Invitation for a walk through microscopy. Sebastian Schuchmann Jörg Rösner
|
|
|
- Harold Edwards
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Invitation for a walk through microscopy Sebastian Schuchmann Jörg Rösner joerg.roesner@charite.de
2 Techniques in microscopy Conventional (light) microscopy bright & dark field, phase & interference contrast Fluorescence microscopy light sources, fluorescence detectors, digital image, objectives Single- & two-photon confocal microscopy basic idea & differences, advantages & disadvantages What is the optimal technique (for my question)?
3 ( Conventional (light) microscopy
4 Light microscope: general structure I Illumination Magnification Specimen (with modification
5 Light microscope: general structure II 2f imaginary image f (magnifying glass) object Illumination Magnification specimen ocular objective condensor light source object F 2f F f real image
6 A light microscope is a combination of a slide projector with a magnifying glass Intermediate (real) image (on the projector screen) ocular (magnifying glass) Final (imaginary) image objective (slide projector) light Total magnification = M objective x M ocular
7 Bright and dark field illumination bright field with specimen objective object plane specimen condensor
8 Bright and dark field illumination dark field without specimen dark field with specimen objective object plane specimen condensor - ring diaphragm (usually) - dark field condensor
9 Bright and dark field illumination Bright field total illumination of the specimen direct light collection by objective dark/colored object on bright background Dark field part-illumination of the specimen scattered light collected by objective bright object on dark background Objects with high contrast Objects with a sharp rise in refraction index (with modification
10 Microscopy illumination after Köhler (or the mystery condensor adjustment) conjugate planes in the image path A. Köhler ( ) retina optical elements (eye) objective specimen condensor diaphragm intermediate image plane focused specimen field diaphragm ocular objective condensor aperture diaphragm light source
11 How to do adjust the Köhler illumination 1.Light source on 2.Open up fully field diaphragm and aperture diaphragm 3. Choose prefered objective (at least 10x), focus specimen 4.Close down field diaphragm; focus the image of the field diaphragm sharply onto the already focused specimen 5.If neccessary center the condensor; then open the field diaphragm until it just disappears from view 6.Take out one of the eyepieces, look down the tube and adjust the aperture diaphragm Diaphragm should be 2/3 to 3/4 open (compromise between resolution & contrast)
12 Amplitude and phase objects influence light waves: Basic principle for phase & interference contrast amplitude object amplitude Reduction in amplitude is equal with a reduction in light intensity (used in bright field microscopy!) phase object amplitude phase Slow down of light wave passing the phase object
13 intermediate image plane Phase contrast scattered light slowed down, unscattered light phase ring objective focussed specimen condensor and light source phase diaphragm
14 Differential interference contrast (DIC) Prisma (Nomarski) Specimen (inhomogen phase object) DIC prisma (Nomarski) Polarisator Phase difference Analysator unpolarized light linear polarized light two vertical polarized waves linear polarized light (analysator vertical vs. polarisator)
15 Phase contrast vs. DIC Buccal epithelial cell (monolayer) Kidney tissue (tubule with some cells > 100 µm thick section) Phase contrast DIC (with modification
16 Light microscopy: illumination & contrast techniques Illumination Try to optimise your illumination (condensor adjustment after Köhler) Bright field illumination: standard technique for most specimen Dark field illumination: specific technique for monolayer specimen with distinct differences in the refraction index Contrast Check and improve all contrast techniques available at your microscope Phase contrast: standard technique for low-contrast monolayer specimen DIC: standard technique for low-contrast specimen, in particularily for thick (non-monolayer) preparations
17 Fluorescence microscopy
18 Basic idea of fluorescence microscopy: Stokes shift excitation level 1 E1 E = hν E1 E2 excitation level 2 E2 c = λν λ 1 λ 2 E ~ 1 / λ Stokes shift base level E0
19 The use of the Stokes shift in fluorescence microscopy Detection system (eye, conventional camera, CCD, photo diode, PMT) (filter) emission wavelenght λ em > λ ex light source (arc lamp, laser) dichroic mirror excitation wavelenght λ ex fluorescence object/dye
20 Fluorescence microscopy requires... Fluorochrome (or autofluorescence) Light source
21 Light source Arc lamps Xenon Mercury Laser types UV IR Argon Blue diode Helium-Cadmium Krypton-Argon Green Helium-Neon 543 Yellow Helium-Neon 594 Orange Helium-Neon 612 Red Helium-Neon 633 Red diode Ti:Sapphire
22 Fluorescence microscopy requires... Fluorochrome (or autofluorescence) see Molecular Probes ( Light source Fluorescence detection
23 Fluorescence detector systems... Temporal resolution photo diode PMT CCD conventional photography Spartial resolution
24 Fluorescence detector systems produce digital images Analog Image Digital Sampling Pixel Quantization - observer eye - conventional photography - CCD - PMT (in combination with scan technique) (with modification
25 Fluorescence detector systems produce digital images pixel counts normal contrast low contrast high contrast grey level grey level grey level (with modification
26 Mainly fluorescence detector systems are color-blind! (Colors are based on a [pseudo-]color look-up table)
27 Fluorescence microscopy requires... Fluorochrome (or autofluorescence) see Molecular Probes ( Light source Fluorescence detection (prefers) immersion objectives
28 Immersion objectives: Remember the refraction index! α α β β α β = α n 1 n 2 sin α = n 2 n 1 < n 2 sin β n 1 total reflection
29 Immersion objectives: Remember the refraction index! water or oil immersion objective medium (water or oil) specimen Emission Light source Excitation DM refraction index (n) air 1.00 water = 1.37 oil = 1.5 glass = 1.5 Immersion objective with specimen
30 Conventional fluorescence microscopy Advantage low cost uncomplicated handling fast imaging technique Disadvantage no 3-dimentional imaging possible low depth of light penetration bleaching
31 (Schmitz et al., 2001) Confocal microscopy
32 Basic idea of confocal microscopy I Conventional fluorescence microscope Laser scanning microscope full field detection point scan detection specimen full field illumination Arc lamp (Hg, Xe) + excitation filter point scan illumination laser light source
