Analog Circuits and Systems
|
|
|
- Liliana Small
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Analog Circuits and Systems Prof. K Radhakrishna Rao Lecture 3 Role of Analog Signal Processing in Electronic Products Part 11 1
2 Cell Phone o The most dominant product of present day world o Its basic function is to make and receive telephone calls over a radio link while moving around a wide geographic area. o It connects to a cellular network provided by a mobile phone operator, allowing access to the public telephone network. o They also support a wide variety of other services such as text messaging, multimedia messaging, , Internet access, short-range wireless communications (infrared and Bluetooth), business applications, gaming, and photography. o Mobile phones that offer these and more general computing capabilities are referred to as smart phones. 2
3 Cell Phone Block Diagram (Md Whaiduzzaman, Abdulla Gani: A Study of Anatomy of Smartphone; Computer Communication and Collaboration, 2013) 3
4 Radio and Analog Base Band Block Diagram 4
5 RF Front End o Typical path consists of, after diplexer, a tunable band pass filter, RF low transmitting power of cell phone is 500mW o RF filter in the transmission path is a tunable band pass filter o Antenna is connected to transmitter and receiver through a diplexer o Low noise amplifier (LNA) 5
6 IF Block o The output of the LNA goes to a mixer to generate IF signal using the local oscillator that is under the control of digital base band processor to produce a sinusoidal signal at ( IF ). o The IF signal is amplified by IF amplifier which is a fixed frequency band pass filter o The IF amplifier output is demodulated using local oscillator which down converts the signal to analog/digital base band. 6
7 Analog Back-End and Baseband o The output of the demodulator may represent the digitally coded speech, video or data. o The video signal and speech signal are reconstructed using D/A converter. The digital data directly goes to the digital base band processor o The output from IF amplifier whose input is from the Modulator is up converted to the radio frequency of transmission by a mixer and power amplified before getting connected to the antenna. 7
8 Analog Back-End and Baseband (contd..) o Speech and video signals generated by the user are converted into digital data using Analog-to-Digital converter. o Digital data goes to the Modulator and to digital base band processor 8
9 Digital Baseband o Human interface (keyboard and display), dialing, memory and power management are controlled by digital baseband processor 9
10 Power Management o Power management system consists of battery charging, battery monitoring and efficient power distribution o Digitally controlled analog sub-systems. 10
11 Electrocardiogram (ECG) o An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a non-invasive procedure for recording of the electrical activity on the body surface generated by the heart. o An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) shows a series of waves that relate to the electrical impulses of heartbeat. 11
12 Idealized version of ECG Waveform o It has features defined as the P, QRS, and T for each heartbeat. o The amplitude and relative timing of the various segments (PQRST) are used for diagnosis. 12
13 Important Components of ECG o Heart rate: Hz (i.e beats per minute) o P-wave: Hz o QRS: Hz o T-wave: 1 7 Hz o High frequency potentials: Hz 13
14 Artifacts and Noise in ECG o Muscle: 5 50 Hz o Respiratory: Hz (e.g bpm) o External electrical: 50 or 60 Hz (A/C mains or line frequency) o Other electrical: typically >10 Hz (muscle stimulators, strong magnetic fields, pacemakers with impedance monitoring) 14
15 ECG Recording o It uses several electrodes o The machine detects and amplifies the electrical impulses picked up by electrodes that occur at each heartbeat and records them on to a paper, computer or any storage device. (google images) 15
16 Positioning of Electrodes o A differential recording between two points on the body are made o They are defined as V I, V II and V III (google images) where RA = right arm, LA = left arm, and LL = left leg 16
17 ECG Signal Characteristics 17
18 ECG Block Diagram 18
