GATE 2014: General Instructions during Examination
|
|
|
- Amie Newman
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GATE 2014: General Instructions during Examination 1. Total duration of the GATE examination is 180 minutes. 2. The clock will be set at the server. The countdown timer at the top right corner of screen will display the remaining time available for you to complete the examination. When the timer reaches zero, the examination will end by itself. You need not terminate the examination or submit your paper. 3. Any useful data required for your paper can be viewed by clicking on the Useful Common Data button that appears on the screen. 4. Use the scribble pad provided to you for any rough work. Submit the scribble pad at the end of the examination. 5. You are allowed to use a non-programmable type calculator, however, sharing of calculators is not allowed. 6. The Question Palette displayed on the right side of screen will show the status of each question using one of the following symbols: The Marked for Review status for a question simply indicates that you would like to look at that question again. If a question is answered, but marked for review, then the answer will be considered for evaluation unless the status is modified by the candidate. Navigating to a Question : 7. To answer a question, do the following: a. Click on the question number in the Question Palette to go to that question directly. b. Select an answer for a multiple choice type question by clicking on the bubble placed before the 4 choices, namely A, B, C and D. Use the virtual numeric keypad to enter a number as answer for a numerical type question. c. Click on Save & Next to save your answer for the current question and then go to the next question. d. Click on Mark for Review & Next to save your answer for the current question and also mark it for review, and then go to the next question.
2 Caution: Note that your answer for the current question will not be saved, if you navigate to another question directly by clicking on a question number without saving the answer to the previous question. You can view all the questions by clicking on the Question Paper button. This feature is provided, so that if you want you can just see the entire question paper at a glance. Answering a Question : 8. Procedure for answering a multiple choice (MCQ) type question: a. Choose one answer from the 4 options (A,B,C,D) given below the question, click on the bubble placed before the chosen option. b. To deselect your chosen answer, click on the bubble of the chosen option again or click on the Clear Response button. c. To change your chosen answer, click on the bubble of another option. d. To save your answer, you MUST click on the Save & Next button. 9. Procedure for answering a numerical answer type question: a. To enter a number as your answer, use the virtual numerical keypad. b. A fraction (e.g or -.3) can be entered as an answer with or without '0' before the decimal point. As many as four decimal points, e.g or or or can be entered. c. To clear your answer, click on the Clear Response button. d. To save your answer, you MUST click on the Save & Next button 10. To mark a question for review, click on the Mark for Review & Next button. If an answer is selected (for MCQ) or entered (for numerical answer type) for a question that is Marked for Review, that answer will be considered in the evaluation unless the status is modified by the candidate. 11. To change your answer to a question that has already been answered, first select that question for answering and then follow the procedure for answering that type of question. 12. Note that ONLY Questions for which answers are saved or marked for review after answering will be considered for evaluation. Choosing a Section : 13. Sections in this question paper are displayed on the top bar of the screen. Questions in a Section can be viewed by clicking on the name of that Section. The Section you are currently viewing will be highlighted. 14. A checkbox is displayed for every optional Section, if any, in the Question Paper. To select the optional Section for answering, click on the checkbox for that Section. 15. If the checkbox for an optional Section is not selected, the Save & Next button and the Mark for Review & Next button will NOT be enabled for that Section. You will
3 only be able to see questions in this Section, but you will not be able to answer questions in the Section. 16. After clicking the Save & Next button for the last question in a Section, you will automatically be taken to the first question of the next Section in sequence. 17. You can move the mouse cursor over the name of a Section to view the answering status for that Section. Changing the Optional Section : 18. After answering the chosen optional Section, partially or completely, you can change the optional Section by selecting the checkbox for a new Section that you want to attempt. A warning message will appear along with a table showing the number of questions answered in each of the previously chosen optional Sections and a checkbox against each of these Sections. Click on a checkbox against a Section that you want to reset and then click on the RESET button. Note that RESETTING a Section will DELETE all the answers for questions in that Section. Hence, if you think that you may want to select this Section again later, you will have to note down your answers for questions in that Section. If you do not want to reset the Section and want to continue answering the previously chosen optional Section, then click on the BACK button. 19. If you deselect the checkbox for an optional Section in the top bar, the following warning message will appear: "Deselecting the checkbox will DELETE all the answers for questions in this Section. Do you want to deselect this Section? If you want to deselect, click on the RESET button. If you do not want to deselect, click on the BACK button. 20. You can shuffle between different Sections or change the optional Sections any number of times.
4 GATE 2014 Examination EC: Electronics & Communications Engineering Duration: 180 minutes Maximum Marks: 100 Read the following instructions carefully. 1. To login, enter your Registration Number and password provided to you. Kindly go through the various symbols used in the test and understand their meaning before you start the examination. 2. Once you login and after the start of the examination, you can view all the questions in the question paper, by clicking on the View All Questions button in the screen. 3. This question paper consists of 2 sections, General Aptitude (GA) for 15 marks and the subject specific GATE paper for 85 marks. Both these sections are compulsory. The GA section consists of 10 questions. Question numbers 1 to 5 are of 1-mark each, while question numbers 6 to 10 are of 2-mark each. The subject specific GATE paper section consists of 55 questions, out of which question numbers 1 to 25 are of 1-mark each, while question numbers 26 to 55 are of 2-mark each. 4. Depending upon the GATE paper, there may be useful common data that may be required for answering the questions. If the paper has such useful data, the same can be viewed by clicking on the Useful Common Data button that appears at the top, right hand side of the screen. 5. The computer allotted to you at the examination center runs specialized software that permits only one answer to be selected for multiple-choice questions using a mouse and to enter a suitable number for the numerical answer type questions using the virtual keyboard and mouse. 6. Your answers shall be updated and saved on a server periodically and also at the end of the examination. The examination will stop automatically at the end of 180 minutes. 7. In each paper a candidate can answer a total of 65 questions carrying 100 marks. 8. The question paper may consist of questions of multiple choice type (MCQ) and numerical answer type. 9. Multiple choice type questions will have four choices against A, B, C, D, out of which only ONE is the correct answer. The candidate has to choose the correct answer by clicking on the bubble ( ) placed before the choice. 10. For numerical answer type questions, each question will have a numerical answer and there will not be any choices. For these questions, the answer should be enteredby using the virtual keyboard that appears on the monitor and the mouse. 11. All questions that are not attempted will result in zero marks. However, wrong answers for multiple choice type questions (MCQ) will result in NEGATIVE marks. For all MCQ questions a wrong answer will result in deduction of⅓ marks for a 1-mark question and ⅔ marks for a 2-mark question. 12. There is NO NEGATIVE MARKING for questions of NUMERICAL ANSWER TYPE. 13. Non-programmable type Calculator is allowed. Charts, graph sheets, and mathematical tables are NOT allowed in the Examination Hall. You must use the Scribble pad provided to you at the examination centre for all your rough work. The Scribble Pad has to be returned at the end of the examination. Declaration by the candidate: I have read and understood all the above instructions. I have also read and understood clearly the instructions given on the admit card and shall follow the same. I also understand that in case I am found to violate any of these instructions, my candidature is liable to be cancelled. I also confirm that at the start of the examination all the computer hardware allotted to me are in proper working condition.