33 Laser: light source for confocal microscopy Laser (Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation) = highly precise light source in direction, frequency, phase, polarisation - monochromatic = light has the same wavelength (continuous-wave lasers) - coherent = light is oscilating in the same phase - linear polarized = light is oscilating in the same direction - can be focussed to a very high density power (compared to arc lamps) Different wavelengths require different laser, for example... visible spectrum ultra violet infra red Argon Green Helium-Neon 543 Red Helium-Neon 633
34 Basic idea of confocal microscopy II laser y z x y x point scan illumination (fluorescence excitation) point scan detection (fluorescence emission)
35 Confocal microscope: general structure PMT excitation emission pinhole filter laser source x/y-scanning device and dichroic mirror objective focal plane specimen z y x
36 Confocal microscope: the power of the pinhole PMT PMT pinhole pinhole objective objective specimen focal plane specimen
37 Confocal microscope: excitation profil in z-direction focal plane A(x) ~ 1/I(x)
38 Confocal microscope: depth of light penetration visible light depth of light penetration (µm) UV IR wavelenght (µm)
39 Confocal fluorescence microscopy Advantage improved spartial resolution 3-dimentional scanning Disadvantage more complicated imaging control low depth of light penetration bleaching
40 Two-photon microscopy A B 5 µm 100 ms
41 Basic idea of two-photon microscopy single-photon excitation two-photon excitation Absorbtion hν Emission hν Absorbtion hν* hν* Emission hν E = hν c = λν E ~ 1 / λ E* = 1/2 E E* ~ 1 / 2λ Two photons at the same time and at the same place with doubled wavelenght photons from the infra red spectrum (> 750 nm) high photon density
42 Light source for two-photon microscopy: Ti/Sa-laser Pump laser: solid-state cw laser, 532 nm, 5 W (Millennia, Spectra Physics) Mode-locked Titan-Sapphire laser (Tsunami, Spectra Physics) avarage power > 0.7 W at 800 nm pulsewidth < 100 fs nominal repetition rate 80 MHz turning range nm Titan-Sapphire spectra Excitation Emission
43 Two-photon excitation (with modification Piston, 1999) laser pulse focal plane photon non-excited dye molecule 2p-excited dye molecule the required photon density for two-photon excitation can be established only in the focal plan and within a laser puls
44 Single vs. two-photon microscope: general structure emission excitation PMT PMT emission excitation pinhole IR laser x/y-scanning device and dichroic mirror z y x
45 Fluorescence detection using 2-photon excitation descanned detection Non descanned detection (NDD) point scan detection full field detection specimen point scan illumination pulsed Ti:Sa laser point scan illumination pulsed Ti:Sa laser
46 Two-photon microscopy with descanned and NDD-PMT excitation beam x/y-scanning device & dichroic mirror (DM) prisma for spectral analyse DM DM descanned PMT 1 & 2 non-descanned (NDD) PMT 3 & 4 objective specimen condensor DM trans-non-descanned (NDD) PMT 5 (with modification Oertner, 2002)
47 Single vs. two-photon excitation: excitation profile single-photon excitation two-photon excitation focal plane A(x) ~ 1/I(x) A(x) ~ 1/I 2 (x)
48 Two-photon microscope: depth of light penetration visible light depth of ligh penetration (µm) UV IR wavelenght (µm)
49 Single vs. two-photon microscopy: bleaching (3D-FITC-dextran gel; irradiated area ~ 10 x 20 µm) single-photon absorbtion (488 nm; Ar) focal plane y x x z two-photon absorbtion (760 nm; Ti:Sa) focal plane 20 µm 10 µm (with modification Kubitscheck et al., 1996)
50 Two-photon microscope: excitation spectra Simply doubling the excitation wavelenght? Absorbtion hν hν Emission hν Two-photon cross section Calcium green (506/533) Fluo-3 (505/526) Lucifer yellow (428/533) Cascade blue (400/420) Excitation wavelenght (nm) (with modification
51 Two-photon microscopy Advantage optimized z-resolution reduced bleaching higher efficiency (removed pinhole) higher depth of light penetration Disadvantage complicate combination of laser and imaging control cost reduced temporal resolution
52 Limitations of fluorescence microscopy Eternal triangle of compromise (Shotton, 1995) light source & fluorescence dye Intensity and spectral resolution (dynamic range, signal-to-noise-ratio) Spatial resolution fluorescence detection Temporal resolution
53 What is the proper technique for my question? Fluorescence microscopy conventional confocal (single-photon) two-photon spatial resolution depth of penetration bleaching temporal resolution available dyes ++ + (+) cost increasing
54 What is the proper technique for my question? conventional fluorescence imaging - fast and full frame imaging - dual-wavelenght functional imaging (Fura-2, BCECF, etc.) confocal (single-photon) fluorescence imaging - thin preparation (< 100 µm): cell culture (monolayer), fixed preparations - multilabling using different dyes (require of different wavelenght) two-photon fluorescence imaging - thick preparation: acute and cultured brain slice - in vivo imaging with interest on deeper structures
55 Spinning Disk Microscope Advantage -fast scanning (300 frames/s) -low phototoxicity Disadvantage -fixated pinhole -no FRAP source Duke University
56 TIRF Microscope TIRF Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence Advantage -improved axial resolution (50-150nm) -signal to noise ratio Disadvantage -very low depth of light penetration (< 150nm) Nikon sourcenikon
57 STED Microscope STED Stimulated Emission Depletion Advantage -improved lateral resolution (50-70nm) as compared with a fluorescence- or confocal microscope Disadvantage -cost -bleaching Grafik: Max-Planck-Institut für biophysikalische Chemie"
58 PALM Microscope PALM Photoactivated Localization Microscopy Advantage -high lateral resolution ( 20nm) -multi channel recording Disadvantage -cost -higher background fluorescence than STED source Science 2006
59 Notes on confocal resolution Lateral resolution FWHM = 0.4 * λ / NA Axial resolution FWHM = 0.45 * λ / n (1-cosα) NA = n*sinα FWHM: full width half maximum (or spatial resolution) NA: numeral aperture of the chosen objective n: refraction index of the sample medium (for air: n = 1, for immersion oil: n = 1.5) λ: laser wavelength
60 Notes on confocal resolution The improvement in spatial resolution corresponds lateral to 1.4x and axial to 6x compaired with the conventional fluorescence microscopy. You can adjust the spatial resolution in the LCS software using Zoom and Format. As a simple rule you can use: Lateral: resolution/3 = optimal size of the voxel Axial: resolution/3 = optimal choice of the z-scan Please note: the spatial resolution depends on the used wavelength.
