FLEx18 3.3V 64K/128K/256K/512K x 18 Synchronous Dual-Port RAM Features Functional Description True dual-ported memory cells that allow simultaneous access of the same memory location Synchronous pipelined
72-Mbit QDR II SRAM 4-Word Burst Architecture
 72-Mbit QDR II SRAM 4-Word Burst Architecture Features Separate Independent Read and Write Data Ports Supports concurrent transactions 333 MHz Clock for High Bandwidth 4-word Burst for Reducing Address
72-Mbit QDR II SRAM 4-Word Burst Architecture Features Separate Independent Read and Write Data Ports Supports concurrent transactions 333 MHz Clock for High Bandwidth 4-word Burst for Reducing Address
18-Mbit QDR -II SRAM 2 Word Burst Architecture
 8-Mbit QDR -II SRAM 2 Word Burst Architecture Features Separate Independent read and write data ports Supports concurrent transactions 25 MHz clock for high bandwidth 2 Word Burst on all accesses Double
8-Mbit QDR -II SRAM 2 Word Burst Architecture Features Separate Independent read and write data ports Supports concurrent transactions 25 MHz clock for high bandwidth 2 Word Burst on all accesses Double
CY7C0851V/CY7C0851AV CY7C0852V/CY7C0852AV CY7C0853V/CY7C0853AV FLEx V, 32K/64K/128K/256K 36 Synchronous Dual-Port RAM
 FLEx36 3.3 V, 32K/64K/128K/256K 36 Synchronous Dual-Port RAM FLEx36 3.3 V, 32K/64K/128K/256K 36 Synchronous Dual-Port RAM Features True dual-ported memory cells that allow simultaneous access of the same
FLEx36 3.3 V, 32K/64K/128K/256K 36 Synchronous Dual-Port RAM FLEx36 3.3 V, 32K/64K/128K/256K 36 Synchronous Dual-Port RAM Features True dual-ported memory cells that allow simultaneous access of the same
72-Mbit QDR II SRAM Four-Word Burst Architecture
 72-Mbit QDR II SRAM Four-Word Burst Architecture 72-Mbit QDR II SRAM Four-Word Burst Architecture Features Separate independent read and write data ports Supports concurrent transactions 333 MHz clock
72-Mbit QDR II SRAM Four-Word Burst Architecture 72-Mbit QDR II SRAM Four-Word Burst Architecture Features Separate independent read and write data ports Supports concurrent transactions 333 MHz clock
I/O 1 I/O 2 I/O 3 I/O 4 I/O 5 I/O 6 I/O 7
 Features High speed t AA = 12 ns Low active power 1320 mw (max.) Low CMOS standby power (Commercial L version) 2.75 mw (max.) 2.0V Data Retention (400 µw at 2.0V retention) Automatic power-down when deselected
Features High speed t AA = 12 ns Low active power 1320 mw (max.) Low CMOS standby power (Commercial L version) 2.75 mw (max.) 2.0V Data Retention (400 µw at 2.0V retention) Automatic power-down when deselected
1K x 8 Dual-Port Static RAM
 Features True Dual-Ported memory cells which allow simultaneous reads of the same memory location 1K x 8 organization 0.65-micron CMOS for optimum speed/power High-speed access: 15 ns ow operating power:
Features True Dual-Ported memory cells which allow simultaneous reads of the same memory location 1K x 8 organization 0.65-micron CMOS for optimum speed/power High-speed access: 15 ns ow operating power:
2Kx8 Dual-Port Static RAM
 1CY 7C13 2/ CY7C1 36 fax id: 5201 CY7C132/CY7C136 Features True Dual-Ported memory cells which allow simultaneous reads of the same memory location 2K x 8 organization 0.65-micron CMOS for optimum speed/power
1CY 7C13 2/ CY7C1 36 fax id: 5201 CY7C132/CY7C136 Features True Dual-Ported memory cells which allow simultaneous reads of the same memory location 2K x 8 organization 0.65-micron CMOS for optimum speed/power
SCAN16512 Low Voltage Universal 16-bit IEEE Bus Transceiver with TRI-STATE Outputs
 SCAN16512 Low Voltage Universal 16-bit IEEE 1149.1 Bus Transceiver with TRI-STATE Outputs General Description The SCAN16512 is a high speed, low-power universal bus transceiver featuring data inputs organized
SCAN16512 Low Voltage Universal 16-bit IEEE 1149.1 Bus Transceiver with TRI-STATE Outputs General Description The SCAN16512 is a high speed, low-power universal bus transceiver featuring data inputs organized
SCAN16512A Low Voltage Universal 16-bit IEEE Bus Transceiver with TRI-STATE Outputs
 Low Voltage Universal 16-bit IEEE 1149.1 Bus Transceiver with TRI-STATE Outputs General Description The SCAN16512A is a high speed, low-power universal bus transceiver featuring data inputs organized into
Low Voltage Universal 16-bit IEEE 1149.1 Bus Transceiver with TRI-STATE Outputs General Description The SCAN16512A is a high speed, low-power universal bus transceiver featuring data inputs organized into
A 4 A 3 A 2 ROW DECODER 64K x 16 RAM Array I/O 1 I/O X 2048 I/O 9 I/O 16
 021 CY7C1021 Features High speed t AA = 12 ns CMOS for optimum speed/power Low active power 1320 mw (max.) Automatic power-down when deselected Independent Control of Upper and Lower bits Available in
021 CY7C1021 Features High speed t AA = 12 ns CMOS for optimum speed/power Low active power 1320 mw (max.) Automatic power-down when deselected Independent Control of Upper and Lower bits Available in
64/256/512/1K/2K/4K/8K x 9 Synchronous FIFOs
 241/42 fax id: 549 CY7C4421/421/4211/4221 64/256/512/1K/2K/4K/8K x 9 Synchronous FIFOs Features High-speed, low-power, first-in, first-out (FIFO) memories 64 x 9 (CY7C4421) 256 x 9 (CY7C421) 512 x 9 (CY7C4211)
241/42 fax id: 549 CY7C4421/421/4211/4221 64/256/512/1K/2K/4K/8K x 9 Synchronous FIFOs Features High-speed, low-power, first-in, first-out (FIFO) memories 64 x 9 (CY7C4421) 256 x 9 (CY7C421) 512 x 9 (CY7C4211)
I/O 1 I/O 2 I/O 3 I/O 4 I/O 5 I/O 6 A 16 I/O 7
 128K x 8 Static RAM Features High speed t AA = 12 ns Low active power 495 mw (max. 12 ns) Low CMOS standby power 55 mw (max.) 4 mw 2.0V Data Retention Automatic power-down when deselected TTL-compatible
128K x 8 Static RAM Features High speed t AA = 12 ns Low active power 495 mw (max. 12 ns) Low CMOS standby power 55 mw (max.) 4 mw 2.0V Data Retention Automatic power-down when deselected TTL-compatible
72-Mbit QDR -II+ SRAM 4-Word Burst Architecture (2.0 Cycle Read Latency)
 72-Mbit QDR -II+ SRAM 4-Word Burst Architecture (2. Cycle Read Latency) Features Separate independent read and write data ports Supports concurrent transactions 375 MHz clock for high bandwidth 4-word
72-Mbit QDR -II+ SRAM 4-Word Burst Architecture (2. Cycle Read Latency) Features Separate independent read and write data ports Supports concurrent transactions 375 MHz clock for high bandwidth 4-word
128K x 8 Static RAM CY7C1019B CY7C10191B. Features. Functional Description. Logic Block Diagram. Pin Configurations
 128K x 8 Static RAM Features High speed t AA = 10, 12, 15 ns CMOS for optimum speed/power Center power/ground pinout Automatic power-down when deselected Easy memory expansion with and OE options Functionally
128K x 8 Static RAM Features High speed t AA = 10, 12, 15 ns CMOS for optimum speed/power Center power/ground pinout Automatic power-down when deselected Easy memory expansion with and OE options Functionally
64K x 1 Static RAM CY7C187. Features. Functional Description. Logic Block Diagram. Pin Configurations. Selection Guide DIP. SOJ Top View.
