June : 2016 (CBCS) Negative terminal for forward bias. Positive terminal for forward bias. Cathode ( n-type)
|
|
|
- Lenard Clement Short
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
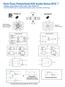
1 s Year : Commo o all raches Jue : 6 (CCS) Noe : Max. marks : 6 (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) emp ay five quesios ou of seve quesios. ll quesios carry equal marks. Draw he ea diagram, wheever ecessary. ssume daa, wherever ecessary. Q. (a) Defie diode. Describe heory of diode operaio. Wha is he applicaio of i? Diode : p jucio forms a popular semicoducor device called p jucio diode. I has wo ermials called elecrodes, oe elecrode each from p regio ad regio hece called diode (Di + elecrode). Posiive ermial for forward bias I F Negaive ermial for forward bias rrowhead idicaes coveioal curre direcio I he symbol of a diode, a arrowhead idicaes he coveioal curre direcio whe i is forward biased. diode allows curre o flow i oly oe direcio. Operaio : Forward bias :. p jucio is forward bias whe a volage is applied posiive o he p side ad egaive o he side.. Whe a diode is coeced i a forward bias, he egaive ermial of he baery pushes he free elecros i regio owards he jucio. Similarly he holes from p regio are repelled by he posiive ermial of he baery ad move owards he jucio. 3. forward biased jucio has a arrow depleio regio. 4. The forward bias applied volage V a origial value V o V V. 5. The elecric field reduces. J 6. The immobile ios i depleio regio reduces. + J a ode ( p-ype) Cahode ( -ype), reduces he barrier poeial across he jucio from is 7. majoriy charge carrier curre flows across a forward bias jucio. V J V a p-regio Depleio regio -regio + V a
2 s Year : Commo o all raches Reverse bias :. p jucio is reverse bias whe a volage is applied posiive o he side ad egaive o he p side. p +. Whe a diode is coeced i a reverse bias, he egaive ermial of he baery aracs he holes i p regio away from he jucio. Similarly he elecros from regio are araced by he posiive ermial of he baery ad move away from he jucio. 3. reverse biased jucio has a wide depleio regio. 4. The reverse bias applied volage V a origial value V o V V. 5. The elecric field icreases. J 6. The immobile ios i depleio regio icreases. J a, icreases he barrier poeial across he jucio from is 7. very small mioriy charge carrier curre flows across a reverse bias jucio. p-regio V J V a V a Depleio regio -regio + pplicaio :. Recifiers which are furher classified as half wave, full wave ad bridge recifiers.. Clipper circuis o remove uwaed porios of waveform. 3. Clamper circuis o add DC level o waveform. 4. Volage mulipliers such as volage doubler, volage ripler ec. 5. Various elecroic ad operaioal amplifier circuis such as volage o curre coverers, log ad ailog amplifiers, precisio recifiers, proecio circuis ec. Q. (b) Wha are he ypes of diode? Lis hem ad draw heir symbol. Types of diode ad heir symbol : V a Name Symbol Geeral purpose diode Zeer diode Schoky diode Varacor/varicap diode
3 3 s Year : Commo o all raches Tuel diode Ligh emiig diode (LED) Phoodiode Pi diode Q. (a) Deermie he decimal umbers represeed by followig biary umbers : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (i) N N N (ii) N N 384 N (iii) () () N N 55 () (55) (iv) N N Q. (b) Perform he followig : (i) ddiio (?) (ii) Subracio (?) (i) ddiio (?)
4 4 s Year : Commo o all raches (ii) Subracio (?) Q.3 (a) Describe he OR, ND, NND gae wih he help of ruh able. ND gae : logic circui whose oupu is HIGH oly whe all ipus are HIGH. Symbol of ND gae : Truh able of ND gae : Ipus Oupu Y Y Oupu is whe all ipus are OR gae : logic circui whose oupu is HIGH whe aleas oe ipu is HIGH. Symbol of OR gae : Truh able of OR gae : Ipus Oupu Y Y Oupu is whe all ipus are NND gae : logic circui whose oupu is LOW whe all ipus are HIGH. Symbol of ipu NND gae : Y Truh able : Ipus Oupu Y Oupu is whe all ipus are
5 5 s Year : Commo o all raches Q.3 (b) Give he logical equaio Y ( C)( C). Desig a circui usig gaes o realize his fucio. Give oolea fucio is, Y ( C)( C) Y CCC C Y C C [ND law : X X X ad X X ] Y C Y C ( ) C ( ) C ( C) [OR law : X X ] Y C C C C C C Y C C C C Y C ( ) C ( ) [OR law : X X ] Logic diagram : Y C C C C C C Q.4 (a) Defie aalog ad digial commuicaios. Draw he basic block diagram of rasmier ad receivers. alog commuicaio : alog commuicaio is ha ypes of commuicaio i which he rasmied message or iformaio sigal is aalog i aure. This meas ha i aalog commuicaio he modulaig sigal i.e. base bad sigal is a aalog sigal. This aalog message sigal may be obaied from sources such as speech, video shooig ec. Digial commuicaio : I digial commuicaio, he message sigal o be rasmied is digial i aure. This meas ha digial commuicaio ivolves he rasmissio of iformaio i digial form. The immuiy o chael oise ad exeral ierferece is beer ha aalog commuicaio. lock diagram of rasmier ad receiver :. Radio rasmier : radio rasmier cosiss of several elemes ha work ogeher o geerae radio waves ha coai useful iformaio such as audio, video, or digial daa. (i) Power supply : I provides he ecessary elecrical power o operae he rasmier. (ii) Oscillaor : I creaes aleraig curre a he frequecy o which he rasmier will rasmi. The oscillaor usually geeraes a sie wave, which is referred o as a carrier wave. (iii) Modulaor : I adds useful iformaio o he carrier wave. There are wo mai ways o add his iformaio. The firs, called ampliude modulaio or M, makes sligh icreases or decreases o he ampliude of he carrier wave. The secod, called frequecy modulaio or FM, makes sligh icreases or decreases he frequecy of he carrier wave. (iv) mplifier : I amplifies he modulaed carrier wave o icrease is power. The more powerful he amplifier, he more powerful he broadcas. (v) ea : I covers he amplified sigal o radio waves.
6 6 s Year : Commo o all raches ea Power supply Oscillaor Modulaor mplifier udio or video iformaio Fig. lock diagram of rasmier. Radio receiver : radio receiver is he opposie of a radio rasmier. I uses a aea o capure radio waves, processes hose waves o exrac oly hose waves ha are vibraig a he desired frequecy, exracs he audio sigals ha were added o hose waves, amplifies he sigals. (i) ea : I capures he radio waves. Typically, he aea is simply a legh of wire. Whe his wire is exposed o radio waves, he waves iduce a very small aleraig curre i he aea. (ii) RF amplifier : sesiive amplifier ha amplifies he very weak radio frequecy (RF) sigal from he aea so ha he sigal ca be processed by he uer. (iii) Tuer : circui ha ca exrac sigals of a paricular frequecy from a mix of sigals of differe frequecies. O is ow, he aea capures radio waves of all frequecies ad seds hem o he RF amplifier, which duifully amplifies hem all. (iv) Deecor : I is resposible for separaig he audio iformaio from he carrier wave. For M sigals, his ca be doe wih a diode ha jus recifies he aleraig curre sigal. (v) udio amplifier : This compoeʹs ask is o amplify he weak sigal ha comes from he deecor so ha i ca be heard. This ca be doe usig a simple rasisor amplifier circui. ea RF amplifier Tuer Deecor Fig. lock diagram of receiver udio amplifier Q.4 (b) Draw he various RF bads of IEEE specrum ad wrie heir applicaios. I wireless commuicaio, elecromageic waves are used as a media for rasfer of iformaio. Thus i such a commuicaio, he iformaio sigal is covered io he elecromageic sigal before rasmissio. The elecromageic (EM) waves cosis of boh elecric ad mageic fields ad hey ca ravel a log disace hrough space. The rage of all possible frequecies of EM waves is called he elecromageic specrum, show i he figure below. I exeds from he frequecies used for moder radio (a he log wavelegh ed) o gamma radiaio (a he shor wavelegh ed). I he mid rage icludes mos commoly used radio frequecies for wo way commuicaios, elevisio ad oher applicaios.
