An 8-Channel Parallel Multispectral TCSPC FLIM System
|
|
|
- Wilfrid Washington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 An 8-Channel Parallel Multispectral TCSPC FLIM System Abstract. We describe a TCSPC FLIM system that uses 8 parallel TCSPC channels to record FLIM data at a peak count rate on the order of s -1. By using a polychromator for spectral dispersion and a multi-channel PMT for detection we obtain multi-spectral FLIM data at acquisition times on the order of one second. We demonstrate the system for recording transient lifetime effects in the chloroplasts in live plants. Count Rates in TCSPC FLIM Experiments TCSPC FLIM [3, 6] delivers single- and multi-wavelength fluorescence lifetime images at an accuracy essentially limited by the photon statistics [1, 11], and a time resolution limited by the transit-time-spread of the detector [4, 5, 12]. This is a clear advantage in the typical FLIM applications, such as FRET measurements, investigation of membrane proteins, or autofluorescence imaging. All these applications have in common that the fluorophore concentration is low. Moreover, the excitation power has to be kept low to avoid cell damage and lifetime changes by photobleaching. The count rates available from the samples are therefore on the order of only 10 4 s -1 to a few 10 5 s -1. This is one to two orders of magnitude lower than the counting capability of a single TCSPC FLIM device [5]. Consequently, the acquisition time required to achieve a given lifetime accuracy is exclusively given by the photostability of the sample, not by the counting capability of the TCSPC module. Technical efforts to increase the counting capability of the TCSPC FLIM electronics therefore do not result in shorter acquisition times in these applications. There are, however, certain classes of FLIM experiments that can be run at very high count rate. One of these is imaging of chlorophyll in plant tissue. Chlorophyll is highly photostable and emits strong fluorescence around 700 nm. The fluorescence lifetime of chlorophyll in live plants changes with the time of exposure [9]. Recording these changes requires fast FLIM [10]. Another potential application is, surprisingly, autofluorescence. Autofluorescence signals are usually weak, but exceptions do exist. Fig. 1 shows autofluorescence FLIM images of live yeast cells. The bright cells (probably apoptotic ones) are about 50 times brighter than the dim ones (visible only in Fig. 1, right). Fig. 1: FLIM images of yeast cells. Left: Intensity scale 0 to 3000 counts per pixel. Right: Intensity scale 0 to 300 counts per pixel. The bright cells are about 50 times brighter than the dim ones. Becker & Hickl DCS-120 confocal scanning FLIM system, excitation at 407 nm. eight-channel-flim-apn01.doc Oct
2 Recording lifetimes for both types of cells in the same image requires the count rate of the bright cells to be kept below about 4 MHz. The count rate in the dim cells is then less than 100 khz. The high contrast thus results in an unnecessarily long acquisition time. The Way to Higher Counting Capability The count rate of TCSPC FLIM is limited by counting loss due to the dead time of the TCSPC electronics, by pile-up effects, and saturation in the detector [4, 5, 10]. Counting loss could, in principle, be reduced by decreasing the dead time of the electronics. Pile-up-effects could be reduced by recording more than one photon per signal period. Unfortunately, both approaches have detrimental effects on the accuracy of the FLIM data. Reducing the dead time increases the background caused by the afterpulsing of the detector [4]. Recording several photons per laser period leads to an overlap of subsequent single-photon pulses and thus causes count-rate-dependent distortions of the decay curves [10]. In any case, detector nonlinearity and detector overload preclude the use of a single detector at count rates much higher than 10 7 s -1. A better way to increase the counting capability of TCSPC FLIM is therefore to use several parallel TCSPC channels. Standard FLIM systems for the bh DCS-120 confocal scanner [7] or the Zeiss LSM 710 NLO [8] system therefore have two parallel TCSPC channels. Four-channel FLIM systems are available as well [5] and have been shown to record FLIM at an average count rate of 13 MHz [2]. 8-Channel Parallel FLIM To further increase the counting capability of TCSPC FLIM we built an eight-channel parallel FLIM system. The architecture of the system is described below. We use the Becker & Hickl DC-120 confocal scanning FLIM system [7], see Fig. 2, left. An LOT MS 125 polychromator is attached to one confocal output of the DCS-120 scanner. The polychromator is used without an input slit; the light focused into the slit plane by a lens. from confocal pinhole Slit plane Mirror Mirror Lens LOT MS 125 Grating R5900-L16 Detector Fig. 2: Eight-channel FLIM system. Left: DCS-120 scanner. Middle: Principle of spectral dispersion. Right: FLIM electronics. The spectrum at the polychromator output is detected by a Hamamatsu R5900-L16-01 multichannel PMT. Only eight of the 16 channels of the R5900 are used; the remaining ones are terminated via 50 Ω into ground. Alternatively, connecting every two PMT channels in parallel is possible, but not recommended. The PMT channels have slightly different signal transit times. Connecting channels in parallel thus impairs the time resolution. Moreover, combining channels would also combine the dark counts and thus result in an unwanted increase of the thermal background. The electronics of the 8-channel FLIM system is shown in Fig. 2, right. We use two Simple- Tau 154 bus extension boxes holding four bh SPC-150 TCSPC modules each. The boxes are connected to a standard Pentium PC via bus extension cables. The PC also contains a DCC-100 detector controller card [5] and the scan controller card of the DCS-120 system [7]. 2 eight-channel-flim-apn01.doc Oct. 2009
3 Fig. 3 shows autofluorescence FLIM of a Drosophila eye. The excitation wavelength was 407 nm. The images were scanned at a resolution of 256 x 256 pixels and a rate of 500 ms per frame. The intensities were normalised on the brightest pixels. Fig. 3: Multi-wavelength FLIM of a Drosophila eye. Autofluorescence, excitation at 407 nm. Double-exponential decay model. Left: Amplitude weighted mean lifetime. Right: Relative amplitude of fast decay component. The total count rate (summed over all TCSPC channels and averaged over the image) obtained from the Drosophila eye was about s -1. That means the rate in the brightest pixels was more than s -1. A single-channel FLIM system would still deliver reasonable lifetimes under these conditions but inevitably develop visible intensity nonlinearity. A time-series recording with the 8-channel system is shown in Fig. 4. A moss leaf was scanned with 407 nm excitation wavelength, and at a scan rate of 4 frames per second. The data format of the TCSPC data was 256 x 256 pixels x 256 time channels. The lifetime shown is an amplitudeweighted average of the two lifetime components of a double-exponential fit. The intensity scale of all images was normalised on the intensity of the brightest pixel. Fig. 4: Multi-wavelength time-series FLIM obtained from a moss leaf. Each image is 256 x 256 pixels, 256 time channels. Left to right: Wavelength, from 580 nm to 720 nm. Top to bottom: First four steps of the time series, acquisition time 5 seconds per step. eight-channel-flim-apn01.doc Oct