5 GATE 2014 SET- 5 General Aptitude -GA Q. 1 Q. 5 carry one mark each. Q.1 India is a country of rich heritage and cultural diversity. Which one of the following facts best supports the claim made in the above sentence? (A) India is a union of 28 states and 7 union territories. (B) India has a population of over 1.1 billion. (C) India is home to 22 official languages and thousands of dialects. (D) The Indian cricket team draws players from over ten states. Q.2 The value of one U.S. dollar is 65 Indian Rupees today, compared to 60 last year. The Indian Rupee has. (A) depressed (B) depreciated (C) appreciated (D) stabilized Q.3 'Advice' is. (A) a verb (B) a noun (C) an adjective (D) both a verb and a noun Q.4 The next term in the series 81, 54, 36, 24, is Q.5 In which of the following options will the expression P < M be definitely true? (A) M < R > P > S (B) M > S < P < F (C) Q < M < F = P (D) P = A < R < M Q. 6 Q. 10 carry two marks each. Q.6 Find the next term in the sequence: 7G, 11K, 13M, (A) 15Q (B) 17Q (C) 15P (D) 17P GA05 (GATE 2014) GA 1/3
6 GATE 2014 SET- 5 General Aptitude -GA Q.7 The multi-level hierarchical pie chart shows the population of animals in a reserve forest. The correct conclusions from this information are: (i) Butterflies are birds (ii) There are more tigers in this forest than red ants (iii) All reptiles in this forest are either snakes or crocodiles (iv) Elephants are the largest mammals in this forest (A) (i) and (ii) only (C) (i), (iii) and (iv) only (B) (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) (D) (i), (ii) and (iii) only Q.8 A man can row at 8 km per hour in still water. If it takes him thrice as long to row upstream, as to row downstream, then find the stream velocity in km per hour. GA05 (GATE 2014) GA 2/3
7 GATE 2014 SET- 5 General Aptitude -GA Q.9 A firm producing air purifiers sold 200 units in The following pie chart presents the share of raw material, labour, energy, plant & machinery, and transportation costs in the total manufacturing cost of the firm in The expenditure on labour in 2012 is Rs. 4,50,000. In 2013, the raw material expenses increased by 30% and all other expenses increased by 20%. If the company registered a profit of Rs. 10 lakhs in 2012, at what price (in Rs.) was each air purifier sold? Q.10 A batch of one hundred bulbs is inspected by testing four randomly chosen bulbs. The batch is rejected if even one of the bulbs is defective. A batch typically has five defective bulbs. The probability that the current batch is accepted is END OF THE QUESTION PAPER GA05 (GATE 2014) GA 3/3
8 Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 The maximum value of the function ff(xx) = llll(1 + xx) xx (where xx > 1) occurs at xx =. Q.2 Which ONE of the following is a linear non-homogeneous differential equation, where x and y are the independent and dependent variables respectively? (A) dddd + xxxx = ee xx dddd (B) dddd + xxxx = 0 dddd (C) dddd + xxxx = ee yy dddd (D) dddd + dddd ee yy = 0 Q.3 Match the application to appropriate numerical method. Application Numerical Method P1: Numerical integration M1: Newton-Raphson Method P2: Solution to a transcendental equation M2: Runge-Kutta Method P3: Solution to a system of linear equations M3: Simpson s 1/3-rule P4: Solution to a differential equation M4: Gauss Elimination Method (A) P1 M3, P2 M2, P3 M4, P4 M1 (B) P1 M3, P2 M1, P3 M4, P4 M2 (C) P1 M4, P2 M1, P3 M3, P4 M2 (D) P1 M2, P2 M1, P3 M3, P4 M4 Q.4 An unbiased coin is tossed an infinite number of times. The probability that the fourth head appears at the tenth toss is (A) (B) (C) (D) Q.5 If z = xy ln( xy), then z z (A) x + y = 0 x y z z (C) x = y x y z z (B) y = x x y z z (D) y + x = 0 x y EC 1/14
9 Q.6 A series RC circuit is connected to a DC voltage source at time t = 0. The relation between the source voltage V S, the resistance R, the capacitance C, and the current i(t) is given below: tt oo VV ss = RR ii(tt) + 1 CC ii(uu)dddd. Which one of the following represents the current i(t)? (A) (B) (C) i(t) 0 i(t) 0 t Q.7 In the figure shown, the value of the current I (in Amperes) is. t (D) i(t) 0 i(t) 0 t t Q.8 In MOSFET fabrication, the channel length is defined during the process of (A) isolation oxide growth (B) channel stop implantation (C) poly-silicon gate patterning (D) lithography step leading to the contact pads EC 2/14
10 Q.9 A thin P-type silicon sample is uniformly illuminated with light which generates excess carriers. The recombination rate is directly proportional to (A) the minority carrier mobility (B) the minority carrier recombination lifetime (C) the majority carrier concentration (D) the excess minority carrier concentration Q.10 At T = 300 K, the hole mobility of a semiconductor μμ pp = 500 cm 2 /V-s and kkkk qq hole diffusion constant DD pp in cm 2 /s is Q.11 The desirable characteristics of a transconductance amplifier are (A) high input resistance and high output resistance (B) high input resistance and low output resistance (C) low input resistance and high output resistance (D) low input resistance and low output resistance = 26 mv. The Q.12 In the circuit shown, the PNP transistor has VV BBBB = 0.7 Vand β = 50. Assume that RR BB = 100 kkω. For V 0 to be 5 V, the value of RR CC (in kkω) is R B R C V EE = 10 V Q.13 The figure shows a half-wave rectifier. The diode D is ideal. The average steady-state current (in Amperes) through the diode is approximately. V 0 Q.14 An analog voltage in the range 0 to 8 V is divided in 16 equal intervals for conversion to 4-bit digital output. The maximum quantization error (in V) is EC 3/14
11 Q.15 The circuit shown in the figure is a D En D Latch Q Q En D Latch Q Q Clk (A) Toggle Flip Flop (B) JK Flip Flop (C) SR Latch (D) Master-Slave D Flip Flop Q.16 Consider the multiplexer based logic circuit shown in the figure. Which one of the following Boolean functions is realized by the circuit? (A) FF = WWSS 1 SS 2 (B) FF = WWSS 1 + WWSS 2 + SS 1 SS 2 (C) FF = WW + SS 1 + SS 2 (D) FF = WW SS 1 SS 2 Q.17 Let xx(tt) = cos(10ππππ) + cos(30ππππ) be sampled at 20 Hz and reconstructed using an ideal low-pass filter with cut-off frequency of 20 Hz. The frequency/frequencies present in the reconstructed signal is/are Q.18 W (A) 5 Hz and 15 Hz only (C) 5 Hz, 10 Hz and 15 Hz only (zz 1 bb ) 0 MUX 1 (B) 10 Hz and 15 Hz only (D) 5 Hz only For an all-pass system HH(zz) =, where (1 aazz 1 ) HH ee jjjj = 1, for all ωω. If Re(aa) 0, Im(aa) 0, then b equals (A) aa (B) aa (C) 1/aa (D) 1/aa S 1 0 MUX 1 S 2 F EC 4/14
12 Q.19 A modulated signal is yy(tt) = mm(tt) cos(40000ππππ), where the baseband signal mm(tt) has frequency components less than 5 khz only. The minimum required rate (in khz) at which yy(tt) should be sampled to recover mm(tt) is. Q.20 Consider the following block diagram in the figure. The transfer function CC(ss) (A) GG 1GG 2 1+GG 1 GG 2 (B)GG 1 GG 2 + GG (C)GG 1 GG 2 + GG GG (D) 1 1+GG 1 GG 2 RR(ss) is Q.21 The input 3e 2tt uu(tt), where uu(tt) is the unit step function, is applied to a system with transfer function ss 2. If the initial value of the output is 2, then the value of the output at steady state is ss+3. Q.22 The phase response of a passband waveform at the receiver is given by φφ(ff) = 2ππππ(ff ff cc ) 2ππππff cc where ff cc is the centre frequency, and αα and ββ are positive constants. The actual signal propagation delay from the transmitter to receiver is (A) αα ββ αα+ββ (B) αααα αα+ββ (C) αα (D) ββ Q.23 Consider an FM signal ff(tt) = cos[2ππff cc tt + ββ 1 sin 2ππff 1 tt + ββ 2 sin 2ππff 2 tt ]. The maximum deviation of the instantaneous frequency from the carrier frequency ff cc is (A) ββ 1 ff 1 + ββ 2 ff 2 (B) ββ 1 ff 2 + ββ 2 ff 1 (C) ββ 1 + ββ 2 (D) ff 1 + ff 2 Q.24 Consider an air filled rectangular waveguide with a cross-section of 5 cm 3 cm. For this waveguide, the cut-off frequency (in MHz) of TE 21 mode is. EC 5/14
