Based with permission on lectures by John Getty Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX262) Spring 2011 Lecture 9 Page 1
|
|
|
- Augusta West
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Today 3// Lecture 9 Analog Digital Conversion Sampled Data Acquisition Systems Discrete Sampling and Nyquist Digital to Analog Conversion Analog to Digital Conversion Homework Study for Exam next week (in class 3/9/) Covers everything up through Lecture 8 and Lab 7 Reading A/D converters (pages 6-64). Lab Do DAC pre-lab before lab meeting. Graded at start of lab!!! Sequential logic lab book due 3/5 at 0am. Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX6) Spring 0 Lecture 9 Page
2 Analog Digital Analog Why convert from analog to digital Digital transmission and storage of analog signals Compression, Reliability, Error Correction Digital signal processing Powerful algorithm, adaptable, ease of implementation Why convert from digital to analog We live (see, hear, and feel) in an analog world Replay stored, transmitted, or processed data Music, messages, movies Relay information from computers to humans Digital control of analog systems Convert virtual worlds to reality Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX6) Spring 0 Lecture 9 Page
3 Key Elements of a Sampled Signal Processing System * *ref: Analog Devices; Application Note AN-8 Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX6) Spring 0 Lecture 9 Page 3
4 In many systems the signal is Converts the analog signal converted Key back Elements into analog of a Sampled into a digital Data representation: System (sometimes The final after part short of the or process long A DSP is a term storage includes in additional memory): conditioning Sample microprocessor and Hold * is in the analog domain. Interface to sampled analog optimized circuitry system: for that Latch holds the digital data Precision buffer/gain ensures manipulating the amplifiers ADC digitized sees a until the Some D/A can D/As finish can produce the inband glitches This also that allows must be preserve the stable, integrity analog unchanging signals: of analog conversion. signal. Sometimes signal Perform auto-scale the time operations input the DSP removed processor at this to move stage. required to accurately on to Anti-alias filter perform is such a the LPF, as conversion. typically digital other Analog tasks. filtering can be used with steep roll-off (allows to ensure filtering for undersampling Often >f there and are FFTs. no The D/A to reverses compensate the for the signal components sample advanced is also /. process discrete used on nature the input of the D/A, used for side of improving the system. overall system topic in system A/D) control. fidelity. Some systems are made to A/D can Vector be any processors. of a wide faithfully reproduce (CD range of Field devices. programmable More players) or improve (noise on this gate later. arrays (FPGA). cancelling headphones) on *ref: Analog Devices; Application Note AN-8 the original analog input. Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX6) Spring 0 Lecture 9 Page 4
5 Discrete Sampling of 0 Hz Signal at 5Hz fsignal 0Hz 5Hz fsample Sample interval = 00mS Sample Rate = 5Hz Milliseconds Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX6) Spring 0 Lecture 9 Page 5
6 Discrete Sampling of 0Hz signal at 0Hz fsignal 0Hz 0Hz fsample Sample interval = 00mS Sample Rate = 0Hz Milliseconds Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX6) Spring 0 Lecture 9 Page 6
7 Discrete Sampling at 0Hz fsignal 0Hz fsample 0Hz Milliseconds Sample interval = 50mS Sample Rate = 0Hz Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX6) Spring 0 Lecture 9 Page 7
8 Nyquist Sampling Theorem The sampling theorem states that for a limited bandwidth (band-limited) signal with maximum frequency f max, the equally spaced sampling frequency f sample must be GREATER THAN twice the maximum frequency of the signal, f max, in order to uniquely reconstruct the signal without aliasing. fsample f max => f max is called the Nyquist sampling rate. Half of the sampling rate of an A/D is sometimes called its Nyquist frequency, and is the max frequency that a A/D can record. Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX6) Spring 0 Lecture 9 Page 8
9 Discrete Sampling at f s =f max f F 0Hz f 0Hz S Sample interval = 50mS Sample Rate = 0Hz Milliseconds f s =f max is not sufficient, Nyquist sampling requires f s f max Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX6) Spring 0 Lecture 9 Page 9
10 Aliasing Original Signal fsig Hz Seconds Sample Freq. fsamp 0Hz Sample Period TSamp 50mS Sample_Rate_.XLS Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX6) Spring 0 Lecture 9 Page 0
11 Aliasing in the Frequency Domain The frequency of aliased signals is the difference between and sum of the sampling frequency f S and signal being sampled, f F. These aliased signals repeat around each integer multiple of the sampling frequency. f F f A L f 8 S f F f f and f f f 4 S S f F fs f F F fs.5 A f AL H f S S f AH f F Nyquist Frequency If you low pass filtered at f s, the you know only f<f s are real. Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX6) Spring 0 Lecture 9 Page Hz
12 Digital to Analog Converter (DAC) Terminology Number of Bits: A DAC with n bits provides n discrete output steps or counts. For example an 8 bit DAC has 56 possible output values. Output Range: Difference between the maximum and minimum output values. Resolution: Also known as the step size, represents the minimum change in output voltage. Typically equal to output range / ( n -) Dynamic Range: Output Range divided by Resolution or Noise Voltage. Would be ( n -) if the noise was less than step size of DAC. Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX6) Spring 0 Lecture 9 Page
13 In-Class Exercise Assume a 0 bit DAC is set up to output a voltage from -V dc to +V dc. Determine the resolution. The 0 bits produce a total of 0 = 04 steps. The range is +V dc -(-V dc ) = +4V dc. Therefore the resolution is 4Vdc/03 = V. 3.5mV/step! Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX6) Spring 0 Lecture 9 Page 3
14 One Approach to DAC: R-R Ladder Circuit Vout kohm kohm kohm kohm kohm kohm kohm kohm Key = D Key = C Key = B Key = A V ref 5V V out A B C D V What is V max? V max =V ref *5/6=4.69V V min =0 Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX6) Spring 0 Lecture 9 Page 4
15 nd Approach to DAC: Scaled Summing Junction DAC 50kohm 3 Vout V 0kohm 0kohm 40kohm 80kohm Key = D Key = C Key = B Key = A This approach is the one we will implement in lab. V out A50k B50k C50k D50k V 80k 40k 0k 0k A B C D V What is Range? V max =0, V min =-0V*5/6=-4.69V Range=4.69V Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX6) Spring 0 Lecture 9 Page 5