Bio 407. Applied microscopy. Introduction into light microscopy. José María Mateos. Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis
 Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Bio 407 Applied Introduction into light José María Mateos Fundamentals of light Compound microscope Microscope composed of an objective and an additional lens (eyepiece,
Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Bio 407 Applied Introduction into light José María Mateos Fundamentals of light Compound microscope Microscope composed of an objective and an additional lens (eyepiece,
INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY. Urs Ziegler THE PROBLEM
 INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch THE PROBLEM 1 ORGANISMS ARE LARGE LIGHT AND ELECTRONS: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES v = Wavelength ( ) Speed (v) Frequency ( ) Amplitude (A) Propagation
INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch THE PROBLEM 1 ORGANISMS ARE LARGE LIGHT AND ELECTRONS: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES v = Wavelength ( ) Speed (v) Frequency ( ) Amplitude (A) Propagation
Basics of confocal imaging (part I)
 Basics of confocal imaging (part I) Swiss Institute of Technology (EPFL) Faculty of Life Sciences Head of BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS BIOP arne.seitz@epfl.ch Lateral resolution BioImaging &Optics Platform Light
Basics of confocal imaging (part I) Swiss Institute of Technology (EPFL) Faculty of Life Sciences Head of BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS BIOP arne.seitz@epfl.ch Lateral resolution BioImaging &Optics Platform Light
LSM 510 META in Chang Gung University
 Content LSM 510 META in Chang ung University LSM 510 META 路 理 The features and applications of LSM 510 META 01-09 Introduction of the hardware 10-12 Fluorescence observation in conventional microscope
Content LSM 510 META in Chang ung University LSM 510 META 路 理 The features and applications of LSM 510 META 01-09 Introduction of the hardware 10-12 Fluorescence observation in conventional microscope
Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev. Microscopy course, Michmoret Dec 2005
 Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Why use confocal microscopy? Principles of the laser scanning confocal microscope. Image resolution. Manipulating the
Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Why use confocal microscopy? Principles of the laser scanning confocal microscope. Image resolution. Manipulating the
Examination, TEN1, in courses SK2500/SK2501, Physics of Biomedical Microscopy,
 KTH Applied Physics Examination, TEN1, in courses SK2500/SK2501, Physics of Biomedical Microscopy, 2009-06-05, 8-13, FB51 Allowed aids: Compendium Imaging Physics (handed out) Compendium Light Microscopy
KTH Applied Physics Examination, TEN1, in courses SK2500/SK2501, Physics of Biomedical Microscopy, 2009-06-05, 8-13, FB51 Allowed aids: Compendium Imaging Physics (handed out) Compendium Light Microscopy
Final Exam, 150 points PMB 185: Techniques in Light Microscopy
 Final Exam, 150 points Name PMB 185: Techniques in Light Microscopy Point value is in parentheses at the end of each question. Note: GFP = green fluorescent protein ; CFP = cyan fluorescent protein ; YFP
Final Exam, 150 points Name PMB 185: Techniques in Light Microscopy Point value is in parentheses at the end of each question. Note: GFP = green fluorescent protein ; CFP = cyan fluorescent protein ; YFP
BASICS OF CONFOCAL IMAGING (PART I)
 BASICS OF CONFOCAL IMAGING (PART I) INTERNAL COURSE 2012 LIGHT MICROSCOPY Lateral resolution Transmission Fluorescence d min 1.22 NA obj NA cond 0 0 rairy 0.61 NAobj Ernst Abbe Lord Rayleigh Depth of field
BASICS OF CONFOCAL IMAGING (PART I) INTERNAL COURSE 2012 LIGHT MICROSCOPY Lateral resolution Transmission Fluorescence d min 1.22 NA obj NA cond 0 0 rairy 0.61 NAobj Ernst Abbe Lord Rayleigh Depth of field
Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement
 Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY BioVis Uppsala, 2017 Jeremy Adler Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Widefield & Confocal Microscopy
Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY BioVis Uppsala, 2017 Jeremy Adler Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Widefield & Confocal Microscopy
TRAINING MANUAL. Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO
 TRAINING MANUAL Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO September 2010 Multiphoton Microscopy Training Manual Multiphoton microscopy is only available on the LSM 510 META-NLO system. This system is equipped
TRAINING MANUAL Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO September 2010 Multiphoton Microscopy Training Manual Multiphoton microscopy is only available on the LSM 510 META-NLO system. This system is equipped
Fundamentals of Light Microscopy II: Fluorescence, Deconvolution, Confocal, Multiphoton, Spectral microscopy. Integrated Microscopy Course
 Fundamentals of Light Microscopy II: Fluorescence, Deconvolution, Confocal, Multiphoton, Spectral microscopy Integrated Microscopy Course Review Lecture 1: Microscopy Basics Light train Kohler illumination*
Fundamentals of Light Microscopy II: Fluorescence, Deconvolution, Confocal, Multiphoton, Spectral microscopy Integrated Microscopy Course Review Lecture 1: Microscopy Basics Light train Kohler illumination*
Maria Smedh, Centre for Cellular Imaging. Maria Smedh, Centre for Cellular Imaging
 Nonlinear microscopy I: Two-photon fluorescence microscopy Multiphoton Microscopy What is multiphoton imaging? Applications Different imaging modes Advantages/disadvantages Scattering of light in thick
Nonlinear microscopy I: Two-photon fluorescence microscopy Multiphoton Microscopy What is multiphoton imaging? Applications Different imaging modes Advantages/disadvantages Scattering of light in thick
Introduction to light microscopy
 Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light microscopy Basic concepts of imaging with light Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction Diffraction
Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light microscopy Basic concepts of imaging with light Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction Diffraction
Introduction to light microscopy
 Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light Basic concepts of imaging with light Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Microscopy with light 1 Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction
Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light Basic concepts of imaging with light Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Microscopy with light 1 Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction
Light Microscopy. Upon completion of this lecture, the student should be able to:
 Light Light microscopy is based on the interaction of light and tissue components and can be used to study tissue features. Upon completion of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1- Explain the
Light Light microscopy is based on the interaction of light and tissue components and can be used to study tissue features. Upon completion of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1- Explain the
Point Spread Function. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy. Confocal Aperture. Optical aberrations. Alternative Scanning Microscopy
 Bi177 Lecture 5 Adding the Third Dimension Wide-field Imaging Point Spread Function Deconvolution Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Confocal Aperture Optical aberrations Alternative Scanning Microscopy
Bi177 Lecture 5 Adding the Third Dimension Wide-field Imaging Point Spread Function Deconvolution Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Confocal Aperture Optical aberrations Alternative Scanning Microscopy
Microscopy. Matti Hotokka Department of Physical Chemistry Åbo Akademi University
 Microscopy Matti Hotokka Department of Physical Chemistry Åbo Akademi University What s coming Anatomy of a microscope Modes of illumination Practicalities Special applications Basic microscope Ocular
Microscopy Matti Hotokka Department of Physical Chemistry Åbo Akademi University What s coming Anatomy of a microscope Modes of illumination Practicalities Special applications Basic microscope Ocular