 64K x 1 Static RAM Features High speed 15 ns CMOS for optimum speed/power Low active power 495 mw Low standby power 110 mw TTL compatible inputs and outputs Automatic power-down when deselected Available
64K x 1 Static RAM Features High speed 15 ns CMOS for optimum speed/power Low active power 495 mw Low standby power 110 mw TTL compatible inputs and outputs Automatic power-down when deselected Available
8K x 8 Static RAM CY6264. Features. Functional Description
 8K x 8 Static RAM Features 55, 70 ns access times CMOS for optimum speed/power Easy memory expansion with CE 1, CE 2, and OE features TTL-compatible inputs and outputs Automatic power-down when deselected
8K x 8 Static RAM Features 55, 70 ns access times CMOS for optimum speed/power Easy memory expansion with CE 1, CE 2, and OE features TTL-compatible inputs and outputs Automatic power-down when deselected
SENSE AMPS POWER DOWN
 185 CY7C185 8K x 8 Static RAM Features High speed 15 ns Fast t DOE Low active power 715 mw Low standby power 220 mw CMOS for optimum speed/power Easy memory expansion with,, and OE features TTL-compatible
185 CY7C185 8K x 8 Static RAM Features High speed 15 ns Fast t DOE Low active power 715 mw Low standby power 220 mw CMOS for optimum speed/power Easy memory expansion with,, and OE features TTL-compatible
1 Mbit (128K x 8) Static RAM
 1 Mbit (128K x 8) Static RAM Features Temperature Ranges Industrial: 40 C to 85 C Automotive-A: 40 C to 85 C Pin and Function compatible with CY7C1019BV33 High Speed t AA = 10 ns CMOS for optimum Speed
1 Mbit (128K x 8) Static RAM Features Temperature Ranges Industrial: 40 C to 85 C Automotive-A: 40 C to 85 C Pin and Function compatible with CY7C1019BV33 High Speed t AA = 10 ns CMOS for optimum Speed
I/O 1 I/O 2 I/O 3 I/O 4 I/O 5 I/O 6 A 16 I/O 7 A 15 7
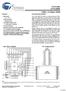 Features High speed t AA = 12 ns Low active power 495 mw (max.) Low CMOS standby power 11 mw (max.) (L Version) 2.0V Data Retention Automatic power-down when deselected TTL-compatible inputs and outputs
Features High speed t AA = 12 ns Low active power 495 mw (max.) Low CMOS standby power 11 mw (max.) (L Version) 2.0V Data Retention Automatic power-down when deselected TTL-compatible inputs and outputs
PRELIMINARY C106A 1. 7C106A 12 7C106A 15 7C106A 20 7C106A 25 7C106A 35 Maximum Access Time (ns) Maximum Operating
 1CY 7C10 6A Features High speed t AA = 12 ns CMOS for optimum speed/power Low active power 910 mw Low standby power 275 mw 2.0V data retention (optional) 100 µw Automatic power-down when deselected TTL-compatible
1CY 7C10 6A Features High speed t AA = 12 ns CMOS for optimum speed/power Low active power 910 mw Low standby power 275 mw 2.0V data retention (optional) 100 µw Automatic power-down when deselected TTL-compatible
64K x V Static RAM Module
 831V33 Features High-density 3.3V 2-megabit SRAM module High-speed SRAMs Access time of 12 ns Low active power 1.512W (max.) at 12 ns 64 pins Available in ZIP format Functional Description CYM1831V33 64K
831V33 Features High-density 3.3V 2-megabit SRAM module High-speed SRAMs Access time of 12 ns Low active power 1.512W (max.) at 12 ns 64 pins Available in ZIP format Functional Description CYM1831V33 64K
2M Async Fast SRAM. Rev. No. History Issue Date 1.0 Initial issue Apr..15,2014
 Revision History Rev. No. History Issue Date 1.0 Initial issue Apr..15,2014 1 Rev. 1.0 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The and are a 2,097,152-bit high-speed Static Random Access Memory organized as 128K(256) words
Revision History Rev. No. History Issue Date 1.0 Initial issue Apr..15,2014 1 Rev. 1.0 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The and are a 2,097,152-bit high-speed Static Random Access Memory organized as 128K(256) words
4M Async Fast SRAM. Rev. No. History Issue Date 1.0 Initial issue Apr.15,2014
 Revision History Rev. No. History Issue Date 1.0 Initial issue Apr.15,2014 1 Rev. 1.0 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The and are a 4,194,304-bit high-speed Static Random Access Memory organized as 256K(512) words
Revision History Rev. No. History Issue Date 1.0 Initial issue Apr.15,2014 1 Rev. 1.0 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The and are a 4,194,304-bit high-speed Static Random Access Memory organized as 256K(512) words
1M Async Fast SRAM. Revision History CS16FS1024(3/5/W) Rev. No. History Issue Date
 Revision History Rev. No. History Issue Date 1.0 Initial issue Apr.15,2014 2.0 Add 32TSOPII-400mil pin configuration and outline May 26, 2014 3.0 Delete 128kx8 products May 22, 2015 4.0 Add part no. CS16FS10245GC(I)-12
Revision History Rev. No. History Issue Date 1.0 Initial issue Apr.15,2014 2.0 Add 32TSOPII-400mil pin configuration and outline May 26, 2014 3.0 Delete 128kx8 products May 22, 2015 4.0 Add part no. CS16FS10245GC(I)-12
 Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. 2K x 8 Dual-Port Static RAM Features True Dual-Ported memory cells which
Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. 2K x 8 Dual-Port Static RAM Features True Dual-Ported memory cells which
I/O 1 I/O 2 I/O 3 A 10 6
 Features High speed 12 ns Fast t DOE CMOS for optimum speed/power Low active power 495 mw (Max, L version) Low standby power 0.275 mw (Max, L version) 2V data retention ( L version only) Easy memory expansion
Features High speed 12 ns Fast t DOE CMOS for optimum speed/power Low active power 495 mw (Max, L version) Low standby power 0.275 mw (Max, L version) 2V data retention ( L version only) Easy memory expansion
