GATE 2002 Electronics and Communication Engineering
|
|
|
- Esther Morrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GATE 22 Electronics and Communication Engineering SECTION A (75 MARKS ). This question consists of TWENTY FIVE sub-question (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A, B, C and D) are given, out of which only one is correct. Indicate the correct answer by darkening the appropriate bubble against the question number on the left hand side of the objective Response Sheet (ORS). You may use the answer book provided for any rough work, if needed.. The dependent current source shown in given figure. 5Ω - V =2V I 5Ω V 5 A (A) Delivers 8 W (B) absorbs 8W (C) Delivers 4 W (D) absorbs 4 W Page :
2 .2 In given figure.2, the switch was closed for a long time before opening at t =.The voltage Vx at t = is t= 2Ω 2.5A 5H _ 2Ω V x (A) 25 V (B) 5V (C) 5 V (D) V.3 Convolution of x(t5) with impulse function δ(t-7) is equal to (A) x(t 2) (C) x(t 2) (B) x(t 2) (D) x(t 2).4 Which of the following cannot be the Fourier series expansion of a periodic signal? (A) x(t) = 2cos t 3 cos3t (C) x(t) = cost.5 (B) x(t) = 2cos πt 7 cost (D) x(t) = 2cos.5π t sin3.5πt.5 In given figure a silicon diode is carrying a constant current of ma. When the temperature of the diode is 2 C, V is found to be 7 mv. If the temperature rises to 4 C, V becomes approximately equal to ma V D (A) 74 mv (B) 66mV (C) 68 mv (D) 7 mv Page : 2
3 .6 In a negative feedback amplifier using voltage-series (i.e. Voltage-sampling, series mixing) feedback. (A) R i decreases and R o decreases (C) R i increases and R o decreases (B) R i decreases and R o increases (D) R i increases and R o increases (R i and R o denote the input and output resistances respectively ).7 A 74-type opamp has a gain-bandwidth product of MHz. A non-inverting amplifier using this opamp and having a voltage gain of 2 db will exhibit a 3-dB bandwidth of (A) 5 khz (C) khz (B) khz (D). khz.8 Three identical RC-coupled transistor amplifiers are cascaded. If each of the amplifiers has a frequency response as shown in the figure is the overall frequency response is as given in A V db 3 2Hz KHz f (A) A V db 3 4Hz. 5KHz f Page : 3
4 (B) A V db 3 4Hz KHz f (C) A V db 3 4Hz 2KHz f (D) A V db 3 Hz. 5KHz f.9 4-bit 2 s complement representation of a decimal number is. The number is (A) 8 (C) 7 (B) (D) 8 Page : 4
5 . If the input to the digital circuit the figure, consisting of a cascade of 2 XOR-gates is X, then the output Y is equal to y X (A) (B) (C) X (D) X. The number of comparators required in a 3-bit comparator type ADC is (A) 2 (C) 7 (B) 3 (D) 8.2 If the transistor in the figure is in saturation, then I C C I B B β dc Denotes the dc current gain E (A) I C is always equal to β dc I B (B) I C is always equal to β dc I B (C) I C is greater than or equal to β dc I B (D) I C is less than or equal to β dc I B Page : 5
6 .3 Consider a system with the transfer function G(s) = the value of k is (A) 2/6 (B) 3 (C) /6 (D) 6. Is damping ratio will be.5 when.4 Which of the following points is NOT on the root locus of a system with the open-loop transfer function G(s) H(s) = (A) s = - j 3 (B) s = -.5 ()( ) (C) s = - 3 (D) s = -.5 The phase margin of a system with the open-loop transfer function G(s) H(s) = (A) (B) 63.4 (C) 9 (D) () ()( ) is.6 The transfer function Y(s) / U(s) of a system described by the state equations x(t) = - 2x(t) 2u(t) and y(t) =.5x(t) is (A).5/(s 2) (C).5/(s 2) (B) /(s 2) (D) /(s 2).7 The Fourier transform F{e u(t)} is equal to (A) e u(f) (B) e u(f) π.therefore, F (C) e u(-f) (D) e u(-f) π.8 A linear phase channel with phase delay T and group delay T must have (A) T = T = constant (B) T f and T f (f denotes frequency) is (C) T = constant and T f (D) T f and t = constant.9 A MHz sinusoidal carrier is amplitude modulated by symmetrical square wave of period µ sec. Which of the following frequencies will NOT be present in the modulated signal? (A) 99 khz (C) 2 khz (B) khz (D) 3 khz Page : 5
7 .2 Consider a sampled signal y(t) = 5 x(t) δ(t nt ) where x(t) = cos (8π )t and T = μsec. When y(t) is passed through an ideal lowpass filter with a cut-off frequency of 5 khz, the output of the filter is (A) 5 cos (8π )t (B) 5 cos (8π )t (C) 5 cos (8π )t (D) cos (8π )t.2 For a bit-rate of 8 kbps, the best possible values of the transmitted frequency in a coherent binary FSK system are (A) 6 khz and 2 khz (C) 2 khz and 4 khz (B) 2 khz and 32 khz (D) 32 khz and 4 khz.22 The line-of-sight communication requires the transmit and receive antennas to face each other. If the transmit antenna is vertically polarized, for best reception the receive antenna should be (A) horizontally polarized (B) vertically polarized (C) at 45 with respect to horizontal polarization. (D) at 45 with respect to vertical polarization..23 The VSWR can have any value between (A) and (B) - and (C) and (D) and.24 In an impedance Smith chart, a clockwise movement along a constant resistance circle gives rise to (A) a decrease in the value of reactance. (B) an increase in the value of reactance. (C) no change in the reactance value. (D) no change in the impedance value..25 The phase velocity for the TE -mode in an air-filled rectangular waveguide is (A) less than c (C) Greater than c (B) Equal to c (D) None of the above ( c is the velocity of plane waves in free space) Page : 6
8 2. This question consists of TWENTY FIVE sub-questions ( ) of TWO marks each. For each of these sub-questions, four alternatives (A, B, C and D) are given, out of which only one is correct. Indicate the correct answer by darkening the appropriate bubble against the question number on the left hand side of the Objective Response Sheet (ORS). You may to use the answer book provided for any rough work, if needed. 2. In the network of the figure is the maximum power is delivered to R L if its value is I 4Ω. 5I 2Ω R L - 5V (A) 6 (B) Ω (C) 6 (D) If the 3-phase balanced source in the figure delivers 5W at a leading power factor of.844, then the value of Z L (in ohm) is approximately Z L Z L 3-PHASE BALANCED SOURCE 4V Z L (A) (B) (C) (D) Page : 7
9 2.3 The Laplace transform of a continuous-time signal x(t) is X(s) = transform of this signal exists, then x(t) is (A) e u(t) 2e u(t) (B) e u( t) 2e u(t). If the Fourier (C) e u( t) 2e u(t) (D) e u( t) 2e u(t) 2.4 If the impulse response of a discrete-time system is h[n] = 5 u[ n ], then the system function H(z) is equal to (A) and the system is stable (C) and the system is unstable (B) and the system is stable (D) and the system is unstable 2.5 An amplifier using an opamp with a slew-rate SR= V/µsec has a gain of 4dB. If this amplifier has to faithfully amplify sinusoidal signals from dc to 2 khz without introducing any slew-rate induced distortion, then the input signal level must not exceed. (A) 795mV (B) 395mV (C) 79.5mV (D) 39.5mV 2.6 The circuit in figure employs positive feedback and is intended to generate sinusoidal oscillation. If at a frequency f, B(f) = () =, then to sustain oscillation at this frequency () R 2 R - V f (f) - Network B(f) V (f) - (A) R = 5R (B) R = 6R (C) R = (D) R = Page : 8
10 2.7 A zener diode regulator in the figure is to be designed to meet the specifications: I = ma, V = V and V m varies from 3V to 5V. The zener diode has V = V and I (knee current) = ma. For satisfactory operation. R I 2 I L =ma V in D z V R L - - (A) R 8Ω (B) 2Ω R 22 W (C) 37Ω R 4Ω (D) R > 4Ω 2.8 The voltage gain A = of the JFET amplifier shown in the figure is V DD =V R D (3KΩ) I D =ma C V C 2 I DSS = ma : V p = - 5V (Assume C,C 2 and C S to be very large) V i R G (MΩ) R S (2.5KΩ) C S - (A) 8 (B) -8 (C) 6 (D) - 6 Page : 9