16 Analog to Digital Converter (ADC) Terminology Number of Bits: An ADC with n bits divides the input range into n discrete steps. For example, an 8 bit ADC can produce a total of 56 different output codes. Full Scale Input Range Difference between the minimum and maximum input voltage that can be measured. Resolution: Quantization, also known as the step size, is the change in input voltage represented by each count at the output. Often referred to as LSB (least significant bit) Dynamic Range: Input Range divided by resolution or noise. Typically equals n -, if noise is less than LSB. Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX6) Spring 0 Lecture 9 Page 6
17 ADC Accuracy QUANTIZATION ERROR Inherent accuracy (±/LSB, least significant bit) INTEGRAL NON-LINEARITY (INL) is a measure of the deviation of each individual code from a line drawn from zero scale or negative full scale ( LSB below the first code transition) through positive full scale ( LSB above the last code transition). The deviation of any given code from this straight line is measured from the center of that code value. DIFFERENTIAL NON-LINEARITY (DNL) is the measure of the maximum deviation from the ideal step size of LSB. DNL is commonly measured at the rated clock frequency with a ramp input. MISSING CODES are output codes that are skipped or never appear at the ADC outputs. These codes cannot be reached by any input value. OFFSET ERROR is the difference between the ideal and actual LSB transition point. FULL SCALE ERROR is how far the last code transition is from the ideal.5 LSB below positive V_ref (V_ref is n times step size) GAIN ERROR is number of LSB gained from conversion from lowest to highest output. It is a measure of the deviation of the ADC from linear (gain = ) conversion. See figure 9.44 in H&H page 65 Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX6) Spring 0 Lecture 9 Page 7
18 Ideal ADC: Quantization Error Quantization Error LSB QUANTIZATION ERROR LSB FULL SCALE ERROR Quantization error is the inherent deviation of the output from a straight line. -Note last transition is.5 LSB from V ref (used to measure full scale error) Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX6) Spring 0 Lecture 9 Page 8
19 Sampled System Errors - INL INL Error Integral Non-Linearity is the deviation of the output from a straight line. Can be measured at each code or stated as maximum for all codes. Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX6) Spring 0 Lecture 9 Page 9
20 Sampled System Errors - DNL DNL Error DNL= LSB (step is correct, but INL of 00 is.0lsb) Differential Non-Linearity is the maximum difference between the expected stepsize ( LSB) and that steps actually produced by the DAC. Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX6) Spring 0 Lecture 9 Page 0
21 Sampled System Errors - Offset Offset Error Offset Error is measured at 000. Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX6) Spring 0 Lecture 9 Page
22 Sampled System Errors - Gain Gain Error Gain Error is measured at. The offset error must be known to compute slope. (y=mx+b) Gain Error is given in LSB over full scale. Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX6) Spring 0 Lecture 9 Page
23 Sampled System Errors - Gain Gain Error LSB offset Gain Error is measured at. The offset error must be known to compute this value. (y=mx+b) Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX6) Spring 0 Lecture 9 Page 3
24 References. Paul Horowitz and Winfield Hill (989). The Art of Electronics, nd Ed., Cambridge. Analog Devices, Fundamentals of Sampled Data Systems, accessed MAR Efunda, Engineering Fundamentals web site; accessed MAR National Semiconductor: accessed MAR Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX6) Spring 0 Lecture 9 Page 4
Analog ó Digital Conversion Sampled Data Acquisition Systems Discrete Sampling and Nyquist Digital to Analog Conversion Analog to Digital Conversion
 Today Analog ó Digital Conversion Sampled Data Acquisition Systems Discrete Sampling and Nyquist Digital to Analog Conversion Analog to Digital Conversion Analog Digital Analog Beneits o digital systems
Today Analog ó Digital Conversion Sampled Data Acquisition Systems Discrete Sampling and Nyquist Digital to Analog Conversion Analog to Digital Conversion Analog Digital Analog Beneits o digital systems
Advantages of Analog Representation. Varies continuously, like the property being measured. Represents continuous values. See Figure 12.
 Analog Signals Signals that vary continuously throughout a defined range. Representative of many physical quantities, such as temperature and velocity. Usually a voltage or current level. Digital Signals
Analog Signals Signals that vary continuously throughout a defined range. Representative of many physical quantities, such as temperature and velocity. Usually a voltage or current level. Digital Signals
Design IV. E232 Spring 07
 Design IV Spring 07 Class 8 Bruce McNair bmcnair@stevens.edu 8-1/38 Computerized Data Acquisition Measurement system architecture System under test sensor sensor sensor sensor signal conditioning signal
Design IV Spring 07 Class 8 Bruce McNair bmcnair@stevens.edu 8-1/38 Computerized Data Acquisition Measurement system architecture System under test sensor sensor sensor sensor signal conditioning signal
Microprocessors & Interfacing
 Lecture overview Microprocessors & Interfacing /Output output PMW Digital-to- (D/A) Conversion input -to-digital (A/D) Conversion Lecturer : Dr. Annie Guo S2, 2008 COMP9032 Week9 1 S2, 2008 COMP9032 Week9
Lecture overview Microprocessors & Interfacing /Output output PMW Digital-to- (D/A) Conversion input -to-digital (A/D) Conversion Lecturer : Dr. Annie Guo S2, 2008 COMP9032 Week9 1 S2, 2008 COMP9032 Week9
The need for Data Converters
 The need for Data Converters ANALOG SIGNAL (Speech, Images, Sensors, Radar, etc.) PRE-PROCESSING (Filtering and analog to digital conversion) DIGITAL PROCESSOR (Microprocessor) POST-PROCESSING (Digital
The need for Data Converters ANALOG SIGNAL (Speech, Images, Sensors, Radar, etc.) PRE-PROCESSING (Filtering and analog to digital conversion) DIGITAL PROCESSOR (Microprocessor) POST-PROCESSING (Digital
EE 421L Digital Electronics Laboratory. Laboratory Exercise #9 ADC and DAC
 EE 421L Digital Electronics Laboratory Laboratory Exercise #9 ADC and DAC Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, at Las Vegas Objective: The purpose of this laboratory
EE 421L Digital Electronics Laboratory Laboratory Exercise #9 ADC and DAC Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, at Las Vegas Objective: The purpose of this laboratory
Digital to Analog Conversion. Data Acquisition
 Digital to Analog Conversion (DAC) Digital to Analog Conversion Data Acquisition DACs or D/A converters are used to convert digital signals representing binary numbers into proportional analog voltages.
Digital to Analog Conversion (DAC) Digital to Analog Conversion Data Acquisition DACs or D/A converters are used to convert digital signals representing binary numbers into proportional analog voltages.
DSP Project. Reminder: Project proposal is due Friday, October 19, 2012 by 5pm in my office (Small 239).