13 Q.25 In the following figure, the transmitter Tx sends a wideband modulated RF signal via a coaxial cable to the receiver Rx. The output impedance Z T of Tx, the characteristic impedance Z 0 of the cable and the input impedance Z R of Rx are all real. Which one of the following statements is TRUE about the distortion of the received signal due to impedance mismatch? (A) The signal gets distorted if Z R Z 0, irrespective of the value of Z T (B) The signal gets distorted if Z T Z 0, irrespective of the value of Z R (C) Signal distortion implies impedance mismatch at both ends: Z T Z 0 and Z R Z 0 (D) Impedance mismatches do NOT result in signal distortion but reduce power transfer efficiency Q. 26 Q. 55 carry two marks each. Q.26 The maximum value of ff(xx) = 2xx 3 9xx xx 3 in the interval 0 xx 3 is. Q.27 Which one of the following statements is NOT true for a square matrix AA? (A) If AA is upper triangular, the eigenvalues of AA are the diagonal elements of it (B) If AA is real symmetric, the eigenvalues of AA are always real and positive (C) If AA is real, the eigenvalues of AA and AA TT are always the same (D) If all the principal minors of AA are positive, all the eigenvalues of AA are also positive Q.28 A fair coin is tossed repeatedly till both head and tail appear at least once. The average number of tosses required is. Q.29 Let X 1, X 2, and X 3 be independent and identically distributed random variables with the uniform distribution on [0, 1]. The probability P{X 1 + X 2 X 3 } is. EC 6/14
14 Q.30 Consider the building block called Network N shown in the figure. Let C = 100 µf and R = 10 kω. Network N + V 1 (s) C R + V 2 (s) - - Two such blocks are connected in cascade, as shown in the figure. The transfer function VV 3(ss) of the cascaded network is (A) ss 1+ss VV 1 (ss) (B) ss 2 1+3ss+ss 2 (C) ss 1+ss 2 Q.31 In the circuit shown in the figure, the value of node voltage VV 2 is + V 1 (s) - C Network R N (A) 22 + j 2 V (B) 2 + j 22 V (C) 22 j 2 V (D) 2 j 22 V Q.32 In the circuit shown in the figure, the angular frequency ω (in rad/s), at which the Norton equivalent impedance as seen from terminals b-b is purely resistive, is. + - Network N + V 3 (s) - (D) ss 2+ss EC 7/14
15 Q.33 For the Y-network shown in the figure, the value of R 1 (in Ω) in the equivalent -network is. R 1 5 Ω 3 Ω Q.34 The donor and accepter impurities in an abrupt junction silicon diode are 1 x cm -3 and 5 x cm -3, respectively. Assume that the intrinsic carrier concentration in silicon n i = 1.5 x cm -3 at 300 K, kkkk = 26 mv and the permittivity of silicon εε qq ssss = F/cm. The built-in potential and the depletion width of the diode under thermal equilibrium conditions, respectively, are (A) 0.7 V and 1 x 10-4 cm (B) 0.86 V and 1 x 10-4 cm (C) 0.7 V and 3.3 x 10-5 cm (D) 0.86 V and 3.3 x 10-5 cm Q.35 The slope of the II DD vs. VV GGGG curve of an n-channel MOSFET in linear regime is 10 3 Ω 1 at VV DDDD = 0.1 V. For the same device, neglecting channel length modulation, the slope of the II DD vs. VV GGGG curve (in A/V) under saturation regime is approximately. Q.36 An ideal MOS capacitor has boron doping-concentration of cm -3 in the substrate. When a gate voltage is applied, a depletion region of width 0.5 µm is formed with a surface (channel) potential of 0.2 V. Given that ε 0 = F/cm and the relative permittivities of silicon and silicon dioxide are 12 and 4, respectively, the peak electric field (in V/µm) in the oxide region is. 7.5 Ω EC 8/14
16 Q.37 In the circuit shown, the silicon BJT has β = 50. Assume V BE = 0.7 V and V CE(sat) = 0.2 V. Which one of the following statements is correct? (A) For R C = 1 kω, the BJT operates in the saturation region (B) For R C = 3 kω, the BJT operates in the saturation region (C) For R C =20 kω, the BJT operates in the cut-off region (D) For R C =20 kω, the BJT operates in the linear region Q.38 Assuming that the Op-amp in the circuit shown is ideal, V o is given by (A) 5 V 2 1 3V 2 (B) 2V 1 5 V 2 2 (C) 3 V V 2 2 (D) 3V V 2 2 Q.39 For the MOSFET M 1 shown in the figure, assume W/L = 2, V DD = 2.0 V, μμ nn CC oooo = 100 μa/v 2 and V TH = 0.5 V. The transistor M 1 switches from saturation region to linear region when V in (in Volts) is. V DD R= 10 kω V out V in M 1 EC 9/14
17 Q.40 If WL is the Word Line and BL the Bit Line, an SRAM cell is shown in (A) (B) (C) Q.41 In the circuit shown, WW and YY are MSBs of the control inputs. The output FF is given by V CC (A) FF = WWXX + WW XX + YY ZZ (B) FF = WWXX + WW XX + YY ZZ (C) FF = WWXX YY + WW XXYY (D) FF = (WW + XX )YY ZZ (D) 4:1 MUX 4:1 MUX I 0 I 1 I 2 I 3 Q I 0 I 1 I 2 I 3 W X Y Z Q F EC 10/14
18 Q.42 If X and Y are inputs and the Difference (D = X Y) and the Borrow (B) are the outputs, which one of the following diagrams implements a half-subtractor? (A) (C) Y Y X Y X Y I 0 I 1 2:1 MUX S S I 0 2:1 MUX I 1 I 0 2:1 MUX I 1 S S I 0 2:1 MUX I 1 D B B D (B) (D) X X Y X Y X I 0 I 1 2:1 MUX S S I 0 2:1 MUX I 1 I 0 2:1 MUX I 1 S S I 0 2:1 MUX I 1 Q.43 Let HH 1 (zz) = (1 ppzz 1 ) 1, HH 2 (zz) = (1 qqzz 1 ) 1, HH(zz) = HH 1 (zz) + rr HH 2 (zz). The quantities pp, qq, rr are real numbers. Consider pp = 1, qq = 1, rr < 1. If the zero of HH(zz) lies on the unit circle, 2 4 then rr = Q.44 Let h(tt) denote the impulse response of a causal system with transfer function 1. Consider the ss+1 following three statements. S1: The system is stable. S2: h (tt+1) is independent of tt for tt > 0. h(tt) S3: A non-causal system with the same transfer function is stable. For the above system, (A) only S1 and S2 are true (C) only S1 and S3 are true (B) only S2 and S3 are true (D) S1, S2 and S3 are true Q.45 1 The z-transform of the sequence xx[nn] is given by X(zz) = (1 2 zz 1 ) 2, with the region of convergence zz > 2. Then, xx[2] is. D B B D EC 11/14
19 Q.46 The steady state error of the system shown in the figure for a unit step input is. Q.47 The state equation of a second-order linear system is given by xx (tt) = AAxx(tt), xx(0) = xx 0 For xx 0 = 1 ee tt, xx(tt) = 1 ee tt and for xx 0 = 0 1, xx(tt) = ee tt ee 2tt ee tt + 2ee 2tt. When xx 0 = 3, xx(tt) is 5 (A) 8ee tt + 11ee 2tt 8ee tt 2tt 22ee (B) (C) 3ee tt 5ee 2tt 3ee tt + 10ee 2tt 11ee tt 8ee 2tt 11ee tt + 16ee 2tt (D) 5ee tt 3ee 2tt 5ee tt + 6ee 2tt Q.48 In the root locus plot shown in the figure, the pole/zero marks and the arrows have been removed. Which one of the following transfer functions has this root locus? (A) (C) ss+1 (ss+2)(ss+4)(ss+7) ss+7 (ss+1)(ss+2)(ss+4) (B) (D) ss+4 (ss+1)(ss+2)(ss+7) (ss+1)(ss+2) (ss+7)(ss+4) Q.49 Let XX(tt) be a wide sense stationary (WSS) random process with power spectral density SS XX (ff). If YY(tt) is the process defined as YY(tt) = XX(2tt 1), the power spectral density SS YY (ff) is (A) SS YY (ff) = 1 SS 2 XX ff 2 ee jjjjjj (B) SS YY (ff) = 1 SS 2 XX ff /2 ee jjjjjj 2 (C) SS YY (ff) = 1 SS 2 XX ff (D) SS 2 YY(ff) = 1 SS 2 XX ff ee jj2ππππ 2 EC 12/14