11 2.9 The gates G and G 2 in the figure have propagation delays of nsec and 2 nsec respectively. If the input V i makes an abrupt change from logic to at time t = t, then the output waveform V is. G G t V V V V (A) t t t t (B) t t t t (C) t t t t (D) t t t t Page :
12 2. The circuit in the figure has two CMOS NOR-gates. This circuit functions as a R V (Output) V ss V ss C V i (A) flip-flop (B) schmitt trigger (C) monostable multivibrator (D) astable multivibrator 2. Consider the following statements in connection with the CMOS inverter in the figure is where both the MOSFETs are of enhancement type and both have a threshold voltage of 2 V. Statement : T conducts when Vi 2 V. Statement 2 : T is always in saturation when V = V. 5 V T 2 V i V T Which of the following is correct? (A) Only statement is TRUE (B) Only statement 2 is TRUE (C) Both the statements are TRUE (D) Both the statements are FALSE Page :
13 2.2 If the input X 3, X 2, X, X to the ROM in the figure are BCD numbers, then the outputs Y 3 Y 2 Y Y are X 3 X 2 X X ROM BCD-to-Decimal DECODER D D D 8 D 9 Y 3 Y 2 Y Y (A) gray code numbers (B) BCD numbers (C) excess-3 code numbers (D) none of the above 2.3 Consider the following assembly language program. MVI B,87H MOV A, B START : JMP NEXT MVI B, H XRA B OUT PORT HLT NEXT : XRA B JP START OUT PORT 2 HLT Page : 2
14 The execution of the above program in an 885 microprocessor will result in (A) An output of 87H at PORT (B) An output of 87H at PORT2 (C) Infinite looping of the program execution with accumulator data remaining at H. (D) Infinite looping of the program execution with accumulator data alternating between H and 87H. 2.4 The system shown in the figure remains stable when R(s) k s Y(s) 3 (A) k < - (B) - < k < (C) < k < 3 (D) K > The transfer function of a system is G(s) = approximate settling time for 2% criterion is (A) sec (B) 4 sec ()(). For a unit-step input to the system the (C) sec (D). sec 2.6 The characteristic polynomial of a system is q(s) = 2s s s s 2s. The system is (A) stable (C) unstable (B) marginally stable (D) oscillatory 2.7 The system with the open loop transfer function G(s) H(s) = (A) -6 db (B) db (C) 3.5 db (D) 6 db ( ) has a gain margin of Page : 3
15 2.8 An angle-modulated signal is given by s(t) = cos 2π(2 t 3 sin 5t 4 cos 5t). The maximum frequency and phase deviations of s(t) are (A).5 khz, 4π rad (B) 6 khz, 8π rad (C).5 khz, π rad (D) 7.5 khz, π rad 2.9 In the figure m(t) =, s(t) = cos 2πt and n(t) =. The output y(t) will be m(t) Lowpass filter y(t) S(t) n(t) S(t) Cutoff frequency =Hz Passband Gain = (A) (B) cos 3πt (C) (D). cos.5πt cos.75πt 2.2 A signal x(t) = cos (24π )t is ideally sampled with a sampling period of 5µsec and then passed through an ideal low pass filter with cut-off frequency of 5 khz. Which of the following frequencies is/are present at the filter output? (A) 2 khz only (B) 8 khz only (C) 2 khz and 9 khz (D) 2 khz and 8 khz 2.2 If the variance σ of d(n) = x(n) x(n ) is one tenth the variance σ of a stationary zero-mean discrete-time signal x(n), then the normalized autocorrelation function R (k)/σ at k= is (A).95 (B).9 (C). (D) A plane wave is characterized by E =.5x ye /2e. This wave is (A) linearly polarized (C) elliptically polarized (B) circularly polarized (D) unpolarized Page : 5
16 2.23 Distilled water at 25 C is characterized by σ =.7 mho/m and ε = 78ε at a frequency of 3 GHz. Its loss tangent tan δ is (A).3 (B).3 (C).7 (D).7 /(78ε ) (ε = /(36π)F/m) 2.24 The electric field on the surface of a perfect conductor is 2V/m. The conductor is immersed in water with ε = 8ε. The surface charge density on the conductor is (A) C/m (C).8 C/m (B) 2 C/m (D).4 C/m (ε = /(36π)F/m) 2.25 A person with a receiver is 5 Km away from the transmitter. What is the distance that this person must move further to detect a 3-dB decrease in signal strength? (A) 942 m (C) 4978 m (B) 27 m (D) 532 m Page : 6
17 SECTION B (75 Marks) This section consists of TWENTY questions (EC3 EC22) of FIVE marks each. Attempt ANY FIFTEEN questions. Answers must be given in the answer book provided. Answer for each question must start on a fresh page and must appear at one place only (Answers to all parts of a question must appear together). 3. The switch in the figure is has been in position for a long time and is, then moved to position 2 at t =. 25 KΩ t = u( t)v - 2 KΩ 5H I L 6V 2μF V c 4H KΩ 5 KΩ (A) Determine V ( ) and I ( ). (B) Determine () at t =. (C) Determine Vc(t) for t >. Page : 7
18 4. For the network shown in the figure is R = KΩ, L = 2 H, L = 5 H, L = H, L = 4 H and C =.2 µf. The mutual inductances are M = 3 H and M = 2 H. Determine (A) the equivalent inductance for the combination of L and L. (B) the equivalent inductance across the points A and B in the network. (C) the resonant frequency of the network. R A L I I 3 I 2 V s (t) ~ M 2 L 2 M 34 L 4 C B 5. Consider the network in the given figure Ω 5Ω 2 I x PORT PORT 2 Ω I 2 I 2I x 2 I 2 (A) Find its short-circuit admittance parameters. (B) Find the open-circuit impedance Z. Page : 8
19 6. A triangular voltage waveform V (t) first figure applied at the input to the circuit of second figure. Assume the diodes to be ideal. V i (t) 2 V V i (t) V t 7V 5V.5 KΩ t (A) Determine the output V (t). (B) Neatly sketch the output waveform superimposed on the input V (t) and label the key points. 7. The given figure shows 2-stage amplifier. The transistors Q and Q are identical with current gain β = ; further β = β = β. The zener diode D has a break-down voltage V =.7 volt. Assume that D is in break-down region and its dynamic resistance r is zero. The capacitors C and C are large and provide negligible impedance at signal frequencies..5 KΩ V cc = V D 2 D KΩ R 93 Ω R C2 4KΩ C 2 D z V EE = V V z Q 2 I c R L V c 4KΩ V D R B Q V s C L 93K Ω V H = V (A) Identify the configuration in each of the amplifier stages (i.e. whether CE, CC, CB etc.) (B) Determine the quiescent quantities I and V. Page : 9
20 (C) Derive an expression for the voltage gain A and determine its value. (Assume V =.7 V, r = and Thermal voltage V = 25 mv) 8. Consider the circuit of the figure is. The opamp used is ideal. 5V V cc2 = 2V V c = 5V R KΩ V i V OP R B 5 Ω Q R F V EE2 I = 2V KΩ R L Ω I V EE I = 5V (A) In which mode is the BJT operating (i.e. active, saturation or cut off)? Justify your answer. (B) Obtain an expression relating the output current I and V if V = 2 volt (V : output of opamp) (Assume β = 99 and V =.7 V) Page : 2
21 9. The inputs to a digital circuit shown in the figure is are the external signals A, B and C. (A, B and C are not available). The 5 V power supply (logic ) and the ground (logic ) are also available. The output of the circuit is X = A B A B C. 5V Table-9 A B C DIGITAL CIRCUIT X D D S Y S Y D D (A) Write down the output function in its canonical SOP and POS forms. (B) Implement the circuit using only two 2: multiplexers shown in the figure where S is the data-select line, D and D are the input data lines and Y is the output line. The function table for the multiplexer is in given Table.. Each transistor in the figure is has dc current gain β = 5, cut-in voltage Vγ =.65 V and V =.75 V. The output voltage V for T in saturation can be as high as.2 V. Assume.7 V drop across a conducting p-n junction. Determine? 5V R B R c2 = KΩ V i I B2 V (output) T T 2 (input) R b = 5 KΩ 2V (A) the minimum value I necessary to keep T saturation. (B) the maximum permissible value for the resistance R. Page : 2