BSI BH62UV8000. Ultra Low Power/High Speed CMOS SRAM 1M X 8 bit
 FEATURES Wide low operation voltage : 1.65V ~ 3.6V Ultra low power consumption : = 3.0V = 2.0V High speed access time : -70 70ns at 1.V at 5 O C Ultra Low Power/High Speed CMOS SRAM 1M X bit Operation
FEATURES Wide low operation voltage : 1.65V ~ 3.6V Ultra low power consumption : = 3.0V = 2.0V High speed access time : -70 70ns at 1.V at 5 O C Ultra Low Power/High Speed CMOS SRAM 1M X bit Operation
DS1270W 3.3V 16Mb Nonvolatile SRAM
 19-5614; Rev 11/10 www.maxim-ic.com 3.3V 16Mb Nonvolatile SRAM FEATURES Five years minimum data retention in the absence of external power Data is automatically protected during power loss Unlimited write
19-5614; Rev 11/10 www.maxim-ic.com 3.3V 16Mb Nonvolatile SRAM FEATURES Five years minimum data retention in the absence of external power Data is automatically protected during power loss Unlimited write
72-Mbit QDR II SRAM 4-Word Burst Architecture
 72-Mbit QDR II SRAM 4-Word Burst Architecture Features Configurations Separate independent Read and Write Data Ports Supports concurrent transactions 3 MHz clock for High Bandwidth 4-word Burst for reducing
72-Mbit QDR II SRAM 4-Word Burst Architecture Features Configurations Separate independent Read and Write Data Ports Supports concurrent transactions 3 MHz clock for High Bandwidth 4-word Burst for reducing
P4C164LL. VERY LOW POWER 8Kx8 STATIC CMOS RAM FEATURES DESCRIPTION V CC. Current (Commercial/Industrial) Operating: 55 ma CMOS Standby: 3 µa
 P4C164LL VERY LOW POWER 8Kx8 STATIC CMOS RAM FEATURES Current (Commercial/Industrial) Operating: 55 ma CMOS Standby: 3 µa Access Times 80/100 (Commercial or Industrial) 90/120 (Military) Single 5 Volts
P4C164LL VERY LOW POWER 8Kx8 STATIC CMOS RAM FEATURES Current (Commercial/Industrial) Operating: 55 ma CMOS Standby: 3 µa Access Times 80/100 (Commercial or Industrial) 90/120 (Military) Single 5 Volts
16M Async Fast SRAM. Rev. No. History Issue Date 1.0 Initial issue Apr. 15,2014
 Revision History Rev. No. History Issue Date 1.0 Initial issue Apr. 15,2014 1 Rev. 1.0 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The and are a 16,789,216-bit high-speed Static Random Access Memory organized as 1M(2M) words
Revision History Rev. No. History Issue Date 1.0 Initial issue Apr. 15,2014 1 Rev. 1.0 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The and are a 16,789,216-bit high-speed Static Random Access Memory organized as 1M(2M) words
ICSSSTUB32S868D Advance Information
 Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. ICSSSTUB3S868 8-Bit Configurable egistered Buffer for ecommended Application: Memory Modules Provides complete IMM solution with ICS97U877 Ideal for 400, 533 and 667 Product
Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. ICSSSTUB3S868 8-Bit Configurable egistered Buffer for ecommended Application: Memory Modules Provides complete IMM solution with ICS97U877 Ideal for 400, 533 and 667 Product
PSRAM 2-Mbit (128K x 16)
 PSRAM 2-Mbit (128K x 16) Features Wide voltage range: 2.7V 3.6V Access Time: 55 ns, 70 ns Ultra-low active power Typical active current: 1mA @ f = 1 MHz Typical active current: 14 ma @ f = fmax (For 55-ns)
PSRAM 2-Mbit (128K x 16) Features Wide voltage range: 2.7V 3.6V Access Time: 55 ns, 70 ns Ultra-low active power Typical active current: 1mA @ f = 1 MHz Typical active current: 14 ma @ f = fmax (For 55-ns)
5V 128K X 8 HIGH SPEED CMOS SRAM
 5V 128K X 8 HIGH SPEED CMOS SRAM Revision History AS7C1024B Revision Details Date Rev 1.0 Preliminary datasheet prior to 2004 Rev 1.1 Die Revision A to B March 2004 Rev 2.0 PCN issued yield issues with
5V 128K X 8 HIGH SPEED CMOS SRAM Revision History AS7C1024B Revision Details Date Rev 1.0 Preliminary datasheet prior to 2004 Rev 1.1 Die Revision A to B March 2004 Rev 2.0 PCN issued yield issues with
P4C1256L LOW POWER 32K X 8 STATIC CMOS RAM FEATURES DESCRIPTION V CC. Current (Commercial/Industrial) Operating: 70mA/85mA CMOS Standby: 100µA/100µA
 FEATURES Current (Commercial/Industrial) Operating: 70mA/85mA CMOS Standby: 100µA/100µA Access Times 55/70/85 Single 5 Volts ±10% Power Supply Easy Memory Expansion Using CE and OE Inputs Common Data I/O
FEATURES Current (Commercial/Industrial) Operating: 70mA/85mA CMOS Standby: 100µA/100µA Access Times 55/70/85 Single 5 Volts ±10% Power Supply Easy Memory Expansion Using CE and OE Inputs Common Data I/O
64/256/512/1K/2K/4K/8K x 9 Synchronous FIFOs
 CY7C4421/421/4211/4221 64/256/512/1K/2K/4K/8K x 9 Synchronous FIFOs Features CY7C4421/421/4211/4221 64/256/512/1K/2K/4K/8K x 9 Synchronous FIFOs High-speed, low-power, First-In, First-Out (FIFO) memories
CY7C4421/421/4211/4221 64/256/512/1K/2K/4K/8K x 9 Synchronous FIFOs Features CY7C4421/421/4211/4221 64/256/512/1K/2K/4K/8K x 9 Synchronous FIFOs High-speed, low-power, First-In, First-Out (FIFO) memories
CY7C2663KV18/CY7C2665KV Mbit QDR II+ SRAM Four-Word Burst Architecture (2.5 Cycle Read Latency) with ODT
 44-Mbit QDR II+ SRAM Four-Word Burst Architecture (2.5 Cycle Read Latency) with ODT 44-Mbit QDR II+ SRAM Four-Word Burst Architecture (2.5 Cycle Read Latency) with ODT Features Separate independent read
44-Mbit QDR II+ SRAM Four-Word Burst Architecture (2.5 Cycle Read Latency) with ODT 44-Mbit QDR II+ SRAM Four-Word Burst Architecture (2.5 Cycle Read Latency) with ODT Features Separate independent read