 DSP Project eminder: Project proposal is due Friday, October 19, 2012 by 5pm in my office (Small 239). Budget: $150 for project. Free parts: Surplus parts from previous year s project are available on
DSP Project eminder: Project proposal is due Friday, October 19, 2012 by 5pm in my office (Small 239). Budget: $150 for project. Free parts: Surplus parts from previous year s project are available on
The Fundamentals of Mixed Signal Testing
 The Fundamentals of Mixed Signal Testing Course Information The Fundamentals of Mixed Signal Testing course is designed to provide the foundation of knowledge that is required for testing modern mixed
The Fundamentals of Mixed Signal Testing Course Information The Fundamentals of Mixed Signal Testing course is designed to provide the foundation of knowledge that is required for testing modern mixed
Analog Input and Output. Lecturer: Sri Parameswaran Notes by: Annie Guo
 Analog Input and Output Lecturer: Sri Parameswaran Notes by: Annie Guo 1 Analog output Lecture overview PMW Digital-to-Analog (D/A) Conversion Analog input Analog-to-Digital (A/D) Conversion 2 PWM Analog
Analog Input and Output Lecturer: Sri Parameswaran Notes by: Annie Guo 1 Analog output Lecture overview PMW Digital-to-Analog (D/A) Conversion Analog input Analog-to-Digital (A/D) Conversion 2 PWM Analog
A-D and D-A Converters
 Chapter 5 A-D and D-A Converters (No mathematical derivations) 04 Hours 08 Marks When digital devices are to be interfaced with analog devices (or vice a versa), Digital to Analog converter and Analog
Chapter 5 A-D and D-A Converters (No mathematical derivations) 04 Hours 08 Marks When digital devices are to be interfaced with analog devices (or vice a versa), Digital to Analog converter and Analog
Data Converters. Dr.Trushit Upadhyaya EC Department, CSPIT, CHARUSAT
 Data Converters Dr.Trushit Upadhyaya EC Department, CSPIT, CHARUSAT Purpose To convert digital values to analog voltages V OUT Digital Value Reference Voltage Digital Value DAC Analog Voltage Analog Quantity:
Data Converters Dr.Trushit Upadhyaya EC Department, CSPIT, CHARUSAT Purpose To convert digital values to analog voltages V OUT Digital Value Reference Voltage Digital Value DAC Analog Voltage Analog Quantity:
ELG3336: Converters Analog to Digital Converters (ADCs) Digital to Analog Converters (DACs)
 ELG3336: Converters Analog to Digital Converters (ADCs) Digital to Analog Converters (DACs) Digital Output Dout 111 110 101 100 011 010 001 000 ΔV, V LSB V ref 8 V FSR 4 V 8 ref 7 V 8 ref Analog Input
ELG3336: Converters Analog to Digital Converters (ADCs) Digital to Analog Converters (DACs) Digital Output Dout 111 110 101 100 011 010 001 000 ΔV, V LSB V ref 8 V FSR 4 V 8 ref 7 V 8 ref Analog Input
P a g e 1. Introduction
 P a g e 1 Introduction 1. Signals in digital form are more convenient than analog form for processing and control operation. 2. Real world signals originated from temperature, pressure, flow rate, force
P a g e 1 Introduction 1. Signals in digital form are more convenient than analog form for processing and control operation. 2. Real world signals originated from temperature, pressure, flow rate, force
Digital Design Laboratory Lecture 7. A/D and D/A
 ECE 280 / CSE 280 Digital Design Laboratory Lecture 7 A/D and D/A Analog/Digital Conversion A/D conversion is the process of sampling a continuous signal Two significant implications 1. The information
ECE 280 / CSE 280 Digital Design Laboratory Lecture 7 A/D and D/A Analog/Digital Conversion A/D conversion is the process of sampling a continuous signal Two significant implications 1. The information
Lecture 9, ANIK. Data converters 1
 Lecture 9, ANIK Data converters 1 What did we do last time? Noise and distortion Understanding the simplest circuit noise Understanding some of the sources of distortion 502 of 530 What will we do today?
Lecture 9, ANIK Data converters 1 What did we do last time? Noise and distortion Understanding the simplest circuit noise Understanding some of the sources of distortion 502 of 530 What will we do today?
EECS 373 Design of Microprocessor-Based Systems
 EECS 373 Design of Microprocessor-Based Systems Prabal Dutta University of Michigan Lecture 11: Sampling, ADCs, and DACs Oct 7, 2014 Some slides adapted from Mark Brehob, Jonathan Hui & Steve Reinhardt
EECS 373 Design of Microprocessor-Based Systems Prabal Dutta University of Michigan Lecture 11: Sampling, ADCs, and DACs Oct 7, 2014 Some slides adapted from Mark Brehob, Jonathan Hui & Steve Reinhardt
Electronics A/D and D/A converters
 Electronics A/D and D/A converters Prof. Márta Rencz, Gábor Takács, Dr. György Bognár, Dr. Péter G. Szabó BME DED December 1, 2014 1 / 26 Introduction The world is analog, signal processing nowadays is
Electronics A/D and D/A converters Prof. Márta Rencz, Gábor Takács, Dr. György Bognár, Dr. Péter G. Szabó BME DED December 1, 2014 1 / 26 Introduction The world is analog, signal processing nowadays is
Fundamentals of Data Converters. DAVID KRESS Director of Technical Marketing
 Fundamentals of Data Converters DAVID KRESS Director of Technical Marketing 9/14/2016 Analog to Electronic Signal Processing Sensor (INPUT) Amp Converter Digital Processor Actuator (OUTPUT) Amp Converter
Fundamentals of Data Converters DAVID KRESS Director of Technical Marketing 9/14/2016 Analog to Electronic Signal Processing Sensor (INPUT) Amp Converter Digital Processor Actuator (OUTPUT) Amp Converter
ADC and DAC converters. Laboratory Instruction
 ADC and DAC converters Laboratory Instruction Prepared by: Łukasz Buczek 05.2015 Rev. 2018 1. Aim of exercise The aim of exercise is to learn the basics of the analog-to-digital (ADC) and digital-to-analog
ADC and DAC converters Laboratory Instruction Prepared by: Łukasz Buczek 05.2015 Rev. 2018 1. Aim of exercise The aim of exercise is to learn the basics of the analog-to-digital (ADC) and digital-to-analog
SIGMA-DELTA CONVERTER
 SIGMA-DELTA CONVERTER (1995: Pacífico R. Concetti Western A. Geophysical-Argentina) The Sigma-Delta A/D Converter is not new in electronic engineering since it has been previously used as part of many
SIGMA-DELTA CONVERTER (1995: Pacífico R. Concetti Western A. Geophysical-Argentina) The Sigma-Delta A/D Converter is not new in electronic engineering since it has been previously used as part of many
FYS3240 PC-based instrumentation and microcontrollers. Signal sampling. Spring 2017 Lecture #5
 FYS3240 PC-based instrumentation and microcontrollers Signal sampling Spring 2017 Lecture #5 Bekkeng, 30.01.2017 Content Aliasing Sampling Analog to Digital Conversion (ADC) Filtering Oversampling Triggering
FYS3240 PC-based instrumentation and microcontrollers Signal sampling Spring 2017 Lecture #5 Bekkeng, 30.01.2017 Content Aliasing Sampling Analog to Digital Conversion (ADC) Filtering Oversampling Triggering
EE251: Tuesday October 10
 EE251: Tuesday October 10 Analog to Digital Conversion Text Chapter 20 through section 20.2 TM4C Data Sheet Chapter 13 Lab #5 Writeup Lab Practical #1 this week Homework #4 is due on Thursday at 4:30 p.m.
EE251: Tuesday October 10 Analog to Digital Conversion Text Chapter 20 through section 20.2 TM4C Data Sheet Chapter 13 Lab #5 Writeup Lab Practical #1 this week Homework #4 is due on Thursday at 4:30 p.m.