22 (C) the worst-case high input (logic ) and the worst-case low input (logic ) for which T will be either in saturation or in cut-off.. It is required to design a binary mod-5 synchronous counter using AB flip-flops such that the output Q Q Q change as. and so on. The excitation table for the AB flipflop is given in the table A B Q n A Q A Q A Q B Q B Q B Q Q n Q n CLOCK (A) Write down the state table for the mod-5 counter. (B) Obtain simplified SOP expressions for the inputs A, B, A, B, A and B in terms of Q, Q, Q and their complements. (C) Hence, complete the circuit diagram for the mod-5 counter given in the figure using minimum number of 2-input NAND-gate only. 2. An 885 microprocessor operating at 5 MHz clock frequency executes the following routine. START : MOVE A, B OUT 55H DCR B STA FFF8H JMP START (A) Determine the total number of machine cycles required to execute this routine till the JMP instruction is executed for the first time. (B) Determine the time interval between two consecutive MEMW signals. Page : 22
23 (C) If the external logic controls the READY line so that three WAIT states are introduced in the I/O WRITE machine cycle, determine the time interval between two consecutive MEMW signals. 3. A unity feedback system has the place transfer function G (s) = ()() (A) Determine the frequency at which the plant has a phase lag of 9. (B) An integral controller with transfer function G (s) = is placed in the feedforward path of the feedback system. Find the value of k such that the compensated system has an open-loop gain margin of 2.5 (C) Determine the steady state errors of the compensated system to unit-step and unit-ramp inputs. 4. The Nyquist plot of an all-pole second order open-loop system is shown in the figure is. Obtain the transfer function of the system. Imag Real ω =.5 ω = ω = Page : 23
24 5. The block diagram of a linear time invariant system is given in the figure is U(s) - - Σ X 2 (s) X (s) /S Σ /S Σ - Y(s) 2 (A) Write down the state variable equations for the system in matrix form assuming the state vector to be [x (t) x (t)] (B) Find out the state transition matrix. (C) Determine y(t), t, When the initial values of the state at time t = are x () =, and x () =. 6. A deterministic signal x(t) = cos 2πt is passed through a differentiator as shown in the figure is x(t) 2 π d dt y(t) (A) Determine the autocorrelation R (T) and the power spectral density S (f). (B) Find the output power spectral density S (f). (C) Evaluate R () and R Page : 24
25 7. A DSBSC modulated signal s(t) = cos (2π t ϕ) m(t ) is corrupted by an additive white Gaussian noise of power spectral density W/Hz. The message power spectral density S (f) is as shown in the figure and ϕ is uniformly distributed over the range to 2π. S mm (f) 3 W/Hz - 3 khz 3 khz f (A) Express the signal autocorrelation function Rss (T) in terms of the message autocorrelation function R (T). Clearly state the necessary assumptions. (B) Determine the signal power spectral density S (f). (C) Find the power of the modulated signal and the noise power in the transmission bandwidth. 8. A continuous-time signal with finite energy, band limited from 3 MHz to 5 MHz, is ideally sampled, encoded by a fixed length PCM coder and then transmitted over a digital channel of capacity 7 Mbps. The probability density function (pdf) at the output of the sampler is uniform over the range 2V to 2V. (A) Determine the minimum sampling rate necessary for perfect reconstruction. (B) Determine the maximum SNR (in db) that may be achieved. 9. A discrete memoryless source generates either or at rate of 6 Kbps; is generated three times more frequently than. A coherent binary PSK modulator is employed to transmit these bits over a noisy channel. The received bits are detected in a correlator fed with the basis function of unit energy (for this binary PSK scheme) as the reference signal. The receiver makes a decision in favour of if the correlator output is positive, else decides in favour of. If and are represented as (6 2 cos 64π t)v and (6 2 cos 64π t)v respectively, then (A) Determine the transmitted signal energy per bit. (B) Determine the basis function of unit energy for this binary PSK scheme. Page : 25
26 (C) Determine the probability that the receiver makes a decision in favour of when the channel noise is characterized as zero-mean AWGN with power spectral density W/Hz = Transmission line transformation of a load Z to Z is given by Z = Z () () (A) Show that the above transformation implies that the impedance Z gets transformed to Z for real Z. (B) What is the importance of the result derived in (a)?. 2. Consider a parallel plate waveguide with plate separation d as shown in the figure electric and magnetic fields for the TEM-mode are given by E = E e Hy = e Where k = ηωε X d ε Z (A) Determine the surface charge densities P on the plates at x = and x = d (B) Determine the surface current densities J on the same plates. (C) Prove that P and J satisfy the current continuity condition. Page : 26
27 22. Consider a linear array of two half-wave dipoles A and B as shown in the figure is. The dipoles are apart and are excited in such a way that the current on element B legs that on element A by 9 in phase. A B λ/4 Y φ = X (A) Obtain the expression for the radiation pattern for E in the XY plane (i.e., θ = 9 ) (B) Sketch the radiation pattern obtained in (a). Page : 27
ECE Branch GATE Paper 2002 SECTION A (75 MARKS )
 SECTION A (75 MARKS ). This question consists of TWENTY FIVE sub-question (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A, B, C and D) are given, out of which only
SECTION A (75 MARKS ). This question consists of TWENTY FIVE sub-question (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A, B, C and D) are given, out of which only
For more files visit
 SECTION A (75 marks). This question consists of TWENTYFIVE subquestions (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these subquestions, four possible alternatives (A,B, C and D) are given, out of which ONLY ONE
SECTION A (75 marks). This question consists of TWENTYFIVE subquestions (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these subquestions, four possible alternatives (A,B, C and D) are given, out of which ONLY ONE
Join discussion of this test paper at
 SECTION A (75 marks). This question consists of TWENTYFIVE subquestions (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these subquestions, four possible alternatives (A,B, C and D) are given, out of which ONLY ONE
SECTION A (75 marks). This question consists of TWENTYFIVE subquestions (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these subquestions, four possible alternatives (A,B, C and D) are given, out of which ONLY ONE
SIR PADAMPAT SINGHANIA UNIVERSITY UDAIPUR Sample Question Paper for Ph.D. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) SPSAT 18
 INSTRUCTIONS SIR PADAMPAT SINGHANIA UNIVERSITY UDAIPUR Sample Question Paper for Ph.D. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) SPSAT 18 The test is 60 minutes long and consists of 40 multiple choice
INSTRUCTIONS SIR PADAMPAT SINGHANIA UNIVERSITY UDAIPUR Sample Question Paper for Ph.D. (Electronics & Communication Engineering) SPSAT 18 The test is 60 minutes long and consists of 40 multiple choice
GATE 2000 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 2 Electronics and ommunication Engineering SETION A (1 Marks) 1. This question consists of 25 (Twenty Five) multiple choice questions, each carrying one mark. For each question (1.1 1.25), four alternatives
GATE 2 Electronics and ommunication Engineering SETION A (1 Marks) 1. This question consists of 25 (Twenty Five) multiple choice questions, each carrying one mark. For each question (1.1 1.25), four alternatives
(i) Determine the admittance parameters of the network of Fig 1 (f) and draw its - equivalent circuit.
