GATE 2004 Electronics and Communication Engineering
|
|
|
- Alexandrina Briggs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GATE 2004 Electronics and Communication Engineering Q Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? (A) Fig. Q.1 (B) (C) (D) 2. The equivalent inductance measured between the terminals 1 and 2 for the circuit shown in the figure is 1 L 1 L 2 2 (A) L 1 + L 2 + M (B) L 1 + L 2 M (C) L 1 + L 2 + 2M (D) L 1 + L 2 2M Page : 1
2 3. The circuit shown in the figure, with R = Ω, L = H, C = 3 F has input voltage υ(t) =sin 2t. The resulting current i(t) is i(t) V(t) R L C (A) 5 sin (2t ) (B) 5 sin (2t 53.1 ) (C) 25 sin (2t ) (D) 25 sin (2t 53.1 ) 4. For the circuit shown in the figure, the time constant RC= 1 ms. The input voltage is υ (t) = 2 sin10 t. The output voltage υ (t) is equal to R V i (t) C V 0 (t) (A) sin (10 t 45 ) (B) sin (10 t + 45 ) (C) sin (10 t 53 ) (D) sin (10 t + 53 ) 5. For the R L circuit shown in the figure, the input voltage υ (t) = u(t). The current i(t) is 1H V i (t) i(t) 2Ω Page : 2
3 (A) i(t) (B) i(t) t(sec) 1/2 t(sec) (C) i(t) (D) i(t) /2 t(sec) 2 t(sec) 6. The impurity commonly used for realizing the base region of a silicon n p n transistor is (A) Gallium (C) Boron (B) Indium (D) Phosphorus 7. If for a silicon n p n transistor, the base to emitter Voltage (V ) is 0.7 V and the collector to base voltage (V ) is 0.2 V, then the transistor is operating in the (A) normal active mode (C) inverse active mode (B) saturation mode (D) cutoff mode 8. Consider the following statements S1 and S2. S1: The β of a bipolar transistor reduces if the base width is increased. S2: The β of a bipolar transistor increases if the doping concentration in the base is increased. Which one of the following is correct? (A) S1 is FALSE and S2 is TRUE (B) Both S1 and S2 are TRUE (C) Both S1 and S2 are FAL5E (D) S1 is TRUE and S2 is FAL5E 9. An ideal op amp is an ideal (A) voltage controlled current source (B) voltage controlled voltage source (C) current controlled current source (D) current controlled voltage source Page : 3
4 10. Voltage series feedback (also called series shunt feedback) results in (A) increase in both input and output impedances (B) decrease in both input and output impedances (C) increase in input impedance and decrease in output impedance (D) decrease in input impedance and increase in output impedance 11. The circuit in the given figure is a R R + V out V in C C (A) low pass filter (B) high pass filter (C) band pass filter. (D) band reject filter Page : 4
5 12. Assuming V = 0.2 V and β = 50, the minimum base current (I ) required to drive the transistor in the given figure to saturation is 3v I C I B 1kΩ (A) 56 µa (B) 140 µa (C) 60 ma (D) 3 ma 13. A master slave flip flop has the characteristic that (A) change in the input immediately reflected in the output (B) change in the output occurs when the state of the master is affected (C) change in the output occurs when the state of the slave is affected (D) both the master and the slave states are affected at the same time 14. The range of signed decimal number that can be represented by 6 bite 1 s complement number is (A) 31 to + 31 (C) 64 to + 63 (B) 62 to + 64 (D) 32 to A digital system is required to amplify a binary encoded audio signal. The user should be able to control the gain of the amplifier from a minimum to a maximum in 100 increments. The minimum number of bits required to encode, in straight binary, is (A) 8 (B) 6 (C) 5 (D) Choose the correct one from among the alternatives A, B, C, D after matching an item from Group 1 with the most appropriate item in Group 2. Group 1 Group 2 P : Shift register Q: Counter R: Decoder (A) P 3, Q 2, R 1 (B) P 3, Q 1, R 2 1 : Frequency division 2 : Addressing in memory chips 3 : Serial to parallel data conversion (C) P 2, Q 1, R 3 (D) P 1, Q 2, R 2 Page : 5
6 17. Figure given below shows the internal schematic of a TTL AND OR Invert (AOI) gate. For the inputs shown in the given figure, the output Y is A B y Inputs are floating { (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) AB (D) AB 18. Given figure is voltage transfer characteristic of V out 0 (A) an NMOS inverter with enhancement mode transistor as load (B) an NMOS inverter with depletion mode transistor as load (C) a CMOS inverter (D) a BJT inverter V in 19. The impulse response h[n] of a linear time invariant system is given by h[n] = u[n + 3] + u[n 2] 2u[n 7] where u[n] is the unit step sequence. The above system is (A) stable but not causal (C) causal but unstable (B) stable and causal (D) unstable and not causal Page : 6
7 20. The distribution function F (x) of a random variable X is shown in the figure. The probability that X = 1 is F x (x) x (A) Zero (B) 0.25 (C) 0.55 (D) The z transform of a system is H z response of the system is (A) (0.2) u[n] (B) (0.2) u[ n 1] z. If the ROC is z < 0.2, then the impulse z 0.2 (C) (0.2) u[n] (D) (0.2) u[ n 1] 22. The Fourier transform of a conjugate symmetric function is always (A) Imaginary (C) real (B) conjugate anti-symmetric (D) conjugate symmetric 23. The gain margin for the system with open loop transfer function G(s) H(z) = (), is (A) (B) 0 (C) 1 (D) 24. Given G(s) H(z) = real axis is (A) 4 (B) 1.33 ()(), the point of intersection of the asymptotes of the root loci with the (C) 1.33 (D) In a PCM system, if the code word length is increased from 6 to 8 bits, the signal to quantization noise ratio improves by the factor (A) 8/6 (C) 16 (B) 12 (D) 8 Page : 7
8 26. An AM signal is detected using an envelope detector. The carrier frequency and modulating signal frequency are 1 MHz and 2 khz respectively. An appropriate value for the time constant of the envelope detector is (A) 500 µsec (B) 20 µsec (C) 0.2 µsec (D) 1 µsec 27. An AM signal and a narrow band FM signal with identical carriers, modulating signals and modulation indices of 0.1 are added together. The resultant signal can be closely approximated by (A) broadband FM (C) DSB SC (B) SSB with carrier (D) SSB without carrier 28. In the output of a DM speech encoder, the consecutive pulses are of opposite polarity during time interval t 1 t t 2.This indicates that during this interval (A) the input to the modulator is essentially constant (B) the modulator is going through slope overload (C) the accumulator is in saturation (D) the speech signal is being sampled at the Nyquist rate 29. The phase velocity of an electromagnetic wave propagating in a hollow metallic rectangular waveguide in the TE mode is (A) equal to its group velocity (B) less than the velocity of light in free space (C) equal to the velocity of light in free space (D) greater than the velocity of light in free space 30. Consider a lossless antenna with a directive gain of + 6 db. If 1 mw of power is fed to it the total power radiated by the antenna will be (A) 4 mw (C) 7 mw (B) 1mW (D) ¼ mw Page : 8
9 Q Carry Two Marks Each 31. For the lattice circuit shown in the figure, Z = j2ω and Z = 2Ω. The values of the open circuit impedance parameters Z = z z z are Z z 1 3 Z Z 2 4 Z (A) 1 j 1 + j 1 + j 1 + j (B) 1 j 1 + j 1 + j 1 j (C) 1 + j 1 + j 1 j 1 j (D) 1 + j 1 + j 1 j 1 j 32. The circuit shown in the figure has initial current i (0 ) =1 A through the inductor and an initial voltage υ (0 ) = 1V across the capacitor. For input υ(t) = u(t), the Laplace transform of the current i(t) for t 0 is (A) (B) (C) (D) + V(t) - 1Ω i(t) 1H + 1F - Page : 9
10 33. Consider the Bode magnitude plot shown in the given figure. The transfer function H(s) is 20log H (j w) 0 20dB/decade ω in rad (A) (B) () ()() () ()() (C) () ()() (D) () ()() 34. The transfer function H(s) = () of an R L C circuit is given by H(s) = () The Quality factor(q factor) of this circuit is (A) 25 (B) 50 (C) 100 (D) For the circuit shown in the figure, the initial conditions are zero. Its transfer function H(s) = () is 1kΩ 10mH () V i (t) 100µF V c (t) (A) (B) (C) (D) Page : 10