19 Analog Front End The inputs from groups of electrodes are multiplexed and processed for common mode rejection by the instrumentation amplifier (INA) The output of INA is amplified by the variable gain amplifier Frequencies lower than 0.05 Hz are eliminated by High Pass Filter Frequencies above 150 Hz are eliminated by Low Pass Filter The noise at power supply frequency is eliminated using a Notch Filter 19
20 Analog Front End (contd..) o The output of the notch filter is amplified and coded to digital form using an Analog-to-Digital Converter o The digital data is suitable processed by a Digital Signal Processor for recording, display or storage. 20
21 Basic Analog Signal Processing Functions o Amplification/Attenuation o Filtering o Comparison o Multiplication o Digital-to-Analog Conversion o Analog-to-Digital Conversion 21
22 Amplification/Attenuation o Output (voltage or current) = K x Input (voltage or current)+offset; where K >1 or K < 1 = a i x Input i where a i can be positive or negative (addition and/or subtraction o If X1 and X2 are two independent variables (inputs) (X1+X2)/2 is known as common mode signal (X1-X2) is known as differential mode signal o Ideal Difference Amplifier: Output=Kd x (X1-X2) 22
23 Amplification/Attenuation (contd..) o Non-ideal Difference Amplifier: Output = Kd x (X1-X2) + Kc x (X1+X2)/2 where Kd is known Differential Mode Gain and Kc is Common Mode Gain o (Kd/Kc) = is known as Common Mode Rejection Ratio. It is normally expressed in decibels as 20log o An ideal difference amplifier should have Common Mode Rejection Ratio of. 23
24 Filtering o Filtering is rejecting or accepting signals in bands of frequencies o Filtering can be Low Pass, High Pass, Band Pass and Band Stop 24
25 Low Pass Filtering o An ideal low pass filter will pass all frequency components below a specified frequency known as upper cut off frequency o A non-deal low pass filter causes varying amplification/ attenuation of frequency components around the upper cut off frequency 25
26 High Pass Filtering o An ideal high pass filter will pass all frequency components above a specified frequency known as lower cut off frequency o A non-deal high pass filter causes varying amplification/ attenuation of frequency components around the lower cut off frequency 26
27 Band Pass Filtering o An ideal band pass filter will pass all frequency components within a upper cut off frequency and lower cut off frequency o A non-deal high pass filter causes varying amplification/ attenuation of frequency components around the upper and lower cut off frequencies 27
28 Band Stop Filtering o An ideal band stop filter will stop all frequency components y within a upper cut off frequency and lower cut off frequency o A non-deal band stop filter causes varying amplification/ attenuation of frequency x components around the upper and lower cut off frequencies 28
29 Comparison o When the input is less than a reference value the output has a specified fixed value and when the input is more than the reference value the output has another specified fixed value 29
30 Multiplication o The output of a multiplier is the product of two inputs o An ideal multiplier has a relationship V = K V V 0 0 X Y o where V X and V Y are two independent inputs o A non-ideal multiplier will have relationship V = V + K V + K V + K V V 0 offset X X Y Y 0 X Y where K X V X and K Y V Y are feed through components 30
31 Multiplication Applications in Communication KVV ( )( ) o p1 p2 a)v ( ) ( ) o = Ko Vp1sin ω1t Vp2sin ω 2t = cos 1 2 t cos 1 2 t 2 ω ω ω +ω DSB, Balance Modulator and Mixer ( )( ) b)v = K V sin ωt V sin ωt sin ω t = K V o o p1 1 p2 2 1 o p1 DSB Demodulation ( 1 cos 2ω1 t ) V sin ω t p2 2 KVV c)vo = Ko Vp1sin ωt Vp2sin ω t +φ = cos cos 2 t 2 φ ω +φ Phase detector, frequency doubler ( )( ( )) o p1 p2 ( ) 2 31
32 Digital to Analog Conversion o The input is n-bit digital data and the output is analog signal o Output = i= 1, n n a 2 V wherea i ref i o It can also be called a multiplier with V ref as analog input = 1 0 and { aa... } 1 2 an is the digital signal 32
33 Analog to Digital Conversion o The output is n-bit digital data and the input is analog signal o A comparator is a one-bit A/D converter 33
34 Analog Systems require o Signal Generation 2 v + 2 Kv = 0 t p ( ) v = V sin Kt +φ ω= K o Power Supplies 34
