(A) 1 and 1 (B) 0 and 1 (C) 1 and 0 (D) 0 and A second order system is described by the equation. (A) 1 rad / sec and 5 (B) 5 rad / sec and 7
|
|
|
- Alice Elisabeth Rose
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EC- Objective Paper-II IES IES-013- Paper-II 1. The D.C. gain and steady state error for step input for ( ) = s + 1 G s are : s + s + 1 (A) 1 and 1 (B) 0 and 1 (C) 1 and 0 (D) 0 and 0. A second order system is described by the equation and damping ratio respectively are d x dx x = 7y. The frequency dt dt (A) 1 rad / sec and 5 (B) 5 rad / sec and 7 (C) 1 rad / sec and 7 (D) 7 rad / sec and Derivative feedback is employed in the control system shown in the figure, to improve its damping. If the required damping factor of the system is 0.5, the value of K d must be adjusted to: R ( s) s4s1 ( + ) Cs ( ) Ks d (A) 4 (B) 19 (C) 0.5 (D) 6 4. The transfer function, of a system is ( ) system will settle in approximately 100 G s =. The unit step response of the s + 10s (A) sec (B) 1 sec (C) 0.8 sec (D) 1.5 sec 5. A feedback system with characteristic equation (A) Stable for all values of K (B) Stable only for K 0 (C) Stable for > K 70 (D) Unstable for all values of K 4 3 s + 0Ks + 5s + 10s + 15 = 0 is : 6. The system having the characteristic equation 3 s + 4s + s 6 + K = 0 will be stable for (A) K > 6 (B) 0 < K < 6 (C) 6 < K < 10 (D) 0 < K <
2 EC- Objective Paper-II IES Consider the transfer function K G( s) H( s) = 3 K. The root-locus plot of the s + 4s + s 6 system passes through s=0. The value of K at this point will be: (A) 10 (B) 0 (C) 6 (D) 8 8. A system has its open-loop transfer function of K ( + + ) s s 6s 10. The break points are s = 1.18 and s =.8, the centroid is at s =, while the asymptotic angles are ± 60 and ± 180. The value of K for the closed loop system to be oscillatory and the frequency of oscillations are respectively : (A) 600 and 10 rad/sec (B) 10 and 5 rad/sec (C) 60 and 3.16 rad/sec (D) 30 and 3.16 rad/sec 9. The open-loop transfer function of a unity feedback control system is ( ) 1 G s =. ( s + ) closed loop transfer function poles are located at: (A), (B), 1 (C), + (D), ± j1 The 10. In control systems, excessive bandwidth is NOT employed because: (A) Noise is proportional to bandwidth (B) It leads to low relative stability (C) It leads to slower response (D) Noise is proportional to the square of the bandwidth 11. Which has one of the following transfer functions the greatest overshoot? 9 (A) s + s (B) s + s (C) s + s (D) s + s The transfer function of a system is. At a frequency of 0.1 rad/sec, the straight line bode 1+ s plot will have a magnitude of: (A) 10 db (B) 0 db (C) 0 db (D) 40 db 13. If the overshoot of the unit-step response of a second order system is 30%, then the time at which peak overshoot occurs ( assuming ω n = 10rad / sec ): (A) 0.36 sec (B) 0.363sec (C) 0.336sec (D) 0.633sec 14. A second order system has maximum value at the frequency: ( ) ( ) C s = R s s s ωn + ξω n + ω n. Its frequency response will have (A) ωn 1 ξ (B) n ω ξ (C) ωn 1 ξ (D) zero 346
3 EC- Objective Paper-II IES The critical value of gain for a system is 40. The system is operating at a gain of 0. The gain margin of the system is: (A) db (B) 3 db (C) 6 db (D) 4 db 16. In a feedback control system, phase margin (PM) is: 1. Directly proportional to ξ. Inversely proportional to ξ 3. Independent of ξ 4 Zero when ξ = 0 Which of the above statements are correct? (A) 1 and (B) and 3 (C) 3 and 4 (D) 1 and The gain margin in db s of a unity feedback control system whose open-loop transfer 1 function, G( s) H( s) = is : s s + 1 ( ) (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) -1 (D) 18. By adding zero to the system transfer function, the improvement to transient response is called as: (A) Phase lead compensation (B) Phase lag compensation (C) Phase lag and phase lead compensation (D) Phase lead and phase lag compensation 19. The network having transfer function G( s) Directions:- Codes frequency of: s 1+ = 4 s 1+ 5 will provide maximum phase lead at a (A) 4 rad/sec (B) 5 rad/sec (C) 10 rad/sec (D) 100 rad/sec Each of next twenty items consists of two statements, one labeled as the statement(i) and other as Statement (II). You are to examine these two statements carefully and select the answers to these items using the codes given below (A) Both Statement (I) and Statement (II) are individually true and Statement (II) is the correct explanation of Statement (I) (B) Both Statement (I) and Statement (II) are individually true but Statement (II) is NOT the correct explanation of Statement (I) (C) Statement (I) is true but Statement (II) is false (D) Statement (I) is false but Statement (II) is true 347
4 EC- Objective Paper-II IES Statement (I): An ideal OP AMP when used to make an inverting amplifier has both input terminals at the same potential. CMRR of the OP AMP is low. 1. Statement (I): A monostable multi-vibrator, when switched on remains in a quasi stable state. Quasi stable state duration is decided by charging time of capacitor.. Statement (I): Emitter-Coupled Logic (ECL) family is designed for high speed. In this logic family, transistor does not operate fully in saturation or cutoff zones. 3. Statement (I): Switching speed of ECL logic family is very high. The transistor used in the family remains unsaturated. 4. Statement (I): In a bipolar junction transistor increase in the collector voltage increases the base width. Increase in the collector voltage increases the space-charge-width at the output junction diode. 5. Statement (I): A flip-flop is a bistable multivibrator. A flip-flop remains in one stable state indefinitely until it is directed by an input signal to switch over to the other stable state. 6. Statement (I): Associative memory is fast memory. Associative memory searches by content and not by accessing of address. 7. Statement (I): PIN photodiodes are preferred to PN photo-diodes. PIN photodiode is a constant voltage generator at a given light level. 8. Statement (I): A derivative controller produces a control action for constant error only. The PD controller increases the damping ratio and reduces the peak overshoot. 9. Statement (I): Nyquist plot is the locus of GH ( jω ) indicating the magnitude and phase angle on the GH ( jω ) plane. Given the values of GH( jω) and GH( jω) using the Nichols chart M, ω and bandwidth can be determined. m m 348
5 EC- Objective Paper-II IES Statement (I): Feedback compensation is preferred to series compensation No amplification is required as the energy flows from higher level to lower level. 31. Statement (I): A PI controller increases the order of a system by units but reduces the steady state error. A PI controller introduces a pole at either the origin or at a desired point on negative real axis. 3. Statement (I): Many of the linear control system transfer functions do not have poles or zeros in the right-half of s-plane. These are called minimum-phase transfer functions. 33. Statement (I): Baud Rate and symbols per second are often used interchangeably. Baud Rate refers to the rate of change of a signal on the transmission medium after encoding and modulation have occurred. 34. Statement (I): Most TDM systems use PCM to transmit analog signals. PCM uses A/D conversion technique to translate analog signals into binary form for serial transmission. 35. Statement (I): Single mode step indexed fibers are widely used for wide band communications. With only path of light along the axis, minimum refraction and no pulse spreading permits high pulse repetition rates. 36. Statement (I): In a conventional transmission line impedance matching can be accomplished by stub matching of adjustable lengths. In practice impedance matching in wave-guides is obtained by tuning screws inserted into the waveguide. 37. Statement (I): Slot antenna is essentially a wave-guide with a slot length of one half lengths with a radiation pattern similar to that of a dipole with plane reflection. Slot antenna has a gain much higher than that of a horn antenna. 38. Statement (I): The data path contains all the circuits to process data within the CPU with the help of which data is suitably transformed. It is the responsibility of the control path to generate control and timing signals as required by the opcode. 39. Statement (I): External fragmentation is NOT possible in paging. Pages of any program are fixed sized and can be located anywhere in memory. 349
