BMB/Bi/Ch 173 Winter 2018
|
|
|
- Grace Oliver
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BMB/Bi/Ch 73 Winter 208 Homework Set 2 (200 Points) Assigned -7-8, due by 0:30 a.m. TA: Rachael Kuintzle. Office hours: SFL 229, Friday /9 4:00-5:00pm and SFL 220, Monday /22 4:00-5:30pm. For the problems that involve plotting, feel free to use your favorite plotting program (Matlab, Excel, Mathematica, etc.). These programs and more are provided to Caltech students for free by the institution. You can also use Wolfram Alpha for free online. Don t forget to label all your axes. If you need help with plotting functions, come to office hours on Friday.. Electron Scattering (20 Points) I. Define amplitude contrast. Which kind of electron scattering (elastic or inelastic) provides amplitude contrast, and why? Both inelastic scattering events and certain types of elastic scattering events provide amplitude contrast by creating differences in percent transmission of electrons through different parts of the sample. Inelastic scattering events provide amplitude contrast because in-elastically scattered electrons are removed from the image primarily by the energy filter. Electrons that are backscattered or elastically scattered at extremely high angles will also not make it to the detector (they will not be able to go through the objective aperture). All of the scattering types mentioned here create regions of low electron density in parts of the image corresponding to strong scattering centers (higher density objects) in the sample. II. Define phase contrast. Which kind of electron scattering (elastic or inelastic) provides phase contrast, and why? Elastic scattering events provide phase contrast because the scattered electron beam interferes with the unscattered beam (constructively or destructively, depending on the phase of the scattered electron) to influence the final image. Note: the phase of elastically scattered electrons can be changed relative to that of un-scattered electrons via two sources of phase shift: o Scattering delays the wave by 90 degrees. o An elastically scattered electron will be scattered at a high angle, which means its path length will be different than that of the unscattered electrons. Therefore, the phase may be shifted further relative to the unscattered beam. Inelastic scattering events do not create phase contrast because inelastically scattered electrons are removed from the image by the energy filter, since their energy is reduced during scattering. 2. Argand Diagrams (30 Points) I. On an Argand diagram, draw each of the following electrons with correct relative phases: ( L = difference in path length between scattered and unscattered radiation). unscattered, L = 0, amplitude of 5 2. scattered, L = 0, amplitude of 3 3. scattered, L = λ/4*, amplitude of 3 (be sure to label your axes correctly)
2 *Assume this electron s phase is further delayed by λ/4. II. Draw the sum of electron () and electron (2). Call this Ψsum,2. Draw the sum of electron () and electron (3). Call this Ψsum,3. Ψ sum,2 Im Ψ Re Ψ sum,3 Re III. The amplitude of Ψsum,2 is about The amplitude of Ψsum,3 is 2. How much more probable is Ψsum,2 to be detected than the Ψsum,3? Probability of detection is proportional to amplitude 2. Therefore, it is ( /2 2 ) = 8.5 times more likely to be detected. 3. Putting the Fun back in Contrast Transfer Function (50 Points) I. How can you figure out what the contrast transfer function (CTF) looks like for a particular image? Get the radial average of intensities from the Thon rings in the power spectrum of your image (power spectrum = FT 2 ). Plot radial average versus spatial frequency, and perform a nonlinear regression to solve for the unknown variable, defocus. II. How can you use the CTF to improve the contrast in an image? You can perform CTF correction, which means that you can divide pixel values in the FT of your image by the corresponding value of the CTF at that spatial frequency, and then take the inverse FT to reproduce the image. III. Why is CTF correction not perfect? Because we can t divide by zero. The spatial frequencies where the contrast transfer = 0 will therefore remain missing from your final image. The contrast transfer function can be written as follows: CTF = sin π z λ k 2 + π C λ 3 k 4 where C is spherical aberration. Assume C is 0.5 mm. z is defocus. λ is the relativistic wavelength of the electron. k is spatial frequency. 2
3 IV. Separately plot the CTFs for a 200 kv electron microscope and a 300 kv electron microscope. The relativistic electron wavelength for each instrument is provided in the table below. Assume the detector is conjugate to the image plane. Plot for the following range of spatial frequencies: < k < 4 4.; 84. Relativistic wavelength (pm) 200 kv potential kv potential.97 It may be useful to first convert all variables with distance units to Angstroms () using this fancy table ( = x 0-0 m): Variable Value () C λ <=> (200 kv) λ <=> (300 kv) z Contrast Transfer 5 x x x Acceleration Potential: 200 kv
4 Contrast Transfer Acceleration Potential: 300 kv V. Based on your understanding of why the CTF oscillates, explain how the electron wavelength affects the CTF shape. Recall that there is a relationship between the wavelength, the angle of scattering, and the path length (the number of wavelengths traveled between the sample and the detector) of a scattered electron. Therefore, the path length difference ( L) between a scattered electron and unscattered electrons depends on the electron wavelength. The contrast you see for a given spatial frequency depends on this path length difference, as we have seen in our Argand diagrams. More detailed answer (not required for full credit): the angle of scattering by objects of a given spatial frequency increases with wavelength; thus, a higher energy electron (shorter wavelength) would be scattered at a smaller angle than would a lower energy electron (longer wavelength) by objects of the same spatial frequency. A difference in scattering angle produces a large difference in the path length of the electron, and therefore changes the path length difference ( L) between the scattered and unscattered beam. This will shift the CTF and alter the range of spatial frequencies between zero points on the CTF. VI. Your CTF function is dampened by the following envelope function: Env BCDEC> FGH=<=IF= k = e 8 K L M N O P Q 8 K R P O S T O UV W Plot the envelope function, assuming an acceleration potential of 300 kv. For the parameter source size (α 4 ), use a value of mrad = x 0-3 radians. For the other parameters, use the same constants as in part (IV). What is the cause of this dampening? Why does the envelope affect higher resolution information more than lower resolution information? Imperfect coherence affects higher resolution information more than low res info. If you shift images of large objects very slightly relative to each other (due to imperfect spatial coherence), the sine waves corresponding to their low spatial frequency will be displaced relative to each other with a very small phase difference, and thus they will all still constructively interfere with each other. Similarly, if you shift images of small objects by the same displacement distance, the sine waves corresponding to their high spatial frequency will also be shifted. However, because their wavelength is small, a small displacement of the images contributed to by different electrons could result in a very large phase difference of the component sine
5 waves. Therefore, the sine waves representing these small objects may interfere constructively, destructively, or anywhere in-between, thereby averaging out (flattening) the sine waves and erasing contrast. CTF Amplitude.0 Acceleration Potential: 300 kv VII. The main advantage of buying a microscope with a higher acceleration potential (e.g. 300 kv instead of 200 kv) is that it has a more generous envelope function. Re-plot the two CTF curves you generated in part (IV), but now plot them dampened by the envelope function above. Which acceleration potential yields greater contrast at high-resolution spatial frequencies: 200 kv or 300 kv? To get the dampened function, multiply the CTF by the envelope function. The 300 kv potential yields greater contrast at high-resolution spatial frequencies. Contrast Transfer Acceleration Potential: 200 kv
6 Contrast Transfer Acceleration Potential: 300 kv VIII. Let s suppose that you are interested in imaging some cytoskeletal filaments inside a cell. These filaments, called MreB and FtsZ, have a 4 nm (40 ) diameter. Based on the CTFs you plotted in part (VII), do you expect it will be easy or hard to see the filaments? Why? It will be hard. The CTF has very low values in the region around 40 -> k = Low CTF values mean poor contrast in your image, due to very little difference in amplitude between elastically scattered electrons and unscattered electrons. Therefore, objects at spatial frequencies with low CTF values will not show up well in the image. Side note: In practice, CTF correction can t be used to recover true amplitudes when contrast is very close to zero, because the signal-to-noise ratio is just too low. IX. You are determined to get a good image of these cytoskeletal filaments. a. Which parameter in the CTF equation can you tune in order to see them better? Defocus ( z) b. Plot a new CTF with the relevant parameter changed so you can see the microtubules better, and write the new value that you used (with units). More specifically, shift the curve so there is a CTF maximum around the spatial frequency of these filaments. Assume you have access to a 300 kv instrument. Zoom in to the region of interest by plotting for < k < 4 W6 84. Helpful hints: Use a negative value. First try changing the parameter in the un-dampened CTF, in order to more clearly see the peaks. You ll get a ballpark parameter value based on this. Try to get a final contrast value above 0.. The value should be around -0,000, or - µm.