Analog to Digital Conversion
 Analog to Digital Conversion Florian Erdinger Lehrstuhl für Schaltungstechnik und Simulation Technische Informatik der Uni Heidelberg VLSI Design - Mixed Mode Simulation F. Erdinger, ZITI, Uni Heidelberg
Analog to Digital Conversion Florian Erdinger Lehrstuhl für Schaltungstechnik und Simulation Technische Informatik der Uni Heidelberg VLSI Design - Mixed Mode Simulation F. Erdinger, ZITI, Uni Heidelberg
System on a Chip. Prof. Dr. Michael Kraft
 System on a Chip Prof. Dr. Michael Kraft Lecture 5: Data Conversion ADC Background/Theory Examples Background Physical systems are typically analogue To apply digital signal processing, the analogue signal
System on a Chip Prof. Dr. Michael Kraft Lecture 5: Data Conversion ADC Background/Theory Examples Background Physical systems are typically analogue To apply digital signal processing, the analogue signal
ELG4139: Converters Analog to Digital Converters (ADCs) Digital to Analog Converters (DACs)
 ELG4139: Converters Analog to Digital Converters (ADCs) Digital to Analog Converters (DACs) Digital Output Dout 111 110 101 100 011 010 001 000 ΔV, V LSB V ref 8 V FS 4 V 8 ref 7 V 8 ref Analog Input V
ELG4139: Converters Analog to Digital Converters (ADCs) Digital to Analog Converters (DACs) Digital Output Dout 111 110 101 100 011 010 001 000 ΔV, V LSB V ref 8 V FS 4 V 8 ref 7 V 8 ref Analog Input V
Chapter 2 Signal Conditioning, Propagation, and Conversion
 09/0 PHY 4330 Instrumentation I Chapter Signal Conditioning, Propagation, and Conversion. Amplification (Review of Op-amps) Reference: D. A. Bell, Operational Amplifiers Applications, Troubleshooting,
09/0 PHY 4330 Instrumentation I Chapter Signal Conditioning, Propagation, and Conversion. Amplification (Review of Op-amps) Reference: D. A. Bell, Operational Amplifiers Applications, Troubleshooting,
UNIT III Data Acquisition & Microcontroller System. Mr. Manoj Rajale
 UNIT III Data Acquisition & Microcontroller System Mr. Manoj Rajale Syllabus Interfacing of Sensors / Actuators to DAQ system, Bit width, Sampling theorem, Sampling Frequency, Aliasing, Sample and hold
UNIT III Data Acquisition & Microcontroller System Mr. Manoj Rajale Syllabus Interfacing of Sensors / Actuators to DAQ system, Bit width, Sampling theorem, Sampling Frequency, Aliasing, Sample and hold
Analog to Digital Conversion
 Analog to Digital Conversion 02534567998 6 4 2 3 4 5 6 ANALOG to DIGITAL CONVERSION Analog variation (Continuous, smooth variation) Digitized Variation (Discrete set of points) N2 N1 Digitization applied
Analog to Digital Conversion 02534567998 6 4 2 3 4 5 6 ANALOG to DIGITAL CONVERSION Analog variation (Continuous, smooth variation) Digitized Variation (Discrete set of points) N2 N1 Digitization applied
Data acquisition and instrumentation. Data acquisition
 Data acquisition and instrumentation START Lecture Sam Sadeghi Data acquisition 1 Humanistic Intelligence Body as a transducer,, data acquisition and signal processing machine Analysis of physiological
Data acquisition and instrumentation START Lecture Sam Sadeghi Data acquisition 1 Humanistic Intelligence Body as a transducer,, data acquisition and signal processing machine Analysis of physiological
CHAPTER ELEVEN - Interfacing With the Analog World
 CHAPTER ELEVEN - Interfacing With the Analog World 11.1 (a) Analog output = (K) x (digital input) (b) Smallest change that can occur in the analog output as a result of a change in the digital input. (c)
CHAPTER ELEVEN - Interfacing With the Analog World 11.1 (a) Analog output = (K) x (digital input) (b) Smallest change that can occur in the analog output as a result of a change in the digital input. (c)
Outline. Analog/Digital Conversion
 Analog/Digital Conversion The real world is analog. Interfacing a microprocessor-based system to real-world devices often requires conversion between the microprocessor s digital representation of values
Analog/Digital Conversion The real world is analog. Interfacing a microprocessor-based system to real-world devices often requires conversion between the microprocessor s digital representation of values
EECS 373 Design of Microprocessor-Based Systems
 EECS 373 Design of Microprocessor-Based Systems Ronald Dreslinski University of Michigan Sampling, ADCs, and DACs and more Some slides adapted from Mark Brehob, Prabal Dutta, Jonathan Hui & Steve Reinhardt
EECS 373 Design of Microprocessor-Based Systems Ronald Dreslinski University of Michigan Sampling, ADCs, and DACs and more Some slides adapted from Mark Brehob, Prabal Dutta, Jonathan Hui & Steve Reinhardt
Computerized Data Acquisition Systems. Chapter 4
 Computerized Data Acquisition Systems Chapter 4 Data Acquisition - Objectives State and discuss in terms a bright high school student would understand the following definitions related to data acquisition
Computerized Data Acquisition Systems Chapter 4 Data Acquisition - Objectives State and discuss in terms a bright high school student would understand the following definitions related to data acquisition
Lab.3. Tutorial : (draft) Introduction to CODECs
 Lab.3. Tutorial : (draft) Introduction to CODECs Fig. Basic digital signal processing system Definition A codec is a device or computer program capable of encoding or decoding a digital data stream or
Lab.3. Tutorial : (draft) Introduction to CODECs Fig. Basic digital signal processing system Definition A codec is a device or computer program capable of encoding or decoding a digital data stream or
Theoretical 1 Bit A/D Converter
 Acquisition 16.1 Chapter 4 - Acquisition D/A converter (or DAC): Digital to Analog converters are used to map a finite number of values onto a physical output range (usually a ) A/D converter (or ADC):
Acquisition 16.1 Chapter 4 - Acquisition D/A converter (or DAC): Digital to Analog converters are used to map a finite number of values onto a physical output range (usually a ) A/D converter (or ADC):
Data Acquisition & Computer Control
 Chapter 4 Data Acquisition & Computer Control Now that we have some tools to look at random data we need to understand the fundamental methods employed to acquire data and control experiments. The personal
Chapter 4 Data Acquisition & Computer Control Now that we have some tools to look at random data we need to understand the fundamental methods employed to acquire data and control experiments. The personal
Chapter 7. Introduction. Analog Signal and Discrete Time Series. Sampling, Digital Devices, and Data Acquisition
 Chapter 7 Sampling, Digital Devices, and Data Acquisition Material from Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements; Figliola, Third Edition Introduction Integrating analog electrical transducers with
Chapter 7 Sampling, Digital Devices, and Data Acquisition Material from Theory and Design for Mechanical Measurements; Figliola, Third Edition Introduction Integrating analog electrical transducers with
Time Matters How Power Meters Measure Fast Signals
 Time Matters How Power Meters Measure Fast Signals By Wolfgang Damm, Product Management Director, Wireless Telecom Group Power Measurements Modern wireless and cable transmission technologies, as well
Time Matters How Power Meters Measure Fast Signals By Wolfgang Damm, Product Management Director, Wireless Telecom Group Power Measurements Modern wireless and cable transmission technologies, as well
Lecture #6: Analog-to-Digital Converter
 Lecture #6: Analog-to-Digital Converter All electrical signals in the real world are analog, and their waveforms are continuous in time. Since most signal processing is done digitally in discrete time,
Lecture #6: Analog-to-Digital Converter All electrical signals in the real world are analog, and their waveforms are continuous in time. Since most signal processing is done digitally in discrete time,
II Year (04 Semester) EE6403 Discrete Time Systems and Signal Processing
 Class Subject Code Subject II Year (04 Semester) EE6403 Discrete Time Systems and Signal Processing 1.CONTENT LIST: Introduction to Unit I - Signals and Systems 2. SKILLS ADDRESSED: Listening 3. OBJECTIVE
Class Subject Code Subject II Year (04 Semester) EE6403 Discrete Time Systems and Signal Processing 1.CONTENT LIST: Introduction to Unit I - Signals and Systems 2. SKILLS ADDRESSED: Listening 3. OBJECTIVE
EE247 Lecture 11. EECS 247 Lecture 11: Intro. to Data Converters & Performance Metrics 2009 H. K. Page 1. Typical Sampling Process C.T. S.D. D.T.