6 EC- Objective Paper-II IES An event has two possible outcomes with probability P 1 =, and P =. The rate of 64 information with 16 outcomes per second is: (A) 38 bits / sec 4 (B) 38 bits / sec 64 (C) 38 bits / sec (D) 38 bits / sec A radio channel has a bandwidth of 10 khz and an S/N ratio of 15 db. The maximum data rate that can be transmitted is: (A) 16.1 kb/sec (B) 4. kb/sec (C) 3.3 kb/sec (D) 50.3 kb/sec 4. Conveniently information I(x) is expressed as (A) ( ) log p( x) Hartleys (B) log ( ) 10 (C) log p( x) Hartleys (D) 10 log 10 p x Hartleys 1 p x ( ) Hartleys A source produces 4 symbols with probabilities,, and. For this source, a practical coding scheme has an average code word length of bits/symbol. The efficiency of the code is (A) 1 (B) 7 8 (C) 1 (D) An analog signal is band limited to 4 khz. It is sampled at a the Nyquist rate and samples are quantized into 4 levels. The quantization levels have probabilities 1, 1, 3 and The information rate of the source is (A) bps (B) 4000 bps (C) bps (D) bps 45. What is the ratio of modulating power to the total power at 100% AM modulation? (A) 1:3 (B) 1: (C) : 3 (D) 1: A bandwidth of 10 khz is required for AM system. If the lowest frequency component in the modulated signal is 555 khz, carrier frequency in khz is: (A) 55 (B) 550 (C) 560 (D) Determine the bandwidth occupied by a sinusoidal frequency modulated carrier for which the modulation index is.4 (A) 4.8 f m (B) 6.8 f m (C).4 f m (D) 3.8 f m 350
7 EC- Objective Paper-II IES An AM signal with a carrier of 1 kw has 00 W in each side band. The percentage of modulation is (A) 0% (B) 89.4% (C) 49.7% (D) 40% 49. An audio signal, 15sin ( 1500t) index will be: 3 π amplitude modulates 60 sin ( π 10 t) (A) 0% (B) 50% (C) 5% (D) 100%. The modulation 50. In a PCM system, the amplitude levels are transmitted as 7 bit code-words. The sampling is done at 10 khz. The bandwidth of the system is: (A) 10 khz (B) 0 khz (C) 35 khz (D) 70 khz 51. What multiplexing method do the CODECs use to transmit two PCM signals in opposite directions over the same transmission line? (A) TDM (B) FDM (C) Amplitude-separation Multiplexing (D) Code Division Multiplexing 5. A radio cab company with its antenna at a height of 15 m communicates with a cab having its antenna 1.5 m. The maximum communication distance without obstacles is roughly: (A) 10 km (B) 0 km (C) 8 km (D) 36 km 53. Assuming that packet transmissions and retransmission can both the described as a Poisson process, calculate the probability that a data packet transmission in an S-ALOHA system will experience a collision with another user. Assume the total traffic rate λ t = 10 packets/sec and the packet duration τ = 10 msec. (A) 0.9 (B) 0.09 (C) (D) In a satellite communication, the uplink power level is generally high and power level of the received down link signal is low because 1. High signal attenuation due to free-space loss. Limited available down link power 3. Finite satellite down link antenna gain, which is dictated by the required coverage are. (A) 1 and only (B) 1 and 3 only (C) and 3 only (D) 1, and A CE amplifier has a resistor R F connected between collector and base R F = 40k Ω, Rc = 4K Ω. Given hfe = 50, rπ = 1K Ω, the output resistance is: (A) 40KΩ (B) 0KΩ (C) 4 KΩ (D) 0.66 KΩ 351
8 EC- Objective Paper-II IES If ICEO = 410µ A, ICBO = 5µ A and IB = 30µ A, then the collector current is (A) 415µ A (B) 440µ A (C) 445µ A (D).84µ A 57. With the increase of reverse bias in a p-n diode, the reverse current (A) Decreases (B) Increases (C) Remains constant (D) May increase or decrease depending upon doping 58. The transistor as shown in the circuit is operating in: (A) Cut-off region +5V (B) Saturation region 5kΩ (C) Active region (D) Either in active or saturation region 5V 100kΩ B C E 59. A monostable multivibrator is frequently used: (A) In memory and timing circuits (B) For regeneration of distorted waves (C) In counting circuits (D) For producing triangular waves 60. When two identical stages with upper cutoff frequency ω H are cascaded, overall cutoff frequency is at: (A) 1 ω H (B) ω H (C) 0.5ω H (D) 0.64ω H 61. Low frequency response of RC coupled amplifier can be improved by: (A) Increasing the value of the coupling capacitor only (B) Increasing the value of the bypass capacitor and coupling capacitor (C) Increasing the value of the bypass capacitor only (D) Decreasing the value of the coupling capacitor 6. In order to increase the bandwidth of tuned amplifiers, one can use 1. Tuned circuit with inductance having high Q factor. Double tuned amplifier with two tuned circuits coupled by mutual inductance 3. Staggered tuned amplifiers in which different tuned circuits which are cascaded are tuned to slightly different frequencies (A) 1, and 3 (B) 1 and only (C) and 3 only (D) 1 and 3 only 35
9 EC- Objective Paper-II IES The amplifier A shown in the figure has open loop gain of 100, input impedance Z i of 1KΩ and output impedance Zo of 100 Ω. If a negative feedback factor β = 0.99 is used, the new values of Z i and Zo are respectively (A) 10 Ω. and 1 Ω (B) 10 Ω. and 10kΩ (C) 100 K Ω. and 1 Ω (D) 100 k Ω. and 10Ω V i + A β V f V o 64. A 5 mv, 1 KHz sinusoidal signal is applied to the input of an OP-AMP integrator for which of R = 100kΩ and C = 1µ F. The output voltage is 1 cos 000 t 1 40π (A) ( π ) (B) cos( 000πt 1) 1 cos 000 t 1 40π (C) ( π ) (D) cos( 000πt 1) 65. A series RLC circuit has 5 ω 0 = 10, Q = 50, R = 400 Ω. The value of C is (A) 50 pf (B) 1000 pf (C) 500 pf (D) 1.5 pf 66. The voltage gain of an amplifier is 100. A negative feedback is applied with β = The overall gain of the amplifier is (A) 70 (B) 5 (C) (D) The open loop transfer function of an amplifier with resistive negative feedback has two poles in the left half s-plane. Then the amplifier (A) Will always be unstable at high frequencies (B) Will be stable at all frequencies (C) May become unstable depending upon feedback factor (D) Will oscillate at low frequencies 68. The ripple factor in case of a full-wave rectifier is (A) 1.1 (B) 0.50 (C) 0.48 (D) Consider the following statements: 1. A differential amplifier is used at the input stage of an operational amplifier. Differential amplifiers have very high CMRR Which of these statements are correct? (A) Both 1 and (B) Neither 1 nor (C) 1 only (D) only 353
10 EC- Objective Paper-II IES The maximum efficiency of a half-wave rectifier is (A) 33.33% (B) 40.60% (C) 50.00% (D) 68.00% 71. If a differential amplifier has a gain of 0,000 and CMRR = 80 db, its common mode gain is (A) (B) 1 (C) 1 (D) 0 7. One of the reasons why vacuum tubes eventually fail at microwave frequencies is that their (A) Transmit time becomes too short (B) Noise figure increases (C) Shunt capacitive reactance becomes too large (D) Series inductive reactance becomes too small 73. The seek time of a disk is 30 msec. It rotates at the rate of 30 rotations per second. Each track has a capacity of 300 words. The access time is (A) 47 msec (B) 50 msec (C) 60 msec (D) 6 msec 74. A parametric amplifier is to be cooled (A) To improve noise performance (B) To increase bandwidth (C) To make it suitable to pulses (D) As it cannot be used at room temperature 75. A wave guide section in microwave circuits will act as a (A) Low-pass filter (B) Band-pass filter (C) Band-stop filter (D) High-pass filter 76. The waveguide modes are usually excited from a signal source through: (A) An antenna (B) An aperture (C) A Coaxial cable (D) Free-space coupling 77. The minimum cut-off frequencies for a rectangular waveguide are obtained when: (A) a > b, m = 0 and n = 1 (B) a > b, m = 1 and n = 0 (C) a < b, m = 0 and n = 1 (D) a < b, m = 1 and n = For any lossless, reciprocal three port network, one port can be terminated in a reactance so that the other two ports are (A) Shorted (B) Decoupled (C) Matched (D) Opened 354
