GATE 2014: General Instructions during Examination
|
|
|
- Octavia Johnston
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GATE 2014: General Instructions during Examination 1. Total duration of the GATE examination is 180 minutes. 2. The clock will be set at the server. The countdown timer at the top right corner of screen will display the remaining time available for you to complete the examination. When the timer reaches zero, the examination will end by itself. You need not terminate the examination or submit your paper. 3. Any useful data required for your paper can be viewed by clicking on the Useful Common Data button that appears on the screen. 4. Use the scribble pad provided to you for any rough work. Submit the scribble pad at the end of the examination. 5. You are allowed to use a non-programmable type calculator, however, sharing of calculators is not allowed. 6. The Question Palette displayed on the right side of screen will show the status of each question using one of the following symbols: The Marked for Review status for a question simply indicates that you would like to look at that question again. If a question is answered, but marked for review, then the answer will be considered for evaluation unless the status is modified by the candidate. Navigating to a Question : 7. To answer a question, do the following: a. Click on the question number in the Question Palette to go to that question directly. b. Select an answer for a multiple choice type question by clicking on the bubble placed before the 4 choices, namely A, B, C and D. Use the virtual numeric keypad to enter a number as answer for a numerical type question. c. Click on Save & Next to save your answer for the current question and then go to the next question. d. Click on Mark for Review & Next to save your answer for the current question and also mark it for review, and then go to the next question.
2 Caution: Note that your answer for the current question will not be saved, if you navigate to another question directly by clicking on a question number without saving the answer to the previous question. You can view all the questions by clicking on the Question Paper button. This feature is provided, so that if you want you can just see the entire question paper at a glance. Answering a Question : 8. Procedure for answering a multiple choice (MCQ) type question: a. Choose one answer from the 4 options (A,B,C,D) given below the question, click on the bubble placed before the chosen option. b. To deselect your chosen answer, click on the bubble of the chosen option again or click on the Clear Response button. c. To change your chosen answer, click on the bubble of another option. d. To save your answer, you MUST click on the Save & Next button. 9. Procedure for answering a numerical answer type question: a. To enter a number as your answer, use the virtual numerical keypad. b. A fraction (e.g or -.3) can be entered as an answer with or without '0' before the decimal point. As many as four decimal points, e.g or or or can be entered. c. To clear your answer, click on the Clear Response button. d. To save your answer, you MUST click on the Save & Next button 10. To mark a question for review, click on the Mark for Review & Next button. If an answer is selected (for MCQ) or entered (for numerical answer type) for a question that is Marked for Review, that answer will be considered in the evaluation unless the status is modified by the candidate. 11. To change your answer to a question that has already been answered, first select that question for answering and then follow the procedure for answering that type of question. 12. Note that ONLY Questions for which answers are saved or marked for review after answering will be considered for evaluation. Choosing a Section : 13. Sections in this question paper are displayed on the top bar of the screen. Questions in a Section can be viewed by clicking on the name of that Section. The Section you are currently viewing will be highlighted. 14. A checkbox is displayed for every optional Section, if any, in the Question Paper. To select the optional Section for answering, click on the checkbox for that Section. 15. If the checkbox for an optional Section is not selected, the Save & Next button and the Mark for Review & Next button will NOT be enabled for that Section. You will
3 only be able to see questions in this Section, but you will not be able to answer questions in the Section. 16. After clicking the Save & Next button for the last question in a Section, you will automatically be taken to the first question of the next Section in sequence. 17. You can move the mouse cursor over the name of a Section to view the answering status for that Section. Changing the Optional Section : 18. After answering the chosen optional Section, partially or completely, you can change the optional Section by selecting the checkbox for a new Section that you want to attempt. A warning message will appear along with a table showing the number of questions answered in each of the previously chosen optional Sections and a checkbox against each of these Sections. Click on a checkbox against a Section that you want to reset and then click on the RESET button. Note that RESETTING a Section will DELETE all the answers for questions in that Section. Hence, if you think that you may want to select this Section again later, you will have to note down your answers for questions in that Section. If you do not want to reset the Section and want to continue answering the previously chosen optional Section, then click on the BACK button. 19. If you deselect the checkbox for an optional Section in the top bar, the following warning message will appear: "Deselecting the checkbox will DELETE all the answers for questions in this Section. Do you want to deselect this Section? If you want to deselect, click on the RESET button. If you do not want to deselect, click on the BACK button. 20. You can shuffle between different Sections or change the optional Sections any number of times.
4 GATE 2014 Examination EC: Electronics & Communications Engineering Duration: 180 minutes Maximum Marks: 100 Read the following instructions carefully. 1. To login, enter your Registration Number and password provided to you. Kindly go through the various symbols used in the test and understand their meaning before you start the examination. 2. Once you login and after the start of the examination, you can view all the questions in the question paper, by clicking on the View All Questions button in the screen. 3. This question paper consists of 2 sections, General Aptitude (GA) for 15 marks and the subject specific GATE paper for 85 marks. Both these sections are compulsory. The GA section consists of 10 questions. Question numbers 1 to 5 are of 1-mark each, while question numbers 6 to 10 are of 2-mark each. The subject specific GATE paper section consists of 55 questions, out of which question numbers 1 to 25 are of 1-mark each, while question numbers 26 to 55 are of 2-mark each. 4. Depending upon the GATE paper, there may be useful common data that may be required for answering the questions. If the paper has such useful data, the same can be viewed by clicking on the Useful Common Data button that appears at the top, right hand side of the screen. 5. The computer allotted to you at the examination center runs specialized software that permits only one answer to be selected for multiple-choice questions using a mouse and to enter a suitable number for the numerical answer type questions using the virtual keyboard and mouse. 6. Your answers shall be updated and saved on a server periodically and also at the end of the examination. The examination will stop automatically at the end of 180 minutes. 7. In each paper a candidate can answer a total of 65 questions carrying 100 marks. 8. The question paper may consist of questions of multiple choice type (MCQ) and numerical answer type. 9. Multiple choice type questions will have four choices against A, B, C, D, out of which only ONE is the correct answer. The candidate has to choose the correct answer by clicking on the bubble ( ) placed before the choice. 10. For numerical answer type questions, each question will have a numerical answer and there will not be any choices. For these questions, the answer should be enteredby using the virtual keyboard that appears on the monitor and the mouse. 11. All questions that are not attempted will result in zero marks. However, wrong answers for multiple choice type questions (MCQ) will result in NEGATIVE marks. For all MCQ questions a wrong answer will result in deduction of⅓ marks for a 1-mark question and ⅔ marks for a 2-mark question. 12. There is NO NEGATIVE MARKING for questions of NUMERICAL ANSWER TYPE. 13. Non-programmable type Calculator is allowed. Charts, graph sheets, and mathematical tables are NOT allowed in the Examination Hall. You must use the Scribble pad provided to you at the examination centre for all your rough work. The Scribble Pad has to be returned at the end of the examination. Declaration by the candidate: I have read and understood all the above instructions. I have also read and understood clearly the instructions given on the admit card and shall follow the same. I also understand that in case I am found to violate any of these instructions, my candidature is liable to be cancelled. I also confirm that at the start of the examination all the computer hardware allotted to me are in proper working condition.
