ELEC Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2015 Logic Synthesis (Chapters 2-5)
|
|
|
- Miles Barker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ELE igital Logic ircuits Fall 2015 Logic Synthesis (hapters 2-5) Vishwani. grawal James J. anaher Professor epartment of Electrical and omputer Engineering uburn University, uburn, L vagrawal@eng.auburn.edu Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 1
2 Logic Synthesis efinition: To design a logic circuit such that it meets the specifications and can be economically manufactured: Performance meets delay specification, or has minimum delay. ost uses minimum hardware, smallest chip area, smallest number of gates or transistors. Power meets power specification, or consumes minimum power. Testablility has no redundant (untestable) logic and is easily testable. Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 2
3 Synthesis Procedure Minimization Obtain MSOP or MPOS. This is also known as two-level minimization because the result can be implemented as a two-level N-OR or NN-NN or NOR-NOR circuit. Technology mapping onsidering design requirements, transform the minimized form into one of the technologically realizable forms: Programmable logic array (PL) Standard cell library Field programmable gate array (FPG) Others... Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 3
4 References on Synthesis G. e Micheli, Synthesis and Optimization of igital ircuits, New York: McGraw-Hill, S. evadas,. Ghosh and K. Keutzer, Logic Synthesis, New York: McGraw-Hill, Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 4
5 Programmable Logic rray (PL) direct implementation of multi-output function as a two-level circuit in MOS technology. PL styles: NN-NN NOR-NOR Textbook, hapter 5. Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 5
6 Example: Two-Output Function Need four products: P1,, P3, P4 F1 F B B Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 6
7 Two-Level N-OR Implementation lso known as technology-independent circuit. INPUTS N OR P1 F1 B P3 P4 F2 Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 7
8 NN-NN Implementation INPUTS NN NN P1 F1 B P3 F2 P4 Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 8
9 NN Gate in nmos Technology V epletion load V Enhancement load V XY XY XY X X X Y Y Y GN GN GN R.. Jaeger and T, N. Blalock, Microelectronic ircuit esign, Boston: McGraw-Hill, 2008, Section Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 9
10 NN-NN PL B F1 F2 V V P1 V V P3 V P4 V GN Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 10
11 NN-NN PL SHEMTI B F1 F2 INPUTS Transistors at cross-points OUTPUTS P1 P3 Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 11 P4 N-plane OR-plane
12 Standard-ell esign Obtain two-level minimized form. Map the design onto predesigned building blocks called standard cells (technology mapping). Standard-cell library contains predesigned logic cells in the technology of manufacture. Examples of technology: 90 nanometer MOS 65 nanometer MOS 45 nanometer MOS... This is known as application-specific integrated circuit (SI). Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 12
13 Technology Mapping Find a common logic element, e.g., two-input NN gate or inverter (one-input NN). MSOP is converted into NN-NN circuit. Split larger input gates into two-input NN gates and inverters. over the circuit with standard cells, also split into two-input NN gates and inverters (graph-matching). Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 13
14 Typical ell Library Name rea units (cost) Inputs Output function, Z Inverter 2 NN2 3, B NN3 4, B, NN4 5, B,, OI21 4, B, OI21 4, B, OI22 5, B,, XOR 4, B Z = Z = Z = Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 14 B B Z = B Z = B + Z = ( + B) Z = B + Z = B + B S. evadas,. Ghosh and K. Keutzer, Logic Synthesis, New York: McGraw-Hill 1994, Section 7.7, pp
15 NN3 ell in Transistors V Z B GN Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 15
16 NN3 ell Graphs irected cyclic Graph (G) (tree) Root Output One-input node (NOT) Two-input node (NN) Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 16
17 NN4 ell Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 17
18 OI21 ell Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 18
19 OI21 ell Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 19
20 OI22 ell in Transistors V Pull-up network B Z Pull-down network Observe that in a MOS circuit, any vector of input variables connects the output Z either to GN or to V, giving it a value 0 or 1, respectively. Examining the pull-down network, we notice that the output is connected to GN if B = 1 or =1. That gives the output function as,. The cell, therefore, is OI22. Z = B+ Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 20 GN
21 OI22 ell Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 21
22 XOR ell Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 22
23 NN Graphs for Library ells Name rea units (cost) Inputs NN graph Inverter 2 NN2 3, B NN3 4, B, NN4 5, B,, OI21 4, B, OI21 4, B, OI22 5, B,, XOR 4, B Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 23
24 Technology Mapping Procedure Obtain MSOP. onvert to two-level N-OR circuit. Transform to two-level NN-NN circuit. Transform to two-input NN and inverter tree network. Perform an optimal pattern matching to obtain a minimum cost tree covering. Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 24
25 Previous Example: 2-Level NN (Slide 8) INPUTS NN NN P1 F1 B P3 F2 P4 Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 25
26 Simple Technology Mapping (2) NN2 (3) NN2 (3) F1 NN3 (4) NN3 (4) B (2) NN2 (3) F2 NN2 (3) ost = 24 Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 26
27 Optimum Mapping: onvert NN ircuit to irected cyclic Graph (G) P1 F1 B P3 P4 F2 Each node is a NN gate. (NOT 1-input NN) Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 27
28 Split G into Trees (Forest) B F1 B F2 ost = 24 Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 28
29 Split Nodes With More Than Two Branches (Use NN3, NN4 Graphs) or F2 or F2 NN4 or Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 29
30 Uniform Branching (1 or 2) F1 B B F2 ost = 32 Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 30
31 Graph Matching (2) OI21 (4) F1 Nodes inserted For pattern matching B NN3 (4) B (2) NN2 (3) NN3 (4) F2 NN2 (3) ost = 22 Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 31
32 Technology Mapping OI21 (4) Inverters inserted For pattern matching (2) B (2) NN3 (4) F1 NN3 (4) B (2) NN2 (3) NN2 (3) Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 32 F2 ost = 22
33 Mapped ircuit (2) OI21 (4) F1 NN3 (4) NN3 (4) B (2) NN2 (3) F2 NN2 (3) ost = 22 Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 33
34 Original Reference K. Keutzer, GON: Technology Binding and Local Optimization by G matching, Proc. 24th esign utomation onf., 1987, pp Fall 2015, Nov 6... ELE Lecture 6 34
VLSI Design. Static CMOS Logic
 VLSI esign Static MOS Logic [dapted from Rabaey s igital Integrated ircuits, 2002, J. Rabaey et al.] EE4121 Static MOS Logic.1 ZLM Review: MOS Process at a Glance efine active areas Etch and fill trenches
