Technology Note ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan
|
|
|
- Roderick Garrett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Technology Note ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan Introducing the Fast Acquisition Mode
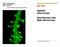
2 ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan Introducing the Fast Acquisition Mode Author: Dr. Annette Bergter Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH, Germany Joseph Huff, PhD Carl Zeiss Microscopy, LLC, Thornwood, NY, USA Date: April 2016 In August 2014, ZEISS introduced Airyscan, a new detector concept for confocal laser scanning microscopy (LSM). Airyscan is a 32 channel GaAsP-PMT area detector, positioned at the pinhole-plane of an LSM. Using Airyscan, additional light and spatial information is collected beyond that of a typical LSM image, resulting in substantial and simultaneous improvements in spatial resolution and signal-to-noise ratio. The introduction of the Fast mode for Airyscan represents the next innovation step for LSM imaging. Airyscan detector technology is utilized along with an illumination shaping approach to enhance acquisition speeds by four times. Airyscan affords researchers access to superresolution, increased signal-to-noise ratio and increased acquisition speeds simultaneously without the traditional compromises. Laser Scanning Microscopy The Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope (LSM) has become one of the most popular instruments in basic biomedical research for fluorescence imaging. The main reason LSM has become so popular is that the technique affords researchers images with high contrast and a versatile optical sectioning capability to investigate three dimensional biological structures [1]. The optical sectioning ability of an LSM is a product of scanning a diffraction limited spot, produced by a focused laser spot, across a sample to create an image one point at a time. The generated fluorescence from each point is collected by the imaging objective and results from fluorophores in the sample that reside both in the desired plane of focus and in out of focus planes. In order to separate the fluorescence emitted from the desired focal plane, an aperture (pinhole) is positioned in the light path to block all out of focus light from reaching the detector (traditionally a PMT) [2]. Based on the application needs, LSM offers tremendous flexibility to fit experimental requirements, such as the choice of the excitation laser wavelengths and scanner movement; magnification and resolution of objective lenses as well as the type and arrangement of the detectors. Hence LSMs can be used to image diverse samples from whole organisms to large tissue sections to single cells and their compartments, labeled with numerous fluorescent markers of diverse emission intensities. During the past couple of decades the LSM has undergone continuous improvement; both usability and technical capa- Figure 1 LSM 880 with Airyscan beam path. For Fast mode imaging, the wheels holding the slit apertures are introduced into the illumination beam path (arrow), shaping the excitation beam into an ellipse. The emission light is captured on the 16 center detector elements (grey) of the Airyscan detector. The remaining 16 detector elements are not used in Fast mode imaging. The Airyscan detector itself remains unchanged and all 32 detector elements are used for Airyscan modes (e.g. superresolution or sensitivity mode). bility of the instruments (to make use of the precious emission light) have been significantly enhanced. These improvements have been the result of constant technical advances, production of high class optical components and improvements in the design of the confocal beam path. But the one ultimate compromise of confocal laser scanning microscopy was not touched until 2014, when ZEISS introduced the Airyscan for its LSM 8 Family systems: the pinhole. 2
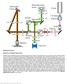
3 Until this point the pinhole would be generally set to a 1 Airy unit (AU) opening diameter; resulting in a good compromise between capturing the scarce emission light and achieving an effective resolution. In theory one can enhance the resolution of a confocal LSM by closing the pinhole below a 1 AU opening. However this is not usually an option, since too much light is rejected resulting in images with unusable signal-to-noise (SNR) ratios. For the first time, the Airyscan detector allowed to combine enhanced resolution and signal to noise for LSM imaging [3]. Airyscan detector The Airyscan detector consists of 32 GaAsP PMT detector elements, which are arranged in a hexagonal array (Figure 1), positioned at a conjugated focal plane in the beam path the detector is functioning as the traditional LSM pinhole. For full flexibility an adjustable optical zoom is present in front of the Airyscan detector which enables adjustment of the number of Airy units that are projected onto the detector. This design made it possible to collect more light (equivalent to a pinhole opened to 1.25 AU), whilst at the same time dramatically enhancing the resolution, with every detector Figure 2 The shape of the laser beam, that enters the back aperture of the objective lens, determines the resulting excitation PSF. Conventionally it is the goal to generate the smallest possible excitation spot with a given objective lens. This is achieved with a laser beam that completely fills the back aperture of the objective lens (left). If the laser beam s diameter is smaller than the back aperture of the objective, the resulting PSF is larger (middle). In order to elongate the excitation PSF only in one direction, an elliptical laser beam is used. This beam is narrowed along one axis, stretching the resulting excitation PSF along that exact axis (right). element acting as an efficient pinhole with a diameter of only 0.2 AU. Instead of facing an either / or decision, a simultaneous enhancement of resolution by the factor of 1.7 x and signal-to-noise by 4 8x was introduced to LSM imaging. Superresolution imaging under gentle conditions, with low laser powers, became part of the confocal LSM repertoire. Flexibility was added with the zoom optic, which allowed researchers to decide if resolution or sensitivity was the priority for the experiment; adapting the Airyscan advantages to the specific experimental needs. Using either multiphoton or single photon excitation without altering the well-established LSM sample preparation and labelling protocols, further broadened the experimental prospects. Detailed descriptions of the theory and technology of Airyscanning can be found in these technology notes [4, 5]. Limitations of acquisition speed in conventional LSM Research objectives can dictate the acquisition of fast, dynamic processes or the quick capture of many fields-ofview (FOV). In both cases, the challenge for the imaging system is to collect sufficient fluorescence for an image with good SNR but in a very limited period of time. Conversely, because traditional LSMs create images one point at a time, image acquisition can be relatively slow. To improve the acquisition speed of LSM instruments, several strategies can be pursued; such as limiting the field of view, sacrificing image resolution (using fewer image pixels) and scanning the laser spot faster. When scanning the laser spot faster across a FOV, the pixel dwell time is shortened. Consequently, the amount of time per pixel spent collecting fluorescence is also shorted which impacts the resulting SNR of the image. As the acquisition speed is increased, fewer and fewer photons will be available resulting in a deterioration of image SNR. The outcome is not only a noisy image but also a compromised spatial resolution, in which fine structures cannot be properly resolved. To compensate for the deteriorating SNR the laser power can be increased but this too has disadvantages; the danger of bleaching the fluorophore and / or damaging live samples by phototoxic effects (e.g. free oxygen radicals) becomes more prevalent at higher laser powers and thus the risk of influencing experimental outcomes is increased [6, 7, 8,]. Therefore, traditional techniques to improve image acquisition speeds demand that a researcher compromises image SNR, resolution, FOV and laser exposure, all of which will likely impede the research goal. 3
