Index. b beam quality 951 f beam-stop 86 beat frequency 492 Beer s law 851 bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) 166, 795 ff
|
|
|
- Berniece Rose
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 967 Index a Abbe focometer 890 Abbe number 645 absorption 331 ff absorption coefficient 332 attenuation coefficient 333 Lambert-Beer law 333 scattering coefficient 333 volume scattering function 333 accuracy bias 169 Hartmann sensor 214 Hartmann-Shack sensor 197 linearity 169 overall variation of a measurement system 170 point spread function retrieval 278 precision 170 repeatability 170 reproducibility 170 stability 169 total system variation 173 acousto-optic modulator (AOM) 493 acousto-optic tunable filter 359 ff acousic angle 493 birefringence 363 bragg diffraction at acoustic waves 363 collinear beam AOTF 360 drive power 360 index ellipsoid 362 interaction length 362 non-collinear AOTF 362 peak wavelength 363 phase matching condition 363 polar angel 363 response time 369 spectral resolution 369 transmission 369 tuning range 369 acutance 922 adjustment 907 AIAG (Automotive Industry Action Group) 168 Alvarez lens 756 ff analysis of variance method (ANOVA) 172 angle encoder 524 ff absolute encoder 526 accuracy and error sources 527 basic principles 527 calibration techniques 528 incremental angle encoder 526 angle metrology 524 ff angular resolved scattering (ARS) 795 f aperture size 901 atomic force microscope (AFM) 779, 800 contact mode (static mode) 802 imaging modes 802 non-contact mode 803 principle technique used in an AFM 801 range and resolution of an AFM 804 tapping mode (dynamic mode) 803 autocollimator 528 ff, 910 accuracy and error sources 803 basic principles 803 calibration techniques 532 devices 532 autocorrelation function 939 axial point spread function 918 b beam quality 951 f beam-stop 86 beat frequency 492 Beer s law 851 bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) 166, 795 ff Handbook of Optical Systems: Vol. 5. Metrology of Optical Components and Systems. First Edition. Edited by Herbert Gross. Copyright 2012 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA. Published 2012 by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.
2 968 Index bidirectional scatter distribution function (BSDF) noise equivalent BSDF (NEBSDF) 851 bidirectional scatter distribution function (BSDF) 166, 812 ff bidirectional transmittance distribution function (BTDF) 166 birefringence 664 ff crossed polarizers 166 Fizeau interferometer to measure birefringence 671 indication of drawing 665 ISO Part measurement with electronic polarimeter 672 metrology 672 parallel polarizers 672 residual stress-induced birefringence 664 rotating polarizers setup 666 sample with quadratically rising radial birefringence 666 specifications 666 tolerances 665 bubbles and inclusions 673 ff indication of drawing 674 ISO Part metrology 674 setup to inspect bubbles and inclusions 676 setup to inspect haze caused by inclusions 677 specification of platinum particles 676 specifications 676 c capability of measurement systems 168 carrier-envelope offset frequency (CEO) 505 caustic 35 cavity length 28 ceiling, relative 926 centering 760 ff, 910 ff, 202 adjustment of lens support 28 centering errors 28 centering errors of Hartmann-Shack sensor 202 centering errors of point spread function retrieval 265 centering metrology for aspherical lens elements 28 centering metrology with adjusted lens support 28 centering metrology with unadjusted lens support 28 critical points in centering metrology 28 datum axis 760 datum point 760 indication of drawings 763 inner and outer centering 762 lateral displacement of an aspherical surface 761 lateral displacement of an optical element or subsystem 761 metrology 761 optical axis 760 tilt angle of a spherical surface 760 tilt angle of an aspherical surface 760 tilt angle of an optical element 761 central thickness 689 ff, 907 ff interferometric measurement using short coherent light 761 measurement by contacting (Abbe method) 761 measurement using optical proximity sensors 691 measurement using two chromatical confocal sensors 691 metrology 691 optical measurement from one side 692 specification 689 cesium atomic clock 505 chamfer metrology 776 ff Chebyshev polynomials 702 ff chromatical aberrations 929 coatings 839 ff abrasion resistance 846 absorptance metrology 846 adhesion 846 area imperfections 847 back-surface reflection 867 back-surface reflection suppression 867 band-stop 841 characteristics of an AR multi-layer coating 841 coating tolerance 846 cross-hatch resistance 846 data analysis 846 definition of coatings by function. 846 detector surface reflection 864 diffuse interface 864 graded interfaces 864 integrating sphere setup 864 ISO laser calorimetry arrangement 877 line-like imperfections 847 Magnesium Fluoride MgF2 841 material designation 841
3 Index 969 metrology 841 monochromatic unpolarized photometer setup 859 photothermal effect 877 point-like imperfections 847 quarter-wave system 841 reflectance metrology 841 solubility 846 specification 846 spectral absorptance 846 spectral photometer or polarimeter arrangement 846 spectral polarized photometer setup 860 spectral reflectance 860 spectral scatter 845 spectral transmittance 845 stationary Helmholtz equation 849 surface roughness 854 Tantalum Pentoxide Ta2O5 841 total transfer matrix 850 transfer-matrix method 850 transition matrix 850 transmittance metrology 850 transmittance of plane-parallel elements 850 V-N setup 850 volume imperfections 847 V-W setup 871 coefficients of thermal expansion (CTE) 153 coherence coherence function 19 coherence length 19 coherence time 19 correlation function 19 partial coherence in Hartmann sensor 216 colored glas filter band-pass filter 19 edge wavelength 345 internal transmission 344 Limit of blocking range 344 Limit of pass range 346 long-pass filter 345 luminescense 348 short-pass filter 345 solarization 348 temperature influence on colored glass filters 348 combined distance and Aagle metrology 540 ff compensator 589 ff Babinet compensator 348 Babinet-Soleil compensator 348 photoelastic modulator (PEM) 590 compensator plate 56 ff complex numbers 8 computer-generated hologram (CGH) 122, 729 ff amplitude grating 8 calculating the structures of a CGH 8 CGH with ring-shaped focus control zone 740 deflection angle as a function of groove density 733 groove depth 731 Littrow angle as a function of groove density 734 Littrow arrangement 733 local grating period 732 maximum grating density in a CGH 740 off-axis CGH as a null corrector 734 phase grating 734 theoretical diffraction efficiencies 732 confocal sensor 517 ff, 892 chromatic confocal sensor 122 coaxial interferometric sensor 122 monochromatic confocal sensor 122 conic surface with elliptical principal sections 752 ff contrast 897 corner cube 493 ff criterion 893 focus 893 f Hopkins 941 MTF 941 SQF 942 Thomas 920 d dead path 497 deflectometer 432, 890 accuracy and error sources 497 algorithms 469 basic setups 469 calibration 469 deflectometer to test mirrors 467 deflectometer to test strongly curved surfaces 468 geometric parameters for a deflectometer 466 resolution 471 to test transmissive test samples 465 depolarization 560, 572 depolarizer 591 ff Cornu depolarizer 572 Lyot depolarizer 592 quartz-silica wedge depolarizer 592
4 970 Index detection of flux 338 ff light guide value 592 diameter metrology 776 ff diattenuation 560, 957 of tilted glass plates 574 dispersion-free material 22 displacement metrology absolute displacement-measuring Interferometer 22 short-range 22 thickness 22 to measure the tilt of a plane mirror 22 distortion metrology accuracy and error sources 22 basic setups 22 calibration 463 correlation masks 463 correlation method 463 cross-correlation 463 dynamic range 463 MoirØ technique 463 of systems 929 sinusoidal masks 463 Doppler effect 19 Doppler shift 492 double-frequency grating 80 Duffieux integral 939 dynameter 902 dynamic range improvements 143 improvements 143 in surface topometry 140 lateral dynamic range 143 lateral resolution 143 limitations 143 maximum fringe density 142 of Hartmann-Shack sensor 194 using a single point detector 141 e edge 230, 688, 917 f, 932 defect 922 displacement 928 measurement 917 model function 935 steepness 921 width 920 edge spread function 919 f, 933 EdlØn formula 153 electro-optic effect 587 ff elementary beam of radiation 323 f ellipsometer 622 ff accuracy and error sources 153 calibration techniques 153 null ellipsometer 629 PCm SAr arrangement 631 PCmSA arrangement 634 PCrSCr A arrangement 633 Pr SA arrangement 633 PrCSA arrangement 633 PSCmA arrangement 634 PSCrA arrangement 632 rotating analyzer ellipsometer (RAE) 632 spectroscopic ellipsometer 632 systematic errors 636 to measure complex reflectivities 628 encircled energy (EE) 443, 917 energy of radiation 305 ff electric field strength 306 dielectricity 306 electromagnetic field 306 energy density 306 irradiance 308 magnetic field strength 306 magnetic permeability 306 phase velocity 307 Poynting vector 307 refraction index 307 wave vector 306 entropy 897 envelope detection 502 environmental limitations 496 error sources Abbe error 62 acoustics 160 air turbulence 496 conduction 159 convection 157 cosine error 157 dark current noise 162 data age uncertainty 499 environmental noise 167 erroneous reflections 167 figure error of the mirror surface 497 fixed-pattern noise 162 Hartmann-Shack sensor 195 imperfect components 497 imperfections in AR-coatings 497 instrument errors 499 misalignment of components 498 overlap error 498 polarization leakage error 497 radiation 158 readout noise 162 sound 160 thermal stability 153