11 36. A system described by the following differential equation For input x(t) = 2u(t), the output y(t) is (A) (1 2e + e ) u(t) (B) (1 + 2e 2e ) u(t) +3 +2y = x(t) is initially at rest. (C) (0.5 + e + 1.5e ) u(t) (D) ( e + 2e ) u(t) 37. Consider the following statements S1 and S2 S1: At the resonant frequency the impedance of a series R L C circuit is zero. S2: In a parallel G L C circuit, increasing the conductance G results in increase in its Q factor. Which one of the following is correct? (A) S1 is FLASE and S2 is TRUE (B) Both S1 and S2 are TRUE (C) S1 is TRUE and S2 is FALSE (D) Both S1 and S2 are FALSE 38. In an abrupt p n junction, doping concentrations on p side and n side are N = 9 10 /cm and N = 1 10 /cm respectively. The p n junction is reverse biased and the total depletion width is 3 µm. The depletion width on the p side is (A) 2.7 μm (B) 0.3 μm (C) 2.25 μm (D) 0.75 μm 39. The resistivity of a uniformly doped n-type silicon sample is 0.5Ω-cm. If the electron mobility µ is 1250 cm /V-sec and the charge of an electron is Coulomb, the donor impurity concentration (N )in the sample is (A) 2 10 /cm (B) 1 10 /cm (C) /cm (D) 2 10 /cm 40. Consider an abrupt p-junction. Let V be the built-it potential of this junction and V be the applied reverse bias. If the junction capacitance (C j ) is 1pF for V bi + V R = 1V, than for V bi + V R = 4V, C j will be (A) 4pF (B) 2pF (C) 0.25pF (D) 0.5pF 41. Consider the following statements S1 and S2. S1: The threshold voltage (V ) of the MOS capacitor decreases with increase in gate oxide thickness S2 : The threshold voltage (V )of a MOS capacitor decreases with increase in substrate doping concentration. Which one of the following is correct? (A) S1 is FALSE and S2 is TRUE (B) Both S1 and S2 are TRUE (C) Both S1 and S2 are FAL5E (D) S1 is TRUE and S2 is FAL5E Page : 11
12 42. The drain of an n-channel MOSFET is shorted to the gate so that V =V. The threshold voltage (V )of MOSFET is 1 V. If the drain current (I ) is 1 ma for V =2V, then for V =3V, I is (A) 2mA (B) 3mA (C) 9mA (D) 4mA 43. The longest wavelength that can be absorbed by silicon, which has the bandgap of 1.12 ev, is 1.1 µm. If the longest wavelength that can be absorbed by another material is 0.87 µm, then the bandgap of this material is (A) ev (B) ev (C) ev (D) ev 44. The neutral base width of a bipolar transistor, biased in the active region, is 0.5 μm. The maximum electron concentration and the diffusion constant in the base are 10 /cm and D =25cm /sec respectively. Assuming negligible recombination in the base, the collector current density is (the electron charge is coulomb) (A) 800A/cm (B) 8 A/cm (C) 200A/cm (D) 2 A/cm 45. Assuming that the β of the transistor is extremely large and V =0.7V,I in the circuit shown in the figure are 5V I C 4kΩ 2.2kΩ + V CE _ - 1kΩ 300Ω (A) I = 1mA, V = 4.7V (B) I = 0.5mA, V = 3.75V (C) I = 1mA, V = 2.5V (D) I = 0.5mA, V = 3.9V Page : 12
13 46. A bipolar transistor is operating in the active region with a collector current of 1mA. Assuming that the β of the transistor is 100 and the thermal voltage (V ) is 25mV, the transconductance (g ) and the input resistance (r π ) of the transistor in the common emitter configuration, are (A) g = 25mA/V and r π =15.625kΩ) (B) g =40mA/V andr π =4.0kΩ (C) g =25mA/V and r π =2.5kΩ (D) g =40mA/V and r π =2.5kΩ 47. The value of C required for sinusoidal oscillations of frequency 1kHz in the circuit of given figure is 1 k 2.1 kω V 1 k 1 k (A) π µf (B) 2π µf (C) µf (D) 2π 6 µf 48. In the op-amp circuit given in the figure, the load current i is R V R 1 R 2 R L i L R 2 (A) υ (B) υ (C) υ (D) υ Page : 13
14 49. In the voltage regulator shown in the given figure, the load current can vary from 100 ma to 500 ma. Assuming that the Zener diode is ideal (i.e., the Zener knee current is negligibly small and Zener resistance is zero in the breakdown region), the value of R is R Variable Load 100 to 500A (A) 7 Ω (B) 70 Ω (C) Ω (D) 14Ω 50. In a full-wave rectifier using two ideal diodes, V and V are the dc and peak of the voltage respectively across a resistive load. If PIV is the peak inverse voltage of the diode, then the appropriate relationships for this rectifier are (A) V = π, PIV = 2V (C) V = 2, PIV = V π (B) V = 2, PIV = 2V π (D) V = π, PIV = V 51. The minimum number of 2- to -1 multiplexers required to realize a 4- to 1 multiplexer is (A) 1 (C) 3 (B) 2 (D) The Boolean expression AC + BC is equivalent to (A) AC + BC + AC (B) BC + AC + BC + ACB (C) AC + BC + BC + ABC (D) ABC + ABC + ABC + ABC , 1001 and correspond to the 2 s complement representation of which one of the following sets of number? (A) 25, 9 and 57 respectively (C) -7, -7 and -7 respectively (B) -6, -6 and -6 respectively (D) -25, -9 and -57 respectively Page : 14
15 54. The 8255 Programmable Peripheral Interface is used as described below. (I) An A/D converter is interfaced to a microprocessor through an The conversion is initiated by a signal from the 8255 on Port C. A signal on Port C causes data to be strobed into Port A. (II) Two computers exchange data using a pair of 8255s. Port A works as a bidirectional data port supported by appropriate handshaking signals. The appropriate modes of operation of the 8255 for (I) and (II) would be (A) Mode 0 for (I) and Mode 1 for (II) (B) Mode 1 for (I) and Mode 0 for (II) (C) Mode 2 for (I) and Mode 0 for (II) (D) Mode 2 for (I) and Mode 1 for (II) 55. The number of memory cycles required to execute the following 8085 instructions (I) LDA 3000 H (II) LXI D, F0F 1 H would be (A) 2 for (I) and 2 for (II) (B) 4 for (I) and 3 for (II) (C) 3 for (I) and 3 for (II) (D) 3 for (I) and 4 for (II) 56. In the modulo-6 ripple counters shown in the given figure, the output of the 2-input gate is used to clear the J-K flip-flops. Cl oc k 2- input The 2-input gate gate is (A) a NAND gate (B) a NOR gate (C) an OR gate (D) an AND gate 57. Consider the sequence of 8085 instructions given below. LXIH, 9258, MOV A, M, CMA, MOV M, A Which one of the following is performed by this sequence? (A) Contents of location 9258 are moved to the accumulator (B) Contents of location 9258 are compared with the contents of the accumulator (C) Contents of location 8529 are complemented and stored in location 8529 (D) Contents of location 5892 are complemented and stored in location 5892 Page : 15
16 58. A Boolean function f of two variables x and y is defined as follows: F(0,0) = f(0,1) = f(1, 1) = 1; f(1, 0) = 0 Assuming complements of x and y are not available, a minimum cost solution for realizing f using only 2-input NOR gates and 2-input OR gates (each having unit cost) would have a total cost of (A) 1 unit (B) 4 unit (C) 3 unit (D) 2 unit 59. It is desired to multiply the numbers 0AHby 0BH and store the result in the accumulator. The numbers are available in registers B and C respectively. A Part of the 8085 program for this purpose is given below: MVI A, 00H Loop; HLT END The sequence of instruction to the complete the program would be (A) JNZ LOOP, ADD B, DCR C (B) ADD B, JNZ LOOP, DCR C (C) DCRC, JNZ LOOP, ADD B (D) ADD B, DCR C, JNZ LOOP 60. A 1 khz sinusoidal signal is ideally sampled at 1500 samples/sec and the sampled signal is passed through an ideal low-pass filter with cut-off frequency 800 Hz. The output signal has the frequency (A) zero Hz (B) 0.75 khz (C) 0.5 khz (D) 0.25 khz 61. A rectangular pulse train s(t) as shown in the figure is convolved signal with the signal cos (4p 10 3 t). The convolved signal will be a s 0.1 (A) DC (B) 12 khz sinusoid (C) 8 khz sinusoid (D) 14kHz sinusoid Page : 16
17 62. Consider the sequence x[n] = [-4 j j2 4] The conjugate anti-symmetric part of the sequence is (A) [ -4 j2.5 j2 4 j2.5] (B) [ -j2.5 1 j2.5] (C) [ -j5 j2 0] (D) [ ] 63. A casual LTI system is described by the difference equation 2y[n] = αy[n-2] 2x[n] + βx[n-1] The system is stable only if (A) α = 2, β < 2 (C) α < 2, any value of β (B) α > 2, β > 2 (D) β < 2, any value of α 64. A casual system having the transfer function H(s) = is excited with 10u(t). The time at which the output reaches 99% of its steady state value is (A) 2.7 sec (C) 2.3 sec (B) 2.5 sec (D) 2.1 sec 65. The impulse response h[n] of a linear time invariant system is given as 2 2 n = 1, 1 h[n] = 4 2 n = 2, 2 0, otherwise If the input to the above system is the sequence e jπn 4, then the output is (A) 4 2e jπn 4 (B) 4 2e jπn 4 (C) 4e jπn 4 (D) 4e jπn 4 Page : 17