5 GATE 2014 SET- 4 General Aptitude -GA Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 Choose the most appropriate word from the options given below to complete the following sentence. Communication and interpersonal skills are important in their own ways. (A) each (B) both (C) all (D) either Q.2 Which of the options given below best completes the following sentence? She will feel much better if she. (A) will get some rest (C) will be getting some rest (B) gets some rest (D) is getting some rest Q.3 Choose the most appropriate pair of words from the options given below to complete the following sentence. She could not the thought of the election to her bitter rival. (A) bear, loosing (B) bare, loosing (C) bear, losing (D) bare, losing Q.4 A regular die has six sides with numbers 1 to 6 marked on its sides. If a very large number of throws show the following frequencies of occurrence: ; ; ; ; ; We call this die (A) irregular (B) biased (C) Gaussian (D) insufficient Q.5 Fill in the missing number in the series Q. 6 Q. 10 carry two marks each. Q.6 Find the odd one in the following group Q,W,Z,B B,H,K,M W,C,G,J M,S,V,X (A) Q,W,Z,B (B) B,H,K,M (C) W,C,G,J (D) M,S,V,X GA04 (GATE 2014) Q.7 Lights of four colors (red, blue, green, yellow) are hung on a ladder. On every step of the ladder there are two lights. If one of the lights is red, the other light on that step will always be blue. If one of the lights on a step is green, the other light on that step will always be yellow. Which of the following statements is not necessarily correct? (A) The number of red lights is equal to the number of blue lights (B) The number of green lights is equal to the number of yellow lights (C) The sum of the red and green lights is equal to the sum of the yellow and blue lights (D) The sum of the red and blue lights is equal to the sum of the green and yellow lights Q.8 The sum of eight consecutive odd numbers is 656. The average of four consecutive even numbers is 87. What is the sum of the smallest odd number and second largest even number? GA 1/2
6 GATE 2014 SET- 4 General Aptitude -GA Q.9 The total exports and revenues from the exports of a country are given in the two charts shown below. The pie chart for exports shows the quantity of each item exported as a percentage of the total quantity of exports. The pie chart for the revenues shows the percentage of the total revenue generated through export of each item. The total quantity of exports of all the items is 500 thousand tonnes and the total revenues are 250 crore rupees. Which item among the following has generated the maximum revenue per kg? Exports Revenues Item 5 12% Item 6 16% Item 4 22% Item 1 11% Item 3 19% (A) Item 2 (B) Item 3 (C) Item 6 (D) Item 5 Q.10 It takes 30 minutes to empty a half-full tank by draining it at a constant rate. It is decided to simultaneously pump water into the half-full tank while draining it. What is the rate at which water has to be pumped in so that it gets fully filled in 10 minutes? (A) 4 times the draining rate (C) 2.5 times the draining rate Item 2 20% (B) 3 times the draining rate (D) 2 times the draining rate END OF THE QUESTION PAPER Item 6 19% Item 5 20% Item 4 6% Item 1 12% Item 3 23% Item 2 20% GA04 (GATE 2014) GA 2/2
7 Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 The determinant of matrix A is 5 and the determinant of matrix B is 40. The determinant of matrix AB is. Q.2 Let X be a random variable which is uniformly chosen from the set of positive odd numbers less than 100. The expectation, E[X], is. Q.3 For 0 t <, the maximum value of the function f(t) = e t 2 e 2t occurs at (A) t = log e 4 (B) t = log e 2 (C) t = 0 (D) t = log e 8 Q.4 The value of is lim x x x (A) ln2 (B) 1.0 (C) e (D) Q.5 If the characteristic equation of the differential equation d 2 y dy + 2 α dx2 dx + y = 0 has two equal roots, then the values of α are (A) ±1 (B) 0,0 (C) ±j (D) ±1/2 Q.6 Norton s theorem states that a complex network connected to a load can be replaced with an equivalent impedance (A) in series with a current source (B) in parallel with a voltage source (C) in series with a voltage source (D) in parallel with a current source Q.7 In the figure shown, the ideal switch has been open for a long time. If it is closed at t = 0, then the magnitude of the current (in ma) through the 4 kω resistor at t = 0 + is. Q.8 A silicon bar is doped with donor impurities N D = 2.25 x atoms / cm 3. Given the intrinsic carrier concentration of silicon at T = 300 K is n i = 1.5 x cm -3. Assuming complete impurity ionization, the equilibrium electron and hole concentrations are (A) n 0 = 1.5 x cm -3, p 0 = 1.5 x 10 5 cm -3 (B) n 0 = 1.5 x cm -3, p 0 = 1.5 x cm -3 (C) n 0 = 2.25 x cm -3, p 0 = 1.5 x cm -3 (D) n 0 = 2.25 x cm -3, p 0 = 1 x 10 5 cm -3 EC 1/12
8 Q.9 An increase in the base recombination of a BJT will increase (A) the common emitter dc current gain β (B) the breakdown voltage BV CEO (C) the unity-gain cut-off frequency f T (D) the transconductance g m Q.10 In CMOS technology, shallow P-well or N-well regions can be formed using (A) low pressure chemical vapour deposition (B) low energy sputtering (C) low temperature dry oxidation (D) low energy ion-implantation Q.11 The feedback topology in the amplifier circuit ( the base bias circuit is not shown for simplicity) in the figure is (A) Voltage shunt feedback (B) Current series feedback (C) Current shunt feedback (D) Voltage series feedback EC 2/12
9 Q.12 In the differential amplifier shown in the figure, the magnitudes of the common-mode and differential-mode gains are A cm and A d, respectively. If the resistance R E is increased, then (A) A cm increases (C) A d increases (B) common-mode rejection ratio increases (D) common-mode rejection ratio decreases Q.13 A cascade connection of two voltage amplifiers A1 and A2 is shown in the figure. The open-loop gain A v0, input resistance R in, and output resistance R o for A1 and A2 are as follows: A1: A v0 = 10, R in = 10 kω, R o = 1 kω. A2: A v0 = 5, R in = 5 kω, R o = 200 Ω. The approximate overall voltage gain v out /v in is. Q.14 For an n-variable Boolean function, the maximum number of prime implicants is (A) 2(n-1) (B) n/2 (C) 2 n (D) 2 (n-1) Q.15 The number of bytes required to represent the decimal number in packed BCD (Binary Coded Decimal) form is. Q.16 In a half-subtractor circuit with X and Y as inputs, the Borrow (M) and Difference (N = X - Y) are given by (A) M = X Y, N = XY (B) M = XY, N = X Y (C) M = X Y, N = X Y (D) M = XY, N = X Y Q.17 An FIR system is described by the system function The system is H(z) = z z 2 (A) maximum phase (B) minimum phase (C) mixed phase (D) zero phase EC 3/12
10 Q.18 Let x[n] = x[ n]. Let X(z) be the z-transform of x[n]. If j 0.25 is a zero of X(z), which one of the following must also be a zero of X(z). (A) 0.5 j 0.25 (B) 1/(0.5 + j 0.25) (C) 1/(0.5 j 0.25) (D) 2+j 4 Q.19 Consider the periodic square wave in the figure shown. The ratio of the power in the 7 th harmonic to the power in the 5 th harmonic for this waveform is closest in value to. Q.20 The natural frequency of an undamped second-order system is 40 rad/s. If the system is damped with a damping ratio 0.3, the damped natural frequency in rad/s is. Q.21 For the following system, X 1 (s) when X 1 (s) = 0, the transfer function Y(s) (A) s s 2 (B) 1 s+1 s s+1 X 2 (s) is (C) s+2 s(s+1) + + X 2 (s) (D) s+1 s(s+2) Q.22 The capacity of a band-limited additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) channel is given by P C = W log bits per second (bps), where W is the channel bandwidth, P is the σ 2 W average power received and σ 2 is the one-sided power spectral density of the AWGN. For a fixed P σ2 = 1000, the channel capacity (in kbps) with infinite bandwidth (W ) is approximately (A) 1.44 (B) 1.08 (C) 0.72 (D) 0.36 Q.23 Consider sinusoidal modulation in an AM system. Assuming no overmodulation, the modulation index (μ) when the maximum and minimum values of the envelope, respectively, are 3 V and 1 V, is. 1 s Y(s) EC 4/12