5 Index 971 transfer noise 162 vibrations 149 ESF 919 f f F-number 51 Fabry-PØrot resonator 37 Fabry-PØrot-etalon 349 ff finesse 37 free spectral range 350 FWHM 350 multiple FabryPØrot-etalon 350 spectral resolution 351 tuning Fabry-PØrot-etalon 352 Faraday effect 588 femtosecond frequency combs 504 femtosecond pulse laser 504 five-sample-adaptive algorithm (FSA) 502 Fizeau interferferometer 49 Fizeau surface 49, 122 focal length 887 ff focimeter 889 focometer 890 focus criterion 893 Foucault test 230 f, 688, 917 f Fourier spectrometer 411 ff spatially modulated Fourier spectrometer 51 spectral resolution 51 temporally modulated Fourier spectrometer 51 Fresnel equations 37, 39 fringe analysis asymmetric kernel 101 CarrØ algorithm 107 convolution kernel 101 detuning error 101 discrete convolution 101 erroneous fringes 101 error sources 97 Gaussian window 99 indicator function 116 lateral resolution 116 least-squares phase detection 95 least-squares procedure 95 multi-fringe interferogram 108 nonlinearity error 105 phase-shifting interferometry 98 simultaneous phase-shifting interferometry 112 spatial carrier frequency analysis 107 statistical phase fluctuations 107 synchronous detection 107 Takeda algorithm 108 two-dimensional convolution kernel 110 unwrapped phase 115 unwrapping 115 unwrapping in the presence of noise 118 von Hann window 99 window function 99 wrapped phase 115 fringes bright fringes 115 concentric circular interference rings 41 dark fringes 41 fluffing fringe contrast 23 fringe contrast 16 fringe profile 16 fringe spacing 16 fringe visibility 16 Haidinger fringes 16 Newton fringes 16 of equal inclination 16 of equal thickness 16 of two waves with different wavelengths 18 sinusoidal shape 18 straight parallel and equally spaced 18 full-well capacity 163 fundamental law of radiometry 321 ff g Gauge capability ratio (GCR) 175 Gauge R&R analysis 170 Gauss method 888 Gaussian irradiance profile 85 Gaussian oscillator 852 geometry of optical components 679 ff Gerchberg-Saxton 270 f ghost image 950 glare index 950 glare spread function 950 goniometer spectrometer Abbe arrangement 650 goniometer spectrometer 647 ff grating image 936 grating monochromator 387 ff angular dispersion 650 blazed diffraction grating 650 concave grating monochromator 650 configurations of grating monochromators 650 constant deflection angle 650 Czerny-Turner monochromator 400 diffraction at gratings 400 diffraction efficiency 395
6 972 Index Fastie-Ebert monochromator 395 free spectral range 395 grating equation 388 linear dispersion 397 resolving power 397 spectral bandwidth 398 spectral resolution 398 throughput 398 h harmonic oscillator 852 Hartmann sensor 208 ff accuracy 214 apodization 218 partial coherence 216 Hartmann-Shack sensor 183 ff averaging 197 calibration 204 centering error 202 cross-talk 195 diameter adaptation 189 dynamic range 194 error sources 195 layout 192 relay lens 190 setup 187 Height Transfer Function 112 Hindle test 132 ff holographic modal sensor 240 Hopkins factor 941 Huygens principle 34, 37 i IFTA 270 f illumination 948 image contrast 931 degradation 926 gradient 895, 897 quality 912 ff, 941 image analysis 432 ff, 912 ff calibration principles 435 mask-projecting system 433 performance criteria 912 ff system setup 432 image gradient 895, 897 image location 892 f image quality 912 ff infinite series 38, 40 inhomogeneity 655 ff Fizeau interferometer to measure inhomogeneity 432 indication of drawing 657 ISO Part measurement at polished samples 660 measurement in immersion tank 661 metrology 661 oil-on-plates sandwich method 661 specification 656 integrating sphere 821, 946 intensity moments 915 interface-radiation through 324 ff Fresnel equations 656 polarization 326 reflectivity 326 transmissivity 326 interference contrast 19 of non-spherical wavefronts 33 of two monochromatic waves with statistically phase 20 of two plane waves 12 of two spherical waves 14 of two waves which have a spectrum 21 of waves having different polarization 31 with extended monochromatic light sources 27 interference filter 352 ff all-dielectric interference filter 27 central wavelength 357 circular wedge filters 357 effective refraction index 356 FWHM 357 linear wedge filters 357 peak transmission wavelength 354 thermo-optic tuning 358 interference microscope 804 ff differential interference contrast microscope (DIC) 358 examples of interference microscope objectives 806 for very rough surfaces 811 Linnik interference microscope 807 Michelson objective 807 Mirau objective 807 Nomarski arrangement 807 reference-free interference microscope 807 interferometer absolute displacement-measuring interferometer 807 accuracy 807 common-path 44 compensating system 121 cyclic Interferometer 121
7 Index 973 displacement-measuring interferometer 121 double-pass 121 environmental limitations 148 equal-path 44 error sources 44 Fizeau interferometer 49 grating angle shearing interferometer 78 heterodyne 491 homodyne 491 Jamin interferometer 491 lateral-shear 44 low-coherence 44 Mach-Zehnder interferometer 44 mechanical stability 149 Michelson interferometer 149 multiple-beam 44 multiple-pass 44 Newton interferometer 44 null-system 121 point diffraction interferometer (PDI) 121 radial-shear 44 reversal-shear 44 rotational-shear 44 shearing interferometer 44 single-pass 44 Smartt interferometer 44, 235 two-beam 44 Twyman-Green interferometer 44 unequal-path 44 Williams interferometer 60 interferometer calibration averaging of non-rotationally symmetric errors 126 ball averaging 131 calibration of non-rotationally symmetric errors 124 calibration procedures to determine element deviations 122 calibration techniques 120 cat s eye position 123 deviation of a reference element 121 liquid surface 121 non-rotationally symmetric deviations 124 reference elements with known residual error 121 retrace error of an interferometer 121 rotating sphere 131 rotationally symmetric deviations 124 shift-rotation technique 125 three-flat test 128 three-flat test extended to spherical surfaces 129 three-position technique 122 well-known reference surface 121 interferometer design beam expansion 85 bulls eye 93 distortion 91 field curvature 89 holographic optical element 94 lateral resolution 86 reduction of coherent artefacts 91 rotating diffuser disk 93 internal transmittance 335 optical density 335 ISO standard 885 j Jamin interferometer 491 Jones calculus 561 ff, 956 Jones matrix 563 ff determination from measured Jones vectors 567 for different polarizing elements 566 measurement of the Jones matrix 566 of selected optical components 566 Jones pupil 956 Jones vector 561 measurement of Jones vector 566 measurement with compensator and rotating polarizer 599 k Kepler-type telescope 58, 63 Kerr effect 588 knife edge method (Foucault test) 230, 688, 917 f, 932 kurtosis 954 l Lambertian radiator 321 Larkin, Kieran 502 laser tracker 544 ff accuracy and error sources 502 basic principles 545 calibration techniques 547 devices 547 lens position 907 line spread function 919, 923 ff, 936 linear encoder absolute type 514 accuracy and error sources 514 calibration techniques 515 diffraction scale encoder 513 hologram scale encoder 513
8 974 Index incremental type 513 MoirØ method 512 reference mark 513 liquid crystal polarization grating free spectral range 513 spectral resolution 513 tuning range 513 liquid crystal tunable filter 369 ff free spectral range 373 FWHM 373 Lyot-Ohman filter 373 response time 373 spectral resolution 373 tuning range 373 Lorentz oscillator 852 LSF 919, 923 ff, 936 Lyot test 235 Lçber, August f m M2 951 f Mach, Ernst 62 Mach-Zehnder interferometer 44 magneto-optic effect 587 ff magnification 900 f Maltese cross 957 manufacturing specifications 886 matt surface 787 Maxwell s equations 4 mean radial profile 706 f measurement system analysis (MSA) 168 Michelson, Albert 56 Michelson interferometer 149 microdefects 787 microlens array 183 microscope lens 904 minimum deflection angle of a prism 648 modal method 285 modulation transfer function 930 ff moire deflectometry 890 moments of intensity 915 monochromatic wave 7 monochromator 341 f absorption filter 7 colored glass filter 7 mount techniques for optical elements 710 f three-ball mount to support lens elements 712 Mueller matrix 570, 959 measurement of complete Mueller matrix 712 measurement of Mueller matrix elements 712 of selected optical components 712 of systems 954 n Newton interferometer 44 noise CCD Noise Sources 162 non-ambiguity range 507 null corrector 727 ff in a Fizeau interferometer 728 matrix system in a Fizeau interferometer 728 null-system of interferometers 121 Nyquist limit 86 f, 112, 142 o OCT 908 oil plates 54 optical profile metrology 548 ff accuracy and error sources 550, 554 calibration techniques 550, 555 CMM with optical sensors 555 deflectometry 555 devices using angle sensors 555 extended shear angle difference method (ESAD) 555 long trace profiler (LTP) 555 multiple-distance sensor module (MDS) 555 setup to measure optical freeform surfaces 549 traceable multi-sensor technique (TMS) 549 optical transfer function (OTF) 443, 930 ff OTF 443, 930 ff p pattern and fringe projectors accuracy and error sources 443 algorithms 479 basic setups 471 calibration 479 calibration plate with well-known fiducials 482 central projection 475 intrinsic and extrinsic parameters 480 invisible regions 477 pattern projection 477 photogrammetry 478 resolution 484 Scheimpflug condition 476 telecentric projection 474 triangulation 474