18 66. Let x(t) and y(t) (with Fourier transforms X(f) and Y(f) respectively) be related as shown in the given figure. Then Y(f) is x ( y ( (A) X(f 2 )e (B) X(f 2) e (C) X(f 2) e (D) -X(f 2) e 67. A system has poles at 0.01Hz, 1Hz and 80 Hz; zeros at 5 Hz, 100Hz and 200 Hz. The approximate phase of the system response at 20 Hz is (A) -90 (B) 0 (C) 90 (D) Consider the signal flow graph shown in the figure. The gain is x x x x x e f g (A) (B) ( ) ( ) (C) (D) ( ) ( ) Page : 18
19 69. If A = 2 2, then sin At is 1 3 (A) + 2 sin ( t) 2 sin( 4t) + 2 sin ( t) sin( 4t) sin( 4t) + sin ( t) 2 sin( 4t) + sin ( t) sin ( 2t) (B) sin(2t) sin (t) sin( 3t) (C) sin(4t) + 2 sin (t) 2 sin( 4t) 2 sin ( t) sin( 4t) + sin (t) 2 sin(4t) + sin ( t) (D) cos( t) + 2 cos (t) 2 cos( 4t) + 2 sin ( t) cos( 4t) + sin ( t) 2 cos( 4t) + cos ( t) 70. The open-loop transfer function of a unity feedback system is G(s) = of K for which the system is stable is (A) > K > 0 (B) 13 > K > 0 (C) < K < (D) -6 < K < ( )(). The range 71. For the polynomial P(s) = s + s + 2s + 2s + 3s + 15, the number of roots which lie in the right half of the s-plane is (A) 4 (C) 3 (B) 2 (D) The state variable equation of a system are: 1. x = -3x - x + u 2. x = 2x y = x + u The system is (A) controllable but not observable (B) observable but not controllable (C) neither controllable nor observable (D) controllable and observable 73. Given A = , the state transition matrix e is given by (A) 0 e e 0 (C) e 0 0 e (B) e 0 0 e (D) 0 e e 0 Page : 19
20 74. Consider the signal x(t) shown in the figure. Let h(t) denote the impulse response of the filter matched to x(t), with h(t) being non-zero only in the interval 0 to 4 sec. The slope of h(t) in the interval 3 < t< 4 sec is x(t) - t(sec) (A) sec (B) -1sec (C) sec (D) 1 sec 75. A 1 mw video signal having a bandwidth of 100MHz is transmitted to a receiver through a cable that has 40 db loss. If the effective one-sided noise spectral density at the receiver is 10 Watt/Hz, then the signal-to-noise ratio at the receiver is (A) 50 db (B) 30 db (C) 40 db (D) 60 db 76. A 100 MHz carrier of 1V amplitude and a 1MHz modulating signal of 1V amplitude are fed to a balanced modulator. The output of the modulator is passed through an ideal high-pass filter with cut-off frequency of 100 MHz. The output of the filter is added with 100 MHz signal of 1V amplitude and 90 phase shift as shown in the given figure. The envelope of the resultant signal is 1MHz Balance d 100MH HPF 100M Hz 100MHz 0 (A) Constant (B) 1 + sin (2π X 10 t) (C) sin (2π X 10 t) (D) cos (2π X 10 t) 77. Two sinusoidal signals of same amplitude and frequencies 10 khz and 10.1 khz are added together. The combined signal is given to an ideal frequency detector. The output of the detector is (A) 0.1 khz sinusoid (B) 20.1 khz sinusoid (C) a linear function of time (D) a constant Page : 20
21 78. Consider a binary digital communication system with equally likely 0 s and 1 s. When binary 0 is transmitted the voltage at the detector input can lie between the levels V and V with equal probability: when binary 1 is transmitted, the voltage at the detector can have any value between 0 and 1V with equal probability. If the detector has a threshold of 2.0V (i.e., if the received signal is greater than 0.2V, the bit is taken as 1), the average bit error probability is (A) 0.15 (B) 0.2 (C) 0.05 (D) A random variable X with uniform density in the interval 0 to 1 is quantized value of X. If 0 < X < 0.3, x = 0 If 0.3 < X < 1, x = 0.7 Where x is the quantized value of X. The root-mean square value of the quantization noise is (A) (B) (C) (D) Choose the correct one from among the alternatives A, B, C, D after matching an item from Group 1 with the most appropriate item in Group 2. Group 1 Group 2 1 : FM P : Slope overload 2 : DM Q : μ-law 3 : PSK R : Envelope detector 4 : PCM S : Capture effect T : Hilbert transform U : Matched filter (A) 1-T, 2-P, 3-U, 4-S (B) 1-S, 2-U, 3-P, 4-T (C) 1-S, 2-P, 3-U, 4-Q (D) 1-U, 2-R, 3-S,4-Q 81. Three analog signals, having bandwidths 1200Hz, 600 Hz and 600 Hz, are sampled at their respective Nyquist rates, encoded with 12 bit words, and time division multiplexed. The bit rate for the multiplexed signal is (A) kbps (B) 28.8 kbps (C) 57.6 kbps (D) 38.4 kbps Page : 21
22 82. Consider a system shown in the figure. Let X(f) and Y(f) denote the Fourier transforms of x(f) and y(t) respectively. The ideal HPF has the cutoff frequency 10 khz. x(t) Balanced Modulator HPF 10kHz Balanced Modulator y(t) ~ 10 khz ~ 13 khz X(f) The positive frequencies where Y(f) has spectral peaks are (A) 1 khz and 24 khz (C) 1 khz and 14 khz (B) 2 khz and 24 khz (D) 2 khz and 14 khz f(khz) 83. A parallel plate air-filled capacitor has plate area of 10 m and plate separation of 10 m. it is connected to a 0.5V, 3.6 GHz source. The magnitude of the displacement current is(ε = 1/36π 10 F/m) (A) 10 ma (B) 100 ma (C) 10A (D) 1.59 ma 84. A source produces binary data at the rate of 10 kbps. The binary symbols are represented as shown in the figure 1 Binary 1 Binary t(msec) - t(msec) Page : 22
23 The source output is transmitted using two modulation schemes, namely Binary PSK (BPSK) and Quadrature PSK (QPSK), let B and B be the bandwidth requirements of BPSK and QPSK respectively. Assuming that the bandwidth of the above rectangular pulses is 10 khz, B and B are (A) B = 20 khz, B = 20 khz (B) B = 10 khz, B = 20 khz (C) B = 20 khz, B = 10 khz (D) B = 20 khz, B = 10 khz 85. Consider a 300 Ω, quarter-wave long (at 1 GHz) transmission line as shown in the figure. It is connected to a 10 V, 50 Ω source at one end and is left open circuited at the other end. The magnitude of the voltage at the open circuit end of the line is (A) 10 V (B) 5V 10V, 50Ω source λ 4 Z 0 = 300Ω (C) 60 V (D) 60/7 V 86. In a microwave test bench, way is the microwave signal amplitude modulated at 1 khz? (A) To increase the sensitivity of measurement (B) To transmit the signal to a far-off place (C) To study amplitude modulation (D) Because crystal detector fails at microwave frequencies 87. If E = a + ja e and H = a + ja e vector is (A) null vector (B) a (C) a (D) a The time averaged Poynting Page : 23
24 88. Consider an impedance Z=R + jx marked with point P in an impedance Smith chart as shown in the figure. The movement from the point P along a constant resistance circle in the clockwise direction by an angle 45 is equivalent to x = 0.5 x = x = x = x P (A) adding an inductance in series with Z (B) adding an capacitance in series with Z (C) adding an inductance in shunt across Z (D) adding a capacitance in shunt across Z 89. A plane electromagnetic wave propagating in free space in incident normally on a large slab of loss-less, non-magnetic, dielectric material with ε > ε. Maxima and minima are observed when the electric field is measured in front of the slab. The maximum electric field is found to be 5 times the minimum field. The intrinsic impedance of the medium should be (A) 120πΩ (B) 60 πω (C) 600 πω (D) 24 πω 90. A lossless transmission line is terminated in a load which reflects a part of the incident power. The measured VSWR is 2. The percentage of the power that is reflected back is (A) (C) 0.11 (B) (D) Page : 24
ECE Branch GATE Paper 2004
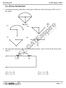 Q. 1 30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? Fig. Q.1 2. The equivalent inductance measured between the terminals
Q. 1 30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? Fig. Q.1 2. The equivalent inductance measured between the terminals
Q.1 Q.30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in figure. Which one of the following is NOT a tree of this graph?