7 Contrast Transfer c. What do you need to physically change within the EM column in order to change the value of this parameter? You need to change the distance between the detector and the image plane. You can do this by changing the strength of the objective lens, which shifts the image plane relative to the detector.
No part of this material may be reproduced without explicit written permission.
 This material is provided for educational use only. The information in these slides including all data, images and related materials are the property of : Robert M. Glaeser Department of Molecular & Cell
This material is provided for educational use only. The information in these slides including all data, images and related materials are the property of : Robert M. Glaeser Department of Molecular & Cell
GBS765 Hybrid methods
 GBS765 Hybrid methods Lecture 3 Contrast and image formation 10/20/14 4:37 PM The lens ray diagram Magnification M = A/a = v/u and 1/u + 1/v = 1/f where f is the focal length The lens ray diagram So we
GBS765 Hybrid methods Lecture 3 Contrast and image formation 10/20/14 4:37 PM The lens ray diagram Magnification M = A/a = v/u and 1/u + 1/v = 1/f where f is the focal length The lens ray diagram So we
Contrast transfer. Contrast transfer and CTF correction. Lecture 6 H Saibil
 Lecture 6 H Saibil Contrast transfer Contrast transfer and CTF correction The weak phase approximation Contrast transfer function Determining defocus CTF correction methods Image processing for cryo microscopy
Lecture 6 H Saibil Contrast transfer Contrast transfer and CTF correction The weak phase approximation Contrast transfer function Determining defocus CTF correction methods Image processing for cryo microscopy
CTF Correction with IMOD
 CTF Correction with IMOD CTF Correction When microscope is operated in underfocus to produce phase contrast, the contrast is inverted in some spatial frequency ranges 1 We See Only Amplitudes, Not Phases,
CTF Correction with IMOD CTF Correction When microscope is operated in underfocus to produce phase contrast, the contrast is inverted in some spatial frequency ranges 1 We See Only Amplitudes, Not Phases,
PHY 431 Homework Set #5 Due Nov. 20 at the start of class
 PHY 431 Homework Set #5 Due Nov. 0 at the start of class 1) Newton s rings (10%) The radius of curvature of the convex surface of a plano-convex lens is 30 cm. The lens is placed with its convex side down
PHY 431 Homework Set #5 Due Nov. 0 at the start of class 1) Newton s rings (10%) The radius of curvature of the convex surface of a plano-convex lens is 30 cm. The lens is placed with its convex side down
SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY AND X-RAY MICROANALYSIS
 SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY AND X-RAY MICROANALYSIS Robert Edward Lee Electron Microscopy Center Department of Anatomy and Neurobiology Colorado State University P T R Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs,
SCANNING ELECTRON MICROSCOPY AND X-RAY MICROANALYSIS Robert Edward Lee Electron Microscopy Center Department of Anatomy and Neurobiology Colorado State University P T R Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs,
(Refer Slide Time: 00:10)
 Fundamentals of optical and scanning electron microscopy Dr. S. Sankaran Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module 03 Unit-6 Instrumental details
Fundamentals of optical and scanning electron microscopy Dr. S. Sankaran Department of Metallurgical and Materials Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Module 03 Unit-6 Instrumental details
Cs-corrector. Felix de Haas
 Cs-corrector. Felix de Haas Content Non corrector systems Lens aberrations and how to minimize? Corrector systems How is it done? Lens aberrations Spherical aberration Astigmatism Coma Chromatic Quality
Cs-corrector. Felix de Haas Content Non corrector systems Lens aberrations and how to minimize? Corrector systems How is it done? Lens aberrations Spherical aberration Astigmatism Coma Chromatic Quality
Chapter 1. Basic Electron Optics (Lecture 2)
 Chapter 1. Basic Electron Optics (Lecture 2) Basic concepts of microscope (Cont ) Fundamental properties of electrons Electron Scattering Instrumentation Basic conceptions of microscope (Cont ) Ray diagram
Chapter 1. Basic Electron Optics (Lecture 2) Basic concepts of microscope (Cont ) Fundamental properties of electrons Electron Scattering Instrumentation Basic conceptions of microscope (Cont ) Ray diagram
Microscope anatomy, image formation and resolution
 Microscope anatomy, image formation and resolution Ian Dobbie Buy this book for your lab: D.B. Murphy, "Fundamentals of light microscopy and electronic imaging", ISBN 0-471-25391-X Visit these websites:
Microscope anatomy, image formation and resolution Ian Dobbie Buy this book for your lab: D.B. Murphy, "Fundamentals of light microscopy and electronic imaging", ISBN 0-471-25391-X Visit these websites:
Image Contrast Theory
 Image Contrast Theory Wah Chiu wah@bcm.tmc.edu National Center for Macromolecular Imaging References Jiang, W. & Chiu, W. Web-based simulation for contrast transfer function and envelope functions. Microsc
Image Contrast Theory Wah Chiu wah@bcm.tmc.edu National Center for Macromolecular Imaging References Jiang, W. & Chiu, W. Web-based simulation for contrast transfer function and envelope functions. Microsc
The electric field for the wave sketched in Fig. 3-1 can be written as
 ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Light consists of an electric field and a magnetic field that oscillate at very high rates, of the order of 10 14 Hz. These fields travel in wavelike fashion at very high speeds.
ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES Light consists of an electric field and a magnetic field that oscillate at very high rates, of the order of 10 14 Hz. These fields travel in wavelike fashion at very high speeds.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 Q1. Just over two hundred years ago Thomas Young demonstrated the interference of light by illuminating two closely spaced narrow slits with light from a single light source.
