RISC Central Processing Unit
|
|
|
- Poppy Higgins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RISC Central Processing Unit Lan-Da Van ( 范倫達 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Taiwan, R.O.C. Spring, 2014 ldvan@cs.nctu.edu.tw Source: Prof. M. Morris Mano and Prof. Charles R. Kime, Logic and Computer Design Fundamentals, 3rd Edition, 2004, Prentice Hall.
2 Outline Introduction Pipelined Datapath Pipelined Control The Reduced Instruction Set Computer (RISC) Summary 2
3 Introduction CPU: Datapath and control unit Datapath: Consist of a function unit, regs, and internal buses May be nonpiplined or pipelined Control unit: Consist of a program counter, an instr reg, and control logic May be hardwired, microprogrammed, or pipelined (if the datapath is pipelined) 3
4 Conventional datapath v.s. Pipelined datapath Fig
5 Detailed block diagram of the pipelined datapath: the increased cost: the pipeline platforms Fig
6 Pipeline Execution Pattern (1/2) Execution of pipeline -ops: Fig
7 Pipeline Execution Pattern (2/2) In the first two clock cycles, not all of the pipeline stages are active. => filling In the next five clock cycles, all stages of the pipeline are active. => fully utilized In the last two clock cycles, not all pipeline stages are active. => emptying Speedup = (7 12)/ (9 5) = 1.9 More pipelines, much better?? No The delay contributed by the pipeline platforms The difference between the delay of the logic assigned to each stage Thus, there exists one optimized pipelined stages. 7
8 Pipelined Control Based on the single-cycle computer: (hardwired control) Fig Fig
9 Block diagram of pipelined computer: 9
10 Pipeline Stages Stage 1: Instr fetch (IF) Stage 2: Instr decoder & reg file read (DOF) (decode & operand fetch) Stage 3: The function unit & data mem read and write (EX) Stage 4: Reg file write (WB) Pipeleine Principle: The location of the pipeline platforms has balanced the partitioning of the delays. Timing: 5 ns/stage 200 MHz, speedup = 3.4 (w.r.t single-cycle) 10
11 Pipeline Programming and Performance (1/3) E.g.: Load constants 1 ~ 7 into regs R1 ~ R7 1 LDI R1, 1 2 LDI R2, 2 3 LDI R3, 3 4 LDI R4, 4 5 LDI R5, 5 6 LDI R6, 6 7 LDI R7, 7 11
12 Pipeline Programming and Performance (2/3) In the first 4 clk periods: 20 ns 1/4 + 1/2 + 3/4 + 1 = 2.5 instrs completed Overall time: 50 ns 10 clk cycles for 7 instrs Speedup = (7 17) / 50 = 2.38 Filling: the first 3 clks Fully utilized: the next 4 clks Speedup = (4 17) / 20 = 3.4 Emptying: the last 3 clks 12
13 Pipeline Programming and Performance (3/3) For a k-stage pipelined computer: The speedup is not k w.r.t. the single-cycle computer The delays cannot be divided into k equal pieces. The delays of the added pipeline platforms The delay of the function unit is larger than that of ideal k equal delays. The filling and emptying of the pipeline Data hazard Control hazard 13
14 Design goal: The Reduced Instruction Set Computer A RISC with a pipelined datapath and control unit The instr set arch: load/store mem access, 4 addressing modes, A single instr format length, Instrs that require only elementary ops. The ops, resembling those that can be performed by the single-cycle computer, can be performed by a single pass through the pipeline. 14
15 Instruction Set Architecture The CPU regs accessible to the programmer: Fig12-6 Reg file: 32 regs, 32 bits/reg, R0 = 0 The size of the reg file: RISC > CISC, load/store instr set arch PC: 32 bits No stack pointer or status reg 15
16 Instruction Format Instr formats: 3-reg type 2-reg type Branch: target addr = PC + target offset 16
17 Instructions (1/2) 17
18 Instructions (2/2) All of the ops are elementary and can be described by a single reg transfer statement. The only ops that can access memory: Load & Store The immediate field: 15 bits 32 bits and using zero fill or sign extension BZ, BNZ, SLT: handle the absence of stored versions of status bits JML: Jump and Link 18
19 Addressing Modes 4 addressing modes: specified by the opcode i. Register: the 3-operand data manipulation instrs ii. Register indirect: load and store instrs iii. Immediate: the 2-reg format instrs iv. Relative: branch and jump instrs Implement an addressing mode not directly provided: Use a sequence of RISC instrs E.g.: Indexed addressing, R15 M[R5 + 0 I] AIU R9, R5, I LD R15, R9 19
20 Datapath Organization The Pipelined computer in Fig 12-4: 16-bit version 20
21 Modifications of datapath: Fig 12-4 Fig 12-8: 32-bit version Register file Function unit Bus structure Modifications of control unit: Instruction decoder Control logic related to the PC Modified Datapath and Control Unit Pipeline platforms 21
22 Register File and Function Unit Reg file: bit regs & all regs are identical in function bit regs & R0 = 0 edge triggered read-after-write reg file Function unit: ALU: 16 bits 32 bits Shifter: Single-bit position shifter Barrel shifter with lsr or lsl of 0 ~ 31 positions (SH: IR[4:0]) 22
23 32-bit Barrel Shifter Left/right: a control signal decoded from OPCODE SH: = IR(4:0), the shift amount field Perform both the left and right shift by using a right rotate: p-position right shift rotate p position to the right p-position left shift rotate 64 p position to the right 23
24 Bus structure: Bus Structure zero fill constant unit: CS = 0, zero fill ; CS = 1, sign extension 0 IM se IM MUX A is added: provide a path for PC 1 to the reg file for implementing JML instr Jump and Link: PC PC + se IM, R[DR] PC + 1 MUX D is extended: help implement SLT instr Set if Less Than: If R[SA] < R [SB] then R[DR] = 1 24
25 Instruction Decoder Instruction decoder: to deal with the new instr set SH is added as an IR field. A 1-bit CS field is added to the instr decoder. A 1-bit MA field is added to the instr decoder. MD is expanded to two bits. A new pipeline platform for SH & expanded 2-bit platforms for MD 25
26 Control Logic (1/2) Control logic related to the PC: Permit the loading of addrs into the PC for implementing branches and jumps MUX C: in EX stage, selects from 3 different sources for the next value of PC (BS, PS) PC + 1 BrA: for branches and jumps R[AA]: for reg jump Pipeline regs PC 1 & PC 2 PC PC se IM PC R[AA] 26
27 Control Logic (2/2) 27
28 Control Words for Instrs 28
29 29
30 Data Hazards Data hazard example: Solutions of data hazard: Program-based solution Data hazard stall Data forwarding 30
31 Program-Based Solution Disadv. of program-based sol.: The program is longer (unless some unrelated instrs may be placed in the NOP positions) Reduce the throughput 31
32 Data Hazard Stall (1/4) Data hazard stall: HW-based sol. 32
33 Data Hazard Stall (2/4) When an operand is found at the DOF stage that has not been written back yet, the associated execution and write-back are delayed by stalling the pipeline flow in IF and DOF for one clock cycle. The pipeline is said to be stalled, i.e., contain a bubble in subsequent clock cycles and stages for that instr. Disadv.: Has the same throughput penalty as the program w/ the NOPs 33
