Reflecting optical system to increase signal intensity. in confocal microscopy
|
|
|
- Lindsey Byrd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Reflecting optical system to increase signal intensity in confocal microscopy DongKyun Kang *, JungWoo Seo, DaeGab Gweon Nano Opto Mechatronics Laboratory, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, Taejon, Korea ABSTRACT In fluorescence mode confocal microscopes, only 0.0% of emitted signal can be detected in best case. So, we proposed reflecting optical system to increase signal intensity detected in photon detector. In this paper, we evaluate the proposed reflecting optical system using optical transfer function. To evaluate the proposed system, we used the modeling method based on wave optics. We first calculated point spread function of total system, and calculated optical transfer function of total system. When we use the proposed reflecting optical system, we can increase the signal intensity detected in photon detector. Amount of increased signal intensity depends on the ratio of NA of objective in the original confocal microscopy to NA of objective in reflecting optical system. We also simulated axial response of total system. FWHM of axial response increased a little when using reflecting optical system. The amount of increased FWHM also depends on the ratio of NA, mentioned above. Maximum increase in FWHM of axial response is about 5%. Keywords: Confocal microscopy, Reflecting optical system, Optical transfer function, Signal intensity 1. INTRODUCTION Confocal microscopy is first invented by M. Minsky. Due to the aid of development of various laser and computer, confocal microscopy is widely used in cell biology, physiology, cytogenetics, diagnostic pathology and the material sciences. 1 The main advantage of confocal microscopy over conventional optical microscopy is the ability of optical sectioning. With pinhole aperture, light from out of focus plane can be rejected, thus only the thin slice in focal plane can be imaged in the thick specimen. Using this optical sectioning ability, true three-dimensional image of specimen can be achieved. But confocal microscopy has some disadvantages. It takes time to perform a scan particularly for high resolution imaging over a large area or volume of a specimen. And it has low optical transfer efficiency, which means only small * godogo@mail.kaist.ac.kr ; phone ; fax ; ; Nano Opto Mechatronics Laboratory, KAIST, Yusung-gu, Taejon, Korea Optical Design and Testing, Zhicheng Weng, Jose M. Sasian, Yongtian Wang, Editors, Proceedings of SPIE Vol. 497 (00) 00 SPIE X/0/$15.00
2 part of emitted fluorescence can be detected. To overcome the low quantum efficiency, we proposed the reflecting optical system before 3. In the first part of this paper, we describe the proposed reflecting optical system briefly. And in the next section, we analyze the performance of reflecting optical system.. REFLECTING OPTICAL SYSTEM In fluorescence mode confocal microscopy, which is a very popular instrument in biology, optical transfer efficiency is very low 4. Amount of light emitted from fluorophore is limited by photodynamic property of given fluorophore. Fluorescence photobleaching limits the emitted photons and excited-state saturation limits the available imaging intensity. So, we can t get more emitted photons by increasing intensity of illumination light over fluorescence saturation level. In case of limited available photons, it is very important to detect as many photons as possible to enhance good image quality. For confocal microscopy, optical transfer efficiency, ratio of detected fluorescence to emitted fluorescence, is usually much less than 0.3% even for maximum-size detector aperture. There were several methods proposed to increase the amount of detected fluorescence or to increase sensitivity of photon detector. Art (1989) demonstrated a simple trans-illuminated confocal design in which emitted fluorescence propagating forward is captured by second objective and collimated to be reflected by plane mirror 4. Reflected fluorescence is focused by second objective and collimated again by first objective to be detected by photon detector. S.W. Hell et al. proposed 4Pi-confocal microscopy, which has good axial resolution and increased number of detected photons 5. But these methods are only applicable to the object scanning. If fast scanning speed is necessary, beam scanning type is preferred, and we need different method to increase detected fluorescence intensity. As one of the solutions to this problem, we proposed reflecting optical system behind the specimen 3. Proposed reflecting optical system is described in Fig. 1. Objective Specimen Spherical lens Objective Spherical mirror Figure 1 : Schematics diagram of proposed reflecting optical system Fluorescence propagating forward passes proposed reflecting optical system so that it is focused at the point where it came from. Now, this focused beam passes through the first objective and beam scanning system to reach the pinhole aperture. Because this beam came from where illumination spot was, it can pass through the pinhole and can be detected Proc. SPIE Vol
3 by photon detector. So, detected intensity is increased. This property doesn t depend on specific scanning point, so the proposed reflecting optical system can be used in beam scanning confocal microscopy. 3. PERFORMANCE OF REFLECTING OPTICAL SYSTEM The reflecting optical system proposed in this paper is expected to increase detected intensity. To analyze performance of proposed reflecting optical system, we used the concept of point spread function, optical transfer function, and axial response. In this chapter, we present the modeling of proposed reflecting optical system for wave optical analysis. And we explain the concept of point spread function briefly. At the end of this chapter, we describe the optical transfer function and axial response of proposed reflecting optical system to compare its performance with the confocal microscopy without reflecting optical system. 3.1 Modeling for wave optical analysis Simplified model for beam scanning confocal microscopy with proposed reflecting optical system can be easily understood by Fig.. In this model, beam scanning mechanism is replaced with moving light source and moving pinhole aperture which are conjugate to each other. Scanning surface is considered as curved due to the aberration of beam scanning optical system. Reflecting optical system is designed so that the surface of spherical mirror is conjugate surface to the curved scanning surface. Objective lens Scanning dish Specimen Objective lens Spherical mirror Source Collecting lens Pinhole Figure : Simplified model concerning scanning surface 398 Proc. SPIE Vol. 497
4 If we assume that objective has no aberration, the curved scanning surface made by beam scanning optical system can be considered to be made by objective with only field curvature. But if we consider the curved scanning surface as a reference plane, then this field curvature can be eliminated so that scanning surface can be considered simply as a plane 6. Once scanning surface is considered as a plane, the spherical mirror in reflecting optical system can be considered as a plane, since it is the conjugate plane to the scanning surface. So, simplified model with plane scanning region is described in Fig. 3. We use this simplified model to analyze the performance of reflecting optical system. Objective lens Scanning plane Specimen Objective lens Mirror Source Collecting lens Pinhole Figure 3 : Simplified model with plane scanning surface 3. PSF of overall optical system with proposed reflecting optical system For fluorescence type confocal microscopy, relation between detected intensity and object function for point detector is usually expressed as Eq. (1) 7. I( rs ) = h1 ( M r1 ) o f ( rs r1 ) h ( r1 ) d r1 (1) Similar equation can be established for simplified model with reflecting optical system, which we are considering now. Proc. SPIE Vol