9 Index 975 pattern projection 432 performance specifications 886 phase retrieval 249 ff accuracy 278 algorithms 270 apodization 274 centering 265 illumination 254 image processing 262 model 258 object space defocusing 275 principle 251 pinhole deconvolution 267 setup 253 phase space analyzer 219 ff layout 222 wave optical description 227 phase-stabilized frequency comb 505 photometric quantities 314 ff v-lambda function 315 aqueous humour 314 candela 314 CIE standard photometric observer 316 cones 316 cornea 314 eye 314 iris 314 mesopic vision 315 photopic vision 315 retina 314 rods 314 scotopic vision 315 spectral luminous efficacy of radiation 316 vitreous humour 314 plane parallel plate transmittance through 335 ff plane wave 6 planotoric or cylindrical surface 751 point diffraction interferometer (PDI) 121 point diffraction plate 67 ff point image filtering 230 f point spread function (PSF) 443 ff, 914 ff axial 918 intensity moments 915 phase retrieval 249 ff Strehl ratio 915 f polarimeter 605 ff, 622 ff complete/incomplete Mueller polarimeter 622 dual-pem setup PCmSCmA 627 PCmSA arrangement 627 PCrSCrA arrangement 627 PrCSA arrangement 627 PrSA arrangement 627 PrSAr arrangement 627 PSrA arrangement 627 used to measure birefringence 622 using PEMs 622 polarization aberrations 954 by reflection 573 birefringent polarizer 575 dichroic polarizer 575 Glan-Foucault prism 575 Glan-Taylor prism 575 Glan-Thompson prism 575 Nicol prism 576 of systems 954 of tilted glass plates 573 polarizing beam-splitter cubes 576 Rochon prism 576 thin-film or interference polarizer 579 wire-grid polarizer 579 Wollaston prism 579 polarizer 572 ff polarizing beam-splitter 574 f polarizing elements 572 ff power in the bucket 917 power spectral density (PSD) 789 ff 1D power spectral density function 790 2D power spectral density function 790 2D-isotropical PSD 790 precision to tolerance ratio P/T 175 principal planes 898 prism monochromator 375 ff Abbe prism 175 angular dispersion 175 constant deflection by a dispersion prism 175 deflection by a prism 175 dispersion 383 linear dispersion 383 minimum deflection of a dispersion prism 383 Pellin-Broca prism 379 resolving power 379 spectral bandwidth 384 spectral resolution 384 throughput 384 Wadsworth arrangement 378 PSD 789 ff PSF 443 ff, 914 ff pupil location 901 pyramid curvature sensor 239
10 976 Index q quantum characteristics of radiation actinometry 319 Avogadro number 320 dose 320 Einstein 320 electron volt 320 photon 320 Planck s constant f r radiance invariance 324 radiometric quantities 309 ff irradiance 309 projection of irradiance 310 radiance 310 radiant energy 312 radiant exitance 310 radiant exposure 312 radiant flux 309 radiant intensity 309 radiant power 309 solid angle 309 spectral radiometric quantities 314 radius of curvature 681 ff as a function of temperature 688 bar spherometer 685 deflectometry 688 error sources 687 Foucault test (knife-edge test) 230, 688, 917 f interferometry against a plane reference surface 688 ISO Part metrology 681 relative radius error 685 sagitta error 681 specification 681 spherometer 683 test-glass method 683 test-glass method in a Fizeau interferometer 683 three-leg spherometer 683 total surface deviation function 681 traveling microscope method 688 two-position test 688 Rayleigh criterion 30 refractive index immersion compensation 647 metrology 647 of the prism 648 specification 645 subscripts for associated wavelength 645 tolerances 646 relative ceiling 926 retardance 560, 957 retarder 582 ff circular retarder 560 Fresnel double rhomb 585 Fresnel rhomb 585 half-waveplate 583 linear retarder 583 optically active component 587 Pockels cell 587 quarter-waveplate 583 rhomb 583 waveplate 583 Ritchey-Common test in different angular positions 583 with a circular-shaped mirror under test 583 with a non-circular-shaped mirror under test 583 Ronchi grating 890, 894, 903 Ronchi test 230 f rotationally symmetric aspherical surfaces 735 ff s scanning probe microscopy (SPM) 800 ff characteristics of SPMs 583 SPM for large samples 802 scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) 800 scattering by optical surfaces 794 ff scatterometer 812 ff ARS scatterometer 800 ASTM standard for TIS 818 backward scatter TIS measurement 818 BSDF scatterometer 818 calibration 816 Coblentz sphere 816 forward scatter TIS measurement 819 integrating sphere factor M 819 near specular geometry 815 receiver unit configuration 814 signature of BSDF scatterometer 815 TIS scatterometer 817 TS and TIS measurement with integrating sphere 821 Ulbricht sphere (integrating sphere) 821 second-order surface 751 Sellmeier equation 646 Senarmont method 623 f shearing interferometer 44 shear plate 77 signal-to-noise ratio (S/N or SNR) 162 f
11 Index 977 slope measurement 287 Smartt interferometer 235 Sommargren, Gary 70 specific OPD changes 156 specifications 884 manufacturing 886 of optical materials 644 ff performance 886 speckle effects 165 spectral transmission 947 spectrometer 402 ff calibrarion of wavelength scale 165 calibration of radiant flux 165 chopper 406 detection monochromator 404 double-beam spectrometer 404 illumination monochromator 403 multi-channel device 403 multi-channel spectrometer 403 photometric accuracy 403 single channel device 403 single-beam spectrometer 405 single-channel spectrometer 405 spectral reflectance 404 spectral resolution of multichannel spectrometers 409 spectral transmittance 404 spectrophotometer 402 spectroradiometer 402 wavelength accuracy 420 specular surface 787 spherical wave 8, 14 SQF criterion 942 star test, slit test 442 ff, 787 f, 914 ff, 923 ff accuracy and error sources 787 Airy pattern 787 annular aperture 437 array of point sources 442 calibration 442 dimensions of star mask 442 image deconvolution 443 star image irradiance distribution 443 to test afocal systems 443 steepness 921 stitching technique 145 ff Stokes vector 568 ff measurement of Stokes vector 443 measurement of Stokes vector using PEM and polarizer 443 Stokes/Mueller calculus 568 ff stray light 50 ff, 86, 950 Strehl ratio 915 f striae 655 ff indication of drawing 657 ISO Part metrology 657 shadowgraph image simulation 664 shadowgraph setup 664 specification 657 striae model 657 structural content 944 Struve ratio 925 super luminescent diode (SLD) 503 surface form and figure irregularities 694 ff Alvarez lens to test second-order and toric surfaces 757 approximating aspherical surface 695 approximating spherical surface 695 concentric lens elements 695 D/R-diagram for transmission spheres 721 decomposition 698 effective reference surface 698 environmental conditions 712 finite element method (FEM) 709 Fizeau surface 719 geometrical parameters for ring-zone testing of aspheres 749 gravity and orientation 749 horizontal interferometer and a vertical test beam 711 horizontal interferometric setup 710 indication of drawing 697 interferograms for surfaces using transmission sphere 723 interferometer using short coherent light to test 716 interferometric setup to test aspherical back surfaces 742 irregularity 695 irregularity function 695 ISO Part limitations for surfaces to test by transmission sphere 720 local retrace error 747 metrology 747 misalignment when testing surfaces 747 misalignments of spherical surfaces 747 oblique incidence interferometer by means of a prism 718 peak-to-valley (PV) difference 695 principal surface of a transmission sphere 695 productivity 695 retrace error compensation 747 ring-zone testing 747
12 978 Index rms asymmetry, RMSa 696 rms irregularity, RMSi 696 rotationally symmetric irregularity 695 sagitta error 695 specification 695 spherical lens elements with problematic geometry 726 spurious reflections 714 subaperture testing 714 surface-form deviation 694 surface-form measuring interferometers 694 test tower arrangement 724 testing freeform surfaces 724 testing generalized second-order and toric surfaces 724 testing in oblique incidence 717 testing plane surfaces 717 testing rotationally symmetric aspherical surfaces 717 testing surfaces with full compensation 755 testing surfaces with partial compensation 759 testing surfaces with refractive null systems 759 testing spherical surfaces 759 testing with diffractive null systems (CGHs) 759 testing with fully compensated setup 759 testing with partially compensated 759 testing with refractive null systems 759 total rms deviation, RMSt 695 total surface deviation function 695 transmission spheres 695 uncompensated testing 695 uncompensated testing of surfaces 759 various null systems to measure aspherical surfaces 737 wavefront error function 698 surface imperfections 823 ff analogue microscope image comparator (MIC) 698 bright-field detector 828 comparison of methods I and II 835 dark-field detector 829 indication in drawings 829 inspection using a stray-light sensor 830 inspection using an integrating sphere (method II) 830 metrology 830 obscured or affected area method (method I) 830 size designation for surface imperfections 824 specification 824 visibility class designations 826 visibility method (method II) 823 surface texture 785 ff band limited roughness 790 bandwidths of texture measuring instruments 797 grade numbers, permissible number of microdefects 793 indication in drawings 793 metrology 793 microdefects 793 power spectral density (PSD) 793 specification 793 surface roughness Rq 793 surface waviness 793 tactile profilometer 793 typical parameters of tactile profilometers 799 system performance 883 t tabletop compliance 152 Talbot effect 244 f, 891 telecentricity 905 f Tenengrad 895 test glass 45 ff test pattern 432 ff, 543 ff, 932 accuracy and error sources 543 amplitude modulation 543 basic principles 543 calibration techniques 544 checkerboard 152 chirped circular grid 434 chirped linear grid 434 circular spot grid 434 concentric equidistant rings 434 devices 544 polarization modulation 543 random pattern 434 rings and spokes 433 Siemens star 434 single circular spot 433 single slit 433 time-of-flight 541 uniform equidistant grid 433 USAF target 433 theodolite and total station 541 ff thermal coefficients of different materials 154 Thomas criterion 920
13 Index 979 Ti:sapphire (titanium-sapphire) laser 505 ff tilt metrology 524 ff, 910 ff accuracy and error sources 154 calibration techniques 534 differential heterodyne laser interferometer 534 displacement-measuring interferometer 534 surface-measuring interferometer 534 time-of-flight measurement 505 ff toric surface 752 ff toroidal lens 221 total integrated scatter (TIS) 795 f total internal reflection 904 total scatter (TS) 795 f transfer function 930 ff transmission 945 f transmission flat 53, 85, 128, 714 ff transmission sphere 49 ff, 719 ff transmittance absorption coefficient 654 internal transmittance 654 metrology 654 of systems 945 f photochromic sample 655 reflection factor 651 specification 651 spectral photometer 654 transmittance photometer light sources 653 transport of intensity equation 249 triangulation 432 triangulator 515 ff tunable repetition rate 509 Twyman-Green interferometer 44 v V-edge surface 752 ff vector perturbation theories (VPT) 796 veiling glare 950 Verdet constant 588 vertex position 909 vibration specifications 150 vibration-isolation system 149 ff vignetting 948 visual inspection 450 w wavefront 912 wavefront sensor 183 ff Williams interferometer 60 wire test 230 f Wolter test 235 z Zehnder, Ludwig 62 Zeiss, Carl 45 Zernike polynomials 283 ff, 288 ff, 699 ff, 894, 959 calculation 288 normalization radius 291 propagation 292 Zernike test 235 zonal method 284