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1995 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Some useful data: Electron charge: 1.6 10 19 Coulomb Free space permeability: 4 10 7 H/m Free space permittivity: 8.85 pf/m Velocity
Electronics Eingineering
 Electronics Eingineering 1. The output of a two-input gate is 0 if and only if its inputs are unequal. It is true for (A) XOR gate (B) NAND gate (C) NOR gate (D) XNOR gate 2. In K-map simplification, a
Electronics Eingineering 1. The output of a two-input gate is 0 if and only if its inputs are unequal. It is true for (A) XOR gate (B) NAND gate (C) NOR gate (D) XNOR gate 2. In K-map simplification, a
ECE Branch GATE Paper 2004
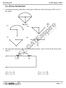 Q. 1 30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? Fig. Q.1 2. The equivalent inductance measured between the terminals
Q. 1 30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? Fig. Q.1 2. The equivalent inductance measured between the terminals
ECE Branch GATE Paper (C) exp ( t ) sin (25t) (B) 4cos (20t + 3) + 2 sin (710t)
 Question 30 Carry One Mark Each. The following differential equation has 2 3 d y dy 2 3 4 y 2 2 dt degree = 2, order = degree = 3, order = 2 + + + = x dt degree = 4, order = 3 degree = 2, order = 3 2.
Question 30 Carry One Mark Each. The following differential equation has 2 3 d y dy 2 3 4 y 2 2 dt degree = 2, order = degree = 3, order = 2 + + + = x dt degree = 4, order = 3 degree = 2, order = 3 2.
GATE 1999 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 1999 Electronics and Communication Engineering SECTION A (75 Marks) 1. This question consists of 25 (Twenty Five) multiple choice questions, each carrying one mark. For each questions (1.1 1.25),
GATE 1999 Electronics and Communication Engineering SECTION A (75 Marks) 1. This question consists of 25 (Twenty Five) multiple choice questions, each carrying one mark. For each questions (1.1 1.25),
Downloaded From All JNTU World
 Code: 9A02403 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of a nuclear plant as compared to other conventional power plants. 2 Explain about: (a) Solar distillation. (b) Solar
Code: 9A02403 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of a nuclear plant as compared to other conventional power plants. 2 Explain about: (a) Solar distillation. (b) Solar
R.B.V.R.R. WOMEN S COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS) Narayanaguda, Hyderabad. ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS
 R.B.V.R.R. WOMEN S COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS) Narayanaguda, Hyderabad. DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS QUESTION BANK FOR SEMESTER V PHYSICS PAPER VI (A) ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS UNIT I: SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
R.B.V.R.R. WOMEN S COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS) Narayanaguda, Hyderabad. DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS QUESTION BANK FOR SEMESTER V PHYSICS PAPER VI (A) ELECTRONIC PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS UNIT I: SEMICONDUCTOR DEVICES
IENGINEERS- CONSULTANTS GATE QUESTION PAPER EC 2001
 SECTION - A. This question consists of TWENTY-FIVE sub-questions (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A,B, C and D) are given, out of which ONLY ONE is
SECTION - A. This question consists of TWENTY-FIVE sub-questions (..25) of ONE mark each. For each of these sub-questions, four possible alternatives (A,B, C and D) are given, out of which ONLY ONE is
GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13)
 GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13) 1. Removing bypass capacitor across the emitter leg resistor in a CE amplifier causes a. increase in current gain b. decrease in current gain c. increase
GATE: Electronics MCQs (Practice Test 1 of 13) 1. Removing bypass capacitor across the emitter leg resistor in a CE amplifier causes a. increase in current gain b. decrease in current gain c. increase
Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All questions carry equal marks
 Code: 9A02401 PRINCIPLES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Common to EIE, E.Con.E, ECE & ECC) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 1 In a series RLC circuit, R = 5 Ω, L = 1 H and C = 1 F. A dc v ltage f 20 V is applied
Code: 9A02401 PRINCIPLES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Common to EIE, E.Con.E, ECE & ECC) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 1 In a series RLC circuit, R = 5 Ω, L = 1 H and C = 1 F. A dc v ltage f 20 V is applied
GATE 2004 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 2004 Electronics and Communication Engineering Q. 1 30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? (A) Fig. Q.1
GATE 2004 Electronics and Communication Engineering Q. 1 30 Carry One Mark Each 1. Consider the network graph shown in the figure. Which one of the following is NOT a 'tree' of this graph? (A) Fig. Q.1
ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS. Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100
 EC 40 MODEL TEST PAPER - 1 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Answer five questions, taking ANY TWO from Group A, any two from Group B and all from Group C. All parts of a question
EC 40 MODEL TEST PAPER - 1 ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 100 Answer five questions, taking ANY TWO from Group A, any two from Group B and all from Group C. All parts of a question
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-2013 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-03 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: PART - A 0. What does the arrow mark indicate
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-03 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: PART - A 0. What does the arrow mark indicate
Downloaded From JNTU World. B.Tech II Year II Semester (R09) Supplementary Examinations December/January 2014/2015 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER
 Downloaded From Code: 9A02403 B.Tech II Year II Semester () Supplementary Examinations December/January 2014/2015 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER Answer any FIVE questions 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages
Downloaded From Code: 9A02403 B.Tech II Year II Semester () Supplementary Examinations December/January 2014/2015 GENERATION OF ELECTRIC POWER Answer any FIVE questions 1 Discuss the advantages and disadvantages
Linear Algebra, Calculus, Differential Equations and Vector Analysis. Complex Anaysis, Numerical Methods and Probability and Statistics.
 Test No Topic code Topic EC-01 GEM (Engineering Mathematics) Topic wise Tests Each test carries 25 marks and 45 minutes duration Test consists of 5 one mark questions and 10 two marks questions Tests will
Test No Topic code Topic EC-01 GEM (Engineering Mathematics) Topic wise Tests Each test carries 25 marks and 45 minutes duration Test consists of 5 one mark questions and 10 two marks questions Tests will
6. A low pass filter having a frequency response does not produce any phase distortion, if (A) A(ω)
 1. The rank of the matrix is 0 1 2. P, where P is a vector, is equal to 2 P P P 2 P+ P ( ) 2 3 2 P+ P 2 ( P) P 3. ( P) ds, where P is a vector, is equal to P dl P dl Pdv ax 4. A probability density function
1. The rank of the matrix is 0 1 2. P, where P is a vector, is equal to 2 P P P 2 P+ P ( ) 2 3 2 P+ P 2 ( P) P 3. ( P) ds, where P is a vector, is equal to P dl P dl Pdv ax 4. A probability density function
B.E. SEMESTER III (ELECTRICAL) SUBJECT CODE: X30902 Subject Name: Analog & Digital Electronics
 B.E. SEMESTER III (ELECTRICAL) SUBJECT CODE: X30902 Subject Name: Analog & Digital Electronics Sr. No. Date TITLE To From Marks Sign 1 To verify the application of op-amp as an Inverting Amplifier 2 To
B.E. SEMESTER III (ELECTRICAL) SUBJECT CODE: X30902 Subject Name: Analog & Digital Electronics Sr. No. Date TITLE To From Marks Sign 1 To verify the application of op-amp as an Inverting Amplifier 2 To
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-2007 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - II Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt Question No. 1 which is compulsory and FOUR more questions
I.E.S-(Conv.)-2007 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - II Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt Question No. 1 which is compulsory and FOUR more questions
HIGH LOW Astable multivibrators HIGH LOW 1:1
 1. Multivibrators A multivibrator circuit oscillates between a HIGH state and a LOW state producing a continuous output. Astable multivibrators generally have an even 50% duty cycle, that is that 50% of
1. Multivibrators A multivibrator circuit oscillates between a HIGH state and a LOW state producing a continuous output. Astable multivibrators generally have an even 50% duty cycle, that is that 50% of
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-2012 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: Qn. PART - A 0. Which is the largest of three
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: Qn. PART - A 0. Which is the largest of three
Downloaded From All JNTU World
 Code: 9A02401 PRINCIPLES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Common to ECE, EIE, E.Con.E & ECC) 1 Find initial conditions for voltage across capacitor, the currents i 1, i 2 and the derivatives for the circuit
Code: 9A02401 PRINCIPLES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Common to ECE, EIE, E.Con.E & ECC) 1 Find initial conditions for voltage across capacitor, the currents i 1, i 2 and the derivatives for the circuit
QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION (15EC61)
 QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION (15EC61) Module 1 1. Explain Digital communication system with a neat block diagram. 2. What are the differences between digital and analog communication systems?