20 Q.50 A real band-limited random process XX(tt) has two-sided power spectral density SS XX (ff) = 10 6 (3000 ff ) Watts/Hz for ff 3 khz 0 otherwise where ff is the frequency expressed in Hz. The signal XX(tt) modulates a carrier cos ππππ and the resultant signal is passed through an ideal band-pass filter of unity gain with centre frequency of 8 khz and band-width of 2 khz. The output power (in Watts) is. Q.51 In a PCM system, the signal mm(tt) = {sin(100ππππ) + cos(100ππππ)} V is sampled at the Nyquist rate. The samples are processed by a uniform quantizer with step size 0.75 V. The minimum data rate of the PCM system in bits per second is. Q.52 A binary random variable XX takes the value of 1 with probability 1 3. XX is input to a cascade of 2 independent identical binary symmetric channels (BSCs) each with crossover probability 1 2. The output of BSCs are the random variables YY 1 and YY 2 as shown in the figure. X Y1 2 BSC The value of HH(YY 1 ) + HH(YY 2 ) in bits is. Q.53 Given the vector AA = (cos xx)(sin yy)aa xx + (sin xx)(cos yy)aa yy, whereaa xx, aa yy denote unit vectors along x,y directions, respectively. The magnitude of curl of AA is Q.54 A region shown below contains a perfect conducting half-space and air. The surface current KK ss on the surface of the perfect conductor is KK ss = xx 2 amperes per meter. The tangential HH field in the air just above the perfect conductor is KK ss y Air BSC Perfect conductor x Y (A) (xx + zz )2 amperes per meter (B) xx 2 amperes per meter (C) zz 2 amperes per meter (D) zz 2 amperes per meter EC 13/14
21 Q.55 Assume that a plane wave in air with an electric field E = 10 cos( ωt 3x 3z) aˆ y V/m is incident on a non-magnetic dielectric slab of relative permittivity 3 which covers the region z > 0. The angle of transmission in the dielectric slab is degrees. END OF THE QUESTION PAPER EC 14/14
GATE 2014 QUESTION PAPERS EC: Electronics & Communications Engineering - 16th February 2014 (Morning)
 ENGISTAN.COM GATE 2014 QUESTION PAPERS EC: Electronics & Communications Engineering - 16th February 2014 (Morning) All GATE 2014 Question Papers & Answers keys are Original Papers & Keys as provided by
ENGISTAN.COM GATE 2014 QUESTION PAPERS EC: Electronics & Communications Engineering - 16th February 2014 (Morning) All GATE 2014 Question Papers & Answers keys are Original Papers & Keys as provided by
GATE 2014: General Instructions during Examination
 GATE 2014: General Instructions during Examination 1. Total duration of the GATE examination is 180 minutes. 2. The clock will be set at the server. The countdown timer at the top right corner of screen
GATE 2014: General Instructions during Examination 1. Total duration of the GATE examination is 180 minutes. 2. The clock will be set at the server. The countdown timer at the top right corner of screen
GATE 2014: General Instructions during Examination
 GATE 2014: General Instructions during Examination 1. Total duration of the GATE examination is 180 minutes. 2. The clock will be set at the server. The countdown timer at the top right corner of screen
GATE 2014: General Instructions during Examination 1. Total duration of the GATE examination is 180 minutes. 2. The clock will be set at the server. The countdown timer at the top right corner of screen
GATE 2014: General Instructions during Examination
 GATE 2014: General Instructions during Examination 1. Total duration of the GATE examination is 180 minutes. 2. The clock will be set at the server. The countdown timer at the top right corner of screen
GATE 2014: General Instructions during Examination 1. Total duration of the GATE examination is 180 minutes. 2. The clock will be set at the server. The countdown timer at the top right corner of screen
Physical Structure of CMOS Integrated Circuits
 Physical Structure of CMOS Integrated Circuits Dae Hyun Kim EECS Washington State University References John P. Uyemura, Introduction to VLSI Circuits and Systems, 2002. Chapter 3 Neil H. Weste and David
Physical Structure of CMOS Integrated Circuits Dae Hyun Kim EECS Washington State University References John P. Uyemura, Introduction to VLSI Circuits and Systems, 2002. Chapter 3 Neil H. Weste and David
ECE Branch GATE Paper Q2. The trigonometric Fourier series for the waveform shown below contains
 Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each. Q1. The eigen values of a skew-symmetric matrix are Always zero Always pure imaginary Either zero or pure imaginary Always real Q2. The trigonometric Fourier series for the
Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each. Q1. The eigen values of a skew-symmetric matrix are Always zero Always pure imaginary Either zero or pure imaginary Always real Q2. The trigonometric Fourier series for the
b) discrete-time iv) aperiodic (finite energy)
 EE 464 Frequency Analysis of Signals and Systems Fall 2018 Read Text, Chapter. Study suggestion: Use Matlab to plot several of the signals and their DTFT in the examples to follow. Some types of signal
EE 464 Frequency Analysis of Signals and Systems Fall 2018 Read Text, Chapter. Study suggestion: Use Matlab to plot several of the signals and their DTFT in the examples to follow. Some types of signal
Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras
 Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Sample Questions on Semiconductor Devices EE3 applicants who are interested to pursue their research in microelectronics devices area (fabrication and/or
Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Sample Questions on Semiconductor Devices EE3 applicants who are interested to pursue their research in microelectronics devices area (fabrication and/or
ECE Branch GATE Paper (C) exp ( t ) sin (25t) (B) 4cos (20t + 3) + 2 sin (710t)
 Question 30 Carry One Mark Each. The following differential equation has 2 3 d y dy 2 3 4 y 2 2 dt degree = 2, order = degree = 3, order = 2 + + + = x dt degree = 4, order = 3 degree = 2, order = 3 2.
Question 30 Carry One Mark Each. The following differential equation has 2 3 d y dy 2 3 4 y 2 2 dt degree = 2, order = degree = 3, order = 2 + + + = x dt degree = 4, order = 3 degree = 2, order = 3 2.
EJERCICIOS DE COMPONENTES ELECTRÓNICOS. 1 er cuatrimestre
 EJECICIOS DE COMPONENTES ELECTÓNICOS. 1 er cuatrimestre 2 o Ingeniería Electrónica Industrial Juan Antonio Jiménez Tejada Índice 1. Basic concepts of Electronics 1 2. Passive components 1 3. Semiconductors.
EJECICIOS DE COMPONENTES ELECTÓNICOS. 1 er cuatrimestre 2 o Ingeniería Electrónica Industrial Juan Antonio Jiménez Tejada Índice 1. Basic concepts of Electronics 1 2. Passive components 1 3. Semiconductors.
SIR PADAMPAT SINGHANIA UNIVERSITY UDAIPUR Sample Question Paper for Ph.D. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) SPSAT 18
 INSTRUCTIONS SIR PADAMPAT SINGHANIA UNIVERSITY UDAIPUR Sample Question Paper for Ph.D. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) SPSAT 18 The test is 60 minutes long and consists of 40 multiple choice
INSTRUCTIONS SIR PADAMPAT SINGHANIA UNIVERSITY UDAIPUR Sample Question Paper for Ph.D. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) SPSAT 18 The test is 60 minutes long and consists of 40 multiple choice
Project 6 Capacitance of a PN Junction Diode
 Project 6 Capacitance of a PN Junction Diode OVERVIEW: In this project, we will characterize the capacitance of a reverse-biased PN diode. We will see that this capacitance is voltage-dependent and we
Project 6 Capacitance of a PN Junction Diode OVERVIEW: In this project, we will characterize the capacitance of a reverse-biased PN diode. We will see that this capacitance is voltage-dependent and we
 COMBO ONLINE TEST SERIES GATE 2019 SCHEDULE: ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Syllabus Test Date Test Type [ EB-Engineering Branch ; EM- No. of Engineering Mathematics; GA- General Question Marks
COMBO ONLINE TEST SERIES GATE 2019 SCHEDULE: ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Syllabus Test Date Test Type [ EB-Engineering Branch ; EM- No. of Engineering Mathematics; GA- General Question Marks
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each.
