FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY
|
|
|
- Kelly Summers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY Methods for Cell Analysis Course BioVis Uppsala, 2015 Matyas Molnar and Dirk Pacholsky 1
2 Information This lecture contains images and information from the following internet homepages
3 3
4 Light phenomenon 4
5 Light phenomenon 5
6 The human eye perceives app nm; best at around 500 nm (green) Has a general resolution down to μm (human hair: μm) We need a tool to see smaller things or more of the spectral range Microscope (Objective/Filter) Camera/Film 6
7 Light phenomenon Light photon particle and electromagnetic wave. λ E White light comprises of light of different λ (nm,color). Light travels in vacuum C = km/sec Seems to slows down in denser matter. Refractive index n = C/v (v= speed in matter) light is 1.5 x slower at n=1.5 Light changes direction between different dense materials : shorter λ refract more than longer λ Optic lenses, effects in sample... shorter wavelength (blue) has higher energy 7
8 WHY FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY? 8
9 Microscopical techniques Brightfield - low contrast for thin or transparent specimen - staining to enhance contrast needed (histochemical staining) Phase contrast - contrast via optical element (Phase ring) - intracellular structures can be seen - good for cell culture applications - negative: halos around cell bodies - combining with other techniques is generally poor (e.g. overlay with fluorescent image) 9
10 Microscopical techniques DIC/Nomarski - contrast via polarized light & optical element (Wollaston prism) - gives a (fake) topographical view - excellent for combination with fluorescence and histochemical staining Fluorescence - contrast via fluorescent staining - You see only what you stain (...in the perfect world) - special optical elements are needed (filter cubes) high resolution, high contrast, good for quantification (area + intensity) - Staining is sensitive - it can fade. 10
11 THE MICROSCOPE 11
12 Optical pathway of a microscope Objective projects image of specimen via Tube lens to Primary image plane Eyepiece magnifies this image. * Objectives are not interchangeable 12
13 Optical pathway of a microscope 1) Illuminator light source and different filters 2) Light conditioner e.g. phase annulus, FL excitation filter, polarizer 3) Condensor e.g. resolution, aberration 4) Specimen properties of specimen, immersion media, CS 5) Objective e.g. resolution, magnification, aberration working distance 6) Image filter e.g. Phase plate, FL emission filter, analyzer 7) Eyepiece e.g. magnification, field size 8) Detector human eye, camera 13
14 Optical pathway of a microscope 14
15 The objective or lens The heart of a microscope, may contain up to e.g. 12 lenses Specification and Identification - Magnification (enlargement) - Numerical aperture (resolution) - Immersion medium (should fit to embedding medium) - corrections (spherical; chromatical) - working distance - tube length (infinity or 160 mm) - coverslip thickness 15
16 Objective magnification and resolution A microscope magnifies a specimen with a certain resolution. 10x / high NA 10x / low NA objectives 20x N.A µm resolution 40x N.A µm resolution 60x N.A µm resolution Magnification without resolution is useless : empty magnification! 16
17 Illumination of the specimen Lens Light to/ from point source focal point in XZ Sample Z view Focal point Focal plane resolution in XY approx 2 x better than in Z The better the objective the smaller the focal point better means Numerical Aperture See next slide Field of view 17
18 Illumination of the specimen - resolution d = λ 2nsin θ d: point resolution, the shorter the lenght is better for us [nm] λ: wavelength of light used ([nm], visible light nm) n: refractive index (air: 1, water: 1.3, oil: ) ѳ: the maximum cone of light that can enter or exit the lens nsin(2 ѳ) : numerical aperture (NA) 18
19 Illumination of the specimen Lens hour glass shaped light cone indicates N.A. Larger N.A. Collects more photons sample Z direction Focal plane F Information (light) coming from above/below focus disturbs focus information. unsharp images get overlaid with sharp images from focus Blurred image in total Get rid of that extra to see only information from Focal plane by Calculations (e.g. Deconvolution) or Technique LSM...PINHOLE 19
20 Objective aberrations Chromatic aberration: color fringes light in different wavelength travels with different speed (refraction) therefore they won t meet in one focal point Spherical abberations: unsharp images Different focus of paraxial and peripheral light rays Corrections are possible 20
21 Objective aberrations - correction 21
22 Objective names Achromat, Planachromat chromatical corrected for RB, spherical corrected RB Fluar, Fluorite, Planfluorite chromatical corrected for RGB, spherical corrected RB Apochromat, Planapochromat high N.A. objectives, chromatical corrected for RGB+UV, spherical corrected RGB Different brands will have their own (confusing and abbreviated) objective names Planapochromates are the objectives to use if resolution and high quality photomicroscopy is needed. Plan objectives: normal lenses project a curved image. Plan lenses are flat-field corrected, both the center and the edge of the field is in focus. Plan-Neofluar is a fine universal objective for FL-microscopy. Use correct coverslip (1.5 = 170µm thickness), immersion for best imaging. 22
23 Resolution, Airy disk, NA & WD WD 23
24 Objective Resolution and Airy disk A point of light will not be a point of light Light originally coming from a point and passing through lenses etc. will not be a point again in the image, but rather a dot (1st maxima, AiryDisk) with several side maxima separated by mininima (interference pattern). he yellow dots shall indicate infinite points, where light originally came from. z Airy disk in XZ x The Spreading from Point light source to a Airy disk Image is called Point Spread Function (PSF). PSF gets bigger with mismatch of embedding medium and objective
25 Objective NA - Resolution and Airy disk One gains better Optical resolution by Increase of Numerical aperture (N.A.) of the objective used 25
26 Wavelength- Resolution and Airy disk One gains better Optical resolution by Decrease of wavelength of fluorophore used maximum resolution is approx µm lateral and 0.40 µm axial 26
27 Match embedding medium to objective. Light coming from high to low density medium (glas vs air) gets refracted away from the vertical of the incident angle, eventually misses the lense and is lost for imaging. Appliance of immersion (oil, glycerin, water) between Coverslip and Lense with similar refractive index as Glas will reduce refraction and enhance light yield which in turn gives better Airy pattern (resolution) Light coming from one point source will get scattered and refracted into different angles the point gets spreaded. By applying High Numerical Aperture this effects are kept to a minimum. PSF gets bigger with mismatch of embedding medium and objective
28 Practical tips Bad approach Match objective with correct - Immersion media - Coverslip thickness - Embedding media - Imaging setup - Sample preparation good approach - Objectives indicate for which immersion media they are made for - Objectives indicate for which coverslip thickness they are made for - Embedding medium has optimally same RI like immersion media - Place the sample as close as possible towards the objective lens - RI of sub-cellular components considerably lower than that of immersion media, and in many cases these RI are uncertain and vary throughout the specimen. Different fixations might destroy antigen to be targeted or might quench fluorescence (of e.g. GFP)
29 Resolution summary BEST RESOLUTION - NA as high as possible (1.4 max) - Refractive index of embedding medium like glass /oil - Use of immersion oil objective - Excitation/emission wavelength as short as possible (shift to blue region) d = λ 2nsin θ 29
30 Applications for fluorescent probes Proteins using antibodies Receptors using conjugated ligands DNA RNA Lipids Lectins to detect proteoglycans and glycolipids Cytoskeleton Organelles Tracers for cells and fluids Viability, proliferation Ions (Ca 2+,,Mg 2+, Zn 2+,Na +, K +, Cl -.) ROS ph Membrane potential 30
31 THE FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPE 31
32 Fluorescence Examples of fluorescent probes Principle of fluorescence Principle of fluorescent microscope Excitation-Emission filter cube
33 The fluorescence microscope Human eye perceives nm Camera/detector will do better mercury lamp Mercury (Xenon) lamp spectrum: (1300) nm Filtercube with band-pass-filter to choose wavelength for Excitation and Emission, including a special (dichroic) mirror.
