Computed tomography with single-shot dual-energy sandwich detectors
|
|
|
- Jasper Nathaniel Barber
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Computed tomography with single-shot dual-energy sandwich detectors Seung Ho Kim, a Hanbean Youn, b,c Daecheon Kim, a Dong Woon Kim, a Hosang Jeon, b,c Ho Kyung Kim a,c a School of Mechanical Engineering, Pusan National University, Busan 46241, South Korea b Department of Radiation Oncology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Gyeongsangnam-do 50612, South Korea c Center for Advanced Medical Engineering, Pusan National University, Busan 46241, South Korea ABSTRACT Single-shot dual-energy sandwich detector can produce sharp images because of subtraction of images from two sub-detector layers, which have different thick x-ray converters, of the sandwich detector. Inspired by this observation, the authors have developed a microtomography system with the sandwich detector in pursuit of highresolution bone-enhanced small-animal imaging. The preliminary results show that the bone-enhanced images reconstructed with the subtracted projection data are better in visibility of bone details than the conventionally reconstructed images. In addition, the bone-enhanced images obtained from the sandwich detector are relatively immune to the artifacts caused by photon starvation. The microtomography with the single-shot dual-energy sandwich detector will be useful for the high-resolution bone imaging. Keywords: Computed tomography, microtomography, micro-ct, sandwich detector, dual-energy imaging, single-shot dual-energy imaging, mouse imaging 1. INTRODUCTION We previously described the multilayer ( sandwich ) detector by stacking two flat-panel detectors (FPDs) and demonstrated its prospect for motion-artifact-free single-shot dual-energy imaging (DEI) by obtaining bone and soft-tissue images of a postmortem mouse. 1, 2 While the front FPD measures relatively low energy, as shown in Fig. 1, the rear one measures relatively high energy because of x-ray beam hardening through the front FPD. Onto the same CMOS photodiode platform, thus, we placed a thicker scintillator in the rear FPD than the front one to achieve high quantum efficiency with the relatively higher-energy x-ray spectrum. An intermediate copper (Cu) filter can be used to further increase spectral separation between the two FPD measurements, which may provides a better contrast-to-noise performance in the subtracted images. As shown in Fig. 2, the conventional dual-shot image obtained by switching the applied tube voltages (40/70 kvp) showed superior signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) performance but the single-shot image obtained from the sandwich detector was almost as good and had the advantage of being less susceptible to motion artifacts. We also observed that the single-shot method showed better SNR at higher spatial frequencies (e.g. edge regions and bone details) than the double-shot method. The reason can be explained by the inherent unsharp masking effect of the sandwich detector; 2 the rear FPD with a thicker scintillator provides a blurrier image than the front FPD, hence subtraction of the two images enhances edges in the resultant image. Since the physical characteristics of bone are affected by numerous factors, such as age, hormones, arthritis, and exercise, 3 a preclinical study with small animals with respect to those various factors would be helpful for theoretical and computational models of bone. 4 Moreover, longitudinal, histological studies without sacrificing animals are essential. 5, 6 In these regards, the x-ray microtomography (or micro-ct) has been popular for smallanimal bone studies Inspired by the aforementioned observation, we have applied the sandwich-detector concept to the microtomography (or micro-ct) for small-animal bone imaging. hokyung@pusan.ac.kr; phone ; fax
2 Figure 1. Conceptual illustration of the sandwich detector operation. Figure 2. Comparison of dual-energy postmortem mouse images obtained from (a) dual-shot (40/70 kvp switching) and (b) single-shot (using the sandwich detector at 70 kvp) methods. 2. MATERIALS AND METHODS As shown in Fig. 3, we have developed a bench-top micro-ct system with the sandwich detector. During continuous x-ray irradiation, the object rotates on its axis by an amount of prescribed step angle and then the rotation stays until the sandwich detector produces two projection images. These motion and image readout were computer-controlled and lasted till a single rotation completed. The distances from the x-ray focal spot to the detector (dsd ) and to the axis of rotation (dsa ) were computer-controlled variables. The traveling ranges of the object jig were 600, 300, and 75 mm along the x, y, and z directions, respectively. The x-ray source (Series 5000 XTF5011, Oxford Instruments, Inc., US) employed a tungsten anode and could operate up to the maximum power of 50 Watts. The tungsten x-ray spectra were further tailored by an additional 1-mm thick aluminum filter. According to the manufacturer, the nominal focal-spot size was mm. Each FPD layer constituting the sandwich detector employed a combination of a Gd2 O2 S:Tb phosphor screen for conversion of x-ray into optical quanta and a photodiode array for detection of them. The thicknesses of the front and rear phosphors were 34 and 67 mg cm 2, respectively. The same photodiode arrays (RadEye1TM, Teledyne Rad-icon Imaging Corp., Sunnyvale, US) were used for the front and rear FPDs. The pixel pitch of the photodiode array was mm, and the magnification of the pixel pitch of the rear detector was negligible. The active area of the sandwich detector was mm2. For a small-animal imaging, we prepared a postmortem mouse phantom ( 40 g) by replacing blood by paraformaldehyde as shown in Fig. 3. Bone-enhanced tomographic images may be obtained by reconstructing bone-enhanced projection data fbone (r) = FDK {WPF PR }, (1) where Pj denotes the projection data in a matrix form obtained from the jth FPD layer and W is a diagonal matrix consisting of weighting factors determined at each projection angle w(θ). The operator FDK { } implies the approximate filtered backprojection operation11 with the Hann filter. The w(θ) was determined by minimizing
3 Figure 3. Picture describing the micro-ct system with the sandwich detector. The enlarged views show the sandwich detector and a postmortem mouse phantom. contrast between the soft tissue to be subtracted and background. 2 If the weighting factor is independent upon the rotation angle, W becomes a scalar w. Head part of a mouse was scanned using two different designs of sandwich detector; one design used no intermediate filter and the other used a Cu filter with a thickness of 0.3 mm. Irradiation x-ray spectrum was from a tungsten target at 50 kvp/1 mm aluminum filter. 360 projection views were obtained for a single circular scan and they were used for reconstruction. All the reconstructed images were calibrated into the Hounsfield units (HU) using separate scans of water phantom. 3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Figure 4 compares projection images obtained from the each FPD layer of the two designs of sandwich detectors (i.e. one design included a 0.3 mm-thick Cu filter and the other did not) and their resultant DE images for the postmortem mouse phantom. The images were displayed with the level of their mean value (µ) and a window of two times their standard deviation (σ) (other images below were displayed with the same level and window). It was observed that the projections from the front FPD were sharper than those from the rear FPD as the font FPD employed a thinner phosphor than the rear FPD. Comparing Figs. 4(b) with (e), use of the intermediate filter resulted in higher noise in the rear FPD image, and the reason could be explained by the reduction in the number of x-ray photons reaching the rear FPD due to the attenuation through the filter layer. Weighted logarithmic subtraction successfully provided bone-enhanced images as shown in Figs. 4(c) and (f). Tomographic images reconstructed using each projection dataset, as exemplary shown in Fig. 4, are summarized in Fig. 5. The characteristics observed from the projection data were well reflected into the tomographic images. Comparing Figs. 5(c) with (f), use of the intermediate filter gave rise to a more reduction of soft tissues. It was also observed that the DE tomographic images showed less streak artifacts due to photon starvation compared to the images obtained using the front FPD. As shown in Fig. 6, the regions indicated as boxes in Fig. 5(d) have been investigated in detail. The rear FPD with a thick phosphor provided a blur image as shown in Fig. 6(b), and it became noisier, as shown in Fig. 6(e), when the Cu filter was additionally used. The DE tomographic image obtained form the sandwich detector without any filter layers showed the best visual performance for bone details. Figure 7 compares profiles extracted along the line A A (as possible as we can), as designated in Fig. 5(a), for each reconstruction image. Bone signal in the reconstructed image with projections from the front FPD was the largest, the rear FPD the second, and then the DE results. Although the DE tomographic image signals were noisy, they consisted mostly of bone signals. As observed from Figs. 4(e) and 5(e), the images obtained from the rear FPD of the sandwich detector with the Cu filter were noisy.