 EE247 Lecture Data converters Sampling, aliasing, reconstruction Amplitude quantization Static converter error sources Offset Full-scale error Differential non-linearity (DNL) Integral non-linearity (INL)
EE247 Lecture Data converters Sampling, aliasing, reconstruction Amplitude quantization Static converter error sources Offset Full-scale error Differential non-linearity (DNL) Integral non-linearity (INL)
DIGITAL FILTERING OF MULTIPLE ANALOG CHANNELS
 DIGITAL FILTERING OF MULTIPLE ANALOG CHANNELS Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Hicks, William T. Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal International Telemetering Conference Proceedings
DIGITAL FILTERING OF MULTIPLE ANALOG CHANNELS Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Hicks, William T. Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal International Telemetering Conference Proceedings
ANALOG TO DIGITAL (ADC) and DIGITAL TO ANALOG CONVERTERS (DAC)
 COURSE / CODE DIGITAL SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS (ECE421) DIGITAL ELECTRONICS FUNDAMENTAL (ECE422) ANALOG TO DIGITAL (ADC) and DIGITAL TO ANALOG CONVERTERS (DAC) Connecting digital circuitry to sensor devices
COURSE / CODE DIGITAL SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS (ECE421) DIGITAL ELECTRONICS FUNDAMENTAL (ECE422) ANALOG TO DIGITAL (ADC) and DIGITAL TO ANALOG CONVERTERS (DAC) Connecting digital circuitry to sensor devices
EEE312: Electrical measurement & instrumentation
 University of Turkish Aeronautical Association Faculty of Engineering EEE department EEE312: Electrical measurement & instrumentation Digital Electronic meters BY Ankara March 2017 1 Introduction The digital
University of Turkish Aeronautical Association Faculty of Engineering EEE department EEE312: Electrical measurement & instrumentation Digital Electronic meters BY Ankara March 2017 1 Introduction The digital
Working with ADCs, OAs and the MSP430
 Working with ADCs, OAs and the MSP430 Bonnie Baker HPA Senior Applications Engineer Texas Instruments 2006 Texas Instruments Inc, Slide 1 Agenda An Overview of the MSP430 Data Acquisition System SAR Converters
Working with ADCs, OAs and the MSP430 Bonnie Baker HPA Senior Applications Engineer Texas Instruments 2006 Texas Instruments Inc, Slide 1 Agenda An Overview of the MSP430 Data Acquisition System SAR Converters
Analog to Digital Conversion
 Analog to Digital Conversion Why It s Needed Embedded systems often need to measure values of physical parameters These parameters are usually continuous (analog) and not in a digital form which computers
Analog to Digital Conversion Why It s Needed Embedded systems often need to measure values of physical parameters These parameters are usually continuous (analog) and not in a digital form which computers
FYS3240 PC-based instrumentation and microcontrollers. Signal sampling. Spring 2015 Lecture #5
 FYS3240 PC-based instrumentation and microcontrollers Signal sampling Spring 2015 Lecture #5 Bekkeng, 29.1.2015 Content Aliasing Nyquist (Sampling) ADC Filtering Oversampling Triggering Analog Signal Information
FYS3240 PC-based instrumentation and microcontrollers Signal sampling Spring 2015 Lecture #5 Bekkeng, 29.1.2015 Content Aliasing Nyquist (Sampling) ADC Filtering Oversampling Triggering Analog Signal Information
! Where are we on course map? ! What we did in lab last week. " How it relates to this week. ! Sampling/Quantization Review
 ! Where are we on course map?! What we did in lab last week " How it relates to this week! Sampling/Quantization Review! Nyquist Shannon Sampling Rate! Next Lab! References Lecture #2 Nyquist-Shannon Sampling
! Where are we on course map?! What we did in lab last week " How it relates to this week! Sampling/Quantization Review! Nyquist Shannon Sampling Rate! Next Lab! References Lecture #2 Nyquist-Shannon Sampling
Figure 1: Block diagram of Digital signal processing
 Experiment 3. Digital Process of Continuous Time Signal. Introduction Discrete time signal processing algorithms are being used to process naturally occurring analog signals (like speech, music and images).
Experiment 3. Digital Process of Continuous Time Signal. Introduction Discrete time signal processing algorithms are being used to process naturally occurring analog signals (like speech, music and images).
