A Brief Handout for Introduction to
|
|
|
- Charla Sheryl Rogers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Brief Handout for Introduction to Electric cal Engineering Course This handout is a compilation of PSPICE, A Brief Primer, Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering, University of Pennsylvania and Introduction to OrCAD PSpice 9.2, Department of Electrical Engineeringg and Computer Sciences, University of California Berkeley, with some additional examples. R. Nasiri, M. Alizadeh, A. Asgari, P. Molavi Department of Electrical Engineering, Sharif University of Technology 10/ /14/2007
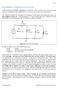
2 I. Introduction SPICE is a powerful general purpose analog and mixed-mode circuit simulator that is used to verify circuit designs and to predict the circuit behavior. This is of particular importance for integrated circuits. It was for this reason that SPICE was originally developed at the Electronics Research Laboratory of the University of California, Berkeley (1975), as its name implies: Simulation Program for Integrated Circuits Emphasis. PSpice is a PC version of SPICE (which is currently available from OrCAD Corp. of Cadence Design Systems, Inc.). A student version (with limited capabilities) comes with various textbooks. The OrCAD student edition is called PSpice AD Lite. Information about PSpice AD is available from the OrCAD website: The PSpice Light version has the following limitations: circuits have a maximum of 64 nodes, 10 transistors and 2 operational amplifiers. SPICE can do several types of circuit analyses. Here are the most important ones: Non-linear DC analysis: calculates the DC transfer curve. Non-linear transient and Fourier analysis: calculates the voltage and current as a function of time when a large signal is applied; Fourier analysis gives the frequency spectrum. Linear AC Analysis: calculates the output as a function of frequency. A bode plot is generated. Noise analysis Parametric analysis Monte Carlo Analysis In addition, PSpice has analog and digital libraries of standard components (such as NAND, NOR, flip-flops, MUXes, FPGA, PLDs and many more digital components). This makes it a useful tool for a wide range of analog and digital applications. All analyses can be done at different temperatures. The default temperature is 300K. The circuit can contain the following components: Independent and dependent voltage and current sources Resistors Capacitors Inductors Mutual inductors Transmission lines Operational amplifiers Switches Diodes Bipolar transistors MOS transistors JFET MESFET Digital gates Other components (see user s manual).
3 II. PSpice with OrCAD Capture Before one can simulate a circuit one needs to specify the circuit configuration. This can be done in a variety of ways. One way is to enter the circuit description as a text file in terms of the elements, connections, the models of the elements and the type of analysis. This file is called the SPICE input file or source file and will not be discussed here (interested reader can refer to for an introductory text on SPICE source file). An alternative way is to use a schematic entry program such as OrCAD Capture. OrCAD Capture is usually bundled with PSpice Lite AD on the same CD. Capture is a user-friendly program that allows you to capture the schematic of the circuits and to specify the type of simulation. Capture is not only intended to generate the input for PSpice but also for PCD layout design programs. The following figure summarizes the different steps involved in simulating a circuit with Capture and PSpice. We'll describe each of these briefly through a couple of examples. Step 1: Circuit Creation with Capture Create a new Analog, mixed AD project Place circuit parts Connect the parts Specify values and names Step 2: Specify type of simulation Create a simulation profile Select type of analysis: Bias, DC sweep, Transient, AC sweep Run PSpice Step 3: View the results Add traces to the probe window Use cursors to analyze waveforms Check the output file, if needed Save or print the results Figure 1. Steps involved in simulating a circuit with PSpice. The values of elements can be specified using scaling factors (upper or lower case): T or Tera (= ) G or Giga (= ) MEG or Mega (= ) K or Kilo (= ) M or Milli (= ) U or Micro (= ) N or Nano (= ) P or Pico (= ) F of Femto (= ) Both upper and lower case letters are allowed in PSpice. As an example, one can specify a capacitor of 225 picofarad in the following ways: 225P, 225p, 225pF; 225pFarad; 225E-12; 0.225N Notice that Mega is written as MEG, e.g. a 15 megaohm resistor can be specified as 15MEG, 15MEGohm, 15meg, or 15E6. Be careful not to use M for Mega! When you write 15Mohm or 15M, Spice will read this as 15 milliohm! We'll illustrate the different types of simulations for the following circuit:
4 Figure 2. Circuit to be simulated (screen shot from OrCAD Capture) Step 1: Creating the circuit in Capture 1. Create a new project a) Open OrCAD Capture b) Create a new Project: FILE MENU/NEW_PROJECT c) Enter the name of the project d) Select Analog or Mixed-AD e) When the Create PSpice Project box opens, select "Create Blank Project". A new page will open in the Project Design Manager as shown below. Figure 3. Design manager with schematic window and toolbars (OrCAD screen capture) 2. Place the components and connect the parts a) Click on the Schematic window in Capture. b) To Place a part go to PLACE/PART menu or click on the Place Part Icon. This will open a dialog box shown below.
5 Figure 4. Place Part window c) Select the library that contains the required components. Type the beginning of the name in the Part box. The part list will scroll to the components whose name contains the same letters. If the library is not available, you need to add the library, by clicking on the Add Library button. This will bring up the Add Library window. Select the desired library. For Spice you should select the libraries from the Capture/Library/PSpice folder. Some of the most commonly used libraries are listed below: ANALOG: contains the passive components (R, L, C), mutual inductance, transmission line, and voltage and current dependent sources (voltage dependent voltage source E, current-dependent current source F, voltage-dependent current source G and current-dependent voltage source H). SOURCE: gives the different types of independent voltage and current sources, such as Vdc, Idc, Vac, Iac, Vsin, Vexp, pulse, piecewise linear, etc. Browse the library to see what is available. BREAKOUT: provides diodes (D ), bipolar transistors (Q ), MOS transistors, JFETs (J ), real opamp such as the u741, switches (SW_tClose, SW_tOpen), various digital gates and components. ABM: contains a selection of interesting mathematical operators that can be applied to signals, such as multiplication (MULT), summation (SUM), Square Root (SWRT), Laplace (LAPLACE), arctan (ARCTAN), and many more. SPECIAL: contains a variety of other components, such as PARAM, NODESET, etc. d) Place the resistors, capacitor (from the Analog library), and the DC voltage and current source. You can place the part by the left mouse click. You can rotate the components by clicking on the R key. To place another instance of the same part, click the left mouse button again. Hit the ESC key when done with a particular element. You can add initial conditions to the capacitor. Double-click on the part; this will open the Property window that looks like a spreadsheet. Under the column, labeled IC, enter the value of the initial condition, e.g. 2V. For our example we assume that IC was 0V (this is the default value). e) After placing all parts, you need to place the Ground terminal by clicking on the GND icon (on the right side toolbar see Fig. 3). When the Place Ground window opens, select GND/CAPSYM and give it the name 0 (i.e. zero). Do not forget to change the name to 0, otherwise PSpice will give an error or "Floating Node". The reason is that SPICE needs a ground terminal as the reference node that has the node number or name 0 (zero).