4 In the wavelength intervals from 580 nm to 640 nm the fluorescence comes from the cell membranes. At 660 nm fluorescence of the chloroplasts starts to show up. From 680 nm to 720 nm the images are totally dominated by chlorophyll fluorescence. The lifetime of the chloroplasts decreases over the time of exposure, due to induction of a non-photochemical quenching transient. The lifetime in the cell membranes remains constant. The variation of the lifetime can be seen more clearly in Fig. 5. The figure shows lifetime images in the 700 nm interval for the first four steps of the time series. The lifetime scale has been stretched to 200 ps to 400 ps. Decay curves in a selected spot of the images are shown in the second row. Fig. 5: First four steps of the time series, 700 nm interval. Upper row: Lifetime images. Lower row: Decay curve in pixel position X=51, Y=147. Summary The results presented show that an eight-channel parallel TCSPC FLIM system is feasible and operable. The advantage over a single-channel multispectral FLIM system [5, 6] is that the applicable count rate is 8 times higher. Moreover, possible saturation in a single spectral channel does not cause artefacts in other channels. The parallel-channel architecture allows relatively large FLIM data formats to be used. However, large pixel and time channel numbers in combination with the eight channels result in large data file size. Every single recording step of the time-series shown in Fig. 4 produces 260 Mbytes of data. The rate at which a time series can be recorded is thus limited by the speed at which the computer can save the data. The rate scales with the image format; for images of 128 x 128 pixels x 256 time channels a speed of about 1.3 seconds per step is reached. It should be noted that the 8-channel system is built from standard components of the bh modular FLIM systems. Moreover, the application of the system is not restricted to bh DCS-120 confocal scanning system. It can be used with any confocal or multiphoton laser scanning microscope that gives the user access to the fluorescence light via an optical port. 4 eight-channel-flim-apn01.doc Oct. 2009
5 References 1. R.M. Ballew, J.N. Demas, An error analysis of the rapid lifetime determination method for the evaluation of single exponential decays, Anal. Chem. 61, 30 (1989) 2. W. Becker, A. Bergmann, G. Biscotti, K. Koenig, I. Riemann, L. Kelbauskas, C. Biskup, High-speed FLIM data acquisition by time-correlated single photon counting, Proc. SPIE 5323, (2004) 3. W. Becker, A. Bergmann, M.A. Hink, K. König, K. Benndorf, C. Biskup, Fluorescence lifetime imaging by timecorrelated single photon counting, Micr. Res. Techn. 63, (2004) 4. W. Becker, Advanced time-correlated single-photon counting techniques. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, W. Becker, The bh TCSPC handbook, third edition. Becker & Hickl GmbH (2006), available on 6. W. Becker, A. Bergmann, C. Biskup, Multi-Spectral Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging by TCSPC, Micr. Res. Tech. 70, (2007) 7. Becker & Hickl GmbH, DCS-120 confocal scanning FLIM systems, user handbook. Available on 8. Becker & Hickl GmbH, Modular FLIM systems for Zeiss LSM 510 and LSM 710 laser scanning microscopes. User handbook. Available on 9. Govindjee, Sixty-three Years Since Kautsky: Chlorophyll Fluorescence, Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 22, (1995) 10. V. Katsoulidou, A. Bergmann, W. Becker, How fast can TCSPC FLIM be made? Proc. SPIE 6771, 67710B-1 to 67710B-7 (2007) 11. M. Köllner, J. Wolfrum, How many photons are necessary for fluorescence-lifetime measurements?, Phys. Chem. Lett. 200, (1992) 12. D.V. O Connor, D. Phillips, Time-correlated single photon counting, Academic Press, London (1984) eight-channel-flim-apn01.doc Oct
Non-Descanned FLIM Detection in Multiphoton Microscopes
 Non-Descanned FLIM Detection in Multiphoton Microscopes Abstract. Multiphoton microscopes use a femtosecond NIR laser to excite fluorescence in the sample. Excitation is performed via a multi-photon absorption
Non-Descanned FLIM Detection in Multiphoton Microscopes Abstract. Multiphoton microscopes use a femtosecond NIR laser to excite fluorescence in the sample. Excitation is performed via a multi-photon absorption
Megapixel FLIM with bh TCSPC Modules
 Megapixel FLIM with bh TCSPC Modules The New SPCM 64-bit Software Abstract: Becker & Hickl have recently introduced version 9.60 of their SPCM TCSPC data acquisition software. SPCM version 9.60 not only
Megapixel FLIM with bh TCSPC Modules The New SPCM 64-bit Software Abstract: Becker & Hickl have recently introduced version 9.60 of their SPCM TCSPC data acquisition software. SPCM version 9.60 not only
TCSPC at Wavelengths from 900 nm to 1700 nm
 TCSPC at Wavelengths from 900 nm to 1700 nm We describe picosecond time-resolved optical signal recording in the spectral range from 900 nm to 1700 nm. The system consists of an id Quantique id220 InGaAs
TCSPC at Wavelengths from 900 nm to 1700 nm We describe picosecond time-resolved optical signal recording in the spectral range from 900 nm to 1700 nm. The system consists of an id Quantique id220 InGaAs
Instrument response function. Left linear scale, right logarithmic scale. FWHM is 120 ps.
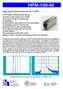 High Speed Hybrid Detector for TCSPC HPM-100-40 GaAsP cathode: Excellent detection efficiency Instrument response function 120 ps FWHM Clean response, no tails or secondary peaks No afterpulsing Excellent
High Speed Hybrid Detector for TCSPC HPM-100-40 GaAsP cathode: Excellent detection efficiency Instrument response function 120 ps FWHM Clean response, no tails or secondary peaks No afterpulsing Excellent
DCS-120. Confocal Scanning FLIM Systems. Based on bh s Multidimensional Megapixel FLIM Technology
 Based on bh s Multidimensional Megapixel FLIM Technology Complete Laser Scanning FLIM Microscopes FLIM Upgrades for Existing Conventional Microscopes Multidimensional TCSPC technique High throughput dual-channel
Based on bh s Multidimensional Megapixel FLIM Technology Complete Laser Scanning FLIM Microscopes FLIM Upgrades for Existing Conventional Microscopes Multidimensional TCSPC technique High throughput dual-channel
DCS-120. Confocal Scanning FLIM Systems. Based on bh s Multidimensional Megapixel FLIM Technology
 DCS-120 Based on bh s Multidimensional Megapixel FLIM Technology Complete Laser Scanning FLIM Microscopes FLIM Upgrades for Existing Conventional Microscopes FLIM with up to 2048 x 2048 pixels Decay curves
DCS-120 Based on bh s Multidimensional Megapixel FLIM Technology Complete Laser Scanning FLIM Microscopes FLIM Upgrades for Existing Conventional Microscopes FLIM with up to 2048 x 2048 pixels Decay curves
The DCS-120 Confocal Scanning FLIM System
 he DCS-120 Confocal Scanning FLIM System he bh DCS-120 confocal scanning FLIM system converts a conventional microscope into a high-performance fluorescence lifetime imaging system. he system is based
he DCS-120 Confocal Scanning FLIM System he bh DCS-120 confocal scanning FLIM system converts a conventional microscope into a high-performance fluorescence lifetime imaging system. he system is based
PZ-FLIM-110. Piezo Scanning FLIM System. Based on bh s Megapixel FLIM Technology. Complete FLIM Microscopes FLIM Upgrades for Existing Microscopes
 Based on bh s Megapixel FLIM Technology Complete FLIM Microscopes FLIM Upgrades for Existing Microscopes Multidimensional TCSPC technique Sample Scanning by Piezo Stage Compact Electronics, Controlled
Based on bh s Megapixel FLIM Technology Complete FLIM Microscopes FLIM Upgrades for Existing Microscopes Multidimensional TCSPC technique Sample Scanning by Piezo Stage Compact Electronics, Controlled