7 7 s Year : Commo o all raches m m m m m m m m 4 3 Wavelegh m m m 3 m 4 m 5.4 x m(viole) 6.7 x m(red) 6 ELF VF VLF LF MF HF VHF UHF SHF EHF Millimeer waves Ifrared Visible ligh Ulraviole X-rays Gamma rays Cosmic rays 3Hz 3Hz 3kHz Fig. Elecromageic specrum The able below shows he radio frequecy specrum ad is applicaio accordig o various frequecy bads. Frequecy bad Frequecy Wavelegh pplicaios Exremely low frequecy (ELF) 3 3 Hz 4 3 km km Commuicaio wih submaries 3 Voice frequecy (VF) 3 3 Hz km km udio applicaio Very low frequecy (VLF) 3 3 khz km km Submarie commuicaio, avalache beacos, wireless hear rae moiors, geophysics Low frequecy (LF) 3 3 khz km km Navigaio, ime sigals, M log wave broadcasig Medium frequecy (MF) 3 3 khz km m M (Medium wave) broadcass High frequecy (HF) 3 3 MHz m m Shorwave broadcass, amaeur radio ad over he horizo aviaio commuicaios Very high frequecy (VHF) Ulra high frequecy (UHF) Super high frequecy (SHF) Exremely high frequecy (EHF) 3kHz 3 khz 3MHz 3MHz 3 MHz 3 3 MHz m m FM, elevisio broadcass ad lie of sigh groud o aircraf ad aircraf o aircraf commuicaios 3 3 MHz 3GHz 3GHz Frequecy 3 GHz m mm Televisio broadcass, mobile phoes, wireless LN, blueooh ad wo way radio such as FRS ad GMRS radios 3 3 GHz mm mm Microwave device, wireless LN, mos moder radars 3 3 GHz mm mm Radio asroomy, high speed microwave radio relay
8 8 s Year : Commo o all raches Q.5 (a) How NOT operaio ca be performed usig rasisor? Describe. Whe ipu X, he base of he rasisor is low () ad herefore rasisor operaes i cu off regio IC. Hece o volage drop across R C ad oupu Y is V CC (HIGH). Whe ipu X, he base of he rasisor is high () ad herefore rasisor operaes i sauraio regio. I he sauraio regio V. V. Hece oupu volage. V, i.e. CE logic (Low). Thus for he circui show i figure oupu is compleme of ipu ad we ca say ha i represes NOT gae. Q.5 (b) Describe various oolea ideiies. Draw he ND circui usig diode logics. Laws of oolea algebra are used for simplifyig a complex oolea expressio. The differe oolea laws are discussed as follows :. OR law : The followig heorems impleme he OR law : (i) Ou of wo variables o be ORed, if ay oe variable is low (), he he oupu value is he oher variable i.e. (ii) Ou of wo variables o be ORed, if ay oe variable is high (), he he oupu value is high i.e. (iii) If boh variables o be ORed have he same value, he he oupu value is of oe ipu variable i.e. (iv) Ou of wo variables o be ORed, if ay oe variable is he compleme of he oher, he he oupu value is high i.e.. ND law : The followig heorems impleme he ND law : (i) Ou of wo variables o be NDded, if ay oe variable is low (), he he oupu value is zero i.e. (ii) Ou of wo variables o be NDed, if ay oe variable is high (), he he oupu value is oher variable i.e. (iii) If boh variables o be NDed have he same value, he he oupu value is also he same of oe of he variable i.e. (iv) Ou of wo variables o be NDed, if ay oe variable is he compleme of he oher, he he oupu value is zero i.e. 3. Commuaive law : I saes ha chagig he sequece of he variables o perform logic operaio does o chage he oupu, which meas ha chage of variable sequece is allowed i.e. X V CC + R C V CE Fig. NOT gae usig rasisor Y
9 9 s Year : Commo o all raches 4. ssociaive law : I saes ha chagig he order of logic operaios does o chage he oupu, which meas ha chagig he order of logic operaios is allowed i.e. ( C) ( ) C ( C) ( ) C 5. Disribuive law : I saes ha NDig he resul of several ORed variables wih a sigle variable is he same as NDig resul wih a idividual variable wih each of he muliple variables, ad is produc is a ORed variable i.e. ( C) C ( C) ( ) ( C) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 6. Complemeaio law : I saes ha he compleme of is, of is, ad of is i.e. 7. bsorpio law : I saes he followig properies : ( ) 8. Idempoecy law : I saes he followig properies : 9. Iversio law : I saes ha if a variable is subjeced o a double iversio ha i will resul i he origial variable iself i.e. ND gae circui usig diode : +5V R + 5V= V = C D D Y Fig. Diode ND gae circui usig posiive logic D 3 I Fig. for posiive logic, if ay of he hree ipus is a V (logic ), he correspodig diode becomes forward biased or coducig showig zero resisace ad hece he volage a Y becomes zero. If all he ipus, ad C are a +5 V (logic ), he diodes are i reversed bias, hece o diode coducs ad he volage a Y will be +V (logic ) This is described wih he help of he ruh able show i Fig..
10 s Year : Commo o all raches C Y Fig. Truh able for ND gae Q.6 (a) Compare half wave recifier wih full wave recifier wih ea skech. S. No. Pariculars HWR FWR. Number of diodes. DC curre I m / Im / 3. DC volage Vm / Vm / 4. RMS curre I m / I / 5. Ripple facor Maximum efficiecy 4.6% 8.% 7. TUF PIV Vm V m 9. Oupu frequecy f f. Form facor.57.. Peak facor.44 m. Figure D R L v + M G V m D i C Ipu N V m D i + R L Q.6 (b) Wha is sigal? Defie. mpliude is impora variable parameers of sigal. Wha kid of operaios ca be performed wih ampliude? Describe. Sigal is a fucio which coveys some iformaio. sigal is defied as a physical quaiy ha varies wih ime, space or ay oher idepede variable. Example : (i) Elecric volage or curre, such as radio sigal, TV sigal, elephoe sigal, compuer sigal ec. (i) Pressure sigal, soud sigal ec. are o elecric sigals. Mahemaically, a sigal is represeed as a fucio of a idepede variable. Usually, represe ime. Thus, a sigal is deoed by x(). Classificaio of sigals :. Coiuous ad discree ime sigals. alog ad digial sigals 3. Deermiisic ad radom sigals 4. Eve ad odd sigals 5. Periodic ad o periodic sigals 6. Eergy ad power sigals
11 s Year : Commo o all raches mpliude scalig : Cosider a sigal x() is provided ad we have o scale or muliply i by facor, where ca be ay value., he ampliude compress by a facor., he he ampliude is sreched by facor. 4 x () x () x () / mpliude iversio : x () x () Example : Cosider a sigal x(). Time For x () mpliude x () x () x () x () x() For x(), muliply ampliude wih. Q.7 (a) Describe differe aalog ad digial sigal i deail. alog sigal : (i) Ui sep sigal : for Ui sep sigal is defied as, u ().5 for for The ui sep sigal is discoiuous a ad a is value is udefied. So, u( ) u( ) u() The ui sep fucio is also kow as Heaviside ui fucio. u () (ii) Ui ramp sigal : Ui ramp sigal is defied as, for r () for
12 s Year : Commo o all raches 3 r () (iii) Ui impulse sigal : The impulse sigal is a sigal wih ifiie magiude ad zero duraio, bu wih ui area. The ui impulse fucio is also kow as he Dirac dela fucio. a Mahemaically, δ( ) ad () d a (iv) Expoeial sigal : Expoeial sigals are of wo ypes : (a) Real expoeial sigal : x() e If, he x() is a growig expoeial, ad if, he x() is a decayig expoeial. x () e ; 3 x () e ; () j (b) Complex expoeial sigal : x() e cos jsi The sigal x() is kow as complex expoeial sigal whose real par is cos ad imagiary par is si. I is periodic wih ime period T π / ω. The geeral complex expoeial sigal is, x e e e j s ( j) () (cos si ) where real par e cos ad imagiary par e si The real par of complex frequecy variable is called aeuaio or growh cosa. I deoes by how much amou ampliude of he sigal is icreased or decreased. The imagiary par of a complex frequecy variable is called agular frequecy wih a usual meaig. Wih ad, x() i.e. cosa ampliude sigal. Wih ad s ad, x() e i.e. expoeially growig sigal. Wih ad s ad, x() e i.e. expoeially decayig sigal. j Wih s j, x () e, i.e. purely siusoidal sigal wih susaied oscillaios. Wih s j ad, we ge siusoidal sigal wih decayig oscillaios. Wih s j ad, we ge siusoidal sigal wih growig oscillaios.
13 3 s Year : Commo o all raches e si ; e si ; Digial sigal : (i) Ui sep sequece : Ui sep sequece is mahemaically defied as, for u ( ) for The value of u ( ) a is defied ad equals uiy. (ii) Ui ramp sequece : Ui ramp sequece is defied as, for r ( ) for r ( ) 3 (iii) Ui sample sequece : Ui sample sequece is defied as, a ( ) a 3 ( ) (iv) Expoeial sequece : Expoeial sequeces are of wo ypes : (a) Real expoeial sequece : x( ) e If, he x( ) is a growig expoeial. If, he x( ) is a decayig expoeial. x ( ) e ; x ( ) e ;
14 4 s Year : Commo o all raches j (b) Complex expoeial sequece : x( ) e cos jsi The sigal x( ) is kow as complex expoeial sigal whose real par is cos ad imagiary par is si. The geeral complex expoeial sigal is, x e e e j s ( j) ( ) (cos si ) whose real par e cos ad imagiary par e si are expoeially icreasig if ad expoeially decreasig if. e si ; e si ; (v) Recagular pulse sequece : Le L be a posiive odd ieger. impora example of a discree ime sigal is he discree ime recagular pulse fucio rec[ ] of legh L defied by,, ( L)/,...,,,,...( L)/ rec[ ], all oher The discree ime recagular pulse is show i figure. rec [ ] ( L ) 3 3 L Q.8 (b) How aalog sigal ca be covered io a digial oe? Describe. alog sigal ca be covered io digial sigal by followig procedure as show i figure below. Sampler Quaizer Ecoder m () m s () m q () T s T s T s 3T s Fig. lock diagram of aalog o digial coverer Sampler : I covers coiuous ampliude coiuous ime sigal io coiuous ampliude discree ime sigal.
15 s Year : Commo o all raches 5 Quaizer : I covers coiuous ampliude discree ime sigal io discree ampliude discree ime sigal. I approximaes each sample io is eares sadard volage level called quaizaio level. I is a process of roudig off he sigal. Ecoder : ecoder covers each quaized sample io disic code word. Thus a he oupu of he ecoder we ge digial code words.