6 Figure 5. Place the ground terminal box; the ground terminal should have the name 0 f) Now connect the elements using the Place Wire command from the menu (PLACE/WIRE) or by clicking on the Place Wire icon. g) You can assign names to nets or nodes using the Place Net Alias command (PLACE/NET ALIAS menu). We will do this for the output node and input node. Name these Out and In, as shown in Figure Assign Values and Names to the parts a) Change the values of the resistors by double-clicking on the number next to the resistor. You can also change the name of the resistor. Do the same for the capacitor and voltage and current source. b) If you haven't done so yet, you can (if you want) assign names to nodes (e.g. Out and In nodes). c) Save the project 4. Netlist The netlist gives the list of all elements using the simple format: R_name node1 node2 value C_name nodex nodey value, etc. 1. You can generate the netlist by going to the PSPICE/CREATE NETLIST menu. 2. Look at the netlist by double clicking on the Output/name.net file in the Project Manager Window (in the left side File window). Note on Current Directions in elements: The positive current direction in an element such as a resistor is from node 1 to node 2. Node 1 is either the left pin or the top pin for a horizontal or vertical positioned element (e.g. a resistor). By rotating the element 180 degrees one can switch the pin numbers. To verify the node numbers you can look at the netlist: e.g. R_R2 node1 node2 10k e.g. R_R2 0 OUT 10k
7 Since we are interested in the current direction from the OUT node to the ground, we need to rotate the resistor R2 twice so that the node numbers are interchanged: R_R2 OUT 0 10k Step 2: Specifying the type of analysis and simulation As mentioned in the introduction, Spice allows you do to a DC bias, DC Sweep, Transient with Fourier analysis, AC analysis, Montecarlo/worst case sweep, Parameter sweep and Temperature sweep. We will first explain how to do the Bias and DC Sweep on the circuit of Figure BIAS or DC analysis a) With the schematic open, go to the PSPICE menu and choose NEW SIMULATION PROFILE. b) In the Name text box, type a descriptive name, e.g. Bias c) From the Inherit From List: select none and click Create. d) When the Simulation Setting window opens, for the Analysis Type, choose Bias Point and click OK. e) Now you are ready to run the simulation: PSPICE/RUN f) A window will open, letting you know if the simulation was successful. If there are errors, consult the Simulation Output file. g) To see the result of the DC bias point simulation, you can open the Simulation Output file or go back to the schematic and click on the V icon (Enable Bias Voltage Display) and I icon (Enable Bias Current Display) to show the voltage and currents (see Figure 6). To check the direction of the current, you need to look at the netlist: the current is positive flowing from node1 to node1 (see note on Current Direction above). Figure 6. Results of the Bias simulation displayed on the schematic 2. DC Sweep simulation We will be using the same circuit but will evaluate the effect of sweeping the voltage source between 0 and 20V. We'll keep the current source constant at 1mA. a) Create a new New Simulation Profile (from the PSpice Menu); We'll call it DC Sweep b) For analysis select DC Sweep; enter the name of the voltage source to be swept: V1. The start
8 and end values and the step need to be specified: 0, 20 and 0.1V, respectively (see Fig. 7 below). Figure 7. Setting for the DC Sweep simulation c) Run the simulation. PSpice will generate an output file that contains the values of all voltages and currents in the circuit. Step 3: Displaying the simulation results PSpice has a user-friendly interface to show the results of the simulations. Once the simulation is finished a Probe window will open. Figure 8. Probe window a) From the TRACE menu select ADD TRACE and select the voltages and current you like to display. In our case we'll add V(out) and V(in). Click OK.
9 Figure 9. Add Traces window b) You can also add traces using the "Voltage Markers" in the schematic. From the PSPICE menu select MARKERS/VOLTAGE LEVELS. Place the makers on the Out and In node. When done, right click and select End Mode. Figure 10. Using Voltage Markers to show the simulation result of V(out) and V(in) c) Go back to PSpice. You will notice that the waveforms have appeared. d) You can add a second Y Axis and use this to display e.g. the current in Resistor R2, as shown below. Go to PLOT/Add Y Axis. Next, add the trace for I(R2). e) You can also use the cursors on the graphs for Vout and Vin to display the actual values at certain points. Go to TRACE/CURSORS/DISPLAY f) The cursors will be associated with the first trace, as indicated by the small rectangle around the legend for V(out) at the bottom of the window. Left click on the first trace. The value of the x and y axes are displayed in the Probe window. When you right click on V(out) the value of the second cursor will be given together with the difference between the first and second cursor. g) To place the second cursor on the second trace (for V(in)), right click the legend for V(in). You'll notice the outline around V(in) at the bottom of the window. When you right click the second trace the cursor will snap to it. The values of the first and second cursors will be shown in Probe window.
10 h) You can chance the X and Y axes by double clicking on them. i) When adding traces you can perform mathematical calculations on the traces, as indicated in the Add Trace Window to the right of Figure 9. Figure 11. Result of the DC sweep, showing Vout, Vin and the current through resistor R2. Cursors were used for V(out) and V(in) Other Types of Analysis 1. Transient Analysis We'll be using the same circuit as for the DC sweep, except that we'll apply the voltage and current sources by closing a switch, as shown in Figure 12. Figure 12. Circuit used for the transient simulation a) Insert the SW_TCLOSE switch from the ANL_MISC Library as shown above. Double click on the switch TCLOSE value and enter the value when the switch closes. Let s make TCLOSE = 5ms. b) Set up the Transient Analysis: go to the PSPICE/NEW SIMULATION PROFILE. c) Give it a name (e.g. Transient). When the Simulation Settings window opens, select "Time Domain (Transient)" Analysis. Enter also the Run Time. Let s make it 50ms. For the Max Step size, you can leave it blank or enter 10us. d) Run PSpice. e) A Probe window in PSpice will open. You can now add the traces to display the results. In the figure below we have plotted the current through the capacitor in the top window and the voltage over the capacitor on the bottom one.
11 Figure 13. Results of the transient simulation of Figure 12 f) Instead of using a switch we can also use a voltage source that changes over time. This was done in Figure 14 where we used the VPULSE and IPULSE sources from the SOURCE Library. We entered the voltage levels (V1 and V2), the delay (TD), Rise and Fall Times, Pulse Width (PW) and the Period (PER). The values are indicated in the figure below. Figure 14. Circuit with a PULSE voltage and current source g) After doing the transient simulation results can be displayed as was done before h) The last example of a transient analysis is with a sinusoidal signal VSIN. The circuit is shown below. We made the amplitude 10V and frequency 10 Hz. Figure 15. Circuit with a sinusoidal input i) Create a Simulation Profiler for the transient analysis and run PSpice. j) The result of the simulation for Vout and Vin are given in the figure below.
12 Figure 16. Transient simulation with a sinusoidal input 2. AC Sweep Analysis The AC analysis will apply a sinusoidal voltage whose frequency is swept over a specified range. The simulation calculates the corresponding voltage and current amplitude and phases for each frequency. In contrast to a sinusoidal transient analysis, the AC analysis is not a time domain simulation but rather a simulation of the sinusoidal steady state of the circuit. In the first example, we'll show a simple RC filter corresponding to the circuit of Figure 17. Figure 17. Circuit for the AC sweep simulation a) Create a new project and build the circuit b) For the voltage source use VAC from the SOURCE library. c) Make the amplitude of the input source 1V. d) Create a Simulation Profile. In the Simulation Settings window, select AC Sweep/Noise. e) Enter the start and end frequencies and the number of points per decade. For our example we use 0.1Hz, 10 khz and 11, respectively. f) Run the simulation. g) In the Probe window, add the traces for the input voltage. We added a second window to display the phase in addition to the magnitude of the output voltage. The voltage can be displayed in db by specifying Vdb(out) in the Add Trace window (type Vdb(out) in the Trace Expression box. For the phase, type VP(out)).
13 h) An alternative way to show the voltage in db and phase is to use markers on the schematics: PSPICE/MARKERS/ADVANCED/dB Magnitude or Phase of voltage, or current. Place the markers on the node of interest. i) The db Magnitude and Phase of output voltage are displayed in the following figure. Figure 18. Results of the AC sweep analysis of figure 17
Introduction to PSpice
 Electric Circuit I Lab Manual 4 Session # 5 Introduction to PSpice 1 PART A INTRODUCTION TO PSPICE Objective: The objective of this experiment is to be familiar with Pspice (learn how to connect circuits,
Electric Circuit I Lab Manual 4 Session # 5 Introduction to PSpice 1 PART A INTRODUCTION TO PSPICE Objective: The objective of this experiment is to be familiar with Pspice (learn how to connect circuits,
Electronics I LAB. Lab 1: Lab 1 : Introduction to PsPise
 Electronics I LAB Lab 1: Lab 1 : Introduction to PsPise 1-Introduction to PsPise : SPICE (Simulation Program for Integrated Circuits Emphasis.) is a po werful general purpo se analog and mixed-mode circuit
Electronics I LAB Lab 1: Lab 1 : Introduction to PsPise 1-Introduction to PsPise : SPICE (Simulation Program for Integrated Circuits Emphasis.) is a po werful general purpo se analog and mixed-mode circuit
Introduction to OrCAD. Simulation Program With Integrated Circuits Emphasis.
