PCS-150 / PCI-200 High Speed Boxcar Modules
|
|
|
- Alban Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Becker & Hickl GmbH Kolonnenstr Berlin Tel. 030 / Fax. 030 / info@becker-hickl.de PCSAPP.DOC PCS-150 / PCI-200 High Speed Boxcar Modules Recovery of s from Noise Resolution down to 150 ps Recording of High Speed Optical s Luminescence Decay Measurements Energy Measurement of ps and fs Pulses Nonlinear Optical Absorption Measurements Introduction The PCS-150 and the PCI-200 are PC plug-in modules for signal recording by the sampling or boxcar technique. They are intended for the measurement of repetitive signals with high bandwidth and time resolution. To record the signal, a sequential sampling technique is used. By using a high speed linear gate, one sample is taken from the signal in each signal period. To record the signal as a function of time, the sample point is shifted over the signal in small time increments. To measure the signal value at a selected point of the signal, the sampling point can also be fixed. In this case the signal voltage at the selected moment as a function of an externally varied parameter is recorded. In all modes the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) the of the result can be enhanced by repeatedly sampling each signal point and averaging the samples. The PCS-150 / PCI-200 modules contain two signal channels which are controlled by a common gate pulse. This enables the module to record two input signals at the same time. The gate width of the PCS-150 is <150 ps (typically 120 ps), the gate width of the PCI-200 can be selected from 2 ns to 50 ns. To record high speed optical signals, a wide variety of detectors is available. Depending on the required speed and sensitivity, pin and avalanche photodiode modules, PMT modules and energy proportional pin photodiode modules with fj sensitivity can be connected directly to the PCS-150 and the PCI-200. The trigger pulse can be either derived from the signal of the channel A, or an external trigger pulse can be used. For accurate triggering on optical pulses, an optical 'constant fraction' trigger module is available. All functions are controlled by the software delivered with the module. The software controls the measurement procedure, provides the selection of operation modes and measurement parameters and performs the display, evaluation and storage of the results. 1
2 Method of Recording Sampling The principle of the sampling method is shown in the figure below. In each signal period one sample is taken from the signal. From period to period the sample location is shifted by a small amount, to sample a somewhat later point of the signal. After n signal periods n samples have been taken to recover the waveform of the signal. If the sample point is shifted in sufficiently small steps the signal bandwidth is determined by the gate width only. Because the processing time of the particular samples does not affect the time resolution, the sampling method provides a very high bandwidth and an extremely high virtual sample rate at a moderate hardware effort. In fact, the virtual sample rate and the signal bandwidth can be 10 to 100 times higher than with digital oscilloscopes of comparable price. To improve the signal to noise ratio the sampling method can be combined with signal averaging. For that purpose, the procedure described above is repeated several times and the obtained curves are averaged. Averaging of n curves improves the signal to noise ratio by a factor of n. Boxcar The boxcar method uses the same principle as the sampling method. It differs only in the strategy of signal averaging. While the sampling method immediately proceeds to the next signal point and averages the complete curves, the boxcar method averages the samples of one signal point first and than proceeds to the next point. The method is shown in the next figure. At each sample point several (in the figure 100) samples are taken and averaged with the same delay setting. When the averaging for this signal point is complete the delay is increased. The SNR improvement is n1/2. The practical difference compared to the sampling method is the different effect of a possible amplitude or time drift of the signal. period: Sample Sampling Method period: Sample Boxcar method: 100 samples / step averaged Result Result after 100 signal periods Boxcar with Fixed Delay In some applications only one particular point of the signal rather than the complete waveform is recorded. The signal value at this point is recorded as a function of the time or any other externally variable parameter. For such applications the PCS-150 and PCI-200 modules can be operated in the 'Fixed Delay' mode. The principle is shown in the figure below. 2
3 In the example shown the signal has a different shape in the signal periods 3 to 8. This results in a different sample value at the fixed sample point. In the result the sample value as a function of the signal period number is displayed. The method can be combined with a signal averaging technique in the same way as the boxcar method. period: Sample 9 10 Boxcar measurement with fixed delay Result Applications Basic Measurement Setup The PCS-150 and PCI-200 modules can be used in the same way as a normal sampling oscilloscope. Thus, the modules need a trigger signal as a reference for the temporal location of the signal. The trigger signal must appear at least 20 to 40 ns preceding the signal in order to compensate the internal delay of the trigger circuit and the delay unit (see figure below). If the signal has a repetition rate of more than 50 MHz this delay is no problem. If the trigger is too late, simply the next Recorded Interval signal period is displayed. For signals with low repetition rates, however, trigger and signal must be in the correct Delayed time relation. This can be achieved by two different ways. The simplest way is to delay the measured signals through Internal Delay Recorded Interval delay lines by ns m of high quality 50 Ohm cable is required for that purpose. The second way is a delayed triggering of the experiment. This can be achieved by an external delay generator or simply by delay cables. The signals from the experiment are fed directly to the PCS-150 or PCI-200 and the external trigger input is connected to the output of the generator that triggers the experiment. The second method avoids signal distortions by the delay lines in the signal path. Delay Delay Experiment PCS Source Experiment PCS Delaying the Delaying the Experiment 3
4 Measurement of noisy signals The next figure shows an example for the measurement of a noisy signal. The investigated device (experiment) is excited by a pulse generator. The experiment delivers a noisy output signal on each input pulse. Due to the noise the signal from the experiment cannot be used for triggering the PCS-150 / PCI-200. Therefore, the module is triggered externally by the same pulse generator that triggers the experiment. To compensate the internal delay of the PCS-150 or PCI-200, the experiment trigger is delayed in relation to the PCS-150 / PCI-200 trigger. Pulse Generator Experiment A PCS-150 Measurement of a noisy signal The figure above shows an example of the noise suppression which is achieved by signal averaging. By averaging 4096 samples per delay step the signal-to-noise ratio improved by a factor of 64. Measurements with PMTs Photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) are used to record low level light signals with a resolution down to 1ns (FWHM). The typical gain of a PMT is in the order of 10 5 to With this gain one single photon yields an output pulse from 16 ua to 1.6 ma or 0.8 mv to 80 mv at a load resistor of 50 Ω. Thus, only a few photons can be detected within the linear range of the PMT and the signal is very noisy. Often the PMT output signal consists only of random current pulses due to the detection of the individual photons of the light signal (Figure right). Any attempt to improve the signal by additional amplifiers or by increasing the gain of the PMT in this situation results in increased noise or decreased dynamic range. There is only one remedy: To detect more photons either by decreasing the PMT gain while increasing the light intensity or by averaging many periods of the signal. In the figure right a typical example is shown. A fast PMT was illuminated with a light pulse of 0.3 ns FWHM from a laser diode. The intensity was reduced to keep the PMT signal within the linear range of the output current. The upper recording shows the noise due to the sampling of the random single photon pulses of the PMT. By averaging 4096 signal periods the number of photons is increased accordingly, and the shape of the PMT response is shown clearly. Light Pulse PMT Output PMT output signal for a low level light signal PMT signal recorded without and with 4096 accumulations per point 4