QUESTION BANK SUBJECT: DIGITAL COMMUNICATION (15EC61) Module 1 1. Explain Digital communication system with a neat block diagram. 2. What are the differences between digital and analog communication systems?
GATE 2009 Instrumentation Engineering
 GATE 2009 Instrumentation Engineering Q. Q20 carry one mark each.. If z = x jy, where x and y are real, the value of e is (A) (C) e (B) e x y (D) e 2. The value of origin, is (A) 0 (B) 2πj dz, where the
GATE 2009 Instrumentation Engineering Q. Q20 carry one mark each.. If z = x jy, where x and y are real, the value of e is (A) (C) e (B) e x y (D) e 2. The value of origin, is (A) 0 (B) 2πj dz, where the
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS
 OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS Q.1 The breakdown mechanism in a lightly doped p-n junction under reverse biased condition is called (A) avalanche breakdown. (B) zener breakdown. (C) breakdown by tunnelling.
LINEAR IC APPLICATIONS
 1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2013
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 2013
GATE 2009 Electrical Engineering
 Q. No. 1 20 Carry One Mark Each GATE 2009 Electrical Engineering 1. The pressure coil of a dynamometer type wattmeter is (A) highly inductive (B) highly resistive (C) purely resistive (D) purely inductive
Q. No. 1 20 Carry One Mark Each GATE 2009 Electrical Engineering 1. The pressure coil of a dynamometer type wattmeter is (A) highly inductive (B) highly resistive (C) purely resistive (D) purely inductive
GATE SOLVED PAPER - IN
 YEAR 202 ONE MARK Q. The i-v characteristics of the diode in the circuit given below are : v -. A v 0.7 V i 500 07 $ = * 0 A, v < 0.7 V The current in the circuit is (A) 0 ma (C) 6.67 ma (B) 9.3 ma (D)
YEAR 202 ONE MARK Q. The i-v characteristics of the diode in the circuit given below are : v -. A v 0.7 V i 500 07 $ = * 0 A, v < 0.7 V The current in the circuit is (A) 0 ma (C) 6.67 ma (B) 9.3 ma (D)
EE Branch GATE Paper 2001 SECTION A (TOTAL MARKS = 75)
 SECTION A (TOTAL MARKS = 75) 1. This question consists of 25 (TWENTY-FIVE) sub-questions (1.1-1.25) of ONE mark each. (25 1 = 25 ) 1.1 In a series RLC circuit at resonance, the magnitude of the voltage
SECTION A (TOTAL MARKS = 75) 1. This question consists of 25 (TWENTY-FIVE) sub-questions (1.1-1.25) of ONE mark each. (25 1 = 25 ) 1.1 In a series RLC circuit at resonance, the magnitude of the voltage
 COMBO ONLINE TEST SERIES GATE 2019 SCHEDULE: ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Syllabus Test Date Test Type [ EB-Engineering Branch ; EM- No. of Engineering Mathematics; GA- General Question Marks
COMBO ONLINE TEST SERIES GATE 2019 SCHEDULE: ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Syllabus Test Date Test Type [ EB-Engineering Branch ; EM- No. of Engineering Mathematics; GA- General Question Marks
Problem Sheets: Communication Systems
 Problem Sheets: Communication Systems Professor A. Manikas Chair of Communications and Array Processing Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London v.11 1 Topic: Introductory
Problem Sheets: Communication Systems Professor A. Manikas Chair of Communications and Array Processing Department of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Imperial College London v.11 1 Topic: Introductory
Q.1: Power factor of a linear circuit is defined as the:
 Q.1: Power factor of a linear circuit is defined as the: a. Ratio of real power to reactive power b. Ratio of real power to apparent power c. Ratio of reactive power to apparent power d. Ratio of resistance
Q.1: Power factor of a linear circuit is defined as the: a. Ratio of real power to reactive power b. Ratio of real power to apparent power c. Ratio of reactive power to apparent power d. Ratio of resistance
Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All questions carry equal marks *****
 Code: 9A04601 DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) 1 (a) Explain in detail about non-uniform quantization. (b) What is the disadvantage of uniform quantization over the non-uniform
Code: 9A04601 DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) 1 (a) Explain in detail about non-uniform quantization. (b) What is the disadvantage of uniform quantization over the non-uniform
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1996 Some useful data:
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1996 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt question ONE which is compulsory and any FOUR of the remaining
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1996 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt question ONE which is compulsory and any FOUR of the remaining
Electronics & Communication Engineering
 A SET EC - 6 Booklet No. : Electronics & Communication Engineering Duration of Test : Hours Max. Marks : 0 Hall Ticket No. Name of the Candidate : Date of Examination : OMR Answer Sheet No. : Signature
A SET EC - 6 Booklet No. : Electronics & Communication Engineering Duration of Test : Hours Max. Marks : 0 Hall Ticket No. Name of the Candidate : Date of Examination : OMR Answer Sheet No. : Signature
The steeper the phase shift as a function of frequency φ(ω) the more stable the frequency of oscillation
 It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
It should be noted that the frequency of oscillation ω o is determined by the phase characteristics of the feedback loop. the loop oscillates at the frequency for which the phase is zero The steeper the
 Code No: Y0221/R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, Apr/May 2013 BASIC ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
Code No: Y0221/R07 Set No. 1 I B.Tech Supplementary Examinations, Apr/May 2013 BASIC ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS (Electrical & Electronics Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions
Difference between BJTs and FETs. Junction Field Effect Transistors (JFET)
 Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
Oscillators. An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier.