34 Data Hazard Stall (3/4) The following events must all occur for HA. MA in the DOF stage must be 0, meaning that the A operand is coming from the register file. AA in the DOF stage equals DA in the EX stage, meaning that there is potentially a register being read in the DOF stage that is to be written in the next clock cycle. RW in the EX stage is 1, meaning that register DA in the EX stage will definitely be written in WB during the next clock cycle. The OR of all bits of DA is 1, meaning that the register to be written is not R0 and so is a register that must be written before being read. 34
35 Data Hazard Stall (4/4) Pipelined RISC with Data hazard stall: Added or modified hardware: Data hazard detection: DHS DHS HA HB HA MA HB MB DOF DOF ( DA ( DA EX EX AA BA DOF DOF ) RW ) RW EX EX 4 i 0 4 i 0 ( DA ( DA EX EX ) ) i i Pipeline stalling: DHS is inverted to initiate a bubble in the pipeline for the instr currently in the IR and to stop the PC and IR from changing. 35
36 36
37 Data Forwarding (1/2) Data forwarding: HW-based sol. 37
38 Data Forwarding (2/2) Pipelined RISC w/ Data forwarding: Added or modified hardware: Data hazard detection: HA, HB Data forwarding: The information needed to form the result is available on the inputs to the pipeline platform that provides the inputs to MUX D. MUX D is added to produce the result on Bus D Add an additional input to MUX A & MUX B from Bus D 38
39 39
40 Control Hazards Control hazard example: If R1 = 0 1 BZ R1, 18 2 MOVA R2, R3 3 MOVA R1, R2 20 MOVA R5, R6 Solutions of control hazard: Program-based solution Branch hazard stall Branch prediction 40
41 Program-Based Solution 2 NOPs are inserted after the branch instr. (These wasted cycles can sometimes be avoided by rearranging the order of instrs.) 41
42 Branch Hazard Stall Branch hazard stall: HW-based sol. Just as in the case of the data hazard, a stall can be used to deal w/ the control hazard. Produce 2 bubbles after the branch instr Disadv.: The reduction in throughput will be the same as w/ the insertion of NOPs. 42
43 Branch Prediction (1/3) Branch prediction Simplest form: predict that branches will never be taken Instrs will be fetched and decoded and operands fetched on the basis of +1 to the value of the PC. If the branch is not taken, the instrs already in the pipeline due to the prediction will be allowed to proceed. If the branch is taken, the instrs following the branch instr need to be cancelled. The cancellation may be done by inserting bubbles into EX & WB stages. 43
44 Branch Prediction (2/3) E.g.: Branch prediction with branch non-taken Figure 12-16, p.555 If the branch is taken 44
45 Branch Prediction (3/3) Pipelined RISC w/ Branch prediction Figure 12-17, p.556 Added or modified hardware: Branch detection: EX stage the selection values on the inputs to MUX C are not 00 Instruction canceling: IF & DOF stages 45
46 46
47 Summary Widely discussed in the following topics. Pipelined Datapath Pieplined Control RISC Instruction Set Architecture Addressing Modes Datapath Data Hazard Control Hazard 47
Computer Hardware. Pipeline
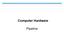 Computer Hardware Pipeline Conventional Datapath 2.4 ns is required to perform a single operation (i.e. 416.7 MHz). Register file MUX B 0.6 ns Clock 0.6 ns 0.2 ns Function unit 0.8 ns MUX D 0.2 ns c. Production
Computer Hardware Pipeline Conventional Datapath 2.4 ns is required to perform a single operation (i.e. 416.7 MHz). Register file MUX B 0.6 ns Clock 0.6 ns 0.2 ns Function unit 0.8 ns MUX D 0.2 ns c. Production
7/11/2012. Single Cycle (Review) CSE 2021: Computer Organization. Multi-Cycle Implementation. Single Cycle with Jump. Pipelining Analogy
 CSE 2021: Computer Organization Single Cycle (Review) Lecture-10 CPU Design : Pipelining-1 Overview, Datapath and control Shakil M. Khan CSE-2021 July-12-2012 2 Single Cycle with Jump Multi-Cycle Implementation
CSE 2021: Computer Organization Single Cycle (Review) Lecture-10 CPU Design : Pipelining-1 Overview, Datapath and control Shakil M. Khan CSE-2021 July-12-2012 2 Single Cycle with Jump Multi-Cycle Implementation
Lecture Topics. Announcements. Today: Pipelined Processors (P&H ) Next: continued. Milestone #4 (due 2/23) Milestone #5 (due 3/2)
 Lecture Topics Today: Pipelined Processors (P&H 4.5-4.10) Next: continued 1 Announcements Milestone #4 (due 2/23) Milestone #5 (due 3/2) 2 1 ISA Implementations Three different strategies: single-cycle
Lecture Topics Today: Pipelined Processors (P&H 4.5-4.10) Next: continued 1 Announcements Milestone #4 (due 2/23) Milestone #5 (due 3/2) 2 1 ISA Implementations Three different strategies: single-cycle
Chapter 4. Pipelining Analogy. The Processor. Pipelined laundry: overlapping execution. Parallelism improves performance. Four loads: Non-stop:
 Chapter 4 The Processor Part II Pipelining Analogy Pipelined laundry: overlapping execution Parallelism improves performance Four loads: Speedup = 8/3.5 = 2.3 Non-stop: Speedup p = 2n/(0.5n + 1.5) 4 =
Chapter 4 The Processor Part II Pipelining Analogy Pipelined laundry: overlapping execution Parallelism improves performance Four loads: Speedup = 8/3.5 = 2.3 Non-stop: Speedup p = 2n/(0.5n + 1.5) 4 =
CS 110 Computer Architecture Lecture 11: Pipelining
 CS 110 Computer Architecture Lecture 11: Pipelining Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger http://shtech.org/courses/ca/ School of Information Science and Technology SIST ShanghaiTech University Slides based on
CS 110 Computer Architecture Lecture 11: Pipelining Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger http://shtech.org/courses/ca/ School of Information Science and Technology SIST ShanghaiTech University Slides based on
Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture An Introduction Virendra Singh Associate Professor Computer Architecture and Dependable Systems Lab Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay http://www.ee.iitb.ac.in/~viren/
Computer Architecture An Introduction Virendra Singh Associate Professor Computer Architecture and Dependable Systems Lab Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay http://www.ee.iitb.ac.in/~viren/
Pipelining A B C D. Readings: Example: Doing the laundry. Ann, Brian, Cathy, & Dave. each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold
 Pipelining Readings: 4.5-4.8 Example: Doing the laundry Ann, Brian, Cathy, & Dave A B C D each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder takes
Pipelining Readings: 4.5-4.8 Example: Doing the laundry Ann, Brian, Cathy, & Dave A B C D each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder takes
7/19/2012. IF for Load (Review) CSE 2021: Computer Organization. EX for Load (Review) ID for Load (Review) WB for Load (Review) MEM for Load (Review)
 CSE 2021: Computer Organization IF for Load (Review) Lecture-11 CPU Design : Pipelining-2 Review, Hazards Shakil M. Khan CSE-2021 July-19-2012 2 ID for Load (Review) EX for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-19-2012
CSE 2021: Computer Organization IF for Load (Review) Lecture-11 CPU Design : Pipelining-2 Review, Hazards Shakil M. Khan CSE-2021 July-19-2012 2 ID for Load (Review) EX for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-19-2012
CSE 2021: Computer Organization
 CSE 2021: Computer Organization Lecture-11 CPU Design : Pipelining-2 Review, Hazards Shakil M. Khan IF for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-14-2011 2 ID for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-14-2011 3 EX for Load
