Live Leak - SSC Scientific Assistant Electronics and Telecommunication Model Question Paper 2017
|
|
|
- Berenice Dennis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Live Leak - SSC Scientific Assistant Electronics and Telecommunication Model Question Paper 2017 Q1. In a p-n diode, holes diffuse from p-region to n-region because. 1. There is higher concentration of holes in the p-region 2. Holes are positively charged 3. Holes are urged to move by the barrier potential 4. Free-electron in the n-region attract the holes Q2. Thermal runaway is not encountered in FETs because. 1. IDS has a zero temperature coefficient 2. IDS has a negative temperature coefficient 3. IDS has a positive temperature coefficient 4. The mobility of the carries decreases with increase in temperature Q3. The electron and hole concentrations in a intrinsic semiconductor are Click and drag to move and Click and drag to move respectively. When doped with a p-type material, these change to n and p respectively, then 1. n + p = n i + p i 2. n + n i = p + p i 3. np i = n i p 4. np = n i p i 1 P a g e
2 Q4. The static characteristics of an adequately forward biased pn junction is a straight line if the plot is of 1. ln Ivsln V 2. ln IvsV 3. Ivsln V 4. IvsV Q5. A CMOS amplifier when compared to an N channel MOSFET, has the advantage of 1. Higher cut off frequency 2. Higher voltage gain 3. Higher current gain 4. Lower current drain from the power supply, thereby less dissipation Q6. The effective channel length of MOSFET in saturation decreases with increase in 1. Gate voltage 2. Drain voltage 3. Source voltage 4. Body voltage Q7. Choose proper substitutes for X and Y to make the following statement correct Tunnel diode and Avalanche photodiode are operated in X bias and Y bias respectively 1. X : reverse, Y : reverse 2 P a g e
3 2. X : reverse, Y : forward 3. X : forward, Y: reverse 4. X : forward, Y: forward Q8. Small increase in temperature in the CE connected transistor causes 1. Increase in I CEO 2. Increase in ac current gain 3. Decrease in ac current gain 4. Increase in output resistance Q9. P channel FETs are less superior than N channel FETs because 1. They have higher input impedance 2. They have high switching time 3. They consume less power 4. Mobility of elections is greater than that of holes Q10. In an enhancement type MOSFET, the output V I characteristics has 1. Only an ohmic region 2. Only a saturation region 3. Only ohmic region at lower voltage value followed by a saturation region at higher voltages 4. An ohmic region at large voltage values preceded by a saturation region at lower voltages Q11. When an NPN transistor is properly biased then most of the electrons from the emitter 3 P a g e
4 1. Recombine with holes in the base 2. Recombine in the emitter itself 3. Pass through the base to the collector 4. Are stopped by the junction barrier Q12. Intrinsic semiconductors are those which 1. Are available locally 2. Are made of the semiconductor material in its purest from 3. Have more electrons than holes 4. Have zero energy gaps Q13. The SiO2 layer in an IC acts as a/an 1. Resistor 2. An insulting layer 3. Mechanical output 4. None Q14. In the study of BJT as an amplifier, if α = i c i e and β = i c i b, where i c, i e, i b are the collector, emitter and base currents, then 1. β = (1 α)/α 2. β = α/(1 α) 3. β = α/(1 + α) 4. β = (1 + α)/α 4 P a g e
5 Q15. The leakage current in Si is 10μA at 10 C. The leakage current when T = 30 C is 1. 10μA 2. 20μA 3. 40μA 4. 80μA Q16. The drift velocity of holes is 5cm/sec5cm/sec under a field of 100V/cm100V/cm. The mobility is cm 2 /Vsec cm 2 /Vsec 3. 20cm 2 /Vsec 4. 5m 2 /Vsec Q17. A Common Base amplifier is characterized by 1. High current gain and High Voltage gain 2. Low current gain and Low Voltage gain 3. Low current gain and High Voltage gain 4. High current gain and Low Voltage gain Q18. Hartley oscillator is commonly used in a 1. TV receivers 2. Radio transmitters 3. Radio Receivers 5 P a g e
6 4. TV transmitters Q19. The advantage of bridge rectifier over full wave rectifier is 1. Higher Average current 2. Lower PIV (Peak Inverse Voltage) 3. Lower ripple factor 4. Higher efficiency Q20. An amplifier without feedback has a gain of 100 ± 10 and negative feedback is provided such that the gain variations remain within 0.2%. Then the amount of feedback β is given as Q21. When three amplifiers each if bandwidth f H = 20kHz are cascaded the overall bandwidth becomes khz khz khz khz Q22. Negative feedback is generally used in 1. Oscillators 2. Comparator 6 P a g e
7 3. Amplifiers 4. Multivibrator Q23. The power amplifier which is having Maximum distortion is 1. A 2. B 3. C 4. AB Q24. The control signal of a sample and hold circuit is applied to the- 1. Triac 2. Silicon Controlled Rectifier 3. Diac 4. MOS Q25. UV radiation is used in which process of IC fabrication? 1. Diffusion 2. Masking 3. Ion Implantation 4. Oxidation Q26. Which of the following statement is false regarding Common Collector amplifier 1. Output is taken from the emitter terminal 2. Input and output signals are in phase 7 P a g e
8 3. Input resistance is high 4. Voltage gain is relatively high Q27. An FET is a better chopper than a BJT because it has 1. Lower Off-set voltage 2. Lower gain and bandwidth product 3. Lower input current 4. Higher input impedance Q28. For a tuned radio frequency applications generally we use 1. Class A amplifier 2. Class C amplifier 3. Class AB amplifier 4. Class B amplifier Q29. To obtain very High Input and Low Output Impedances in a feedback amplifier, the topology mostly used is 1. Voltage Series Feedback 2. Current Series Feedback 3. Voltage Shunt Feedback 4. Current Shunt Feedback Q30. Three identical RC coupled amplifiers each having a lower cut off frequency f is cascaded with negligible loading. What is the lower cut off frequency of the overall amplifier? 8 P a g e
9 1. f f f f Q31. The full scale output of a 10 bit DAC is 5V. the resolution is 1. 5 mv mv mv mv Q32. The network shown below implements. 1. NOR gate 9 P a g e
10 2. NAND gate 3. XOR gate 4. XNOR gate Q33. The MUX shown below is a 4 1 multiplexer. The output Z is 1. A C 2. A C 3. B C 4. B C Q34. It is required to construct a 2 n to 1 multiplexer by using 2 to 1 multiplexers only. How many of 2 to 1 multiplexers are needed? n 3. 2 n n 1 Q35. The parity of binary number P a g e