 Oscillators An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier. An amplifier delivers an output signal whose waveform corresponds to the input signal but
Oscillators An oscillator may be described as a source of alternating voltage. It is different than amplifier. An amplifier delivers an output signal whose waveform corresponds to the input signal but
(A) 1 and 1 (B) 0 and 1 (C) 1 and 0 (D) 0 and A second order system is described by the equation. (A) 1 rad / sec and 5 (B) 5 rad / sec and 7
 EC- Objective Paper-II IES-013 www.gateforum.com IES-013- Paper-II 1. The D.C. gain and steady state error for step input for ( ) = s + 1 G s are : s + s + 1 (A) 1 and 1 (B) 0 and 1 (C) 1 and 0 (D) 0 and
EC- Objective Paper-II IES-013 www.gateforum.com IES-013- Paper-II 1. The D.C. gain and steady state error for step input for ( ) = s + 1 G s are : s + s + 1 (A) 1 and 1 (B) 0 and 1 (C) 1 and 0 (D) 0 and
UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus
 UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus PAPER I 1. Circuit Theory: Circuit components; network graphs; KCL, KVL; circuit analysis methods: nodal analysis, mesh analysis;
UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus PAPER I 1. Circuit Theory: Circuit components; network graphs; KCL, KVL; circuit analysis methods: nodal analysis, mesh analysis;
Problem Sheet 1 Probability, random processes, and noise
 Problem Sheet 1 Probability, random processes, and noise 1. If F X (x) is the distribution function of a random variable X and x 1 x 2, show that F X (x 1 ) F X (x 2 ). 2. Use the definition of the cumulative
Problem Sheet 1 Probability, random processes, and noise 1. If F X (x) is the distribution function of a random variable X and x 1 x 2, show that F X (x 1 ) F X (x 2 ). 2. Use the definition of the cumulative
Total No. of Questions : 40 ] [ Total No. of Printed Pages : 7. March, Time : 3 Hours 15 Minutes ] [ Max. Marks : 90
![Total No. of Questions : 40 ] [ Total No. of Printed Pages : 7. March, Time : 3 Hours 15 Minutes ] [ Max. Marks : 90 Total No. of Questions : 40 ] [ Total No. of Printed Pages : 7. March, Time : 3 Hours 15 Minutes ] [ Max. Marks : 90](/thumbs/93/111664408.jpg) Code No. 40 Total No. of Questions : 40 ] [ Total No. of Printed Pages : 7 March, 2009 ELECTRONICS Time : 3 Hours 15 Minutes ] [ Max. Marks : 90 Note : i) The question paper has four Parts A, B, C & D.
Code No. 40 Total No. of Questions : 40 ] [ Total No. of Printed Pages : 7 March, 2009 ELECTRONICS Time : 3 Hours 15 Minutes ] [ Max. Marks : 90 Note : i) The question paper has four Parts A, B, C & D.
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-2005 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - II Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt Question No. 1 which is compulsory and FOUR more questions
I.E.S-(Conv.)-2005 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - II Time Allowed: 3 hours Maximum Marks : 200 Candidates should attempt Question No. 1 which is compulsory and FOUR more questions
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering 1
 UNIT I SAMPLING AND QUANTIZATION Pulse Modulation 1. Explain in detail the generation of PWM and PPM signals (16) (M/J 2011) 2. Explain in detail the concept of PWM and PAM (16) (N/D 2012) 3. What is the
UNIT I SAMPLING AND QUANTIZATION Pulse Modulation 1. Explain in detail the generation of PWM and PPM signals (16) (M/J 2011) 2. Explain in detail the concept of PWM and PAM (16) (N/D 2012) 3. What is the
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-2012 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 40 Subject: PART - A 0. Which region of the transistor
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 40 Subject: PART - A 0. Which region of the transistor
PROPOSED SCHEME OF COURSE WORK
 PROPOSED SCHEME OF COURSE WORK Course Details: Course Title : LINEAR AND DIGITAL IC APPLICATIONS Course Code : 13EC1146 L T P C : 4 0 0 3 Program: : B.Tech. Specialization: : Electrical and Electronics
PROPOSED SCHEME OF COURSE WORK Course Details: Course Title : LINEAR AND DIGITAL IC APPLICATIONS Course Code : 13EC1146 L T P C : 4 0 0 3 Program: : B.Tech. Specialization: : Electrical and Electronics
B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering)
 Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
 SET - 1 1. a) Write the application of attenuator b) State the clamping theorem c) Write the application of Monostable multi vibrator d) Draw the diagram for Diode two input AND gate e) Define the terms
SET - 1 1. a) Write the application of attenuator b) State the clamping theorem c) Write the application of Monostable multi vibrator d) Draw the diagram for Diode two input AND gate e) Define the terms
ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Q1. A transmission line of characteristic impedance 50 Ω is terminated by a 50 Ω load. When excited by a sinusoidal voltage source at 10 GHz the phase difference
ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING Q1. A transmission line of characteristic impedance 50 Ω is terminated by a 50 Ω load. When excited by a sinusoidal voltage source at 10 GHz the phase difference
Transistor Digital Circuits
 Recapitulation Transistor Digital Circuits The transistor Operating principle and regions Utilization of the transistor Transfer characteristics, symbols Controlled switch model BJT digital circuits MOSFET
Recapitulation Transistor Digital Circuits The transistor Operating principle and regions Utilization of the transistor Transfer characteristics, symbols Controlled switch model BJT digital circuits MOSFET
BSNL TTA Question Paper Control Systems Specialization 2007
 BSNL TTA Question Paper Control Systems Specialization 2007 1. An open loop control system has its (a) control action independent of the output or desired quantity (b) controlling action, depending upon
BSNL TTA Question Paper Control Systems Specialization 2007 1. An open loop control system has its (a) control action independent of the output or desired quantity (b) controlling action, depending upon
Gechstudentszone.wordpress.com
 8.1 Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) UNIT 8: Operational Amplifier An operational amplifier ("op-amp") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended
8.1 Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp) UNIT 8: Operational Amplifier An operational amplifier ("op-amp") is a DC-coupled high-gain electronic voltage amplifier with a differential input and, usually, a single-ended
The University of Texas at Austin Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Exam
 The University of Texas at Austin Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Exam Date: December 18, 2017 Course: EE 313 Evans Name: Last, First The exam is scheduled to last three hours. Open
The University of Texas at Austin Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering Final Exam Date: December 18, 2017 Course: EE 313 Evans Name: Last, First The exam is scheduled to last three hours. Open
OSCILLATORS AND WAVEFORM-SHAPING CIRCUITS
 OSILLATORS AND WAVEFORM-SHAPING IRUITS Signals having prescribed standard waveforms (e.g., sinusoidal, square, triangle, pulse, etc). To generate sinusoidal waveforms: o Positive feedback loop with non-linear
OSILLATORS AND WAVEFORM-SHAPING IRUITS Signals having prescribed standard waveforms (e.g., sinusoidal, square, triangle, pulse, etc). To generate sinusoidal waveforms: o Positive feedback loop with non-linear
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER PREPARED BY, PROF. CHIRAG H. RAVAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR NIRMA UNIVRSITY
