Electromechanical Systems and Mechatronics Signal Conditioning: Lecture 3
|
|
|
- Veronica Elliott
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Electromechanical ystems and Mechatronics ignal Conditioning: Lecture 3 ignal Conditioning Processes The Operational Amplifier Filtering Digital ignals Multiplexers Data Acquisition Digital ignal Processing Pulse Modulation eferences Giorgio izzoni, Principles and Applications of Electrical Engineering, Fourth Edition, 2003 W. Bolton, Mechatronics: Electronic Control ystems in Mechanical and Electrical Engineering, Prentice Hall, 2003.
2 Instrumentation ystem Physical signal Transducer Analog processing Analog channels Multiplexer Digital output Analog-to-digital conersion Digital computer Display and record Analog output Analog processing Digital-to-analog conersion
3 ensors: ignal Classification ensor design always inoles the application of some law or principle of physics or chemistry that relates the quantity of interest to some measurement eent. Motion, position and dimensional ariable: Potentiometers; stress and strain gages; capacitie sensors; differential transformers, optical sensors. Force, torque, pressure and flow: train gages; piezoelectric sensors; capacitie sensors. Flow: Turbine meters; electromagnetic sensors; imaging sensors. Temperature: Thermocouples; thermometers. Liquid leel: Motion transducers; Force transducers. Humidity: emiconductor sensors and MEM. Chemical composition: Gas analysis equipment; semiconductor gas sensors.
4 Instrumentation: ensors and Transducers An important component in mechatronic systems that is linked to instrumentation is the sensor, whose function is to proide a mechanism for collecting information about a particular process. ensors transform real-world data into electrical signals. The sensor may be defined as a deice that produces an output signal for the purpose of sensing of a physical phenomenon. ensors are also referred as transducers. The extent to which sensors and transducers are used depends upon the leel of automation and the complexity of the control system. There is always a need for faster, sensitie, and precise measuring deices, accordingly, sensors are being miniaturized in solid state form by combing seeral sensors and signal processing mechanisms.
5 Types of ensors Actie ensors: They require external power for their operation. Passie ensors: Examples include piezoelectric, thermoelectric, and radioactie. Analog ensors: They hae an output that is proportional to the ariable being measured. Digital ensors: They are accurate and precision. Deflection ensors: They are used in a physical setup where the output is proportional to the measured quantity that is displayed. Null ensors: In this type, any deflection due to the measured quantity is balanced by the opposing calibrated force so that any imbalance is detected.
6 esistance Transducers A displacement transducer that uses the ariable resistance transduction principle may be manufactured with a rotary or linear potentiometer (rotation or displacement is conerted into a potential difference). uch potentiometers consist of a wiper that makes contact with a resistie element, and as this point of contact moes, the resistance between the wiper and end leads of the deice changes in proportion to the angular displacement. Through oltage diision, the change in resistance can be used to create an output oltage that is directly proportional to the input displacement. wiper
7 Inductance Transducers Inductance transducers are used for proximity sensing when the presence or absence of an object must be detected with an electronic non-contact sensor. They are also used for motion position detection, motion control, and process control applications. Variable inductance transducers are based on Faraday s law of induction in a coil: the induced oltage is equal to the rate at which the magnetic flux through the circuit changes dφ d( BA) dn( φ) dϕ V N N dt dt dt dt ( ψ is the total flux linkage in the circuit) ψ L i Ni φ L N 2 Nφ i ; 1 µ A N A µ l 2
8 The bridge conerts a relatie change of resistance δ / into a proportional oltage output V o Wheatstone Bridge I M I I 1 I I I 2 3 I I I V i I 1 I 2 I 3 I M V o
9 Temperature Effect in train Gage The strain gauge enironment is often influenced by temperature change. The electrical resistiity of most alloys changes with temperature, increasing as temperature rises and decreasing as it falls. Usually metals used in strain gauges hae a temperature coefficient (αo) on the order of 0.004/ o C. The resistance at temperature T is gien by T T T o (1 + α T ) T o α T o o (esistance change due to change in Temperature)
10 Velocity Measurement: Tachometer A permanent magnet DC generator can be used for analog measurement of angular elocity. ω is the angular elocity to be measured, T is the torque required to drie the generator, L and are the inductance and the capacitance of the rotor, I is the current in the rotor windings, and V is the oltage output at the rotor windings terminals. L i N V T, ω
11 ignal Conditioning Processes Protection to preent damage to the next element. Preparing the signal into the right type of signal. Proiding the right leel of signal. Eliminating or reducing the noise. ignal manipulation or making it a linear function of some ariable.
12 Inerting Amplifier Non-Inerting Amplifier umming Amplifier Integrating Amplifier Differential Amplifier Logarithmic Amplifier Comparator Operational Amplifier
13 Operational Amplifier Operational amplifier is an amplifier whose output oltage is proportional to the negatie of its input oltage and that boosts the amplitude of an input signal, many times, i.e., has a ery high gain.high-gain amplifiers. They were deeloped to be used in synthesizing mathematical operations in early analog computers, hence their name. Typified by the series 741 (The integrated circuit contains 8-pin mini- DIP, 20 transistors and 11 resistors). Used for amplifications, as switches, as filters, as rectifiers, and in digital circuits. Take adantage of large open-loop gain. It is usually connected so that part of the output is fed back to the input. Can be used with positie feedback to produce oscillation.
14 Figure 8.2, 8.3 A Voltage Amplifier imple Voltage Amplifier Model in L in L out L in in L L out L in L in in in A A A ; ; ;
15 Operational Amplifier Model ymbols and Circuit Diagram Figure 8.4
16 The Ideal and eal Op-Amp Ideal Amplifier: Two Inputs: Inerting. Non-inerting. V o A (V + -V - ) Gain A is large ( ). V o 0, when V + V - Infinite input resistance, which produces no currents at the inputs. The output resistance is zero, so it does not affect the output of the amplifier by loading. The gain A is independent of the frequency. eal Amplifier: Gain ( ). Input resistance 10 6 for BJTs Output resistance: Ω.
17 Figur e 8.5 Inerting Amplifier F out F out F out out in F in F out F in A A i i i i i i i i i ; ; 0 ; ;
18 A Practical Application: Why Feedback elf-balancing mechanism, which allows the amplifier to presere zero potential difference between its input terminals. A practical example that illustrates a common application of negatie feedback is the thermostat. This simple temperature control system operates by comparing the desired ambient temperature and the temperature measured by the thermometer and turning a heat source on and off to maintain the difference between actual and desired temperature as close to zero as possible.
19 Figure 8.7 umming Amplifier N n F out F out F n F N n n n n i N n i i i i i ,2,
20 Noninerting Amplifier Voltage Follower Figu re 8.8, 8.9 out 1+ F out
21 Differential Amplifier out ( ) Figure 8.10
22 Instrumentation Amplifier Input (a) and output (b) stages of Instrumentation amplifier Figure 8.14, 8.15 A V out 1 2 F
23 Op-amp Circuits Employing Complex Impedances V V V V out out ( ( jω) jω) Z Z 1+ F Z Z F Figure 8.20
24 Op-amp Integrator t 1 out ( t) ( t) dt C F Figure 8.30
25 Op-amp Differentiator out ( t) F C d ( t) dt Figure 8.35
26 Protection There are cases where the connection of a sensor to the next unit can lead to the possibility of damage as a result of high current or high oltage. The high current can be protected against by the incorporation in the input line of a series resistor to limit the current to certain leel and a fuse to break if the current does exceed a safe leel. High oltage and wrong polarity may be protected against by the use of a Zener diode circuit. Zerner diodes behae like ordinary diodes up to some breakdown oltage when they become conducting.
