Lecture #20 Analog Inputs Embedded System Engineering Philip Koopman Wednesday, 30-March-2016
|
|
|
- Warren Armstrong
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lecture #20 Analog Inputs Embedded System Engineering Philip Koopman Wednesday, 30-March-2016 Electrical& Computer ENGINEEING Copyright , Philip Koopman, All ights eserved
2 Commercial HVAC Is Networked For Monitoring [Emerson Climate Technology Copeland ] 2
3 Centralized Monitoring For etail Cooling How much does it cost to replace a freezer case full of spoiled seafood? How much energy can you save by detecting inefficient compressors? Processes millions of automated alerts per year [Emerson Climate Technology Copeland ] Emerson ProAct Service Center, Atlanta GA 3
4 Where Are We Now? Where we ve been: Analog Output Where we re going today: Analog Input Filters Where we re going next: Human I/O and misc I/O stuff Gentle introduction to control Embedded networks Test #2; last project 4
5 Preview Analog to Digital Converters ADC; A/D General components analog mux, signal sample, ADC Operating parameters Types of ADCs Flash ADC Successive Approximation ADC Engineering consideration Triggering sample and determining when sample is done esolution, accuracy Brief reminder of Nyquist Criterion A very gentle introduction to filters 5
6 Why Is Digital Data A Good Thing? Once encoded as a digital number, noise doesn t matter The value is exact and can be encoded as a binary value It won t change over time or with noise it is an exact value You can have as many bits of precision as you want It can be stored and transmitted Storing a digital value is easy series of ones and zeros rather than analog value Sending it down a network requires only ability to see a zero or one, not analog value Error correction works Can use error detection to tell if value is corrupted (can t really do that on analog values) Can use error correction in some cases to compensate for errors But, the world is analog, so Need to get the data from analog to digital as accurately as possible 6
7 Analog Input Protection Usually analog inputs must have compatible voltage with CPU E.g., analog input must be between 0V and +5V If input is outside this voltage, it can damage CPU Often every company has different approaches but end goal is the same elated considerations Protection against static electricity discharge Protection against reverse power supply voltage (e.g. battery in backward) Protection against power supply over-voltage (e.g., 24V jump start voltage) [Valvano] 7
8 Analog To Digital Conversion Analog inputs permit CPU to sense external world Note that analog inputs are usually changing values ( moving targets ) Analog input components: ADC Analog to Digital Converter S/H Sample and Hold MUX analog multiplex to share use of ADC among many inputs [Valvano] 8
9 Analog Mux Same idea as digital mux, except passes analog values Important parameter: number of channels (often 8 to 12 channels) Select: V V 5.00V 4.85V 1.66V 3.14V 2.98V Analog Inputs Select=5 Analog Output Analog Value 3.14V 4.17V Various unrelated inputs Mux picks one input to sample 7 Analog Mux 9
10 Sample & Hold Need to keep a constant analog value for measurement even if input changes Approach: charge an internal capacitor to match input voltage and hold value S/H stage 1: input amplifier precharge capacitor close to input voltage S/H stage 2: connect capacitor to input to exactly match voltage S/H stage 3: hold charge, isolating it from input after the sample is complete and then run ADC process Sample Hold Vinput Switch Vsample Vinput Switch Vsample C C Ground (0V) Ground (0V) 10
11 ADC Specifications (examples are from course processor) esolution how many bits of input value? Often 8 to 12 bits of resolution For k bits of resolution, each quantum of input value is ~V range /2 k Conversion time Time from sample available (S/H complete) to answer Might vary depending on value! E.g., 7 µsec, 10-bit single conversion time Conversion approach Multiple approaches to conversion, each with cost/performance tradeoffs Flash fast but expensive Successive Approximation (SA) slower, but cheaper Other methods as well 11
12 Integrating ADC Two-part operation 1. amp up capacitor voltage from Vin input through a for fixed amount of time 2. Bleed down capacitor to negative Vref voltage through b and measure time it takes for op amp to switch to its + input (ground value) Compare time to ramp up with time to ramp down Time ratio tells you the voltage Dual slope so that capacitor variation is averaged out by using the ramping ratio Cheap And slow! AMP UP AMP DOWN [Wikipedia] 12
13 Flash ADC Produces value after one propagation delay through circuit Stack of resistors provides uniformly spaced voltage points from gnd to V ref All resistors same value Every op amp provides saturated comparison value: lower than me = 0 higher than me = 1 Priority encoder gives position of highest 1 value That s the digital version of voltage Priority encoder (optimizations possible, but this is the basic idea) Cost: 2 b resistors + 2 b -1 op amps $9 to $70+ depending on specs Time: almost constant time 13
14 How A Flash ADC Works Vref (+5V) Vinput Vref (+5V) 2.35V Example: Input = 2.35 V Vinput Vref (+5V) 2.35V 4.375V 4.375V V V 3.125V 2.500V 1.875V 1.250V Voltage divider gives evenly space voltage reference points 3.750V 3.125V 2.500V 1.875V 1.250V 2.35V 2.35V V 3.125V 2.500V 1.875V 1.250V 2.35V 2.35V Priority Encoder (position of highest 1 input) Binary Output esult is 3 (1.875V) 0.625V 0.625V V V 0V 0V Ground (0V) Ground (0V) Ground (0V) 14
15 Why Use Different Converter Types? Flash ADC is fast, but expensive Need 2 k copies of sample logic (resistor, op amp) for k bit sample Often only good to 8 bits because resistors have to be closely matched in value 16-bit Flash ADC are common, but quite expensive Other approaches provide slower conversion time for lower cost SA is a common compromise points 15
16 SA Successive Approximation egister Majority of market good cost/performance tradeoff Uses a DAC to generate an analog value a guess Uses Op Amp to compare guess to actual value Generates Dout for whether guess is high or low Use binary search technique to find voltage one iteration per bit of output Usually gives 8 to 16 bits of useful output Guess From CPU Vinput Think of this as: $80 2.5V 0 = Low D/A Converter 3.81V DAC creates what is logically a single point on the flash ADC voltage divider + Instead of trying all possible values at once, use binary search of values 0 or 1 ( High or Low ) 16
17 Successive Approximation ADC Operation Guess a value Do binary search based on guess Time to find value for b bits is b steps Hardware cost: log 2 b (inside the DAC) for b bits [Valvano] 17
18 Course Chip A/D [Freescale]
19 ADC Usage Multi-channel polled A/D reading [Valvano] 19
20 ADC Hardware Interface Two types of interfaces Tell ADC Go and data available some fixed time later Tell ADC Go and monitor done bit (or get interrupt) to know when it is ready 7 [Valvano] 20
21 ADC Example Timer_Init is program 2.10 in [Valvano] Enables TCNT; sets TCNT to 1 microsecond tick rate Timer_Wait is also program 2.10 Waits for N TCNT increments (Timer_Wait(10) waits for 10 microsecs) [Valvano] 21