Introduction to Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
 Wireless Iformaio Trasmissio Sysem Lab. Iroducio o Orhogoal Frequecy Divisio Muliplexig OFDM Isiue of Commuicaios Egieerig aioal Su Ya-se Uiversiy OFDM Overview OFDM Sysem Model Orhogoaliy Oulie Muli-carrier
Wireless Iformaio Trasmissio Sysem Lab. Iroducio o Orhogoal Frequecy Divisio Muliplexig OFDM Isiue of Commuicaios Egieerig aioal Su Ya-se Uiversiy OFDM Overview OFDM Sysem Model Orhogoaliy Oulie Muli-carrier
Field-Effect Transistors (FETs) 3.4 The p-channel MOSFET & COMS
 Field-Effec Trasisors (FETs 3.4 The p-chael MOSFET & COMS A p-chael ehaceme-ype MOSFET is fabricaed o a -ype subsrae wih p+ regios for he drai ad source, ad has holes as charge carriers. The deice operaes
Field-Effec Trasisors (FETs 3.4 The p-chael MOSFET & COMS A p-chael ehaceme-ype MOSFET is fabricaed o a -ype subsrae wih p+ regios for he drai ad source, ad has holes as charge carriers. The deice operaes
Handout 10: Pulse-Code Modulation
 ENGG 31-B: Priciples of Commuicaio Sysems Hadou 1: Pulse-Code Modulaio 17 18 Firs Term Isrucor: Wig-Ki Ma November 1, 17 Suggesed Readig: Chaper 7 of Simo Hayki ad Michael Moher, Commuicaio Sysems (5h
ENGG 31-B: Priciples of Commuicaio Sysems Hadou 1: Pulse-Code Modulaio 17 18 Firs Term Isrucor: Wig-Ki Ma November 1, 17 Suggesed Readig: Chaper 7 of Simo Hayki ad Michael Moher, Commuicaio Sysems (5h
Introduction to Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) Technique
 Wireless Iformaio Trasmissio Sysem Lab. Iroducio o Orhogoal Frequecy Divisio Muliplexig (OFDM Techique Isiue of Commuicaios Egieerig Naioal Su Ya-se Uiversiy OFDM Overview OFDM Sysem Model Orhogoaliy Oulie
Wireless Iformaio Trasmissio Sysem Lab. Iroducio o Orhogoal Frequecy Divisio Muliplexig (OFDM Techique Isiue of Commuicaios Egieerig Naioal Su Ya-se Uiversiy OFDM Overview OFDM Sysem Model Orhogoaliy Oulie
Digital Communications (by B. Sklar)
 Digial Commuicaios by B. Sklar Sug Ho Cho Voice 2 222 39 Cellular 11 412 5178 E mail: drago@hayag.ac.kr Coes 1 Sigals ad Specra Formaig ad Basebad Trasmissio Badpass Modulaio ad Demodulaio Chael Codig
Digial Commuicaios by B. Sklar Sug Ho Cho Voice 2 222 39 Cellular 11 412 5178 E mail: drago@hayag.ac.kr Coes 1 Sigals ad Specra Formaig ad Basebad Trasmissio Badpass Modulaio ad Demodulaio Chael Codig
Introduction to OFDM Systems
 Wireless Iformaio Trasmissio Sysem Lab. Iroducio o OFDM Sysems Isiue of Commuicaios Egieerig Naioal Su Ya-se Uiversiy Oulie OFDM Overview OFDM Sysem Model Orhogoaliy Muli-carrier Equivale Implemeaio by
Wireless Iformaio Trasmissio Sysem Lab. Iroducio o OFDM Sysems Isiue of Commuicaios Egieerig Naioal Su Ya-se Uiversiy Oulie OFDM Overview OFDM Sysem Model Orhogoaliy Muli-carrier Equivale Implemeaio by
Experiment 2: Waveform Analysis
 Specrum aalyzer Experime : Waveform Aalysis 8/3/6 his experime is o familiarize you wih he aalysis of sigals ad eworks usig he HP 358A Specrum Aalyzer. he aalysis of sigals is achieved i he ope loop mode
Specrum aalyzer Experime : Waveform Aalysis 8/3/6 his experime is o familiarize you wih he aalysis of sigals ad eworks usig he HP 358A Specrum Aalyzer. he aalysis of sigals is achieved i he ope loop mode
Walsh Function Based Reconstruction Method of. Command Waveform in PWM Inverter
 Walsh Fucio Based Recosrucio Mehod of Commad Waveform i PWM Iverer Kri Choeisai ad Seiji Kodo Nagaoka Uiversiy of echology 63- Kamiomioka, Nagaoka 94-288, Japa Fa: +8-28-4-9, Phoe: +8-28-4-9 E-Mail: kri@s.agaokau.ac.jp
Walsh Fucio Based Recosrucio Mehod of Commad Waveform i PWM Iverer Kri Choeisai ad Seiji Kodo Nagaoka Uiversiy of echology 63- Kamiomioka, Nagaoka 94-288, Japa Fa: +8-28-4-9, Phoe: +8-28-4-9 E-Mail: kri@s.agaokau.ac.jp
R. W. Erickson. Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder
 R. W. Erickso Deparme of Elecrical, Compuer, ad Eergy Egieerig Uiversiy of Colorado, Boulder 4.2.2. The Power MOSFET Gae Source Gae leghs approachig oe micro p - p Cosiss of may small ehacememode parallelcoeced
R. W. Erickso Deparme of Elecrical, Compuer, ad Eergy Egieerig Uiversiy of Colorado, Boulder 4.2.2. The Power MOSFET Gae Source Gae leghs approachig oe micro p - p Cosiss of may small ehacememode parallelcoeced
An Optimization of Gaussian UWB Pulses
 0 h Ieraioal Coferece o DEVELOPMENT AND APPLICATION SYSTEMS, Suceava, Romaia, May 7-9, 00 A Opimizaio of Gaussia UWB Pulses Adria POPA "Gheorghe Asachi" Techical Uiversiy of Iaşi Bd.Carol No., RO0.506
0 h Ieraioal Coferece o DEVELOPMENT AND APPLICATION SYSTEMS, Suceava, Romaia, May 7-9, 00 A Opimizaio of Gaussia UWB Pulses Adria POPA "Gheorghe Asachi" Techical Uiversiy of Iaşi Bd.Carol No., RO0.506
Solution of ECE 342 Test 2 S12
 Soluion of ECE 342 Tes 2 S2. All quesions regarding superheerodyne receivers refer o his diagram. x c () Anenna B T < B RF < 2 f B = B T Oher Signals f c Mixer f Baseband x RFi RF () x RFo () () () x i
Soluion of ECE 342 Tes 2 S2. All quesions regarding superheerodyne receivers refer o his diagram. x c () Anenna B T < B RF < 2 f B = B T Oher Signals f c Mixer f Baseband x RFi RF () x RFo () () () x i
ITERATIVE RECEIVER FOR SPACE-TIME CODED FLAT FADING CHANNELS. Noura Sellami yz, Mohamed Siala y, David Declercq z, Inbar Fijalkow z
 ITERATIVE RECEIVER FOR SPACE-TIME CODED FLAT FADING CHANNELS Noura Sellami yz, Mohamed Siala y, David Declercq z, Ibar Fijalkow z y Frace Telecom R&D, 38-40 rue du Gééral Leclerc 92794 Issy les Moulieaux,
ITERATIVE RECEIVER FOR SPACE-TIME CODED FLAT FADING CHANNELS Noura Sellami yz, Mohamed Siala y, David Declercq z, Ibar Fijalkow z y Frace Telecom R&D, 38-40 rue du Gééral Leclerc 92794 Issy les Moulieaux,
ECE ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS - INVESTIGATION 7 INTRODUCTION TO AMPLITUDE MODULATION - PART II
 ECE 405 - ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS - INVESTIGATION 7 INTRODUCTION TO AMPLITUDE MODULATION - PART II FALL 2005 A.P. FELZER To do "well" on his invesigaion you mus no only ge he righ answers bu mus also do
ECE 405 - ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS - INVESTIGATION 7 INTRODUCTION TO AMPLITUDE MODULATION - PART II FALL 2005 A.P. FELZER To do "well" on his invesigaion you mus no only ge he righ answers bu mus also do
EE123 Digital Signal Processing
 Aoucemes EE3 Digial Sigal Processig Lecure Miderm: Friday ex week Ope everyhig... bu chea shee recommeded isead Who ca o say ill pm? Opioal homework ex week Will give you miderm ad pracice quesios How
Aoucemes EE3 Digial Sigal Processig Lecure Miderm: Friday ex week Ope everyhig... bu chea shee recommeded isead Who ca o say ill pm? Opioal homework ex week Will give you miderm ad pracice quesios How
A1 K. 12V rms. 230V rms. 2 Full Wave Rectifier. Fig. 2.1: FWR with Transformer. Fig. 2.2: Transformer. Aim: To Design and setup a full wave rectifier.