4 Figure 4. Projection images obtained from the each FPD layer of the sandwich detectors without and with a Cu filter layer and their resultant DE images for the postmortem mouse phantom. (L/W = µ/ ± 2σ).
5 Figure 5. Comparison of tomographic images reconstructed from the corresponding projection dataset. Figure 6. Enlarged images indicated by the boxes Fig. 5(d) for more detailed displays of tomographic images.
6 Figure 7. Profiles extracted along the line A A, as designated in Fig. 5(a), for each corresponding reconstruction image. In the present work, the bone-enhanced tomographic image was obtained by reconstructing weighted-subtraction sinogram. Alternatively, the bone-enhanced images may also be obtained by subtraction of two tomographic images reconstructed with projections obtained from the front and rear FPDs f bone (r) = wfdk {P F } FDK {P R }. (2) This approach is under progress and comparison with the present method will be made. Furthermore, the boneenhanced DE tomographic images may be combined with the images reconstructed with projections obtained from the front FPD as the conventional unsharp masking digital image processing. The authors anticipate the resultant images will be conventional tomographic images which include more pronounced bone details. These further studies will be a separate future study. 4. CONCLUSION Bone-enhanced tomographic images have been obtained using dual-energy sandwich detectors for a postmortem mouse phantom, and they outperformed the tomographic images obtained from the conventional detectors (i.e. the front and rear flat-panel detectors constituting the sandwich detectors) for bone details. Although use of an intermediate filter, which was placed between the front and rear flat-panel detectors, resulted in less residual soft tissues in the reconstructed bone-enhanced images, it degraded the visual image quality of bone details because of increased noise. Optimal filter design in terms of material and thickness is required for a more tissue separability and less noise performance in images. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) grants funded by the Korea government (MSIP) (No. 2013M2A2A and No. 2014R1A2A2A ). REFERENCES 1. S. Yun, J. C. Han, D. W. Kim, H. Youn, H. K. Kim, J. Tanguay, and I. A. Cunningham, Feasibility of active sandwich detectors for single-shot dual-energy imaging, Proc. SPIE 9033, pp T 90335T 8, 2014.
7 2. J. C. Han, H. K. Kim, D. W. Kim, S. Yun, H. Youn, S. Kam, J. Tanguay, and I. A. Cunningham, Singleshot dual-energy x-ray imaging with a flat-panel sandwich detector for preclinical imaging, Cur. Appl. Phys. 14(12), pp , J.-T. Hsu, Y.-J. Chen, J.-T. Ho, H.-L. Huang, S.-P. Wang, F.-C. Cheng, J. Wu, and M.-T. Tsai, A comparison of micro-ct and dental CT in assessing cortical bone morphology and trabecular bone microarchitecture, PLoS ONE 9, p. e107545, N. A. Hanson and C. M. Bagi, Alternative approach to assessment of bone quality using micro-computed tomography, Bone 35(1), pp , E. L. Ritman, Molecular imaging in small animals - Roles for micro-ct, J. Cell. Biochem. 87(S39), pp , S. C. Lee, H. K. Kim, I. K. Chun, M. H. Cho, S. Y. Lee, and M. H. Cho, A flat-panel detector based micro- CT system: Performance evaluation for small-animal imaging, Phy. Med. Biol. 48(24), pp , M. J. Paulus, S. S. Gleason, S. J. Kennel, P. R. Hunsicker, and D. K. Johnson, High resolution x-ray computed tomography: An emerging tool for small animal cancer research, Neoplasia 2(1-2), pp , D. W. Holdsworth and M. M. Thornton, Micro-CT in small animal and specimen imaging, Trends Biotechnol. 20(8), pp. S34 S39, E. L. Ritman, Micro-computed tomography - Current status and developments, Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 6(1), pp , D. Clark and C. Badea, Micro-CT of rodents: State-of-the-art and future perspectives, Phys. Medica 30(6), pp , L. A. Feldkamp, L. C. Davis, and J. W. Kress, Practical cone-beam algorithm, J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 1, pp , Jun 1984.
MTF and NPS of single-shot dual-energy sandwich detectors
 MTF and NPS of single-shot dual-energy sandwich detectors Junwoo Kim, a Dong Woon Kim, a Hanbean Youn, b,c Ho Kyung Kim a,c a School of Mechanical Engineering, Pusan National University, Busan 609-735,
MTF and NPS of single-shot dual-energy sandwich detectors Junwoo Kim, a Dong Woon Kim, a Hanbean Youn, b,c Ho Kyung Kim a,c a School of Mechanical Engineering, Pusan National University, Busan 609-735,
VOLUMETRIC computed tomography (CT) based on flatpanel
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NUCLEAR SCIENCE, VOL. 56, NO. 3, JUNE 2009 1179 Radiation Effects on the Performance of CMOS Photodiode Array Detectors and the Role of Gain-Offset Corrections Ho Kyung Kim, Min Kook
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NUCLEAR SCIENCE, VOL. 56, NO. 3, JUNE 2009 1179 Radiation Effects on the Performance of CMOS Photodiode Array Detectors and the Role of Gain-Offset Corrections Ho Kyung Kim, Min Kook
Performance Evaluation of a Flat-panel Detector-based Microtomography System for Small-animal Imaging
 Performance Evaluation of a Flat-panel Detector-based Microtomography System for Small-animal Imaging Ho Kyung Kim, Sang Chul Lee, In Kon Chun, Myung Hye Cho, Min Hyoung Cho, Member, IEEE, Soo Yeol Lee
Performance Evaluation of a Flat-panel Detector-based Microtomography System for Small-animal Imaging Ho Kyung Kim, Sang Chul Lee, In Kon Chun, Myung Hye Cho, Min Hyoung Cho, Member, IEEE, Soo Yeol Lee
Optimization of Energy Modulation Filter for Dual Energy CBCT Using Geant4 Monte-Carlo Simulation
 Original Article PROGRESS in MEDICAL PHYSICS 27(3), Sept. 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2016.27.3.125 pissn 2508-4445, eissn 2508-4453 Optimization of Energy Modulation Filter for Dual Energy CBCT
Original Article PROGRESS in MEDICAL PHYSICS 27(3), Sept. 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2016.27.3.125 pissn 2508-4445, eissn 2508-4453 Optimization of Energy Modulation Filter for Dual Energy CBCT
Introduction. Chapter 16 Diagnostic Radiology. Primary radiological image. Primary radiological image
 Introduction Chapter 16 Diagnostic Radiology Radiation Dosimetry I Text: H.E Johns and J.R. Cunningham, The physics of radiology, 4 th ed. http://www.utoledo.edu/med/depts/radther In diagnostic radiology
Introduction Chapter 16 Diagnostic Radiology Radiation Dosimetry I Text: H.E Johns and J.R. Cunningham, The physics of radiology, 4 th ed. http://www.utoledo.edu/med/depts/radther In diagnostic radiology
Digital Detector Array Image Quality for Various GOS Scintillators
 Digital Detector Array Image Quality for Various GOS Scintillators More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=22768 Brian S. White 1, Mark E. Shafer 2, William H. Russel 3, Eric Fallet 4, Jacques
Digital Detector Array Image Quality for Various GOS Scintillators More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=22768 Brian S. White 1, Mark E. Shafer 2, William H. Russel 3, Eric Fallet 4, Jacques
The effect of focal spot size on the spatial resolution of variable resolution X-ray CT scanner
 The effect of focal spot size on the spatial resolution of variable resolution X-ray CT scanner H. Arabi, A.R. Kamali Asl *, S.M. Aghamiri Iran. J. Radiat. Res., 2010; 8 (1): 37-43 Radiation Medicine Department,