 Q. Q.30 arry One Mark Each. onsider the network graph shown in figure. Which one of the following is NOT a tree of this graph?. The equivalent inductance measured between the terminals and for the circuit
Q. Q.30 arry One Mark Each. onsider the network graph shown in figure. Which one of the following is NOT a tree of this graph?. The equivalent inductance measured between the terminals and for the circuit
ECE Branch GATE Paper (C) exp ( t ) sin (25t) (B) 4cos (20t + 3) + 2 sin (710t)
 Question 30 Carry One Mark Each. The following differential equation has 2 3 d y dy 2 3 4 y 2 2 dt degree = 2, order = degree = 3, order = 2 + + + = x dt degree = 4, order = 3 degree = 2, order = 3 2.
Question 30 Carry One Mark Each. The following differential equation has 2 3 d y dy 2 3 4 y 2 2 dt degree = 2, order = degree = 3, order = 2 + + + = x dt degree = 4, order = 3 degree = 2, order = 3 2.
(i) Determine the admittance parameters of the network of Fig 1 (f) and draw its - equivalent circuit.
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras
 Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Sample Questions on Semiconductor Devices EE3 applicants who are interested to pursue their research in microelectronics devices area (fabrication and/or
Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Sample Questions on Semiconductor Devices EE3 applicants who are interested to pursue their research in microelectronics devices area (fabrication and/or
Electronics Eingineering
 Electronics Eingineering 1. The output of a two-input gate is 0 if and only if its inputs are unequal. It is true for (A) XOR gate (B) NAND gate (C) NOR gate (D) XNOR gate 2. In K-map simplification, a
Electronics Eingineering 1. The output of a two-input gate is 0 if and only if its inputs are unequal. It is true for (A) XOR gate (B) NAND gate (C) NOR gate (D) XNOR gate 2. In K-map simplification, a
ECE Branch GATE Paper 2002 SECTION A (75 MARKS )
 SECTION A (75 MARKS ). This question consists of TWENTY FIVE sub-question (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A, B, C and D) are given, out of which only
SECTION A (75 MARKS ). This question consists of TWENTY FIVE sub-question (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A, B, C and D) are given, out of which only
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2013
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2013
GATE 2000 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 2 Electronics and ommunication Engineering SETION A (1 Marks) 1. This question consists of 25 (Twenty Five) multiple choice questions, each carrying one mark. For each question (1.1 1.25), four alternatives
GATE 2 Electronics and ommunication Engineering SETION A (1 Marks) 1. This question consists of 25 (Twenty Five) multiple choice questions, each carrying one mark. For each question (1.1 1.25), four alternatives
6. A low pass filter having a frequency response does not produce any phase distortion, if (A) A(ω)
 1. The rank of the matrix is 0 1 2. P, where P is a vector, is equal to 2 P P P 2 P+ P ( ) 2 3 2 P+ P 2 ( P) P 3. ( P) ds, where P is a vector, is equal to P dl P dl Pdv ax 4. A probability density function
1. The rank of the matrix is 0 1 2. P, where P is a vector, is equal to 2 P P P 2 P+ P ( ) 2 3 2 P+ P 2 ( P) P 3. ( P) ds, where P is a vector, is equal to P dl P dl Pdv ax 4. A probability density function
GATE 1999 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 1999 Electronics and Communication Engineering SECTION A (75 Marks) 1. This question consists of 25 (Twenty Five) multiple choice questions, each carrying one mark. For each questions (1.1 1.25),
GATE 1999 Electronics and Communication Engineering SECTION A (75 Marks) 1. This question consists of 25 (Twenty Five) multiple choice questions, each carrying one mark. For each questions (1.1 1.25),
GATE 2002 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 22 Electronics and Communication Engineering SECTION A (75 MARKS ). This question consists of TWENTY FIVE sub-question (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives
GATE 22 Electronics and Communication Engineering SECTION A (75 MARKS ). This question consists of TWENTY FIVE sub-question (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 GATE-2010 Question Paper & Answer Keys GATE-2010 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
GATE-2010 Question Paper & Answer Keys GATE-2010 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
 Code No: Y0221/R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, Apr/May 2013 BASIC ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
Code No: Y0221/R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, Apr/May 2013 BASIC ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
EJERCICIOS DE COMPONENTES ELECTRÓNICOS. 1 er cuatrimestre
 EJECICIOS DE COMPONENTES ELECTÓNICOS. 1 er cuatrimestre 2 o Ingeniería Electrónica Industrial Juan Antonio Jiménez Tejada Índice 1. Basic concepts of Electronics 1 2. Passive components 1 3. Semiconductors.
EJECICIOS DE COMPONENTES ELECTÓNICOS. 1 er cuatrimestre 2 o Ingeniería Electrónica Industrial Juan Antonio Jiménez Tejada Índice 1. Basic concepts of Electronics 1 2. Passive components 1 3. Semiconductors.