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering department Digital Electronics Lab (EELE 3121) Eng. Mohammed S. Jouda Eng. Amani S. abu reyala Experiment 1 Introduction to OrCAD
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Electrical Engineering department Digital Electronics Lab (EELE 3121) Eng. Mohammed S. Jouda Eng. Amani S. abu reyala Experiment 1 Introduction to OrCAD
PSPICE A brief primer
 PSPICE A brief primer Contents 1. Introduction 2. Use of PSpice with OrCAD Capture 2.1 Step 1: Creating the circuit in Capture 2.2 Step 2: Specifying the type of analysis and simulation BIAS or DC analysis
PSPICE A brief primer Contents 1. Introduction 2. Use of PSpice with OrCAD Capture 2.1 Step 1: Creating the circuit in Capture 2.2 Step 2: Specifying the type of analysis and simulation BIAS or DC analysis
Engineering 3821 Fall Pspice TUTORIAL 1. Prepared by: J. Tobin (Class of 2005) B. Jeyasurya E. Gill
 Engineering 3821 Fall 2003 Pspice TUTORIAL 1 Prepared by: J. Tobin (Class of 2005) B. Jeyasurya E. Gill 2 INTRODUCTION The PSpice program is a member of the SPICE (Simulation Program with Integrated Circuit
Engineering 3821 Fall 2003 Pspice TUTORIAL 1 Prepared by: J. Tobin (Class of 2005) B. Jeyasurya E. Gill 2 INTRODUCTION The PSpice program is a member of the SPICE (Simulation Program with Integrated Circuit
Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology. Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering AUST/EEE
 Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering LABORATORY MANUAL FOR ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC SESSIONAL COURSE Student Name : Student ID : Course no
Ahsanullah University of Science and Technology Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering LABORATORY MANUAL FOR ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONIC SESSIONAL COURSE Student Name : Student ID : Course no
EXPERIMENT NUMBER 10 TRANSIENT ANALYSIS USING PSPICE
 EXPERIMENT NUMBER 10 TRANSIENT ANALYSIS USING PSPICE Objective: To learn to use a circuit simulator package for plotting the response of a circuit in the time domain. Preliminary: Revise laboratory 8 to
EXPERIMENT NUMBER 10 TRANSIENT ANALYSIS USING PSPICE Objective: To learn to use a circuit simulator package for plotting the response of a circuit in the time domain. Preliminary: Revise laboratory 8 to
PSPICE T UTORIAL P ART I: INTRODUCTION AND DC ANALYSIS. for the Orcad PSpice Release 9.2 Lite Edition
 PSPICE T UTORIAL P ART I: INTRODUCTION AND DC ANALYSIS for the Orcad PSpice Release 9.2 Lite Edition INTRODUCTION The Simulation Program with Integrated Circuit Emphasis (SPICE) circuit simulation tool
PSPICE T UTORIAL P ART I: INTRODUCTION AND DC ANALYSIS for the Orcad PSpice Release 9.2 Lite Edition INTRODUCTION The Simulation Program with Integrated Circuit Emphasis (SPICE) circuit simulation tool
OrCAD PSpice - Tutorial. TA: 黃玉龍
 OrCAD PSpice - Tutorial TA: 黃玉龍 r9994320@ntu.edu.tw Outline 2 Introduction Preparation Schematic Simulation Conclusion Introduction 3 OrCAD PSpice is developed by Cadence Analog circuit simulation tool
OrCAD PSpice - Tutorial TA: 黃玉龍 r9994320@ntu.edu.tw Outline 2 Introduction Preparation Schematic Simulation Conclusion Introduction 3 OrCAD PSpice is developed by Cadence Analog circuit simulation tool
14:332:223 Principles of Electrical Engineering I Instructions for using PSPICE Tools Sharanya Chandrasekar February 1, 2006
 14:332:223 Principles of Electrical Engineering I Instructions for using PSPICE Tools Sharanya Chandrasekar February 1, 2006 1. Getting Started PSPICE is available on the ECE Computer labs in EE 103, DSV
14:332:223 Principles of Electrical Engineering I Instructions for using PSPICE Tools Sharanya Chandrasekar February 1, 2006 1. Getting Started PSPICE is available on the ECE Computer labs in EE 103, DSV
ECE 201 LAB 6 INTRODUCTION TO SPICE/PSPICE
 Version 1.1 1 of 33 BEFORE YOU BEGIN PREREQUISITE LABS Resistive Circuits EXPECTED KNOWLEDGE ECE 201 LAB 6 INTRODUCTION TO SPICE/PSPICE Ohm's Law: v = ir Node Voltage and Mesh Current Methods of Circuit
Version 1.1 1 of 33 BEFORE YOU BEGIN PREREQUISITE LABS Resistive Circuits EXPECTED KNOWLEDGE ECE 201 LAB 6 INTRODUCTION TO SPICE/PSPICE Ohm's Law: v = ir Node Voltage and Mesh Current Methods of Circuit
Background Theory and Simulation Practice
 CAD and Simulation Objectives Experiment Topic: CAD and Simulation PSpice 9.1 Student Version To obtain your free copy of the software and user s guide, go to Electronics Lab website ( http://www.electronics-lab.com/downloads/schematic/013/
CAD and Simulation Objectives Experiment Topic: CAD and Simulation PSpice 9.1 Student Version To obtain your free copy of the software and user s guide, go to Electronics Lab website ( http://www.electronics-lab.com/downloads/schematic/013/
Since transmission lines can be modeled using PSpice, you can do your analysis by downloading the student version of this excellent program.
 PSpice Analysis Since transmission lines can be modeled using PSpice, you can do your analysis by downloading the student version of this excellent program. PSpice can be downloaded from the following
PSpice Analysis Since transmission lines can be modeled using PSpice, you can do your analysis by downloading the student version of this excellent program. PSpice can be downloaded from the following
Introduction to SPICE. Simulator of Electronic devices
 Introduction to SPICE Simulator of Electronic devices Main steps: Download Instalation Open OrCAD capture CIS Lite Create a circuit. Place parts. Design a Simulation Profile Run PSpice F11 View simulation
Introduction to SPICE Simulator of Electronic devices Main steps: Download Instalation Open OrCAD capture CIS Lite Create a circuit. Place parts. Design a Simulation Profile Run PSpice F11 View simulation
Fig. 1-1 show the main window of Orcad Capture. Every project you work on will start from Orcad Capture. Fig. 1-1 Orcad Capture Main window.