34 Fluorescent dye spectra Spectra always bell shaped Normalized Intensity Alexa 488 Excitation spectra Which wavelength is best suited to excite this fluorophore? At 490 nm 100 % of fluorophore will get excited, but only 20% at 450 nm Emission spectra Wavelength of output emission it stays the same independent whether excitation was done with 490 nm or 450 nm BUT emission intensity will be lowered. nm
35 Dealing with fluorescence Cell sample Cell images merged RGB image 35
36 Dealing with fluorescence ex Cell sample Cell image* Excitation 350 nm excitates Blue and Green, using BP filter collects them both. *Remember: the camera is color blind. You decide with your choice of filter what it will see. 36
37 Dealing with fluorescence ex Cell sample Cell image* Excitation 350 nm excitates Blue and Green, using BP filter collects only the blue. *Remember: the camera is color blind. You decide with your choice of filter what it will see. 37
38 Dealing with fluorescence ex Cell sample Cell image* Excitation 480 nm excitates Green and Red, using BP filter collects only the green. *Remember: the camera is color blind. You decide with your choice of filter what it will see. 38
39 Combining fluorescent dyes - crosscheck To avoid false positive images in Fluorescence microscopy check for Seeing is Believing BUT Is it true? What s to be seen in pos/neg control stained unstained Crossreact AbX with AbY? AbX AbY(1) X Y AbX X Y AbY(2) Unspecific backgr. by Ab)? cell with - w/out target X X Appropr. fixation? Fixation A) X Fixation B) Crosstalk/ Bleeding through? ex Use quality objectives, correct filter, embedding medium 39
40 Widefield vs Optical section Kidney sample 10µm thick, 63x/NA 1.43, Widefield image and optical section using Apotome technique. 40
41 Bleaching Bleaching before and after 100x imaging same area with Widefield microscopy. Test sample is a strong stain and so bleaching might be subtle and only clearly be see in LUT (look-up-tables) Intensities of emission are shown in LUT Black to white LUT= Blue, over green, yellow, red You might not see the subtle changes But would like to compare Intensities Between image 1 and 2? Be aware... 41
42 IMAGING 42
43 Imaging digital camera - pixel (8bit) All pixels of the camera will be exposed to light at once; image is processed all pixels at once Black&White cameras pixel does not care about color. For Fluorescence microscopy use B&W cameras (with appropriate filtercubes) 43
44 Imaging Features of a digital camera Spatial Resolution: ability to capture fine specimen details without pixels being visible in image (1308x1040 pixel, 6.45x6.45µm pixel on 2/3 chip) Light-Intensity Resolution: dynamic range or number of gray levels that are distinguishable in image. (12 bit or 16 bit) Time Resolution: frame rate - the ability to follow movement or rapid kinetic processes (38 fps) Signal-to-Noise Ratio: visibility and clarity of specimen signals relative to the image background Spectral Sensitivity: range of wavelength on which camera reacts ( nm) (data from Zeiss Axiocam MRm) 44
45 Image quality over/underexposure Sample :3 color staining balanced imaging over/underexposure palette mode visualizing Over/under exposure Remember: all color is based on grey value Red: overexposed Blue: underexposed 45
46 Image quality dynamic range Acquire your image with appropriate grey level (8bit at least) to represent different intensity levels. Incoming photons 12 or 16 ( grey levels )bit images would also allow you e.g. to enhance features lying in the dark to stretch them into the light... 46
47 Image quality - resolution example for aliasing and pixel blocking Image should not appear pixelated have enough pixels not enough pixels result in aliasing (jagged edges) and pixel blocking More pixels needed? Larger Chip more expensive camera Smaller pixels size less sensitive, signal to noise ratio decreases Scientific cameras 6.45x6.45 µm pixel LSM-Systems variable pixel size 47
48 Imaging color vs black&white In Color Cameras each pixel is overlaid by color filter lense pattern The Bayer mosaic. Reduction of sensitivity and actual resolution + +/- +/- +/ Color pixel red only lets pass light in red range (+) signal. Rest of pixels are calculated in respect to surrounding pixels (+/-). i.e. 66% (2 of 3 colors /px). More green in the Bayer mosaic, therefore human eye is more sensitive to green. Problem: Actual resolution is 2x2 pixel i.e. 4x less Solution: camera with moveable chip are used each pixel will sample light from (9) different positions. High resolution Brightfield Black&White cameras pixel does not care about color. For Fluorescence microscopy use B&W cameras (with appropriate filtercubes) 48
49 Publishing photos Use the highest bit depth as possible, and take care about over/underexposure Use the highest quality/resolution as possible Use TIF files Crop image if neccessary Use measure bar to show scale Do not use total magnification, e. g. objective magnification - 60X (which is of course not 60X magnification but 600X at least) Magnification 1000x VS Measure bar ( light years) 49
50 THANKS FOR YOUR ATTENTION! 50
FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY. Matyas Molnar and Dirk Pacholsky
 FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY Matyas Molnar and Dirk Pacholsky 1 The human eye perceives app. 400-700 nm; best at around 500 nm (green) Has a general resolution down to150-300 μm (human hair: 40-250 μm) We need
FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY Matyas Molnar and Dirk Pacholsky 1 The human eye perceives app. 400-700 nm; best at around 500 nm (green) Has a general resolution down to150-300 μm (human hair: 40-250 μm) We need
Imaging Introduction. September 24, 2010
 Imaging Introduction September 24, 2010 What is a microscope? Merriam-Webster: an optical instrument consisting of a lens or combination of lenses for making enlarged images of minute objects; especially:
Imaging Introduction September 24, 2010 What is a microscope? Merriam-Webster: an optical instrument consisting of a lens or combination of lenses for making enlarged images of minute objects; especially:
CCAM Microscope Objectives
 CCAM Microscope Objectives Things to consider when selecting an objective Magnification Numerical Aperture (NA) resolving power and light intensity of the objective Working Distance distance between the
CCAM Microscope Objectives Things to consider when selecting an objective Magnification Numerical Aperture (NA) resolving power and light intensity of the objective Working Distance distance between the
BioVis Core Facility. Fluorescence. Quantitative Microscopy Course CBA Dirk Pacholsky
 BioVis Core Facility Fluorescence Quantitative Microscopy Course CBA 2012 Dirk Pacholsky 1 Information This lecture contains images and information from the following internet homepages http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/index.html
BioVis Core Facility Fluorescence Quantitative Microscopy Course CBA 2012 Dirk Pacholsky 1 Information This lecture contains images and information from the following internet homepages http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/index.html
Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement
 Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY BioVis Uppsala, 2017 Jeremy Adler Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Widefield & Confocal Microscopy
Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY BioVis Uppsala, 2017 Jeremy Adler Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Widefield & Confocal Microscopy
CCAM s Selection of. Zeiss Microscope Objectives
 CCAM s Selection of Zeiss Microscope Objectives 1. Magnification Image scale 2. Resolution The minimum separation distance between two points that are clearly resolved. The resolution of an objective is
CCAM s Selection of Zeiss Microscope Objectives 1. Magnification Image scale 2. Resolution The minimum separation distance between two points that are clearly resolved. The resolution of an objective is
Point Spread Function. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy. Confocal Aperture. Optical aberrations. Alternative Scanning Microscopy
 Bi177 Lecture 5 Adding the Third Dimension Wide-field Imaging Point Spread Function Deconvolution Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Confocal Aperture Optical aberrations Alternative Scanning Microscopy
Bi177 Lecture 5 Adding the Third Dimension Wide-field Imaging Point Spread Function Deconvolution Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Confocal Aperture Optical aberrations Alternative Scanning Microscopy
Light Microscopy. Upon completion of this lecture, the student should be able to:
 Light Light microscopy is based on the interaction of light and tissue components and can be used to study tissue features. Upon completion of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1- Explain the