27 Filtering The term filtering is used to describe the process of remoing a certain band of frequencies from a signal and allowing others to be transmitted. The range of frequencies passed by a filter is known as the pass band. Filters are classifies as. The term cutoff is defined as being that at which the output oltage is 70.7% of that in the passband. Low Pass Filter: Allows frequencies from 0 up to some frequency to pass. High Pass Filter: Allows frequencies from some alue up to infinity to be transmitted. Band Pass Filter: Allows all the frequencies within a specified band to be transmitted. Band-top Filter: tops all frequencies within a particular band from being transmitted.
28 Actie Low-Pass Filter Figure 8.21, 8.23 Normalized esponse of Actie Low-pass Filter
29 Actie High-Pass Filter Figure 8.24, 8.25 Normalized esponse of Actie High-pass Filter
30 Actie Band-Pass Filter Figure 8.26, 8.27 Normalized Amplitude esponse of Actie Band-pass Filter
31 Digital ignal Analog to Digital Conerter: The A/D conerts the information from analog to digital form. Often, the time ariations of the analog signal must be arrested with a sample-and-hold circuit while A/D conersion is taking place. Digital to Analog Conerter: Often, the computer must proide outputs in analog form. If, for example, the data monitor were part of the control system, the computer might furnish analog signals as feedback to the controller of the process affecting the physical measurements.
32 Analog to Digital Conersion ADC, or digitizing, conerts analog waeforms to digital representations that can be processed and stored in digital form. The analog wae is sampled, or read, hundreds or thousands of times per second to map out the wae digitally. Digital music requires extremely high sampling rates (44,100 samples/sec), while it is usually acceptable to sample oice at 11,000 samples/sec or higher. There is also a factor that determines the precision of the captured signal-the more bits used to record the alue of the sampled signal, the higher its resolution and the better its sound when played back. Howeer, the more bits used, the more disk space is required for storage or bandwidth for transmission. For example, one minute of sampling at 44.1 khz using 16 bits per sample requires MB of disk space.
33 The telephone companies conert analog oice to digital at their central offices for transmission across trunk lines to other central offices or to long-distance systems. Voice conerted to digital requires a 64-kbit/sec channel. ADCs are used in a ariety of information-processing applications. Information collected from analog phenomena such as sound, light, temperature, and pressure can be digitized and made aailable for digital processing. A codec (coder/decoder) is the deice that transforms the analog signals to digital signals. The process inoles sampling, quantizing, and digitizing. The amplitude of a signal is measured at arious interals. The tighter these interals, the more accurate the recording.
34 ADC
35 ampling Theorem ADC samples analog signals at regular interals and conert these alues to binary words. The sampling rate should be at least twice that of the highest frequency in the analog signal that the sample gies the original signal. This criterion is known as the Nyquist Criterion or hannon s sampling theorem.
36 Figure An n-bit Digital-to-Analog Conerter
37 A 4-bit DAC Figure 15.25
38 Multiplexers eeral analog channels are processed sequentially through a multiplexer, which is a digitally controlled switch. The multiplexer accepts parallel inputs from seeral channels and proides one analog output at a time for conersion to digital form. Multiplexer ADC Output Channel select signal
39 Data Acquisition ystem The term data Acquisition or DAQ is used for the process of taking data from sensors and moing them into a computer for processing. The sensors are connected ia signal conditioning to data acquisition board which is plugged into the back of a computer. The DAQ board is a printed circuit board that, for analog inputs, basically proides a multiplexer, amplification, ADC, register, and control circuit so that the Figure sampled digital signals are applied to the computer system Computer software is used to control the acquisition of data ia the DAQ board. When the program requires an input from a particular sensor, it actiates the board by sending a control word to the control and status register. uch a word indicates the type of operation the board has to carry out. As a consequence the board switches the multiplexer to the appropriate input channel. The signal from the sensor will moe ia the amplifier to ADC, data register and then processed by the computer. In brief, data Acquisition means storing data from sensors using a microprocessor or a computer.
40 DAQ
41 Actuators elays and Motors DC Motors Permanent magnet eries wound hunt wound eparately excited Compound wound Torque-speed characteristic; speed control; reersible; regeneratie breaking ingle phase quirrel cage Wound rotor AC Motors Three phase Induction ynchronous Uniersal motors
42 List of Mechatronic ystems Air bag safety, antilock break system; remote automatic door locks; cruise control, etc. Copy machines, fax machines, dcanners. MI equipment; ultrasonic probes; and other medical equipment. Autofocus cameras; VCs; CD players; camcoders; and other consumer products. Welding robots; automatic guided ehicles. Flight control actuators; landing gear system; and cockpit control system. Washing machines; dishwashers; automatic ice makers. Garage door openers; security system; and other home support systems. Variable speed drills; digital torque wrenches. Factory automation system. More!
Electronic Instrumentation and Measurements
 Electronic Instrumentation and Measurements A fundamental part of many electromechanical systems is a measurement system that composed of four basic parts: Sensors Signal Conditioning Analog-to-Digital-Conversion
Electronic Instrumentation and Measurements A fundamental part of many electromechanical systems is a measurement system that composed of four basic parts: Sensors Signal Conditioning Analog-to-Digital-Conversion
Chapter 6: Operational Amplifier (Op Amp)
 Chapter 6: Operational Amplifier (Op Amp) 6.1 What is an Op Amp? 6.2 Ideal Op Amp 6.3 Nodal Analysis of Circuits with Op Amps 6.4 Configurations of Op Amp 6.5 Cascaded Op Amp 6.6 Op Amp Circuits & Linear
Chapter 6: Operational Amplifier (Op Amp) 6.1 What is an Op Amp? 6.2 Ideal Op Amp 6.3 Nodal Analysis of Circuits with Op Amps 6.4 Configurations of Op Amp 6.5 Cascaded Op Amp 6.6 Op Amp Circuits & Linear
Electronic Instrumentation Experiment 6 -- Digital Switching
 1 Electronic Instrumentation Experiment 6 -- Digital Switching Part A: Transistor Switches Part B: Comparators and Schmitt Triggers Part C: Digital Switching Part D: Switching a elay Part A: Transistors
1 Electronic Instrumentation Experiment 6 -- Digital Switching Part A: Transistor Switches Part B: Comparators and Schmitt Triggers Part C: Digital Switching Part D: Switching a elay Part A: Transistors
Chapter Goal. Zulfiqar Ali
 Chapter Goal Understand behaior and characteristics of ideal differential and op amps. Demonstrate circuit analysis techniques for ideal op amps. Characterize inerting, non-inerting, summing and instrumentation
Chapter Goal Understand behaior and characteristics of ideal differential and op amps. Demonstrate circuit analysis techniques for ideal op amps. Characterize inerting, non-inerting, summing and instrumentation