5 I( rs ) = hillu ( rs + r1 ) o f ( r1 )( h1det ( rs + r1 ) + hdet ( rs + r1 ) ) d r1 () Eq. () is different from Eq. (1) in two points. Since we are considering beam scanning type confocal system, coordinate of object function is fixed, while coordinate of illumination and detection point spread function changes which stands for the movement of source and detection pinhole respectively. And detection point spread function is composed of two parts. One is usual detection point spread function for confocal microscopy, and the other is point spread function for detection path with reflecting optical system. If we define h a as overall intensity point spread function, we can explain the equation above as follows. I r ) = o ( r ) h ( r ) (3) ( s f s 3 a s This shows that there is no difference of imaging process between object scanning and beam scanning type confocal microscopy when we assume the curved surface as reference plane in beam scanning type. Before we consider overall intensity point spread function, detection point spread function with reflecting optical system, h det, must be considered, since this is the main difference to the conventional confocal microscopy. 3.3 Detection PSF with reflecting optical system Coherent transfer function of detection path with reflecting optical system is multiplication of three CTF, which are two CTF of second objective and CTF of collecting lens. CTF is one in central region and zero in outer region. So, CTF with minimum non-zero region will govern the non-zero region of overall CTF. When NA of second objective is larger than that of collecting lens, NA of returning fluorescence from reflecting optical system is limited by that of collecting lens. Otherwise, when NA of second objective is smaller than that of collecting lens, main bottleneck is second objective. If we assume that NA of second objective is not larger than that of collecting lens, CTF of second detection path is just CTF of second objective. (This doesn t lose generality, since second of objective with larger NA will acts as that with the same NA to collecting lens) So, PSF of second detection path is just PSF of second objective. Letting the ratio of second objective NA to collecting lens NA m, we can get the equation below for PSF of second detection path. h ( v, u) = m h ( mv, m ) (4) det 1det u 400 Proc. SPIE Vol. 497
6 Since m is not larger than one, Eq. (4) means that detection signal by second path, which uses reflecting optical system, can t be larger that that by first path, which is conventional detection path in confocal microscopy. And the shape of PSF is broader than that of first detection path. Using this result we can calculate the optical transfer function and axial response of proposed optical system. 3.4 Performance of confocal microscopy with reflecting optical system Optical transfer function is Fourier transform of intensity point spread function. OTF explains spatial frequency response of given optical system. Practically, it can be calculated by convolution of OTF of illumination path and detection path. Before we actually calculate the OTF, we consider OTF of second path at this point. From the Eq. (4), OTF of second path has the given relation below. l s C det ( l, s) = C1det (, ) (5) m m Eq. (5) shows that OTF of second path has narrower band pass in spatial frequency space, which means it worsen the frequency response property of overall system. Numerical results of OTF are shown in Fig. 4. Absolute size of OTF is doubled when reflecting optical system is used, but there is no apparent difference of shape and pass band. When m is smaller than one, amount of increase in absolute size is decreased compared to the case when m is one. (a) : OTF without reflecting optical system (b) : OTF with reflecting optical system Figure 4 : OTF of overall optical system (a) : OTF without reflecting optical system (b) : OTF with reflecting optical system Proc. SPIE Vol
7 (a) without normalization (b) with normalization Figure 5 : Axial response of overall optical system. (dashed line : m=1, solid line : m=0.5, dotted line : m=0) (a) : axial response without normalization, (b) : normalized axial response Fig. 5 shows axial response of overall optical system. With reflecting optical system, detected intensity increases. But the amount of increase is proportional to m 4, so when m=0.5, there is only 6.5% of increase. With normalization, there looks no difference according to the change of m value. But magnified view of central lobe shows axial response curve is broader when m is 0.5. This means FWHM of axial response is increased. Fig. 6 shows the change of relative FWHM according to the change of m value. As m gets larger, FWHM also gets larger until m is about 0.8. As m gets larger than 0.8, FWHM gets smaller. In any case, FWHM is increased, which worsen the axial response of overall optical system. The maximum increase of FWHM is about 5%. Figure 6 : Relation between relative FWHM with respect to change of m 40 Proc. SPIE Vol. 497
8 4. RESULT We proposed reflecting optical system and analyzed performance of optical system using the concept of PSF, OTF, and axial response. Detected intensity is increased when reflecting optical system is used, and the amount of increase if proportional to m 4. FWHM of axial response is increased and maximum value of increase is 5%. In actual setup, there is movement of optical probe due to the refractive index change in specimen. To compensate this effect, motorized stage to move second objective in reflecting optical system is necessary. 5. REFERENCE 1. C.J.R. Sheppard, D.M. Shotton, Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy, Springer Verlag, New York, John G. Walker, Non-scanning confocal fluorescence microscopy using speckle illumination, Optics Communications. 189, pp. 1-6, D.K. Kang, J.W. Seo, Dae-gab Gweon, Signal increasing method in confocal scanning microscopy in fluorescent mode using curved mirror, Proceeding of International conference on control, Automation and Systems 001, , Oct J.B.Pawley (Ed.), Handbook of Biological Confocal Microscopy, Plenum Publishers, New York, K. Bahlmann, S. Jakobs, S.W. Hell, 4Pi-confocal microscopy of live cells, Ultramicroscopy. 87, pp , Virendra N. Mahajan, Aberration theory made simple, SPIE, Min Gu, Principles of Three-Dimensional Imaging in Confocal Microscopes, World Scientific, 1996 Proc. SPIE Vol
Point Spread Function. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy. Confocal Aperture. Optical aberrations. Alternative Scanning Microscopy
 Bi177 Lecture 5 Adding the Third Dimension Wide-field Imaging Point Spread Function Deconvolution Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Confocal Aperture Optical aberrations Alternative Scanning Microscopy
Bi177 Lecture 5 Adding the Third Dimension Wide-field Imaging Point Spread Function Deconvolution Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy Confocal Aperture Optical aberrations Alternative Scanning Microscopy
Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter
 Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter Michal Balberg +, George Barbastathis*, Sergio Fantini % and David J. Brady University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana,
Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter Michal Balberg +, George Barbastathis*, Sergio Fantini % and David J. Brady University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana,
Zero Focal Shift in High Numerical Aperture Focusing of a Gaussian Laser Beam through Multiple Dielectric Interfaces. Ali Mahmoudi
 1 Zero Focal Shift in High Numerical Aperture Focusing of a Gaussian Laser Beam through Multiple Dielectric Interfaces Ali Mahmoudi a.mahmoudi@qom.ac.ir & amahmodi@yahoo.com Laboratory of Optical Microscopy,
1 Zero Focal Shift in High Numerical Aperture Focusing of a Gaussian Laser Beam through Multiple Dielectric Interfaces Ali Mahmoudi a.mahmoudi@qom.ac.ir & amahmodi@yahoo.com Laboratory of Optical Microscopy,
BASICS OF CONFOCAL IMAGING (PART I)
 BASICS OF CONFOCAL IMAGING (PART I) INTERNAL COURSE 2012 LIGHT MICROSCOPY Lateral resolution Transmission Fluorescence d min 1.22 NA obj NA cond 0 0 rairy 0.61 NAobj Ernst Abbe Lord Rayleigh Depth of field
BASICS OF CONFOCAL IMAGING (PART I) INTERNAL COURSE 2012 LIGHT MICROSCOPY Lateral resolution Transmission Fluorescence d min 1.22 NA obj NA cond 0 0 rairy 0.61 NAobj Ernst Abbe Lord Rayleigh Depth of field
