Point Spread Function. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy. Confocal Aperture. Optical aberrations. Alternative Scanning Microscopy
|
|
|
- Lewis Ray
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bi177 Lecture 5 Adding the Third Dimension Wide-field Imaging Point Spread Function Deconvolution Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Confocal Aperture Optical aberrations Alternative Scanning Microscopy Two-photon Laser Scanning Microscopy
2 Widefield imaging: detail in the image from collecting diffracted light Larger aperture = more diffraction peaks = higher resolution Therefore, for any finite aperture: 1. diffraction limit in size of central maximum 2. Extended point spread function Point Spread Function: Image of a infinitely small object.
3 Point Spread Function is three dimensional Image of subdiffraction limit spot Subdiffraction limit spot Thus, each spot in specimen will be blurred onto the sensor (Aperture and Missing Cone )
4 To reduce contribution of the blurring to the image: Deconvolution Compute model of what might have generated the image Image blurred by PSF Compare and iterate Compute how model would be blurred by PSF
5 Image deconvolution Inputs: 3-D image stack 3-D PSF (bead image) Requires: Time Computer memory Note: z-axis blurring from the missing cone is minimized but not eliminated
6 How else to fill in the missing cone? Need more data in the Z-axis --> Confocal microscopy PMT Detector Detection Pinhole Confocal pinholes Dichroic Beam Splitter Excitation Laser Objective Excitation Pinhole Conjugate Focal Planes
7 Three confocal places Confocal Microscopy (Minsky, 1957)
8 Pinhole: Axial Filtering Identical Lenses Focal Points
9 Aperture trims the PSF: increased resolution in XY plane Cost: Loss of light
10 Aperture trims the PSF: increased resolution in Z direction But at a cost in brightness: Thinner section means less labeled material in image Aperture rejects some in focus light Subtle scattering or distortion rejects more light
11 Optical section thickness vs pinhole size % light passed by aperture Apparent brightness will be the product of these two!!
12 Resolution, Signal and Pinhole Diameter Best Resolution Best Signal to Noise
13 Why does confocal add depth discrimination? Light projected on a single spot in the specimen Good: excitation falls off by the distance from the focus squared Spatial filter in front of the detector Good: detection falls off by the distance from the focus squared Bad: illumination of regions that are not used to generate an image Optical sectioning Combined, sensitivity falls off by (distance from the focus) 4
14 But this arrangement generates an image of only one point in the specimen Only a single point is imaged at a time. Detector signal must be decoded by a computer to reconstruct image. Imaging point needs to be scanned somehow.
15 Scan Specimen Good: Microscope works on axis Best correction for optical aberrations Most uniform light collection efficiency Bad: Slow Sloshes specimen
16 Scan Microscope Head Good: Specimen doesn t move Microscope works on axis Best correction for optical aberrations Most uniform light collection efficiency Bad: Slow Optics can be more complicated
17 Scan Laser Good: Faster Specimen moves slowly less sloshing Bad: Very high requirements on objective Light collection may be nonuniform off-axis More complicated
18 Optical Aberrations: Imperfections in optical systems Chromatic (blue=shorter wavelength) Spherical Curvature of field
19 Spherical Aberration Zone of Confusion
20 Spherical aberration: Light misses aperture (and defocused)
21 Higher index of refraction results in shorter f Chromatic Aberration Lateral (magnification) Axial (focus shift) f Shift of focus i o Change in magnification
22 Lateral chromatic aberration - light misses aperture
23 Curvature of field: Flat object does not project a flat image f i o Results in a port hole image: dimmer at edges
24 Aberrations result in loss of signal and soft focus at depth
25 How to scan the laser beam? Place galvometer mirror at the telencentric point All light travels through the same zone Angle at which the light travels dictates the position in the specimen plane Telencentric Plane
26 Position is critical Place galvometer mirror AT the telencentric point laser If not at the point, Spherical aberration results How can two mirrors be at the same point?? Optical relay (without aberration)
27 1:1 Image relay Focal Point f
28 Position is critical Place galvometer mirrors AT the telencentric point Optically two mirrors can be at the same point Optical relay (without aberration)
29 Limitations: Phototoxicity Sample is continuously exposed to light. Weaker signal within sample requires stronger excitation and causes more toxicity.
30 Limitations: Photobleaching Scanning causes repeated exposure above and below.
31 Loss of sectioning by Scattering
32 How else to do confocal microscopy?
33 Tandem spinning disk scanner Illumination through this side Illumination through this side Alignment is critical Most of light hits mask not hole
34 Nipkow disk with lenslets >>1% pass Yokogawa
35 Nipkow disk with lenslets Yokogawa
36 Optical sectioning without an aperture? Two-Photon laser-scanning microscopy
37 Two-Photon Excited Fluorescence Very low probability: required intense pulsed laser light Requires two photons: excitation is a function of (exciting light) 2 Exciting light falls off by (distance from focus) 2 Thus, Emission falls off by (distance from focus) 4 --> Optical Sectioning without a confocal aperture!!