4 Technology Note Fast mode To solve the traditional trade-off between acquisition speed remains unchanged. In LSM 880 the beam shaping is per- and image SNR, the Airyscan detector is used in a new Fast formed by using slit apertures positioned in the excitation acquisition mode. As an area detector the Airyscan can path of the scanhead. Different slit sizes are provided to capture spatial information that is utilized to parallelize the serve a wide variety of objective lenses. These slit apertures scanning process, collecting 4 image lines simultaneously. are therefore arranged on wheels that position the necessary This means enhancing acquisition speed by a factor of 4 slit width into the laser beam path (Figure 1). The excitation while keeping high pixel dwell times to efficiently collect ellipse is scanned along the x-axis of the image field in the emitted photons. Ordinarily, the focused laser beam is conventional manner; but at the end of each line, the laser moved along the x-axis to acquire one image line, before it beam is shifted by the distance of 4 pixels in y direction be- is moved in the y-axis to acquire the consecutive image line. fore scanning the next line. The imaging time for one frame In Fast mode imaging, four image lines are acquired at the is thus reduced 4-fold without reducing the pixel dwell time same time when moving the laser in the x-direction. in the process. In order to excite the fluorescent dye in four lines at a time, The resulting fluorescence for each 4-pixel column is collect- the excitation spot needs to be broadened slightly along the ed by the Airyscan utilizing 16 detector elements of the y-axis. The broadening is achieved by shaping the laser beam Airyscan detector s center (Figure 3) where three horizontal before it enters the objective lens back aperture (Figure 2). detector elements cover 0.9 AU and the up to 6 vertical If the laser beam is narrowed in its y-axis before entering the elements cover 1.65 AU of the emission Airy disk 1. As a result, objective lens, the resulting excitation beam is stretched into each detector element acts as an individual pinhole with a an ellipse along the y-axis, while its size in x direction diameter of about 0.3 AU. Figure 3 Drosophila melanogaster embryo, Jupiter-GFP (microtubules). The left hand image was acquired with the internal GaAsP detectors of LSM 880. The z-stack (80 images) acquisition took 4:47 minutes. The same z-stack was acquired afterwards in Fast mode imaging in only 1:11 minutes. The comparison (close-up; upper image: Fast mode, lower image: internal GaAsP detectors) shows, that as well image quality in Fast mode is superior to the conventional confocal image. Settings for both images: Optimal sampling: 3372 x 1451pixels; Plan-APOCHROMAT 20x / 0.8; Z-stack: 80; Pixel dwell: 0.62 µs Sample courtesy of B. Erdi, Max F. Perutz Laboratories, University of Vienna, Vienna Biocenter, Austria. 1 For image pixel sizes that correspond to at least Nyquist sampling or superresolution sampling; named Optimal and SR sampling in ZEN. 4
5 The remaining 16 detector elements, of the otherwise unchanged Airyscan detector, are not used and do not produce any digital data. This keeps the data rate lean when streaming it directly onto the hard drive. Each individual detector element of the Airyscan detector is shifted relative to the optical axis by a certain distance. Therefore the captured signal must be reassigned to its point of origin within the resulting image. Consequently emitted photons are not rejected at a pinhole aperture but are rather collected and contribute to the signal of the respective pixel to increase its intensity. This pixel reassignment process, performed on the mathematical basis published by Sheppard et al. [9,10], results in the 4 vertical pixels per laser beam position. The resulting image from the Airyscan in Fast mode shows an enhanced SNR and resolution, because the detector collects more light than with conventional LSM settings, and it combines this with the resolution of a very small pinhole. The concluding deconvolution step therefore profits from both a very small effective PSF and a high SNR. As for conventional point scanning LSM, Fast mode works reliably in thicker samples; and can be used with multiphoton excitation to analyze highly scattering tissue. Using Airyscan in Fast mode enables the use of this unique GaAsP area detector for spatial parallelization to enhance imaging speed without compromising pixel dwell time. Airyscan in Fast mode delivers images with 4 times more SNR at a 4 times increase in acquisition speed. At the same time the characteristic advantages of the Airyscan are preserved and allow for increased resolution by a factor of 1.5 x. Furthermore, these advantages can be realized without making any changes to sample preparation or staining protocols and can be seamlessly integrated into current experimental workflows. The result of simultaneously improving resolution, SNR and speed on an optical sectioning system provides researchers with the unique combination of gentle imaging with high spatial and temporal resolution. This unprecedented combination of functionality promises to meet the growing demand for efficient large volume imaging whilst also addressing large scale structural studies and providing the capability of capturing dynamic processes for functional analysis. With Fast mode for Airyscan, ZEISS expands the potential of the Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope. Conclusion The introduction of Airyscan eliminated the requirement to choose between high resolution and high sensitivity; both could be achieved at once. In the same way, Airyscan Fast mode now takes this one step further by enabling simultaneous improvements in resolution, sensitivity and speed. Fast mode characteristics Fast mode Airyscan detector in Fast mode AU per element LSM 880 with Airyscan acquisition mode to acquire 4 image lines simultaneously, increasing image acquisition by 4-fold 16 central detector elements of the Airyscan detector are active. The remaining 16 detector elements are not used for Fast mode acquisition. ~ 0.3 AU Resolution Enhanced by 1.5 fold x = 145 nm, y = 180 nm, z = 450 nm Sensitivity 4 x enhanced SNR at 4 times faster image acquisition Speed 512 x 512 pixel 19 fps 480 x 480 pixel 27.3 fps 480 x 128 pixel 86.1 fps 1024 x 1024 pixel 6.2 fps 2048 x 2048 pixel 1.6 fps 5
6 Glossary Airy disk Airy pattern Airy Unit (AU) GaAsP LSM Pinhole Pixel dwell PMT PSF SNR The center spot of the Airy pattern. A single point source is imaged by a microscope as a blurred spot with surrounding rings of decreasing intensities, due to the diffraction nature of light. Diameter of the Airy disk, measured from the first surrounding intensity minimum. Gallium arsenide phosphide. Semiconductor material, which is used as a coating for the photocathode of the detector. The photocathode converts photons into electrons. Laser scanning microscope Aperture, positioned in the conjugated focal plane in the emission beam path, blocking out-of-focus light. Duration the laser is illumination one position and the microscope system is collecting emission light, to generate one image pixel Photomultiplier tube; common basis for light detectors in Laser Scanning Microscopes Point spread function. Describes the pattern that is generated by a microscope of a point emitting light source. Signal to noise ratio. References: [1] Conchello, J. A. and Lichtman, J. W., Optical sectioning microscopy. Nature methods, (12): p [2] Minsky, M., Memoir on inventing the confocal scanning microscope. Scanning, (4): p [3] Huff, J., The Airyscan detector from ZEISS: confocal imaging with improved signal-to-noise ratio and super-resolution. Nature methods, [4] Weisshart, K., The basic principle of Airyscanning ZEISS Technology Note [5] Huff, J.; Bathe, W.; Netz, R.; Anhut, T.; Weisshart, K., The Airyscan detector from ZEISS. Confocal imaging with improved signal-to-noise ratio and superresolution ZEISS Technology Note [6] Wäldchen, S. et al., Light-induced cell damage in live-cell super-resolution microscopy. Sci.Rep, : p [7] Li, D. et al., Extended-resolution structured illumination imaging of endocytic and cytoskeletal dynamics. Science, (6251) [8] Kucsko, G. et al., Nanometre-scale thermometry in a living cell. Nature : p [9] Sheppard, C.J., Super-resolution in confocal imaging. Optik, (2): p [10] Sheppard, C.J.; Mehta, S.B., and Heintzmann, R., Superresolution by image scanning microscopy using pixel reassignment. Opt Lett (15): p Title: Right side: Single images of a time series. Drosophila embryo, maximum intensity projection. Microtubules labeled with GFP. Z-stack with 72 slices imaged for 11.5 h at 15 min interval. Courtesy of B. Erdi, Max F. Perutz Laboratories, University of Vienna, Austria Left side: Single images of a time series. Calcium sparks labeled with Fluo 4 imaged in Cardiomyocytes with 50 frames per second. Courtesy of P. Robison, B. Prosser, University of Pennsylvania, USA 6
7 Not for therapeutic, treatment or medical diagnostic evidence. Not all products are available in every country. Contact your local ZEISS representative for more information. EN_41_013_125 CZ Design, scope of delivery and technical progress subject to change without notice. Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH Jena, Germany
Application Note. The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a Z-stack
 The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a Z-stack The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a
The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a Z-stack The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a
Travel to New Dimensions- LSM 880. The Resolution of a Microscope is limited. The Resolution of a Microscope is limited. Image. Image. Object.