 2 Full Wave Recifier Aim: To Design and seup a full wave recifier. Componens Required: Diode(1N4001)(4),Resisor 10k,Capacior 56uF,Breadboard,Power Supplies and CRO and ransformer 230V-12V RMS. + A1 K B1
2 Full Wave Recifier Aim: To Design and seup a full wave recifier. Componens Required: Diode(1N4001)(4),Resisor 10k,Capacior 56uF,Breadboard,Power Supplies and CRO and ransformer 230V-12V RMS. + A1 K B1
Lecture 5: DC-DC Conversion
 1 / 31 Lecure 5: DC-DC Conversion ELEC-E845 Elecric Drives (5 ECTS) Mikko Rouimo (lecurer), Marko Hinkkanen (slides) Auumn 217 2 / 31 Learning Oucomes Afer his lecure and exercises you will be able o:
1 / 31 Lecure 5: DC-DC Conversion ELEC-E845 Elecric Drives (5 ECTS) Mikko Rouimo (lecurer), Marko Hinkkanen (slides) Auumn 217 2 / 31 Learning Oucomes Afer his lecure and exercises you will be able o:
ON THE QAM PARALLEL TURBO-TCM SCHEMES USING RECURSIVE CONVOLUTIONAL GF(2 N ) ENCODERS
 8h Europea Sigal Processig Coferece (EUSIPCO-00) Aalborg, Demark, Augus 3-7, 00 O THE QAM PARAE TURBO-TCM SCHEMES USIG RECURSIVE COVOUTIOA GF( ) ECODERS Adria Flori Pău, Cǎli Vlǎdeau, Io Marghescu, Safwa
8h Europea Sigal Processig Coferece (EUSIPCO-00) Aalborg, Demark, Augus 3-7, 00 O THE QAM PARAE TURBO-TCM SCHEMES USIG RECURSIVE COVOUTIOA GF( ) ECODERS Adria Flori Pău, Cǎli Vlǎdeau, Io Marghescu, Safwa
Notes on the Fourier Transform
 Noes on he Fourier Transform The Fourier ransform is a mahemaical mehod for describing a coninuous funcion as a series of sine and cosine funcions. The Fourier Transform is produced by applying a series
Noes on he Fourier Transform The Fourier ransform is a mahemaical mehod for describing a coninuous funcion as a series of sine and cosine funcions. The Fourier Transform is produced by applying a series
EXPERIMENT #4 AM MODULATOR AND POWER AMPLIFIER
 EXPERIMENT #4 AM MODULATOR AND POWER AMPLIFIER INTRODUCTION: Being able o ransmi a radio frequency carrier across space is of no use unless we can place informaion or inelligence upon i. This las ransmier
EXPERIMENT #4 AM MODULATOR AND POWER AMPLIFIER INTRODUCTION: Being able o ransmi a radio frequency carrier across space is of no use unless we can place informaion or inelligence upon i. This las ransmier
A New Power System Oscillation Type Identification Method Based on Empirical Mode Decomposition and Hilbert Transform
 Proceedigs of he World Cogress o Egieerig ad Compuer Sciece 4 Vol I WCECS 4, -4 Ocober, 4, Sa Fracisco, USA A New Power Sysem Oscillaio Type Ideificaio Mehod Based o Empirical Mode Decomposiio ad Hilber
Proceedigs of he World Cogress o Egieerig ad Compuer Sciece 4 Vol I WCECS 4, -4 Ocober, 4, Sa Fracisco, USA A New Power Sysem Oscillaio Type Ideificaio Mehod Based o Empirical Mode Decomposiio ad Hilber
APPLICATION NOTE UNDERSTANDING EFFECTIVE BITS
 APPLICATION NOTE AN95091 INTRODUCTION UNDERSTANDING EFFECTIVE BITS Toy Girard, Sigatec, Desig ad Applicatios Egieer Oe criteria ofte used to evaluate a Aalog to Digital Coverter (ADC) or data acquisitio
APPLICATION NOTE AN95091 INTRODUCTION UNDERSTANDING EFFECTIVE BITS Toy Girard, Sigatec, Desig ad Applicatios Egieer Oe criteria ofte used to evaluate a Aalog to Digital Coverter (ADC) or data acquisitio
ELEG 3124 SYSTEMS AND SIGNALS Ch. 1 Continuous-Time Signals
 Deparmen of Elecrical Engineering Universiy of Arkansas ELEG 3124 SYSTEMS AND SIGNALS Ch. 1 Coninuous-Time Signals Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Inroducion: wha are signals and sysems? Signals
Deparmen of Elecrical Engineering Universiy of Arkansas ELEG 3124 SYSTEMS AND SIGNALS Ch. 1 Coninuous-Time Signals Dr. Jingxian Wu wuj@uark.edu OUTLINE 2 Inroducion: wha are signals and sysems? Signals
EXPERIMENT #9 FIBER OPTIC COMMUNICATIONS LINK
 EXPERIMENT #9 FIBER OPTIC COMMUNICATIONS LINK INTRODUCTION: Much of daa communicaions is concerned wih sending digial informaion hrough sysems ha normally only pass analog signals. A elephone line is such
EXPERIMENT #9 FIBER OPTIC COMMUNICATIONS LINK INTRODUCTION: Much of daa communicaions is concerned wih sending digial informaion hrough sysems ha normally only pass analog signals. A elephone line is such
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 301 s & Sysems Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #1 Wha is s & Sysems all abou??? 1/9 Do All EE s & CoE s Design Circuis? No!!!! Someone has o figure ou wha funcion hose circuis need o do Someone also needs
EECE 301 s & Sysems Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #1 Wha is s & Sysems all abou??? 1/9 Do All EE s & CoE s Design Circuis? No!!!! Someone has o figure ou wha funcion hose circuis need o do Someone also needs
Fast and Accurate Behavioral Simulation of Fractional-N Frequency Synthesizers and other PLL/DLL Circuits
 Fas ad Accurae Behavioral Simulaio of Fracioal-N Frequecy Syhesizers ad oher PLL/LL Circuis Michael H. Perro Microsysems Techology Laboraory, MIT perro@mi.edu, hp://www-ml.mi.edu/ perro ABSTRACT Techiques
Fas ad Accurae Behavioral Simulaio of Fracioal-N Frequecy Syhesizers ad oher PLL/LL Circuis Michael H. Perro Microsysems Techology Laboraory, MIT perro@mi.edu, hp://www-ml.mi.edu/ perro ABSTRACT Techiques
Self-Interference Cancellation in Full-Duplex Radio Transceivers with Oscillator Phase Noise
 Self-Ierferece Cacellaio i Full-Duplex Radio Trasceivers wih Oscillaor Phase Noise Ville Syrjälä ad Koji Yamamoo Graduae School of Iformaics Kyoo Uiversiy Yoshida-homachi Sakyo-ku Kyoo-shi 606-8501 Kyoo
Self-Ierferece Cacellaio i Full-Duplex Radio Trasceivers wih Oscillaor Phase Noise Ville Syrjälä ad Koji Yamamoo Graduae School of Iformaics Kyoo Uiversiy Yoshida-homachi Sakyo-ku Kyoo-shi 606-8501 Kyoo
Chapter 2 Introduction: From Phase-Locked Loop to Costas Loop
 Chaper 2 Inroducion: From Phase-Locked Loop o Cosas Loop The Cosas loop can be considered an exended version of he phase-locked loop (PLL). The PLL has been invened in 932 by French engineer Henri de Belleszice
Chaper 2 Inroducion: From Phase-Locked Loop o Cosas Loop The Cosas loop can be considered an exended version of he phase-locked loop (PLL). The PLL has been invened in 932 by French engineer Henri de Belleszice
Comparison of Color Features for Image Retrieval
 Compariso of Color Feaures for Image Rerieval S.R. Kodiuwakku 1 Deparme of Saisics & Compuer Sciece, Uiversiy of Peradeiya salukak@pd.ac.lk S.Selvarajah Deparme of Physical Sciece, Vavuiya Campus, Uiversiy
Compariso of Color Feaures for Image Rerieval S.R. Kodiuwakku 1 Deparme of Saisics & Compuer Sciece, Uiversiy of Peradeiya salukak@pd.ac.lk S.Selvarajah Deparme of Physical Sciece, Vavuiya Campus, Uiversiy
Bézier curves with shape parameter *
 Wag e al. / J Zhejiag Uiv SCI 5 6A(6):497-5 497 Joural of Zhejiag Uiversiy SCIENCE ISSN 9-395 hp://www.zju.edu.c/jzus E-mail: jzus@zju.edu.c Bézier curves wih shape parameer * WANG We-ao ( 王文涛 ) WANG Guo-zhao
Wag e al. / J Zhejiag Uiv SCI 5 6A(6):497-5 497 Joural of Zhejiag Uiversiy SCIENCE ISSN 9-395 hp://www.zju.edu.c/jzus E-mail: jzus@zju.edu.c Bézier curves wih shape parameer * WANG We-ao ( 王文涛 ) WANG Guo-zhao
Phase-Shifting Control of Double Pulse in Harmonic Elimination Wei Peng1, a*, Junhong Zhang1, Jianxin gao1, b, Guangyi Li1, c
 Inernaional Symposium on Mechanical Engineering and Maerial Science (ISMEMS 016 Phase-Shifing Conrol of Double Pulse in Harmonic Eliminaion Wei Peng1, a*, Junhong Zhang1, Jianxin gao1, b, Guangyi i1, c
Inernaional Symposium on Mechanical Engineering and Maerial Science (ISMEMS 016 Phase-Shifing Conrol of Double Pulse in Harmonic Eliminaion Wei Peng1, a*, Junhong Zhang1, Jianxin gao1, b, Guangyi i1, c
PRINCIPLES OF COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS. Lecture 1- Introduction Elements, Modulation, Demodulation, Frequency Spectrum
 PRINCIPLES OF COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Lecture 1- Introduction Elements, Modulation, Demodulation, Frequency Spectrum Topic covered Introduction to subject Elements of Communication system Modulation General
PRINCIPLES OF COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Lecture 1- Introduction Elements, Modulation, Demodulation, Frequency Spectrum Topic covered Introduction to subject Elements of Communication system Modulation General
MULTI USER DETECTION FOR CDMA- OFDM/OQAM SYSTEM COMBINED WITH SPACE TIME CODING