38 TPLSM depth discrimination by selective excitation Light projected on a single spot in the specimen Good: illumination falls off by the distance from the focus squared And Excitation depends on the square of the intensity Spatial filter in front of the detector Good: detection falls off by the distance from the focus squared Bad: illumination of regions that are not used to generate an image Optical sectioning Combined, sensitivity falls off by (distance from the focus) 4
39 Evil test case (David Piston) Deconvolution vs Confocal Fluorescent plastic cube Bleach one plane using TPLSM
40 N.A. and image brightness Epifluorescence N.A. = η sin θ Brightness = fn (NA 4 / magnification 2 ) 10x 0.5 NA is 8 times brighter than 10x 0.3NA θ But time matters Pulses are very short 100fsec x c = 30µm
Rates of excitation, emission, ISC
 Bi177 Lecture 4 Fluorescence Microscopy Phenomenon of Fluorescence Energy Diagram Rates of excitation, emission, ISC Practical Issues Lighting, Filters More on diffraction Point Spread Functions Thus Far,
Bi177 Lecture 4 Fluorescence Microscopy Phenomenon of Fluorescence Energy Diagram Rates of excitation, emission, ISC Practical Issues Lighting, Filters More on diffraction Point Spread Functions Thus Far,
3D light microscopy techniques
 3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 1 1 2! NA = 0.5! NA 2D imaging
3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 1 1 2! NA = 0.5! NA 2D imaging
Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev. Microscopy course, Michmoret Dec 2005
 Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Why use confocal microscopy? Principles of the laser scanning confocal microscope. Image resolution. Manipulating the
Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Why use confocal microscopy? Principles of the laser scanning confocal microscope. Image resolution. Manipulating the
BASICS OF CONFOCAL IMAGING (PART I)
 BASICS OF CONFOCAL IMAGING (PART I) INTERNAL COURSE 2012 LIGHT MICROSCOPY Lateral resolution Transmission Fluorescence d min 1.22 NA obj NA cond 0 0 rairy 0.61 NAobj Ernst Abbe Lord Rayleigh Depth of field
BASICS OF CONFOCAL IMAGING (PART I) INTERNAL COURSE 2012 LIGHT MICROSCOPY Lateral resolution Transmission Fluorescence d min 1.22 NA obj NA cond 0 0 rairy 0.61 NAobj Ernst Abbe Lord Rayleigh Depth of field
High resolution extended depth of field microscopy using wavefront coding
 High resolution extended depth of field microscopy using wavefront coding Matthew R. Arnison *, Peter Török #, Colin J. R. Sheppard *, W. T. Cathey +, Edward R. Dowski, Jr. +, Carol J. Cogswell *+ * Physical
High resolution extended depth of field microscopy using wavefront coding Matthew R. Arnison *, Peter Török #, Colin J. R. Sheppard *, W. T. Cathey +, Edward R. Dowski, Jr. +, Carol J. Cogswell *+ * Physical
Development of a High-speed Super-resolution Confocal Scanner
 Development of a High-speed Super-resolution Confocal Scanner Takuya Azuma *1 Takayuki Kei *1 Super-resolution microscopy techniques that overcome the spatial resolution limit of conventional light microscopy
Development of a High-speed Super-resolution Confocal Scanner Takuya Azuma *1 Takayuki Kei *1 Super-resolution microscopy techniques that overcome the spatial resolution limit of conventional light microscopy
Basics of confocal imaging (part I)
 Basics of confocal imaging (part I) Swiss Institute of Technology (EPFL) Faculty of Life Sciences Head of BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS BIOP arne.seitz@epfl.ch Lateral resolution BioImaging &Optics Platform Light
Basics of confocal imaging (part I) Swiss Institute of Technology (EPFL) Faculty of Life Sciences Head of BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS BIOP arne.seitz@epfl.ch Lateral resolution BioImaging &Optics Platform Light
Confocal Microscopy. Kristin Jensen
 Confocal Microscopy Kristin Jensen 17.11.05 References Cell Biological Applications of Confocal Microscopy, Brian Matsumoto, chapter 1 Studying protein dynamics in living cells,, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz
Confocal Microscopy Kristin Jensen 17.11.05 References Cell Biological Applications of Confocal Microscopy, Brian Matsumoto, chapter 1 Studying protein dynamics in living cells,, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz
Aberrations and adaptive optics for biomedical microscopes
 Aberrations and adaptive optics for biomedical microscopes Martin Booth Department of Engineering Science And Centre for Neural Circuits and Behaviour University of Oxford Outline Rays, wave fronts and
Aberrations and adaptive optics for biomedical microscopes Martin Booth Department of Engineering Science And Centre for Neural Circuits and Behaviour University of Oxford Outline Rays, wave fronts and
Reflecting optical system to increase signal intensity. in confocal microscopy
 Reflecting optical system to increase signal intensity in confocal microscopy DongKyun Kang *, JungWoo Seo, DaeGab Gweon Nano Opto Mechatronics Laboratory, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Korea Advanced
Reflecting optical system to increase signal intensity in confocal microscopy DongKyun Kang *, JungWoo Seo, DaeGab Gweon Nano Opto Mechatronics Laboratory, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Korea Advanced
3D light microscopy techniques
 3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 2D imaging 3D imaging Resolution
3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 2D imaging 3D imaging Resolution
Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement
 Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY BioVis Uppsala, 2017 Jeremy Adler Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Widefield & Confocal Microscopy
Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY BioVis Uppsala, 2017 Jeremy Adler Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Widefield & Confocal Microscopy
Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter
 Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter Michal Balberg +, George Barbastathis*, Sergio Fantini % and David J. Brady University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana,
Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter Michal Balberg +, George Barbastathis*, Sergio Fantini % and David J. Brady University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana,
Bio 407. Applied microscopy. Introduction into light microscopy. José María Mateos. Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis
 Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Bio 407 Applied Introduction into light José María Mateos Fundamentals of light Compound microscope Microscope composed of an objective and an additional lens (eyepiece,
Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Bio 407 Applied Introduction into light José María Mateos Fundamentals of light Compound microscope Microscope composed of an objective and an additional lens (eyepiece,
Introduction to light microscopy
 Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light microscopy Basic concepts of imaging with light Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction Diffraction
Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light microscopy Basic concepts of imaging with light Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction Diffraction
Confocal and 2-photon Imaging. October 15, 2010