 Q. Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q. A random variable XX has probability density function ff(xx) as given below: aa bbbb ffffff 0 < xx < ff(xx) = 0 otherwise If the expected value EE[XX] = 2/3, then PPPP[XX
Q. Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q. A random variable XX has probability density function ff(xx) as given below: aa bbbb ffffff 0 < xx < ff(xx) = 0 otherwise If the expected value EE[XX] = 2/3, then PPPP[XX
Electronics Eingineering
 Electronics Eingineering 1. The output of a two-input gate is 0 if and only if its inputs are unequal. It is true for (A) XOR gate (B) NAND gate (C) NOR gate (D) XNOR gate 2. In K-map simplification, a
Electronics Eingineering 1. The output of a two-input gate is 0 if and only if its inputs are unequal. It is true for (A) XOR gate (B) NAND gate (C) NOR gate (D) XNOR gate 2. In K-map simplification, a
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-2012 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 40 Subject: PART - A 0. Which region of the transistor
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 40 Subject: PART - A 0. Which region of the transistor
1.5 The voltage V is given as V=RI, where R and I are resistance matrix and I current vector. Evaluate V given that
 Sheet (1) 1.1 The voltage across a discharging capacitor is v(t)=10(1 e 0.2t ) Generate a table of voltage, v(t), versus time, t, for t = 0 to 50 seconds with increment of 5 s. 1.2 Use MATLAB to evaluate
Sheet (1) 1.1 The voltage across a discharging capacitor is v(t)=10(1 e 0.2t ) Generate a table of voltage, v(t), versus time, t, for t = 0 to 50 seconds with increment of 5 s. 1.2 Use MATLAB to evaluate
Linear Algebra, Calculus, Differential Equations and Vector Analysis. Complex Anaysis, Numerical Methods and Probability and Statistics.
 Test No Topic code Topic EC-01 GEM (Engineering Mathematics) Topic wise Tests Each test carries 25 marks and 45 minutes duration Test consists of 5 one mark questions and 10 two marks questions Tests will
Test No Topic code Topic EC-01 GEM (Engineering Mathematics) Topic wise Tests Each test carries 25 marks and 45 minutes duration Test consists of 5 one mark questions and 10 two marks questions Tests will
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-2007 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - II Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt Question No. 1 which is compulsory and FOUR more questions
I.E.S-(Conv.)-2007 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - II Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt Question No. 1 which is compulsory and FOUR more questions
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-2012 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: Qn. PART - A 0. Which is the largest of three
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: Qn. PART - A 0. Which is the largest of three
6. A low pass filter having a frequency response does not produce any phase distortion, if (A) A(ω)
 1. The rank of the matrix is 0 1 2. P, where P is a vector, is equal to 2 P P P 2 P+ P ( ) 2 3 2 P+ P 2 ( P) P 3. ( P) ds, where P is a vector, is equal to P dl P dl Pdv ax 4. A probability density function
1. The rank of the matrix is 0 1 2. P, where P is a vector, is equal to 2 P P P 2 P+ P ( ) 2 3 2 P+ P 2 ( P) P 3. ( P) ds, where P is a vector, is equal to P dl P dl Pdv ax 4. A probability density function
Section 2.3 Bipolar junction transistors - BJTs
 Section 2.3 Bipolar junction transistors - BJTs Single junction devices, such as p-n and Schottkty diodes can be used to obtain rectifying I-V characteristics, and to form electronic switching circuits
Section 2.3 Bipolar junction transistors - BJTs Single junction devices, such as p-n and Schottkty diodes can be used to obtain rectifying I-V characteristics, and to form electronic switching circuits
6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits
 Page 1 of 13 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Final Eam Closed Book: Formula sheet provided;
Page 1 of 13 YOUR NAME Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Final Eam Closed Book: Formula sheet provided;
B.E. SEMESTER III (ELECTRICAL) SUBJECT CODE: X30902 Subject Name: Analog & Digital Electronics
 B.E. SEMESTER III (ELECTRICAL) SUBJECT CODE: X30902 Subject Name: Analog & Digital Electronics Sr. No. Date TITLE To From Marks Sign 1 To verify the application of op-amp as an Inverting Amplifier 2 To
B.E. SEMESTER III (ELECTRICAL) SUBJECT CODE: X30902 Subject Name: Analog & Digital Electronics Sr. No. Date TITLE To From Marks Sign 1 To verify the application of op-amp as an Inverting Amplifier 2 To
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 GATE-2010 Question Paper & Answer Keys GATE-2010 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
GATE-2010 Question Paper & Answer Keys GATE-2010 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
Georgia Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Midterm Exam
 Georgia Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Midterm Exam ECE-3400 Fall 2013 Tue, September 24, 2013 Duration: 80min First name Solutions Last name Solutions ID number
Georgia Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Midterm Exam ECE-3400 Fall 2013 Tue, September 24, 2013 Duration: 80min First name Solutions Last name Solutions ID number
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-2005 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - II Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt Question No. 1 which is compulsory and FOUR more questions
I.E.S-(Conv.)-2005 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - II Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt Question No. 1 which is compulsory and FOUR more questions
(i) Determine the admittance parameters of the network of Fig 1 (f) and draw its - equivalent circuit.
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
Lecture 4 -- Tuesday, Sept. 19: Non-uniform injection and/or doping. Diffusion. Continuity/conservation. The five basic equations.
 6.012 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS Schedule -- Fall 1995 (8/31/95 version) Recitation 1 -- Wednesday, Sept. 6: Review of 6.002 models for BJT. Discussion of models and modeling; motivate need to go
6.012 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS Schedule -- Fall 1995 (8/31/95 version) Recitation 1 -- Wednesday, Sept. 6: Review of 6.002 models for BJT. Discussion of models and modeling; motivate need to go
* GATE 2017 ONLINE TEST SERIES
 * GATE 2017 ONLINE TEST SERIES Complete with best... Our proficient faculties have done extensive research to prepare and shape these test series. An opportunity for students to come across their strengths
* GATE 2017 ONLINE TEST SERIES Complete with best... Our proficient faculties have done extensive research to prepare and shape these test series. An opportunity for students to come across their strengths
Unit WorkBook 4 Level 4 ENG U19 Electrical and Electronic Principles LO4 Digital & Analogue Electronics 2018 Unicourse Ltd. All Rights Reserved.
 Pearson BTEC Levels 4 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 19: Electrical and Electronic Principles Unit Workbook 4 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 4 Digital & Analogue Electronics
Pearson BTEC Levels 4 Higher Nationals in Engineering (RQF) Unit 19: Electrical and Electronic Principles Unit Workbook 4 in a series of 4 for this unit Learning Outcome 4 Digital & Analogue Electronics
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
 OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
Field Effect Transistors
 Field Effect Transistors Purpose In this experiment we introduce field effect transistors (FETs). We will measure the output characteristics of a FET, and then construct a common-source amplifier stage,
Field Effect Transistors Purpose In this experiment we introduce field effect transistors (FETs). We will measure the output characteristics of a FET, and then construct a common-source amplifier stage,
ECE Branch GATE Paper 2004
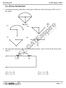 Q. 1 30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? Fig. Q.1 2. The equivalent inductance measured between the terminals
Q. 1 30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? Fig. Q.1 2. The equivalent inductance measured between the terminals
TECHNO INDIA BATANAGAR (DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING) QUESTION BANK- 2018
 TECHNO INDIA BATANAGAR (DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING) QUESTION BANK- 2018 Paper Setter Detail Name Designation Mobile No. E-mail ID Raina Modak Assistant Professor 6290025725 raina.modak@tib.edu.in
TECHNO INDIA BATANAGAR (DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING) QUESTION BANK- 2018 Paper Setter Detail Name Designation Mobile No. E-mail ID Raina Modak Assistant Professor 6290025725 raina.modak@tib.edu.in
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-2013 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-03 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: PART - A 0. What does the arrow mark indicate
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-03 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: PART - A 0. What does the arrow mark indicate
SAMPLE FINAL EXAMINATION FALL TERM
 ENGINEERING SCIENCES 154 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS SAMPLE FINAL EXAMINATION FALL TERM 2001-2002 NAME Some Possible Solutions a. Please answer all of the questions in the spaces provided. If you need
ENGINEERING SCIENCES 154 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS SAMPLE FINAL EXAMINATION FALL TERM 2001-2002 NAME Some Possible Solutions a. Please answer all of the questions in the spaces provided. If you need
Special-Purpose Operational Amplifier Circuits
 Special-Purpose Operational Amplifier Circuits Instrumentation Amplifier An instrumentation amplifier (IA) is a differential voltagegain device that amplifies the difference between the voltages existing
Special-Purpose Operational Amplifier Circuits Instrumentation Amplifier An instrumentation amplifier (IA) is a differential voltagegain device that amplifies the difference between the voltages existing
NAME: Last First Signature
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE 130: IC Devices Spring 2003 FINAL EXAMINATION NAME: Last First Signature STUDENT
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE 130: IC Devices Spring 2003 FINAL EXAMINATION NAME: Last First Signature STUDENT
Fan in: The number of inputs of a logic gate can handle.