5 Fluorescence Lifetime Measurements In the figure below a simple setup for the measurement of fluorescence decay functions is shown. N2 Laser P1 P2 C M F1 F2 F3 OCF-400 PDM-400 PDM-400 APM-400 APM-400 Del1 Del2 Trg A B PC with PCS-150 Flourescence Decay Measurement with the PCS-150 The nitrogen laser generates light pulses with less than 1ns duration and a repetition rate of Hz. The light pulses excite the sample cell C. The fluorescence light from the sample cell is detected by a photodiode module PDM-400 or APM-400. The signal is fed to channel B of the PCS-150. P1 and P2 are glass plates which reflect a part of the laser radiation to the a second photodiode module and to the 'Optical Constant Fraction ' OCF-400. The signal from OCF-400 is used as a trigger for the PCS-150. The signal from the second PDM- 400 (or APM-400) is used to record the shape of the excitation pulse. The filters F1..F3 are provided to adjust the signal amplitudes, and the monochromator M selects an appropriate wavelength of the fluorescence light. The apparatus shown records fluorescence decay functions, time resolved fluorescence spectra or multiple decay curves at different wavelengths i.e. the complete wavelength-time behaviour of the fluorescence. For recording decay functions the sampling or boxcar mode is used. To suppress noise and amplitude fluctuations of the laser pulses 'Samples averaged' is chosen as high as possible with regard to the measuring time. The measurement delivers the decay function at the selected wavelength and the shape of the exciting laser pulse. A typical result is shown in the figure below. 5
6 Recording of time resolved spectra is achieved in the 'Fixed Delay' mode of the PCS-150. The sample point is set to the desired point of the decay function. Instead of the sample point the wavelength of the monochromator is scanned during the measurement, thus recording of the fluorescence intensity at the selected time as a function of the wavelength. The operation mode 'Block Increment' can be used to obtain the entire wavelength-time dependence of the fluorescence. In this mode the PCS / PCI performs subsequent measurements of the input waveform using the sampling or boxcar method. The curves are stored in different memory blocks. By scanning the wavelength, full information about the fluorescence behaviour of the sample is obtained. Transient Absorption Measurements In the figure below a simple arrangement for transient absorption measurements is shown. Prism Pulsed Laser P1 Dye Laser Optical Delay M2 Probe Beam Filter D1 PDM-400 M1 Pump Beam P2 Sample P3 D2 PDI-400 D3 PDI-400 PCI-200 Channel A Channel B Transient Absorption Measurement The output of a high power pulsed laser (i.e. N2 laser, excimer laser or frequency multiplied diode laser pumped YAG) is divided into two parts. One part is used to pump the sample, the other part pumps a dye laser which generates a light pulse of the appropriate wavelength to probe the absorption of the excited molecules in the sample. The detector D1 is a fast PDM- 400 photodiode module which generates a trigger pulse for the PCI-200 Boxcar Module. The absorption in the sample is measured by the detectors D2 and D3. D1 and D2 are PDI-400 integrating photodiode modules and deliver energy proportional output pulses of some 100ns duration. The amplitudes of these pulses are recorded by the two signal channels of the PCI-200 Boxcar module. The PCI-200 is run in the Fixed Delay mode. Thus, it records a curve consisting of subsequent averages over a selectable number of D2 and D3 intensity values. If the optical delay is continuously changed during the measurement and the quotient A/B is displayed the result shows the decay of the abasorption of the excited state species in the sample. 6
7 Nonlinear Optical Absorption Measurements Another example for the fixed delay mode and the wide gate width of the PCI-200 is given in the next figure. The shown setup is used for the measurement of the intensity-dependence of the light absorption in organic dyes. A high power pulsed laser (i.e. nitrogen laser or pulsed dye laser) generates short pulses (< 1ns) with high energy (1mJ). The intensity is controlled by a suitable optical attenuator. The beam is split into two parts by the glass plate P2. The main part of the light is focused into the sample cell C1. The other part is fed through the reference cell C2. Both light signals are fed through a filter to the Detectors D1 and D2. D1 and D2 are PDI-400 integrating photodiode modules and deliver energy proportional output pulses of some 100ns duration. These pulses are recorded by the two signal channels of the PCI-200. The trigger pulse for the PCI-200 is generated by the photodiode PD3. Due to the long duration of the signal pulses, delay lines in the signal path are not required. The gate width and the delay of the PCI-200 are set to sample a signal portion near the peak of the input pulses. The main problem in non-linear optical absorption measurements is, that an absorption accuracy of better than one percent over several orders of magnitude of the intensity is required. To reach the required absorption accuracy, the shown setup uses a second signal path trough a reference cell and the detector module D3. By using a common replaceable filter for both channels the signal intensity can be held inside the useful input voltage range of the PCI-200 without degrading the accuracy of the measured absorption values. Pulsed Laser P1 optical Attenuator P2 C1 C2 Filter D1 D2 PDI-400 PDI-400 D3 PDM-400 M PCI-200 Measurement of non-linear absorption Channel B Channel A The measurement delivers pairs of signal values from which the intensity and the ratio of small signal and large signal absorption can be derived. By referring the A value (large signal absorption) to the B value (intensity and small signal absorption) the influence of the laser instability and the error of the optical attenuator do not appear in the measured absorption values. The apparatus is able to measure absorption variations as small as 1 %. 7
8 Accessories DCA Series Preamplifiers These DC coupled preamplifiers have an excellent input offset stability and a bandwidth of up to 400 MHz. Inverting and noninverting versions with gains up to 10 (20 db) are available. ACA Series Preamlifiers The ACA preamplifiers are AC coupled and have a bandwidth up to 2 GHz and a gain up to 70 (37 db). PDM-400 Photodiode Modules The PDM-400 is a PIN photodiode module with 400 ps FWHM and a spectral range from 330 to 1000 nm. The modules do not require a special power supply, the operating voltage is taken from a connector at the PCS / PCI module. APM-400 Avalanche Photodiode Modules The APM-400 is an avalanche photodiode module with an internal gain up to 100. Different versions with detector areas from 0.03 to 7 mm 2 are available. Depending on the detector area, the speed is from 0.32 to 3 ns FWHM. PDI-400 Integrating Photodiode Modules The PDI-400 is an integrating detector for pulsed light signals in the fj range. The PDI-400 includes a high performance photodiode, a low noise charge sensitive amplifier and an active high pass filter. Due to filtering, most of the amplifier noise and low frequency background signals are rejected and the PDI-400 is insensitive to roomlight. Its high sensitivity, low noise and wide dynamic range makes it extremely useful in all applications where accurate and reproducable measurements of light pulse energies are essential. OCF-400 Optical Constant Fraction The OCF-400 is used to derive electrical trigger pulses from optical pulses with variable amplitude. Due to the constant fraction trigger principle the trigger point is widely independent of the pulse amplitude. Compared to a simple photodiode, the OCF-400 offers negligible influence of the light pulse energy on the trigger delay. It is used for measurements with Nitrogen Lasers or Dye Lasers with unstable pulse energy. 8
SHM-180 Eight Channel Sample & Hold Module
 Becker & Hickl GmbH April 2003 Printer HP 4500 PS High Performance Photon Counting Tel. +49 / 30 / 787 56 32 FAX +49 / 30 / 787 57 34 http://www.becker-hickl.com email: info@becker-hickl.com SHM-180 Eight
Becker & Hickl GmbH April 2003 Printer HP 4500 PS High Performance Photon Counting Tel. +49 / 30 / 787 56 32 FAX +49 / 30 / 787 57 34 http://www.becker-hickl.com email: info@becker-hickl.com SHM-180 Eight
PML Channel Detector Head for Time-Correlated Single Photon Counting
 Becker & Hickl GmbH Nahmitzer Damm 30 12277 Berlin Tel +49 30 787 56 32 Fax +49 30 787 57 34 email: info@becker-hicklde http://wwwbecker-hicklde PML16DOC PML-16 16 Channel Detector Head for Time-Correlated
Becker & Hickl GmbH Nahmitzer Damm 30 12277 Berlin Tel +49 30 787 56 32 Fax +49 30 787 57 34 email: info@becker-hicklde http://wwwbecker-hicklde PML16DOC PML-16 16 Channel Detector Head for Time-Correlated
OCF-401 Optical Constant Fraction Discriminator
 Becker & Hickl GmbH March. 2002 Printer HP 4500 PS Intelligent Measurement and Control Systems Tel. 49 / 30 / 787 56 32 FAX 49 / 30 / 787 57 34 http://www.beckerhickl.com email: info@beckerhickl.com OCF401
Becker & Hickl GmbH March. 2002 Printer HP 4500 PS Intelligent Measurement and Control Systems Tel. 49 / 30 / 787 56 32 FAX 49 / 30 / 787 57 34 http://www.beckerhickl.com email: info@beckerhickl.com OCF401
TCSPC at Wavelengths from 900 nm to 1700 nm