VLSI esign Static MOS Logic [dapted from Rabaey s igital Integrated ircuits, 2002, J. Rabaey et al.] EE4121 Static MOS Logic.1 ZLM Review: MOS Process at a Glance efine active areas Etch and fill trenches
Copyright 2000 N. AYDIN. All rights reserved. 1
 Introduction to igital Prof Nizamettin IN naydin@yildizedutr naydin@ieeeorg ourse Outline igital omputers, Number Systems, rithmetic Operations, ecimal, lphanumeric, and Gray odes 2 inary, Gates, oolean
Introduction to igital Prof Nizamettin IN naydin@yildizedutr naydin@ieeeorg ourse Outline igital omputers, Number Systems, rithmetic Operations, ecimal, lphanumeric, and Gray odes 2 inary, Gates, oolean
ECE520 VLSI Design. Lecture 11: Combinational Static Logic. Prof. Payman Zarkesh-Ha
 EE520 VLSI esign Lecture 11: ombinational Static Logic Prof. Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: EE ldg. 230 Office hours: Wednesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: pzarkesh@unm.edu Slide: 1 eview of Last
EE520 VLSI esign Lecture 11: ombinational Static Logic Prof. Payman Zarkesh-Ha Office: EE ldg. 230 Office hours: Wednesday 2:00-3:00PM or by appointment E-mail: pzarkesh@unm.edu Slide: 1 eview of Last
Synthesis of Combinational Logic
 Synthesis of ombinational Logic 6.4 Gates F = xor Handouts: Lecture Slides, PS3, Lab2 6.4 - Spring 2 2/2/ L5 Logic Synthesis Review: K-map Minimization ) opy truth table into K-Map 2) Identify subcubes,
Synthesis of ombinational Logic 6.4 Gates F = xor Handouts: Lecture Slides, PS3, Lab2 6.4 - Spring 2 2/2/ L5 Logic Synthesis Review: K-map Minimization ) opy truth table into K-Map 2) Identify subcubes,
EE260: Digital Design, Spring n More Logic Gates n NAND and NOR Gates
 EE26: igital esign, Spring 28 -eb-8 EE 26: Introduction to igital esign oolean lgebra: Logic Synthesis and Timing Hazards ao Zheng epartment of Electrical Engineering University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Overview
EE26: igital esign, Spring 28 -eb-8 EE 26: Introduction to igital esign oolean lgebra: Logic Synthesis and Timing Hazards ao Zheng epartment of Electrical Engineering University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa Overview
ELEC Digital Logic Circuits Fall 2015 Delay and Power
 ELEC - Digital Logic Circuits Fall 5 Delay and Power Vishwani D. Agrawal James J. Danaher Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Auburn University, Auburn, AL 36849 http://www.eng.auburn.edu/~vagrawal
ELEC - Digital Logic Circuits Fall 5 Delay and Power Vishwani D. Agrawal James J. Danaher Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Auburn University, Auburn, AL 36849 http://www.eng.auburn.edu/~vagrawal
Integrated Circuits & Systems
 Federal University of Santa atarina enter for Technology omputer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated ircuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 16 MOS ombinational ircuits - 2 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br Pass
Federal University of Santa atarina enter for Technology omputer Science & Electronics Engineering Integrated ircuits & Systems INE 5442 Lecture 16 MOS ombinational ircuits - 2 guntzel@inf.ufsc.br Pass
Programmable Logic Arrays (PLAs)
 Programmable Logic Regular logic Programmable Logic rrays Multiplexers/ecoders ROMs Field Programmable Gate rrays Xilinx Vertex Random Logic Full ustom esign S 5 - Fall 25 Lec. #3: Programmable Logic -
Programmable Logic Regular logic Programmable Logic rrays Multiplexers/ecoders ROMs Field Programmable Gate rrays Xilinx Vertex Random Logic Full ustom esign S 5 - Fall 25 Lec. #3: Programmable Logic -
Programmable Logic Arrays (PLAs)
 Programmable Logic! Regular logic " Programmable Logic rrays " Multiplexers/ecoders " ROMs! Field Programmable Gate rrays " Xilinx Vertex Random Logic Full ustom esign S 5 - Spring 27 Lec. #3: Programmable
Programmable Logic! Regular logic " Programmable Logic rrays " Multiplexers/ecoders " ROMs! Field Programmable Gate rrays " Xilinx Vertex Random Logic Full ustom esign S 5 - Spring 27 Lec. #3: Programmable
CMOS Digital Logic Design with Verilog. Chapter1 Digital IC Design &Technology
 CMOS Digital Logic Design with Verilog Chapter1 Digital IC Design &Technology Chapter Overview: In this chapter we study the concept of digital hardware design & technology. This chapter deals the standard
CMOS Digital Logic Design with Verilog Chapter1 Digital IC Design &Technology Chapter Overview: In this chapter we study the concept of digital hardware design & technology. This chapter deals the standard
Logic Restructuring Revisited. Glitching in an RCA. Glitching in Static CMOS Networks
 Logic Restructuring Revisited Low Power VLSI System Design Lectures 4 & 5: Logic-Level Power Optimization Prof. R. Iris ahar September 8 &, 7 Logic restructuring: hanging the topology of a logic network
Logic Restructuring Revisited Low Power VLSI System Design Lectures 4 & 5: Logic-Level Power Optimization Prof. R. Iris ahar September 8 &, 7 Logic restructuring: hanging the topology of a logic network
CS8803: Advanced Digital Design for Embedded Hardware
 HPTER II-6 MO MO WITHE WITH NETWORK -WITHE IN ERIE -WITHE IN PRLLEL -INPUT ELETOR 883: dvanced Digital Design for Embedded Hardware Lecture : MO Transistors and Layout The idea is to use the series and
HPTER II-6 MO MO WITHE WITH NETWORK -WITHE IN ERIE -WITHE IN PRLLEL -INPUT ELETOR 883: dvanced Digital Design for Embedded Hardware Lecture : MO Transistors and Layout The idea is to use the series and
Digital Integrated CircuitDesign
 Digital Integrated CircuitDesign Lecture 11 BiCMOS PMOS rray Q1 NMOS rray Y NMOS rray Q2 dib brishamifar EE Department IUST Contents Introduction BiCMOS Devices BiCMOS Inverters BiCMOS Gates BiCMOS Drivers
Digital Integrated CircuitDesign Lecture 11 BiCMOS PMOS rray Q1 NMOS rray Y NMOS rray Q2 dib brishamifar EE Department IUST Contents Introduction BiCMOS Devices BiCMOS Inverters BiCMOS Gates BiCMOS Drivers
SYNTHESIS OF COMBINATIONAL CIRCUITS
 HPTER 6 SYNTHESIS O OMINTIONL IRUITS 6.1 Introduction oolean functions can be expressed in the forms of sum-of-products and productof-sums. These expressions can also be minimized using algebraic manipulations
HPTER 6 SYNTHESIS O OMINTIONL IRUITS 6.1 Introduction oolean functions can be expressed in the forms of sum-of-products and productof-sums. These expressions can also be minimized using algebraic manipulations
Novel Library of Logic Gates with Ambipolar CNTFETs: Opportunities for Multi-Level Logic Synthesis
 Novel Library of ates with mbipolar NTFETs: Opportunities for Multi-Level ynthesis M. Haykel en Jamaa, Kartik Mohanram, and iovanni e Micheli wiss Federal Institute of Technology, Lausanne, witzerland
Novel Library of ates with mbipolar NTFETs: Opportunities for Multi-Level ynthesis M. Haykel en Jamaa, Kartik Mohanram, and iovanni e Micheli wiss Federal Institute of Technology, Lausanne, witzerland
Domino CMOS Implementation of Power Optimized and High Performance CLA adder
 Domino CMOS Implementation of Power Optimized and High Performance CLA adder Kistipati Karthik Reddy 1, Jeeru Dinesh Reddy 2 1 PG Student, BMS College of Engineering, Bull temple Road, Bengaluru, India
Domino CMOS Implementation of Power Optimized and High Performance CLA adder Kistipati Karthik Reddy 1, Jeeru Dinesh Reddy 2 1 PG Student, BMS College of Engineering, Bull temple Road, Bengaluru, India