11 1. is even 2. is not known 3. is odd 4. is as the number of zeros Q36. With which decoder it is possible to obtain many code conversions? 1. 2 line to 4 line decoder 2. 3 line to 8 line decoder 3. Not possible with any decoder 4. 4 line to 16 line decoder Q37. Two of the four synchronous modes of operation of clocked JK flip flops are SET, HOLD. The other two are 1. PRESET and CLEAR 2. PRESET and RESET 3. PRESET and TOGGLE 4. RESET and TOGGLE Q38. The decimal equivalent of hexadecimal number 2A0F is Q39. Given the logical function of four variables 11 P a g e
12 f(a, B, C, D) = (A + BC)(B + CD) The function as a sum of product will be 1. AB + BC + ACD + BCD 2. AB + AB + ACD + BCD 3. AB + AB + ACD + BCD 4. AB + AB + ACD + BCD Q40. If x y = 0, then which one of the following is true? 1. xy + yx + xz = xy + yz 2. xyz + xyz = xyz + xyz 3. xy + yx = xy + xy 4. xyz = 1 Q41. A 4-bit modulo 16 ripple counter uses JK flip flop. If the propagation delay of each flip flop is 50 ns, The maximum clock frequency that can be used is MHz MHz 3. 5 MHz 4. 4 MHz Q42. Logic 1 in positive logic system is represented by 1. zero level 2. lower voltage level 12 P a g e
13 3. higher voltage level 4. negative voltage Q43. Synchronous counters eliminate the delay problems encountered with asynchronous (ripple) counter because the 1. Input clock pulses are applied only to the first and the last stages 2. Input clock pulses are applied only to the last stage 3. Input clock pulses are not used to activated any of the counter stages 4. Input clock pulses are applied simultaneously Q44. The Boolean expression reduces to F = A + B + C + A + B + C + A + B + C + ABC reduces to 1. A 2. B 3. C 4. A + B + C Q45. What are the values respectively, of R 1 andr 2 in the expression (235) R1 = (565) 10 = (1065) R2? 1. 8, , , , 8 Q46. Which one of the following statements in not correct? 13 P a g e
14 Conversion of EXCESS-3 code to BCD can be achieved by using 1. Discrete gates 2. 4 : 16 de-multiplexer 3. A 4 bit full adder 4. A 4 bit half adder Q47. A, B, C and D are input, and Y is the output bit in the XOR gate circuit of the figure below. Which of the following statements about the sum S of A, B, C, D and Y is correct? 1. S is always with zero or odd 2. S is always either zero or even 3. S = 1 only if the sum of A, B, C and D is even 4. S = 1 only if the sum A, B, C and D is odd Q48. A cary look ahead adder is frequently used to addition because it 1. is faster 2. is more accurate 3. uses fewer gates 4. costs less Q49. The reduced form of the Boolean expression 14 P a g e
15 A[B + C(AB + AC)] 1. AB 2. AB 3. AB 4. AB + AC Q50. Consider the following: Any combination circuit can be built using NAND gates 2. NOR gates 3. EX OR gates 4. Multiplexers Which of these are correct? 1. 1, 2 and , 3 and , 3 and , 2 and 4 Q51. A Delta connected network with its Wye-equivalent is shown in figure. The resistance R 1, R 2 and R 3 (in ohms) are respectively 15 P a g e
16 1. 1.5, 3 and , 9 and , 3 and , 1.5 and 9 Q52. For two two-port networks have their inputs in series connection and their outputs in parallel connection. Which of the following is true about the network? 1. The overall z parameter is the sum of individual z parameter matrices. 2. The overall y parameter is the sum of individual y parameter matrices. 3. The overall h parameter is the sum of individual h parameter matrices. 4. The overall ABCD parameter is the product of individual ABCD parameter matrices. Q53. If the scattering matrix [S] of a two port network is [S] = [ ] Then the network is 1. lossless and reciprocal 2. lossless but not reciprocal 3. not lossless but reciprocal 16 P a g e
17 4. neither lossless nor reciprocal Q54. For the ideal transformer shown below, the input impedance V 1 I 1 is 1. nr 2. n 2 R 3. R n 2 4. R n Q55. If P m is the maximum power transferred, then loss of the system is 1. P m 4 2. P m P m 4 4. P m Q56. A 4μF capacitor is charged by a constant current 2μA for 6sec. The voltage across the capacitor at the end of the charging interval will be 1. 2V 2. 3V 3. 4V 17 P a g e
18 4. 0.5V Q57. The peak value of a sine wave is 200 V. Its average value is V V V V Q58. The current flowing through the voltage source in the circuit shown is A A A A Q59. A series RLC circuit resonates at 1000 khz. At frequency of 1005 khz, the circuit impedance is 1. Resistive 2. Capacitive 3. Inductive 18 P a g e
19 4. Minimum Q60. Superposition theorem can be applied only to circuits having elements. 1. Non-linear 2. Passive 3. Linear bilateral 4. Resistive Q61. The voltage V in the following figure is equal to 1. 3 V V 3. 5 V 4. None of the above Q62. The ratio of resistances of a 100 W, 220 V lamps to that of a 100 W, 110 V lamps will be at respective voltages ½ 19 P a g e
20 4. ¼ Q63. An active element is circuit is 1. Voltage source 2. Resistance 3. Capacitor 4. Inductor Q64. Transient current in a circuit results from 1. Voltage applied to the circuit 2. Impedance of the circuit 3. Resistance of the circuit 4. Changes in the stored energy in inductors and capacitors Q65. Equivalent Inductance of the circuit at terminals a-b is 1. 4 H H 3. 8 H 4. 6 H Q66. An inductor at time t = 0+, with non-zero initial current act as a 20 P a g e
21 1. Short circuit 2. Open circuit 3. Constant current source 4. Constant voltage source Q67. Resistance of earth should be 1. Infinite 2. Medium 3. Low 4. The minimum possible Q68. Phase difference between the two wave forms can be compared only when they have the same. 1. Frequency 2. Peak value 3. Effective value 4. RMS Value Q69. The value of Voltage across 3A current source in the circuit shown in below is 21 P a g e
22 1. 1 V 2. 2 V 3. 3 V 4. 4 V Q70. In the given circuit, voltage across capacitor C at time t = is 1. 5 V V Zero Q71. If the number of bits per sample in a PCM system is increased from n to n+1, then quantization noise power becomes 1. Half 2. Two times 3. One fourth 4. Four times Q72. The power spectral density of a deterministic signal is given by ( frequency. The auto correlation function of this signal in the time domain is sin f f )2 where f is 22 P a g e
23 1. A rectangular pulse 2. A delta function 3. A sine pulse 4. A triangular pulse Q73. A sinusoidal signal with peak-to-peak amplitude of V is quantized into 128 levels using a mid-rise uniform quantizer. The quantization-noise power is V V V V Q74. If the carrier of a 100 percent modulated AM wave is suppressed, the percentage power saving will be Q75. A random process obeys Poisson s distribution. It is given that the mean of the process is 5. Then the variance of the process is P a g e