 TCSPC at Wavelengths from 900 nm to 1700 nm We describe picosecond time-resolved optical signal recording in the spectral range from 900 nm to 1700 nm. The system consists of an id Quantique id220 InGaAs
TCSPC at Wavelengths from 900 nm to 1700 nm We describe picosecond time-resolved optical signal recording in the spectral range from 900 nm to 1700 nm. The system consists of an id Quantique id220 InGaAs
Time Correlated Single Photon Counting Systems
 Boston Electronics Corporation 91 Boylston Street, Brookline MA 02445 USA (800)347-5445 or (617)566-3821 fax (617)731-0935 www.boselec.com boselec@world.std.com Time Correlated Single Photon Counting Systems
Boston Electronics Corporation 91 Boylston Street, Brookline MA 02445 USA (800)347-5445 or (617)566-3821 fax (617)731-0935 www.boselec.com boselec@world.std.com Time Correlated Single Photon Counting Systems
IR Antibunching Measurements with id201 InGaAs Gated SPAD Detectors
 IR Antibunching Measurements with id201 GaAs Gated SPAD Detectors Abstract. Antibunching measurements with GaAs SPAD detectors are faced with the problems of high background count rate, afterpulsing, and
IR Antibunching Measurements with id201 GaAs Gated SPAD Detectors Abstract. Antibunching measurements with GaAs SPAD detectors are faced with the problems of high background count rate, afterpulsing, and
Setting up High Gain Detector Electronics for TCSPC
 Becker & Hickl GmbH Sept. 2000 higain1.doc Nahmitzer Damm 30 12277 Berlin Tel. +49 / 30 / 787 56 32 Fax. +49 / 30 / 787 57 34 email: info@becker-hickl.de http://www.becker-hickl.de Setting up High Gain
Becker & Hickl GmbH Sept. 2000 higain1.doc Nahmitzer Damm 30 12277 Berlin Tel. +49 / 30 / 787 56 32 Fax. +49 / 30 / 787 57 34 email: info@becker-hickl.de http://www.becker-hickl.de Setting up High Gain
BDS-MM Family Picosecond Diode Lasers
 BDS-MM Family Picosecond Diode s Optical power up to 60 mw at MHz Wavelengths 405, 445, 525, 640, 685, 785, 915 nm Power up to 60mW, multi-mode Small-size laser module, 40 mm x 40 mm x 120 mm Free-beam
BDS-MM Family Picosecond Diode s Optical power up to 60 mw at MHz Wavelengths 405, 445, 525, 640, 685, 785, 915 nm Power up to 60mW, multi-mode Small-size laser module, 40 mm x 40 mm x 120 mm Free-beam
400 MHz Photoreceiver with Si PIN Photodiode
 The picture shows the -FS. The photoreceiver will be delivered without post holder and post. Features Si PIN Detector, 0.8 mm Active Diameter Spectral Range 320... 1000 nm Bandwidth DC... 400 MHz Amplifier
The picture shows the -FS. The photoreceiver will be delivered without post holder and post. Features Si PIN Detector, 0.8 mm Active Diameter Spectral Range 320... 1000 nm Bandwidth DC... 400 MHz Amplifier
MSA-200 MSA-300 MSA-1000 Ultrafast Photon Counters / Multiscalers
 Becker & Hickl GmbH Aug. 2001 Printer: HP 4000 TN PS Nahmitzer Damm 30 12277 Berlin Tel. +49 / 30 / 787 56 32 FAX +49 / 30 / 787 57 34 Email info@becker-hickl.de http//www.becker-hickl.de MSA-200 MSA-300
Becker & Hickl GmbH Aug. 2001 Printer: HP 4000 TN PS Nahmitzer Damm 30 12277 Berlin Tel. +49 / 30 / 787 56 32 FAX +49 / 30 / 787 57 34 Email info@becker-hickl.de http//www.becker-hickl.de MSA-200 MSA-300
Time-Correlated Single Photon Counting
 UK Agents: Photonic Solutions plc TCSPC1.DOC 24. Apr. 2001 40 Captains Rd Edinburgh, EH17 8QF Tel. 0131 664 8122 Fax. 0131 664 8144 email: sales@psplc.com http://www.psplc.com i n t e l l i g e n t measurement
UK Agents: Photonic Solutions plc TCSPC1.DOC 24. Apr. 2001 40 Captains Rd Edinburgh, EH17 8QF Tel. 0131 664 8122 Fax. 0131 664 8144 email: sales@psplc.com http://www.psplc.com i n t e l l i g e n t measurement
High-Speed Photoreceiver with Si PIN Photodiode
 The photoreceiver will be delivered without post holder and post Features Si PIN Detector, 0.8 mm Active Diameter Spectral Range 320... 1000 nm Bandwidth DC... 200 MHz Amplifier Transimpedance (Gain) 2.0
The photoreceiver will be delivered without post holder and post Features Si PIN Detector, 0.8 mm Active Diameter Spectral Range 320... 1000 nm Bandwidth DC... 200 MHz Amplifier Transimpedance (Gain) 2.0
400 MHz Photoreceiver with InGaAs PIN Photodiode
 The picture shows the -FS with free space input. The photoreceiver will be delivered without post holder and post. Features InGaAs PIN detector Spectral range 900... 1700 nm Bandwidth DC... 400 MHz Amplifier
The picture shows the -FS with free space input. The photoreceiver will be delivered without post holder and post. Features InGaAs PIN detector Spectral range 900... 1700 nm Bandwidth DC... 400 MHz Amplifier
PZ-FLIM-110. Piezo Scanning FLIM System. Based on bh s Megapixel FLIM Technology. Complete FLIM Microscopes FLIM Upgrades for Existing Microscopes
 Based on bh s Megapixel FLIM Technology Complete FLIM Microscopes FLIM Upgrades for Existing Microscopes Multidimensional TCSPC technique Sample Scanning by Piezo Stage Compact Electronics, Controlled
Based on bh s Megapixel FLIM Technology Complete FLIM Microscopes FLIM Upgrades for Existing Microscopes Multidimensional TCSPC technique Sample Scanning by Piezo Stage Compact Electronics, Controlled
BDS-SM Family Picosecond Diode Lasers
 BDS-SM Family Picosecond Diode s BDS-SM Small-size OEM Module, 40 mm x 40 mm x 120 mm Wavelengths 375 nm, 405 nm, 445 nm, 473 nm, 488 nm, 515 nm, 640 nm, 685 nm, 785 nm, 1064 nm Free-beam or single-mode
BDS-SM Family Picosecond Diode s BDS-SM Small-size OEM Module, 40 mm x 40 mm x 120 mm Wavelengths 375 nm, 405 nm, 445 nm, 473 nm, 488 nm, 515 nm, 640 nm, 685 nm, 785 nm, 1064 nm Free-beam or single-mode
8.2 Common Forms of Noise
 8.2 Common Forms of Noise Johnson or thermal noise shot or Poisson noise 1/f noise or drift interference noise impulse noise real noise 8.2 : 1/19 Johnson Noise Johnson noise characteristics produced by
8.2 Common Forms of Noise Johnson or thermal noise shot or Poisson noise 1/f noise or drift interference noise impulse noise real noise 8.2 : 1/19 Johnson Noise Johnson noise characteristics produced by
taccor Optional features Overview Turn-key GHz femtosecond laser
 taccor Turn-key GHz femtosecond laser Self-locking and maintaining Stable and robust True hands off turn-key system Wavelength tunable Integrated pump laser Overview The taccor is a unique turn-key femtosecond
taccor Turn-key GHz femtosecond laser Self-locking and maintaining Stable and robust True hands off turn-key system Wavelength tunable Integrated pump laser Overview The taccor is a unique turn-key femtosecond
Simple setup for nano-second time-resolved spectroscopic measurements by a digital storage oscilloscope
 NOTE Simple setup for nano-second time-resolved spectroscopic measurements by a digital storage oscilloscope Goro Nishimura and Mamoru Tamura Biophysics, Research Institute for Electronic Science, Hokkaido
NOTE Simple setup for nano-second time-resolved spectroscopic measurements by a digital storage oscilloscope Goro Nishimura and Mamoru Tamura Biophysics, Research Institute for Electronic Science, Hokkaido
BDS-SM Family Picosecond Diode Lasers
 BDS-SM Family Picosecond Diode s BDS-SM Small-size OEM Module, 40 mm x 40 mm x 120 mm Wavelengths 375 nm, 405 nm, 445 nm, 473 nm, 488 nm, 515 nm, 640 nm, 685 nm, 785 nm, 1064 nm Free-beam or single-mode
BDS-SM Family Picosecond Diode s BDS-SM Small-size OEM Module, 40 mm x 40 mm x 120 mm Wavelengths 375 nm, 405 nm, 445 nm, 473 nm, 488 nm, 515 nm, 640 nm, 685 nm, 785 nm, 1064 nm Free-beam or single-mode
improved stability (compared with
 Picosecond Tunable Systems Nanosecond Lasers NT230 SERIES NT230 series lasers deliver high up to 10 mj energy pulses at 100 Hz pulse repetition rate, tunable over a broad spectral range. Integrated into
Picosecond Tunable Systems Nanosecond Lasers NT230 SERIES NT230 series lasers deliver high up to 10 mj energy pulses at 100 Hz pulse repetition rate, tunable over a broad spectral range. Integrated into
DCS-120. Confocal Scanning FLIM Systems. Based on bh s Multidimensional Megapixel FLIM Technology
 Based on bh s Multidimensional Megapixel FLIM Technology Complete Laser Scanning FLIM Microscopes FLIM Upgrades for Existing Conventional Microscopes Multidimensional TCSPC technique High throughput dual-channel
Based on bh s Multidimensional Megapixel FLIM Technology Complete Laser Scanning FLIM Microscopes FLIM Upgrades for Existing Conventional Microscopes Multidimensional TCSPC technique High throughput dual-channel
Theoretical Approach. Why do we need ultra short technology?? INTRODUCTION:
 Theoretical Approach Why do we need ultra short technology?? INTRODUCTION: Generating ultrashort laser pulses that last a few femtoseconds is a highly active area of research that is finding applications
Theoretical Approach Why do we need ultra short technology?? INTRODUCTION: Generating ultrashort laser pulses that last a few femtoseconds is a highly active area of research that is finding applications
HF Upgrade Studies: Characterization of Photo-Multiplier Tubes
 HF Upgrade Studies: Characterization of Photo-Multiplier Tubes 1. Introduction Photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) are very sensitive light detectors which are commonly used in high energy physics experiments.