14
Handbook of Optical Systems
 Handbook of Optical Systems Volume 5: Metrology of Optical Components and Systems von Herbert Gross, Bernd Dörband, Henriette Müller 1. Auflage Handbook of Optical Systems Gross / Dörband / Müller schnell
Handbook of Optical Systems Volume 5: Metrology of Optical Components and Systems von Herbert Gross, Bernd Dörband, Henriette Müller 1. Auflage Handbook of Optical Systems Gross / Dörband / Müller schnell
J. C. Wyant Fall, 2012 Optics Optical Testing and Testing Instrumentation
 J. C. Wyant Fall, 2012 Optics 513 - Optical Testing and Testing Instrumentation Introduction 1. Measurement of Paraxial Properties of Optical Systems 1.1 Thin Lenses 1.1.1 Measurements Based on Image Equation
J. C. Wyant Fall, 2012 Optics 513 - Optical Testing and Testing Instrumentation Introduction 1. Measurement of Paraxial Properties of Optical Systems 1.1 Thin Lenses 1.1.1 Measurements Based on Image Equation
Optics and Lasers. Matt Young. Including Fibers and Optical Waveguides
 Matt Young Optics and Lasers Including Fibers and Optical Waveguides Fourth Revised Edition With 188 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Contents
Matt Young Optics and Lasers Including Fibers and Optical Waveguides Fourth Revised Edition With 188 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Contents
Index. Optical Shop Testing, Third Edition Edited by Daniel Malacara Copyright # 2007 John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Index Aberration function, 499 Aberration, spherical of aspherical surfaces, 839 Aberration function secondary, 504 Schwarzschild, 504 Aberrations, 83, 259, 348, 408, 410, 416 astigmatism of a concave
Index Aberration function, 499 Aberration, spherical of aspherical surfaces, 839 Aberration function secondary, 504 Schwarzschild, 504 Aberrations, 83, 259, 348, 408, 410, 416 astigmatism of a concave
Metrology and Sensing
 Metrology and Sensing Lecture 10: Holography 2017-12-21 Herbert Gross Winter term 2017 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule No Date Subject Detailed Content 1 19.10. Introduction Introduction, optical
Metrology and Sensing Lecture 10: Holography 2017-12-21 Herbert Gross Winter term 2017 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule No Date Subject Detailed Content 1 19.10. Introduction Introduction, optical
Optical Signal Processing
 Optical Signal Processing ANTHONY VANDERLUGT North Carolina State University Raleigh, North Carolina A Wiley-Interscience Publication John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York / Chichester / Brisbane / Toronto
Optical Signal Processing ANTHONY VANDERLUGT North Carolina State University Raleigh, North Carolina A Wiley-Interscience Publication John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York / Chichester / Brisbane / Toronto
Gerhard K. Ackermann and Jurgen Eichler. Holography. A Practical Approach BICENTENNIAL. WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA
 Gerhard K. Ackermann and Jurgen Eichler Holography A Practical Approach BICENTENNIAL BICENTENNIAL WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Contents Preface XVII Part 1 Fundamentals of Holography 1 1 Introduction
Gerhard K. Ackermann and Jurgen Eichler Holography A Practical Approach BICENTENNIAL BICENTENNIAL WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Contents Preface XVII Part 1 Fundamentals of Holography 1 1 Introduction
Basics of INTERFEROMETRY
 Basics of INTERFEROMETRY P Hariharan CSIRO Division of Applied Sydney, Australia Physics ACADEMIC PRESS, INC. Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, Publishers Boston San Diego New York London Sydney Tokyo Toronto
Basics of INTERFEROMETRY P Hariharan CSIRO Division of Applied Sydney, Australia Physics ACADEMIC PRESS, INC. Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, Publishers Boston San Diego New York London Sydney Tokyo Toronto
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS AND OPTICAL DESIGN
 GEOMETRICAL OPTICS AND OPTICAL DESIGN Pantazis Mouroulis Associate Professor Center for Imaging Science Rochester Institute of Technology John Macdonald Senior Lecturer Physics Department University of
GEOMETRICAL OPTICS AND OPTICAL DESIGN Pantazis Mouroulis Associate Professor Center for Imaging Science Rochester Institute of Technology John Macdonald Senior Lecturer Physics Department University of
Metrology and Sensing
 Metrology and Sensing Lecture 7: Wavefront sensors 2016-11-29 Herbert Gross Winter term 2016 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule No Date Subject Detailed Content 1 18.10. Introduction Introduction,
Metrology and Sensing Lecture 7: Wavefront sensors 2016-11-29 Herbert Gross Winter term 2016 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule No Date Subject Detailed Content 1 18.10. Introduction Introduction,
instruments Solar Physics course lecture 3 May 4, 2010 Frans Snik BBL 415 (710)
 Solar Physics course lecture 3 May 4, 2010 Frans Snik BBL 415 (710) f.snik@astro.uu.nl www.astro.uu.nl/~snik info from photons spatial (x,y) temporal (t) spectral (λ) polarization ( ) usually photon starved
Solar Physics course lecture 3 May 4, 2010 Frans Snik BBL 415 (710) f.snik@astro.uu.nl www.astro.uu.nl/~snik info from photons spatial (x,y) temporal (t) spectral (λ) polarization ( ) usually photon starved
R.B.V.R.R. WOMEN S COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS) Narayanaguda, Hyderabad.
 R.B.V.R.R. WOMEN S COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS) Narayanaguda, Hyderabad. DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS QUESTION BANK FOR SEMESTER III PAPER III OPTICS UNIT I: 1. MATRIX METHODS IN PARAXIAL OPTICS 2. ABERATIONS UNIT II
R.B.V.R.R. WOMEN S COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS) Narayanaguda, Hyderabad. DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS QUESTION BANK FOR SEMESTER III PAPER III OPTICS UNIT I: 1. MATRIX METHODS IN PARAXIAL OPTICS 2. ABERATIONS UNIT II
Will contain image distance after raytrace Will contain image height after raytrace
 Name: LASR 51 Final Exam May 29, 2002 Answer all questions. Module numbers are for guidance, some material is from class handouts. Exam ends at 8:20 pm. Ynu Raytracing The first questions refer to the
Name: LASR 51 Final Exam May 29, 2002 Answer all questions. Module numbers are for guidance, some material is from class handouts. Exam ends at 8:20 pm. Ynu Raytracing The first questions refer to the
Basics of INTERFEROMETRY
 Basics of INTERFEROMETRY Second Edition P. HARIHARAN School ofphysics, Sydney, Australia University of Sydney CPi AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE
Basics of INTERFEROMETRY Second Edition P. HARIHARAN School ofphysics, Sydney, Australia University of Sydney CPi AMSTERDAM BOSTON HEIDELBERG LONDON NEW YORK OXFORD PARIS SAN DIEGO SAN FRANCISCO SINGAPORE
Optical Information Processing. Adolf W. Lohmann. Edited by Stefan Sinzinger. Ch>
 Optical Information Processing Adolf W. Lohmann Edited by Stefan Sinzinger Ch> Universitätsverlag Ilmenau 2006 Contents Preface to the 2006 edition 13 Preface to the third edition 15 Preface volume 1 17
Optical Information Processing Adolf W. Lohmann Edited by Stefan Sinzinger Ch> Universitätsverlag Ilmenau 2006 Contents Preface to the 2006 edition 13 Preface to the third edition 15 Preface volume 1 17
Opti 415/515. Introduction to Optical Systems. Copyright 2009, William P. Kuhn
 Opti 415/515 Introduction to Optical Systems 1 Optical Systems Manipulate light to form an image on a detector. Point source microscope Hubble telescope (NASA) 2 Fundamental System Requirements Application
Opti 415/515 Introduction to Optical Systems 1 Optical Systems Manipulate light to form an image on a detector. Point source microscope Hubble telescope (NASA) 2 Fundamental System Requirements Application
3.0 Alignment Equipment and Diagnostic Tools:
 3.0 Alignment Equipment and Diagnostic Tools: Alignment equipment The alignment telescope and its use The laser autostigmatic cube (LACI) interferometer A pin -- and how to find the center of curvature
3.0 Alignment Equipment and Diagnostic Tools: Alignment equipment The alignment telescope and its use The laser autostigmatic cube (LACI) interferometer A pin -- and how to find the center of curvature
06SurfaceQuality.nb Optics James C. Wyant (2012) 1
 06SurfaceQuality.nb Optics 513 - James C. Wyant (2012) 1 Surface Quality SQ-1 a) How is surface profile data obtained using the FECO interferometer? Your explanation should include diagrams with the appropriate
06SurfaceQuality.nb Optics 513 - James C. Wyant (2012) 1 Surface Quality SQ-1 a) How is surface profile data obtained using the FECO interferometer? Your explanation should include diagrams with the appropriate
Difrotec Product & Services. Ultra high accuracy interferometry & custom optical solutions
 Difrotec Product & Services Ultra high accuracy interferometry & custom optical solutions Content 1. Overview 2. Interferometer D7 3. Benefits 4. Measurements 5. Specifications 6. Applications 7. Cases
Difrotec Product & Services Ultra high accuracy interferometry & custom optical solutions Content 1. Overview 2. Interferometer D7 3. Benefits 4. Measurements 5. Specifications 6. Applications 7. Cases
Lens Design I. Lecture 3: Properties of optical systems II Herbert Gross. Summer term
 Lens Design I Lecture 3: Properties of optical systems II 205-04-8 Herbert Gross Summer term 206 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule 04.04. Basics 2.04. Properties of optical systrems I 3 8.04.