Imaging Retreat - UMASS Customized real-time confocal and 2-photon imaging
 Imaging Retreat - UMASS 2012 Customized real-time confocal and 2-photon imaging Mike Sanderson Department of Microbiology and Physiological Systems University of Massachusetts Medical School Thanks for
Imaging Retreat - UMASS 2012 Customized real-time confocal and 2-photon imaging Mike Sanderson Department of Microbiology and Physiological Systems University of Massachusetts Medical School Thanks for
Very short introduction to light microscopy and digital imaging
 Very short introduction to light microscopy and digital imaging Hernan G. Garcia August 1, 2005 1 Light Microscopy Basics In this section we will briefly describe the basic principles of operation and
Very short introduction to light microscopy and digital imaging Hernan G. Garcia August 1, 2005 1 Light Microscopy Basics In this section we will briefly describe the basic principles of operation and
FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY. Matyas Molnar and Dirk Pacholsky
 FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY Matyas Molnar and Dirk Pacholsky 1 The human eye perceives app. 400-700 nm; best at around 500 nm (green) Has a general resolution down to150-300 μm (human hair: 40-250 μm) We need
FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY Matyas Molnar and Dirk Pacholsky 1 The human eye perceives app. 400-700 nm; best at around 500 nm (green) Has a general resolution down to150-300 μm (human hair: 40-250 μm) We need
Practical work no. 3: Confocal Live Cell Microscopy
 Practical work no. 3: Confocal Live Cell Microscopy Course Instructor: Mikko Liljeström (MIU) 1 Background Confocal microscopy: The main idea behind confocality is that it suppresses the signal outside
Practical work no. 3: Confocal Live Cell Microscopy Course Instructor: Mikko Liljeström (MIU) 1 Background Confocal microscopy: The main idea behind confocality is that it suppresses the signal outside
microscopy A great online resource Molecular Expressions, a Microscope Primer Partha Roy
 Fundamentals of optical microscopy A great online resource Molecular Expressions, a Microscope Primer http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/index.html Partha Roy 1 Why microscopy Topics Functions of a microscope
Fundamentals of optical microscopy A great online resource Molecular Expressions, a Microscope Primer http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/index.html Partha Roy 1 Why microscopy Topics Functions of a microscope
Confocal Microscopy. Kristin Jensen
 Confocal Microscopy Kristin Jensen 17.11.05 References Cell Biological Applications of Confocal Microscopy, Brian Matsumoto, chapter 1 Studying protein dynamics in living cells,, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz
Confocal Microscopy Kristin Jensen 17.11.05 References Cell Biological Applications of Confocal Microscopy, Brian Matsumoto, chapter 1 Studying protein dynamics in living cells,, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz
Components of confocal and two-photon microscopes
 Components of confocal and two-photon microscopes Internal training 07/04/2016 A. GRICHINE Platform Optical microscopy Cell imaging, IAB, ISdV Plan Confocal laser scanning microscope o o o Principle Main
Components of confocal and two-photon microscopes Internal training 07/04/2016 A. GRICHINE Platform Optical microscopy Cell imaging, IAB, ISdV Plan Confocal laser scanning microscope o o o Principle Main
5/4/2015 INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY. Urs Ziegler MICROSCOPY WITH LIGHT. Image formation in a nutshell. Overview of techniques
 INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch MICROSCOPY WITH LIGHT INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY Image formation in a nutshell Overview of techniques Widefield microscopy Resolution
INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch MICROSCOPY WITH LIGHT INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY Image formation in a nutshell Overview of techniques Widefield microscopy Resolution
3D light microscopy techniques
 3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 1 1 2! NA = 0.5! NA 2D imaging
3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 1 1 2! NA = 0.5! NA 2D imaging
Imaging Introduction. September 24, 2010
 Imaging Introduction September 24, 2010 What is a microscope? Merriam-Webster: an optical instrument consisting of a lens or combination of lenses for making enlarged images of minute objects; especially:
Imaging Introduction September 24, 2010 What is a microscope? Merriam-Webster: an optical instrument consisting of a lens or combination of lenses for making enlarged images of minute objects; especially:
Zeiss 780 Training Notes
 Zeiss 780 Training Notes Turn on Main Switch, System PC and Components Switches 780 Start up sequence Do you need the argon laser (458, 488, 514 nm lines)? Yes Turn on the laser s main power switch and
Zeiss 780 Training Notes Turn on Main Switch, System PC and Components Switches 780 Start up sequence Do you need the argon laser (458, 488, 514 nm lines)? Yes Turn on the laser s main power switch and
Zeiss 880 Training Notes Zen 2.3
 Zeiss 880 Training Notes Zen 2.3 1 Turn on the HXP 120V Lamp 2 Turn on Main Power Switch Turn on the Systems PC Switch Turn on the Components Switch. 3 4 5 Turn on the PC and log into your account. Start
Zeiss 880 Training Notes Zen 2.3 1 Turn on the HXP 120V Lamp 2 Turn on Main Power Switch Turn on the Systems PC Switch Turn on the Components Switch. 3 4 5 Turn on the PC and log into your account. Start
OPTICAL PRINCIPLES OF MICROSCOPY. Interuniversity Course 28 December 2003 Aryeh M. Weiss Bar Ilan University
 OPTICAL PRINCIPLES OF MICROSCOPY Interuniversity Course 28 December 2003 Aryeh M. Weiss Bar Ilan University FOREWORD This slide set was originally presented at the ISM Workshop on Theoretical and Experimental
OPTICAL PRINCIPLES OF MICROSCOPY Interuniversity Course 28 December 2003 Aryeh M. Weiss Bar Ilan University FOREWORD This slide set was originally presented at the ISM Workshop on Theoretical and Experimental
Confocal Microscopy and Related Techniques
 Confocal Microscopy and Related Techniques Chau-Hwang Lee Associate Research Fellow Research Center for Applied Sciences, Academia Sinica 128 Sec. 2, Academia Rd., Nankang, Taipei 11529, Taiwan E-mail:
Confocal Microscopy and Related Techniques Chau-Hwang Lee Associate Research Fellow Research Center for Applied Sciences, Academia Sinica 128 Sec. 2, Academia Rd., Nankang, Taipei 11529, Taiwan E-mail:
Observing Microorganisms through a Microscope LIGHT MICROSCOPY: This type of microscope uses visible light to observe specimens. Compound Light Micros
 PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY JIGAR SHAH INSTITUTE OF PHARMACY NIRMA UNIVERSITY Observing Microorganisms through a Microscope LIGHT MICROSCOPY: This type of microscope uses visible light to observe specimens.
PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY JIGAR SHAH INSTITUTE OF PHARMACY NIRMA UNIVERSITY Observing Microorganisms through a Microscope LIGHT MICROSCOPY: This type of microscope uses visible light to observe specimens.
Rates of excitation, emission, ISC
 Bi177 Lecture 4 Fluorescence Microscopy Phenomenon of Fluorescence Energy Diagram Rates of excitation, emission, ISC Practical Issues Lighting, Filters More on diffraction Point Spread Functions Thus Far,
Bi177 Lecture 4 Fluorescence Microscopy Phenomenon of Fluorescence Energy Diagram Rates of excitation, emission, ISC Practical Issues Lighting, Filters More on diffraction Point Spread Functions Thus Far,
Akinori Mitani and Geoff Weiner BGGN 266 Spring 2013 Non-linear optics final report. Introduction and Background
 Akinori Mitani and Geoff Weiner BGGN 266 Spring 2013 Non-linear optics final report Introduction and Background Two-photon microscopy is a type of fluorescence microscopy using two-photon excitation. It
Akinori Mitani and Geoff Weiner BGGN 266 Spring 2013 Non-linear optics final report Introduction and Background Two-photon microscopy is a type of fluorescence microscopy using two-photon excitation. It
Things to check before start-up.