ECE Branch GATE Paper Q2. The trigonometric Fourier series for the waveform shown below contains
 Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each. Q1. The eigen values of a skew-symmetric matrix are Always zero Always pure imaginary Either zero or pure imaginary Always real Q2. The trigonometric Fourier series for the
Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each. Q1. The eigen values of a skew-symmetric matrix are Always zero Always pure imaginary Either zero or pure imaginary Always real Q2. The trigonometric Fourier series for the
SIR PADAMPAT SINGHANIA UNIVERSITY UDAIPUR Sample Question Paper for Ph.D. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) SPSAT 18
 INSTRUCTIONS SIR PADAMPAT SINGHANIA UNIVERSITY UDAIPUR Sample Question Paper for Ph.D. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) SPSAT 18 The test is 60 minutes long and consists of 40 multiple choice
INSTRUCTIONS SIR PADAMPAT SINGHANIA UNIVERSITY UDAIPUR Sample Question Paper for Ph.D. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) SPSAT 18 The test is 60 minutes long and consists of 40 multiple choice
R.B.V.R.R. WOMEN S COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS) Narayanaguda, Hyderabad. ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS
 R.B.V.R.R. WOMEN S COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS) Narayanaguda, Hyderabad. DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS QUESTION BANK FOR SEMESTER V PHYSICS PAPER VI (A) ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS UNIT I: SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
R.B.V.R.R. WOMEN S COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS) Narayanaguda, Hyderabad. DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS QUESTION BANK FOR SEMESTER V PHYSICS PAPER VI (A) ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS UNIT I: SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1992 Time Allowed : Three Hours
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1992 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time Allowed : Three Hours Maximum Marks: 0 Candidates should attempt question No. 1 which is compulsory and any FOUR of the remaining
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1992 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time Allowed : Three Hours Maximum Marks: 0 Candidates should attempt question No. 1 which is compulsory and any FOUR of the remaining
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
 OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
 Electronic Devices 1. Current flowing in each of the following circuits A and respectively are: (Circuit 1) (Circuit 2) 1) 1A, 2A 2) 2A, 1A 3) 4A, 2A 4) 2A, 4A 2. Among the following one statement is not
Electronic Devices 1. Current flowing in each of the following circuits A and respectively are: (Circuit 1) (Circuit 2) 1) 1A, 2A 2) 2A, 1A 3) 4A, 2A 4) 2A, 4A 2. Among the following one statement is not
Linear Algebra, Calculus, Differential Equations and Vector Analysis. Complex Anaysis, Numerical Methods and Probability and Statistics.
 Test No Topic code Topic EC-01 GEM (Engineering Mathematics) Topic wise Tests Each test carries 25 marks and 45 minutes duration Test consists of 5 one mark questions and 10 two marks questions Tests will
Test No Topic code Topic EC-01 GEM (Engineering Mathematics) Topic wise Tests Each test carries 25 marks and 45 minutes duration Test consists of 5 one mark questions and 10 two marks questions Tests will
GATE SOLVED PAPER - IN
 YEAR 202 ONE MARK Q. The i-v characteristics of the diode in the circuit given below are : v -. A v 0.7 V i 500 07 $ = * 0 A, v < 0.7 V The current in the circuit is (A) 0 ma (C) 6.67 ma (B) 9.3 ma (D)
YEAR 202 ONE MARK Q. The i-v characteristics of the diode in the circuit given below are : v -. A v 0.7 V i 500 07 $ = * 0 A, v < 0.7 V The current in the circuit is (A) 0 ma (C) 6.67 ma (B) 9.3 ma (D)
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS
 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS 1. As compared to a full wave rectifier using 2 diodes, the four diode bridge rectifier has the dominant advantage of (a) Higher current carrying (b) lower peak inverse
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS 1. As compared to a full wave rectifier using 2 diodes, the four diode bridge rectifier has the dominant advantage of (a) Higher current carrying (b) lower peak inverse
 COMBO ONLINE TEST SERIES GATE 2019 SCHEDULE: ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Syllabus Test Date Test Type [ EB-Engineering Branch ; EM- No. of Engineering Mathematics; GA- General Question Marks
COMBO ONLINE TEST SERIES GATE 2019 SCHEDULE: ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Syllabus Test Date Test Type [ EB-Engineering Branch ; EM- No. of Engineering Mathematics; GA- General Question Marks
GATE 2006 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 2006 Electronics and Communication Engineering 1 1 1 1. The rank of the matrix 1 1 0 is (A) 0 (B) 1 1 1 1 2. P, where P is a vector, is equal to 2 P P P (A) 2 P P (B) (C) 2 (D) 3 (C) 2 P P 2 (D) P
GATE 2006 Electronics and Communication Engineering 1 1 1 1. The rank of the matrix 1 1 0 is (A) 0 (B) 1 1 1 1 2. P, where P is a vector, is equal to 2 P P P (A) 2 P P (B) (C) 2 (D) 3 (C) 2 P P 2 (D) P
Homework Assignment 04
 Question 1 (Short Takes) Homework Assignment 04 1. Consider the single-supply op-amp amplifier shown. What is the purpose of R 3? (1 point) Answer: This compensates for the op-amp s input bias current.
Question 1 (Short Takes) Homework Assignment 04 1. Consider the single-supply op-amp amplifier shown. What is the purpose of R 3? (1 point) Answer: This compensates for the op-amp s input bias current.
BJT Amplifier. Superposition principle (linear amplifier)
 BJT Amplifier Two types analysis DC analysis Applied DC voltage source AC analysis Time varying signal source Superposition principle (linear amplifier) The response of a linear amplifier circuit excited
BJT Amplifier Two types analysis DC analysis Applied DC voltage source AC analysis Time varying signal source Superposition principle (linear amplifier) The response of a linear amplifier circuit excited
MICROELECTRONIC CIRCUIT DESIGN Third Edition
 MICROELECTRONIC CIRCUIT DESIGN Third Edition Richard C. Jaeger and Travis N. Blalock Answers to Selected Problems Updated 1/25/08 Chapter 1 1.3 1.52 years, 5.06 years 1.5 1.95 years, 6.46 years 1.8 113
MICROELECTRONIC CIRCUIT DESIGN Third Edition Richard C. Jaeger and Travis N. Blalock Answers to Selected Problems Updated 1/25/08 Chapter 1 1.3 1.52 years, 5.06 years 1.5 1.95 years, 6.46 years 1.8 113
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-2012 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: Qn. PART - A 0. Which is the largest of three
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: Qn. PART - A 0. Which is the largest of three
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All questions carry equal marks *****
 Code: 9A04601 DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) 1 (a) Explain in detail about non-uniform quantization. (b) What is the disadvantage of uniform quantization over the non-uniform
Code: 9A04601 DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) 1 (a) Explain in detail about non-uniform quantization. (b) What is the disadvantage of uniform quantization over the non-uniform
Paper-1 (Circuit Analysis) UNIT-I
 Paper-1 (Circuit Analysis) UNIT-I AC Fundamentals & Kirchhoff s Current and Voltage Laws 1. Explain how a sinusoidal signal can be generated and give the significance of each term in the equation? 2. Define
Paper-1 (Circuit Analysis) UNIT-I AC Fundamentals & Kirchhoff s Current and Voltage Laws 1. Explain how a sinusoidal signal can be generated and give the significance of each term in the equation? 2. Define
IENGINEERS- CONSULTANTS GATE QUESTION PAPER EC 2001
 SECTION - A. This question consists of TWENTY-FIVE sub-questions (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A,B, C and D) are given, out of which ONLY ONE is
SECTION - A. This question consists of TWENTY-FIVE sub-questions (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A,B, C and D) are given, out of which ONLY ONE is
Live Leak - SSC Scientific Assistant Electronics and Telecommunication Model Question Paper 2017
 Live Leak - SSC Scientific Assistant Electronics and Telecommunication Model Question Paper 2017 Q1. In a p-n diode, holes diffuse from p-region to n-region because. 1. There is higher concentration of
Live Leak - SSC Scientific Assistant Electronics and Telecommunication Model Question Paper 2017 Q1. In a p-n diode, holes diffuse from p-region to n-region because. 1. There is higher concentration of
Georgia Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Midterm Exam
 Georgia Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Midterm Exam ECE-3400 Fall 2013 Tue, September 24, 2013 Duration: 80min First name Solutions Last name Solutions ID number
Georgia Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Midterm Exam ECE-3400 Fall 2013 Tue, September 24, 2013 Duration: 80min First name Solutions Last name Solutions ID number
BJT Circuits (MCQs of Moderate Complexity)
 BJT Circuits (MCQs of Moderate Complexity) 1. The current ib through base of a silicon npn transistor is 1+0.1 cos (1000πt) ma. At 300K, the rπ in the small signal model of the transistor is i b B C r
BJT Circuits (MCQs of Moderate Complexity) 1. The current ib through base of a silicon npn transistor is 1+0.1 cos (1000πt) ma. At 300K, the rπ in the small signal model of the transistor is i b B C r
Homework Assignment 07
 Homework Assignment 07 Question 1 (Short Takes). 2 points each unless otherwise noted. 1. A single-pole op-amp has an open-loop low-frequency gain of A = 10 5 and an open loop, 3-dB frequency of 4 Hz.
