7/19/2012. IF for Load (Review) CSE 2021: Computer Organization. EX for Load (Review) ID for Load (Review) WB for Load (Review) MEM for Load (Review)
|
|
|
- Gabriella Davidson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CSE 2021: Computer Organization IF for Load (Review) Lecture-11 CPU Design : Pipelining-2 Review, Hazards Shakil M. Khan CSE-2021 July ID for Load (Review) EX for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July CSE-2021 July MEM for Load (Review) WB for Load (Review) Wrong register number CSE-2021 July CSE-2021 July
2 Corrected Datapath for Load (Review) Pipelined Control (Review) CSE-2021 July CSE-2021 July Data Hazards in ALU Instructions Consider this sequence: sub $2, $1,$3 and $12,$2,$5 or $13,$6,$2 add $14,$2,$2 sw $15,100($2) Dependencies & Forwarding We can resolve hazards with forwarding how do we detect when to forward? CSE-2021 July CSE-2021 July Detecting the Need to Forward Pass register numbers along pipeline e.g., ID/EX.RegisterRs = register number for Rs sitting in ID/EX pipeline register ALU operand register numbers in EX stage are given by ID/EX.RegisterRs, ID/EX.RegisterRt Data hazards when 1a. EX/MEM.RegisterRd = ID/EX.RegisterRs 1b. EX/MEM.RegisterRd = ID/EX.RegisterRt 2a. MEM/WB.RegisterRd = ID/EX.RegisterRs 2b. MEM/WB.RegisterRd = ID/EX.RegisterRt Fwd from EX/MEM pipeline reg Fwd from MEM/WB CSE-2021 July pipeline reg 11 Detecting the Need to Forward But only if forwarding instruction will write to a register! EX/MEM.RegWrite, MEM/WB.RegWrite And only if Rd for that instruction is not $zero EX/MEM.RegisterRd 0, MEM/WB.RegisterRd 0 CSE-2021 July
3 Forwarding Paths Forwarding Conditions EX hazard if (EX/MEM.RegWrite and (EX/MEM.RegisterRd 0) and (EX/MEM.RegisterRd = ID/EX.RegisterRs)) ForwardA = 10 if (EX/MEM.RegWrite and (EX/MEM.RegisterRd 0) and (EX/MEM.RegisterRd = ID/EX.RegisterRt)) ForwardB = 10 CSE-2021 July CSE-2021 July Forwarding Conditions MEM hazard and (MEM/WB.RegisterRd = ID/EX.RegisterRs)) ForwardA = 01 and (MEM/WB.RegisterRd = ID/EX.RegisterRt)) ForwardB = 01 Double Data Hazard Consider the sequence: add $1,$1,$2 add $1,$1,$3 add $1,$1,$4 Both hazards occur want to use the most recent Revise MEM hazard condition only fwd if EX hazard condition isn t true CSE-2021 July CSE-2021 July Revised Forwarding Condition Datapath with Forwarding MEM hazard and not (EX/MEM.RegWrite and (EX/MEM.RegisterRd 0) and (EX/MEM.RegisterRd = ID/EX.RegisterRs)) and (MEM/WB.RegisterRd = ID/EX.RegisterRs)) ForwardA = 01 and not (EX/MEM.RegWrite and (EX/MEM.RegisterRd 0) and (EX/MEM.RegisterRd = ID/EX.RegisterRt)) and (MEM/WB.RegisterRd = ID/EX.RegisterRt)) ForwardB = 01 CSE-2021 July CSE-2021 July
4 Load-Use Data Hazard Load-Use Hazard Detection Check when using instruction is decoded in ID stage Need to stall for one cycle ALU operand register numbers in ID stage are given by IF/ID.RegisterRs, IF/ID.RegisterRt Load-use hazard when ID/EX.MemRead and ((ID/EX.RegisterRt = IF/ID.RegisterRs) or (ID/EX.RegisterRt = IF/ID.RegisterRt)) If detected, stall and insert bubble CSE-2021 July CSE-2021 July How to Stall the Pipeline Force control values in ID/EX register to 0 EX, MEM and WB do nop (no-operation) Prevent update of PC and IF/ID register using instruction is decoded again following instruction is fetched again 1-cycle stall allows MEM to read data for lw can subsequently forward to EX stage Stall/Bubble in the Pipeline Stall inserted here CSE-2021 July CSE-2021 July Stall/Bubble in the Pipeline Datapath with Hazard Detection Or, more accurately CSE-2021 July CSE-2021 July
5 Stalls and Performance Stalls reduce performance but are required to get correct results Branch Hazards If branch outcome determined in MEM Compiler can arrange code to avoid hazards and stalls requires knowledge of the pipeline structure The BIG Picture Flush these instructions (Set control values to 0) CSE-2021 July PC CSE-2021 July Reducing Branch Delay Move hardware to determine outcome to ID stage move target address adder (easy) add register comparator (hard) need additional forwarding h/w as operands might depend on previous instruction Example: Branch Taken 36: sub $10, $4, $8 40: beq $1, $3, 7 44: and $12, $2, $5 48: or $13, $2, $6 52: add $14, $4, $2 56: slt $15, $6, $ : lw $4, 50($7) CSE-2021 July CSE-2021 July Example: Branch Taken Example: Branch Taken CSE-2021 July CSE-2021 July
6 Data Hazards for Branches If a comparison register is a destination of 2 nd or 3 rd preceding ALU instruction add $1, $2, $3 add $4, $5, $6 beq $1, $4, target Can resolve using forwarding Data Hazards for Branches If a comparison register is a destination of preceding ALU instruction or 2 nd preceding load instruction need 1 stall cycle lw $1, addr add $4, $5, $6 beq stalled beq $1, $4, target IF ID ID EX MEM WB CSE-2021 July CSE-2021 July Data Hazards for Branches If a comparison register is a destination of immediately preceding load instruction need 2 stall cycles lw $1, addr beq stalled beq stalled beq $1, $0, target IF ID ID ID EX MEM WB CSE-2021 July Dynamic Branch Prediction In deeper and superscalar pipelines, branch penalty is more significant Use dynamic prediction branch prediction buffer (aka branch history table) indexed by recent branch instruction addresses stores outcome (taken/not taken) to execute a branch check table, expect the same outcome start fetching from fall-through or target if wrong, flush pipeline and flip prediction CSE-2021 July Bit Predictor: Shortcoming Inner loop branches mispredicted twice! outer: inner: beq,, inner beq,, outer 2-Bit Predictor Only change prediction on two successive mispredictions Mispredict as taken on last iteration of inner loop Then mispredict as not taken on first iteration of inner loop next time around CSE-2021 July CSE-2021 July
7 Calculating the Branch Target Concluding Remarks Even with predictor, still need to calculate the target address 1-cycle penalty for a taken branch Branch target buffer cache of target addresses indexed by PC when instruction fetched if hit and instruction is branch predicted taken, can fetch target immediately ISA influences design of datapath and control Datapath and control influence design of ISA Pipelining improves instruction throughput using parallelism more instructions completed per second latency for each instruction not reduced Hazards: structural, data, control Multiple issue and dynamic scheduling (ILP) dependencies limit achievable parallelism complexity leads to the power wall CSE-2021 July CSE-2021 July
CSE 2021: Computer Organization
 CSE 2021: Computer Organization Lecture-11 CPU Design : Pipelining-2 Review, Hazards Shakil M. Khan IF for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-14-2011 2 ID for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-14-2011 3 EX for Load
CSE 2021: Computer Organization Lecture-11 CPU Design : Pipelining-2 Review, Hazards Shakil M. Khan IF for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-14-2011 2 ID for Load (Review) CSE-2021 July-14-2011 3 EX for Load
7/11/2012. Single Cycle (Review) CSE 2021: Computer Organization. Multi-Cycle Implementation. Single Cycle with Jump. Pipelining Analogy