 Byeong Cha Page 1 11/24/2009 Manual for Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Enter you name, the date, the time, and the account number in the user log book. Things to check before start-up. Make sure that your
Byeong Cha Page 1 11/24/2009 Manual for Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Enter you name, the date, the time, and the account number in the user log book. Things to check before start-up. Make sure that your
EUV microscopy - a user s perspective Dimitri Scholz EUV,
 EUV microscopy - a user s perspective Dimitri Scholz EUV, 09.11.2011 Imaging technologies: available at UCD now and in the next future Begin ab ovo - Simple approaches direct to the goal - Standard methods
EUV microscopy - a user s perspective Dimitri Scholz EUV, 09.11.2011 Imaging technologies: available at UCD now and in the next future Begin ab ovo - Simple approaches direct to the goal - Standard methods
MULTIPHOTON MICROSCOPY. Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky
 MULTIPHOTON MICROSCOPY Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Information Information given here about 2 Photon microscopy were mainly taken from these sources: Background information on 2-Photon microscopy: http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/techniques/fluorescence/multiphoton/
MULTIPHOTON MICROSCOPY Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Information Information given here about 2 Photon microscopy were mainly taken from these sources: Background information on 2-Photon microscopy: http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/techniques/fluorescence/multiphoton/
Development of a High-speed Super-resolution Confocal Scanner
 Development of a High-speed Super-resolution Confocal Scanner Takuya Azuma *1 Takayuki Kei *1 Super-resolution microscopy techniques that overcome the spatial resolution limit of conventional light microscopy
Development of a High-speed Super-resolution Confocal Scanner Takuya Azuma *1 Takayuki Kei *1 Super-resolution microscopy techniques that overcome the spatial resolution limit of conventional light microscopy
CCAM Microscope Objectives
 CCAM Microscope Objectives Things to consider when selecting an objective Magnification Numerical Aperture (NA) resolving power and light intensity of the objective Working Distance distance between the
CCAM Microscope Objectives Things to consider when selecting an objective Magnification Numerical Aperture (NA) resolving power and light intensity of the objective Working Distance distance between the
ANSWER KEY Lab 2 (IGB): Bright Field and Fluorescence Optical Microscopy and Sectioning
 Phys598BP Spring 2016 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign ANSWER KEY Lab 2 (IGB): Bright Field and Fluorescence Optical Microscopy and Sectioning Location: IGB Core Microscopy Facility Microscope:
Phys598BP Spring 2016 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign ANSWER KEY Lab 2 (IGB): Bright Field and Fluorescence Optical Microscopy and Sectioning Location: IGB Core Microscopy Facility Microscope:
Light microscopy BMB 173, Lecture 14, Feb. 21, 2018
 Light microscopy The Structural Biology Continuum Next two lectures: Light microscopy Many slides taken from Scott Fraser, Murphy s Fundamentals of light microscopy, Alberts Molecular Biology of the Cell,
Light microscopy The Structural Biology Continuum Next two lectures: Light microscopy Many slides taken from Scott Fraser, Murphy s Fundamentals of light microscopy, Alberts Molecular Biology of the Cell,
Microscopy Techniques that make it easy to see things this small.
 Microscopy Techniques that make it easy to see things this small. What is a Microscope? An instrument for viewing objects that are too small to be seen easily by the naked eye. Dutch spectacle-makers Hans
Microscopy Techniques that make it easy to see things this small. What is a Microscope? An instrument for viewing objects that are too small to be seen easily by the naked eye. Dutch spectacle-makers Hans
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE DEPTH STUDY: ELECTRON MICROSCOPES
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE DEPTH STUDY: ELECTRON MICROSCOPES Shortly after the experimental confirmation of the wave properties of the electron, it was suggested that the electron could be used to examine objects
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE DEPTH STUDY: ELECTRON MICROSCOPES Shortly after the experimental confirmation of the wave properties of the electron, it was suggested that the electron could be used to examine objects
Bi/BE 227 Winter Assignment #3. Adding the third dimension: 3D Confocal Imaging
 Bi/BE 227 Winter 2016 Assignment #3 Adding the third dimension: 3D Confocal Imaging Schedule: Jan 20: Assignment Jan 20-Feb 8: Work on assignment Feb 10: Student PowerPoint presentations. Goals for this
Bi/BE 227 Winter 2016 Assignment #3 Adding the third dimension: 3D Confocal Imaging Schedule: Jan 20: Assignment Jan 20-Feb 8: Work on assignment Feb 10: Student PowerPoint presentations. Goals for this
Operation Guide for the Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Bio-Imaging Facility Hunter College October 2009
 Operation Guide for the Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Bio-Imaging Facility Hunter College October 2009 Introduction of Fluoresence Confocal Microscopy The first confocal microscope was invented by Princeton
Operation Guide for the Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Bio-Imaging Facility Hunter College October 2009 Introduction of Fluoresence Confocal Microscopy The first confocal microscope was invented by Princeton
Supplementary Information for. Surface Waves. Angelo Angelini, Elsie Barakat, Peter Munzert, Luca Boarino, Natascia De Leo,
 Supplementary Information for Focusing and Extraction of Light mediated by Bloch Surface Waves Angelo Angelini, Elsie Barakat, Peter Munzert, Luca Boarino, Natascia De Leo, Emanuele Enrico, Fabrizio Giorgis,
Supplementary Information for Focusing and Extraction of Light mediated by Bloch Surface Waves Angelo Angelini, Elsie Barakat, Peter Munzert, Luca Boarino, Natascia De Leo, Emanuele Enrico, Fabrizio Giorgis,
Administrative details:
 Administrative details: Anything from your side? www.photonics.ethz.ch 1 What are we actually doing here? Optical imaging: Focusing by a lens Angular spectrum Paraxial approximation Gaussian beams Method
Administrative details: Anything from your side? www.photonics.ethz.ch 1 What are we actually doing here? Optical imaging: Focusing by a lens Angular spectrum Paraxial approximation Gaussian beams Method
Lecture 23 MNS 102: Techniques for Materials and Nano Sciences
 Lecture 23 MNS 102: Techniques for Materials and Nano Sciences Reference: #1 C. R. Brundle, C. A. Evans, S. Wilson, "Encyclopedia of Materials Characterization", Butterworth-Heinemann, Toronto (1992),
Lecture 23 MNS 102: Techniques for Materials and Nano Sciences Reference: #1 C. R. Brundle, C. A. Evans, S. Wilson, "Encyclopedia of Materials Characterization", Butterworth-Heinemann, Toronto (1992),
INTRODUCTION TO OPTICAL MICROSCOPY
 Experimental Biophysics TEK265, FYST23, TNF060, FAF010F Lab Exercise Supervisor: Karl Adolfsson Written by Peter Jönsson and Jason Beech Updated by Henrik Persson, Karl Adolfsson and Zhen Li karl.adolfsson@ftf.lth.se
Experimental Biophysics TEK265, FYST23, TNF060, FAF010F Lab Exercise Supervisor: Karl Adolfsson Written by Peter Jönsson and Jason Beech Updated by Henrik Persson, Karl Adolfsson and Zhen Li karl.adolfsson@ftf.lth.se
Supplemental Figure 1: Histogram of 63x Objective Lens z axis Calculated Resolutions. Results from the MetroloJ z axis fits for 5 beads from each
 Supplemental Figure 1: Histogram of 63x Objective Lens z axis Calculated Resolutions. Results from the MetroloJ z axis fits for 5 beads from each lens with a 1 Airy unit pinhole setting. Many water lenses
Supplemental Figure 1: Histogram of 63x Objective Lens z axis Calculated Resolutions. Results from the MetroloJ z axis fits for 5 beads from each lens with a 1 Airy unit pinhole setting. Many water lenses
Introduction to light microscopy
 Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light Imaging with light / Overview of techniques Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction Diffraction
Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light Imaging with light / Overview of techniques Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction Diffraction
Chapter 2 The Study of Microbial Structure: Microscopy and Specimen Preparation