 Travel to New Dimensions- LSM 880 LSM 880: The Power of Sensitivity Our Latest Member of the LSM 880 with GaAsP Detectors Sensitivity, and Ease of Use Innovative High-End Laser Scanning Microscopes from
Travel to New Dimensions- LSM 880 LSM 880: The Power of Sensitivity Our Latest Member of the LSM 880 with GaAsP Detectors Sensitivity, and Ease of Use Innovative High-End Laser Scanning Microscopes from
Point Spread Function. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy. Confocal Aperture. Optical aberrations. Alternative Scanning Microscopy
 Bi177 Lecture 5 Adding the Third Dimension Wide-field Imaging Point Spread Function Deconvolution Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Confocal Aperture Optical aberrations Alternative Scanning Microscopy
Bi177 Lecture 5 Adding the Third Dimension Wide-field Imaging Point Spread Function Deconvolution Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Confocal Aperture Optical aberrations Alternative Scanning Microscopy
3D light microscopy techniques
 3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 1 1 2! NA = 0.5! NA 2D imaging
3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 1 1 2! NA = 0.5! NA 2D imaging
The Zeiss AiryScan System, Confocal Four.
 The Zeiss AiryScan System, Confocal Four. Overview. The Zeiss AiryScan module is a segmented, radially stacked GaASP detector and collector system designed to subsample the airy disk of a point emission
The Zeiss AiryScan System, Confocal Four. Overview. The Zeiss AiryScan module is a segmented, radially stacked GaASP detector and collector system designed to subsample the airy disk of a point emission
Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev. Microscopy course, Michmoret Dec 2005
 Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Why use confocal microscopy? Principles of the laser scanning confocal microscope. Image resolution. Manipulating the
Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Why use confocal microscopy? Principles of the laser scanning confocal microscope. Image resolution. Manipulating the
Practical work no. 3: Confocal Live Cell Microscopy
 Practical work no. 3: Confocal Live Cell Microscopy Course Instructor: Mikko Liljeström (MIU) 1 Background Confocal microscopy: The main idea behind confocality is that it suppresses the signal outside
Practical work no. 3: Confocal Live Cell Microscopy Course Instructor: Mikko Liljeström (MIU) 1 Background Confocal microscopy: The main idea behind confocality is that it suppresses the signal outside
Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 5 LIVE Confocal Microscope
 Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 5 LIVE Confocal Microscope AIM 4.2 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Verify that main power switches on the
Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 5 LIVE Confocal Microscope AIM 4.2 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Verify that main power switches on the
Training Guide for Leica SP8 Confocal/Multiphoton Microscope
 Training Guide for Leica SP8 Confocal/Multiphoton Microscope LAS AF v3.3 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON power switch for epifluorescence
Training Guide for Leica SP8 Confocal/Multiphoton Microscope LAS AF v3.3 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON power switch for epifluorescence
Inside the LSM 880 NLO + Airyscan
 Inside the LSM 880 NLO + Airyscan Overview of the Newest High-End Point Scanning Solution from Carl Zeiss Microscopy Matt Curtis 3D Imaging Specialist John Dirnberger Account Manager Washington University
Inside the LSM 880 NLO + Airyscan Overview of the Newest High-End Point Scanning Solution from Carl Zeiss Microscopy Matt Curtis 3D Imaging Specialist John Dirnberger Account Manager Washington University
LSM 710 Confocal Microscope Standard Operation Protocol
 LSM 710 Confocal Microscope Standard Operation Protocol Basic Operation Turning on the system 1. Switch on Main power switch 2. Switch on System / PC power button 3. Switch on Components power button 4.
LSM 710 Confocal Microscope Standard Operation Protocol Basic Operation Turning on the system 1. Switch on Main power switch 2. Switch on System / PC power button 3. Switch on Components power button 4.
Shreyash Tandon M.S. III Year
 Shreyash Tandon M.S. III Year 20091015 Confocal microscopy is a powerful tool for generating high-resolution images and 3-D reconstructions of a specimen by using point illumination and a spatial pinhole
Shreyash Tandon M.S. III Year 20091015 Confocal microscopy is a powerful tool for generating high-resolution images and 3-D reconstructions of a specimen by using point illumination and a spatial pinhole
Development of a High-speed Super-resolution Confocal Scanner
 Development of a High-speed Super-resolution Confocal Scanner Takuya Azuma *1 Takayuki Kei *1 Super-resolution microscopy techniques that overcome the spatial resolution limit of conventional light microscopy
Development of a High-speed Super-resolution Confocal Scanner Takuya Azuma *1 Takayuki Kei *1 Super-resolution microscopy techniques that overcome the spatial resolution limit of conventional light microscopy
Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement
 Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY BioVis Uppsala, 2017 Jeremy Adler Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Widefield & Confocal Microscopy
Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY BioVis Uppsala, 2017 Jeremy Adler Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Widefield & Confocal Microscopy
Confocal Microscopy. (Increasing contrast and resolu6on using op6cal sec6oning) Lecture 7. November 2017
 Confocal Microscopy (Increasing contrast and resolu6on using op6cal sec6oning) Lecture 7 November 2017 3 Flavours of Microscope Confocal Laser Scanning Problem: Out of Focus Light Spinning disc 2-Photon
Confocal Microscopy (Increasing contrast and resolu6on using op6cal sec6oning) Lecture 7 November 2017 3 Flavours of Microscope Confocal Laser Scanning Problem: Out of Focus Light Spinning disc 2-Photon
3D light microscopy techniques
 3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 2D imaging 3D imaging Resolution
3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 2D imaging 3D imaging Resolution
1 Co Localization and Working flow with the lsm700
 1 Co Localization and Working flow with the lsm700 Samples -1 slide = mousse intestine, Dapi / Ki 67 with Cy3/ BrDU with alexa 488. -1 slide = mousse intestine, Dapi / Ki 67 with Cy3/ no BrDU (but with
1 Co Localization and Working flow with the lsm700 Samples -1 slide = mousse intestine, Dapi / Ki 67 with Cy3/ BrDU with alexa 488. -1 slide = mousse intestine, Dapi / Ki 67 with Cy3/ no BrDU (but with
Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 880 with AiryScan FAST
 Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 880 with AiryScan FAST ZEN 2.3 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2018) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON Main Switch from the remote control
Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 880 with AiryScan FAST ZEN 2.3 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2018) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON Main Switch from the remote control
BASICS OF CONFOCAL IMAGING (PART I)
 BASICS OF CONFOCAL IMAGING (PART I) INTERNAL COURSE 2012 LIGHT MICROSCOPY Lateral resolution Transmission Fluorescence d min 1.22 NA obj NA cond 0 0 rairy 0.61 NAobj Ernst Abbe Lord Rayleigh Depth of field
BASICS OF CONFOCAL IMAGING (PART I) INTERNAL COURSE 2012 LIGHT MICROSCOPY Lateral resolution Transmission Fluorescence d min 1.22 NA obj NA cond 0 0 rairy 0.61 NAobj Ernst Abbe Lord Rayleigh Depth of field
Megapixel FLIM with bh TCSPC Modules
 Megapixel FLIM with bh TCSPC Modules The New SPCM 64-bit Software Abstract: Becker & Hickl have recently introduced version 9.60 of their SPCM TCSPC data acquisition software. SPCM version 9.60 not only
Megapixel FLIM with bh TCSPC Modules The New SPCM 64-bit Software Abstract: Becker & Hickl have recently introduced version 9.60 of their SPCM TCSPC data acquisition software. SPCM version 9.60 not only
Multifluorescence The Crosstalk Problem and Its Solution