HF Upgrade Studies: Characterization of Photo-Multiplier Tubes 1. Introduction Photomultiplier tubes (PMTs) are very sensitive light detectors which are commonly used in high energy physics experiments.
Instrument response function. Left linear scale, right logarithmic scale. FWHM is 120 ps.
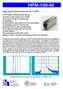 High Speed Hybrid Detector for TCSPC HPM-100-40 GaAsP cathode: Excellent detection efficiency Instrument response function 120 ps FWHM Clean response, no tails or secondary peaks No afterpulsing Excellent
High Speed Hybrid Detector for TCSPC HPM-100-40 GaAsP cathode: Excellent detection efficiency Instrument response function 120 ps FWHM Clean response, no tails or secondary peaks No afterpulsing Excellent
GFT1504 4/8/10 channel Delay Generator
 Features 4 independent Delay Channels (10 in option) 100 ps resolution (1ps in option) 25 ps RMS jitter (channel to channel) 10 second range Channel Output pulse 6 V/50 Ω, 3 ns rise time Independent control
Features 4 independent Delay Channels (10 in option) 100 ps resolution (1ps in option) 25 ps RMS jitter (channel to channel) 10 second range Channel Output pulse 6 V/50 Ω, 3 ns rise time Independent control
pulsecheck The Modular Autocorrelator
 pulsecheck The Modular Autocorrelator Pulse Measurement Perfection with the Multitalent from APE It is good to have plenty of options at hand. Suitable for the characterization of virtually any ultrafast
pulsecheck The Modular Autocorrelator Pulse Measurement Perfection with the Multitalent from APE It is good to have plenty of options at hand. Suitable for the characterization of virtually any ultrafast
Characterisation of SiPM Index :
 Characterisation of SiPM --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Index : 1. Basics of SiPM* 2. SiPM module 3. Working principle 4. Experimental setup
Characterisation of SiPM --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Index : 1. Basics of SiPM* 2. SiPM module 3. Working principle 4. Experimental setup
Testing with Femtosecond Pulses
 Testing with Femtosecond Pulses White Paper PN 200-0200-00 Revision 1.3 January 2009 Calmar Laser, Inc www.calmarlaser.com Overview Calmar s femtosecond laser sources are passively mode-locked fiber lasers.
Testing with Femtosecond Pulses White Paper PN 200-0200-00 Revision 1.3 January 2009 Calmar Laser, Inc www.calmarlaser.com Overview Calmar s femtosecond laser sources are passively mode-locked fiber lasers.
PMT tests at UMD. Vlasios Vasileiou Version st May 2006
 PMT tests at UMD Vlasios Vasileiou Version 1.0 1st May 2006 Abstract This memo describes the tests performed on three Milagro PMTs in UMD. Initially, pulse-height distributions of the PMT signals were
PMT tests at UMD Vlasios Vasileiou Version 1.0 1st May 2006 Abstract This memo describes the tests performed on three Milagro PMTs in UMD. Initially, pulse-height distributions of the PMT signals were
Wide-Field TCSPC FLIM with bh SPC-150 N TCSPC System and Photek FGN Detector
 Wide-Field TCSPC FLIM with bh SPC-150 N TCSPC System and Photek FGN 392-1000 Detector Abstract: We present a wide-field TCSPC FLIM system consisting of a position-sensitive MCP PMT of the delay-line type,
Wide-Field TCSPC FLIM with bh SPC-150 N TCSPC System and Photek FGN 392-1000 Detector Abstract: We present a wide-field TCSPC FLIM system consisting of a position-sensitive MCP PMT of the delay-line type,
Working in Visible NHMFL
 Working in Visible Optics @ NHMFL NHMFL Summer School 05-19-2016 Stephen McGill Optical Energy Range Energy of Optical Spectroscopy Range SCM3 Optics Facility Energy Range of Optical Spectroscopy SCM3
Working in Visible Optics @ NHMFL NHMFL Summer School 05-19-2016 Stephen McGill Optical Energy Range Energy of Optical Spectroscopy Range SCM3 Optics Facility Energy Range of Optical Spectroscopy SCM3
DETECTORS Important characteristics: 1) Wavelength response 2) Quantum response how light is detected 3) Sensitivity 4) Frequency of response
 DETECTORS Important characteristics: 1) Wavelength response 2) Quantum response how light is detected 3) Sensitivity 4) Frequency of response (response time) 5) Stability 6) Cost 7) convenience Photoelectric
DETECTORS Important characteristics: 1) Wavelength response 2) Quantum response how light is detected 3) Sensitivity 4) Frequency of response (response time) 5) Stability 6) Cost 7) convenience Photoelectric
Measure the roll-off frequency of an acousto-optic modulator
 Slide 1 Goals of the Lab: Get to know some of the properties of pin photodiodes Measure the roll-off frequency of an acousto-optic modulator Measure the cut-off frequency of a pin photodiode as a function
Slide 1 Goals of the Lab: Get to know some of the properties of pin photodiodes Measure the roll-off frequency of an acousto-optic modulator Measure the cut-off frequency of a pin photodiode as a function
NON-AMPLIFIED HIGH SPEED PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE
 NON-AMPLIFIED HIGH SPEED PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE Thank you for purchasing your Non-amplified High Speed Photodetector. This user s guide will help answer any questions you may have regarding the safe
NON-AMPLIFIED HIGH SPEED PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE Thank you for purchasing your Non-amplified High Speed Photodetector. This user s guide will help answer any questions you may have regarding the safe
PoS(PhotoDet 2012)051
 Optical to electrical detection delay in avalanche photodiode based detector and its interpretation Josef Blažej 1 E-mail: blazej@fjfi.cvut.cz Ivan Procházka Jan Kodet Technical University in Munich FSG,
Optical to electrical detection delay in avalanche photodiode based detector and its interpretation Josef Blažej 1 E-mail: blazej@fjfi.cvut.cz Ivan Procházka Jan Kodet Technical University in Munich FSG,
Great Britain: LASER COMPONENTS (UK) Ltd., Phone: , Fax: , France: LASER COMPONENTS
 F E M T O P H O T O R E C E I V E R O V E R V I E W 2 0 0 5 S O P H I S T I C A T E D T O O L S F O R S I G N A L R E C O V E R Y Selection Guide Photoreceivers Model Spectral Calibration Bandwidth Min.