Chapter 11 Operational Amplifiers and Applications
 Chapter Operational Amplifiers and Applications Chapter Goals Understand the magic of negatie feedback and the characteristics of ideal op amps. Understand the conditions for non-ideal op amp behaior so
Chapter Operational Amplifiers and Applications Chapter Goals Understand the magic of negatie feedback and the characteristics of ideal op amps. Understand the conditions for non-ideal op amp behaior so
Circuit produces an amplified negative version of v IN = R R R
 Inerting Amplifier Circuit produces an amplified negatie ersion of i = i, = 2 0 = 2 OUT OUT = 2 Example: Calculate OUT / and I for = 0.5V Solution: A V OUT 2 = = = 0 kω = 0 kω i 05. V = = = kω 05. ma
Inerting Amplifier Circuit produces an amplified negatie ersion of i = i, = 2 0 = 2 OUT OUT = 2 Example: Calculate OUT / and I for = 0.5V Solution: A V OUT 2 = = = 0 kω = 0 kω i 05. V = = = kω 05. ma
Amplifiers with Negative Feedback
 13 Amplifiers with Negatie Feedback 335 Amplifiers with Negatie Feedback 13.1 Feedback 13.2 Principles of Negatie Voltage Feedback In Amplifiers 13.3 Gain of Negatie Voltage Feedback Amplifier 13.4 Adantages
13 Amplifiers with Negatie Feedback 335 Amplifiers with Negatie Feedback 13.1 Feedback 13.2 Principles of Negatie Voltage Feedback In Amplifiers 13.3 Gain of Negatie Voltage Feedback Amplifier 13.4 Adantages
5. Transducers Definition and General Concept of Transducer Classification of Transducers
 5.1. Definition and General Concept of Definition The transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form. Examples: Mechanical transducer and Electrical transducer Electrical A
5.1. Definition and General Concept of Definition The transducer is a device which converts one form of energy into another form. Examples: Mechanical transducer and Electrical transducer Electrical A
55:041 Electronic Circuits
 55:04 Electronic Circuits Lecture -5 eiew of Op-Amps Sections of Chapters 9 & 4 A. Kruger Op-Amp eiew- eal-world Op-Amp In earlier courses, op-amp were often considered ideal Infinite input resistance
55:04 Electronic Circuits Lecture -5 eiew of Op-Amps Sections of Chapters 9 & 4 A. Kruger Op-Amp eiew- eal-world Op-Amp In earlier courses, op-amp were often considered ideal Infinite input resistance
Introduction. ELCT903, Sensor Technology Electronics and Electrical Engineering Department 1. Dr.-Eng. Hisham El-Sherif
 Introduction In automation industry every mechatronic system has some sensors to measure the status of the process variables. The analogy between the human controlled system and a computer controlled system
Introduction In automation industry every mechatronic system has some sensors to measure the status of the process variables. The analogy between the human controlled system and a computer controlled system
ECE:3410 Electronic Circuits
 ECE:3410 Electronic Circuits Reiew of Op-Amps Sections of Chapters 9 & 14 A. Kruger Op-Amp Reiew-1 Real-World Op-Amp In earlier courses, op-amp were often considered ideal Infinite input resistance Infinite
ECE:3410 Electronic Circuits Reiew of Op-Amps Sections of Chapters 9 & 14 A. Kruger Op-Amp Reiew-1 Real-World Op-Amp In earlier courses, op-amp were often considered ideal Infinite input resistance Infinite
Signal Conditioning Systems
 Note-13 1 Signal Conditioning Systems 2 Generalized Measurement System: The output signal from a sensor has generally to be processed or conditioned to make it suitable for the next stage Signal conditioning
Note-13 1 Signal Conditioning Systems 2 Generalized Measurement System: The output signal from a sensor has generally to be processed or conditioned to make it suitable for the next stage Signal conditioning
Week 7: Common-Collector Amplifier, MOS Field Effect Transistor
 EE 2110A Electronic Circuits Week 7: Common-Collector Amplifier, MOS Field Effect Transistor ecture 07-1 Topics to coer Common-Collector Amplifier MOS Field Effect Transistor Physical Operation and I-V
EE 2110A Electronic Circuits Week 7: Common-Collector Amplifier, MOS Field Effect Transistor ecture 07-1 Topics to coer Common-Collector Amplifier MOS Field Effect Transistor Physical Operation and I-V
55:041 Electronic Circuits
 55:041 Electronic Circuits Reiew of Op-Amps Sections of Chapters 9 & 14 A. Kruger Op-Amp Reiew-1 Real-World Op-Amp In earlier courses, op-amp were often considered ideal Infinite input resistance Infinite
55:041 Electronic Circuits Reiew of Op-Amps Sections of Chapters 9 & 14 A. Kruger Op-Amp Reiew-1 Real-World Op-Amp In earlier courses, op-amp were often considered ideal Infinite input resistance Infinite
IT.MLD900 SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS TRAINER. Signal Conditioning
 SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS TRAINER IT.MLD900 The s and Instrumentation Trainer introduces students to input sensors, output actuators, signal conditioning circuits, and display devices through a wide range
SENSORS AND TRANSDUCERS TRAINER IT.MLD900 The s and Instrumentation Trainer introduces students to input sensors, output actuators, signal conditioning circuits, and display devices through a wide range
ELECTRONIC DEVICES. Assist. prof. Laura-Nicoleta IVANCIU, Ph.D. C8 Summing and differential amplifiers with OpAmp
 ELECTNIC DEVICES Assist. prof. Laura-Nicoleta IVANCIU, Ph.D. C8 Summing and differential amplifiers with pamp C8 Summing and differential amplifs w/ pamp Contents Summing amplifiers with pamp Inerting
ELECTNIC DEVICES Assist. prof. Laura-Nicoleta IVANCIU, Ph.D. C8 Summing and differential amplifiers with pamp C8 Summing and differential amplifs w/ pamp Contents Summing amplifiers with pamp Inerting
MECE 3320 Measurements & Instrumentation. Data Acquisition
 MECE 3320 Measurements & Instrumentation Data Acquisition Dr. Isaac Choutapalli Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Texas Pan American Sampling Concepts 1 f s t Sampling Rate f s 2 f m or
MECE 3320 Measurements & Instrumentation Data Acquisition Dr. Isaac Choutapalli Department of Mechanical Engineering University of Texas Pan American Sampling Concepts 1 f s t Sampling Rate f s 2 f m or
ELECTRONIC DEVICES. Assist. prof. Laura-Nicoleta IVANCIU, Ph.D. C10 Applications with OpAmp - 2
 ELECNC DEVCE Assist. prof. Laura-Nicoleta VANCU, Ph.D. C10 Applications with pamp - 2 Contents Half-wae and full-wae precision rectifiers Precision peak detectors Current sources Logarithmic and exponential
ELECNC DEVCE Assist. prof. Laura-Nicoleta VANCU, Ph.D. C10 Applications with pamp - 2 Contents Half-wae and full-wae precision rectifiers Precision peak detectors Current sources Logarithmic and exponential
AC Voltage Standards With Quantum Traceability
 NPL Electromagnetics day 29/11/2007 AC Voltage Standards With Quantum Traceability Kein Marshall, Dale Henderson, Prain Patel and Jonathan Williams. Background To Quantum Voltage Metrology Existing DC
NPL Electromagnetics day 29/11/2007 AC Voltage Standards With Quantum Traceability Kein Marshall, Dale Henderson, Prain Patel and Jonathan Williams. Background To Quantum Voltage Metrology Existing DC
EIT/FE Exam EE Review 2 nd Session Prof. Richard Spencer. Transformer
 EIT/FE Exam EE eiew 2 nd ession Prof. ichard pencer Transformer Assume two coils are wound on the same core and that it has low reluctance (high permeability) If a current flows in one of the windings,