 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER PREPARED BY, PROF. CHIRAG H. RAVAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR NIRMA UNIVRSITY INTRODUCTION Op-Amp means Operational Amplifier. Operational stands for mathematical operation like addition,
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER PREPARED BY, PROF. CHIRAG H. RAVAL ASSISTANT PROFESSOR NIRMA UNIVRSITY INTRODUCTION Op-Amp means Operational Amplifier. Operational stands for mathematical operation like addition,
Digital Modulation Schemes
 Digital Modulation Schemes 1. In binary data transmission DPSK is preferred to PSK because (a) a coherent carrier is not required to be generated at the receiver (b) for a given energy per bit, the probability
Digital Modulation Schemes 1. In binary data transmission DPSK is preferred to PSK because (a) a coherent carrier is not required to be generated at the receiver (b) for a given energy per bit, the probability
CHAPTER 6 DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS
 CHAPTER 6 DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS 1 LECTURE CONTENTS 6.1 Logic Gates 6.2 Digital Instruments 6.3 Analog to Digital Converter 6.4 Electronic Counter 6.6 Digital Multimeters 2 6.1 Logic Gates 3 AND Gate The
CHAPTER 6 DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS 1 LECTURE CONTENTS 6.1 Logic Gates 6.2 Digital Instruments 6.3 Analog to Digital Converter 6.4 Electronic Counter 6.6 Digital Multimeters 2 6.1 Logic Gates 3 AND Gate The
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 8-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 29
Question Paper & Answer Keys Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 8-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com ANALYSIS OF GATE 29
Experiment 1: Amplifier Characterization Spring 2019
 Experiment 1: Amplifier Characterization Spring 2019 Objective: The objective of this experiment is to develop methods for characterizing key properties of operational amplifiers Note: We will be using
Experiment 1: Amplifier Characterization Spring 2019 Objective: The objective of this experiment is to develop methods for characterizing key properties of operational amplifiers Note: We will be using
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad
 1 P a g e INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Name : INTEGRATED CIRCUITS APPLICATIONS Code
1 P a g e INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Name : INTEGRATED CIRCUITS APPLICATIONS Code
EC Transmission Lines And Waveguides
 EC6503 - Transmission Lines And Waveguides UNIT I - TRANSMISSION LINE THEORY A line of cascaded T sections & Transmission lines - General Solution, Physical Significance of the Equations 1. Define Characteristic
EC6503 - Transmission Lines And Waveguides UNIT I - TRANSMISSION LINE THEORY A line of cascaded T sections & Transmission lines - General Solution, Physical Significance of the Equations 1. Define Characteristic
ELECTRONICS ADVANCED SUPPLEMENTARY LEVEL
 ELECTRONICS ADVANCED SUPPLEMENTARY LEVEL AIMS The general aims of the subject are : 1. to foster an interest in and an enjoyment of electronics as a practical and intellectual discipline; 2. to develop
ELECTRONICS ADVANCED SUPPLEMENTARY LEVEL AIMS The general aims of the subject are : 1. to foster an interest in and an enjoyment of electronics as a practical and intellectual discipline; 2. to develop
GATE 2006 Electronics and Communication Engineering
 GATE 2006 Electronics and Communication Engineering 1 1 1 1. The rank of the matrix 1 1 0 is (A) 0 (B) 1 1 1 1 2. P, where P is a vector, is equal to 2 P P P (A) 2 P P (B) (C) 2 (D) 3 (C) 2 P P 2 (D) P
GATE 2006 Electronics and Communication Engineering 1 1 1 1. The rank of the matrix 1 1 0 is (A) 0 (B) 1 1 1 1 2. P, where P is a vector, is equal to 2 P P P (A) 2 P P (B) (C) 2 (D) 3 (C) 2 P P 2 (D) P
Thus there are three basic modulation techniques: 1) AMPLITUDE SHIFT KEYING 2) FREQUENCY SHIFT KEYING 3) PHASE SHIFT KEYING
 CHAPTER 5 Syllabus 1) Digital modulation formats 2) Coherent binary modulation techniques 3) Coherent Quadrature modulation techniques 4) Non coherent binary modulation techniques. Digital modulation formats:
CHAPTER 5 Syllabus 1) Digital modulation formats 2) Coherent binary modulation techniques 3) Coherent Quadrature modulation techniques 4) Non coherent binary modulation techniques. Digital modulation formats:
QUESTION BANK EC 1351 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION YEAR / SEM : III / VI UNIT I- PULSE MODULATION PART-A (2 Marks) 1. What is the purpose of sample and hold
 QUESTION BANK EC 1351 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION YEAR / SEM : III / VI UNIT I- PULSE MODULATION PART-A (2 Marks) 1. What is the purpose of sample and hold circuit 2. What is the difference between natural sampling
QUESTION BANK EC 1351 DIGITAL COMMUNICATION YEAR / SEM : III / VI UNIT I- PULSE MODULATION PART-A (2 Marks) 1. What is the purpose of sample and hold circuit 2. What is the difference between natural sampling
EC6503 Transmission Lines and WaveguidesV Semester Question Bank
 UNIT I TRANSMISSION LINE THEORY A line of cascaded T sections & Transmission lines General Solution, Physicasignificance of the equations 1. Derive the two useful forms of equations for voltage and current
UNIT I TRANSMISSION LINE THEORY A line of cascaded T sections & Transmission lines General Solution, Physicasignificance of the equations 1. Derive the two useful forms of equations for voltage and current
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS UNIT-1 SUBJECT : ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS SUBJECT CODE : EC6202 BRANCH: EEE PART -A 1. What is meant by diffusion current in a semi conductor? (APR/MAY 2010, 2011, NOV/DEC
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS UNIT-1 SUBJECT : ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS SUBJECT CODE : EC6202 BRANCH: EEE PART -A 1. What is meant by diffusion current in a semi conductor? (APR/MAY 2010, 2011, NOV/DEC
Code: 9A Answer any FIVE questions All questions carry equal marks *****
 II B. Tech II Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations, April/May 2012 ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS (Common to EIE, E. Con. E & ECE) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All
II B. Tech II Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations, April/May 2012 ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT ANALYSIS (Common to EIE, E. Con. E & ECE) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All
GATE Question Paper & Answer Keys
 GATE-2015 Question Paper & Answer Keys GATE-2015 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
GATE-2015 Question Paper & Answer Keys GATE-2015 Index 1. Question Paper Analysis 2. Question Paper & Answer keys : 080-617 66 222, info@thegateacademy.com Copyright reserved. Web:www.thegateacademy.com
Conventional Paper-II-2011 Part-1A
 Conventional Paper-II-2011 Part-1A 1(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) The purpose of providing dummy coils in the armature of a DC machine is to: (A) Increase voltage induced (B) Decrease the armature resistance
Conventional Paper-II-2011 Part-1A 1(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) The purpose of providing dummy coils in the armature of a DC machine is to: (A) Increase voltage induced (B) Decrease the armature resistance
Electronic Circuits EE359A
 Electronic Circuits EE359A Bruce McNair B206 bmcnair@stevens.edu 201-216-5549 1 Memory and Advanced Digital Circuits - 2 Chapter 11 2 Figure 11.1 (a) Basic latch. (b) The latch with the feedback loop opened.
Electronic Circuits EE359A Bruce McNair B206 bmcnair@stevens.edu 201-216-5549 1 Memory and Advanced Digital Circuits - 2 Chapter 11 2 Figure 11.1 (a) Basic latch. (b) The latch with the feedback loop opened.