The effect of focal spot size on the spatial resolution of variable resolution X-ray CT scanner H. Arabi, A.R. Kamali Asl *, S.M. Aghamiri Iran. J. Radiat. Res., 2010; 8 (1): 37-43 Radiation Medicine Department,
HISTORY. CT Physics with an Emphasis on Application in Thoracic and Cardiac Imaging SUNDAY. Shawn D. Teague, MD
 CT Physics with an Emphasis on Application in Thoracic and Cardiac Imaging Shawn D. Teague, MD DISCLOSURES 3DR- advisory committee CT PHYSICS WITH AN EMPHASIS ON APPLICATION IN THORACIC AND CARDIAC IMAGING
CT Physics with an Emphasis on Application in Thoracic and Cardiac Imaging Shawn D. Teague, MD DISCLOSURES 3DR- advisory committee CT PHYSICS WITH AN EMPHASIS ON APPLICATION IN THORACIC AND CARDIAC IMAGING
An aging study of the signal and noise characteristics in large-area CMOS detectors
 An aging study of the signal and noise characteristics in large-area CMOS detectors Jong Chul Han a, Seungman Yun a, Chang Hwy Lim a, Tae Gyun Youm a, Sung Kyn Heo b, Tae Woo Kim b, Ian Cunningham c, Ho
An aging study of the signal and noise characteristics in large-area CMOS detectors Jong Chul Han a, Seungman Yun a, Chang Hwy Lim a, Tae Gyun Youm a, Sung Kyn Heo b, Tae Woo Kim b, Ian Cunningham c, Ho
Geometric image distortion in flat-panel X-ray detectors and its influence on the accuracy of CT-based dimensional measurements
 Geometric image distortion in flat-panel X-ray detectors and its influence on the accuracy of CT-based dimensional measurements Daniel Weiß, Ronald Lonardoni, Andreas Deffner, Christoph Kuhn Carl Zeiss
Geometric image distortion in flat-panel X-ray detectors and its influence on the accuracy of CT-based dimensional measurements Daniel Weiß, Ronald Lonardoni, Andreas Deffner, Christoph Kuhn Carl Zeiss
Four-dimensional Computed Tomography (4D CT) Concepts and Preliminary Development
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ORIGINAL ARTICLE Radiation Medicine: Vol. 21 No. 1, 17 22 p.p., 2003 Four-dimensional Computed Tomography (4D CT) Concepts and Preliminary Development Masahiro Endo,* Takanori Tsunoo,*
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ORIGINAL ARTICLE Radiation Medicine: Vol. 21 No. 1, 17 22 p.p., 2003 Four-dimensional Computed Tomography (4D CT) Concepts and Preliminary Development Masahiro Endo,* Takanori Tsunoo,*
Data. microcat +SPECT
 Data microcat +SPECT microcat at a Glance Designed to meet the throughput, resolution and image quality requirements of academic and pharmaceutical research, the Siemens microcat sets the standard for
Data microcat +SPECT microcat at a Glance Designed to meet the throughput, resolution and image quality requirements of academic and pharmaceutical research, the Siemens microcat sets the standard for
Reconstruction Filtering in Industrial gamma-ray CT Application
 Reconstruction Filtering in Industrial gamma-ray CT Application Lakshminarayana Yenumula *, Rajesh V Acharya, Umesh Kumar, and Ashutosh Dash Industrial Tomography and Instrumentation Section, Isotope Production
Reconstruction Filtering in Industrial gamma-ray CT Application Lakshminarayana Yenumula *, Rajesh V Acharya, Umesh Kumar, and Ashutosh Dash Industrial Tomography and Instrumentation Section, Isotope Production
MC SIMULATION OF SCATTER INTENSITIES IN A CONE-BEAM CT SYSTEM EMPLOYING A 450 kv X-RAY TUBE
 MC SIMULATION OF SCATTER INTENSITIES IN A CONE-BEAM CT SYSTEM EMPLOYING A 450 kv X-RAY TUBE A. Miceli ab, R. Thierry a, A. Flisch a, U. Sennhauser a, F. Casali b a Empa - Swiss Federal Laboratories for
MC SIMULATION OF SCATTER INTENSITIES IN A CONE-BEAM CT SYSTEM EMPLOYING A 450 kv X-RAY TUBE A. Miceli ab, R. Thierry a, A. Flisch a, U. Sennhauser a, F. Casali b a Empa - Swiss Federal Laboratories for
Pitfalls and Remedies of MDCT Scanners as Quantitative Instruments
 intensity m(e) m (/cm) 000 00 0 0. 0 50 0 50 Pitfalls and Remedies of MDCT Scanners as Jiang Hsieh, PhD GE Healthcare Technology University of Wisconsin-Madison Root-Causes of CT Number Inaccuracies Nature
intensity m(e) m (/cm) 000 00 0 0. 0 50 0 50 Pitfalls and Remedies of MDCT Scanners as Jiang Hsieh, PhD GE Healthcare Technology University of Wisconsin-Madison Root-Causes of CT Number Inaccuracies Nature
Scatter Correction by Modulation of Primary Radiation in Industrial X-ray CT: Beam-hardening Effects and their Correction
 International Symposium on Digital Industrial Radiology and Computed Tomography - Mo.3.2 Scatter Correction by Modulation of Primary Radiation in Industrial X-ray CT: Beam-hardening Effects and their Correction
International Symposium on Digital Industrial Radiology and Computed Tomography - Mo.3.2 Scatter Correction by Modulation of Primary Radiation in Industrial X-ray CT: Beam-hardening Effects and their Correction
SECTION I - CHAPTER 2 DIGITAL IMAGING PROCESSING CONCEPTS
 RADT 3463 - COMPUTERIZED IMAGING Section I: Chapter 2 RADT 3463 Computerized Imaging 1 SECTION I - CHAPTER 2 DIGITAL IMAGING PROCESSING CONCEPTS RADT 3463 COMPUTERIZED IMAGING Section I: Chapter 2 RADT
RADT 3463 - COMPUTERIZED IMAGING Section I: Chapter 2 RADT 3463 Computerized Imaging 1 SECTION I - CHAPTER 2 DIGITAL IMAGING PROCESSING CONCEPTS RADT 3463 COMPUTERIZED IMAGING Section I: Chapter 2 RADT
X-RAY COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY
 X-RAY COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Bc. Jan Kratochvíla Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering Abstract Computed tomography is a powerful tool for imaging the inner
X-RAY COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Bc. Jan Kratochvíla Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Nuclear Sciences and Physical Engineering Abstract Computed tomography is a powerful tool for imaging the inner
Amorphous Selenium Direct Radiography for Industrial Imaging
 DGZfP Proceedings BB 67-CD Paper 22 Computerized Tomography for Industrial Applications and Image Processing in Radiology March 15-17, 1999, Berlin, Germany Amorphous Selenium Direct Radiography for Industrial
DGZfP Proceedings BB 67-CD Paper 22 Computerized Tomography for Industrial Applications and Image Processing in Radiology March 15-17, 1999, Berlin, Germany Amorphous Selenium Direct Radiography for Industrial
DOUBLE gated in vivo small animal cone beam micro
 Low Dose Phase Correlated Cone Beam Micro CT of Small Animals Stefan Sawall, Frank Bergner, Robert Lapp, Markus Mronz, Marek Karolczak, Andreas Hess, and Marc Kachelrieß, Member, IEEE I. INTRODUCTION DOUBLE
Low Dose Phase Correlated Cone Beam Micro CT of Small Animals Stefan Sawall, Frank Bergner, Robert Lapp, Markus Mronz, Marek Karolczak, Andreas Hess, and Marc Kachelrieß, Member, IEEE I. INTRODUCTION DOUBLE
Mammography is a radiographic procedure specially designed for detecting breast pathology Approximately 1 woman in 8 will develop breast cancer over
 Mammography is a radiographic procedure specially designed for detecting breast pathology Approximately 1 woman in 8 will develop breast cancer over a lifetime Breast cancer screening programs rely on
Mammography is a radiographic procedure specially designed for detecting breast pathology Approximately 1 woman in 8 will develop breast cancer over a lifetime Breast cancer screening programs rely on
Breast Tomosynthesis. Bob Liu, Ph.D. Department of Radiology Massachusetts General Hospital And Harvard Medical School
 Breast Tomosynthesis Bob Liu, Ph.D. Department of Radiology Massachusetts General Hospital And Harvard Medical School Outline Physics aspects of breast tomosynthesis Quality control of breast tomosynthesis