 Multifluorescence The Crosstalk Problem and Its Solution If a specimen is labeled with more than one fluorochrome, each image channel should only show the emission signal of one of them. If, in a specimen
Multifluorescence The Crosstalk Problem and Its Solution If a specimen is labeled with more than one fluorochrome, each image channel should only show the emission signal of one of them. If, in a specimen
Akinori Mitani and Geoff Weiner BGGN 266 Spring 2013 Non-linear optics final report. Introduction and Background
 Akinori Mitani and Geoff Weiner BGGN 266 Spring 2013 Non-linear optics final report Introduction and Background Two-photon microscopy is a type of fluorescence microscopy using two-photon excitation. It
Akinori Mitani and Geoff Weiner BGGN 266 Spring 2013 Non-linear optics final report Introduction and Background Two-photon microscopy is a type of fluorescence microscopy using two-photon excitation. It
Bio 407. Applied microscopy. Introduction into light microscopy. José María Mateos. Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis
 Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Bio 407 Applied Introduction into light José María Mateos Fundamentals of light Compound microscope Microscope composed of an objective and an additional lens (eyepiece,
Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Bio 407 Applied Introduction into light José María Mateos Fundamentals of light Compound microscope Microscope composed of an objective and an additional lens (eyepiece,
Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 510 META Confocal Microscope
 Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 510 META Confocal Microscope AIM 4.2 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON Components and System/PC switches
Training Guide for Carl Zeiss LSM 510 META Confocal Microscope AIM 4.2 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON Components and System/PC switches
Technology Note. The Airyscan Detector from ZEISS Confocal Imaging with Improved Signal-to-Noise Ratio and Superresolution
 Technology Note Confocal The Airyscan Detector from ZEISS Confocal Imaging with Improved Signal-to-Noise Ratio and Superresolution Airyscan The Airyscan Detector from ZEISS Confocal Imaging with Improved
Technology Note Confocal The Airyscan Detector from ZEISS Confocal Imaging with Improved Signal-to-Noise Ratio and Superresolution Airyscan The Airyscan Detector from ZEISS Confocal Imaging with Improved
Imaging Retreat - UMASS Customized real-time confocal and 2-photon imaging
 Imaging Retreat - UMASS 2012 Customized real-time confocal and 2-photon imaging Mike Sanderson Department of Microbiology and Physiological Systems University of Massachusetts Medical School Thanks for
Imaging Retreat - UMASS 2012 Customized real-time confocal and 2-photon imaging Mike Sanderson Department of Microbiology and Physiological Systems University of Massachusetts Medical School Thanks for
Basics of confocal imaging (part I)
 Basics of confocal imaging (part I) Swiss Institute of Technology (EPFL) Faculty of Life Sciences Head of BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS BIOP arne.seitz@epfl.ch Lateral resolution BioImaging &Optics Platform Light
Basics of confocal imaging (part I) Swiss Institute of Technology (EPFL) Faculty of Life Sciences Head of BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS BIOP arne.seitz@epfl.ch Lateral resolution BioImaging &Optics Platform Light
LSM 780 Confocal Microscope Standard Operation Protocol
 LSM 780 Confocal Microscope Standard Operation Protocol Basic Operation Turning on the system 1. Sign on log sheet according to Actual start time 2. Check Compressed Air supply for the air table 3. Switch
LSM 780 Confocal Microscope Standard Operation Protocol Basic Operation Turning on the system 1. Sign on log sheet according to Actual start time 2. Check Compressed Air supply for the air table 3. Switch
Operation Guide for the Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Bio-Imaging Facility Hunter College October 2009
 Operation Guide for the Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Bio-Imaging Facility Hunter College October 2009 Introduction of Fluoresence Confocal Microscopy The first confocal microscope was invented by Princeton
Operation Guide for the Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Bio-Imaging Facility Hunter College October 2009 Introduction of Fluoresence Confocal Microscopy The first confocal microscope was invented by Princeton
Confocal and 2-photon Imaging. October 15, 2010
 Confocal and 2-photon Imaging October 15, 2010 Review Optical Elements Adapted from Sluder & Nordberg 2007 Review Optical Elements Collector Lens Adapted from Sluder & Nordberg 2007 Review Optical Elements
Confocal and 2-photon Imaging October 15, 2010 Review Optical Elements Adapted from Sluder & Nordberg 2007 Review Optical Elements Collector Lens Adapted from Sluder & Nordberg 2007 Review Optical Elements
Instant super-resolution imaging in live cells and embryos via analog image processing
 Nature Methods Instant super-resolution imaging in live cells and embryos via analog image processing Andrew G. York, Panagiotis Chandris, Damian Dalle Nogare, Jeffrey Head, Peter Wawrzusin, Robert S.
Nature Methods Instant super-resolution imaging in live cells and embryos via analog image processing Andrew G. York, Panagiotis Chandris, Damian Dalle Nogare, Jeffrey Head, Peter Wawrzusin, Robert S.
Opterra II Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope. Innovation with Integrity
 Opterra II Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Enabling 4D Live-Cell Fluorescence Imaging through Speed, Sensitivity, Viability and Simplicity Innovation with Integrity Fluorescence Microscopy The
Opterra II Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Enabling 4D Live-Cell Fluorescence Imaging through Speed, Sensitivity, Viability and Simplicity Innovation with Integrity Fluorescence Microscopy The
ADVANCED METHODS FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY II. Jean-Yves Chatton Sept. 2006
 ADVANCED METHODS FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY II Jean-Yves Chatton Sept. 2006 Workshop outline Confocal microscopy of living cells and tissues X-Z scanning Time series Bleach: FRAP, photoactivation Emission
ADVANCED METHODS FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY II Jean-Yves Chatton Sept. 2006 Workshop outline Confocal microscopy of living cells and tissues X-Z scanning Time series Bleach: FRAP, photoactivation Emission
Zeiss 880 Training Notes Zen 2.3
 Zeiss 880 Training Notes Zen 2.3 1 Turn on the HXP 120V Lamp 2 Turn on Main Power Switch Turn on the Systems PC Switch Turn on the Components Switch. 3 4 5 Turn on the PC and log into your account. Start
Zeiss 880 Training Notes Zen 2.3 1 Turn on the HXP 120V Lamp 2 Turn on Main Power Switch Turn on the Systems PC Switch Turn on the Components Switch. 3 4 5 Turn on the PC and log into your account. Start
Bi/BE 227 Winter Assignment #3. Adding the third dimension: 3D Confocal Imaging
 Bi/BE 227 Winter 2016 Assignment #3 Adding the third dimension: 3D Confocal Imaging Schedule: Jan 20: Assignment Jan 20-Feb 8: Work on assignment Feb 10: Student PowerPoint presentations. Goals for this
Bi/BE 227 Winter 2016 Assignment #3 Adding the third dimension: 3D Confocal Imaging Schedule: Jan 20: Assignment Jan 20-Feb 8: Work on assignment Feb 10: Student PowerPoint presentations. Goals for this
Microscopy from Carl Zeiss
 Microscopy from Carl Zeiss Contents Page Contents... 1 Introduction... 1 Starting the System... 2 Introduction to ZEN Efficient Navigation... 5 Setting up the microscope... 10 Configuring the beam path
Microscopy from Carl Zeiss Contents Page Contents... 1 Introduction... 1 Starting the System... 2 Introduction to ZEN Efficient Navigation... 5 Setting up the microscope... 10 Configuring the beam path
Leica SP8 Resonant Confocal. Quick-Start Guide
 Leica SP8 Resonant Confocal Quick-Start Guide Contents Start-up Preparing for Imaging Part 1 On the scope Part 2 Software interface Part 3 Heat & CO2 incubation Part 4 Other hardware options Shut-down
Leica SP8 Resonant Confocal Quick-Start Guide Contents Start-up Preparing for Imaging Part 1 On the scope Part 2 Software interface Part 3 Heat & CO2 incubation Part 4 Other hardware options Shut-down
Things to check before start-up.