11 EC- Objective Paper-II IES A micro-strip line consists of a single ground plane and a thin strip conductor on a (A) Conducting plane (B) Semi conductor slab (C) Low-loss dielectric substrate (D) High-loss dielectric substrate 80. Parabolic reflectors use Cassegrain feed to (A) Increase the gain of the system (B) Increase the beam width of the system (C) Reduce the size of the main reflector (D) Allow the feed to be placed at a convenient point 81. A Ruby Maser is preferred to Ammonia Maser for microwave amplification because it has: (A) Much greater bandwidth (B) Lower noise figure (C) Better frequency stability (D) No need for a circulator 8. Laser is based on the principle of (A Stimulated emission (B) Spontaneous emission (C) Radiation (D) Polarization 83. Magnetron is a (A) High power microwave amplifier (B) Low power microwave amplifier (C) Low power microwave oscillator (D) High power microwave oscillator 84. Optical fibers are preferred as communication links for Lasers because they (A) Prevent interference by other Lasers (B) Ensure that the beam does not spread (C) Prevent atmospheric interference (D) Ensure amplification of the signal 85. Microwave links are used for TV transmission because (A) They have small S/N ratio (B) They produce less phase distortion (C) They are relatively cheaper (D) They are free from impulse noise 355
12 EC- Objective Paper-II IES The switching speed of ECL is very high, because the transistors A) Are switched between cut-off and saturation region (B) Are switched between active and saturation region (C) Are switched between active and cut-off region (D) May operate in any of the three regions 87. The rise time of a transistor switch is the time for the current to rise from A) Zero value to peak value (B) 10% of peak value to peak value (C) 10% of peak value to 90% peak value (D) 10% of peak value to 80% peak value 88. The frequency of oscillation of a stable multivibrator with component values R = k Ω, R = 0k Ω, C = 0.01µ F and C = 0.05 µ F is 1 1 (A) Hz (B) Hz (C) Hz (D) Hz 89. Which of the following regions of operation are mainly responsible for heating of the transistor under switching operation? 1. Saturation operation Cut-off region 3. Transition from saturation to cut-off 4. Transition from cut-off to saturation (A) 1, and 4 (B) 1, 3and 4 (C) and 3 only (D) 1 and 3 only 90. The BCD code for a decimal number is (A) ( (C) ( ) BCD (B) ( ) BCD ) BCD (D) ( ) BCD 91. Logic function ( A + B)( A + B) can be reduced to (A) B (B) B (C) A (D) A 9. Logic function ABD + ABD can be reduced to (A) AB (B) AB (C) BD (D) AD 93. The minimum number of NAND gates required to implement A + AB + ABC is (A) 0 (B) 1 (C) 4 (D) 7 356
13 EC- Objective Paper-II IES The logic function f ( A,B,C,D) = ( A + BC)( B + CD) can be expressed to: (A) AB + BC + ACD + BCD (B) AB + AB + ACD + BCD (C AB + AB + ACD + BCD (D) AB + AB + ACD + BCD 95. The logic function (A+B) can be expressed in terms of min terms as: (A) AB + BA (B) AB + BA + AB (C) AB + AB (D) AB + BA 96. A 3-variable truth table has a high output for the inputs: 010, 011 and 110. The Boolean expression for sum of products (SOP) can be written as (A) A B + BC (B) AB + BC (C) AB + BC (D) AB + BC 97. Which of the following are the characteristics of a Junction Field Effect Transistor? 1. High input resistance. Good thermal stability 3. High current gain 4. More noisy than bipolar junction transistor (A) 1and 3 (B) 1 and (C) and 3 (D) 3 and The minterms for AB +ACD are: (A) ABCD + ABCD + ABCD + ABCD + ABCD (B) ABCD + ABCD + ABCD + ABCD + ABCD (C) ABCD + ABCD + ABCD + ABCD + ABCD (D) ABCD + ABCD + ABCD + ABCD + ABCD 99. A binary full-subtractor (A) Consists of two cascaded half-subtractors (B) Contains two half-substractors and one OR gate (C) Can subtract any binary number (D) Can be made out of a full-adder 100. A digital multiplexer can be used for 1. Parallel to serial conversion. Many-to-one switch 3. Generating memory chip select 4. Code conversion (A) 1, and 3 (B) and 3 only (C) 1 and only (D) 1 and 3 only 357
14 EC- Objective Paper-II IES Which one of the following statements is correct? (A) PROM contains a programmable AND array and a fixed OR array (B) PLA contains a fixed AND array and a programmable OR array (C) PROM contains a fixed AND array and programmable OR array (D) PLA contains a programmable AND array and a programmable OR array 10. The output Q n of a J-K flip-flop is zero. It changes to 1 when a clock pulse is applied. The input Jn and K n are respectively (X represents don t care condition) (A) 1 and X (B) 0 and X (C) X and 0 (D) X and In a sequential circuit, the output at any instant of time depends (A) Only on the inputs presents at that instant of time (B) On past outputs as well as present inputs (C) Only on the past inputs (D) Only on the present outputs 104. Dual slope integration type Analog-to-Digital converters provide: (A) Higher speeds compared to all other types of A/D converters (B) Very good accuracy without putting extreme requirements on component stability (C) Poor rejection of power supply (D) Better resolution compared to all other types of A/D converters for the same number of bits The decimal equivalent of binary number is (A) (B) 0.75 (C) (D) Hexadecimal conversion of decimal number 7 will be (A) A3 (B) E3 (C) CC (D) C A seven-bit Hamming code is received as What is the correct code? (A) (B) (C) (D) An analog signal has a bit rate of 8000 bps and a baud rate of 1000 baud. The data elements carried by each signal and signal elements needed are respectively. (A) 8 and 56 (B) 4 and 16 (C) and 4 (D) 7 and A computer system has a 4 K word cache organized in block-set associative manner with 4 blocks per set, 64 words per block. The numbers of bits in the SET and WORD fields of the main memory address formula are respectively. (A) 15 and 4 (B) 6 and 4 (C) 7 and (D) 4 and 6 358
15 EC- Objective Paper-II IES The program counter (PC) in a micro-processor (A) Counts the number of programs being executed by the micro processor (B) Counts the number of instructions being executed by the microprocessor (C) Counts the number of interrupts handled by the microprocessor (D) Keeps the address of the next instruction to be fetched 111. An interrupt in which an external device supplies its address and the interrupt request, is called (A) Poll interrupt (C) Non-maskable interrupt (B) Maskable interrupt (D) vectored interrupt 11. Aliasing in the context of programming language refers to multiple variables having the same (A) Memory location (B) Value (C) Identifier (D) None of these 113. In a microprocessor, the register which holds the address of the next instruction to be fetched is (A) Accumulator (C) Stack pointer (B) Program counter (D) Instructor register 114. With reference to 8085 microprocessor, which of the following statements are correct? 1. The DAD instruction adds the contents of the specified register pair to the contents of the DE register pair.. The program counter is an instruction pointer 3. Whenever an instruction uses the HL pointer, the addressing is called indirect addressing 4. HL register pair is also called data pointer. (A) 1 and only (B) 1, and 3 (C), 3 and 4 (D) and 4 only 115. On the 8085, which of the following machine cycles are not used in the CALL instruction? 1. Instruction fetch. I/O 3. Memory Read 4. Memory Write (A) only (B) 1 and 4 only (C), 3 and 4 (D) 1,,3 and The stack pointer will be affected by instructions: 1. PUSH PSW. CALL ADDR 3. XTHL 4. RST n (A) 1,,3 and 4 (B) 1 and 3 only (C) 1, and 4 only (D),3 and 4 only 359
16 EC- Objective Paper-II IES TRAP is an interrupt in Which one of the following statements is true about the TRAP? (A) It is level triggered (B) It is negative edge triggered (C) It is positive edge triggered (D) It is both positive and negative edge triggered 118. Which one of the following instruction uses implied addressing mode? (A) CMA (B) JMP (C) ADC (D) SBB 119. An array multiplier is used to find the product of a 3 bit number with a 4 bit number. How many 4 bits adders are required to perform multiplication? (A) 1 (B) (C) 3 (D) During direct memory access (DMA), the INTR and INTA (interrupt and interrupt acknowledge) lines (A) Are never used (B) Are used by the DMA controller to acquire the data and address bus from the microprocessor (C) Are used by the IO device to invoke an error routine if a problem occurs during DMA transfer (D) Are used by the DMA controller to signal the microprocessor about the end of the current data transfer 360
Electronics Eingineering
 Electronics Eingineering 1. The output of a two-input gate is 0 if and only if its inputs are unequal. It is true for (A) XOR gate (B) NAND gate (C) NOR gate (D) XNOR gate 2. In K-map simplification, a
Electronics Eingineering 1. The output of a two-input gate is 0 if and only if its inputs are unequal. It is true for (A) XOR gate (B) NAND gate (C) NOR gate (D) XNOR gate 2. In K-map simplification, a
(i) Determine the admittance parameters of the network of Fig 1 (f) and draw its - equivalent circuit.