 Subject Code: 17333 Model Answer Page 1/ 29 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model
Subject Code: 17333 Model Answer Page 1/ 29 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model
ECE-342 Test 1: Sep 27, :00-8:00, Closed Book. Name : SOLUTION
 ECE-342 Test 1: Sep 27, 2011 6:00-8:00, Closed Book Name : SOLUTION All solutions must provide units as appropriate. Use the physical constants and data as provided on the formula sheet the last page of
ECE-342 Test 1: Sep 27, 2011 6:00-8:00, Closed Book Name : SOLUTION All solutions must provide units as appropriate. Use the physical constants and data as provided on the formula sheet the last page of
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective. The Devices. Digital Integrated Circuits 2nd Devices
 Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective The Devices The Diode The diodes are rarely explicitly used in modern integrated circuits However, a MOS transistor contains at least two reverse biased
Digital Integrated Circuits A Design Perspective The Devices The Diode The diodes are rarely explicitly used in modern integrated circuits However, a MOS transistor contains at least two reverse biased
FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR (FET) 1. JUNCTION FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR (JFET)
 FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR (FET) The field-effect transistor (FET) is a three-terminal device used for a variety of applications that match, to a large extent, those of the BJT transistor. Although there
FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR (FET) The field-effect transistor (FET) is a three-terminal device used for a variety of applications that match, to a large extent, those of the BJT transistor. Although there
ECE Branch GATE Paper 2002 SECTION A (75 MARKS )
 SECTION A (75 MARKS ). This question consists of TWENTY FIVE sub-question (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A, B, C and D) are given, out of which only
SECTION A (75 MARKS ). This question consists of TWENTY FIVE sub-question (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A, B, C and D) are given, out of which only
Course Number Section. Electronics I ELEC 311 BB Examination Date Time # of pages. Final August 12, 2005 Three hours 3 Instructor
 Course Number Section Electronics ELEC 311 BB Examination Date Time # of pages Final August 12, 2005 Three hours 3 nstructor Dr. R. Raut M aterials allowed: No Yes X (Please specify) Calculators allowed:
Course Number Section Electronics ELEC 311 BB Examination Date Time # of pages Final August 12, 2005 Three hours 3 nstructor Dr. R. Raut M aterials allowed: No Yes X (Please specify) Calculators allowed:
SRM INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (DEEMED UNIVERSITY)
 SRM INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (DEEMED UNIVERSITY) QUESTION BANK I YEAR B.Tech (II Semester) ELECTRONIC DEVICES (COMMON FOR EC102, EE104, IC108, BM106) UNIT-I PART-A 1. What are intrinsic and
SRM INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (DEEMED UNIVERSITY) QUESTION BANK I YEAR B.Tech (II Semester) ELECTRONIC DEVICES (COMMON FOR EC102, EE104, IC108, BM106) UNIT-I PART-A 1. What are intrinsic and
R. W. Erickson. Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder
 R. W. Erickson Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder pn junction! Junction diode consisting of! p-doped silicon! n-doped silicon! A p-n junction where
R. W. Erickson Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, Boulder pn junction! Junction diode consisting of! p-doped silicon! n-doped silicon! A p-n junction where
Homework Assignment 09
 Question 1 (2 points each unless noted otherwise) Homework Assignment 09 1. For SPICE, Explain very briefly the difference between the multiplier M and Meg, as in a resistor has value 2M versus a resistor
Question 1 (2 points each unless noted otherwise) Homework Assignment 09 1. For SPICE, Explain very briefly the difference between the multiplier M and Meg, as in a resistor has value 2M versus a resistor
BJT Circuits (MCQs of Moderate Complexity)
 BJT Circuits (MCQs of Moderate Complexity) 1. The current ib through base of a silicon npn transistor is 1+0.1 cos (1000πt) ma. At 300K, the rπ in the small signal model of the transistor is i b B C r
BJT Circuits (MCQs of Moderate Complexity) 1. The current ib through base of a silicon npn transistor is 1+0.1 cos (1000πt) ma. At 300K, the rπ in the small signal model of the transistor is i b B C r
ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Q1. A transmission line of characteristic impedance 50 Ω is terminated by a 50 Ω load. When excited by a sinusoidal voltage source at 10 GHz the phase difference
ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Q1. A transmission line of characteristic impedance 50 Ω is terminated by a 50 Ω load. When excited by a sinusoidal voltage source at 10 GHz the phase difference
 Electronic Devices 1. Current flowing in each of the following circuits A and respectively are: (Circuit 1) (Circuit 2) 1) 1A, 2A 2) 2A, 1A 3) 4A, 2A 4) 2A, 4A 2. Among the following one statement is not
Electronic Devices 1. Current flowing in each of the following circuits A and respectively are: (Circuit 1) (Circuit 2) 1) 1A, 2A 2) 2A, 1A 3) 4A, 2A 4) 2A, 4A 2. Among the following one statement is not
If You Give A Mouse A Letter He ll Want The Whole Alphabet By
 If You Give A Mouse A Letter He ll Want The Whole Alphabet By a TeachWithMe.com A If you give a mouse an A he will want a Bb. AAAA aaaa B If you give a mouse an B he will want a Cc. BBBB bbbb C If you
If You Give A Mouse A Letter He ll Want The Whole Alphabet By a TeachWithMe.com A If you give a mouse an A he will want a Bb. AAAA aaaa B If you give a mouse an B he will want a Cc. BBBB bbbb C If you
Diode Circuits Recent GATE Problems
 Diode Circuits Recent GATE Problems 1. The diodes and capacitors in the circuit shown are ideal. The voltage v(t) across the diode DD 1 is CC 1 DD 2 cos(ωωωω) AC DD 1 CC 1 (a) cos(ωωωω) 1 (b) sin(ωωωω)
Diode Circuits Recent GATE Problems 1. The diodes and capacitors in the circuit shown are ideal. The voltage v(t) across the diode DD 1 is CC 1 DD 2 cos(ωωωω) AC DD 1 CC 1 (a) cos(ωωωω) 1 (b) sin(ωωωω)
Downloaded From All JNTU World
 Code: 9A02403 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of a nuclear plant as compared to other conventional power plants. 2 Explain about: (a) Solar distillation. (b) Solar
Code: 9A02403 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of a nuclear plant as compared to other conventional power plants. 2 Explain about: (a) Solar distillation. (b) Solar
GATE 2004 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 2004 Electronics and Communication Engineering Q. 1 30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? (A) Fig. Q.1
GATE 2004 Electronics and Communication Engineering Q. 1 30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? (A) Fig. Q.1
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2013
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2013
AE103 ELECTRONIC DEVICES & CIRCUITS DEC 2014
 Q.2 a. State and explain the Reciprocity Theorem and Thevenins Theorem. a. Reciprocity Theorem: If we consider two loops A and B of network N and if an ideal voltage source E in loop A produces current
Q.2 a. State and explain the Reciprocity Theorem and Thevenins Theorem. a. Reciprocity Theorem: If we consider two loops A and B of network N and if an ideal voltage source E in loop A produces current
ELEC351 Lecture Notes Set 1
 ELEC351 Lecture Notes Set 1 There is a tutorial on Monday September 10! You will do the first workshop problem in the tutorial. Bring a calculator. The course web site is: www.ece.concordia.ca/~trueman/web_page_351.htm
ELEC351 Lecture Notes Set 1 There is a tutorial on Monday September 10! You will do the first workshop problem in the tutorial. Bring a calculator. The course web site is: www.ece.concordia.ca/~trueman/web_page_351.htm
GATE 2000 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 2 Electronics and ommunication Engineering SETION A (1 Marks) 1. This question consists of 25 (Twenty Five) multiple choice questions, each carrying one mark. For each question (1.1 1.25), four alternatives
GATE 2 Electronics and ommunication Engineering SETION A (1 Marks) 1. This question consists of 25 (Twenty Five) multiple choice questions, each carrying one mark. For each question (1.1 1.25), four alternatives
EE301 Electronics I , Fall
 EE301 Electronics I 2018-2019, Fall 1. Introduction to Microelectronics (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Introduction, Historical Background, Basic Consepts 2. Rewiev of Semiconductors (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Semiconductor materials
EE301 Electronics I 2018-2019, Fall 1. Introduction to Microelectronics (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Introduction, Historical Background, Basic Consepts 2. Rewiev of Semiconductors (1 Week/3 Hrs.) Semiconductor materials
Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters
 Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters Goal: In circuits with a time-varying voltage, the relationship between current and voltage is more complicated
Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters Goal: In circuits with a time-varying voltage, the relationship between current and voltage is more complicated
Difference between BJTs and FETs. Junction Field Effect Transistors (JFET)
 Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
Q.1: Power factor of a linear circuit is defined as the:
 Q.1: Power factor of a linear circuit is defined as the: a. Ratio of real power to reactive power b. Ratio of real power to apparent power c. Ratio of reactive power to apparent power d. Ratio of resistance
Q.1: Power factor of a linear circuit is defined as the: a. Ratio of real power to reactive power b. Ratio of real power to apparent power c. Ratio of reactive power to apparent power d. Ratio of resistance
UNIT I Introduction to DC & AC circuits
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207) Year & Sem: II-B.