24 4. 0 Q76. A sinusoidal signal with peak-to-peak amplitude of V is quantized into 128 levels using a mid-rise uniform quantizer. The quantization-noise power is V V V V Q77. The bandwidth, BW of ASK, PSK and FSK for the same bit rate R b follows which of the following inequalities: 1. BW bask = BW bpsk > BW bfsk 2. BW bask = BW bpsk > BW bfsk 3. BW bask = BW bpsk < BW bfsk 4. BW bask = BW bpsk = BW bfsk Q78. We have the carrier power and message signal power given as P c and P m respectively. The power of wide band FM generated using the carrier and message signal is Q79. Two symbols are separated by a minimum euclidean distance, d min in the signal space, such that the channel is disturbed by an additive white Gaussian noise of power spectral density η/2 and mean zero. The probability of error is given by 1. P e = Q( d 2 min ) η 2. P e = Q( 2d min 2 η ) 24 P a g e
25 3. P e = Q( d 2 min ) 2η 4. P e = Q( d 2 min ) 4η Q80. The main advantage of DM over PCM is 1. Less bandwidth 2. Less power 3. Better S/N ratio 4. Simple circuitry Q81. Figure of merit is always unity in 1. SSB SC 2. AM 3. FM 4. All of these Q82. The main advantage of super heterodyne receiver is 1. Simple circuit 2. Better tracking 3. Improvement in selectivity and sensi 4. Better alignment Q83. Four voice signals, each limited to 4 khz and sampled by Nyquist rate are converted 25 P a g e into binary PCM using 256 quantization levels. The bit transmission rate for the time division multiplexed signal will be
26 1. 8 kbps kbps kbps kbps Q84. An analog signal is sampled at 36 khz and quantized into 256 levels. The time duration of a bit of the binary coded signal is μ s μ s ms ms Q85. If carrier modulated by a digital bit stream had one of the possible phases of 0, 90, 180 and 270 degrees, then the modulation is called 1. BPSK 2. QPSK 3. QAM 4. MSK Q86. g(t) = 5cos (10 6 πt)sin (10 3 πt) represents 1. DSB suppressed carrier signal 2. AM signal 3. SSB upper sideband signal 4. Narrow band FM signal 26 P a g e
27 Q87. A carrier voltage of unmodulated carrier power 1 kw on being amplitude modulated by an audio sinusoidal voltage to a depth of 100% has total modulated carrier power of kw kw 3. 2 kw 4. 4 kw Q88. A band limited signal when sampled is represented as f s (t). Its frequency spectrum will show no overlaps if the sampling time is 1. 1 f max 2. 1 f max f max f max Q89. If the transmission bandwidth is doubled in FM, then the figure of merit (FOM) is 1. Also doubled 2. Improved four fold 3. Improved four fold 4. Unaffected Q90. If the number of bits per sample in a PCM system is increased from n to n + 1, the improvement in signal-to-quantisation noise ratio will be 27 P a g e
28 1. 3 db 2. 6 db 3. 2n db 4. n db Q91. For transmission of normal speech signal, the PCM channel needs a bandwidth khz khz 3. 8 khz khz Q92. In a PCM system, signal is sampled at a rate f s and the number of pulses in one codegroup is p. then the number of pulses per second is 1. f s 2. pf s 3. f s /p 4. p/f s Q93. PPM may be converted into PWM by using 1. Monostable multivibrator 2. Bistable multivibrator 3. Astable multivibrator 4. Integrator Q94. Practical bandwidth of a narrow band FM signal (β < 1) equals 28 P a g e
29 1. f m 2. 2f m 3. f d 4. 2f d Q95. Which of the following statements is not true for FM? 1. Carrier component never becomes zero 2. J-coefficients occasionally are negative 3. Total power remains constant in-spite of change of modulation index 4. Total bandwidth increases with increase in modulation index Q96. The current flowing through a time varying capacitor having voltage V" equals to 1. d dt (CV) 2. C d dt (V) CV t Vdt C Q97. The power factor of an AC circuit is given by: 1. R Z 2. X L R 3. Z R 4. R X L 29 P a g e
30 Q98. Find the current through 5 Ω resistor is A A 3. 5 A A Q99. The RMS value of the alternating current given by the equation i = 50sin (314t 10 ) + 30sin (157t 20 ) A A A A Q100. For RLC Series circuits at resonance the current is 1. Minimum at leading power factor 2. Minimum at lagging power factor 3. Maximum at unity power factor 4. Maximum at leading power factor 30 P a g e
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
 OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
4. Forward bias of a silicon P-N junction will produce a barrier voltage of approximately how many volts? A. 0.2 B. 0.3 C. 0.7 D. 0.
 1. The dc current through each diode in a bridge rectifier equals A. the load current B. half the dc load current C. twice the dc load current D. one-fourth the dc load current 2. When matching polarity
1. The dc current through each diode in a bridge rectifier equals A. the load current B. half the dc load current C. twice the dc load current D. one-fourth the dc load current 2. When matching polarity
R & D Electronics DIGITAL IC TRAINER. Model : DE-150. Feature: Object: Specification:
 DIGITAL IC TRAINER Model : DE-150 Object: To Study the Operation of Digital Logic ICs TTL and CMOS. To Study the All Gates, Flip-Flops, Counters etc. To Study the both the basic and advance digital electronics
DIGITAL IC TRAINER Model : DE-150 Object: To Study the Operation of Digital Logic ICs TTL and CMOS. To Study the All Gates, Flip-Flops, Counters etc. To Study the both the basic and advance digital electronics
R09. 1.a) State and explain Kirchoff s laws. b) In the circuit given below Figure 1 find the current through 5 Ω resistor. [7+8] FIRSTRANKER.
![R09. 1.a) State and explain Kirchoff s laws. b) In the circuit given below Figure 1 find the current through 5 Ω resistor. [7+8] FIRSTRANKER. R09. 1.a) State and explain Kirchoff s laws. b) In the circuit given below Figure 1 find the current through 5 Ω resistor. [7+8] FIRSTRANKER.](/thumbs/95/125797779.jpg) SET - 1 1.a) State and explain Kirchoff s laws. b) In the circuit given below find the current through 5 Ω resistor. [7+8] 2.a) Find the impedance between terminals A and B in the following circuit ().
SET - 1 1.a) State and explain Kirchoff s laws. b) In the circuit given below find the current through 5 Ω resistor. [7+8] 2.a) Find the impedance between terminals A and B in the following circuit ().