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS. Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100
 EC 40 MODEL TEST PAPER - 1 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Answer five questions, taking ANY TWO from Group A, any two from Group B and all from Group C. All parts of a question
EC 40 MODEL TEST PAPER - 1 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Answer five questions, taking ANY TWO from Group A, any two from Group B and all from Group C. All parts of a question
GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13)
 GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13) 1. Removing bypass capacitor across the emitter leg resistor in a CE amplifier causes a. increase in current gain b. decrease in current gain c. increase
GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13) 1. Removing bypass capacitor across the emitter leg resistor in a CE amplifier causes a. increase in current gain b. decrease in current gain c. increase
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-2012 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: Qn. PART - A 0. Which is the largest of three
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: Qn. PART - A 0. Which is the largest of three
LINEAR IC APPLICATIONS
 1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
 OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
R.B.V.R.R. WOMEN S COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS) Narayanaguda, Hyderabad. ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS
 R.B.V.R.R. WOMEN S COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS) Narayanaguda, Hyderabad. DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS QUESTION BANK FOR SEMESTER V PHYSICS PAPER VI (A) ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS UNIT I: SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
R.B.V.R.R. WOMEN S COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS) Narayanaguda, Hyderabad. DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS QUESTION BANK FOR SEMESTER V PHYSICS PAPER VI (A) ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS UNIT I: SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-2013 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-03 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: PART - A 0. What does the arrow mark indicate
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-03 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: PART - A 0. What does the arrow mark indicate
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-2012 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 40 Subject: PART - A 0. Which region of the transistor
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 40 Subject: PART - A 0. Which region of the transistor
ECE Branch GATE Paper (C) exp ( t ) sin (25t) (B) 4cos (20t + 3) + 2 sin (710t)
 Question 30 Carry One Mark Each. The following differential equation has 2 3 d y dy 2 3 4 y 2 2 dt degree = 2, order = degree = 3, order = 2 + + + = x dt degree = 4, order = 3 degree = 2, order = 3 2.
Question 30 Carry One Mark Each. The following differential equation has 2 3 d y dy 2 3 4 y 2 2 dt degree = 2, order = degree = 3, order = 2 + + + = x dt degree = 4, order = 3 degree = 2, order = 3 2.
ELECTRONICS ADVANCED SUPPLEMENTARY LEVEL
 ELECTRONICS ADVANCED SUPPLEMENTARY LEVEL AIMS The general aims of the subject are : 1. to foster an interest in and an enjoyment of electronics as a practical and intellectual discipline; 2. to develop
ELECTRONICS ADVANCED SUPPLEMENTARY LEVEL AIMS The general aims of the subject are : 1. to foster an interest in and an enjoyment of electronics as a practical and intellectual discipline; 2. to develop
Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All questions carry equal marks
 Code: 9A02401 PRINCIPLES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Common to EIE, E.Con.E, ECE & ECC) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 1 In a series RLC circuit, R = 5 Ω, L = 1 H and C = 1 F. A dc v ltage f 20 V is applied
Code: 9A02401 PRINCIPLES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Common to EIE, E.Con.E, ECE & ECC) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 1 In a series RLC circuit, R = 5 Ω, L = 1 H and C = 1 F. A dc v ltage f 20 V is applied
Downloaded From All JNTU World
 Code: 9A02403 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of a nuclear plant as compared to other conventional power plants. 2 Explain about: (a) Solar distillation. (b) Solar
Code: 9A02403 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of a nuclear plant as compared to other conventional power plants. 2 Explain about: (a) Solar distillation. (b) Solar
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-2007 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - II Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt Question No. 1 which is compulsory and FOUR more questions
I.E.S-(Conv.)-2007 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - II Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt Question No. 1 which is compulsory and FOUR more questions
ASTABLE MULTIVIBRATOR
 555 TIMER ASTABLE MULTIIBRATOR MONOSTABLE MULTIIBRATOR 555 TIMER PHYSICS (LAB MANUAL) PHYSICS (LAB MANUAL) 555 TIMER Introduction The 555 timer is an integrated circuit (chip) implementing a variety of
555 TIMER ASTABLE MULTIIBRATOR MONOSTABLE MULTIIBRATOR 555 TIMER PHYSICS (LAB MANUAL) PHYSICS (LAB MANUAL) 555 TIMER Introduction The 555 timer is an integrated circuit (chip) implementing a variety of
GATE 2000 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 2 Electronics and ommunication Engineering SETION A (1 Marks) 1. This question consists of 25 (Twenty Five) multiple choice questions, each carrying one mark. For each question (1.1 1.25), four alternatives
GATE 2 Electronics and ommunication Engineering SETION A (1 Marks) 1. This question consists of 25 (Twenty Five) multiple choice questions, each carrying one mark. For each question (1.1 1.25), four alternatives
SIR PADAMPAT SINGHANIA UNIVERSITY UDAIPUR Sample Question Paper for Ph.D. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) SPSAT 18
 INSTRUCTIONS SIR PADAMPAT SINGHANIA UNIVERSITY UDAIPUR Sample Question Paper for Ph.D. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) SPSAT 18 The test is 60 minutes long and consists of 40 multiple choice
INSTRUCTIONS SIR PADAMPAT SINGHANIA UNIVERSITY UDAIPUR Sample Question Paper for Ph.D. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) SPSAT 18 The test is 60 minutes long and consists of 40 multiple choice
IES Digital Mock Test
 . The circuit given below work as IES Digital Mock Test - 4 Logic A B C x y z (a) Binary to Gray code converter (c) Binary to ECESS- converter (b) Gray code to Binary converter (d) ECESS- To Gray code
. The circuit given below work as IES Digital Mock Test - 4 Logic A B C x y z (a) Binary to Gray code converter (c) Binary to ECESS- converter (b) Gray code to Binary converter (d) ECESS- To Gray code
B.E. SEMESTER III (ELECTRICAL) SUBJECT CODE: X30902 Subject Name: Analog & Digital Electronics
 B.E. SEMESTER III (ELECTRICAL) SUBJECT CODE: X30902 Subject Name: Analog & Digital Electronics Sr. No. Date TITLE To From Marks Sign 1 To verify the application of op-amp as an Inverting Amplifier 2 To
B.E. SEMESTER III (ELECTRICAL) SUBJECT CODE: X30902 Subject Name: Analog & Digital Electronics Sr. No. Date TITLE To From Marks Sign 1 To verify the application of op-amp as an Inverting Amplifier 2 To
Conventional Paper-II-2011 Part-1A
 Conventional Paper-II-2011 Part-1A 1(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) The purpose of providing dummy coils in the armature of a DC machine is to: (A) Increase voltage induced (B) Decrease the armature resistance
Conventional Paper-II-2011 Part-1A 1(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) The purpose of providing dummy coils in the armature of a DC machine is to: (A) Increase voltage induced (B) Decrease the armature resistance
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 1 P a g e INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Name : INTEGRATED CIRCUITS APPLICATIONS Code
1 P a g e INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Name : INTEGRATED CIRCUITS APPLICATIONS Code
Downloaded From All JNTU World
 Code: 9A02401 PRINCIPLES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Common to ECE, EIE, E.Con.E & ECC) 1 Find initial conditions for voltage across capacitor, the currents i 1, i 2 and the derivatives for the circuit
Code: 9A02401 PRINCIPLES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Common to ECE, EIE, E.Con.E & ECC) 1 Find initial conditions for voltage across capacitor, the currents i 1, i 2 and the derivatives for the circuit
HIGH LOW Astable multivibrators HIGH LOW 1:1
 1. Multivibrators A multivibrator circuit oscillates between a HIGH state and a LOW state producing a continuous output. Astable multivibrators generally have an even 50% duty cycle, that is that 50% of
1. Multivibrators A multivibrator circuit oscillates between a HIGH state and a LOW state producing a continuous output. Astable multivibrators generally have an even 50% duty cycle, that is that 50% of