11 Q.24 To maximize power transfer, a lossless transmission line is to be matched to a resistive load impedance via a λ/4 transformer as shown. lossless transmission line λ/4 transformer Z in =50 Ω Z L = 100 Ω The characteristic impedance (in Ω) of the λ/4 transformer is. Q.25 Which one of the following field patterns represents a TEM wave travelling in the positive x direction? (A) E = +8y, H = 4z (C) E = +2z, H = +2y Q. 26 Q. 55 carry two marks each. Q.26 The system of linear equations a b = 4 has c 14 (A) a unique solution (B) infinitely many solutions (C) no solution (D) exactly two solutions (B) E = 2y, H = 3z (D) E = 3y, H = +4z Q.27 The real part of an analytic function f(z) where z = x + jy is given by e y cos(x). The imaginary part of f(z) is (A) e y cos(x) (B) e y sin(x) (C) e y sin(x) (D) e y sin(x) Q.28 The maximum value of the determinant among all 2 2 real symmetric matrices with trace 14 is. Q.29 If r = xaˆ + yaˆ + zaˆ and r = r, then div r 2 (ln r) =. x y z Q.30 A series LCR circuit is operated at a frequency different from its resonant frequency. The operating frequency is such that the current leads the supply voltage. The magnitude of current is half the value at resonance. If the values of L, C and R are 1 H, 1 F and 1 Ω, respectively, the operating angular frequency (in rad/s) is. EC 5/12
12 Q.31 In the h-parameter model of the 2-port network given in the figure shown, the value of h 22 (in S) is. 3 Ω 1 3 Ω 3 Ω 2 2 Ω 1' 2 Ω 2 Ω 2' Q.32 In the figure shown, the capacitor is initially uncharged. Which one of the following expressions describes the current I(t) (in ma) for t > 0? (A) I(t) = e t/τ, τ = 2 3 msec (C) I(t) = e t/τ, τ = 3 msec (B) I(t) = e t/τ, τ = 2 3 msec (D) I(t) = e t/τ, τ = 3 msec Q.33 In the magnetically coupled circuit shown in the figure, 56 % of the total flux emanating from one coil links the other coil. The value of the mutual inductance (in H) is. 0 60cos(4t + 30 ) V 10 Ω 4 H M 5 H (1/16) F Q.34 Assume electronic charge q = C, kt/q = 25 mv and electron mobility µ n = 1000 cm 2 /V-s. If the concentration gradient of electrons injected into a P-type silicon sample is /cm 4, the magnitude of electron diffusion current density (in A/cm 2 ) is. Q.35 Consider an abrupt PN junction (at T = 300 K) shown in the figure. The depletion region width X n on the N-side of the junction is 0.2 µm and the permittivity of silicon (ε si ) is F/cm. At the junction, the approximate value of the peak electric field (in kv/cm) is. EC 6/12
13 Q.36 When a silicon diode having a doping concentration of N A = cm -3 on p-side and N D = cm -3 on n-side is reverse biased, the total depletion width is found to be 3 µm. Given that the permittivity of silicon is F/cm, the depletion width on the p-side and the maximum electric field in the depletion region, respectively, are (A) 2.7 µm and V/cm (B) 0.3 µm and V/cm (C) 0.3 µm and V/cm (D) 2.1 µm and V/cm Q.37 The diode in the circuit shown has V on = 0.7 Volts but is ideal otherwise. If V i = 5 sin(ωt)volts, the minimum and maximum values of V o (in Volts) are, respectively, (A) 5 and 2.7 (B) 2.7 and 5 (C) 5 and 3.85 (D) 1.3 and 5 Q.38 For the n-channel MOS transistor shown in the figure, the threshold voltage V Th is 0.8 V. Neglect channel length modulation effects. When the drain voltage V D = 1.6 V, the drain current I D was found to be 0.5 ma. If V D is adjusted to be 2 V by changing the values of R and V DD, the new value of I D (in ma) is (A) (B) 0.75 (C) (D) 1.5 EC 7/12
14 Q.39 For the MOSFETs shown in the figure, the threshold voltage V t = 2 V and 1 W K = µ Cox 2 L = 0.1 ma/v2. The value of I D (in ma) is. V DD = +12 V R 1 10 kω R 2 10 kω I D V SS = 5 V Q.40 In the circuit shown, choose the correct timing diagram of the output (y) from the given waveforms W1, W2, W3 and W4. (A) W1 (B) W2 (C) W3 (D) W4 EC 8/12
15 Q.41 The outputs of the two flip-flops Q1, Q2 in the figure shown are initialized to 0, 0. The sequence generated at Q1 upon application of clock signal is J1 Q1 Q1 J2 Q2 K1 Q1 K2 Q2 CLK (A) (B) (C) (D) Q.42 For the 8085 microprocessor, the interfacing circuit to input 8-bit digital data (DI 0 DI 7 ) from an external device is shown in the figure. The instruction for correct data transfer is A 3 A 2 A 1 A 0 IO/M RD A 5 A 4 A 6 A 7 3-to-8 7 Decoder 6 C 5 4 B 3 2 A 1 0 G G G 1 2A 2B A 8 Digital Inputs A 10 A 9 A 11 A 12 A13 A 14 A15 I/O Device DI Data Bus 0 DI 7 DO 0 DO 7 (D 0 D 7 ) DS DS 2 (A) MVI A, F8H (B) IN F8H (C) OUT F8H (D) LDA F8F8H Q.43 Consider a discrete-time signal n for 0 n 10 x[n] =. 0 otherwise If y[n] is the convolution of x[n] with itself, the value of y[4] is. 1 Q.44 The input-output relationship of a causal stable LTI system is given as y[n] = α y[n 1] + β x[n] If the impulse response h[n] of this system satisfies the condition between α and β is n=0 h[n] = 2, the relationship (A) α = 1 β/2 (B) α = 1 + β/2 (C) α = 2β (D) α = 2β EC 9/12
16 Q.45 The value of the integral sinc 2 (5t) dt is. Q.46 An unforced linear time invariant (LTI) system is represented by x 1 = 1 0 x x 1 x 2 If the initial conditions are x 1 (0) = 1 and x 2 (0) = 1, the solution of the state equation is (A) x 1 (t) = 1, x 2 (t) = 2 (B) x 1 (t) = e t, x 2 (t) = 2e t (C) x 1 (t) = e t, x 2 (t) = e 2t (D) x 1 (t) = e t, x 2 (t) = 2e t Q.47 The Bode asymptotic magnitude plot of a minimum phase system is shown in the figure. If the system is connected in a unity negative feedback configuration, the steady state error of the closed loop system, to a unit ramp input, is. Q.48 Consider the state space system expressed by the signal flow diagram shown in the figure. The corresponding system is (A) always controllable (C) always stable (B) always observable (D) always unstable EC 10/12
17 Q.49 The input to a 1-bit quantizer is a random variable X with pdf f X (x) = 2e 2x for x 0 and f X (x) = 0 for x < 0. For outputs to be of equal probability, the quantizer threshold should be. Q.50 Coherent orthogonal binary FSK modulation is used to transmit two equiprobable symbol waveforms s 1 (t) = α cos 2πf 1 t and s 2 (t) = α cos 2πf 2 t, where α = 4 mv. Assume an AWGN channel with two-sided noise power spectral density N 0 = W/Hz. Using an optimal receiver and the relation Q(v) = 1 2π e u2 2 du, the bit error probability for a data rate of v 500 kbps is (A) Q(2) (B) Q 2 2 (C) Q(4) (D) Q 4 2 Q.51 The power spectral density of a real stationary random process X(t) is given by The value of the expectation E π X(t) X t 1 S X (f) =, f W W 0, f > W. 1 4W is. Q.52 In the figure, M(f) is the Fourier transform of the message signal m(t) where A = 100 Hz and B = 40 Hz. Given v(t) = cos (2πf c t) and w(t) = cos (2π(f c + A)t), where f c > A. The cutoff frequencies of both the filters are f c. m(t) v(t) High Pass Filter M(f) 1 -A -B B A w(t) Low Pass Filter The bandwidth of the signal at the output of the modulator (in Hz) is. Q.53 If the electric field of a plane wave is E (z, t) = x 3cos(ωt kz + 30 ) y 4sin(ωt kz + 45 ) (mv/m), the polarization state of the plane wave is (A) left elliptical (B) left circular (C) right elliptical (D) right circular f s(t) EC 11/12
18 Q.54 In the transmission line shown, the impedance Z in (in ohms) between node A and the ground is. Q.55 For a rectangular waveguide of internal dimensions a b (a > b), the cut-off frequency for the TE11 mode is the arithmetic mean of the cut-off frequencies for TE10 mode and TE20 mode. If a = 5 cm, the value of b (in cm) is. END OF THE QUESTION PAPER EC 12/12
GATE 2014: General Instructions during Examination
 GATE 2014: General Instructions during Examination 1. Total duration of the GATE examination is 180 minutes. 2. The clock will be set at the server. The countdown timer at the top right corner of screen
GATE 2014: General Instructions during Examination 1. Total duration of the GATE examination is 180 minutes. 2. The clock will be set at the server. The countdown timer at the top right corner of screen
ECE Branch GATE Paper Q2. The trigonometric Fourier series for the waveform shown below contains
 Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each. Q1. The eigen values of a skew-symmetric matrix are Always zero Always pure imaginary Either zero or pure imaginary Always real Q2. The trigonometric Fourier series for the
Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each. Q1. The eigen values of a skew-symmetric matrix are Always zero Always pure imaginary Either zero or pure imaginary Always real Q2. The trigonometric Fourier series for the
ECE Branch GATE Paper (C) exp ( t ) sin (25t) (B) 4cos (20t + 3) + 2 sin (710t)
 Question 30 Carry One Mark Each. The following differential equation has 2 3 d y dy 2 3 4 y 2 2 dt degree = 2, order = degree = 3, order = 2 + + + = x dt degree = 4, order = 3 degree = 2, order = 3 2.