 Ieraioal Joural of Wireless & Mobile Neworks (IJWMN) Vol. 4, No. 4, Augus 212 MULTI USER DETECTION FOR CDMA- OFDM/OQAM SYSTEM COMBINED WITH SPACE TIME CODING Radhia GHARSALLAH 1 ad Ridha BOUALLEGUE 2 1
Ieraioal Joural of Wireless & Mobile Neworks (IJWMN) Vol. 4, No. 4, Augus 212 MULTI USER DETECTION FOR CDMA- OFDM/OQAM SYSTEM COMBINED WITH SPACE TIME CODING Radhia GHARSALLAH 1 ad Ridha BOUALLEGUE 2 1
Analog Circuits EC / EE / IN. For
 Analog Circuis For EC / EE / IN By www.hegaeacademy.com Syllabus Syllabus for Analog Circuis Small Signal Equivalen Circuis of Diodes, BJTs, MOSFETs and Analog CMOS. Simple Diode Circuis, Clipping, Clamping,
Analog Circuis For EC / EE / IN By www.hegaeacademy.com Syllabus Syllabus for Analog Circuis Small Signal Equivalen Circuis of Diodes, BJTs, MOSFETs and Analog CMOS. Simple Diode Circuis, Clipping, Clamping,
Creating a Channel for Current Flow
 10/10/2005 Creaing a Channel for Curren Flow 1/5 Creaing a Channel for Curren Flow When we firs look a an NMOS deice, i appears ha no curren can flow from he Drain elecrode o he Source elecrode (or ice
10/10/2005 Creaing a Channel for Curren Flow 1/5 Creaing a Channel for Curren Flow When we firs look a an NMOS deice, i appears ha no curren can flow from he Drain elecrode o he Source elecrode (or ice
Synchronization of single-channel stepper motor drivers reduces noise and interference
 hronizaion of single-channel sepper moor drivers reduces noise and inerference n mos applicaions, a non-synchronized operaion causes no problems. However, in some cases he swiching of he wo channels inerfere,
hronizaion of single-channel sepper moor drivers reduces noise and inerference n mos applicaions, a non-synchronized operaion causes no problems. However, in some cases he swiching of he wo channels inerfere,
In Color We Live C IP E I. In Color We Live. t n. In Color We Live
 I r We Live Eviro me I r We Live IP E I 0 12 I 2 T E vir ome 0 12 I 2 T IPEI Evirome IPEI 012 I 2 T I r We Live Iesiy Idepede RGB-o-XYZ ur amera alibraio Bria FUNT, ad Pouya BSTNI School of ompuig Sciece,
I r We Live Eviro me I r We Live IP E I 0 12 I 2 T E vir ome 0 12 I 2 T IPEI Evirome IPEI 012 I 2 T I r We Live Iesiy Idepede RGB-o-XYZ ur amera alibraio Bria FUNT, ad Pouya BSTNI School of ompuig Sciece,
Moment-Based Bound on Peak-to-Average Power Ratio and Reduction with Unitary Matrix
 Mome-Based Boud o Peak-o-Average Power Raio ad Reducio wih Uiary Marix Hirofumi Tsuda Deparme of Applied Mahemaics ad Physics Graduae School of Iformaics Kyoo Uiversiy Kyoo Japa suda.hirofumi.38u@s.kyoo-u.ac.jp
Mome-Based Boud o Peak-o-Average Power Raio ad Reducio wih Uiary Marix Hirofumi Tsuda Deparme of Applied Mahemaics ad Physics Graduae School of Iformaics Kyoo Uiversiy Kyoo Japa suda.hirofumi.38u@s.kyoo-u.ac.jp
ECE3204 Microelectronics II Bitar / McNeill. ECE 3204 / Term D-2017 Problem Set 7
 EE3204 Microelecronics II Biar / McNeill Due: Monday, May 1, 2017 EE 3204 / Term D-2017 Problem Se 7 All ex problems from Sedra and Smih, Microelecronic ircuis, 7h ediion. NOTES: Be sure your NAME and
EE3204 Microelecronics II Biar / McNeill Due: Monday, May 1, 2017 EE 3204 / Term D-2017 Problem Se 7 All ex problems from Sedra and Smih, Microelecronic ircuis, 7h ediion. NOTES: Be sure your NAME and
Lab 3 Acceleration. What You Need To Know: Physics 211 Lab
 b Lab 3 Acceleraion Wha You Need To Know: The Physics In he previous lab you learned ha he velociy of an objec can be deermined by finding he slope of he objec s posiion vs. ime graph. x v ave. = v ave.
b Lab 3 Acceleraion Wha You Need To Know: The Physics In he previous lab you learned ha he velociy of an objec can be deermined by finding he slope of he objec s posiion vs. ime graph. x v ave. = v ave.
MEDIUM VOLTAGE CABLES TO IEC60502, BS6622, VDE0276
 IEC2, BS22, VDE2 Sigle Core Cables o VDE 2 The sigle core cables are desiged for disribuio of elecrical power wih Applicaio: omial volage Uo/U ragig from./.kv o 9/KV ad frequecy Hz. They are suiable for
IEC2, BS22, VDE2 Sigle Core Cables o VDE 2 The sigle core cables are desiged for disribuio of elecrical power wih Applicaio: omial volage Uo/U ragig from./.kv o 9/KV ad frequecy Hz. They are suiable for
f t 2cos 2 Modulator Figure 21: DSB-SC modulation.
 4.5 Ampliude modulaion: AM 4.55. DSB-SC ampliude modulaion (which is summarized in Figure 21) is easy o undersand and analyze in boh ime and frequency domains. However, analyical simpliciy is no always
4.5 Ampliude modulaion: AM 4.55. DSB-SC ampliude modulaion (which is summarized in Figure 21) is easy o undersand and analyze in boh ime and frequency domains. However, analyical simpliciy is no always
Signal Characteristics
 Signal Characerisics Analog Signals Analog signals are always coninuous (here are no ime gaps). The signal is of infinie resoluion. Discree Time Signals SignalCharacerisics.docx 8/28/08 10:41 AM Page 1
Signal Characerisics Analog Signals Analog signals are always coninuous (here are no ime gaps). The signal is of infinie resoluion. Discree Time Signals SignalCharacerisics.docx 8/28/08 10:41 AM Page 1
ANALOG AND DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING LABORATORY EXPERIMENTS : CHAPTER 3
 Laboraory # Chap 3 Objecives Linear Sysem Response: general case Undersand he difference and he relaionship beween a sep and impulse response. Deermine he limis of validiy of an approximaed impulse response.
Laboraory # Chap 3 Objecives Linear Sysem Response: general case Undersand he difference and he relaionship beween a sep and impulse response. Deermine he limis of validiy of an approximaed impulse response.
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 3 Signals & Sysems Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #8 C-T Sysems: Frequency-Domain Analysis of Sysems Reading Assignmen: Secion 5.2 of Kamen and Heck /2 Course Flow Diagram The arrows here show concepual
EECE 3 Signals & Sysems Prof. Mark Fowler Noe Se #8 C-T Sysems: Frequency-Domain Analysis of Sysems Reading Assignmen: Secion 5.2 of Kamen and Heck /2 Course Flow Diagram The arrows here show concepual
Communications II Lecture 7: Performance of digital modulation
 Communicaions II Lecure 7: Performance of digial modulaion Professor Kin K. Leung EEE and Compuing Deparmens Imperial College London Copyrigh reserved Ouline Digial modulaion and demodulaion Error probabiliy
Communicaions II Lecure 7: Performance of digial modulaion Professor Kin K. Leung EEE and Compuing Deparmens Imperial College London Copyrigh reserved Ouline Digial modulaion and demodulaion Error probabiliy
Modulation exercises. Chapter 3
 Chaper 3 Modulaion exercises Each problem is annoaed wih he leer E, T, C which sands for exercise, requires some hough, requires some concepualizaion. Problems labeled E are usually mechanical, hose labeled
Chaper 3 Modulaion exercises Each problem is annoaed wih he leer E, T, C which sands for exercise, requires some hough, requires some concepualizaion. Problems labeled E are usually mechanical, hose labeled
Analysis of Current Starved Voltage Controlled Oscillator using 45nm CMOS Technology
 SSN (Pri) : 30 3765 SSN (Olie): 78 8875 eraioal Joural of Advaced Research i Elecrical, Elecroics ad srumeaio Egieerig (A SO 397: 007 erified Orgaizaio) ol. 3, ssue 3, March 014 Aalysis of urre Sarved
SSN (Pri) : 30 3765 SSN (Olie): 78 8875 eraioal Joural of Advaced Research i Elecrical, Elecroics ad srumeaio Egieerig (A SO 397: 007 erified Orgaizaio) ol. 3, ssue 3, March 014 Aalysis of urre Sarved
A New Adaptive Medical Image Coding with Orthogonal Polynomials
 Ieraioal Joural of Compuer Applicaios (975 8887) Volume 46 No., May A New Adapive Medical Image Codig wih Orhogoal Polyomials Krishamoorhy R Deparme of CSE Aa Uiversiy of Techology - Tiruchirappalli Tiruchirappalli,
Ieraioal Joural of Compuer Applicaios (975 8887) Volume 46 No., May A New Adapive Medical Image Codig wih Orhogoal Polyomials Krishamoorhy R Deparme of CSE Aa Uiversiy of Techology - Tiruchirappalli Tiruchirappalli,
Lecture #7: Discrete-time Signals and Sampling
 EEL335: Discree-Time Signals and Sysems Lecure #7: Discree-ime Signals and Sampling. Inroducion Lecure #7: Discree-ime Signals and Sampling Unlike coninuous-ime signals, discree-ime signals have defined
EEL335: Discree-Time Signals and Sysems Lecure #7: Discree-ime Signals and Sampling. Inroducion Lecure #7: Discree-ime Signals and Sampling Unlike coninuous-ime signals, discree-ime signals have defined
AM Demodulation (peak detect.)