Breast Tomosynthesis Bob Liu, Ph.D. Department of Radiology Massachusetts General Hospital And Harvard Medical School Outline Physics aspects of breast tomosynthesis Quality control of breast tomosynthesis
Chromatic X-Ray imaging with a fine pitch CdTe sensor coupled to a large area photon counting pixel ASIC
 Chromatic X-Ray imaging with a fine pitch CdTe sensor coupled to a large area photon counting pixel ASIC R. Bellazzini a,b, G. Spandre a*, A. Brez a, M. Minuti a, M. Pinchera a and P. Mozzo b a INFN Pisa
Chromatic X-Ray imaging with a fine pitch CdTe sensor coupled to a large area photon counting pixel ASIC R. Bellazzini a,b, G. Spandre a*, A. Brez a, M. Minuti a, M. Pinchera a and P. Mozzo b a INFN Pisa
Gas scintillation Glass GEM detector for high-resolution X-ray imaging and CT
 Gas scintillation Glass GEM detector for high-resolution X-ray imaging and CT Takeshi Fujiwara 1, Yuki Mitsuya 2, Hiroyuki Takahashi 2, and Hiroyuki Toyokawa 2 1 National Institute of Advanced Industrial
Gas scintillation Glass GEM detector for high-resolution X-ray imaging and CT Takeshi Fujiwara 1, Yuki Mitsuya 2, Hiroyuki Takahashi 2, and Hiroyuki Toyokawa 2 1 National Institute of Advanced Industrial
Moving from film to digital: A study of digital x-ray benefits, challenges and best practices
 Moving from film to digital: A study of digital x-ray benefits, challenges and best practices H.U. Pöhler 1 and N. D Ademo 2 DÜRR NDT GmbH & Co. KG, Höpfigheimer Straße 22, Bietigheim-Bissingen, 74321,
Moving from film to digital: A study of digital x-ray benefits, challenges and best practices H.U. Pöhler 1 and N. D Ademo 2 DÜRR NDT GmbH & Co. KG, Höpfigheimer Straße 22, Bietigheim-Bissingen, 74321,
Detector technology in simultaneous spectral imaging
 Computed tomography Detector technology in simultaneous spectral imaging Philips IQon Spectral CT Z. Romman, I. Uman, Y. Yagil, D. Finzi, N. Wainer, D. Milstein; Philips Healthcare While CT has become
Computed tomography Detector technology in simultaneous spectral imaging Philips IQon Spectral CT Z. Romman, I. Uman, Y. Yagil, D. Finzi, N. Wainer, D. Milstein; Philips Healthcare While CT has become
diagnostic examination
 RADIOLOGICAL PHYSICS 2011 Raphex diagnostic examination Adel A. Mustafa, Ph.D., Editor PUBLISHED FOR: RAMPS (Radiological and Medical Physics Society of New York) preface The RAPHEX Diagnostic exam 2011
RADIOLOGICAL PHYSICS 2011 Raphex diagnostic examination Adel A. Mustafa, Ph.D., Editor PUBLISHED FOR: RAMPS (Radiological and Medical Physics Society of New York) preface The RAPHEX Diagnostic exam 2011
Thermionic x-ray. Alternative technologies. Electron Field Emission. CNT Based Field Emission X-Ray Source
 Energy Level (ev) Multi-beam x-ray source array based on carbon nanotube field emission O. Zhou, JP Lu, X. Calderon-Colon, X. Qian, G. Yang, G. Cao, E. Gidcumb, A. Tucker, J. Shan University of North Carolina
Energy Level (ev) Multi-beam x-ray source array based on carbon nanotube field emission O. Zhou, JP Lu, X. Calderon-Colon, X. Qian, G. Yang, G. Cao, E. Gidcumb, A. Tucker, J. Shan University of North Carolina
Current technology in digital image production (CR/DR and other modalities) Jaroonroj Wongnil 25 Mar 2016
 Current technology in digital image production (CR/DR and other modalities) Jaroonroj Wongnil 25 Mar 2016 Current technology in digital image production (CR/DR and other modalities) 2/ Overview Digital
Current technology in digital image production (CR/DR and other modalities) Jaroonroj Wongnil 25 Mar 2016 Current technology in digital image production (CR/DR and other modalities) 2/ Overview Digital
CHAPTER 2 COMMISSIONING OF KILO-VOLTAGE CONE BEAM COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY FOR IMAGE-GUIDED RADIOTHERAPY
 14 CHAPTER 2 COMMISSIONING OF KILO-VOLTAGE CONE BEAM COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY FOR IMAGE-GUIDED RADIOTHERAPY 2.1 INTRODUCTION kv-cbct integrated with linear accelerators as a tool for IGRT, was developed to
14 CHAPTER 2 COMMISSIONING OF KILO-VOLTAGE CONE BEAM COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY FOR IMAGE-GUIDED RADIOTHERAPY 2.1 INTRODUCTION kv-cbct integrated with linear accelerators as a tool for IGRT, was developed to
Niklas Norrby 12/17/2010
 LINKÖPINGS UNIVERSITET Nanotomography Synchrotron radiation course project Niklas Norrby 12/17/2010 Introduction Tomography is a method to image three-dimensional objects by illumination from different
LINKÖPINGS UNIVERSITET Nanotomography Synchrotron radiation course project Niklas Norrby 12/17/2010 Introduction Tomography is a method to image three-dimensional objects by illumination from different
DALLA LUCE VISIBILE AI RAGGI X: NUOVI RIVELATORI DI IMMAGINI PER RAGGI X A DISCRIMINAZIONE IN ENERGIA ED APPLICAZIONI
 DALLA LUCE VISIBILE AI RAGGI X: NUOVI RIVELATORI DI IMMAGINI PER RAGGI X A DISCRIMINAZIONE IN ENERGIA ED APPLICAZIONI D. Pacella ENEA - Frascati LIMS, Frascati 14-15 ottobre 2015 Come per la fotografia:
DALLA LUCE VISIBILE AI RAGGI X: NUOVI RIVELATORI DI IMMAGINI PER RAGGI X A DISCRIMINAZIONE IN ENERGIA ED APPLICAZIONI D. Pacella ENEA - Frascati LIMS, Frascati 14-15 ottobre 2015 Come per la fotografia:
Photon Counting and Energy Discriminating X-Ray Detectors - Benefits and Applications
 19 th World Conference on Non-Destructive Testing 2016 Photon Counting and Energy Discriminating X-Ray Detectors - Benefits and Applications David WALTER 1, Uwe ZSCHERPEL 1, Uwe EWERT 1 1 BAM Bundesanstalt
19 th World Conference on Non-Destructive Testing 2016 Photon Counting and Energy Discriminating X-Ray Detectors - Benefits and Applications David WALTER 1, Uwe ZSCHERPEL 1, Uwe EWERT 1 1 BAM Bundesanstalt
Suppression of metal artifacts using image-based monoenergetic DECT imaging
 Suppression of metal artifacts using image-based monoenergetic DECT imaging Poster No.: C-0519 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: B. Krauss, B. Schmidt, M. Sedlmair, T. Flohr; Forchheim/DE
Suppression of metal artifacts using image-based monoenergetic DECT imaging Poster No.: C-0519 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: B. Krauss, B. Schmidt, M. Sedlmair, T. Flohr; Forchheim/DE
I. PERFORMANCE OF X-RAY PRODUCTION COMPONENTS FLUOROSCOPIC ACCEPTANCE TESTING: TEST PROCEDURES & PERFORMANCE CRITERIA
 FLUOROSCOPIC ACCEPTANCE TESTING: TEST PROCEDURES & PERFORMANCE CRITERIA EDWARD L. NICKOLOFF DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY NEW YORK, NY ACCEPTANCE TESTING GOALS PRIOR TO 1st CLINICAL USAGE
FLUOROSCOPIC ACCEPTANCE TESTING: TEST PROCEDURES & PERFORMANCE CRITERIA EDWARD L. NICKOLOFF DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY NEW YORK, NY ACCEPTANCE TESTING GOALS PRIOR TO 1st CLINICAL USAGE
Tomosynthesis. Energy Subtraction. Long View Imaging
 Freedom and Flexibility in Imaging Experience a wide range of applications targeted to improve diagnostic capabilities combined with a precise design that facilitates imaging. With unique image processing
Freedom and Flexibility in Imaging Experience a wide range of applications targeted to improve diagnostic capabilities combined with a precise design that facilitates imaging. With unique image processing
Studies on reduction of exposure dose using digital scattered X-ray removal processing
 Studies on reduction of exposure dose using digital scattered X-ray removal processing Poster No.: C-1834 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Kashiyama, M. Funahashi, T. Nakaoka, T.