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 Q1. Just over two hundred years ago Thomas Young demonstrated the interference of light by illuminating two closely spaced narrow slits with light from a single light source.
Modulation Transfer Function
 Modulation Transfer Function The resolution and performance of an optical microscope can be characterized by a quantity known as the modulation transfer function (MTF), which is a measurement of the microscope's
Modulation Transfer Function The resolution and performance of an optical microscope can be characterized by a quantity known as the modulation transfer function (MTF), which is a measurement of the microscope's
Lecture 2: Interference
 Lecture 2: Interference λ S 1 d S 2 Lecture 2, p.1 Today Interference of sound waves Two-slit interference Lecture 2, p.2 Review: Wave Summary ( ) ( ) The formula y x,t = Acoskx ωt describes a harmonic
Lecture 2: Interference λ S 1 d S 2 Lecture 2, p.1 Today Interference of sound waves Two-slit interference Lecture 2, p.2 Review: Wave Summary ( ) ( ) The formula y x,t = Acoskx ωt describes a harmonic
Tutorial on Linear Image Simulations of Phase-Contrast and Incoherent Imaging by convolutions
 Tutorial on Linear Image Simulations of Phase-Contrast and Incoherent Imaging by convolutions Huolin Xin, David Muller, based on Appendix A of Kirkland s book This tutorial covers the use of temcon and
Tutorial on Linear Image Simulations of Phase-Contrast and Incoherent Imaging by convolutions Huolin Xin, David Muller, based on Appendix A of Kirkland s book This tutorial covers the use of temcon and
microscopy A great online resource Molecular Expressions, a Microscope Primer Partha Roy
 Fundamentals of optical microscopy A great online resource Molecular Expressions, a Microscope Primer http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/index.html Partha Roy 1 Why microscopy Topics Functions of a microscope
Fundamentals of optical microscopy A great online resource Molecular Expressions, a Microscope Primer http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/primer/index.html Partha Roy 1 Why microscopy Topics Functions of a microscope
The Formation of an Aerial Image, part 3
 T h e L i t h o g r a p h y T u t o r (July 1993) The Formation of an Aerial Image, part 3 Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, Austin, Texas In the last two issues, we described how a projection system
T h e L i t h o g r a p h y T u t o r (July 1993) The Formation of an Aerial Image, part 3 Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, Austin, Texas In the last two issues, we described how a projection system
Notes on the VPPEM electron optics
 Notes on the VPPEM electron optics Raymond Browning 2/9/2015 We are interested in creating some rules of thumb for designing the VPPEM instrument in terms of the interaction between the field of view at
Notes on the VPPEM electron optics Raymond Browning 2/9/2015 We are interested in creating some rules of thumb for designing the VPPEM instrument in terms of the interaction between the field of view at
Chapter Ray and Wave Optics
 109 Chapter Ray and Wave Optics 1. An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to [2002] reduce spherical aberration have high resolution increase span of observation have low dispersion. 2. If two
109 Chapter Ray and Wave Optics 1. An astronomical telescope has a large aperture to [2002] reduce spherical aberration have high resolution increase span of observation have low dispersion. 2. If two
Optical Coherence: Recreation of the Experiment of Thompson and Wolf
 Optical Coherence: Recreation of the Experiment of Thompson and Wolf David Collins Senior project Department of Physics, California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo June 2010 Abstract The purpose
Optical Coherence: Recreation of the Experiment of Thompson and Wolf David Collins Senior project Department of Physics, California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo June 2010 Abstract The purpose
Analytical analysis of modulated signal in apertureless scanning near-field optical microscopy C. H. Chuang and Y. L. Lo *
 Research Express@NCKU Volume 5 Issue 10 - October 3, 2008 [ http://research.ncku.edu.tw/re/articles/e/20081003/2.html ] Analytical analysis of modulated signal in apertureless scanning near-field optical
Research Express@NCKU Volume 5 Issue 10 - October 3, 2008 [ http://research.ncku.edu.tw/re/articles/e/20081003/2.html ] Analytical analysis of modulated signal in apertureless scanning near-field optical
ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. 13:10 16:00, Oct. 6, 2008 Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica. Tung Hsu
 ELECTRON MICROSCOPY 13:10 16:00, Oct. 6, 2008 Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica Tung Hsu Department of Materials Science and Engineering National Tsing Hua University Hsinchu 300, TAIWAN Tel. 03-5742564
ELECTRON MICROSCOPY 13:10 16:00, Oct. 6, 2008 Institute of Physics, Academia Sinica Tung Hsu Department of Materials Science and Engineering National Tsing Hua University Hsinchu 300, TAIWAN Tel. 03-5742564
Digital Camera Technologies for Scientific Bio-Imaging. Part 2: Sampling and Signal
 Digital Camera Technologies for Scientific Bio-Imaging. Part 2: Sampling and Signal Yashvinder Sabharwal, 1 James Joubert 2 and Deepak Sharma 2 1. Solexis Advisors LLC, Austin, TX, USA 2. Photometrics
Digital Camera Technologies for Scientific Bio-Imaging. Part 2: Sampling and Signal Yashvinder Sabharwal, 1 James Joubert 2 and Deepak Sharma 2 1. Solexis Advisors LLC, Austin, TX, USA 2. Photometrics
Lab Report 3: Speckle Interferometry LIN PEI-YING, BAIG JOVERIA
 Lab Report 3: Speckle Interferometry LIN PEI-YING, BAIG JOVERIA Abstract: Speckle interferometry (SI) has become a complete technique over the past couple of years and is widely used in many branches of
Lab Report 3: Speckle Interferometry LIN PEI-YING, BAIG JOVERIA Abstract: Speckle interferometry (SI) has become a complete technique over the past couple of years and is widely used in many branches of
ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB
 ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB Lab 2: Imaging 1 the Telescope Original Version: Prof. McLeod SUMMARY: In this lab you will become familiar with the use of one or more lenses to create images of distant
ECEN 4606, UNDERGRADUATE OPTICS LAB Lab 2: Imaging 1 the Telescope Original Version: Prof. McLeod SUMMARY: In this lab you will become familiar with the use of one or more lenses to create images of distant
ECE 185 ELECTRO-OPTIC MODULATION OF LIGHT
 ECE 185 ELECTRO-OPTIC MODULATION OF LIGHT I. Objective: To study the Pockels electro-optic (E-O) effect, and the property of light propagation in anisotropic medium, especially polarization-rotation effects.
ECE 185 ELECTRO-OPTIC MODULATION OF LIGHT I. Objective: To study the Pockels electro-optic (E-O) effect, and the property of light propagation in anisotropic medium, especially polarization-rotation effects.