Lens Design I Lecture 3: Properties of optical systems II 205-04-8 Herbert Gross Summer term 206 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule 04.04. Basics 2.04. Properties of optical systrems I 3 8.04.
CONTENTS. Chapter 1 Wave Nature of Light 19
 CONTENTS Chapter 1 Wave Nature of Light 19 1.1 Light Waves in a Homogeneous Medium 19 A. Plane Electromagnetic Wave 19 B. Maxwell's Wave Equation and Diverging Waves 22 Example 1.1.1 A diverging laser
CONTENTS Chapter 1 Wave Nature of Light 19 1.1 Light Waves in a Homogeneous Medium 19 A. Plane Electromagnetic Wave 19 B. Maxwell's Wave Equation and Diverging Waves 22 Example 1.1.1 A diverging laser
Use of Computer Generated Holograms for Testing Aspheric Optics
 Use of Computer Generated Holograms for Testing Aspheric Optics James H. Burge and James C. Wyant Optical Sciences Center, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721 http://www.optics.arizona.edu/jcwyant,
Use of Computer Generated Holograms for Testing Aspheric Optics James H. Burge and James C. Wyant Optical Sciences Center, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ 85721 http://www.optics.arizona.edu/jcwyant,
Optical Design with Zemax
 Optical Design with Zemax Lecture : Correction II 3--9 Herbert Gross Summer term www.iap.uni-jena.de Correction II Preliminary time schedule 6.. Introduction Introduction, Zemax interface, menues, file
Optical Design with Zemax Lecture : Correction II 3--9 Herbert Gross Summer term www.iap.uni-jena.de Correction II Preliminary time schedule 6.. Introduction Introduction, Zemax interface, menues, file
Handbook of Optical Systems
 Handbook of Optical Systems Edited by Herbert Gross Volume 3: Aberration Theory and Correction of Optical Systems Herbert Cross, Hannfried Zügge, Martin Peschka, Fritz Blechinger BICENTENNIAL BICENTENNIA
Handbook of Optical Systems Edited by Herbert Gross Volume 3: Aberration Theory and Correction of Optical Systems Herbert Cross, Hannfried Zügge, Martin Peschka, Fritz Blechinger BICENTENNIAL BICENTENNIA
INTRODUCTION TO ABERRATIONS IN OPTICAL IMAGING SYSTEMS
 INTRODUCTION TO ABERRATIONS IN OPTICAL IMAGING SYSTEMS JOSE SASIÄN University of Arizona ШШ CAMBRIDGE Щ0 UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface Acknowledgements Harold H. Hopkins Roland V. Shack Symbols 1 Introduction
INTRODUCTION TO ABERRATIONS IN OPTICAL IMAGING SYSTEMS JOSE SASIÄN University of Arizona ШШ CAMBRIDGE Щ0 UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface Acknowledgements Harold H. Hopkins Roland V. Shack Symbols 1 Introduction
Computer Generated Holograms for Optical Testing
 Computer Generated Holograms for Optical Testing Dr. Jim Burge Associate Professor Optical Sciences and Astronomy University of Arizona jburge@optics.arizona.edu 520-621-8182 Computer Generated Holograms
Computer Generated Holograms for Optical Testing Dr. Jim Burge Associate Professor Optical Sciences and Astronomy University of Arizona jburge@optics.arizona.edu 520-621-8182 Computer Generated Holograms
Metrology and Sensing
 Metrology and Sensing Lecture 13: Metrology of aspheres and freeforms 017-01-17 Herbert Gross Winter term 016 www.iap.uni-jena.de Preliminary Schedule No Date Subject Detailed Content 1 18.10. Introduction
Metrology and Sensing Lecture 13: Metrology of aspheres and freeforms 017-01-17 Herbert Gross Winter term 016 www.iap.uni-jena.de Preliminary Schedule No Date Subject Detailed Content 1 18.10. Introduction
Lens Design I. Lecture 3: Properties of optical systems II Herbert Gross. Summer term
 Lens Design I Lecture 3: Properties of optical systems II 207-04-20 Herbert Gross Summer term 207 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule - Lens Design I 207 06.04. Basics 2 3.04. Properties of optical
Lens Design I Lecture 3: Properties of optical systems II 207-04-20 Herbert Gross Summer term 207 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule - Lens Design I 207 06.04. Basics 2 3.04. Properties of optical
OPTICAL IMAGING AND ABERRATIONS
 OPTICAL IMAGING AND ABERRATIONS PARTI RAY GEOMETRICAL OPTICS VIRENDRA N. MAHAJAN THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION AND THE UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA SPIE O P T I C A L E N G I N E E R I N G P R E S S A
OPTICAL IMAGING AND ABERRATIONS PARTI RAY GEOMETRICAL OPTICS VIRENDRA N. MAHAJAN THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION AND THE UNIVERSITY OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA SPIE O P T I C A L E N G I N E E R I N G P R E S S A
Metrology and Sensing
 Metrology and Sensing Lecture 1: Phase retrieval 018-01-18 Herbert Gross Winter term 017 www.iap.uni-jena.de Preliminary Schedule No Date Subject Detailed Content 1 19.10. Introduction Introduction, optical
Metrology and Sensing Lecture 1: Phase retrieval 018-01-18 Herbert Gross Winter term 017 www.iap.uni-jena.de Preliminary Schedule No Date Subject Detailed Content 1 19.10. Introduction Introduction, optical
Warren J. Smith Chief Scientist, Consultant Rockwell Collins Optronics Carlsbad, California
 Modern Optical Engineering The Design of Optical Systems Warren J. Smith Chief Scientist, Consultant Rockwell Collins Optronics Carlsbad, California Fourth Edition Me Graw Hill New York Chicago San Francisco
Modern Optical Engineering The Design of Optical Systems Warren J. Smith Chief Scientist, Consultant Rockwell Collins Optronics Carlsbad, California Fourth Edition Me Graw Hill New York Chicago San Francisco
Index. Cambridge University Press An Introduction to Practical Laboratory Optics J. F. James. Index.
 aberrations 13 chromatic 14, 171 lateral 14, 163 longitudinal 14, 163 geometric, 50, 75, 90, 92 off-axis 14, 26, 30 optical 162 et seq. Seidel 162 spherical 13, 163 albedo 41 alignment 80, 92 aperture
aberrations 13 chromatic 14, 171 lateral 14, 163 longitudinal 14, 163 geometric, 50, 75, 90, 92 off-axis 14, 26, 30 optical 162 et seq. Seidel 162 spherical 13, 163 albedo 41 alignment 80, 92 aperture
Section 5 ISO Drawings ISO 10110
 Section 5 ISO 10110 Drawings Optical Drawings provide a precise Definition of your optic for fabrication. Standards allow for a common language to be used between you and the optician so there is no confusion
Section 5 ISO 10110 Drawings Optical Drawings provide a precise Definition of your optic for fabrication. Standards allow for a common language to be used between you and the optician so there is no confusion
TSBB09 Image Sensors 2018-HT2. Image Formation Part 1
 TSBB09 Image Sensors 2018-HT2 Image Formation Part 1 Basic physics Electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves With energy That propagate through space The waves consist of transversal
TSBB09 Image Sensors 2018-HT2 Image Formation Part 1 Basic physics Electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves With energy That propagate through space The waves consist of transversal
Testing Aspheric Lenses: New Approaches
 Nasrin Ghanbari OPTI 521 - Synopsis of a published Paper November 5, 2012 Testing Aspheric Lenses: New Approaches by W. Osten, B. D orband, E. Garbusi, Ch. Pruss, and L. Seifert Published in 2010 Introduction
Nasrin Ghanbari OPTI 521 - Synopsis of a published Paper November 5, 2012 Testing Aspheric Lenses: New Approaches by W. Osten, B. D orband, E. Garbusi, Ch. Pruss, and L. Seifert Published in 2010 Introduction
Why is There a Black Dot when Defocus = 1λ?