CSE 2021: Computer Organization Lecture-11 CPU Design : Pipelining-2 Review, Hazards Shakil M. Khan IF for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-14-2011 2 ID for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-14-2011 3 EX for Load
RISC Design: Pipelining
 RISC Design: Pipelining Virendra Singh Associate Professor Computer Architecture and Dependable Systems Lab Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay http://www.ee.iitb.ac.in/~viren/
RISC Design: Pipelining Virendra Singh Associate Professor Computer Architecture and Dependable Systems Lab Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay http://www.ee.iitb.ac.in/~viren/
Pipelined Processor Design
 Pipelined Processor Design COE 38 Computer Architecture Prof. Muhamed Mudawar Computer Engineering Department King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Presentation Outline Pipelining versus Serial
Pipelined Processor Design COE 38 Computer Architecture Prof. Muhamed Mudawar Computer Engineering Department King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Presentation Outline Pipelining versus Serial
A B C D. Ann, Brian, Cathy, & Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold. Time
 Pipelining Readings: 4.5-4.8 Example: Doing the laundry A B C D Ann, Brian, Cathy, & Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder takes
Pipelining Readings: 4.5-4.8 Example: Doing the laundry A B C D Ann, Brian, Cathy, & Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder takes
EECE 321: Computer Organiza5on
 EECE 321: Computer Organiza5on Mohammad M. Mansour Dept. of Electrical and Compute Engineering American University of Beirut Lecture 21: Pipelining Processor Pipelining Same principles can be applied to
EECE 321: Computer Organiza5on Mohammad M. Mansour Dept. of Electrical and Compute Engineering American University of Beirut Lecture 21: Pipelining Processor Pipelining Same principles can be applied to
IF ID EX MEM WB 400 ps 225 ps 350 ps 450 ps 300 ps
 CSE 30321 Computer Architecture I Fall 2011 Homework 06 Pipelined Processors 75 points Assigned: November 1, 2011 Due: November 8, 2011 PLEASE DO THE ASSIGNMENT ON THIS HANDOUT!!! Problem 1: (15 points)
CSE 30321 Computer Architecture I Fall 2011 Homework 06 Pipelined Processors 75 points Assigned: November 1, 2011 Due: November 8, 2011 PLEASE DO THE ASSIGNMENT ON THIS HANDOUT!!! Problem 1: (15 points)
IF ID EX MEM WB 400 ps 225 ps 350 ps 450 ps 300 ps
 CSE 30321 Computer Architecture I Fall 2010 Homework 06 Pipelined Processors 85 points Assigned: November 2, 2010 Due: November 9, 2010 PLEASE DO THE ASSIGNMENT ON THIS HANDOUT!!! Problem 1: (25 points)
CSE 30321 Computer Architecture I Fall 2010 Homework 06 Pipelined Processors 85 points Assigned: November 2, 2010 Due: November 9, 2010 PLEASE DO THE ASSIGNMENT ON THIS HANDOUT!!! Problem 1: (25 points)
LECTURE 8. Pipelining: Datapath and Control
 LECTURE 8 Pipelining: Datapath and Control PIPELINED DATAPATH As with the single-cycle and multi-cycle implementations, we will start by looking at the datapath for pipelining. We already know that pipelining
LECTURE 8 Pipelining: Datapath and Control PIPELINED DATAPATH As with the single-cycle and multi-cycle implementations, we will start by looking at the datapath for pipelining. We already know that pipelining
Instruction Level Parallelism. Data Dependence Static Scheduling
 Instruction Level Parallelism Data Dependence Static Scheduling Basic Block A straight line code sequence with no branches in except to the entry and no branches out except at the exit Loop: L.D ADD.D
Instruction Level Parallelism Data Dependence Static Scheduling Basic Block A straight line code sequence with no branches in except to the entry and no branches out except at the exit Loop: L.D ADD.D
Lecture 4: Introduction to Pipelining
 Lecture 4: Introduction to Pipelining Pipelining Laundry Example Ann, Brian, Cathy, Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes A B C D Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder
Lecture 4: Introduction to Pipelining Pipelining Laundry Example Ann, Brian, Cathy, Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes A B C D Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder
6.S084 Tutorial Problems L19 Control Hazards in Pipelined Processors
 6.S084 Tutorial Problems L19 Control Hazards in Pipelined Processors Options for dealing with data and control hazards: stall, bypass, speculate 6.S084 Worksheet - 1 of 10 - L19 Control Hazards in Pipelined
6.S084 Tutorial Problems L19 Control Hazards in Pipelined Processors Options for dealing with data and control hazards: stall, bypass, speculate 6.S084 Worksheet - 1 of 10 - L19 Control Hazards in Pipelined
ECE473 Computer Architecture and Organization. Pipeline: Introduction
 Computer Architecture and Organization Pipeline: Introduction Lecturer: Prof. Yifeng Zhu Fall, 2015 Portions of these slides are derived from: Dave Patterson UCB Lec 11.1 The Laundry Analogy Student A,
Computer Architecture and Organization Pipeline: Introduction Lecturer: Prof. Yifeng Zhu Fall, 2015 Portions of these slides are derived from: Dave Patterson UCB Lec 11.1 The Laundry Analogy Student A,
Selected Solutions to Problem-Set #3 COE 608: Computer Organization and Architecture Single Cycle Datapath and Control
 Selected Solutions to Problem-Set #3 COE 608: Computer Organization and Architecture Single Cycle Datapath and Control 4.1. Done in the class 4.2. Try it yourself Q4.3. 4.3.1 a. Logic Only b. Logic Only
Selected Solutions to Problem-Set #3 COE 608: Computer Organization and Architecture Single Cycle Datapath and Control 4.1. Done in the class 4.2. Try it yourself Q4.3. 4.3.1 a. Logic Only b. Logic Only
Pipelined Beta. Handouts: Lecture Slides. Where are the registers? Spring /10/01. L16 Pipelined Beta 1
 Pipelined Beta Where are the registers? Handouts: Lecture Slides L16 Pipelined Beta 1 Increasing CPU Performance MIPS = Freq CPI MIPS = Millions of Instructions/Second Freq = Clock Frequency, MHz CPI =
Pipelined Beta Where are the registers? Handouts: Lecture Slides L16 Pipelined Beta 1 Increasing CPU Performance MIPS = Freq CPI MIPS = Millions of Instructions/Second Freq = Clock Frequency, MHz CPI =
Suggested Readings! Lecture 12" Introduction to Pipelining! Example: We have to build x cars...! ...Each car takes 6 steps to build...! ! Readings!
 1! CSE 30321 Lecture 12 Introduction to Pipelining! CSE 30321 Lecture 12 Introduction to Pipelining! 2! Suggested Readings!! Readings!! H&P: Chapter 4.5-4.7!! (Over the next 3-4 lectures)! Lecture 12"
1! CSE 30321 Lecture 12 Introduction to Pipelining! CSE 30321 Lecture 12 Introduction to Pipelining! 2! Suggested Readings!! Readings!! H&P: Chapter 4.5-4.7!! (Over the next 3-4 lectures)! Lecture 12"
Understanding Engineers #2
 Understanding Engineers #! The graduate with a Science degree asks, "Why does it work?"! The graduate with an Engineering degree asks, "How does it work?"! The graduate with an Accounting degree asks,
Understanding Engineers #! The graduate with a Science degree asks, "Why does it work?"! The graduate with an Engineering degree asks, "How does it work?"! The graduate with an Accounting degree asks,
Asanovic/Devadas Spring Pipeline Hazards. Krste Asanovic Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T.