LECTURE 26: Interference
 ANNOUNCEMENT *Final: Thursday December 14, 2017, 1 PM 3 PM *Location: Elliot Hall of Music *Covers all readings, lectures, homework from Chapters 28.6 through 33. *The exam will be multiple choice. Be
ANNOUNCEMENT *Final: Thursday December 14, 2017, 1 PM 3 PM *Location: Elliot Hall of Music *Covers all readings, lectures, homework from Chapters 28.6 through 33. *The exam will be multiple choice. Be
Single Slit Diffraction
 PC1142 Physics II Single Slit Diffraction 1 Objectives Investigate the single-slit diffraction pattern produced by monochromatic laser light. Determine the wavelength of the laser light from measurements
PC1142 Physics II Single Slit Diffraction 1 Objectives Investigate the single-slit diffraction pattern produced by monochromatic laser light. Determine the wavelength of the laser light from measurements
1 ONE- and TWO-DIMENSIONAL HARMONIC OSCIL- LATIONS
 SIMG-232 LABORATORY #1 Writeup Due 3/23/2004 (T) 1 ONE- and TWO-DIMENSIONAL HARMONIC OSCIL- LATIONS 1.1 Rationale: This laboratory (really a virtual lab based on computer software) introduces the concepts
SIMG-232 LABORATORY #1 Writeup Due 3/23/2004 (T) 1 ONE- and TWO-DIMENSIONAL HARMONIC OSCIL- LATIONS 1.1 Rationale: This laboratory (really a virtual lab based on computer software) introduces the concepts
Chapter 17 Waves in Two and Three Dimensions
 Chapter 17 Waves in Two and Three Dimensions Slide 17-1 Chapter 17: Waves in Two and Three Dimensions Concepts Slide 17-2 Section 17.1: Wavefronts The figure shows cutaway views of a periodic surface wave
Chapter 17 Waves in Two and Three Dimensions Slide 17-1 Chapter 17: Waves in Two and Three Dimensions Concepts Slide 17-2 Section 17.1: Wavefronts The figure shows cutaway views of a periodic surface wave
Optical design of a high resolution vision lens
 Optical design of a high resolution vision lens Paul Claassen, optical designer, paul.claassen@sioux.eu Marnix Tas, optical specialist, marnix.tas@sioux.eu Prof L.Beckmann, l.beckmann@hccnet.nl Summary:
Optical design of a high resolution vision lens Paul Claassen, optical designer, paul.claassen@sioux.eu Marnix Tas, optical specialist, marnix.tas@sioux.eu Prof L.Beckmann, l.beckmann@hccnet.nl Summary:
Microscope Imaging. Colin Sheppard Nano- Physics Department Italian Ins:tute of Technology (IIT) Genoa, Italy
 Microscope Imaging Colin Sheppard Nano- Physics Department Italian Ins:tute of Technology (IIT) Genoa, Italy colinjrsheppard@gmail.com Objec:ve lens Op:cal microscope Numerical aperture (n sin α) Air /
Microscope Imaging Colin Sheppard Nano- Physics Department Italian Ins:tute of Technology (IIT) Genoa, Italy colinjrsheppard@gmail.com Objec:ve lens Op:cal microscope Numerical aperture (n sin α) Air /
Lab 8 - INTRODUCTION TO AC CURRENTS AND VOLTAGES
 08-1 Name Date Partners ab 8 - INTRODUCTION TO AC CURRENTS AND VOTAGES OBJECTIVES To understand the meanings of amplitude, frequency, phase, reactance, and impedance in AC circuits. To observe the behavior
08-1 Name Date Partners ab 8 - INTRODUCTION TO AC CURRENTS AND VOTAGES OBJECTIVES To understand the meanings of amplitude, frequency, phase, reactance, and impedance in AC circuits. To observe the behavior
Introduction to Electron Microscopy
 Introduction to Electron Microscopy Prof. David Muller, dm24@cornell.edu Rm 274 Clark Hall, 255-4065 Ernst Ruska and Max Knoll built the first electron microscope in 1931 (Nobel Prize to Ruska in 1986)
Introduction to Electron Microscopy Prof. David Muller, dm24@cornell.edu Rm 274 Clark Hall, 255-4065 Ernst Ruska and Max Knoll built the first electron microscope in 1931 (Nobel Prize to Ruska in 1986)
High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM) Summary 4/11/2018. Thomas LaGrange Faculty Lecturer and Senior Staff Scientist
 Thomas LaGrange Faculty Lecturer and Senior Staff Scientist High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM) Doctoral Course MS-637 April 16-18th, 2018 Summary Contrast in TEM images results from
Thomas LaGrange Faculty Lecturer and Senior Staff Scientist High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy (HRTEM) Doctoral Course MS-637 April 16-18th, 2018 Summary Contrast in TEM images results from
OPTICAL IMAGE FORMATION
 GEOMETRICAL IMAGING First-order image is perfect object (input) scaled (by magnification) version of object optical system magnification = image distance/object distance no blurring object distance image
GEOMETRICAL IMAGING First-order image is perfect object (input) scaled (by magnification) version of object optical system magnification = image distance/object distance no blurring object distance image
TSBB09 Image Sensors 2018-HT2. Image Formation Part 1
 TSBB09 Image Sensors 2018-HT2 Image Formation Part 1 Basic physics Electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves With energy That propagate through space The waves consist of transversal
TSBB09 Image Sensors 2018-HT2 Image Formation Part 1 Basic physics Electromagnetic radiation consists of electromagnetic waves With energy That propagate through space The waves consist of transversal
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE DEPTH STUDY: ELECTRON MICROSCOPES
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE DEPTH STUDY: ELECTRON MICROSCOPES Shortly after the experimental confirmation of the wave properties of the electron, it was suggested that the electron could be used to examine objects
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE DEPTH STUDY: ELECTRON MICROSCOPES Shortly after the experimental confirmation of the wave properties of the electron, it was suggested that the electron could be used to examine objects
Name: Lab Partner: Section:
 Chapter 11 Wave Phenomena Name: Lab Partner: Section: 11.1 Purpose Wave phenomena using sound waves will be explored in this experiment. Standing waves and beats will be examined. The speed of sound will
Chapter 11 Wave Phenomena Name: Lab Partner: Section: 11.1 Purpose Wave phenomena using sound waves will be explored in this experiment. Standing waves and beats will be examined. The speed of sound will
ELECTRON MICROSCOPY. 14:10 17:00, Apr. 3, 2007 Department of Physics, National Taiwan University. Tung Hsu
 ELECTRON MICROSCOPY 14:10 17:00, Apr. 3, 2007 Department of Physics, National Taiwan University Tung Hsu Department of Materials Science and Engineering National Tsinghua University Hsinchu 300, TAIWAN
ELECTRON MICROSCOPY 14:10 17:00, Apr. 3, 2007 Department of Physics, National Taiwan University Tung Hsu Department of Materials Science and Engineering National Tsinghua University Hsinchu 300, TAIWAN
Interference [Hecht Ch. 9]
![Interference [Hecht Ch. 9] Interference [Hecht Ch. 9]](/thumbs/79/79365345.jpg) Interference [Hecht Ch. 9] Note: Read Ch. 3 & 7 E&M Waves and Superposition of Waves and Meet with TAs and/or Dr. Lai if necessary. General Consideration 1 2 Amplitude Splitting Interferometers If a lightwave
Interference [Hecht Ch. 9] Note: Read Ch. 3 & 7 E&M Waves and Superposition of Waves and Meet with TAs and/or Dr. Lai if necessary. General Consideration 1 2 Amplitude Splitting Interferometers If a lightwave
Shaping light in microscopy:
 Shaping light in microscopy: Adaptive optical methods and nonconventional beam shapes for enhanced imaging Martí Duocastella planet detector detector sample sample Aberrated wavefront Beamsplitter Adaptive
Shaping light in microscopy: Adaptive optical methods and nonconventional beam shapes for enhanced imaging Martí Duocastella planet detector detector sample sample Aberrated wavefront Beamsplitter Adaptive
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Mechanical Engineering Department. 2.71/2.710 Final Exam. May 21, Duration: 3 hours (9 am-12 noon)
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Mechanical Engineering Department 2.71/2.710 Final Exam May 21, 2013 Duration: 3 hours (9 am-12 noon) CLOSED BOOK Total pages: 5 Name: PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET WITH