 T. K. Ha PSpice Lecture #1 1 Objective: By the end of this lecture, it is hope that the students will have a rudimentary knowledge of using and running PSpice. The student will be able to draw and edit
T. K. Ha PSpice Lecture #1 1 Objective: By the end of this lecture, it is hope that the students will have a rudimentary knowledge of using and running PSpice. The student will be able to draw and edit
EE 210 Lab Exercise #3 Introduction to PSPICE
 EE 210 Lab Exercise #3 Introduction to PSPICE Appending 4 in your Textbook contains a short tutorial on PSPICE. Additional information, tutorials and a demo version of PSPICE can be found at the manufacturer
EE 210 Lab Exercise #3 Introduction to PSPICE Appending 4 in your Textbook contains a short tutorial on PSPICE. Additional information, tutorials and a demo version of PSPICE can be found at the manufacturer
ET 304A Laboratory Tutorial-Circuitmaker For Transient and Frequency Analysis
 ET 304A Laboratory Tutorial-Circuitmaker For Transient and Frequency Analysis All circuit simulation packages that use the Pspice engine allow users to do complex analysis that were once impossible to
ET 304A Laboratory Tutorial-Circuitmaker For Transient and Frequency Analysis All circuit simulation packages that use the Pspice engine allow users to do complex analysis that were once impossible to
ENEE207 Electric Circuits Lab Manual
 ENEE207 Electric Circuits Lab Manual Department of Engineering, Physical & Computer Sciences Montgomery College Version 3 Copyright Lan Xiang (Do not distribute without permission) 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
ENEE207 Electric Circuits Lab Manual Department of Engineering, Physical & Computer Sciences Montgomery College Version 3 Copyright Lan Xiang (Do not distribute without permission) 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS
Laboratory #2 PSpice Analyses
 Laboratory #2 PSpice Analyses I. Objectives 1. Know the development of SPICE. 2. Learn to install the PSpice software. 3. Learn to use the Capture CIS to draw circuit. 4. Learn to use the four analyses
Laboratory #2 PSpice Analyses I. Objectives 1. Know the development of SPICE. 2. Learn to install the PSpice software. 3. Learn to use the Capture CIS to draw circuit. 4. Learn to use the four analyses
Introduction to LT Spice IV with Examples
 Introduction to LT Spice IV with Examples 400D - Fall 2015 Purpose Part of Electronics & Control Division Technical Training Series by Nicholas Lombardo The purpose of this document is to give a basic
Introduction to LT Spice IV with Examples 400D - Fall 2015 Purpose Part of Electronics & Control Division Technical Training Series by Nicholas Lombardo The purpose of this document is to give a basic
An Introductory Guide to Circuit Simulation using NI Multisim 12
 School of Engineering and Technology An Introductory Guide to Circuit Simulation using NI Multisim 12 This booklet belongs to: This document provides a brief overview and introductory tutorial for circuit
School of Engineering and Technology An Introductory Guide to Circuit Simulation using NI Multisim 12 This booklet belongs to: This document provides a brief overview and introductory tutorial for circuit
Introduction to SwitcherCAD
 Introduction to SwitcherCAD 1 PREFACE 1.1 What is SwitcherCAD? SwitcherCAD III is a new Spice based program that was developed for modelling board level switching regulator systems. The program consists
Introduction to SwitcherCAD 1 PREFACE 1.1 What is SwitcherCAD? SwitcherCAD III is a new Spice based program that was developed for modelling board level switching regulator systems. The program consists
Electric Circuit Fall 2015 Pingqiang Zhou. ShanghaiTech University. School of Information Science and Technology. Professor Pingqiang Zhou
 ShanghaiTech University School of Information Science and Technology Professor Pingqiang Zhou LABORATORY 2 CAD Tools Guide Practical circuit design occurs in three stages: 1. Design of an appropriate circuit
ShanghaiTech University School of Information Science and Technology Professor Pingqiang Zhou LABORATORY 2 CAD Tools Guide Practical circuit design occurs in three stages: 1. Design of an appropriate circuit
Chapter 12: Electronic Circuit Simulation and Layout Software
 Chapter 12: Electronic Circuit Simulation and Layout Software In this chapter, we introduce the use of analog circuit simulation software and circuit layout software. I. Introduction So far we have designed
Chapter 12: Electronic Circuit Simulation and Layout Software In this chapter, we introduce the use of analog circuit simulation software and circuit layout software. I. Introduction So far we have designed
EECS 312: Digital Integrated Circuits Lab Project 1 Introduction to Schematic Capture and Analog Circuit Simulation
 EECS 312: Digital Integrated Circuits Lab Project 1 Introduction to Schematic Capture and Analog Circuit Simulation Teacher: Robert Dick GSI: Shengshuo Lu Assigned: 5 September 2013 Due: 17 September 2013
EECS 312: Digital Integrated Circuits Lab Project 1 Introduction to Schematic Capture and Analog Circuit Simulation Teacher: Robert Dick GSI: Shengshuo Lu Assigned: 5 September 2013 Due: 17 September 2013
Lab 7 PSpice: Time Domain Analysis
 Lab 7 PSpice: Time Domain Analysis OBJECTIVES 1. Use PSpice Circuit Simulator to simulate circuits containing capacitors and inductors in the time domain. 2. Practice using a switch, and a Pulse & Sinusoidal
Lab 7 PSpice: Time Domain Analysis OBJECTIVES 1. Use PSpice Circuit Simulator to simulate circuits containing capacitors and inductors in the time domain. 2. Practice using a switch, and a Pulse & Sinusoidal
LTSpice Basic Tutorial
 Index: I. Opening LTSpice II. Drawing the circuit A. Making Sure You Have a GND B. Getting the Parts C. Placing the Parts D. Connecting the Circuit E. Changing the Name of the Part F. Changing the Value
Index: I. Opening LTSpice II. Drawing the circuit A. Making Sure You Have a GND B. Getting the Parts C. Placing the Parts D. Connecting the Circuit E. Changing the Name of the Part F. Changing the Value
LT Spice Getting Started Very Quickly. First Get the Latest Software!
 LT Spice Getting Started Very Quickly First Get the Latest Software! 1. After installing LT Spice, run it and check to make sure you have the latest version with respect to the latest version available
LT Spice Getting Started Very Quickly First Get the Latest Software! 1. After installing LT Spice, run it and check to make sure you have the latest version with respect to the latest version available
EXPERIMENT 9 Problem Solving: First-order Transient Circuits
 EXPERIMENT 9 Problem Solving: First-order Transient Circuits I. Introduction In transient analyses, we determine voltages and currents as functions of time. Typically, the time dependence is demonstrated
EXPERIMENT 9 Problem Solving: First-order Transient Circuits I. Introduction In transient analyses, we determine voltages and currents as functions of time. Typically, the time dependence is demonstrated
Introduction to NI Multisim & Ultiboard Software version 14.1
 School of Engineering and Applied Science Electrical and Computer Engineering Department Introduction to NI Multisim & Ultiboard Software version 14.1 Dr. Amir Aslani August 2018 Parts Probes Tools Outline
School of Engineering and Applied Science Electrical and Computer Engineering Department Introduction to NI Multisim & Ultiboard Software version 14.1 Dr. Amir Aslani August 2018 Parts Probes Tools Outline
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING LAB SHEET
 FACULTY OF ENGINEERING LAB SHEET CIRCUITS AND SIGNALS EEL 2186 TRIMESTER 1 (218/219) -Circuit analysis using ORCAD PSpice *Note: You will be given an assessment sheet during the lab session to be completed
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING LAB SHEET CIRCUITS AND SIGNALS EEL 2186 TRIMESTER 1 (218/219) -Circuit analysis using ORCAD PSpice *Note: You will be given an assessment sheet during the lab session to be completed
Simulating Circuits James Lamberti 5/4/2014
 Simulating Circuits James Lamberti (jal416@lehigh.edu) 5/4/2014 There are many simulation and design platforms for circuits. The two big ones are Altium and Cadence. This tutorial will focus on Altium,
Simulating Circuits James Lamberti (jal416@lehigh.edu) 5/4/2014 There are many simulation and design platforms for circuits. The two big ones are Altium and Cadence. This tutorial will focus on Altium,
Figure 1. Main window (Common Interface Window), CIW opens and from the pull down menus you can start your design. Figure 2.