22 ADC Sharing Mutex Approach ADC is a shared resource Need to worry about concurrency! Here are some common approaches One approach: Use a mutex to control access to ADC Task waits for ADC to be free, then gets a sample Stalls tasks if they get unlucky Complicates real time scheduling Priority inversion Longer blocking time for each task based on resource Gets complicated if you want to ensure fair (round robin) or prioritized access Generally this is an event triggered approach ADC sample based on the event of a task wanting a sample 22
23 ADC Sharing Time Triggered Approach Instead, use: periodic background ADC sampling task and mailboxes Background task does round robin ADC for all possible inputs Possibly at different rates depending on input time constants Think multi rate cooperative scheduling for inputs esults of ADC are put in a global variable array, e.g., ADCout[8] Other tasks just use value on ADCout[i] for Analog sample Time Triggered because samples happen based on time, not based on task request Pros: Blocking time limited to interrupts masked while reading ADCout[i] value Tasks don t have to request an ADC value and wait for conversion Much simpler to design and get right for real time operation Creates periodic samples, which are what you need for filtering (see later slides) Cons: Samples might be stale (what if you look at ADCout just before next sample?) Not all samples will be processed only most recent sample Need a way to deal with errors (mark ADCout[i] as stale ) Overall, this is a good way to go 23
24 How Good Are Samples? Sample quality depends on hardware quality esolution size of one measurement quantum e.g., 1/256 of V ref for 8-bit Accuracy how close measured value is to actual value Can t do better than resolution Very often do several bits worse For example, 12-bit ADC might only give 8-bits of clean output data Example: course processor Data sheet summary says: 8 bit or 10 bit resolution with 7 microsecond conversion time But take a look at Appendix A Electrical Characteristics 24
25 Conversion Time If we just wait 10 µsec, will that code always work? [Freescale] 25
26 Accuracy This specification is a pretty good A/D Do we believe the spec in real-world applications? Assumes perfect signal input doesn t account for noise in signal itself [Freescale] 26
27 How Fast Do We Need To Sample? Nyquist criterion sample at least 2x signal frequency Sampling too slowly results in alias problems Sampling at least 2x faster avoids aliasing. But isn t perfect [Valvano] Practical sampling rates For non-sinusoidal signals, need at least 2x of highest frequency component you want to reproduce (that s Nyquist criterion which is a theoretical bound) But, also usually want to sample perhaps 5x-10x faster than the basic signal, if you can, to get a good smooth curve 27
28 A Very Gentle Introduction To Filters Analog inputs have noise Quantization noise Noise in the signal itself Noise in the conversion process (which is an analog process) What if we want to get a better value? In other words what s the input version of the /C analog low pass output filter? Well, it s a filter! (but for inputs we want a digital filter) Input filtering Look at multiple sequential inputs and use that information to make a better guess as to the actual signal value Generally requires storing most recent n samples and combining them 28
29 Finite Impulse esponse (FI) Filter Simple FI: moving average (most frequently used filter in practice) Take most recent n samples and average them Filters out noise by reducing effect of any single errant data point + Simple, intuitive, fast; this is usually what you see in embedded systems Single outlier can make it way off; time lag proportional to # samples Embellishments: Weighted average (weight newest samples more than old ones) Drop outliers (obviously way off data points; e.g., drop highest & lowest) Generalized FI Each input has a gain and is summed to create output Simple moving average: all the gains are the same [Wikipedia] 29
30 Infinite Impulse esponse (II) Filter Note that FI is only based on input values Values older than n samples cannot affect output II includes feedback from output That means that all previous inputs affect output (to some degree) In other words, even a single pulse input will affect infinitely many outputs Simple example: /C low pass filter is an analog II But, in practice, effect decays to nearly zero over time In general, II has some form of integrator that remembers all previous history II implementation: Take a signals course! Bring some math with you applies here [Wikipedia] 30
31 Filtering Tradeoffs Latency The more samples in your filter, the longer it takes to see an output Simplistically, you have to wait about n samples to see a filtered output That means you need to sample at least n times faster than system time constant! Memory All those samples have to be stored in AM, which might be limited Analysis complexity You need to know the math to use a complex filter (Or, get the code from the Internet and hope it actually works!) un-time complexity More complex math means more computation But, complex filters often give more accurate estimates of real input value 31
32 A Word About DSP Chips DSP = Digital Signal Processing Special chips to support DSP They are also a microcontroller (e.g., have a program counter) Hardware optimized for DSP tasks filtering, FFT, etc. Codec = Coder/Decoder ; just an A/D, D/A pair [TI] 32
33 A Word About Careers Embedded System Engineers, 2013 data: [payscale.com] 33
34 Embedded System Engineer Salary Profile [payscale.com] 34
35 Software-Only Skills Pays Less Than SW+HW [payscale.com] 35
36 equirements & Design Worth More Than Coding [payscale.com] 36
37 [payscale.com] 37
38 CIT Salary Data (Excerpts) 38
39 Don t Forget elative Cost of Living Other factors: Opportunity density oom-mate more common in high-cost area 39
40 eview Analog to Digital Converters ADC; A/D Know general components and what they do Understand operating parameters Types of ADCs Know how an integrating ADC works Know how a Flash ADC works Know how a Successive Approximation ADC works Engineering considerations Understand tradeoff between Flash and SA approaches Speed Cost Understand difference between resolution and accuracy Be able to apply Nyquist Criterion Understand tradeoffs of moving average filters 40
Lecture 6: Digital/Analog Techniques
 Lecture 6: Digital/Analog Techniques The electronics signals that we ve looked at so far have been analog that means the information is continuous. A voltage of 5.3V represents different information that
Lecture 6: Digital/Analog Techniques The electronics signals that we ve looked at so far have been analog that means the information is continuous. A voltage of 5.3V represents different information that
EE251: Tuesday October 10
 EE251: Tuesday October 10 Analog to Digital Conversion Text Chapter 20 through section 20.2 TM4C Data Sheet Chapter 13 Lab #5 Writeup Lab Practical #1 this week Homework #4 is due on Thursday at 4:30 p.m.
EE251: Tuesday October 10 Analog to Digital Conversion Text Chapter 20 through section 20.2 TM4C Data Sheet Chapter 13 Lab #5 Writeup Lab Practical #1 this week Homework #4 is due on Thursday at 4:30 p.m.