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Mechanical Engineering Department 2.71/2.710 Final Exam May 21, 2013 Duration: 3 hours (9 am-12 noon) CLOSED BOOK Total pages: 5 Name: PLEASE RETURN THIS BOOKLET WITH
Atomic Resolution Imaging with a sub-50 pm Electron Probe
 Atomic Resolution Imaging with a sub-50 pm Electron Probe Rolf Erni, Marta D. Rossell, Christian Kisielowski, Ulrich Dahmen National Center for Electron Microscopy, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Atomic Resolution Imaging with a sub-50 pm Electron Probe Rolf Erni, Marta D. Rossell, Christian Kisielowski, Ulrich Dahmen National Center for Electron Microscopy, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
The Principle of Superposition
 The Principle of Superposition If wave 1 displaces a particle in the medium by D 1 and wave 2 simultaneously displaces it by D 2, the net displacement of the particle is simply D 1 + D 2. Standing Waves
The Principle of Superposition If wave 1 displaces a particle in the medium by D 1 and wave 2 simultaneously displaces it by D 2, the net displacement of the particle is simply D 1 + D 2. Standing Waves
Copyright 2000 Society of Photo Instrumentation Engineers.
 Copyright 2000 Society of Photo Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in SPIE Proceedings, Volume 4043 and is made available as an electronic reprint with permission of SPIE. One print or
Copyright 2000 Society of Photo Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in SPIE Proceedings, Volume 4043 and is made available as an electronic reprint with permission of SPIE. One print or
G1 THE NATURE OF EM WAVES AND LIGHT SOURCES
 G1 THE NATURE OF EM WAVES AND LIGHT SOURCES G2 OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS HW/Study Packet Required: READ Tsokos, pp 598-620 SL/HL Supplemental: Hamper, pp 411-450 DO Questions p 605 #1,3 pp 621-623 #6,8,15,18,19,24,26
G1 THE NATURE OF EM WAVES AND LIGHT SOURCES G2 OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS HW/Study Packet Required: READ Tsokos, pp 598-620 SL/HL Supplemental: Hamper, pp 411-450 DO Questions p 605 #1,3 pp 621-623 #6,8,15,18,19,24,26
Sound Waves and Beats
 Physics Topics Sound Waves and Beats If necessary, review the following topics and relevant textbook sections from Serway / Jewett Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 9th Ed. Traveling Waves (Serway
Physics Topics Sound Waves and Beats If necessary, review the following topics and relevant textbook sections from Serway / Jewett Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 9th Ed. Traveling Waves (Serway
Physics 431 Final Exam Examples (3:00-5:00 pm 12/16/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 120 MINUTES Name: Signature:
 Physics 431 Final Exam Examples (3:00-5:00 pm 12/16/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 120 MINUTES Name: PID: Signature: CLOSED BOOK. TWO 8 1/2 X 11 SHEET OF NOTES (double sided is allowed), AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR
Physics 431 Final Exam Examples (3:00-5:00 pm 12/16/2009) TIME ALLOTTED: 120 MINUTES Name: PID: Signature: CLOSED BOOK. TWO 8 1/2 X 11 SHEET OF NOTES (double sided is allowed), AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR
DOPPLER RADAR. Doppler Velocities - The Doppler shift. if φ 0 = 0, then φ = 4π. where
 Q: How does the radar get velocity information on the particles? DOPPLER RADAR Doppler Velocities - The Doppler shift Simple Example: Measures a Doppler shift - change in frequency of radiation due to
Q: How does the radar get velocity information on the particles? DOPPLER RADAR Doppler Velocities - The Doppler shift Simple Example: Measures a Doppler shift - change in frequency of radiation due to
A few concepts in TEM and STEM explained
 A few concepts in TEM and STEM explained Martin Ek November 23, 2011 1 Introduction This is a collection of short, qualitative explanations of key concepts in TEM and STEM. Most of them are beyond what
A few concepts in TEM and STEM explained Martin Ek November 23, 2011 1 Introduction This is a collection of short, qualitative explanations of key concepts in TEM and STEM. Most of them are beyond what
DESIGN NOTE: DIFFRACTION EFFECTS
 NASA IRTF / UNIVERSITY OF HAWAII Document #: TMP-1.3.4.2-00-X.doc Template created on: 15 March 2009 Last Modified on: 5 April 2010 DESIGN NOTE: DIFFRACTION EFFECTS Original Author: John Rayner NASA Infrared
NASA IRTF / UNIVERSITY OF HAWAII Document #: TMP-1.3.4.2-00-X.doc Template created on: 15 March 2009 Last Modified on: 5 April 2010 DESIGN NOTE: DIFFRACTION EFFECTS Original Author: John Rayner NASA Infrared
ANTENNA INTRODUCTION / BASICS
 ANTENNA INTRODUCTION / BASICS RULES OF THUMB: 1. The Gain of an antenna with losses is given by: 2. Gain of rectangular X-Band Aperture G = 1.4 LW L = length of aperture in cm Where: W = width of aperture
ANTENNA INTRODUCTION / BASICS RULES OF THUMB: 1. The Gain of an antenna with losses is given by: 2. Gain of rectangular X-Band Aperture G = 1.4 LW L = length of aperture in cm Where: W = width of aperture
Properties of Structured Light
 Properties of Structured Light Gaussian Beams Structured light sources using lasers as the illumination source are governed by theories of Gaussian beams. Unlike incoherent sources, coherent laser sources
Properties of Structured Light Gaussian Beams Structured light sources using lasers as the illumination source are governed by theories of Gaussian beams. Unlike incoherent sources, coherent laser sources
point at zero displacement string 80 scale / cm Fig. 4.1
 1 (a) Fig. 4.1 shows a section of a uniform string under tension at one instant of time. A progressive wave of wavelength 80 cm is moving along the string from left to right. At the instant shown, the
1 (a) Fig. 4.1 shows a section of a uniform string under tension at one instant of time. A progressive wave of wavelength 80 cm is moving along the string from left to right. At the instant shown, the
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2003 Final Exam. Name:
 EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2003 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. THREE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
EE119 Introduction to Optical Engineering Spring 2003 Final Exam Name: SID: CLOSED BOOK. THREE 8 1/2 X 11 SHEETS OF NOTES, AND SCIENTIFIC POCKET CALCULATOR PERMITTED. TIME ALLOTTED: 180 MINUTES Fundamental
6 Experiment II: Law of Reflection
 Lab 6: Microwaves 3 Suggested Reading Refer to the relevant chapters, 1 Introduction Refer to Appendix D for photos of the apparatus This lab allows you to test the laws of reflection, refraction and diffraction
Lab 6: Microwaves 3 Suggested Reading Refer to the relevant chapters, 1 Introduction Refer to Appendix D for photos of the apparatus This lab allows you to test the laws of reflection, refraction and diffraction
Collimation Tester Instructions
 Description Use shear-plate collimation testers to examine and adjust the collimation of laser light, or to measure the wavefront curvature and divergence/convergence magnitude of large-radius optical
Description Use shear-plate collimation testers to examine and adjust the collimation of laser light, or to measure the wavefront curvature and divergence/convergence magnitude of large-radius optical
PHYSICS. Chapter 35 Lecture FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E RANDALL D. KNIGHT
 PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 35 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 35 Optical Instruments IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about some common optical instruments and
PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEERS A STRATEGIC APPROACH 4/E Chapter 35 Lecture RANDALL D. KNIGHT Chapter 35 Optical Instruments IN THIS CHAPTER, you will learn about some common optical instruments and
Katarina Logg, Kristofer Bodvard, Mikael Käll. Dept. of Applied Physics. 12 September Optical Microscopy. Supervisor s signature:...