 CSE 2021: Computer Organization Single Cycle (Review) Lecture-10 CPU Design : Pipelining-1 Overview, Datapath and control Shakil M. Khan CSE-2021 July-12-2012 2 Single Cycle with Jump Multi-Cycle Implementation
CSE 2021: Computer Organization Single Cycle (Review) Lecture-10 CPU Design : Pipelining-1 Overview, Datapath and control Shakil M. Khan CSE-2021 July-12-2012 2 Single Cycle with Jump Multi-Cycle Implementation
Chapter 4. Pipelining Analogy. The Processor. Pipelined laundry: overlapping execution. Parallelism improves performance. Four loads: Non-stop:
 Chapter 4 The Processor Part II Pipelining Analogy Pipelined laundry: overlapping execution Parallelism improves performance Four loads: Speedup = 8/3.5 = 2.3 Non-stop: Speedup p = 2n/(0.5n + 1.5) 4 =
Chapter 4 The Processor Part II Pipelining Analogy Pipelined laundry: overlapping execution Parallelism improves performance Four loads: Speedup = 8/3.5 = 2.3 Non-stop: Speedup p = 2n/(0.5n + 1.5) 4 =
Pipelined Processor Design
 Pipelined Processor Design COE 38 Computer Architecture Prof. Muhamed Mudawar Computer Engineering Department King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Presentation Outline Pipelining versus Serial
Pipelined Processor Design COE 38 Computer Architecture Prof. Muhamed Mudawar Computer Engineering Department King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals Presentation Outline Pipelining versus Serial
Lecture Topics. Announcements. Today: Pipelined Processors (P&H ) Next: continued. Milestone #4 (due 2/23) Milestone #5 (due 3/2)
 Lecture Topics Today: Pipelined Processors (P&H 4.5-4.10) Next: continued 1 Announcements Milestone #4 (due 2/23) Milestone #5 (due 3/2) 2 1 ISA Implementations Three different strategies: single-cycle
Lecture Topics Today: Pipelined Processors (P&H 4.5-4.10) Next: continued 1 Announcements Milestone #4 (due 2/23) Milestone #5 (due 3/2) 2 1 ISA Implementations Three different strategies: single-cycle
LECTURE 8. Pipelining: Datapath and Control
 LECTURE 8 Pipelining: Datapath and Control PIPELINED DATAPATH As with the single-cycle and multi-cycle implementations, we will start by looking at the datapath for pipelining. We already know that pipelining
LECTURE 8 Pipelining: Datapath and Control PIPELINED DATAPATH As with the single-cycle and multi-cycle implementations, we will start by looking at the datapath for pipelining. We already know that pipelining
EECE 321: Computer Organiza5on
 EECE 321: Computer Organiza5on Mohammad M. Mansour Dept. of Electrical and Compute Engineering American University of Beirut Lecture 21: Pipelining Processor Pipelining Same principles can be applied to
EECE 321: Computer Organiza5on Mohammad M. Mansour Dept. of Electrical and Compute Engineering American University of Beirut Lecture 21: Pipelining Processor Pipelining Same principles can be applied to
Lecture 4: Introduction to Pipelining
 Lecture 4: Introduction to Pipelining Pipelining Laundry Example Ann, Brian, Cathy, Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes A B C D Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder
Lecture 4: Introduction to Pipelining Pipelining Laundry Example Ann, Brian, Cathy, Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes A B C D Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder
IF ID EX MEM WB 400 ps 225 ps 350 ps 450 ps 300 ps
 CSE 30321 Computer Architecture I Fall 2011 Homework 06 Pipelined Processors 75 points Assigned: November 1, 2011 Due: November 8, 2011 PLEASE DO THE ASSIGNMENT ON THIS HANDOUT!!! Problem 1: (15 points)
CSE 30321 Computer Architecture I Fall 2011 Homework 06 Pipelined Processors 75 points Assigned: November 1, 2011 Due: November 8, 2011 PLEASE DO THE ASSIGNMENT ON THIS HANDOUT!!! Problem 1: (15 points)
IF ID EX MEM WB 400 ps 225 ps 350 ps 450 ps 300 ps
 CSE 30321 Computer Architecture I Fall 2010 Homework 06 Pipelined Processors 85 points Assigned: November 2, 2010 Due: November 9, 2010 PLEASE DO THE ASSIGNMENT ON THIS HANDOUT!!! Problem 1: (25 points)
CSE 30321 Computer Architecture I Fall 2010 Homework 06 Pipelined Processors 85 points Assigned: November 2, 2010 Due: November 9, 2010 PLEASE DO THE ASSIGNMENT ON THIS HANDOUT!!! Problem 1: (25 points)
Computer Architecture
 Computer Architecture An Introduction Virendra Singh Associate Professor Computer Architecture and Dependable Systems Lab Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay http://www.ee.iitb.ac.in/~viren/
Computer Architecture An Introduction Virendra Singh Associate Professor Computer Architecture and Dependable Systems Lab Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay http://www.ee.iitb.ac.in/~viren/
RISC Design: Pipelining
 RISC Design: Pipelining Virendra Singh Associate Professor Computer Architecture and Dependable Systems Lab Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay http://www.ee.iitb.ac.in/~viren/
RISC Design: Pipelining Virendra Singh Associate Professor Computer Architecture and Dependable Systems Lab Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay http://www.ee.iitb.ac.in/~viren/
A B C D. Ann, Brian, Cathy, & Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold. Time
 Pipelining Readings: 4.5-4.8 Example: Doing the laundry A B C D Ann, Brian, Cathy, & Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder takes
Pipelining Readings: 4.5-4.8 Example: Doing the laundry A B C D Ann, Brian, Cathy, & Dave each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder takes
Pipelining A B C D. Readings: Example: Doing the laundry. Ann, Brian, Cathy, & Dave. each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold
 Pipelining Readings: 4.5-4.8 Example: Doing the laundry Ann, Brian, Cathy, & Dave A B C D each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder takes
Pipelining Readings: 4.5-4.8 Example: Doing the laundry Ann, Brian, Cathy, & Dave A B C D each have one load of clothes to wash, dry, and fold Washer takes 30 minutes Dryer takes 40 minutes Folder takes
CS 110 Computer Architecture Lecture 11: Pipelining
 CS 110 Computer Architecture Lecture 11: Pipelining Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger http://shtech.org/courses/ca/ School of Information Science and Technology SIST ShanghaiTech University Slides based on
CS 110 Computer Architecture Lecture 11: Pipelining Instructor: Sören Schwertfeger http://shtech.org/courses/ca/ School of Information Science and Technology SIST ShanghaiTech University Slides based on
ECE 2300 Digital Logic & Computer Organization. More Pipelined Microprocessor
 ECE 2300 Digital ogic & Computer Organization Spring 2018 ore Pipelined icroprocessor ecture 18: 1 nnouncements No instructor office hour today Rescheduled to onday pril 16, 4:00-5:30pm Prelim 2 review
ECE 2300 Digital ogic & Computer Organization Spring 2018 ore Pipelined icroprocessor ecture 18: 1 nnouncements No instructor office hour today Rescheduled to onday pril 16, 4:00-5:30pm Prelim 2 review
Suggested Readings! Lecture 12" Introduction to Pipelining! Example: We have to build x cars...! ...Each car takes 6 steps to build...! ! Readings!