Homework Assignment 07 Question 1 (Short Takes). 2 points each unless otherwise noted. 1. A single-pole op-amp has an open-loop low-frequency gain of A = 10 5 and an open loop, 3-dB frequency of 4 Hz.
UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus
 UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus PAPER I 1. Circuit Theory: Circuit components; network graphs; KCL, KVL; circuit analysis methods: nodal analysis, mesh analysis;
UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus PAPER I 1. Circuit Theory: Circuit components; network graphs; KCL, KVL; circuit analysis methods: nodal analysis, mesh analysis;
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-2012 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 40 Subject: PART - A 0. Which region of the transistor
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 40 Subject: PART - A 0. Which region of the transistor
Q.1: Power factor of a linear circuit is defined as the:
 Q.1: Power factor of a linear circuit is defined as the: a. Ratio of real power to reactive power b. Ratio of real power to apparent power c. Ratio of reactive power to apparent power d. Ratio of resistance
Q.1: Power factor of a linear circuit is defined as the: a. Ratio of real power to reactive power b. Ratio of real power to apparent power c. Ratio of reactive power to apparent power d. Ratio of resistance
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) MODEL ANSWER
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Difference between BJTs and FETs. Junction Field Effect Transistors (JFET)
 Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Q1. A transmission line of characteristic impedance 50 Ω is terminated by a 50 Ω load. When excited by a sinusoidal voltage source at 10 GHz the phase difference
ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Q1. A transmission line of characteristic impedance 50 Ω is terminated by a 50 Ω load. When excited by a sinusoidal voltage source at 10 GHz the phase difference
Level 6 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Electronics and telecommunications
 9210-116 Level 6 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Electronics and telecommunications Sample Paper You should have the following for this examination one answer book non-programmable calculator pen, pencil,
9210-116 Level 6 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Electronics and telecommunications Sample Paper You should have the following for this examination one answer book non-programmable calculator pen, pencil,
SAMPLE FINAL EXAMINATION FALL TERM
 ENGINEERING SCIENCES 154 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS SAMPLE FINAL EXAMINATION FALL TERM 2001-2002 NAME Some Possible Solutions a. Please answer all of the questions in the spaces provided. If you need
ENGINEERING SCIENCES 154 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS SAMPLE FINAL EXAMINATION FALL TERM 2001-2002 NAME Some Possible Solutions a. Please answer all of the questions in the spaces provided. If you need
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 GATE-2015 Question Paper & Answer Keys GATE-2015 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
GATE-2015 Question Paper & Answer Keys GATE-2015 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2011
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2011
UMAINE ECE Morse Code ROM and Transmitter at ISM Band Frequency
 UMAINE ECE Morse Code ROM and Transmitter at ISM Band Frequency Jamie E. Reinhold December 15, 2011 Abstract The design, simulation and layout of a UMAINE ECE Morse code Read Only Memory and transmitter
UMAINE ECE Morse Code ROM and Transmitter at ISM Band Frequency Jamie E. Reinhold December 15, 2011 Abstract The design, simulation and layout of a UMAINE ECE Morse code Read Only Memory and transmitter
Electronic Devices & Circuit and Digital Electronics
 QUESTION BANK Electronic Devices & Circuit and Digital Electronics 1. Consider the following four statement i) In the 2 s complement representation, negative numbers are stored in sign magnitude form ii)
QUESTION BANK Electronic Devices & Circuit and Digital Electronics 1. Consider the following four statement i) In the 2 s complement representation, negative numbers are stored in sign magnitude form ii)
Electronics Question Bank-2
 Electronics Question Bank-2 Questions Collected from Candidates Appeared for Various Competitive Examinations Compiled by Vishnu.N.V 1. The concentration of minority carriers in an extrinsic semiconductor
Electronics Question Bank-2 Questions Collected from Candidates Appeared for Various Competitive Examinations Compiled by Vishnu.N.V 1. The concentration of minority carriers in an extrinsic semiconductor
Microelectronic Circuits
 SECOND EDITION ISHBWHBI \ ' -' Microelectronic Circuits Adel S. Sedra University of Toronto Kenneth С Smith University of Toronto HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON, INC. New York Chicago
SECOND EDITION ISHBWHBI \ ' -' Microelectronic Circuits Adel S. Sedra University of Toronto Kenneth С Smith University of Toronto HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON, INC. New York Chicago
Electronics & Communication Engineering
 A SET EC - 6 Booklet No. : Electronics & Communication Engineering Duration of Test : Hours Max. Marks : 0 Hall Ticket No. Name of the Candidate : Date of Examination : OMR Answer Sheet No. : Signature
A SET EC - 6 Booklet No. : Electronics & Communication Engineering Duration of Test : Hours Max. Marks : 0 Hall Ticket No. Name of the Candidate : Date of Examination : OMR Answer Sheet No. : Signature
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-2005 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - II Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt Question No. 1 which is compulsory and FOUR more questions
I.E.S-(Conv.)-2005 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - II Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt Question No. 1 which is compulsory and FOUR more questions
Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All questions carry equal marks
 Code: 9A02401 PRINCIPLES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Common to EIE, E.Con.E, ECE & ECC) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 1 In a series RLC circuit, R = 5 Ω, L = 1 H and C = 1 F. A dc v ltage f 20 V is applied
Code: 9A02401 PRINCIPLES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Common to EIE, E.Con.E, ECE & ECC) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 1 In a series RLC circuit, R = 5 Ω, L = 1 H and C = 1 F. A dc v ltage f 20 V is applied
Homework Assignment 07
 Homework Assignment 07 Question 1 (Short Takes). 2 points each unless otherwise noted. 1. A single-pole op-amp has an open-loop low-frequency gain of A = 10 5 and an open loop, 3-dB frequency of 4 Hz.
Homework Assignment 07 Question 1 (Short Takes). 2 points each unless otherwise noted. 1. A single-pole op-amp has an open-loop low-frequency gain of A = 10 5 and an open loop, 3-dB frequency of 4 Hz.