 Pipeline Hazards Krste Asanovic Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. Pipelined DLX Datapath without interlocks and jumps 31 0x4 RegDst RegWrite inst Inst rs1 rs2 rd1 ws wd rd2 GPRs Imm Ext A B OpSel
Pipeline Hazards Krste Asanovic Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. Pipelined DLX Datapath without interlocks and jumps 31 0x4 RegDst RegWrite inst Inst rs1 rs2 rd1 ws wd rd2 GPRs Imm Ext A B OpSel
CMSC 611: Advanced Computer Architecture
 CMSC 611: Advanced Computer Architecture Pipelining Some material adapted from Mohamed Younis, UMBC CMSC 611 Spr 2003 course slides Some material adapted from Hennessy & Patterson / 2003 Elsevier Science
CMSC 611: Advanced Computer Architecture Pipelining Some material adapted from Mohamed Younis, UMBC CMSC 611 Spr 2003 course slides Some material adapted from Hennessy & Patterson / 2003 Elsevier Science
Basic Symbols for Register Transfers. Symbol Description Examples
 T-58 Basic Symbols for Register Trasfers TABLE 7- Basic Symbols for Register Trasfers Symbol Descriptio Examples Letters Deotes a register AR, R2, DR, IR (ad umerals) Paretheses Deotes a part of a register
T-58 Basic Symbols for Register Trasfers TABLE 7- Basic Symbols for Register Trasfers Symbol Descriptio Examples Letters Deotes a register AR, R2, DR, IR (ad umerals) Paretheses Deotes a part of a register
CS420/520 Computer Architecture I
 CS42/52 Computer rchitecture I Designing a Pipeline Processor (C4: ppendix ) Dr. Xiaobo Zhou Department of Computer Science CS42/52 pipeline. UC. Colorado Springs dapted from UCB97 & UCB3 Branch Jump Recap:
CS42/52 Computer rchitecture I Designing a Pipeline Processor (C4: ppendix ) Dr. Xiaobo Zhou Department of Computer Science CS42/52 pipeline. UC. Colorado Springs dapted from UCB97 & UCB3 Branch Jump Recap:
CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture
 CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr. Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Last updated: November 8, 2017 at 09:27 CS429 Slideset 14: 1 Overview What s wrong
CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr. Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Last updated: November 8, 2017 at 09:27 CS429 Slideset 14: 1 Overview What s wrong
Controller Implementation--Part I. Cascading Edge-triggered Flip-Flops
 Controller Implementation--Part I Alternative controller FSM implementation approaches based on: Classical Moore and Mealy machines Time state: Divide and Counter Jump counters Microprogramming (ROM) based
Controller Implementation--Part I Alternative controller FSM implementation approaches based on: Classical Moore and Mealy machines Time state: Divide and Counter Jump counters Microprogramming (ROM) based
Low-Power CMOS VLSI Design
 Low-Power CMOS VLSI Design ( 范倫達 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science, National Chiao Tung University, Taiwan, R.O.C. Fall, 2017 ldvan@cs.nctu.edu.tw http://www.cs.nctu.tw/~ldvan/ Outline Introduction
Low-Power CMOS VLSI Design ( 范倫達 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science, National Chiao Tung University, Taiwan, R.O.C. Fall, 2017 ldvan@cs.nctu.edu.tw http://www.cs.nctu.tw/~ldvan/ Outline Introduction
ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization. More Pipelined Microprocessor
 ECE 2300 Digital ogic & Computer Organization Spring 2018 ore Pipelined icroprocessor ecture 18: 1 nnouncements No instructor office hour today Rescheduled to onday pril 16, 4:00-5:30pm Prelim 2 review
ECE 2300 Digital ogic & Computer Organization Spring 2018 ore Pipelined icroprocessor ecture 18: 1 nnouncements No instructor office hour today Rescheduled to onday pril 16, 4:00-5:30pm Prelim 2 review
Computer Elements and Datapath. Microarchitecture Implementation of an ISA
 6.823, L5--1 Computer Elements and atapath Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 status lines Microarchitecture Implementation of an ISA ler control points 6.823, L5--2
6.823, L5--1 Computer Elements and atapath Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 status lines Microarchitecture Implementation of an ISA ler control points 6.823, L5--2
EE382V-ICS: System-on-a-Chip (SoC) Design
 EE38V-CS: System-on-a-Chip (SoC) Design Hardware Synthesis and Architectures Source: D. Gajski, S. Abdi, A. Gerstlauer, G. Schirner, Embedded System Design: Modeling, Synthesis, Verification, Chapter 6:
EE38V-CS: System-on-a-Chip (SoC) Design Hardware Synthesis and Architectures Source: D. Gajski, S. Abdi, A. Gerstlauer, G. Schirner, Embedded System Design: Modeling, Synthesis, Verification, Chapter 6:
Project 5: Optimizer Jason Ansel
 Project 5: Optimizer Jason Ansel Overview Project guidelines Benchmarking Library OoO CPUs Project Guidelines Use optimizations from lectures as your arsenal If you decide to implement one, look at Whale
Project 5: Optimizer Jason Ansel Overview Project guidelines Benchmarking Library OoO CPUs Project Guidelines Use optimizations from lectures as your arsenal If you decide to implement one, look at Whale
Computer Science 246. Advanced Computer Architecture. Spring 2010 Harvard University. Instructor: Prof. David Brooks
 Advanced Computer Architecture Spring 2010 Harvard University Instructor: Prof. dbrooks@eecs.harvard.edu Lecture Outline Instruction-Level Parallelism Scoreboarding (A.8) Instruction Level Parallelism
Advanced Computer Architecture Spring 2010 Harvard University Instructor: Prof. dbrooks@eecs.harvard.edu Lecture Outline Instruction-Level Parallelism Scoreboarding (A.8) Instruction Level Parallelism
EE 457 Homework 5 Redekopp Name: Score: / 100_
 EE 457 Homework 5 Redekopp Name: Score: / 100_ Single-Cycle CPU The following exercises are taken from Hennessy and Patterson, CO&D 2 nd, 3 rd, and 4 th Ed. 1.) (6 pts.) Review your class notes. a. Is
EE 457 Homework 5 Redekopp Name: Score: / 100_ Single-Cycle CPU The following exercises are taken from Hennessy and Patterson, CO&D 2 nd, 3 rd, and 4 th Ed. 1.) (6 pts.) Review your class notes. a. Is
Chapter 16 - Instruction-Level Parallelism and Superscalar Processors
 Chapter 16 - Instruction-Level Parallelism and Superscalar Processors Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 16 - Superscalar Processors 1 / 78 Table of Contents I 1 Overview
Chapter 16 - Instruction-Level Parallelism and Superscalar Processors Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 16 - Superscalar Processors 1 / 78 Table of Contents I 1 Overview
Pipelined Architecture (2A) Young Won Lim 4/10/18
 Pipelined Architecture (2A) Copyright (c) 2014-2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2
Pipelined Architecture (2A) Copyright (c) 2014-2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2
Pipelined Architecture (2A) Young Won Lim 4/7/18
 Pipelined Architecture (2A) Copyright (c) 2014-2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2
Pipelined Architecture (2A) Copyright (c) 2014-2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2
EN164: Design of Computing Systems Lecture 22: Processor / ILP 3
 EN164: Design of Computing Systems Lecture 22: Processor / ILP 3 Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University
EN164: Design of Computing Systems Lecture 22: Processor / ILP 3 Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University
Single vs. Mul2- cycle MIPS. Single Clock Cycle Length
 Single vs. Mul2- cycle MIPS Single Clock Cycle Length Suppose we have 2ns 2ns ister read 2ns ister write 2ns ory read 2ns ory write 2ns 2ns What is the clock cycle length? 1 Single Cycle Length Worst case
Single vs. Mul2- cycle MIPS Single Clock Cycle Length Suppose we have 2ns 2ns ister read 2ns ister write 2ns ory read 2ns ory write 2ns 2ns What is the clock cycle length? 1 Single Cycle Length Worst case
Computer Architecture and Organization: L08: Design Control Lines
 Computer Architecture and Organization: L08: Design Control Lines By: A. H. Abdul Hafez Abdul.hafez@hku.edu.tr, ah.abdulhafez@gmail.com, hafez@research.iiit.ac.in 1 CAO, by Dr. A.H. Abdul Hafez, CE Dept.