Laboratory Assignment 1 Sampling Phenomena
 1 Main Topics Signal Acquisition Audio Processing Aliasing, Anti-Aliasing Filters Laboratory Assignment 1 Sampling Phenomena 2.171 Analysis and Design of Digital Control Systems Digital Filter Design and
1 Main Topics Signal Acquisition Audio Processing Aliasing, Anti-Aliasing Filters Laboratory Assignment 1 Sampling Phenomena 2.171 Analysis and Design of Digital Control Systems Digital Filter Design and
Analog-to-Digital i Converters
 CSE 577 Spring 2011 Analog-to-Digital i Converters Jaehyun Lim, Kyusun Choi Department t of Computer Science and Engineering i The Pennsylvania State University ADC Glossary DNL (differential nonlinearity)
CSE 577 Spring 2011 Analog-to-Digital i Converters Jaehyun Lim, Kyusun Choi Department t of Computer Science and Engineering i The Pennsylvania State University ADC Glossary DNL (differential nonlinearity)
In The Name of Almighty. Lec. 2: Sampling
 In The Name of Almighty Lec. 2: Sampling Lecturer: Hooman Farkhani Department of Electrical Engineering Islamic Azad University of Najafabad Feb. 2016. Email: H_farkhani@yahoo.com A/D and D/A Conversion
In The Name of Almighty Lec. 2: Sampling Lecturer: Hooman Farkhani Department of Electrical Engineering Islamic Azad University of Najafabad Feb. 2016. Email: H_farkhani@yahoo.com A/D and D/A Conversion
LAB Week 7: Data Acquisition
 LAB Week 7: Data Acquisition Wright State University: Mechanical Engineering ME 3600L Section 01 Report and experiment by: Nicholas Smith Experiment performed on February 23, 2015 Due: March 16, 2015 Instructor:
LAB Week 7: Data Acquisition Wright State University: Mechanical Engineering ME 3600L Section 01 Report and experiment by: Nicholas Smith Experiment performed on February 23, 2015 Due: March 16, 2015 Instructor:
EE 230 Lecture 39. Data Converters. Time and Amplitude Quantization
 EE 230 Lecture 39 Data Converters Time and Amplitude Quantization Review from Last Time: Time Quantization How often must a signal be sampled so that enough information about the original signal is available
EE 230 Lecture 39 Data Converters Time and Amplitude Quantization Review from Last Time: Time Quantization How often must a signal be sampled so that enough information about the original signal is available
APPLICATION NOTE. Atmel AVR127: Understanding ADC Parameters. Atmel 8-bit Microcontroller. Features. Introduction
 APPLICATION NOTE Atmel AVR127: Understanding ADC Parameters Atmel 8-bit Microcontroller Features Getting introduced to ADC concepts Understanding various ADC parameters Understanding the effect of ADC
APPLICATION NOTE Atmel AVR127: Understanding ADC Parameters Atmel 8-bit Microcontroller Features Getting introduced to ADC concepts Understanding various ADC parameters Understanding the effect of ADC
AD9772A - Functional Block Diagram
 F FEATURES single 3.0 V to 3.6 V supply 14-Bit DAC Resolution 160 MPS Input Data Rate 67.5 MHz Reconstruction Passband @ 160 MPS 74 dbc FDR @ 25 MHz 2 Interpolation Filter with High- or Low-Pass Response
F FEATURES single 3.0 V to 3.6 V supply 14-Bit DAC Resolution 160 MPS Input Data Rate 67.5 MHz Reconstruction Passband @ 160 MPS 74 dbc FDR @ 25 MHz 2 Interpolation Filter with High- or Low-Pass Response
Analyzing A/D and D/A converters
 Analyzing A/D and D/A converters 2013. 10. 21. Pálfi Vilmos 1 Contents 1 Signals 3 1.1 Periodic signals 3 1.2 Sampling 4 1.2.1 Discrete Fourier transform... 4 1.2.2 Spectrum of sampled signals... 5 1.2.3
Analyzing A/D and D/A converters 2013. 10. 21. Pálfi Vilmos 1 Contents 1 Signals 3 1.1 Periodic signals 3 1.2 Sampling 4 1.2.1 Discrete Fourier transform... 4 1.2.2 Spectrum of sampled signals... 5 1.2.3
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Final Exam EECS 247 H. Khorramabadi Tues., Dec. 14, 2010 FALL 2010 Name: SID: Total number of
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Final Exam EECS 247 H. Khorramabadi Tues., Dec. 14, 2010 FALL 2010 Name: SID: Total number of
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA. EECS 145M: Microcomputer Interfacing Lab
 NAME (please print) STUDENT (SID) NUMBER UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Berkeley EECS 145M: Microcomputer Interfacing Lab LAB REPORTS: 1 (100
NAME (please print) STUDENT (SID) NUMBER UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Berkeley EECS 145M: Microcomputer Interfacing Lab LAB REPORTS: 1 (100
Music 270a: Fundamentals of Digital Audio and Discrete-Time Signals
 Music 270a: Fundamentals of Digital Audio and Discrete-Time Signals Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego October 3, 2016 1 Continuous vs. Discrete signals
Music 270a: Fundamentals of Digital Audio and Discrete-Time Signals Tamara Smyth, trsmyth@ucsd.edu Department of Music, University of California, San Diego October 3, 2016 1 Continuous vs. Discrete signals
ANALOGUE AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION
 ANALOGUE AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION Syed M. Zafi S. Shah Umair M. Qureshi Lecture xxx: Analogue to Digital Conversion Topics Pulse Modulation Systems Advantages & Disadvantages Pulse Code Modulation Pulse
ANALOGUE AND DIGITAL COMMUNICATION Syed M. Zafi S. Shah Umair M. Qureshi Lecture xxx: Analogue to Digital Conversion Topics Pulse Modulation Systems Advantages & Disadvantages Pulse Code Modulation Pulse
Analog I/O. ECE 153B Sensor & Peripheral Interface Design Winter 2016
 Analog I/O ECE 153B Sensor & Peripheral Interface Design Introduction Anytime we need to monitor or control analog signals with a digital system, we require analogto-digital (ADC) and digital-to-analog
Analog I/O ECE 153B Sensor & Peripheral Interface Design Introduction Anytime we need to monitor or control analog signals with a digital system, we require analogto-digital (ADC) and digital-to-analog
SYLLABUS of the course BASIC ELECTRONICS AND DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING. Master in Computer Science, University of Bolzano-Bozen, a.y.
 SYLLABUS of the course BASIC ELECTRONICS AND DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Master in Computer Science, University of Bolzano-Bozen, a.y. 2017-2018 Lecturer: LEONARDO RICCI (last updated on November 27, 2017)
SYLLABUS of the course BASIC ELECTRONICS AND DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Master in Computer Science, University of Bolzano-Bozen, a.y. 2017-2018 Lecturer: LEONARDO RICCI (last updated on November 27, 2017)
Workshop ESSCIRC. Low-Power Data Acquisition System For Very Small Signals At Low Frequencies With12-Bit- SAR-ADC. 17. September 2010.
 Workshop ESSCIRC Low-Power Data Acquisition System For Very Small Signals At Low Frequencies With12-Bit- SAR-ADC 17. September 2010 Christof Dohmen Outline System Overview Analog-Front-End Chopper-Amplifier
Workshop ESSCIRC Low-Power Data Acquisition System For Very Small Signals At Low Frequencies With12-Bit- SAR-ADC 17. September 2010 Christof Dohmen Outline System Overview Analog-Front-End Chopper-Amplifier
!"!#"#$% Lecture 2: Media Creation. Some materials taken from Prof. Yao Wang s slides RECAP
 Lecture 2: Media Creation Some materials taken from Prof. Yao Wang s slides RECAP #% A Big Umbrella Content Creation: produce the media, compress it to a format that is portable/ deliverable Distribution:
Lecture 2: Media Creation Some materials taken from Prof. Yao Wang s slides RECAP #% A Big Umbrella Content Creation: produce the media, compress it to a format that is portable/ deliverable Distribution:
Chapter 5: Signal conversion