F E M T O P H O T O R E C E I V E R O V E R V I E W 2 0 0 5 S O P H I S T I C A T E D T O O L S F O R S I G N A L R E C O V E R Y Selection Guide Photoreceivers Model Spectral Calibration Bandwidth Min.
High Performance Photon Counting. User Manual PML-16-C. 16 Channel Detector Head for Time-Correlated Single Photon Counting. Becker & Hickl GmbH
 High Performance Photon Counting User Manual PML-16-C 16 Channel Detector Head for Time-Correlated Single Photon Counting Becker & Hickl GmbH PML-16C User Handbook 1 Becker & Hickl GmbH March 2006 High
High Performance Photon Counting User Manual PML-16-C 16 Channel Detector Head for Time-Correlated Single Photon Counting Becker & Hickl GmbH PML-16C User Handbook 1 Becker & Hickl GmbH March 2006 High
Picosecond Time Analyzer Applications in...
 ORTEC AN52 Picosecond Time Analyzer Applications in... LIDAR and DIAL Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Fluorescence/Phosphorescence Lifetime Spectrometry Pulse or Signal Jitter Analysis CONTENTS of this
ORTEC AN52 Picosecond Time Analyzer Applications in... LIDAR and DIAL Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry Fluorescence/Phosphorescence Lifetime Spectrometry Pulse or Signal Jitter Analysis CONTENTS of this
Spectral phase shaping for high resolution CARS spectroscopy around 3000 cm 1
 Spectral phase shaping for high resolution CARS spectroscopy around 3 cm A.C.W. van Rhijn, S. Postma, J.P. Korterik, J.L. Herek, and H.L. Offerhaus Mesa + Research Institute for Nanotechnology, University
Spectral phase shaping for high resolution CARS spectroscopy around 3 cm A.C.W. van Rhijn, S. Postma, J.P. Korterik, J.L. Herek, and H.L. Offerhaus Mesa + Research Institute for Nanotechnology, University
NON-AMPLIFIED PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE
 NON-AMPLIFIED PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE Thank you for purchasing your Non-amplified Photodetector. This user s guide will help answer any questions you may have regarding the safe use and optimal operation
NON-AMPLIFIED PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE Thank you for purchasing your Non-amplified Photodetector. This user s guide will help answer any questions you may have regarding the safe use and optimal operation
 1 of 6 03/12/2012 14:56 2012-12-03 HAMEG > Products > Accessories > Probes http://www.hameg.com/186.0.html P R O B E S H Z 5 6-2 * AC/ DC Current Clamps This AC/DC Current Probe is used to measure currents
1 of 6 03/12/2012 14:56 2012-12-03 HAMEG > Products > Accessories > Probes http://www.hameg.com/186.0.html P R O B E S H Z 5 6-2 * AC/ DC Current Clamps This AC/DC Current Probe is used to measure currents
Redefining Measurement ID101 OEM Visible Photon Counter
 Redefining Measurement ID OEM Visible Photon Counter Miniature Photon Counter for OEM Applications Intended for large-volume OEM applications, the ID is the smallest, most reliable and most efficient single-photon
Redefining Measurement ID OEM Visible Photon Counter Miniature Photon Counter for OEM Applications Intended for large-volume OEM applications, the ID is the smallest, most reliable and most efficient single-photon
High collection efficiency MCPs for photon counting detectors
 High collection efficiency MCPs for photon counting detectors D. A. Orlov, * T. Ruardij, S. Duarte Pinto, R. Glazenborg and E. Kernen PHOTONIS Netherlands BV, Dwazziewegen 2, 9301 ZR Roden, The Netherlands
High collection efficiency MCPs for photon counting detectors D. A. Orlov, * T. Ruardij, S. Duarte Pinto, R. Glazenborg and E. Kernen PHOTONIS Netherlands BV, Dwazziewegen 2, 9301 ZR Roden, The Netherlands
200 MHz Photoreceiver with Si PIN Photodiode
 The picture shows the -FS with free space input. The photoreceiver will be delivered without post holder and post. Features Si PIN Detector, 0.8 mm Active Diameter Spectral Range 320... 1000 nm Bandwidth
The picture shows the -FS with free space input. The photoreceiver will be delivered without post holder and post. Features Si PIN Detector, 0.8 mm Active Diameter Spectral Range 320... 1000 nm Bandwidth
Supplemental Information
 Optically Activated Delayed Fluorescence Blake C. Fleischer, Jeffrey T. Petty, Jung-Cheng Hsiang, Robert M. Dickson, * School of Chemistry & Biochemistry and Petit Institute for Bioengineering and Bioscience,
Optically Activated Delayed Fluorescence Blake C. Fleischer, Jeffrey T. Petty, Jung-Cheng Hsiang, Robert M. Dickson, * School of Chemistry & Biochemistry and Petit Institute for Bioengineering and Bioscience,
combustion diagnostics
 3. Instrumentation t ti for optical combustion diagnostics Equipment for combustion laser diagnostics 1) Laser/Laser system 2) Optics Lenses Polarizer Filters Mirrors Etc. 3) Detector CCD-camera Spectrometer
3. Instrumentation t ti for optical combustion diagnostics Equipment for combustion laser diagnostics 1) Laser/Laser system 2) Optics Lenses Polarizer Filters Mirrors Etc. 3) Detector CCD-camera Spectrometer
Mass Spectrometry and the Modern Digitizer
 Mass Spectrometry and the Modern Digitizer The scientific field of Mass Spectrometry (MS) has been under constant research and development for over a hundred years, ever since scientists discovered that
Mass Spectrometry and the Modern Digitizer The scientific field of Mass Spectrometry (MS) has been under constant research and development for over a hundred years, ever since scientists discovered that
Solea. Supercontinuum Laser. Applications
 Solea Supercontinuum Laser Extended Spectral range: 525 nm - 900 nm (ECO mode), 480 nm - 900 nm (BOOST mode) Extended 2-year worldwide warranty* Supercontinuum output or wavelength selected output through
Solea Supercontinuum Laser Extended Spectral range: 525 nm - 900 nm (ECO mode), 480 nm - 900 nm (BOOST mode) Extended 2-year worldwide warranty* Supercontinuum output or wavelength selected output through
MEASURING HUM MODULATION USING MATRIX MODEL HD-500 HUM DEMODULATOR
 MEASURING HUM MODULATION USING MATRIX MODEL HD-500 HUM DEMODULATOR The SCTE defines hum modulation as, The amplitude distortion of a signal caused by the modulation of the signal by components of the power
MEASURING HUM MODULATION USING MATRIX MODEL HD-500 HUM DEMODULATOR The SCTE defines hum modulation as, The amplitude distortion of a signal caused by the modulation of the signal by components of the power
High Power Supercontinuum Fiber Laser Series. Visible Power [W]
![High Power Supercontinuum Fiber Laser Series. Visible Power [W] High Power Supercontinuum Fiber Laser Series. Visible Power [W]](/thumbs/90/101224915.jpg) Visible Power [W] Crystal Fibre aerolase Koheras SuperK SuperK EXTREME High Power Supercontinuum Fiber Laser Series 400-2400nm white light single mode spectrum Highest visible power Unsurpassed reliability
Visible Power [W] Crystal Fibre aerolase Koheras SuperK SuperK EXTREME High Power Supercontinuum Fiber Laser Series 400-2400nm white light single mode spectrum Highest visible power Unsurpassed reliability
DDG-210 Preliminary Manual Version A4
 General Information DDG-210 is a Digital Delay which can control experiments as a master device. Timing is referenced to the leading edge of the START pulse. There are 6 signal outputs available on which
General Information DDG-210 is a Digital Delay which can control experiments as a master device. Timing is referenced to the leading edge of the START pulse. There are 6 signal outputs available on which
Fast Raman Spectral Imaging Using Chirped Femtosecond Lasers
 Fast Raman Spectral Imaging Using Chirped Femtosecond Lasers Dan Fu 1, Gary Holtom 1, Christian Freudiger 1, Xu Zhang 2, Xiaoliang Sunney Xie 1 1. Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Harvard
Fast Raman Spectral Imaging Using Chirped Femtosecond Lasers Dan Fu 1, Gary Holtom 1, Christian Freudiger 1, Xu Zhang 2, Xiaoliang Sunney Xie 1 1. Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Harvard
Photon Counters SR430 5 ns multichannel scaler/averager
 Photon Counters SR430 5 ns multichannel scaler/averager SR430 Multichannel Scaler/Averager 5 ns to 10 ms bin width Count rates up to 100 MHz 1k to 32k bins per record Built-in discriminator No interchannel