FLEx V 128 K/256 K 72 Synchronous Dual-Port RAM
 FLEx72 3.3 V 128 K/256 K 72 Synchronous Dual-Port RAM Features Functional Description True dual-ported memory cells that allow simultaneous access of the same memory location Synchronous pipelined operation
FLEx72 3.3 V 128 K/256 K 72 Synchronous Dual-Port RAM Features Functional Description True dual-ported memory cells that allow simultaneous access of the same memory location Synchronous pipelined operation
64, 256, 512, 1K, 2K, 4K x 18 Synchronous FIFOs
 1CY 7C42 25 fax id: 5410 CY7C4425/4205/4215 64, 256, 512, 1K, 2K, 4K x 18 Synchronous FIFOs Features High-speed, low-power, first-in first-out (FIFO) memories 64 x 18 (CY7C4425) 256 x 18 (CY7C4205) 512
1CY 7C42 25 fax id: 5410 CY7C4425/4205/4215 64, 256, 512, 1K, 2K, 4K x 18 Synchronous FIFOs Features High-speed, low-power, first-in first-out (FIFO) memories 64 x 18 (CY7C4425) 256 x 18 (CY7C4205) 512
I/O 1 I/O 2 I/O 3 A 10 6
 Features High speed 12 ns Fast t DOE CMOS for optimum speed/power Low active power 467 mw (max, 12 ns L version) Low standby power 0.275 mw (max, L version) 2V data retention ( L version only) Easy memory
Features High speed 12 ns Fast t DOE CMOS for optimum speed/power Low active power 467 mw (max, 12 ns L version) Low standby power 0.275 mw (max, L version) 2V data retention ( L version only) Easy memory
DS1073 3V EconOscillator/Divider
 3V EconOscillator/Divider wwwmaxim-iccom FEATURES Dual fixed-frequency outputs (30kHz to 100MHz) User-programmable on-chip dividers (from 1 to 513) User-programmable on-chip prescaler (1, 2, 4) No external
3V EconOscillator/Divider wwwmaxim-iccom FEATURES Dual fixed-frequency outputs (30kHz to 100MHz) User-programmable on-chip dividers (from 1 to 513) User-programmable on-chip prescaler (1, 2, 4) No external
DS1642 Nonvolatile Timekeeping RAM
 www.dalsemi.com Nonvolatile Timekeeping RAM FEATURES Integrated NV SRAM, real time clock, crystal, power fail control circuit and lithium energy source Standard JEDEC bytewide 2K x 8 static RAM pinout
www.dalsemi.com Nonvolatile Timekeeping RAM FEATURES Integrated NV SRAM, real time clock, crystal, power fail control circuit and lithium energy source Standard JEDEC bytewide 2K x 8 static RAM pinout
IS61WV25632ALL/ALS IS61WV25632BLL/BLS IS64WV25632BLL/BLS
 256K x 32 HIGH-SPEED ASYNCHRONOUS CMOS STATIC RAM WITH 3.3V SUPPLY PRELIMINARY INFORMATION APRIL 2008 FEATURES High-speed access times: 8, 10, 20 ns High-performance, low-power CMOS process Multiple center
256K x 32 HIGH-SPEED ASYNCHRONOUS CMOS STATIC RAM WITH 3.3V SUPPLY PRELIMINARY INFORMATION APRIL 2008 FEATURES High-speed access times: 8, 10, 20 ns High-performance, low-power CMOS process Multiple center
72-Mbit QDR II SRAM Two-Word Burst Architecture
 72-Mbit QDR II SRAM Two-Word Burst Architecture 72-Mbit QDR II SRAM Two-Word Burst Architecture Features Separate independent read and write data ports Supports concurrent transactions 35 MHz clock for
72-Mbit QDR II SRAM Two-Word Burst Architecture 72-Mbit QDR II SRAM Two-Word Burst Architecture Features Separate independent read and write data ports Supports concurrent transactions 35 MHz clock for
Very Low Power CMOS SRAM 2M X 8 bit. Pb-Free and Green package materials are compliant to RoHS. STANDBY (ICCSB1, Max) V CC=3.0V
 Very Low Power CMOS SRAM 2M X bit Pb-Free and Green package materials are compliant to RoHS BS62LV1600 FEATURES Wide operation voltage : 2.4V ~ 5.5V Very low power consumption : = 3.0V Operation current
Very Low Power CMOS SRAM 2M X bit Pb-Free and Green package materials are compliant to RoHS BS62LV1600 FEATURES Wide operation voltage : 2.4V ~ 5.5V Very low power consumption : = 3.0V Operation current
P4C1041 HIGH SPEED 256K x 16 (4 MEG) STATIC CMOS RAM
 HIGH SPEED 256K x 16 (4 MEG) STATIC CMOS RAM FEATURES High Speed (Equal Access and Cycle Times) 10/12/15/20 ns (Commercial) 12/15/20 ns (Industrial/Military) Low Power Single 5.0V ± 10% Power Supply 2.0V
HIGH SPEED 256K x 16 (4 MEG) STATIC CMOS RAM FEATURES High Speed (Equal Access and Cycle Times) 10/12/15/20 ns (Commercial) 12/15/20 ns (Industrial/Military) Low Power Single 5.0V ± 10% Power Supply 2.0V
 Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. 256K (32K x 8) Static RAM Features Temperature Ranges Commercial: 0 C to
Distributed by: www.jameco.com 1-800-831-4242 The content and copyrights of the attached material are the property of its owner. 256K (32K x 8) Static RAM Features Temperature Ranges Commercial: 0 C to
SCAN18374T D-Type Flip-Flop with 3-STATE Outputs
 SCAN18374T D-Type Flip-Flop with 3-STATE Outputs General Description The SCAN18374T is a high speed, low-power D-type flipflop featuring separate D-type inputs organized into dual 9- bit bytes with byte-oriented
SCAN18374T D-Type Flip-Flop with 3-STATE Outputs General Description The SCAN18374T is a high speed, low-power D-type flipflop featuring separate D-type inputs organized into dual 9- bit bytes with byte-oriented
SCAN182373A Transparent Latch with 25Ω Series Resistor Outputs
 January 1993 Revised August 2000 SCAN182373A Traparent Latch with 25Ω Series Resistor Outputs General Description The SCAN182373A is a high performance BiCMOS traparent latch featuring separate data inputs
January 1993 Revised August 2000 SCAN182373A Traparent Latch with 25Ω Series Resistor Outputs General Description The SCAN182373A is a high performance BiCMOS traparent latch featuring separate data inputs