Studies on reduction of exposure dose using digital scattered X-ray removal processing Poster No.: C-1834 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Kashiyama, M. Funahashi, T. Nakaoka, T.
Studies on reduction of exposure dose using digital scattered X-ray removal processing
 Studies on reduction of exposure dose using digital scattered X-ray removal processing Poster No.: C-1834 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Kashiyama, M. Funahashi, T. Nakaoka, T.
Studies on reduction of exposure dose using digital scattered X-ray removal processing Poster No.: C-1834 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Kashiyama, M. Funahashi, T. Nakaoka, T.
Distributed source x-ray tube technology for tomosynthesis imaging
 Distributed source x-ray tube technology for tomosynthesis imaging Authors: F. Sprenger a*, X. Calderon-Colon b, Y. Cheng a, K. Englestad a, J. Lu b, J. Maltz c, A. Paidi c, X. Qian b, D. Spronk a, S.
Distributed source x-ray tube technology for tomosynthesis imaging Authors: F. Sprenger a*, X. Calderon-Colon b, Y. Cheng a, K. Englestad a, J. Lu b, J. Maltz c, A. Paidi c, X. Qian b, D. Spronk a, S.
Philip Sperling. Sales Science and New Materials, YXLON International GmbH, Essener Bogen 15, Hamburg, Germany.
 A new generation of x-ray computed tomography devices for quality inspection and metrology inspection in the field of additive manufacturing and other sciences Philip Sperling Sales Science and New Materials,
A new generation of x-ray computed tomography devices for quality inspection and metrology inspection in the field of additive manufacturing and other sciences Philip Sperling Sales Science and New Materials,
K-edge subtraction X-ray imaging with a pixellated spectroscopic detector
 K-edge subtraction X-ray imaging with a pixellated spectroscopic detector Silvia Pani Department of Physics, University of Surrey Summary Hyperspectral imaging K-edge subtraction X-ray imaging for mammography
K-edge subtraction X-ray imaging with a pixellated spectroscopic detector Silvia Pani Department of Physics, University of Surrey Summary Hyperspectral imaging K-edge subtraction X-ray imaging for mammography
Metal Artifact Reduction for Orthopedic Implants (O-MAR)
 Metal Artifact Reduction for Orthopedic Implants () Summary Since the inception of CT, numerous methods have been proposed to suppress metal artifacts with varying degrees of success. 1-4 (Metal Artifact
Metal Artifact Reduction for Orthopedic Implants () Summary Since the inception of CT, numerous methods have been proposed to suppress metal artifacts with varying degrees of success. 1-4 (Metal Artifact
12/21/2016. Siemens Medical Systems Research Agreement Philips Healthcare Research Agreement AAN and ASN Committees
 Joseph V. Fritz, PhD Nandor Pintor, MD Dent Neurologic Institute ASN 2017 Friday, January 20, 2017 Siemens Medical Systems Research Agreement Philips Healthcare Research Agreement AAN and ASN Committees
Joseph V. Fritz, PhD Nandor Pintor, MD Dent Neurologic Institute ASN 2017 Friday, January 20, 2017 Siemens Medical Systems Research Agreement Philips Healthcare Research Agreement AAN and ASN Committees
CT Basics: Data Acquisition Module 3
 Module 3 Transcript For educational and institutional use. This transcript is licensed for noncommercial, educational inhouse or online educational course use only in educational and corporate institutions.
Module 3 Transcript For educational and institutional use. This transcript is licensed for noncommercial, educational inhouse or online educational course use only in educational and corporate institutions.
Maximizing clinical outcomes
 Maximizing clinical outcomes Digital Tomosynthesis Dual Energy Subtraction Automated Long Length Imaging Improved image quality at a low dose Xray Xray Patented ISS capture technology promotes high sensitivity
Maximizing clinical outcomes Digital Tomosynthesis Dual Energy Subtraction Automated Long Length Imaging Improved image quality at a low dose Xray Xray Patented ISS capture technology promotes high sensitivity
Development of a large-area CMOS-based detector for real-time x-ray imaging
 Development of a large-area CMOS-based detector for real-time x-ray imaging Sung Kyn Heo a, Sung Kyu Park a, Sung Ha Hwang a, Dong Ak Im a, Jari Kosonen a, Tae Woo Kim a, Seungman Yun b, Ho Kyung Kim b*
Development of a large-area CMOS-based detector for real-time x-ray imaging Sung Kyn Heo a, Sung Kyu Park a, Sung Ha Hwang a, Dong Ak Im a, Jari Kosonen a, Tae Woo Kim a, Seungman Yun b, Ho Kyung Kim b*
Uncertainty in CT Metrology: Visualizations for Exploration and Analysis of Geometric Tolerances
 Uncertainty in CT Metrology: Visualizations for Exploration and Analysis of Geometric Tolerances Artem Amirkhanov 1, Bernhard Fröhler 1, Michael Reiter 1, Johann Kastner 1, M. Eduard Grӧller 2, Christoph
Uncertainty in CT Metrology: Visualizations for Exploration and Analysis of Geometric Tolerances Artem Amirkhanov 1, Bernhard Fröhler 1, Michael Reiter 1, Johann Kastner 1, M. Eduard Grӧller 2, Christoph
Synchrotron X-ray tomographic microscopy Theory vs. practice
 Synchrotron X-ray tomographic microscopy Theory vs. practice Federica Marone Swiss Light Source, Paul Scherrer Institut, Villigen, Switzerland Theory Radon transform Rf x = Beer-Lambert law I E = I 0 (E)e
Synchrotron X-ray tomographic microscopy Theory vs. practice Federica Marone Swiss Light Source, Paul Scherrer Institut, Villigen, Switzerland Theory Radon transform Rf x = Beer-Lambert law I E = I 0 (E)e
Applications of the Cracow X-Ray Microprobe in Tomography
 Vol. 115 (2009) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 2 Proceedings of the XLII Zakopane School of Physics, Zakopane 2008 Applications of the Cracow X-Ray Microprobe in Tomography J. Bielecki a, S. Bożek a,b, J.
Vol. 115 (2009) ACTA PHYSICA POLONICA A No. 2 Proceedings of the XLII Zakopane School of Physics, Zakopane 2008 Applications of the Cracow X-Ray Microprobe in Tomography J. Bielecki a, S. Bożek a,b, J.
An Introduction to TG-142 Imaging QA Using Standard Imaging Products. Mark Wiesmeyer, PhD, DABR Technical Product Manager Standard Imaging, Inc.