 Running Cadence Once the Cadence environment has been setup you can start working with Cadence. You can run cadence from your directory by typing Figure 1. Main window (Common Interface Window), CIW opens
Running Cadence Once the Cadence environment has been setup you can start working with Cadence. You can run cadence from your directory by typing Figure 1. Main window (Common Interface Window), CIW opens
EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response
 EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of active signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Active Filters, Op-Amp Filters, Bode plots Suggested
EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of active signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Active Filters, Op-Amp Filters, Bode plots Suggested
MultiSim and Analog Discovery 2 Manual
 MultiSim and Analog Discovery 2 Manual 1 MultiSim 1.1 Running Windows Programs Using Mac Obtain free Microsoft Windows from: http://software.tamu.edu Set up a Windows partition on your Mac: https://support.apple.com/en-us/ht204009
MultiSim and Analog Discovery 2 Manual 1 MultiSim 1.1 Running Windows Programs Using Mac Obtain free Microsoft Windows from: http://software.tamu.edu Set up a Windows partition on your Mac: https://support.apple.com/en-us/ht204009
Week 1: Preparing for PSpice Simulations
 Week 1: Preparing for PSpice Simulations Week 1 is composed of two experiments from the lab manual Experiment 1: Breadboard Basics Experiment 3: Ohm s Law Separate lectures on Modules will be posted for
Week 1: Preparing for PSpice Simulations Week 1 is composed of two experiments from the lab manual Experiment 1: Breadboard Basics Experiment 3: Ohm s Law Separate lectures on Modules will be posted for
1. Hand Calculations (in a manner suitable for submission) For the circuit in Fig. 1 with f = 7.2 khz and a source vin () t 1.
 Objectives The purpose of this laboratory project is to introduce to equipment, measurement techniques, and simulations commonly used in AC circuit analysis. In this laboratory session, each student will:
Objectives The purpose of this laboratory project is to introduce to equipment, measurement techniques, and simulations commonly used in AC circuit analysis. In this laboratory session, each student will:
Lab #2 First Order RC Circuits Week of 27 January 2015
 ECE214: Electrical Circuits Laboratory Lab #2 First Order RC Circuits Week of 27 January 2015 1 Introduction In this lab you will investigate the magnitude and phase shift that occurs in an RC circuit
ECE214: Electrical Circuits Laboratory Lab #2 First Order RC Circuits Week of 27 January 2015 1 Introduction In this lab you will investigate the magnitude and phase shift that occurs in an RC circuit
Lab 3: Circuit Simulation with PSPICE
 Page 1 of 11 Laboratory Goals Introduce text-based PSPICE as a design tool Create transistor circuits using PSPICE Simulate output response for the designed circuits Introduce the Curve Tracer functionality.
Page 1 of 11 Laboratory Goals Introduce text-based PSPICE as a design tool Create transistor circuits using PSPICE Simulate output response for the designed circuits Introduce the Curve Tracer functionality.
ECE4902 Lab 5 Simulation. Simulation. Export data for use in other software tools (e.g. MATLAB or excel) to compare measured data with simulation
 ECE4902 Lab 5 Simulation Simulation Export data for use in other software tools (e.g. MATLAB or excel) to compare measured data with simulation Be sure to have your lab data available from Lab 5, Common
ECE4902 Lab 5 Simulation Simulation Export data for use in other software tools (e.g. MATLAB or excel) to compare measured data with simulation Be sure to have your lab data available from Lab 5, Common
OrCAD 17.2 Pspice Tutorial. High-Speed Circuits & Systems Lab. Yonsei University
 OrCAD 17.2 Pspice Tutorial High-Speed Circuits & Systems Lab. Yonsei University Installation Move to http://www.orcad.com/resources/orcaddownloads#demo Installation Click Download FREE-OrCAD 17.2 Lite
OrCAD 17.2 Pspice Tutorial High-Speed Circuits & Systems Lab. Yonsei University Installation Move to http://www.orcad.com/resources/orcaddownloads#demo Installation Click Download FREE-OrCAD 17.2 Lite
SPICE FOR POWER ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRIC POWER
 SPICE FOR POWER ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRIC POWER SECOND EDITION MUHAMMAD H. RASHID University of West Florida Pensacola, Florida, U.S.A. HASAN M. RASHID University of Florida Gainesville, Florida, U.S.A.
SPICE FOR POWER ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRIC POWER SECOND EDITION MUHAMMAD H. RASHID University of West Florida Pensacola, Florida, U.S.A. HASAN M. RASHID University of Florida Gainesville, Florida, U.S.A.
Electronic Circuit Simulation Tools Using Pspice On Ac Analysis
 Electronic Circuit Simulation Tools Using Pspice On Ac Analysis This Design Idea shows it can handle digital filter simulation too. PSpice has become an industry standard tool for analog circuit simulations.
Electronic Circuit Simulation Tools Using Pspice On Ac Analysis This Design Idea shows it can handle digital filter simulation too. PSpice has become an industry standard tool for analog circuit simulations.
EE 2274 RC and Op Amp Circuit Completed Prior to Coming to Lab. Prelab Part I: RC Circuit
 EE 2274 RC and Op Amp Circuit Completed Prior to Coming to Lab Prelab Part I: RC Circuit 1. Design a high pass filter (Fig. 1) which has a break point f b = 1 khz at 3dB below the midband level (the -3dB
EE 2274 RC and Op Amp Circuit Completed Prior to Coming to Lab Prelab Part I: RC Circuit 1. Design a high pass filter (Fig. 1) which has a break point f b = 1 khz at 3dB below the midband level (the -3dB
SPICE for Power Electronics and Electric Power
 SPICE for Power Electronics and Electric Power Third Edition Muhammad H. Rashid Life Fellow IEEE /^0\ \Cf*' CRC Press I Taylor & Francis eis Crou Group Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint
SPICE for Power Electronics and Electric Power Third Edition Muhammad H. Rashid Life Fellow IEEE /^0\ \Cf*' CRC Press I Taylor & Francis eis Crou Group Boca Raton London New York CRC Press is an imprint
Lab 6: Building a Function Generator
 ECE 212 Spring 2010 Circuit Analysis II Names: Lab 6: Building a Function Generator Objectives In this lab exercise you will build a function generator capable of generating square, triangle, and sine
ECE 212 Spring 2010 Circuit Analysis II Names: Lab 6: Building a Function Generator Objectives In this lab exercise you will build a function generator capable of generating square, triangle, and sine
Introduction to Pspice
 1. Objectives Introduction to Pspice The learning objectives for this laboratory are to give the students a brief introduction to using Pspice as a tool to analyze circuits and also to demonstrate the
1. Objectives Introduction to Pspice The learning objectives for this laboratory are to give the students a brief introduction to using Pspice as a tool to analyze circuits and also to demonstrate the
Faculty of Engineering 4 th Year, Fall 2010
 4. Inverter Schematic a) After you open the previously created Inverter schematic, an empty window appears where you should place your components. To place an NMOS, select Add- >Instance or use shortcut
4. Inverter Schematic a) After you open the previously created Inverter schematic, an empty window appears where you should place your components. To place an NMOS, select Add- >Instance or use shortcut
Mor M. Peretz Power Electronics Laboratory Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, ISRAEL
 Mor M. Peretz Power Electronics Laboratory Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, ISRAEL [1] PSpice A/D simulation program allows to analyze electrical circuits
Mor M. Peretz Power Electronics Laboratory Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, ISRAEL [1] PSpice A/D simulation program allows to analyze electrical circuits
EE320L Electronics I. Laboratory. Laboratory Exercise #2. Basic Op-Amp Circuits. Angsuman Roy. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 EE320L Electronics I Laboratory Laboratory Exercise #2 Basic Op-Amp Circuits By Angsuman Roy Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, Las Vegas Objective: The purpose of