Computer Architecture and Organization: L08: Design Control Lines By: A. H. Abdul Hafez Abdul.hafez@hku.edu.tr, ah.abdulhafez@gmail.com, hafez@research.iiit.ac.in 1 CAO, by Dr. A.H. Abdul Hafez, CE Dept.
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology
 A digital audio signal processor for cellular phone application Jeongsik Yang, Chanhong Park Beomsup Kim Department of Electrical Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering Korea Advanced Institute
A digital audio signal processor for cellular phone application Jeongsik Yang, Chanhong Park Beomsup Kim Department of Electrical Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering Korea Advanced Institute
Instruction Level Parallelism Part II - Scoreboard
 Course on: Advanced Computer Architectures Instruction Level Parallelism Part II - Scoreboard Prof. Cristina Silvano Politecnico di Milano email: cristina.silvano@polimi.it 1 Basic Assumptions We consider
Course on: Advanced Computer Architectures Instruction Level Parallelism Part II - Scoreboard Prof. Cristina Silvano Politecnico di Milano email: cristina.silvano@polimi.it 1 Basic Assumptions We consider
On the Rules of Low-Power Design
 On the Rules of Low-Power Design (and Why You Should Break Them) Prof. Todd Austin University of Michigan austin@umich.edu A long time ago, in a not so far away place The Rules of Low-Power Design P =
On the Rules of Low-Power Design (and Why You Should Break Them) Prof. Todd Austin University of Michigan austin@umich.edu A long time ago, in a not so far away place The Rules of Low-Power Design P =
CS521 CSE IITG 11/23/2012
 Parallel Decoding and issue Parallel execution Preserving the sequential consistency of execution and exception processing 1 slide 2 Decode/issue data Issue bound fetch Dispatch bound fetch RS RS RS RS
Parallel Decoding and issue Parallel execution Preserving the sequential consistency of execution and exception processing 1 slide 2 Decode/issue data Issue bound fetch Dispatch bound fetch RS RS RS RS
Single-Cycle CPU The following exercises are taken from Hennessy and Patterson, CO&D 2 nd, 3 rd, and 4 th Ed.
 EE 357 Homework 7 Redekopp Name: Lec: 9:30 / 11:00 Score: Submit answers via Blackboard for all problems except 5.) and 6.). For those questions, submit a hardcopy with your answers, diagrams, circuit
EE 357 Homework 7 Redekopp Name: Lec: 9:30 / 11:00 Score: Submit answers via Blackboard for all problems except 5.) and 6.). For those questions, submit a hardcopy with your answers, diagrams, circuit
CMP 301B Computer Architecture. Appendix C
 CMP 301B Computer Architecture Appendix C Dealing with Exceptions What should be done when an exception arises and many instructions are in the pipeline??!! Force a trap instruction in the next IF stage
CMP 301B Computer Architecture Appendix C Dealing with Exceptions What should be done when an exception arises and many instructions are in the pipeline??!! Force a trap instruction in the next IF stage
Topics. Low Power Techniques. Based on Penn State CSE477 Lecture Notes 2002 M.J. Irwin and adapted from Digital Integrated Circuits 2002 J.
 Topics Low Power Techniques Based on Penn State CSE477 Lecture Notes 2002 M.J. Irwin and adapted from Digital Integrated Circuits 2002 J. Rabaey Review: Energy & Power Equations E = C L V 2 DD P 0 1 +
Topics Low Power Techniques Based on Penn State CSE477 Lecture Notes 2002 M.J. Irwin and adapted from Digital Integrated Circuits 2002 J. Rabaey Review: Energy & Power Equations E = C L V 2 DD P 0 1 +
Some material adapted from Mohamed Younis, UMBC CMSC 611 Spr 2003 course slides Some material adapted from Hennessy & Patterson / 2003 Elsevier
 Some material adapted from Mohamed Younis, UMBC CMSC 611 Spr 2003 course slides Some material adapted from Hennessy & Patterson / 2003 Elsevier Science !!! Basic MIPS integer pipeline Branches with one
Some material adapted from Mohamed Younis, UMBC CMSC 611 Spr 2003 course slides Some material adapted from Hennessy & Patterson / 2003 Elsevier Science !!! Basic MIPS integer pipeline Branches with one
COSC4201. Scoreboard
 COSC4201 Scoreboard Prof. Mokhtar Aboelaze York University Based on Slides by Prof. L. Bhuyan (UCR) Prof. M. Shaaban (RIT) 1 Overcoming Data Hazards with Dynamic Scheduling In the pipeline, if there is
COSC4201 Scoreboard Prof. Mokhtar Aboelaze York University Based on Slides by Prof. L. Bhuyan (UCR) Prof. M. Shaaban (RIT) 1 Overcoming Data Hazards with Dynamic Scheduling In the pipeline, if there is
EECS 470 Lecture 4. Pipelining & Hazards II. Winter Prof. Ronald Dreslinski h8p://
 Wenisch 26 -- Portions ustin, Brehob, Falsafi, Hill, Hoe, ipasti, artin, Roth, Shen, Smith, Sohi, Tyson, Vijaykumar EECS 4 ecture 4 Pipelining & Hazards II Winter 29 GS STTION Prof. Ronald Dreslinski h8p://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs4
Wenisch 26 -- Portions ustin, Brehob, Falsafi, Hill, Hoe, ipasti, artin, Roth, Shen, Smith, Sohi, Tyson, Vijaykumar EECS 4 ecture 4 Pipelining & Hazards II Winter 29 GS STTION Prof. Ronald Dreslinski h8p://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs4
Pipelining and ISA Design
 Pipelined instuc.on Execu.on 1 Pipelining and ISA Design MIPS Instuc:on Set designed fo pipelining All instuc:ons ae 32- bits Easie to fetch and decode in one cycle x86: 1- to 17- byte instuc:ons (x86
Pipelined instuc.on Execu.on 1 Pipelining and ISA Design MIPS Instuc:on Set designed fo pipelining All instuc:ons ae 32- bits Easie to fetch and decode in one cycle x86: 1- to 17- byte instuc:ons (x86
Design of Microprogrammed Control Units (MCU) using VHDL Description. Arvutitehnika erikusus
 Design of Microprogrammed Control Units (MCU) using VHDL Description Arvutitehnika erikusus 1 Hardwired control unit S5 A S6 & D Q Q D Q Q CLOCK A hardwired control unit accomplishes a conditional transfer
Design of Microprogrammed Control Units (MCU) using VHDL Description Arvutitehnika erikusus 1 Hardwired control unit S5 A S6 & D Q Q D Q Q CLOCK A hardwired control unit accomplishes a conditional transfer
Dynamic Scheduling II
 so far: dynamic scheduling (out-of-order execution) Scoreboard omasulo s algorithm register renaming: removing artificial dependences (WAR/WAW) now: out-of-order execution + precise state advanced topic:
so far: dynamic scheduling (out-of-order execution) Scoreboard omasulo s algorithm register renaming: removing artificial dependences (WAR/WAW) now: out-of-order execution + precise state advanced topic:
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture. Pipelining Hazards. Instructor: Senior Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia
 CS 61C: Geat Ideas in Compute Achitectue Pipelining Hazads Instucto: Senio Lectue SOE Dan Gacia 1 Geat Idea #4: Paallelism So9wae Paallel Requests Assigned to compute e.g. seach Gacia Paallel Theads Assigned
CS 61C: Geat Ideas in Compute Achitectue Pipelining Hazads Instucto: Senio Lectue SOE Dan Gacia 1 Geat Idea #4: Paallelism So9wae Paallel Requests Assigned to compute e.g. seach Gacia Paallel Theads Assigned