 Chapter 2 The Study of Microbial Structure: Microscopy and Specimen Preparation 1 Lenses and the Bending of Light light is refracted (bent) when passing from one medium to another refractive index a measure
Chapter 2 The Study of Microbial Structure: Microscopy and Specimen Preparation 1 Lenses and the Bending of Light light is refracted (bent) when passing from one medium to another refractive index a measure
Tissue Preparation ORGANISM IMAGE TISSUE PREPARATION. 1) Fixation: halts cell metabolism, preserves cell/tissue structure
 Lab starts this week! ANNOUNCEMENTS - Tuesday or Wednesday 1:25 ISB 264 - Read Lab 1: Microscopy and Imaging (see Web Page) - Getting started on Lab Group project - Organ for investigation - Lab project
Lab starts this week! ANNOUNCEMENTS - Tuesday or Wednesday 1:25 ISB 264 - Read Lab 1: Microscopy and Imaging (see Web Page) - Getting started on Lab Group project - Organ for investigation - Lab project
ADVANCED METHODS FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY II. Jean-Yves Chatton Sept. 2006
 ADVANCED METHODS FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY II Jean-Yves Chatton Sept. 2006 Workshop outline Confocal microscopy of living cells and tissues X-Z scanning Time series Bleach: FRAP, photoactivation Emission
ADVANCED METHODS FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY II Jean-Yves Chatton Sept. 2006 Workshop outline Confocal microscopy of living cells and tissues X-Z scanning Time series Bleach: FRAP, photoactivation Emission
Microscopy: Fundamental Principles and Practical Approaches
 Microscopy: Fundamental Principles and Practical Approaches Simon Atkinson Online Resource: http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/index.html Book: Murphy, D.B. Fundamentals of Light Microscopy and Electronic
Microscopy: Fundamental Principles and Practical Approaches Simon Atkinson Online Resource: http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/index.html Book: Murphy, D.B. Fundamentals of Light Microscopy and Electronic
Resolution. Diffraction from apertures limits resolution. Rayleigh criterion θ Rayleigh = 1.22 λ/d 1 peak at 2 nd minimum. θ f D
 Microscopy Outline 1. Resolution and Simple Optical Microscope 2. Contrast enhancement: Dark field, Fluorescence (Chelsea & Peter), Phase Contrast, DIC 3. Newer Methods: Scanning Tunneling microscopy (STM),
Microscopy Outline 1. Resolution and Simple Optical Microscope 2. Contrast enhancement: Dark field, Fluorescence (Chelsea & Peter), Phase Contrast, DIC 3. Newer Methods: Scanning Tunneling microscopy (STM),
Microscopy Training & Overview
 Microscopy Training & Overview Product Marketing October 2011 Stephan Briggs - PLE OVERVIEW AND PRESENTATION FLOW Glossary and Important Terms Introduction Timeline Innovation and Advancement Primary Components
Microscopy Training & Overview Product Marketing October 2011 Stephan Briggs - PLE OVERVIEW AND PRESENTATION FLOW Glossary and Important Terms Introduction Timeline Innovation and Advancement Primary Components
3D light microscopy techniques
 3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 2D imaging 3D imaging Resolution
3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 2D imaging 3D imaging Resolution
Advanced Optical Microscopy
 Nanosystems I - Seminar TU München 8th December 2008 1 Introduction to Classical Optical Microscopy Denitions in Optical Microscopy Contrast and Contrast Enhancement 1 Introduction to Classical Optical
Nanosystems I - Seminar TU München 8th December 2008 1 Introduction to Classical Optical Microscopy Denitions in Optical Microscopy Contrast and Contrast Enhancement 1 Introduction to Classical Optical
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup.
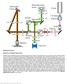 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup. Excitation from a femtosecond laser is passed through intensity control and shuttering optics (1/2 λ wave plate, polarizing beam splitting
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup. Excitation from a femtosecond laser is passed through intensity control and shuttering optics (1/2 λ wave plate, polarizing beam splitting
Education in Microscopy and Digital Imaging
 Contact Us Carl Zeiss Education in Microscopy and Digital Imaging ZEISS Home Products Solutions Support Online Shop ZEISS International ZEISS Campus Home Interactive Tutorials Basic Microscopy Spectral
Contact Us Carl Zeiss Education in Microscopy and Digital Imaging ZEISS Home Products Solutions Support Online Shop ZEISS International ZEISS Campus Home Interactive Tutorials Basic Microscopy Spectral
Microscopic Structures
 Microscopic Structures Image Analysis Metal, 3D Image (Red-Green) The microscopic methods range from dark field / bright field microscopy through polarisation- and inverse microscopy to techniques like
Microscopic Structures Image Analysis Metal, 3D Image (Red-Green) The microscopic methods range from dark field / bright field microscopy through polarisation- and inverse microscopy to techniques like
Quick Start Guide. Leica SP5 X
 Quick Start Guide Leica SP5 X Please note: Some of the information in this guide was taken from Leica Microsystems Leica TCS SP5 LAS AF Guide for New Users. This work is licensed under the Creative Commons
Quick Start Guide Leica SP5 X Please note: Some of the information in this guide was taken from Leica Microsystems Leica TCS SP5 LAS AF Guide for New Users. This work is licensed under the Creative Commons
Operating Checklist for using the Laser Scanning Confocal Microscope. Leica TCS SP5.
 Smith College August 2010 Operating Checklist for using the Laser Scanning Confocal Microscope Leica TCS SP5. CONTENT, page no. Startup, 1 Initial set-up, 1 Software, 2 Microscope Specimen observation
Smith College August 2010 Operating Checklist for using the Laser Scanning Confocal Microscope Leica TCS SP5. CONTENT, page no. Startup, 1 Initial set-up, 1 Software, 2 Microscope Specimen observation
Introduction to Light Microscopy. (Image: T. Wittman, Scripps)
 Introduction to Light Microscopy (Image: T. Wittman, Scripps) The Light Microscope Four centuries of history Vibrant current development One of the most widely used research tools A. Khodjakov et al. Major
Introduction to Light Microscopy (Image: T. Wittman, Scripps) The Light Microscope Four centuries of history Vibrant current development One of the most widely used research tools A. Khodjakov et al. Major
BASICS IN BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS PLATFORM EPFL SV PTBIOP LIGHT MICROSCOPY
 BASICS IN LIGHT MICROSCOPY OVERVIEW 1. Motivation 2. Basic in optics 3. How microscope works 4. Illumination and resolution 5. Microscope optics 6. Contrasting methods -2- MOTIVATION Why do we need microscopy?
BASICS IN LIGHT MICROSCOPY OVERVIEW 1. Motivation 2. Basic in optics 3. How microscope works 4. Illumination and resolution 5. Microscope optics 6. Contrasting methods -2- MOTIVATION Why do we need microscopy?
Prof. Enrico Gratton - Lecture 6 Fluorescence Microscopy
 Prof. Enrico Gratton - Lecture 6 Fluorescence Microscopy Instrumentation Light Sources: One-photon and Multi-photon Excitation Applications in Cells Lifetime Imaging Figures acknowledgements: E.D. Salmon
Prof. Enrico Gratton - Lecture 6 Fluorescence Microscopy Instrumentation Light Sources: One-photon and Multi-photon Excitation Applications in Cells Lifetime Imaging Figures acknowledgements: E.D. Salmon
Travel to New Dimensions- LSM 880. The Resolution of a Microscope is limited. The Resolution of a Microscope is limited. Image. Image. Object.
 Travel to New Dimensions- LSM 880 LSM 880: The Power of Sensitivity Our Latest Member of the LSM 880 with GaAsP Detectors Sensitivity, and Ease of Use Innovative High-End Laser Scanning Microscopes from
Travel to New Dimensions- LSM 880 LSM 880: The Power of Sensitivity Our Latest Member of the LSM 880 with GaAsP Detectors Sensitivity, and Ease of Use Innovative High-End Laser Scanning Microscopes from
Ratio Imaging. Dividing one image by another to detect changing conditions. Images collected at different times, wavelengths, polarities, etc
 Ratio Imaging Dividing one image by another to detect changing conditions Images collected at different times, wavelengths, polarities, etc Most common use of ratio imaging is to provide a quick spectral
Ratio Imaging Dividing one image by another to detect changing conditions Images collected at different times, wavelengths, polarities, etc Most common use of ratio imaging is to provide a quick spectral
Observing Microorganisms through a Microscope
 2016/2/19 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College CHAPTER 3 Observing Microorganisms through a Microscope 1 Figure 3.2 Microscopes and Magnification.