EE320L Electronics I Laboratory Laboratory Exercise #2 Basic Op-Amp Circuits By Angsuman Roy Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, Las Vegas Objective: The purpose of
LABORATORY 4. Palomar College ENGR210 Spring 2017 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17
 LABORATORY 4 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17 OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this lab is to evaluate the transient and steady-state circuit response of first order and second order circuits. MINIMUM EQUIPMENT LIST: You will
LABORATORY 4 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17 OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this lab is to evaluate the transient and steady-state circuit response of first order and second order circuits. MINIMUM EQUIPMENT LIST: You will
EECE Circuits and Signals: Biomedical Applications. Lab 3. Basic Instruments, Components and Circuits. Introduction to Spice and AC circuits
 EECE 2150 - Circuits and Signals: Biomedical Applications Lab 3 Basic Instruments, Components and Circuits. Introduction to Spice and AC circuits Introduction and Preamble: In this lab you will experiment
EECE 2150 - Circuits and Signals: Biomedical Applications Lab 3 Basic Instruments, Components and Circuits. Introduction to Spice and AC circuits Introduction and Preamble: In this lab you will experiment
Lab 3: Very Brief Introduction to Micro-Cap SPICE
 Lab 3: Very Brief Introduction to Micro-Cap SPICE Starting Micro-Cap SPICE Micro-Cap SPICE is available on CoE machines under the Spectrum Software menu: Programs Spectrum Software Micro-Cap 10 Evaluation
Lab 3: Very Brief Introduction to Micro-Cap SPICE Starting Micro-Cap SPICE Micro-Cap SPICE is available on CoE machines under the Spectrum Software menu: Programs Spectrum Software Micro-Cap 10 Evaluation
Tsung-Chu Huang. Department of Electronic Engineering National Changhua University of Education /10/4-5 TCH NCUE
 Digital IC Design Tsung-Chu Huang Department of Electronic Engineering National Changhua University of Education Email: tch@cc.ncue.edu.tw 2004/10/4-5 Page 1 Circuit Simulation Tools 1. Switch Level: Verilog,
Digital IC Design Tsung-Chu Huang Department of Electronic Engineering National Changhua University of Education Email: tch@cc.ncue.edu.tw 2004/10/4-5 Page 1 Circuit Simulation Tools 1. Switch Level: Verilog,
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING LAB SHEET
 FACULTY OF ENGINEERING LAB SHEET CIRCUITS AND SIGNALS EEL 286 TRIMESTER (26/27) -Circuit analysis using ORCAD PSpice Experiment : Circuit analysis using ORCAD Pspice PRECAUTIONARY STEPS:. Read this experiment
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING LAB SHEET CIRCUITS AND SIGNALS EEL 286 TRIMESTER (26/27) -Circuit analysis using ORCAD PSpice Experiment : Circuit analysis using ORCAD Pspice PRECAUTIONARY STEPS:. Read this experiment
Lab Reference Manual. ECEN 326 Electronic Circuits. Texas A&M University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 Lab Reference Manual ECEN 326 Electronic Circuits Texas A&M University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Contents 1. Circuit Analysis in PSpice 3 1.1 Transient and DC Analysis 3 1.2 Measuring
Lab Reference Manual ECEN 326 Electronic Circuits Texas A&M University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Contents 1. Circuit Analysis in PSpice 3 1.1 Transient and DC Analysis 3 1.2 Measuring
John von Neumann Faculty of Informatics F1. Basics of MicroCap. After the launching of the MicroCap 9 the following screen appears:
 Basics of MicroCap 1. MicroCap Based on the Electronics lectures the student learn the acquired knowledge in practice. For this the MicroCap simulation software will be used in the practical courses. The
Basics of MicroCap 1. MicroCap Based on the Electronics lectures the student learn the acquired knowledge in practice. For this the MicroCap simulation software will be used in the practical courses. The
SIMULATIONS WITH THE BUCK-BOOST TOPOLOGY EE562: POWER ELECTRONICS I COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY. Modified February 2006
 SIMULATIONS WITH THE BUCK-BOOST TOPOLOGY EE562: POWER ELECTRONICS I COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Modified February 2006 Page 1 of 13 PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to simulate the Buck-Boost converter
SIMULATIONS WITH THE BUCK-BOOST TOPOLOGY EE562: POWER ELECTRONICS I COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Modified February 2006 Page 1 of 13 PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to simulate the Buck-Boost converter
ECE 310L : LAB 9. Fall 2012 (Hay)
 ECE 310L : LAB 9 PRELAB ASSIGNMENT: Read the lab assignment in its entirety. 1. For the circuit shown in Figure 3, compute a value for R1 that will result in a 1N5230B zener diode current of approximately
ECE 310L : LAB 9 PRELAB ASSIGNMENT: Read the lab assignment in its entirety. 1. For the circuit shown in Figure 3, compute a value for R1 that will result in a 1N5230B zener diode current of approximately
The default account setup for the class should allow you to run HSPICE without any further configuration. To verify this, type:
 UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences HW #1: Circuit Simulation NTU IC541CA (Spring 2004) 1 Objective The objective of this homework
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences HW #1: Circuit Simulation NTU IC541CA (Spring 2004) 1 Objective The objective of this homework
Experiment 2 Introduction to PSpice
 Experiment 2 Introduction to PSpice W.T. Yeung and R.T. Howe UC Berkeley EE 105 Fall 2004 1.0 Objective One of the CAD tools you will be using as a circuit designer is SPICE, a Berkeleydeveloped industry-standard
Experiment 2 Introduction to PSpice W.T. Yeung and R.T. Howe UC Berkeley EE 105 Fall 2004 1.0 Objective One of the CAD tools you will be using as a circuit designer is SPICE, a Berkeleydeveloped industry-standard
Using LTSPICE to Analyze Circuits
 Using LTSPICE to Analyze Circuits Overview: LTSPICE is circuit simulation software that automatically constructs circuit equations using circuit element models (built in or downloadable). In its modern
Using LTSPICE to Analyze Circuits Overview: LTSPICE is circuit simulation software that automatically constructs circuit equations using circuit element models (built in or downloadable). In its modern
Mor M. Peretz Power Electronics Laboratory Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, ISRAEL
 Mor M. Peretz Power Electronics Laboratory Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, ISRAEL [1] Models and Devices A model defines the electrical behavior of
Mor M. Peretz Power Electronics Laboratory Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, ISRAEL [1] Models and Devices A model defines the electrical behavior of
Simulation Guide. The notes in this document are intended to give guidance to those using the demonstration files provided for
 Simulation Guide The notes in this document are intended to give guidance to those using the demonstration files provided for Electronics: A Systems Approach 2nd Edition by Neil Storey. Demonstration files
Simulation Guide The notes in this document are intended to give guidance to those using the demonstration files provided for Electronics: A Systems Approach 2nd Edition by Neil Storey. Demonstration files
University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2009 LAB 2 NON IDEAL OPAMPS
 University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2009 LAB 2 NON IDEAL OPAMPS Issued 10/5/2008 Pre Lab Completed 10/12/2008 Lab Due in Lecture 10/21/2008 Introduction In this lab you will characterize
University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2009 LAB 2 NON IDEAL OPAMPS Issued 10/5/2008 Pre Lab Completed 10/12/2008 Lab Due in Lecture 10/21/2008 Introduction In this lab you will characterize
Using LTspice a Short Intro with Examples
 Using LTspice a Short Intro with Examples LTspice, also called SwitcherCAD, is a powerful and easy to use schematic capture program and SPICE engine, which is a general-purpose circuit simulation program