Intelligent Systems Group Department of Electronics. An Evolvable, Field-Programmable Full Custom Analogue Transistor Array (FPTA)
 Department of Electronics n Evolvable, Field-Programmable Full Custom nalogue Transistor rray (FPT) Outline What`s Behind nalog? Evolution Substrate custom made configurable transistor array (FPT) Ways
Department of Electronics n Evolvable, Field-Programmable Full Custom nalogue Transistor rray (FPT) Outline What`s Behind nalog? Evolution Substrate custom made configurable transistor array (FPT) Ways
EC 1354-Principles of VLSI Design
 EC 1354-Principles of VLSI Design UNIT I MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY AND PROCESS TECHNOLOGY PART-A 1. What are the four generations of integrated circuits? 2. Give the advantages of IC. 3. Give the variety of
EC 1354-Principles of VLSI Design UNIT I MOS TRANSISTOR THEORY AND PROCESS TECHNOLOGY PART-A 1. What are the four generations of integrated circuits? 2. Give the advantages of IC. 3. Give the variety of
CMOS LOGIC Inside the CMOS inverter, no I D current flows through transistors when input is logic 1 or logic 0, because
 EEC 40 pring 2003 Lecture 22. Ross EEC 40 pring 2003 Lecture 22. Ross CMO LOGIC Inside the CMO inverter, no I current flows through transistors when input is logic 1 or logic 0, because the NMO transistor
EEC 40 pring 2003 Lecture 22. Ross EEC 40 pring 2003 Lecture 22. Ross CMO LOGIC Inside the CMO inverter, no I current flows through transistors when input is logic 1 or logic 0, because the NMO transistor
EE 330 Lecture 5. Other Logic Styles. Improved Device Models. complex logic gates pass transistor logic
 EE 330 Lecture 5 Other Logic Styles complex logic gates pass transistor logic Improved evice Models Review from Last Time MOS Transistor Qualitative iscussion of n-channel Operation Source Gate rain rain
EE 330 Lecture 5 Other Logic Styles complex logic gates pass transistor logic Improved evice Models Review from Last Time MOS Transistor Qualitative iscussion of n-channel Operation Source Gate rain rain
EE 330 Lecture 5. Other Logic Styles Improved Device Models Stick Diagrams
 EE 330 Lecture 5 Other Logic Styles Improved evice Models Stick iagrams Review from Last Time MOS Transistor Qualitative iscussion of n-channel Operation ulk Source Gate rain rain Gate n-channel MOSFET
EE 330 Lecture 5 Other Logic Styles Improved evice Models Stick iagrams Review from Last Time MOS Transistor Qualitative iscussion of n-channel Operation ulk Source Gate rain rain Gate n-channel MOSFET
Lecture # 16 Logic with a State Dependent Device. Logic Gates How are they built in practice?
 EECS 42 Introduction to Digital Electronics Andrew R. Neureuther These viewgraphs will be handed out in class 1/21/ Lecture # 16 Logic with a State Dependent Device S&O pp. 9-9, 4-6 (read for graphs and
EECS 42 Introduction to Digital Electronics Andrew R. Neureuther These viewgraphs will be handed out in class 1/21/ Lecture # 16 Logic with a State Dependent Device S&O pp. 9-9, 4-6 (read for graphs and
EE 330 Lecture 44. Digital Circuits. Ring Oscillators Sequential Logic Array Logic Memory Arrays. Final: Tuesday May 2 7:30-9:30
 EE 330 Lecture 44 igital Circuits Ring Oscillators Sequential Logic Array Logic Memory Arrays Final: Tuesday May 2 7:30-9:30 Review from Last Time ynamic Logic Basic ynamic Logic Gate V F A n PN Any of
EE 330 Lecture 44 igital Circuits Ring Oscillators Sequential Logic Array Logic Memory Arrays Final: Tuesday May 2 7:30-9:30 Review from Last Time ynamic Logic Basic ynamic Logic Gate V F A n PN Any of
Learning Outcomes. Spiral 2 8. Digital Design Overview LAYOUT
 2-8.1 2-8.2 Spiral 2 8 Cell Mark Redekopp earning Outcomes I understand how a digital circuit is composed of layers of materials forming transistors and wires I understand how each layer is expressed as
2-8.1 2-8.2 Spiral 2 8 Cell Mark Redekopp earning Outcomes I understand how a digital circuit is composed of layers of materials forming transistors and wires I understand how each layer is expressed as
Digital Fundamentals
 Digital Fundamentals Tenth Edition Floyd hapter 5 Floyd, Digital Fundamentals, th ed 28 Pearson Education 29 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 7458. ll Rights Reserved ombinational Logic ircuits
Digital Fundamentals Tenth Edition Floyd hapter 5 Floyd, Digital Fundamentals, th ed 28 Pearson Education 29 Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ 7458. ll Rights Reserved ombinational Logic ircuits
Engr354: Digital Logic Circuits
 Engr354: Digital Logic Circuits Chapter 3: Implementation Technology Curtis Nelson Chapter 3 Overview In this chapter you will learn about: How transistors are used as switches; Integrated circuit technology;
Engr354: Digital Logic Circuits Chapter 3: Implementation Technology Curtis Nelson Chapter 3 Overview In this chapter you will learn about: How transistors are used as switches; Integrated circuit technology;
EXPERIMENT #5 COMBINATIONAL and SEQUENTIAL LOGIC CIRCUITS Hardware implementation and software design
 PH-315 La Rosa EXPERIMENT #5 COMINTIONL and SEUENTIL LOGIC CIRCUITS Hardware implementation and software design I PURPOSE: To familiarize with combinational and sequential logic circuits Combinational
PH-315 La Rosa EXPERIMENT #5 COMINTIONL and SEUENTIL LOGIC CIRCUITS Hardware implementation and software design I PURPOSE: To familiarize with combinational and sequential logic circuits Combinational
Low power high speed hybrid CMOS Full Adder By using sub-micron technology
 Low power high speed hybrid CMOS Full Adder By using sub-micron technology Ch.Naveen Kumar 1 Assistant professor,ece department GURUNANAK institutions technical campus Hyderabad-501506 A.V. Rameshwar Rao
Low power high speed hybrid CMOS Full Adder By using sub-micron technology Ch.Naveen Kumar 1 Assistant professor,ece department GURUNANAK institutions technical campus Hyderabad-501506 A.V. Rameshwar Rao
General Structure of MOS Inverter
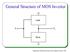 General Structure of MOS Inverter Load V i Drive Department of Microelectronics and omputer Science, TUL Digital MOS ircuits Families Digital MOS ircuits PMOS NMOS MOS BiMOS Depletion mode load Enhancement
General Structure of MOS Inverter Load V i Drive Department of Microelectronics and omputer Science, TUL Digital MOS ircuits Families Digital MOS ircuits PMOS NMOS MOS BiMOS Depletion mode load Enhancement
Implementation of High Performance Carry Save Adder Using Domino Logic
 Page 136 Implementation of High Performance Carry Save Adder Using Domino Logic T.Jayasimha 1, Daka Lakshmi 2, M.Gokula Lakshmi 3, S.Kiruthiga 4 and K.Kaviya 5 1 Assistant Professor, Department of ECE,
Page 136 Implementation of High Performance Carry Save Adder Using Domino Logic T.Jayasimha 1, Daka Lakshmi 2, M.Gokula Lakshmi 3, S.Kiruthiga 4 and K.Kaviya 5 1 Assistant Professor, Department of ECE,
In this lecture: Lecture 8: ROM & Programmable Logic Devices
 In this lecture: Lecture 8: ROM Programmable Logic Devices Dr Pete Sedcole Department of EE Engineering Imperial College London http://caseeicacuk/~nps/ (Floyd, 3 5, 3) (Tocci 2, 24, 25, 27, 28, 3 34)