3D light microscopy techniques
 3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 1 1 2! NA = 0.5! NA 2D imaging
3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 1 1 2! NA = 0.5! NA 2D imaging
Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev. Microscopy course, Michmoret Dec 2005
 Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Why use confocal microscopy? Principles of the laser scanning confocal microscope. Image resolution. Manipulating the
Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Why use confocal microscopy? Principles of the laser scanning confocal microscope. Image resolution. Manipulating the
Examination, TEN1, in courses SK2500/SK2501, Physics of Biomedical Microscopy,
 KTH Applied Physics Examination, TEN1, in courses SK2500/SK2501, Physics of Biomedical Microscopy, 2009-06-05, 8-13, FB51 Allowed aids: Compendium Imaging Physics (handed out) Compendium Light Microscopy
KTH Applied Physics Examination, TEN1, in courses SK2500/SK2501, Physics of Biomedical Microscopy, 2009-06-05, 8-13, FB51 Allowed aids: Compendium Imaging Physics (handed out) Compendium Light Microscopy
Basics of confocal imaging (part I)
 Basics of confocal imaging (part I) Swiss Institute of Technology (EPFL) Faculty of Life Sciences Head of BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS BIOP arne.seitz@epfl.ch Lateral resolution BioImaging &Optics Platform Light
Basics of confocal imaging (part I) Swiss Institute of Technology (EPFL) Faculty of Life Sciences Head of BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS BIOP arne.seitz@epfl.ch Lateral resolution BioImaging &Optics Platform Light
Advanced Optical Microscopy lecture. 03. December 2012 Kai Wicker
 Advanced Optical Microscopy lecture 03. December 2012 Kai Wicker Today: Optical transfer functions (OTF) and point spread functions (PSF) in incoherent imaging. 1. Quick revision: the incoherent wide-field
Advanced Optical Microscopy lecture 03. December 2012 Kai Wicker Today: Optical transfer functions (OTF) and point spread functions (PSF) in incoherent imaging. 1. Quick revision: the incoherent wide-field
Confocal and 2-photon Imaging. October 15, 2010
 Confocal and 2-photon Imaging October 15, 2010 Review Optical Elements Adapted from Sluder & Nordberg 2007 Review Optical Elements Collector Lens Adapted from Sluder & Nordberg 2007 Review Optical Elements
Confocal and 2-photon Imaging October 15, 2010 Review Optical Elements Adapted from Sluder & Nordberg 2007 Review Optical Elements Collector Lens Adapted from Sluder & Nordberg 2007 Review Optical Elements
Development of a new multi-wavelength confocal surface profilometer for in-situ automatic optical inspection (AOI)
 Development of a new multi-wavelength confocal surface profilometer for in-situ automatic optical inspection (AOI) Liang-Chia Chen 1#, Chao-Nan Chen 1 and Yi-Wei Chang 1 1. Institute of Automation Technology,
Development of a new multi-wavelength confocal surface profilometer for in-situ automatic optical inspection (AOI) Liang-Chia Chen 1#, Chao-Nan Chen 1 and Yi-Wei Chang 1 1. Institute of Automation Technology,
Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement
 Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY BioVis Uppsala, 2017 Jeremy Adler Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Widefield & Confocal Microscopy
Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY BioVis Uppsala, 2017 Jeremy Adler Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Widefield & Confocal Microscopy
PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE. Three-dimensional transfer functions
 PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE SPIEDigitalLibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie Three-dimensional transfer functions Colin J. R. Sheppard Colin J. R. Sheppard, "Three-dimensional transfer functions," Proc. SPIE
PROCEEDINGS OF SPIE SPIEDigitalLibrary.org/conference-proceedings-of-spie Three-dimensional transfer functions Colin J. R. Sheppard Colin J. R. Sheppard, "Three-dimensional transfer functions," Proc. SPIE
More fancy SPIM, Even fancier SPIM
 More fancy SPIM, Even fancier SPIM Last class Light sheet microscopy Fancy SPIM (ispim, dspim, etc ) This class Multi camera SPIM SIM SPIM Bessels d x,y = λ em 2 NA d z = 2 NA λ ex + n(1 cosθ λ em 1 IsoView
More fancy SPIM, Even fancier SPIM Last class Light sheet microscopy Fancy SPIM (ispim, dspim, etc ) This class Multi camera SPIM SIM SPIM Bessels d x,y = λ em 2 NA d z = 2 NA λ ex + n(1 cosθ λ em 1 IsoView
Operation Guide for the Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Bio-Imaging Facility Hunter College October 2009
 Operation Guide for the Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Bio-Imaging Facility Hunter College October 2009 Introduction of Fluoresence Confocal Microscopy The first confocal microscope was invented by Princeton
Operation Guide for the Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Bio-Imaging Facility Hunter College October 2009 Introduction of Fluoresence Confocal Microscopy The first confocal microscope was invented by Princeton
Optimal Pupil Design for Confocal Microscopy
 Optimal Pupil Design for Confocal Microscopy Yogesh G. Patel 1, Milind Rajadhyaksha 3, and Charles A. DiMarzio 1,2 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 2 Department of Mechanical and Industrial
Optimal Pupil Design for Confocal Microscopy Yogesh G. Patel 1, Milind Rajadhyaksha 3, and Charles A. DiMarzio 1,2 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, 2 Department of Mechanical and Industrial
Maria Smedh, Centre for Cellular Imaging. Maria Smedh, Centre for Cellular Imaging
 Nonlinear microscopy I: Two-photon fluorescence microscopy Multiphoton Microscopy What is multiphoton imaging? Applications Different imaging modes Advantages/disadvantages Scattering of light in thick
Nonlinear microscopy I: Two-photon fluorescence microscopy Multiphoton Microscopy What is multiphoton imaging? Applications Different imaging modes Advantages/disadvantages Scattering of light in thick
Development of a High-speed Super-resolution Confocal Scanner
 Development of a High-speed Super-resolution Confocal Scanner Takuya Azuma *1 Takayuki Kei *1 Super-resolution microscopy techniques that overcome the spatial resolution limit of conventional light microscopy
Development of a High-speed Super-resolution Confocal Scanner Takuya Azuma *1 Takayuki Kei *1 Super-resolution microscopy techniques that overcome the spatial resolution limit of conventional light microscopy
MOM#3: LIGHT SHEET MICROSCOPY (LSM) Stanley Cohen, MD
 MOM#3: LIGHT SHEET MICROSCOPY (LSM) Stanley Cohen, MD Introduction. Although the technical details of light sheet imaging and its various permutations appear at first glance to be complex and require some
MOM#3: LIGHT SHEET MICROSCOPY (LSM) Stanley Cohen, MD Introduction. Although the technical details of light sheet imaging and its various permutations appear at first glance to be complex and require some
attocfm I for Surface Quality Inspection NANOSCOPY APPLICATION NOTE M01 RELATED PRODUCTS G
 APPLICATION NOTE M01 attocfm I for Surface Quality Inspection Confocal microscopes work by scanning a tiny light spot on a sample and by measuring the scattered light in the illuminated volume. First,
APPLICATION NOTE M01 attocfm I for Surface Quality Inspection Confocal microscopes work by scanning a tiny light spot on a sample and by measuring the scattered light in the illuminated volume. First,
Multicolor 4D Fluorescence Microscopy using Ultrathin Bessel Light sheets
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multicolor 4D Fluorescence Microscopy using Ultrathin Bessel Light sheets Teng Zhao, Sze Cheung Lau, Ying Wang, Yumian Su, Hao Wang, Aifang Cheng, Karl Herrup, Nancy Y. Ip, Shengwang
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multicolor 4D Fluorescence Microscopy using Ultrathin Bessel Light sheets Teng Zhao, Sze Cheung Lau, Ying Wang, Yumian Su, Hao Wang, Aifang Cheng, Karl Herrup, Nancy Y. Ip, Shengwang
TRAINING MANUAL. Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO
 TRAINING MANUAL Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO September 2010 Multiphoton Microscopy Training Manual Multiphoton microscopy is only available on the LSM 510 META-NLO system. This system is equipped
TRAINING MANUAL Multiphoton Microscopy LSM 510 META-NLO September 2010 Multiphoton Microscopy Training Manual Multiphoton microscopy is only available on the LSM 510 META-NLO system. This system is equipped
A 3D Profile Parallel Detecting System Based on Differential Confocal Microscopy. Y.H. Wang, X.F. Yu and Y.T. Fei
 Key Engineering Materials Online: 005-10-15 ISSN: 166-9795, Vols. 95-96, pp 501-506 doi:10.408/www.scientific.net/kem.95-96.501 005 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland A 3D Profile Parallel Detecting
Key Engineering Materials Online: 005-10-15 ISSN: 166-9795, Vols. 95-96, pp 501-506 doi:10.408/www.scientific.net/kem.95-96.501 005 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland A 3D Profile Parallel Detecting
Heisenberg) relation applied to space and transverse wavevector
 2. Optical Microscopy 2.1 Principles A microscope is in principle nothing else than a simple lens system for magnifying small objects. The first lens, called the objective, has a short focal length (a
2. Optical Microscopy 2.1 Principles A microscope is in principle nothing else than a simple lens system for magnifying small objects. The first lens, called the objective, has a short focal length (a
Shreyash Tandon M.S. III Year
 Shreyash Tandon M.S. III Year 20091015 Confocal microscopy is a powerful tool for generating high-resolution images and 3-D reconstructions of a specimen by using point illumination and a spatial pinhole
Shreyash Tandon M.S. III Year 20091015 Confocal microscopy is a powerful tool for generating high-resolution images and 3-D reconstructions of a specimen by using point illumination and a spatial pinhole
High-speed 1-frame ms scanning confocal microscope with a microlens and Nipkow disks
 High-speed 1-framems scanning confocal microscope with a microlens and Nipkow disks Takeo Tanaami, Shinya Otsuki, Nobuhiro Tomosada, Yasuhito Kosugi, Mizuho Shimizu, and Hideyuki Ishida We have developed
High-speed 1-framems scanning confocal microscope with a microlens and Nipkow disks Takeo Tanaami, Shinya Otsuki, Nobuhiro Tomosada, Yasuhito Kosugi, Mizuho Shimizu, and Hideyuki Ishida We have developed
Microscopy. Lecture 2: Optical System of the Microscopy II Herbert Gross. Winter term
 Microscopy Lecture 2: Optical System of the Microscopy II 212-1-22 Herbert Gross Winter term 212 www.iap.uni-jena.de Preliminary time schedule 2 No Date Main subject Detailed topics Lecturer 1 15.1. Optical
Microscopy Lecture 2: Optical System of the Microscopy II 212-1-22 Herbert Gross Winter term 212 www.iap.uni-jena.de Preliminary time schedule 2 No Date Main subject Detailed topics Lecturer 1 15.1. Optical
:... resolution is about 1.4 μm, assumed an excitation wavelength of 633 nm and a numerical aperture of 0.65 at 633 nm.
 PAGE 30 & 2008 2007 PRODUCT CATALOG Confocal Microscopy - CFM fundamentals :... Over the years, confocal microscopy has become the method of choice for obtaining clear, three-dimensional optical images
PAGE 30 & 2008 2007 PRODUCT CATALOG Confocal Microscopy - CFM fundamentals :... Over the years, confocal microscopy has become the method of choice for obtaining clear, three-dimensional optical images
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Opt Lett. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2010 August 9.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Opt Lett. 2010 January 1; 35(1): 67 69. Autoconfocal transmission microscopy based on two-photon induced photocurrent of Si photodiodes
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Opt Lett. 2010 January 1; 35(1): 67 69. Autoconfocal transmission microscopy based on two-photon induced photocurrent of Si photodiodes
Introduction to light microscopy
 Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light microscopy Basic concepts of imaging with light Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction Diffraction
Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light microscopy Basic concepts of imaging with light Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction Diffraction
Study of self-interference incoherent digital holography for the application of retinal imaging
 Study of self-interference incoherent digital holography for the application of retinal imaging Jisoo Hong and Myung K. Kim Department of Physics, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL, US 33620 ABSTRACT
Study of self-interference incoherent digital holography for the application of retinal imaging Jisoo Hong and Myung K. Kim Department of Physics, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL, US 33620 ABSTRACT
Aberrations and adaptive optics for biomedical microscopes
 Aberrations and adaptive optics for biomedical microscopes Martin Booth Department of Engineering Science And Centre for Neural Circuits and Behaviour University of Oxford Outline Rays, wave fronts and
Aberrations and adaptive optics for biomedical microscopes Martin Booth Department of Engineering Science And Centre for Neural Circuits and Behaviour University of Oxford Outline Rays, wave fronts and
Introduction to Light Microscopy. (Image: T. Wittman, Scripps)
 Introduction to Light Microscopy (Image: T. Wittman, Scripps) The Light Microscope Four centuries of history Vibrant current development One of the most widely used research tools A. Khodjakov et al. Major
Introduction to Light Microscopy (Image: T. Wittman, Scripps) The Light Microscope Four centuries of history Vibrant current development One of the most widely used research tools A. Khodjakov et al. Major
Flatness of Dichroic Beamsplitters Affects Focus and Image Quality
 Flatness of Dichroic Beamsplitters Affects Focus and Image Quality Flatness of Dichroic Beamsplitters Affects Focus and Image Quality 1. Introduction Even though fluorescence microscopy has become a routine
Flatness of Dichroic Beamsplitters Affects Focus and Image Quality Flatness of Dichroic Beamsplitters Affects Focus and Image Quality 1. Introduction Even though fluorescence microscopy has become a routine
No part of this material may be reproduced without explicit written permission.
 This material is provided for educational use only. The information in these slides including all data, images and related materials are the property of : Robert M. Glaeser Department of Molecular & Cell
This material is provided for educational use only. The information in these slides including all data, images and related materials are the property of : Robert M. Glaeser Department of Molecular & Cell
TCSPC at Wavelengths from 900 nm to 1700 nm
 TCSPC at Wavelengths from 900 nm to 1700 nm We describe picosecond time-resolved optical signal recording in the spectral range from 900 nm to 1700 nm. The system consists of an id Quantique id220 InGaAs
TCSPC at Wavelengths from 900 nm to 1700 nm We describe picosecond time-resolved optical signal recording in the spectral range from 900 nm to 1700 nm. The system consists of an id Quantique id220 InGaAs
Optical sectioning by two-pinhole confocal fluorescence microscopy
 Micron 34 (2003) 313 318 www.elsevier.com/locate/micron Optical sectioning by two-pinhole confocal fluorescence microscopy M. Martínez-Corral a, *, M.T. Caballero b, C. Ibáñez-López a, V. Sarafis c a Departamento
Micron 34 (2003) 313 318 www.elsevier.com/locate/micron Optical sectioning by two-pinhole confocal fluorescence microscopy M. Martínez-Corral a, *, M.T. Caballero b, C. Ibáñez-López a, V. Sarafis c a Departamento
High resolution extended depth of field microscopy using wavefront coding
 High resolution extended depth of field microscopy using wavefront coding Matthew R. Arnison *, Peter Török #, Colin J. R. Sheppard *, W. T. Cathey +, Edward R. Dowski, Jr. +, Carol J. Cogswell *+ * Physical
High resolution extended depth of field microscopy using wavefront coding Matthew R. Arnison *, Peter Török #, Colin J. R. Sheppard *, W. T. Cathey +, Edward R. Dowski, Jr. +, Carol J. Cogswell *+ * Physical
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup.