Light Light microscopy is based on the interaction of light and tissue components and can be used to study tissue features. Upon completion of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1- Explain the
LSM 510 META in Chang Gung University
 Content LSM 510 META in Chang ung University LSM 510 META 路 理 The features and applications of LSM 510 META 01-09 Introduction of the hardware 10-12 Fluorescence observation in conventional microscope
Content LSM 510 META in Chang ung University LSM 510 META 路 理 The features and applications of LSM 510 META 01-09 Introduction of the hardware 10-12 Fluorescence observation in conventional microscope
Microscopy: Fundamental Principles and Practical Approaches
 Microscopy: Fundamental Principles and Practical Approaches Simon Atkinson Online Resource: http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/index.html Book: Murphy, D.B. Fundamentals of Light Microscopy and Electronic
Microscopy: Fundamental Principles and Practical Approaches Simon Atkinson Online Resource: http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/index.html Book: Murphy, D.B. Fundamentals of Light Microscopy and Electronic
Microscope anatomy, image formation and resolution
 Microscope anatomy, image formation and resolution Ian Dobbie Buy this book for your lab: D.B. Murphy, "Fundamentals of light microscopy and electronic imaging", ISBN 0-471-25391-X Visit these websites:
Microscope anatomy, image formation and resolution Ian Dobbie Buy this book for your lab: D.B. Murphy, "Fundamentals of light microscopy and electronic imaging", ISBN 0-471-25391-X Visit these websites:
microscopy A great online resource Molecular Expressions, a Microscope Primer Partha Roy
 Fundamentals of optical microscopy A great online resource Molecular Expressions, a Microscope Primer http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/index.html Partha Roy 1 Why microscopy Topics Functions of a microscope
Fundamentals of optical microscopy A great online resource Molecular Expressions, a Microscope Primer http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/index.html Partha Roy 1 Why microscopy Topics Functions of a microscope
Education in Microscopy and Digital Imaging
 Contact Us Carl Zeiss Education in Microscopy and Digital Imaging ZEISS Home Products Solutions Support Online Shop ZEISS International ZEISS Campus Home Interactive Tutorials Basic Microscopy Spectral
Contact Us Carl Zeiss Education in Microscopy and Digital Imaging ZEISS Home Products Solutions Support Online Shop ZEISS International ZEISS Campus Home Interactive Tutorials Basic Microscopy Spectral
BASICS IN BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS PLATFORM EPFL SV PTBIOP LIGHT MICROSCOPY
 BASICS IN LIGHT MICROSCOPY OVERVIEW 1. Motivation 2. Basic in optics 3. How microscope works 4. Illumination and resolution 5. Microscope optics 6. Contrasting methods -2- MOTIVATION Why do we need microscopy?
BASICS IN LIGHT MICROSCOPY OVERVIEW 1. Motivation 2. Basic in optics 3. How microscope works 4. Illumination and resolution 5. Microscope optics 6. Contrasting methods -2- MOTIVATION Why do we need microscopy?
Reflection! Reflection and Virtual Image!
 1/30/14 Reflection - wave hits non-absorptive surface surface of a smooth water pool - incident vs. reflected wave law of reflection - concept for all electromagnetic waves - wave theory: reflected back
1/30/14 Reflection - wave hits non-absorptive surface surface of a smooth water pool - incident vs. reflected wave law of reflection - concept for all electromagnetic waves - wave theory: reflected back
ANSWER KEY Lab 2 (IGB): Bright Field and Fluorescence Optical Microscopy and Sectioning
 Phys598BP Spring 2016 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign ANSWER KEY Lab 2 (IGB): Bright Field and Fluorescence Optical Microscopy and Sectioning Location: IGB Core Microscopy Facility Microscope:
Phys598BP Spring 2016 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign ANSWER KEY Lab 2 (IGB): Bright Field and Fluorescence Optical Microscopy and Sectioning Location: IGB Core Microscopy Facility Microscope:
Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev. Microscopy course, Michmoret Dec 2005
 Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Why use confocal microscopy? Principles of the laser scanning confocal microscope. Image resolution. Manipulating the
Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Why use confocal microscopy? Principles of the laser scanning confocal microscope. Image resolution. Manipulating the
Very short introduction to light microscopy and digital imaging
 Very short introduction to light microscopy and digital imaging Hernan G. Garcia August 1, 2005 1 Light Microscopy Basics In this section we will briefly describe the basic principles of operation and
Very short introduction to light microscopy and digital imaging Hernan G. Garcia August 1, 2005 1 Light Microscopy Basics In this section we will briefly describe the basic principles of operation and
MULTIPHOTON MICROSCOPY. Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky
 MULTIPHOTON MICROSCOPY Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Information Information given here about 2 Photon microscopy were mainly taken from these sources: Background information on 2-Photon microscopy: http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/techniques/fluorescence/multiphoton/
MULTIPHOTON MICROSCOPY Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Information Information given here about 2 Photon microscopy were mainly taken from these sources: Background information on 2-Photon microscopy: http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/techniques/fluorescence/multiphoton/
Lecture 23 MNS 102: Techniques for Materials and Nano Sciences
 Lecture 23 MNS 102: Techniques for Materials and Nano Sciences Reference: #1 C. R. Brundle, C. A. Evans, S. Wilson, "Encyclopedia of Materials Characterization", Butterworth-Heinemann, Toronto (1992),
Lecture 23 MNS 102: Techniques for Materials and Nano Sciences Reference: #1 C. R. Brundle, C. A. Evans, S. Wilson, "Encyclopedia of Materials Characterization", Butterworth-Heinemann, Toronto (1992),
The Nature of Light. Light and Energy
 The Nature of Light Light and Energy - dependent on energy from the sun, directly and indirectly - solar energy intimately associated with existence of life -light absorption: dissipate as heat emitted
The Nature of Light Light and Energy - dependent on energy from the sun, directly and indirectly - solar energy intimately associated with existence of life -light absorption: dissipate as heat emitted
1 Co Localization and Working flow with the lsm700
 1 Co Localization and Working flow with the lsm700 Samples -1 slide = mousse intestine, Dapi / Ki 67 with Cy3/ BrDU with alexa 488. -1 slide = mousse intestine, Dapi / Ki 67 with Cy3/ no BrDU (but with
1 Co Localization and Working flow with the lsm700 Samples -1 slide = mousse intestine, Dapi / Ki 67 with Cy3/ BrDU with alexa 488. -1 slide = mousse intestine, Dapi / Ki 67 with Cy3/ no BrDU (but with
Microscopy Training & Overview
 Microscopy Training & Overview Product Marketing October 2011 Stephan Briggs - PLE OVERVIEW AND PRESENTATION FLOW Glossary and Important Terms Introduction Timeline Innovation and Advancement Primary Components
Microscopy Training & Overview Product Marketing October 2011 Stephan Briggs - PLE OVERVIEW AND PRESENTATION FLOW Glossary and Important Terms Introduction Timeline Innovation and Advancement Primary Components
INTRODUCTION TO OPTICAL MICROSCOPY
 Experimental Biophysics TEK265, FYST23, TNF060, FAF010F Lab Exercise Supervisor: Karl Adolfsson Written by Peter Jönsson and Jason Beech Updated by Henrik Persson, Karl Adolfsson and Zhen Li karl.adolfsson@ftf.lth.se
Experimental Biophysics TEK265, FYST23, TNF060, FAF010F Lab Exercise Supervisor: Karl Adolfsson Written by Peter Jönsson and Jason Beech Updated by Henrik Persson, Karl Adolfsson and Zhen Li karl.adolfsson@ftf.lth.se
Examination, TEN1, in courses SK2500/SK2501, Physics of Biomedical Microscopy,
 KTH Applied Physics Examination, TEN1, in courses SK2500/SK2501, Physics of Biomedical Microscopy, 2009-06-05, 8-13, FB51 Allowed aids: Compendium Imaging Physics (handed out) Compendium Light Microscopy
KTH Applied Physics Examination, TEN1, in courses SK2500/SK2501, Physics of Biomedical Microscopy, 2009-06-05, 8-13, FB51 Allowed aids: Compendium Imaging Physics (handed out) Compendium Light Microscopy
Introduction to Light Microscopy. (Image: T. Wittman, Scripps)
 Introduction to Light Microscopy (Image: T. Wittman, Scripps) The Light Microscope Four centuries of history Vibrant current development One of the most widely used research tools A. Khodjakov et al. Major
Introduction to Light Microscopy (Image: T. Wittman, Scripps) The Light Microscope Four centuries of history Vibrant current development One of the most widely used research tools A. Khodjakov et al. Major
a) How big will that physical image of the cells be your camera sensor?