 1! CSE 30321 Lecture 12 Introduction to Pipelining! CSE 30321 Lecture 12 Introduction to Pipelining! 2! Suggested Readings!! Readings!! H&P: Chapter 4.5-4.7!! (Over the next 3-4 lectures)! Lecture 12"
1! CSE 30321 Lecture 12 Introduction to Pipelining! CSE 30321 Lecture 12 Introduction to Pipelining! 2! Suggested Readings!! Readings!! H&P: Chapter 4.5-4.7!! (Over the next 3-4 lectures)! Lecture 12"
Instruction Level Parallelism. Data Dependence Static Scheduling
 Instruction Level Parallelism Data Dependence Static Scheduling Basic Block A straight line code sequence with no branches in except to the entry and no branches out except at the exit Loop: L.D ADD.D
Instruction Level Parallelism Data Dependence Static Scheduling Basic Block A straight line code sequence with no branches in except to the entry and no branches out except at the exit Loop: L.D ADD.D
RISC Central Processing Unit
 RISC Central Processing Unit Lan-Da Van ( 范倫達 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Taiwan, R.O.C. Spring, 2014 ldvan@cs.nctu.edu.tw http://www.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~ldvan/
RISC Central Processing Unit Lan-Da Van ( 范倫達 ), Ph. D. Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Taiwan, R.O.C. Spring, 2014 ldvan@cs.nctu.edu.tw http://www.cs.nctu.edu.tw/~ldvan/
Computer Hardware. Pipeline
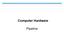 Computer Hardware Pipeline Conventional Datapath 2.4 ns is required to perform a single operation (i.e. 416.7 MHz). Register file MUX B 0.6 ns Clock 0.6 ns 0.2 ns Function unit 0.8 ns MUX D 0.2 ns c. Production
Computer Hardware Pipeline Conventional Datapath 2.4 ns is required to perform a single operation (i.e. 416.7 MHz). Register file MUX B 0.6 ns Clock 0.6 ns 0.2 ns Function unit 0.8 ns MUX D 0.2 ns c. Production
6.S084 Tutorial Problems L19 Control Hazards in Pipelined Processors
 6.S084 Tutorial Problems L19 Control Hazards in Pipelined Processors Options for dealing with data and control hazards: stall, bypass, speculate 6.S084 Worksheet - 1 of 10 - L19 Control Hazards in Pipelined
6.S084 Tutorial Problems L19 Control Hazards in Pipelined Processors Options for dealing with data and control hazards: stall, bypass, speculate 6.S084 Worksheet - 1 of 10 - L19 Control Hazards in Pipelined
CSEN 601: Computer System Architecture Summer 2014
 CSEN 601: Cmputer System Architecture Summer 2014 Practice Assignment 7 Slutin Exercise 7-1: Based n the MIPS pipeline implementatin yu studied, what are the cntrl signals that have t be stred in the ID/EX
CSEN 601: Cmputer System Architecture Summer 2014 Practice Assignment 7 Slutin Exercise 7-1: Based n the MIPS pipeline implementatin yu studied, what are the cntrl signals that have t be stred in the ID/EX
Project 5: Optimizer Jason Ansel
 Project 5: Optimizer Jason Ansel Overview Project guidelines Benchmarking Library OoO CPUs Project Guidelines Use optimizations from lectures as your arsenal If you decide to implement one, look at Whale
Project 5: Optimizer Jason Ansel Overview Project guidelines Benchmarking Library OoO CPUs Project Guidelines Use optimizations from lectures as your arsenal If you decide to implement one, look at Whale
EN164: Design of Computing Systems Lecture 22: Processor / ILP 3
 EN164: Design of Computing Systems Lecture 22: Processor / ILP 3 Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University
EN164: Design of Computing Systems Lecture 22: Processor / ILP 3 Professor Sherief Reda http://scale.engin.brown.edu Electrical Sciences and Computer Engineering School of Engineering Brown University
CMP 301B Computer Architecture. Appendix C
 CMP 301B Computer Architecture Appendix C Dealing with Exceptions What should be done when an exception arises and many instructions are in the pipeline??!! Force a trap instruction in the next IF stage
CMP 301B Computer Architecture Appendix C Dealing with Exceptions What should be done when an exception arises and many instructions are in the pipeline??!! Force a trap instruction in the next IF stage
Out-of-Order Execution. Register Renaming. Nima Honarmand
 Out-of-Order Execution & Register Renaming Nima Honarmand Out-of-Order (OOO) Execution (1) Essence of OOO execution is Dynamic Scheduling Dynamic scheduling: processor hardware determines instruction execution
Out-of-Order Execution & Register Renaming Nima Honarmand Out-of-Order (OOO) Execution (1) Essence of OOO execution is Dynamic Scheduling Dynamic scheduling: processor hardware determines instruction execution
Some material adapted from Mohamed Younis, UMBC CMSC 611 Spr 2003 course slides Some material adapted from Hennessy & Patterson / 2003 Elsevier
 Some material adapted from Mohamed Younis, UMBC CMSC 611 Spr 2003 course slides Some material adapted from Hennessy & Patterson / 2003 Elsevier Science !!! Basic MIPS integer pipeline Branches with one
Some material adapted from Mohamed Younis, UMBC CMSC 611 Spr 2003 course slides Some material adapted from Hennessy & Patterson / 2003 Elsevier Science !!! Basic MIPS integer pipeline Branches with one
CMSC 611: Advanced Computer Architecture
 CMSC 611: Advanced Computer Architecture Pipelining Some material adapted from Mohamed Younis, UMBC CMSC 611 Spr 2003 course slides Some material adapted from Hennessy & Patterson / 2003 Elsevier Science
CMSC 611: Advanced Computer Architecture Pipelining Some material adapted from Mohamed Younis, UMBC CMSC 611 Spr 2003 course slides Some material adapted from Hennessy & Patterson / 2003 Elsevier Science
Dynamic Scheduling I
 basic pipeline started with single, in-order issue, single-cycle operations have extended this basic pipeline with multi-cycle operations multiple issue (superscalar) now: dynamic scheduling (out-of-order
basic pipeline started with single, in-order issue, single-cycle operations have extended this basic pipeline with multi-cycle operations multiple issue (superscalar) now: dynamic scheduling (out-of-order
Asanovic/Devadas Spring Pipeline Hazards. Krste Asanovic Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T.