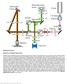 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup. Excitation from a femtosecond laser is passed through intensity control and shuttering optics (1/2 λ wave plate, polarizing beam splitting
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup. Excitation from a femtosecond laser is passed through intensity control and shuttering optics (1/2 λ wave plate, polarizing beam splitting
Nikon Instruments Europe
 Nikon Instruments Europe Recommendations for N-SIM sample preparation and image reconstruction Dear customer, We hope you find the following guidelines useful in order to get the best performance out of
Nikon Instruments Europe Recommendations for N-SIM sample preparation and image reconstruction Dear customer, We hope you find the following guidelines useful in order to get the best performance out of
Confocal Microscopy. Kristin Jensen
 Confocal Microscopy Kristin Jensen 17.11.05 References Cell Biological Applications of Confocal Microscopy, Brian Matsumoto, chapter 1 Studying protein dynamics in living cells,, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz
Confocal Microscopy Kristin Jensen 17.11.05 References Cell Biological Applications of Confocal Microscopy, Brian Matsumoto, chapter 1 Studying protein dynamics in living cells,, Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz
Resolution. Diffraction from apertures limits resolution. Rayleigh criterion θ Rayleigh = 1.22 λ/d 1 peak at 2 nd minimum. θ f D
 Microscopy Outline 1. Resolution and Simple Optical Microscope 2. Contrast enhancement: Dark field, Fluorescence (Chelsea & Peter), Phase Contrast, DIC 3. Newer Methods: Scanning Tunneling microscopy (STM),
Microscopy Outline 1. Resolution and Simple Optical Microscope 2. Contrast enhancement: Dark field, Fluorescence (Chelsea & Peter), Phase Contrast, DIC 3. Newer Methods: Scanning Tunneling microscopy (STM),
Opterra II Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope. Innovation with Integrity
 Opterra II Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Enabling 4D Live-Cell Fluorescence Imaging through Speed, Sensitivity, Viability and Simplicity Innovation with Integrity Fluorescence Microscopy The
Opterra II Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Enabling 4D Live-Cell Fluorescence Imaging through Speed, Sensitivity, Viability and Simplicity Innovation with Integrity Fluorescence Microscopy The
INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY. Urs Ziegler THE PROBLEM
 INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch THE PROBLEM 1 ORGANISMS ARE LARGE LIGHT AND ELECTRONS: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES v = Wavelength ( ) Speed (v) Frequency ( ) Amplitude (A) Propagation
INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch THE PROBLEM 1 ORGANISMS ARE LARGE LIGHT AND ELECTRONS: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES v = Wavelength ( ) Speed (v) Frequency ( ) Amplitude (A) Propagation
Bio 407. Applied microscopy. Introduction into light microscopy. José María Mateos. Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis
 Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Bio 407 Applied Introduction into light José María Mateos Fundamentals of light Compound microscope Microscope composed of an objective and an additional lens (eyepiece,
Center for Microscopy and Image Analysis Bio 407 Applied Introduction into light José María Mateos Fundamentals of light Compound microscope Microscope composed of an objective and an additional lens (eyepiece,
Supplementary Information. Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy Imaging of Microtubule Arrays in Intact Arabidopsis thaliana Seedling Roots
 Supplementary Information Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy Imaging of Microtubule Arrays in Intact Arabidopsis thaliana Seedling Roots Bin Dong 1,, Xiaochen Yang 2,, Shaobin Zhu 1, Diane C.
Supplementary Information Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy Imaging of Microtubule Arrays in Intact Arabidopsis thaliana Seedling Roots Bin Dong 1,, Xiaochen Yang 2,, Shaobin Zhu 1, Diane C.
Light Microscopy. Upon completion of this lecture, the student should be able to:
 Light Light microscopy is based on the interaction of light and tissue components and can be used to study tissue features. Upon completion of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1- Explain the
Light Light microscopy is based on the interaction of light and tissue components and can be used to study tissue features. Upon completion of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1- Explain the
Training Guide for Leica SP8 Confocal/Multiphoton Microscope
 Training Guide for Leica SP8 Confocal/Multiphoton Microscope LAS AF v3.3 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON power switch for epifluorescence
Training Guide for Leica SP8 Confocal/Multiphoton Microscope LAS AF v3.3 Optical Imaging & Vital Microscopy Core Baylor College of Medicine (2017) Power ON Routine 1 2 Turn ON power switch for epifluorescence
Lenses Design Basics. Introduction. RONAR-SMITH Laser Optics. Optics for Medical. System. Laser. Semiconductor Spectroscopy.
 Introduction Optics Application Lenses Design Basics a) Convex lenses Convex lenses are optical imaging components with positive focus length. After going through the convex lens, parallel beam of light
Introduction Optics Application Lenses Design Basics a) Convex lenses Convex lenses are optical imaging components with positive focus length. After going through the convex lens, parallel beam of light
Optical-Sectioning Improvement in Two-Color Excitation Scanning Microscopy
 MICROSCOPY RESEARCH AND TECHNIQUE 64:96 102 (2004) Optical-Sectioning Improvement in Two-Color Excitation Scanning Microscopy CRISTINA IBÁÑEZ-LÓPEZ, ISABEL ESCOBAR, GENARO SAAVEDRA, AND MANUEL MARTÍNEZ-CORRAL*
MICROSCOPY RESEARCH AND TECHNIQUE 64:96 102 (2004) Optical-Sectioning Improvement in Two-Color Excitation Scanning Microscopy CRISTINA IBÁÑEZ-LÓPEZ, ISABEL ESCOBAR, GENARO SAAVEDRA, AND MANUEL MARTÍNEZ-CORRAL*
3D light microscopy techniques
 3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 2D imaging 3D imaging Resolution
3D light microscopy techniques The image of a point is a 3D feature In-focus image Out-of-focus image The image of a point is not a point Point Spread Function (PSF) 1D imaging 2D imaging 3D imaging Resolution
The DCS-120 Confocal Scanning FLIM System
 he DCS-120 Confocal Scanning FLIM System he bh DCS-120 confocal scanning FLIM system converts a conventional microscope into a high-performance fluorescence lifetime imaging system. he system is based
he DCS-120 Confocal Scanning FLIM System he bh DCS-120 confocal scanning FLIM system converts a conventional microscope into a high-performance fluorescence lifetime imaging system. he system is based
Adaptive optics two-photon fluorescence microscopy
 Adaptive optics two-photon fluorescence microscopy Yaopeng Zhou 1, Thomas Bifano 1 and Charles Lin 2 1. Manufacturing Engineering Department, Boston University 15 Saint Mary's Street, Brookline MA, 02446