 1. Consider a regular wide-field microscope set up with a 60x, NA = 1.4 objective and a monochromatic digital camera with 8 um pixels, properly positioned in the primary image plane. This microscope is
1. Consider a regular wide-field microscope set up with a 60x, NA = 1.4 objective and a monochromatic digital camera with 8 um pixels, properly positioned in the primary image plane. This microscope is
Microscopy Techniques that make it easy to see things this small.
 Microscopy Techniques that make it easy to see things this small. What is a Microscope? An instrument for viewing objects that are too small to be seen easily by the naked eye. Dutch spectacle-makers Hans
Microscopy Techniques that make it easy to see things this small. What is a Microscope? An instrument for viewing objects that are too small to be seen easily by the naked eye. Dutch spectacle-makers Hans
Chapter 2 The Study of Microbial Structure: Microscopy and Specimen Preparation
 Chapter 2 The Study of Microbial Structure: Microscopy and Specimen Preparation 1 Lenses and the Bending of Light light is refracted (bent) when passing from one medium to another refractive index a measure
Chapter 2 The Study of Microbial Structure: Microscopy and Specimen Preparation 1 Lenses and the Bending of Light light is refracted (bent) when passing from one medium to another refractive index a measure
3D light microscopy techniques
 3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 1 1 2! NA = 0.5! NA 2D imaging
3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 1 1 2! NA = 0.5! NA 2D imaging
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE DEPTH STUDY: ELECTRON MICROSCOPES
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE DEPTH STUDY: ELECTRON MICROSCOPES Shortly after the experimental confirmation of the wave properties of the electron, it was suggested that the electron could be used to examine objects
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE DEPTH STUDY: ELECTRON MICROSCOPES Shortly after the experimental confirmation of the wave properties of the electron, it was suggested that the electron could be used to examine objects
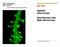
Figure 3.4 Approximate size of various types of cells. ~10 um. Red Blood Cells = mm 1500 um. Width of penny Pearson Education, Inc.
 Figure 3.4 Approximate size of various types of cells. ~10 um Red Blood Cells 1.5mm 1500 um Width of penny = 1500 Figure 4.3 The limits of resolution (and some representative objects within those ranges)
Figure 3.4 Approximate size of various types of cells. ~10 um Red Blood Cells 1.5mm 1500 um Width of penny = 1500 Figure 4.3 The limits of resolution (and some representative objects within those ranges)
MULTIPHOTON MICROSCOPY
 MULTIPHOTON MICROSCOPY Methods for Cell Analysis Course BioVis Uppsala, 2014 Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Information Information given here about 2 Photon microscopy were mainly taken from these sources:
MULTIPHOTON MICROSCOPY Methods for Cell Analysis Course BioVis Uppsala, 2014 Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Information Information given here about 2 Photon microscopy were mainly taken from these sources:
Microscopy. Matti Hotokka Department of Physical Chemistry Åbo Akademi University
 Microscopy Matti Hotokka Department of Physical Chemistry Åbo Akademi University What s coming Anatomy of a microscope Modes of illumination Practicalities Special applications Basic microscope Ocular
Microscopy Matti Hotokka Department of Physical Chemistry Åbo Akademi University What s coming Anatomy of a microscope Modes of illumination Practicalities Special applications Basic microscope Ocular
Tissue Preparation ORGANISM IMAGE TISSUE PREPARATION. 1) Fixation: halts cell metabolism, preserves cell/tissue structure
 Lab starts this week! ANNOUNCEMENTS - Tuesday or Wednesday 1:25 ISB 264 - Read Lab 1: Microscopy and Imaging (see Web Page) - Getting started on Lab Group project - Organ for investigation - Lab project
Lab starts this week! ANNOUNCEMENTS - Tuesday or Wednesday 1:25 ISB 264 - Read Lab 1: Microscopy and Imaging (see Web Page) - Getting started on Lab Group project - Organ for investigation - Lab project
Invitation for a walk through microscopy. Sebastian Schuchmann Jörg Rösner
 Invitation for a walk through microscopy Sebastian Schuchmann Jörg Rösner joerg.roesner@charite.de Techniques in microscopy Conventional (light) microscopy bright & dark field, phase & interference contrast
Invitation for a walk through microscopy Sebastian Schuchmann Jörg Rösner joerg.roesner@charite.de Techniques in microscopy Conventional (light) microscopy bright & dark field, phase & interference contrast
LSM 510 Meta Training Notes
 LSM 510 Meta Training Notes Turning on the system Turn on X-Cite power supply. This supplies light for epifluorescence for viewing your samples through the microscope. Turn on the remote control switch.
LSM 510 Meta Training Notes Turning on the system Turn on X-Cite power supply. This supplies light for epifluorescence for viewing your samples through the microscope. Turn on the remote control switch.
High resolution extended depth of field microscopy using wavefront coding
 High resolution extended depth of field microscopy using wavefront coding Matthew R. Arnison *, Peter Török #, Colin J. R. Sheppard *, W. T. Cathey +, Edward R. Dowski, Jr. +, Carol J. Cogswell *+ * Physical
High resolution extended depth of field microscopy using wavefront coding Matthew R. Arnison *, Peter Török #, Colin J. R. Sheppard *, W. T. Cathey +, Edward R. Dowski, Jr. +, Carol J. Cogswell *+ * Physical
LSM 510 Training Notes
 LSM 510 Training Notes Turning on the system Turn on the arc lamp, found on the bench top left of the microscope. This supplies light for epifluorescence for viewing your samples through the microscope.