EIT/FE Exam EE eiew 2 nd ession Prof. ichard pencer Transformer Assume two coils are wound on the same core and that it has low reluctance (high permeability) If a current flows in one of the windings,
Electronic Systems - B1 23/04/ /04/ SisElnB DDC. Chapter 2
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS. Introduction. B1 - Sensors and actuators. Introduction
 Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Politecnico di Torino - ICT school Goup B - goals ELECTRONIC SYSTEMS B INFORMATION PROCESSING B.1 Systems, sensors, and actuators» System block diagram» Analog and digital signals» Examples of sensors»
Chapter 6: Converter circuits
 hapter 6. onerter ircuits 6.. ircuit manipulations 6.. A short list of conerters 6.3. Transformer isolation 6.4. onerter ealuation and design 6.5. Summary of key points Where do the boost, buck-boost,
hapter 6. onerter ircuits 6.. ircuit manipulations 6.. A short list of conerters 6.3. Transformer isolation 6.4. onerter ealuation and design 6.5. Summary of key points Where do the boost, buck-boost,
Paralleled three-phase inverters
 Paralleled three-phase inerters Hoff, E., Skjellnes, T. & Norum, L. Department of Electrical Power Engineering, Norwegian Uniersity of Science and Technology, NTNU 749 Trondheim, NORWAY Phone (+47) 73
Paralleled three-phase inerters Hoff, E., Skjellnes, T. & Norum, L. Department of Electrical Power Engineering, Norwegian Uniersity of Science and Technology, NTNU 749 Trondheim, NORWAY Phone (+47) 73
9/28/2010. Chapter , The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
 Chapter 4 Sensors are are used to detect, and often to measure, the magnitude of something. They basically operate by converting mechanical, magnetic, thermal, optical, and chemical variations into electric
Chapter 4 Sensors are are used to detect, and often to measure, the magnitude of something. They basically operate by converting mechanical, magnetic, thermal, optical, and chemical variations into electric
Signal Conditioning Fundamentals for PC-Based Data Acquisition Systems
 Application Note 048 Signal Conditioning Fundamentals for PC-Based Data Acquisition Systems Introduction PC-based data acquisition (DAQ) systems and plugin boards are used in a very wide range of applications
Application Note 048 Signal Conditioning Fundamentals for PC-Based Data Acquisition Systems Introduction PC-based data acquisition (DAQ) systems and plugin boards are used in a very wide range of applications
Lecture 1 Introduction to Electronic
 Lecture 1 Introduction to Electronic Present by : Thawatchai Thongleam Faculty of Science and Technology Nakhon Pathom Rajabhat Uniersity Electronic Engineering Lecture 1 Introduction to Electronic Lecture
Lecture 1 Introduction to Electronic Present by : Thawatchai Thongleam Faculty of Science and Technology Nakhon Pathom Rajabhat Uniersity Electronic Engineering Lecture 1 Introduction to Electronic Lecture
Industrial Sensors. Proximity Mechanical Optical Inductive/Capacitive. Position/Velocity Potentiometer LVDT Encoders Tachogenerator
 Proximity Mechanical Optical Inductive/Capacitive Position/Velocity Potentiometer LVDT Encoders Tachogenerator Force/Pressure Vibration/acceleration Industrial Sensors 1 Definitions Accuracy: The agreement
Proximity Mechanical Optical Inductive/Capacitive Position/Velocity Potentiometer LVDT Encoders Tachogenerator Force/Pressure Vibration/acceleration Industrial Sensors 1 Definitions Accuracy: The agreement
Elektronika (TKE 4012)
 Operational Amplifier & aplikasinya Elektronika (TKE 40) Eka Maulana maulana.lecture.ub.ac.id Op Amp Op Amp is short for operational amplifier Amplifiers proide gains in oltage or current Op amps can conert
Operational Amplifier & aplikasinya Elektronika (TKE 40) Eka Maulana maulana.lecture.ub.ac.id Op Amp Op Amp is short for operational amplifier Amplifiers proide gains in oltage or current Op amps can conert
M.D. Singh J.G. Joshi MECHATRONICS
 M.D. Singh J.G. Joshi MECHATRONICS MECHATRONICS MECHATRONICS M.D. SINGH Formerly Principal Sagar Institute of Technology and Research Bhopal J.G. JOSHI Lecturer Department of Electronics and Telecommunication
M.D. Singh J.G. Joshi MECHATRONICS MECHATRONICS MECHATRONICS M.D. SINGH Formerly Principal Sagar Institute of Technology and Research Bhopal J.G. JOSHI Lecturer Department of Electronics and Telecommunication
ELECTRONIC DEVICES. Assist. prof. Laura-Nicoleta IVANCIU, Ph.D. C9 Applications with OpAmp - 1
 ELECTONIC DEVICES Assist. prof. Laura-Nicoleta IVANCIU, Ph.D. C9 Applications with OpAmp - C9 Applications with OpAmp - Contents Voltage domain conersion circuits Capacitiely coupled amplifiers Op-amp
ELECTONIC DEVICES Assist. prof. Laura-Nicoleta IVANCIU, Ph.D. C9 Applications with OpAmp - C9 Applications with OpAmp - Contents Voltage domain conersion circuits Capacitiely coupled amplifiers Op-amp
Part 10: Transducers
 Part 10: Transducers 10.1: Classification of Transducers An instrument may be defined as a device or a system which is designed to maintain a functional relationship between prescribed properties of physical
Part 10: Transducers 10.1: Classification of Transducers An instrument may be defined as a device or a system which is designed to maintain a functional relationship between prescribed properties of physical
Mechatronics 421/780. Department of Mechanical and Aeronautical Engineering. Page 1 of 10
 Mechatronics 421/780 Department of Mechanical and Aeronautical Engineering Page 1 of 10 OVERVIEW AND OBJECTIVES 1. Course Overview Mechatronics (MEG 421 or MEG 780) is a multidisciplinary field of engineering
Mechatronics 421/780 Department of Mechanical and Aeronautical Engineering Page 1 of 10 OVERVIEW AND OBJECTIVES 1. Course Overview Mechatronics (MEG 421 or MEG 780) is a multidisciplinary field of engineering
ELECTRONIC FUNDAMENTALS
 Part 66 Cat. B1 Module 4 ELECTRONIC FUNDAMENTALS Vilnius-2017 Issue 1. Effective date 2017-02-28 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY Page 1 of 67 Figure 1-4. Standard diode color code system Color Digit Diode suffix
Part 66 Cat. B1 Module 4 ELECTRONIC FUNDAMENTALS Vilnius-2017 Issue 1. Effective date 2017-02-28 FOR TRAINING PURPOSES ONLY Page 1 of 67 Figure 1-4. Standard diode color code system Color Digit Diode suffix
ni.com Sensor Measurement Fundamentals Series
 Sensor Measurement Fundamentals Series Introduction to Data Acquisition Basics and Terminology Litkei Márton District Sales Manager National Instruments What Is Data Acquisition (DAQ)? 3 Why Measure? Engineers
Sensor Measurement Fundamentals Series Introduction to Data Acquisition Basics and Terminology Litkei Márton District Sales Manager National Instruments What Is Data Acquisition (DAQ)? 3 Why Measure? Engineers
Study Guide for the First Exam
 Study Guide or the First Exam Chemistry 838 Fall 005 T V Atkinson Department o Chemistry Michigan State Uniersity East Lansing, MI 4884 The leel o knowledge and detail expected or the exam is that o the
Study Guide or the First Exam Chemistry 838 Fall 005 T V Atkinson Department o Chemistry Michigan State Uniersity East Lansing, MI 4884 The leel o knowledge and detail expected or the exam is that o the
DC Machine Construction. Figure 1 General arrangement of a dc machine
 1 DC Motor The direct current (dc) machine can be used as a motor or as a generator. DC Machine is most often used for a motor. The major adantages of dc machines are the easy speed and torque regulation.