In this lecture: Lecture 8: ROM Programmable Logic Devices Dr Pete Sedcole Department of EE Engineering Imperial College London http://caseeicacuk/~nps/ (Floyd, 3 5, 3) (Tocci 2, 24, 25, 27, 28, 3 34)
Low Power System-On-Chip-Design Chapter 12: Physical Libraries
 1 Low Power System-On-Chip-Design Chapter 12: Physical Libraries Friedemann Wesner 2 Outline Standard Cell Libraries Modeling of Standard Cell Libraries Isolation Cells Level Shifters Memories Power Gating
1 Low Power System-On-Chip-Design Chapter 12: Physical Libraries Friedemann Wesner 2 Outline Standard Cell Libraries Modeling of Standard Cell Libraries Isolation Cells Level Shifters Memories Power Gating
TESTABLE VLSI CIRCUIT DESIGN FOR CELLULAR ARRAYS
 12-08-98 SENIOR DESIGN PROJECT PROPOSAL PROJECT SUMMARY The main objective of this project is to design testability features that can potentially be included in any CMOS chip. For this particular design
12-08-98 SENIOR DESIGN PROJECT PROPOSAL PROJECT SUMMARY The main objective of this project is to design testability features that can potentially be included in any CMOS chip. For this particular design
Implementation of Carry Select Adder using CMOS Full Adder
 Implementation of Carry Select Adder using CMOS Full Adder Smitashree.Mohapatra Assistant professor,ece department MVSR Engineering College Nadergul,Hyderabad-510501 R. VaibhavKumar PG Scholar, ECE department(es&vlsid)
Implementation of Carry Select Adder using CMOS Full Adder Smitashree.Mohapatra Assistant professor,ece department MVSR Engineering College Nadergul,Hyderabad-510501 R. VaibhavKumar PG Scholar, ECE department(es&vlsid)
! MOS Device Layout. ! Inverter Layout. ! Gate Layout and Stick Diagrams. ! Design Rules. ! Standard Cells. ! CMOS Process Enhancements
 EE 570: igital Integrated Circuits and VLI Fundamentals Lec 3: January 18, 2018 MO Fabrication pt. 2: esign Rules and Layout Lecture Outline! MO evice Layout! Inverter Layout! Gate Layout and tick iagrams!
EE 570: igital Integrated Circuits and VLI Fundamentals Lec 3: January 18, 2018 MO Fabrication pt. 2: esign Rules and Layout Lecture Outline! MO evice Layout! Inverter Layout! Gate Layout and tick iagrams!
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 5: Logic
 Harris Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 5: Logic David Harris Harvey Mudd College David_Harris@hmc.edu Based on EE271 developed by Mark Horowitz, Stanford University MAH E158 Lecture 5 1
Harris Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design (E158) Lecture 5: Logic David Harris Harvey Mudd College David_Harris@hmc.edu Based on EE271 developed by Mark Horowitz, Stanford University MAH E158 Lecture 5 1
ECE380 Digital Logic. Logic values as voltage levels
 ECE380 Digital Logic Implementation Technology: NMOS and PMOS Transistors, CMOS logic gates Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 13-1 Logic values as voltage levels V ss is the minimum voltage that can exist in the
ECE380 Digital Logic Implementation Technology: NMOS and PMOS Transistors, CMOS logic gates Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 13-1 Logic values as voltage levels V ss is the minimum voltage that can exist in the
Overview ECE 553: TESTING AND TESTABLE DESIGN OF DIGITAL SYSTES. Motivation. Modeling Levels. Hierarchical Model: A Full-Adder 9/6/2002
 Overview ECE 3: TESTING AND TESTABLE DESIGN OF DIGITAL SYSTES Logic and Fault Modeling Motivation Logic Modeling Model types Models at different levels of abstractions Models and definitions Fault Modeling
Overview ECE 3: TESTING AND TESTABLE DESIGN OF DIGITAL SYSTES Logic and Fault Modeling Motivation Logic Modeling Model types Models at different levels of abstractions Models and definitions Fault Modeling
Lecture 0: Introduction
 Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture : Introduction David Harris Steven Levitan Harvey Mudd College University of Pittsburgh Spring 24 Fall 28 Administrivia Professor Steven Levitan TA: Bo Zhao Syllabus
Introduction to CMOS VLSI Design Lecture : Introduction David Harris Steven Levitan Harvey Mudd College University of Pittsburgh Spring 24 Fall 28 Administrivia Professor Steven Levitan TA: Bo Zhao Syllabus
Gates and Circuits 1
 1 Gates and Circuits Chapter Goals Identify the basic gates and describe the behavior of each Describe how gates are implemented using transistors Combine basic gates into circuits Describe the behavior
1 Gates and Circuits Chapter Goals Identify the basic gates and describe the behavior of each Describe how gates are implemented using transistors Combine basic gates into circuits Describe the behavior
EE 330 Lecture 44. Digital Circuits. Dynamic Logic Circuits. Course Evaluation Reminder - All Electronic
 EE 330 Lecture 44 Digital Circuits Dynamic Logic Circuits Course Evaluation Reminder - All Electronic Digital Building Blocks Shift Registers Sequential Logic Shift Registers (stack) Array Logic Memory
EE 330 Lecture 44 Digital Circuits Dynamic Logic Circuits Course Evaluation Reminder - All Electronic Digital Building Blocks Shift Registers Sequential Logic Shift Registers (stack) Array Logic Memory
VLSI DESIGN OF DIGIT-SERIAL FPGA ARCHITECTURE
 Journal of Circuits, Systems, and Computers Vol. 3, No. (24) 7 52 c World Scientific Publishing Company VLSI ESIGN OF IGIT-SERIAL FPGA ARCHITECTURE HANHO LEE School of Information and Communication Engineering,
Journal of Circuits, Systems, and Computers Vol. 3, No. (24) 7 52 c World Scientific Publishing Company VLSI ESIGN OF IGIT-SERIAL FPGA ARCHITECTURE HANHO LEE School of Information and Communication Engineering,
Low Power &High Speed Domino XOR Cell
 Low Power &High Speed Domino XOR Cell Payal Soni Electronics and Communication Department, FET- Mody University Lakshmangarh, Dist.-Sikar, India E-mail: payal.soni3091@gmail.com Abstract Shiwani Singh
Low Power &High Speed Domino XOR Cell Payal Soni Electronics and Communication Department, FET- Mody University Lakshmangarh, Dist.-Sikar, India E-mail: payal.soni3091@gmail.com Abstract Shiwani Singh
Topics. Memory Reliability and Yield Control Logic. John A. Chandy Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Connecticut
 Topics Memory Reliability and Yield Control Logic Reliability and Yield Noise Sources in T DRam BL substrate Adjacent BL C WBL α-particles WL leakage C S electrode C cross Transposed-Bitline Architecture
Topics Memory Reliability and Yield Control Logic Reliability and Yield Noise Sources in T DRam BL substrate Adjacent BL C WBL α-particles WL leakage C S electrode C cross Transposed-Bitline Architecture
High Performance VLSI Design Using Body Biasing in Domino Logic Circuits
 Salendra.Govindarajulu et. al. / (IJS) International Journal on omputer Science and ngineering Vol. 2, No. 5, 21, 1741-1745 High Performance VLSI esign Using ody iasing in omino Logic ircuits Salendra.Govindarajulu
Salendra.Govindarajulu et. al. / (IJS) International Journal on omputer Science and ngineering Vol. 2, No. 5, 21, 1741-1745 High Performance VLSI esign Using ody iasing in omino Logic ircuits Salendra.Govindarajulu
Design For Test. VLSI Design I. Design for Test. page 1. What can we do to increase testability?