 An Introduction to TG-142 Imaging QA Using Standard Imaging Products Mark Wiesmeyer, PhD, DABR Technical Product Manager Standard Imaging, Inc. Goals Understand the nature and intent of TG 142 imaging
An Introduction to TG-142 Imaging QA Using Standard Imaging Products Mark Wiesmeyer, PhD, DABR Technical Product Manager Standard Imaging, Inc. Goals Understand the nature and intent of TG 142 imaging
Mammography: Physics of Imaging
 Mammography: Physics of Imaging Robert G. Gould, Sc.D. Professor and Vice Chair Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging University of California San Francisco, California Mammographic Imaging: Uniqueness
Mammography: Physics of Imaging Robert G. Gould, Sc.D. Professor and Vice Chair Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging University of California San Francisco, California Mammographic Imaging: Uniqueness
Efficacy of Beam-Hardening Correction for Vascular Morphometry Using 3D Conebeam Micro-CT
 Marquette University e-publications@marquette Biomedical Engineering Faculty Research and Publications Biomedical Engineering, Department of 1-1-1999 Efficacy of Beam-Hardening Correction for Vascular
Marquette University e-publications@marquette Biomedical Engineering Faculty Research and Publications Biomedical Engineering, Department of 1-1-1999 Efficacy of Beam-Hardening Correction for Vascular
Digital Radiography : Flat Panel
 Digital Radiography : Flat Panel Flat panels performances & operation How does it work? - what is a sensor? - ideal sensor Flat panels limits and solutions - offset calibration - gain calibration - non
Digital Radiography : Flat Panel Flat panels performances & operation How does it work? - what is a sensor? - ideal sensor Flat panels limits and solutions - offset calibration - gain calibration - non
An EM Reconstruction with Improved Signal-to. to-noise Ratio for Coded Aperture Imaging
 An EM Reconstruction with Improved Signal-to to-noise Ratio for Coded Aperture Imaging Cynthia Tozian, PhD UMass Lowell Bristol-Myers Squibb Medical Imaging Young Investigators Symposium April 12, 2006
An EM Reconstruction with Improved Signal-to to-noise Ratio for Coded Aperture Imaging Cynthia Tozian, PhD UMass Lowell Bristol-Myers Squibb Medical Imaging Young Investigators Symposium April 12, 2006
Seminar 8. Radiology S8 1
 Seminar 8 Radiology Medical imaging. X-ray image formation. Energizing and controlling the X-ray tube. Image detectors. The acquisition of analog and digital images. Digital image processing. Selected
Seminar 8 Radiology Medical imaging. X-ray image formation. Energizing and controlling the X-ray tube. Image detectors. The acquisition of analog and digital images. Digital image processing. Selected
TDI Imaging: An Efficient AOI and AXI Tool
 TDI Imaging: An Efficient AOI and AXI Tool Yakov Bulayev Hamamatsu Corporation Bridgewater, New Jersey Abstract As a result of heightened requirements for quality, integrity and reliability of electronic
TDI Imaging: An Efficient AOI and AXI Tool Yakov Bulayev Hamamatsu Corporation Bridgewater, New Jersey Abstract As a result of heightened requirements for quality, integrity and reliability of electronic
Migrating from traditional to Digital Radiography in Aerospace
 Migrating from traditional to Digital Radiography in Aerospace More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=22663 Abstract Lennart Schulenburg VisiConsult X-ray System & Solutions GmbH Brandenbrooker
Migrating from traditional to Digital Radiography in Aerospace More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=22663 Abstract Lennart Schulenburg VisiConsult X-ray System & Solutions GmbH Brandenbrooker
Acceptance Testing of a Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Unit
 Acceptance Testing of a Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Unit 2012 AAPM Spring Clinical Meeting Jessica Clements, M.S., DABR Objectives Review of technology and clinical advantages Acceptance Testing Procedures
Acceptance Testing of a Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Unit 2012 AAPM Spring Clinical Meeting Jessica Clements, M.S., DABR Objectives Review of technology and clinical advantages Acceptance Testing Procedures
Observational Astronomy
 Observational Astronomy Instruments The telescope- instruments combination forms a tightly coupled system: Telescope = collecting photons and forming an image Instruments = registering and analyzing the
Observational Astronomy Instruments The telescope- instruments combination forms a tightly coupled system: Telescope = collecting photons and forming an image Instruments = registering and analyzing the
PD233: Design of Biomedical Devices and Systems
 PD233: Design of Biomedical Devices and Systems (Lecture-8 Medical Imaging Systems) (Imaging Systems Basics, X-ray and CT) Dr. Manish Arora CPDM, IISc Course Website: http://cpdm.iisc.ac.in/utsaah/courses/
PD233: Design of Biomedical Devices and Systems (Lecture-8 Medical Imaging Systems) (Imaging Systems Basics, X-ray and CT) Dr. Manish Arora CPDM, IISc Course Website: http://cpdm.iisc.ac.in/utsaah/courses/
Development of Solid-State Detector for X-ray Computed Tomography
 Proceedings of the Korea Nuclear Society Autumn Meeting Seoul, Korea, October 2001 Development of Solid-State Detector for X-ray Computed Tomography S.W Kwak 1), H.K Kim 1), Y. S Kim 1), S.C Jeon 1), G.
Proceedings of the Korea Nuclear Society Autumn Meeting Seoul, Korea, October 2001 Development of Solid-State Detector for X-ray Computed Tomography S.W Kwak 1), H.K Kim 1), Y. S Kim 1), S.C Jeon 1), G.
Evaluation of a Chip LED Sensor Module at 770 nm for Fat Thickness Measurement of Optical Tissue Phantoms and Human Body Tissue
 Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 51, No. 5, November 2007, pp. 1663 1667 Evaluation of a Chip LED Sensor Module at 770 nm for Fat Thickness Measurement of Optical Tissue Phantoms and Human
Journal of the Korean Physical Society, Vol. 51, No. 5, November 2007, pp. 1663 1667 Evaluation of a Chip LED Sensor Module at 770 nm for Fat Thickness Measurement of Optical Tissue Phantoms and Human
Enhanced Functionality of High-Speed Image Processing Engine SUREengine PRO. Sharpness (spatial resolution) Graininess (noise intensity)
 Vascular Enhanced Functionality of High-Speed Image Processing Engine SUREengine PRO Medical Systems Division, Shimadzu Corporation Yoshiaki Miura 1. Introduction In recent years, digital cardiovascular
Vascular Enhanced Functionality of High-Speed Image Processing Engine SUREengine PRO Medical Systems Division, Shimadzu Corporation Yoshiaki Miura 1. Introduction In recent years, digital cardiovascular
LECTURE 1 The Radiographic Image
 LECTURE 1 The Radiographic Image Prepared by:- KAMARUL AMIN ABDULLAH @ ABU BAKAR UiTM Faculty of Health Sciences Medical Imaging Department 11/23/2011 KAMARUL AMIN (C) 1 Lesson Objectives At the end of
LECTURE 1 The Radiographic Image Prepared by:- KAMARUL AMIN ABDULLAH @ ABU BAKAR UiTM Faculty of Health Sciences Medical Imaging Department 11/23/2011 KAMARUL AMIN (C) 1 Lesson Objectives At the end of
An Activity in Computed Tomography
 Pre-lab Discussion An Activity in Computed Tomography X-rays X-rays are high energy electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths smaller than those in the visible spectrum (0.01-10nm and 4000-800nm respectively).
Pre-lab Discussion An Activity in Computed Tomography X-rays X-rays are high energy electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths smaller than those in the visible spectrum (0.01-10nm and 4000-800nm respectively).
Modeling detector performance in digital mammography using the linear cascaded systems approach
 51 Modeling detector performance in digital mammography using the linear cascaded systems approach V. Spyropoulou a,b, N. Kalivas a,b, A. Gaitanis a,b, C. Michail a,b, G. Panayiotakis b, I. Kandarakis
51 Modeling detector performance in digital mammography using the linear cascaded systems approach V. Spyropoulou a,b, N. Kalivas a,b, A. Gaitanis a,b, C. Michail a,b, G. Panayiotakis b, I. Kandarakis
Digital Images & Image Quality
 Introduction to Medical Engineering (Medical Imaging) Suetens 1 Digital Images & Image Quality Ho Kyung Kim Pusan National University Radiation imaging DR & CT: x-ray Nuclear medicine: gamma-ray Ultrasound
Introduction to Medical Engineering (Medical Imaging) Suetens 1 Digital Images & Image Quality Ho Kyung Kim Pusan National University Radiation imaging DR & CT: x-ray Nuclear medicine: gamma-ray Ultrasound
CT Basics: Image Quality Module 6
 Module 6 For educational and institutional use. This transcript is licensed for noncommercial, educational inhouse or online educational course use only in educational and corporate institutions. Any broadcast,
Module 6 For educational and institutional use. This transcript is licensed for noncommercial, educational inhouse or online educational course use only in educational and corporate institutions. Any broadcast,
Exposure Indices and Target Values in Radiography: What Are They and How Can You Use Them?