2016/2/19 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College CHAPTER 3 Observing Microorganisms through a Microscope 1 Figure 3.2 Microscopes and Magnification.
Multifluorescence The Crosstalk Problem and Its Solution
 Multifluorescence The Crosstalk Problem and Its Solution If a specimen is labeled with more than one fluorochrome, each image channel should only show the emission signal of one of them. If, in a specimen
Multifluorescence The Crosstalk Problem and Its Solution If a specimen is labeled with more than one fluorochrome, each image channel should only show the emission signal of one of them. If, in a specimen
Confocal and 2-photon Imaging. October 15, 2010
 Confocal and 2-photon Imaging October 15, 2010 Review Optical Elements Adapted from Sluder & Nordberg 2007 Review Optical Elements Collector Lens Adapted from Sluder & Nordberg 2007 Review Optical Elements
Confocal and 2-photon Imaging October 15, 2010 Review Optical Elements Adapted from Sluder & Nordberg 2007 Review Optical Elements Collector Lens Adapted from Sluder & Nordberg 2007 Review Optical Elements
CFIM MICROSCOPY COURSE PROGRAMME PRINCIPLES OF MICROSCOPY CONFOCAL AND FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY
 CFIM MICROSCOPY COURSE PROGRAMME PRINCIPLES OF MICROSCOPY 11.01.16-15.01.2016 CONFOCAL AND FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY 25.01.16-29.01.2016 PhD Course - University of Copenhagen Department of Biomedical Sciences
CFIM MICROSCOPY COURSE PROGRAMME PRINCIPLES OF MICROSCOPY 11.01.16-15.01.2016 CONFOCAL AND FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY 25.01.16-29.01.2016 PhD Course - University of Copenhagen Department of Biomedical Sciences
IC 2 S High Performance Objectives
 M i c r o s c o p y f r o m C a r l Z e i s s IC 2 S igh Performance Objectives for Biomedical Applications with Laser Based Imaging Systems LSM,, ConfoCor, TIRF and ELYRA Carl Zeiss offers a large range
M i c r o s c o p y f r o m C a r l Z e i s s IC 2 S igh Performance Objectives for Biomedical Applications with Laser Based Imaging Systems LSM,, ConfoCor, TIRF and ELYRA Carl Zeiss offers a large range
You won t be able to measure the incident power precisely. The readout of the power would be lower than the real incident power.
 1. a) Given the transfer function of a detector (below), label and describe these terms: i. dynamic range ii. linear dynamic range iii. sensitivity iv. responsivity b) Imagine you are using an optical
1. a) Given the transfer function of a detector (below), label and describe these terms: i. dynamic range ii. linear dynamic range iii. sensitivity iv. responsivity b) Imagine you are using an optical
Guide to Confocal 5. Starting session
 Guide to Confocal 5 Remember that when booking and before starting session you can check for any problems at https://www.bris.ac.uk/biochemistry/uobonly/cif/index.html Starting session Switch on microscope
Guide to Confocal 5 Remember that when booking and before starting session you can check for any problems at https://www.bris.ac.uk/biochemistry/uobonly/cif/index.html Starting session Switch on microscope
 Microscopy http://www.microscopyu.com/articles/phasecontrast/phasemicroscopy.html http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/anatomy/anatomy.html 2005, Dr. Jack Ikeda & Dr. Gail Grabner 9 Nikon Labophot (Question
Microscopy http://www.microscopyu.com/articles/phasecontrast/phasemicroscopy.html http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/anatomy/anatomy.html 2005, Dr. Jack Ikeda & Dr. Gail Grabner 9 Nikon Labophot (Question
Single-photon excitation of morphology dependent resonance
 Single-photon excitation of morphology dependent resonance 3.1 Introduction The examination of morphology dependent resonance (MDR) has been of considerable importance to many fields in optical science.
Single-photon excitation of morphology dependent resonance 3.1 Introduction The examination of morphology dependent resonance (MDR) has been of considerable importance to many fields in optical science.
More fancy SPIM, Even fancier SPIM
 More fancy SPIM, Even fancier SPIM Last class Light sheet microscopy Fancy SPIM (ispim, dspim, etc ) This class Multi camera SPIM SIM SPIM Bessels d x,y = λ em 2 NA d z = 2 NA λ ex + n(1 cosθ λ em 1 IsoView
More fancy SPIM, Even fancier SPIM Last class Light sheet microscopy Fancy SPIM (ispim, dspim, etc ) This class Multi camera SPIM SIM SPIM Bessels d x,y = λ em 2 NA d z = 2 NA λ ex + n(1 cosθ λ em 1 IsoView
Nature Protocols: doi: /nprot Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic diagram of Kőhler illumination.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic diagram of Kőhler illumination. The green beam path represents the excitation path and the red represents the emission path. Supplementary Figure 2 Microscope base components
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic diagram of Kőhler illumination. The green beam path represents the excitation path and the red represents the emission path. Supplementary Figure 2 Microscope base components
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy
 Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
Bandpass Edge Dichroic Notch & More
 Edmund Optics BROCHURE Filters COPYRIGHT 217 EDMUND OPTICS, INC. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 1/17 Bandpass Edge Dichroic Notch & More Contact us for a Stock or Custom Quote Today! USA: +1-856-547-3488 EUROPE:
Edmund Optics BROCHURE Filters COPYRIGHT 217 EDMUND OPTICS, INC. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED 1/17 Bandpass Edge Dichroic Notch & More Contact us for a Stock or Custom Quote Today! USA: +1-856-547-3488 EUROPE:
Nikon E800 Operating Instructions.