EC4205 Microprocessor and Microcontroller
 EC4205 Microprocessor and Microcontroller Webcast link: https://sites.google.com/a/bitmesra.ac.in/aminulislam/home All announcement made through webpage: check back often Students are welcome outside the
EC4205 Microprocessor and Microcontroller Webcast link: https://sites.google.com/a/bitmesra.ac.in/aminulislam/home All announcement made through webpage: check back often Students are welcome outside the
EECS 470. Lecture 9. MIPS R10000 Case Study. Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont
 MIPS R10000 Case Study Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 Multiprocessor SGI Origin Using MIPS R10K Many thanks to Prof. Martin and Roth of University of Pennsylvania for
MIPS R10000 Case Study Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 Multiprocessor SGI Origin Using MIPS R10K Many thanks to Prof. Martin and Roth of University of Pennsylvania for
8-bit Microcontroller with 512/1024 Bytes In-System Programmable Flash. ATtiny4/5/9/10
 Features High Performance, Low Power AVR 8-Bit Microcontroller Advanced RISC Architecture 54 Powerful Instructions Most Single Clock Cycle Execution 16 x 8 General Purpose Working Registers Fully Static
Features High Performance, Low Power AVR 8-Bit Microcontroller Advanced RISC Architecture 54 Powerful Instructions Most Single Clock Cycle Execution 16 x 8 General Purpose Working Registers Fully Static
SCALCORE: DESIGNING A CORE
 SCALCORE: DESIGNING A CORE FOR VOLTAGE SCALABILITY Bhargava Gopireddy, Choungki Song, Josep Torrellas, Nam Sung Kim, Aditya Agrawal, Asit Mishra University of Illinois, University of Wisconsin, Nvidia,
SCALCORE: DESIGNING A CORE FOR VOLTAGE SCALABILITY Bhargava Gopireddy, Choungki Song, Josep Torrellas, Nam Sung Kim, Aditya Agrawal, Asit Mishra University of Illinois, University of Wisconsin, Nvidia,
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 3: ReviewTechnology & Delay Modeling. September 3, 1997
 CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 3: ReviewTechnology & Delay Modeling September 3, 1997 Dave Patterson (httpcsberkeleyedu/~patterson) lecture slides: http://www-insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs152/
CS152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 3: ReviewTechnology & Delay Modeling September 3, 1997 Dave Patterson (httpcsberkeleyedu/~patterson) lecture slides: http://www-insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs152/
CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture. Lecture 9 - Scoreboard
 CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture Lecture 9 - Scoreboard Michela Taufer http://www.cis.udel.edu/~taufer/teaching/cis662f07 Powerpoint Lecture tes from John Hennessy and David Patterson s: Computer
CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture Lecture 9 - Scoreboard Michela Taufer http://www.cis.udel.edu/~taufer/teaching/cis662f07 Powerpoint Lecture tes from John Hennessy and David Patterson s: Computer
Multiple Predictors: BTB + Branch Direction Predictors
 Constructive Computer Architecture: Branch Prediction: Direction Predictors Arvind Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab. Massachusetts Institute of Technology October 28, 2015 http://csg.csail.mit.edu/6.175
Constructive Computer Architecture: Branch Prediction: Direction Predictors Arvind Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab. Massachusetts Institute of Technology October 28, 2015 http://csg.csail.mit.edu/6.175
EECS 470 Lecture 8. P6 µarchitecture. Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont Core 2 Microarchitecture
 P6 µarchitecture Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 Core 2 Microarchitecture Many thanks to Prof. Martin and Roth of University of Pennsylvania for most of these slides. Portions
P6 µarchitecture Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 Core 2 Microarchitecture Many thanks to Prof. Martin and Roth of University of Pennsylvania for most of these slides. Portions
EECS 427 Lecture 13: Leakage Power Reduction Readings: 6.4.2, CBF Ch.3. EECS 427 F09 Lecture Reminders
 EECS 427 Lecture 13: Leakage Power Reduction Readings: 6.4.2, CBF Ch.3 [Partly adapted from Irwin and Narayanan, and Nikolic] 1 Reminders CAD assignments Please submit CAD5 by tomorrow noon CAD6 is due
EECS 427 Lecture 13: Leakage Power Reduction Readings: 6.4.2, CBF Ch.3 [Partly adapted from Irwin and Narayanan, and Nikolic] 1 Reminders CAD assignments Please submit CAD5 by tomorrow noon CAD6 is due
[Krishna, 2(9): September, 2013] ISSN: Impact Factor: INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY
![[Krishna, 2(9): September, 2013] ISSN: Impact Factor: INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY [Krishna, 2(9): September, 2013] ISSN: Impact Factor: INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY](/thumbs/77/74980115.jpg) IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY Design of Wallace Tree Multiplier using Compressors K.Gopi Krishna *1, B.Santhosh 2, V.Sridhar 3 gopikoleti@gmail.com Abstract
IJESRT INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES & RESEARCH TECHNOLOGY Design of Wallace Tree Multiplier using Compressors K.Gopi Krishna *1, B.Santhosh 2, V.Sridhar 3 gopikoleti@gmail.com Abstract
CSE502: Computer Architecture CSE 502: Computer Architecture
 CSE 502: Computer Architecture Speculation and raps in Out-of-Order Cores What is wrong with omasulo s? Branch instructions Need branch prediction to guess what to fetch next Need speculative execution
CSE 502: Computer Architecture Speculation and raps in Out-of-Order Cores What is wrong with omasulo s? Branch instructions Need branch prediction to guess what to fetch next Need speculative execution
Clock-Powered CMOS: A Hybrid Adiabatic Logic Style for Energy-Efficient Computing
 Clock-Powered CMOS: A Hybrid Adiabatic Logic Style for Energy-Efficient Computing Nestoras Tzartzanis and Bill Athas nestoras@isiedu, athas@isiedu http://wwwisiedu/acmos Information Sciences Institute
Clock-Powered CMOS: A Hybrid Adiabatic Logic Style for Energy-Efficient Computing Nestoras Tzartzanis and Bill Athas nestoras@isiedu, athas@isiedu http://wwwisiedu/acmos Information Sciences Institute
8-bit Microcontroller with 2K Bytes In-System Programmable Flash. ATtiny20
 Features High Performance, Low Power AVR 8-bit Microcontroller Advanced RISC Architecture 112 Powerful Instructions Most Single Clock Cycle Execution 16 x 8 General Purpose Working Registers Fully Static
Features High Performance, Low Power AVR 8-bit Microcontroller Advanced RISC Architecture 112 Powerful Instructions Most Single Clock Cycle Execution 16 x 8 General Purpose Working Registers Fully Static
Instructor: Dr. Mainak Chaudhuri. Instructor: Dr. S. K. Aggarwal. Instructor: Dr. Rajat Moona
 NPTEL Online - IIT Kanpur Instructor: Dr. Mainak Chaudhuri Instructor: Dr. S. K. Aggarwal Course Name: Department: Program Optimization for Multi-core Architecture Computer Science and Engineering IIT