1 DC Motor The direct current (dc) machine can be used as a motor or as a generator. DC Machine is most often used for a motor. The major adantages of dc machines are the easy speed and torque regulation.
ME 3200 Mechatronics I Laboratory Lab 8: Angular Position and Velocity Sensors
 ME 3200 Mechatronics I Laboratory Lab 8: Angular Position and Velocity Sensors In this exercise you will explore the use of the potentiometer and the tachometer as angular position and velocity sensors.
ME 3200 Mechatronics I Laboratory Lab 8: Angular Position and Velocity Sensors In this exercise you will explore the use of the potentiometer and the tachometer as angular position and velocity sensors.
ELG 2135 ELECTRONICS I FOURTH CHAPTER : BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS
 ELG 2135 ELECTRONICS I FOURTH CHAPTER : BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS Session WINTER 2003 Dr M. YAGOUB Fourth Chapter: Bipolar Junction Transistors IV - 2 _ Haing studied the junction diode, which is the
ELG 2135 ELECTRONICS I FOURTH CHAPTER : BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTORS Session WINTER 2003 Dr M. YAGOUB Fourth Chapter: Bipolar Junction Transistors IV - 2 _ Haing studied the junction diode, which is the
Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors
 Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors Sander Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Department of Electrical Engineering Electronic Systems INDUCTIVE SENSORS (Chapter 3.4, 7.3) 3 Inductive sensors 4 Inductive
Sensors and Actuators Introduction to sensors Sander Stuijk (s.stuijk@tue.nl) Department of Electrical Engineering Electronic Systems INDUCTIVE SENSORS (Chapter 3.4, 7.3) 3 Inductive sensors 4 Inductive
CRN: MET-487 Instrumentation and Automatic Control June 28, 2010 August 5, 2010 Professor Paul Lin
 CRN: 32030 MET-487 Instrumentation and Automatic Control June 28, 2010 August 5, 2010 Professor Paul Lin Course Description: Class 2, Lab 2, Cr. 3, Junior class standing and 216 Instrumentation for pressure,
CRN: 32030 MET-487 Instrumentation and Automatic Control June 28, 2010 August 5, 2010 Professor Paul Lin Course Description: Class 2, Lab 2, Cr. 3, Junior class standing and 216 Instrumentation for pressure,
Introduction to Measurement Systems
 MFE 3004 Mechatronics I Measurement Systems Dr Conrad Pace Page 4.1 Introduction to Measurement Systems Role of Measurement Systems Detection receive an external stimulus (ex. Displacement) Selection measurement
MFE 3004 Mechatronics I Measurement Systems Dr Conrad Pace Page 4.1 Introduction to Measurement Systems Role of Measurement Systems Detection receive an external stimulus (ex. Displacement) Selection measurement
COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING
 COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MCE 527 DISCLAIMER The contents of this document are intended for practice and leaning purposes at the
COVENANT UNIVERSITY NIGERIA TUTORIAL KIT OMEGA SEMESTER PROGRAMME: MECHANICAL ENGINEERING COURSE: MCE 527 DISCLAIMER The contents of this document are intended for practice and leaning purposes at the
Question Paper Code : B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER Third Semester. Electrical and Electronics Engineering
 Question Paper Code : 31391 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2013. Third Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 2201/EE 33/EI 1202/10133 EE 302/080280016 MEASUREMENTS AND
Question Paper Code : 31391 B.E./B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION, NOVEMBER/DECEMBER 2013. Third Semester Electrical and Electronics Engineering EE 2201/EE 33/EI 1202/10133 EE 302/080280016 MEASUREMENTS AND
COURSE INFORMATION. Course Prefix/Number: EET 231. Lecture Hours/Week: 3.0 Lab Hours/Week: 3.0 Credit Hours/Semester: 4.0
 COURSE INFORMATION Course Prefix/Number: EET 231 Course Title: Industrial Electronics Lecture Hours/Week: 3.0 Lab Hours/Week: 3.0 Credit Hours/Semester: 4.0 VA Statement/Distance Learning Attendance Textbook
COURSE INFORMATION Course Prefix/Number: EET 231 Course Title: Industrial Electronics Lecture Hours/Week: 3.0 Lab Hours/Week: 3.0 Credit Hours/Semester: 4.0 VA Statement/Distance Learning Attendance Textbook
Position Sensors. The Potentiometer.
 Position Sensors In this tutorial we will look at a variety of devices which are classed as Input Devices and are therefore called "Sensors" and in particular those sensors which are Positional in nature
Position Sensors In this tutorial we will look at a variety of devices which are classed as Input Devices and are therefore called "Sensors" and in particular those sensors which are Positional in nature
Indigenous Design of Electronic Circuit for Electrocardiograph
 Indigenous Design of Electronic Circuit for Electrocardiograph Raman Gupta 1, Sandeep Singh 2, Kashish Garg 3, Shruti Jain 4 U.G student, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering,Jaypee
Indigenous Design of Electronic Circuit for Electrocardiograph Raman Gupta 1, Sandeep Singh 2, Kashish Garg 3, Shruti Jain 4 U.G student, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering,Jaypee
CHAPTER SIX SOLUTIONS
 CHAPTE SIX SOLUTIONS. The first step is to perform a simple source transformation, so that a 0.5-V source in series with a 50-Ω resistor is connected to the inerting pin of the ideal op amp. 00 50 Then,
CHAPTE SIX SOLUTIONS. The first step is to perform a simple source transformation, so that a 0.5-V source in series with a 50-Ω resistor is connected to the inerting pin of the ideal op amp. 00 50 Then,
Linear Voltage Regulators
 8/6/ inearoltageegulators(oeriew).doc / 8/6/ inearoltageegulators(oeriew).doc / inear oltage egulators The schematic below shows a pretty darn good design for a linear regulator. t has good regulation,
8/6/ inearoltageegulators(oeriew).doc / 8/6/ inearoltageegulators(oeriew).doc / inear oltage egulators The schematic below shows a pretty darn good design for a linear regulator. t has good regulation,
DSC Lab 2: Force and Displacement Measurement Page 1
 DSC Lab 2: Force and Displacement Measurement Page 1 Overview of Laboratory on Force and Displacement Measurement This lab course introduces concepts in force and motion measurement using strain-gauge
DSC Lab 2: Force and Displacement Measurement Page 1 Overview of Laboratory on Force and Displacement Measurement This lab course introduces concepts in force and motion measurement using strain-gauge
Study Guide for the First Exam
 Study Guide or the First Exam Chemistry 838 Fall 27 T V Atkinson Department o Chemistry Michigan State Uniersity East Lansing, MI 48824 Table o Contents Table o Contents...1 Table o Tables...1 Table o
Study Guide or the First Exam Chemistry 838 Fall 27 T V Atkinson Department o Chemistry Michigan State Uniersity East Lansing, MI 48824 Table o Contents Table o Contents...1 Table o Tables...1 Table o
Differential Amplifier : input. resistance. Differential amplifiers are widely used in engineering instrumentation
 Differential Amplifier : input resistance Differential amplifiers are widely used in engineering instrumentation Differential Amplifier : input resistance v 2 v 1 ir 1 ir 1 2iR 1 R in v 2 i v 1 2R 1 Differential
Differential Amplifier : input resistance Differential amplifiers are widely used in engineering instrumentation Differential Amplifier : input resistance v 2 v 1 ir 1 ir 1 2iR 1 R in v 2 i v 1 2R 1 Differential
VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER
 VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER These are based on a change in the magnetic characteristic of an electrical circuit in response to a measurand which may be displacement, velocity, acceleration, etc. 1.