 AM Deodulaion (peak deec.) Deodulaion is abou recovering he original signal--crysal Radio Exaple Anenna = Long Wire FM AM Tuning Circui A siple Diode! Deodulaion Circui (envelop of AM Signal) Filer (Mechanical)
AM Deodulaion (peak deec.) Deodulaion is abou recovering he original signal--crysal Radio Exaple Anenna = Long Wire FM AM Tuning Circui A siple Diode! Deodulaion Circui (envelop of AM Signal) Filer (Mechanical)
Chapter 4: Angle Modulation
 Tes 2 Review Tes 2 Review Professor Deepa Kundur Universiy of Torono Reference: Secions: 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, 4.4, 4.6, 4.7, 4.8 of 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.5 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4, 6.5, 6.6 S. Haykin and M. Moher,
Tes 2 Review Tes 2 Review Professor Deepa Kundur Universiy of Torono Reference: Secions: 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, 4.4, 4.6, 4.7, 4.8 of 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.5 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4, 6.5, 6.6 S. Haykin and M. Moher,
Chapter 4: Angle Modulation
 Tes 2 Review Tes 2 Review Professor Deepa Kundur Universiy of Torono Reference: Secions: 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, 4.4, 4.6, 4.7, 4.8 of 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.5 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4, 6.5, 6.6 S. Haykin and M. Moher,
Tes 2 Review Tes 2 Review Professor Deepa Kundur Universiy of Torono Reference: Secions: 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, 4.4, 4.6, 4.7, 4.8 of 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.5 6.1, 6.2, 6.3, 6.4, 6.5, 6.6 S. Haykin and M. Moher,
LECTURE 1 CMOS PHASE LOCKED LOOPS
 Lecure 01 (8/9/18) Page 1-1 Objecive LECTURE 1 CMOS PHASE LOCKED LOOPS OVERVIEW Undersand he principles and applicaions of phase locked loops using inegraed circui echnology wih emphasis on CMOS echnology.
Lecure 01 (8/9/18) Page 1-1 Objecive LECTURE 1 CMOS PHASE LOCKED LOOPS OVERVIEW Undersand he principles and applicaions of phase locked loops using inegraed circui echnology wih emphasis on CMOS echnology.
Chapter 2: Sample Questions, Problems and Solutions Bölüm 2: Örnek Sorular, Problemler ve Çözümleri
 Chapter : Sample Questios, Problems ad Solutios Bölüm : Örek Sorular, Problemler ve Çözümleri Örek Sorular (Sample Questios): Fourier series What is a badwidth? What is a voice-grade? Nyquist theorem Shao
Chapter : Sample Questios, Problems ad Solutios Bölüm : Örek Sorular, Problemler ve Çözümleri Örek Sorular (Sample Questios): Fourier series What is a badwidth? What is a voice-grade? Nyquist theorem Shao
Elements of Communication System Channel Fig: 1: Block Diagram of Communication System Terminology in Communication System
 Content:- Fundamentals of Communication Engineering : Elements of a Communication System, Need of modulation, electromagnetic spectrum and typical applications, Unit V (Communication terminologies in communication
Content:- Fundamentals of Communication Engineering : Elements of a Communication System, Need of modulation, electromagnetic spectrum and typical applications, Unit V (Communication terminologies in communication
Power Conversion and Signal Transmission Integration Method Based on Dual Modulation of DC-DC Converters
 IEEE TRANSATIONS ON INDUSTRIAL ELETRONIS 1 Power oversio ad Sigal Trasmissio Iegraio Mehod Based o Dual Modulaio of D-D overers Jiade Wu, Member, IEEE, Ji Du, Sude Member, IEEE, Zhegyu Li, Seior Member,
IEEE TRANSATIONS ON INDUSTRIAL ELETRONIS 1 Power oversio ad Sigal Trasmissio Iegraio Mehod Based o Dual Modulaio of D-D overers Jiade Wu, Member, IEEE, Ji Du, Sude Member, IEEE, Zhegyu Li, Seior Member,
信號與系統 Signals and Systems
 Sprig 2 信號與系統 Sigals ad Systems Chapter SS- Sigals ad Systems Feg-Li Lia NTU-EE Feb Ju Figures ad images used i these lecture otes are adopted from Sigals & Systems by Ala V. Oppeheim ad Ala S. Willsky,
Sprig 2 信號與系統 Sigals ad Systems Chapter SS- Sigals ad Systems Feg-Li Lia NTU-EE Feb Ju Figures ad images used i these lecture otes are adopted from Sigals & Systems by Ala V. Oppeheim ad Ala S. Willsky,
Detection of Pulsed Radar in a Time Division Duplexed System
 Deecio of Pulsed Radar i a Time Divisio Duplexed Sysem Brad W. Zarikoff Hamilo Isiue Naioal Uiversiy of Irelad Mayooh Email: Brad.Zarikoff@uim.ie David Weldo Wireless R&D, Vecima Neworks, Ic. Vicoria,
Deecio of Pulsed Radar i a Time Divisio Duplexed Sysem Brad W. Zarikoff Hamilo Isiue Naioal Uiversiy of Irelad Mayooh Email: Brad.Zarikoff@uim.ie David Weldo Wireless R&D, Vecima Neworks, Ic. Vicoria,
SystemC-AMS Hands-On Lab Part 2
 SysemC-AMS Hands-On Lab Par 2 Markus Damm, Chrisoph Grimm Compuer Technology Vienna Universiy of Technology, Ausria François Pecheux Laboraoire d Informaique de Paris 6 Universié Pierre & Marie Curie Compuer
SysemC-AMS Hands-On Lab Par 2 Markus Damm, Chrisoph Grimm Compuer Technology Vienna Universiy of Technology, Ausria François Pecheux Laboraoire d Informaique de Paris 6 Universié Pierre & Marie Curie Compuer
M2 3 Introduction to Switching Regulators. 1. What is a switching power supply? 2. What types of switchers are available?
 M2 3 Inroducion o Swiching Regulaors Objecive is o answerhe following quesions: 1. Wha is a swiching power supply? 2. Wha ypes of swichers are available? 3. Why is a swicher needed? 4. How does a swicher
M2 3 Inroducion o Swiching Regulaors Objecive is o answerhe following quesions: 1. Wha is a swiching power supply? 2. Wha ypes of swichers are available? 3. Why is a swicher needed? 4. How does a swicher
Chapter 1: Introduction
 Second ediion ober W. Erickson Dragan Maksimovic Universiy of Colorado, Boulder.. Inroducion o power processing.. Some applicaions of power elecronics.3. Elemens of power elecronics Summary of he course.
Second ediion ober W. Erickson Dragan Maksimovic Universiy of Colorado, Boulder.. Inroducion o power processing.. Some applicaions of power elecronics.3. Elemens of power elecronics Summary of he course.
Simulation Analysis of DC-DC Circuit Based on Simulink in Intelligent Vehicle Terminal
 Open Access Library Journal 218, Volume 5, e4682 ISSN Online: 2333-9721 ISSN Prin: 2333-975 Simulai Analysis of DC-DC Circui Based Simulink in Inelligen Vehicle erminal Weiran Li, Guoping Yang College
Open Access Library Journal 218, Volume 5, e4682 ISSN Online: 2333-9721 ISSN Prin: 2333-975 Simulai Analysis of DC-DC Circui Based Simulink in Inelligen Vehicle erminal Weiran Li, Guoping Yang College
信號與系統 Signals and Systems
 Sprig 24 信號與系統 Sigals ad Systems Chapter SS- Sigals ad Systems Feg-Li Lia NTU-EE Feb4 Ju4 Figures ad images used i these lecture otes are adopted from Sigals & Systems by Ala V. Oppeheim ad Ala S. Willsky,
Sprig 24 信號與系統 Sigals ad Systems Chapter SS- Sigals ad Systems Feg-Li Lia NTU-EE Feb4 Ju4 Figures ad images used i these lecture otes are adopted from Sigals & Systems by Ala V. Oppeheim ad Ala S. Willsky,
Negative frequency communication
 Negaive frequency communicaion Fanping DU Email: dufanping@homail.com Qing Huo Liu arxiv:2.43v5 [cs.it] 26 Sep 2 Deparmen of Elecrical and Compuer Engineering Duke Universiy Email: Qing.Liu@duke.edu Absrac
Negaive frequency communicaion Fanping DU Email: dufanping@homail.com Qing Huo Liu arxiv:2.43v5 [cs.it] 26 Sep 2 Deparmen of Elecrical and Compuer Engineering Duke Universiy Email: Qing.Liu@duke.edu Absrac
EEO 401 Digital Signal Processing Prof. Mark Fowler
 EEO 40 Digial Proceing Pro. Mark Fowler Noe Se #3 Baic Sampling heory Reading Aignmen: Sec. 6. o Proaki & Manolaki /9 Sampling i Key o Much o oday echnology Analog Elecronic ADC DSP Compuer DAC C- C- Syem
EEO 40 Digial Proceing Pro. Mark Fowler Noe Se #3 Baic Sampling heory Reading Aignmen: Sec. 6. o Proaki & Manolaki /9 Sampling i Key o Much o oday echnology Analog Elecronic ADC DSP Compuer DAC C- C- Syem
10. The Series Resistor and Inductor Circuit
 Elecronicsab.nb 1. he Series esisor and Inducor Circui Inroducion he las laboraory involved a resisor, and capacior, C in series wih a baery swich on or off. I was simpler, as a pracical maer, o replace
Elecronicsab.nb 1. he Series esisor and Inducor Circui Inroducion he las laboraory involved a resisor, and capacior, C in series wih a baery swich on or off. I was simpler, as a pracical maer, o replace
Introduction: Analog Communication: Goal: Transmit a message from one location to another.