Photon Counters SR430 5 ns multichannel scaler/averager SR430 Multichannel Scaler/Averager 5 ns to 10 ms bin width Count rates up to 100 MHz 1k to 32k bins per record Built-in discriminator No interchannel
SHF Communication Technologies AG
 SHF Communication Technologies AG Wilhelm-von-Siemens-Str. 23 Aufgang D 12277 Berlin Marienfelde Germany Phone ++49 30 / 772 05 10 Fax ++49 30 / 753 10 78 E-Mail: sales@shf.biz Web: http://www.shf.biz
SHF Communication Technologies AG Wilhelm-von-Siemens-Str. 23 Aufgang D 12277 Berlin Marienfelde Germany Phone ++49 30 / 772 05 10 Fax ++49 30 / 753 10 78 E-Mail: sales@shf.biz Web: http://www.shf.biz
SIGNAL RECOVERY: Sensors, Signals, Noise and Information Recovery
 SIGNAL RECOVERY: Sensors, Signals, Noise and Information Recovery http://home.deib.polimi.it/cova/ 1 Signal Recovery COURSE OUTLINE Scenery preview: typical examples and problems of Sensors and Signal
SIGNAL RECOVERY: Sensors, Signals, Noise and Information Recovery http://home.deib.polimi.it/cova/ 1 Signal Recovery COURSE OUTLINE Scenery preview: typical examples and problems of Sensors and Signal
Voltage-to-Frequency and Frequency-to-Voltage Converter ADVFC32
 a FEATURES High Linearity 0.01% max at 10 khz FS 0.05% max at 100 khz FS 0.2% max at 500 khz FS Output TTL/CMOS Compatible V/F or F/V Conversion 6 Decade Dynamic Range Voltage or Current Input Reliable
a FEATURES High Linearity 0.01% max at 10 khz FS 0.05% max at 100 khz FS 0.2% max at 500 khz FS Output TTL/CMOS Compatible V/F or F/V Conversion 6 Decade Dynamic Range Voltage or Current Input Reliable
GFT Channel Digital Delay Generator
 Features 20 independent delay Channels 100 ps resolution 25 ps rms jitter 10 second range Output pulse up to 6 V/50 Ω Independent trigger for every channel Four triggers Three are repetitive from three
Features 20 independent delay Channels 100 ps resolution 25 ps rms jitter 10 second range Output pulse up to 6 V/50 Ω Independent trigger for every channel Four triggers Three are repetitive from three
Non-Descanned FLIM Detection in Multiphoton Microscopes
 Non-Descanned FLIM Detection in Multiphoton Microscopes Abstract. Multiphoton microscopes use a femtosecond NIR laser to excite fluorescence in the sample. Excitation is performed via a multi-photon absorption
Non-Descanned FLIM Detection in Multiphoton Microscopes Abstract. Multiphoton microscopes use a femtosecond NIR laser to excite fluorescence in the sample. Excitation is performed via a multi-photon absorption
HIGH SPEED FIBER PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE
 HIGH SPEED FIBER PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE Thank you for purchasing your High Speed Fiber Photodetector. This user s guide will help answer any questions you may have regarding the safe use and optimal
HIGH SPEED FIBER PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE Thank you for purchasing your High Speed Fiber Photodetector. This user s guide will help answer any questions you may have regarding the safe use and optimal
Optical Receivers Theory and Operation
 Optical Receivers Theory and Operation Photo Detectors Optical receivers convert optical signal (light) to electrical signal (current/voltage) Hence referred O/E Converter Photodetector is the fundamental
Optical Receivers Theory and Operation Photo Detectors Optical receivers convert optical signal (light) to electrical signal (current/voltage) Hence referred O/E Converter Photodetector is the fundamental
Picosecond Light Sources
 91 Boylston Street, Brookline, MA 02445 tel: (617)566-3821 fax: (617)731-0935 www.boselec.com tcspc@boselec.com Picosecond Light Sources Available with single mode fiber output coupling From Becker & Hickl
91 Boylston Street, Brookline, MA 02445 tel: (617)566-3821 fax: (617)731-0935 www.boselec.com tcspc@boselec.com Picosecond Light Sources Available with single mode fiber output coupling From Becker & Hickl
Multiphoton FLIM with the Leica HyD RLD Detectors
 Multiphoton FLIM with the Leica HyD RLD Detectors Leica have recently introduced hybrid detectors for the non-descanned (RLD) ports their SP5 and SP8 multiphoton laser scanning microscopes. We have tested
Multiphoton FLIM with the Leica HyD RLD Detectors Leica have recently introduced hybrid detectors for the non-descanned (RLD) ports their SP5 and SP8 multiphoton laser scanning microscopes. We have tested
Agilent 83440B/C/D High-Speed Lightwave Converters
 Agilent 8344B/C/D High-Speed Lightwave Converters DC-6/2/3 GHz, to 6 nm Technical Specifications Fast optical detector for characterizing lightwave signals Fast 5, 22, or 73 ps full-width half-max (FWHM)
Agilent 8344B/C/D High-Speed Lightwave Converters DC-6/2/3 GHz, to 6 nm Technical Specifications Fast optical detector for characterizing lightwave signals Fast 5, 22, or 73 ps full-width half-max (FWHM)
Instytut Fizyki Doświadczalnej Wydział Matematyki, Fizyki i Informatyki UNIWERSYTET GDAŃSKI
 Instytut Fizyki Doświadczalnej Wydział Matematyki, Fizyki i Informatyki UNIWERSYTET GDAŃSKI I. Background theory. 1. The temporal and spatial coherence of light. 2. Interaction of electromagnetic waves
Instytut Fizyki Doświadczalnej Wydział Matematyki, Fizyki i Informatyki UNIWERSYTET GDAŃSKI I. Background theory. 1. The temporal and spatial coherence of light. 2. Interaction of electromagnetic waves
Vertical External Cavity Surface Emitting Laser
 Chapter 4 Optical-pumped Vertical External Cavity Surface Emitting Laser The booming laser techniques named VECSEL combine the flexibility of semiconductor band structure and advantages of solid-state
Chapter 4 Optical-pumped Vertical External Cavity Surface Emitting Laser The booming laser techniques named VECSEL combine the flexibility of semiconductor band structure and advantages of solid-state
APE Autocorrelator Product Family
 APE Autocorrelator Product Family APE Autocorrelators The autocorrelator product family by APE includes a variety of impressive features and properties, designed to cater for a wide range of ultrafast
APE Autocorrelator Product Family APE Autocorrelators The autocorrelator product family by APE includes a variety of impressive features and properties, designed to cater for a wide range of ultrafast
User Handbook. DPC Channel Photon Correlator
 High Performance Photon Counting User Handbook DPC-230 16 Channel Photon Correlator Becker & Hickl GmbH (c) Becker & Hickl GmbH Becker & Hickl GmbH April 2008 High Performance Photon Counting Tel. +49
High Performance Photon Counting User Handbook DPC-230 16 Channel Photon Correlator Becker & Hickl GmbH (c) Becker & Hickl GmbH Becker & Hickl GmbH April 2008 High Performance Photon Counting Tel. +49
Confocal Microscopy. Kristin Jensen
 Confocal Microscopy Kristin Jensen 17.11.05 References Cell Biological Applications of Confocal Microscopy, Brian Matsumoto, chapter 1 Studying protein dynamics in living cells,, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz
Confocal Microscopy Kristin Jensen 17.11.05 References Cell Biological Applications of Confocal Microscopy, Brian Matsumoto, chapter 1 Studying protein dynamics in living cells,, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz
SHF Communication Technologies AG
 SHF Communication Technologies AG Wilhelm-von-Siemens-Str. 23 Aufgang D 12277 Berlin Marienfelde Germany Phone ++49 30 / 772 05 10 Fax ++49 30 / 753 10 78 E-Mail: sales@shf.biz Web: http://www.shf.biz
SHF Communication Technologies AG Wilhelm-von-Siemens-Str. 23 Aufgang D 12277 Berlin Marienfelde Germany Phone ++49 30 / 772 05 10 Fax ++49 30 / 753 10 78 E-Mail: sales@shf.biz Web: http://www.shf.biz
Silicon Photomultiplier
 Silicon Photomultiplier Operation, Performance & Possible Applications Slawomir Piatek Technical Consultant, Hamamatsu Corp. Introduction Very high intrinsic gain together with minimal excess noise make
Silicon Photomultiplier Operation, Performance & Possible Applications Slawomir Piatek Technical Consultant, Hamamatsu Corp. Introduction Very high intrinsic gain together with minimal excess noise make