NPTEL Online - IIT Kanpur Instructor: Dr. Mainak Chaudhuri Instructor: Dr. S. K. Aggarwal Course Name: Department: Program Optimization for Multi-core Architecture Computer Science and Engineering IIT
EECS 470. Tomasulo s Algorithm. Lecture 4 Winter 2018
 omasulo s Algorithm Winter 2018 Slides developed in part by Profs. Austin, Brehob, Falsafi, Hill, Hoe, Lipasti, Martin, Roth, Shen, Smith, Sohi, yson, Vijaykumar, and Wenisch of Carnegie Mellon University,
omasulo s Algorithm Winter 2018 Slides developed in part by Profs. Austin, Brehob, Falsafi, Hill, Hoe, Lipasti, Martin, Roth, Shen, Smith, Sohi, yson, Vijaykumar, and Wenisch of Carnegie Mellon University,
Datapath Components. Multipliers, Counters, Timers, Register Files
 Datapath Components Multipliers, Counters, Timers, Register Files Multipliers An N x N multiplier Multiplies two N bit binary inputs Generates an NN bit result Creating a multiplier using two-level logic
Datapath Components Multipliers, Counters, Timers, Register Files Multipliers An N x N multiplier Multiplies two N bit binary inputs Generates an NN bit result Creating a multiplier using two-level logic
Computer Architecture and Organization:
 Computer Architecture and Organization: L03: Register transfer and System Bus By: A. H. Abdul Hafez Abdul.hafez@hku.edu.tr, ah.abdulhafez@gmail.com 1 CAO, by Dr. A.H. Abdul Hafez, CE Dept. HKU Outlines
Computer Architecture and Organization: L03: Register transfer and System Bus By: A. H. Abdul Hafez Abdul.hafez@hku.edu.tr, ah.abdulhafez@gmail.com 1 CAO, by Dr. A.H. Abdul Hafez, CE Dept. HKU Outlines
Unit-6 PROGRAMMABLE INTERRUPT CONTROLLERS 8259A-PROGRAMMABLE INTERRUPT CONTROLLER (PIC) INTRODUCTION
 M i c r o p r o c e s s o r s a n d M i c r o c o n t r o l l e r s P a g e 1 PROGRAMMABLE INTERRUPT CONTROLLERS 8259A-PROGRAMMABLE INTERRUPT CONTROLLER (PIC) INTRODUCTION Microcomputer system design requires
M i c r o p r o c e s s o r s a n d M i c r o c o n t r o l l e r s P a g e 1 PROGRAMMABLE INTERRUPT CONTROLLERS 8259A-PROGRAMMABLE INTERRUPT CONTROLLER (PIC) INTRODUCTION Microcomputer system design requires
How a processor can permute n bits in O(1) cycles
 How a processor can permute n bits in O(1) cycles Ruby Lee, Zhijie Shi, Xiao Yang Princeton Architecture Lab for Multimedia and Security (PALMS) Department of Electrical Engineering Princeton University
How a processor can permute n bits in O(1) cycles Ruby Lee, Zhijie Shi, Xiao Yang Princeton Architecture Lab for Multimedia and Security (PALMS) Department of Electrical Engineering Princeton University
Novel Low-Overhead Operand Isolation Techniques for Low-Power Datapath Synthesis
 Novel Low-Overhead Operand Isolation Techniques for Low-Power Datapath Synthesis N. Banerjee, A. Raychowdhury, S. Bhunia, H. Mahmoodi, and K. Roy School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Purdue University,
Novel Low-Overhead Operand Isolation Techniques for Low-Power Datapath Synthesis N. Banerjee, A. Raychowdhury, S. Bhunia, H. Mahmoodi, and K. Roy School of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Purdue University,
ECOM 4311 Digital System Design using VHDL. Chapter 9 Sequential Circuit Design: Practice
 ECOM 4311 Digital System Design using VHDL Chapter 9 Sequential Circuit Design: Practice Outline 1. Poor design practice and remedy 2. More counters 3. Register as fast temporary storage 4. Pipelined circuit
ECOM 4311 Digital System Design using VHDL Chapter 9 Sequential Circuit Design: Practice Outline 1. Poor design practice and remedy 2. More counters 3. Register as fast temporary storage 4. Pipelined circuit
Department Computer Science and Engineering IIT Kanpur
 NPTEL Online - IIT Bombay Course Name Parallel Computer Architecture Department Computer Science and Engineering IIT Kanpur Instructor Dr. Mainak Chaudhuri file:///e /parallel_com_arch/lecture1/main.html[6/13/2012
NPTEL Online - IIT Bombay Course Name Parallel Computer Architecture Department Computer Science and Engineering IIT Kanpur Instructor Dr. Mainak Chaudhuri file:///e /parallel_com_arch/lecture1/main.html[6/13/2012
Parallel architectures Electronic Computers LM
 Parallel architectures Electronic Computers LM 1 Architecture Architecture: functional behaviour of a computer. For instance a processor which executes DLX code Implementation: a logical network implementing
Parallel architectures Electronic Computers LM 1 Architecture Architecture: functional behaviour of a computer. For instance a processor which executes DLX code Implementation: a logical network implementing
A LOW POWER DESIGN FOR ARITHMETIC AND LOGIC UNIT
 A LOW POWER DESIGN FOR ARITHMETIC AND LOGIC UNIT NG KAR SIN (B.Tech. (Hons.), NUS) A THESIS SUBMITTED FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING NATIONAL
A LOW POWER DESIGN FOR ARITHMETIC AND LOGIC UNIT NG KAR SIN (B.Tech. (Hons.), NUS) A THESIS SUBMITTED FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING NATIONAL
2002 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference 2002 IEEE
 Outline 802.11a Overview Medium Access Control Design Baseband Transmitter Design Baseband Receiver Design Chip Details What is 802.11a? IEEE standard approved in September, 1999 12 20MHz channels at 5.15-5.35
Outline 802.11a Overview Medium Access Control Design Baseband Transmitter Design Baseband Receiver Design Chip Details What is 802.11a? IEEE standard approved in September, 1999 12 20MHz channels at 5.15-5.35
Topics Introduction to Microprocessors
 Topics 2244 Introduction to Microprocessors Chapter 8253 Programmable Interval Timer/Counter Suree Pumrin,, Ph.D. Interfacing with 886/888 Programming Mode 2244 Introduction to Microprocessors 2 8253/54
Topics 2244 Introduction to Microprocessors Chapter 8253 Programmable Interval Timer/Counter Suree Pumrin,, Ph.D. Interfacing with 886/888 Programming Mode 2244 Introduction to Microprocessors 2 8253/54
8-bit Microcontroller with 4K Bytes In-System Programmable Flash and Boost Converter. ATtiny43U. Preliminary
 Features High Performance, Low Power AVR 8-Bit Microcontroller Advanced RISC Architecture 120 Powerful Instructions Most Single Clock Cycle Execution 32 x 8 General Purpose Working Registers Fully Static
Features High Performance, Low Power AVR 8-Bit Microcontroller Advanced RISC Architecture 120 Powerful Instructions Most Single Clock Cycle Execution 32 x 8 General Purpose Working Registers Fully Static
ELEC 204 Digital Systems Design
 Fall 2013, Koç Uiversity ELEC 204 Digital Systems Desig Egi Erzi College of Egieerig Koç Uiversity,Istabul,Turkey eerzi@ku.edu.tr KU College of Egieerig Elec 204: Digital Systems Desig 1 Today: Datapaths
Fall 2013, Koç Uiversity ELEC 204 Digital Systems Desig Egi Erzi College of Egieerig Koç Uiversity,Istabul,Turkey eerzi@ku.edu.tr KU College of Egieerig Elec 204: Digital Systems Desig 1 Today: Datapaths
EE241 - Spring 2004 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits. Announcements. Borivoje Nikolic. Lecture 15 Low-Power Design: Supply Voltage Scaling