Level 6 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Electronics and telecommunications
 9210-116 Level 6 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Electronics and telecommunications Sample Paper You should have the following for this examination one answer book non-programmable calculator pen, pencil,
9210-116 Level 6 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Electronics and telecommunications Sample Paper You should have the following for this examination one answer book non-programmable calculator pen, pencil,
LM125 Precision Dual Tracking Regulator
 LM125 Precision Dual Tracking Regulator INTRODUCTION The LM125 is a precision, dual, tracking, monolithic voltage regulator. It provides separate positive and negative regulated outputs, thus simplifying
LM125 Precision Dual Tracking Regulator INTRODUCTION The LM125 is a precision, dual, tracking, monolithic voltage regulator. It provides separate positive and negative regulated outputs, thus simplifying
Live Leak - SSC Scientific Assistant Electronics and Telecommunication Model Question Paper 2017
 Live Leak - SSC Scientific Assistant Electronics and Telecommunication Model Question Paper 2017 Q1. In a p-n diode, holes diffuse from p-region to n-region because. 1. There is higher concentration of
Live Leak - SSC Scientific Assistant Electronics and Telecommunication Model Question Paper 2017 Q1. In a p-n diode, holes diffuse from p-region to n-region because. 1. There is higher concentration of
The steeper the phase shift as a function of frequency φ(ω) the more stable the frequency of oscillation
 It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
Difference between BJTs and FETs. Junction Field Effect Transistors (JFET)
 Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
ECE Branch GATE Paper 2002 SECTION A (75 MARKS )
 SECTION A (75 MARKS ). This question consists of TWENTY FIVE sub-question (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A, B, C and D) are given, out of which only
SECTION A (75 MARKS ). This question consists of TWENTY FIVE sub-question (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A, B, C and D) are given, out of which only
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS Academic Planner for odd Semesters Semester : I Subject : Electronics(ELT1). Course: B.Sc. (PME) Introduction to Number systems B Construction and types, working Review of P type
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS Academic Planner for odd Semesters Semester : I Subject : Electronics(ELT1). Course: B.Sc. (PME) Introduction to Number systems B Construction and types, working Review of P type
BJT Circuits (MCQs of Moderate Complexity)
 BJT Circuits (MCQs of Moderate Complexity) 1. The current ib through base of a silicon npn transistor is 1+0.1 cos (1000πt) ma. At 300K, the rπ in the small signal model of the transistor is i b B C r
BJT Circuits (MCQs of Moderate Complexity) 1. The current ib through base of a silicon npn transistor is 1+0.1 cos (1000πt) ma. At 300K, the rπ in the small signal model of the transistor is i b B C r
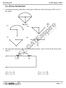
For the mechanical system of figure shown above:
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-00 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks : 0 Candidates should attempt any FIVE questions. Some useful data: Electron charge : 1.6
I.E.S-(Conv.)-00 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time Allowed: Three Hours Maximum Marks : 0 Candidates should attempt any FIVE questions. Some useful data: Electron charge : 1.6
Associate In Applied Science In Electronics Engineering Technology Expiration Date:
 PROGRESS RECORD Study your lessons in the order listed below. Associate In Applied Science In Electronics Engineering Technology Expiration Date: 1 2330A Current and Voltage 2 2330B Controlling Current
PROGRESS RECORD Study your lessons in the order listed below. Associate In Applied Science In Electronics Engineering Technology Expiration Date: 1 2330A Current and Voltage 2 2330B Controlling Current
Q.P. Code : [ TURN OVER]
![Q.P. Code : [ TURN OVER] Q.P. Code : [ TURN OVER]](/thumbs/90/103239233.jpg) Q.P. Code : 587801 8ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC70 6308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703
Q.P. Code : 587801 8ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC70 6308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703193679392A86308ADF85B2CAF8DDC703
GATE SOLVED PAPER - IN
 YEAR 202 ONE MARK Q. The i-v characteristics of the diode in the circuit given below are : v -. A v 0.7 V i 500 07 $ = * 0 A, v < 0.7 V The current in the circuit is (A) 0 ma (C) 6.67 ma (B) 9.3 ma (D)
YEAR 202 ONE MARK Q. The i-v characteristics of the diode in the circuit given below are : v -. A v 0.7 V i 500 07 $ = * 0 A, v < 0.7 V The current in the circuit is (A) 0 ma (C) 6.67 ma (B) 9.3 ma (D)
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS 1. A cordless telephone using separate frequencies for transmission in base and portable units is known as A. duplex arrangement B. half duplex arrangement C. either (a) or (b) D.
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS 1. A cordless telephone using separate frequencies for transmission in base and portable units is known as A. duplex arrangement B. half duplex arrangement C. either (a) or (b) D.
Downloaded From JNTU World. B.Tech II Year II Semester (R09) Supplementary Examinations December/January 2014/2015 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER
 Downloaded From Code: 9A02403 B.Tech II Year II Semester () Supplementary Examinations December/January 2014/2015 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER Answer any FIVE questions 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages
Downloaded From Code: 9A02403 B.Tech II Year II Semester () Supplementary Examinations December/January 2014/2015 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER Answer any FIVE questions 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages
Frequently Asked Questions GE6252 BEEE UNIT I ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS AND MEASUREMENTS
 Frequently Asked Questions GE6252 BEEE UNIT I ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS AND MEASUREMENTS 1. What is charge? 2. Define current. 3. Under what condition AC circuit said to be resonant? 4. What do you meant by
Frequently Asked Questions GE6252 BEEE UNIT I ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS AND MEASUREMENTS 1. What is charge? 2. Define current. 3. Under what condition AC circuit said to be resonant? 4. What do you meant by
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EC6202 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EC6202 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS UNIT-I - PN DIODEAND ITSAPPLICATIONS 1. What is depletion region in PN junction?
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EC6202 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS UNIT-I - PN DIODEAND ITSAPPLICATIONS 1. What is depletion region in PN junction?
ELC224 Final Review (12/10/2009) Name:
 ELC224 Final Review (12/10/2009) Name: Select the correct answer to the problems 1 through 20. 1. A common-emitter amplifier that uses direct coupling is an example of a dc amplifier. 2. The frequency
ELC224 Final Review (12/10/2009) Name: Select the correct answer to the problems 1 through 20. 1. A common-emitter amplifier that uses direct coupling is an example of a dc amplifier. 2. The frequency
shorted to ground In an NPN transistor, the majority carriers in the base are:
 الدورة الشتوية لعام 0 00.. 3. 4. 5. A silicon diode measures a high value of resistance with the meter leads in both positions. The trouble, if any, the diode is: open internally shorted shorted to ground
الدورة الشتوية لعام 0 00.. 3. 4. 5. A silicon diode measures a high value of resistance with the meter leads in both positions. The trouble, if any, the diode is: open internally shorted shorted to ground
BSNL TTA Question Paper Control Systems Specialization 2007
 BSNL TTA Question Paper Control Systems Specialization 2007 1. An open loop control system has its (a) control action independent of the output or desired quantity (b) controlling action, depending upon
BSNL TTA Question Paper Control Systems Specialization 2007 1. An open loop control system has its (a) control action independent of the output or desired quantity (b) controlling action, depending upon
Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators
 Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators FEATURES Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for Single-ended or Push-pull Applications Low Standby Current 8mA Typical Interchangeable with
Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators FEATURES Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for Single-ended or Push-pull Applications Low Standby Current 8mA Typical Interchangeable with
Linear Algebra, Calculus, Differential Equations and Vector Analysis. Complex Anaysis, Numerical Methods and Probability and Statistics.