PERFORMANCE OF PHOTODIGM S DBR SEMICONDUCTOR LASERS FOR PICOSECOND AND NANOSECOND PULSING APPLICATIONS
 PERFORMANCE OF PHOTODIGM S DBR SEMICONDUCTOR LASERS FOR PICOSECOND AND NANOSECOND PULSING APPLICATIONS By Jason O Daniel, Ph.D. TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction...1 2. Pulse Measurements for Pulse Widths
PERFORMANCE OF PHOTODIGM S DBR SEMICONDUCTOR LASERS FOR PICOSECOND AND NANOSECOND PULSING APPLICATIONS By Jason O Daniel, Ph.D. TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction...1 2. Pulse Measurements for Pulse Widths
Tutors Dominik Dannheim, Thibault Frisson (CERN, Geneva, Switzerland)
 Danube School on Instrumentation in Elementary Particle & Nuclear Physics University of Novi Sad, Serbia, September 8 th 13 th, 2014 Lab Experiment: Characterization of Silicon Photomultipliers Dominik
Danube School on Instrumentation in Elementary Particle & Nuclear Physics University of Novi Sad, Serbia, September 8 th 13 th, 2014 Lab Experiment: Characterization of Silicon Photomultipliers Dominik
Data sheet for TDS 10XX system THz Time Domain Spectrometer TDS 10XX
 THz Time Domain Spectrometer TDS 10XX TDS10XX 16/02/2018 www.batop.de Page 1 of 11 Table of contents 0. The TDS10XX family... 3 1. Basic TDS system... 3 1.1 Option SHR - Sample Holder Reflection... 4 1.2
THz Time Domain Spectrometer TDS 10XX TDS10XX 16/02/2018 www.batop.de Page 1 of 11 Table of contents 0. The TDS10XX family... 3 1. Basic TDS system... 3 1.1 Option SHR - Sample Holder Reflection... 4 1.2
CHAPTER 8 PHOTOMULTIPLIER TUBE MODULES
 CHAPTER 8 PHOTOMULTIPLIER TUBE MODULES This chapter describes the structure, usage, and characteristics of photomultiplier tube () modules. These modules consist of a photomultiplier tube, a voltage-divider
CHAPTER 8 PHOTOMULTIPLIER TUBE MODULES This chapter describes the structure, usage, and characteristics of photomultiplier tube () modules. These modules consist of a photomultiplier tube, a voltage-divider
Variable-Gain High Speed Current Amplifier
 Features Transimpedance (Gain) Switchable from 1 x 10 2 to 1 x 10 8 V/A Bandwidth from DC up to 200 MHz Upper Cut-Off Frequency Switchable to 1 MHz, 10 MHz or Full Bandwidth Switchable AC/DC Coupling Adjustable
Features Transimpedance (Gain) Switchable from 1 x 10 2 to 1 x 10 8 V/A Bandwidth from DC up to 200 MHz Upper Cut-Off Frequency Switchable to 1 MHz, 10 MHz or Full Bandwidth Switchable AC/DC Coupling Adjustable
Interface Electronic Circuits
 Lecture (5) Interface Electronic Circuits Part: 1 Prof. Kasim M. Al-Aubidy Philadelphia University-Jordan AMSS-MSc Prof. Kasim Al-Aubidy 1 Interface Circuits: An interface circuit is a signal conditioning
Lecture (5) Interface Electronic Circuits Part: 1 Prof. Kasim M. Al-Aubidy Philadelphia University-Jordan AMSS-MSc Prof. Kasim Al-Aubidy 1 Interface Circuits: An interface circuit is a signal conditioning
Operation and Service Manual. 350 MHz Preamplifier SIM914. Stanford Research Systems
 Operation and Service Manual Stanford Research Systems Revision 1.8 August 24, 2006 Certification Stanford Research Systems certifies that this product met its published specifications at the time of shipment.
Operation and Service Manual Stanford Research Systems Revision 1.8 August 24, 2006 Certification Stanford Research Systems certifies that this product met its published specifications at the time of shipment.
Application Note (A12)
 Application Note (A2) The Benefits of DSP Lock-in Amplifiers Revision: A September 996 Gooch & Housego 4632 36 th Street, Orlando, FL 328 Tel: 47 422 37 Fax: 47 648 542 Email: sales@goochandhousego.com
Application Note (A2) The Benefits of DSP Lock-in Amplifiers Revision: A September 996 Gooch & Housego 4632 36 th Street, Orlando, FL 328 Tel: 47 422 37 Fax: 47 648 542 Email: sales@goochandhousego.com
Boston Electronics Corporation 91 Boylston Street, Brookline MA USA (800) or (617) fax (617)
 Single Photon Counting APD, MCP & PMT Detectors plus High Speed Amplifiers, Routers, Trigger Detectors, Constant Fraction Discriminators From Becker & Hickl, id Quantique and Hamamatsu F Boston Electronics
Single Photon Counting APD, MCP & PMT Detectors plus High Speed Amplifiers, Routers, Trigger Detectors, Constant Fraction Discriminators From Becker & Hickl, id Quantique and Hamamatsu F Boston Electronics
Isolated, Linearized RTD Input 7B34 FEATURES APPLICATIONS PRODUCT OVERVIEW FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
 Isolated, Linearized RTD Input 7B34 FEATURES Amplifies, Protects, Filters, and interfaces input voltages from a wide variety of two and three-wire platinum, copper and nickel Resistor Temperature Detectors
Isolated, Linearized RTD Input 7B34 FEATURES Amplifies, Protects, Filters, and interfaces input voltages from a wide variety of two and three-wire platinum, copper and nickel Resistor Temperature Detectors
Features. Applications. Optional Features
 Features Compact, Rugged Design TEM Beam with M 2 < 1.2 Pulse Rates from Single Shot to 15 khz IR, Green, UV, and Deep UV Wavelengths Available RS232 Computer Control Patented Harmonic Generation Technology
Features Compact, Rugged Design TEM Beam with M 2 < 1.2 Pulse Rates from Single Shot to 15 khz IR, Green, UV, and Deep UV Wavelengths Available RS232 Computer Control Patented Harmonic Generation Technology
High-Power Femtosecond Lasers
 High-Power Femtosecond Lasers PHAROS is a single-unit integrated femtosecond laser system combining millijoule pulse energies and high average power. PHAROS features a mechanical and optical design optimized
High-Power Femtosecond Lasers PHAROS is a single-unit integrated femtosecond laser system combining millijoule pulse energies and high average power. PHAROS features a mechanical and optical design optimized
Variable Gain 100 MHz Wideband Voltage Amplifier
 Features 10 to 60 db, Switchable in 10 db Steps Bandwidth DC... 100 MHz, Switchable to 10 MHz Built-In Temperature Compensation for Low Drift of 0.6 µv/k 2.5 nv/ Hz Input Noise Switchable AC/DC-Coupling
Features 10 to 60 db, Switchable in 10 db Steps Bandwidth DC... 100 MHz, Switchable to 10 MHz Built-In Temperature Compensation for Low Drift of 0.6 µv/k 2.5 nv/ Hz Input Noise Switchable AC/DC-Coupling
STUDY ON SAW ATTENUATION OF PMMA USING LASER ULTRASONIC
 STUDY ON SAW ATTENUATION OF PMMA USING LASER ULTRASONIC TECHNIQUE INTRODUCTION D. F ei, X. R. Zhang, C. M. Gan, and S. Y. Zhang Lab of Modern Acoustics and Institute of Acoustics Nanjing University, Nanjing,
STUDY ON SAW ATTENUATION OF PMMA USING LASER ULTRASONIC TECHNIQUE INTRODUCTION D. F ei, X. R. Zhang, C. M. Gan, and S. Y. Zhang Lab of Modern Acoustics and Institute of Acoustics Nanjing University, Nanjing,
Measuring Kinetics of Luminescence with TDS 744 oscilloscope
 Measuring Kinetics of Luminescence with TDS 744 oscilloscope Eex Nex Luminescence Photon E 0 Disclaimer Safety the first!!! This presentation is not manual. It is just brief set of rule to remind procedure
Measuring Kinetics of Luminescence with TDS 744 oscilloscope Eex Nex Luminescence Photon E 0 Disclaimer Safety the first!!! This presentation is not manual. It is just brief set of rule to remind procedure
3.003 Lab 3 Part A. Measurement of Speed of Light
 3.003 Lab 3 Part A. Measurement of Speed of Light Objective: To measure the speed of light in free space Experimental Apparatus: Feb. 18, 2010 Due Mar. 2, 2010 Components: 1 Laser, 4 mirrors, 1 beam splitter
3.003 Lab 3 Part A. Measurement of Speed of Light Objective: To measure the speed of light in free space Experimental Apparatus: Feb. 18, 2010 Due Mar. 2, 2010 Components: 1 Laser, 4 mirrors, 1 beam splitter
200 MHz Variable Gain Photoreceiver
 The image shows model -FST with 1.035-40 threaded flange and coupler ring. Features Applications Adjustable transimpedance gain from 10 2 to 10 8 V/A Wide bandwidth up to 200 MHz Si-PIN photodiode covering
The image shows model -FST with 1.035-40 threaded flange and coupler ring. Features Applications Adjustable transimpedance gain from 10 2 to 10 8 V/A Wide bandwidth up to 200 MHz Si-PIN photodiode covering
Photon Count. for Brainies.