VARIABLE INDUCTANCE TRANSDUCER These are based on a change in the magnetic characteristic of an electrical circuit in response to a measurand which may be displacement, velocity, acceleration, etc. 1.
Department of Mechatronics Engineering
 Department of Mechatronics Engineering COURSES COVERED CONTROL SYSTEM POWER ELECTRONICS ELECTROMECHANICAL SYSTEM SENSORS AND INTRUMENTATION LAB SUPERVISOR: ENGR. MOEZ UL HASSAN NI ELVIS II The NI Educational
Department of Mechatronics Engineering COURSES COVERED CONTROL SYSTEM POWER ELECTRONICS ELECTROMECHANICAL SYSTEM SENSORS AND INTRUMENTATION LAB SUPERVISOR: ENGR. MOEZ UL HASSAN NI ELVIS II The NI Educational
Developer Techniques Sessions
 1 Developer Techniques Sessions Physical Measurements and Signal Processing Control Systems Logging and Networking 2 Abstract This session covers the technologies and configuration of a physical measurement
1 Developer Techniques Sessions Physical Measurements and Signal Processing Control Systems Logging and Networking 2 Abstract This session covers the technologies and configuration of a physical measurement
Prof. Paolo Colantonio a.a
 Pro. Paolo Colantonio a.a. 03 4 Operational ampliiers (op amps) are among the most widely used building blocks in electronics they are integrated circuits (ICs) oten DIL (or DIP) or SMT (or SMD) DIL (or
Pro. Paolo Colantonio a.a. 03 4 Operational ampliiers (op amps) are among the most widely used building blocks in electronics they are integrated circuits (ICs) oten DIL (or DIP) or SMT (or SMD) DIL (or
Lecture 1. EE 215 Electronic Devices & Circuits. Semiconductor Devices: Diodes. The Ideal Diode
 Lecture 1 EE 215 Electronic Deices & Circuits Asst Prof Muhammad Anis Chaudhary EE 215 Electronic Deices & Circuits Credit Hours: 3 1 Course Book: Adel S. Sedra and Kenneth C. Smith, Microelectronic Circuits,
Lecture 1 EE 215 Electronic Deices & Circuits Asst Prof Muhammad Anis Chaudhary EE 215 Electronic Deices & Circuits Credit Hours: 3 1 Course Book: Adel S. Sedra and Kenneth C. Smith, Microelectronic Circuits,
Synchronous Machines Study Material
 Synchronous machines: The machines generating alternating emf from the mechanical input are called alternators or synchronous generators. They are also known as AC generators. All modern power stations
Synchronous machines: The machines generating alternating emf from the mechanical input are called alternators or synchronous generators. They are also known as AC generators. All modern power stations
GATE 2019 ONLINE TEST SERIES
 GATE 29 ONLINE TEST SERIES Compete with the be... Our proficient faculties have done extensive research to prepare and shape these te series. An opportunity for udents to come across their rengths and
GATE 29 ONLINE TEST SERIES Compete with the be... Our proficient faculties have done extensive research to prepare and shape these te series. An opportunity for udents to come across their rengths and
UNIT III Data Acquisition & Microcontroller System. Mr. Manoj Rajale
 UNIT III Data Acquisition & Microcontroller System Mr. Manoj Rajale Syllabus Interfacing of Sensors / Actuators to DAQ system, Bit width, Sampling theorem, Sampling Frequency, Aliasing, Sample and hold
UNIT III Data Acquisition & Microcontroller System Mr. Manoj Rajale Syllabus Interfacing of Sensors / Actuators to DAQ system, Bit width, Sampling theorem, Sampling Frequency, Aliasing, Sample and hold
1. A transducer converts
 1. A transducer converts a. temperature to resistance b. force into current c. position into voltage d. one form of energy to another 2. Whose of the following transducers the output is a change in resistance?
1. A transducer converts a. temperature to resistance b. force into current c. position into voltage d. one form of energy to another 2. Whose of the following transducers the output is a change in resistance?
Operational Amplifiers
 Operational Amplifiers Spring 2008 Sean Lynch Lambros Samouris Tom Groshans History of Op Amps Non Named for their originally intended functions: performing mathematical operations and amplification Addition
Operational Amplifiers Spring 2008 Sean Lynch Lambros Samouris Tom Groshans History of Op Amps Non Named for their originally intended functions: performing mathematical operations and amplification Addition
Robot Sensors Introduction to Robotics Lecture Handout September 20, H. Harry Asada Massachusetts Institute of Technology
 Robot Sensors 2.12 Introduction to Robotics Lecture Handout September 20, 2004 H. Harry Asada Massachusetts Institute of Technology Touch Sensor CCD Camera Vision System Ultrasonic Sensor Photo removed
Robot Sensors 2.12 Introduction to Robotics Lecture Handout September 20, 2004 H. Harry Asada Massachusetts Institute of Technology Touch Sensor CCD Camera Vision System Ultrasonic Sensor Photo removed
RA / /6. Replaces: Table of contents RA /06.98
 Electronic amplifier for the control of proportional directional ales with electrical position feedback Models VT 5024 and VT 5025, Series 1X RA 29 958/06.98 Replaces: 11.97 The amplifiers VT 5024 and
Electronic amplifier for the control of proportional directional ales with electrical position feedback Models VT 5024 and VT 5025, Series 1X RA 29 958/06.98 Replaces: 11.97 The amplifiers VT 5024 and
MODEL ANSWER WINTER 17 EXAMINATION 17414
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Implementation of a Single-phase Unipolar Inverter Using DSP TMS320F241
 U J.T. 8(4): 995 (pr. 25) Implementation of a Singlephase Unipolar Inerter Using DSP TMS32F24 Narong phiratsakun, Sanjia ao Bhaganagarapu and Kittiphan Techakittiroj Faculty of Engineering, ssumption Uniersity
U J.T. 8(4): 995 (pr. 25) Implementation of a Singlephase Unipolar Inerter Using DSP TMS32F24 Narong phiratsakun, Sanjia ao Bhaganagarapu and Kittiphan Techakittiroj Faculty of Engineering, ssumption Uniersity
Figure 1.1 Mechatronic system components (p. 3)
 Figure 1.1 Mechatronic system components (p. 3) Example 1.2 Measurement System Digital Thermometer (p. 5) Figure 2.2 Electric circuit terminology (p. 13) Table 2.2 Resistor color band codes (p. 18) Figure
Figure 1.1 Mechatronic system components (p. 3) Example 1.2 Measurement System Digital Thermometer (p. 5) Figure 2.2 Electric circuit terminology (p. 13) Table 2.2 Resistor color band codes (p. 18) Figure
EE3301 Experiment 5 A BRIDGE RECTIFIER POWER SUPPLY
 Fall 2000 Releant sections of textbook: Chapter 10 Output Stages and Power Supplies 10.5 inear oltage regulators 10.6 inear-power-supply design EE3301 Experiment 5 A BRIDGE RECTIFIER POWER SUPPY 1 Introduction
Fall 2000 Releant sections of textbook: Chapter 10 Output Stages and Power Supplies 10.5 inear oltage regulators 10.6 inear-power-supply design EE3301 Experiment 5 A BRIDGE RECTIFIER POWER SUPPY 1 Introduction
Instrumentation (ch. 4 in Lecture notes)
 TMR7 Experimental methods in Marine Hydrodynamics week 35 Instrumentation (ch. 4 in Lecture notes) Measurement systems short introduction Measurement using strain gauges Calibration Data acquisition Different
TMR7 Experimental methods in Marine Hydrodynamics week 35 Instrumentation (ch. 4 in Lecture notes) Measurement systems short introduction Measurement using strain gauges Calibration Data acquisition Different
ACTUATORS AND SENSORS. Joint actuating system. Servomotors. Sensors
 ACTUATORS AND SENSORS Joint actuating system Servomotors Sensors JOINT ACTUATING SYSTEM Transmissions Joint motion low speeds high torques Spur gears change axis of rotation and/or translate application
ACTUATORS AND SENSORS Joint actuating system Servomotors Sensors JOINT ACTUATING SYSTEM Transmissions Joint motion low speeds high torques Spur gears change axis of rotation and/or translate application
Chap. 5 Electronic Components and Sensing Devices
 1 Chap. 5 Electronic Components and Sensing Devices Today, practically all mechanical devices contain some sort of electronic components. The function of a product often relies on the integration of mechanical
1 Chap. 5 Electronic Components and Sensing Devices Today, practically all mechanical devices contain some sort of electronic components. The function of a product often relies on the integration of mechanical
ECET 211 Electric Machines & Controls Lecture 4-2 Motor Control Devices: Lecture 4 Motor Control Devices
 ECET 211 Electric Machines & Controls Lecture 4-2 Motor Control Devices: Part 3. Sensors, Part 4. Actuators Text Book: Electric Motors and Control Systems, by Frank D. Petruzella, published by McGraw Hill,
ECET 211 Electric Machines & Controls Lecture 4-2 Motor Control Devices: Part 3. Sensors, Part 4. Actuators Text Book: Electric Motors and Control Systems, by Frank D. Petruzella, published by McGraw Hill,
Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering. MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers. Final Examination.