 Test No Topic code Topic EC-01 GEM (Engineering Mathematics) Topic wise Tests Each test carries 25 marks and 45 minutes duration Test consists of 5 one mark questions and 10 two marks questions Tests will
Test No Topic code Topic EC-01 GEM (Engineering Mathematics) Topic wise Tests Each test carries 25 marks and 45 minutes duration Test consists of 5 one mark questions and 10 two marks questions Tests will
PESIT BANGALORE SOUTH CAMPUS BASIC ELECTRONICS
 PESIT BANGALORE SOUTH CAMPUS QUESTION BANK BASIC ELECTRONICS Sub Code: 17ELN15 / 17ELN25 IA Marks: 20 Hrs/ Week: 04 Exam Marks: 80 Total Hours: 50 Exam Hours: 03 Name of Faculty: Mr. Udoshi Basavaraj Module
PESIT BANGALORE SOUTH CAMPUS QUESTION BANK BASIC ELECTRONICS Sub Code: 17ELN15 / 17ELN25 IA Marks: 20 Hrs/ Week: 04 Exam Marks: 80 Total Hours: 50 Exam Hours: 03 Name of Faculty: Mr. Udoshi Basavaraj Module
Preface... iii. Chapter 1: Diodes and Circuits... 1
 Table of Contents Preface... iii Chapter 1: Diodes and Circuits... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Structure of an Atom... 2 1.3 Classification of Solid Materials on the Basis of Conductivity... 2 1.4 Atomic
Table of Contents Preface... iii Chapter 1: Diodes and Circuits... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Structure of an Atom... 2 1.3 Classification of Solid Materials on the Basis of Conductivity... 2 1.4 Atomic
Number of Lessons:155 #14B (P) Electronics Technology with Digital and Microprocessor Laboratory Completion Time: 42 months
 PROGRESS RECORD Study your lessons in the order listed below. Number of Lessons:155 #14B (P) Electronics Technology with Digital and Microprocessor Laboratory Completion Time: 42 months 1 2330A Current
PROGRESS RECORD Study your lessons in the order listed below. Number of Lessons:155 #14B (P) Electronics Technology with Digital and Microprocessor Laboratory Completion Time: 42 months 1 2330A Current
Fan in: The number of inputs of a logic gate can handle.
 Subject Code: 17333 Model Answer Page 1/ 29 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model
Subject Code: 17333 Model Answer Page 1/ 29 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1992 Time Allowed : Three Hours
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1992 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time Allowed : Three Hours Maximum Marks: 0 Candidates should attempt question No. 1 which is compulsory and any FOUR of the remaining
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1992 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time Allowed : Three Hours Maximum Marks: 0 Candidates should attempt question No. 1 which is compulsory and any FOUR of the remaining
NOORUL ISLAM COLLEGE OF ENGG, KUMARACOIL. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGG. SUBJECT CODE: EC 1251 SUBJECT NAME: ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS-II
 NOORUL ISLAM COLLEGE OF ENGG, KUMARACOIL. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGG. SUBJECT CODE: EC 1251 SUBJECT NAME: ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS-II Prepared by, C.P.SREE BALA LEKSHMI (Lect/ECE) ELECTRONICS
NOORUL ISLAM COLLEGE OF ENGG, KUMARACOIL. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGG. SUBJECT CODE: EC 1251 SUBJECT NAME: ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS-II Prepared by, C.P.SREE BALA LEKSHMI (Lect/ECE) ELECTRONICS
Operational Amplifiers
 Operational Amplifiers Table of contents 1. Design 1.1. The Differential Amplifier 1.2. Level Shifter 1.3. Power Amplifier 2. Characteristics 3. The Opamp without NFB 4. Linear Amplifiers 4.1. The Non-Inverting
Operational Amplifiers Table of contents 1. Design 1.1. The Differential Amplifier 1.2. Level Shifter 1.3. Power Amplifier 2. Characteristics 3. The Opamp without NFB 4. Linear Amplifiers 4.1. The Non-Inverting
UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus
 UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus PAPER I 1. Circuit Theory: Circuit components; network graphs; KCL, KVL; circuit analysis methods: nodal analysis, mesh analysis;
UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus PAPER I 1. Circuit Theory: Circuit components; network graphs; KCL, KVL; circuit analysis methods: nodal analysis, mesh analysis;
State the application of negative feedback and positive feedback (one in each case)
 (ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Subject Code: 073 Model wer Page No: / N Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
(ISO/IEC - 700-005 Certified) Subject Code: 073 Model wer Page No: / N Important Instructions to examiners: ) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer
CHAPTER 6 DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS
 CHAPTER 6 DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS 1 LECTURE CONTENTS 6.1 Logic Gates 6.2 Digital Instruments 6.3 Analog to Digital Converter 6.4 Electronic Counter 6.6 Digital Multimeters 2 6.1 Logic Gates 3 AND Gate The
CHAPTER 6 DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS 1 LECTURE CONTENTS 6.1 Logic Gates 6.2 Digital Instruments 6.3 Analog to Digital Converter 6.4 Electronic Counter 6.6 Digital Multimeters 2 6.1 Logic Gates 3 AND Gate The
ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Q1. A transmission line of characteristic impedance 50 Ω is terminated by a 50 Ω load. When excited by a sinusoidal voltage source at 10 GHz the phase difference
ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Q1. A transmission line of characteristic impedance 50 Ω is terminated by a 50 Ω load. When excited by a sinusoidal voltage source at 10 GHz the phase difference
Electrical Materials may be referred to a metal, dielectrics,electrical insulators or conductors,paramagnetic materials and many other.
 Electrical Engineering Paper-1 Syllabus : This part is for both objective and conventional types papers : 1) EM Theory- The electromagnetic force is said to be one of the fundamental interactions in nature
Electrical Engineering Paper-1 Syllabus : This part is for both objective and conventional types papers : 1) EM Theory- The electromagnetic force is said to be one of the fundamental interactions in nature
Document Name: Electronic Circuits Lab. Facebook: Twitter:
 Document Name: Electronic Circuits Lab www.vidyathiplus.in Facebook: www.facebook.com/vidyarthiplus Twitter: www.twitter.com/vidyarthiplus Copyright 2011-2015 Vidyarthiplus.in (VP Group) Page 1 CIRCUIT
Document Name: Electronic Circuits Lab www.vidyathiplus.in Facebook: www.facebook.com/vidyarthiplus Twitter: www.twitter.com/vidyarthiplus Copyright 2011-2015 Vidyarthiplus.in (VP Group) Page 1 CIRCUIT
Q.1: Power factor of a linear circuit is defined as the:
 Q.1: Power factor of a linear circuit is defined as the: a. Ratio of real power to reactive power b. Ratio of real power to apparent power c. Ratio of reactive power to apparent power d. Ratio of resistance
Q.1: Power factor of a linear circuit is defined as the: a. Ratio of real power to reactive power b. Ratio of real power to apparent power c. Ratio of reactive power to apparent power d. Ratio of resistance
OBJECTIVE PAPER-II. Key: (C)
 ESE-06 EC Objective Paper-II OBJECTIVE PAPER-II. The closed-loop transfer function of a certain control system is given by C 00 (s). R s 0s 00 Then the settling time for a % tolerance band is given by
ESE-06 EC Objective Paper-II OBJECTIVE PAPER-II. The closed-loop transfer function of a certain control system is given by C 00 (s). R s 0s 00 Then the settling time for a % tolerance band is given by
Oscillators. An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier.