Outline. Analog/Digital Conversion
 Analog/Digital Conversion The real world is analog. Interfacing a microprocessor-based system to real-world devices often requires conversion between the microprocessor s digital representation of values
Analog/Digital Conversion The real world is analog. Interfacing a microprocessor-based system to real-world devices often requires conversion between the microprocessor s digital representation of values
Analog to Digital Conversion
 Analog to Digital Conversion 02534567998 6 4 2 3 4 5 6 ANALOG to DIGITAL CONVERSION Analog variation (Continuous, smooth variation) Digitized Variation (Discrete set of points) N2 N1 Digitization applied
Analog to Digital Conversion 02534567998 6 4 2 3 4 5 6 ANALOG to DIGITAL CONVERSION Analog variation (Continuous, smooth variation) Digitized Variation (Discrete set of points) N2 N1 Digitization applied
ELG3336: Converters Analog to Digital Converters (ADCs) Digital to Analog Converters (DACs)
 ELG3336: Converters Analog to Digital Converters (ADCs) Digital to Analog Converters (DACs) Digital Output Dout 111 110 101 100 011 010 001 000 ΔV, V LSB V ref 8 V FSR 4 V 8 ref 7 V 8 ref Analog Input
ELG3336: Converters Analog to Digital Converters (ADCs) Digital to Analog Converters (DACs) Digital Output Dout 111 110 101 100 011 010 001 000 ΔV, V LSB V ref 8 V FSR 4 V 8 ref 7 V 8 ref Analog Input
Analog I/O. ECE 153B Sensor & Peripheral Interface Design Winter 2016
 Analog I/O ECE 153B Sensor & Peripheral Interface Design Introduction Anytime we need to monitor or control analog signals with a digital system, we require analogto-digital (ADC) and digital-to-analog
Analog I/O ECE 153B Sensor & Peripheral Interface Design Introduction Anytime we need to monitor or control analog signals with a digital system, we require analogto-digital (ADC) and digital-to-analog
Analog to Digital Converters
 Analog to Digital Converters By: Byron Johns, Danny Carpenter Stephanie Pohl, Harry Bo Marr http://ume.gatech.edu/mechatronics_course/fadc_f05.ppt (unless otherwise marked) Presentation Outline Introduction:
Analog to Digital Converters By: Byron Johns, Danny Carpenter Stephanie Pohl, Harry Bo Marr http://ume.gatech.edu/mechatronics_course/fadc_f05.ppt (unless otherwise marked) Presentation Outline Introduction:
ELG4139: Converters Analog to Digital Converters (ADCs) Digital to Analog Converters (DACs)
 ELG4139: Converters Analog to Digital Converters (ADCs) Digital to Analog Converters (DACs) Digital Output Dout 111 110 101 100 011 010 001 000 ΔV, V LSB V ref 8 V FS 4 V 8 ref 7 V 8 ref Analog Input V
ELG4139: Converters Analog to Digital Converters (ADCs) Digital to Analog Converters (DACs) Digital Output Dout 111 110 101 100 011 010 001 000 ΔV, V LSB V ref 8 V FS 4 V 8 ref 7 V 8 ref Analog Input V
UNIT III Data Acquisition & Microcontroller System. Mr. Manoj Rajale
 UNIT III Data Acquisition & Microcontroller System Mr. Manoj Rajale Syllabus Interfacing of Sensors / Actuators to DAQ system, Bit width, Sampling theorem, Sampling Frequency, Aliasing, Sample and hold
UNIT III Data Acquisition & Microcontroller System Mr. Manoj Rajale Syllabus Interfacing of Sensors / Actuators to DAQ system, Bit width, Sampling theorem, Sampling Frequency, Aliasing, Sample and hold
CENG4480 Lecture 04: Analog/Digital Conversions
 CENG4480 Lecture 04: Analog/Digital Conversions Bei Yu byu@cse.cuhk.edu.hk (Latest update: October 3, 2018) Fall 2018 1 / 31 Overview Preliminaries Comparator Digital to Analog Conversion (DAC) Analog
CENG4480 Lecture 04: Analog/Digital Conversions Bei Yu byu@cse.cuhk.edu.hk (Latest update: October 3, 2018) Fall 2018 1 / 31 Overview Preliminaries Comparator Digital to Analog Conversion (DAC) Analog
Lecture #19 Digital To Analog, PWM, Stepper Motors Embedded System Engineering Philip Koopman Monday, 28-March-2016
 Lecture #19 Digital To Analog, PWM, Stepper Motors 18-348 Embedded System Engineering Philip Koopman Monday, 28-March-2016 Electrical& Computer ENGINEERING Copyright 2006-2016, Philip Koopman, All Rights
Lecture #19 Digital To Analog, PWM, Stepper Motors 18-348 Embedded System Engineering Philip Koopman Monday, 28-March-2016 Electrical& Computer ENGINEERING Copyright 2006-2016, Philip Koopman, All Rights
PHYS225 Lecture 22. Electronic Circuits
 PHYS225 Lecture 22 Electronic Circuits Last lecture Digital to Analog Conversion DAC Converts digital signal to an analog signal Computer control of everything! Various types/techniques for conversion
PHYS225 Lecture 22 Electronic Circuits Last lecture Digital to Analog Conversion DAC Converts digital signal to an analog signal Computer control of everything! Various types/techniques for conversion
Analog to Digital Conversion
 Analog to Digital Conversion Why It s Needed Embedded systems often need to measure values of physical parameters These parameters are usually continuous (analog) and not in a digital form which computers
Analog to Digital Conversion Why It s Needed Embedded systems often need to measure values of physical parameters These parameters are usually continuous (analog) and not in a digital form which computers
Data Converters. Dr.Trushit Upadhyaya EC Department, CSPIT, CHARUSAT
 Data Converters Dr.Trushit Upadhyaya EC Department, CSPIT, CHARUSAT Purpose To convert digital values to analog voltages V OUT Digital Value Reference Voltage Digital Value DAC Analog Voltage Analog Quantity:
Data Converters Dr.Trushit Upadhyaya EC Department, CSPIT, CHARUSAT Purpose To convert digital values to analog voltages V OUT Digital Value Reference Voltage Digital Value DAC Analog Voltage Analog Quantity:
Data Acquisition: A/D & D/A Conversion
 Data Acquisition: A/D & D/A Conversion Mark Colton ME 363 Spring 2011 Sampling: A Review In order to store and process measured variables in a computer, the computer must sample the variables 10 Continuous
Data Acquisition: A/D & D/A Conversion Mark Colton ME 363 Spring 2011 Sampling: A Review In order to store and process measured variables in a computer, the computer must sample the variables 10 Continuous
EE 435. Lecture 41. ADC Design
 EE 435 Lecture 4 ADC Design Nyqyist ate Usage Structures. eview from last lecture. 0 esolution 6 SA Pipeline 8 4 Flash K 0K 00K M 0M 00M G 0G Speed . eview from last lecture. SA ADC C LK IN EF DAC n DAC
EE 435 Lecture 4 ADC Design Nyqyist ate Usage Structures. eview from last lecture. 0 esolution 6 SA Pipeline 8 4 Flash K 0K 00K M 0M 00M G 0G Speed . eview from last lecture. SA ADC C LK IN EF DAC n DAC
EEE312: Electrical measurement & instrumentation
 University of Turkish Aeronautical Association Faculty of Engineering EEE department EEE312: Electrical measurement & instrumentation Digital Electronic meters BY Ankara March 2017 1 Introduction The digital
University of Turkish Aeronautical Association Faculty of Engineering EEE department EEE312: Electrical measurement & instrumentation Digital Electronic meters BY Ankara March 2017 1 Introduction The digital
Digital to Analog Conversion. Data Acquisition
 Digital to Analog Conversion (DAC) Digital to Analog Conversion Data Acquisition DACs or D/A converters are used to convert digital signals representing binary numbers into proportional analog voltages.
Digital to Analog Conversion (DAC) Digital to Analog Conversion Data Acquisition DACs or D/A converters are used to convert digital signals representing binary numbers into proportional analog voltages.
Basic Operational Amplifier Circuits
 Basic Operational Amplifier Circuits Comparators A comparator is a specialized nonlinear op-amp circuit that compares two input voltages and produces an output state that indicates which one is greater.
Basic Operational Amplifier Circuits Comparators A comparator is a specialized nonlinear op-amp circuit that compares two input voltages and produces an output state that indicates which one is greater.