 Katarina Logg, Kristofer Bodvard, Mikael Käll Dept. of Applied Physics 12 September 2007 O1 Optical Microscopy Name:.. Date:... Supervisor s signature:... Introduction Over the past decades, the number
Katarina Logg, Kristofer Bodvard, Mikael Käll Dept. of Applied Physics 12 September 2007 O1 Optical Microscopy Name:.. Date:... Supervisor s signature:... Introduction Over the past decades, the number
INTRODUCTION THIN LENSES. Introduction. given by the paraxial refraction equation derived last lecture: Thin lenses (19.1) = 1. Double-lens systems
 Chapter 9 OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS Introduction Thin lenses Double-lens systems Aberrations Camera Human eye Compound microscope Summary INTRODUCTION Knowledge of geometrical optics, diffraction and interference,
Chapter 9 OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS Introduction Thin lenses Double-lens systems Aberrations Camera Human eye Compound microscope Summary INTRODUCTION Knowledge of geometrical optics, diffraction and interference,
Testing Aspherics Using Two-Wavelength Holography
 Reprinted from APPLIED OPTICS. Vol. 10, page 2113, September 1971 Copyright 1971 by the Optical Society of America and reprinted by permission of the copyright owner Testing Aspherics Using Two-Wavelength
Reprinted from APPLIED OPTICS. Vol. 10, page 2113, September 1971 Copyright 1971 by the Optical Society of America and reprinted by permission of the copyright owner Testing Aspherics Using Two-Wavelength
Experiment 5: Spark Gap Microwave Generator Dipole Radiation, Polarization, Interference W14D2
 Experiment 5: Spark Gap Microwave Generator Dipole Radiation, Polarization, Interference W14D2 1 Announcements Week 14 Prepset due Fri at 8:30 am PS 11 due Week 14 Friday at 9 pm in boxes outside 26-152
Experiment 5: Spark Gap Microwave Generator Dipole Radiation, Polarization, Interference W14D2 1 Announcements Week 14 Prepset due Fri at 8:30 am PS 11 due Week 14 Friday at 9 pm in boxes outside 26-152
OPTICAL PRINCIPLES OF MICROSCOPY. Interuniversity Course 28 December 2003 Aryeh M. Weiss Bar Ilan University
 OPTICAL PRINCIPLES OF MICROSCOPY Interuniversity Course 28 December 2003 Aryeh M. Weiss Bar Ilan University FOREWORD This slide set was originally presented at the ISM Workshop on Theoretical and Experimental
OPTICAL PRINCIPLES OF MICROSCOPY Interuniversity Course 28 December 2003 Aryeh M. Weiss Bar Ilan University FOREWORD This slide set was originally presented at the ISM Workshop on Theoretical and Experimental
Introduction to Transmission Electron Microscopy (Physical Sciences)
 Introduction to Transmission Electron Microscopy (Physical Sciences) Centre for Advanced Microscopy Program 9:30 10:45 Lecture 1 Basics of TEM 10:45 11:00 Morning tea 11:00 12:15 Lecture 2 Diffraction
Introduction to Transmission Electron Microscopy (Physical Sciences) Centre for Advanced Microscopy Program 9:30 10:45 Lecture 1 Basics of TEM 10:45 11:00 Morning tea 11:00 12:15 Lecture 2 Diffraction
NanoSpective, Inc Progress Drive Suite 137 Orlando, Florida
 TEM Techniques Summary The TEM is an analytical instrument in which a thin membrane (typically < 100nm) is placed in the path of an energetic and highly coherent beam of electrons. Typical operating voltages
TEM Techniques Summary The TEM is an analytical instrument in which a thin membrane (typically < 100nm) is placed in the path of an energetic and highly coherent beam of electrons. Typical operating voltages
Figure1. To construct a light pulse, the electric component of the plane wave should be multiplied with a bell shaped function.
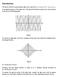 Introduction The Electric field of a monochromatic plane wave is given by is the angular frequency of the plane wave. The plot of this function is given by a cosine function as shown in the following graph.
Introduction The Electric field of a monochromatic plane wave is given by is the angular frequency of the plane wave. The plot of this function is given by a cosine function as shown in the following graph.