 Oscillators An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier. An amplifier delivers an output signal whose waveform corresponds to the input signal but
Oscillators An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier. An amplifier delivers an output signal whose waveform corresponds to the input signal but
About the Tutorial. Audience. Prerequisites. Copyright & Disclaimer. Linear Integrated Circuits Applications
 About the Tutorial Linear Integrated Circuits are solid state analog devices that can operate over a continuous range of input signals. Theoretically, they are characterized by an infinite number of operating
About the Tutorial Linear Integrated Circuits are solid state analog devices that can operate over a continuous range of input signals. Theoretically, they are characterized by an infinite number of operating
LM13600 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers
 LM13600 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers General Description The LM13600 series consists of two current controlled transconductance amplifiers each with
LM13600 Dual Operational Transconductance Amplifiers with Linearizing Diodes and Buffers General Description The LM13600 series consists of two current controlled transconductance amplifiers each with
 free Online GATE coaching www.egate.ws Online IES coaching for free I.E.S-(Conv.)-2000 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - II Candidates should attempt question no. 1 which is compulsory
free Online GATE coaching www.egate.ws Online IES coaching for free I.E.S-(Conv.)-2000 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - II Candidates should attempt question no. 1 which is compulsory
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-2005 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - II Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt Question No. 1 which is compulsory and FOUR more questions
I.E.S-(Conv.)-2005 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - II Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt Question No. 1 which is compulsory and FOUR more questions
free I.E.S-(OBJ) Online GATE 2007 coaching Online IES coaching for 1 of free 13 PAPER-II
 free I.E.S-(OBJ) Online GATE 007 coaching www.egate.ws Online IES coaching for 1 of free 13 ELECTRONICS & TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER-II 1. In which unit is the performance of cache memory measured?
free I.E.S-(OBJ) Online GATE 007 coaching www.egate.ws Online IES coaching for 1 of free 13 ELECTRONICS & TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER-II 1. In which unit is the performance of cache memory measured?
EC Objective Paper II (Set - D) 2 10 Hz (C)
 EC Objective Paper II (Set - D) 1. Techniques that automatically move program and data blocks into the physical main memory when they are required for execution are called Main Memory techniques Cache
EC Objective Paper II (Set - D) 1. Techniques that automatically move program and data blocks into the physical main memory when they are required for execution are called Main Memory techniques Cache
ELECTRONICS & TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER-II
 I.E.S. (OBJ)-003 1 of 15 ELECTRONICS & TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING 1. Match List I (Circuit) with List II (Property) and select the correct answer : List I A. R-C coupled single-stage amplifier B. Emitter
I.E.S. (OBJ)-003 1 of 15 ELECTRONICS & TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING 1. Match List I (Circuit) with List II (Property) and select the correct answer : List I A. R-C coupled single-stage amplifier B. Emitter
UNIT 2. Q.1) Describe the functioning of standard signal generator. Ans. Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation
 UNIT 2 Q.1) Describe the functioning of standard signal generator Ans. STANDARD SIGNAL GENERATOR A standard signal generator produces known and controllable voltages. It is used as power source for the
UNIT 2 Q.1) Describe the functioning of standard signal generator Ans. STANDARD SIGNAL GENERATOR A standard signal generator produces known and controllable voltages. It is used as power source for the
Emitter base bias. Collector base bias Active Forward Reverse Saturation forward Forward Cut off Reverse Reverse Inverse Reverse Forward
 SEMICONDUCTOR PHYSICS-2 [Transistor, constructional characteristics, biasing of transistors, transistor configuration, transistor as an amplifier, transistor as a switch, transistor as an oscillator] Transistor
SEMICONDUCTOR PHYSICS-2 [Transistor, constructional characteristics, biasing of transistors, transistor configuration, transistor as an amplifier, transistor as a switch, transistor as an oscillator] Transistor
Analog Electronic Circuits Lab-manual
 2014 Analog Electronic Circuits Lab-manual Prof. Dr Tahir Izhar University of Engineering & Technology LAHORE 1/09/2014 Contents Experiment-1:...4 Learning to use the multimeter for checking and indentifying
2014 Analog Electronic Circuits Lab-manual Prof. Dr Tahir Izhar University of Engineering & Technology LAHORE 1/09/2014 Contents Experiment-1:...4 Learning to use the multimeter for checking and indentifying
PAPER-II (Subjective)
 PAPER-II (Subjective) 1.(A) Choose and write the correct answer from among the four options given in each case for (a) to (j) below: (a) Improved commutation in d.c machines cannot be achieved by (i) Use
PAPER-II (Subjective) 1.(A) Choose and write the correct answer from among the four options given in each case for (a) to (j) below: (a) Improved commutation in d.c machines cannot be achieved by (i) Use
Low Pass Filter Introduction
 Low Pass Filter Introduction Basically, an electrical filter is a circuit that can be designed to modify, reshape or reject all unwanted frequencies of an electrical signal and accept or pass only those
Low Pass Filter Introduction Basically, an electrical filter is a circuit that can be designed to modify, reshape or reject all unwanted frequencies of an electrical signal and accept or pass only those
Multivibrators. Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Amrita School of Engineering
 Multivibrators Multivibrators Multivibrator is an electronic circuit that generates square, rectangular, pulse waveforms. Also called as nonlinear oscillators or function generators. Multivibrator is basically
Multivibrators Multivibrators Multivibrator is an electronic circuit that generates square, rectangular, pulse waveforms. Also called as nonlinear oscillators or function generators. Multivibrator is basically
Operational Amplifier BME 360 Lecture Notes Ying Sun
 Operational Amplifier BME 360 Lecture Notes Ying Sun Characteristics of Op-Amp An operational amplifier (op-amp) is an analog integrated circuit that consists of several stages of transistor amplification
Operational Amplifier BME 360 Lecture Notes Ying Sun Characteristics of Op-Amp An operational amplifier (op-amp) is an analog integrated circuit that consists of several stages of transistor amplification
8-Bit A/D Converter AD673 REV. A FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
 a FEATURES Complete 8-Bit A/D Converter with Reference, Clock and Comparator 30 s Maximum Conversion Time Full 8- or 16-Bit Microprocessor Bus Interface Unipolar and Bipolar Inputs No Missing Codes Over
a FEATURES Complete 8-Bit A/D Converter with Reference, Clock and Comparator 30 s Maximum Conversion Time Full 8- or 16-Bit Microprocessor Bus Interface Unipolar and Bipolar Inputs No Missing Codes Over
Electronics Question Bank-2
 Electronics Question Bank-2 Questions Collected from Candidates Appeared for Various Competitive Examinations Compiled by Vishnu.N.V 1. The concentration of minority carriers in an extrinsic semiconductor
Electronics Question Bank-2 Questions Collected from Candidates Appeared for Various Competitive Examinations Compiled by Vishnu.N.V 1. The concentration of minority carriers in an extrinsic semiconductor
Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Lesson Four Lesson Five PREVIEW COPY
 Oscillators Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Introduction to Oscillators...3 Flip-Flops...19 Logic Clocks...37 Lesson Four Filters and Waveforms...53 Lesson Five Troubleshooting Oscillators...69
Oscillators Table of Contents Lesson One Lesson Two Lesson Three Introduction to Oscillators...3 Flip-Flops...19 Logic Clocks...37 Lesson Four Filters and Waveforms...53 Lesson Five Troubleshooting Oscillators...69
Introductory Electronics for Scientists and Engineers
 Introductory Electronics for Scientists and Engineers Second Edition ROBERT E. SIMPSON University of New Hampshire Allyn and Bacon, Inc. Boston London Sydney Toronto Contents Preface xiü 1 Direct Current
Introductory Electronics for Scientists and Engineers Second Edition ROBERT E. SIMPSON University of New Hampshire Allyn and Bacon, Inc. Boston London Sydney Toronto Contents Preface xiü 1 Direct Current
WINTER 14 EXAMINATION
 Subject Code:173 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The
Subject Code:173 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The
ECE Branch GATE Paper 2004
 Q. 1 30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? Fig. Q.1 2. The equivalent inductance measured between the terminals
Q. 1 30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? Fig. Q.1 2. The equivalent inductance measured between the terminals
Gechstudentszone.wordpress.com
 8.1 Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) UNIT 8: Operational Amplifier An operational amplifier ("op-amp") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended
8.1 Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) UNIT 8: Operational Amplifier An operational amplifier ("op-amp") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended
R a) Explain the operation of RC high-pass circuit when exponential input is applied.