Using LTspice a Short Intro with Examples LTspice, also called SwitcherCAD, is a powerful and easy to use schematic capture program and SPICE engine, which is a general-purpose circuit simulation program
Getting Started with Qucs
 Getting Started with Qucs Graham Edge University of Toronto After downloading Qucs, installing it, and running for the first time you should see a window that looks something like this: The large yellow
Getting Started with Qucs Graham Edge University of Toronto After downloading Qucs, installing it, and running for the first time you should see a window that looks something like this: The large yellow
LABORATORY 2: Bridge circuits, Superposition, Thevenin Circuits, and Amplifier Circuits
 LABORATORY 2: Bridge circuits, Superposition, Thevenin Circuits, and Amplifier Circuits Note: If your partner is no longer in the class, please talk to the instructor. Material covered: Bridge circuits
LABORATORY 2: Bridge circuits, Superposition, Thevenin Circuits, and Amplifier Circuits Note: If your partner is no longer in the class, please talk to the instructor. Material covered: Bridge circuits
ETIN25 Analogue IC Design. Laboratory Manual Lab 2
 Department of Electrical and Information Technology LTH ETIN25 Analogue IC Design Laboratory Manual Lab 2 Jonas Lindstrand Martin Liliebladh Markus Törmänen September 2011 Laboratory 2: Design and Simulation
Department of Electrical and Information Technology LTH ETIN25 Analogue IC Design Laboratory Manual Lab 2 Jonas Lindstrand Martin Liliebladh Markus Törmänen September 2011 Laboratory 2: Design and Simulation
LAB EXERCISE 3 FET Amplifier Design and Linear Analysis
 ADS 2012 Workspaces and Simulation Tools (v.1 Oct 2012) LAB EXERCISE 3 FET Amplifier Design and Linear Analysis Topics: More schematic capture, DC and AC simulation, more on libraries and cells, using
ADS 2012 Workspaces and Simulation Tools (v.1 Oct 2012) LAB EXERCISE 3 FET Amplifier Design and Linear Analysis Topics: More schematic capture, DC and AC simulation, more on libraries and cells, using
The analysis of the linear voltage regulators
 The analysis of the linear voltage regulators 1. Theoretical aspects The voltage regulator is an electronic circuit which, ideally, it provides a constant output voltage. The value of the output voltage
The analysis of the linear voltage regulators 1. Theoretical aspects The voltage regulator is an electronic circuit which, ideally, it provides a constant output voltage. The value of the output voltage
Laboratory Project 1: AC Circuit Measurements and Simulation
 Objectives The purpose of this laboratory project is to introduce to equipment, measurement techniques, and simulations commonly used in C circuit analysis. In this laboratory session, each student will:
Objectives The purpose of this laboratory project is to introduce to equipment, measurement techniques, and simulations commonly used in C circuit analysis. In this laboratory session, each student will:
EECE 488: Short HSPICE Tutorial. Last updated by: Mohammad Beikahmadi January 2013
 EECE 488: Short HSPICE Tutorial Last updated by: Mohammad Beikahmadi January 2013 SPICE? Simulation Program with Integrated Circuit Emphasis An open source analog circuit simulator Predicts circuit behavior,
EECE 488: Short HSPICE Tutorial Last updated by: Mohammad Beikahmadi January 2013 SPICE? Simulation Program with Integrated Circuit Emphasis An open source analog circuit simulator Predicts circuit behavior,
DC Operating Point, I-V Curve Trace. Author: Nate Turner
 DC Operating Point, I-V Curve Trace Author: Nate Turner Description: This tutorial demonstrates how to print the DC-Operating Point as well as trace the I-V curves for a transistor in the tsmc 180nm process.
DC Operating Point, I-V Curve Trace Author: Nate Turner Description: This tutorial demonstrates how to print the DC-Operating Point as well as trace the I-V curves for a transistor in the tsmc 180nm process.
Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 11: Lab Projects
 Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 11: Lab Projects 11.2.1: Signals with Multiple Frequency Components Overview: In this lab project, we will calculate the magnitude response of an electrical circuit and
Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 11: Lab Projects 11.2.1: Signals with Multiple Frequency Components Overview: In this lab project, we will calculate the magnitude response of an electrical circuit and
EECE 488: Short HSPICE. Tutorial. Last updated by: Mohammad Beikahmadi January Original presentation by: Jack Shiah
 EECE 488: Short HSPICE Tutorial Last updated by: Mohammad Beikahmadi January 2012 Original presentation by: Jack Shiah SPICE? Simulation Program with Integrated Circuit Emphasis An open source analog circuit
EECE 488: Short HSPICE Tutorial Last updated by: Mohammad Beikahmadi January 2012 Original presentation by: Jack Shiah SPICE? Simulation Program with Integrated Circuit Emphasis An open source analog circuit
PSPICE SIMULATIONS WITH THE RESONANT INVERTER POWER ELECTRONICS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY. Created by Colorado State University student
 PSPICE SIMULATIONS WITH THE RESONANT INVERTER POWER ELECTRONICS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Created by Colorado State University student Page 1 of 13 PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to simulate the resonant
PSPICE SIMULATIONS WITH THE RESONANT INVERTER POWER ELECTRONICS COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Created by Colorado State University student Page 1 of 13 PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to simulate the resonant
Class #7: Experiment L & C Circuits: Filters and Energy Revisited
 Class #7: Experiment L & C Circuits: Filters and Energy Revisited In this experiment you will revisit the voltage oscillations of a simple LC circuit. Then you will address circuits made by combining resistors
Class #7: Experiment L & C Circuits: Filters and Energy Revisited In this experiment you will revisit the voltage oscillations of a simple LC circuit. Then you will address circuits made by combining resistors
Appendix: PSPICE and EXCEL Using a Low-pass Filter Example
 Appendix: PSPICE and EXCEL Using a Low-pass Filter Example Introduction... 2 Problem... 2 Analysis... 2 Organization of a project in CAPTURE... 4 Placing files... 4 The project manager... 5 Naming files...
Appendix: PSPICE and EXCEL Using a Low-pass Filter Example Introduction... 2 Problem... 2 Analysis... 2 Organization of a project in CAPTURE... 4 Placing files... 4 The project manager... 5 Naming files...
Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Technology. EET 3086C Circuit Analysis Laboratory Experiments. Masood Ejaz
 Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Technology EET 3086C Circuit Analysis Laboratory Experiments Masood Ejaz Experiment # 1 DC Measurements of a Resistive Circuit and Proof of Thevenin Theorem
Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Technology EET 3086C Circuit Analysis Laboratory Experiments Masood Ejaz Experiment # 1 DC Measurements of a Resistive Circuit and Proof of Thevenin Theorem
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING. Date: Assistant A2: PSpice 2 PC Pool
 University of Applied Sciences Hamburg Group No : DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Laboratory for Instrumentation and Measurement L1: in charge of the report PSpice 2 PC Pool Date: Assistant A2: Professor:
University of Applied Sciences Hamburg Group No : DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Laboratory for Instrumentation and Measurement L1: in charge of the report PSpice 2 PC Pool Date: Assistant A2: Professor:
NGSPICE- Usage and Examples
 NGSPICE- Usage and Examples Debapratim Ghosh deba21pratim@gmail.com Electronic Systems Group Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay February 2013 Debapratim Ghosh Dept.
NGSPICE- Usage and Examples Debapratim Ghosh deba21pratim@gmail.com Electronic Systems Group Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Bombay February 2013 Debapratim Ghosh Dept.