Question 30 Carry One Mark Each. The following differential equation has 2 3 d y dy 2 3 4 y 2 2 dt degree = 2, order = degree = 3, order = 2 + + + = x dt degree = 4, order = 3 degree = 2, order = 3 2.
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 GATE-2010 Question Paper & Answer Keys GATE-2010 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
GATE-2010 Question Paper & Answer Keys GATE-2010 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras
 Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Sample Questions on Semiconductor Devices EE3 applicants who are interested to pursue their research in microelectronics devices area (fabrication and/or
Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Sample Questions on Semiconductor Devices EE3 applicants who are interested to pursue their research in microelectronics devices area (fabrication and/or
Electronics Eingineering
 Electronics Eingineering 1. The output of a two-input gate is 0 if and only if its inputs are unequal. It is true for (A) XOR gate (B) NAND gate (C) NOR gate (D) XNOR gate 2. In K-map simplification, a
Electronics Eingineering 1. The output of a two-input gate is 0 if and only if its inputs are unequal. It is true for (A) XOR gate (B) NAND gate (C) NOR gate (D) XNOR gate 2. In K-map simplification, a
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2013
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2013
ECE Branch GATE Paper 2004
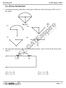 Q. 1 30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? Fig. Q.1 2. The equivalent inductance measured between the terminals
Q. 1 30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? Fig. Q.1 2. The equivalent inductance measured between the terminals
ECE Branch GATE Paper 2002 SECTION A (75 MARKS )
 SECTION A (75 MARKS ). This question consists of TWENTY FIVE sub-question (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A, B, C and D) are given, out of which only
SECTION A (75 MARKS ). This question consists of TWENTY FIVE sub-question (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A, B, C and D) are given, out of which only
6. A low pass filter having a frequency response does not produce any phase distortion, if (A) A(ω)
 1. The rank of the matrix is 0 1 2. P, where P is a vector, is equal to 2 P P P 2 P+ P ( ) 2 3 2 P+ P 2 ( P) P 3. ( P) ds, where P is a vector, is equal to P dl P dl Pdv ax 4. A probability density function
1. The rank of the matrix is 0 1 2. P, where P is a vector, is equal to 2 P P P 2 P+ P ( ) 2 3 2 P+ P 2 ( P) P 3. ( P) ds, where P is a vector, is equal to P dl P dl Pdv ax 4. A probability density function
Georgia Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Midterm Exam
 Georgia Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Midterm Exam ECE-3400 Fall 2013 Tue, September 24, 2013 Duration: 80min First name Solutions Last name Solutions ID number
Georgia Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Midterm Exam ECE-3400 Fall 2013 Tue, September 24, 2013 Duration: 80min First name Solutions Last name Solutions ID number
GATE 2004 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 2004 Electronics and Communication Engineering Q. 1 30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? (A) Fig. Q.1
GATE 2004 Electronics and Communication Engineering Q. 1 30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? (A) Fig. Q.1
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-2007 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - II Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt Question No. 1 which is compulsory and FOUR more questions
I.E.S-(Conv.)-2007 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - II Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt Question No. 1 which is compulsory and FOUR more questions
 Code No: Y0221/R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, Apr/May 2013 BASIC ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
Code No: Y0221/R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, Apr/May 2013 BASIC ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
Linear Algebra, Calculus, Differential Equations and Vector Analysis. Complex Anaysis, Numerical Methods and Probability and Statistics.
 Test No Topic code Topic EC-01 GEM (Engineering Mathematics) Topic wise Tests Each test carries 25 marks and 45 minutes duration Test consists of 5 one mark questions and 10 two marks questions Tests will
Test No Topic code Topic EC-01 GEM (Engineering Mathematics) Topic wise Tests Each test carries 25 marks and 45 minutes duration Test consists of 5 one mark questions and 10 two marks questions Tests will
 COMBO ONLINE TEST SERIES GATE 2019 SCHEDULE: ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Syllabus Test Date Test Type [ EB-Engineering Branch ; EM- No. of Engineering Mathematics; GA- General Question Marks
COMBO ONLINE TEST SERIES GATE 2019 SCHEDULE: ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Syllabus Test Date Test Type [ EB-Engineering Branch ; EM- No. of Engineering Mathematics; GA- General Question Marks
GATE 2000 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 2 Electronics and ommunication Engineering SETION A (1 Marks) 1. This question consists of 25 (Twenty Five) multiple choice questions, each carrying one mark. For each question (1.1 1.25), four alternatives
GATE 2 Electronics and ommunication Engineering SETION A (1 Marks) 1. This question consists of 25 (Twenty Five) multiple choice questions, each carrying one mark. For each question (1.1 1.25), four alternatives
GATE 2002 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 22 Electronics and Communication Engineering SECTION A (75 MARKS ). This question consists of TWENTY FIVE sub-question (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives
GATE 22 Electronics and Communication Engineering SECTION A (75 MARKS ). This question consists of TWENTY FIVE sub-question (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives
EJERCICIOS DE COMPONENTES ELECTRÓNICOS. 1 er cuatrimestre
 EJECICIOS DE COMPONENTES ELECTÓNICOS. 1 er cuatrimestre 2 o Ingeniería Electrónica Industrial Juan Antonio Jiménez Tejada Índice 1. Basic concepts of Electronics 1 2. Passive components 1 3. Semiconductors.
EJECICIOS DE COMPONENTES ELECTÓNICOS. 1 er cuatrimestre 2 o Ingeniería Electrónica Industrial Juan Antonio Jiménez Tejada Índice 1. Basic concepts of Electronics 1 2. Passive components 1 3. Semiconductors.