 Byeong Cha Page 1 11/24/2009 Manual for Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Enter you name, the date, the time, and the account number in the user log book. Things to check before start-up. Make sure that your
Byeong Cha Page 1 11/24/2009 Manual for Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Enter you name, the date, the time, and the account number in the user log book. Things to check before start-up. Make sure that your
Confocal imaging on the Leica TCS SP8. 1) Turn the system on. 2) Use TCS user account. 3) Start LAS X software:
 Confocal imaging on the Leica TCS SP8 1) Turn the system on. 2) Use TCS user account. 3) Start LAS X software: 4) Do not touch the microscope while the software is initializing. Choose your options: Turn
Confocal imaging on the Leica TCS SP8 1) Turn the system on. 2) Use TCS user account. 3) Start LAS X software: 4) Do not touch the microscope while the software is initializing. Choose your options: Turn
Zeiss 780 Training Notes
 Zeiss 780 Training Notes Turn on Main Switch, System PC and Components Switches 780 Start up sequence Do you need the argon laser (458, 488, 514 nm lines)? Yes Turn on the laser s main power switch and
Zeiss 780 Training Notes Turn on Main Switch, System PC and Components Switches 780 Start up sequence Do you need the argon laser (458, 488, 514 nm lines)? Yes Turn on the laser s main power switch and
Leica TCS SP8 Quick Start Guide
 Leica TCS SP8 Quick Start Guide Leica TCS SP8 System Overview Start-Up Procedure 1. Turn on the CTR Control Box, Fluorescent Light for the microscope stand. 2. Turn on the Scanner Power (1) on the front
Leica TCS SP8 Quick Start Guide Leica TCS SP8 System Overview Start-Up Procedure 1. Turn on the CTR Control Box, Fluorescent Light for the microscope stand. 2. Turn on the Scanner Power (1) on the front
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup. Excitation from a femtosecond laser is passed through intensity control and shuttering optics (1/2 λ wave plate, polarizing beam splitting
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup. Excitation from a femtosecond laser is passed through intensity control and shuttering optics (1/2 λ wave plate, polarizing beam splitting
Digital Camera Technologies for Scientific Bio-Imaging. Part 2: Sampling and Signal
 Digital Camera Technologies for Scientific Bio-Imaging. Part 2: Sampling and Signal Yashvinder Sabharwal, 1 James Joubert 2 and Deepak Sharma 2 1. Solexis Advisors LLC, Austin, TX, USA 2. Photometrics
Digital Camera Technologies for Scientific Bio-Imaging. Part 2: Sampling and Signal Yashvinder Sabharwal, 1 James Joubert 2 and Deepak Sharma 2 1. Solexis Advisors LLC, Austin, TX, USA 2. Photometrics
IC 2 S High Performance Objectives
 M i c r o s c o p y f r o m C a r l Z e i s s IC 2 S igh Performance Objectives for Biomedical Applications with Laser Based Imaging Systems LSM,, ConfoCor, TIRF and ELYRA Carl Zeiss offers a large range
M i c r o s c o p y f r o m C a r l Z e i s s IC 2 S igh Performance Objectives for Biomedical Applications with Laser Based Imaging Systems LSM,, ConfoCor, TIRF and ELYRA Carl Zeiss offers a large range
Confocal, hyperspectral, spinning disk
 Confocal, hyperspectral, spinning disk Administrative HW 6 due on Fri Midterm on Wed Covers everything since previous midterm 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed, 1 side Guest lecture by Joe Dragavon on Mon 10/30 Last
Confocal, hyperspectral, spinning disk Administrative HW 6 due on Fri Midterm on Wed Covers everything since previous midterm 8.5 x 11 sheet allowed, 1 side Guest lecture by Joe Dragavon on Mon 10/30 Last
Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter
 Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter Michal Balberg +, George Barbastathis*, Sergio Fantini % and David J. Brady University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana,
Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter Michal Balberg +, George Barbastathis*, Sergio Fantini % and David J. Brady University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana,
TRAINING MANUAL. Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO
 TRAINING MANUAL Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO September 2010 Multiphoton Microscopy Training Manual Multiphoton microscopy is only available on the LSM 510 META-NLO system. This system is equipped
TRAINING MANUAL Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO September 2010 Multiphoton Microscopy Training Manual Multiphoton microscopy is only available on the LSM 510 META-NLO system. This system is equipped
Quick Guide. LSM 5 MP, LSM 510 and LSM 510 META. Laser Scanning Microscopes. We make it visible. M i c r o s c o p y f r o m C a r l Z e i s s
 LSM 5 MP, LSM 510 and LSM 510 META M i c r o s c o p y f r o m C a r l Z e i s s Quick Guide Laser Scanning Microscopes LSM Software ZEN 2007 August 2007 We make it visible. Contents Page Contents... 1
LSM 5 MP, LSM 510 and LSM 510 META M i c r o s c o p y f r o m C a r l Z e i s s Quick Guide Laser Scanning Microscopes LSM Software ZEN 2007 August 2007 We make it visible. Contents Page Contents... 1
Zeiss LSM880 Operating Instructions. UTMB Optical Microscopy Core Jan. 16, 2018
 Zeiss LSM880 Operating Instructions UTMB Optical Microscopy Core Jan. 16, 2018 1 1. Power up the microscope Sing the LOGBOOK Steps below will provide power to the computer and all of the microscope components.
Zeiss LSM880 Operating Instructions UTMB Optical Microscopy Core Jan. 16, 2018 1 1. Power up the microscope Sing the LOGBOOK Steps below will provide power to the computer and all of the microscope components.