 Confocal and 2-photon Imaging October 15, 2010 Review Optical Elements Adapted from Sluder & Nordberg 2007 Review Optical Elements Collector Lens Adapted from Sluder & Nordberg 2007 Review Optical Elements
Confocal and 2-photon Imaging October 15, 2010 Review Optical Elements Adapted from Sluder & Nordberg 2007 Review Optical Elements Collector Lens Adapted from Sluder & Nordberg 2007 Review Optical Elements
Confocal Microscopy. (Increasing contrast and resolu6on using op6cal sec6oning) Lecture 7. November 2017
 Confocal Microscopy (Increasing contrast and resolu6on using op6cal sec6oning) Lecture 7 November 2017 3 Flavours of Microscope Confocal Laser Scanning Problem: Out of Focus Light Spinning disc 2-Photon
Confocal Microscopy (Increasing contrast and resolu6on using op6cal sec6oning) Lecture 7 November 2017 3 Flavours of Microscope Confocal Laser Scanning Problem: Out of Focus Light Spinning disc 2-Photon
More fancy SPIM, Even fancier SPIM
 More fancy SPIM, Even fancier SPIM Last class Light sheet microscopy Fancy SPIM (ispim, dspim, etc ) This class Multi camera SPIM SIM SPIM Bessels d x,y = λ em 2 NA d z = 2 NA λ ex + n(1 cosθ λ em 1 IsoView
More fancy SPIM, Even fancier SPIM Last class Light sheet microscopy Fancy SPIM (ispim, dspim, etc ) This class Multi camera SPIM SIM SPIM Bessels d x,y = λ em 2 NA d z = 2 NA λ ex + n(1 cosθ λ em 1 IsoView
Imaging Retreat - UMASS Customized real-time confocal and 2-photon imaging
 Imaging Retreat - UMASS 2012 Customized real-time confocal and 2-photon imaging Mike Sanderson Department of Microbiology and Physiological Systems University of Massachusetts Medical School Thanks for
Imaging Retreat - UMASS 2012 Customized real-time confocal and 2-photon imaging Mike Sanderson Department of Microbiology and Physiological Systems University of Massachusetts Medical School Thanks for
Development of a new multi-wavelength confocal surface profilometer for in-situ automatic optical inspection (AOI)
 Development of a new multi-wavelength confocal surface profilometer for in-situ automatic optical inspection (AOI) Liang-Chia Chen 1#, Chao-Nan Chen 1 and Yi-Wei Chang 1 1. Institute of Automation Technology,
Development of a new multi-wavelength confocal surface profilometer for in-situ automatic optical inspection (AOI) Liang-Chia Chen 1#, Chao-Nan Chen 1 and Yi-Wei Chang 1 1. Institute of Automation Technology,
Shreyash Tandon M.S. III Year
 Shreyash Tandon M.S. III Year 20091015 Confocal microscopy is a powerful tool for generating high-resolution images and 3-D reconstructions of a specimen by using point illumination and a spatial pinhole
Shreyash Tandon M.S. III Year 20091015 Confocal microscopy is a powerful tool for generating high-resolution images and 3-D reconstructions of a specimen by using point illumination and a spatial pinhole
TRAINING MANUAL. Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO
 TRAINING MANUAL Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO September 2010 Multiphoton Microscopy Training Manual Multiphoton microscopy is only available on the LSM 510 META-NLO system. This system is equipped
TRAINING MANUAL Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO September 2010 Multiphoton Microscopy Training Manual Multiphoton microscopy is only available on the LSM 510 META-NLO system. This system is equipped
Introduction to Light Microscopy. (Image: T. Wittman, Scripps)
 Introduction to Light Microscopy (Image: T. Wittman, Scripps) The Light Microscope Four centuries of history Vibrant current development One of the most widely used research tools A. Khodjakov et al. Major
Introduction to Light Microscopy (Image: T. Wittman, Scripps) The Light Microscope Four centuries of history Vibrant current development One of the most widely used research tools A. Khodjakov et al. Major
Examination, TEN1, in courses SK2500/SK2501, Physics of Biomedical Microscopy,
 KTH Applied Physics Examination, TEN1, in courses SK2500/SK2501, Physics of Biomedical Microscopy, 2009-06-05, 8-13, FB51 Allowed aids: Compendium Imaging Physics (handed out) Compendium Light Microscopy
KTH Applied Physics Examination, TEN1, in courses SK2500/SK2501, Physics of Biomedical Microscopy, 2009-06-05, 8-13, FB51 Allowed aids: Compendium Imaging Physics (handed out) Compendium Light Microscopy
Application Note. The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a Z-stack
 The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a Z-stack The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a
The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a Z-stack The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a
High-speed 1-frame ms scanning confocal microscope with a microlens and Nipkow disks
 High-speed 1-framems scanning confocal microscope with a microlens and Nipkow disks Takeo Tanaami, Shinya Otsuki, Nobuhiro Tomosada, Yasuhito Kosugi, Mizuho Shimizu, and Hideyuki Ishida We have developed
High-speed 1-framems scanning confocal microscope with a microlens and Nipkow disks Takeo Tanaami, Shinya Otsuki, Nobuhiro Tomosada, Yasuhito Kosugi, Mizuho Shimizu, and Hideyuki Ishida We have developed
Fundamentals of Light Microscopy II: Fluorescence, Deconvolution, Confocal, Multiphoton, Spectral microscopy. Integrated Microscopy Course
 Fundamentals of Light Microscopy II: Fluorescence, Deconvolution, Confocal, Multiphoton, Spectral microscopy Integrated Microscopy Course Review Lecture 1: Microscopy Basics Light train Kohler illumination*
Fundamentals of Light Microscopy II: Fluorescence, Deconvolution, Confocal, Multiphoton, Spectral microscopy Integrated Microscopy Course Review Lecture 1: Microscopy Basics Light train Kohler illumination*
Practical Flatness Tech Note
 Practical Flatness Tech Note Understanding Laser Dichroic Performance BrightLine laser dichroic beamsplitters set a new standard for super-resolution microscopy with λ/10 flatness per inch, P-V. We ll
Practical Flatness Tech Note Understanding Laser Dichroic Performance BrightLine laser dichroic beamsplitters set a new standard for super-resolution microscopy with λ/10 flatness per inch, P-V. We ll
Imaging Introduction. September 24, 2010
 Imaging Introduction September 24, 2010 What is a microscope? Merriam-Webster: an optical instrument consisting of a lens or combination of lenses for making enlarged images of minute objects; especially:
Imaging Introduction September 24, 2010 What is a microscope? Merriam-Webster: an optical instrument consisting of a lens or combination of lenses for making enlarged images of minute objects; especially:
Training Guide for Leica SP8 Confocal/Multiphoton Microscope
 Training Guide for Leica SP8 Confocal/Multiphoton Microscope LAS AF v3.3 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON power switch for epifluorescence
Training Guide for Leica SP8 Confocal/Multiphoton Microscope LAS AF v3.3 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON power switch for epifluorescence
Instant super-resolution imaging in live cells and embryos via analog image processing
 Nature Methods Instant super-resolution imaging in live cells and embryos via analog image processing Andrew G. York, Panagiotis Chandris, Damian Dalle Nogare, Jeffrey Head, Peter Wawrzusin, Robert S.
Nature Methods Instant super-resolution imaging in live cells and embryos via analog image processing Andrew G. York, Panagiotis Chandris, Damian Dalle Nogare, Jeffrey Head, Peter Wawrzusin, Robert S.
FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY. Matyas Molnar and Dirk Pacholsky
 FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY Matyas Molnar and Dirk Pacholsky 1 The human eye perceives app. 400-700 nm; best at around 500 nm (green) Has a general resolution down to150-300 μm (human hair: 40-250 μm) We need
FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY Matyas Molnar and Dirk Pacholsky 1 The human eye perceives app. 400-700 nm; best at around 500 nm (green) Has a general resolution down to150-300 μm (human hair: 40-250 μm) We need
Optical Components for Laser Applications. Günter Toesko - Laserseminar BLZ im Dezember
 Günter Toesko - Laserseminar BLZ im Dezember 2009 1 Aberrations An optical aberration is a distortion in the image formed by an optical system compared to the original. It can arise for a number of reasons
Günter Toesko - Laserseminar BLZ im Dezember 2009 1 Aberrations An optical aberration is a distortion in the image formed by an optical system compared to the original. It can arise for a number of reasons
Bi/BE 227 Winter Assignment #3. Adding the third dimension: 3D Confocal Imaging
 Bi/BE 227 Winter 2016 Assignment #3 Adding the third dimension: 3D Confocal Imaging Schedule: Jan 20: Assignment Jan 20-Feb 8: Work on assignment Feb 10: Student PowerPoint presentations. Goals for this
Bi/BE 227 Winter 2016 Assignment #3 Adding the third dimension: 3D Confocal Imaging Schedule: Jan 20: Assignment Jan 20-Feb 8: Work on assignment Feb 10: Student PowerPoint presentations. Goals for this
Cardinal Points of an Optical System--and Other Basic Facts
 Cardinal Points of an Optical System--and Other Basic Facts The fundamental feature of any optical system is the aperture stop. Thus, the most fundamental optical system is the pinhole camera. The image
Cardinal Points of an Optical System--and Other Basic Facts The fundamental feature of any optical system is the aperture stop. Thus, the most fundamental optical system is the pinhole camera. The image
Parallel Mode Confocal System for Wafer Bump Inspection
 Parallel Mode Confocal System for Wafer Bump Inspection ECEN5616 Class Project 1 Gao Wenliang wen-liang_gao@agilent.com 1. Introduction In this paper, A parallel-mode High-speed Line-scanning confocal
Parallel Mode Confocal System for Wafer Bump Inspection ECEN5616 Class Project 1 Gao Wenliang wen-liang_gao@agilent.com 1. Introduction In this paper, A parallel-mode High-speed Line-scanning confocal
ANSWER KEY Lab 2 (IGB): Bright Field and Fluorescence Optical Microscopy and Sectioning
 Phys598BP Spring 2016 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign ANSWER KEY Lab 2 (IGB): Bright Field and Fluorescence Optical Microscopy and Sectioning Location: IGB Core Microscopy Facility Microscope:
Phys598BP Spring 2016 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign ANSWER KEY Lab 2 (IGB): Bright Field and Fluorescence Optical Microscopy and Sectioning Location: IGB Core Microscopy Facility Microscope:
Technology Note ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan
 Technology Note ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan Introducing the Fast Acquisition Mode ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan Introducing the Fast Acquisition Mode Author: Dr. Annette Bergter Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH,
Technology Note ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan Introducing the Fast Acquisition Mode ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan Introducing the Fast Acquisition Mode Author: Dr. Annette Bergter Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH,
Some of the important topics needed to be addressed in a successful lens design project (R.R. Shannon: The Art and Science of Optical Design)
 Lens design Some of the important topics needed to be addressed in a successful lens design project (R.R. Shannon: The Art and Science of Optical Design) Focal length (f) Field angle or field size F/number
Lens design Some of the important topics needed to be addressed in a successful lens design project (R.R. Shannon: The Art and Science of Optical Design) Focal length (f) Field angle or field size F/number
Introduction to light microscopy
 Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light Basic concepts of imaging with light Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Microscopy with light 1 Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction
Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light Basic concepts of imaging with light Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Microscopy with light 1 Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction
Travel to New Dimensions- LSM 880. The Resolution of a Microscope is limited. The Resolution of a Microscope is limited. Image. Image. Object.
 Travel to New Dimensions- LSM 880 LSM 880: The Power of Sensitivity Our Latest Member of the LSM 880 with GaAsP Detectors Sensitivity, and Ease of Use Innovative High-End Laser Scanning Microscopes from
Travel to New Dimensions- LSM 880 LSM 880: The Power of Sensitivity Our Latest Member of the LSM 880 with GaAsP Detectors Sensitivity, and Ease of Use Innovative High-End Laser Scanning Microscopes from
Optical System Design
 Phys 531 Lecture 12 14 October 2004 Optical System Design Last time: Surveyed examples of optical systems Today, discuss system design Lens design = course of its own (not taught by me!) Try to give some
Phys 531 Lecture 12 14 October 2004 Optical System Design Last time: Surveyed examples of optical systems Today, discuss system design Lens design = course of its own (not taught by me!) Try to give some
INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY. Urs Ziegler THE PROBLEM
 INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch THE PROBLEM 1 ORGANISMS ARE LARGE LIGHT AND ELECTRONS: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES v = Wavelength ( ) Speed (v) Frequency ( ) Amplitude (A) Propagation
INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch THE PROBLEM 1 ORGANISMS ARE LARGE LIGHT AND ELECTRONS: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES v = Wavelength ( ) Speed (v) Frequency ( ) Amplitude (A) Propagation
BEAM HALO OBSERVATION BY CORONAGRAPH
 BEAM HALO OBSERVATION BY CORONAGRAPH T. Mitsuhashi, KEK, TSUKUBA, Japan Abstract We have developed a coronagraph for the observation of the beam halo surrounding a beam. An opaque disk is set in the beam
BEAM HALO OBSERVATION BY CORONAGRAPH T. Mitsuhashi, KEK, TSUKUBA, Japan Abstract We have developed a coronagraph for the observation of the beam halo surrounding a beam. An opaque disk is set in the beam
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE DEPTH STUDY: ELECTRON MICROSCOPES
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE DEPTH STUDY: ELECTRON MICROSCOPES Shortly after the experimental confirmation of the wave properties of the electron, it was suggested that the electron could be used to examine objects
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE DEPTH STUDY: ELECTRON MICROSCOPES Shortly after the experimental confirmation of the wave properties of the electron, it was suggested that the electron could be used to examine objects
Light Microscopy. Upon completion of this lecture, the student should be able to:
 Light Light microscopy is based on the interaction of light and tissue components and can be used to study tissue features. Upon completion of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1- Explain the
Light Light microscopy is based on the interaction of light and tissue components and can be used to study tissue features. Upon completion of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1- Explain the
VC 11/12 T2 Image Formation
 VC 11/12 T2 Image Formation Mestrado em Ciência de Computadores Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia de Redes e Sistemas Informáticos Miguel Tavares Coimbra Outline Computer Vision? The Human Visual System
VC 11/12 T2 Image Formation Mestrado em Ciência de Computadores Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia de Redes e Sistemas Informáticos Miguel Tavares Coimbra Outline Computer Vision? The Human Visual System
a) How big will that physical image of the cells be your camera sensor?