ECE-342 Test 1: Sep 27, :00-8:00, Closed Book. Name : SOLUTION
 ECE-342 Test 1: Sep 27, 2011 6:00-8:00, Closed Book Name : SOLUTION All solutions must provide units as appropriate. Use the physical constants and data as provided on the formula sheet the last page of
ECE-342 Test 1: Sep 27, 2011 6:00-8:00, Closed Book Name : SOLUTION All solutions must provide units as appropriate. Use the physical constants and data as provided on the formula sheet the last page of
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
 OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 GATE-2015 Question Paper & Answer Keys GATE-2015 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
GATE-2015 Question Paper & Answer Keys GATE-2015 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
BJT Circuits (MCQs of Moderate Complexity)
 BJT Circuits (MCQs of Moderate Complexity) 1. The current ib through base of a silicon npn transistor is 1+0.1 cos (1000πt) ma. At 300K, the rπ in the small signal model of the transistor is i b B C r
BJT Circuits (MCQs of Moderate Complexity) 1. The current ib through base of a silicon npn transistor is 1+0.1 cos (1000πt) ma. At 300K, the rπ in the small signal model of the transistor is i b B C r
BJT Amplifier. Superposition principle (linear amplifier)
 BJT Amplifier Two types analysis DC analysis Applied DC voltage source AC analysis Time varying signal source Superposition principle (linear amplifier) The response of a linear amplifier circuit excited
BJT Amplifier Two types analysis DC analysis Applied DC voltage source AC analysis Time varying signal source Superposition principle (linear amplifier) The response of a linear amplifier circuit excited
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2011
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2011
SAMPLE FINAL EXAMINATION FALL TERM
 ENGINEERING SCIENCES 154 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS SAMPLE FINAL EXAMINATION FALL TERM 2001-2002 NAME Some Possible Solutions a. Please answer all of the questions in the spaces provided. If you need
ENGINEERING SCIENCES 154 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS SAMPLE FINAL EXAMINATION FALL TERM 2001-2002 NAME Some Possible Solutions a. Please answer all of the questions in the spaces provided. If you need
ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Q1. A transmission line of characteristic impedance 50 Ω is terminated by a 50 Ω load. When excited by a sinusoidal voltage source at 10 GHz the phase difference
ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Q1. A transmission line of characteristic impedance 50 Ω is terminated by a 50 Ω load. When excited by a sinusoidal voltage source at 10 GHz the phase difference
UNIT I Introduction to DC & AC circuits
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207) Year & Sem: II-B.
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207) Year & Sem: II-B.
(i) Determine the admittance parameters of the network of Fig 1 (f) and draw its - equivalent circuit.
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
GATE 2014: General Instructions during Examination
 GATE 2014: General Instructions during Examination 1. Total duration of the GATE examination is 180 minutes. 2. The clock will be set at the server. The countdown timer at the top right corner of screen
GATE 2014: General Instructions during Examination 1. Total duration of the GATE examination is 180 minutes. 2. The clock will be set at the server. The countdown timer at the top right corner of screen
6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 Page 1 of 13 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Final Eam Closed Book: Formula sheet provided;
Page 1 of 13 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Final Eam Closed Book: Formula sheet provided;
Electronics Question Bank-2
 Electronics Question Bank-2 Questions Collected from Candidates Appeared for Various Competitive Examinations Compiled by Vishnu.N.V 1. The concentration of minority carriers in an extrinsic semiconductor
Electronics Question Bank-2 Questions Collected from Candidates Appeared for Various Competitive Examinations Compiled by Vishnu.N.V 1. The concentration of minority carriers in an extrinsic semiconductor
Section 2.3 Bipolar junction transistors - BJTs
 Section 2.3 Bipolar junction transistors - BJTs Single junction devices, such as p-n and Schottkty diodes can be used to obtain rectifying I-V characteristics, and to form electronic switching circuits
Section 2.3 Bipolar junction transistors - BJTs Single junction devices, such as p-n and Schottkty diodes can be used to obtain rectifying I-V characteristics, and to form electronic switching circuits
Paper-1 (Circuit Analysis) UNIT-I
 Paper-1 (Circuit Analysis) UNIT-I AC Fundamentals & Kirchhoff s Current and Voltage Laws 1. Explain how a sinusoidal signal can be generated and give the significance of each term in the equation? 2. Define
Paper-1 (Circuit Analysis) UNIT-I AC Fundamentals & Kirchhoff s Current and Voltage Laws 1. Explain how a sinusoidal signal can be generated and give the significance of each term in the equation? 2. Define
Veer Narmad South Gujarat University, Surat
 Unit I: Passive circuit elements (With effect from June 2017) Syllabus for: F Y B Sc (Electronics) Semester- 1 PAPER I: Basic Electrical Circuits Resistors, resistor types, power ratings, resistor colour
Unit I: Passive circuit elements (With effect from June 2017) Syllabus for: F Y B Sc (Electronics) Semester- 1 PAPER I: Basic Electrical Circuits Resistors, resistor types, power ratings, resistor colour
Q.1: Power factor of a linear circuit is defined as the:
 Q.1: Power factor of a linear circuit is defined as the: a. Ratio of real power to reactive power b. Ratio of real power to apparent power c. Ratio of reactive power to apparent power d. Ratio of resistance
Q.1: Power factor of a linear circuit is defined as the: a. Ratio of real power to reactive power b. Ratio of real power to apparent power c. Ratio of reactive power to apparent power d. Ratio of resistance
UNIT 3: FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS
 FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR: UNIT 3: FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS The field effect transistor is a semiconductor device, which depends for its operation on the control of current by an electric field. There are
FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR: UNIT 3: FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS The field effect transistor is a semiconductor device, which depends for its operation on the control of current by an electric field. There are
GATE 2006 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 2006 Electronics and Communication Engineering 1 1 1 1. The rank of the matrix 1 1 0 is (A) 0 (B) 1 1 1 1 2. P, where P is a vector, is equal to 2 P P P (A) 2 P P (B) (C) 2 (D) 3 (C) 2 P P 2 (D) P
GATE 2006 Electronics and Communication Engineering 1 1 1 1. The rank of the matrix 1 1 0 is (A) 0 (B) 1 1 1 1 2. P, where P is a vector, is equal to 2 P P P (A) 2 P P (B) (C) 2 (D) 3 (C) 2 P P 2 (D) P
Electronics I. Midterm #1
 The University of Toledo s6ms_elct7.fm - Electronics I Midterm # Problems Points. 4 2. 5 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo s6ms_elct7.fm - 2 Problem 4 points For full credit,
The University of Toledo s6ms_elct7.fm - Electronics I Midterm # Problems Points. 4 2. 5 3. 6 Total 5 Was the exam fair? yes no The University of Toledo s6ms_elct7.fm - 2 Problem 4 points For full credit,
GATE 1999 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 1999 Electronics and Communication Engineering SECTION A (75 Marks) 1. This question consists of 25 (Twenty Five) multiple choice questions, each carrying one mark. For each questions (1.1 1.25),
GATE 1999 Electronics and Communication Engineering SECTION A (75 Marks) 1. This question consists of 25 (Twenty Five) multiple choice questions, each carrying one mark. For each questions (1.1 1.25),
 Electronic Devices 1. Current flowing in each of the following circuits A and respectively are: (Circuit 1) (Circuit 2) 1) 1A, 2A 2) 2A, 1A 3) 4A, 2A 4) 2A, 4A 2. Among the following one statement is not
Electronic Devices 1. Current flowing in each of the following circuits A and respectively are: (Circuit 1) (Circuit 2) 1) 1A, 2A 2) 2A, 1A 3) 4A, 2A 4) 2A, 4A 2. Among the following one statement is not
Live Leak - SSC Scientific Assistant Electronics and Telecommunication Model Question Paper 2017
 Live Leak - SSC Scientific Assistant Electronics and Telecommunication Model Question Paper 2017 Q1. In a p-n diode, holes diffuse from p-region to n-region because. 1. There is higher concentration of
Live Leak - SSC Scientific Assistant Electronics and Telecommunication Model Question Paper 2017 Q1. In a p-n diode, holes diffuse from p-region to n-region because. 1. There is higher concentration of
PART-A UNIT I Introduction to DC & AC circuits
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207)
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207)
Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All questions carry equal marks
 Code: 9A02401 PRINCIPLES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Common to EIE, E.Con.E, ECE & ECC) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 1 In a series RLC circuit, R = 5 Ω, L = 1 H and C = 1 F. A dc v ltage f 20 V is applied
Code: 9A02401 PRINCIPLES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Common to EIE, E.Con.E, ECE & ECC) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 1 In a series RLC circuit, R = 5 Ω, L = 1 H and C = 1 F. A dc v ltage f 20 V is applied
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-2005 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - II Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt Question No. 1 which is compulsory and FOUR more questions
I.E.S-(Conv.)-2005 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - II Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt Question No. 1 which is compulsory and FOUR more questions
Part A: Question & Answers UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION
 PANDIAN SARASWATHI YADAV ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATON ENGG. Branch: ECE EC6402 COMMUNICATION THEORY Semester: IV Part A: Question & Answers UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION 1.