Preface... iii. Chapter 1: Diodes and Circuits... 1
 Table of Contents Preface... iii Chapter 1: Diodes and Circuits... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Structure of an Atom... 2 1.3 Classification of Solid Materials on the Basis of Conductivity... 2 1.4 Atomic
Table of Contents Preface... iii Chapter 1: Diodes and Circuits... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Structure of an Atom... 2 1.3 Classification of Solid Materials on the Basis of Conductivity... 2 1.4 Atomic
Veer Narmad South Gujarat University, Surat
 Unit I: Passive circuit elements (With effect from June 2017) Syllabus for: F Y B Sc (Electronics) Semester- 1 PAPER I: Basic Electrical Circuits Resistors, resistor types, power ratings, resistor colour
Unit I: Passive circuit elements (With effect from June 2017) Syllabus for: F Y B Sc (Electronics) Semester- 1 PAPER I: Basic Electrical Circuits Resistors, resistor types, power ratings, resistor colour
Electronics Eingineering
 Electronics Eingineering 1. The output of a two-input gate is 0 if and only if its inputs are unequal. It is true for (A) XOR gate (B) NAND gate (C) NOR gate (D) XNOR gate 2. In K-map simplification, a
Electronics Eingineering 1. The output of a two-input gate is 0 if and only if its inputs are unequal. It is true for (A) XOR gate (B) NAND gate (C) NOR gate (D) XNOR gate 2. In K-map simplification, a
Paper-1 (Circuit Analysis) UNIT-I
 Paper-1 (Circuit Analysis) UNIT-I AC Fundamentals & Kirchhoff s Current and Voltage Laws 1. Explain how a sinusoidal signal can be generated and give the significance of each term in the equation? 2. Define
Paper-1 (Circuit Analysis) UNIT-I AC Fundamentals & Kirchhoff s Current and Voltage Laws 1. Explain how a sinusoidal signal can be generated and give the significance of each term in the equation? 2. Define
ELECTRONICS ADVANCED SUPPLEMENTARY LEVEL
 ELECTRONICS ADVANCED SUPPLEMENTARY LEVEL AIMS The general aims of the subject are : 1. to foster an interest in and an enjoyment of electronics as a practical and intellectual discipline; 2. to develop
ELECTRONICS ADVANCED SUPPLEMENTARY LEVEL AIMS The general aims of the subject are : 1. to foster an interest in and an enjoyment of electronics as a practical and intellectual discipline; 2. to develop
R.B.V.R.R. WOMEN S COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS) Narayanaguda, Hyderabad. ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS
 R.B.V.R.R. WOMEN S COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS) Narayanaguda, Hyderabad. DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS QUESTION BANK FOR SEMESTER V PHYSICS PAPER VI (A) ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS UNIT I: SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
R.B.V.R.R. WOMEN S COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS) Narayanaguda, Hyderabad. DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS QUESTION BANK FOR SEMESTER V PHYSICS PAPER VI (A) ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS UNIT I: SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
PESIT BANGALORE SOUTH CAMPUS BASIC ELECTRONICS
 PESIT BANGALORE SOUTH CAMPUS QUESTION BANK BASIC ELECTRONICS Sub Code: 17ELN15 / 17ELN25 IA Marks: 20 Hrs/ Week: 04 Exam Marks: 80 Total Hours: 50 Exam Hours: 03 Name of Faculty: Mr. Udoshi Basavaraj Module
PESIT BANGALORE SOUTH CAMPUS QUESTION BANK BASIC ELECTRONICS Sub Code: 17ELN15 / 17ELN25 IA Marks: 20 Hrs/ Week: 04 Exam Marks: 80 Total Hours: 50 Exam Hours: 03 Name of Faculty: Mr. Udoshi Basavaraj Module
Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras
 Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Sample Questions on Semiconductor Devices EE3 applicants who are interested to pursue their research in microelectronics devices area (fabrication and/or
Department of Electrical Engineering IIT Madras Sample Questions on Semiconductor Devices EE3 applicants who are interested to pursue their research in microelectronics devices area (fabrication and/or
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-2012 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 40 Subject: PART - A 0. Which region of the transistor
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 40 Subject: PART - A 0. Which region of the transistor
The steeper the phase shift as a function of frequency φ(ω) the more stable the frequency of oscillation
 It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1992 Time Allowed : Three Hours
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1992 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time Allowed : Three Hours Maximum Marks: 0 Candidates should attempt question No. 1 which is compulsory and any FOUR of the remaining
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1992 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time Allowed : Three Hours Maximum Marks: 0 Candidates should attempt question No. 1 which is compulsory and any FOUR of the remaining
SEMESTER SYSTEM, A. PROPOSED SCHEME FOR B.Sc. ELECTRONICS (PASS) COURSE. B.Sc. (ELECTRONICS MAINTENANCE) COURSE
 SEMESTER SYSTEM, 2010-2013 A PROPOSED SCHEME FOR B.Sc. ELECTRONICS (PASS) COURSE B.Sc. (ELECTRONICS MAINTENANCE) COURSE CLASS/ SEMESTER Sem -I Sem-II B. Sc (Elex) B. Sc (Elex. Maint) EL-1101 Components
SEMESTER SYSTEM, 2010-2013 A PROPOSED SCHEME FOR B.Sc. ELECTRONICS (PASS) COURSE B.Sc. (ELECTRONICS MAINTENANCE) COURSE CLASS/ SEMESTER Sem -I Sem-II B. Sc (Elex) B. Sc (Elex. Maint) EL-1101 Components
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-2013 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-03 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: PART - A 0. What does the arrow mark indicate
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-03 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: PART - A 0. What does the arrow mark indicate
R a) Draw and explain VI characteristics of Si & Ge diode. (8M) b) Explain the operation of SCR & its characteristics (8M)
 SET - 1 1. a) Define i) transient capacitance ii) Diffusion capacitance (4M) b) Explain Fermi level in intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductor (4M) c) Derive the expression for ripple factor of Half wave
SET - 1 1. a) Define i) transient capacitance ii) Diffusion capacitance (4M) b) Explain Fermi level in intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductor (4M) c) Derive the expression for ripple factor of Half wave
Electronic Devices & Circuit and Digital Electronics
 QUESTION BANK Electronic Devices & Circuit and Digital Electronics 1. Consider the following four statement i) In the 2 s complement representation, negative numbers are stored in sign magnitude form ii)
QUESTION BANK Electronic Devices & Circuit and Digital Electronics 1. Consider the following four statement i) In the 2 s complement representation, negative numbers are stored in sign magnitude form ii)
S-[F] NPW-02 June All Syllabus B.Sc. [Electronics] Ist Year Semester-I & II.doc - 1 -
![S-[F] NPW-02 June All Syllabus B.Sc. [Electronics] Ist Year Semester-I & II.doc - 1 - S-[F] NPW-02 June All Syllabus B.Sc. [Electronics] Ist Year Semester-I & II.doc - 1 -](/thumbs/79/79759849.jpg) - 1 - - 2 - - 3 - DR. BABASAHEB AMBEDKAR MARATHWADA UNIVERSITY, AURANGABAD SYLLABUS of B.Sc. FIRST & SECOND SEMESTER [ELECTRONICS (OPTIONAL)] {Effective from June- 2013 onwards} - 4 - B.Sc. Electronics
- 1 - - 2 - - 3 - DR. BABASAHEB AMBEDKAR MARATHWADA UNIVERSITY, AURANGABAD SYLLABUS of B.Sc. FIRST & SECOND SEMESTER [ELECTRONICS (OPTIONAL)] {Effective from June- 2013 onwards} - 4 - B.Sc. Electronics
 Code No: Y0221/R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, Apr/May 2013 BASIC ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
Code No: Y0221/R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, Apr/May 2013 BASIC ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EC6202 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EC6202 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS UNIT-I - PN DIODEAND ITSAPPLICATIONS 1. What is depletion region in PN junction?
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EC6202 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS UNIT-I - PN DIODEAND ITSAPPLICATIONS 1. What is depletion region in PN junction?
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS 1. A cordless telephone using separate frequencies for transmission in base and portable units is known as A. duplex arrangement B. half duplex arrangement C. either (a) or (b) D.
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS 1. A cordless telephone using separate frequencies for transmission in base and portable units is known as A. duplex arrangement B. half duplex arrangement C. either (a) or (b) D.