Analogue Interfacing. What is a signal? Continuous vs. Discrete Time. Continuous time signals
 Analogue Interfacing What is a signal? Signal: Function of one or more independent variable(s) such as space or time Examples include images and speech Continuous vs. Discrete Time Continuous time signals
Analogue Interfacing What is a signal? Signal: Function of one or more independent variable(s) such as space or time Examples include images and speech Continuous vs. Discrete Time Continuous time signals
Microprocessors & Interfacing
 Lecture overview Microprocessors & Interfacing /Output output PMW Digital-to- (D/A) Conversion input -to-digital (A/D) Conversion Lecturer : Dr. Annie Guo S2, 2008 COMP9032 Week9 1 S2, 2008 COMP9032 Week9
Lecture overview Microprocessors & Interfacing /Output output PMW Digital-to- (D/A) Conversion input -to-digital (A/D) Conversion Lecturer : Dr. Annie Guo S2, 2008 COMP9032 Week9 1 S2, 2008 COMP9032 Week9
Analog Input and Output. Lecturer: Sri Parameswaran Notes by: Annie Guo
 Analog Input and Output Lecturer: Sri Parameswaran Notes by: Annie Guo 1 Analog output Lecture overview PMW Digital-to-Analog (D/A) Conversion Analog input Analog-to-Digital (A/D) Conversion 2 PWM Analog
Analog Input and Output Lecturer: Sri Parameswaran Notes by: Annie Guo 1 Analog output Lecture overview PMW Digital-to-Analog (D/A) Conversion Analog input Analog-to-Digital (A/D) Conversion 2 PWM Analog
145M Final Exam Solutions page 1 May 11, 2010 S. Derenzo R/2. Vref. Address encoder logic. Exclusive OR. Digital output (8 bits) V 1 2 R/2
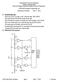 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Department 145M Microcomputer Interfacing Lab Final Exam Solutions May 11, 2010 1.1 Handshaking steps: When
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences Department 145M Microcomputer Interfacing Lab Final Exam Solutions May 11, 2010 1.1 Handshaking steps: When
Data Converters. Lecture Fall2013 Page 1
 Data Converters Lecture Fall2013 Page 1 Lecture Fall2013 Page 2 Representing Real Numbers Limited # of Bits Many physically-based values are best represented with realnumbers as opposed to a discrete number
Data Converters Lecture Fall2013 Page 1 Lecture Fall2013 Page 2 Representing Real Numbers Limited # of Bits Many physically-based values are best represented with realnumbers as opposed to a discrete number
6.111 Lecture # 15. Operational Amplifiers. Uses of Op Amps
 6.111 Lecture # 15 Operational Amplifiers Parameter Ideal '741 '357 Int Gain A Infinity 200,000/f(Hz) 20x10^6/f(Hz) Uses of Op Amps Analog uses employ negative feedback to drive + input to (nearly) the
6.111 Lecture # 15 Operational Amplifiers Parameter Ideal '741 '357 Int Gain A Infinity 200,000/f(Hz) 20x10^6/f(Hz) Uses of Op Amps Analog uses employ negative feedback to drive + input to (nearly) the
Real Time Embedded Systems. Lecture 1 January 17, 2012
 Analog Real Time Embedded Systems www.atomicrhubarb.com/embedded Lecture 1 January 17, 2012 Topic Section Topic Where in the books Catsoulis chapter/page Simon chapter/page Zilog UM197 (ZNEO Z16F Series
Analog Real Time Embedded Systems www.atomicrhubarb.com/embedded Lecture 1 January 17, 2012 Topic Section Topic Where in the books Catsoulis chapter/page Simon chapter/page Zilog UM197 (ZNEO Z16F Series
Chapter 5: Signal conversion
 Chapter 5: Signal conversion Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you will be able to: explain the need for signal conversion between analogue and digital form in communications and microprocessors
Chapter 5: Signal conversion Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you will be able to: explain the need for signal conversion between analogue and digital form in communications and microprocessors
Chapter 2 Signal Conditioning, Propagation, and Conversion
 09/0 PHY 4330 Instrumentation I Chapter Signal Conditioning, Propagation, and Conversion. Amplification (Review of Op-amps) Reference: D. A. Bell, Operational Amplifiers Applications, Troubleshooting,
09/0 PHY 4330 Instrumentation I Chapter Signal Conditioning, Propagation, and Conversion. Amplification (Review of Op-amps) Reference: D. A. Bell, Operational Amplifiers Applications, Troubleshooting,
Last Time. P and N type semiconductors Diode internals Transistors NPN PNP
 Last Time P and N type semiconductors Diode internals Transistors NPN PNP Device of the Day... Piezo microphone Device of the Day... Transistor Recap Transistors operate as current amplifiers With the
Last Time P and N type semiconductors Diode internals Transistors NPN PNP Device of the Day... Piezo microphone Device of the Day... Transistor Recap Transistors operate as current amplifiers With the
Advantages of Analog Representation. Varies continuously, like the property being measured. Represents continuous values. See Figure 12.
 Analog Signals Signals that vary continuously throughout a defined range. Representative of many physical quantities, such as temperature and velocity. Usually a voltage or current level. Digital Signals
Analog Signals Signals that vary continuously throughout a defined range. Representative of many physical quantities, such as temperature and velocity. Usually a voltage or current level. Digital Signals
Analog to Digital Conversion
 Analog to Digital Conversion Florian Erdinger Lehrstuhl für Schaltungstechnik und Simulation Technische Informatik der Uni Heidelberg VLSI Design - Mixed Mode Simulation F. Erdinger, ZITI, Uni Heidelberg
Analog to Digital Conversion Florian Erdinger Lehrstuhl für Schaltungstechnik und Simulation Technische Informatik der Uni Heidelberg VLSI Design - Mixed Mode Simulation F. Erdinger, ZITI, Uni Heidelberg
IFB270 Advanced Electronic Circuits
 IFB270 Advanced Electronic Circuits Chapter 13: Basic op-amp circuits Prof. Manar Mohaisen Department of EEC Engineering Introduction Review of the Precedent Lecture Op-amp operation modes and parameters
IFB270 Advanced Electronic Circuits Chapter 13: Basic op-amp circuits Prof. Manar Mohaisen Department of EEC Engineering Introduction Review of the Precedent Lecture Op-amp operation modes and parameters
RESIDUE AMPLIFIER PIPELINE ADC
 RESIDUE AMPLIFIER PIPELINE ADC A direct-conversion ADC designed only with Op-Amps Abstract This project explores the design of a type of direct-conversion ADC called a Residue Amplifier Pipeline ADC. Direct-conversion
RESIDUE AMPLIFIER PIPELINE ADC A direct-conversion ADC designed only with Op-Amps Abstract This project explores the design of a type of direct-conversion ADC called a Residue Amplifier Pipeline ADC. Direct-conversion
Electronics A/D and D/A converters
 Electronics A/D and D/A converters Prof. Márta Rencz, Gábor Takács, Dr. György Bognár, Dr. Péter G. Szabó BME DED December 1, 2014 1 / 26 Introduction The world is analog, signal processing nowadays is
Electronics A/D and D/A converters Prof. Márta Rencz, Gábor Takács, Dr. György Bognár, Dr. Péter G. Szabó BME DED December 1, 2014 1 / 26 Introduction The world is analog, signal processing nowadays is
EE445L Fall 2015 Quiz 2 Page 1 of 5
 EE445L Fall 2015 Quiz 2 Page 1 of 5 Jonathan W. Valvano First: Last: November 20, 2015, 10:00-10:50am. Open book, open notes, calculator (no laptops, phones, devices with screens larger than a TI-89 calculator,
EE445L Fall 2015 Quiz 2 Page 1 of 5 Jonathan W. Valvano First: Last: November 20, 2015, 10:00-10:50am. Open book, open notes, calculator (no laptops, phones, devices with screens larger than a TI-89 calculator,
Data Acquisition & Computer Control
 Chapter 4 Data Acquisition & Computer Control Now that we have some tools to look at random data we need to understand the fundamental methods employed to acquire data and control experiments. The personal
Chapter 4 Data Acquisition & Computer Control Now that we have some tools to look at random data we need to understand the fundamental methods employed to acquire data and control experiments. The personal
EECS 473 Advanced Embedded Systems