 EE241 - Spring 2004 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Borivoje Nikolic Lecture 15 Low-Power Design: Supply Voltage Scaling Announcements Homework #2 due today Midterm project reports due next Thursday
EE241 - Spring 2004 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Borivoje Nikolic Lecture 15 Low-Power Design: Supply Voltage Scaling Announcements Homework #2 due today Midterm project reports due next Thursday
OOO Execution & Precise State MIPS R10000 (R10K)
 OOO Execution & Precise State in MIPS R10000 (R10K) Nima Honarmand CDB. CDB.V Spring 2018 :: CSE 502 he Problem with P6 Map able + Regfile value R value Head Retire Dispatch op RS 1 2 V1 FU V2 ail Dispatch
OOO Execution & Precise State in MIPS R10000 (R10K) Nima Honarmand CDB. CDB.V Spring 2018 :: CSE 502 he Problem with P6 Map able + Regfile value R value Head Retire Dispatch op RS 1 2 V1 FU V2 ail Dispatch
The Metrics and Designs of an Arithmetic Logic Function over
 The Metrics and Designs of an Arithmetic Logic Function over 2002-2015 Jimmy Vallejo Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Central Flida Orlando, FL 32816-2362 Abstract There
The Metrics and Designs of an Arithmetic Logic Function over 2002-2015 Jimmy Vallejo Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Central Flida Orlando, FL 32816-2362 Abstract There
Microprocessor & Interfacing Lecture Programmable Interval Timer
 Microprocessor & Interfacing Lecture 30 8254 Programmable Interval Timer P A R U L B A N S A L A S S T P R O F E S S O R E C S D E P A R T M E N T D R O N A C H A R Y A C O L L E G E O F E N G I N E E
Microprocessor & Interfacing Lecture 30 8254 Programmable Interval Timer P A R U L B A N S A L A S S T P R O F E S S O R E C S D E P A R T M E N T D R O N A C H A R Y A C O L L E G E O F E N G I N E E
EECS 470 Lecture 5. Intro to Dynamic Scheduling (Scoreboarding) Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont
 Intro to Dynamic Scheduling (Scoreboarding) Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 Many thanks to Prof. Martin and Roth of University of Pennsylvania for most of these slides.
Intro to Dynamic Scheduling (Scoreboarding) Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 Many thanks to Prof. Martin and Roth of University of Pennsylvania for most of these slides.
Vector Arithmetic Logic Unit Amit Kumar Dutta JIS College of Engineering, Kalyani, WB, India
 Vol. 2 Issue 2, December -23, pp: (75-8), Available online at: www.erpublications.com Vector Arithmetic Logic Unit Amit Kumar Dutta JIS College of Engineering, Kalyani, WB, India Abstract: Real time operation
Vol. 2 Issue 2, December -23, pp: (75-8), Available online at: www.erpublications.com Vector Arithmetic Logic Unit Amit Kumar Dutta JIS College of Engineering, Kalyani, WB, India Abstract: Real time operation
Evolution of DSP Processors. Kartik Kariya EE, IIT Bombay
 Evolution of DSP Processors Kartik Kariya EE, IIT Bombay Agenda Expected features of DSPs Brief overview of early DSPs Multi-issue DSPs Case Study: VLIW based Processor (SPXK5) for Mobile Applications
Evolution of DSP Processors Kartik Kariya EE, IIT Bombay Agenda Expected features of DSPs Brief overview of early DSPs Multi-issue DSPs Case Study: VLIW based Processor (SPXK5) for Mobile Applications
Architectural Core Salvaging in a Multi-Core Processor for Hard-Error Tolerance
 Architectural Core Salvaging in a Multi-Core Processor for Hard-Error Tolerance Michael D. Powell, Arijit Biswas, Shantanu Gupta, and Shubu Mukherjee SPEARS Group, Intel Massachusetts EECS, University
Architectural Core Salvaging in a Multi-Core Processor for Hard-Error Tolerance Michael D. Powell, Arijit Biswas, Shantanu Gupta, and Shubu Mukherjee SPEARS Group, Intel Massachusetts EECS, University
CZ3001 ADVANCED COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE
 CZ3001 ADVANCED COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lab 3 Report Abstract Pipelining is a process in which successive steps of an instruction sequence are executed in turn by a sequence of modules able to operate concurrently,
CZ3001 ADVANCED COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lab 3 Report Abstract Pipelining is a process in which successive steps of an instruction sequence are executed in turn by a sequence of modules able to operate concurrently,
Tomasolu s s Algorithm
 omasolu s s Algorithm Fall 2007 Prof. homas Wenisch http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs4 70 Floating Point Buffers (FLB) ag ag ag Storage Bus Floating Point 4 3 Buffers FLB 6 5 5 4 Control 2 1 1 Result
omasolu s s Algorithm Fall 2007 Prof. homas Wenisch http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs4 70 Floating Point Buffers (FLB) ag ag ag Storage Bus Floating Point 4 3 Buffers FLB 6 5 5 4 Control 2 1 1 Result
Advanced Digital Logic Design
 \ / Advanced Digital Logic Design Using VHDL, State Machines, and Synthesis for FPGAs Sunggu Lee С ENGAGE 1% Learning" Australia Canada Mexico Singapore Spain United Kingdom United States Ф Ф ФФтшш»» '
\ / Advanced Digital Logic Design Using VHDL, State Machines, and Synthesis for FPGAs Sunggu Lee С ENGAGE 1% Learning" Australia Canada Mexico Singapore Spain United Kingdom United States Ф Ф ФФтшш»» '
Tomasulo s Algorithm. Tomasulo s Algorithm
 Tomasulo s Algorithm Load and store buffers Contain data and addresses, act like reservation stations Branch Prediction Top-level design: 56 Tomasulo s Algorithm Three Steps: Issue Get next instruction
Tomasulo s Algorithm Load and store buffers Contain data and addresses, act like reservation stations Branch Prediction Top-level design: 56 Tomasulo s Algorithm Three Steps: Issue Get next instruction
8-bit Atmel tinyavr Microcontroller with 16K Bytes In-System Programmable Flash. ATtiny1634
 8-bit Atmel tinyavr Microcontroller with 16K Bytes In-System Programmable Flash Features High Performance, Low Power AVR 8-bit Microcontroller Advanced RISC Architecture 125 Powerful Instructions Most
8-bit Atmel tinyavr Microcontroller with 16K Bytes In-System Programmable Flash Features High Performance, Low Power AVR 8-bit Microcontroller Advanced RISC Architecture 125 Powerful Instructions Most
CSE502: Computer Architecture CSE 502: Computer Architecture
 CSE 502: Computer Architecture Out-of-Order Schedulers Data-Capture Scheduler Dispatch: read available operands from ARF/ROB, store in scheduler Commit: Missing operands filled in from bypass Issue: When
CSE 502: Computer Architecture Out-of-Order Schedulers Data-Capture Scheduler Dispatch: read available operands from ARF/ROB, store in scheduler Commit: Missing operands filled in from bypass Issue: When
CS61C : Machine Structures
 Election Data is now available Puple Ameica! inst.eecs.bekeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Stuctues Lectue 31 Pipelined Execution, pat II 2004-11-10 Lectue PSOE Dan Gacia www.cs.bekeley.edu/~ddgacia The
Election Data is now available Puple Ameica! inst.eecs.bekeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Stuctues Lectue 31 Pipelined Execution, pat II 2004-11-10 Lectue PSOE Dan Gacia www.cs.bekeley.edu/~ddgacia The