 COMBO ONLINE TEST SERIES GATE 2019 SCHEDULE: ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Syllabus Test Date Test Type [ EB-Engineering Branch ; EM- No. of Engineering Mathematics; GA- General Question Marks
COMBO ONLINE TEST SERIES GATE 2019 SCHEDULE: ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Syllabus Test Date Test Type [ EB-Engineering Branch ; EM- No. of Engineering Mathematics; GA- General Question Marks
Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All questions carry equal marks
 Code: 9A02401 PRINCIPLES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Common to EIE, E.Con.E, ECE & ECC) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 1 In a series RLC circuit, R = 5 Ω, L = 1 H and C = 1 F. A dc v ltage f 20 V is applied
Code: 9A02401 PRINCIPLES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Common to EIE, E.Con.E, ECE & ECC) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 1 In a series RLC circuit, R = 5 Ω, L = 1 H and C = 1 F. A dc v ltage f 20 V is applied
SIR PADAMPAT SINGHANIA UNIVERSITY UDAIPUR Sample Question Paper for Ph.D. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) SPSAT 18
 INSTRUCTIONS SIR PADAMPAT SINGHANIA UNIVERSITY UDAIPUR Sample Question Paper for Ph.D. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) SPSAT 18 The test is 60 minutes long and consists of 40 multiple choice
INSTRUCTIONS SIR PADAMPAT SINGHANIA UNIVERSITY UDAIPUR Sample Question Paper for Ph.D. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) SPSAT 18 The test is 60 minutes long and consists of 40 multiple choice
MTLE-6120: Advanced Electronic Properties of Materials. Semiconductor transistors for logic and memory. Reading: Kasap
 MTLE-6120: Advanced Electronic Properties of Materials 1 Semiconductor transistors for logic and memory Reading: Kasap 6.6-6.8 Vacuum tube diodes 2 Thermionic emission from cathode Electrons collected
MTLE-6120: Advanced Electronic Properties of Materials 1 Semiconductor transistors for logic and memory Reading: Kasap 6.6-6.8 Vacuum tube diodes 2 Thermionic emission from cathode Electrons collected
EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS
 EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS Pulse Code Modulation: 1. Draw the block diagram of basic digital communication system. How it is different from analog communication system. 2. What are the advantages of
EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS Pulse Code Modulation: 1. Draw the block diagram of basic digital communication system. How it is different from analog communication system. 2. What are the advantages of
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS Academic Planner for odd Semesters Semester : I Subject : Electronics(ELT1). Course: B.Sc. (PME) Introduction to Number systems B Construction and types, working Review of P type
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS Academic Planner for odd Semesters Semester : I Subject : Electronics(ELT1). Course: B.Sc. (PME) Introduction to Number systems B Construction and types, working Review of P type
UNIT I Introduction to DC & AC circuits
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207) Year & Sem: II-B.
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207) Year & Sem: II-B.
NORTH MAHARASHTRA UNIVERSITY, JALGAON
 , JALGAON Syllabus for F.Y.B.Sc. Semester I and II ELECTRONICS (w. e. f. June 2012) F.Y. B. Sc. Subject Electronics Syllabus Structure Semester Code Title Number of Lectures ELE-111 Paper I : Analog Electronics
, JALGAON Syllabus for F.Y.B.Sc. Semester I and II ELECTRONICS (w. e. f. June 2012) F.Y. B. Sc. Subject Electronics Syllabus Structure Semester Code Title Number of Lectures ELE-111 Paper I : Analog Electronics
Linear Algebra, Calculus, Differential Equations and Vector Analysis. Complex Anaysis, Numerical Methods and Probability and Statistics.
 Test No Topic code Topic EC-01 GEM (Engineering Mathematics) Topic wise Tests Each test carries 25 marks and 45 minutes duration Test consists of 5 one mark questions and 10 two marks questions Tests will
Test No Topic code Topic EC-01 GEM (Engineering Mathematics) Topic wise Tests Each test carries 25 marks and 45 minutes duration Test consists of 5 one mark questions and 10 two marks questions Tests will
Syllabus for: Electronics for F Y B Sc (Electronics) Semester- 1 (With effect from June 2014) PAPER I: Basic Electrical Circuits
 Unit I: Passive Devices Syllabus for: Electronics for F Y B Sc (Electronics) Semester- 1 (With effect from June 2014) PAPER I: Basic Electrical Circuits Resistors, Fixed resistors & variable resistors,
Unit I: Passive Devices Syllabus for: Electronics for F Y B Sc (Electronics) Semester- 1 (With effect from June 2014) PAPER I: Basic Electrical Circuits Resistors, Fixed resistors & variable resistors,
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING Question Bank
 Programme Subject DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING Question Bank Semester / Branch : BE : GE6252-BASICELECTRICALANDELECTRONICS ENGINEERING : II-Civil and Mechanical Engineering PART
Programme Subject DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING Question Bank Semester / Branch : BE : GE6252-BASICELECTRICALANDELECTRONICS ENGINEERING : II-Civil and Mechanical Engineering PART
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) Summer 2016 EXAMINATIONS.