LSM 510 Training Notes Turning on the system Turn on the arc lamp, found on the bench top left of the microscope. This supplies light for epifluorescence for viewing your samples through the microscope.
Basics of confocal imaging (part I)
 Basics of confocal imaging (part I) Swiss Institute of Technology (EPFL) Faculty of Life Sciences Head of BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS BIOP arne.seitz@epfl.ch Lateral resolution BioImaging &Optics Platform Light
Basics of confocal imaging (part I) Swiss Institute of Technology (EPFL) Faculty of Life Sciences Head of BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS BIOP arne.seitz@epfl.ch Lateral resolution BioImaging &Optics Platform Light
Rates of excitation, emission, ISC
 Bi177 Lecture 4 Fluorescence Microscopy Phenomenon of Fluorescence Energy Diagram Rates of excitation, emission, ISC Practical Issues Lighting, Filters More on diffraction Point Spread Functions Thus Far,
Bi177 Lecture 4 Fluorescence Microscopy Phenomenon of Fluorescence Energy Diagram Rates of excitation, emission, ISC Practical Issues Lighting, Filters More on diffraction Point Spread Functions Thus Far,
INTRODUCTION THIN LENSES. Introduction. given by the paraxial refraction equation derived last lecture: Thin lenses (19.1) = 1. Double-lens systems
 Chapter 9 OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS Introduction Thin lenses Double-lens systems Aberrations Camera Human eye Compound microscope Summary INTRODUCTION Knowledge of geometrical optics, diffraction and interference,
Chapter 9 OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS Introduction Thin lenses Double-lens systems Aberrations Camera Human eye Compound microscope Summary INTRODUCTION Knowledge of geometrical optics, diffraction and interference,
Practical work no. 3: Confocal Live Cell Microscopy
 Practical work no. 3: Confocal Live Cell Microscopy Course Instructor: Mikko Liljeström (MIU) 1 Background Confocal microscopy: The main idea behind confocality is that it suppresses the signal outside
Practical work no. 3: Confocal Live Cell Microscopy Course Instructor: Mikko Liljeström (MIU) 1 Background Confocal microscopy: The main idea behind confocality is that it suppresses the signal outside
SETTING UP OF A TOTAL INTERNAL REFLECTION FLUORESCENT MICROSCOPE (TIRFM) SYSTEM: A DETAILED OVERVIEW
 PK ISSN 0022-2941; CODEN JNSMAC Vol. 51, (2011) PP 31-45 SETTING UP OF A TOTAL INTERNAL REFLECTION FLUORESCENT MICROSCOPE (TIRFM) SYSTEM: A DETAILED OVERVIEW A. R. KHAN 1 *, S. AKHLAQ 1, M. N. B. ABID
PK ISSN 0022-2941; CODEN JNSMAC Vol. 51, (2011) PP 31-45 SETTING UP OF A TOTAL INTERNAL REFLECTION FLUORESCENT MICROSCOPE (TIRFM) SYSTEM: A DETAILED OVERVIEW A. R. KHAN 1 *, S. AKHLAQ 1, M. N. B. ABID
Operating Instructions for Zeiss LSM 510
 Operating Instructions for Zeiss LSM 510 Location: GNL 6.312q (BSL3) Questions? Contact: Maxim Ivannikov, maivanni@utmb.edu 1 Attend A Complementary Training Before Using The Microscope All future users
Operating Instructions for Zeiss LSM 510 Location: GNL 6.312q (BSL3) Questions? Contact: Maxim Ivannikov, maivanni@utmb.edu 1 Attend A Complementary Training Before Using The Microscope All future users
Observing Microorganisms through a Microscope LIGHT MICROSCOPY: This type of microscope uses visible light to observe specimens. Compound Light Micros
 PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY JIGAR SHAH INSTITUTE OF PHARMACY NIRMA UNIVERSITY Observing Microorganisms through a Microscope LIGHT MICROSCOPY: This type of microscope uses visible light to observe specimens.
PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY JIGAR SHAH INSTITUTE OF PHARMACY NIRMA UNIVERSITY Observing Microorganisms through a Microscope LIGHT MICROSCOPY: This type of microscope uses visible light to observe specimens.
Applications of Optics
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 26 Applications of Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Applications of Optics Many devices are based on the principles of optics
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 26 Applications of Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Applications of Optics Many devices are based on the principles of optics
PHYSICS. Chapter 35 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 35 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 35 Optical Instruments IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about some common optical instruments and
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 35 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 35 Optical Instruments IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about some common optical instruments and
Biology 29 Cell Structure and Function Spring, 2009 Springer LABORATORY 1: THE LIGHT MICROSCOPE
 Biology 29 Cell Structure and Function Spring, 2009 Springer LABORATORY 1: THE LIGHT MICROSCOPE Prior to lab: 1) Read these instructions (p 1-6) 2) Go through the online tutorial, the microscopy pre-lab
Biology 29 Cell Structure and Function Spring, 2009 Springer LABORATORY 1: THE LIGHT MICROSCOPE Prior to lab: 1) Read these instructions (p 1-6) 2) Go through the online tutorial, the microscopy pre-lab
Bio 407. Applied microscopy. Introduction into light microscopy. José María Mateos. Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis
 Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Bio 407 Applied Introduction into light José María Mateos Fundamentals of light Compound microscope Microscope composed of an objective and an additional lens (eyepiece,
Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Bio 407 Applied Introduction into light José María Mateos Fundamentals of light Compound microscope Microscope composed of an objective and an additional lens (eyepiece,
TRAINING MANUAL. Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO
 TRAINING MANUAL Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO September 2010 Multiphoton Microscopy Training Manual Multiphoton microscopy is only available on the LSM 510 META-NLO system. This system is equipped
TRAINING MANUAL Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO September 2010 Multiphoton Microscopy Training Manual Multiphoton microscopy is only available on the LSM 510 META-NLO system. This system is equipped
ZEISS LSM510META confocal manual
 ZEISS LSM510META confocal manual Switching on the system 1) Switch on the Remote Control button located on the table to the right of the microscope. This is the main switch for the whole system including
ZEISS LSM510META confocal manual Switching on the system 1) Switch on the Remote Control button located on the table to the right of the microscope. This is the main switch for the whole system including
Chapter 17: Wave Optics. What is Light? The Models of Light 1/11/13
 Chapter 17: Wave Optics Key Terms Wave model Ray model Diffraction Refraction Fringe spacing Diffraction grating Thin-film interference What is Light? Light is the chameleon of the physical world. Under
Chapter 17: Wave Optics Key Terms Wave model Ray model Diffraction Refraction Fringe spacing Diffraction grating Thin-film interference What is Light? Light is the chameleon of the physical world. Under
BASICS OF CONFOCAL IMAGING (PART I)
 BASICS OF CONFOCAL IMAGING (PART I) INTERNAL COURSE 2012 LIGHT MICROSCOPY Lateral resolution Transmission Fluorescence d min 1.22 NA obj NA cond 0 0 rairy 0.61 NAobj Ernst Abbe Lord Rayleigh Depth of field
BASICS OF CONFOCAL IMAGING (PART I) INTERNAL COURSE 2012 LIGHT MICROSCOPY Lateral resolution Transmission Fluorescence d min 1.22 NA obj NA cond 0 0 rairy 0.61 NAobj Ernst Abbe Lord Rayleigh Depth of field
Zeiss LSM 510 Confocor III Training Notes. Center for Cell Analysis & Modeling
 Zeiss LSM 510 Confocor III Training Notes Center for Cell Analysis & Modeling Confocor 3 Start Up Go to System Module Turn on Main Switch, System/ PC, and Components Switches Do you need the arc lamp?