 Chapter 5: Signal conversion Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you will be able to: explain the need for signal conversion between analogue and digital form in communications and microprocessors
Chapter 5: Signal conversion Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you will be able to: explain the need for signal conversion between analogue and digital form in communications and microprocessors
Cyber-Physical Systems ADC / DAC
 Cyber-Physical Systems ADC / DAC ICEN 553/453 Fall 2018 Prof. Dola Saha 1 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) Ø ADC is important almost to all application fields Ø Converts a continuous-time voltage signal
Cyber-Physical Systems ADC / DAC ICEN 553/453 Fall 2018 Prof. Dola Saha 1 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) Ø ADC is important almost to all application fields Ø Converts a continuous-time voltage signal
In this lecture, we will look at how different electronic modules communicate with each other. We will consider the following topics:
 In this lecture, we will look at how different electronic modules communicate with each other. We will consider the following topics: Links between Digital and Analogue Serial vs Parallel links Flow control
In this lecture, we will look at how different electronic modules communicate with each other. We will consider the following topics: Links between Digital and Analogue Serial vs Parallel links Flow control
Analog to Digital Converters
 Analog to Digital Converters By: Byron Johns, Danny Carpenter Stephanie Pohl, Harry Bo Marr http://ume.gatech.edu/mechatronics_course/fadc_f05.ppt (unless otherwise marked) Presentation Outline Introduction:
Analog to Digital Converters By: Byron Johns, Danny Carpenter Stephanie Pohl, Harry Bo Marr http://ume.gatech.edu/mechatronics_course/fadc_f05.ppt (unless otherwise marked) Presentation Outline Introduction:
Data Converter Topics. Suggested Reference Texts
 Data Converter Topics Basic Operation of Data Converters Uniform sampling and reconstruction Uniform amplitude quantization Characterization and Testing Common ADC/DAC Architectures Selected Topics in
Data Converter Topics Basic Operation of Data Converters Uniform sampling and reconstruction Uniform amplitude quantization Characterization and Testing Common ADC/DAC Architectures Selected Topics in
Analog-Digital Interface
 Analog-Digital Interface Tuesday 24 November 15 Summary Previous Class Dependability Today: Redundancy Error Correcting Codes Analog-Digital Interface Converters, Sensors / Actuators Sampling DSP Frequency
Analog-Digital Interface Tuesday 24 November 15 Summary Previous Class Dependability Today: Redundancy Error Correcting Codes Analog-Digital Interface Converters, Sensors / Actuators Sampling DSP Frequency
Lecture Schedule: Week Date Lecture Title
 http://elec3004.org Sampling & More 2014 School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering at The University of Queensland Lecture Schedule: Week Date Lecture Title 1 2-Mar Introduction 3-Mar
http://elec3004.org Sampling & More 2014 School of Information Technology and Electrical Engineering at The University of Queensland Lecture Schedule: Week Date Lecture Title 1 2-Mar Introduction 3-Mar
EE247 Lecture 11. Example: Switched-capacitor filters in CODEC integrated circuits. Switched-capacitor filter design summary
 EE47 Lecture 11 Filters (continued) Example: Switched-capacitor filters in CODEC integrated circuits Switched-capacitor filter design summary Comparison of various filter topologies New Topic: Data Converters
EE47 Lecture 11 Filters (continued) Example: Switched-capacitor filters in CODEC integrated circuits Switched-capacitor filter design summary Comparison of various filter topologies New Topic: Data Converters
APPLICATION BULLETIN PRINCIPLES OF DATA ACQUISITION AND CONVERSION. Reconstructed Wave Form
 APPLICATION BULLETIN Mailing Address: PO Box 11400 Tucson, AZ 85734 Street Address: 6730 S. Tucson Blvd. Tucson, AZ 85706 Tel: (60) 746-1111 Twx: 910-95-111 Telex: 066-6491 FAX (60) 889-1510 Immediate
APPLICATION BULLETIN Mailing Address: PO Box 11400 Tucson, AZ 85734 Street Address: 6730 S. Tucson Blvd. Tucson, AZ 85706 Tel: (60) 746-1111 Twx: 910-95-111 Telex: 066-6491 FAX (60) 889-1510 Immediate
Media Devices: Audio. CTEC1465/2018S Computer System Support
 Media Devices: Audio CTEC1465/2018S Computer System Support Learning Objective Describe how to implement sound in a PC Introduction The process by which sounds are stored in electronic format on your PC
Media Devices: Audio CTEC1465/2018S Computer System Support Learning Objective Describe how to implement sound in a PC Introduction The process by which sounds are stored in electronic format on your PC
Continuous vs. Discrete signals. Sampling. Analog to Digital Conversion. CMPT 368: Lecture 4 Fundamentals of Digital Audio, Discrete-Time Signals
 Continuous vs. Discrete signals CMPT 368: Lecture 4 Fundamentals of Digital Audio, Discrete-Time Signals Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 22,
Continuous vs. Discrete signals CMPT 368: Lecture 4 Fundamentals of Digital Audio, Discrete-Time Signals Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 22,
Sampling and Reconstruction of Analog Signals
 Sampling and Reconstruction of Analog Signals Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes: (i) Ability to convert an analog signal to a discrete-time sequence via sampling (ii) Ability to construct an analog signal
Sampling and Reconstruction of Analog Signals Chapter Intended Learning Outcomes: (i) Ability to convert an analog signal to a discrete-time sequence via sampling (ii) Ability to construct an analog signal
Analog to Digital Converters (ADC) Rferences. Types of AD converters Direct (voltage comparison)
 Analog to Digital Converters (ADC) Lecture 7 Rferences U. Tietze, Ch.Schenk, Electronics Circuits Handbook for Design and Applications, Springer,2010 Advertisement materials and Application notes of: Linear
Analog to Digital Converters (ADC) Lecture 7 Rferences U. Tietze, Ch.Schenk, Electronics Circuits Handbook for Design and Applications, Springer,2010 Advertisement materials and Application notes of: Linear
Summary Last Lecture
 Interleaved ADCs EE47 Lecture 4 Oversampled ADCs Why oversampling? Pulse-count modulation Sigma-delta modulation 1-Bit quantization Quantization error (noise) spectrum SQNR analysis Limit cycle oscillations
Interleaved ADCs EE47 Lecture 4 Oversampled ADCs Why oversampling? Pulse-count modulation Sigma-delta modulation 1-Bit quantization Quantization error (noise) spectrum SQNR analysis Limit cycle oscillations
Linear Integrated Circuits
 Linear Integrated Circuits Single Slope ADC Comparator checks input voltage with integrated reference voltage, V REF At the same time the number of clock cycles is being counted. When the integrator output
Linear Integrated Circuits Single Slope ADC Comparator checks input voltage with integrated reference voltage, V REF At the same time the number of clock cycles is being counted. When the integrator output
NPTEL. VLSI Data Conversion Circuits - Video course. Electronics & Communication Engineering.
 NPTEL Syllabus VLSI Data Conversion Circuits - Video course COURSE OUTLINE This course covers the analysis and design of CMOS Analog-to-Digital and Digital-to-Analog Converters,with about 7 design assigments.
NPTEL Syllabus VLSI Data Conversion Circuits - Video course COURSE OUTLINE This course covers the analysis and design of CMOS Analog-to-Digital and Digital-to-Analog Converters,with about 7 design assigments.