Operating Instructions for Zeiss LSM 510
 Operating Instructions for Zeiss LSM 510 Location: GNL 6.312q (BSL3) Questions? Contact: Maxim Ivannikov, maivanni@utmb.edu 1 Attend A Complementary Training Before Using The Microscope All future users
Operating Instructions for Zeiss LSM 510 Location: GNL 6.312q (BSL3) Questions? Contact: Maxim Ivannikov, maivanni@utmb.edu 1 Attend A Complementary Training Before Using The Microscope All future users
Reflecting optical system to increase signal intensity. in confocal microscopy
 Reflecting optical system to increase signal intensity in confocal microscopy DongKyun Kang *, JungWoo Seo, DaeGab Gweon Nano Opto Mechatronics Laboratory, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Korea Advanced
Reflecting optical system to increase signal intensity in confocal microscopy DongKyun Kang *, JungWoo Seo, DaeGab Gweon Nano Opto Mechatronics Laboratory, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Korea Advanced
Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
 Name of the Core Facility: Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy CORE Forschungszentrum Immunologie Mainz Welcome to the CSLM Core Facility: The CLSM Core Facility enables working groups to incorporate high
Name of the Core Facility: Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy CORE Forschungszentrum Immunologie Mainz Welcome to the CSLM Core Facility: The CLSM Core Facility enables working groups to incorporate high
Quick Guide for Zeiss 710 Laser Scanning Confocal MGH Cancer Center
 Quick Guide for Zeiss 710 Laser Scanning Confocal MGH Cancer Center For any questions or concerns, please contact: Linda Nieman lnieman@mgh.harvard.edu Office: (617) 643-9684 Cell: (512) 565-8076 Chenyue
Quick Guide for Zeiss 710 Laser Scanning Confocal MGH Cancer Center For any questions or concerns, please contact: Linda Nieman lnieman@mgh.harvard.edu Office: (617) 643-9684 Cell: (512) 565-8076 Chenyue
INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY. Urs Ziegler THE PROBLEM
 INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch THE PROBLEM 1 ORGANISMS ARE LARGE LIGHT AND ELECTRONS: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES v = Wavelength ( ) Speed (v) Frequency ( ) Amplitude (A) Propagation
INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch THE PROBLEM 1 ORGANISMS ARE LARGE LIGHT AND ELECTRONS: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES v = Wavelength ( ) Speed (v) Frequency ( ) Amplitude (A) Propagation
The DCS-120 Confocal Scanning FLIM System
 he DCS-120 Confocal Scanning FLIM System he bh DCS-120 confocal scanning FLIM system converts a conventional microscope into a high-performance fluorescence lifetime imaging system. he system is based
he DCS-120 Confocal Scanning FLIM System he bh DCS-120 confocal scanning FLIM system converts a conventional microscope into a high-performance fluorescence lifetime imaging system. he system is based
Confocal Microscopy. Kristin Jensen
 Confocal Microscopy Kristin Jensen 17.11.05 References Cell Biological Applications of Confocal Microscopy, Brian Matsumoto, chapter 1 Studying protein dynamics in living cells,, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz
Confocal Microscopy Kristin Jensen 17.11.05 References Cell Biological Applications of Confocal Microscopy, Brian Matsumoto, chapter 1 Studying protein dynamics in living cells,, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz
Competition for the Confocal Microscope?
 Competition for the Confocal Microscope? M. Schropp 1,2, Ch. Seebacher 1,2, A. Deeg 2, A. Dovzhenko 3, Olaf Tietz 3, K. Palme 3, and R. Uhl 1,2 1 Bioimaging Zentrum der LMU München, Grosshadernerstrasse
Competition for the Confocal Microscope? M. Schropp 1,2, Ch. Seebacher 1,2, A. Deeg 2, A. Dovzhenko 3, Olaf Tietz 3, K. Palme 3, and R. Uhl 1,2 1 Bioimaging Zentrum der LMU München, Grosshadernerstrasse
Quick Guide for Zeiss 710 Laser Scanning Confocal MGH Cancer Center
 Quick Guide for Zeiss 710 Laser Scanning Confocal MGH Cancer Center For any questions or concerns, please contact: Linda Nieman lnieman@mgh.harvard.edu Office: (617) 643-9684 Cell: (512) 565-8076 Chenyue
Quick Guide for Zeiss 710 Laser Scanning Confocal MGH Cancer Center For any questions or concerns, please contact: Linda Nieman lnieman@mgh.harvard.edu Office: (617) 643-9684 Cell: (512) 565-8076 Chenyue
Zeiss LSM 780 Protocol
 Zeiss LSM 780 Protocol 1) System Startup F Please note the sign-up policy. You must inform the facility at least 24 hours beforehand if you can t come; otherwise, you will receive a charge for unused time.
Zeiss LSM 780 Protocol 1) System Startup F Please note the sign-up policy. You must inform the facility at least 24 hours beforehand if you can t come; otherwise, you will receive a charge for unused time.
Confocal, Airyscan and Structured Illumination Superresolution microscopy Mayandi Sivaguru
 Confocal, Airyscan and Structured Illumination Superresolution microscopy Mayandi Sivaguru Theory, Light Path, Resolution Comparison Performance comparison Why and When Choose Airyscan OR SR-SIM Superresolution
Confocal, Airyscan and Structured Illumination Superresolution microscopy Mayandi Sivaguru Theory, Light Path, Resolution Comparison Performance comparison Why and When Choose Airyscan OR SR-SIM Superresolution
LSM 800 Confocal Microscope Standard Operation Protocol
 LSM 800 Confocal Microscope Standard Operation Protocol Turning on the system 1. Switch on the Main switch (labeled 1 and 2 ) mounted on the wall. 2. Turn the Laser Key (labeled 3 ) 90 clockwise for power
LSM 800 Confocal Microscope Standard Operation Protocol Turning on the system 1. Switch on the Main switch (labeled 1 and 2 ) mounted on the wall. 2. Turn the Laser Key (labeled 3 ) 90 clockwise for power
Zeiss LSM 880 Protocol
 Zeiss LSM 880 Protocol 1) System Startup Please note put sign-up policy. You must inform the facility at least 24 hours beforehand if you can t come; otherwise, you will receive a charge for unused time.
Zeiss LSM 880 Protocol 1) System Startup Please note put sign-up policy. You must inform the facility at least 24 hours beforehand if you can t come; otherwise, you will receive a charge for unused time.
MULTIPHOTON MICROSCOPY. Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky
 MULTIPHOTON MICROSCOPY Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Information Information given here about 2 Photon microscopy were mainly taken from these sources: Background information on 2-Photon microscopy: http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/techniques/fluorescence/multiphoton/
MULTIPHOTON MICROSCOPY Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Information Information given here about 2 Photon microscopy were mainly taken from these sources: Background information on 2-Photon microscopy: http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/techniques/fluorescence/multiphoton/
EUV microscopy - a user s perspective Dimitri Scholz EUV,
 EUV microscopy - a user s perspective Dimitri Scholz EUV, 09.11.2011 Imaging technologies: available at UCD now and in the next future Begin ab ovo - Simple approaches direct to the goal - Standard methods
EUV microscopy - a user s perspective Dimitri Scholz EUV, 09.11.2011 Imaging technologies: available at UCD now and in the next future Begin ab ovo - Simple approaches direct to the goal - Standard methods
Zeiss LSM 510 Confocor III Training Notes. Center for Cell Analysis & Modeling
 Zeiss LSM 510 Confocor III Training Notes Center for Cell Analysis & Modeling Confocor 3 Start Up Go to System Module Turn on Main Switch, System/ PC, and Components Switches Do you need the arc lamp?
Zeiss LSM 510 Confocor III Training Notes Center for Cell Analysis & Modeling Confocor 3 Start Up Go to System Module Turn on Main Switch, System/ PC, and Components Switches Do you need the arc lamp?