Adaptive optics two-photon fluorescence microscopy Yaopeng Zhou 1, Thomas Bifano 1 and Charles Lin 2 1. Manufacturing Engineering Department, Boston University 15 Saint Mary's Street, Brookline MA, 02446
Parallel Mode Confocal System for Wafer Bump Inspection
 Parallel Mode Confocal System for Wafer Bump Inspection ECEN5616 Class Project 1 Gao Wenliang wen-liang_gao@agilent.com 1. Introduction In this paper, A parallel-mode High-speed Line-scanning confocal
Parallel Mode Confocal System for Wafer Bump Inspection ECEN5616 Class Project 1 Gao Wenliang wen-liang_gao@agilent.com 1. Introduction In this paper, A parallel-mode High-speed Line-scanning confocal
Dynamic beam shaping with programmable diffractive optics
 Dynamic beam shaping with programmable diffractive optics Bosanta R. Boruah Dept. of Physics, GU Page 1 Outline of the talk Introduction Holography Programmable diffractive optics Laser scanning confocal
Dynamic beam shaping with programmable diffractive optics Bosanta R. Boruah Dept. of Physics, GU Page 1 Outline of the talk Introduction Holography Programmable diffractive optics Laser scanning confocal
Some of the important topics needed to be addressed in a successful lens design project (R.R. Shannon: The Art and Science of Optical Design)
 Lens design Some of the important topics needed to be addressed in a successful lens design project (R.R. Shannon: The Art and Science of Optical Design) Focal length (f) Field angle or field size F/number
Lens design Some of the important topics needed to be addressed in a successful lens design project (R.R. Shannon: The Art and Science of Optical Design) Focal length (f) Field angle or field size F/number
Dual-detection confocal fluorescence microscopy: fluorescence axial imaging without axial scanning
 Dual-detection confocal fluorescence microscopy: fluorescence axial imaging without axial scanning Dong-Ryoung Lee, 1 Young-Duk Kim, 1 Dae-Gab Gweon, 1,3 and Hongki Yoo, 2,* 1 Nano Opto-Mechatronics Laboratory,
Dual-detection confocal fluorescence microscopy: fluorescence axial imaging without axial scanning Dong-Ryoung Lee, 1 Young-Duk Kim, 1 Dae-Gab Gweon, 1,3 and Hongki Yoo, 2,* 1 Nano Opto-Mechatronics Laboratory,
Application Note. The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a Z-stack
 The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a Z-stack The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a
The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a Z-stack The New 2D Superresolution Mode for ZEISS Airyscan 120 nm Lateral Resolution without Acquiring a
Laboratory Experiment of a High-contrast Imaging Coronagraph with. New Step-transmission Filters
 Laboratory Experiment of a High-contrast Imaging Coronagraph with New Step-transmission Filters Jiangpei Dou *a,b,c, Deqing Ren a,b,d, Yongtian Zhu a,b & Xi Zhang a,b,c a. National Astronomical Observatories/Nanjing
Laboratory Experiment of a High-contrast Imaging Coronagraph with New Step-transmission Filters Jiangpei Dou *a,b,c, Deqing Ren a,b,d, Yongtian Zhu a,b & Xi Zhang a,b,c a. National Astronomical Observatories/Nanjing
Applications of Optics
 Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 26 Applications of Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Applications of Optics Many devices are based on the principles of optics
Nicholas J. Giordano www.cengage.com/physics/giordano Chapter 26 Applications of Optics Marilyn Akins, PhD Broome Community College Applications of Optics Many devices are based on the principles of optics
Beam Scanning Confocal Differential Heterodyne Interferometry
 Beam Scanning Confocal Differential Heterodyne Interferometry Cheol Song, Tae Joong Kim, Dae-Gab Gweon Nano opto mechatronics Lab., Dept. of Mechanical Eng, KAIST, Daejeon, 305-701, Korea (e-mail: feloveyou@kaist.ac.kr,
Beam Scanning Confocal Differential Heterodyne Interferometry Cheol Song, Tae Joong Kim, Dae-Gab Gweon Nano opto mechatronics Lab., Dept. of Mechanical Eng, KAIST, Daejeon, 305-701, Korea (e-mail: feloveyou@kaist.ac.kr,
Imaging Introduction. September 24, 2010
 Imaging Introduction September 24, 2010 What is a microscope? Merriam-Webster: an optical instrument consisting of a lens or combination of lenses for making enlarged images of minute objects; especially:
Imaging Introduction September 24, 2010 What is a microscope? Merriam-Webster: an optical instrument consisting of a lens or combination of lenses for making enlarged images of minute objects; especially:
Introduction to light microscopy
 Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light Basic concepts of imaging with light Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Microscopy with light 1 Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction
Center for Microscopy and Image Anaylsis Introduction to light Basic concepts of imaging with light Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch Microscopy with light 1 Light interacting with matter Absorbtion Refraction
Fluorescence Imaging of Single Spins in Nitrogen-Vacancy centers using a Confocal Microscope. Advanced Lab Course University of Basel
 Fluorescence Imaging of Single Spins in Nitrogen-Vacancy centers using a Confocal Microscope Advanced Lab Course University of Basel October 6, 2015 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 The Confocal Microscope
Fluorescence Imaging of Single Spins in Nitrogen-Vacancy centers using a Confocal Microscope Advanced Lab Course University of Basel October 6, 2015 Contents 1 Introduction 2 2 The Confocal Microscope
Technology Note ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan
 Technology Note ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan Introducing the Fast Acquisition Mode ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan Introducing the Fast Acquisition Mode Author: Dr. Annette Bergter Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH,
Technology Note ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan Introducing the Fast Acquisition Mode ZEISS LSM 880 with Airyscan Introducing the Fast Acquisition Mode Author: Dr. Annette Bergter Carl Zeiss Microscopy GmbH,
Administrative details:
 Administrative details: Anything from your side? www.photonics.ethz.ch 1 What are we actually doing here? Optical imaging: Focusing by a lens Angular spectrum Paraxial approximation Gaussian beams Method
Administrative details: Anything from your side? www.photonics.ethz.ch 1 What are we actually doing here? Optical imaging: Focusing by a lens Angular spectrum Paraxial approximation Gaussian beams Method
1.6 Beam Wander vs. Image Jitter
 8 Chapter 1 1.6 Beam Wander vs. Image Jitter It is common at this point to look at beam wander and image jitter and ask what differentiates them. Consider a cooperative optical communication system that
8 Chapter 1 1.6 Beam Wander vs. Image Jitter It is common at this point to look at beam wander and image jitter and ask what differentiates them. Consider a cooperative optical communication system that
a) How big will that physical image of the cells be your camera sensor?