 Nikon E800 Operating Instructions. You can request electronic copies of this manual by contacting lshats@jhsph.edu Copies are also available on the JHU MMI Department web site. Please send your comments
Nikon E800 Operating Instructions. You can request electronic copies of this manual by contacting lshats@jhsph.edu Copies are also available on the JHU MMI Department web site. Please send your comments
Biology 29 Cell Structure and Function Spring, 2009 Springer LABORATORY 1: THE LIGHT MICROSCOPE
 Biology 29 Cell Structure and Function Spring, 2009 Springer LABORATORY 1: THE LIGHT MICROSCOPE Prior to lab: 1) Read these instructions (p 1-6) 2) Go through the online tutorial, the microscopy pre-lab
Biology 29 Cell Structure and Function Spring, 2009 Springer LABORATORY 1: THE LIGHT MICROSCOPE Prior to lab: 1) Read these instructions (p 1-6) 2) Go through the online tutorial, the microscopy pre-lab
Confocal Microscopy. (Increasing contrast and resolu6on using op6cal sec6oning) Lecture 7. November 2017
 Confocal Microscopy (Increasing contrast and resolu6on using op6cal sec6oning) Lecture 7 November 2017 3 Flavours of Microscope Confocal Laser Scanning Problem: Out of Focus Light Spinning disc 2-Photon
Confocal Microscopy (Increasing contrast and resolu6on using op6cal sec6oning) Lecture 7 November 2017 3 Flavours of Microscope Confocal Laser Scanning Problem: Out of Focus Light Spinning disc 2-Photon
Quick Guide. LSM 5 MP, LSM 510 and LSM 510 META. Laser Scanning Microscopes. We make it visible. M i c r o s c o p y f r o m C a r l Z e i s s
 LSM 5 MP, LSM 510 and LSM 510 META M i c r o s c o p y f r o m C a r l Z e i s s Quick Guide Laser Scanning Microscopes LSM Software ZEN 2007 August 2007 We make it visible. Contents Page Contents... 1
LSM 5 MP, LSM 510 and LSM 510 META M i c r o s c o p y f r o m C a r l Z e i s s Quick Guide Laser Scanning Microscopes LSM Software ZEN 2007 August 2007 We make it visible. Contents Page Contents... 1
Systems Biology. Optical Train, Köhler Illumination
 McGill University Life Sciences Complex Imaging Facility Systems Biology Microscopy Workshop Tuesday December 7 th, 2010 Simple Lenses, Transmitted Light Optical Train, Köhler Illumination What Does a
McGill University Life Sciences Complex Imaging Facility Systems Biology Microscopy Workshop Tuesday December 7 th, 2010 Simple Lenses, Transmitted Light Optical Train, Köhler Illumination What Does a
a) How big will that physical image of the cells be your camera sensor?
 1. Consider a regular wide-field microscope set up with a 60x, NA = 1.4 objective and a monochromatic digital camera with 8 um pixels, properly positioned in the primary image plane. This microscope is
1. Consider a regular wide-field microscope set up with a 60x, NA = 1.4 objective and a monochromatic digital camera with 8 um pixels, properly positioned in the primary image plane. This microscope is
Training Guide for Leica SP8 Confocal/Multiphoton Microscope
 Training Guide for Leica SP8 Confocal/Multiphoton Microscope LAS AF v3.3 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON power switch for epifluorescence
Training Guide for Leica SP8 Confocal/Multiphoton Microscope LAS AF v3.3 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON power switch for epifluorescence
Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
 Name of the Core Facility: Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy CORE Forschungszentrum Immunologie Mainz Welcome to the CSLM Core Facility: The CLSM Core Facility enables working groups to incorporate high
Name of the Core Facility: Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy CORE Forschungszentrum Immunologie Mainz Welcome to the CSLM Core Facility: The CLSM Core Facility enables working groups to incorporate high
Non-Descanned FLIM Detection in Multiphoton Microscopes
 Non-Descanned FLIM Detection in Multiphoton Microscopes Abstract. Multiphoton microscopes use a femtosecond NIR laser to excite fluorescence in the sample. Excitation is performed via a multi-photon absorption
Non-Descanned FLIM Detection in Multiphoton Microscopes Abstract. Multiphoton microscopes use a femtosecond NIR laser to excite fluorescence in the sample. Excitation is performed via a multi-photon absorption
Nikon. King s College London. Imaging Centre. N-SIM guide NIKON IMAGING KING S COLLEGE LONDON
 N-SIM guide NIKON IMAGING CENTRE @ KING S COLLEGE LONDON Starting-up / Shut-down The NSIM hardware is calibrated after system warm-up occurs. It is recommended that you turn-on the system for at least
N-SIM guide NIKON IMAGING CENTRE @ KING S COLLEGE LONDON Starting-up / Shut-down The NSIM hardware is calibrated after system warm-up occurs. It is recommended that you turn-on the system for at least
Leica TCS SP8 Quick Start Guide
 Leica TCS SP8 Quick Start Guide Leica TCS SP8 System Overview Start-Up Procedure 1. Turn on the CTR Control Box, Fluorescent Light for the microscope stand. 2. Turn on the Scanner Power (1) on the front
Leica TCS SP8 Quick Start Guide Leica TCS SP8 System Overview Start-Up Procedure 1. Turn on the CTR Control Box, Fluorescent Light for the microscope stand. 2. Turn on the Scanner Power (1) on the front
The Nature of Light. Light and Energy
 The Nature of Light Light and Energy - dependent on energy from the sun, directly and indirectly - solar energy intimately associated with existence of life -light absorption: dissipate as heat emitted
The Nature of Light Light and Energy - dependent on energy from the sun, directly and indirectly - solar energy intimately associated with existence of life -light absorption: dissipate as heat emitted
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
 Zeiss LSM 510 M eta Confocal M icroscope OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS Starting the System: 1. Turn the black knob on the laser box one-quarter turn from Off to On. You will hear the laser cooling mechanisms
Zeiss LSM 510 M eta Confocal M icroscope OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS Starting the System: 1. Turn the black knob on the laser box one-quarter turn from Off to On. You will hear the laser cooling mechanisms
Compound Light Microscopy. Microscopy. Things to remember... 1/22/2017. This is what we use in the laboratory
 Compound Light Microscopy This is what we use in the laboratory Microscopy Chapter 3 BIO 440 A series of finely ground lenses is used to form a magnified image Specimen is illuminated with visible light
Compound Light Microscopy This is what we use in the laboratory Microscopy Chapter 3 BIO 440 A series of finely ground lenses is used to form a magnified image Specimen is illuminated with visible light
INTRODUCTION THIN LENSES. Introduction. given by the paraxial refraction equation derived last lecture: Thin lenses (19.1) = 1. Double-lens systems
 Chapter 9 OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS Introduction Thin lenses Double-lens systems Aberrations Camera Human eye Compound microscope Summary INTRODUCTION Knowledge of geometrical optics, diffraction and interference,
Chapter 9 OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS Introduction Thin lenses Double-lens systems Aberrations Camera Human eye Compound microscope Summary INTRODUCTION Knowledge of geometrical optics, diffraction and interference,
Femtosecond laser microfabrication in. Prof. Dr. Cleber R. Mendonca
 Femtosecond laser microfabrication in polymers Prof. Dr. Cleber R. Mendonca laser microfabrication focus laser beam on material s surface laser microfabrication laser microfabrication laser microfabrication
Femtosecond laser microfabrication in polymers Prof. Dr. Cleber R. Mendonca laser microfabrication focus laser beam on material s surface laser microfabrication laser microfabrication laser microfabrication
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Optically reconfigurable metasurfaces and photonic devices based on phase change materials S1: Schematic diagram of the experimental setup. A Ti-Sapphire femtosecond laser (Coherent Chameleon Vision S)
Optically reconfigurable metasurfaces and photonic devices based on phase change materials S1: Schematic diagram of the experimental setup. A Ti-Sapphire femtosecond laser (Coherent Chameleon Vision S)
Operating Instructions for Zeiss LSM 510
 Operating Instructions for Zeiss LSM 510 Location: GNL 6.312q (BSL3) Questions? Contact: Maxim Ivannikov, maivanni@utmb.edu 1 Attend A Complementary Training Before Using The Microscope All future users
Operating Instructions for Zeiss LSM 510 Location: GNL 6.312q (BSL3) Questions? Contact: Maxim Ivannikov, maivanni@utmb.edu 1 Attend A Complementary Training Before Using The Microscope All future users