 Pipeline Hazards Krste Asanovic Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. Pipelined DLX Datapath without interlocks and jumps 31 0x4 RegDst RegWrite inst Inst rs1 rs2 rd1 ws wd rd2 GPRs Imm Ext A B OpSel
Pipeline Hazards Krste Asanovic Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. Pipelined DLX Datapath without interlocks and jumps 31 0x4 RegDst RegWrite inst Inst rs1 rs2 rd1 ws wd rd2 GPRs Imm Ext A B OpSel
ECE473 Computer Architecture and Organization. Pipeline: Introduction
 Computer Architecture and Organization Pipeline: Introduction Lecturer: Prof. Yifeng Zhu Fall, 2015 Portions of these slides are derived from: Dave Patterson UCB Lec 11.1 The Laundry Analogy Student A,
Computer Architecture and Organization Pipeline: Introduction Lecturer: Prof. Yifeng Zhu Fall, 2015 Portions of these slides are derived from: Dave Patterson UCB Lec 11.1 The Laundry Analogy Student A,
Computer Science 246. Advanced Computer Architecture. Spring 2010 Harvard University. Instructor: Prof. David Brooks
 Advanced Computer Architecture Spring 2010 Harvard University Instructor: Prof. dbrooks@eecs.harvard.edu Lecture Outline Instruction-Level Parallelism Scoreboarding (A.8) Instruction Level Parallelism
Advanced Computer Architecture Spring 2010 Harvard University Instructor: Prof. dbrooks@eecs.harvard.edu Lecture Outline Instruction-Level Parallelism Scoreboarding (A.8) Instruction Level Parallelism
Chapter 16 - Instruction-Level Parallelism and Superscalar Processors
 Chapter 16 - Instruction-Level Parallelism and Superscalar Processors Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 16 - Superscalar Processors 1 / 78 Table of Contents I 1 Overview
Chapter 16 - Instruction-Level Parallelism and Superscalar Processors Luis Tarrataca luis.tarrataca@gmail.com CEFET-RJ L. Tarrataca Chapter 16 - Superscalar Processors 1 / 78 Table of Contents I 1 Overview
Pipelining and ISA Design
 Pipelined instuc.on Execu.on 1 Pipelining and ISA Design MIPS Instuc:on Set designed fo pipelining All instuc:ons ae 32- bits Easie to fetch and decode in one cycle x86: 1- to 17- byte instuc:ons (x86
Pipelined instuc.on Execu.on 1 Pipelining and ISA Design MIPS Instuc:on Set designed fo pipelining All instuc:ons ae 32- bits Easie to fetch and decode in one cycle x86: 1- to 17- byte instuc:ons (x86
Dynamic Scheduling II
 so far: dynamic scheduling (out-of-order execution) Scoreboard omasulo s algorithm register renaming: removing artificial dependences (WAR/WAW) now: out-of-order execution + precise state advanced topic:
so far: dynamic scheduling (out-of-order execution) Scoreboard omasulo s algorithm register renaming: removing artificial dependences (WAR/WAW) now: out-of-order execution + precise state advanced topic:
Department Computer Science and Engineering IIT Kanpur
 NPTEL Online - IIT Bombay Course Name Parallel Computer Architecture Department Computer Science and Engineering IIT Kanpur Instructor Dr. Mainak Chaudhuri file:///e /parallel_com_arch/lecture1/main.html[6/13/2012
NPTEL Online - IIT Bombay Course Name Parallel Computer Architecture Department Computer Science and Engineering IIT Kanpur Instructor Dr. Mainak Chaudhuri file:///e /parallel_com_arch/lecture1/main.html[6/13/2012
Instruction Level Parallelism Part II - Scoreboard
 Course on: Advanced Computer Architectures Instruction Level Parallelism Part II - Scoreboard Prof. Cristina Silvano Politecnico di Milano email: cristina.silvano@polimi.it 1 Basic Assumptions We consider
Course on: Advanced Computer Architectures Instruction Level Parallelism Part II - Scoreboard Prof. Cristina Silvano Politecnico di Milano email: cristina.silvano@polimi.it 1 Basic Assumptions We consider
EECS 470 Lecture 4. Pipelining & Hazards II. Winter Prof. Ronald Dreslinski h8p://
 Wenisch 26 -- Portions ustin, Brehob, Falsafi, Hill, Hoe, ipasti, artin, Roth, Shen, Smith, Sohi, Tyson, Vijaykumar EECS 4 ecture 4 Pipelining & Hazards II Winter 29 GS STTION Prof. Ronald Dreslinski h8p://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs4
Wenisch 26 -- Portions ustin, Brehob, Falsafi, Hill, Hoe, ipasti, artin, Roth, Shen, Smith, Sohi, Tyson, Vijaykumar EECS 4 ecture 4 Pipelining & Hazards II Winter 29 GS STTION Prof. Ronald Dreslinski h8p://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs4
CSE502: Computer Architecture CSE 502: Computer Architecture
 CSE 502: Computer Architecture Out-of-Order Execution and Register Rename In Search of Parallelism rivial Parallelism is limited What is trivial parallelism? In-order: sequential instructions do not have
CSE 502: Computer Architecture Out-of-Order Execution and Register Rename In Search of Parallelism rivial Parallelism is limited What is trivial parallelism? In-order: sequential instructions do not have
CSE502: Computer Architecture CSE 502: Computer Architecture
 CSE 502: Computer Architecture Out-of-Order Execution and Register Rename In Search of Parallelism rivial Parallelism is limited What is trivial parallelism? In-order: sequential instructions do not have
CSE 502: Computer Architecture Out-of-Order Execution and Register Rename In Search of Parallelism rivial Parallelism is limited What is trivial parallelism? In-order: sequential instructions do not have
Computer Architecture ( L), Fall 2017 HW 3: Branch handling and GPU SOLUTIONS
 Computer Architecture (263-2210-00L), Fall 2017 HW 3: Branch handling and GPU SOLUTIONS Instructor: Prof. Onur Mutlu TAs: Hasan Hassan, Arash Tavakkol, Mohammad Sadr, Lois Orosa, Juan Gomez Luna Assigned:
Computer Architecture (263-2210-00L), Fall 2017 HW 3: Branch handling and GPU SOLUTIONS Instructor: Prof. Onur Mutlu TAs: Hasan Hassan, Arash Tavakkol, Mohammad Sadr, Lois Orosa, Juan Gomez Luna Assigned:
Instructor: Dr. Mainak Chaudhuri. Instructor: Dr. S. K. Aggarwal. Instructor: Dr. Rajat Moona
 NPTEL Online - IIT Kanpur Instructor: Dr. Mainak Chaudhuri Instructor: Dr. S. K. Aggarwal Course Name: Department: Program Optimization for Multi-core Architecture Computer Science and Engineering IIT
NPTEL Online - IIT Kanpur Instructor: Dr. Mainak Chaudhuri Instructor: Dr. S. K. Aggarwal Course Name: Department: Program Optimization for Multi-core Architecture Computer Science and Engineering IIT
On the Rules of Low-Power Design
 On the Rules of Low-Power Design (and Why You Should Break Them) Prof. Todd Austin University of Michigan austin@umich.edu A long time ago, in a not so far away place The Rules of Low-Power Design P =
On the Rules of Low-Power Design (and Why You Should Break Them) Prof. Todd Austin University of Michigan austin@umich.edu A long time ago, in a not so far away place The Rules of Low-Power Design P =
CS420/520 Computer Architecture I
 CS42/52 Computer rchitecture I Designing a Pipeline Processor (C4: ppendix ) Dr. Xiaobo Zhou Department of Computer Science CS42/52 pipeline. UC. Colorado Springs dapted from UCB97 & UCB3 Branch Jump Recap:
CS42/52 Computer rchitecture I Designing a Pipeline Processor (C4: ppendix ) Dr. Xiaobo Zhou Department of Computer Science CS42/52 pipeline. UC. Colorado Springs dapted from UCB97 & UCB3 Branch Jump Recap:
Instruction Level Parallelism III: Dynamic Scheduling
 Instruction Level Parallelism III: Dynamic Scheduling Reading: Appendix A (A-67) H&P Chapter 2 Instruction Level Parallelism III: Dynamic Scheduling 1 his Unit: Dynamic Scheduling Application OS Compiler
Instruction Level Parallelism III: Dynamic Scheduling Reading: Appendix A (A-67) H&P Chapter 2 Instruction Level Parallelism III: Dynamic Scheduling 1 his Unit: Dynamic Scheduling Application OS Compiler
EECS 470. Tomasulo s Algorithm. Lecture 4 Winter 2018
 omasulo s Algorithm Winter 2018 Slides developed in part by Profs. Austin, Brehob, Falsafi, Hill, Hoe, Lipasti, Martin, Roth, Shen, Smith, Sohi, yson, Vijaykumar, and Wenisch of Carnegie Mellon University,
omasulo s Algorithm Winter 2018 Slides developed in part by Profs. Austin, Brehob, Falsafi, Hill, Hoe, Lipasti, Martin, Roth, Shen, Smith, Sohi, yson, Vijaykumar, and Wenisch of Carnegie Mellon University,
EECS 470 Lecture 5. Intro to Dynamic Scheduling (Scoreboarding) Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont
 Intro to Dynamic Scheduling (Scoreboarding) Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 Many thanks to Prof. Martin and Roth of University of Pennsylvania for most of these slides.