 ECE-5 Phil Schnier January 6, 8 Inroducion: Goal: Transmi a rom one locaion o anoher When is coninuous waveorm analog comm (eg, FM radio), sequence o numbers digial comm (eg, mp ile), hough he sequence
ECE-5 Phil Schnier January 6, 8 Inroducion: Goal: Transmi a rom one locaion o anoher When is coninuous waveorm analog comm (eg, FM radio), sequence o numbers digial comm (eg, mp ile), hough he sequence
Diodes. Diodes, Page 1
 Diodes, Page 1 Diodes V-I Characerisics signal diode Measure he volage-curren characerisic of a sandard signal diode, he 1N914, using he circui shown below. The purpose of he back-o-back power supplies
Diodes, Page 1 Diodes V-I Characerisics signal diode Measure he volage-curren characerisic of a sandard signal diode, he 1N914, using he circui shown below. The purpose of he back-o-back power supplies
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 3 Sigals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler Note Set #6 D-T Systems: DTFT Aalysis of DT Systems Readig Assigmet: Sectios 5.5 & 5.6 of Kame ad Heck / Course Flow Diagram The arrows here show coceptual flow
EECE 3 Sigals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler Note Set #6 D-T Systems: DTFT Aalysis of DT Systems Readig Assigmet: Sectios 5.5 & 5.6 of Kame ad Heck / Course Flow Diagram The arrows here show coceptual flow
Analog/Digital Communications Primer
 for Amaeur Radio Virginia Polyechnic Insiue & Sae Universiy March 19, 2013 # include //... in main() { floa kf = 0.1f; // modulaion facor liquid_freqdem_ype ype = LIQUID_FREQDEM_DELAYCONJ;
for Amaeur Radio Virginia Polyechnic Insiue & Sae Universiy March 19, 2013 # include //... in main() { floa kf = 0.1f; // modulaion facor liquid_freqdem_ype ype = LIQUID_FREQDEM_DELAYCONJ;
MIMO-OFDM with Pilot-Aided Channel Estimation for WiMax Systems
 Fir Ieraioal Workhop o he Performace Ehaceme i MIMO-OFDM Syem MIMO-OFDM wih Pilo-Aided Chael Eimaio for WiMax Syem Fabie Delere ad Yichuag Su School of Egieerig ad echology Uiveriy of Herfordhire, Hafield,
Fir Ieraioal Workhop o he Performace Ehaceme i MIMO-OFDM Syem MIMO-OFDM wih Pilo-Aided Chael Eimaio for WiMax Syem Fabie Delere ad Yichuag Su School of Egieerig ad echology Uiveriy of Herfordhire, Hafield,
Communication Systems. Department of Electronics and Electrical Engineering
 COMM 704: Communicaion Lecure : Analog Mulipliers Dr Mohamed Abd El Ghany Dr. Mohamed Abd El Ghany, Mohamed.abdel-ghany@guc.edu.eg nroducion Nonlinear operaions on coninuous-valued analog signals are ofen
COMM 704: Communicaion Lecure : Analog Mulipliers Dr Mohamed Abd El Ghany Dr. Mohamed Abd El Ghany, Mohamed.abdel-ghany@guc.edu.eg nroducion Nonlinear operaions on coninuous-valued analog signals are ofen
Potato IC. Contact Potato Semiconductor for IP or detail. PotatoSemi High frequency noise cancellation technology.
 How oes PoaoSemi Kill inside Of I? Volage mode differenial Logic. New Paen IP. d MOS logic by using high frequency noise cancellaion echnology Poao I Normal I 2 1 20 19 Inpu1 Inpu2 Inpu3 ie Oupu1 Oupu2
How oes PoaoSemi Kill inside Of I? Volage mode differenial Logic. New Paen IP. d MOS logic by using high frequency noise cancellaion echnology Poao I Normal I 2 1 20 19 Inpu1 Inpu2 Inpu3 ie Oupu1 Oupu2
Power losses in pulsed voltage source inverters/rectifiers with sinusoidal currents
 ree-wheeling diode Turn-off power dissipaion: off/d = f s * E off/d (v d, i LL, T j/d ) orward power dissipaion: fw/t = 1 T T 1 v () i () d Neglecing he load curren ripple will resul in: fw/d = i Lavg
ree-wheeling diode Turn-off power dissipaion: off/d = f s * E off/d (v d, i LL, T j/d ) orward power dissipaion: fw/t = 1 T T 1 v () i () d Neglecing he load curren ripple will resul in: fw/d = i Lavg
EE 40 Final Project Basic Circuit
 EE 0 Spring 2006 Final Projec EE 0 Final Projec Basic Circui Par I: General insrucion 1. The final projec will coun 0% of he lab grading, since i s going o ake lab sessions. All oher individual labs will
EE 0 Spring 2006 Final Projec EE 0 Final Projec Basic Circui Par I: General insrucion 1. The final projec will coun 0% of he lab grading, since i s going o ake lab sessions. All oher individual labs will
Revision: June 11, E Main Suite D Pullman, WA (509) Voice and Fax
 2.5.3: Sinusoidal Signals and Complex Exponenials Revision: June 11, 2010 215 E Main Suie D Pullman, W 99163 (509) 334 6306 Voice and Fax Overview Sinusoidal signals and complex exponenials are exremely
2.5.3: Sinusoidal Signals and Complex Exponenials Revision: June 11, 2010 215 E Main Suie D Pullman, W 99163 (509) 334 6306 Voice and Fax Overview Sinusoidal signals and complex exponenials are exremely
(2) The MOSFET. Review of. Learning Outcome. (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor) 2.0) Field Effect Transistor (FET)
 EEEB73 Electroics Aalysis & esig II () Review of The MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semicoductor Field Effect Trasistor) Referece: Neame, Chapter 3 ad Chapter 4 Learig Outcome Able to describe ad use the followig:
EEEB73 Electroics Aalysis & esig II () Review of The MOSFET (Metal-Oxide-Semicoductor Field Effect Trasistor) Referece: Neame, Chapter 3 ad Chapter 4 Learig Outcome Able to describe ad use the followig:
EE201 Circuit Theory I Fall
 EE1 Circui Theory I 17 Fall 1. Basic Conceps Chaper 1 of Nilsson - 3 Hrs. Inroducion, Curren and Volage, Power and Energy. Basic Laws Chaper &3 of Nilsson - 6 Hrs. Volage and Curren Sources, Ohm s Law,
EE1 Circui Theory I 17 Fall 1. Basic Conceps Chaper 1 of Nilsson - 3 Hrs. Inroducion, Curren and Volage, Power and Energy. Basic Laws Chaper &3 of Nilsson - 6 Hrs. Volage and Curren Sources, Ohm s Law,
Wrap Up. Fourier Transform Sampling, Modulation, Filtering Noise and the Digital Abstraction Binary signaling model and Shannon Capacity
 Wrap Up Fourier ransorm Sampling, Modulaion, Filering Noise and he Digial Absracion Binary signaling model and Shannon Capaciy Copyrigh 27 by M.H. Perro All righs reserved. M.H. Perro 27 Wrap Up, Slide
Wrap Up Fourier ransorm Sampling, Modulaion, Filering Noise and he Digial Absracion Binary signaling model and Shannon Capaciy Copyrigh 27 by M.H. Perro All righs reserved. M.H. Perro 27 Wrap Up, Slide
UNIT IV DIGITAL MODULATION SCHEME
 UNI IV DIGIAL MODULAION SCHEME Geomeric Represenaion of Signals Ojecive: o represen any se of M energy signals {s i (} as linear cominaions of N orhogonal asis funcions, where N M Real value energy signals
UNI IV DIGIAL MODULAION SCHEME Geomeric Represenaion of Signals Ojecive: o represen any se of M energy signals {s i (} as linear cominaions of N orhogonal asis funcions, where N M Real value energy signals
Antenna & Propagation. Basic Radio Wave Propagation
 For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Antenna & Propagation Basic Radio Wave Propagation by Nor Hadzfizah Binti Mohd Radi Faculty of Electric & Electronics Engineering hadzfizah@ump.edu.my
For updated version, please click on http://ocw.ump.edu.my Antenna & Propagation Basic Radio Wave Propagation by Nor Hadzfizah Binti Mohd Radi Faculty of Electric & Electronics Engineering hadzfizah@ump.edu.my
INF 5460 Electronic noise Estimates and countermeasures. Lecture 11 (Mot 8) Sensors Practical examples
 IF 5460 Electroic oise Estimates ad coutermeasures Lecture 11 (Mot 8) Sesors Practical examples Six models are preseted that "ca be geeralized to cover all types of sesors." amig: Sesor: All types Trasducer:
IF 5460 Electroic oise Estimates ad coutermeasures Lecture 11 (Mot 8) Sesors Practical examples Six models are preseted that "ca be geeralized to cover all types of sesors." amig: Sesor: All types Trasducer:
MEASUREMENT AND CONTORL OF TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION IN FREQUENCY RANGE 0,02-10KHZ.