 1. Consider a regular wide-field microscope set up with a 60x, NA = 1.4 objective and a monochromatic digital camera with 8 um pixels, properly positioned in the primary image plane. This microscope is
1. Consider a regular wide-field microscope set up with a 60x, NA = 1.4 objective and a monochromatic digital camera with 8 um pixels, properly positioned in the primary image plane. This microscope is
Confocal Microscopy Confocal Microscopy Acousto-optic products
 Confocal Microscopy Confocal Microscopy Acousto-optic products AA OPTO-ELECTRONIC QUANTA TECH Introduction Confocal microscopy is an imaging technique used to increase micrograph contrast and/or to reconstruct
Confocal Microscopy Confocal Microscopy Acousto-optic products AA OPTO-ELECTRONIC QUANTA TECH Introduction Confocal microscopy is an imaging technique used to increase micrograph contrast and/or to reconstruct
Resolution. Diffraction from apertures limits resolution. Rayleigh criterion θ Rayleigh = 1.22 λ/d 1 peak at 2 nd minimum. θ f D
 Microscopy Outline 1. Resolution and Simple Optical Microscope 2. Contrast enhancement: Dark field, Fluorescence (Chelsea & Peter), Phase Contrast, DIC 3. Newer Methods: Scanning Tunneling microscopy (STM),
Microscopy Outline 1. Resolution and Simple Optical Microscope 2. Contrast enhancement: Dark field, Fluorescence (Chelsea & Peter), Phase Contrast, DIC 3. Newer Methods: Scanning Tunneling microscopy (STM),
Microscope anatomy, image formation and resolution
 Microscope anatomy, image formation and resolution Ian Dobbie Buy this book for your lab: D.B. Murphy, "Fundamentals of light microscopy and electronic imaging", ISBN 0-471-25391-X Visit these websites:
Microscope anatomy, image formation and resolution Ian Dobbie Buy this book for your lab: D.B. Murphy, "Fundamentals of light microscopy and electronic imaging", ISBN 0-471-25391-X Visit these websites:
Invitation for a walk through microscopy. Sebastian Schuchmann Jörg Rösner
 Invitation for a walk through microscopy Sebastian Schuchmann Jörg Rösner joerg.roesner@charite.de Techniques in microscopy Conventional (light) microscopy bright & dark field, phase & interference contrast
Invitation for a walk through microscopy Sebastian Schuchmann Jörg Rösner joerg.roesner@charite.de Techniques in microscopy Conventional (light) microscopy bright & dark field, phase & interference contrast
ADVANCED METHODS FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY II. Jean-Yves Chatton Sept. 2006
 ADVANCED METHODS FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY II Jean-Yves Chatton Sept. 2006 Workshop outline Confocal microscopy of living cells and tissues X-Z scanning Time series Bleach: FRAP, photoactivation Emission
ADVANCED METHODS FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY II Jean-Yves Chatton Sept. 2006 Workshop outline Confocal microscopy of living cells and tissues X-Z scanning Time series Bleach: FRAP, photoactivation Emission
attocfm I for Surface Quality Inspection NANOSCOPY APPLICATION NOTE M01 RELATED PRODUCTS G
 APPLICATION NOTE M01 attocfm I for Surface Quality Inspection Confocal microscopes work by scanning a tiny light spot on a sample and by measuring the scattered light in the illuminated volume. First,
APPLICATION NOTE M01 attocfm I for Surface Quality Inspection Confocal microscopes work by scanning a tiny light spot on a sample and by measuring the scattered light in the illuminated volume. First,
Advanced Optical Microscopy lecture. 03. December 2012 Kai Wicker
 Advanced Optical Microscopy lecture 03. December 2012 Kai Wicker Today: Optical transfer functions (OTF) and point spread functions (PSF) in incoherent imaging. 1. Quick revision: the incoherent wide-field
Advanced Optical Microscopy lecture 03. December 2012 Kai Wicker Today: Optical transfer functions (OTF) and point spread functions (PSF) in incoherent imaging. 1. Quick revision: the incoherent wide-field
CCAM Microscope Objectives
 CCAM Microscope Objectives Things to consider when selecting an objective Magnification Numerical Aperture (NA) resolving power and light intensity of the objective Working Distance distance between the
CCAM Microscope Objectives Things to consider when selecting an objective Magnification Numerical Aperture (NA) resolving power and light intensity of the objective Working Distance distance between the
Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics. Geometrical Approximation. Lenses. Mirrors. Optical Systems. Images and Pupils. Aberrations.
 Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics Outline 1 Geometrical Approximation 2 Lenses 3 Mirrors 4 Optical Systems 5 Images and Pupils 6 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden Observatory, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics Outline 1 Geometrical Approximation 2 Lenses 3 Mirrors 4 Optical Systems 5 Images and Pupils 6 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden Observatory, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Heisenberg) relation applied to space and transverse wavevector
 2. Optical Microscopy 2.1 Principles A microscope is in principle nothing else than a simple lens system for magnifying small objects. The first lens, called the objective, has a short focal length (a
2. Optical Microscopy 2.1 Principles A microscope is in principle nothing else than a simple lens system for magnifying small objects. The first lens, called the objective, has a short focal length (a
Ron Liu OPTI521-Introductory Optomechanical Engineering December 7, 2009
 Synopsis of METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR IMPROVING VISION AND THE RESOLUTION OF RETINAL IMAGES by David R. Williams and Junzhong Liang from the US Patent Number: 5,777,719 issued in July 7, 1998 Ron Liu OPTI521-Introductory
Synopsis of METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR IMPROVING VISION AND THE RESOLUTION OF RETINAL IMAGES by David R. Williams and Junzhong Liang from the US Patent Number: 5,777,719 issued in July 7, 1998 Ron Liu OPTI521-Introductory
Reflection! Reflection and Virtual Image!