Intro to Dynamic Scheduling (Scoreboarding) Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 Many thanks to Prof. Martin and Roth of University of Pennsylvania for most of these slides.
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture. Pipelining Hazards. Instructor: Senior Lecturer SOE Dan Garcia
 CS 61C: Geat Ideas in Compute Achitectue Pipelining Hazads Instucto: Senio Lectue SOE Dan Gacia 1 Geat Idea #4: Paallelism So9wae Paallel Requests Assigned to compute e.g. seach Gacia Paallel Theads Assigned
CS 61C: Geat Ideas in Compute Achitectue Pipelining Hazads Instucto: Senio Lectue SOE Dan Gacia 1 Geat Idea #4: Paallelism So9wae Paallel Requests Assigned to compute e.g. seach Gacia Paallel Theads Assigned
EE 457 Homework 5 Redekopp Name: Score: / 100_
 EE 457 Homework 5 Redekopp Name: Score: / 100_ Single-Cycle CPU The following exercises are taken from Hennessy and Patterson, CO&D 2 nd, 3 rd, and 4 th Ed. 1.) (6 pts.) Review your class notes. a. Is
EE 457 Homework 5 Redekopp Name: Score: / 100_ Single-Cycle CPU The following exercises are taken from Hennessy and Patterson, CO&D 2 nd, 3 rd, and 4 th Ed. 1.) (6 pts.) Review your class notes. a. Is
U. Wisconsin CS/ECE 752 Advanced Computer Architecture I
 U. Wisconsin CS/ECE 752 Advanced Computer Architecture I Prof. Karu Sankaralingam Unit 5: Dynamic Scheduling I Slides developed by Amir Roth of University of Pennsylvania with sources that included University
U. Wisconsin CS/ECE 752 Advanced Computer Architecture I Prof. Karu Sankaralingam Unit 5: Dynamic Scheduling I Slides developed by Amir Roth of University of Pennsylvania with sources that included University
FMP For More Practice
 FP 6.-6 For ore Practice Labeling Pipeline Diagrams with 6.5 [2] < 6.3> To understand how pipeline works, let s consider these five instructions going through the pipeline: lw $, 2($) sub $, $2, $3 and
FP 6.-6 For ore Practice Labeling Pipeline Diagrams with 6.5 [2] < 6.3> To understand how pipeline works, let s consider these five instructions going through the pipeline: lw $, 2($) sub $, $2, $3 and
Problem: hazards delay instruction completion & increase the CPI. Compiler scheduling (static scheduling) reduces impact of hazards
 Dynamic Scheduling Pipelining: Issue instructions in every cycle (CPI 1) Problem: hazards delay instruction completion & increase the CPI Compiler scheduling (static scheduling) reduces impact of hazards
Dynamic Scheduling Pipelining: Issue instructions in every cycle (CPI 1) Problem: hazards delay instruction completion & increase the CPI Compiler scheduling (static scheduling) reduces impact of hazards
ECE 4750 Computer Architecture, Fall 2016 T09 Advanced Processors: Superscalar Execution
 ECE 4750 Computer Architecture, Fall 2016 T09 Advanced Processors: Superscalar Execution School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cornell University revision: 2016-11-28-17-33 1 In-Order Dual-Issue
ECE 4750 Computer Architecture, Fall 2016 T09 Advanced Processors: Superscalar Execution School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Cornell University revision: 2016-11-28-17-33 1 In-Order Dual-Issue
Pipelined Beta. Handouts: Lecture Slides. Where are the registers? Spring /10/01. L16 Pipelined Beta 1
 Pipelined Beta Where are the registers? Handouts: Lecture Slides L16 Pipelined Beta 1 Increasing CPU Performance MIPS = Freq CPI MIPS = Millions of Instructions/Second Freq = Clock Frequency, MHz CPI =
Pipelined Beta Where are the registers? Handouts: Lecture Slides L16 Pipelined Beta 1 Increasing CPU Performance MIPS = Freq CPI MIPS = Millions of Instructions/Second Freq = Clock Frequency, MHz CPI =
COSC4201. Scoreboard
 COSC4201 Scoreboard Prof. Mokhtar Aboelaze York University Based on Slides by Prof. L. Bhuyan (UCR) Prof. M. Shaaban (RIT) 1 Overcoming Data Hazards with Dynamic Scheduling In the pipeline, if there is
COSC4201 Scoreboard Prof. Mokhtar Aboelaze York University Based on Slides by Prof. L. Bhuyan (UCR) Prof. M. Shaaban (RIT) 1 Overcoming Data Hazards with Dynamic Scheduling In the pipeline, if there is
Single-Cycle CPU The following exercises are taken from Hennessy and Patterson, CO&D 2 nd, 3 rd, and 4 th Ed.