ECE-342 Test 1: Sep 27, :00-8:00, Closed Book. Name : SOLUTION
 ECE-342 Test 1: Sep 27, 2011 6:00-8:00, Closed Book Name : SOLUTION All solutions must provide units as appropriate. Use the physical constants and data as provided on the formula sheet the last page of
ECE-342 Test 1: Sep 27, 2011 6:00-8:00, Closed Book Name : SOLUTION All solutions must provide units as appropriate. Use the physical constants and data as provided on the formula sheet the last page of
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-2013 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-03 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: PART - A 0. What does the arrow mark indicate
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-03 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: PART - A 0. What does the arrow mark indicate
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R05010204 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplimentary Examinations, Aug/Sep 2007 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS ( Common to Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Electronics & Communication Engineering,
Code No: R05010204 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplimentary Examinations, Aug/Sep 2007 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS ( Common to Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Electronics & Communication Engineering,
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1996 Some useful data:
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1996 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt question ONE which is compulsory and any FOUR of the remaining
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1996 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt question ONE which is compulsory and any FOUR of the remaining
Section 2.3 Bipolar junction transistors - BJTs
 Section 2.3 Bipolar junction transistors - BJTs Single junction devices, such as p-n and Schottkty diodes can be used to obtain rectifying I-V characteristics, and to form electronic switching circuits
Section 2.3 Bipolar junction transistors - BJTs Single junction devices, such as p-n and Schottkty diodes can be used to obtain rectifying I-V characteristics, and to form electronic switching circuits
Downloaded From All JNTU World
 Code: 9A02401 PRINCIPLES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Common to ECE, EIE, E.Con.E & ECC) 1 Find initial conditions for voltage across capacitor, the currents i 1, i 2 and the derivatives for the circuit
Code: 9A02401 PRINCIPLES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Common to ECE, EIE, E.Con.E & ECC) 1 Find initial conditions for voltage across capacitor, the currents i 1, i 2 and the derivatives for the circuit
GATE 2009 Electrical Engineering
 Q. No. 1 20 Carry One Mark Each GATE 2009 Electrical Engineering 1. The pressure coil of a dynamometer type wattmeter is (A) highly inductive (B) highly resistive (C) purely resistive (D) purely inductive
Q. No. 1 20 Carry One Mark Each GATE 2009 Electrical Engineering 1. The pressure coil of a dynamometer type wattmeter is (A) highly inductive (B) highly resistive (C) purely resistive (D) purely inductive
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (CODE NO. 10) PAPER - I
 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (CODE NO. 10) PAPER - I 1. Circuit theory Circuit Components, Network graphs, KCL, KVL, Circuit analysis methods: Nodal analysis, mesh analysis, basic network theorems; transient
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (CODE NO. 10) PAPER - I 1. Circuit theory Circuit Components, Network graphs, KCL, KVL, Circuit analysis methods: Nodal analysis, mesh analysis, basic network theorems; transient
GATE 2009 Instrumentation Engineering
 GATE 2009 Instrumentation Engineering Q. Q20 carry one mark each.. If z = x jy, where x and y are real, the value of e is (A) (C) e (B) e x y (D) e 2. The value of origin, is (A) 0 (B) 2πj dz, where the
GATE 2009 Instrumentation Engineering Q. Q20 carry one mark each.. If z = x jy, where x and y are real, the value of e is (A) (C) e (B) e x y (D) e 2. The value of origin, is (A) 0 (B) 2πj dz, where the
Index. Small-Signal Models, 14 saturation current, 3, 5 Transistor Cutoff Frequency, 18 transconductance, 16, 22 transit time, 10
 Index A absolute value, 308 additional pole, 271 analog multiplier, 190 B BiCMOS,107 Bode plot, 266 base-emitter voltage, 16, 50 base-emitter voltages, 296 bias current, 111, 124, 133, 137, 166, 185 bipolar
Index A absolute value, 308 additional pole, 271 analog multiplier, 190 B BiCMOS,107 Bode plot, 266 base-emitter voltage, 16, 50 base-emitter voltages, 296 bias current, 111, 124, 133, 137, 166, 185 bipolar
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS UNIT-1 SUBJECT : ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS SUBJECT CODE : EC6202 BRANCH: EEE PART -A 1. What is meant by diffusion current in a semi conductor? (APR/MAY 2010, 2011, NOV/DEC
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS UNIT-1 SUBJECT : ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS SUBJECT CODE : EC6202 BRANCH: EEE PART -A 1. What is meant by diffusion current in a semi conductor? (APR/MAY 2010, 2011, NOV/DEC
Preface... iii. Chapter 1: Diodes and Circuits... 1
 Table of Contents Preface... iii Chapter 1: Diodes and Circuits... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Structure of an Atom... 2 1.3 Classification of Solid Materials on the Basis of Conductivity... 2 1.4 Atomic
Table of Contents Preface... iii Chapter 1: Diodes and Circuits... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Structure of an Atom... 2 1.3 Classification of Solid Materials on the Basis of Conductivity... 2 1.4 Atomic
Chapter 8. Field Effect Transistor
 Chapter 8. Field Effect Transistor Field Effect Transistor: The field effect transistor is a semiconductor device, which depends for its operation on the control of current by an electric field. There
Chapter 8. Field Effect Transistor Field Effect Transistor: The field effect transistor is a semiconductor device, which depends for its operation on the control of current by an electric field. There
Downloaded From All JNTU World
 Code: 9A02403 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of a nuclear plant as compared to other conventional power plants. 2 Explain about: (a) Solar distillation. (b) Solar
Code: 9A02403 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of a nuclear plant as compared to other conventional power plants. 2 Explain about: (a) Solar distillation. (b) Solar
LINEAR IC APPLICATIONS
 1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
Homework Assignment 11
 Homework Assignment 11 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. What is the 3-dB bandwidth of the amplifier shown below if r π = 2.5K, r o = 100K, g m = 40 ms, and C L =
Homework Assignment 11 Question 1 (Short Takes) Two points each unless otherwise indicated. 1. What is the 3-dB bandwidth of the amplifier shown below if r π = 2.5K, r o = 100K, g m = 40 ms, and C L =
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-2007 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - II Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt Question No. 1 which is compulsory and FOUR more questions
I.E.S-(Conv.)-2007 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - II Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt Question No. 1 which is compulsory and FOUR more questions
The steeper the phase shift as a function of frequency φ(ω) the more stable the frequency of oscillation
 It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
UNIT 3: FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS
 FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR: UNIT 3: FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS The field effect transistor is a semiconductor device, which depends for its operation on the control of current by an electric field. There are
FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR: UNIT 3: FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS The field effect transistor is a semiconductor device, which depends for its operation on the control of current by an electric field. There are
UNIT I Introduction to DC & AC circuits
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207) Year & Sem: II-B.
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207) Year & Sem: II-B.
MTLE-6120: Advanced Electronic Properties of Materials. Semiconductor transistors for logic and memory. Reading: Kasap
 MTLE-6120: Advanced Electronic Properties of Materials 1 Semiconductor transistors for logic and memory Reading: Kasap 6.6-6.8 Vacuum tube diodes 2 Thermionic emission from cathode Electrons collected
MTLE-6120: Advanced Electronic Properties of Materials 1 Semiconductor transistors for logic and memory Reading: Kasap 6.6-6.8 Vacuum tube diodes 2 Thermionic emission from cathode Electrons collected
GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13)
 GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13) 1. Removing bypass capacitor across the emitter leg resistor in a CE amplifier causes a. increase in current gain b. decrease in current gain c. increase
GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13) 1. Removing bypass capacitor across the emitter leg resistor in a CE amplifier causes a. increase in current gain b. decrease in current gain c. increase
Conventional Paper-II-2011 Part-1A
 Conventional Paper-II-2011 Part-1A 1(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) The purpose of providing dummy coils in the armature of a DC machine is to: (A) Increase voltage induced (B) Decrease the armature resistance
Conventional Paper-II-2011 Part-1A 1(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) The purpose of providing dummy coils in the armature of a DC machine is to: (A) Increase voltage induced (B) Decrease the armature resistance
Analog Integrated Circuit Design Exercise 1
 Analog Integrated Circuit Design Exercise 1 Integrated Electronic Systems Lab Prof. Dr.-Ing. Klaus Hofmann M.Sc. Katrin Hirmer, M.Sc. Sreekesh Lakshminarayanan Status: 21.10.2015 Pre-Assignments The lecture
Analog Integrated Circuit Design Exercise 1 Integrated Electronic Systems Lab Prof. Dr.-Ing. Klaus Hofmann M.Sc. Katrin Hirmer, M.Sc. Sreekesh Lakshminarayanan Status: 21.10.2015 Pre-Assignments The lecture
AE103 ELECTRONIC DEVICES & CIRCUITS DEC 2014
 Q.2 a. State and explain the Reciprocity Theorem and Thevenins Theorem. a. Reciprocity Theorem: If we consider two loops A and B of network N and if an ideal voltage source E in loop A produces current
Q.2 a. State and explain the Reciprocity Theorem and Thevenins Theorem. a. Reciprocity Theorem: If we consider two loops A and B of network N and if an ideal voltage source E in loop A produces current
MICROELECTRONIC CIRCUIT DESIGN Fifth Edition
 MICROELECTRONIC CIRCUIT DESIGN Fifth Edition Richard C. Jaeger and Travis N. Blalock Answers to Selected Problems Updated 07/05/15 Chapter 1 1.5 1.52 years, 5.06 years 1.6 1.95 years, 6.52 years 1.9 402
MICROELECTRONIC CIRCUIT DESIGN Fifth Edition Richard C. Jaeger and Travis N. Blalock Answers to Selected Problems Updated 07/05/15 Chapter 1 1.5 1.52 years, 5.06 years 1.6 1.95 years, 6.52 years 1.9 402
EE Branch GATE Paper 2001 SECTION A (TOTAL MARKS = 75)
 SECTION A (TOTAL MARKS = 75) 1. This question consists of 25 (TWENTY-FIVE) sub-questions (1.1-1.25) of ONE mark each. (25 1 = 25 ) 1.1 In a series RLC circuit at resonance, the magnitude of the voltage
SECTION A (TOTAL MARKS = 75) 1. This question consists of 25 (TWENTY-FIVE) sub-questions (1.1-1.25) of ONE mark each. (25 1 = 25 ) 1.1 In a series RLC circuit at resonance, the magnitude of the voltage
Figure Responsivity (A/W) Figure E E-09.