Zeiss LSM 510 Confocor III Training Notes Center for Cell Analysis & Modeling Confocor 3 Start Up Go to System Module Turn on Main Switch, System/ PC, and Components Switches Do you need the arc lamp?
Things to check before start-up.
 Byeong Cha Page 1 11/24/2009 Manual for Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Enter you name, the date, the time, and the account number in the user log book. Things to check before start-up. Make sure that your
Byeong Cha Page 1 11/24/2009 Manual for Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Enter you name, the date, the time, and the account number in the user log book. Things to check before start-up. Make sure that your
Resolution. Diffraction from apertures limits resolution. Rayleigh criterion θ Rayleigh = 1.22 λ/d 1 peak at 2 nd minimum. θ f D
 Microscopy Outline 1. Resolution and Simple Optical Microscope 2. Contrast enhancement: Dark field, Fluorescence (Chelsea & Peter), Phase Contrast, DIC 3. Newer Methods: Scanning Tunneling microscopy (STM),
Microscopy Outline 1. Resolution and Simple Optical Microscope 2. Contrast enhancement: Dark field, Fluorescence (Chelsea & Peter), Phase Contrast, DIC 3. Newer Methods: Scanning Tunneling microscopy (STM),
 Microscopy http://www.microscopyu.com/articles/phasecontrast/phasemicroscopy.html http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/anatomy/anatomy.html 2005, Dr. Jack Ikeda & Dr. Gail Grabner 9 Nikon Labophot (Question
Microscopy http://www.microscopyu.com/articles/phasecontrast/phasemicroscopy.html http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/anatomy/anatomy.html 2005, Dr. Jack Ikeda & Dr. Gail Grabner 9 Nikon Labophot (Question
BASICS IN LIGHT MICROSCOPY
 BASICS IN LIGHT MICROSCOPY INTERNAL COURSE 2015 26 TH JANUARY OVERVIEW Light microscopy Why do we need it? How does it work? What are its limitations? What do we need to consider? - 2 - HUMAN EYE Normal
BASICS IN LIGHT MICROSCOPY INTERNAL COURSE 2015 26 TH JANUARY OVERVIEW Light microscopy Why do we need it? How does it work? What are its limitations? What do we need to consider? - 2 - HUMAN EYE Normal
Observing Microorganisms through a Microscope
 2016/2/19 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College CHAPTER 3 Observing Microorganisms through a Microscope 1 Figure 3.2 Microscopes and Magnification.
2016/2/19 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College CHAPTER 3 Observing Microorganisms through a Microscope 1 Figure 3.2 Microscopes and Magnification.
Fundamentals of Light Microscopy II: Fluorescence, Deconvolution, Confocal, Multiphoton, Spectral microscopy. Integrated Microscopy Course
 Fundamentals of Light Microscopy II: Fluorescence, Deconvolution, Confocal, Multiphoton, Spectral microscopy Integrated Microscopy Course Review Lecture 1: Microscopy Basics Light train Kohler illumination*
Fundamentals of Light Microscopy II: Fluorescence, Deconvolution, Confocal, Multiphoton, Spectral microscopy Integrated Microscopy Course Review Lecture 1: Microscopy Basics Light train Kohler illumination*
Final Exam, 150 points PMB 185: Techniques in Light Microscopy
 Final Exam, 150 points Name PMB 185: Techniques in Light Microscopy Point value is in parentheses at the end of each question. Note: GFP = green fluorescent protein ; CFP = cyan fluorescent protein ; YFP
Final Exam, 150 points Name PMB 185: Techniques in Light Microscopy Point value is in parentheses at the end of each question. Note: GFP = green fluorescent protein ; CFP = cyan fluorescent protein ; YFP
Nikon. King s College London. Imaging Centre. N-SIM guide NIKON IMAGING KING S COLLEGE LONDON
 N-SIM guide NIKON IMAGING CENTRE @ KING S COLLEGE LONDON Starting-up / Shut-down The NSIM hardware is calibrated after system warm-up occurs. It is recommended that you turn-on the system for at least
N-SIM guide NIKON IMAGING CENTRE @ KING S COLLEGE LONDON Starting-up / Shut-down The NSIM hardware is calibrated after system warm-up occurs. It is recommended that you turn-on the system for at least
Compound Light Microscopy. Microscopy. Things to remember... 1/22/2017. This is what we use in the laboratory
 Compound Light Microscopy This is what we use in the laboratory Microscopy Chapter 3 BIO 440 A series of finely ground lenses is used to form a magnified image Specimen is illuminated with visible light
Compound Light Microscopy This is what we use in the laboratory Microscopy Chapter 3 BIO 440 A series of finely ground lenses is used to form a magnified image Specimen is illuminated with visible light
Motorized Axio Observer Start-up instructions
 Start-up instructions 1. If using fluorescence turn on Fluorescent light source. TL light Source (Hal 100) 2. Turn on microscope using switch on lower left side of the microscope. 3. If imaging, turn on
Start-up instructions 1. If using fluorescence turn on Fluorescent light source. TL light Source (Hal 100) 2. Turn on microscope using switch on lower left side of the microscope. 3. If imaging, turn on
2/4/15. Brightfield Microscopy! It s all about Magnification..! or is it?!
 Brightfield Microscopy It s all about Magnification.. or is it? 1 What actually does go into chosing a microscope Choice depends on what you need the microscope to do. Do you want to magnify stained specimens?
Brightfield Microscopy It s all about Magnification.. or is it? 1 What actually does go into chosing a microscope Choice depends on what you need the microscope to do. Do you want to magnify stained specimens?