 EE 357 Homework 7 Redekopp Name: Lec: 9:30 / 11:00 Score: Submit answers via Blackboard for all problems except 5.) and 6.). For those questions, submit a hardcopy with your answers, diagrams, circuit
EE 357 Homework 7 Redekopp Name: Lec: 9:30 / 11:00 Score: Submit answers via Blackboard for all problems except 5.) and 6.). For those questions, submit a hardcopy with your answers, diagrams, circuit
CSE502: Computer Architecture CSE 502: Computer Architecture
 CSE 502: Computer Architecture Speculation and raps in Out-of-Order Cores What is wrong with omasulo s? Branch instructions Need branch prediction to guess what to fetch next Need speculative execution
CSE 502: Computer Architecture Speculation and raps in Out-of-Order Cores What is wrong with omasulo s? Branch instructions Need branch prediction to guess what to fetch next Need speculative execution
CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture. Lecture 9 - Scoreboard
 CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture Lecture 9 - Scoreboard Michela Taufer http://www.cis.udel.edu/~taufer/teaching/cis662f07 Powerpoint Lecture tes from John Hennessy and David Patterson s: Computer
CISC 662 Graduate Computer Architecture Lecture 9 - Scoreboard Michela Taufer http://www.cis.udel.edu/~taufer/teaching/cis662f07 Powerpoint Lecture tes from John Hennessy and David Patterson s: Computer
Parallel architectures Electronic Computers LM
 Parallel architectures Electronic Computers LM 1 Architecture Architecture: functional behaviour of a computer. For instance a processor which executes DLX code Implementation: a logical network implementing
Parallel architectures Electronic Computers LM 1 Architecture Architecture: functional behaviour of a computer. For instance a processor which executes DLX code Implementation: a logical network implementing
Selected Solutions to Problem-Set #3 COE 608: Computer Organization and Architecture Single Cycle Datapath and Control
 Selected Solutions to Problem-Set #3 COE 608: Computer Organization and Architecture Single Cycle Datapath and Control 4.1. Done in the class 4.2. Try it yourself Q4.3. 4.3.1 a. Logic Only b. Logic Only
Selected Solutions to Problem-Set #3 COE 608: Computer Organization and Architecture Single Cycle Datapath and Control 4.1. Done in the class 4.2. Try it yourself Q4.3. 4.3.1 a. Logic Only b. Logic Only
Tomasolu s s Algorithm
 omasolu s s Algorithm Fall 2007 Prof. homas Wenisch http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs4 70 Floating Point Buffers (FLB) ag ag ag Storage Bus Floating Point 4 3 Buffers FLB 6 5 5 4 Control 2 1 1 Result
omasolu s s Algorithm Fall 2007 Prof. homas Wenisch http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs4 70 Floating Point Buffers (FLB) ag ag ag Storage Bus Floating Point 4 3 Buffers FLB 6 5 5 4 Control 2 1 1 Result
CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture
 CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr. Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Last updated: November 8, 2017 at 09:27 CS429 Slideset 14: 1 Overview What s wrong
CS429: Computer Organization and Architecture Dr. Bill Young Department of Computer Sciences University of Texas at Austin Last updated: November 8, 2017 at 09:27 CS429 Slideset 14: 1 Overview What s wrong
Precise State Recovery. Out-of-Order Pipelines
 Precise State Recovery in Out-of-Order Pipelines Nima Honarmand Recall Our Generic OOO Pipeline Instruction flow (pipeline front-end) is in-order Register and memory execution are OOO And, we need a final
Precise State Recovery in Out-of-Order Pipelines Nima Honarmand Recall Our Generic OOO Pipeline Instruction flow (pipeline front-end) is in-order Register and memory execution are OOO And, we need a final
CS61C : Machine Structures
 Election Data is now available Puple Ameica! inst.eecs.bekeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Stuctues Lectue 31 Pipelined Execution, pat II 2004-11-10 Lectue PSOE Dan Gacia www.cs.bekeley.edu/~ddgacia The
Election Data is now available Puple Ameica! inst.eecs.bekeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Stuctues Lectue 31 Pipelined Execution, pat II 2004-11-10 Lectue PSOE Dan Gacia www.cs.bekeley.edu/~ddgacia The
SATSim: A Superscalar Architecture Trace Simulator Using Interactive Animation
 SATSim: A Superscalar Architecture Trace Simulator Using Interactive Animation Mark Wolff Linda Wills School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology {wolff,linda.wills}@ece.gatech.edu
SATSim: A Superscalar Architecture Trace Simulator Using Interactive Animation Mark Wolff Linda Wills School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology {wolff,linda.wills}@ece.gatech.edu
CMSC 611: Advanced Computer Architecture
 CMSC 611: Advanced Compute Achitectue Pipelining Some mateial adapted fom Mohamed Younis, UMBC CMSC 611 Sp 2003 couse slides Some mateial adapted fom Hennessy & Patteson / 2003 Elsevie Science Pipeline
CMSC 611: Advanced Compute Achitectue Pipelining Some mateial adapted fom Mohamed Younis, UMBC CMSC 611 Sp 2003 couse slides Some mateial adapted fom Hennessy & Patteson / 2003 Elsevie Science Pipeline
EECS 470. Lecture 9. MIPS R10000 Case Study. Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont
 MIPS R10000 Case Study Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 Multiprocessor SGI Origin Using MIPS R10K Many thanks to Prof. Martin and Roth of University of Pennsylvania for
MIPS R10000 Case Study Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 Multiprocessor SGI Origin Using MIPS R10K Many thanks to Prof. Martin and Roth of University of Pennsylvania for
Multiple Predictors: BTB + Branch Direction Predictors
 Constructive Computer Architecture: Branch Prediction: Direction Predictors Arvind Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab. Massachusetts Institute of Technology October 28, 2015 http://csg.csail.mit.edu/6.175
Constructive Computer Architecture: Branch Prediction: Direction Predictors Arvind Computer Science & Artificial Intelligence Lab. Massachusetts Institute of Technology October 28, 2015 http://csg.csail.mit.edu/6.175
EECS150 - Digital Design Lecture 2 - Synchronous Digital Systems Review Part 1. Outline
 EECS5 - Digital Design Lecture 2 - Synchronous Digital Systems Review Part January 2, 2 John Wawrzynek Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley http://www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs5
EECS5 - Digital Design Lecture 2 - Synchronous Digital Systems Review Part January 2, 2 John Wawrzynek Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California, Berkeley http://www-inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs5
Pipelined Architecture (2A) Young Won Lim 4/10/18
 Pipelined Architecture (2A) Copyright (c) 2014-2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2
Pipelined Architecture (2A) Copyright (c) 2014-2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2
Pipelined Architecture (2A) Young Won Lim 4/7/18
 Pipelined Architecture (2A) Copyright (c) 2014-2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2
Pipelined Architecture (2A) Copyright (c) 2014-2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2
CS521 CSE IITG 11/23/2012
 Parallel Decoding and issue Parallel execution Preserving the sequential consistency of execution and exception processing 1 slide 2 Decode/issue data Issue bound fetch Dispatch bound fetch RS RS RS RS
Parallel Decoding and issue Parallel execution Preserving the sequential consistency of execution and exception processing 1 slide 2 Decode/issue data Issue bound fetch Dispatch bound fetch RS RS RS RS
CSE502: Computer Architecture CSE 502: Computer Architecture
 CSE 502: Computer Architecture Out-of-Order Schedulers Data-Capture Scheduler Dispatch: read available operands from ARF/ROB, store in scheduler Commit: Missing operands filled in from bypass Issue: When
CSE 502: Computer Architecture Out-of-Order Schedulers Data-Capture Scheduler Dispatch: read available operands from ARF/ROB, store in scheduler Commit: Missing operands filled in from bypass Issue: When
CS61c: Introduction to Synchronous Digital Systems
 CS61c: Introduction to Synchronous Digital Systems J. Wawrzynek March 4, 2006 Optional Reading: P&H, Appendix B 1 Instruction Set Architecture Among the topics we studied thus far this semester, was the
CS61c: Introduction to Synchronous Digital Systems J. Wawrzynek March 4, 2006 Optional Reading: P&H, Appendix B 1 Instruction Set Architecture Among the topics we studied thus far this semester, was the
Topics. Low Power Techniques. Based on Penn State CSE477 Lecture Notes 2002 M.J. Irwin and adapted from Digital Integrated Circuits 2002 J.