 VLS esign esign for Test esign For Test What can we do to increase ability? He s dead Jim... Overview design for architectures ad-hoc, scan based, built-in in Goal: You are familiar with ability metrics
VLS esign esign for Test esign For Test What can we do to increase ability? He s dead Jim... Overview design for architectures ad-hoc, scan based, built-in in Goal: You are familiar with ability metrics
Digital Integrated Circuits Designing Combinational Logic Circuits. Fuyuzhuo
 Digital Integrated Circuits Designing Combinational Logic Circuits Fuyuzhuo Introduction Digital IC Combinational vs. Sequential Logic In Combinational Logic Circuit Out In Combinational Logic Circuit
Digital Integrated Circuits Designing Combinational Logic Circuits Fuyuzhuo Introduction Digital IC Combinational vs. Sequential Logic In Combinational Logic Circuit Out In Combinational Logic Circuit
EE241 - Spring 2006 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits. Notes. Lecture 7: Logic Families for Performance
 EE241 - Spring 2006 dvanced Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 7: Logic Families for Performance Notes Hw 1 due tomorrow Feedback on projects will be sent out by the end of the weekend Some thoughts on
EE241 - Spring 2006 dvanced Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 7: Logic Families for Performance Notes Hw 1 due tomorrow Feedback on projects will be sent out by the end of the weekend Some thoughts on
Electronic Circuits EE359A
 Electronic Circuits EE359A Bruce McNair B206 bmcnair@stevens.edu 201-216-5549 1 Memory and Advanced Digital Circuits - 2 Chapter 11 2 Figure 11.1 (a) Basic latch. (b) The latch with the feedback loop opened.
Electronic Circuits EE359A Bruce McNair B206 bmcnair@stevens.edu 201-216-5549 1 Memory and Advanced Digital Circuits - 2 Chapter 11 2 Figure 11.1 (a) Basic latch. (b) The latch with the feedback loop opened.
EE 330 Lecture 5. Improved Device Models Propagation Delay in Logic Circuits
 EE 330 Lecture 5 Improved evice Models Propagation elay in Logic Circuits Review from Last Time MO Transistor Qualitative iscussion of n-channel Operation rain rain ulk Cross-ectional View n-channel MOFET
EE 330 Lecture 5 Improved evice Models Propagation elay in Logic Circuits Review from Last Time MO Transistor Qualitative iscussion of n-channel Operation rain rain ulk Cross-ectional View n-channel MOFET
Digital Microelectronic Circuits ( ) CMOS Digital Logic. Lecture 6: Presented by: Adam Teman
 Digital Microelectronic Circuits (361-1-3021 ) Presented by: Adam Teman Lecture 6: CMOS Digital Logic 1 Last Lectures The CMOS Inverter CMOS Capacitance Driving a Load 2 This Lecture Now that we know all
Digital Microelectronic Circuits (361-1-3021 ) Presented by: Adam Teman Lecture 6: CMOS Digital Logic 1 Last Lectures The CMOS Inverter CMOS Capacitance Driving a Load 2 This Lecture Now that we know all
Pass Transistor and CMOS Logic Configuration based De- Multiplexers
 Abstract: Pass Transistor and CMOS Logic Configuration based De- Multiplexers 1 K Rama Krishna, 2 Madanna, 1 PG Scholar VLSI System Design, Geethanajali College of Engineering and Technology, 2 HOD Dept
Abstract: Pass Transistor and CMOS Logic Configuration based De- Multiplexers 1 K Rama Krishna, 2 Madanna, 1 PG Scholar VLSI System Design, Geethanajali College of Engineering and Technology, 2 HOD Dept
Digital Integrated Circuits Designing Combinational Logic Circuits. Fuyuzhuo
 Digital Integrated Circuits Designing Combinational Logic Circuits Fuyuzhuo Introduction Digital IC Combinational vs. Sequential Logic In Combinational Logic Circuit Out In Combinational Logic Circuit
Digital Integrated Circuits Designing Combinational Logic Circuits Fuyuzhuo Introduction Digital IC Combinational vs. Sequential Logic In Combinational Logic Circuit Out In Combinational Logic Circuit
Spiral Content Mapping. Spiral 1 / Unit 8. Outcomes DEMORGAN'S THEOREM. Transistor Implementations CMOS Logic Gates
 18.1 18.2 Spiral ontent Mapping Spiral Theory ombinational esign Sequential esign System Level esign Implementation and Tools Project Spiral 1 / Unit 8 Transistor Implementations MOS Logic Gates Performance
18.1 18.2 Spiral ontent Mapping Spiral Theory ombinational esign Sequential esign System Level esign Implementation and Tools Project Spiral 1 / Unit 8 Transistor Implementations MOS Logic Gates Performance
A Highly Efficient Carry Select Adder
 IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 2 Issue 4 October 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-784X A Highly Efficient Carry Select Adder Shiya Andrews V PG Student Department of Electronics
IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 2 Issue 4 October 2015 ISSN (online): 2349-784X A Highly Efficient Carry Select Adder Shiya Andrews V PG Student Department of Electronics
Topic 6. CMOS Static & Dynamic Logic Gates. Static CMOS Circuit. NMOS Transistors in Series/Parallel Connection
 NMOS Transistors in Series/Parallel Connection Topic 6 CMOS Static & Dynamic Logic Gates Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London Transistors can be thought
NMOS Transistors in Series/Parallel Connection Topic 6 CMOS Static & Dynamic Logic Gates Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London Transistors can be thought
Implementation of Full Adder using Cmos Logic
 ISSN: 232-9653; IC Value: 45.98; SJ Impact Factor:6.887 Volume 5 Issue VIII, July 27- Available at www.ijraset.com Implementation of Full Adder using Cmos Logic Ravika Gupta Undergraduate Student, Dept
ISSN: 232-9653; IC Value: 45.98; SJ Impact Factor:6.887 Volume 5 Issue VIII, July 27- Available at www.ijraset.com Implementation of Full Adder using Cmos Logic Ravika Gupta Undergraduate Student, Dept
Outcomes. Spiral 1 / Unit 8. DeMorgan s Theorem DEMORGAN'S THEOREM. Transistor Implementations CMOS Logic Gates
 18.1 18.2 Spiral 1 / Unit 8 Transistor Implementations MOS Logic Gates Mark Redekopp Outcomes I know the difference between combinational and sequential logic and can name examples of each. I understand
18.1 18.2 Spiral 1 / Unit 8 Transistor Implementations MOS Logic Gates Mark Redekopp Outcomes I know the difference between combinational and sequential logic and can name examples of each. I understand
Layout - Line of Diffusion. Where are we? Line of Diffusion in General. Line of Diffusion in General. Stick Diagrams. Line of Diffusion in General
 Where are we? Lots of Layout issues Line of diffusion style Power pitch it-slice pitch Routing strategies Transistor sizing Wire sizing Layout - Line of Diffusion Very common layout method Start with a
Where are we? Lots of Layout issues Line of diffusion style Power pitch it-slice pitch Routing strategies Transistor sizing Wire sizing Layout - Line of Diffusion Very common layout method Start with a
Preface to Third Edition Deep Submicron Digital IC Design p. 1 Introduction p. 1 Brief History of IC Industry p. 3 Review of Digital Logic Gate
 Preface to Third Edition p. xiii Deep Submicron Digital IC Design p. 1 Introduction p. 1 Brief History of IC Industry p. 3 Review of Digital Logic Gate Design p. 6 Basic Logic Functions p. 6 Implementation
Preface to Third Edition p. xiii Deep Submicron Digital IC Design p. 1 Introduction p. 1 Brief History of IC Industry p. 3 Review of Digital Logic Gate Design p. 6 Basic Logic Functions p. 6 Implementation