512 x 8 Registered PROM
 512 x 8 Registered PROM Features CMOS for optimum speed/power High speed 25 ns address set-up 12 ns clock to output Low power 495 mw (Commercial) 660 mw (Military) Synchronous and asynchronous output enables
512 x 8 Registered PROM Features CMOS for optimum speed/power High speed 25 ns address set-up 12 ns clock to output Low power 495 mw (Commercial) 660 mw (Military) Synchronous and asynchronous output enables
LM12L Bit + Sign Data Acquisition System with Self-Calibration
 LM12L458 12-Bit + Sign Data Acquisition System with Self-Calibration General Description The LM12L458 is a highly integrated 3.3V Data Acquisition System. It combines a fully-differential self-calibrating
LM12L458 12-Bit + Sign Data Acquisition System with Self-Calibration General Description The LM12L458 is a highly integrated 3.3V Data Acquisition System. It combines a fully-differential self-calibrating
DS1075 EconOscillator/Divider
 EconOscillator/Divider www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Dual Fixed frequency outputs (30 KHz - 100 MHz) User-programmable on-chip dividers (from 1-513) User-programmable on-chip prescaler (1, 2, 4) No external
EconOscillator/Divider www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Dual Fixed frequency outputs (30 KHz - 100 MHz) User-programmable on-chip dividers (from 1-513) User-programmable on-chip prescaler (1, 2, 4) No external
18-Mbit DDR II SRAM Four-Word Burst Architecture
 8-Mbit DDR II SRAM Four-Word Burst Architecture 8-Mbit DDR II SRAM Four-Word Burst Architecture Features 8-Mbit density (M 8, 52K 36) 333-MHz clock for high bandwidth Four-word burst for reducing address
8-Mbit DDR II SRAM Four-Word Burst Architecture 8-Mbit DDR II SRAM Four-Word Burst Architecture Features 8-Mbit density (M 8, 52K 36) 333-MHz clock for high bandwidth Four-word burst for reducing address
Ultra Low Power/High Speed CMOS SRAM 512K X 16 bit. Pb-Free and Green package materials are compliant to RoHS. STANDBY (ICCSB1, Max) V CC=3.
 Ultra Low Power/High Speed CMOS SRAM 512K X 16 bit Pb-Free and Green package materials are compliant to RoHS BH616UV8010 FEATURES Wide low operation voltage : 165V ~ 36V Ultra low power consumption : =
Ultra Low Power/High Speed CMOS SRAM 512K X 16 bit Pb-Free and Green package materials are compliant to RoHS BH616UV8010 FEATURES Wide low operation voltage : 165V ~ 36V Ultra low power consumption : =
IS61QDPB24M18A/A1/A2 IS61QDPB22M36A/A1/A2. 4Mx18, 2Mx36 72Mb QUADP (Burst 2) Synchronous SRAM (2.5 CYCLE READ LATENCY)
 4Mx18, 2Mx36 72Mb QUADP (Burst 2) Synchronous SRAM (2.5 CYCLE READ LATENCY) FEATURES 2Mx36 and 4Mx18 configuration available. On-chip Delay-Locked Loop (DLL) for wide data valid window. Separate independent
4Mx18, 2Mx36 72Mb QUADP (Burst 2) Synchronous SRAM (2.5 CYCLE READ LATENCY) FEATURES 2Mx36 and 4Mx18 configuration available. On-chip Delay-Locked Loop (DLL) for wide data valid window. Separate independent
Very Low Power CMOS SRAM 64K X 16 bit. Pb-Free and Green package materials are compliant to RoHS. STANDBY (ICCSB1, Max) V CC=3.0V
 Very Low Power CMOS SRAM 64K X 16 bit Pb-Free and Green package materials are compliant to RoHS BS616LV1010 FEATURES Wide operation voltage : 24V ~ 55V Very low power consumption : = 30V Operation current
Very Low Power CMOS SRAM 64K X 16 bit Pb-Free and Green package materials are compliant to RoHS BS616LV1010 FEATURES Wide operation voltage : 24V ~ 55V Very low power consumption : = 30V Operation current
256K (32K x 8) Static RAM
 256K (32K x 8) Static RAM Features High speed 55 ns Temperature Ranges Commercial: 0 C to 70 C Industrial: 40 C to 85 C Automotive: 40 C to 125 C Voltage range 4.5V 5.5V Low active power and standby power
256K (32K x 8) Static RAM Features High speed 55 ns Temperature Ranges Commercial: 0 C to 70 C Industrial: 40 C to 85 C Automotive: 40 C to 125 C Voltage range 4.5V 5.5V Low active power and standby power
General Purpose Clock Synthesizer
 1CY 290 7 fax id: 3521 CY2907 General Purpose Clock Synthesizer Features Highly configurable single PLL clock synthesizer provides all clocking requirements for numerous applications Compatible with all
1CY 290 7 fax id: 3521 CY2907 General Purpose Clock Synthesizer Features Highly configurable single PLL clock synthesizer provides all clocking requirements for numerous applications Compatible with all
DS1075. EconOscillator/Divider PRELIMINARY FEATURES PIN ASSIGNMENT FREQUENCY OPTIONS
 PRELIMINARY EconOscillator/Divider FEATURES Dual Fixed frequency outputs (200 KHz 100 MHz) User programmable on chip dividers (from 1 513) User programmable on chip prescaler (1, 2, 4) No external components
PRELIMINARY EconOscillator/Divider FEATURES Dual Fixed frequency outputs (200 KHz 100 MHz) User programmable on chip dividers (from 1 513) User programmable on chip prescaler (1, 2, 4) No external components
144-Mbit DDR II SRAM Two-Word Burst Architecture
 44-Mbit DDR II SRAM Two-Word Burst Architecture 44-Mbit DDR II SRAM Two-Word Burst Architecture Features 44-Mbit density (8M 8, 4M 36) 333 MHz clock for high bandwidth Two-word burst for reducing address
44-Mbit DDR II SRAM Two-Word Burst Architecture 44-Mbit DDR II SRAM Two-Word Burst Architecture Features 44-Mbit density (8M 8, 4M 36) 333 MHz clock for high bandwidth Two-word burst for reducing address
64/256/512/1K/2K/4K x 18 Synchronous FIFOs