 EECS 473 Advanced Embedded Systems Lecture 15: Power review & Switching power supplies (again) A number of slides taken from UT-Austin s EE462L power electronics class. http://users.ece.utexas.edu/~kwasinski/ee462ls14.html
EECS 473 Advanced Embedded Systems Lecture 15: Power review & Switching power supplies (again) A number of slides taken from UT-Austin s EE462L power electronics class. http://users.ece.utexas.edu/~kwasinski/ee462ls14.html
Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) And Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC)
 1 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) And Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) 2 1. DAC In an electronic circuit, a combination of high voltage (+5V) and low voltage (0V) is usually used to represent a binary
1 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) And Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) 2 1. DAC In an electronic circuit, a combination of high voltage (+5V) and low voltage (0V) is usually used to represent a binary
EE 421L Digital Electronics Laboratory. Laboratory Exercise #9 ADC and DAC
 EE 421L Digital Electronics Laboratory Laboratory Exercise #9 ADC and DAC Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, at Las Vegas Objective: The purpose of this laboratory
EE 421L Digital Electronics Laboratory Laboratory Exercise #9 ADC and DAC Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, at Las Vegas Objective: The purpose of this laboratory
Analogue to Digital Conversion
 Analogue to Digital Conversion Turns electrical input (voltage/current) into numeric value Parameters and requirements Resolution the granularity of the digital values Integral NonLinearity proportionality
Analogue to Digital Conversion Turns electrical input (voltage/current) into numeric value Parameters and requirements Resolution the granularity of the digital values Integral NonLinearity proportionality
II Year (04 Semester) EE6403 Discrete Time Systems and Signal Processing
 Class Subject Code Subject II Year (04 Semester) EE6403 Discrete Time Systems and Signal Processing 1.CONTENT LIST: Introduction to Unit I - Signals and Systems 2. SKILLS ADDRESSED: Listening 3. OBJECTIVE
Class Subject Code Subject II Year (04 Semester) EE6403 Discrete Time Systems and Signal Processing 1.CONTENT LIST: Introduction to Unit I - Signals and Systems 2. SKILLS ADDRESSED: Listening 3. OBJECTIVE
Module 13: Interfacing ADC. Introduction ADC Programming DAC Programming Sensor Interfacing
 Module 13: Interfacing ADC Introduction ADC Programming DAC Programming Sensor Interfacing Introduction ADC Devices o Analog-to-digital converters (ADC) are among the most widely used devices for data
Module 13: Interfacing ADC Introduction ADC Programming DAC Programming Sensor Interfacing Introduction ADC Devices o Analog-to-digital converters (ADC) are among the most widely used devices for data
Digital Design Laboratory Lecture 7. A/D and D/A
 ECE 280 / CSE 280 Digital Design Laboratory Lecture 7 A/D and D/A Analog/Digital Conversion A/D conversion is the process of sampling a continuous signal Two significant implications 1. The information
ECE 280 / CSE 280 Digital Design Laboratory Lecture 7 A/D and D/A Analog/Digital Conversion A/D conversion is the process of sampling a continuous signal Two significant implications 1. The information
Module 3. Embedded Systems I/O. Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1
 Module 3 Embedded Systems I/O Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 esson 19 Analog Interfacing Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would be able
Module 3 Embedded Systems I/O Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 1 esson 19 Analog Interfacing Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 2 Instructional Objectives After going through this lesson the student would be able
Chapter 7: From Digital-to-Analog and Back Again
 Chapter 7: From Digital-to-Analog and Back Again Overview Often the information you want to capture in an experiment originates in the laboratory as an analog voltage or a current. Sometimes you want to
Chapter 7: From Digital-to-Analog and Back Again Overview Often the information you want to capture in an experiment originates in the laboratory as an analog voltage or a current. Sometimes you want to
Real Time Operating Systems Lecture 29.1
 Real Time Operating Systems Lecture 29.1 EE345M Final Exam study guide (Spring 2014): Final is both a closed and open book exam. During the closed book part you can have a pencil, pen and eraser. During
Real Time Operating Systems Lecture 29.1 EE345M Final Exam study guide (Spring 2014): Final is both a closed and open book exam. During the closed book part you can have a pencil, pen and eraser. During
Data acquisition and instrumentation. Data acquisition
 Data acquisition and instrumentation START Lecture Sam Sadeghi Data acquisition 1 Humanistic Intelligence Body as a transducer,, data acquisition and signal processing machine Analysis of physiological
Data acquisition and instrumentation START Lecture Sam Sadeghi Data acquisition 1 Humanistic Intelligence Body as a transducer,, data acquisition and signal processing machine Analysis of physiological
Chapter 2 Analog-to-Digital Conversion...
 Chapter... 5 This chapter examines general considerations for analog-to-digital converter (ADC) measurements. Discussed are the four basic ADC types, providing a general description of each while comparing
Chapter... 5 This chapter examines general considerations for analog-to-digital converter (ADC) measurements. Discussed are the four basic ADC types, providing a general description of each while comparing
A-D and D-A Converters
 Chapter 5 A-D and D-A Converters (No mathematical derivations) 04 Hours 08 Marks When digital devices are to be interfaced with analog devices (or vice a versa), Digital to Analog converter and Analog
Chapter 5 A-D and D-A Converters (No mathematical derivations) 04 Hours 08 Marks When digital devices are to be interfaced with analog devices (or vice a versa), Digital to Analog converter and Analog
Analogue to Digital Conversion
 Analogue to Digital Conversion Turns electrical input (voltage/current) into numeric value Parameters and requirements Resolution the granularity of the digital values Integral NonLinearity proportionality
Analogue to Digital Conversion Turns electrical input (voltage/current) into numeric value Parameters and requirements Resolution the granularity of the digital values Integral NonLinearity proportionality
EE 308 Spring Using the HCS12 PWM
 Using the HCS12 PWM 1. Choose 8-bit mode (PWMCTL = x) 2. Choose high polarity (PWMPOL = xff) 3. Choose left-aligned (PWMCAE = x) 4. Select clock mode in PWMCLK: PCLKn = for 2 N, PCLKn = 1 for 2 (N+1) M,
Using the HCS12 PWM 1. Choose 8-bit mode (PWMCTL = x) 2. Choose high polarity (PWMPOL = xff) 3. Choose left-aligned (PWMCAE = x) 4. Select clock mode in PWMCLK: PCLKn = for 2 N, PCLKn = 1 for 2 (N+1) M,
Linear Integrated Circuits
 Linear Integrated Circuits Single Slope ADC Comparator checks input voltage with integrated reference voltage, V REF At the same time the number of clock cycles is being counted. When the integrator output
Linear Integrated Circuits Single Slope ADC Comparator checks input voltage with integrated reference voltage, V REF At the same time the number of clock cycles is being counted. When the integrator output
Introduction to Real-Time Systems
 Introduction to Real-Time Systems Real-Time Systems, Lecture 1 Martina Maggio and Karl-Erik Årzén 16 January 2018 Lund University, Department of Automatic Control Content [Real-Time Control System: Chapter
Introduction to Real-Time Systems Real-Time Systems, Lecture 1 Martina Maggio and Karl-Erik Årzén 16 January 2018 Lund University, Department of Automatic Control Content [Real-Time Control System: Chapter
Lecture 9, ANIK. Data converters 1
 Lecture 9, ANIK Data converters 1 What did we do last time? Noise and distortion Understanding the simplest circuit noise Understanding some of the sources of distortion 502 of 530 What will we do today?