 Topics Low Power Techniques Based on Penn State CSE477 Lecture Notes 2002 M.J. Irwin and adapted from Digital Integrated Circuits 2002 J. Rabaey Review: Energy & Power Equations E = C L V 2 DD P 0 1 +
Topics Low Power Techniques Based on Penn State CSE477 Lecture Notes 2002 M.J. Irwin and adapted from Digital Integrated Circuits 2002 J. Rabaey Review: Energy & Power Equations E = C L V 2 DD P 0 1 +
Memory-Level Parallelism Aware Fetch Policies for Simultaneous Multithreading Processors
 Memory-Level Parallelism Aware Fetch Policies for Simultaneous Multithreading Processors STIJN EYERMAN and LIEVEN EECKHOUT Ghent University A thread executing on a simultaneous multithreading (SMT) processor
Memory-Level Parallelism Aware Fetch Policies for Simultaneous Multithreading Processors STIJN EYERMAN and LIEVEN EECKHOUT Ghent University A thread executing on a simultaneous multithreading (SMT) processor
CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.bekeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Stuctues Lectue 29 Intoduction to Pipelined Execution Lectue PSOE Dan Gacia www.cs.bekeley.edu/~ddgacia Bionic Eyes let blind see! Johns Hopkins eseaches have
inst.eecs.bekeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Stuctues Lectue 29 Intoduction to Pipelined Execution Lectue PSOE Dan Gacia www.cs.bekeley.edu/~ddgacia Bionic Eyes let blind see! Johns Hopkins eseaches have
EECS 470 Lecture 8. P6 µarchitecture. Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont Core 2 Microarchitecture
 P6 µarchitecture Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 Core 2 Microarchitecture Many thanks to Prof. Martin and Roth of University of Pennsylvania for most of these slides. Portions
P6 µarchitecture Fall 2018 Jon Beaumont http://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 Core 2 Microarchitecture Many thanks to Prof. Martin and Roth of University of Pennsylvania for most of these slides. Portions
Computer Elements and Datapath. Microarchitecture Implementation of an ISA
 6.823, L5--1 Computer Elements and atapath Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 status lines Microarchitecture Implementation of an ISA ler control points 6.823, L5--2
6.823, L5--1 Computer Elements and atapath Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 status lines Microarchitecture Implementation of an ISA ler control points 6.823, L5--2
How a processor can permute n bits in O(1) cycles
 How a processor can permute n bits in O(1) cycles Ruby Lee, Zhijie Shi, Xiao Yang Princeton Architecture Lab for Multimedia and Security (PALMS) Department of Electrical Engineering Princeton University
How a processor can permute n bits in O(1) cycles Ruby Lee, Zhijie Shi, Xiao Yang Princeton Architecture Lab for Multimedia and Security (PALMS) Department of Electrical Engineering Princeton University
A Static Power Model for Architects
 A Static Power Model for Architects J. Adam Butts and Guri Sohi University of Wisconsin-Madison {butts,sohi}@cs.wisc.edu 33rd International Symposium on Microarchitecture Monterey, California December,
A Static Power Model for Architects J. Adam Butts and Guri Sohi University of Wisconsin-Madison {butts,sohi}@cs.wisc.edu 33rd International Symposium on Microarchitecture Monterey, California December,
CSE502: Computer Architecture Welcome to CSE 502
 Welcome to CSE 502 Introduction & Review Today s Lecture Course Overview Course Topics Grading Logistics Academic Integrity Policy Homework Quiz Key basic concepts for Computer Architecture Course Overview
Welcome to CSE 502 Introduction & Review Today s Lecture Course Overview Course Topics Grading Logistics Academic Integrity Policy Homework Quiz Key basic concepts for Computer Architecture Course Overview
Single vs. Mul2- cycle MIPS. Single Clock Cycle Length
 Single vs. Mul2- cycle MIPS Single Clock Cycle Length Suppose we have 2ns 2ns ister read 2ns ister write 2ns ory read 2ns ory write 2ns 2ns What is the clock cycle length? 1 Single Cycle Length Worst case
Single vs. Mul2- cycle MIPS Single Clock Cycle Length Suppose we have 2ns 2ns ister read 2ns ister write 2ns ory read 2ns ory write 2ns 2ns What is the clock cycle length? 1 Single Cycle Length Worst case
EE382V-ICS: System-on-a-Chip (SoC) Design
 EE38V-CS: System-on-a-Chip (SoC) Design Hardware Synthesis and Architectures Source: D. Gajski, S. Abdi, A. Gerstlauer, G. Schirner, Embedded System Design: Modeling, Synthesis, Verification, Chapter 6:
EE38V-CS: System-on-a-Chip (SoC) Design Hardware Synthesis and Architectures Source: D. Gajski, S. Abdi, A. Gerstlauer, G. Schirner, Embedded System Design: Modeling, Synthesis, Verification, Chapter 6:
DAT105: Computer Architecture
 Department of Computer Science & Engineering Chalmers University of Techlogy DAT05: Computer Architecture Exercise 6 (Old exam questions) By Minh Quang Do 2007-2-2 Question 4a [2006/2/22] () Loop: LD F0,0(R)
Department of Computer Science & Engineering Chalmers University of Techlogy DAT05: Computer Architecture Exercise 6 (Old exam questions) By Minh Quang Do 2007-2-2 Question 4a [2006/2/22] () Loop: LD F0,0(R)
Lecture Topics. Announcements. Today: Memory Management (Stallings, chapter ) Next: continued. Self-Study Exercise #6. Project #4 (due 10/11)
 Lecture Topics Today: Memory Management (Stallings, chapter 7.1-7.4) Next: continued 1 Announcements Self-Study Exercise #6 Project #4 (due 10/11) Project #5 (due 10/18) 2 Memory Hierarchy 3 Memory Hierarchy
Lecture Topics Today: Memory Management (Stallings, chapter 7.1-7.4) Next: continued 1 Announcements Self-Study Exercise #6 Project #4 (due 10/11) Project #5 (due 10/18) 2 Memory Hierarchy 3 Memory Hierarchy
Instructor: Randy H. Katz hap://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c/fa13. Fall Lecture #20. Warehouse Scale Computer
 CS 61C: Geat Ideas in Compute Achitectue Contol and Pipelining Instucto: Randy H. Katz hap://inst.eecs.bekeley.edu/~cs61c/fa13 11/5/13 Fall 2013 - - Lectue #20 1 So0wae Paallel Requests Assigned to compute
CS 61C: Geat Ideas in Compute Achitectue Contol and Pipelining Instucto: Randy H. Katz hap://inst.eecs.bekeley.edu/~cs61c/fa13 11/5/13 Fall 2013 - - Lectue #20 1 So0wae Paallel Requests Assigned to compute
Improving GPU Performance via Large Warps and Two-Level Warp Scheduling
 Improving GPU Performance via Large Warps and Two-Level Warp Scheduling Veynu Narasiman The University of Texas at Austin Michael Shebanow NVIDIA Chang Joo Lee Intel Rustam Miftakhutdinov The University