 1/30/14 Reflection - wave hits non-absorptive surface surface of a smooth water pool - incident vs. reflected wave law of reflection - concept for all electromagnetic waves - wave theory: reflected back
1/30/14 Reflection - wave hits non-absorptive surface surface of a smooth water pool - incident vs. reflected wave law of reflection - concept for all electromagnetic waves - wave theory: reflected back
Photolithography II ( Part 2 )
 1 Photolithography II ( Part 2 ) Chapter 14 : Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology by M. Quirk & J. Serda Saroj Kumar Patra, Department of Electronics and Telecommunication, Norwegian University of Science
1 Photolithography II ( Part 2 ) Chapter 14 : Semiconductor Manufacturing Technology by M. Quirk & J. Serda Saroj Kumar Patra, Department of Electronics and Telecommunication, Norwegian University of Science
Opti 415/515. Introduction to Optical Systems. Copyright 2009, William P. Kuhn
 Opti 415/515 Introduction to Optical Systems 1 Optical Systems Manipulate light to form an image on a detector. Point source microscope Hubble telescope (NASA) 2 Fundamental System Requirements Application
Opti 415/515 Introduction to Optical Systems 1 Optical Systems Manipulate light to form an image on a detector. Point source microscope Hubble telescope (NASA) 2 Fundamental System Requirements Application
Image Formation. Light from distant things. Geometrical optics. Pinhole camera. Chapter 36
 Light from distant things Chapter 36 We learn about a distant thing from the light it generates or redirects. The lenses in our eyes create images of objects our brains can process. This chapter concerns
Light from distant things Chapter 36 We learn about a distant thing from the light it generates or redirects. The lenses in our eyes create images of objects our brains can process. This chapter concerns
CCAM s Selection of. Zeiss Microscope Objectives
 CCAM s Selection of Zeiss Microscope Objectives 1. Magnification Image scale 2. Resolution The minimum separation distance between two points that are clearly resolved. The resolution of an objective is
CCAM s Selection of Zeiss Microscope Objectives 1. Magnification Image scale 2. Resolution The minimum separation distance between two points that are clearly resolved. The resolution of an objective is
Applications of Optics
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 26 Applications of Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Applications of Optics Many devices are based on the principles of optics
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 26 Applications of Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Applications of Optics Many devices are based on the principles of optics
Operation Guide for the Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Bio-Imaging Facility Hunter College October 2009
 Operation Guide for the Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Bio-Imaging Facility Hunter College October 2009 Introduction of Fluoresence Confocal Microscopy The first confocal microscope was invented by Princeton
Operation Guide for the Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Bio-Imaging Facility Hunter College October 2009 Introduction of Fluoresence Confocal Microscopy The first confocal microscope was invented by Princeton
Digital Camera Technologies for Scientific Bio-Imaging. Part 2: Sampling and Signal
 Digital Camera Technologies for Scientific Bio-Imaging. Part 2: Sampling and Signal Yashvinder Sabharwal, 1 James Joubert 2 and Deepak Sharma 2 1. Solexis Advisors LLC, Austin, TX, USA 2. Photometrics
Digital Camera Technologies for Scientific Bio-Imaging. Part 2: Sampling and Signal Yashvinder Sabharwal, 1 James Joubert 2 and Deepak Sharma 2 1. Solexis Advisors LLC, Austin, TX, USA 2. Photometrics
Confocal, hyperspectral, spinning disk
 Confocal, hyperspectral, spinning disk Administrative HW 6 due on Fri Midterm on Wed Covers everything since previous midterm 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed, 1 side Guest lecture by Joe Dragavon on Mon 10/30 Last
Confocal, hyperspectral, spinning disk Administrative HW 6 due on Fri Midterm on Wed Covers everything since previous midterm 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed, 1 side Guest lecture by Joe Dragavon on Mon 10/30 Last
Very short introduction to light microscopy and digital imaging
 Very short introduction to light microscopy and digital imaging Hernan G. Garcia August 1, 2005 1 Light Microscopy Basics In this section we will briefly describe the basic principles of operation and
Very short introduction to light microscopy and digital imaging Hernan G. Garcia August 1, 2005 1 Light Microscopy Basics In this section we will briefly describe the basic principles of operation and
Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics. Geometrical Approximation. Lenses. Mirrors. Optical Systems. Images and Pupils. Aberrations.
 Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics Outline 1 Geometrical Approximation 2 Lenses 3 Mirrors 4 Optical Systems 5 Images and Pupils 6 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden Observatory, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics Outline 1 Geometrical Approximation 2 Lenses 3 Mirrors 4 Optical Systems 5 Images and Pupils 6 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden Observatory, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Opterra II Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope. Innovation with Integrity
 Opterra II Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Enabling 4D Live-Cell Fluorescence Imaging through Speed, Sensitivity, Viability and Simplicity Innovation with Integrity Fluorescence Microscopy The
Opterra II Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Enabling 4D Live-Cell Fluorescence Imaging through Speed, Sensitivity, Viability and Simplicity Innovation with Integrity Fluorescence Microscopy The
Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 5 LIVE Confocal Microscope
 Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 5 LIVE Confocal Microscope AIM 4.2 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Verify that main power switches on the
Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 5 LIVE Confocal Microscope AIM 4.2 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Verify that main power switches on the
Laboratory experiment aberrations
 Laboratory experiment aberrations Obligatory laboratory experiment on course in Optical design, SK2330/SK3330, KTH. Date Name Pass Objective This laboratory experiment is intended to demonstrate the most
Laboratory experiment aberrations Obligatory laboratory experiment on course in Optical design, SK2330/SK3330, KTH. Date Name Pass Objective This laboratory experiment is intended to demonstrate the most
Multiphoton Microscopy
 Multiphoton Microscopy A. Neumann, Y. Kuznetsova Introduction Multi-Photon Fluorescence Microscopy is a relatively novel imaging technique in cell biology. It relies on the quasi-simultaneous absorption
Multiphoton Microscopy A. Neumann, Y. Kuznetsova Introduction Multi-Photon Fluorescence Microscopy is a relatively novel imaging technique in cell biology. It relies on the quasi-simultaneous absorption
You won t be able to measure the incident power precisely. The readout of the power would be lower than the real incident power.