 OSI Optoelectronics, is a leading manufacturer of fiber optic components for communication systems. The products offer range for Silicon, GaAs and InGaAs to full turnkey solutions. Photodiodes are semiconductor
OSI Optoelectronics, is a leading manufacturer of fiber optic components for communication systems. The products offer range for Silicon, GaAs and InGaAs to full turnkey solutions. Photodiodes are semiconductor
Homework Assignment 12
 Homework Assignment 12 Question 1 Shown the is Bode plot of the magnitude of the gain transfer function of a constant GBP amplifier. By how much will the amplifier delay a sine wave with the following
Homework Assignment 12 Question 1 Shown the is Bode plot of the magnitude of the gain transfer function of a constant GBP amplifier. By how much will the amplifier delay a sine wave with the following
ELECTRONIC SCIENCE. Time : 1 Hour 15 Minutes Maximum Marks: 100. Instructions for the Candidates
 Roll No. 2117 (Write Roll Number from left side exactly as in the Admit Card) Subject Code : 21 PAPER II Signature of Invigilators 1. 2. Question Booklet Series Question Booklet No. (Identical with OMR
Roll No. 2117 (Write Roll Number from left side exactly as in the Admit Card) Subject Code : 21 PAPER II Signature of Invigilators 1. 2. Question Booklet Series Question Booklet No. (Identical with OMR
(A) 1 and 1 (B) 0 and 1 (C) 1 and 0 (D) 0 and A second order system is described by the equation. (A) 1 rad / sec and 5 (B) 5 rad / sec and 7
 EC- Objective Paper-II IES-013 www.gateforum.com IES-013- Paper-II 1. The D.C. gain and steady state error for step input for ( ) = s + 1 G s are : s + s + 1 (A) 1 and 1 (B) 0 and 1 (C) 1 and 0 (D) 0 and
EC- Objective Paper-II IES-013 www.gateforum.com IES-013- Paper-II 1. The D.C. gain and steady state error for step input for ( ) = s + 1 G s are : s + s + 1 (A) 1 and 1 (B) 0 and 1 (C) 1 and 0 (D) 0 and
EC Transmission Lines And Waveguides
 EC6503 - Transmission Lines And Waveguides UNIT I - TRANSMISSION LINE THEORY A line of cascaded T sections & Transmission lines - General Solution, Physical Significance of the Equations 1. Define Characteristic
EC6503 - Transmission Lines And Waveguides UNIT I - TRANSMISSION LINE THEORY A line of cascaded T sections & Transmission lines - General Solution, Physical Significance of the Equations 1. Define Characteristic
NAME: Last First Signature
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE 130: IC Devices Spring 2003 FINAL EXAMINATION NAME: Last First Signature STUDENT
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EE 130: IC Devices Spring 2003 FINAL EXAMINATION NAME: Last First Signature STUDENT
WINTER 14 EXAMINATION. Model Answer. 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the
 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 17213 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 17213 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
Veer Narmad South Gujarat University, Surat
 Unit I: Passive circuit elements (With effect from June 2017) Syllabus for: F Y B Sc (Electronics) Semester- 1 PAPER I: Basic Electrical Circuits Resistors, resistor types, power ratings, resistor colour
Unit I: Passive circuit elements (With effect from June 2017) Syllabus for: F Y B Sc (Electronics) Semester- 1 PAPER I: Basic Electrical Circuits Resistors, resistor types, power ratings, resistor colour
EC6503 Transmission Lines and WaveguidesV Semester Question Bank
 UNIT I TRANSMISSION LINE THEORY A line of cascaded T sections & Transmission lines General Solution, Physicasignificance of the equations 1. Derive the two useful forms of equations for voltage and current
UNIT I TRANSMISSION LINE THEORY A line of cascaded T sections & Transmission lines General Solution, Physicasignificance of the equations 1. Derive the two useful forms of equations for voltage and current
FET Channel. - simplified representation of three terminal device called a field effect transistor (FET)
 FET Channel - simplified representation of three terminal device called a field effect transistor (FET) - overall horizontal shape - current levels off as voltage increases - two regions of operation 1.
FET Channel - simplified representation of three terminal device called a field effect transistor (FET) - overall horizontal shape - current levels off as voltage increases - two regions of operation 1.
Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Basics- GATE Problems
 Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Basics- GATE Problems One Mark Questions 1. The break down voltage of a transistor with its base open is BV CEO and that with emitter open is BV CBO, then (a) BV CEO =
Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Basics- GATE Problems One Mark Questions 1. The break down voltage of a transistor with its base open is BV CEO and that with emitter open is BV CBO, then (a) BV CEO =
FUNDAMENTALS OF MODERN VLSI DEVICES
 19-13- FUNDAMENTALS OF MODERN VLSI DEVICES YUAN TAUR TAK H. MING CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Physical Constants and Unit Conversions List of Symbols Preface page xi xiii xxi 1 INTRODUCTION I 1.1 Evolution
19-13- FUNDAMENTALS OF MODERN VLSI DEVICES YUAN TAUR TAK H. MING CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Physical Constants and Unit Conversions List of Symbols Preface page xi xiii xxi 1 INTRODUCTION I 1.1 Evolution
GATE 2008 Instrumentation Engineering
 GATE 2008 Instrumentation Engineering Q. 1 Q. 20 Carry One Mark Each. 1. Given y = x 2x 10, the value of is equal to (A) 0 (B) 4 (C) 12 (D) 13 2. lim is (A) Indeterminate (B) 0 (C) 1 (D) 3. The power supplied
GATE 2008 Instrumentation Engineering Q. 1 Q. 20 Carry One Mark Each. 1. Given y = x 2x 10, the value of is equal to (A) 0 (B) 4 (C) 12 (D) 13 2. lim is (A) Indeterminate (B) 0 (C) 1 (D) 3. The power supplied
ECE4902 B2015 HW Set 1
 ECE4902 B2015 HW Set 1 Due in class Tuesday November 3. To make life easier on the graders: Be sure your NAME and ECE MAILBOX NUMBER are prominently displayed on the upper right of what you hand in. When
ECE4902 B2015 HW Set 1 Due in class Tuesday November 3. To make life easier on the graders: Be sure your NAME and ECE MAILBOX NUMBER are prominently displayed on the upper right of what you hand in. When
SEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS: MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS. Class XII : PHYSICS WORKSHEET
 SEMICONDUCT ELECTRONICS: MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS Class XII : PHYSICS WKSHEET 1. How is a n-p-n transistor represented symbolically? (1) 2. How does conductivity of a semiconductor change
SEMICONDUCT ELECTRONICS: MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS Class XII : PHYSICS WKSHEET 1. How is a n-p-n transistor represented symbolically? (1) 2. How does conductivity of a semiconductor change
* GATE 2017 ONLINE TEST SERIES
 * GATE 2017 ONLINE TEST SERIES Complete with best... Our proficient faculties have done extensive research to prepare and shape these test series. An opportunity for students to come across their strengths
* GATE 2017 ONLINE TEST SERIES Complete with best... Our proficient faculties have done extensive research to prepare and shape these test series. An opportunity for students to come across their strengths
Three Terminal Devices
 Three Terminal Devices - field effect transistor (FET) - bipolar junction transistor (BJT) - foundation on which modern electronics is built - active devices - devices described completely by considering
Three Terminal Devices - field effect transistor (FET) - bipolar junction transistor (BJT) - foundation on which modern electronics is built - active devices - devices described completely by considering
Final Exam: Electronics 323 December 14, 2010
 Final Exam: Electronics 323 December 4, 200 Formula sheet provided. In all questions give at least some explanation of what you are doing to receive full value. You may answer some questions ON the question
Final Exam: Electronics 323 December 4, 200 Formula sheet provided. In all questions give at least some explanation of what you are doing to receive full value. You may answer some questions ON the question