 64/256/512/1K/2K/4K x 18 Synchronous FIFOs Features High speed, low power, first-in first-out (FIFO) memories 64 x 18 (CY7C4425) 256 x 18 (CY7C4205) 512 x 18 (CY7C4215) 1K x 18 (CY7C4225) 2K x 18 (CY7C4235)
64/256/512/1K/2K/4K x 18 Synchronous FIFOs Features High speed, low power, first-in first-out (FIFO) memories 64 x 18 (CY7C4425) 256 x 18 (CY7C4205) 512 x 18 (CY7C4215) 1K x 18 (CY7C4225) 2K x 18 (CY7C4235)
32M Async Fast SRAM. Rev. No. History Issue Date 1.0 Initial issue Apr. 26,2017
 Revision History Rev. No. History Issue Date 1.0 Initial issue Apr. 26,2017 1 Rev. 1.0 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The and are a 33,578,432-bit high-speed Static Random Access Memory organized as 4M(2M) words
Revision History Rev. No. History Issue Date 1.0 Initial issue Apr. 26,2017 1 Rev. 1.0 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The and are a 33,578,432-bit high-speed Static Random Access Memory organized as 4M(2M) words
18-Mbit QDR II SRAM Two-Word Burst Architecture
 8-Mbit QDR II SRAM Two-Word Burst Architecture 8-Mbit QDR II SRAM Two-Word Burst Architecture Features Separate independent read and write data ports Supports concurrent transactions 333 MHz clock for
8-Mbit QDR II SRAM Two-Word Burst Architecture 8-Mbit QDR II SRAM Two-Word Burst Architecture Features Separate independent read and write data ports Supports concurrent transactions 333 MHz clock for
72-Mbit DDR II+ SRAM Two-Word Burst Architecture (2.5 Cycle Read Latency)
 72-Mbit DDR II+ SRAM Two-Word Burst Architecture (2.5 Cycle Read Latency) 72-Mbit DDR II+ SRAM Two-Word Burst Architecture (2.5 Cycle Read Latency) Features 72-Mbit density (4 M 8, 2 M 36) 55 MHz clock
72-Mbit DDR II+ SRAM Two-Word Burst Architecture (2.5 Cycle Read Latency) 72-Mbit DDR II+ SRAM Two-Word Burst Architecture (2.5 Cycle Read Latency) Features 72-Mbit density (4 M 8, 2 M 36) 55 MHz clock
PT7C4563 Real-time Clock Module (I 2 C Bus)
 Features Using external 32.768kHz quartz crystal Supports I 2 -Bus's high speed mode (400 khz) Description The PT74563 serial real-time clock is a low-power clock/calendar with a programmable square-wave
Features Using external 32.768kHz quartz crystal Supports I 2 -Bus's high speed mode (400 khz) Description The PT74563 serial real-time clock is a low-power clock/calendar with a programmable square-wave
XC2C32 CoolRunner-II CPLD
 0 XC2C32 Coolunner-II CPLD DS091 (v1.4) January 27, 2003 0 0 Advance Product Specification Features Optimized for 1.8V systems - As fast as 3.5 ns pin-to-pin logic delays - As low as 14 µa quiescent current
0 XC2C32 Coolunner-II CPLD DS091 (v1.4) January 27, 2003 0 0 Advance Product Specification Features Optimized for 1.8V systems - As fast as 3.5 ns pin-to-pin logic delays - As low as 14 µa quiescent current
2K x 8 Dual-Port Static RAM
 2K x 8 Dual-Port Static RAM Features True dual-ported memory cells that enable simultaneous reads of the same memory location 2K x 8 organization 0.65 micron CMOS for optimum speed and power High speed
2K x 8 Dual-Port Static RAM Features True dual-ported memory cells that enable simultaneous reads of the same memory location 2K x 8 organization 0.65 micron CMOS for optimum speed and power High speed
TOSHIBA MOS DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUIT SILICON GATE CMOS
 TENTATIVE TOSHIBA MOS DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUIT SILICON GATE CMOS 262,144-WORD BY 16-BIT FULL CMOS STATIC RAM DESCRIPTION The TC55YEM216ABXN is a 4,194,304-bit static random access memory (SRAM) organized
TENTATIVE TOSHIBA MOS DIGITAL INTEGRATED CIRCUIT SILICON GATE CMOS 262,144-WORD BY 16-BIT FULL CMOS STATIC RAM DESCRIPTION The TC55YEM216ABXN is a 4,194,304-bit static random access memory (SRAM) organized
Very Low Power/Voltage CMOS SRAM 128K x 16 or 256K x 8 bit switchable DESCRIPTION. SPEED ( ns ) STANDBY. ( ICCSB1, Max ) BLOCK DIAGRAM
 Very Low Power/Voltage CMOS SRAM 128K x 16 or 256K x 8 bit switchable FEATURES DESCRIPTION Very low operation voltage : 45 ~ 55V Very low power consumption : = 50V C-grade: 40mA (Max) operating current
Very Low Power/Voltage CMOS SRAM 128K x 16 or 256K x 8 bit switchable FEATURES DESCRIPTION Very low operation voltage : 45 ~ 55V Very low power consumption : = 50V C-grade: 40mA (Max) operating current
32K x 8 Reprogrammable Registered PROM
 1CY7C277 CY7C277 32K x 8 Reprogrammable Registered PROM Features Windowed for reprogrammability CMOS for optimum speed/power High speed 30-ns address set-up 15-ns clock to output Low power 60 mw (commercial)
1CY7C277 CY7C277 32K x 8 Reprogrammable Registered PROM Features Windowed for reprogrammability CMOS for optimum speed/power High speed 30-ns address set-up 15-ns clock to output Low power 60 mw (commercial)
64/256/512/1K/2K/4K x18 Low-Voltage Synchronous FIFOs
 CY7C4425V /4205V/4215V CY7C4225V /4235V/4245V64/256/512/1K/2K/4K x18 Low-Voltage Synchronous FIFOs CY7C4225V/4205V/4215V 64/256/512/1K/2K/4K x18 Low-Voltage Synchronous FIFOs Features 3.3V operation for
CY7C4425V /4205V/4215V CY7C4225V /4235V/4245V64/256/512/1K/2K/4K x18 Low-Voltage Synchronous FIFOs CY7C4225V/4205V/4215V 64/256/512/1K/2K/4K x18 Low-Voltage Synchronous FIFOs Features 3.3V operation for
32K Word x 8 Bit. Rev. No. History Issue Date Remark 2.0 Initial issue with new naming rule Dec.27,2004
 Revision History Rev. No. History Issue Date Remark 2.0 Initial issue with new naming rule Dec.27,2004 1 Rev. 2.0 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a high performance, high speed and super low power CMOS Static