 Exposure Indices and Target Values in Radiography: What Are They and How Can You Use Them? Definition and Validation of Exposure Indices Ingrid Reiser, PhD DABR Department of Radiology University of Chicago
Exposure Indices and Target Values in Radiography: What Are They and How Can You Use Them? Definition and Validation of Exposure Indices Ingrid Reiser, PhD DABR Department of Radiology University of Chicago
Radiology Physics Lectures: Digital Radiography. Digital Radiography. D. J. Hall, Ph.D. x20893
 Digital Radiography D. J. Hall, Ph.D. x20893 djhall@ucsd.edu Background Common Digital Modalities Digital Chest Radiograph - 4096 x 4096 x 12 bit CT - 512 x 512 x 12 bit SPECT - 128 x 128 x 8 bit MRI -
Digital Radiography D. J. Hall, Ph.D. x20893 djhall@ucsd.edu Background Common Digital Modalities Digital Chest Radiograph - 4096 x 4096 x 12 bit CT - 512 x 512 x 12 bit SPECT - 128 x 128 x 8 bit MRI -
An Activity in Computed Tomography
 Pre-lab Discussion An Activity in Computed Tomography X-rays X-rays are high energy electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths smaller than those in the visible spectrum (0.01-10nm and 4000-800nm respectively).
Pre-lab Discussion An Activity in Computed Tomography X-rays X-rays are high energy electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths smaller than those in the visible spectrum (0.01-10nm and 4000-800nm respectively).
X-rays. X-rays are produced when electrons are accelerated and collide with a target. X-rays are sometimes characterized by the generating voltage
 X-rays Ouch! 1 X-rays X-rays are produced when electrons are accelerated and collide with a target Bremsstrahlung x-rays Characteristic x-rays X-rays are sometimes characterized by the generating voltage
X-rays Ouch! 1 X-rays X-rays are produced when electrons are accelerated and collide with a target Bremsstrahlung x-rays Characteristic x-rays X-rays are sometimes characterized by the generating voltage
HIGH RESOLUTION COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY SYSTEM USING AN IMAGING PLATE
 HIGH RESOLUTION COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY SYSTEM USING AN IMAGING PLATE Takeyuki Hashimoto 1), Morio Onoe 2), Hiroshi Nakamura 3), Tamon Inouye 4), Hiromichi Jumonji 5), Iwao Takahashi 6); 1)Yokohama Soei
HIGH RESOLUTION COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY SYSTEM USING AN IMAGING PLATE Takeyuki Hashimoto 1), Morio Onoe 2), Hiroshi Nakamura 3), Tamon Inouye 4), Hiromichi Jumonji 5), Iwao Takahashi 6); 1)Yokohama Soei
Electronic Noise in CT Detectors: Impact on Image Noise and Artifacts
 Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research Duan et al. Electronic Noise in CT Detectors Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research Xinhui Duan 1 Jia Wang 1,2 Shuai Leng 1 ernhard Schmidt
Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research Duan et al. Electronic Noise in CT Detectors Medical Physics and Informatics Original Research Xinhui Duan 1 Jia Wang 1,2 Shuai Leng 1 ernhard Schmidt
Dose Reduction and Image Preservation After the Introduction of a 0.1 mm Cu Filter into the LODOX Statscan unit above 110 kvp
 Dose Reduction and Image Preservation After the Introduction of a into the LODOX Statscan unit above 110 kvp Abstract: CJ Trauernicht 1, C Rall 1, T Perks 2, G Maree 1, E Hering 1, S Steiner 3 1) Division
Dose Reduction and Image Preservation After the Introduction of a into the LODOX Statscan unit above 110 kvp Abstract: CJ Trauernicht 1, C Rall 1, T Perks 2, G Maree 1, E Hering 1, S Steiner 3 1) Division
High Energy Digital Radiography & 3D-CT for Industrial Systems
 DIR 2007 - International Symposium on Digital industrial Radiology and Computed Tomography, June 25-27, 2007, Lyon, France High Energy Digital Radiography & 3D-CT for Industrial Systems Non-Destructive
DIR 2007 - International Symposium on Digital industrial Radiology and Computed Tomography, June 25-27, 2007, Lyon, France High Energy Digital Radiography & 3D-CT for Industrial Systems Non-Destructive
Investigation of Effective DQE (edqe) parameters for a flat panel detector
 Investigation of Effective DQE (edqe) parameters for a flat panel detector Poster No.: C-1892 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit D. Bor 1, S. Cubukcu 1, A. Yalcin 1, O.
Investigation of Effective DQE (edqe) parameters for a flat panel detector Poster No.: C-1892 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit D. Bor 1, S. Cubukcu 1, A. Yalcin 1, O.
Related topics Beam hardening, cupping effect, Beam hardening correction, metal artefacts, photon starvation
 Beam hardening and metal artefacts TEP Related topics Beam hardening, cupping effect, Beam hardening correction, metal artefacts, photon starvation Principle X-ray sources produce a polychromatic spectrum
Beam hardening and metal artefacts TEP Related topics Beam hardening, cupping effect, Beam hardening correction, metal artefacts, photon starvation Principle X-ray sources produce a polychromatic spectrum
Phase Imaging Using Focused Polycapillary Optics
 Phase Imaging Using Focused Polycapillary Optics Sajid Bashir, Sajjad Tahir, Jonathan C. Petruccelli, C.A. MacDonald Dept. of Physics, University at Albany, Albany, New York Abstract Contrast in conventional
Phase Imaging Using Focused Polycapillary Optics Sajid Bashir, Sajjad Tahir, Jonathan C. Petruccelli, C.A. MacDonald Dept. of Physics, University at Albany, Albany, New York Abstract Contrast in conventional
Simulated validation and quantitative analysis of the blur of an integral image related to the pickup sampling effects
 J. Europ. Opt. Soc. Rap. Public. 9, 14037 (2014) www.jeos.org Simulated validation and quantitative analysis of the blur of an integral image related to the pickup sampling effects Y. Chen School of Physics
J. Europ. Opt. Soc. Rap. Public. 9, 14037 (2014) www.jeos.org Simulated validation and quantitative analysis of the blur of an integral image related to the pickup sampling effects Y. Chen School of Physics
Lecture 25. Wind Lidar (3) Direct Detection Doppler Lidar
 Lecture 25. Wind Lidar (3) Direct Detection Doppler Lidar Overview of Direct Detection Doppler Lidar (DDL) Fringe imaging DDL Scanning FPI DDL FPI edge-filter DDL Iodine absorption-line edge-filter DDL
Lecture 25. Wind Lidar (3) Direct Detection Doppler Lidar Overview of Direct Detection Doppler Lidar (DDL) Fringe imaging DDL Scanning FPI DDL FPI edge-filter DDL Iodine absorption-line edge-filter DDL
Performance of Image Intensifiers in Radiographic Systems
 DOE/NV/11718--396 LA-UR-00-211 Performance of Image Intensifiers in Radiographic Systems Stuart A. Baker* a, Nicholas S. P. King b, Wilfred Lewis a, Stephen S. Lutz c, Dane V. Morgan a, Tim Schaefer a,
DOE/NV/11718--396 LA-UR-00-211 Performance of Image Intensifiers in Radiographic Systems Stuart A. Baker* a, Nicholas S. P. King b, Wilfred Lewis a, Stephen S. Lutz c, Dane V. Morgan a, Tim Schaefer a,
Objective Evaluation of Radiographic Contrast- Enhancement Masks
 Chapter 8 Objective Evaluation of Radiographic Contrast- Enhancement Masks The development and application of radiographic contrast-enhancement masks (RCMs) in digital radiography (DR) were discussed in
Chapter 8 Objective Evaluation of Radiographic Contrast- Enhancement Masks The development and application of radiographic contrast-enhancement masks (RCMs) in digital radiography (DR) were discussed in
SYLLABUS. 1. Identification of Subject:
 SYLLABUS Date/ Revision : 30 January 2017/1 Faculty : Life Sciences Approval : Dean, Faculty of Life Sciences SUBJECT : Biophysics 1. Identification of Subject: Name of Subject : Biophysics Code of Subject
SYLLABUS Date/ Revision : 30 January 2017/1 Faculty : Life Sciences Approval : Dean, Faculty of Life Sciences SUBJECT : Biophysics 1. Identification of Subject: Name of Subject : Biophysics Code of Subject