Testing Digital Systems II
 Lecture : Introduction Instructor: M. Tahoori Copyright 206, M. Tahoori TDS II: Lecture Today s Lecture Logistics Course Outline Review from TDS I Copyright 206, M. Tahoori TDS II: Lecture 2 Lecture Logistics
Lecture : Introduction Instructor: M. Tahoori Copyright 206, M. Tahoori TDS II: Lecture Today s Lecture Logistics Course Outline Review from TDS I Copyright 206, M. Tahoori TDS II: Lecture 2 Lecture Logistics
Course Objectives and Outcomes
 Course Objectives and Outcomes Course Objectives and Outcomes 1. Course code and title: EE3019 Integrated Electronics 2. Number of AUs: 3 3. Course type: Elective 4. Course schedule: Lecture: 2 hours/week
Course Objectives and Outcomes Course Objectives and Outcomes 1. Course code and title: EE3019 Integrated Electronics 2. Number of AUs: 3 3. Course type: Elective 4. Course schedule: Lecture: 2 hours/week
High Performance Low-Power Signed Multiplier
 High Performance Low-Power Signed Multiplier Amir R. Attarha Mehrdad Nourani VLSI Circuits & Systems Laboratory Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Tehran, IRAN Email: attarha@khorshid.ece.ut.ac.ir
High Performance Low-Power Signed Multiplier Amir R. Attarha Mehrdad Nourani VLSI Circuits & Systems Laboratory Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Tehran, IRAN Email: attarha@khorshid.ece.ut.ac.ir
MOS CURRENT MODE LOGIC BASED PRIORITY ENCODERS
 MOS CURRENT MODE LOGIC BASED PRIORITY ENCODERS Neeta Pandey 1, Kirti Gupta 2, Stuti Gupta 1, Suman Kumari 1 1 Dept. of Electronics and Communication, Delhi Technological University, New Delhi (India) 2
MOS CURRENT MODE LOGIC BASED PRIORITY ENCODERS Neeta Pandey 1, Kirti Gupta 2, Stuti Gupta 1, Suman Kumari 1 1 Dept. of Electronics and Communication, Delhi Technological University, New Delhi (India) 2
AREA AND DELAY EFFICIENT DESIGN FOR PARALLEL PREFIX FINITE FIELD MULTIPLIER
 AREA AND DELAY EFFICIENT DESIGN FOR PARALLEL PREFIX FINITE FIELD MULTIPLIER 1 CH.JAYA PRAKASH, 2 P.HAREESH, 3 SK. FARISHMA 1&2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, 3 M.Tech-Student, Sir CR Reddy College
AREA AND DELAY EFFICIENT DESIGN FOR PARALLEL PREFIX FINITE FIELD MULTIPLIER 1 CH.JAYA PRAKASH, 2 P.HAREESH, 3 SK. FARISHMA 1&2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, 3 M.Tech-Student, Sir CR Reddy College
Introduction to Electronic Design Automation
 Introduction to Electronic Design Automation Jie-Hong Roland Jiang 江介宏 Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University Spring 2014 1 Design Automation? 2 Course Info (1/4) Instructor Jie-Hong
Introduction to Electronic Design Automation Jie-Hong Roland Jiang 江介宏 Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University Spring 2014 1 Design Automation? 2 Course Info (1/4) Instructor Jie-Hong
Gates and and Circuits
 Chapter 4 Gates and Circuits Chapter Goals Identify the basic gates and describe the behavior of each Describe how gates are implemented using transistors Combine basic gates into circuits Describe the
Chapter 4 Gates and Circuits Chapter Goals Identify the basic gates and describe the behavior of each Describe how gates are implemented using transistors Combine basic gates into circuits Describe the
ECE/CoE 0132: FETs and Gates
 ECE/CoE 0132: FETs and Gates Kartik Mohanram September 6, 2017 1 Physical properties of gates Over the next 2 lectures, we will discuss some of the physical characteristics of integrated circuits. We will
ECE/CoE 0132: FETs and Gates Kartik Mohanram September 6, 2017 1 Physical properties of gates Over the next 2 lectures, we will discuss some of the physical characteristics of integrated circuits. We will
Low Power, Area Efficient FinFET Circuit Design
 Low Power, Area Efficient FinFET Circuit Design Michael C. Wang, Princeton University Abstract FinFET, which is a double-gate field effect transistor (DGFET), is more versatile than traditional single-gate
Low Power, Area Efficient FinFET Circuit Design Michael C. Wang, Princeton University Abstract FinFET, which is a double-gate field effect transistor (DGFET), is more versatile than traditional single-gate
Field Effect Transistor Characterization EE251 Laboratory Report #3 <name> May 26, 2008
 Field Effect Transistor Characterization EE251 Laboratory Report #3 May 26, 2008 Abstract The low frequency characteristics of the 2N7000 N channel MOS Transistor were measured and compared to published
Field Effect Transistor Characterization EE251 Laboratory Report #3 May 26, 2008 Abstract The low frequency characteristics of the 2N7000 N channel MOS Transistor were measured and compared to published
ECE 471/571 Combinatorial Circuits Lecture-7. Gurjeet Singh
 ECE 471/571 Combinatorial Circuits Lecture-7 Gurjeet Singh Propagation Delay of CMOS Gates Propagation delay of Four input NAND Gate Disadvantages of Complementary CMOS Design Increase in complexity Larger
ECE 471/571 Combinatorial Circuits Lecture-7 Gurjeet Singh Propagation Delay of CMOS Gates Propagation delay of Four input NAND Gate Disadvantages of Complementary CMOS Design Increase in complexity Larger
POWER GATING. Power-gating parameters
 POWER GATING Power Gating is effective for reducing leakage power [3]. Power gating is the technique wherein circuit blocks that are not in use are temporarily turned off to reduce the overall leakage
POWER GATING Power Gating is effective for reducing leakage power [3]. Power gating is the technique wherein circuit blocks that are not in use are temporarily turned off to reduce the overall leakage
Design and Implementation of Complex Multiplier Using Compressors
 Design and Implementation of Complex Multiplier Using Compressors Abstract: In this paper, a low-power high speed Complex Multiplier using compressor circuit is proposed for fast digital arithmetic integrated
Design and Implementation of Complex Multiplier Using Compressors Abstract: In this paper, a low-power high speed Complex Multiplier using compressor circuit is proposed for fast digital arithmetic integrated
A Low Power Array Multiplier Design using Modified Gate Diffusion Input (GDI)
 A Low Power Array Multiplier Design using Modified Gate Diffusion Input (GDI) Mahendra Kumar Lariya 1, D. K. Mishra 2 1 M.Tech, Electronics and instrumentation Engineering, Shri G. S. Institute of Technology
A Low Power Array Multiplier Design using Modified Gate Diffusion Input (GDI) Mahendra Kumar Lariya 1, D. K. Mishra 2 1 M.Tech, Electronics and instrumentation Engineering, Shri G. S. Institute of Technology
Detecting Resistive Shorts for CMOS Domino Circuits
 Detecting Resistive Shorts for MOS Domino ircuits Jonathan T.-Y. hang and Edward J. Mcluskey enter for Reliable omputing Stanford University Gates Hall 2 Stanford, 94305 STRT We investigate defects in
Detecting Resistive Shorts for MOS Domino ircuits Jonathan T.-Y. hang and Edward J. Mcluskey enter for Reliable omputing Stanford University Gates Hall 2 Stanford, 94305 STRT We investigate defects in
Abstract. 1 Introduction
 Variable Input Delay CMOS Logic for Low Power Design Tezaswi Raja Vishwani D. Agrawal Michael L. Bushnell Transmeta Corp. Auburn University, Dept. of ECE Rutgers University, Dept. of ECE Santa Clara, CA