 ELECTRONICS 00 September, Sozopol, BLGARIA MEASREMENT AND CONTORL OF TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION IN FREQENCY RANGE 0,0-0KHZ. Plame Agelov Agelov Faculty for Computer Sciece, Egieerig ad Natural Studies,
ELECTRONICS 00 September, Sozopol, BLGARIA MEASREMENT AND CONTORL OF TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION IN FREQENCY RANGE 0,0-0KHZ. Plame Agelov Agelov Faculty for Computer Sciece, Egieerig ad Natural Studies,
READING ASSIGNMENTS LECTURE OBJECTIVES. Problem Solving Skills. x(t) = cos(αt 2 ) ELEG-212 Signal Processing and Communications
 ELEG- Signal Processing and Communicaions Lecure 5 Periodic Signals, Harmonics & ime-varying Sinusoids READING ASSIGNMENS his Lecure: Chaper 3, Secions 3- and 3-3 Chaper 3, Secions 3-7 and 3-8 Lab sars
ELEG- Signal Processing and Communicaions Lecure 5 Periodic Signals, Harmonics & ime-varying Sinusoids READING ASSIGNMENS his Lecure: Chaper 3, Secions 3- and 3-3 Chaper 3, Secions 3-7 and 3-8 Lab sars
Medical signal processing
 signal is any kd o physical quaniy ha conveys/ ransmis/sores ormaion Medical signal processg eg () elecrical volage, ha can be measured on he surace o he sk/head as a resul o he hear-/muscle-/bra aciviies
signal is any kd o physical quaniy ha conveys/ ransmis/sores ormaion Medical signal processg eg () elecrical volage, ha can be measured on he surace o he sk/head as a resul o he hear-/muscle-/bra aciviies
Microwave Transistor Oscillator Design
 Tuorial on Modern Ulra Low Noise Microwave Transisor Oscillaor Design olumbia Universiy Sepember, 9 Ulrich L. Rohde, Ph.D.* hairman Synergy Microwave orp. *Prof. of RF ircui and Microwave ircui Design
Tuorial on Modern Ulra Low Noise Microwave Transisor Oscillaor Design olumbia Universiy Sepember, 9 Ulrich L. Rohde, Ph.D.* hairman Synergy Microwave orp. *Prof. of RF ircui and Microwave ircui Design
Estimation of electromagnetic compatibility and efficiency of the adjustable load systems of PMSG in wind turbines
 Ihor SHCHUR Naioal Uiversiy Lviv olyechic, Deparme of ower Egieerig ad Corol Sysems Esimaio of elecromageic compaibiliy ad efficiecy of he adjusable load sysems of MSG i wid urbies Absrac. I wid urbie
Ihor SHCHUR Naioal Uiversiy Lviv olyechic, Deparme of ower Egieerig ad Corol Sysems Esimaio of elecromageic compaibiliy ad efficiecy of he adjusable load sysems of MSG i wid urbies Absrac. I wid urbie
IEEE JOURNAL ON SELECTED AREAS IN COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 32, NO. 5, MAY
 IEEE JOURNAL ON SELECTED AREAS IN COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 32, NO. 5, MAY 2014 1 Updae-Efficiecy ad Local Repairabiliy Limis for Capaciy Approachig Codes Arya Mazumdar Member, IEEE, Veka Chadar, ad Gregory
IEEE JOURNAL ON SELECTED AREAS IN COMMUNICATIONS, VOL. 32, NO. 5, MAY 2014 1 Updae-Efficiecy ad Local Repairabiliy Limis for Capaciy Approachig Codes Arya Mazumdar Member, IEEE, Veka Chadar, ad Gregory
Test 1 Review. Test 1 Review. Communication Systems: Foundational Theories. Communication System. Reference: Sections and
 Tes 1 Review Tes 1 Review Proessor Deepa Kundur Universiy o Torono Reerence: Secions 2.2-2.7 and 3.1-3.6 o S. Haykin and M. Moher, Inroducion o Analog & Digial Communicaions, 2nd ed., John iley & Sons,
Tes 1 Review Tes 1 Review Proessor Deepa Kundur Universiy o Torono Reerence: Secions 2.2-2.7 and 3.1-3.6 o S. Haykin and M. Moher, Inroducion o Analog & Digial Communicaions, 2nd ed., John iley & Sons,
ISSCC 2007 / SESSION 29 / ANALOG AND POWER MANAGEMENT TECHNIQUES / 29.8
 ISSCC 27 / SESSION 29 / ANALOG AND POWER MANAGEMENT TECHNIQUES / 29.8 29.8 A 3GHz Swiching DC-DC Converer Using Clock- Tree Charge-Recycling in 9nm CMOS wih Inegraed Oupu Filer Mehdi Alimadadi, Samad Sheikhaei,
ISSCC 27 / SESSION 29 / ANALOG AND POWER MANAGEMENT TECHNIQUES / 29.8 29.8 A 3GHz Swiching DC-DC Converer Using Clock- Tree Charge-Recycling in 9nm CMOS wih Inegraed Oupu Filer Mehdi Alimadadi, Samad Sheikhaei,
Receiver Architectures
 27/Dec/26 1 Receiver Archiecures Image-Rejec Receivers Shif-by-9 o For narrowband signal: sin cos +j /2 +j (a) T / 4 X = j j /2 G( ) = j sgn( ) 1/2 (b) Figure 5.23 Shif by 9 o in (a) ime and (b) frequency
27/Dec/26 1 Receiver Archiecures Image-Rejec Receivers Shif-by-9 o For narrowband signal: sin cos +j /2 +j (a) T / 4 X = j j /2 G( ) = j sgn( ) 1/2 (b) Figure 5.23 Shif by 9 o in (a) ime and (b) frequency
Simulation Series Termination
 ESE370: Circui-Level Modeling, Design, and Opimizaion for Digial Sysems Day 35: December 5, 2012 Transmission Lines Implicaions 1 Transmission Line Agenda Where arise? General wire formulaion Lossless
ESE370: Circui-Level Modeling, Design, and Opimizaion for Digial Sysems Day 35: December 5, 2012 Transmission Lines Implicaions 1 Transmission Line Agenda Where arise? General wire formulaion Lossless
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS FOR PRACTICAL EXAMINATION Subject : Electronics-I ( EC 112)
 OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS FOR PRACTICAL EXAMINATION Subject : Electronics-I ( EC 112) 1. Which mathematical notation specifies the condition of periodicity for a continuous time signal? a. x(t) = x( t +T)
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS FOR PRACTICAL EXAMINATION Subject : Electronics-I ( EC 112) 1. Which mathematical notation specifies the condition of periodicity for a continuous time signal? a. x(t) = x( t +T)
Communication Systems. Communication Systems
 Communicaion Sysems Analog communicaion Transmi and receive analog waveforms Ampliude Modulaion (AM Phase Modulaion (PM Freq. Modulaion (FM Quadraure Ampliude Modulaion (QAM Pulse Ampliude Modulaion (PAM
Communicaion Sysems Analog communicaion Transmi and receive analog waveforms Ampliude Modulaion (AM Phase Modulaion (PM Freq. Modulaion (FM Quadraure Ampliude Modulaion (QAM Pulse Ampliude Modulaion (PAM
Generating Polar Modulation with R&S SMU200A
 Rohde & Schwarz producs: SMU00 Generaing Polar Modulaion wih R&S SMU00 Polar modulaion is a mehod where digial modulaion is realized as a combinaion of phase and ampliude modulaion, raher han using an
Rohde & Schwarz producs: SMU00 Generaing Polar Modulaion wih R&S SMU00 Polar modulaion is a mehod where digial modulaion is realized as a combinaion of phase and ampliude modulaion, raher han using an
A Channel Estimation Method for MIMO-OFDM Mobile WiMax Systems
 A Chael Eimaio Mehod for MIMO-OFDM Mobile WiMax Syem Fabie Delere ad Yichuag Su School of Egieerig ad echology Uiveriy of Herfordhire, Hafield, Her, AL0 9AB, UK Abrac I hi paper, chael eimaio for Space-ime
A Chael Eimaio Mehod for MIMO-OFDM Mobile WiMax Syem Fabie Delere ad Yichuag Su School of Egieerig ad echology Uiveriy of Herfordhire, Hafield, Her, AL0 9AB, UK Abrac I hi paper, chael eimaio for Space-ime
Single Bit DACs in a Nutshell. Part I DAC Basics
 Sigle Bit DACs i a Nutshell Part I DAC Basics By Dave Va Ess, Pricipal Applicatio Egieer, Cypress Semicoductor May embedded applicatios require geeratig aalog outputs uder digital cotrol. It may be a DC
Sigle Bit DACs i a Nutshell Part I DAC Basics By Dave Va Ess, Pricipal Applicatio Egieer, Cypress Semicoductor May embedded applicatios require geeratig aalog outputs uder digital cotrol. It may be a DC
Lab 2: Common Source Amplifier.
 epartet of Electrical ad Coputer Egieerig Fall 1 Lab : Coo Source plifier. 1. OBJECTIVES Study ad characterize Coo Source aplifier: Bias CS ap usig MOSFET curret irror; Measure gai of CS ap with resistive
epartet of Electrical ad Coputer Egieerig Fall 1 Lab : Coo Source plifier. 1. OBJECTIVES Study ad characterize Coo Source aplifier: Bias CS ap usig MOSFET curret irror; Measure gai of CS ap with resistive
weight: amplitude of sine curve
 Joseph Fourier s claim: all signals are sums of sinusoids of differen frequencies. weighed sine curves weigh: ampliude of sine curve all : no exacly bu doesn maer for us in pracice Example: 3 sin() + sin(*)
Joseph Fourier s claim: all signals are sums of sinusoids of differen frequencies. weighed sine curves weigh: ampliude of sine curve all : no exacly bu doesn maer for us in pracice Example: 3 sin() + sin(*)
Sound so far: 10/13/2013. Sound and stringed instruments
 0/3/203 Sound and ed insrumens Sound so far: Sound is a pressure or densiy flucuaion carried (usually) by air molecules sound wae is longdiudinal Wha is he difference beween a hud and a musical noe? ecure
0/3/203 Sound and ed insrumens Sound so far: Sound is a pressure or densiy flucuaion carried (usually) by air molecules sound wae is longdiudinal Wha is he difference beween a hud and a musical noe? ecure