PANDIAN SARASWATHI YADAV ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATON ENGG. Branch: ECE EC6402 COMMUNICATION THEORY Semester: IV Part A: Question & Answers UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION 1.
(Refer Slide Time: 01:33)
 Solid State Devices Dr. S. Karmalkar Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 31 Bipolar Junction Transistor (Contd ) So, we have been discussing
Solid State Devices Dr. S. Karmalkar Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 31 Bipolar Junction Transistor (Contd ) So, we have been discussing
Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Basics- GATE Problems
 Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Basics- GATE Problems One Mark Questions 1. The break down voltage of a transistor with its base open is BV CEO and that with emitter open is BV CBO, then (a) BV CEO =
Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Basics- GATE Problems One Mark Questions 1. The break down voltage of a transistor with its base open is BV CEO and that with emitter open is BV CBO, then (a) BV CEO =
ES 330 Electronics II Homework # 1 (Fall 2016 SOLUTIONS)
 SOLUTIONS ES 330 Electronics II Homework # 1 (Fall 2016 SOLUTIONS) Problem 1 (20 points) We know that a pn junction diode has an exponential I-V behavior when forward biased. The diode equation relating
SOLUTIONS ES 330 Electronics II Homework # 1 (Fall 2016 SOLUTIONS) Problem 1 (20 points) We know that a pn junction diode has an exponential I-V behavior when forward biased. The diode equation relating
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1992 Time Allowed : Three Hours
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1992 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time Allowed : Three Hours Maximum Marks: 0 Candidates should attempt question No. 1 which is compulsory and any FOUR of the remaining
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1992 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time Allowed : Three Hours Maximum Marks: 0 Candidates should attempt question No. 1 which is compulsory and any FOUR of the remaining
Difference between BJTs and FETs. Junction Field Effect Transistors (JFET)
 Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
Field-Effect Transistor (FET) is one of the two major transistors; FET derives its name from its working mechanism;
 Chapter 3 Field-Effect Transistors (FETs) 3.1 Introduction Field-Effect Transistor (FET) is one of the two major transistors; FET derives its name from its working mechanism; The concept has been known
Chapter 3 Field-Effect Transistors (FETs) 3.1 Introduction Field-Effect Transistor (FET) is one of the two major transistors; FET derives its name from its working mechanism; The concept has been known
Downloaded From All JNTU World
 Code: 9A02403 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of a nuclear plant as compared to other conventional power plants. 2 Explain about: (a) Solar distillation. (b) Solar
Code: 9A02403 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of a nuclear plant as compared to other conventional power plants. 2 Explain about: (a) Solar distillation. (b) Solar
MTLE-6120: Advanced Electronic Properties of Materials. Semiconductor transistors for logic and memory. Reading: Kasap
 MTLE-6120: Advanced Electronic Properties of Materials 1 Semiconductor transistors for logic and memory Reading: Kasap 6.6-6.8 Vacuum tube diodes 2 Thermionic emission from cathode Electrons collected
MTLE-6120: Advanced Electronic Properties of Materials 1 Semiconductor transistors for logic and memory Reading: Kasap 6.6-6.8 Vacuum tube diodes 2 Thermionic emission from cathode Electrons collected
GATE 2009 Electrical Engineering
 Q. No. 1 20 Carry One Mark Each GATE 2009 Electrical Engineering 1. The pressure coil of a dynamometer type wattmeter is (A) highly inductive (B) highly resistive (C) purely resistive (D) purely inductive
Q. No. 1 20 Carry One Mark Each GATE 2009 Electrical Engineering 1. The pressure coil of a dynamometer type wattmeter is (A) highly inductive (B) highly resistive (C) purely resistive (D) purely inductive
* GATE 2017 ONLINE TEST SERIES
 * GATE 2017 ONLINE TEST SERIES Complete with best... Our proficient faculties have done extensive research to prepare and shape these test series. An opportunity for students to come across their strengths
* GATE 2017 ONLINE TEST SERIES Complete with best... Our proficient faculties have done extensive research to prepare and shape these test series. An opportunity for students to come across their strengths
Three Terminal Devices
 Three Terminal Devices - field effect transistor (FET) - bipolar junction transistor (BJT) - foundation on which modern electronics is built - active devices - devices described completely by considering
Three Terminal Devices - field effect transistor (FET) - bipolar junction transistor (BJT) - foundation on which modern electronics is built - active devices - devices described completely by considering
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) PART - A
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207) Year & Sem: II-B.
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207) Year & Sem: II-B.
MICROELECTRONIC CIRCUIT DESIGN Third Edition
 MICROELECTRONIC CIRCUIT DESIGN Third Edition Richard C. Jaeger and Travis N. Blalock Answers to Selected Problems Updated 1/25/08 Chapter 1 1.3 1.52 years, 5.06 years 1.5 1.95 years, 6.46 years 1.8 113
MICROELECTRONIC CIRCUIT DESIGN Third Edition Richard C. Jaeger and Travis N. Blalock Answers to Selected Problems Updated 1/25/08 Chapter 1 1.3 1.52 years, 5.06 years 1.5 1.95 years, 6.46 years 1.8 113
Learning Outcomes. Spiral 2-6. Current, Voltage, & Resistors DIODES
 26.1 26.2 Learning Outcomes Spiral 26 Semiconductor Material MOS Theory I underst why a diode conducts current under forward bias but does not under reverse bias I underst the three modes of operation
26.1 26.2 Learning Outcomes Spiral 26 Semiconductor Material MOS Theory I underst why a diode conducts current under forward bias but does not under reverse bias I underst the three modes of operation
S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Control System Engineering SYLLABUS
![S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Control System Engineering SYLLABUS S.E. Sem. III [ETRX] Control System Engineering SYLLABUS](/thumbs/86/94736291.jpg) Oral : 25 Marks Control System Engineering 1. Introduction to control system analysis Introduction, examples of control systems, open loop control systems, closed loop control systems, Transfer function.
Oral : 25 Marks Control System Engineering 1. Introduction to control system analysis Introduction, examples of control systems, open loop control systems, closed loop control systems, Transfer function.