Variable Input Delay CMOS Logic for Low Power Design Tezaswi Raja Vishwani D. Agrawal Michael L. Bushnell Transmeta Corp. Auburn University, Dept. of ECE Rutgers University, Dept. of ECE Santa Clara, CA
Lecture 12 Memory Circuits. Memory Architecture: Decoders. Semiconductor Memory Classification. Array-Structured Memory Architecture RWM NVRWM ROM
 Semiconductor Memory Classification Lecture 12 Memory Circuits RWM NVRWM ROM Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London Reading: Weste Ch 8.3.1-8.3.2, Rabaey
Semiconductor Memory Classification Lecture 12 Memory Circuits RWM NVRWM ROM Peter Cheung Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London Reading: Weste Ch 8.3.1-8.3.2, Rabaey
Energy Efficient Multiplier Design Using Multi-Gate MOSFETs
 Energy Efficient Multiplier Design Using Multi-Gate MOSFETs Y.E. Vasanth Kumar 1,. Nandini 2,. Hyndhavi 3 ssistant Professor, Department of Electronics and ommunication Engineering, Wellfare Institute
Energy Efficient Multiplier Design Using Multi-Gate MOSFETs Y.E. Vasanth Kumar 1,. Nandini 2,. Hyndhavi 3 ssistant Professor, Department of Electronics and ommunication Engineering, Wellfare Institute
EE 42/100 Lecture 23: CMOS Transistors and Logic Gates. Rev A 4/15/2012 (10:39 AM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad
 A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EE 100 / 42 Lecture 23 p. 1/16 EE 42/100 Lecture 23: CMOS Transistors and Logic Gates ELECTRONICS Rev A 4/15/2012 (10:39 AM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University
A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EE 100 / 42 Lecture 23 p. 1/16 EE 42/100 Lecture 23: CMOS Transistors and Logic Gates ELECTRONICS Rev A 4/15/2012 (10:39 AM) Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University
A Fine Grain Configurable Logic Block
 VLSI DESIGN 2001, Vol. 12, No. 4, pp. 527-536 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 2001 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published by license
VLSI DESIGN 2001, Vol. 12, No. 4, pp. 527-536 Reprints available directly from the publisher Photocopying permitted by license only (C) 2001 OPA (Overseas Publishers Association) N.V. Published by license
ECE 683 Project Report. Winter Professor Steven Bibyk. Team Members. Saniya Bhome. Mayank Katyal. Daniel King. Gavin Lim.
 ECE 683 Project Report Winter 2006 Professor Steven Bibyk Team Members Saniya Bhome Mayank Katyal Daniel King Gavin Lim Abstract This report describes the use of Cadence software to simulate logic circuits
ECE 683 Project Report Winter 2006 Professor Steven Bibyk Team Members Saniya Bhome Mayank Katyal Daniel King Gavin Lim Abstract This report describes the use of Cadence software to simulate logic circuits
ECE 334: Electronic Circuits Lecture 10: Digital CMOS Circuits
 Faculty of Engineering ECE 334: Electronic Circuits Lecture 10: Digital CMOS Circuits CMOS Technology Complementary MOS, or CMOS, needs both PMOS and NMOS FET devices for their logic gates to be realized
Faculty of Engineering ECE 334: Electronic Circuits Lecture 10: Digital CMOS Circuits CMOS Technology Complementary MOS, or CMOS, needs both PMOS and NMOS FET devices for their logic gates to be realized
A Highly-Efficient Technique for Reducing Soft Errors in Static CMOS Circuits
 A Highly-Efficient Technique for Reducing Soft Errors in Static MOS ircuits Srivathsan Krishnamohan and Nihar R. Mahapatra E-mail: {krishn37, nrm}@egr.msu.edu Department of Electrical & omputer Engineering,
A Highly-Efficient Technique for Reducing Soft Errors in Static MOS ircuits Srivathsan Krishnamohan and Nihar R. Mahapatra E-mail: {krishn37, nrm}@egr.msu.edu Department of Electrical & omputer Engineering,
The Design and Realization of Basic nmos Digital Devices
 Proceedings of The National Conference On Undergraduate Research (NCUR) 2004 Indiana University Purdue University Indianapolis, Indiana April 15-17, 2004 The Design and Realization of Basic nmos Digital
Proceedings of The National Conference On Undergraduate Research (NCUR) 2004 Indiana University Purdue University Indianapolis, Indiana April 15-17, 2004 The Design and Realization of Basic nmos Digital
Low-Power and Process Variation Tolerant Memories in sub-90nm Technologies
 Low-Power and Process Variation Tolerant Memories in sub-9nm Technologies Saibal Mukhopadhyay, Swaroop Ghosh, Keejong Kim, and Kaushik Roy Dept. of ECE, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, @ecn.purdue.edu
Low-Power and Process Variation Tolerant Memories in sub-9nm Technologies Saibal Mukhopadhyay, Swaroop Ghosh, Keejong Kim, and Kaushik Roy Dept. of ECE, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, @ecn.purdue.edu
Memory, Latches, & Registers
 Memory, Latches, & Registers 1) Structured Logic Arrays 2) Memory Arrays 3) Transparent Latches 4) Saving a few bucks at toll booths 5) Edge-triggered Registers 1 General Table Lookup Synthesis A B 00
Memory, Latches, & Registers 1) Structured Logic Arrays 2) Memory Arrays 3) Transparent Latches 4) Saving a few bucks at toll booths 5) Edge-triggered Registers 1 General Table Lookup Synthesis A B 00
EE241 - Spring 2002 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits
 EE241 - Spring 2002 dvanced Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 7 MOS Logic Styles nnouncements Homework #1 due 2/19 1 Reading Chapter 7 in the text by K. ernstein ackground material from Rabaey References»
EE241 - Spring 2002 dvanced Digital Integrated Circuits Lecture 7 MOS Logic Styles nnouncements Homework #1 due 2/19 1 Reading Chapter 7 in the text by K. ernstein ackground material from Rabaey References»
Digital Systems Design
 Digital Systems Design Digital Systems Design and Test Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 1-1 Introduction Traditional digital design Manual process of designing and capturing circuits Schematic entry System-level
Digital Systems Design Digital Systems Design and Test Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 1-1 Introduction Traditional digital design Manual process of designing and capturing circuits Schematic entry System-level
Subthreshold Voltage High-k CMOS Devices Have Lowest Energy and High Process Tolerance
 Subthreshold Voltage High-k CMOS Devices Have Lowest Energy and High Process Tolerance Muralidharan Venkatasubramanian Auburn University vmn0001@auburn.edu Vishwani D. Agrawal Auburn University vagrawal@eng.auburn.edu
Subthreshold Voltage High-k CMOS Devices Have Lowest Energy and High Process Tolerance Muralidharan Venkatasubramanian Auburn University vmn0001@auburn.edu Vishwani D. Agrawal Auburn University vagrawal@eng.auburn.edu
Subtractor Logic Schematic
 Function Of Xor Gate In Parallel Adder Subtractor Logic Schematic metic functions, including half adder, half subtractor, full adder, independent logic gates to form desired circuits based on dif- by integrating
Function Of Xor Gate In Parallel Adder Subtractor Logic Schematic metic functions, including half adder, half subtractor, full adder, independent logic gates to form desired circuits based on dif- by integrating
Zhan Chen and Israel Koren ABSTRACT. proposed algorithm has been implemented in the framework of the Berkeley logic optimization package SIS.