 SET - 1 1. a) Explain the operation of RC high-pass circuit when exponential input is applied. 2x V ( e 1) V b) Verify V2 = = tanhx for a symmetrical square wave applied to a RC low 2x 2 ( e + 2 pass circuit.
SET - 1 1. a) Explain the operation of RC high-pass circuit when exponential input is applied. 2x V ( e 1) V b) Verify V2 = = tanhx for a symmetrical square wave applied to a RC low 2x 2 ( e + 2 pass circuit.
ECE-342 Test 1: Sep 27, :00-8:00, Closed Book. Name : SOLUTION
 ECE-342 Test 1: Sep 27, 2011 6:00-8:00, Closed Book Name : SOLUTION All solutions must provide units as appropriate. Use the physical constants and data as provided on the formula sheet the last page of
ECE-342 Test 1: Sep 27, 2011 6:00-8:00, Closed Book Name : SOLUTION All solutions must provide units as appropriate. Use the physical constants and data as provided on the formula sheet the last page of
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (CODE NO. 10) PAPER - I
 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (CODE NO. 10) PAPER - I 1. Circuit theory Circuit Components, Network graphs, KCL, KVL, Circuit analysis methods: Nodal analysis, mesh analysis, basic network theorems; transient
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (CODE NO. 10) PAPER - I 1. Circuit theory Circuit Components, Network graphs, KCL, KVL, Circuit analysis methods: Nodal analysis, mesh analysis, basic network theorems; transient
Microelectronic Circuits
 SECOND EDITION ISHBWHBI \ ' -' Microelectronic Circuits Adel S. Sedra University of Toronto Kenneth С Smith University of Toronto HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON, INC. New York Chicago
SECOND EDITION ISHBWHBI \ ' -' Microelectronic Circuits Adel S. Sedra University of Toronto Kenneth С Smith University of Toronto HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON, INC. New York Chicago
PRINCIPLES OF RADAR. By Members of the Staff of the Radar School Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Third Edition by J.
 PRINCIPLES OF RADAR By Members of the Staff of the Radar School Massachusetts Institute of Technology Third Edition by J. Francis Reintjes ASSISTANT PBOFESSOR OF COMMUNICATIONS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE
PRINCIPLES OF RADAR By Members of the Staff of the Radar School Massachusetts Institute of Technology Third Edition by J. Francis Reintjes ASSISTANT PBOFESSOR OF COMMUNICATIONS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1996 Some useful data:
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1996 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt question ONE which is compulsory and any FOUR of the remaining
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1996 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt question ONE which is compulsory and any FOUR of the remaining
Physical electronics, various electronics devices, ICs form the core of Electronics and Telecommunication branch. This part includes
 Paper-1 Syllabus for Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering: This part is for both objective and conventional type papers: 1) Materials and Components Materials and Components are the vertebral column
Paper-1 Syllabus for Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering: This part is for both objective and conventional type papers: 1) Materials and Components Materials and Components are the vertebral column
Chapter 13 Oscillators and Data Converters
 Chapter 13 Oscillators and Data Converters 13.1 General Considerations 13.2 Ring Oscillators 13.3 LC Oscillators 13.4 Phase Shift Oscillator 13.5 Wien-Bridge Oscillator 13.6 Crystal Oscillators 13.7 Chapter
Chapter 13 Oscillators and Data Converters 13.1 General Considerations 13.2 Ring Oscillators 13.3 LC Oscillators 13.4 Phase Shift Oscillator 13.5 Wien-Bridge Oscillator 13.6 Crystal Oscillators 13.7 Chapter
Single Supply, Rail to Rail Low Power FET-Input Op Amp AD820
 a FEATURES True Single Supply Operation Output Swings Rail-to-Rail Input Voltage Range Extends Below Ground Single Supply Capability from + V to + V Dual Supply Capability from. V to 8 V Excellent Load
a FEATURES True Single Supply Operation Output Swings Rail-to-Rail Input Voltage Range Extends Below Ground Single Supply Capability from + V to + V Dual Supply Capability from. V to 8 V Excellent Load
UMAINE ECE Morse Code ROM and Transmitter at ISM Band Frequency
 UMAINE ECE Morse Code ROM and Transmitter at ISM Band Frequency Jamie E. Reinhold December 15, 2011 Abstract The design, simulation and layout of a UMAINE ECE Morse code Read Only Memory and transmitter
UMAINE ECE Morse Code ROM and Transmitter at ISM Band Frequency Jamie E. Reinhold December 15, 2011 Abstract The design, simulation and layout of a UMAINE ECE Morse code Read Only Memory and transmitter
Final Exam: Electronics 323 December 14, 2010
 Final Exam: Electronics 323 December 4, 200 Formula sheet provided. In all questions give at least some explanation of what you are doing to receive full value. You may answer some questions ON the question
Final Exam: Electronics 323 December 4, 200 Formula sheet provided. In all questions give at least some explanation of what you are doing to receive full value. You may answer some questions ON the question
Lab Exercises. Exercise 1. Objective. Theory. Lab Exercises
 Lab Exercises Exercise 1 Objective! Study the generation of differential binary signal.! Study the differential PSK modulation.! Study the differential PSK demodulation. Lab Exercises Theory Carrier and
Lab Exercises Exercise 1 Objective! Study the generation of differential binary signal.! Study the differential PSK modulation.! Study the differential PSK demodulation. Lab Exercises Theory Carrier and
Summer 2015 Examination
 Summer 2015 Examination Subject Code: 17445 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
Summer 2015 Examination Subject Code: 17445 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
SUMMER 13 EXAMINATION Subject Code: Model Answer Page No: / N
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Exam Booklet. Pulse Circuits
 Exam Booklet Pulse Circuits Pulse Circuits STUDY ASSIGNMENT This booklet contains two examinations for the six lessons entitled Pulse Circuits. The material is intended to provide the last training sought
Exam Booklet Pulse Circuits Pulse Circuits STUDY ASSIGNMENT This booklet contains two examinations for the six lessons entitled Pulse Circuits. The material is intended to provide the last training sought
 Electronic Devices 1. Current flowing in each of the following circuits A and respectively are: (Circuit 1) (Circuit 2) 1) 1A, 2A 2) 2A, 1A 3) 4A, 2A 4) 2A, 4A 2. Among the following one statement is not
Electronic Devices 1. Current flowing in each of the following circuits A and respectively are: (Circuit 1) (Circuit 2) 1) 1A, 2A 2) 2A, 1A 3) 4A, 2A 4) 2A, 4A 2. Among the following one statement is not
R & D Electronics DIGITAL IC TRAINER. Model : DE-150. Feature: Object: Specification:
 DIGITAL IC TRAINER Model : DE-150 Object: To Study the Operation of Digital Logic ICs TTL and CMOS. To Study the All Gates, Flip-Flops, Counters etc. To Study the both the basic and advance digital electronics
DIGITAL IC TRAINER Model : DE-150 Object: To Study the Operation of Digital Logic ICs TTL and CMOS. To Study the All Gates, Flip-Flops, Counters etc. To Study the both the basic and advance digital electronics
OSCILLATORS AND WAVEFORM-SHAPING CIRCUITS
 OSILLATORS AND WAVEFORM-SHAPING IRUITS Signals having prescribed standard waveforms (e.g., sinusoidal, square, triangle, pulse, etc). To generate sinusoidal waveforms: o Positive feedback loop with non-linear
OSILLATORS AND WAVEFORM-SHAPING IRUITS Signals having prescribed standard waveforms (e.g., sinusoidal, square, triangle, pulse, etc). To generate sinusoidal waveforms: o Positive feedback loop with non-linear