Improving GPU Performance via Large Warps and Two-Level Warp Scheduling Veynu Narasiman The University of Texas at Austin Michael Shebanow NVIDIA Chang Joo Lee Intel Rustam Miftakhutdinov The University
Meltdown & Spectre. Side-channels considered harmful. Qualcomm Mobile Security Summit May, San Diego, CA. Moritz Lipp
 Meltdown & Spectre Side-channels considered harmful Qualcomm Mobile Security Summit 2018 17 May, 2018 - San Diego, CA Moritz Lipp (@mlqxyz) Michael Schwarz (@misc0110) Flashback Qualcomm Mobile Security
Meltdown & Spectre Side-channels considered harmful Qualcomm Mobile Security Summit 2018 17 May, 2018 - San Diego, CA Moritz Lipp (@mlqxyz) Michael Schwarz (@misc0110) Flashback Qualcomm Mobile Security
You are Here! Processor Design Process. Agenda. Agenda 10/25/12. CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Single Cycle MIPS CPU Part II
 /26/2 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Single Cycle MIPS CPU Part II /25/2 ructors: Krste Asanovic, Randy H. Katz hcp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs6c/fa2 Fall 22 - - Lecture #26 Parallel Requests
/26/2 CS 6C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Single Cycle MIPS CPU Part II /25/2 ructors: Krste Asanovic, Randy H. Katz hcp://inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs6c/fa2 Fall 22 - - Lecture #26 Parallel Requests
Tomasulo s Algorithm. Tomasulo s Algorithm
 Tomasulo s Algorithm Load and store buffers Contain data and addresses, act like reservation stations Branch Prediction Top-level design: 56 Tomasulo s Algorithm Three Steps: Issue Get next instruction
Tomasulo s Algorithm Load and store buffers Contain data and addresses, act like reservation stations Branch Prediction Top-level design: 56 Tomasulo s Algorithm Three Steps: Issue Get next instruction
Metrics How to improve performance? CPI MIPS Benchmarks CSC3501 S07 CSC3501 S07. Louisiana State University 4- Performance - 1
 Performance of Computer Systems Dr. Arjan Durresi Louisiana State University Baton Rouge, LA 70810 Durresi@Csc.LSU.Edu LSUEd These slides are available at: http://www.csc.lsu.edu/~durresi/csc3501_07/ Louisiana
Performance of Computer Systems Dr. Arjan Durresi Louisiana State University Baton Rouge, LA 70810 Durresi@Csc.LSU.Edu LSUEd These slides are available at: http://www.csc.lsu.edu/~durresi/csc3501_07/ Louisiana
Best Instruction Per Cycle Formula >>>CLICK HERE<<<
 Best Instruction Per Cycle Formula 6 Performance tuning, 7 Perceived performance, 8 Performance Equation, 9 See also is the average instructions per cycle (IPC) for this benchmark. Even. Click Card to
Best Instruction Per Cycle Formula 6 Performance tuning, 7 Perceived performance, 8 Performance Equation, 9 See also is the average instructions per cycle (IPC) for this benchmark. Even. Click Card to
CZ3001 ADVANCED COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE
 CZ3001 ADVANCED COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lab 3 Report Abstract Pipelining is a process in which successive steps of an instruction sequence are executed in turn by a sequence of modules able to operate concurrently,
CZ3001 ADVANCED COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE Lab 3 Report Abstract Pipelining is a process in which successive steps of an instruction sequence are executed in turn by a sequence of modules able to operate concurrently,
Issue. Execute. Finish
 Specula1on & Precise Interrupts Fall 2017 Prof. Ron Dreslinski h6p://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 In Order Out of Order In Order Issue Execute Finish Fetch Decode Dispatch Complete Retire Instruction/Decode
Specula1on & Precise Interrupts Fall 2017 Prof. Ron Dreslinski h6p://www.eecs.umich.edu/courses/eecs470 In Order Out of Order In Order Issue Execute Finish Fetch Decode Dispatch Complete Retire Instruction/Decode
Compiler Optimisation
 Compiler Optimisation 6 Instruction Scheduling Hugh Leather IF 1.18a hleather@inf.ed.ac.uk Institute for Computing Systems Architecture School of Informatics University of Edinburgh 2018 Introduction This
Compiler Optimisation 6 Instruction Scheduling Hugh Leather IF 1.18a hleather@inf.ed.ac.uk Institute for Computing Systems Architecture School of Informatics University of Edinburgh 2018 Introduction This
Power Issues with Embedded Systems. Rabi Mahapatra Computer Science
 Power Issues with Embedded Systems Rabi Mahapatra Computer Science Plan for today Some Power Models Familiar with technique to reduce power consumption Reading assignment: paper by Bill Moyer on Low-Power
Power Issues with Embedded Systems Rabi Mahapatra Computer Science Plan for today Some Power Models Familiar with technique to reduce power consumption Reading assignment: paper by Bill Moyer on Low-Power
Flexibility, Speed and Accuracy in VLIW Architectures Simulation and Modeling
 Flexibility, Speed and Accuracy in VLIW Architectures Simulation and Modeling IVANO BARBIERI, MASSIMO BARIANI, ALBERTO CABITTO, MARCO RAGGIO Department of Biophysical and Electronic Engineering University
Flexibility, Speed and Accuracy in VLIW Architectures Simulation and Modeling IVANO BARBIERI, MASSIMO BARIANI, ALBERTO CABITTO, MARCO RAGGIO Department of Biophysical and Electronic Engineering University
Outline Single Cycle Processor Design Multi cycle Processor. Pipelined Processor Design. Overall clock period. Analyzing performance 3/18/2015
 3/8/5 Pipelined Processor Design. Sahu CSE, T Guwahai Please be updaed wih hp://ainga.iig.erne.in/~asahu/c/ Ouline Single Cycle Processor Design Muli cycle Processor Merging M and, emoving dder and dder
3/8/5 Pipelined Processor Design. Sahu CSE, T Guwahai Please be updaed wih hp://ainga.iig.erne.in/~asahu/c/ Ouline Single Cycle Processor Design Muli cycle Processor Merging M and, emoving dder and dder
An Evaluation of Speculative Instruction Execution on Simultaneous Multithreaded Processors
 An Evaluation of Speculative Instruction Execution on Simultaneous Multithreaded Processors STEVEN SWANSON, LUKE K. McDOWELL, MICHAEL M. SWIFT, SUSAN J. EGGERS and HENRY M. LEVY University of Washington
An Evaluation of Speculative Instruction Execution on Simultaneous Multithreaded Processors STEVEN SWANSON, LUKE K. McDOWELL, MICHAEL M. SWIFT, SUSAN J. EGGERS and HENRY M. LEVY University of Washington