 1. a) Given the transfer function of a detector (below), label and describe these terms: i. dynamic range ii. linear dynamic range iii. sensitivity iv. responsivity b) Imagine you are using an optical
1. a) Given the transfer function of a detector (below), label and describe these terms: i. dynamic range ii. linear dynamic range iii. sensitivity iv. responsivity b) Imagine you are using an optical
Lecture 4: Geometrical Optics 2. Optical Systems. Images and Pupils. Rays. Wavefronts. Aberrations. Outline
 Lecture 4: Geometrical Optics 2 Outline 1 Optical Systems 2 Images and Pupils 3 Rays 4 Wavefronts 5 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl Lecture 4: Geometrical
Lecture 4: Geometrical Optics 2 Outline 1 Optical Systems 2 Images and Pupils 3 Rays 4 Wavefronts 5 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden University, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl Lecture 4: Geometrical
Dynamic beam shaping with programmable diffractive optics
 Dynamic beam shaping with programmable diffractive optics Bosanta R. Boruah Dept. of Physics, GU Page 1 Outline of the talk Introduction Holography Programmable diffractive optics Laser scanning confocal
Dynamic beam shaping with programmable diffractive optics Bosanta R. Boruah Dept. of Physics, GU Page 1 Outline of the talk Introduction Holography Programmable diffractive optics Laser scanning confocal
Final Exam, 150 points PMB 185: Techniques in Light Microscopy
 Final Exam, 150 points Name PMB 185: Techniques in Light Microscopy Point value is in parentheses at the end of each question. Note: GFP = green fluorescent protein ; CFP = cyan fluorescent protein ; YFP
Final Exam, 150 points Name PMB 185: Techniques in Light Microscopy Point value is in parentheses at the end of each question. Note: GFP = green fluorescent protein ; CFP = cyan fluorescent protein ; YFP
VC 14/15 TP2 Image Formation
 VC 14/15 TP2 Image Formation Mestrado em Ciência de Computadores Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia de Redes e Sistemas Informáticos Miguel Tavares Coimbra Outline Computer Vision? The Human Visual System
VC 14/15 TP2 Image Formation Mestrado em Ciência de Computadores Mestrado Integrado em Engenharia de Redes e Sistemas Informáticos Miguel Tavares Coimbra Outline Computer Vision? The Human Visual System
BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS PLATFORM EPFL SV PTBIOP LASER SCANNING CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY PRACTICAL CONSIDERATIONS
 LASER SCANNING CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY PRACTICAL CONSIDERATIONS IMPORTANT PARAMETERS Pixel dwell time Zoom and pixel number PIXEL DWELL TIME How much time signal is collected at every pixel Very small values,
LASER SCANNING CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY PRACTICAL CONSIDERATIONS IMPORTANT PARAMETERS Pixel dwell time Zoom and pixel number PIXEL DWELL TIME How much time signal is collected at every pixel Very small values,
PHY 431 Homework Set #5 Due Nov. 20 at the start of class
 PHY 431 Homework Set #5 Due Nov. 0 at the start of class 1) Newton s rings (10%) The radius of curvature of the convex surface of a plano-convex lens is 30 cm. The lens is placed with its convex side down
PHY 431 Homework Set #5 Due Nov. 0 at the start of class 1) Newton s rings (10%) The radius of curvature of the convex surface of a plano-convex lens is 30 cm. The lens is placed with its convex side down
ECEG105/ECEU646 Optics for Engineers Course Notes Part 4: Apertures, Aberrations Prof. Charles A. DiMarzio Northeastern University Fall 2008
 ECEG105/ECEU646 Optics for Engineers Course Notes Part 4: Apertures, Aberrations Prof. Charles A. DiMarzio Northeastern University Fall 2008 July 2003+ Chuck DiMarzio, Northeastern University 11270-04-1
ECEG105/ECEU646 Optics for Engineers Course Notes Part 4: Apertures, Aberrations Prof. Charles A. DiMarzio Northeastern University Fall 2008 July 2003+ Chuck DiMarzio, Northeastern University 11270-04-1
The Zeiss AiryScan System, Confocal Four.
 The Zeiss AiryScan System, Confocal Four. Overview. The Zeiss AiryScan module is a segmented, radially stacked GaASP detector and collector system designed to subsample the airy disk of a point emission
The Zeiss AiryScan System, Confocal Four. Overview. The Zeiss AiryScan module is a segmented, radially stacked GaASP detector and collector system designed to subsample the airy disk of a point emission
Big League Cryogenics and Vacuum The LHC at CERN
 Big League Cryogenics and Vacuum The LHC at CERN A typical astronomical instrument must maintain about one cubic meter at a pressure of
Big League Cryogenics and Vacuum The LHC at CERN A typical astronomical instrument must maintain about one cubic meter at a pressure of
Administrative details:
 Administrative details: Anything from your side? www.photonics.ethz.ch 1 What are we actually doing here? Optical imaging: Focusing by a lens Angular spectrum Paraxial approximation Gaussian beams Method
Administrative details: Anything from your side? www.photonics.ethz.ch 1 What are we actually doing here? Optical imaging: Focusing by a lens Angular spectrum Paraxial approximation Gaussian beams Method
Opto Engineering S.r.l.
 TUTORIAL #1 Telecentric Lenses: basic information and working principles On line dimensional control is one of the most challenging and difficult applications of vision systems. On the other hand, besides
TUTORIAL #1 Telecentric Lenses: basic information and working principles On line dimensional control is one of the most challenging and difficult applications of vision systems. On the other hand, besides
Properties of Structured Light
 Properties of Structured Light Gaussian Beams Structured light sources using lasers as the illumination source are governed by theories of Gaussian beams. Unlike incoherent sources, coherent laser sources
Properties of Structured Light Gaussian Beams Structured light sources using lasers as the illumination source are governed by theories of Gaussian beams. Unlike incoherent sources, coherent laser sources
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup.