Lecture 9, ANIK Data converters 1 What did we do last time? Noise and distortion Understanding the simplest circuit noise Understanding some of the sources of distortion 502 of 530 What will we do today?
The simplest DAC can be constructed using a number of resistors with binary weighted values. X[3:0] is the 4-bit digital value to be converter to an
![The simplest DAC can be constructed using a number of resistors with binary weighted values. X[3:0] is the 4-bit digital value to be converter to an The simplest DAC can be constructed using a number of resistors with binary weighted values. X[3:0] is the 4-bit digital value to be converter to an](/thumbs/73/68151962.jpg) 1 Although digital technology dominates modern electronic systems, the physical world remains mostly analogue in nature. The most important components that link the analogue world to digital systems are
1 Although digital technology dominates modern electronic systems, the physical world remains mostly analogue in nature. The most important components that link the analogue world to digital systems are
16.2 DIGITAL-TO-ANALOG CONVERSION
 240 16. DC MEASUREMENTS In the context of contemporary instrumentation systems, a digital meter measures a voltage or current by performing an analog-to-digital (A/D) conversion. A/D converters produce
240 16. DC MEASUREMENTS In the context of contemporary instrumentation systems, a digital meter measures a voltage or current by performing an analog-to-digital (A/D) conversion. A/D converters produce
EE445L Fall 2015 Quiz 2A Solution Page 1
 EE445L Fall 2015 Quiz 2A Solution Page 1 Jonathan W. Valvano First: Last: Solution November 20, 2015, 10:00-10:50am. Open book, open notes, calculator (no laptops, phones, devices with screens larger than
EE445L Fall 2015 Quiz 2A Solution Page 1 Jonathan W. Valvano First: Last: Solution November 20, 2015, 10:00-10:50am. Open book, open notes, calculator (no laptops, phones, devices with screens larger than
Ch 5 Hardware Components for Automation
 Ch 5 Hardware Components for Automation Sections: 1. Sensors 2. Actuators 3. Analog-to-Digital Conversion 4. Digital-to-Analog Conversion 5. Input/Output Devices for Discrete Data Computer-Process Interface
Ch 5 Hardware Components for Automation Sections: 1. Sensors 2. Actuators 3. Analog-to-Digital Conversion 4. Digital-to-Analog Conversion 5. Input/Output Devices for Discrete Data Computer-Process Interface
Analytical Chemistry II
 Analytical Chemistry II L3: Signal processing (selected slides) Semiconductor devices Apart from resistors and capacitors, electronic circuits often contain nonlinear devices: transistors and diodes. The
Analytical Chemistry II L3: Signal processing (selected slides) Semiconductor devices Apart from resistors and capacitors, electronic circuits often contain nonlinear devices: transistors and diodes. The
Lecture 6: Electronics Beyond the Logic Switches Xufeng Kou School of Information Science and Technology ShanghaiTech University
 Lecture 6: Electronics Beyond the Logic Switches Xufeng Kou School of Information Science and Technology ShanghaiTech University EE 224 Solid State Electronics II Lecture 3: Lattice and symmetry 1 Outline
Lecture 6: Electronics Beyond the Logic Switches Xufeng Kou School of Information Science and Technology ShanghaiTech University EE 224 Solid State Electronics II Lecture 3: Lattice and symmetry 1 Outline
DSP Project. Reminder: Project proposal is due Friday, October 19, 2012 by 5pm in my office (Small 239).
 DSP Project eminder: Project proposal is due Friday, October 19, 2012 by 5pm in my office (Small 239). Budget: $150 for project. Free parts: Surplus parts from previous year s project are available on
DSP Project eminder: Project proposal is due Friday, October 19, 2012 by 5pm in my office (Small 239). Budget: $150 for project. Free parts: Surplus parts from previous year s project are available on
ANALOG TO DIGITAL (ADC) and DIGITAL TO ANALOG CONVERTERS (DAC)
 COURSE / CODE DIGITAL SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS (ECE421) DIGITAL ELECTRONICS FUNDAMENTAL (ECE422) ANALOG TO DIGITAL (ADC) and DIGITAL TO ANALOG CONVERTERS (DAC) Connecting digital circuitry to sensor devices
COURSE / CODE DIGITAL SYSTEM FUNDAMENTALS (ECE421) DIGITAL ELECTRONICS FUNDAMENTAL (ECE422) ANALOG TO DIGITAL (ADC) and DIGITAL TO ANALOG CONVERTERS (DAC) Connecting digital circuitry to sensor devices
EE445L Spring 2018 Final EID: Page 1 of 7
 EE445L Spring 2018 Final EID: Page 1 of 7 Jonathan W. Valvano First: Last: This is the closed book section. Calculator is allowed (no laptops, phones, devices with wireless communication). You must put
EE445L Spring 2018 Final EID: Page 1 of 7 Jonathan W. Valvano First: Last: This is the closed book section. Calculator is allowed (no laptops, phones, devices with wireless communication). You must put
Electronics II Physics 3620 / 6620
 Electronics II Physics 3620 / 6620 Feb 09, 2009 Part 1 Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADC) 2/8/2009 1 Why ADC? Digital Signal Processing is more popular Easy to implement, modify, Low cost Data from real
Electronics II Physics 3620 / 6620 Feb 09, 2009 Part 1 Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADC) 2/8/2009 1 Why ADC? Digital Signal Processing is more popular Easy to implement, modify, Low cost Data from real
The need for Data Converters
 The need for Data Converters ANALOG SIGNAL (Speech, Images, Sensors, Radar, etc.) PRE-PROCESSING (Filtering and analog to digital conversion) DIGITAL PROCESSOR (Microprocessor) POST-PROCESSING (Digital
The need for Data Converters ANALOG SIGNAL (Speech, Images, Sensors, Radar, etc.) PRE-PROCESSING (Filtering and analog to digital conversion) DIGITAL PROCESSOR (Microprocessor) POST-PROCESSING (Digital
Analog to Digital (ADC) and Digital to Analog (DAC) Converters
 Analog to Digital (ADC) and Digital to Analog (DAC) Converters 1)Vandana yadav Research scholar singhinia university pachri (Raj. ) 2)Amit yadav (Dept. of physics) Electric voltage and current signals
Analog to Digital (ADC) and Digital to Analog (DAC) Converters 1)Vandana yadav Research scholar singhinia university pachri (Raj. ) 2)Amit yadav (Dept. of physics) Electric voltage and current signals
Hello, and welcome to this presentation of the STM32 Digital Filter for Sigma-Delta modulators interface. The features of this interface, which
 Hello, and welcome to this presentation of the STM32 Digital Filter for Sigma-Delta modulators interface. The features of this interface, which behaves like ADC with external analog part and configurable
Hello, and welcome to this presentation of the STM32 Digital Filter for Sigma-Delta modulators interface. The features of this interface, which behaves like ADC with external analog part and configurable
A DSP IMPLEMENTED DIGITAL FM MULTIPLEXING SYSTEM
 A DSP IMPLEMENTED DIGITAL FM MULTIPLEXING SYSTEM Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Rosenthal, Glenn K. Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal International Telemetering Conference
A DSP IMPLEMENTED DIGITAL FM MULTIPLEXING SYSTEM Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Rosenthal, Glenn K. Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal International Telemetering Conference
Computerized Data Acquisition Systems. Chapter 4