 Name: Number: Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers Final Examination December 12, 2003 Closed Book and Notes 1. Be sure to fill in your
Name: Number: Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering MAE334 - Introduction to Instrumentation and Computers Final Examination December 12, 2003 Closed Book and Notes 1. Be sure to fill in your
electronics for computer engineering (Sensor) by KrisMT Computer Engineering, ICT, University of Phayao
 305222 electronics for computer engineering (Sensor) by KrisMT Computer Engineering, ICT, University of Phayao ห วข อ Sensor =? Each type of sensor Technology Interpolation Sensor =? is a device that measures
305222 electronics for computer engineering (Sensor) by KrisMT Computer Engineering, ICT, University of Phayao ห วข อ Sensor =? Each type of sensor Technology Interpolation Sensor =? is a device that measures
Sensors (Transducer) Introduction By Sintayehu Challa
 Sensors (Transducer) Introduction What are Sensors? Basically the quantities to be measured are Non-Electrical quantities such as temperature, pressure,displacement,humidity, fluid flow, speed etc, but
Sensors (Transducer) Introduction What are Sensors? Basically the quantities to be measured are Non-Electrical quantities such as temperature, pressure,displacement,humidity, fluid flow, speed etc, but
Introduction to Internet of Things Prof. Sudip Misra Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur
 Introduction to Internet of Things Prof. Sudip Misra Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 03 Sensing So, we have already understood the basics
Introduction to Internet of Things Prof. Sudip Misra Department of Computer Science & Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 03 Sensing So, we have already understood the basics
MEASUREMENT AND INSTRUMENTATION QUESTION BANK UNIT I INTRODUCTION. Part A
 MEASUREMENT AND INSTRUMENTATION QUESTION BANK UNIT I INTRODUCTION Part A 1. Define Standard deviation. 2. Why calibration of instrument is important? 3. What are the different calibration methodologies?
MEASUREMENT AND INSTRUMENTATION QUESTION BANK UNIT I INTRODUCTION Part A 1. Define Standard deviation. 2. Why calibration of instrument is important? 3. What are the different calibration methodologies?
Lab 2A: Introduction to Sensing and Data Acquisition
 Lab 2A: Introduction to Sensing and Data Acquisition Prof. R.G. Longoria Department of Mechanical Engineering The University of Texas at Austin June 12, 2014 1 Lab 2A 2 Sensors 3 DAQ 4 Experimentation
Lab 2A: Introduction to Sensing and Data Acquisition Prof. R.G. Longoria Department of Mechanical Engineering The University of Texas at Austin June 12, 2014 1 Lab 2A 2 Sensors 3 DAQ 4 Experimentation
Preface... iii. Chapter 1: Diodes and Circuits... 1
 Table of Contents Preface... iii Chapter 1: Diodes and Circuits... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Structure of an Atom... 2 1.3 Classification of Solid Materials on the Basis of Conductivity... 2 1.4 Atomic
Table of Contents Preface... iii Chapter 1: Diodes and Circuits... 1 1.1 Introduction... 1 1.2 Structure of an Atom... 2 1.3 Classification of Solid Materials on the Basis of Conductivity... 2 1.4 Atomic
ELG3336 Design of Mechatronics System
 ELG3336 Design of Mechatronics System Elements of a Data Acquisition System 2 Analog Signal Data Acquisition Hardware Your Signal Data Acquisition DAQ Device System Computer Cable Terminal Block Data Acquisition
ELG3336 Design of Mechatronics System Elements of a Data Acquisition System 2 Analog Signal Data Acquisition Hardware Your Signal Data Acquisition DAQ Device System Computer Cable Terminal Block Data Acquisition
Downloaded from Downloaded from
 IV SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION- 2002 SUBJECT: BEG232EC, Instrumentation Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as far as practicable. The figure in the margin indicates full marks.
IV SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION- 2002 SUBJECT: BEG232EC, Instrumentation Candidates are required to give their answers in their own words as far as practicable. The figure in the margin indicates full marks.
Sensors. Chapter 3. Storey: Electrical & Electronic Systems Pearson Education Limited 2004 OHT 3.1
 Sensors Chapter 3 Introduction Describing Sensor Performance Temperature Sensors Light Sensors Force Sensors Displacement Sensors Motion Sensors Sound Sensors Sensor Interfacing Storey: Electrical & Electronic
Sensors Chapter 3 Introduction Describing Sensor Performance Temperature Sensors Light Sensors Force Sensors Displacement Sensors Motion Sensors Sound Sensors Sensor Interfacing Storey: Electrical & Electronic
1. Explain in detail the constructional details and working of DC motor.
 DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY, PERAMBALUR DEPT OF ECE EC6352-ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT 1 PART B 1. Explain in detail the constructional details and
DHANALAKSHMI SRINIVASAN INSTITUTE OF RESEARCH AND TECHNOLOGY, PERAMBALUR DEPT OF ECE EC6352-ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND INSTRUMENTATION UNIT 1 PART B 1. Explain in detail the constructional details and
Ultrasonic. Advantages
 Ultrasonic Advantages Non-Contact: Nothing touches the target object Measures Distance: The distance to the target is measured, not just its presence Long and Short Range: Objects can be sensed from 2
Ultrasonic Advantages Non-Contact: Nothing touches the target object Measures Distance: The distance to the target is measured, not just its presence Long and Short Range: Objects can be sensed from 2
Special-Purpose Operational Amplifier Circuits
 Special-Purpose Operational Amplifier Circuits Instrumentation Amplifier An instrumentation amplifier (IA) is a differential voltagegain device that amplifies the difference between the voltages existing
Special-Purpose Operational Amplifier Circuits Instrumentation Amplifier An instrumentation amplifier (IA) is a differential voltagegain device that amplifies the difference between the voltages existing
ELECTRONIC DEVICES. Assist. prof. Laura-Nicoleta IVANCIU, Ph.D. C6 Hysteresis comparators with OpAmp.