The University of Texas at Austin Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Exam
 The University of Texas at Austin Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Exam Date: December 18, 2017 Course: EE 313 Evans Name: Last, First The exam is scheduled to last three hours. Open
The University of Texas at Austin Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Exam Date: December 18, 2017 Course: EE 313 Evans Name: Last, First The exam is scheduled to last three hours. Open
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS
 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS 1. As compared to a full wave rectifier using 2 diodes, the four diode bridge rectifier has the dominant advantage of (a) Higher current carrying (b) lower peak inverse
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS 1. As compared to a full wave rectifier using 2 diodes, the four diode bridge rectifier has the dominant advantage of (a) Higher current carrying (b) lower peak inverse
Basic Electronics. Introductory Lecture Course for. Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011
 Basic Electronics Introductory Lecture Course for Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 2011 Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011 Presented By Gary Drake Argonne National Laboratory Session 3
Basic Electronics Introductory Lecture Course for Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 2011 Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011 Presented By Gary Drake Argonne National Laboratory Session 3
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All questions carry equal marks *****
 Code: 9A04601 DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) 1 (a) Explain in detail about non-uniform quantization. (b) What is the disadvantage of uniform quantization over the non-uniform
Code: 9A04601 DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) 1 (a) Explain in detail about non-uniform quantization. (b) What is the disadvantage of uniform quantization over the non-uniform
Semiconductor Physics and Devices
 Metal-Semiconductor and Semiconductor Heterojunctions The Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (MOSFET) is one of two major types of transistors. The MOSFET is used in digital circuit, because
Metal-Semiconductor and Semiconductor Heterojunctions The Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (MOSFET) is one of two major types of transistors. The MOSFET is used in digital circuit, because
EE 5611 Introduction to Microelectronic Technologies Fall Thursday, September 04, 2014 Lecture 02
 EE 5611 Introduction to Microelectronic Technologies Fall 2014 Thursday, September 04, 2014 Lecture 02 1 Lecture Outline Review on semiconductor materials Review on microelectronic devices Example of microelectronic
EE 5611 Introduction to Microelectronic Technologies Fall 2014 Thursday, September 04, 2014 Lecture 02 1 Lecture Outline Review on semiconductor materials Review on microelectronic devices Example of microelectronic
NAME: Last First Signature
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE 130: IC Devices Spring 2003 FINAL EXAMINATION NAME: Last First Signature STUDENT
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE 130: IC Devices Spring 2003 FINAL EXAMINATION NAME: Last First Signature STUDENT
Analog Integrated Circuit Design Exercise 1
 Analog Integrated Circuit Design Exercise 1 Integrated Electronic Systems Lab Prof. Dr.-Ing. Klaus Hofmann M.Sc. Katrin Hirmer, M.Sc. Sreekesh Lakshminarayanan Status: 21.10.2015 Pre-Assignments The lecture
Analog Integrated Circuit Design Exercise 1 Integrated Electronic Systems Lab Prof. Dr.-Ing. Klaus Hofmann M.Sc. Katrin Hirmer, M.Sc. Sreekesh Lakshminarayanan Status: 21.10.2015 Pre-Assignments The lecture
Electronics Review Flashcards
 November 21, 2011 1 Op Amps 2 Diodes 3 Silicon 4 pn Junctions 5 BJTs 6 MOSFETs Open Loop Characteristics Open-Loop Op-Amp Characteristics (first-order model) Closed Loop Characteristics Closed-Loop Op-Amp
November 21, 2011 1 Op Amps 2 Diodes 3 Silicon 4 pn Junctions 5 BJTs 6 MOSFETs Open Loop Characteristics Open-Loop Op-Amp Characteristics (first-order model) Closed Loop Characteristics Closed-Loop Op-Amp
Course Number Section. Electronics I ELEC 311 BB Examination Date Time # of pages. Final August 12, 2005 Three hours 3 Instructor
 Course Number Section Electronics ELEC 311 BB Examination Date Time # of pages Final August 12, 2005 Three hours 3 nstructor Dr. R. Raut M aterials allowed: No Yes X (Please specify) Calculators allowed:
Course Number Section Electronics ELEC 311 BB Examination Date Time # of pages Final August 12, 2005 Three hours 3 nstructor Dr. R. Raut M aterials allowed: No Yes X (Please specify) Calculators allowed:
AN 1651 Analysis and design Of Analog Integrated Circuits. Two Mark Questions & Answers. Prepared By M.P.Flower queen Lecturer,EEE Dept.
 AN 1651 Analysis and design Of Analog Integrated Circuits Two Mark Questions & Answers Prepared By M.P.Flower queen Lecturer,EEE Dept. 1.write the poissons equation. UNIT I = charge density = electron
AN 1651 Analysis and design Of Analog Integrated Circuits Two Mark Questions & Answers Prepared By M.P.Flower queen Lecturer,EEE Dept. 1.write the poissons equation. UNIT I = charge density = electron
QUESTION BANK for Analog Electronics 4EC111 *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m54983 1 QUESTION BANK for Analog Electronics 4EC111 * Bijay_Kumar Sharma This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 Abstract
OpenStax-CNX module: m54983 1 QUESTION BANK for Analog Electronics 4EC111 * Bijay_Kumar Sharma This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 Abstract
ECE4902 B2015 HW Set 1
 ECE4902 B2015 HW Set 1 Due in class Tuesday November 3. To make life easier on the graders: Be sure your NAME and ECE MAILBOX NUMBER are prominently displayed on the upper right of what you hand in. When
ECE4902 B2015 HW Set 1 Due in class Tuesday November 3. To make life easier on the graders: Be sure your NAME and ECE MAILBOX NUMBER are prominently displayed on the upper right of what you hand in. When
Syllabus for: Electronics for F Y B Sc (Electronics) Semester- 1 (With effect from June 2014) PAPER I: Basic Electrical Circuits
 Unit I: Passive Devices Syllabus for: Electronics for F Y B Sc (Electronics) Semester- 1 (With effect from June 2014) PAPER I: Basic Electrical Circuits Resistors, Fixed resistors & variable resistors,
Unit I: Passive Devices Syllabus for: Electronics for F Y B Sc (Electronics) Semester- 1 (With effect from June 2014) PAPER I: Basic Electrical Circuits Resistors, Fixed resistors & variable resistors,
Chapter 8. Field Effect Transistor
 Chapter 8. Field Effect Transistor Field Effect Transistor: The field effect transistor is a semiconductor device, which depends for its operation on the control of current by an electric field. There
Chapter 8. Field Effect Transistor Field Effect Transistor: The field effect transistor is a semiconductor device, which depends for its operation on the control of current by an electric field. There
Improving Amplifier Voltage Gain
 15.1 Multistage ac-coupled Amplifiers 1077 TABLE 15.3 Three-Stage Amplifier Summary HAND ANALYSIS SPICE RESULTS Voltage gain 998 1010 Input signal range 92.7 V Input resistance 1 M 1M Output resistance
15.1 Multistage ac-coupled Amplifiers 1077 TABLE 15.3 Three-Stage Amplifier Summary HAND ANALYSIS SPICE RESULTS Voltage gain 998 1010 Input signal range 92.7 V Input resistance 1 M 1M Output resistance
Objective Type Questions 1. Why pure semiconductors are insulators at 0 o K? 2. What is effect of temperature on barrier voltage? 3.
 Objective Type Questions 1. Why pure semiconductors are insulators at 0 o K? 2. What is effect of temperature on barrier voltage? 3. What is difference between electron and hole? 4. Why electrons have
Objective Type Questions 1. Why pure semiconductors are insulators at 0 o K? 2. What is effect of temperature on barrier voltage? 3. What is difference between electron and hole? 4. Why electrons have
EE70 - Intro. Electronics
 EE70 - Intro. Electronics Course website: ~/classes/ee70/fall05 Today s class agenda (November 28, 2005) review Serial/parallel resonant circuits Diode Field Effect Transistor (FET) f 0 = Qs = Qs = 1 2π
EE70 - Intro. Electronics Course website: ~/classes/ee70/fall05 Today s class agenda (November 28, 2005) review Serial/parallel resonant circuits Diode Field Effect Transistor (FET) f 0 = Qs = Qs = 1 2π
R. W. Erickson. Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder
 R. W. Erickson Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder pn junction! Junction diode consisting of! p-doped silicon! n-doped silicon! A p-n junction where
R. W. Erickson Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder pn junction! Junction diode consisting of! p-doped silicon! n-doped silicon! A p-n junction where
EC6202-ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS YEAR/SEM: II/III UNIT 1 TWO MARKS. 1. Define diffusion current.