 Computerized Data Acquisition Systems Chapter 4 Data Acquisition - Objectives State and discuss in terms a bright high school student would understand the following definitions related to data acquisition
Computerized Data Acquisition Systems Chapter 4 Data Acquisition - Objectives State and discuss in terms a bright high school student would understand the following definitions related to data acquisition
Based with permission on lectures by John Getty Laboratory Electronics II (PHSX262) Spring 2011 Lecture 9 Page 1
 Today 3// Lecture 9 Analog Digital Conversion Sampled Data Acquisition Systems Discrete Sampling and Nyquist Digital to Analog Conversion Analog to Digital Conversion Homework Study for Exam next week
Today 3// Lecture 9 Analog Digital Conversion Sampled Data Acquisition Systems Discrete Sampling and Nyquist Digital to Analog Conversion Analog to Digital Conversion Homework Study for Exam next week
TUTORIAL 283 INL/DNL Measurements for High-Speed Analog-to- Digital Converters (ADCs)
 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Tutorials > A/D and D/A Conversion/Sampling Circuits > APP 283 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Tutorials > High-Speed Signal Processing > APP
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Tutorials > A/D and D/A Conversion/Sampling Circuits > APP 283 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Tutorials > High-Speed Signal Processing > APP
ENGR 210 Lab 12: Analog to Digital Conversion
 ENGR 210 Lab 12: Analog to Digital Conversion In this lab you will investigate the operation and quantization effects of an A/D and D/A converter. A. BACKGROUND 1. LED Displays We have been using LEDs
ENGR 210 Lab 12: Analog to Digital Conversion In this lab you will investigate the operation and quantization effects of an A/D and D/A converter. A. BACKGROUND 1. LED Displays We have been using LEDs
CHAPTER ELEVEN - Interfacing With the Analog World
 CHAPTER ELEVEN - Interfacing With the Analog World 11.1 (a) Analog output = (K) x (digital input) (b) Smallest change that can occur in the analog output as a result of a change in the digital input. (c)
CHAPTER ELEVEN - Interfacing With the Analog World 11.1 (a) Analog output = (K) x (digital input) (b) Smallest change that can occur in the analog output as a result of a change in the digital input. (c)
WebSeminar: Sept. 24, 2003
 The New Digitally Controlled Programmable Gain Amplifier (PGA) 2003 Microchip Technology Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. MCP6S21/2/6/8 The New Digitally Controlled Amplifier (PGA) 1 The New Digitally
The New Digitally Controlled Programmable Gain Amplifier (PGA) 2003 Microchip Technology Incorporated. All Rights Reserved. MCP6S21/2/6/8 The New Digitally Controlled Amplifier (PGA) 1 The New Digitally
Grundlagen Microcontroller Analog I/O. Günther Gridling Bettina Weiss
 Grundlagen Microcontroller Analog I/O Günther Gridling Bettina Weiss 1 Analog I/O Lecture Overview A/D Conversion Design Issues Representation Conversion Techniques ADCs in Microcontrollers Analog Comparators
Grundlagen Microcontroller Analog I/O Günther Gridling Bettina Weiss 1 Analog I/O Lecture Overview A/D Conversion Design Issues Representation Conversion Techniques ADCs in Microcontrollers Analog Comparators
EECS 373 Design of Microprocessor-Based Systems
 EECS 373 Design of Microprocessor-Based Systems Prabal Dutta University of Michigan Lecture 11: Sampling, ADCs, and DACs Oct 7, 2014 Some slides adapted from Mark Brehob, Jonathan Hui & Steve Reinhardt
EECS 373 Design of Microprocessor-Based Systems Prabal Dutta University of Michigan Lecture 11: Sampling, ADCs, and DACs Oct 7, 2014 Some slides adapted from Mark Brehob, Jonathan Hui & Steve Reinhardt
Lecture #3 Basic Op-Amp Circuits
 Spring 2015 Benha University Faculty of Engineering at Shoubra ECE-322 Electronic Circuits (B) Lecture #3 Basic Op-Amp Circuits Instructor: Dr. Ahmad El-Banna Agenda Comparators Summing Amplifiers Integrators
Spring 2015 Benha University Faculty of Engineering at Shoubra ECE-322 Electronic Circuits (B) Lecture #3 Basic Op-Amp Circuits Instructor: Dr. Ahmad El-Banna Agenda Comparators Summing Amplifiers Integrators
System on a Chip. Prof. Dr. Michael Kraft
 System on a Chip Prof. Dr. Michael Kraft Lecture 5: Data Conversion ADC Background/Theory Examples Background Physical systems are typically analogue To apply digital signal processing, the analogue signal
System on a Chip Prof. Dr. Michael Kraft Lecture 5: Data Conversion ADC Background/Theory Examples Background Physical systems are typically analogue To apply digital signal processing, the analogue signal
Cyber-Physical Systems ADC / DAC
 Cyber-Physical Systems ADC / DAC ICEN 553/453 Fall 2018 Prof. Dola Saha 1 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) Ø ADC is important almost to all application fields Ø Converts a continuous-time voltage signal
Cyber-Physical Systems ADC / DAC ICEN 553/453 Fall 2018 Prof. Dola Saha 1 Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) Ø ADC is important almost to all application fields Ø Converts a continuous-time voltage signal
How do ADCs work? Martin Rowe, Senior Technical Editor -- 7/1/2002 Test & Measurement World

EE283 Electrical Measurement Laboratory Laboratory Exercise #7: Digital Counter
 EE283 Electrical Measurement Laboratory Laboratory Exercise #7: al Counter Objectives: 1. To familiarize students with sequential digital circuits. 2. To show how digital devices can be used for measurement
EE283 Electrical Measurement Laboratory Laboratory Exercise #7: al Counter Objectives: 1. To familiarize students with sequential digital circuits. 2. To show how digital devices can be used for measurement
Section 4: Operational Amplifiers
 Section 4: Operational Amplifiers Op Amps Integrated circuits Simpler to understand than transistors Get back to linear systems, but now with gain Come in various forms Comparators Full Op Amps Differential
Section 4: Operational Amplifiers Op Amps Integrated circuits Simpler to understand than transistors Get back to linear systems, but now with gain Come in various forms Comparators Full Op Amps Differential
Page 1. Midterm #2. OpAmp Review. Inverting & Non-inverting Circuits CS/ECE 6780/5780. Al Davis. Almost ubiquitous analog circuit element since ~1968
 Midterm #2 Midterm 2 hints CS/ECE 6780/5780 Al Davis Today s topics: no practice midterm since it didn t help last time ADC s and DAC s chapter 11 of your text your kit has an A/D (Port D w/ DDR set to
Midterm #2 Midterm 2 hints CS/ECE 6780/5780 Al Davis Today s topics: no practice midterm since it didn t help last time ADC s and DAC s chapter 11 of your text your kit has an A/D (Port D w/ DDR set to
Exercise 3: Sound volume robot
 ETH Course 40-048-00L: Electronics for Physicists II (Digital) 1: Setup uc tools, introduction : Solder SMD Arduino Nano board 3: Build application around ATmega38P 4: Design your own PCB schematic 5:
ETH Course 40-048-00L: Electronics for Physicists II (Digital) 1: Setup uc tools, introduction : Solder SMD Arduino Nano board 3: Build application around ATmega38P 4: Design your own PCB schematic 5:
PreLab 6 PWM Design for H-bridge Driver (due Oct 23)
 GOAL PreLab 6 PWM Design for H-bridge Driver (due Oct 23) The overall goal of Lab6 is to demonstrate a DC motor controller that can adjust speed and direction. You will design the PWM waveform and digital