 Summer 2016 EXAMINATIONS Subject Code: 17321 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the answer scheme. 2) The
Summer 2016 EXAMINATIONS Subject Code: 17321 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the answer scheme. 2) The
Objective Questions. (a) Light (b) Temperature (c) Sound (d) all of these
 Objective Questions Module 1: Introduction 1. Which of the following is an analog quantity? (a) Light (b) Temperature (c) Sound (d) all of these 2. Which of the following is a digital quantity? (a) Electrical
Objective Questions Module 1: Introduction 1. Which of the following is an analog quantity? (a) Light (b) Temperature (c) Sound (d) all of these 2. Which of the following is a digital quantity? (a) Electrical
AE53/AC53/AT53/AE103 ELECT. DEVICES & CIRCUITS DEC 2015
 Q.2 a. By using Norton s theorem, find the current in the load resistor R L for the circuit shown in Fig.1. (8) Fig.1 IETE 1 b. Explain Z parameters and also draw an equivalent circuit of the Z parameter
Q.2 a. By using Norton s theorem, find the current in the load resistor R L for the circuit shown in Fig.1. (8) Fig.1 IETE 1 b. Explain Z parameters and also draw an equivalent circuit of the Z parameter
ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Q1. A transmission line of characteristic impedance 50 Ω is terminated by a 50 Ω load. When excited by a sinusoidal voltage source at 10 GHz the phase difference
ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Q1. A transmission line of characteristic impedance 50 Ω is terminated by a 50 Ω load. When excited by a sinusoidal voltage source at 10 GHz the phase difference
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-2012 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: Qn. PART - A 0. Which is the largest of three
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: Qn. PART - A 0. Which is the largest of three
Frequently Asked Questions GE6252 BEEE UNIT I ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS AND MEASUREMENTS
 Frequently Asked Questions GE6252 BEEE UNIT I ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS AND MEASUREMENTS 1. What is charge? 2. Define current. 3. Under what condition AC circuit said to be resonant? 4. What do you meant by
Frequently Asked Questions GE6252 BEEE UNIT I ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS AND MEASUREMENTS 1. What is charge? 2. Define current. 3. Under what condition AC circuit said to be resonant? 4. What do you meant by
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1996 Some useful data:
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1996 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt question ONE which is compulsory and any FOUR of the remaining
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1996 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt question ONE which is compulsory and any FOUR of the remaining
Transistor Digital Circuits
 Recapitulation Transistor Digital Circuits The transistor Operating principle and regions Utilization of the transistor Transfer characteristics, symbols Controlled switch model BJT digital circuits MOSFET
Recapitulation Transistor Digital Circuits The transistor Operating principle and regions Utilization of the transistor Transfer characteristics, symbols Controlled switch model BJT digital circuits MOSFET
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) MODEL ANSWER
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
ASTABLE MULTIVIBRATOR
 555 TIMER ASTABLE MULTIIBRATOR MONOSTABLE MULTIIBRATOR 555 TIMER PHYSICS (LAB MANUAL) PHYSICS (LAB MANUAL) 555 TIMER Introduction The 555 timer is an integrated circuit (chip) implementing a variety of
555 TIMER ASTABLE MULTIIBRATOR MONOSTABLE MULTIIBRATOR 555 TIMER PHYSICS (LAB MANUAL) PHYSICS (LAB MANUAL) 555 TIMER Introduction The 555 timer is an integrated circuit (chip) implementing a variety of
Difference between BJTs and FETs. Junction Field Effect Transistors (JFET)
 Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS. Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100
 EC 40 MODEL TEST PAPER - 1 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Answer five questions, taking ANY TWO from Group A, any two from Group B and all from Group C. All parts of a question
EC 40 MODEL TEST PAPER - 1 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Answer five questions, taking ANY TWO from Group A, any two from Group B and all from Group C. All parts of a question
WINTER 14 EXAMINATION. Model Answer. 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the
 WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 17213 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
WINTER 14 EXAMINATION Subject Code: 17213 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus
 UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus PAPER I 1. Circuit Theory: Circuit components; network graphs; KCL, KVL; circuit analysis methods: nodal analysis, mesh analysis;
UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus PAPER I 1. Circuit Theory: Circuit components; network graphs; KCL, KVL; circuit analysis methods: nodal analysis, mesh analysis;
HIGH LOW Astable multivibrators HIGH LOW 1:1
 1. Multivibrators A multivibrator circuit oscillates between a HIGH state and a LOW state producing a continuous output. Astable multivibrators generally have an even 50% duty cycle, that is that 50% of
1. Multivibrators A multivibrator circuit oscillates between a HIGH state and a LOW state producing a continuous output. Astable multivibrators generally have an even 50% duty cycle, that is that 50% of
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS UNIT-1 SUBJECT : ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS SUBJECT CODE : EC6202 BRANCH: EEE PART -A 1. What is meant by diffusion current in a semi conductor? (APR/MAY 2010, 2011, NOV/DEC
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS UNIT-1 SUBJECT : ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS SUBJECT CODE : EC6202 BRANCH: EEE PART -A 1. What is meant by diffusion current in a semi conductor? (APR/MAY 2010, 2011, NOV/DEC
 Electronic Devices 1. Current flowing in each of the following circuits A and respectively are: (Circuit 1) (Circuit 2) 1) 1A, 2A 2) 2A, 1A 3) 4A, 2A 4) 2A, 4A 2. Among the following one statement is not
Electronic Devices 1. Current flowing in each of the following circuits A and respectively are: (Circuit 1) (Circuit 2) 1) 1A, 2A 2) 2A, 1A 3) 4A, 2A 4) 2A, 4A 2. Among the following one statement is not
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R05010204 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplimentary Examinations, Aug/Sep 2007 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS ( Common to Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Electronics & Communication Engineering,
Code No: R05010204 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplimentary Examinations, Aug/Sep 2007 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS ( Common to Electrical & Electronic Engineering, Electronics & Communication Engineering,
Section:A Very short answer question
 Section:A Very short answer question 1.What is the order of energy gap in a conductor, semi conductor, and insulator?. Conductor - no energy gap Semi Conductor - It is of the order of 1 ev. Insulator -
Section:A Very short answer question 1.What is the order of energy gap in a conductor, semi conductor, and insulator?. Conductor - no energy gap Semi Conductor - It is of the order of 1 ev. Insulator -
SRM INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (DEEMED UNIVERSITY)
 SRM INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (DEEMED UNIVERSITY) QUESTION BANK I YEAR B.Tech (II Semester) ELECTRONIC DEVICES (COMMON FOR EC102, EE104, IC108, BM106) UNIT-I PART-A 1. What are intrinsic and
SRM INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY (DEEMED UNIVERSITY) QUESTION BANK I YEAR B.Tech (II Semester) ELECTRONIC DEVICES (COMMON FOR EC102, EE104, IC108, BM106) UNIT-I PART-A 1. What are intrinsic and
GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13)
 GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13) 1. Removing bypass capacitor across the emitter leg resistor in a CE amplifier causes a. increase in current gain b. decrease in current gain c. increase
GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13) 1. Removing bypass capacitor across the emitter leg resistor in a CE amplifier causes a. increase in current gain b. decrease in current gain c. increase
ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
 ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING 1. Just as a voltage amplifier signal voltage a power amplifier. 1.amplifier power 2.amplifier signal 3.converts the signal ac power into DC power 4.converts a dc power into useful
ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING 1. Just as a voltage amplifier signal voltage a power amplifier. 1.amplifier power 2.amplifier signal 3.converts the signal ac power into DC power 4.converts a dc power into useful
PART-A UNIT I Introduction to DC & AC circuits
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207)
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR (AUTONOMOUS) Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code : Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207)
NORTH MAHARASHTRA UNIVERSITY. F.Y. B. Sc. Electronics. Syllabus. Wieth effect from june2015
 Syllabus Wieth effect from june2015 Paper- I, Semester I ELE-111: Analog Electronics I Unit- I:Introduction to Basic Circuit Components Definition and unit, Circuit Symbol, Working Principle, Classification
Syllabus Wieth effect from june2015 Paper- I, Semester I ELE-111: Analog Electronics I Unit- I:Introduction to Basic Circuit Components Definition and unit, Circuit Symbol, Working Principle, Classification
multivibrator; Introduction to silicon-controlled rectifiers (SCRs).
 Appendix The experiments of which details are given in this book are based largely on a set of 'modules' specially designed by Dr. K.J. Close. These 'modules' are now made and marketed by Irwin-Desman
Appendix The experiments of which details are given in this book are based largely on a set of 'modules' specially designed by Dr. K.J. Close. These 'modules' are now made and marketed by Irwin-Desman
Downloaded From All JNTU World
 Code: 9A02401 PRINCIPLES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Common to ECE, EIE, E.Con.E & ECC) 1 Find initial conditions for voltage across capacitor, the currents i 1, i 2 and the derivatives for the circuit
Code: 9A02401 PRINCIPLES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Common to ECE, EIE, E.Con.E & ECC) 1 Find initial conditions for voltage across capacitor, the currents i 1, i 2 and the derivatives for the circuit
(i) Determine the admittance parameters of the network of Fig 1 (f) and draw its - equivalent circuit.