3D light microscopy techniques
 3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 2D imaging 3D imaging Resolution
3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 2D imaging 3D imaging Resolution
Light microscopy BMB 173, Lecture 14, Feb. 21, 2018
 Light microscopy The Structural Biology Continuum Next two lectures: Light microscopy Many slides taken from Scott Fraser, Murphy s Fundamentals of light microscopy, Alberts Molecular Biology of the Cell,
Light microscopy The Structural Biology Continuum Next two lectures: Light microscopy Many slides taken from Scott Fraser, Murphy s Fundamentals of light microscopy, Alberts Molecular Biology of the Cell,
Confocal Microscopy and Related Techniques
 Confocal Microscopy and Related Techniques Chau-Hwang Lee Associate Research Fellow Research Center for Applied Sciences, Academia Sinica 128 Sec. 2, Academia Rd., Nankang, Taipei 11529, Taiwan E-mail:
Confocal Microscopy and Related Techniques Chau-Hwang Lee Associate Research Fellow Research Center for Applied Sciences, Academia Sinica 128 Sec. 2, Academia Rd., Nankang, Taipei 11529, Taiwan E-mail:
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2003 Final Exam. Name:
 EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2003 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. THREE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2003 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. THREE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
Introduction to light microscopy
 Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light Basic concepts of imaging with light Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Microscopy with light 1 Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction
Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light Basic concepts of imaging with light Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Microscopy with light 1 Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction
Life Science Chapter 2 Study Guide
 Key concepts and definitions Waves and the Electromagnetic Spectrum Wave Energy Medium Mechanical waves Amplitude Wavelength Frequency Speed Properties of Waves (pages 40-41) Trough Crest Hertz Electromagnetic
Key concepts and definitions Waves and the Electromagnetic Spectrum Wave Energy Medium Mechanical waves Amplitude Wavelength Frequency Speed Properties of Waves (pages 40-41) Trough Crest Hertz Electromagnetic
3. are adherent cells (ie. cells in suspension are too far away from the coverslip)
 Before you begin, make sure your sample... 1. is seeded on #1.5 coverglass (thickness = 0.17) 2. is an aqueous solution (ie. fixed samples mounted on a slide will not work - not enough difference in refractive
Before you begin, make sure your sample... 1. is seeded on #1.5 coverglass (thickness = 0.17) 2. is an aqueous solution (ie. fixed samples mounted on a slide will not work - not enough difference in refractive
LlIGHT REVIEW PART 2 DOWNLOAD, PRINT and submit for 100 points
 WRITE ON SCANTRON WITH NUMBER 2 PENCIL DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST LlIGHT REVIEW PART 2 DOWNLOAD, PRINT and submit for 100 points Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or
WRITE ON SCANTRON WITH NUMBER 2 PENCIL DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST LlIGHT REVIEW PART 2 DOWNLOAD, PRINT and submit for 100 points Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or
Lecture 16. OMX - Structured Illumination Microscopy Ian Dobbie x Microscopy Course Lecture 16 1
 Lecture 16 OMX - Structured Illumination Microscopy Ian Dobbie x13323 Microscopy Course 2014 - Lecture 16 1 Super-resolution fluorescence microscopy Specificity Sensitivity Non-invasive (in situ & in vivo)
Lecture 16 OMX - Structured Illumination Microscopy Ian Dobbie x13323 Microscopy Course 2014 - Lecture 16 1 Super-resolution fluorescence microscopy Specificity Sensitivity Non-invasive (in situ & in vivo)
Instruction Manual T Binocular Acromat Research Scope T Trinocular Acromat Research Scope
 Research Scope Instruction Manual T-29031 Binocular Acromat Research Scope T-29041 Trinocular Acromat Research Scope T-29032 Binocular Semi-Plan Research Scope T-29042 Trinocular Semi-Plan Research Scope
Research Scope Instruction Manual T-29031 Binocular Acromat Research Scope T-29041 Trinocular Acromat Research Scope T-29032 Binocular Semi-Plan Research Scope T-29042 Trinocular Semi-Plan Research Scope
Overview of the Microscope Objective
 Overview of the Microscope Objective Item Type text; Electronic Thesis Authors Niu, Ruijuan Publisher The University of Arizona. Rights Copyright is held by the author. Digital access to this material
Overview of the Microscope Objective Item Type text; Electronic Thesis Authors Niu, Ruijuan Publisher The University of Arizona. Rights Copyright is held by the author. Digital access to this material
Chapter 25. Optical Instruments
 Chapter 25 Optical Instruments Optical Instruments Analysis generally involves the laws of reflection and refraction Analysis uses the procedures of geometric optics To explain certain phenomena, the wave
Chapter 25 Optical Instruments Optical Instruments Analysis generally involves the laws of reflection and refraction Analysis uses the procedures of geometric optics To explain certain phenomena, the wave
Script Bio 407 Applied Microscopy Light microscopy
 Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Dr. José María Mateos Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Winterthurerstrasse 190 CH-8057 Zurich Phone 044 635 98 20 mateos@zmb.uzh.ch www.zmb.uzh.ch Script
Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Dr. José María Mateos Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Winterthurerstrasse 190 CH-8057 Zurich Phone 044 635 98 20 mateos@zmb.uzh.ch www.zmb.uzh.ch Script
OPELCO OPtical ELements COrporation LB Objective Series for Biological Use
 LB Objective Series for Biological Use 105 Executive Drive Suite 100 Dulles, VA 20166-9558 Tel: (703) 471-0080 S PLAN APOCHROMAT OBJECTIVES These objectives compensate for three wavelength of chromatic
LB Objective Series for Biological Use 105 Executive Drive Suite 100 Dulles, VA 20166-9558 Tel: (703) 471-0080 S PLAN APOCHROMAT OBJECTIVES These objectives compensate for three wavelength of chromatic
Optical Design of. Microscopes. George H. Seward. Tutorial Texts in Optical Engineering Volume TT88. SPIE PRESS Bellingham, Washington USA
 Optical Design of Microscopes George H. Seward Tutorial Texts in Optical Engineering Volume TT88 SPIE PRESS Bellingham, Washington USA Preface xiii Chapter 1 Optical Design Concepts /1 1.1 A Value Proposition
Optical Design of Microscopes George H. Seward Tutorial Texts in Optical Engineering Volume TT88 SPIE PRESS Bellingham, Washington USA Preface xiii Chapter 1 Optical Design Concepts /1 1.1 A Value Proposition
The following units are required for an ApoTome imaging workstation:
 V VKN fã~öé=^åèìáëáíáçå=jççìäéë= ^éçqçãé= déåéê~ä= The ApoTome software module controls the ApoTome hardware (control box and slider) and coordinated image acquisition using a digital camera, such as the
V VKN fã~öé=^åèìáëáíáçå=jççìäéë= ^éçqçãé= déåéê~ä= The ApoTome software module controls the ApoTome hardware (control box and slider) and coordinated image acquisition using a digital camera, such as the
Objectives from Carl Zeiss Exceeding Your Expectations
 Microscopy from Carl Zeiss bjectives from Carl Zeiss Exceeding Your Expectations Brilliant Imaging for Research and Routine Work in Life Sciences When Your Research Pushes the Boundaries of What Is Visible,
Microscopy from Carl Zeiss bjectives from Carl Zeiss Exceeding Your Expectations Brilliant Imaging for Research and Routine Work in Life Sciences When Your Research Pushes the Boundaries of What Is Visible,
MICROSCOPE LAB. Resolving Power How well specimen detail is preserved during the magnifying process.
 AP BIOLOGY Cells ACTIVITY #2 MICROSCOPE LAB OBJECTIVES 1. Demonstrate proper care and use of a compound microscope. 2. Identify the parts of the microscope and describe the function of each part. 3. Compare
AP BIOLOGY Cells ACTIVITY #2 MICROSCOPE LAB OBJECTIVES 1. Demonstrate proper care and use of a compound microscope. 2. Identify the parts of the microscope and describe the function of each part. 3. Compare
Supplemental Figure 1: Histogram of 63x Objective Lens z axis Calculated Resolutions. Results from the MetroloJ z axis fits for 5 beads from each
 Supplemental Figure 1: Histogram of 63x Objective Lens z axis Calculated Resolutions. Results from the MetroloJ z axis fits for 5 beads from each lens with a 1 Airy unit pinhole setting. Many water lenses
Supplemental Figure 1: Histogram of 63x Objective Lens z axis Calculated Resolutions. Results from the MetroloJ z axis fits for 5 beads from each lens with a 1 Airy unit pinhole setting. Many water lenses
BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS PLATFORM EPFL SV PTBIOP BASICS IN LIGHT MICROSCOPY
 BASICS IN LIGHT MICROSCOPY INTERNAL COURSE 2014 13 TH JANUARY OVERVIEW 1. Motivation 2. Basic in optics 3. How microscope works 4. Illumination and resolution 5. Microscope optics 6. Contrasting methods
BASICS IN LIGHT MICROSCOPY INTERNAL COURSE 2014 13 TH JANUARY OVERVIEW 1. Motivation 2. Basic in optics 3. How microscope works 4. Illumination and resolution 5. Microscope optics 6. Contrasting methods
Katarina Logg, Kristofer Bodvard, Mikael Käll. Dept. of Applied Physics. 12 September Optical Microscopy. Supervisor s signature:...