Revision History Rev. No. History Issue Date Remark 2.0 Initial issue with new naming rule Dec.27,2004 1 Rev. 2.0 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The is a high performance, high speed and super low power CMOS Static
Dual Programmable Clock Generator
 1I CD20 51 fax id: 3512 Features Dual Programmable Clock Generator Functional Description Two independent clock outputs ranging from 320 khz to 100 MHz Individually programmable PLLs use 22-bit serial
1I CD20 51 fax id: 3512 Features Dual Programmable Clock Generator Functional Description Two independent clock outputs ranging from 320 khz to 100 MHz Individually programmable PLLs use 22-bit serial
CY Features. Logic Block Diagram
 Features Temperature Ranges -Commercial:0 to 70 -Industrial: -40 to 85 -Automotive: -40 to 125 High speed: 55ns and 70 ns Voltage range : 4.5V 5.5V operation Low active power (70ns, LL version, Com l and
Features Temperature Ranges -Commercial:0 to 70 -Industrial: -40 to 85 -Automotive: -40 to 125 High speed: 55ns and 70 ns Voltage range : 4.5V 5.5V operation Low active power (70ns, LL version, Com l and
LY61L K X 16 BIT HIGH SPEED CMOS SRAM
 Y6125616 REVISION HISTORY Revision Description Issue Date Rev. 1.0 Initial Issue May.24.2006 Rev. 1.1 Added Extended Grade Jan.22.2007 Rev. 1.2 Added PKG Type : 48-ball 6mm x 8mm TFBGA Jan.30.2007 Rev.
Y6125616 REVISION HISTORY Revision Description Issue Date Rev. 1.0 Initial Issue May.24.2006 Rev. 1.1 Added Extended Grade Jan.22.2007 Rev. 1.2 Added PKG Type : 48-ball 6mm x 8mm TFBGA Jan.30.2007 Rev.
256K (32K x 8) Static RAM
 256K (32K x 8) Static RAM Features Temperature Ranges Commercial: 0 C to 70 C Industrial: 40 C to 85 C Automotive-A: 40 C to 85 C Automotive-E: 40 C to 125 C Speed: 70 ns Low Voltage Range: 2.7V to 3.6V
256K (32K x 8) Static RAM Features Temperature Ranges Commercial: 0 C to 70 C Industrial: 40 C to 85 C Automotive-A: 40 C to 85 C Automotive-E: 40 C to 125 C Speed: 70 ns Low Voltage Range: 2.7V to 3.6V
256K x 8 Static RAM Module
 41 CYM1441 Features High-density 2-megabit module High-speed CMOS s Access time of 20 ns Low active power 5.3W (max.) SMD technology Separate data I/O 60-pin ZIP package TTL-compatible inputs and outputs
41 CYM1441 Features High-density 2-megabit module High-speed CMOS s Access time of 20 ns Low active power 5.3W (max.) SMD technology Separate data I/O 60-pin ZIP package TTL-compatible inputs and outputs
DS1307/DS X 8 Serial Real Time Clock
 DS1307/DS1308 64 X 8 Serial Real Time Clock www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Real time clock counts seconds, minutes, hours, date of the month, month, day of the week, and year with leap year compensation valid
DS1307/DS1308 64 X 8 Serial Real Time Clock www.dalsemi.com FEATURES Real time clock counts seconds, minutes, hours, date of the month, month, day of the week, and year with leap year compensation valid
LY61L25616A 256K X 16 BIT HIGH SPEED CMOS SRAM
 REVISION HISTORY Revision Description Issue Date Rev. 1.0 Initial Issue Jul.12.2012 Rev. 1.1 VCC - 0.2V revised as 0.2V for TEST CONDITION Jul.19.2012 of Average Operating Power supply Current ICC1 on
REVISION HISTORY Revision Description Issue Date Rev. 1.0 Initial Issue Jul.12.2012 Rev. 1.1 VCC - 0.2V revised as 0.2V for TEST CONDITION Jul.19.2012 of Average Operating Power supply Current ICC1 on
2Mx18, 1Mx36 36Mb QUAD (Burst 4) SYNCHRONOUS SRAM
 2Mx18, 1Mx36 36Mb QUAD (Burst 4) SYNCHRONOUS SRAM FEATURES DESCRIPTION APRIL 2016 1Mx36 and 2Mx18 configuration available. On-chip Delay-Locked Loop (DLL) for wide data valid window. Separate independent
2Mx18, 1Mx36 36Mb QUAD (Burst 4) SYNCHRONOUS SRAM FEATURES DESCRIPTION APRIL 2016 1Mx36 and 2Mx18 configuration available. On-chip Delay-Locked Loop (DLL) for wide data valid window. Separate independent
LY V 128K X 16 BIT HIGH SPEED CMOS SRAM
 Y6112816 REVISION HISTORY Revision Description Issue Date Rev. 1.0 Initial Issue Aug.12.2007 Rev. 1.1 Apr. 17.2009 Revised TEST CONDITION of ICC Revised FEATURES & ORDERING INFORMATION ead free and green
Y6112816 REVISION HISTORY Revision Description Issue Date Rev. 1.0 Initial Issue Aug.12.2007 Rev. 1.1 Apr. 17.2009 Revised TEST CONDITION of ICC Revised FEATURES & ORDERING INFORMATION ead free and green
P4C1299/P4C1299L. ULTRA HIGH SPEED 64K x 4 STATIC CMOS RAM FEATURES DESCRIPTION. Full CMOS, 6T Cell. Data Retention with 2.0V Supply (P4C1299L)
 FEATURES Full CMOS, 6T Cell High Speed (Equal Access and Cycle Times) 15/20/25/35 ns (Commercial/Industrial) 15/20/25/35/45 ns (Military) Low Power Operation Single 5V±10% Power Supply Output Enable (OE)
FEATURES Full CMOS, 6T Cell High Speed (Equal Access and Cycle Times) 15/20/25/35 ns (Commercial/Industrial) 15/20/25/35/45 ns (Military) Low Power Operation Single 5V±10% Power Supply Output Enable (OE)
2Mx18, 1Mx36 36Mb QUAD (Burst 4) SYNCHRONOUS SRAM
 2Mx18, 1Mx36 36Mb QUAD (Burst 4) SYNCHRONOUS SRAM FEATURES DESCRIPTION APRIL 2016 1Mx36 and 2Mx18 configuration available. On-chip Delay-Locked Loop (DLL) for wide data valid window. Separate independent
2Mx18, 1Mx36 36Mb QUAD (Burst 4) SYNCHRONOUS SRAM FEATURES DESCRIPTION APRIL 2016 1Mx36 and 2Mx18 configuration available. On-chip Delay-Locked Loop (DLL) for wide data valid window. Separate independent
ICSSSTV DDR 24-Bit to 48-Bit Registered Buffer. Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. Pin Configuration. Truth Table 1.
 Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. ICSSSTV32852 DDR 24-Bit to 48-Bit Registered Buffer Recommended Application: DDR Memory Modules Provides complete DDR DIMM logic solution with ICS93V857 or ICS95V857 SSTL_2
Integrated Circuit Systems, Inc. ICSSSTV32852 DDR 24-Bit to 48-Bit Registered Buffer Recommended Application: DDR Memory Modules Provides complete DDR DIMM logic solution with ICS93V857 or ICS95V857 SSTL_2
Very Low Power/Voltage CMOS SRAM 1M X 16 bit DESCRIPTION. SPEED (ns) 55ns : 3.0~3.6V 70ns : 2.7~3.6V BLOCK DIAGRAM
 Very Low Power/Voltage CMOS SRAM 1M X 16 bit (Dual CE Pins) FEATURES operation voltage : 27~36V Very low power consumption : = 30V C-grade: 45mA (@55ns) operating current I -grade: 46mA (@55ns) operating
Very Low Power/Voltage CMOS SRAM 1M X 16 bit (Dual CE Pins) FEATURES operation voltage : 27~36V Very low power consumption : = 30V C-grade: 45mA (@55ns) operating current I -grade: 46mA (@55ns) operating
Classic. Feature. EPLD Family. Table 1. Classic Device Features
 Classic EPLD Family May 1999, ver. 5 Data Sheet Features Complete device family with logic densities of 300 to 900 usable gates (see Table 1) Device erasure and reprogramming with non-volatile EPROM configuration
Classic EPLD Family May 1999, ver. 5 Data Sheet Features Complete device family with logic densities of 300 to 900 usable gates (see Table 1) Device erasure and reprogramming with non-volatile EPROM configuration
HY5V56D(L/S)FP. Revision History. No. History Draft Date Remark. 0.1 Defined Target Spec. May Rev. 0.1 / Jan
 Revision History No. History Draft Date Remark 0.1 Defined Target Spec. May 2003 Rev. 0.1 / Jan. 2005 1 Series 4 Banks x 4M x 16bits Synchronous DRAM DESCRIPTION The HY5V56D(L/S)FP is a 268,435,456bit
Revision History No. History Draft Date Remark 0.1 Defined Target Spec. May 2003 Rev. 0.1 / Jan. 2005 1 Series 4 Banks x 4M x 16bits Synchronous DRAM DESCRIPTION The HY5V56D(L/S)FP is a 268,435,456bit
IDT71P74804 IDT71P74604
 Features 8Mb Density (Mx8, 52kx36) Separate, Independent Read and Write Data Ports - Supports concurrent transactions Dual Echo Clock Output 4-Word Burst on all SRAM accesses Multiplexed Address Bus One
Features 8Mb Density (Mx8, 52kx36) Separate, Independent Read and Write Data Ports - Supports concurrent transactions Dual Echo Clock Output 4-Word Burst on all SRAM accesses Multiplexed Address Bus One
P4C1257/P4C1257L. ULTRA HIGH SPEED 256K x 1 STATIC CMOS RAMS FEATURES DESCRIPTION. Full CMOS. Separate Data I/O
 P4C1257/P4C1257L ULTRA HIGH SPEED 256K x 1 STATIC CMOS RAMS FEATURES Full CMOS High Speed (Equal Access and Cycle s) 12/15/20/25 ns (Commercial) 12/15/20/25 ns (Industrial) 25/35/45/55/70 ns (Military)
P4C1257/P4C1257L ULTRA HIGH SPEED 256K x 1 STATIC CMOS RAMS FEATURES Full CMOS High Speed (Equal Access and Cycle s) 12/15/20/25 ns (Commercial) 12/15/20/25 ns (Industrial) 25/35/45/55/70 ns (Military)
DS1482S. 1-Wire Level Shifter and Line Driver with Load Sensor PIN ASSIGNMENT
 www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Works with All ibuttons and 1-Wire Devices Communicates at Regular and Overdrive 1- Wire Speed (ost-dependent) Separate Interface Power Supply to evel Shift to Non-5V Systems
www.maxim-ic.com FEATURES Works with All ibuttons and 1-Wire Devices Communicates at Regular and Overdrive 1- Wire Speed (ost-dependent) Separate Interface Power Supply to evel Shift to Non-5V Systems
Functional Block Diagram. Row Decoder. 512 x 512 Memory Array. Column I/O. Input Data Circuit. Column Decoder A 9 A 14. Control Circuit
 32K X 8 STATIC RAM PRELIMINARY Features High-speed: 35, 70 ns Ultra low DC operating current of 5mA (max.) Low Power Dissipation: TTL Standby: 3 ma (Max.) CMOS Standby: 20 µa (Max.) Fully static operation
32K X 8 STATIC RAM PRELIMINARY Features High-speed: 35, 70 ns Ultra low DC operating current of 5mA (max.) Low Power Dissipation: TTL Standby: 3 ma (Max.) CMOS Standby: 20 µa (Max.) Fully static operation
IS61QDPB22M18C/C1/C2 IS61QDPB21M36C/C1/C2 2Mx18, 1Mx36 36Mb QUADP (Burst 2) Synchronous SRAM (2.5 CYCLE READ LATENCY)
 IS61QDPB21M36C/C1/C2 2Mx18, 1Mx36 36Mb QUADP (Burst 2) Synchronous SRAM (2.5 CYCLE READ LATENCY) APRIL 2016 FEATURES 1Mx36 and 2Mx18 configuration available. On-chip Delay-Locked Loop (DLL) for wide data
IS61QDPB21M36C/C1/C2 2Mx18, 1Mx36 36Mb QUADP (Burst 2) Synchronous SRAM (2.5 CYCLE READ LATENCY) APRIL 2016 FEATURES 1Mx36 and 2Mx18 configuration available. On-chip Delay-Locked Loop (DLL) for wide data

 Features All output pair skew
Features All output pair skew