Multiphoton FLIM with the Leica HyD RLD Detectors
 Multiphoton FLIM with the Leica HyD RLD Detectors Leica have recently introduced hybrid detectors for the non-descanned (RLD) ports their SP5 and SP8 multiphoton laser scanning microscopes. We have tested
Multiphoton FLIM with the Leica HyD RLD Detectors Leica have recently introduced hybrid detectors for the non-descanned (RLD) ports their SP5 and SP8 multiphoton laser scanning microscopes. We have tested
IR Antibunching Measurements with id201 InGaAs Gated SPAD Detectors
 IR Antibunching Measurements with id201 GaAs Gated SPAD Detectors Abstract. Antibunching measurements with GaAs SPAD detectors are faced with the problems of high background count rate, afterpulsing, and
IR Antibunching Measurements with id201 GaAs Gated SPAD Detectors Abstract. Antibunching measurements with GaAs SPAD detectors are faced with the problems of high background count rate, afterpulsing, and
Wide-Field TCSPC FLIM with bh SPC-150 N TCSPC System and Photek FGN Detector
 Wide-Field TCSPC FLIM with bh SPC-150 N TCSPC System and Photek FGN 392-1000 Detector Abstract: We present a wide-field TCSPC FLIM system consisting of a position-sensitive MCP PMT of the delay-line type,
Wide-Field TCSPC FLIM with bh SPC-150 N TCSPC System and Photek FGN 392-1000 Detector Abstract: We present a wide-field TCSPC FLIM system consisting of a position-sensitive MCP PMT of the delay-line type,
Multi-wavelength TCSPC lifetime imaging Wolfgang Becker a, Axel Bergmann a, Christoph Biskup b, Thomas Zimmer b, Nikolaj Klöcker c, Klaus Benndorf b
 Multi-wavelength TCSPC lifetime imaging Wolfgang Becker a, Axel Bergmann a, Christoph Biskup b, Thomas Zimmer b, Nikolaj Klöcker c, Klaus Benndorf b a Becker & Hickl GmbH, Nahmitzer Damm 30, D-12277 Berlin,
Multi-wavelength TCSPC lifetime imaging Wolfgang Becker a, Axel Bergmann a, Christoph Biskup b, Thomas Zimmer b, Nikolaj Klöcker c, Klaus Benndorf b a Becker & Hickl GmbH, Nahmitzer Damm 30, D-12277 Berlin,
Becker & Hickl GmbH DCS-120. Confocal Scanning FLIM Systems. An Overview
 Becker & Hickl GmbH DCS-120 Confocal Scanning FLIM Systems An Overview 2015 The DCS-120 Confocal Scanning FLIM System An Overview Abstract: The DCS-120 system uses excitation by ps diode lasers or femtosecond
Becker & Hickl GmbH DCS-120 Confocal Scanning FLIM Systems An Overview 2015 The DCS-120 Confocal Scanning FLIM System An Overview Abstract: The DCS-120 system uses excitation by ps diode lasers or femtosecond
High Performance Photon Counting. User Manual PML-16-C. 16 Channel Detector Head for Time-Correlated Single Photon Counting. Becker & Hickl GmbH
 High Performance Photon Counting User Manual PML-16-C 16 Channel Detector Head for Time-Correlated Single Photon Counting Becker & Hickl GmbH PML-16C User Handbook 1 Becker & Hickl GmbH March 2006 High
High Performance Photon Counting User Manual PML-16-C 16 Channel Detector Head for Time-Correlated Single Photon Counting Becker & Hickl GmbH PML-16C User Handbook 1 Becker & Hickl GmbH March 2006 High
BDS-SM Family Picosecond Diode Lasers
 BDS-SM Family Picosecond Diode s BDS-SM Small-size OEM Module, 40 mm x 40 mm x 120 mm Wavelengths 375 nm, 405 nm, 445 nm, 473 nm, 488 nm, 515 nm, 640 nm, 685 nm, 785 nm, 1064 nm Free-beam or single-mode
BDS-SM Family Picosecond Diode s BDS-SM Small-size OEM Module, 40 mm x 40 mm x 120 mm Wavelengths 375 nm, 405 nm, 445 nm, 473 nm, 488 nm, 515 nm, 640 nm, 685 nm, 785 nm, 1064 nm Free-beam or single-mode
TCSPC for FLIM and FRET in Microscopy
 91 Boylston Street, Brookline, MA 02445 tel: (617)566-3821 fax: (617)731-0935 www.boselec.com tcspc@boselec.com TCSPC for FLIM and FRET in Microscopy The Becker & Hickl SPC Series Module Family PC Based
91 Boylston Street, Brookline, MA 02445 tel: (617)566-3821 fax: (617)731-0935 www.boselec.com tcspc@boselec.com TCSPC for FLIM and FRET in Microscopy The Becker & Hickl SPC Series Module Family PC Based
Practical work no. 3: Confocal Live Cell Microscopy
 Practical work no. 3: Confocal Live Cell Microscopy Course Instructor: Mikko Liljeström (MIU) 1 Background Confocal microscopy: The main idea behind confocality is that it suppresses the signal outside
Practical work no. 3: Confocal Live Cell Microscopy Course Instructor: Mikko Liljeström (MIU) 1 Background Confocal microscopy: The main idea behind confocality is that it suppresses the signal outside
Time-Correlated Single Photon Counting
 UK Agents: Photonic Solutions plc TCSPC1.DOC 24. Apr. 2001 40 Captains Rd Edinburgh, EH17 8QF Tel. 0131 664 8122 Fax. 0131 664 8144 email: sales@psplc.com http://www.psplc.com i n t e l l i g e n t measurement
UK Agents: Photonic Solutions plc TCSPC1.DOC 24. Apr. 2001 40 Captains Rd Edinburgh, EH17 8QF Tel. 0131 664 8122 Fax. 0131 664 8144 email: sales@psplc.com http://www.psplc.com i n t e l l i g e n t measurement
Becker & Hickl GmbH. Technology Leader in Photon Counting
 Becker & Hickl GmbH Technology Leader in Photon Counting Contents Overview TCSPC Module Gated Photon Counter / Multiscaler Spectral Lifetime Detection Picosecond Diode Laser FLIM System Technology Leader
Becker & Hickl GmbH Technology Leader in Photon Counting Contents Overview TCSPC Module Gated Photon Counter / Multiscaler Spectral Lifetime Detection Picosecond Diode Laser FLIM System Technology Leader
BDS-MM Family Picosecond Diode Lasers
 BDS-MM Family Picosecond Diode s Optical power up to 60 mw at MHz Wavelengths 405, 445, 525, 640, 685, 785, 915 nm Power up to 60mW, multi-mode Small-size laser module, 40 mm x 40 mm x 120 mm Free-beam
BDS-MM Family Picosecond Diode s Optical power up to 60 mw at MHz Wavelengths 405, 445, 525, 640, 685, 785, 915 nm Power up to 60mW, multi-mode Small-size laser module, 40 mm x 40 mm x 120 mm Free-beam
BDS-SM Family Picosecond Diode Lasers
 BDS-SM Family Picosecond Diode s BDS-SM Small-size OEM Module, 40 mm x 40 mm x 120 mm Wavelengths 375 nm, 405 nm, 445 nm, 473 nm, 488 nm, 515 nm, 640 nm, 685 nm, 785 nm, 1064 nm Free-beam or single-mode
BDS-SM Family Picosecond Diode s BDS-SM Small-size OEM Module, 40 mm x 40 mm x 120 mm Wavelengths 375 nm, 405 nm, 445 nm, 473 nm, 488 nm, 515 nm, 640 nm, 685 nm, 785 nm, 1064 nm Free-beam or single-mode
Ultraviolet and Blue Picosecond Diode Laser Modules
 Becker & Hickl GmbH August 2004 Printer HP 4500 PS High Performance Photon Counting Tel. +49 / 30 / 787 56 32 FAX +49 / 30 / 787 57 34 http://www.becker-hickl.com email: info@becker-hickl.com BDL-375 BDL-405
Becker & Hickl GmbH August 2004 Printer HP 4500 PS High Performance Photon Counting Tel. +49 / 30 / 787 56 32 FAX +49 / 30 / 787 57 34 http://www.becker-hickl.com email: info@becker-hickl.com BDL-375 BDL-405
Multifluorescence The Crosstalk Problem and Its Solution
 Multifluorescence The Crosstalk Problem and Its Solution If a specimen is labeled with more than one fluorochrome, each image channel should only show the emission signal of one of them. If, in a specimen
Multifluorescence The Crosstalk Problem and Its Solution If a specimen is labeled with more than one fluorochrome, each image channel should only show the emission signal of one of them. If, in a specimen
3D light microscopy techniques
 3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 1 1 2! NA = 0.5! NA 2D imaging
3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 1 1 2! NA = 0.5! NA 2D imaging
NUV and Blue ps Diode Lasers
 High Performance Photon Counting User Manual NUV and Blue ps Diode Lasers Designed and manufactured in cooperation with BDL-SMC Picosecond Diode Lasers 1 BDL-375-SMC BDL-405-SMC BDL-440-SMC BDL-473-SMC