 Technology Mapping for Hot-Carrier Reliability Enhancement Zhan Chen and Israel Koren Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA 0003 ABSTRACT As semiconductor
Technology Mapping for Hot-Carrier Reliability Enhancement Zhan Chen and Israel Koren Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Massachusetts, Amherst, MA 0003 ABSTRACT As semiconductor
Lab 7 (Hands-On Experiment): CMOS Inverter, NAND Gate, and NOR Gate
 Lab 7 (Hands-On Experiment): CMOS Inverter, NAND Gate, and NOR Gate EECS 170LB, Wed. 5:00 PM TA: Elsharkasy, Wael Ryan Morrison Buu Truong Jonathan Lam 03/05/14 Introduction The purpose of this lab is
Lab 7 (Hands-On Experiment): CMOS Inverter, NAND Gate, and NOR Gate EECS 170LB, Wed. 5:00 PM TA: Elsharkasy, Wael Ryan Morrison Buu Truong Jonathan Lam 03/05/14 Introduction The purpose of this lab is
Generation of Digital System Test Patterns Based on VHDL Simulations
 POSTER 2006, PRAGUE MAY 18 1 Generation of Digital System Test Patterns Based on VHDL Simulations Miljana SOKOLOVIĆ 1, Andy KUIPER 2 1 LEDA laboratory, aculty of Electronic Engineering, University of Niš,
POSTER 2006, PRAGUE MAY 18 1 Generation of Digital System Test Patterns Based on VHDL Simulations Miljana SOKOLOVIĆ 1, Andy KUIPER 2 1 LEDA laboratory, aculty of Electronic Engineering, University of Niš,
MOS IC Amplifiers. Token Ring LAN JSSC 12/89
 MO IC Amplifiers MOFETs are inferior to BJTs for analog design in terms of quality per silicon area But MO is the technology of choice for digital applications Therefore, most analog portions of mixed-signal
MO IC Amplifiers MOFETs are inferior to BJTs for analog design in terms of quality per silicon area But MO is the technology of choice for digital applications Therefore, most analog portions of mixed-signal
ECE380 Digital Logic
 ECE380 Digital Logic Implementation Technology: Standard Chips and Programmable Logic Devices Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 10-1 Standard chips A number of chips, each with a few logic gates, are commonly
ECE380 Digital Logic Implementation Technology: Standard Chips and Programmable Logic Devices Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 10-1 Standard chips A number of chips, each with a few logic gates, are commonly
Shorthand Notation for NMOS and PMOS Transistors
 Shorthand Notation for NMOS and PMOS Transistors Terminal Voltages Mode of operation depends on V g, V d, V s V gs = V g V s V gd = V g V d V ds = V d V s = V gs - V gd Source and drain are symmetric diffusion
Shorthand Notation for NMOS and PMOS Transistors Terminal Voltages Mode of operation depends on V g, V d, V s V gs = V g V s V gd = V g V d V ds = V d V s = V gs - V gd Source and drain are symmetric diffusion
Outline. EECS Components and Design Techniques for Digital Systems. Lec 12 - Timing. General Model of Synchronous Circuit
 Outline EES 5 - omponents and esign Techniques for igital Systems Lec 2 - Timing avid uller Electrical Engineering and omputer Sciences University of alifornia, erkeley Performance Limits of Synchronous
Outline EES 5 - omponents and esign Techniques for igital Systems Lec 2 - Timing avid uller Electrical Engineering and omputer Sciences University of alifornia, erkeley Performance Limits of Synchronous
A HIGH SPEED & LOW POWER 16T 1-BIT FULL ADDER CIRCUIT DESIGN BY USING MTCMOS TECHNIQUE IN 45nm TECHNOLOGY
 A HIGH SPEED & LOW POWER 16T 1-BIT FULL ADDER CIRCUIT DESIGN BY USING MTCMOS TECHNIQUE IN 45nm TECHNOLOGY Jasbir kaur 1, Neeraj Singla 2 1 Assistant Professor, 2 PG Scholar Electronics and Communication
A HIGH SPEED & LOW POWER 16T 1-BIT FULL ADDER CIRCUIT DESIGN BY USING MTCMOS TECHNIQUE IN 45nm TECHNOLOGY Jasbir kaur 1, Neeraj Singla 2 1 Assistant Professor, 2 PG Scholar Electronics and Communication
EE40 Lecture 35. Prof. Chang-Hasnain. 12/5/07 Reading: Ch 7, Supplementary Reader
 EE4 Lecture 35 2/5/7 Reading: Ch 7, Supplementary Reader EE4 all 26 Slide Week 5 OUTLINE Need for Input Controlled Pull-Up CMOS Inverter nalysis CMOS Voltage Transfer Characteristic Combinatorial logic
EE4 Lecture 35 2/5/7 Reading: Ch 7, Supplementary Reader EE4 all 26 Slide Week 5 OUTLINE Need for Input Controlled Pull-Up CMOS Inverter nalysis CMOS Voltage Transfer Characteristic Combinatorial logic
Lecture 12 - Digital Circuits (I) The inverter. October 20, 2005
 6.12 - Microelectronic Devices and Circuits - Fall 25 Lecture 12-1 Lecture 12 - Digital Circuits (I) The inverter October 2, 25 Contents: 1. Introduction to digital electronics: the inverter 2. NMOS inverter
6.12 - Microelectronic Devices and Circuits - Fall 25 Lecture 12-1 Lecture 12 - Digital Circuits (I) The inverter October 2, 25 Contents: 1. Introduction to digital electronics: the inverter 2. NMOS inverter