GOAL PreLab 6 PWM Design for H-bridge Driver (due Oct 23) The overall goal of Lab6 is to demonstrate a DC motor controller that can adjust speed and direction. You will design the PWM waveform and digital
Memory, Latches, & Registers
 Memory, Latches, & Registers 1) Structured Logic Arrays 2) Memory Arrays 3) Transparent Latches 4) Saving a few bucks at toll booths 5) Edge-triggered Registers Friday s class will be a lecture rather
Memory, Latches, & Registers 1) Structured Logic Arrays 2) Memory Arrays 3) Transparent Latches 4) Saving a few bucks at toll booths 5) Edge-triggered Registers Friday s class will be a lecture rather
Analog/Digital and Sampling
 Analog/Digital and Sampling Alexander Nelson October 22, 2018 University of Arkansas - Department of Computer Science and Computer Engineering Analog Signals in the real world are analog signals Process
Analog/Digital and Sampling Alexander Nelson October 22, 2018 University of Arkansas - Department of Computer Science and Computer Engineering Analog Signals in the real world are analog signals Process
(Refer Slide Time: 3:11)
 Digital Communication. Professor Surendra Prasad. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi. Lecture-2. Digital Representation of Analog Signals: Delta Modulation. Professor:
Digital Communication. Professor Surendra Prasad. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi. Lecture-2. Digital Representation of Analog Signals: Delta Modulation. Professor:
Fig 1: The symbol for a comparator
 INTRODUCTION A comparator is a device that compares two voltages or currents and switches its output to indicate which is larger. They are commonly used in devices such as They are commonly used in devices
INTRODUCTION A comparator is a device that compares two voltages or currents and switches its output to indicate which is larger. They are commonly used in devices such as They are commonly used in devices
DATA CONVERSION AND LAB (17.368) Fall Class # 07. October 16, 2008
 DATA CONVERSION AND LAB (17.368) Fall 2008 Class # 07 October 16, 2008 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture Outline Course Admin Lab #3 next week Exam in two weeks 10/30/08 Detailed Technical Discussions Digital
DATA CONVERSION AND LAB (17.368) Fall 2008 Class # 07 October 16, 2008 Dohn Bowden 1 Today s Lecture Outline Course Admin Lab #3 next week Exam in two weeks 10/30/08 Detailed Technical Discussions Digital
Ideal Op Amps. The Two Golden Rules for circuits with ideal op-amps*
 Ideal Op Amps The Two Golden Rules for circuits with ideal op-amps* No voltage difference between op-amp input terminals No current into op-amp inputs * when used in negative feedback amplifiers 1 Approach
Ideal Op Amps The Two Golden Rules for circuits with ideal op-amps* No voltage difference between op-amp input terminals No current into op-amp inputs * when used in negative feedback amplifiers 1 Approach
Learning Objectives:
 Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you will be able to; Analyse and design a DAC based on an op-amp summing amplifier to meet a given specification. 1 Digital and Analogue Information Module
Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you will be able to; Analyse and design a DAC based on an op-amp summing amplifier to meet a given specification. 1 Digital and Analogue Information Module
Section 1. Fundamentals of DDS Technology
 Section 1. Fundamentals of DDS Technology Overview Direct digital synthesis (DDS) is a technique for using digital data processing blocks as a means to generate a frequency- and phase-tunable output signal
Section 1. Fundamentals of DDS Technology Overview Direct digital synthesis (DDS) is a technique for using digital data processing blocks as a means to generate a frequency- and phase-tunable output signal
SYLLABUS of the course BASIC ELECTRONICS AND DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING. Master in Computer Science, University of Bolzano-Bozen, a.y.
 SYLLABUS of the course BASIC ELECTRONICS AND DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Master in Computer Science, University of Bolzano-Bozen, a.y. 2017-2018 Lecturer: LEONARDO RICCI (last updated on November 27, 2017)
SYLLABUS of the course BASIC ELECTRONICS AND DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSING Master in Computer Science, University of Bolzano-Bozen, a.y. 2017-2018 Lecturer: LEONARDO RICCI (last updated on November 27, 2017)
Design of Pipeline Analog to Digital Converter
 Design of Pipeline Analog to Digital Converter Vivek Tripathi, Chandrajit Debnath, Rakesh Malik STMicroelectronics The pipeline analog-to-digital converter (ADC) architecture is the most popular topology
Design of Pipeline Analog to Digital Converter Vivek Tripathi, Chandrajit Debnath, Rakesh Malik STMicroelectronics The pipeline analog-to-digital converter (ADC) architecture is the most popular topology
Mixed-Signal-Electronics
 1 Mixed-Signal-Electronics PD Dr.-Ing. Stephan Henzler 2 Chapter 6 Nyquist Rate Analog-to-Digital Converters 3 Analog-to-Digital Converter Families Architecture Variant Speed Precision Counting Operation
1 Mixed-Signal-Electronics PD Dr.-Ing. Stephan Henzler 2 Chapter 6 Nyquist Rate Analog-to-Digital Converters 3 Analog-to-Digital Converter Families Architecture Variant Speed Precision Counting Operation
Memory, Latches, & Registers
 Memory, Latches, & Registers 1) Structured Logic Arrays 2) Memory Arrays 3) Transparent Latches 4) Saving a few bucks at toll booths 5) Edge-triggered Registers 1 General Table Lookup Synthesis A B 00
Memory, Latches, & Registers 1) Structured Logic Arrays 2) Memory Arrays 3) Transparent Latches 4) Saving a few bucks at toll booths 5) Edge-triggered Registers 1 General Table Lookup Synthesis A B 00
EE445L Fall 2014 Quiz 2A Page 1 of 5
 EE445L Fall 2014 Quiz 2A Page 1 of 5 Jonathan W. Valvano First: Last: November 21, 2014, 10:00-10:50am. Open book, open notes, calculator (no laptops, phones, devices with screens larger than a TI-89 calculator,
EE445L Fall 2014 Quiz 2A Page 1 of 5 Jonathan W. Valvano First: Last: November 21, 2014, 10:00-10:50am. Open book, open notes, calculator (no laptops, phones, devices with screens larger than a TI-89 calculator,
The University of Texas at Arlington Lecture 10 ADC and DAC
 The University of Texas at Arlington Lecture 10 ADC and DAC CSE 3442/5442 Measuring Physical Quantities (Digital) computers use discrete values, and use these to emulate continuous values if needed. In
The University of Texas at Arlington Lecture 10 ADC and DAC CSE 3442/5442 Measuring Physical Quantities (Digital) computers use discrete values, and use these to emulate continuous values if needed. In
EEE3410 Microcontroller Applications Department of Electrical Engineering. Lecture 10. Analogue Interfacing. Vocational Training Council, Hong Kong.
 Department of Electrical Engineering Lecture 10 Analogue Interfacing 1 In this Lecture. Interface 8051 with the following Input/Output Devices Transducer/Sensors Analogue-to-Digital Conversion (ADC) Digital-to-Analogue
Department of Electrical Engineering Lecture 10 Analogue Interfacing 1 In this Lecture. Interface 8051 with the following Input/Output Devices Transducer/Sensors Analogue-to-Digital Conversion (ADC) Digital-to-Analogue