High Performance Photon Counting User Manual NUV and Blue ps Diode Lasers Designed and manufactured in cooperation with BDL-SMC Picosecond Diode Lasers 1 BDL-375-SMC BDL-405-SMC BDL-440-SMC BDL-473-SMC
Time-Correlated Single Photon Counting Systems
 91 Boylston Street, Brookline, MA 02445 tel: (617)566-3821 fax: (617)731-0935 www.boselec.com tcspc@boselec.com Time-Correlated Single Photon Counting Systems PC Based Systems 12277 Berlin, Gemany Tel:
91 Boylston Street, Brookline, MA 02445 tel: (617)566-3821 fax: (617)731-0935 www.boselec.com tcspc@boselec.com Time-Correlated Single Photon Counting Systems PC Based Systems 12277 Berlin, Gemany Tel:
Boston Electronics Corporation 91 Boylston Street, Brookline MA USA (800) or (617) fax (617)
 Single Photon Counting APD, MCP & PMT Detectors plus High Speed Amplifiers, Routers, Trigger Detectors, Constant Fraction Discriminators From Becker & Hickl, id Quantique and Hamamatsu F Boston Electronics
Single Photon Counting APD, MCP & PMT Detectors plus High Speed Amplifiers, Routers, Trigger Detectors, Constant Fraction Discriminators From Becker & Hickl, id Quantique and Hamamatsu F Boston Electronics
Time Correlated Single Photon Counting Systems
 Boston Electronics Corporation 91 Boylston Street, Brookline MA 02445 USA (800)347-5445 or (617)566-3821 fax (617)731-0935 www.boselec.com boselec@world.std.com Time Correlated Single Photon Counting Systems
Boston Electronics Corporation 91 Boylston Street, Brookline MA 02445 USA (800)347-5445 or (617)566-3821 fax (617)731-0935 www.boselec.com boselec@world.std.com Time Correlated Single Photon Counting Systems
Picosecond Light Sources
 91 Boylston Street, Brookline, MA 02445 tel: (617)566-3821 fax: (617)731-0935 www.boselec.com tcspc@boselec.com Picosecond Light Sources Available with single mode fiber output coupling From Becker & Hickl
91 Boylston Street, Brookline, MA 02445 tel: (617)566-3821 fax: (617)731-0935 www.boselec.com tcspc@boselec.com Picosecond Light Sources Available with single mode fiber output coupling From Becker & Hickl
TCSPC measurements with the InGaAs/InP Single- photon counter
 TCSPC measurements with the InGaAs/InP Single-photon counter A typical setup in which the InGaAs/InP Single- Photon Detection Module is widely employed is a photon- timing one, as illustrated in Figure
TCSPC measurements with the InGaAs/InP Single-photon counter A typical setup in which the InGaAs/InP Single- Photon Detection Module is widely employed is a photon- timing one, as illustrated in Figure
Simultaneous Phosphorescence and Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging by Multi-Dimensional TCSPC and Multi-Pulse Excitation
 Simultaneous Phosphorescence and Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging by Multi-Dimensional TCSPC and Multi-Pulse Excitation Abstract. We present a fluorescence and phosphorescence lifetime imaging (FLIM / PLIM)
Simultaneous Phosphorescence and Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging by Multi-Dimensional TCSPC and Multi-Pulse Excitation Abstract. We present a fluorescence and phosphorescence lifetime imaging (FLIM / PLIM)
PML Channel Detector Head for Time-Correlated Single Photon Counting
 Becker & Hickl GmbH Nahmitzer Damm 30 12277 Berlin Tel +49 30 787 56 32 Fax +49 30 787 57 34 email: info@becker-hicklde http://wwwbecker-hicklde PML16DOC PML-16 16 Channel Detector Head for Time-Correlated
Becker & Hickl GmbH Nahmitzer Damm 30 12277 Berlin Tel +49 30 787 56 32 Fax +49 30 787 57 34 email: info@becker-hicklde http://wwwbecker-hicklde PML16DOC PML-16 16 Channel Detector Head for Time-Correlated
Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev. Microscopy course, Michmoret Dec 2005
 Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Why use confocal microscopy? Principles of the laser scanning confocal microscope. Image resolution. Manipulating the
Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Why use confocal microscopy? Principles of the laser scanning confocal microscope. Image resolution. Manipulating the
Confocal Microscopy. Kristin Jensen
 Confocal Microscopy Kristin Jensen 17.11.05 References Cell Biological Applications of Confocal Microscopy, Brian Matsumoto, chapter 1 Studying protein dynamics in living cells,, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz
Confocal Microscopy Kristin Jensen 17.11.05 References Cell Biological Applications of Confocal Microscopy, Brian Matsumoto, chapter 1 Studying protein dynamics in living cells,, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz
TRAINING MANUAL. Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO
 TRAINING MANUAL Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO September 2010 Multiphoton Microscopy Training Manual Multiphoton microscopy is only available on the LSM 510 META-NLO system. This system is equipped
TRAINING MANUAL Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO September 2010 Multiphoton Microscopy Training Manual Multiphoton microscopy is only available on the LSM 510 META-NLO system. This system is equipped
PCS-150 / PCI-200 High Speed Boxcar Modules
 Becker & Hickl GmbH Kolonnenstr. 29 10829 Berlin Tel. 030 / 787 56 32 Fax. 030 / 787 57 34 email: info@becker-hickl.de http://www.becker-hickl.de PCSAPP.DOC PCS-150 / PCI-200 High Speed Boxcar Modules
Becker & Hickl GmbH Kolonnenstr. 29 10829 Berlin Tel. 030 / 787 56 32 Fax. 030 / 787 57 34 email: info@becker-hickl.de http://www.becker-hickl.de PCSAPP.DOC PCS-150 / PCI-200 High Speed Boxcar Modules
WHITE PAPER FAST PROTEIN INTERACTION BINDING CURVES WITH INO S F-HS CONFOCAL MICROSCOPE
 WHITE PAPER FAST PROTEIN INTERACTION BINDING CURVES WITH INO S F-HS CONFOCAL MICROSCOPE Christian Tardif, Jean-Pierre Bouchard Pascal Gallant, Sebastien Roy, Ozzy Mermut September 2017 Introduction Protein-protein
WHITE PAPER FAST PROTEIN INTERACTION BINDING CURVES WITH INO S F-HS CONFOCAL MICROSCOPE Christian Tardif, Jean-Pierre Bouchard Pascal Gallant, Sebastien Roy, Ozzy Mermut September 2017 Introduction Protein-protein
Confocal, hyperspectral, spinning disk
 Confocal, hyperspectral, spinning disk Administrative HW 6 due on Fri Midterm on Wed Covers everything since previous midterm 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed, 1 side Guest lecture by Joe Dragavon on Mon 10/30 Last
Confocal, hyperspectral, spinning disk Administrative HW 6 due on Fri Midterm on Wed Covers everything since previous midterm 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed, 1 side Guest lecture by Joe Dragavon on Mon 10/30 Last
3D light microscopy techniques
 3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 2D imaging 3D imaging Resolution
3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 2D imaging 3D imaging Resolution
Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 510 META Confocal Microscope
 Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 510 META Confocal Microscope AIM 4.2 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON Components and System/PC switches
Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 510 META Confocal Microscope AIM 4.2 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON Components and System/PC switches
Solea. Supercontinuum Laser. Applications
 Solea Supercontinuum Laser Extended Spectral range: 525 nm - 900 nm (ECO mode), 480 nm - 900 nm (BOOST mode) Extended 2-year worldwide warranty* Supercontinuum output or wavelength selected output through
Solea Supercontinuum Laser Extended Spectral range: 525 nm - 900 nm (ECO mode), 480 nm - 900 nm (BOOST mode) Extended 2-year worldwide warranty* Supercontinuum output or wavelength selected output through