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207) Year & Sem: II-B.
Objective Questions. (a) Light (b) Temperature (c) Sound (d) all of these
 Objective Questions Module 1: Introduction 1. Which of the following is an analog quantity? (a) Light (b) Temperature (c) Sound (d) all of these 2. Which of the following is a digital quantity? (a) Electrical
Objective Questions Module 1: Introduction 1. Which of the following is an analog quantity? (a) Light (b) Temperature (c) Sound (d) all of these 2. Which of the following is a digital quantity? (a) Electrical
4. Differential Amplifiers. Electronic Circuits. Prof. Dr. Qiuting Huang Integrated Systems Laboratory
 4. Differential Amplifiers Electronic Circuits Prof. Dr. Qiuting Huang Integrated Systems Laboratory Differential Signaling Basics and Motivation Transmitting information with two complementary signals
4. Differential Amplifiers Electronic Circuits Prof. Dr. Qiuting Huang Integrated Systems Laboratory Differential Signaling Basics and Motivation Transmitting information with two complementary signals
Electronics Question Bank-2
 Electronics Question Bank-2 Questions Collected from Candidates Appeared for Various Competitive Examinations Compiled by Vishnu.N.V 1. The concentration of minority carriers in an extrinsic semiconductor
Electronics Question Bank-2 Questions Collected from Candidates Appeared for Various Competitive Examinations Compiled by Vishnu.N.V 1. The concentration of minority carriers in an extrinsic semiconductor
Review Energy Bands Carrier Density & Mobility Carrier Transport Generation and Recombination
 Review Energy Bands Carrier Density & Mobility Carrier Transport Generation and Recombination Current Transport: Diffusion, Thermionic Emission & Tunneling For Diffusion current, the depletion layer is
Review Energy Bands Carrier Density & Mobility Carrier Transport Generation and Recombination Current Transport: Diffusion, Thermionic Emission & Tunneling For Diffusion current, the depletion layer is
(Refer Slide Time: 05:47)
 Solid State Devices Dr. S. Karmalkar Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 29 Bipolar Junction Transistor (Contd ) So we have been discussing
Solid State Devices Dr. S. Karmalkar Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 29 Bipolar Junction Transistor (Contd ) So we have been discussing
ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
 ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING 1. Just as a voltage amplifier signal voltage a power amplifier. 1.amplifier power 2.amplifier signal 3.converts the signal ac power into DC power 4.converts a dc power into useful
ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING 1. Just as a voltage amplifier signal voltage a power amplifier. 1.amplifier power 2.amplifier signal 3.converts the signal ac power into DC power 4.converts a dc power into useful
CONTENTS Sl. No. Experiment Page No
 CONTENTS Sl. No. Experiment Page No 1a Given a 4-variable logic expression, simplify it using Entered Variable Map and realize the simplified logic expression using 8:1 multiplexer IC. 2a 3a 4a 5a 6a 1b
CONTENTS Sl. No. Experiment Page No 1a Given a 4-variable logic expression, simplify it using Entered Variable Map and realize the simplified logic expression using 8:1 multiplexer IC. 2a 3a 4a 5a 6a 1b
PATCH ANTENNA DESIGN
 FACULTY OF ELECTRONICS, TELECOMMUNICATIONS, AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Department of Telecommunications and Information Technology Laboratory of Antennas and Propagation Prof. dr. ing. Ion BOGDAN PATCH
FACULTY OF ELECTRONICS, TELECOMMUNICATIONS, AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY Department of Telecommunications and Information Technology Laboratory of Antennas and Propagation Prof. dr. ing. Ion BOGDAN PATCH
Field-Effect Transistor (FET) is one of the two major transistors; FET derives its name from its working mechanism;
 Chapter 3 Field-Effect Transistors (FETs) 3.1 Introduction Field-Effect Transistor (FET) is one of the two major transistors; FET derives its name from its working mechanism; The concept has been known
Chapter 3 Field-Effect Transistors (FETs) 3.1 Introduction Field-Effect Transistor (FET) is one of the two major transistors; FET derives its name from its working mechanism; The concept has been known
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1996 Some useful data:
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1996 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt question ONE which is compulsory and any FOUR of the remaining
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1996 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt question ONE which is compulsory and any FOUR of the remaining
Basic Electronics. Introductory Lecture Course for. Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011
 Basic Electronics Introductory Lecture Course for Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 2011 Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011 Presented By Gary Drake Argonne National Laboratory Session 3
Basic Electronics Introductory Lecture Course for Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 2011 Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011 Presented By Gary Drake Argonne National Laboratory Session 3
MODULE-2: Field Effect Transistors (FET)
 FORMAT-1B Definition: MODULE-2: Field Effect Transistors (FET) FET is a three terminal electronic device used for variety of applications that match with BJT. In FET, an electric field is established by
FORMAT-1B Definition: MODULE-2: Field Effect Transistors (FET) FET is a three terminal electronic device used for variety of applications that match with BJT. In FET, an electric field is established by
Chapter 14 Semiconductor Electronics Materials Devices And Simple Circuits
 Class XII Chapter 14 Semiconductor Electronics Materials Devices And Simple Circuits Physics Question 14.1: In an n-type silicon, which of the following statement is true: (a) Electrons are majority carriers
Class XII Chapter 14 Semiconductor Electronics Materials Devices And Simple Circuits Physics Question 14.1: In an n-type silicon, which of the following statement is true: (a) Electrons are majority carriers
ECE 3040 Dr. Alan Doolittle.
 ECE 3040 Dr. Alan Doolittle I have thoroughly enjoyed meeting each of you and hope that I have had a positive influence on your carriers. Please feel free to consult with me in your future work. If I can
ECE 3040 Dr. Alan Doolittle I have thoroughly enjoyed meeting each of you and hope that I have had a positive influence on your carriers. Please feel free to consult with me in your future work. If I can
Memory characteristics of silicon nanowire transistors generated by weak impact ionization
 Supplementary information for Memory characteristics of silicon nanowire transistors generated by weak impact ionization Doohyeok Lim, Minsuk Kim, Yoonjoong Kim, and Sangsig Kim* Department of Electrical
Supplementary information for Memory characteristics of silicon nanowire transistors generated by weak impact ionization Doohyeok Lim, Minsuk Kim, Yoonjoong Kim, and Sangsig Kim* Department of Electrical
IES Digital Mock Test
 . The circuit given below work as IES Digital Mock Test - 4 Logic A B C x y z (a) Binary to Gray code converter (c) Binary to ECESS- converter (b) Gray code to Binary converter (d) ECESS- To Gray code
. The circuit given below work as IES Digital Mock Test - 4 Logic A B C x y z (a) Binary to Gray code converter (c) Binary to ECESS- converter (b) Gray code to Binary converter (d) ECESS- To Gray code
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2011
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2011
Microelectronic Circuits - Fifth Edition Sedra/Smith Copyright 2004 by Oxford University Press, Inc.