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL) paper 2
 Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL) paper 2 1. VSWR on a transmission line is always 1. Equal to 1 2. Equal to 0 3. Less than 1 4. Greater than 1 2. In a amplitude modulated wave, the value of Vmax is 10V and
Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL) paper 2 1. VSWR on a transmission line is always 1. Equal to 1 2. Equal to 0 3. Less than 1 4. Greater than 1 2. In a amplitude modulated wave, the value of Vmax is 10V and
B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering)
 Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
Number of Lessons:155 #14B (P) Electronics Technology with Digital and Microprocessor Laboratory Completion Time: 42 months
 PROGRESS RECORD Study your lessons in the order listed below. Number of Lessons:155 #14B (P) Electronics Technology with Digital and Microprocessor Laboratory Completion Time: 42 months 1 2330A Current
PROGRESS RECORD Study your lessons in the order listed below. Number of Lessons:155 #14B (P) Electronics Technology with Digital and Microprocessor Laboratory Completion Time: 42 months 1 2330A Current
Objective Type Questions 1. Why pure semiconductors are insulators at 0 o K? 2. What is effect of temperature on barrier voltage? 3.
 Objective Type Questions 1. Why pure semiconductors are insulators at 0 o K? 2. What is effect of temperature on barrier voltage? 3. What is difference between electron and hole? 4. Why electrons have
Objective Type Questions 1. Why pure semiconductors are insulators at 0 o K? 2. What is effect of temperature on barrier voltage? 3. What is difference between electron and hole? 4. Why electrons have
Electrical, Electronic and Communications Engineering Technology/Technician CIP Task Grid
 Secondary Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Describe OSHA safety regulations. 102 Identify, select, and demonstrate proper hand tool use for electronics work. 103 Recognize the types and usages of fire extinguishers.
Secondary Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Describe OSHA safety regulations. 102 Identify, select, and demonstrate proper hand tool use for electronics work. 103 Recognize the types and usages of fire extinguishers.
Downloaded from
 Question 14.1: In an n-type silicon, which of the following statement is true: (a) Electrons are majority carriers and trivalent atoms are the dopants. (b) Electrons are minority carriers and pentavalent
Question 14.1: In an n-type silicon, which of the following statement is true: (a) Electrons are majority carriers and trivalent atoms are the dopants. (b) Electrons are minority carriers and pentavalent
Q.1: Power factor of a linear circuit is defined as the:
 Q.1: Power factor of a linear circuit is defined as the: a. Ratio of real power to reactive power b. Ratio of real power to apparent power c. Ratio of reactive power to apparent power d. Ratio of resistance
Q.1: Power factor of a linear circuit is defined as the: a. Ratio of real power to reactive power b. Ratio of real power to apparent power c. Ratio of reactive power to apparent power d. Ratio of resistance
LINEAR IC APPLICATIONS
 1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) PART - A
 SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207) Year & Sem: II-B.
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583 QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE) Subject with Code: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (16EE207) Year & Sem: II-B.
ECE Branch GATE Paper 2004
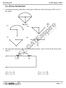 Q. 1 30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? Fig. Q.1 2. The equivalent inductance measured between the terminals
Q. 1 30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? Fig. Q.1 2. The equivalent inductance measured between the terminals
Homework Assignment 04
 Question 1 (Short Takes) Homework Assignment 04 1. Consider the single-supply op-amp amplifier shown. What is the purpose of R 3? (1 point) Answer: This compensates for the op-amp s input bias current.
Question 1 (Short Takes) Homework Assignment 04 1. Consider the single-supply op-amp amplifier shown. What is the purpose of R 3? (1 point) Answer: This compensates for the op-amp s input bias current.
EC6202-ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS YEAR/SEM: II/III UNIT 1 TWO MARKS. 1. Define diffusion current.
 EC6202-ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS YEAR/SEM: II/III UNIT 1 TWO MARKS 1. Define diffusion current. A movement of charge carriers due to the concentration gradient in a semiconductor is called process
EC6202-ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS YEAR/SEM: II/III UNIT 1 TWO MARKS 1. Define diffusion current. A movement of charge carriers due to the concentration gradient in a semiconductor is called process
Number system: the system used to count discrete units is called number. Decimal system: the number system that contains 10 distinguished
 Number system: the system used to count discrete units is called number system Decimal system: the number system that contains 10 distinguished symbols that is 0-9 or digits is called decimal system. As
Number system: the system used to count discrete units is called number system Decimal system: the number system that contains 10 distinguished symbols that is 0-9 or digits is called decimal system. As
Level 6 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Electronics and telecommunications
 9210-116 Level 6 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Electronics and telecommunications Sample Paper You should have the following for this examination one answer book non-programmable calculator pen, pencil,
9210-116 Level 6 Graduate Diploma in Engineering Electronics and telecommunications Sample Paper You should have the following for this examination one answer book non-programmable calculator pen, pencil,
Exam Booklet. Pulse Circuits
 Exam Booklet Pulse Circuits Pulse Circuits STUDY ASSIGNMENT This booklet contains two examinations for the six lessons entitled Pulse Circuits. The material is intended to provide the last training sought
Exam Booklet Pulse Circuits Pulse Circuits STUDY ASSIGNMENT This booklet contains two examinations for the six lessons entitled Pulse Circuits. The material is intended to provide the last training sought
DIGITAL ELECTRONICS ANALOG ELECTRONICS
 DIGITAL ELECTRONICS 1. N10 4 Bit Binary Universal shift register. 2. N22- Random Access Memory (16*4). 3. N23- Read Only Memory. 4. N4-R-S/D-T Flip flop, characteristic and comparison. 5. Master Slave
DIGITAL ELECTRONICS 1. N10 4 Bit Binary Universal shift register. 2. N22- Random Access Memory (16*4). 3. N23- Read Only Memory. 4. N4-R-S/D-T Flip flop, characteristic and comparison. 5. Master Slave
NEW HORIZON PRE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LESSON PLAN FOR THE ACADEMIC YEAR Department of ELECTRONICS
 NEW HORIZON PRE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LESSON PLAN FOR THE ACADEMIC YEAR 2017 2018 Department of ELECTRONICS I PUC Month: JUNE I 1. INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRONICS Electronics and its scope: Development of vacuum
NEW HORIZON PRE UNIVERSITY COLLEGE LESSON PLAN FOR THE ACADEMIC YEAR 2017 2018 Department of ELECTRONICS I PUC Month: JUNE I 1. INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRONICS Electronics and its scope: Development of vacuum
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 WINTER 16 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code: 17213 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
WINTER 16 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code: 17213 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2)
SEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS: MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS. Class XII : PHYSICS WORKSHEET
 SEMICONDUCT ELECTRONICS: MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS Class XII : PHYSICS WKSHEET 1. How is a n-p-n transistor represented symbolically? (1) 2. How does conductivity of a semiconductor change