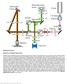 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup. Excitation from a femtosecond laser is passed through intensity control and shuttering optics (1/2 λ wave plate, polarizing beam splitting
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup. Excitation from a femtosecond laser is passed through intensity control and shuttering optics (1/2 λ wave plate, polarizing beam splitting
Maria Smedh, Centre for Cellular Imaging. Maria Smedh, Centre for Cellular Imaging
 Nonlinear microscopy I: Two-photon fluorescence microscopy Multiphoton Microscopy What is multiphoton imaging? Applications Different imaging modes Advantages/disadvantages Scattering of light in thick
Nonlinear microscopy I: Two-photon fluorescence microscopy Multiphoton Microscopy What is multiphoton imaging? Applications Different imaging modes Advantages/disadvantages Scattering of light in thick
LENSES. INEL 6088 Computer Vision
 LENSES INEL 6088 Computer Vision Digital camera A digital camera replaces film with a sensor array Each cell in the array is a Charge Coupled Device light-sensitive diode that converts photons to electrons
LENSES INEL 6088 Computer Vision Digital camera A digital camera replaces film with a sensor array Each cell in the array is a Charge Coupled Device light-sensitive diode that converts photons to electrons
5/4/2015 INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY. Urs Ziegler MICROSCOPY WITH LIGHT. Image formation in a nutshell. Overview of techniques
 INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch MICROSCOPY WITH LIGHT INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY Image formation in a nutshell Overview of techniques Widefield microscopy Resolution
INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch MICROSCOPY WITH LIGHT INTRODUCTION TO LIGHT MICROSCOPY Image formation in a nutshell Overview of techniques Widefield microscopy Resolution
Test procedures Page: 1 of 5
 Test procedures Page: 1 of 5 1 Scope This part of document establishes uniform requirements for measuring the numerical aperture of optical fibre, thereby assisting in the inspection of fibres and cables
Test procedures Page: 1 of 5 1 Scope This part of document establishes uniform requirements for measuring the numerical aperture of optical fibre, thereby assisting in the inspection of fibres and cables
SETTING UP OF A TOTAL INTERNAL REFLECTION FLUORESCENT MICROSCOPE (TIRFM) SYSTEM: A DETAILED OVERVIEW
 PK ISSN 0022-2941; CODEN JNSMAC Vol. 51, (2011) PP 31-45 SETTING UP OF A TOTAL INTERNAL REFLECTION FLUORESCENT MICROSCOPE (TIRFM) SYSTEM: A DETAILED OVERVIEW A. R. KHAN 1 *, S. AKHLAQ 1, M. N. B. ABID
PK ISSN 0022-2941; CODEN JNSMAC Vol. 51, (2011) PP 31-45 SETTING UP OF A TOTAL INTERNAL REFLECTION FLUORESCENT MICROSCOPE (TIRFM) SYSTEM: A DETAILED OVERVIEW A. R. KHAN 1 *, S. AKHLAQ 1, M. N. B. ABID
MOM#3: LIGHT SHEET MICROSCOPY (LSM) Stanley Cohen, MD
 MOM#3: LIGHT SHEET MICROSCOPY (LSM) Stanley Cohen, MD Introduction. Although the technical details of light sheet imaging and its various permutations appear at first glance to be complex and require some
MOM#3: LIGHT SHEET MICROSCOPY (LSM) Stanley Cohen, MD Introduction. Although the technical details of light sheet imaging and its various permutations appear at first glance to be complex and require some
Enhancement of the lateral resolution and the image quality in a line-scanning tomographic optical microscope
 Summary of the PhD thesis Enhancement of the lateral resolution and the image quality in a line-scanning tomographic optical microscope Author: Dudás, László Supervisors: Prof. Dr. Szabó, Gábor and Dr.
Summary of the PhD thesis Enhancement of the lateral resolution and the image quality in a line-scanning tomographic optical microscope Author: Dudás, László Supervisors: Prof. Dr. Szabó, Gábor and Dr.
ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB
 ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB Lab 2: Imaging 1 the Telescope Original Version: Prof. McLeod SUMMARY: In this lab you will become familiar with the use of one or more lenses to create images of distant
ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB Lab 2: Imaging 1 the Telescope Original Version: Prof. McLeod SUMMARY: In this lab you will become familiar with the use of one or more lenses to create images of distant
1 Co Localization and Working flow with the lsm700
 1 Co Localization and Working flow with the lsm700 Samples -1 slide = mousse intestine, Dapi / Ki 67 with Cy3/ BrDU with alexa 488. -1 slide = mousse intestine, Dapi / Ki 67 with Cy3/ no BrDU (but with
1 Co Localization and Working flow with the lsm700 Samples -1 slide = mousse intestine, Dapi / Ki 67 with Cy3/ BrDU with alexa 488. -1 slide = mousse intestine, Dapi / Ki 67 with Cy3/ no BrDU (but with
Mirrors and Lenses. Images can be formed by reflection from mirrors. Images can be formed by refraction through lenses.
 Mirrors and Lenses Images can be formed by reflection from mirrors. Images can be formed by refraction through lenses. Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object
Mirrors and Lenses Images can be formed by reflection from mirrors. Images can be formed by refraction through lenses. Notation for Mirrors and Lenses The object distance is the distance from the object
OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES
 101 L7 OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES Aims Your aim here should be to acquire a working knowledge of the basic components of optical systems and understand their purpose, function and limitations in terms
101 L7 OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES Aims Your aim here should be to acquire a working knowledge of the basic components of optical systems and understand their purpose, function and limitations in terms
Chapter 2 The Study of Microbial Structure: Microscopy and Specimen Preparation
 Chapter 2 The Study of Microbial Structure: Microscopy and Specimen Preparation 1 Lenses and the Bending of Light light is refracted (bent) when passing from one medium to another refractive index a measure
Chapter 2 The Study of Microbial Structure: Microscopy and Specimen Preparation 1 Lenses and the Bending of Light light is refracted (bent) when passing from one medium to another refractive index a measure