LSM 510 META in Chang Gung University
 Content LSM 510 META in Chang ung University LSM 510 META 路 理 The features and applications of LSM 510 META 01-09 Introduction of the hardware 10-12 Fluorescence observation in conventional microscope
Content LSM 510 META in Chang ung University LSM 510 META 路 理 The features and applications of LSM 510 META 01-09 Introduction of the hardware 10-12 Fluorescence observation in conventional microscope
Rates of excitation, emission, ISC
 Bi177 Lecture 4 Fluorescence Microscopy Phenomenon of Fluorescence Energy Diagram Rates of excitation, emission, ISC Practical Issues Lighting, Filters More on diffraction Point Spread Functions Thus Far,
Bi177 Lecture 4 Fluorescence Microscopy Phenomenon of Fluorescence Energy Diagram Rates of excitation, emission, ISC Practical Issues Lighting, Filters More on diffraction Point Spread Functions Thus Far,
Multicolor 4D Fluorescence Microscopy using Ultrathin Bessel Light sheets
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multicolor 4D Fluorescence Microscopy using Ultrathin Bessel Light sheets Teng Zhao, Sze Cheung Lau, Ying Wang, Yumian Su, Hao Wang, Aifang Cheng, Karl Herrup, Nancy Y. Ip, Shengwang
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multicolor 4D Fluorescence Microscopy using Ultrathin Bessel Light sheets Teng Zhao, Sze Cheung Lau, Ying Wang, Yumian Su, Hao Wang, Aifang Cheng, Karl Herrup, Nancy Y. Ip, Shengwang
Leica SP8 TCS Users Manual
 Leica SP8 TCS Users Manual Follow the procedure for start up and log on as posted in the lab. Please log on with your account only and do not share your password with anyone. We track and confirm usage
Leica SP8 TCS Users Manual Follow the procedure for start up and log on as posted in the lab. Please log on with your account only and do not share your password with anyone. We track and confirm usage
Spectral Imaging with the Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal
 Spectral Imaging with the Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal Outline Opterra design overview Scan Modes Light Path Spectral Imaging with Opterra Drosophila larva heart. Opterra Design Overview Supravideo
Spectral Imaging with the Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal Outline Opterra design overview Scan Modes Light Path Spectral Imaging with Opterra Drosophila larva heart. Opterra Design Overview Supravideo
Contents. Introduction
 Contents Page Contents... 1 Introduction... 1 Starting the System... 2 Introduction to ZEN Efficient Navigation... 5 Setting up the microscope... 10 Configuring the beam path and lasers... 12 Scanning
Contents Page Contents... 1 Introduction... 1 Starting the System... 2 Introduction to ZEN Efficient Navigation... 5 Setting up the microscope... 10 Configuring the beam path and lasers... 12 Scanning
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Opt Lett. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2010 August 9.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Opt Lett. 2010 January 1; 35(1): 67 69. Autoconfocal transmission microscopy based on two-photon induced photocurrent of Si photodiodes
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Opt Lett. 2010 January 1; 35(1): 67 69. Autoconfocal transmission microscopy based on two-photon induced photocurrent of Si photodiodes
Supplemental Method Information Zeiss LSM710
 Supplemental Method Information Zeiss LSM710 1 Under the Light Path window set up the confocal for imaging a green dye (Alexa488-EGFP). For example, set up the light path as shown here using the 488 nm
Supplemental Method Information Zeiss LSM710 1 Under the Light Path window set up the confocal for imaging a green dye (Alexa488-EGFP). For example, set up the light path as shown here using the 488 nm
Imaging Beyond the Basics: Optimizing Settings on the Leica SP8 Confocal
 Imaging Beyond the Basics: Optimizing Settings on the Leica SP8 Confocal Todays Goal: Introduce some additional functionalities of the Leica SP8 confocal HyD vs. PMT detectors Dye Assistant Scanning By
Imaging Beyond the Basics: Optimizing Settings on the Leica SP8 Confocal Todays Goal: Introduce some additional functionalities of the Leica SP8 confocal HyD vs. PMT detectors Dye Assistant Scanning By
ZEN 2012 SP5 black edition Hotfix 12
 Information about the software ZEN 2012 SP5 black edition Hotfix 12 Software name: ZEN 2012 Service Pack 5 black edition Hotfix 12 Software version: The software version in ZEN Help About changes to 14.0.12.201
Information about the software ZEN 2012 SP5 black edition Hotfix 12 Software name: ZEN 2012 Service Pack 5 black edition Hotfix 12 Software version: The software version in ZEN Help About changes to 14.0.12.201
ANSWER KEY Lab 2 (IGB): Bright Field and Fluorescence Optical Microscopy and Sectioning
 Phys598BP Spring 2016 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign ANSWER KEY Lab 2 (IGB): Bright Field and Fluorescence Optical Microscopy and Sectioning Location: IGB Core Microscopy Facility Microscope:
Phys598BP Spring 2016 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign ANSWER KEY Lab 2 (IGB): Bright Field and Fluorescence Optical Microscopy and Sectioning Location: IGB Core Microscopy Facility Microscope:
Fast, high-contrast imaging of animal development with scanned light sheet based structured-illumination microscopy
 nature methods Fast, high-contrast imaging of animal development with scanned light sheet based structured-illumination microscopy Philipp J Keller, Annette D Schmidt, Anthony Santella, Khaled Khairy,
nature methods Fast, high-contrast imaging of animal development with scanned light sheet based structured-illumination microscopy Philipp J Keller, Annette D Schmidt, Anthony Santella, Khaled Khairy,
DIC Imaging using Laser Scanning Microscopes (LSMs) on Axio Imager Stands
 DIC Imaging using Laser Scanning Microscopes (LSMs) on Axio Imager Stands Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) imaging is a technique used to increase contrast in brightfield images. In confocal systems,
DIC Imaging using Laser Scanning Microscopes (LSMs) on Axio Imager Stands Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) imaging is a technique used to increase contrast in brightfield images. In confocal systems,
Introduction to light microscopy
 Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light microscopy Basic concepts of imaging with light Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction Diffraction
Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light microscopy Basic concepts of imaging with light Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction Diffraction
Axio Zoom.V16 The Fluorescence Zoom Microscope for Large Fields
 Product Information Interactive PDF internet-link video/animation Release 1.0 It s About Brilliance. Because Only the Best Is Good Enough In Brief The Advantages The Applications In 1994, the molecular
Product Information Interactive PDF internet-link video/animation Release 1.0 It s About Brilliance. Because Only the Best Is Good Enough In Brief The Advantages The Applications In 1994, the molecular
Non-Descanned FLIM Detection in Multiphoton Microscopes
 Non-Descanned FLIM Detection in Multiphoton Microscopes Abstract. Multiphoton microscopes use a femtosecond NIR laser to excite fluorescence in the sample. Excitation is performed via a multi-photon absorption
Non-Descanned FLIM Detection in Multiphoton Microscopes Abstract. Multiphoton microscopes use a femtosecond NIR laser to excite fluorescence in the sample. Excitation is performed via a multi-photon absorption
Supplementary Information. Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy Imaging of Microtubule Arrays in Intact Arabidopsis thaliana Seedling Roots
 Supplementary Information Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy Imaging of Microtubule Arrays in Intact Arabidopsis thaliana Seedling Roots Bin Dong 1,, Xiaochen Yang 2,, Shaobin Zhu 1, Diane C.
Supplementary Information Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy Imaging of Microtubule Arrays in Intact Arabidopsis thaliana Seedling Roots Bin Dong 1,, Xiaochen Yang 2,, Shaobin Zhu 1, Diane C.
Supplemental Figure 1: Histogram of 63x Objective Lens z axis Calculated Resolutions. Results from the MetroloJ z axis fits for 5 beads from each
 Supplemental Figure 1: Histogram of 63x Objective Lens z axis Calculated Resolutions. Results from the MetroloJ z axis fits for 5 beads from each lens with a 1 Airy unit pinhole setting. Many water lenses
Supplemental Figure 1: Histogram of 63x Objective Lens z axis Calculated Resolutions. Results from the MetroloJ z axis fits for 5 beads from each lens with a 1 Airy unit pinhole setting. Many water lenses
LSM 510 Meta Training Notes
 LSM 510 Meta Training Notes Turning on the system Turn on X-Cite power supply. This supplies light for epifluorescence for viewing your samples through the microscope. Turn on the remote control switch.