 Katarina Logg, Kristofer Bodvard, Mikael Käll Dept. of Applied Physics 12 September 2007 O1 Optical Microscopy Name:.. Date:... Supervisor s signature:... Introduction Over the past decades, the number
Katarina Logg, Kristofer Bodvard, Mikael Käll Dept. of Applied Physics 12 September 2007 O1 Optical Microscopy Name:.. Date:... Supervisor s signature:... Introduction Over the past decades, the number
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Fall 2009 Final Exam. Name:
 EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Fall 2009 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. THREE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Fall 2009 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. THREE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics. Geometrical Approximation. Lenses. Mirrors. Optical Systems. Images and Pupils. Aberrations.
 Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics Outline 1 Geometrical Approximation 2 Lenses 3 Mirrors 4 Optical Systems 5 Images and Pupils 6 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden Observatory, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics Outline 1 Geometrical Approximation 2 Lenses 3 Mirrors 4 Optical Systems 5 Images and Pupils 6 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden Observatory, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Zeiss Axiovert 135 Fluorescence Microscope Quick Guide / Operations Manual (v. 1.0 February 09)
 University of Chicago Integrated Light Microscopy Core Dr. Vytas Bindokas, Director http://digital.bsd.uchicago.edu By: Christine Labno, Assistant Director Room: AB-129 Phone: 4-9040 Zeiss Axiovert 135
University of Chicago Integrated Light Microscopy Core Dr. Vytas Bindokas, Director http://digital.bsd.uchicago.edu By: Christine Labno, Assistant Director Room: AB-129 Phone: 4-9040 Zeiss Axiovert 135
Bi/BE 227 Winter Assignment #3. Adding the third dimension: 3D Confocal Imaging
 Bi/BE 227 Winter 2016 Assignment #3 Adding the third dimension: 3D Confocal Imaging Schedule: Jan 20: Assignment Jan 20-Feb 8: Work on assignment Feb 10: Student PowerPoint presentations. Goals for this
Bi/BE 227 Winter 2016 Assignment #3 Adding the third dimension: 3D Confocal Imaging Schedule: Jan 20: Assignment Jan 20-Feb 8: Work on assignment Feb 10: Student PowerPoint presentations. Goals for this
SUBJECT: PHYSICS. Use and Succeed.
 SUBJECT: PHYSICS I hope this collection of questions will help to test your preparation level and useful to recall the concepts in different areas of all the chapters. Use and Succeed. Navaneethakrishnan.V
SUBJECT: PHYSICS I hope this collection of questions will help to test your preparation level and useful to recall the concepts in different areas of all the chapters. Use and Succeed. Navaneethakrishnan.V
Chapter 3 Op,cal Instrumenta,on
 Imaging by an Op,cal System Change in curvature of wavefronts by a thin lens Chapter 3 Op,cal Instrumenta,on 3-1 Stops, Pupils, and Windows 3-4 The Camera 3-5 Simple Magnifiers and Eyepieces 1. Magnifiers
Imaging by an Op,cal System Change in curvature of wavefronts by a thin lens Chapter 3 Op,cal Instrumenta,on 3-1 Stops, Pupils, and Windows 3-4 The Camera 3-5 Simple Magnifiers and Eyepieces 1. Magnifiers
ABC Math Student Copy. N. May ABC Math Student Copy. Physics Week 13(Sem. 2) Name. Light Chapter Summary Cont d 2
 Page 1 of 12 Physics Week 13(Sem. 2) Name Light Chapter Summary Cont d 2 Lens Abberation Lenses can have two types of abberation, spherical and chromic. Abberation occurs when the rays forming an image
Page 1 of 12 Physics Week 13(Sem. 2) Name Light Chapter Summary Cont d 2 Lens Abberation Lenses can have two types of abberation, spherical and chromic. Abberation occurs when the rays forming an image
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup.
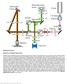 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup. Excitation from a femtosecond laser is passed through intensity control and shuttering optics (1/2 λ wave plate, polarizing beam splitting
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup. Excitation from a femtosecond laser is passed through intensity control and shuttering optics (1/2 λ wave plate, polarizing beam splitting
IC 2 S High Performance Objectives
 M i c r o s c o p y f r o m C a r l Z e i s s IC 2 S igh Performance Objectives for Biomedical Applications with Laser Based Imaging Systems LSM,, ConfoCor, TIRF and ELYRA Carl Zeiss offers a large range
M i c r o s c o p y f r o m C a r l Z e i s s IC 2 S igh Performance Objectives for Biomedical Applications with Laser Based Imaging Systems LSM,, ConfoCor, TIRF and ELYRA Carl Zeiss offers a large range
START-UP PROCEDURE 1 THE MICROSCOPE STAND 3 OBJECTIVES 5 STARTING WITH LAS (SOFTWARE) AND SETTING UP THE MICROSCOPE STAND 7
 Leica DMI AF6000LX Table of contents START-UP PROCEDURE 1 THE MICROSCOPE STAND 3 OBJECTIVES 5 STARTING WITH LAS (SOFTWARE) AND SETTING UP THE MICROSCOPE STAND 7 ACQUIRE MODULE 6 SETTING THE LIGHTPATH 6
Leica DMI AF6000LX Table of contents START-UP PROCEDURE 1 THE MICROSCOPE STAND 3 OBJECTIVES 5 STARTING WITH LAS (SOFTWARE) AND SETTING UP THE MICROSCOPE STAND 7 ACQUIRE MODULE 6 SETTING THE LIGHTPATH 6
Introduction to light microscopy
 Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light microscopy Basic concepts of imaging with light Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction Diffraction
Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light microscopy Basic concepts of imaging with light Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction Diffraction
Chapter 3 Op+cal Instrumenta+on
 Chapter 3 Op+cal Instrumenta+on 3-1 Stops, Pupils, and Windows 3-4 The Camera 3-5 Simple Magnifiers and Eyepieces 3-6 Microscopes 3-7 Telescopes Today (2011-09-22) 1. Magnifiers 2. Camera 3. Resolution
Chapter 3 Op+cal Instrumenta+on 3-1 Stops, Pupils, and Windows 3-4 The Camera 3-5 Simple Magnifiers and Eyepieces 3-6 Microscopes 3-7 Telescopes Today (2011-09-22) 1. Magnifiers 2. Camera 3. Resolution
BEAM HALO OBSERVATION BY CORONAGRAPH
 BEAM HALO OBSERVATION BY CORONAGRAPH T. Mitsuhashi, KEK, TSUKUBA, Japan Abstract We have developed a coronagraph for the observation of the beam halo surrounding a beam. An opaque disk is set in the beam
BEAM HALO OBSERVATION BY CORONAGRAPH T. Mitsuhashi, KEK, TSUKUBA, Japan Abstract We have developed a coronagraph for the observation of the beam halo surrounding a beam. An opaque disk is set in the beam