Time-Correlated Single Photon Counting
 Becker & Hickl GmbH TCSPC1DOC July 2002 Printer HP 4500 PS Nahmitzer Damm 12277 Berlin Tel +49 30 787 56 32 Fax +49 30 787 57 34 email: info@becker-hicklcom http://wwwbecker-hicklcom i n t e l l i g e
Becker & Hickl GmbH TCSPC1DOC July 2002 Printer HP 4500 PS Nahmitzer Damm 12277 Berlin Tel +49 30 787 56 32 Fax +49 30 787 57 34 email: info@becker-hicklcom http://wwwbecker-hicklcom i n t e l l i g e
Training Guide for Leica SP8 Confocal/Multiphoton Microscope
 Training Guide for Leica SP8 Confocal/Multiphoton Microscope LAS AF v3.3 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON power switch for epifluorescence
Training Guide for Leica SP8 Confocal/Multiphoton Microscope LAS AF v3.3 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON power switch for epifluorescence
Detectors for High-Speed Photon Counting
 Detectors for High-Speed Photon Counting Wolfgang Becker, Axel Bergmann Becker & Hickl GmbH, Berlin, becker@becker-hickl.com, bergmann@becker-hickl.com Detectors for photon counting must have sufficient
Detectors for High-Speed Photon Counting Wolfgang Becker, Axel Bergmann Becker & Hickl GmbH, Berlin, becker@becker-hickl.com, bergmann@becker-hickl.com Detectors for photon counting must have sufficient
FLIM Protocol. 1. Install IRF sample on the microscope using the stage insert. IRF sample options include urea crystals or BBO crystal.
 Data Collection FLIM Protocol 1. Install IRF sample on the microscope using the stage insert. IRF sample options include urea crystals or BBO crystal. 2. Install appropriate SHG filter. (890nm = 445/20nm,
Data Collection FLIM Protocol 1. Install IRF sample on the microscope using the stage insert. IRF sample options include urea crystals or BBO crystal. 2. Install appropriate SHG filter. (890nm = 445/20nm,
SHM-180 Eight Channel Sample & Hold Module
 Becker & Hickl GmbH April 2003 Printer HP 4500 PS High Performance Photon Counting Tel. +49 / 30 / 787 56 32 FAX +49 / 30 / 787 57 34 http://www.becker-hickl.com email: info@becker-hickl.com SHM-180 Eight
Becker & Hickl GmbH April 2003 Printer HP 4500 PS High Performance Photon Counting Tel. +49 / 30 / 787 56 32 FAX +49 / 30 / 787 57 34 http://www.becker-hickl.com email: info@becker-hickl.com SHM-180 Eight
DeltaMyc. Fluorescence Lifetime Mapping Microscope. Affordable Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy (FLIM)
 DeltaMyc Fluorescence Lifetime Mapping Microscope Affordable Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy (FLIM) DeltaMyc Affordable Fluorescence Imaging Lifetime Microscopy (FLIM) At last, an affordable yet
DeltaMyc Fluorescence Lifetime Mapping Microscope Affordable Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy (FLIM) DeltaMyc Affordable Fluorescence Imaging Lifetime Microscopy (FLIM) At last, an affordable yet
Confocal Microscopy. (Increasing contrast and resolu6on using op6cal sec6oning) Lecture 7. November 2017
 Confocal Microscopy (Increasing contrast and resolu6on using op6cal sec6oning) Lecture 7 November 2017 3 Flavours of Microscope Confocal Laser Scanning Problem: Out of Focus Light Spinning disc 2-Photon
Confocal Microscopy (Increasing contrast and resolu6on using op6cal sec6oning) Lecture 7 November 2017 3 Flavours of Microscope Confocal Laser Scanning Problem: Out of Focus Light Spinning disc 2-Photon
Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement
 Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY BioVis Uppsala, 2017 Jeremy Adler Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Widefield & Confocal Microscopy
Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY BioVis Uppsala, 2017 Jeremy Adler Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Widefield & Confocal Microscopy
Boston Electronics Corporation 91 Boylston Street, Brookline MA USA (800) or (617) fax (617)
 Single Photon Counting APD, MCP & PMT Detectors plus High Speed Amplifiers, Routers, Trigger Detectors, Constant Fraction Discriminators From Becker & Hickl, id Quantique and Hamamatsu F Boston Electronics
Single Photon Counting APD, MCP & PMT Detectors plus High Speed Amplifiers, Routers, Trigger Detectors, Constant Fraction Discriminators From Becker & Hickl, id Quantique and Hamamatsu F Boston Electronics
Bio 407. Applied microscopy. Introduction into light microscopy. José María Mateos. Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis
 Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Bio 407 Applied Introduction into light José María Mateos Fundamentals of light Compound microscope Microscope composed of an objective and an additional lens (eyepiece,
Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Bio 407 Applied Introduction into light José María Mateos Fundamentals of light Compound microscope Microscope composed of an objective and an additional lens (eyepiece,
User Handbook. DPC Channel Photon Correlator
 High Performance Photon Counting User Handbook DPC-230 16 Channel Photon Correlator Becker & Hickl GmbH (c) Becker & Hickl GmbH Becker & Hickl GmbH April 2008 High Performance Photon Counting Tel. +49
High Performance Photon Counting User Handbook DPC-230 16 Channel Photon Correlator Becker & Hickl GmbH (c) Becker & Hickl GmbH Becker & Hickl GmbH April 2008 High Performance Photon Counting Tel. +49
Shreyash Tandon M.S. III Year
 Shreyash Tandon M.S. III Year 20091015 Confocal microscopy is a powerful tool for generating high-resolution images and 3-D reconstructions of a specimen by using point illumination and a spatial pinhole
Shreyash Tandon M.S. III Year 20091015 Confocal microscopy is a powerful tool for generating high-resolution images and 3-D reconstructions of a specimen by using point illumination and a spatial pinhole
ADVANCED METHODS FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY II. Jean-Yves Chatton Sept. 2006
 ADVANCED METHODS FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY II Jean-Yves Chatton Sept. 2006 Workshop outline Confocal microscopy of living cells and tissues X-Z scanning Time series Bleach: FRAP, photoactivation Emission
ADVANCED METHODS FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY II Jean-Yves Chatton Sept. 2006 Workshop outline Confocal microscopy of living cells and tissues X-Z scanning Time series Bleach: FRAP, photoactivation Emission
Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 5 LIVE Confocal Microscope
 Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 5 LIVE Confocal Microscope AIM 4.2 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Verify that main power switches on the
Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 5 LIVE Confocal Microscope AIM 4.2 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Verify that main power switches on the
Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 880 with AiryScan FAST
 Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 880 with AiryScan FAST ZEN 2.3 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2018) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON Main Switch from the remote control
Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 880 with AiryScan FAST ZEN 2.3 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2018) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON Main Switch from the remote control
Maria Smedh, Centre for Cellular Imaging. Maria Smedh, Centre for Cellular Imaging
 Nonlinear microscopy I: Two-photon fluorescence microscopy Multiphoton Microscopy What is multiphoton imaging? Applications Different imaging modes Advantages/disadvantages Scattering of light in thick