Influence of different iteration levels in fourth generation iterative reconstruction technique on image noise in CT examinations of the neck
 Influence of different iteration levels in fourth generation iterative reconstruction technique on image noise in CT examinations of the neck Poster No.: C-2205 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper
Influence of different iteration levels in fourth generation iterative reconstruction technique on image noise in CT examinations of the neck Poster No.: C-2205 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Paper
COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY 1
 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY 1 Why CT? Conventional X ray picture of a chest 2 Introduction Why CT? In a normal X-ray picture, most soft tissue doesn't show up clearly. To focus in on organs, or to examine the
COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY 1 Why CT? Conventional X ray picture of a chest 2 Introduction Why CT? In a normal X-ray picture, most soft tissue doesn't show up clearly. To focus in on organs, or to examine the
X-rays in medical diagnostics
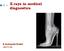 X-rays in medical diagnostics S.Dolanski Babić 2017/18. History W.C.Röntgen (1845-1923) discovered a new type of radiation Nature, Jan. 23. 1896.; Science, Feb.14. 1896. X- rays: Induced the ionization
X-rays in medical diagnostics S.Dolanski Babić 2017/18. History W.C.Röntgen (1845-1923) discovered a new type of radiation Nature, Jan. 23. 1896.; Science, Feb.14. 1896. X- rays: Induced the ionization
Development of a Virtual Simulation Environment for Radiation Treatment Planning
 Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering, 25(2): 61-66 61 Development of a Virtual Simulation Environment for Radiation Treatment Planning Tai-Sin Su De- Kai Chen Wen-Hsu Sung Ching-Fen Jiang * Shuh-Ping
Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering, 25(2): 61-66 61 Development of a Virtual Simulation Environment for Radiation Treatment Planning Tai-Sin Su De- Kai Chen Wen-Hsu Sung Ching-Fen Jiang * Shuh-Ping
X-ray detectors in healthcare and their applications
 X-ray detectors in healthcare and their applications Pixel 2012, Inawashiro September 4th, 2012 Martin Spahn, PhD Clinical applications of X-ray imaging Current X-ray detector technology (case study radiography
X-ray detectors in healthcare and their applications Pixel 2012, Inawashiro September 4th, 2012 Martin Spahn, PhD Clinical applications of X-ray imaging Current X-ray detector technology (case study radiography
Rad-icon Imaging Corp A Division of DALSA Corporation
 Rad-icon Imaging Corp A Division of DALSA Corporation el: 408-486-0886 Fax: 408-486-0882 www.rad-icon.com PRELIMINARY DAA SHEE SkiaGraph 8 Very Large Area X-Ray Camera Key Features: Active area of 20 cm
Rad-icon Imaging Corp A Division of DALSA Corporation el: 408-486-0886 Fax: 408-486-0882 www.rad-icon.com PRELIMINARY DAA SHEE SkiaGraph 8 Very Large Area X-Ray Camera Key Features: Active area of 20 cm
REAL-TIME X-RAY IMAGE PROCESSING; TECHNIQUES FOR SENSITIVITY
 REAL-TIME X-RAY IMAGE PROCESSING; TECHNIQUES FOR SENSITIVITY IMPROVEMENT USING LOW-COST EQUIPMENT R.M. Wallingford and J.N. Gray Center for Aviation Systems Reliability Iowa State University Ames,IA 50011
REAL-TIME X-RAY IMAGE PROCESSING; TECHNIQUES FOR SENSITIVITY IMPROVEMENT USING LOW-COST EQUIPMENT R.M. Wallingford and J.N. Gray Center for Aviation Systems Reliability Iowa State University Ames,IA 50011
X-ray phase-contrast imaging
 ...early-stage tumors and associated vascularization can be visualized via this imaging scheme Introduction As the selection of high-sensitivity scientific detectors, custom phosphor screens, and advanced
...early-stage tumors and associated vascularization can be visualized via this imaging scheme Introduction As the selection of high-sensitivity scientific detectors, custom phosphor screens, and advanced
Clinical Importance on CT
 183 Truncated-View Clinical Importance on CT..,..,.... Artifacts:.... James L. Lehr1 A truncated-view artifact in CT is produced whenever any part of the patient or imaged object is present in some but
183 Truncated-View Clinical Importance on CT..,..,.... Artifacts:.... James L. Lehr1 A truncated-view artifact in CT is produced whenever any part of the patient or imaged object is present in some but
Manufacturing Metrology Team
 The Team has a range of state-of-the-art equipment for the measurement of surface texture and form. We are happy to discuss potential measurement issues and collaborative research Manufacturing Metrology
The Team has a range of state-of-the-art equipment for the measurement of surface texture and form. We are happy to discuss potential measurement issues and collaborative research Manufacturing Metrology
Preliminary Modulation Transfer Function Study on Amorphous Silicon Flat Panel System for Industrial Digital Radiography
 ECNDT 26 - Poster 17 Preliminary Modulation Transfer Function Study on Amorphous Silicon Flat Panel System for Industrial Digital Radiography Khairul Anuar MOHD SALLEH, Ab. Razak HAMZAH and Mohd Ashhar
ECNDT 26 - Poster 17 Preliminary Modulation Transfer Function Study on Amorphous Silicon Flat Panel System for Industrial Digital Radiography Khairul Anuar MOHD SALLEH, Ab. Razak HAMZAH and Mohd Ashhar
CHAPTER 10. DIGITAL SUBTRACTION ANGIOGRAPHY (DSA) 10.1 Introduction
 PHYSICS OF MEDICAL X-RAY IMAGING (1)Chapter 10 CHAPTER 10. DIGITAL SUBTRACTION ANGIOGRAPHY (DSA) 10.1 Introduction In this chapter we will discuss a technique that is known as digital subtraction angiography
PHYSICS OF MEDICAL X-RAY IMAGING (1)Chapter 10 CHAPTER 10. DIGITAL SUBTRACTION ANGIOGRAPHY (DSA) 10.1 Introduction In this chapter we will discuss a technique that is known as digital subtraction angiography
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING IN X-RAY IMAGING
 DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING IN X-RAY IMAGING Shalini Kumari 1, Bachan Prasad 2,Aliya Nasim 3 Department of Electronics And Communication Engineering R.V.S College of Engineering & Technology, Jamshedpur,
DIGITAL IMAGE PROCESSING IN X-RAY IMAGING Shalini Kumari 1, Bachan Prasad 2,Aliya Nasim 3 Department of Electronics And Communication Engineering R.V.S College of Engineering & Technology, Jamshedpur,
Diffraction-enhanced X-ray Imaging (DEXI) Medical Solutions. More information using less radiation
 Diffraction-enhanced X-ray Imaging (DEXI) Medical Solutions More information using less radiation Medical Small Animal Security NDE/NDT Diffraction-Enhanced X-ray Imaging Medical Solutions Safe non-invasive
Diffraction-enhanced X-ray Imaging (DEXI) Medical Solutions More information using less radiation Medical Small Animal Security NDE/NDT Diffraction-Enhanced X-ray Imaging Medical Solutions Safe non-invasive
This document is published in:
 Institutional Repository This document is published in: Bo Yu (ed.) (01). 01 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC): Anaheim, California, USA. October 9 - November 3, 01.
Institutional Repository This document is published in: Bo Yu (ed.) (01). 01 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC): Anaheim, California, USA. October 9 - November 3, 01.
Principles of CT scan
 Related topics Detector calibration, saturation, CT acquisition, CT reconstruction Principle X-ray computed tomography consists of using X-rays that are converted to a digital signal by a detector and
Related topics Detector calibration, saturation, CT acquisition, CT reconstruction Principle X-ray computed tomography consists of using X-rays that are converted to a digital signal by a detector and