ECE Branch GATE Paper Q2. The trigonometric Fourier series for the waveform shown below contains
 Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each. Q1. The eigen values of a skew-symmetric matrix are Always zero Always pure imaginary Either zero or pure imaginary Always real Q2. The trigonometric Fourier series for the
Q.1 Q.25 carry one mark each. Q1. The eigen values of a skew-symmetric matrix are Always zero Always pure imaginary Either zero or pure imaginary Always real Q2. The trigonometric Fourier series for the
Associate In Applied Science In Electronics Engineering Technology Expiration Date:
 PROGRESS RECORD Study your lessons in the order listed below. Associate In Applied Science In Electronics Engineering Technology Expiration Date: 1 2330A Current and Voltage 2 2330B Controlling Current
PROGRESS RECORD Study your lessons in the order listed below. Associate In Applied Science In Electronics Engineering Technology Expiration Date: 1 2330A Current and Voltage 2 2330B Controlling Current
ASTABLE MULTIVIBRATOR
 555 TIMER ASTABLE MULTIIBRATOR MONOSTABLE MULTIIBRATOR 555 TIMER PHYSICS (LAB MANUAL) PHYSICS (LAB MANUAL) 555 TIMER Introduction The 555 timer is an integrated circuit (chip) implementing a variety of
555 TIMER ASTABLE MULTIIBRATOR MONOSTABLE MULTIIBRATOR 555 TIMER PHYSICS (LAB MANUAL) PHYSICS (LAB MANUAL) 555 TIMER Introduction The 555 timer is an integrated circuit (chip) implementing a variety of
BJT Circuits (MCQs of Moderate Complexity)
 BJT Circuits (MCQs of Moderate Complexity) 1. The current ib through base of a silicon npn transistor is 1+0.1 cos (1000πt) ma. At 300K, the rπ in the small signal model of the transistor is i b B C r
BJT Circuits (MCQs of Moderate Complexity) 1. The current ib through base of a silicon npn transistor is 1+0.1 cos (1000πt) ma. At 300K, the rπ in the small signal model of the transistor is i b B C r
Number of Lessons:155 #14B (P) Electronics Technology with Digital and Microprocessor Laboratory Completion Time: 42 months
 PROGRESS RECORD Study your lessons in the order listed below. Number of Lessons:155 #14B (P) Electronics Technology with Digital and Microprocessor Laboratory Completion Time: 42 months 1 2330A Current
PROGRESS RECORD Study your lessons in the order listed below. Number of Lessons:155 #14B (P) Electronics Technology with Digital and Microprocessor Laboratory Completion Time: 42 months 1 2330A Current
i Intelligent Digitize Emulated Achievement Lab
 Electronics Circuits Equipment Intelligent Digitize Emulated Achievement Lab intelligent digitize emulated achievement lab is a digitized-based training system, which utilizes integrated Hardware Platform,
Electronics Circuits Equipment Intelligent Digitize Emulated Achievement Lab intelligent digitize emulated achievement lab is a digitized-based training system, which utilizes integrated Hardware Platform,
Paper-1 (Circuit Analysis) UNIT-I
 Paper-1 (Circuit Analysis) UNIT-I AC Fundamentals & Kirchhoff s Current and Voltage Laws 1. Explain how a sinusoidal signal can be generated and give the significance of each term in the equation? 2. Define
Paper-1 (Circuit Analysis) UNIT-I AC Fundamentals & Kirchhoff s Current and Voltage Laws 1. Explain how a sinusoidal signal can be generated and give the significance of each term in the equation? 2. Define
EC Objective Paper II (Set - D) 2 10 Hz (C)
 EC Objective Paper II (Set - D) 1. Techniques that automatically move program and data blocks into the physical main memory when they are required for execution are called Main Memory techniques Cache
EC Objective Paper II (Set - D) 1. Techniques that automatically move program and data blocks into the physical main memory when they are required for execution are called Main Memory techniques Cache
Test Your Understanding
 074 Part 2 Analog Electronics EXEISE POBLEM Ex 5.3: For the switched-capacitor circuit in Figure 5.3b), the parameters are: = 30 pf, 2 = 5pF, and F = 2 pf. The clock frequency is 00 khz. Determine the
074 Part 2 Analog Electronics EXEISE POBLEM Ex 5.3: For the switched-capacitor circuit in Figure 5.3b), the parameters are: = 30 pf, 2 = 5pF, and F = 2 pf. The clock frequency is 00 khz. Determine the
R a) Explain the operation of RC high-pass circuit when exponential input is applied.
 SET - 1 1. a) Explain the operation of RC high-pass circuit when exponential input is applied. 2x V ( e 1) V b) Verify V2 = = tanhx for a symmetrical square wave applied to a RC low 2x 2 ( e + 2 pass circuit.
SET - 1 1. a) Explain the operation of RC high-pass circuit when exponential input is applied. 2x V ( e 1) V b) Verify V2 = = tanhx for a symmetrical square wave applied to a RC low 2x 2 ( e + 2 pass circuit.
Final Exam: Electronics 323 December 14, 2010
 Final Exam: Electronics 323 December 4, 200 Formula sheet provided. In all questions give at least some explanation of what you are doing to receive full value. You may answer some questions ON the question
Final Exam: Electronics 323 December 4, 200 Formula sheet provided. In all questions give at least some explanation of what you are doing to receive full value. You may answer some questions ON the question
Transistor Design & Analysis (Inverter)
 Experiment No. 1: DIGITAL ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT Transistor Design & Analysis (Inverter) APPARATUS: Transistor Resistors Connecting Wires Bread Board Dc Power Supply THEORY: Digital electronics circuits operate
Experiment No. 1: DIGITAL ELECTRONIC CIRCUIT Transistor Design & Analysis (Inverter) APPARATUS: Transistor Resistors Connecting Wires Bread Board Dc Power Supply THEORY: Digital electronics circuits operate
Multivibrators. Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering, Amrita School of Engineering
 Multivibrators Multivibrators Multivibrator is an electronic circuit that generates square, rectangular, pulse waveforms. Also called as nonlinear oscillators or function generators. Multivibrator is basically
Multivibrators Multivibrators Multivibrator is an electronic circuit that generates square, rectangular, pulse waveforms. Also called as nonlinear oscillators or function generators. Multivibrator is basically
Electrical Materials may be referred to a metal, dielectrics,electrical insulators or conductors,paramagnetic materials and many other.
 Electrical Engineering Paper-1 Syllabus : This part is for both objective and conventional types papers : 1) EM Theory- The electromagnetic force is said to be one of the fundamental interactions in nature
Electrical Engineering Paper-1 Syllabus : This part is for both objective and conventional types papers : 1) EM Theory- The electromagnetic force is said to be one of the fundamental interactions in nature
hij Teacher Resource Bank GCE Electronics Exemplar Examination Questions ELEC2 Further Electronics
 hij Teacher Resource Bank GCE Electronics Exemplar Examination Questions ELEC2 Further Electronics The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England
hij Teacher Resource Bank GCE Electronics Exemplar Examination Questions ELEC2 Further Electronics The Assessment and Qualifications Alliance (AQA) is a company limited by guarantee registered in England
Summer 2015 Examination
 Summer 2015 Examination Subject Code: 17445 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
Summer 2015 Examination Subject Code: 17445 Model Answer Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme.
Chapter 2: Signal Representation
 Chapter 2: Signal Representation Aveek Dutta Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University at Albany Spring 2018 Images and equations adopted from: Digital Communications
Chapter 2: Signal Representation Aveek Dutta Assistant Professor Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University at Albany Spring 2018 Images and equations adopted from: Digital Communications
Homework Assignment 06
 Question 1 (2 points each unless noted otherwise) Homework Assignment 06 1. True or false: when transforming a circuit s diagram to a diagram of its small-signal model, we replace dc constant current sources
Question 1 (2 points each unless noted otherwise) Homework Assignment 06 1. True or false: when transforming a circuit s diagram to a diagram of its small-signal model, we replace dc constant current sources
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the
 Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
 VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur-603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING EC6503 TRANSMISSION LINES AND WAVEGUIDES YEAR / SEMESTER: III / V ACADEMIC YEAR:
VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur-603 203 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING EC6503 TRANSMISSION LINES AND WAVEGUIDES YEAR / SEMESTER: III / V ACADEMIC YEAR:
PHYS 536 The Golden Rules of Op Amps. Characteristics of an Ideal Op Amp
 PHYS 536 The Golden Rules of Op Amps Introduction The purpose of this experiment is to illustrate the golden rules of negative feedback for a variety of circuits. These concepts permit you to create and
PHYS 536 The Golden Rules of Op Amps Introduction The purpose of this experiment is to illustrate the golden rules of negative feedback for a variety of circuits. These concepts permit you to create and
EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS
 EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS Pulse Code Modulation: 1. Draw the block diagram of basic digital communication system. How it is different from analog communication system. 2. What are the advantages of
EXPERIMENT WISE VIVA QUESTIONS Pulse Code Modulation: 1. Draw the block diagram of basic digital communication system. How it is different from analog communication system. 2. What are the advantages of
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1992 Time Allowed : Three Hours
 I.E.S-(Conv.)-1992 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time Allowed : Three Hours Maximum Marks: 0 Candidates should attempt question No. 1 which is compulsory and any FOUR of the remaining
I.E.S-(Conv.)-1992 ELECTRONICS AND TELECOMMUNICATION ENGINEERING PAPER - I Time Allowed : Three Hours Maximum Marks: 0 Candidates should attempt question No. 1 which is compulsory and any FOUR of the remaining