 ELECTONIC DEICES Assist. prof. Laura-Nicoleta IANCIU, Ph.D. C6 Hysteresis comparators with OpAmp. Contents Hysteresis (PF) comparators with OpAmp Motiation Difference between simple and hysteresis comparators
ELECTONIC DEICES Assist. prof. Laura-Nicoleta IANCIU, Ph.D. C6 Hysteresis comparators with OpAmp. Contents Hysteresis (PF) comparators with OpAmp Motiation Difference between simple and hysteresis comparators
Signal Conditioning Devices
 Lecture 4. Signal Conditioning Devices Signal Conditioning Operations In previous lectures we have studied various sensors and transducers used in a mechatronics system. Transducers sense physical phenomenon
Lecture 4. Signal Conditioning Devices Signal Conditioning Operations In previous lectures we have studied various sensors and transducers used in a mechatronics system. Transducers sense physical phenomenon
Data acquisition and instrumentation. Data acquisition
 Data acquisition and instrumentation START Lecture Sam Sadeghi Data acquisition 1 Humanistic Intelligence Body as a transducer,, data acquisition and signal processing machine Analysis of physiological
Data acquisition and instrumentation START Lecture Sam Sadeghi Data acquisition 1 Humanistic Intelligence Body as a transducer,, data acquisition and signal processing machine Analysis of physiological
Technological Studies. - Applied Electronics (H) TECHNOLOGICAL STUDIES HIGHER APPLIED ELECTRONICS OP-AMPS. Craigmount High School 1
 TECHNOLOGICAL STUDIES HIGHER APPLIED ELECTRONICS OP-AMPS Craigmount High School 1 APPLIED ELECTRONICS Outcome 2 - Design and construct electronic systems, based on operational amplifiers, to meet given
TECHNOLOGICAL STUDIES HIGHER APPLIED ELECTRONICS OP-AMPS Craigmount High School 1 APPLIED ELECTRONICS Outcome 2 - Design and construct electronic systems, based on operational amplifiers, to meet given
PRESENTED BY HUMANOID IIT KANPUR
 SENSORS & ACTUATORS Robotics Club (Science and Technology Council, IITK) PRESENTED BY HUMANOID IIT KANPUR October 11th, 2017 WHAT ARE WE GOING TO LEARN!! COMPARISON between Transducers Sensors And Actuators.
SENSORS & ACTUATORS Robotics Club (Science and Technology Council, IITK) PRESENTED BY HUMANOID IIT KANPUR October 11th, 2017 WHAT ARE WE GOING TO LEARN!! COMPARISON between Transducers Sensors And Actuators.
UNIT I. Operational Amplifiers
 UNIT I Operational Amplifiers Operational Amplifier: The operational amplifier is a direct-coupled high gain amplifier. It is a versatile multi-terminal device that can be used to amplify dc as well as
UNIT I Operational Amplifiers Operational Amplifier: The operational amplifier is a direct-coupled high gain amplifier. It is a versatile multi-terminal device that can be used to amplify dc as well as
Analytical Chemistry II
 Analytical Chemistry II L3: Signal processing (selected slides) Semiconductor devices Apart from resistors and capacitors, electronic circuits often contain nonlinear devices: transistors and diodes. The
Analytical Chemistry II L3: Signal processing (selected slides) Semiconductor devices Apart from resistors and capacitors, electronic circuits often contain nonlinear devices: transistors and diodes. The
P a g e 1. Introduction
 P a g e 1 Introduction 1. Signals in digital form are more convenient than analog form for processing and control operation. 2. Real world signals originated from temperature, pressure, flow rate, force
P a g e 1 Introduction 1. Signals in digital form are more convenient than analog form for processing and control operation. 2. Real world signals originated from temperature, pressure, flow rate, force
Quantity available (A) Quantity required (R) Sl. No. Deficiency (R - A) Description of Equipment
 . 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. (R 203) Semester II EE62 Electric Circuits Laboratory Regulated Power Supply: 0 5 V D.C Function Generator ( MHz) Single Phase Energy Meter Oscilloscope (20 MHz). Digital Storage Oscilloscope
. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. (R 203) Semester II EE62 Electric Circuits Laboratory Regulated Power Supply: 0 5 V D.C Function Generator ( MHz) Single Phase Energy Meter Oscilloscope (20 MHz). Digital Storage Oscilloscope
Job Sheet 2 Servo Control
 Job Sheet 2 Servo Control Electrical actuators are replacing hydraulic actuators in many industrial applications. Electric servomotors and linear actuators can perform many of the same physical displacement
Job Sheet 2 Servo Control Electrical actuators are replacing hydraulic actuators in many industrial applications. Electric servomotors and linear actuators can perform many of the same physical displacement
An Instrumentation System
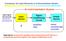 Transducer As Input Elements to Instrumentation System An Instrumentation System Input signal (measurand) electrical or non-electrical Input Device Signal Conditioning Circuit Output Device? -amplifier
Transducer As Input Elements to Instrumentation System An Instrumentation System Input signal (measurand) electrical or non-electrical Input Device Signal Conditioning Circuit Output Device? -amplifier
Advanced Measurements
 Albaha University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department Lecture 5: Displacement measurement Ossama Abouelatta o_abouelatta@yahoo.com Mechanical Engineering Department Faculty of Engineering
Albaha University Faculty of Engineering Mechanical Engineering Department Lecture 5: Displacement measurement Ossama Abouelatta o_abouelatta@yahoo.com Mechanical Engineering Department Faculty of Engineering
Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation. 1. Draw the Maxwell s Bridge Circuit and derives the expression for the unknown element at balance?
 UNIT -6 1. Draw the Maxwell s Bridge Circuit and derives the expression for the unknown element at balance? Ans: Maxwell's bridge, shown in Fig. 1.1, measures an unknown inductance in of standard arm offers
UNIT -6 1. Draw the Maxwell s Bridge Circuit and derives the expression for the unknown element at balance? Ans: Maxwell's bridge, shown in Fig. 1.1, measures an unknown inductance in of standard arm offers
Making Basic Strain Measurements
 IOtech Product Marketing Specialist steve.radecky@iotech.com Making Basic Strain Measurements using 24-Bit IOtech Hardware INTRODUCTION Strain gages are sensing devices used in a variety of physical test
IOtech Product Marketing Specialist steve.radecky@iotech.com Making Basic Strain Measurements using 24-Bit IOtech Hardware INTRODUCTION Strain gages are sensing devices used in a variety of physical test
UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus
 UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus PAPER I 1. Circuit Theory: Circuit components; network graphs; KCL, KVL; circuit analysis methods: nodal analysis, mesh analysis;
UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus UPSC Electrical Engineering Syllabus PAPER I 1. Circuit Theory: Circuit components; network graphs; KCL, KVL; circuit analysis methods: nodal analysis, mesh analysis;