 Why is There a Black Dot when Defocus = 1λ? W = W 020 = a 020 ρ 2 When a 020 = 1λ Sag of the wavefront at full aperture (ρ = 1) = 1λ Sag of the wavefront at ρ = 0.707 = 0.5λ Area of the pupil from ρ =
Why is There a Black Dot when Defocus = 1λ? W = W 020 = a 020 ρ 2 When a 020 = 1λ Sag of the wavefront at full aperture (ρ = 1) = 1λ Sag of the wavefront at ρ = 0.707 = 0.5λ Area of the pupil from ρ =
Fizeau interferometer with spherical reference and CGH correction for measuring large convex aspheres
 Fizeau interferometer with spherical reference and CGH correction for measuring large convex aspheres M. B. Dubin, P. Su and J. H. Burge College of Optical Sciences, The University of Arizona 1630 E. University
Fizeau interferometer with spherical reference and CGH correction for measuring large convex aspheres M. B. Dubin, P. Su and J. H. Burge College of Optical Sciences, The University of Arizona 1630 E. University
LEOK-3 Optics Experiment kit
 LEOK-3 Optics Experiment kit Physical optics, geometrical optics and fourier optics Covering 26 experiments Comprehensive documents Include experiment setups, principles and procedures Cost effective solution
LEOK-3 Optics Experiment kit Physical optics, geometrical optics and fourier optics Covering 26 experiments Comprehensive documents Include experiment setups, principles and procedures Cost effective solution
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2003 Final Exam. Name:
 EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2003 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. THREE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2003 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. THREE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
BEAM HALO OBSERVATION BY CORONAGRAPH
 BEAM HALO OBSERVATION BY CORONAGRAPH T. Mitsuhashi, KEK, TSUKUBA, Japan Abstract We have developed a coronagraph for the observation of the beam halo surrounding a beam. An opaque disk is set in the beam
BEAM HALO OBSERVATION BY CORONAGRAPH T. Mitsuhashi, KEK, TSUKUBA, Japan Abstract We have developed a coronagraph for the observation of the beam halo surrounding a beam. An opaque disk is set in the beam
Some of the important topics needed to be addressed in a successful lens design project (R.R. Shannon: The Art and Science of Optical Design)
 Lens design Some of the important topics needed to be addressed in a successful lens design project (R.R. Shannon: The Art and Science of Optical Design) Focal length (f) Field angle or field size F/number
Lens design Some of the important topics needed to be addressed in a successful lens design project (R.R. Shannon: The Art and Science of Optical Design) Focal length (f) Field angle or field size F/number
The Fiber-Optic Gyroscope
 The Fiber-Optic Gyroscope Second Edition Herve C. Lefevre ARTECH HOUSE BOSTON LONDON artechhouse.com Contents Preface to the First Edition Preface to the Second Edition xvii xix Introduction 1 References
The Fiber-Optic Gyroscope Second Edition Herve C. Lefevre ARTECH HOUSE BOSTON LONDON artechhouse.com Contents Preface to the First Edition Preface to the Second Edition xvii xix Introduction 1 References
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy
 Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
OPAC 202 Optical Design and Instrumentation. Topic 3 Review Of Geometrical and Wave Optics. Department of
 OPAC 202 Optical Design and Instrumentation Topic 3 Review Of Geometrical and Wave Optics Department of http://www.gantep.edu.tr/~bingul/opac202 Optical & Acustical Engineering Gaziantep University Feb
OPAC 202 Optical Design and Instrumentation Topic 3 Review Of Geometrical and Wave Optics Department of http://www.gantep.edu.tr/~bingul/opac202 Optical & Acustical Engineering Gaziantep University Feb
Practical Guide to Specifying Optical Components
 Practical Guide to Specifying Optical Components OPTI 521 Introduction to Opto-Mechanical Engineering Fall 2012 December 10, 2012 Brian Parris Introduction This paper is intended to serve as a practical
Practical Guide to Specifying Optical Components OPTI 521 Introduction to Opto-Mechanical Engineering Fall 2012 December 10, 2012 Brian Parris Introduction This paper is intended to serve as a practical
Lens Design II. Lecture 11: Further topics Herbert Gross. Winter term
 Lens Design II Lecture : Further topics 28--8 Herbert Gross Winter term 27 www.iap.uni-ena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule Lens Design II 27 6.. Aberrations and optimization Repetition 2 23.. Structural modifications
Lens Design II Lecture : Further topics 28--8 Herbert Gross Winter term 27 www.iap.uni-ena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule Lens Design II 27 6.. Aberrations and optimization Repetition 2 23.. Structural modifications
PHY 431 Homework Set #5 Due Nov. 20 at the start of class
 PHY 431 Homework Set #5 Due Nov. 0 at the start of class 1) Newton s rings (10%) The radius of curvature of the convex surface of a plano-convex lens is 30 cm. The lens is placed with its convex side down
PHY 431 Homework Set #5 Due Nov. 0 at the start of class 1) Newton s rings (10%) The radius of curvature of the convex surface of a plano-convex lens is 30 cm. The lens is placed with its convex side down
Interference [Hecht Ch. 9]
![Interference [Hecht Ch. 9] Interference [Hecht Ch. 9]](/thumbs/79/79365345.jpg) Interference [Hecht Ch. 9] Note: Read Ch. 3 & 7 E&M Waves and Superposition of Waves and Meet with TAs and/or Dr. Lai if necessary. General Consideration 1 2 Amplitude Splitting Interferometers If a lightwave
Interference [Hecht Ch. 9] Note: Read Ch. 3 & 7 E&M Waves and Superposition of Waves and Meet with TAs and/or Dr. Lai if necessary. General Consideration 1 2 Amplitude Splitting Interferometers If a lightwave
Sensitive measurement of partial coherence using a pinhole array
 1.3 Sensitive measurement of partial coherence using a pinhole array Paul Petruck 1, Rainer Riesenberg 1, Richard Kowarschik 2 1 Institute of Photonic Technology, Albert-Einstein-Strasse 9, 07747 Jena,
1.3 Sensitive measurement of partial coherence using a pinhole array Paul Petruck 1, Rainer Riesenberg 1, Richard Kowarschik 2 1 Institute of Photonic Technology, Albert-Einstein-Strasse 9, 07747 Jena,
Solution of Exercises Lecture Optical design with Zemax Part 6
 2013-06-17 Prof. Herbert Gross Friedrich Schiller University Jena Institute of Applied Physics Albert-Einstein-Str 15 07745 Jena Solution of Exercises Lecture Optical design with Zemax Part 6 6 Illumination
2013-06-17 Prof. Herbert Gross Friedrich Schiller University Jena Institute of Applied Physics Albert-Einstein-Str 15 07745 Jena Solution of Exercises Lecture Optical design with Zemax Part 6 6 Illumination
Understanding Optical Specifications
 Understanding Optical Specifications Optics can be found virtually everywhere, from fiber optic couplings to machine vision imaging devices to cutting-edge biometric iris identification systems. Despite
Understanding Optical Specifications Optics can be found virtually everywhere, from fiber optic couplings to machine vision imaging devices to cutting-edge biometric iris identification systems. Despite
Lens Design II. Lecture 11: Further topics Herbert Gross. Winter term
 Lens Design II Lecture : Further topics 26--2 Herbert Gross Winter term 25 www.iap.uni-ena.de Preliminary Schedule 2 2.. Aberrations and optimization Repetition 2 27.. Structural modifications Zero operands,
Lens Design II Lecture : Further topics 26--2 Herbert Gross Winter term 25 www.iap.uni-ena.de Preliminary Schedule 2 2.. Aberrations and optimization Repetition 2 27.. Structural modifications Zero operands,
Observational Astronomy
 Observational Astronomy Instruments The telescope- instruments combination forms a tightly coupled system: Telescope = collecting photons and forming an image Instruments = registering and analyzing the
Observational Astronomy Instruments The telescope- instruments combination forms a tightly coupled system: Telescope = collecting photons and forming an image Instruments = registering and analyzing the
Chapter 16 Light Waves and Color
 Chapter 16 Light Waves and Color Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. What causes color? What causes reflection? What causes color?
Chapter 16 Light Waves and Color Lecture PowerPoint Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. What causes color? What causes reflection? What causes color?
Introduction. Geometrical Optics. Milton Katz State University of New York. VfeWorld Scientific New Jersey London Sine Singapore Hong Kong
 Introduction to Geometrical Optics Milton Katz State University of New York VfeWorld Scientific «New Jersey London Sine Singapore Hong Kong TABLE OF CONTENTS PREFACE ACKNOWLEDGMENTS xiii xiv CHAPTER 1:
Introduction to Geometrical Optics Milton Katz State University of New York VfeWorld Scientific «New Jersey London Sine Singapore Hong Kong TABLE OF CONTENTS PREFACE ACKNOWLEDGMENTS xiii xiv CHAPTER 1:
Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics. Geometrical Approximation. Lenses. Mirrors. Optical Systems. Images and Pupils. Aberrations.
 Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics Outline 1 Geometrical Approximation 2 Lenses 3 Mirrors 4 Optical Systems 5 Images and Pupils 6 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden Observatory, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics Outline 1 Geometrical Approximation 2 Lenses 3 Mirrors 4 Optical Systems 5 Images and Pupils 6 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden Observatory, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Introduction to Imaging Spectrometers
 Introduction to Imaging Spectrometers William L. Wolfe Professor Emeritus, Optical Sciences Center, University of Arizona Tutorial Texts in Optical Engineering Volume TT25 Donald С O'Shea, Series Editor
Introduction to Imaging Spectrometers William L. Wolfe Professor Emeritus, Optical Sciences Center, University of Arizona Tutorial Texts in Optical Engineering Volume TT25 Donald С O'Shea, Series Editor
Chemistry 524--"Hour Exam"--Keiderling Mar. 19, pm SES
 Chemistry 524--"Hour Exam"--Keiderling Mar. 19, 2013 -- 2-4 pm -- 170 SES Please answer all questions in the answer book provided. Calculators, rulers, pens and pencils permitted. No open books allowed.
Chemistry 524--"Hour Exam"--Keiderling Mar. 19, 2013 -- 2-4 pm -- 170 SES Please answer all questions in the answer book provided. Calculators, rulers, pens and pencils permitted. No open books allowed.
Cardinal Points of an Optical System--and Other Basic Facts
 Cardinal Points of an Optical System--and Other Basic Facts The fundamental feature of any optical system is the aperture stop. Thus, the most fundamental optical system is the pinhole camera. The image
Cardinal Points of an Optical System--and Other Basic Facts The fundamental feature of any optical system is the aperture stop. Thus, the most fundamental optical system is the pinhole camera. The image
Infra Red Interferometers
 Infra Red Interferometers for performance testing of infra-red materials and optical systems Specialist expertise in testing, analysis, design, development and manufacturing for Optical fabrication, Optical
Infra Red Interferometers for performance testing of infra-red materials and optical systems Specialist expertise in testing, analysis, design, development and manufacturing for Optical fabrication, Optical
Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics. Geometrical Approximation. Lenses. Mirrors. Optical Systems. Images and Pupils. Aberrations.
 Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics Outline 1 Geometrical Approximation 2 Lenses 3 Mirrors 4 Optical Systems 5 Images and Pupils 6 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden Observatory, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Lecture 2: Geometrical Optics Outline 1 Geometrical Approximation 2 Lenses 3 Mirrors 4 Optical Systems 5 Images and Pupils 6 Aberrations Christoph U. Keller, Leiden Observatory, keller@strw.leidenuniv.nl
Chapter Ray and Wave Optics
 109 Chapter Ray and Wave Optics 1. An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to [2002] reduce spherical aberration have high resolution increase span of observation have low dispersion. 2. If two
109 Chapter Ray and Wave Optics 1. An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to [2002] reduce spherical aberration have high resolution increase span of observation have low dispersion. 2. If two
Diffraction. Interference with more than 2 beams. Diffraction gratings. Diffraction by an aperture. Diffraction of a laser beam
 Diffraction Interference with more than 2 beams 3, 4, 5 beams Large number of beams Diffraction gratings Equation Uses Diffraction by an aperture Huygen s principle again, Fresnel zones, Arago s spot Qualitative
Diffraction Interference with more than 2 beams 3, 4, 5 beams Large number of beams Diffraction gratings Equation Uses Diffraction by an aperture Huygen s principle again, Fresnel zones, Arago s spot Qualitative
Physics 431 Final Exam Examples (3:00-5:00 pm 12/16/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 120 MINUTES Name: Signature:
 Physics 431 Final Exam Examples (3:00-5:00 pm 12/16/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 120 MINUTES Name: PID: Signature: CLOSED BOOK. TWO 8 1/2 X 11 SHEET OF NOTES (double sided is allowed), AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR
Physics 431 Final Exam Examples (3:00-5:00 pm 12/16/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 120 MINUTES Name: PID: Signature: CLOSED BOOK. TWO 8 1/2 X 11 SHEET OF NOTES (double sided is allowed), AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR
Optical Design of. Microscopes. George H. Seward. Tutorial Texts in Optical Engineering Volume TT88. SPIE PRESS Bellingham, Washington USA
 Optical Design of Microscopes George H. Seward Tutorial Texts in Optical Engineering Volume TT88 SPIE PRESS Bellingham, Washington USA Preface xiii Chapter 1 Optical Design Concepts /1 1.1 A Value Proposition
Optical Design of Microscopes George H. Seward Tutorial Texts in Optical Engineering Volume TT88 SPIE PRESS Bellingham, Washington USA Preface xiii Chapter 1 Optical Design Concepts /1 1.1 A Value Proposition
2.1.3 Diffraction Limited Systems and Connection to Fresnel Diffraction Point Spread Function (PSF) calculation and dimensions...
 Contents 1 Properties of Optical Systems... 7 1.1 Optical Properties of a Single Spherical Surface... 7 1.1.1 Planar efractive Surfaces... 7 1.1.2 Spherical efractive Surfaces... 7 1.1.3 eflective Surfaces...
Contents 1 Properties of Optical Systems... 7 1.1 Optical Properties of a Single Spherical Surface... 7 1.1.1 Planar efractive Surfaces... 7 1.1.2 Spherical efractive Surfaces... 7 1.1.3 eflective Surfaces...
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Fall 2009 Final Exam. Name:
 EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Fall 2009 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. THREE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Fall 2009 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. THREE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
1.6 Beam Wander vs. Image Jitter
 8 Chapter 1 1.6 Beam Wander vs. Image Jitter It is common at this point to look at beam wander and image jitter and ask what differentiates them. Consider a cooperative optical communication system that
8 Chapter 1 1.6 Beam Wander vs. Image Jitter It is common at this point to look at beam wander and image jitter and ask what differentiates them. Consider a cooperative optical communication system that
Optics and photonics Preparation of drawings for optical elements and systems. Part 5: Surface form tolerances
 Provläsningsexemplar / Preview INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 10110-5 Third edition 2015-08-01 Optics and photonics Preparation of drawings for optical elements and systems Part 5: Surface form tolerances
Provläsningsexemplar / Preview INTERNATIONAL STANDARD ISO 10110-5 Third edition 2015-08-01 Optics and photonics Preparation of drawings for optical elements and systems Part 5: Surface form tolerances
OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES
 101 L7 OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES Aims Your aim here should be to acquire a working knowledge of the basic components of optical systems and understand their purpose, function and limitations in terms
101 L7 OPTICAL SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES Aims Your aim here should be to acquire a working knowledge of the basic components of optical systems and understand their purpose, function and limitations in terms
Reflection! Reflection and Virtual Image!
 1/30/14 Reflection - wave hits non-absorptive surface surface of a smooth water pool - incident vs. reflected wave law of reflection - concept for all electromagnetic waves - wave theory: reflected back
1/30/14 Reflection - wave hits non-absorptive surface surface of a smooth water pool - incident vs. reflected wave law of reflection - concept for all electromagnetic waves - wave theory: reflected back
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2002 Final Exam. Name:
 EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2002 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. FOUR 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2002 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. FOUR 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
The Design, Fabrication, and Application of Diamond Machined Null Lenses for Testing Generalized Aspheric Surfaces
 The Design, Fabrication, and Application of Diamond Machined Null Lenses for Testing Generalized Aspheric Surfaces James T. McCann OFC - Diamond Turning Division 69T Island Street, Keene New Hampshire
The Design, Fabrication, and Application of Diamond Machined Null Lenses for Testing Generalized Aspheric Surfaces James T. McCann OFC - Diamond Turning Division 69T Island Street, Keene New Hampshire
Optical Fibers p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Step-Index Fibers p. 2 Graded-Index Fibers p. 4 Design and Fabrication p. 6 Silica Fibers p.
 Preface p. xiii Optical Fibers p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Step-Index Fibers p. 2 Graded-Index Fibers p. 4 Design and Fabrication p. 6 Silica Fibers p. 6 Plastic Optical Fibers p. 9 Microstructure Optical
Preface p. xiii Optical Fibers p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Step-Index Fibers p. 2 Graded-Index Fibers p. 4 Design and Fabrication p. 6 Silica Fibers p. 6 Plastic Optical Fibers p. 9 Microstructure Optical
LuphoScan platforms. Dr. Gernot Berger (Business Development Manager) APOMA Meeting, Tucson, years of innovation
 125 years of innovation (Business Development Manager) APOMA Meeting, Tucson, 2016 HQ in Berwyn, Pennsylvania $4.0 billion in sales (2015) 15,000 colleagues, 150 manufacturing locations, 30 countries Businesses
125 years of innovation (Business Development Manager) APOMA Meeting, Tucson, 2016 HQ in Berwyn, Pennsylvania $4.0 billion in sales (2015) 15,000 colleagues, 150 manufacturing locations, 30 countries Businesses
Introduction to Light Microscopy. (Image: T. Wittman, Scripps)
 Introduction to Light Microscopy (Image: T. Wittman, Scripps) The Light Microscope Four centuries of history Vibrant current development One of the most widely used research tools A. Khodjakov et al. Major
Introduction to Light Microscopy (Image: T. Wittman, Scripps) The Light Microscope Four centuries of history Vibrant current development One of the most widely used research tools A. Khodjakov et al. Major
A novel tunable diode laser using volume holographic gratings
 A novel tunable diode laser using volume holographic gratings Christophe Moser *, Lawrence Ho and Frank Havermeyer Ondax, Inc. 85 E. Duarte Road, Monrovia, CA 9116, USA ABSTRACT We have developed a self-aligned
A novel tunable diode laser using volume holographic gratings Christophe Moser *, Lawrence Ho and Frank Havermeyer Ondax, Inc. 85 E. Duarte Road, Monrovia, CA 9116, USA ABSTRACT We have developed a self-aligned
Alex Lyubarsky OPTI 521 December 8, 2013
 Alex Lyubarsky OPTI 521 December 8, 2013 Introduction to Optical Specification Standards (Section 1) Sections 2-13 of ISO 10110 Standard Specification ISO 10110 Drawings Q & A ISO 10110 standard created
Alex Lyubarsky OPTI 521 December 8, 2013 Introduction to Optical Specification Standards (Section 1) Sections 2-13 of ISO 10110 Standard Specification ISO 10110 Drawings Q & A ISO 10110 standard created
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 7. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 7 UV to IR Components of Optical Basic components of spectroscopic instruments: stable source of radiant energy transparent container to hold sample device
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 7 UV to IR Components of Optical Basic components of spectroscopic instruments: stable source of radiant energy transparent container to hold sample device
Chapter 34 The Wave Nature of Light; Interference. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 34 The Wave Nature of Light; Interference 34-7 Luminous Intensity The intensity of light as perceived depends not only on the actual intensity but also on the sensitivity of the eye at different