 1. Consider a regular wide-field microscope set up with a 60x, NA = 1.4 objective and a monochromatic digital camera with 8 um pixels, properly positioned in the primary image plane. This microscope is
1. Consider a regular wide-field microscope set up with a 60x, NA = 1.4 objective and a monochromatic digital camera with 8 um pixels, properly positioned in the primary image plane. This microscope is
Adaptive optimisation of illumination beam profiles in fluorescence microscopy
 Adaptive optimisation of illumination beam profiles in fluorescence microscopy T. J. Mitchell a, C. D. Saunter a, W. O Nions a, J. M. Girkin a, G. D. Love a a Centre for Advanced nstrumentation & Biophysical
Adaptive optimisation of illumination beam profiles in fluorescence microscopy T. J. Mitchell a, C. D. Saunter a, W. O Nions a, J. M. Girkin a, G. D. Love a a Centre for Advanced nstrumentation & Biophysical
Akinori Mitani and Geoff Weiner BGGN 266 Spring 2013 Non-linear optics final report. Introduction and Background
 Akinori Mitani and Geoff Weiner BGGN 266 Spring 2013 Non-linear optics final report Introduction and Background Two-photon microscopy is a type of fluorescence microscopy using two-photon excitation. It
Akinori Mitani and Geoff Weiner BGGN 266 Spring 2013 Non-linear optics final report Introduction and Background Two-photon microscopy is a type of fluorescence microscopy using two-photon excitation. It
Single-shot depth-section imaging through chromatic slit-scan confocal microscopy
 Single-shot depth-section imaging through chromatic slit-scan confocal microscopy Paul C. Lin, Pang-Chen Sun, Lijun Zhu, and Yeshaiahu Fainman A chromatic confocal microscope constructed with a white-light
Single-shot depth-section imaging through chromatic slit-scan confocal microscopy Paul C. Lin, Pang-Chen Sun, Lijun Zhu, and Yeshaiahu Fainman A chromatic confocal microscope constructed with a white-light
3-D Quantitative Imaging of the Microvasculature with the Texas Instruments Digital Micromirror Device
 Invited Paper 3-D Quantitative Imaging of the Microvasculature with the Texas Instruments Digital Micromirror Device Y. Fainman, E. Botvinick*, J. Price*, D. Gough* Department of Electrical and Computer
Invited Paper 3-D Quantitative Imaging of the Microvasculature with the Texas Instruments Digital Micromirror Device Y. Fainman, E. Botvinick*, J. Price*, D. Gough* Department of Electrical and Computer
Rates of excitation, emission, ISC
 Bi177 Lecture 4 Fluorescence Microscopy Phenomenon of Fluorescence Energy Diagram Rates of excitation, emission, ISC Practical Issues Lighting, Filters More on diffraction Point Spread Functions Thus Far,
Bi177 Lecture 4 Fluorescence Microscopy Phenomenon of Fluorescence Energy Diagram Rates of excitation, emission, ISC Practical Issues Lighting, Filters More on diffraction Point Spread Functions Thus Far,
Metrology and Sensing
 Metrology and Sensing Lecture 5: Confocal sensors 07-0-3 Herbert Gross Winter term 06 www.iap.uni-jena.de Preliminary Schedule No Date Subject Detailed Content 8.0. Introduction Introduction, optical measurements,
Metrology and Sensing Lecture 5: Confocal sensors 07-0-3 Herbert Gross Winter term 06 www.iap.uni-jena.de Preliminary Schedule No Date Subject Detailed Content 8.0. Introduction Introduction, optical measurements,
Very short introduction to light microscopy and digital imaging
 Very short introduction to light microscopy and digital imaging Hernan G. Garcia August 1, 2005 1 Light Microscopy Basics In this section we will briefly describe the basic principles of operation and
Very short introduction to light microscopy and digital imaging Hernan G. Garcia August 1, 2005 1 Light Microscopy Basics In this section we will briefly describe the basic principles of operation and
Confocal Microscopy and Related Techniques
 Confocal Microscopy and Related Techniques Chau-Hwang Lee Associate Research Fellow Research Center for Applied Sciences, Academia Sinica 128 Sec. 2, Academia Rd., Nankang, Taipei 11529, Taiwan E-mail:
Confocal Microscopy and Related Techniques Chau-Hwang Lee Associate Research Fellow Research Center for Applied Sciences, Academia Sinica 128 Sec. 2, Academia Rd., Nankang, Taipei 11529, Taiwan E-mail:
Finite conjugate spherical aberration compensation in high numerical-aperture optical disc readout
 Finite conjugate spherical aberration compensation in high numerical-aperture optical disc readout Sjoerd Stallinga Spherical aberration arising from deviations of the thickness of an optical disc substrate
Finite conjugate spherical aberration compensation in high numerical-aperture optical disc readout Sjoerd Stallinga Spherical aberration arising from deviations of the thickness of an optical disc substrate
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE DEPTH STUDY: ELECTRON MICROSCOPES
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE DEPTH STUDY: ELECTRON MICROSCOPES Shortly after the experimental confirmation of the wave properties of the electron, it was suggested that the electron could be used to examine objects
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE DEPTH STUDY: ELECTRON MICROSCOPES Shortly after the experimental confirmation of the wave properties of the electron, it was suggested that the electron could be used to examine objects
A wavefront generator for complex pupil function synthesis and point spread function engineering
 Journal of Microscopy, Vol. 197, Pt 3, March 2000, pp. 219±223. Received 27 September 1999; accepted 30 November 1999 SHORT COMMUNICATION A wavefront generator for complex pupil function synthesis and
Journal of Microscopy, Vol. 197, Pt 3, March 2000, pp. 219±223. Received 27 September 1999; accepted 30 November 1999 SHORT COMMUNICATION A wavefront generator for complex pupil function synthesis and
Imaging Retreat - UMASS Customized real-time confocal and 2-photon imaging
 Imaging Retreat - UMASS 2012 Customized real-time confocal and 2-photon imaging Mike Sanderson Department of Microbiology and Physiological Systems University of Massachusetts Medical School Thanks for
Imaging Retreat - UMASS 2012 Customized real-time confocal and 2-photon imaging Mike Sanderson Department of Microbiology and Physiological Systems University of Massachusetts Medical School Thanks for
CREATING ROUND AND SQUARE FLATTOP LASER SPOTS IN MICROPROCESSING SYSTEMS WITH SCANNING OPTICS Paper M305
 CREATING ROUND AND SQUARE FLATTOP LASER SPOTS IN MICROPROCESSING SYSTEMS WITH SCANNING OPTICS Paper M305 Alexander Laskin, Vadim Laskin AdlOptica Optical Systems GmbH, Rudower Chaussee 29, 12489 Berlin,
CREATING ROUND AND SQUARE FLATTOP LASER SPOTS IN MICROPROCESSING SYSTEMS WITH SCANNING OPTICS Paper M305 Alexander Laskin, Vadim Laskin AdlOptica Optical Systems GmbH, Rudower Chaussee 29, 12489 Berlin,
Wide-Field TCSPC FLIM with bh SPC-150 N TCSPC System and Photek FGN Detector
 Wide-Field TCSPC FLIM with bh SPC-150 N TCSPC System and Photek FGN 392-1000 Detector Abstract: We present a wide-field TCSPC FLIM system consisting of a position-sensitive MCP PMT of the delay-line type,
Wide-Field TCSPC FLIM with bh SPC-150 N TCSPC System and Photek FGN 392-1000 Detector Abstract: We present a wide-field TCSPC FLIM system consisting of a position-sensitive MCP PMT of the delay-line type,
BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS PLATFORM EPFL SV PTBIOP LASER SCANNING CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY PRACTICAL CONSIDERATIONS
 LASER SCANNING CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY PRACTICAL CONSIDERATIONS IMPORTANT PARAMETERS Pixel dwell time Zoom and pixel number PIXEL DWELL TIME How much time signal is collected at every pixel Very small values,
LASER SCANNING CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY PRACTICAL CONSIDERATIONS IMPORTANT PARAMETERS Pixel dwell time Zoom and pixel number PIXEL DWELL TIME How much time signal is collected at every pixel Very small values,
Digital Camera Technologies for Scientific Bio-Imaging. Part 2: Sampling and Signal
 Digital Camera Technologies for Scientific Bio-Imaging. Part 2: Sampling and Signal Yashvinder Sabharwal, 1 James Joubert 2 and Deepak Sharma 2 1. Solexis Advisors LLC, Austin, TX, USA 2. Photometrics