Guide to SPEX Optical Spectrometer
 Guide to SPEX Optical Spectrometer GENERAL DESCRIPTION A spectrometer is a device for analyzing an input light beam into its constituent wavelengths. The SPEX model 1704 spectrometer covers a range from
Guide to SPEX Optical Spectrometer GENERAL DESCRIPTION A spectrometer is a device for analyzing an input light beam into its constituent wavelengths. The SPEX model 1704 spectrometer covers a range from
Experiment 1: Fraunhofer Diffraction of Light by a Single Slit
 Experiment 1: Fraunhofer Diffraction of Light by a Single Slit Purpose 1. To understand the theory of Fraunhofer diffraction of light at a single slit and at a circular aperture; 2. To learn how to measure
Experiment 1: Fraunhofer Diffraction of Light by a Single Slit Purpose 1. To understand the theory of Fraunhofer diffraction of light at a single slit and at a circular aperture; 2. To learn how to measure
Laser Speckle Reducer LSR-3000 Series
 Datasheet: LSR-3000 Series Update: 06.08.2012 Copyright 2012 Optotune Laser Speckle Reducer LSR-3000 Series Speckle noise from a laser-based system is reduced by dynamically diffusing the laser beam. A
Datasheet: LSR-3000 Series Update: 06.08.2012 Copyright 2012 Optotune Laser Speckle Reducer LSR-3000 Series Speckle noise from a laser-based system is reduced by dynamically diffusing the laser beam. A
s 2 stigmator: a closed-form solution for single-pass correction of TEM lens astigmatism
 s 2 stigmator: a closed-form solution for single-pass correction of TEM lens astigmatism Rui Yan, Kunpeng Li, Wen Jiang http://cryoem.bio.purdue.edu http://jiang.bio.purdue.edu Purdue Cryo-EM Facility
s 2 stigmator: a closed-form solution for single-pass correction of TEM lens astigmatism Rui Yan, Kunpeng Li, Wen Jiang http://cryoem.bio.purdue.edu http://jiang.bio.purdue.edu Purdue Cryo-EM Facility
ANTENNA INTRODUCTION / BASICS
 Rules of Thumb: 1. The Gain of an antenna with losses is given by: G 0A 8 Where 0 ' Efficiency A ' Physical aperture area 8 ' wavelength ANTENNA INTRODUCTION / BASICS another is:. Gain of rectangular X-Band
Rules of Thumb: 1. The Gain of an antenna with losses is given by: G 0A 8 Where 0 ' Efficiency A ' Physical aperture area 8 ' wavelength ANTENNA INTRODUCTION / BASICS another is:. Gain of rectangular X-Band
Introduction: Why electrons?
 Introduction: Why electrons? 1 Radiations Visible light X-rays Electrons Neutrons Advantages Not very damaging Easily focused Eye wonderful detector Small wavelength (Angstroms) Good penetration Small
Introduction: Why electrons? 1 Radiations Visible light X-rays Electrons Neutrons Advantages Not very damaging Easily focused Eye wonderful detector Small wavelength (Angstroms) Good penetration Small
I look forward to seeing you on August 24!!
 AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment Packet Welcome to AP Physics 1! Your summer assignment is below. You are to complete the entire packet and bring it with you on the first day of school (Monday August 24,
AP Physics 1 Summer Assignment Packet Welcome to AP Physics 1! Your summer assignment is below. You are to complete the entire packet and bring it with you on the first day of school (Monday August 24,
UNIT-II : SIGNAL DEGRADATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS
 UNIT-II : SIGNAL DEGRADATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS The Signal Transmitting through the fiber is degraded by two mechanisms. i) Attenuation ii) Dispersion Both are important to determine the transmission characteristics
UNIT-II : SIGNAL DEGRADATION IN OPTICAL FIBERS The Signal Transmitting through the fiber is degraded by two mechanisms. i) Attenuation ii) Dispersion Both are important to determine the transmission characteristics
Nanotechnology and material science Lecture V
 Most widely used nanoscale microscopy. Based on possibility to create bright electron beam with sub-nm spot size. History: Ernst Ruska (1931), Nobel Prize (1986) For visible light λ=400-700nm, for electrons
Most widely used nanoscale microscopy. Based on possibility to create bright electron beam with sub-nm spot size. History: Ernst Ruska (1931), Nobel Prize (1986) For visible light λ=400-700nm, for electrons
CPSC 425: Computer Vision
 1 / 55 CPSC 425: Computer Vision Instructor: Fred Tung ftung@cs.ubc.ca Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia Lecture Notes 2015/2016 Term 2 2 / 55 Menu January 7, 2016 Topics: Image
1 / 55 CPSC 425: Computer Vision Instructor: Fred Tung ftung@cs.ubc.ca Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia Lecture Notes 2015/2016 Term 2 2 / 55 Menu January 7, 2016 Topics: Image
Holography (A13) Christopher Bronner, Frank Essenberger Freie Universität Berlin Tutor: Dr. Fidder. July 1, 2007 Experiment on July 2, 2007
 Holography (A13) Christopher Bronner, Frank Essenberger Freie Universität Berlin Tutor: Dr. Fidder July 1, 2007 Experiment on July 2, 2007 1 Preparation 1.1 Normal camera If we take a picture with a camera,
Holography (A13) Christopher Bronner, Frank Essenberger Freie Universität Berlin Tutor: Dr. Fidder July 1, 2007 Experiment on July 2, 2007 1 Preparation 1.1 Normal camera If we take a picture with a camera,
Applied Optics. , Physics Department (Room #36-401) , ,
 Applied Optics Professor, Physics Department (Room #36-401) 2290-0923, 019-539-0923, shsong@hanyang.ac.kr Office Hours Mondays 15:00-16:30, Wednesdays 15:00-16:30 TA (Ph.D. student, Room #36-415) 2290-0921,
Applied Optics Professor, Physics Department (Room #36-401) 2290-0923, 019-539-0923, shsong@hanyang.ac.kr Office Hours Mondays 15:00-16:30, Wednesdays 15:00-16:30 TA (Ph.D. student, Room #36-415) 2290-0921,
3. Use your unit circle and fill in the exact values of the cosine function for each of the following angles (measured in radians).
 Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Desmos Activity 1. Use your unit circle and fill in the exact values of the sine function for each of the following angles (measured in radians). sin 0 sin π 2 sin π
Graphing Sine and Cosine Functions Desmos Activity 1. Use your unit circle and fill in the exact values of the sine function for each of the following angles (measured in radians). sin 0 sin π 2 sin π
SECONDARY ELECTRON DETECTION
 SECONDARY ELECTRON DETECTION CAMTEC Workshop Presentation Haitian Xu June 14 th 2010 Introduction SEM Raster scan specimen surface with focused high energy e- beam Signal produced by beam interaction with
SECONDARY ELECTRON DETECTION CAMTEC Workshop Presentation Haitian Xu June 14 th 2010 Introduction SEM Raster scan specimen surface with focused high energy e- beam Signal produced by beam interaction with
Chapter PREPTEST: SHM & WAVE PROPERTIES
 2 4 Chapter 13-14 PREPTEST: SHM & WAVE PROPERTIES Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A load of 45 N attached to a spring that is hanging vertically
2 4 Chapter 13-14 PREPTEST: SHM & WAVE PROPERTIES Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. A load of 45 N attached to a spring that is hanging vertically
... frequency, f speed, v......
 PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. Define the terms wavelength, frequency and speed used to describe a progressive wave. wavelength, λ... frequency, f... speed, v... Hence derive the wave equation v = fλ which
PhysicsAndMathsTutor.com 1 1. Define the terms wavelength, frequency and speed used to describe a progressive wave. wavelength, λ... frequency, f... speed, v... Hence derive the wave equation v = fλ which
FRAUNHOFER AND FRESNEL DIFFRACTION IN ONE DIMENSION
 FRAUNHOFER AND FRESNEL DIFFRACTION IN ONE DIMENSION Revised November 15, 2017 INTRODUCTION The simplest and most commonly described examples of diffraction and interference from two-dimensional apertures
FRAUNHOFER AND FRESNEL DIFFRACTION IN ONE DIMENSION Revised November 15, 2017 INTRODUCTION The simplest and most commonly described examples of diffraction and interference from two-dimensional apertures
R. J. Jones College of Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017
 R. J. Jones College of Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017 Active Modelocking of a Helium-Neon Laser The generation of short optical pulses is important for a wide variety of applications, from time-resolved
R. J. Jones College of Optical Sciences OPTI 511L Fall 2017 Active Modelocking of a Helium-Neon Laser The generation of short optical pulses is important for a wide variety of applications, from time-resolved
Chapter 4 Imaging Lecture 17
 Chapter 4 Imaging Lecture 17 d (110) Imaging Imaging in the TEM Diffraction Contrast in TEM Image HRTEM (High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy) Imaging STEM imaging Imaging in the TEM What is
Chapter 4 Imaging Lecture 17 d (110) Imaging Imaging in the TEM Diffraction Contrast in TEM Image HRTEM (High Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy) Imaging STEM imaging Imaging in the TEM What is
Optical Engineering 421/521 Sample Questions for Midterm 1
 Optical Engineering 421/521 Sample Questions for Midterm 1 Short answer 1.) Sketch a pechan prism. Name a possible application of this prism., write the mirror matrix for this prism (or any other common
Optical Engineering 421/521 Sample Questions for Midterm 1 Short answer 1.) Sketch a pechan prism. Name a possible application of this prism., write the mirror matrix for this prism (or any other common
MAKE SURE TA & TI STAMPS EVERY PAGE BEFORE YOU START
 Laboratory Section: Last Revised on September 21, 2016 Partners Names: Grade: EXPERIMENT 11 Velocity of Waves 1. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1.) What is the longest wavelength at which a sound wave will
Laboratory Section: Last Revised on September 21, 2016 Partners Names: Grade: EXPERIMENT 11 Velocity of Waves 1. Pre-Laboratory Work [2 pts] 1.) What is the longest wavelength at which a sound wave will
Devices & Services Company
 Devices & Services Company 10290 Monroe Drive, Suite 202 - Dallas, Texas 75229 USA - Tel. 214-902-8337 - Fax 214-902-8303 Web: www.devicesandservices.com Email: sales@devicesandservices.com D&S Technical
Devices & Services Company 10290 Monroe Drive, Suite 202 - Dallas, Texas 75229 USA - Tel. 214-902-8337 - Fax 214-902-8303 Web: www.devicesandservices.com Email: sales@devicesandservices.com D&S Technical
Chapter 34 The Wave Nature of Light; Interference. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 34 The Wave Nature of Light; Interference 34-7 Luminous Intensity The intensity of light as perceived depends not only on the actual intensity but also on the sensitivity of the eye at different
Chapter 34 The Wave Nature of Light; Interference 34-7 Luminous Intensity The intensity of light as perceived depends not only on the actual intensity but also on the sensitivity of the eye at different
1 Introduction Installation... 4
 Table of contents 1 Introduction... 3 2 Installation... 4 3 Measurement set up... 5 3.1 Transmissive spatial light modulator...5 3.2 Reflective spatial light modulator...6 4 Software Functions/buttons...
Table of contents 1 Introduction... 3 2 Installation... 4 3 Measurement set up... 5 3.1 Transmissive spatial light modulator...5 3.2 Reflective spatial light modulator...6 4 Software Functions/buttons...
Aberrations and adaptive optics for biomedical microscopes
 Aberrations and adaptive optics for biomedical microscopes Martin Booth Department of Engineering Science And Centre for Neural Circuits and Behaviour University of Oxford Outline Rays, wave fronts and
Aberrations and adaptive optics for biomedical microscopes Martin Booth Department of Engineering Science And Centre for Neural Circuits and Behaviour University of Oxford Outline Rays, wave fronts and
The Formation of an Aerial Image, part 2
 T h e L i t h o g r a p h y T u t o r (April 1993) The Formation of an Aerial Image, part 2 Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, Austin, Texas In the last issue, we began to described how a projection system
T h e L i t h o g r a p h y T u t o r (April 1993) The Formation of an Aerial Image, part 2 Chris A. Mack, FINLE Technologies, Austin, Texas In the last issue, we began to described how a projection system
Coherence of Light and Generation of Speckle Patterns in Photobiology and Photomedicine
 Coherence of Light and Generation of Speckle Patterns in Photobiology and Photomedicine Zeev Zalevsky 1* and Michael Belkin 1 Faculty of Engineering, Bar-Ilan University, Ramat-Gan 5900, Israel, Goldshleger
Coherence of Light and Generation of Speckle Patterns in Photobiology and Photomedicine Zeev Zalevsky 1* and Michael Belkin 1 Faculty of Engineering, Bar-Ilan University, Ramat-Gan 5900, Israel, Goldshleger
Chapter 4: Fourier Optics
 Chapter 4: Fourier Optics P4-1. Calculate the Fourier transform of the function rect(2x)rect(/3) The rectangular function rect(x) is given b 1 x 1/2 rect( x) when 0 x 1/2 P4-2. Assume that ( gx (, )) G
Chapter 4: Fourier Optics P4-1. Calculate the Fourier transform of the function rect(2x)rect(/3) The rectangular function rect(x) is given b 1 x 1/2 rect( x) when 0 x 1/2 P4-2. Assume that ( gx (, )) G
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/2083 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Schramm, Sebastian Markus Title: Imaging with aberration-corrected low energy electron
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/2083 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Schramm, Sebastian Markus Title: Imaging with aberration-corrected low energy electron
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY. 2.71/2.710 Optics Spring 14 Practice Problems Posted May 11, 2014
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 2.71/2.710 Optics Spring 14 Practice Problems Posted May 11, 2014 1. (Pedrotti 13-21) A glass plate is sprayed with uniform opaque particles. When a distant point
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY 2.71/2.710 Optics Spring 14 Practice Problems Posted May 11, 2014 1. (Pedrotti 13-21) A glass plate is sprayed with uniform opaque particles. When a distant point
Light microscopy BMB 173, Lecture 14, Feb. 21, 2018
 Light microscopy The Structural Biology Continuum Next two lectures: Light microscopy Many slides taken from Scott Fraser, Murphy s Fundamentals of light microscopy, Alberts Molecular Biology of the Cell,
Light microscopy The Structural Biology Continuum Next two lectures: Light microscopy Many slides taken from Scott Fraser, Murphy s Fundamentals of light microscopy, Alberts Molecular Biology of the Cell,
Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers. Finite-difference time-domain calculations of the optical transmittance through
Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of the spacer thickness on the resonance properties of the gold and silver metasurface layers. Finite-difference time-domain calculations of the optical transmittance through