LSM 510 Meta Training Notes Turning on the system Turn on X-Cite power supply. This supplies light for epifluorescence for viewing your samples through the microscope. Turn on the remote control switch.
MOM#3: LIGHT SHEET MICROSCOPY (LSM) Stanley Cohen, MD
 MOM#3: LIGHT SHEET MICROSCOPY (LSM) Stanley Cohen, MD Introduction. Although the technical details of light sheet imaging and its various permutations appear at first glance to be complex and require some
MOM#3: LIGHT SHEET MICROSCOPY (LSM) Stanley Cohen, MD Introduction. Although the technical details of light sheet imaging and its various permutations appear at first glance to be complex and require some
長庚大學共軛焦顯微鏡課程 長庚大學共軛焦顯微鏡課程. Spot light 長庚大學
 長庚大學共軛焦顯微鏡課程 Spot light 長庚大學共軛焦顯微鏡課程 20071030 長庚大學 Basic principle of Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy The application of LSM 510 META detector Multiphoton microscopy basic principle and introduction
長庚大學共軛焦顯微鏡課程 Spot light 長庚大學共軛焦顯微鏡課程 20071030 長庚大學 Basic principle of Laser Scanning Confocal Microscopy The application of LSM 510 META detector Multiphoton microscopy basic principle and introduction
Fundamentals of Light Microscopy II: Fluorescence, Deconvolution, Confocal, Multiphoton, Spectral microscopy. Integrated Microscopy Course
 Fundamentals of Light Microscopy II: Fluorescence, Deconvolution, Confocal, Multiphoton, Spectral microscopy Integrated Microscopy Course Review Lecture 1: Microscopy Basics Light train Kohler illumination*
Fundamentals of Light Microscopy II: Fluorescence, Deconvolution, Confocal, Multiphoton, Spectral microscopy Integrated Microscopy Course Review Lecture 1: Microscopy Basics Light train Kohler illumination*
Multi-channel imaging cytometry with a single detector
 Multi-channel imaging cytometry with a single detector Sarah Locknar 1, John Barton 1, Mark Entwistle 2, Gary Carver 1 and Robert Johnson 1 1 Omega Optical, Brattleboro, VT 05301 2 Philadelphia Lightwave,
Multi-channel imaging cytometry with a single detector Sarah Locknar 1, John Barton 1, Mark Entwistle 2, Gary Carver 1 and Robert Johnson 1 1 Omega Optical, Brattleboro, VT 05301 2 Philadelphia Lightwave,
LSM 510 Training Notes
 LSM 510 Training Notes Turning on the system Turn on the arc lamp, found on the bench top left of the microscope. This supplies light for epifluorescence for viewing your samples through the microscope.
LSM 510 Training Notes Turning on the system Turn on the arc lamp, found on the bench top left of the microscope. This supplies light for epifluorescence for viewing your samples through the microscope.
ZEISS LSM 710 NLO Multiphoton microscope Manual/Quick guide
 ZEISS LSM 710 NLO Multiphoton microscope Manual/Quick guide Matyas Molnar, Biovis 2016 Starting the microscpe 1. Check the microscope if everything looks clean and normal. If not, report it in the logbook.
ZEISS LSM 710 NLO Multiphoton microscope Manual/Quick guide Matyas Molnar, Biovis 2016 Starting the microscpe 1. Check the microscope if everything looks clean and normal. If not, report it in the logbook.
Introduction to light microscopy
 Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light Basic concepts of imaging with light Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Microscopy with light 1 Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction
Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light Basic concepts of imaging with light Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Microscopy with light 1 Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction
TCSPC at Wavelengths from 900 nm to 1700 nm
 TCSPC at Wavelengths from 900 nm to 1700 nm We describe picosecond time-resolved optical signal recording in the spectral range from 900 nm to 1700 nm. The system consists of an id Quantique id220 InGaAs
TCSPC at Wavelengths from 900 nm to 1700 nm We describe picosecond time-resolved optical signal recording in the spectral range from 900 nm to 1700 nm. The system consists of an id Quantique id220 InGaAs
Topics. - How to calibrate the LSM scanner. - How to clean the microscope. - How to adjust the pinhole alignment. - How to adjust the Collimator
 Topics - How to calibrate the LSM scanner - How to measure the PSF - How to clean the microscope - How to adjust the pinhole alignment - How to adjust the Collimator How to calibrate the LSM scanner The
Topics - How to calibrate the LSM scanner - How to measure the PSF - How to clean the microscope - How to adjust the pinhole alignment - How to adjust the Collimator How to calibrate the LSM scanner The
BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS PLATFORM EPFL SV PTBIOP LASER SCANNING CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY PRACTICAL CONSIDERATIONS
 LASER SCANNING CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY PRACTICAL CONSIDERATIONS IMPORTANT PARAMETERS Pixel dwell time Zoom and pixel number PIXEL DWELL TIME How much time signal is collected at every pixel Very small values,
LASER SCANNING CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY PRACTICAL CONSIDERATIONS IMPORTANT PARAMETERS Pixel dwell time Zoom and pixel number PIXEL DWELL TIME How much time signal is collected at every pixel Very small values,
Introduction to light microscopy
 Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light microscopy (an overview) Microscopy with light Components of a light microscope 1. Light source 2. Objective 3. Sample or specimen holder
Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light microscopy (an overview) Microscopy with light Components of a light microscope 1. Light source 2. Objective 3. Sample or specimen holder
Practical Flatness Tech Note
 Practical Flatness Tech Note Understanding Laser Dichroic Performance BrightLine laser dichroic beamsplitters set a new standard for super-resolution microscopy with λ/10 flatness per inch, P-V. We ll
Practical Flatness Tech Note Understanding Laser Dichroic Performance BrightLine laser dichroic beamsplitters set a new standard for super-resolution microscopy with λ/10 flatness per inch, P-V. We ll
Flatness of Dichroic Beamsplitters Affects Focus and Image Quality
 Flatness of Dichroic Beamsplitters Affects Focus and Image Quality Flatness of Dichroic Beamsplitters Affects Focus and Image Quality 1. Introduction Even though fluorescence microscopy has become a routine
Flatness of Dichroic Beamsplitters Affects Focus and Image Quality Flatness of Dichroic Beamsplitters Affects Focus and Image Quality 1. Introduction Even though fluorescence microscopy has become a routine
Multidimensional Imaging with the Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal System
 Multidimensional Imaging with the Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal System Outline Opterra design overview Light Path Scan Modes Performance Application data Drosophila larva heart. Courtesy of Nikon
Multidimensional Imaging with the Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal System Outline Opterra design overview Light Path Scan Modes Performance Application data Drosophila larva heart. Courtesy of Nikon
STORM/ PALM ANSWER KEY
 STORM/ PALM ANSWER KEY Phys598BP Spring 2016 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Questions for Lab Report 1. How do you define a resolution in STORM imaging? If you are given a STORM setup, how
STORM/ PALM ANSWER KEY Phys598BP Spring 2016 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Questions for Lab Report 1. How do you define a resolution in STORM imaging? If you are given a STORM setup, how
Dynamic Confocal Imaging of Living Brain. Advantages and risks of multiphoton microscopy in physiology
 Dynamic Confocal Imaging of Living Brain Advantages and risks of multiphoton microscopy in physiology Confocal laser scanning microscopy In conventional optical microscopy focused and out-offocus light
Dynamic Confocal Imaging of Living Brain Advantages and risks of multiphoton microscopy in physiology Confocal laser scanning microscopy In conventional optical microscopy focused and out-offocus light