PC-based controller for Mechatronics System
 Course Code: MDP 454, Course Name:, Second Semester 2014 PC-based controller for Mechatronics System Mechanical System PC Controller Controller in the Mechatronics System Configuration Actuators Power
Course Code: MDP 454, Course Name:, Second Semester 2014 PC-based controller for Mechatronics System Mechanical System PC Controller Controller in the Mechatronics System Configuration Actuators Power
PHYS225 Lecture 22. Electronic Circuits
 PHYS225 Lecture 22 Electronic Circuits Last lecture Digital to Analog Conversion DAC Converts digital signal to an analog signal Computer control of everything! Various types/techniques for conversion
PHYS225 Lecture 22 Electronic Circuits Last lecture Digital to Analog Conversion DAC Converts digital signal to an analog signal Computer control of everything! Various types/techniques for conversion
FFT Analyzer. Gianfranco Miele, Ph.D
 FFT Analyzer Gianfranco Miele, Ph.D www.eng.docente.unicas.it/gianfranco_miele g.miele@unicas.it Introduction It is a measurement instrument that evaluates the spectrum of a time domain signal applying
FFT Analyzer Gianfranco Miele, Ph.D www.eng.docente.unicas.it/gianfranco_miele g.miele@unicas.it Introduction It is a measurement instrument that evaluates the spectrum of a time domain signal applying
Analog to digital and digital to analog converters
 Analog to digital and digital to analog converters A/D converter D/A converter ADC DAC ad da Number bases Decimal, base, numbers - 9 Binary, base, numbers and Oktal, base 8, numbers - 7 Hexadecimal, base
Analog to digital and digital to analog converters A/D converter D/A converter ADC DAC ad da Number bases Decimal, base, numbers - 9 Binary, base, numbers and Oktal, base 8, numbers - 7 Hexadecimal, base
In this lecture. System Model Power Penalty Analog transmission Digital transmission
 System Model Power Penalty Analog transmission Digital transmission In this lecture Analog Data Transmission vs. Digital Data Transmission Analog to Digital (A/D) Conversion Digital to Analog (D/A) Conversion
System Model Power Penalty Analog transmission Digital transmission In this lecture Analog Data Transmission vs. Digital Data Transmission Analog to Digital (A/D) Conversion Digital to Analog (D/A) Conversion
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. AN109 Microprocessor-compatible DACs Dec
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS 1988 Dec DAC products are designed to convert a digital code to an analog signal. Since a common source of digital signals is the data bus of a microprocessor, DAC circuits that are
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS 1988 Dec DAC products are designed to convert a digital code to an analog signal. Since a common source of digital signals is the data bus of a microprocessor, DAC circuits that are
Choosing the Best ADC Architecture for Your Application Part 3:
 Choosing the Best ADC Architecture for Your Application Part 3: Hello, my name is Luis Chioye, I am an Applications Engineer with the Texas Instruments Precision Data Converters team. And I am Ryan Callaway,
Choosing the Best ADC Architecture for Your Application Part 3: Hello, my name is Luis Chioye, I am an Applications Engineer with the Texas Instruments Precision Data Converters team. And I am Ryan Callaway,
ENGR 210 Lab 12: Sampling and Aliasing
 ENGR 21 Lab 12: Sampling and Aliasing In the previous lab you examined how A/D converters actually work. In this lab we will consider some of the consequences of how fast you sample and of the signal processing
ENGR 21 Lab 12: Sampling and Aliasing In the previous lab you examined how A/D converters actually work. In this lab we will consider some of the consequences of how fast you sample and of the signal processing
Specifying A D and D A Converters
 Specifying A D and D A Converters The specification or selection of analog-to-digital (A D) or digital-to-analog (D A) converters can be a chancey thing unless the specifications are understood by the
Specifying A D and D A Converters The specification or selection of analog-to-digital (A D) or digital-to-analog (D A) converters can be a chancey thing unless the specifications are understood by the
Chapter 2 Analog-to-Digital Conversion...
 Chapter... 5 This chapter examines general considerations for analog-to-digital converter (ADC) measurements. Discussed are the four basic ADC types, providing a general description of each while comparing
Chapter... 5 This chapter examines general considerations for analog-to-digital converter (ADC) measurements. Discussed are the four basic ADC types, providing a general description of each while comparing
SAMPLING AND RECONSTRUCTING SIGNALS
 CHAPTER 3 SAMPLING AND RECONSTRUCTING SIGNALS Many DSP applications begin with analog signals. In order to process these analog signals, the signals must first be sampled and converted to digital signals.
CHAPTER 3 SAMPLING AND RECONSTRUCTING SIGNALS Many DSP applications begin with analog signals. In order to process these analog signals, the signals must first be sampled and converted to digital signals.
Data Conversion and Lab (17.368) Fall Lecture Outline
 Data Conversion and Lab (17.368) Fall 2013 Lecture Outline Class # 07 October 17, 2013 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture Outline Administrative Detailed Technical Discussions Digital to Analog Conversion Lab
Data Conversion and Lab (17.368) Fall 2013 Lecture Outline Class # 07 October 17, 2013 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture Outline Administrative Detailed Technical Discussions Digital to Analog Conversion Lab
DATA CONVERSION AND LAB (17.368) Fall Class # 07. October 16, 2008
 DATA CONVERSION AND LAB (17.368) Fall 2008 Class # 07 October 16, 2008 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture Outline Course Admin Lab #3 next week Exam in two weeks 10/30/08 Detailed Technical Discussions Digital
DATA CONVERSION AND LAB (17.368) Fall 2008 Class # 07 October 16, 2008 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture Outline Course Admin Lab #3 next week Exam in two weeks 10/30/08 Detailed Technical Discussions Digital
CMPT 318: Lecture 4 Fundamentals of Digital Audio, Discrete-Time Signals
 CMPT 318: Lecture 4 Fundamentals of Digital Audio, Discrete-Time Signals Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 16, 2006 1 Continuous vs. Discrete
CMPT 318: Lecture 4 Fundamentals of Digital Audio, Discrete-Time Signals Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 16, 2006 1 Continuous vs. Discrete
5 V, 14-Bit Serial, 5 s ADC in SO-8 Package AD7894
 a FEATURES Fast 14-Bit ADC with 5 s Conversion Time 8-Lead SOIC Package Single 5 V Supply Operation High Speed, Easy-to-Use, Serial Interface On-Chip Track/Hold Amplifier Selection of Input Ranges 10 V
a FEATURES Fast 14-Bit ADC with 5 s Conversion Time 8-Lead SOIC Package Single 5 V Supply Operation High Speed, Easy-to-Use, Serial Interface On-Chip Track/Hold Amplifier Selection of Input Ranges 10 V
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
 ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS Definition An analog-to-digital converter is a device which converts continuous signals to discrete digital numbers. Basics An analog-to-digital converter (abbreviated ADC,
ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS Definition An analog-to-digital converter is a device which converts continuous signals to discrete digital numbers. Basics An analog-to-digital converter (abbreviated ADC,
145M Final Exam Solutions page 1 May 11, 2010 S. Derenzo R/2. Vref. Address encoder logic. Exclusive OR. Digital output (8 bits) V 1 2 R/2
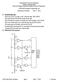 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Department 145M Microcomputer Interfacing Lab Final Exam Solutions May 11, 2010 1.1 Handshaking steps: When
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Department 145M Microcomputer Interfacing Lab Final Exam Solutions May 11, 2010 1.1 Handshaking steps: When
The simplest DAC can be constructed using a number of resistors with binary weighted values. X[3:0] is the 4-bit digital value to be converter to an
![The simplest DAC can be constructed using a number of resistors with binary weighted values. X[3:0] is the 4-bit digital value to be converter to an The simplest DAC can be constructed using a number of resistors with binary weighted values. X[3:0] is the 4-bit digital value to be converter to an](/thumbs/73/68151962.jpg) 1 Although digital technology dominates modern electronic systems, the physical world remains mostly analogue in nature. The most important components that link the analogue world to digital systems are
1 Although digital technology dominates modern electronic systems, the physical world remains mostly analogue in nature. The most important components that link the analogue world to digital systems are