 Page 1/12 Photon Count ounting for Brainies. 0. Preamble This document gives a general overview on InGaAs/InP, APD-based photon counting at telecom wavelengths. In common language, telecom wavelengths
Page 1/12 Photon Count ounting for Brainies. 0. Preamble This document gives a general overview on InGaAs/InP, APD-based photon counting at telecom wavelengths. In common language, telecom wavelengths
Notes on Noise Reduction
 Notes on Noise Reduction When setting out to make a measurement one often finds that the signal, the quantity we want to see, is masked by noise, which is anything that interferes with seeing the signal.
Notes on Noise Reduction When setting out to make a measurement one often finds that the signal, the quantity we want to see, is masked by noise, which is anything that interferes with seeing the signal.
PERFORMANCE OF THE CMS ECAL LASER MONITORING SOURCE IN THE TEST BEAM
 PERFORMANCE OF THE CMS ECAL LASER MONITORING SOURCE IN THE TEST BEAM A. BORNHEIM CALTECH 2 E. California Blvd., Pasadena, CA 925, USA E-mail: bornheim@hep.caltech.edu On behalf of the CMS ECAL Collaboration.
PERFORMANCE OF THE CMS ECAL LASER MONITORING SOURCE IN THE TEST BEAM A. BORNHEIM CALTECH 2 E. California Blvd., Pasadena, CA 925, USA E-mail: bornheim@hep.caltech.edu On behalf of the CMS ECAL Collaboration.
This series of lasers are available with a choice of Nd:YAG, Nd:YLF, and Nd:YVO 4. System Reliability
 Photonics Industries DS Series of UV (351/355 nm) diode pumped solid-state Q-switched lasers offer a compact, hands-free system with the long-term reliability that the manufacturing industry demands. Utilizing
Photonics Industries DS Series of UV (351/355 nm) diode pumped solid-state Q-switched lasers offer a compact, hands-free system with the long-term reliability that the manufacturing industry demands. Utilizing
ModBox Pulse Shaper Arbitrary Optical Waveform Generator
 Delivering Modulation Solutions ModBox The Photline Modbox-Pulse-Shaper is an Optical Modulation Unit to generate short shaped pulses with high extinction ratio at 1030 nm, 1053 nm or 1064 nm. It allows
Delivering Modulation Solutions ModBox The Photline Modbox-Pulse-Shaper is an Optical Modulation Unit to generate short shaped pulses with high extinction ratio at 1030 nm, 1053 nm or 1064 nm. It allows
SECOND HARMONIC GENERATION AND Q-SWITCHING
 SECOND HARMONIC GENERATION AND Q-SWITCHING INTRODUCTION In this experiment, the following learning subjects will be worked out: 1) Characteristics of a semiconductor diode laser. 2) Optical pumping on
SECOND HARMONIC GENERATION AND Q-SWITCHING INTRODUCTION In this experiment, the following learning subjects will be worked out: 1) Characteristics of a semiconductor diode laser. 2) Optical pumping on
DCS-120. Confocal Scanning FLIM Systems. Based on bh s Multidimensional Megapixel FLIM Technology
 DCS-120 Based on bh s Multidimensional Megapixel FLIM Technology Complete Laser Scanning FLIM Microscopes FLIM Upgrades for Existing Conventional Microscopes FLIM with up to 2048 x 2048 pixels Decay curves
DCS-120 Based on bh s Multidimensional Megapixel FLIM Technology Complete Laser Scanning FLIM Microscopes FLIM Upgrades for Existing Conventional Microscopes FLIM with up to 2048 x 2048 pixels Decay curves
The Benefits of Photon Counting... Page -1- Pitfalls... Page -2- APD detectors... Page -2- Hybrid detectors... Page -4- Pitfall table...
 The Benefits of Photon Counting......................................... Page -1- Pitfalls........................................................... Page -2- APD detectors..........................................................
The Benefits of Photon Counting......................................... Page -1- Pitfalls........................................................... Page -2- APD detectors..........................................................
UV AQUAtracka. In-situ PMT Fluorimeter
 Fact Sheet UV AQUAtracka In-situ PMT Fluorimeter The UV AQUAtracka is a highly sensitive in-situ fluorimeter designed to monitor concentrations of hydrocarbons (360nm) & Gelbstoff (440). The UV AQUAtracka
Fact Sheet UV AQUAtracka In-situ PMT Fluorimeter The UV AQUAtracka is a highly sensitive in-situ fluorimeter designed to monitor concentrations of hydrocarbons (360nm) & Gelbstoff (440). The UV AQUAtracka
Evaluation of Scientific Solutions Liquid Crystal Fabry-Perot Etalon
 Evaluation of Scientific Solutions Liquid Crystal Fabry-Perot Etalon Testing of the etalon was done using a frequency stabilized He-Ne laser. The beam from the laser was passed through a spatial filter
Evaluation of Scientific Solutions Liquid Crystal Fabry-Perot Etalon Testing of the etalon was done using a frequency stabilized He-Ne laser. The beam from the laser was passed through a spatial filter
An electrical photon source
 An electrical photon source A word of explanation right at the start is required: the title of this document will not make sense to anyone familiar with even the basic principles in physics. In actual
An electrical photon source A word of explanation right at the start is required: the title of this document will not make sense to anyone familiar with even the basic principles in physics. In actual
MDK EVALUATION KIT FOR METHANE DETECTION INSTRUCTION MANUAL. rev
 MDK EVALUATION KIT FOR METHANE DETECTION INSTRUCTION MANUAL rev. 250516 TABLE OF CONTENTS General Information 3 Application 3 Packaging arrangement 3 Operation conditions 3 Brief overview of the components
MDK EVALUATION KIT FOR METHANE DETECTION INSTRUCTION MANUAL rev. 250516 TABLE OF CONTENTS General Information 3 Application 3 Packaging arrangement 3 Operation conditions 3 Brief overview of the components
APPLICATION NOTE. Synchronization of Two Spectra-Physics Spitfire Pro Amplifiers for Pump-Probe Experiments
 APPLICATION NOTE Synchronization of Two Spectra-Physics Spitfire Pro Amplifiers for Pump-Probe Experiments 43 Technology and Applications Center Newport Corporation Introduction: The invention of nanosecond
APPLICATION NOTE Synchronization of Two Spectra-Physics Spitfire Pro Amplifiers for Pump-Probe Experiments 43 Technology and Applications Center Newport Corporation Introduction: The invention of nanosecond