Digital Camera Technologies for Scientific Bio-Imaging. Part 2: Sampling and Signal Yashvinder Sabharwal, 1 James Joubert 2 and Deepak Sharma 2 1. Solexis Advisors LLC, Austin, TX, USA 2. Photometrics
Metrology and Sensing
 Metrology and Sensing Lecture 5: Confocal sensors 08-0-08 Herbert Gross Winter term 07 www.iap.uni-jena.de Preliminary Schedule No Date Subject Detailed Content 9.0. Introduction Introduction, optical
Metrology and Sensing Lecture 5: Confocal sensors 08-0-08 Herbert Gross Winter term 07 www.iap.uni-jena.de Preliminary Schedule No Date Subject Detailed Content 9.0. Introduction Introduction, optical
Three-dimensional quantitative phase measurement by Commonpath Digital Holographic Microscopy
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 19 (2011) 291 295 International Conference on Optics in Precision Engineering and Nanotechnology Three-dimensional quantitative phase measurement
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 19 (2011) 291 295 International Conference on Optics in Precision Engineering and Nanotechnology Three-dimensional quantitative phase measurement
Study of Graded Index and Truncated Apertures Using Speckle Images
 Study of Graded Index and Truncated Apertures Using Speckle Images A. M. Hamed Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Ain Shams University, Cairo, 11566 Egypt amhamed73@hotmail.com Abstract- In this
Study of Graded Index and Truncated Apertures Using Speckle Images A. M. Hamed Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Ain Shams University, Cairo, 11566 Egypt amhamed73@hotmail.com Abstract- In this
Ron Liu OPTI521-Introductory Optomechanical Engineering December 7, 2009
 Synopsis of METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR IMPROVING VISION AND THE RESOLUTION OF RETINAL IMAGES by David R. Williams and Junzhong Liang from the US Patent Number: 5,777,719 issued in July 7, 1998 Ron Liu OPTI521-Introductory
Synopsis of METHOD AND APPARATUS FOR IMPROVING VISION AND THE RESOLUTION OF RETINAL IMAGES by David R. Williams and Junzhong Liang from the US Patent Number: 5,777,719 issued in July 7, 1998 Ron Liu OPTI521-Introductory
Theoretical modeling and evaluation of the axial resolution of the adaptive optics scanning laser ophthalmoscope
 Journal of Biomedical Optics 9(1), 132 138 (January/February 2004) Theoretical modeling and evaluation of the axial resolution of the adaptive optics scanning laser ophthalmoscope Krishnakumar Venkateswaran
Journal of Biomedical Optics 9(1), 132 138 (January/February 2004) Theoretical modeling and evaluation of the axial resolution of the adaptive optics scanning laser ophthalmoscope Krishnakumar Venkateswaran
Practical Flatness Tech Note
 Practical Flatness Tech Note Understanding Laser Dichroic Performance BrightLine laser dichroic beamsplitters set a new standard for super-resolution microscopy with λ/10 flatness per inch, P-V. We ll
Practical Flatness Tech Note Understanding Laser Dichroic Performance BrightLine laser dichroic beamsplitters set a new standard for super-resolution microscopy with λ/10 flatness per inch, P-V. We ll
Towards 3-Dimensional and time sequenced (4D) live cell imaging
 Towards 3-Dimensional and time sequenced (4D) live cell imaging Colloquium presented by Heather Campbell Supervisor: Alan Greenaway (Waves and Fields Group) In collaboration with the HW Nano-Optics Group;
Towards 3-Dimensional and time sequenced (4D) live cell imaging Colloquium presented by Heather Campbell Supervisor: Alan Greenaway (Waves and Fields Group) In collaboration with the HW Nano-Optics Group;
Confocal microscopy using variable-focal-length microlenses and an optical fiber bundle
 Published in Applied Optics 44, issue 28, 5928-5936, 2005 which should be used for any reference to this work 1 Confocal microscopy using variable-focal-length microlenses and an optical fiber bundle Lisong
Published in Applied Optics 44, issue 28, 5928-5936, 2005 which should be used for any reference to this work 1 Confocal microscopy using variable-focal-length microlenses and an optical fiber bundle Lisong
Adaptive optics in digital micromirror based confocal microscopy P. Pozzi *a, D.Wilding a, O.Soloviev a,b, G.Vdovin a,b, M.
 Adaptive optics in digital micromirror based confocal microscopy P. Pozzi *a, D.Wilding a, O.Soloviev a,b, G.Vdovin a,b, M.Verhaegen a a Delft Center for Systems and Control, Delft University of Technology,
Adaptive optics in digital micromirror based confocal microscopy P. Pozzi *a, D.Wilding a, O.Soloviev a,b, G.Vdovin a,b, M.Verhaegen a a Delft Center for Systems and Control, Delft University of Technology,
ADVANCED METHODS FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY II. Jean-Yves Chatton Sept. 2006
 ADVANCED METHODS FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY II Jean-Yves Chatton Sept. 2006 Workshop outline Confocal microscopy of living cells and tissues X-Z scanning Time series Bleach: FRAP, photoactivation Emission
ADVANCED METHODS FOR CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY II Jean-Yves Chatton Sept. 2006 Workshop outline Confocal microscopy of living cells and tissues X-Z scanning Time series Bleach: FRAP, photoactivation Emission
Pinhole collimator design for nuclear survey system
 Annals of Nuclear Energy 29 (2002) 2029 2040 www.elsevier.com/locate/anucene Pinhole collimator design for nuclear survey system Wanno Lee*, Gyuseong Cho Department of Nuclear Engineering, Korea Advanced
Annals of Nuclear Energy 29 (2002) 2029 2040 www.elsevier.com/locate/anucene Pinhole collimator design for nuclear survey system Wanno Lee*, Gyuseong Cho Department of Nuclear Engineering, Korea Advanced
Dynamic closed-loop system for focus tracking using a spatial light modulator and a deformable membrane mirror
 Dynamic closed-loop system for focus tracking using a spatial light modulator and a deformable membrane mirror Amanda J. Wright, Brett A. Patterson, Simon P. Poland, John M. Girkin Institute of Photonics,
Dynamic closed-loop system for focus tracking using a spatial light modulator and a deformable membrane mirror Amanda J. Wright, Brett A. Patterson, Simon P. Poland, John M. Girkin Institute of Photonics,
Opti 415/515. Introduction to Optical Systems. Copyright 2009, William P. Kuhn
 Opti 415/515 Introduction to Optical Systems 1 Optical Systems Manipulate light to form an image on a detector. Point source microscope Hubble telescope (NASA) 2 Fundamental System Requirements Application
Opti 415/515 Introduction to Optical Systems 1 Optical Systems Manipulate light to form an image on a detector. Point source microscope Hubble telescope (NASA) 2 Fundamental System Requirements Application
ABSTRACT 1. INTRODUCTION
 High-resolulion, multipleoptical mode confocal microscope: I. System design, image acquisition and 3D visualization Carol J. Cogswell, Kiezan G. Larkin, John W. OByrne, and Matthew R. Amison Department
High-resolulion, multipleoptical mode confocal microscope: I. System design, image acquisition and 3D visualization Carol J. Cogswell, Kiezan G. Larkin, John W. OByrne, and Matthew R. Amison Department
Chapter 2 The Study of Microbial Structure: Microscopy and Specimen Preparation
 Chapter 2 The Study of Microbial Structure: Microscopy and Specimen Preparation 1 Lenses and the Bending of Light light is refracted (bent) when passing from one medium to another refractive index a measure
Chapter 2 The Study of Microbial Structure: Microscopy and Specimen Preparation 1 Lenses and the Bending of Light light is refracted (bent) when passing from one medium to another refractive index a measure
INTRODUCTION TO OPTICAL MICROSCOPY
 Experimental Biophysics TEK265, FYST23, TNF060, FAF010F Lab Exercise Supervisor: Karl Adolfsson Written by Peter Jönsson and Jason Beech Updated by Henrik Persson, Karl Adolfsson and Zhen Li karl.adolfsson@ftf.lth.se
Experimental Biophysics TEK265, FYST23, TNF060, FAF010F Lab Exercise Supervisor: Karl Adolfsson Written by Peter Jönsson and Jason Beech Updated by Henrik Persson, Karl Adolfsson and Zhen Li karl.adolfsson@ftf.lth.se