Nonlinear microscopy I: Two-photon fluorescence microscopy Multiphoton Microscopy What is multiphoton imaging? Applications Different imaging modes Advantages/disadvantages Scattering of light in thick
ScanArray Overview. Principle of Operation. Instrument Components
 ScanArray Overview The GSI Lumonics ScanArrayÒ Microarray Analysis System is a scanning laser confocal fluorescence microscope that is used to determine the fluorescence intensity of a two-dimensional
ScanArray Overview The GSI Lumonics ScanArrayÒ Microarray Analysis System is a scanning laser confocal fluorescence microscope that is used to determine the fluorescence intensity of a two-dimensional
Supplemental Information
 Optically Activated Delayed Fluorescence Blake C. Fleischer, Jeffrey T. Petty, Jung-Cheng Hsiang, Robert M. Dickson, * School of Chemistry & Biochemistry and Petit Institute for Bioengineering and Bioscience,
Optically Activated Delayed Fluorescence Blake C. Fleischer, Jeffrey T. Petty, Jung-Cheng Hsiang, Robert M. Dickson, * School of Chemistry & Biochemistry and Petit Institute for Bioengineering and Bioscience,
Fluorescence lifetime imaging for the two-photon microscope: time-domain and frequency-domain methods
 Journal of Biomedical Optics 8(3), 381 390 (July 2003) Fluorescence lifetime imaging for the two-photon microscope: time-domain and frequency-domain methods Enrico Gratton Sophie Breusegem Jason Sutin
Journal of Biomedical Optics 8(3), 381 390 (July 2003) Fluorescence lifetime imaging for the two-photon microscope: time-domain and frequency-domain methods Enrico Gratton Sophie Breusegem Jason Sutin
Simple setup for nano-second time-resolved spectroscopic measurements by a digital storage oscilloscope
 NOTE Simple setup for nano-second time-resolved spectroscopic measurements by a digital storage oscilloscope Goro Nishimura and Mamoru Tamura Biophysics, Research Institute for Electronic Science, Hokkaido
NOTE Simple setup for nano-second time-resolved spectroscopic measurements by a digital storage oscilloscope Goro Nishimura and Mamoru Tamura Biophysics, Research Institute for Electronic Science, Hokkaido
Bi/BE 227 Winter Assignment #3. Adding the third dimension: 3D Confocal Imaging
 Bi/BE 227 Winter 2016 Assignment #3 Adding the third dimension: 3D Confocal Imaging Schedule: Jan 20: Assignment Jan 20-Feb 8: Work on assignment Feb 10: Student PowerPoint presentations. Goals for this
Bi/BE 227 Winter 2016 Assignment #3 Adding the third dimension: 3D Confocal Imaging Schedule: Jan 20: Assignment Jan 20-Feb 8: Work on assignment Feb 10: Student PowerPoint presentations. Goals for this
MULTIPHOTON MICROSCOPY. Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky
 MULTIPHOTON MICROSCOPY Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Information Information given here about 2 Photon microscopy were mainly taken from these sources: Background information on 2-Photon microscopy: http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/techniques/fluorescence/multiphoton/
MULTIPHOTON MICROSCOPY Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Information Information given here about 2 Photon microscopy were mainly taken from these sources: Background information on 2-Photon microscopy: http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/techniques/fluorescence/multiphoton/
Dynamic Confocal Imaging of Living Brain. Advantages and risks of multiphoton microscopy in physiology
 Dynamic Confocal Imaging of Living Brain Advantages and risks of multiphoton microscopy in physiology Confocal laser scanning microscopy In conventional optical microscopy focused and out-offocus light
Dynamic Confocal Imaging of Living Brain Advantages and risks of multiphoton microscopy in physiology Confocal laser scanning microscopy In conventional optical microscopy focused and out-offocus light
Resolution. Diffraction from apertures limits resolution. Rayleigh criterion θ Rayleigh = 1.22 λ/d 1 peak at 2 nd minimum. θ f D
 Microscopy Outline 1. Resolution and Simple Optical Microscope 2. Contrast enhancement: Dark field, Fluorescence (Chelsea & Peter), Phase Contrast, DIC 3. Newer Methods: Scanning Tunneling microscopy (STM),
Microscopy Outline 1. Resolution and Simple Optical Microscope 2. Contrast enhancement: Dark field, Fluorescence (Chelsea & Peter), Phase Contrast, DIC 3. Newer Methods: Scanning Tunneling microscopy (STM),
FLIM on a wide field fluorescence microscope
 FLIM on a wide field fluorescence microscope L.K. van Geest, K.W.J. Stoop Lambert Instruments, Turfweg 4, 933TH Leutingewolde, The Netherlands. Phone: +3 50 50846, Fax: +3 50 500034, e-mail: lkvgeest@lambert-instruments.com
FLIM on a wide field fluorescence microscope L.K. van Geest, K.W.J. Stoop Lambert Instruments, Turfweg 4, 933TH Leutingewolde, The Netherlands. Phone: +3 50 50846, Fax: +3 50 500034, e-mail: lkvgeest@lambert-instruments.com
INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY. Urs Ziegler THE PROBLEM
 INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch THE PROBLEM 1 ORGANISMS ARE LARGE LIGHT AND ELECTRONS: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES v = Wavelength ( ) Speed (v) Frequency ( ) Amplitude (A) Propagation
INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch THE PROBLEM 1 ORGANISMS ARE LARGE LIGHT AND ELECTRONS: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES v = Wavelength ( ) Speed (v) Frequency ( ) Amplitude (A) Propagation
DETECTORS Important characteristics: 1) Wavelength response 2) Quantum response how light is detected 3) Sensitivity 4) Frequency of response
 DETECTORS Important characteristics: 1) Wavelength response 2) Quantum response how light is detected 3) Sensitivity 4) Frequency of response (response time) 5) Stability 6) Cost 7) convenience Photoelectric
DETECTORS Important characteristics: 1) Wavelength response 2) Quantum response how light is detected 3) Sensitivity 4) Frequency of response (response time) 5) Stability 6) Cost 7) convenience Photoelectric
BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS PLATFORM EPFL SV PTBIOP LASER SCANNING CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY PRACTICAL CONSIDERATIONS
 LASER SCANNING CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY PRACTICAL CONSIDERATIONS IMPORTANT PARAMETERS Pixel dwell time Zoom and pixel number PIXEL DWELL TIME How much time signal is collected at every pixel Very small values,
LASER SCANNING CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY PRACTICAL CONSIDERATIONS IMPORTANT PARAMETERS Pixel dwell time Zoom and pixel number PIXEL DWELL TIME How much time signal is collected at every pixel Very small values,
Operating Instructions for Zeiss LSM 510
 Operating Instructions for Zeiss LSM 510 Location: GNL 6.312q (BSL3) Questions? Contact: Maxim Ivannikov, maivanni@utmb.edu 1 Attend A Complementary Training Before Using The Microscope All future users
Operating Instructions for Zeiss LSM 510 Location: GNL 6.312q (BSL3) Questions? Contact: Maxim Ivannikov, maivanni@utmb.edu 1 Attend A Complementary Training Before Using The Microscope All future users
CHAPTER 9 POSITION SENSITIVE PHOTOMULTIPLIER TUBES
 CHAPTER 9 POSITION SENSITIVE PHOTOMULTIPLIER TUBES The current multiplication mechanism offered by dynodes makes photomultiplier tubes ideal for low-light-level measurement. As explained earlier, there
CHAPTER 9 POSITION SENSITIVE PHOTOMULTIPLIER TUBES The current multiplication mechanism offered by dynodes makes photomultiplier tubes ideal for low-light-level measurement. As explained earlier, there
The Zeiss AiryScan System, Confocal Four.