 Feedback 1 Figure 8.1 General structure of the feedback amplifier. This is a signal-flow diagram, and the quantities x represent either voltage or current signals. 2 Figure E8.1 3 Figure 8.2 Illustrating
Feedback 1 Figure 8.1 General structure of the feedback amplifier. This is a signal-flow diagram, and the quantities x represent either voltage or current signals. 2 Figure E8.1 3 Figure 8.2 Illustrating
problem grade total
 Fall 2005 6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. J. A. del Alamo Name: Recitation: November 16, 2005 Quiz #2 problem grade 1 2 3 4 total General guidelines (please read carefully before starting):
Fall 2005 6.012 Microelectronic Devices and Circuits Prof. J. A. del Alamo Name: Recitation: November 16, 2005 Quiz #2 problem grade 1 2 3 4 total General guidelines (please read carefully before starting):
Preliminary Exam, Fall 2013 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Irvine EECS 170B
 Preliminary Exam, Fall 2013 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Irvine EECS 170B Problem 1. Consider the following circuit, where a saw-tooth voltage is applied
Preliminary Exam, Fall 2013 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Irvine EECS 170B Problem 1. Consider the following circuit, where a saw-tooth voltage is applied
Lecture 13 CMOS Power Dissipation
 EE 471: Transport Phenomena in Solid State Devices Spring 2018 Lecture 13 CMOS Power Dissipation Bryan Ackland Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Stevens Institute of Technology Hoboken,
EE 471: Transport Phenomena in Solid State Devices Spring 2018 Lecture 13 CMOS Power Dissipation Bryan Ackland Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Stevens Institute of Technology Hoboken,
ELC224 Final Review (12/10/2009) Name:
 ELC224 Final Review (12/10/2009) Name: Select the correct answer to the problems 1 through 20. 1. A common-emitter amplifier that uses direct coupling is an example of a dc amplifier. 2. The frequency
ELC224 Final Review (12/10/2009) Name: Select the correct answer to the problems 1 through 20. 1. A common-emitter amplifier that uses direct coupling is an example of a dc amplifier. 2. The frequency
In this lecture we will begin a new topic namely the Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor.
 Solid State Devices Dr. S. Karmalkar Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 38 MOS Field Effect Transistor In this lecture we will begin
Solid State Devices Dr. S. Karmalkar Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture - 38 MOS Field Effect Transistor In this lecture we will begin
UMAINE ECE Morse Code ROM and Transmitter at ISM Band Frequency
 UMAINE ECE Morse Code ROM and Transmitter at ISM Band Frequency Jamie E. Reinhold December 15, 2011 Abstract The design, simulation and layout of a UMAINE ECE Morse code Read Only Memory and transmitter
UMAINE ECE Morse Code ROM and Transmitter at ISM Band Frequency Jamie E. Reinhold December 15, 2011 Abstract The design, simulation and layout of a UMAINE ECE Morse code Read Only Memory and transmitter
EE3079 Experiment: Chaos in nonlinear systems
 EE3079 Experiment: Chaos in nonlinear systems Background: November 2, 2016 Revision The theory of nonlinear dynamical systems and Chaos is an intriguing area of mathematics that has received considerable
EE3079 Experiment: Chaos in nonlinear systems Background: November 2, 2016 Revision The theory of nonlinear dynamical systems and Chaos is an intriguing area of mathematics that has received considerable
UNIT 3: FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS
 FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR: UNIT 3: FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS The field effect transistor is a semiconductor device, which depends for its operation on the control of current by an electric field. There are
FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR: UNIT 3: FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS The field effect transistor is a semiconductor device, which depends for its operation on the control of current by an electric field. There are
For the mechanical system of figure shown above:
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-00 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks : 0 Candidates should attempt any FIVE questions. Some useful data: Electron charge : 1.6
I.E.S-(Conv.)-00 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks : 0 Candidates should attempt any FIVE questions. Some useful data: Electron charge : 1.6
Laboratory #5 BJT Basics and MOSFET Basics
 Laboratory #5 BJT Basics and MOSFET Basics I. Objectives 1. Understand the physical structure of BJTs and MOSFETs. 2. Learn to measure I-V characteristics of BJTs and MOSFETs. II. Components and Instruments
Laboratory #5 BJT Basics and MOSFET Basics I. Objectives 1. Understand the physical structure of BJTs and MOSFETs. 2. Learn to measure I-V characteristics of BJTs and MOSFETs. II. Components and Instruments
Chapter 2 : Semiconductor Materials & Devices (II) Feb
 Chapter 2 : Semiconductor Materials & Devices (II) 1 Reference 1. SemiconductorManufacturing Technology: Michael Quirk and Julian Serda (2001) 3. Microelectronic Circuits (5/e): Sedra & Smith (2004) 4.
Chapter 2 : Semiconductor Materials & Devices (II) 1 Reference 1. SemiconductorManufacturing Technology: Michael Quirk and Julian Serda (2001) 3. Microelectronic Circuits (5/e): Sedra & Smith (2004) 4.
Diode conducts when V anode > V cathode. Positive current flow. Diodes (and transistors) are non-linear device: V IR!
 Diodes: What do we use diodes for? Lecture 5: Diodes and Transistors protect circuits by limiting the voltage (clipping and clamping) turn AC into DC (voltage rectifier) voltage multipliers (e.g. double
Diodes: What do we use diodes for? Lecture 5: Diodes and Transistors protect circuits by limiting the voltage (clipping and clamping) turn AC into DC (voltage rectifier) voltage multipliers (e.g. double
INSTRUMENTATION ENGINEERING - IN. , where the contour is the unit circle traversed clockwise, is.
 Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 Let be an matrix with rank (0 < < ). Then = 0 has independent solutions, where is (A) r (B) n (C) (D) + Q.2 The value of 1, where the contour is the unit circle traversed
Q. 1 Q. 25 carry one mark each. Q.1 Let be an matrix with rank (0 < < ). Then = 0 has independent solutions, where is (A) r (B) n (C) (D) + Q.2 The value of 1, where the contour is the unit circle traversed
BJT Amplifier. Superposition principle (linear amplifier)
 BJT Amplifier Two types analysis DC analysis Applied DC voltage source AC analysis Time varying signal source Superposition principle (linear amplifier) The response of a linear amplifier circuit excited
BJT Amplifier Two types analysis DC analysis Applied DC voltage source AC analysis Time varying signal source Superposition principle (linear amplifier) The response of a linear amplifier circuit excited
CHAPTER 6 DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS
 CHAPTER 6 DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS 1 LECTURE CONTENTS 6.1 Logic Gates 6.2 Digital Instruments 6.3 Analog to Digital Converter 6.4 Electronic Counter 6.6 Digital Multimeters 2 6.1 Logic Gates 3 AND Gate The
CHAPTER 6 DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS 1 LECTURE CONTENTS 6.1 Logic Gates 6.2 Digital Instruments 6.3 Analog to Digital Converter 6.4 Electronic Counter 6.6 Digital Multimeters 2 6.1 Logic Gates 3 AND Gate The
PESIT BANGALORE SOUTH CAMPUS BASIC ELECTRONICS
 PESIT BANGALORE SOUTH CAMPUS QUESTION BANK BASIC ELECTRONICS Sub Code: 17ELN15 / 17ELN25 IA Marks: 20 Hrs/ Week: 04 Exam Marks: 80 Total Hours: 50 Exam Hours: 03 Name of Faculty: Mr. Udoshi Basavaraj Module
PESIT BANGALORE SOUTH CAMPUS QUESTION BANK BASIC ELECTRONICS Sub Code: 17ELN15 / 17ELN25 IA Marks: 20 Hrs/ Week: 04 Exam Marks: 80 Total Hours: 50 Exam Hours: 03 Name of Faculty: Mr. Udoshi Basavaraj Module
Microphonics. T. Powers
 Microphonics T. Powers What is microphonics? Microphonics is the time domain variation in cavity frequency driven by external vibrational sources. A 1.5 GHz structure 0.5 m long will change in frequency
Microphonics T. Powers What is microphonics? Microphonics is the time domain variation in cavity frequency driven by external vibrational sources. A 1.5 GHz structure 0.5 m long will change in frequency
EE434 ASIC & Digital Systems
 EE434 ASIC & Digital Systems Partha Pande School of EECS Washington State University pande@eecs.wsu.edu Spring 2015 Dae Hyun Kim daehyun@eecs.wsu.edu 1 Lecture 4 More on CMOS Gates Ref: Textbook chapter
EE434 ASIC & Digital Systems Partha Pande School of EECS Washington State University pande@eecs.wsu.edu Spring 2015 Dae Hyun Kim daehyun@eecs.wsu.edu 1 Lecture 4 More on CMOS Gates Ref: Textbook chapter