 EC6202-ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS YEAR/SEM: II/III UNIT 1 TWO MARKS 1. Define diffusion current. A movement of charge carriers due to the concentration gradient in a semiconductor is called process
EC6202-ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS YEAR/SEM: II/III UNIT 1 TWO MARKS 1. Define diffusion current. A movement of charge carriers due to the concentration gradient in a semiconductor is called process
GATE 2009 Instrumentation Engineering
 GATE 2009 Instrumentation Engineering Q. Q20 carry one mark each.. If z = x jy, where x and y are real, the value of e is (A) (C) e (B) e x y (D) e 2. The value of origin, is (A) 0 (B) 2πj dz, where the
GATE 2009 Instrumentation Engineering Q. Q20 carry one mark each.. If z = x jy, where x and y are real, the value of e is (A) (C) e (B) e x y (D) e 2. The value of origin, is (A) 0 (B) 2πj dz, where the
Problem Sheet 1 Probability, random processes, and noise
 Problem Sheet 1 Probability, random processes, and noise 1. If F X (x) is the distribution function of a random variable X and x 1 x 2, show that F X (x 1 ) F X (x 2 ). 2. Use the definition of the cumulative
Problem Sheet 1 Probability, random processes, and noise 1. If F X (x) is the distribution function of a random variable X and x 1 x 2, show that F X (x 1 ) F X (x 2 ). 2. Use the definition of the cumulative
EIE209 Basic Electronics. Transistor Devices. Contents BJT and FET Characteristics Operations. Prof. C.K. Tse: T ransistor devices
 EIE209 Basic Electronics Transistor Devices Contents BJT and FET Characteristics Operations 1 What is a transistor? Three-terminal device whose voltage-current relationship is controlled by a third voltage
EIE209 Basic Electronics Transistor Devices Contents BJT and FET Characteristics Operations 1 What is a transistor? Three-terminal device whose voltage-current relationship is controlled by a third voltage
Chapter 4. CMOS Cascode Amplifiers. 4.1 Introduction. 4.2 CMOS Cascode Amplifiers
 Chapter 4 CMOS Cascode Amplifiers 4.1 Introduction A single stage CMOS amplifier cannot give desired dc voltage gain, output resistance and transconductance. The voltage gain can be made to attain higher
Chapter 4 CMOS Cascode Amplifiers 4.1 Introduction A single stage CMOS amplifier cannot give desired dc voltage gain, output resistance and transconductance. The voltage gain can be made to attain higher
GATE 2014: General Instructions during Examination
 GATE 2014: General Instructions during Examination 1. Total duration of the GATE examination is 180 minutes. 2. The clock will be set at the server. The countdown timer at the top right corner of screen
GATE 2014: General Instructions during Examination 1. Total duration of the GATE examination is 180 minutes. 2. The clock will be set at the server. The countdown timer at the top right corner of screen
SIR PADAMPAT SINGHANIA UNIVERSITY UDAIPUR Sample Question Paper for Ph.D. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) SPSAT 18
 INSTRUCTIONS SIR PADAMPAT SINGHANIA UNIVERSITY UDAIPUR Sample Question Paper for Ph.D. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) SPSAT 18 The test is 60 minutes long and consists of 40 multiple choice
INSTRUCTIONS SIR PADAMPAT SINGHANIA UNIVERSITY UDAIPUR Sample Question Paper for Ph.D. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) SPSAT 18 The test is 60 minutes long and consists of 40 multiple choice
MOSFET & IC Basics - GATE Problems (Part - I)
 MOSFET & IC Basics - GATE Problems (Part - I) 1. Channel current is reduced on application of a more positive voltage to the GATE of the depletion mode n channel MOSFET. (True/False) [GATE 1994: 1 Mark]
MOSFET & IC Basics - GATE Problems (Part - I) 1. Channel current is reduced on application of a more positive voltage to the GATE of the depletion mode n channel MOSFET. (True/False) [GATE 1994: 1 Mark]
CMOS Cascode Transconductance Amplifier
 CMOS Cascode Transconductance Amplifier Basic topology. 5 V I SUP v s V G2 M 2 iout C L v OUT Device Data V Tn = 1 V V Tp = 1 V µ n C ox = 50 µa/v 2 µ p C ox = 25 µa/v 2 λ n = 0.05 V 1 λ p = 0.02 V 1 @
CMOS Cascode Transconductance Amplifier Basic topology. 5 V I SUP v s V G2 M 2 iout C L v OUT Device Data V Tn = 1 V V Tp = 1 V µ n C ox = 50 µa/v 2 µ p C ox = 25 µa/v 2 λ n = 0.05 V 1 λ p = 0.02 V 1 @
GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13)
 GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13) 1. Removing bypass capacitor across the emitter leg resistor in a CE amplifier causes a. increase in current gain b. decrease in current gain c. increase
GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13) 1. Removing bypass capacitor across the emitter leg resistor in a CE amplifier causes a. increase in current gain b. decrease in current gain c. increase
CHAPTER 8 The pn Junction Diode
 CHAPTER 8 The pn Junction Diode Consider the process by which the potential barrier of a pn junction is lowered when a forward bias voltage is applied, so holes and electrons can flow across the junction
CHAPTER 8 The pn Junction Diode Consider the process by which the potential barrier of a pn junction is lowered when a forward bias voltage is applied, so holes and electrons can flow across the junction
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) MODEL ANSWER
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
In this lecture we will begin a new topic namely the Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor.
 Solid State Devices Dr. S. Karmalkar Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 38 MOS Field Effect Transistor In this lecture we will begin
Solid State Devices Dr. S. Karmalkar Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 38 MOS Field Effect Transistor In this lecture we will begin
CHAPTER 8 The PN Junction Diode
 CHAPTER 8 The PN Junction Diode Consider the process by which the potential barrier of a PN junction is lowered when a forward bias voltage is applied, so holes and electrons can flow across the junction
CHAPTER 8 The PN Junction Diode Consider the process by which the potential barrier of a PN junction is lowered when a forward bias voltage is applied, so holes and electrons can flow across the junction
UMAINE ECE Morse Code ROM and Transmitter at ISM Band Frequency
 UMAINE ECE Morse Code ROM and Transmitter at ISM Band Frequency Jamie E. Reinhold December 15, 2011 Abstract The design, simulation and layout of a UMAINE ECE Morse code Read Only Memory and transmitter
UMAINE ECE Morse Code ROM and Transmitter at ISM Band Frequency Jamie E. Reinhold December 15, 2011 Abstract The design, simulation and layout of a UMAINE ECE Morse code Read Only Memory and transmitter
Operational Amplifier BME 360 Lecture Notes Ying Sun
 Operational Amplifier BME 360 Lecture Notes Ying Sun Characteristics of Op-Amp An operational amplifier (op-amp) is an analog integrated circuit that consists of several stages of transistor amplification
Operational Amplifier BME 360 Lecture Notes Ying Sun Characteristics of Op-Amp An operational amplifier (op-amp) is an analog integrated circuit that consists of several stages of transistor amplification
Gechstudentszone.wordpress.com
 UNIT 4: Small Signal Analysis of Amplifiers 4.1 Basic FET Amplifiers In the last chapter, we described the operation of the FET, in particular the MOSFET, and analyzed and designed the dc response of circuits
UNIT 4: Small Signal Analysis of Amplifiers 4.1 Basic FET Amplifiers In the last chapter, we described the operation of the FET, in particular the MOSFET, and analyzed and designed the dc response of circuits
Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering LAB MANUAL SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION LABORATORY [ECE324] (Branch: ECE)
![Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering LAB MANUAL SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION LABORATORY [ECE324] (Branch: ECE) Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering LAB MANUAL SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION LABORATORY [ECE324] (Branch: ECE)](/thumbs/96/127341232.jpg) Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering LAB MANUAL SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION LABORATORY [ECE324] B.Tech Year 3 rd, Semester - 5 th (Branch: ECE) Version: 01 st August 2018 The LNM Institute
Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering LAB MANUAL SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION LABORATORY [ECE324] B.Tech Year 3 rd, Semester - 5 th (Branch: ECE) Version: 01 st August 2018 The LNM Institute
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 8-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 29
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 8-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 29
For the mechanical system of figure shown above:
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-00 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks : 0 Candidates should attempt any FIVE questions. Some useful data: Electron charge : 1.6
I.E.S-(Conv.)-00 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks : 0 Candidates should attempt any FIVE questions. Some useful data: Electron charge : 1.6