Circuit Simulation with SPICE OPUS
 Circuit Simulation with SPICE OPUS Theory and Practice Tadej Tuma Arpäd Bürmen Birkhäuser Boston Basel Berlin Contents Abbreviations About SPICE OPUS and This Book xiii xv 1 Introduction to Circuit Simulation
Circuit Simulation with SPICE OPUS Theory and Practice Tadej Tuma Arpäd Bürmen Birkhäuser Boston Basel Berlin Contents Abbreviations About SPICE OPUS and This Book xiii xv 1 Introduction to Circuit Simulation
Laboratory Lecture 4
 Gheorghe Asachi Technical University of Iasi Faculty of Electronics, Telecommunications and Information Technology Title of Discipline: Computer-Aided Analysis of Electronic Circuits Laboratory Lecture
Gheorghe Asachi Technical University of Iasi Faculty of Electronics, Telecommunications and Information Technology Title of Discipline: Computer-Aided Analysis of Electronic Circuits Laboratory Lecture
Pulsed Power Engineering Circuit Simulation
 Pulsed Power Engineering Circuit Simulation January 12-16, 2009 Craig Burkhart, PhD Power Conversion Department SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory Circuit Simulation for Pulsed Power Applications Uses
Pulsed Power Engineering Circuit Simulation January 12-16, 2009 Craig Burkhart, PhD Power Conversion Department SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory Circuit Simulation for Pulsed Power Applications Uses
ENGI0531 Lab 2 Tutorial
 ENGI0531 Lab 2 Tutorial Transient Analysis, Operating Points, Parameters and other miscellany Lakehead University Greg Toombs Winter 2009 1. Constructing the Circuit Copying a Cell View Start Cadence as
ENGI0531 Lab 2 Tutorial Transient Analysis, Operating Points, Parameters and other miscellany Lakehead University Greg Toombs Winter 2009 1. Constructing the Circuit Copying a Cell View Start Cadence as
PSpice Tutorial. (usage of simulator ) (common sense) constant. L. Pacher
 PSpice Tutorial (usage of simulator ) (common sense) constant L. Pacher SPICE Simulation Program with Integrated Circuits Emphasis Berkeley University open source code (initially coded in FORTRAN, rewritten
PSpice Tutorial (usage of simulator ) (common sense) constant L. Pacher SPICE Simulation Program with Integrated Circuits Emphasis Berkeley University open source code (initially coded in FORTRAN, rewritten
EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response
 EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of passive signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Passive filters, Frequency domain, Bode plots
EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of passive signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Passive filters, Frequency domain, Bode plots
Circuit Shop v December 2003 Copyright Cherrywood Systems. All rights reserved.
 Circuit Shop v2.02 - December 2003 Copyright 1997-2003 Cherrywood Systems. All rights reserved. This manual is a printable version of Circuit Shop's help file. There are two parts to the manual: The first
Circuit Shop v2.02 - December 2003 Copyright 1997-2003 Cherrywood Systems. All rights reserved. This manual is a printable version of Circuit Shop's help file. There are two parts to the manual: The first
Experiment 8 Frequency Response
 Experiment 8 Frequency Response W.T. Yeung, R.A. Cortina, and R.T. Howe UC Berkeley EE 105 Spring 2005 1.0 Objective This lab will introduce the student to frequency response of circuits. The student will
Experiment 8 Frequency Response W.T. Yeung, R.A. Cortina, and R.T. Howe UC Berkeley EE 105 Spring 2005 1.0 Objective This lab will introduce the student to frequency response of circuits. The student will
EELE 201 Circuits I. Fall 2013 (4 Credits)
 EELE 201 Circuits I Instructor: Fall 2013 (4 Credits) Jim Becker 535 Cobleigh Hall 994-5988 Office hours: Monday 2:30-3:30 pm and Wednesday 3:30-4:30 pm or by appointment EMAIL: For EELE 201-related questions,
EELE 201 Circuits I Instructor: Fall 2013 (4 Credits) Jim Becker 535 Cobleigh Hall 994-5988 Office hours: Monday 2:30-3:30 pm and Wednesday 3:30-4:30 pm or by appointment EMAIL: For EELE 201-related questions,
Revised: Summer 2010
 EE 2274 PRE-LAB EXPERIMENT 5 DIODE OR GATE & CLIPPING CIRCUIT COMPLETE PRIOR TO COMING TO LAB Part I: 1. Design a diode, Figure 1 OR gate in which the maximum input current,, Iin is less than 5mA. Show
EE 2274 PRE-LAB EXPERIMENT 5 DIODE OR GATE & CLIPPING CIRCUIT COMPLETE PRIOR TO COMING TO LAB Part I: 1. Design a diode, Figure 1 OR gate in which the maximum input current,, Iin is less than 5mA. Show
Figure AC circuit to be analyzed.
 7.2(1) MULTISIM DEMO 7.2: INTRODUCTION TO AC ANALYSIS In this section, we ll introduce AC Analysis in Multisim. This is perhaps one of the most useful Analyses that Multisim offers, and we ll use it in
7.2(1) MULTISIM DEMO 7.2: INTRODUCTION TO AC ANALYSIS In this section, we ll introduce AC Analysis in Multisim. This is perhaps one of the most useful Analyses that Multisim offers, and we ll use it in
Week 4: Experiment 24. Using Nodal or Mesh Analysis to Solve AC Circuits with an addition of Equivalent Impedance
 Week 4: Experiment 24 Using Nodal or Mesh Analysis to Solve AC Circuits with an addition of Equivalent Impedance Lab Lectures You have two weeks to complete Experiment 27: Complex Power 2/27/2012 (Pre-Lab
Week 4: Experiment 24 Using Nodal or Mesh Analysis to Solve AC Circuits with an addition of Equivalent Impedance Lab Lectures You have two weeks to complete Experiment 27: Complex Power 2/27/2012 (Pre-Lab
A Short SPICE Tutorial
 A Short SPICE Tutorial Kenneth H. Carpenter Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Kanas State University September 15, 2003 - November 10, 2004 1 Introduction SPICE is an acronym for Simulation
A Short SPICE Tutorial Kenneth H. Carpenter Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Kanas State University September 15, 2003 - November 10, 2004 1 Introduction SPICE is an acronym for Simulation
THE SPICE BOOK. Andrei Vladimirescu. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York Chichester Brisbane Toronto Singapore
 THE SPICE BOOK Andrei Vladimirescu John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York Chichester Brisbane Toronto Singapore CONTENTS Introduction SPICE THE THIRD DECADE 1 1.1 THE EARLY DAYS OF SPICE 1 1.2 SPICE IN THE 1970s
THE SPICE BOOK Andrei Vladimirescu John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York Chichester Brisbane Toronto Singapore CONTENTS Introduction SPICE THE THIRD DECADE 1 1.1 THE EARLY DAYS OF SPICE 1 1.2 SPICE IN THE 1970s
1.3 An Introduction to WinSPICE
 Chapter 1 Introduction to CMOS Design 23 After the GDS file is generated, we can use the Gds2Tlc program to convert the GDS file back into TLC files. In the setups we must specify a directory where the
Chapter 1 Introduction to CMOS Design 23 After the GDS file is generated, we can use the Gds2Tlc program to convert the GDS file back into TLC files. In the setups we must specify a directory where the
1.5k. (a) Resistive Circuit (b) Capacitive Circuit
 Objective Information The purposes of this laboratory project are to become further acquainted with the use of an oscilloscope, and to observe the behavior of resistor and resistor capacitor circuits.
Objective Information The purposes of this laboratory project are to become further acquainted with the use of an oscilloscope, and to observe the behavior of resistor and resistor capacitor circuits.
Lab 1: Non-Ideal Operational Amplifier and Op-Amp Circuits
 Lab 1: Non-Ideal Operational Amplifier and Op-Amp Circuits 1. Learning Outcomes In this lab, the students evaluate characteristics of the non-ideal operational amplifiers. Students use a simulation tool
Lab 1: Non-Ideal Operational Amplifier and Op-Amp Circuits 1. Learning Outcomes In this lab, the students evaluate characteristics of the non-ideal operational amplifiers. Students use a simulation tool
Lab 4: Analysis of the Stereo Amplifier
 ECE 212 Spring 2010 Circuit Analysis II Names: Lab 4: Analysis of the Stereo Amplifier Objectives In this lab exercise you will use the power supply to power the stereo amplifier built in the previous
ECE 212 Spring 2010 Circuit Analysis II Names: Lab 4: Analysis of the Stereo Amplifier Objectives In this lab exercise you will use the power supply to power the stereo amplifier built in the previous