Chapter 34 The Wave Nature of Light; Interference 34-7 Luminous Intensity The intensity of light as perceived depends not only on the actual intensity but also on the sensitivity of the eye at different
Metrology and Sensing
 Metrology and Sensing Lecture 13: Metrology of aspheres and freeforms 018-01-5 Herbert Gross Winter term 017 www.iap.uni-jena.de Preliminary Schedule No Date Subject Detailed Content 1 19.10. Introduction
Metrology and Sensing Lecture 13: Metrology of aspheres and freeforms 018-01-5 Herbert Gross Winter term 017 www.iap.uni-jena.de Preliminary Schedule No Date Subject Detailed Content 1 19.10. Introduction
Sub-nanometer Interferometry Aspheric Mirror Fabrication
 UCRL-JC- 134763 PREPRINT Sub-nanometer Interferometry Aspheric Mirror Fabrication for G. E. Sommargren D. W. Phillion E. W. Campbell This paper was prepared for submittal to the 9th International Conference
UCRL-JC- 134763 PREPRINT Sub-nanometer Interferometry Aspheric Mirror Fabrication for G. E. Sommargren D. W. Phillion E. W. Campbell This paper was prepared for submittal to the 9th International Conference
Heisenberg) relation applied to space and transverse wavevector
 2. Optical Microscopy 2.1 Principles A microscope is in principle nothing else than a simple lens system for magnifying small objects. The first lens, called the objective, has a short focal length (a
2. Optical Microscopy 2.1 Principles A microscope is in principle nothing else than a simple lens system for magnifying small objects. The first lens, called the objective, has a short focal length (a
Optical design of a high resolution vision lens
 Optical design of a high resolution vision lens Paul Claassen, optical designer, paul.claassen@sioux.eu Marnix Tas, optical specialist, marnix.tas@sioux.eu Prof L.Beckmann, l.beckmann@hccnet.nl Summary:
Optical design of a high resolution vision lens Paul Claassen, optical designer, paul.claassen@sioux.eu Marnix Tas, optical specialist, marnix.tas@sioux.eu Prof L.Beckmann, l.beckmann@hccnet.nl Summary:
Technical Infomation on Optics
 page 299 Technical Infomation on Optics Terminology 300 Symbols and Sign Convention 305 Explanation of the Legends on Optical Component Drawings 306 Quality Testing of Optical Components and Systems 309
page 299 Technical Infomation on Optics Terminology 300 Symbols and Sign Convention 305 Explanation of the Legends on Optical Component Drawings 306 Quality Testing of Optical Components and Systems 309
Master program "Optical Design"
 University ITMO, Russia WUT, Poland Department of Applied and Computer Optics Photonics Engineering Division http://zif.mchtr.pw.edu.pl Master program "Optical Design" (ACO Department), St. Petersburg
University ITMO, Russia WUT, Poland Department of Applied and Computer Optics Photonics Engineering Division http://zif.mchtr.pw.edu.pl Master program "Optical Design" (ACO Department), St. Petersburg
Dynamic Phase-Shifting Electronic Speckle Pattern Interferometer
 Dynamic Phase-Shifting Electronic Speckle Pattern Interferometer Michael North Morris, James Millerd, Neal Brock, John Hayes and *Babak Saif 4D Technology Corporation, 3280 E. Hemisphere Loop Suite 146,
Dynamic Phase-Shifting Electronic Speckle Pattern Interferometer Michael North Morris, James Millerd, Neal Brock, John Hayes and *Babak Saif 4D Technology Corporation, 3280 E. Hemisphere Loop Suite 146,
Exam Preparation Guide Geometrical optics (TN3313)
 Exam Preparation Guide Geometrical optics (TN3313) Lectures: September - December 2001 Version of 21.12.2001 When preparing for the exam, check on Blackboard for a possible newer version of this guide.
Exam Preparation Guide Geometrical optics (TN3313) Lectures: September - December 2001 Version of 21.12.2001 When preparing for the exam, check on Blackboard for a possible newer version of this guide.
7 CHAPTER 7: REFRACTIVE INDEX MEASUREMENTS WITH COMMON PATH PHASE SENSITIVE FDOCT SETUP
 7 CHAPTER 7: REFRACTIVE INDEX MEASUREMENTS WITH COMMON PATH PHASE SENSITIVE FDOCT SETUP Abstract: In this chapter we describe the use of a common path phase sensitive FDOCT set up. The phase measurements
7 CHAPTER 7: REFRACTIVE INDEX MEASUREMENTS WITH COMMON PATH PHASE SENSITIVE FDOCT SETUP Abstract: In this chapter we describe the use of a common path phase sensitive FDOCT set up. The phase measurements
j Jacobi matrix 295 Index flattening mirror 258 flint glass 231 form tolerance 598, 605 ff free-form aspheres 456 Fresnel zone plate 499, 503 f
 749 a Abbe number 41, 222, 269, 490, 502 aberrations 2, 216 astigmatism 13, 28 axial chromatic aberration 13, 269 axial color 13, 269 chromatic aberrations 2, 13, 187, 268, 280 chromatic difference in
749 a Abbe number 41, 222, 269, 490, 502 aberrations 2, 216 astigmatism 13, 28 axial chromatic aberration 13, 269 axial color 13, 269 chromatic aberrations 2, 13, 187, 268, 280 chromatic difference in
Reflectors vs. Refractors
 1 Telescope Types - Telescopes collect and concentrate light (which can then be magnified, dispersed as a spectrum, etc). - In the end it is the collecting area that counts. - There are two primary telescope
1 Telescope Types - Telescopes collect and concentrate light (which can then be magnified, dispersed as a spectrum, etc). - In the end it is the collecting area that counts. - There are two primary telescope
Lecture 04: Solar Imaging Instruments
 Hale COLLAGE (NJIT Phys-780) Topics in Solar Observation Techniques Lecture 04: Solar Imaging Instruments Wenda Cao New Jersey Institute of Technology Valentin M. Pillet National Solar Observatory SDO
Hale COLLAGE (NJIT Phys-780) Topics in Solar Observation Techniques Lecture 04: Solar Imaging Instruments Wenda Cao New Jersey Institute of Technology Valentin M. Pillet National Solar Observatory SDO
Lens Design I. Lecture 5: Advanced handling I Herbert Gross. Summer term
 Lens Design I Lecture 5: Advanced handling I 2018-05-17 Herbert Gross Summer term 2018 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule - Lens Design I 2018 1 12.04. Basics 2 19.04. Properties of optical systems
Lens Design I Lecture 5: Advanced handling I 2018-05-17 Herbert Gross Summer term 2018 www.iap.uni-jena.de 2 Preliminary Schedule - Lens Design I 2018 1 12.04. Basics 2 19.04. Properties of optical systems
N.N.Soboleva, S.M.Kozel, G.R.Lockshin, MA. Entin, K.V. Galichsky, P.L. Lebedinsky, P.M. Zhdanovich. Moscow Institute ofphysics and Technology
 Computer assisted optics teaching at the Moscow Institute ofphysics and Technology N.N.Soboleva, S.M.Kozel, G.R.Lockshin, MA. Entin, K.V. Galichsky, P.L. Lebedinsky, P.M. Zhdanovich Moscow Institute ofphysics
Computer assisted optics teaching at the Moscow Institute ofphysics and Technology N.N.Soboleva, S.M.Kozel, G.R.Lockshin, MA. Entin, K.V. Galichsky, P.L. Lebedinsky, P.M. Zhdanovich Moscow Institute ofphysics
Criteria for Optical Systems: Optical Path Difference How do we determine the quality of a lens system? Several criteria used in optical design
 Criteria for Optical Systems: Optical Path Difference How do we determine the quality of a lens system? Several criteria used in optical design Computer Aided Design Several CAD tools use Ray Tracing (see
Criteria for Optical Systems: Optical Path Difference How do we determine the quality of a lens system? Several criteria used in optical design Computer Aided Design Several CAD tools use Ray Tracing (see
APPLICATIONS FOR TELECENTRIC LIGHTING
 APPLICATIONS FOR TELECENTRIC LIGHTING Telecentric lenses used in combination with telecentric lighting provide the most accurate results for measurement of object shapes and geometries. They make attributes
APPLICATIONS FOR TELECENTRIC LIGHTING Telecentric lenses used in combination with telecentric lighting provide the most accurate results for measurement of object shapes and geometries. They make attributes
Absolute distance interferometer in LaserTracer geometry
 Absolute distance interferometer in LaserTracer geometry Corresponding author: Karl Meiners-Hagen Abstract 1. Introduction 1 In this paper, a combination of variable synthetic and two-wavelength interferometry
Absolute distance interferometer in LaserTracer geometry Corresponding author: Karl Meiners-Hagen Abstract 1. Introduction 1 In this paper, a combination of variable synthetic and two-wavelength interferometry
Experiment 1: Fraunhofer Diffraction of Light by a Single Slit
 Experiment 1: Fraunhofer Diffraction of Light by a Single Slit Purpose 1. To understand the theory of Fraunhofer diffraction of light at a single slit and at a circular aperture; 2. To learn how to measure
Experiment 1: Fraunhofer Diffraction of Light by a Single Slit Purpose 1. To understand the theory of Fraunhofer diffraction of light at a single slit and at a circular aperture; 2. To learn how to measure
Fabrication of 6.5 m f/1.25 Mirrors for the MMT and Magellan Telescopes
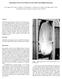 Fabrication of 6.5 m f/1.25 Mirrors for the MMT and Magellan Telescopes H. M. Martin, R. G. Allen, J. H. Burge, L. R. Dettmann, D. A. Ketelsen, W. C. Kittrell, S. M. Miller and S. C. West Steward Observatory,
Fabrication of 6.5 m f/1.25 Mirrors for the MMT and Magellan Telescopes H. M. Martin, R. G. Allen, J. H. Burge, L. R. Dettmann, D. A. Ketelsen, W. C. Kittrell, S. M. Miller and S. C. West Steward Observatory,
Testing Aspherics Using Two-Wavelength Holography
 Reprinted from APPLIED OPTICS. Vol. 10, page 2113, September 1971 Copyright 1971 by the Optical Society of America and reprinted by permission of the copyright owner Testing Aspherics Using Two-Wavelength
Reprinted from APPLIED OPTICS. Vol. 10, page 2113, September 1971 Copyright 1971 by the Optical Society of America and reprinted by permission of the copyright owner Testing Aspherics Using Two-Wavelength