 The Zeiss AiryScan System, Confocal Four. Overview. The Zeiss AiryScan module is a segmented, radially stacked GaASP detector and collector system designed to subsample the airy disk of a point emission
The Zeiss AiryScan System, Confocal Four. Overview. The Zeiss AiryScan module is a segmented, radially stacked GaASP detector and collector system designed to subsample the airy disk of a point emission
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy
 Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
Supplementary Figure S1: Schematic view of the confocal laser scanning STED microscope used for STED-RICS. For a detailed description of our
 Supplementary Figure S1: Schematic view of the confocal laser scanning STED microscope used for STED-RICS. For a detailed description of our home-built STED microscope used for the STED-RICS experiments,
Supplementary Figure S1: Schematic view of the confocal laser scanning STED microscope used for STED-RICS. For a detailed description of our home-built STED microscope used for the STED-RICS experiments,
LSM 710 Confocal Microscope Standard Operation Protocol
 LSM 710 Confocal Microscope Standard Operation Protocol Basic Operation Turning on the system 1. Switch on Main power switch 2. Switch on System / PC power button 3. Switch on Components power button 4.
LSM 710 Confocal Microscope Standard Operation Protocol Basic Operation Turning on the system 1. Switch on Main power switch 2. Switch on System / PC power button 3. Switch on Components power button 4.
Point Spread Function. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy. Confocal Aperture. Optical aberrations. Alternative Scanning Microscopy
 Bi177 Lecture 5 Adding the Third Dimension Wide-field Imaging Point Spread Function Deconvolution Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Confocal Aperture Optical aberrations Alternative Scanning Microscopy
Bi177 Lecture 5 Adding the Third Dimension Wide-field Imaging Point Spread Function Deconvolution Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Confocal Aperture Optical aberrations Alternative Scanning Microscopy
Technology Note ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan
 Technology Note ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan Introducing the Fast Acquisition Mode ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan Introducing the Fast Acquisition Mode Author: Dr. Annette Bergter Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH,
Technology Note ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan Introducing the Fast Acquisition Mode ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan Introducing the Fast Acquisition Mode Author: Dr. Annette Bergter Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH,
Microscopic Structures
 Microscopic Structures Image Analysis Metal, 3D Image (Red-Green) The microscopic methods range from dark field / bright field microscopy through polarisation- and inverse microscopy to techniques like
Microscopic Structures Image Analysis Metal, 3D Image (Red-Green) The microscopic methods range from dark field / bright field microscopy through polarisation- and inverse microscopy to techniques like
Akinori Mitani and Geoff Weiner BGGN 266 Spring 2013 Non-linear optics final report. Introduction and Background
 Akinori Mitani and Geoff Weiner BGGN 266 Spring 2013 Non-linear optics final report Introduction and Background Two-photon microscopy is a type of fluorescence microscopy using two-photon excitation. It
Akinori Mitani and Geoff Weiner BGGN 266 Spring 2013 Non-linear optics final report Introduction and Background Two-photon microscopy is a type of fluorescence microscopy using two-photon excitation. It
Imaging Retreat - UMASS Customized real-time confocal and 2-photon imaging
 Imaging Retreat - UMASS 2012 Customized real-time confocal and 2-photon imaging Mike Sanderson Department of Microbiology and Physiological Systems University of Massachusetts Medical School Thanks for
Imaging Retreat - UMASS 2012 Customized real-time confocal and 2-photon imaging Mike Sanderson Department of Microbiology and Physiological Systems University of Massachusetts Medical School Thanks for
Components of confocal and two-photon microscopes
 Components of confocal and two-photon microscopes Internal training 07/04/2016 A. GRICHINE Platform Optical microscopy Cell imaging, IAB, ISdV Plan Confocal laser scanning microscope o o o Principle Main
Components of confocal and two-photon microscopes Internal training 07/04/2016 A. GRICHINE Platform Optical microscopy Cell imaging, IAB, ISdV Plan Confocal laser scanning microscope o o o Principle Main
Reflecting optical system to increase signal intensity. in confocal microscopy
 Reflecting optical system to increase signal intensity in confocal microscopy DongKyun Kang *, JungWoo Seo, DaeGab Gweon Nano Opto Mechatronics Laboratory, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Korea Advanced
Reflecting optical system to increase signal intensity in confocal microscopy DongKyun Kang *, JungWoo Seo, DaeGab Gweon Nano Opto Mechatronics Laboratory, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Korea Advanced
Zeiss 780 Training Notes
 Zeiss 780 Training Notes Turn on Main Switch, System PC and Components Switches 780 Start up sequence Do you need the argon laser (458, 488, 514 nm lines)? Yes Turn on the laser s main power switch and
Zeiss 780 Training Notes Turn on Main Switch, System PC and Components Switches 780 Start up sequence Do you need the argon laser (458, 488, 514 nm lines)? Yes Turn on the laser s main power switch and
LSM 510 META in Chang Gung University
 Content LSM 510 META in Chang ung University LSM 510 META 路 理 The features and applications of LSM 510 META 01-09 Introduction of the hardware 10-12 Fluorescence observation in conventional microscope
Content LSM 510 META in Chang ung University LSM 510 META 路 理 The features and applications of LSM 510 META 01-09 Introduction of the hardware 10-12 Fluorescence observation in conventional microscope
Examination, TEN1, in courses SK2500/SK2501, Physics of Biomedical Microscopy,
 KTH Applied Physics Examination, TEN1, in courses SK2500/SK2501, Physics of Biomedical Microscopy, 2009-06-05, 8-13, FB51 Allowed aids: Compendium Imaging Physics (handed out) Compendium Light Microscopy
KTH Applied Physics Examination, TEN1, in courses SK2500/SK2501, Physics of Biomedical Microscopy, 2009-06-05, 8-13, FB51 Allowed aids: Compendium Imaging Physics (handed out) Compendium Light Microscopy
LABORATÓRIUMI GYAKORLAT SILLABUSZ SYLLABUS OF A PRACTICAL DEMONSTRATION. financed by the program
 TÁMOP-4.1.1.C-13/1/KONV-2014-0001 projekt Az élettudományi-klinikai felsőoktatás gyakorlatorientált és hallgatóbarát korszerűsítése a vidéki képzőhelyek nemzetközi versenyképességének erősítésére program