SEMICONDUCT ELECTRONICS: MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS Class XII : PHYSICS WKSHEET 1. How is a n-p-n transistor represented symbolically? (1) 2. How does conductivity of a semiconductor change
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS
 ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS 1. At room temperature the current in an intrinsic semiconductor is due to A. holes B. electrons C. ions D. holes and electrons 2. Work function is the maximum energy required
ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS 1. At room temperature the current in an intrinsic semiconductor is due to A. holes B. electrons C. ions D. holes and electrons 2. Work function is the maximum energy required
Microelectronic Circuits
 SECOND EDITION ISHBWHBI \ ' -' Microelectronic Circuits Adel S. Sedra University of Toronto Kenneth С Smith University of Toronto HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON, INC. New York Chicago
SECOND EDITION ISHBWHBI \ ' -' Microelectronic Circuits Adel S. Sedra University of Toronto Kenneth С Smith University of Toronto HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON, INC. New York Chicago
(a) BJT-OPERATING MODES & CONFIGURATIONS
 (a) BJT-OPERATING MODES & CONFIGURATIONS 1. The leakage current I CBO flows in (a) The emitter, base and collector leads (b) The emitter and base leads. (c) The emitter and collector leads. (d) The base
(a) BJT-OPERATING MODES & CONFIGURATIONS 1. The leakage current I CBO flows in (a) The emitter, base and collector leads (b) The emitter and base leads. (c) The emitter and collector leads. (d) The base
Subject Code: Model Answer Page No: / N
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Scheme & Syllabus. New. B.Sc. Electronics. (Pass /Maintenance) Course. I st to IV th Semester. w.e.f. July Devi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya,
 Scheme & Syllabus of New B.Sc. Electronics (Pass /Maintenance) Course I st to IV th Semester w.e.f. July 2011 Devi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya, Indore (M.P.) 452001 SEMESTER SYSTEM, 2011-2014 PROPOSED SCHEME
Scheme & Syllabus of New B.Sc. Electronics (Pass /Maintenance) Course I st to IV th Semester w.e.f. July 2011 Devi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya, Indore (M.P.) 452001 SEMESTER SYSTEM, 2011-2014 PROPOSED SCHEME
BJT Circuits (MCQs of Moderate Complexity)
 BJT Circuits (MCQs of Moderate Complexity) 1. The current ib through base of a silicon npn transistor is 1+0.1 cos (1000πt) ma. At 300K, the rπ in the small signal model of the transistor is i b B C r
BJT Circuits (MCQs of Moderate Complexity) 1. The current ib through base of a silicon npn transistor is 1+0.1 cos (1000πt) ma. At 300K, the rπ in the small signal model of the transistor is i b B C r
Electronic Components And Circuit Analysis
 Theory /Practical Theory Semester /Annual Semester Semester No. I II Swami Ramanand Teerth Marathwada University, Nanded Syllabus B. Sc. First Year ELECTRONICS Semester System (MCQ Pattern) (To Be Implemented
Theory /Practical Theory Semester /Annual Semester Semester No. I II Swami Ramanand Teerth Marathwada University, Nanded Syllabus B. Sc. First Year ELECTRONICS Semester System (MCQ Pattern) (To Be Implemented
UNIT 3: FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS
 FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR: UNIT 3: FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS The field effect transistor is a semiconductor device, which depends for its operation on the control of current by an electric field. There are
FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR: UNIT 3: FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS The field effect transistor is a semiconductor device, which depends for its operation on the control of current by an electric field. There are
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (CODE NO. 10) PAPER - I
 ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (CODE NO. 10) PAPER - I 1. Circuit theory Circuit Components, Network graphs, KCL, KVL, Circuit analysis methods: Nodal analysis, mesh analysis, basic network theorems; transient
ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (CODE NO. 10) PAPER - I 1. Circuit theory Circuit Components, Network graphs, KCL, KVL, Circuit analysis methods: Nodal analysis, mesh analysis, basic network theorems; transient
SUMMER 13 EXAMINATION Subject Code: Model Answer Page No: / N
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Downloaded From All JNTU World
 Code: 9A02403 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of a nuclear plant as compared to other conventional power plants. 2 Explain about: (a) Solar distillation. (b) Solar
Code: 9A02403 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of a nuclear plant as compared to other conventional power plants. 2 Explain about: (a) Solar distillation. (b) Solar
Unit/Standard Number. LEA Task # Alignment
 1 Secondary Competency Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of State and School safety regulations. 102 Practice safety techniques for electronics work. 103 Demonstrate an understanding
1 Secondary Competency Task List 100 SAFETY 101 Demonstrate an understanding of State and School safety regulations. 102 Practice safety techniques for electronics work. 103 Demonstrate an understanding
GATE 2004 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 2004 Electronics and Communication Engineering Q. 1 30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? (A) Fig. Q.1
GATE 2004 Electronics and Communication Engineering Q. 1 30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? (A) Fig. Q.1
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 1 P a g e INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Name : INTEGRATED CIRCUITS APPLICATIONS Code
1 P a g e INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Name : INTEGRATED CIRCUITS APPLICATIONS Code
Unit III FET and its Applications. 2 Marks Questions and Answers
 Unit III FET and its Applications 2 Marks Questions and Answers 1. Why do you call FET as field effect transistor? The name field effect is derived from the fact that the current is controlled by an electric
Unit III FET and its Applications 2 Marks Questions and Answers 1. Why do you call FET as field effect transistor? The name field effect is derived from the fact that the current is controlled by an electric
Introductory Electronics for Scientists and Engineers
 Introductory Electronics for Scientists and Engineers Second Edition ROBERT E. SIMPSON University of New Hampshire Allyn and Bacon, Inc. Boston London Sydney Toronto Contents Preface xiü 1 Direct Current
Introductory Electronics for Scientists and Engineers Second Edition ROBERT E. SIMPSON University of New Hampshire Allyn and Bacon, Inc. Boston London Sydney Toronto Contents Preface xiü 1 Direct Current
B.E. SEMESTER III (ELECTRICAL) SUBJECT CODE: X30902 Subject Name: Analog & Digital Electronics
 B.E. SEMESTER III (ELECTRICAL) SUBJECT CODE: X30902 Subject Name: Analog & Digital Electronics Sr. No. Date TITLE To From Marks Sign 1 To verify the application of op-amp as an Inverting Amplifier 2 To
B.E. SEMESTER III (ELECTRICAL) SUBJECT CODE: X30902 Subject Name: Analog & Digital Electronics Sr. No. Date TITLE To From Marks Sign 1 To verify the application of op-amp as an Inverting Amplifier 2 To
hij Teacher Resource Bank GCE Electronics Exemplar Examination Questions ELEC2 Further Electronics
 hij Teacher Resource Bank GCE Electronics Exemplar Examination Questions ELEC2 Further Electronics The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England
hij Teacher Resource Bank GCE Electronics Exemplar Examination Questions ELEC2 Further Electronics The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England
Basic Electronics. Introductory Lecture Course for. Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011
 Basic Electronics Introductory Lecture Course for Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 2011 Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011 Presented By Gary Drake Argonne National Laboratory Session 3
Basic Electronics Introductory Lecture Course for Technology and Instrumentation in Particle Physics 2011 Chicago, Illinois June 9-14, 2011 Presented By Gary Drake Argonne National Laboratory Session 3