TÁMOP-4.1.1.C-13/1/KONV-2014-0001 projekt Az élettudományi-klinikai felsőoktatás gyakorlatorientált és hallgatóbarát korszerűsítése a vidéki képzőhelyek nemzetközi versenyképességének erősítésére program
1 Co Localization and Working flow with the lsm700
 1 Co Localization and Working flow with the lsm700 Samples -1 slide = mousse intestine, Dapi / Ki 67 with Cy3/ BrDU with alexa 488. -1 slide = mousse intestine, Dapi / Ki 67 with Cy3/ no BrDU (but with
1 Co Localization and Working flow with the lsm700 Samples -1 slide = mousse intestine, Dapi / Ki 67 with Cy3/ BrDU with alexa 488. -1 slide = mousse intestine, Dapi / Ki 67 with Cy3/ no BrDU (but with
Fiber Laser Chirped Pulse Amplifier
 Fiber Laser Chirped Pulse Amplifier White Paper PN 200-0200-00 Revision 1.2 January 2009 Calmar Laser, Inc www.calmarlaser.com Overview Fiber lasers offer advantages in maintaining stable operation over
Fiber Laser Chirped Pulse Amplifier White Paper PN 200-0200-00 Revision 1.2 January 2009 Calmar Laser, Inc www.calmarlaser.com Overview Fiber lasers offer advantages in maintaining stable operation over
Bi Imaging. Multicolor Imaging: The Important Question of Co-Localization. Anna Smallcombe Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hemel Hempstead, UK
 Multicolor Imaging: The Important Question of Co-Localization Anna Smallcombe Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hemel Hempstead, UK The use of specific fluorescent probes, combined with confocal or multiphoton microscopy
Multicolor Imaging: The Important Question of Co-Localization Anna Smallcombe Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hemel Hempstead, UK The use of specific fluorescent probes, combined with confocal or multiphoton microscopy
Light Microscopy for Biomedical Research
 Light Microscopy for Biomedical Research Tuesday 4:30 PM Quantification & Digital Images Michael Hooker Microscopy Facility Michael Chua microscopy@unc.edu 843-3268 6007 Thurston Bowles http://microscopy.unc.edu/lmbr
Light Microscopy for Biomedical Research Tuesday 4:30 PM Quantification & Digital Images Michael Hooker Microscopy Facility Michael Chua microscopy@unc.edu 843-3268 6007 Thurston Bowles http://microscopy.unc.edu/lmbr
A New Single-Photon Avalanche Diode in 90nm Standard CMOS Technology
 A New Single-Photon Avalanche Diode in 90nm Standard CMOS Technology Mohammad Azim Karami* a, Marek Gersbach, Edoardo Charbon a a Dept. of Electrical engineering, Technical University of Delft, Delft,
A New Single-Photon Avalanche Diode in 90nm Standard CMOS Technology Mohammad Azim Karami* a, Marek Gersbach, Edoardo Charbon a a Dept. of Electrical engineering, Technical University of Delft, Delft,
Fundamentals of Light Microscopy II: Fluorescence, Deconvolution, Confocal, Multiphoton, Spectral microscopy. Integrated Microscopy Course
 Fundamentals of Light Microscopy II: Fluorescence, Deconvolution, Confocal, Multiphoton, Spectral microscopy Integrated Microscopy Course Review Lecture 1: Microscopy Basics Light train Kohler illumination*
Fundamentals of Light Microscopy II: Fluorescence, Deconvolution, Confocal, Multiphoton, Spectral microscopy Integrated Microscopy Course Review Lecture 1: Microscopy Basics Light train Kohler illumination*
Cavity QED with quantum dots in semiconductor microcavities
 Cavity QED with quantum dots in semiconductor microcavities M. T. Rakher*, S. Strauf, Y. Choi, N.G. Stolz, K.J. Hennessey, H. Kim, A. Badolato, L.A. Coldren, E.L. Hu, P.M. Petroff, D. Bouwmeester University
Cavity QED with quantum dots in semiconductor microcavities M. T. Rakher*, S. Strauf, Y. Choi, N.G. Stolz, K.J. Hennessey, H. Kim, A. Badolato, L.A. Coldren, E.L. Hu, P.M. Petroff, D. Bouwmeester University
Confocal Microscopy and Related Techniques
 Confocal Microscopy and Related Techniques Chau-Hwang Lee Associate Research Fellow Research Center for Applied Sciences, Academia Sinica 128 Sec. 2, Academia Rd., Nankang, Taipei 11529, Taiwan E-mail:
Confocal Microscopy and Related Techniques Chau-Hwang Lee Associate Research Fellow Research Center for Applied Sciences, Academia Sinica 128 Sec. 2, Academia Rd., Nankang, Taipei 11529, Taiwan E-mail:
Alba v5 Laser Scanning Microscope
 D E S C R I P T I O N Alba v5 Laser Scanning Microscope The instrument for quantitative cell biology at single-molecule detection Alba is a laser scanning microscope that incorporates several measurement
D E S C R I P T I O N Alba v5 Laser Scanning Microscope The instrument for quantitative cell biology at single-molecule detection Alba is a laser scanning microscope that incorporates several measurement
長庚大學共軛焦顯微鏡課程 長庚大學共軛焦顯微鏡課程. Spot light 長庚大學
 長庚大學共軛焦顯微鏡課程 Spot light 長庚大學共軛焦顯微鏡課程 20071030 長庚大學 Basic principle of Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy The application of LSM 510 META detector Multiphoton microscopy basic principle and introduction
長庚大學共軛焦顯微鏡課程 Spot light 長庚大學共軛焦顯微鏡課程 20071030 長庚大學 Basic principle of Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy The application of LSM 510 META detector Multiphoton microscopy basic principle and introduction
Application Note. The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a Z-stack
 The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a Z-stack The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a
The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a Z-stack The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a
ZEISS LSM 710 NLO Multiphoton microscope Manual/Quick guide
 ZEISS LSM 710 NLO Multiphoton microscope Manual/Quick guide Matyas Molnar, Biovis 2016 Starting the microscpe 1. Check the microscope if everything looks clean and normal. If not, report it in the logbook.
ZEISS LSM 710 NLO Multiphoton microscope Manual/Quick guide Matyas Molnar, Biovis 2016 Starting the microscpe 1. Check the microscope if everything looks clean and normal. If not, report it in the logbook.
Real-time Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy Implementation by Analog Mean-Delay Method through Parallel Data Processing
 pissn 2287-5123 eissn 2287-4445 http://dx.doi.org/10.9729/am.2016.46.1.6 Regular Article Real-time Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy Implementation by Analog Mean-Delay Method through Parallel Data
pissn 2287-5123 eissn 2287-4445 http://dx.doi.org/10.9729/am.2016.46.1.6 Regular Article Real-time Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging Microscopy Implementation by Analog Mean-Delay Method through Parallel Data
LSM 780 Confocal Microscope Standard Operation Protocol
 LSM 780 Confocal Microscope Standard Operation Protocol Basic Operation Turning on the system 1. Sign on log sheet according to Actual start time 2. Check Compressed Air supply for the air table 3. Switch
LSM 780 Confocal Microscope Standard Operation Protocol Basic Operation Turning on the system 1. Sign on log sheet according to Actual start time 2. Check Compressed Air supply for the air table 3. Switch