6.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory
 6.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Spring 2015, Instructor Gim Hom Project Proposal Transmitting, Receiving, and Interpreting ECG Waveforms Daniel Moon (dhmoon@mit.edu) Thipok (Ben) Rak-amnouykit
6.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Spring 2015, Instructor Gim Hom Project Proposal Transmitting, Receiving, and Interpreting ECG Waveforms Daniel Moon (dhmoon@mit.edu) Thipok (Ben) Rak-amnouykit
Analog Circuits and Systems
 Analog Circuits and Systems Prof. K Radhakrishna Rao Lecture 21: Filters 1 Review Integrators as building blocks of filters Frequency compensation in negative feedback systems Opamp and LDO frequency compensation
Analog Circuits and Systems Prof. K Radhakrishna Rao Lecture 21: Filters 1 Review Integrators as building blocks of filters Frequency compensation in negative feedback systems Opamp and LDO frequency compensation
Bio-Potential Amplifiers
 Bio-Potential Amplifiers Biomedical Models for Diagnosis Body Signal Sensor Signal Processing Output Diagnosis Body signals and sensors were covered in EE470 The signal processing part is in EE471 Bio-Potential
Bio-Potential Amplifiers Biomedical Models for Diagnosis Body Signal Sensor Signal Processing Output Diagnosis Body signals and sensors were covered in EE470 The signal processing part is in EE471 Bio-Potential
Introduction to Receivers
 Introduction to Receivers Purpose: translate RF signals to baseband Shift frequency Amplify Filter Demodulate Why is this a challenge? Interference Large dynamic range required Many receivers must be capable
Introduction to Receivers Purpose: translate RF signals to baseband Shift frequency Amplify Filter Demodulate Why is this a challenge? Interference Large dynamic range required Many receivers must be capable
Analog Circuits and Systems
 Analog Circuits and Systems Prof. K Radhakrishna Rao Lecture 30: Automatic Tuning of Filters (PLL) and Review of Filter Design 1 Review Frequency Compensation 2 Review (contd.,) Switched Capacitor Filters
Analog Circuits and Systems Prof. K Radhakrishna Rao Lecture 30: Automatic Tuning of Filters (PLL) and Review of Filter Design 1 Review Frequency Compensation 2 Review (contd.,) Switched Capacitor Filters
EE 230 Experiment 10 ECG Measurements Spring 2010
 EE 230 Experiment 10 ECG Measurements Spring 2010 Note: If for any reason the students are uncomfortable with doing this experiment, please talk to the instructor for the course and an alternative experiment
EE 230 Experiment 10 ECG Measurements Spring 2010 Note: If for any reason the students are uncomfortable with doing this experiment, please talk to the instructor for the course and an alternative experiment
PRINCIPLES OF COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS. Lecture 1- Introduction Elements, Modulation, Demodulation, Frequency Spectrum
 PRINCIPLES OF COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Lecture 1- Introduction Elements, Modulation, Demodulation, Frequency Spectrum Topic covered Introduction to subject Elements of Communication system Modulation General
PRINCIPLES OF COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Lecture 1- Introduction Elements, Modulation, Demodulation, Frequency Spectrum Topic covered Introduction to subject Elements of Communication system Modulation General
Course Code: EE-411 Teacher: Engr.Ahmad Bilal Multiple choice & Short Questions notes
 Department of Electrical (POWER) Engineering Swedish College of Engineering & Technology Rahim yar khan Subject: Communication systems Course Code: EE-411 Teacher: Engr.Ahmad Bilal Multiple choice & Short
Department of Electrical (POWER) Engineering Swedish College of Engineering & Technology Rahim yar khan Subject: Communication systems Course Code: EE-411 Teacher: Engr.Ahmad Bilal Multiple choice & Short
Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance
 E5.1 Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance Note: It is strongly recommended that you complete lab E4: Capacitors and the RC Circuit before performing this experiment. Introduction Ohm s law, a well known
E5.1 Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance Note: It is strongly recommended that you complete lab E4: Capacitors and the RC Circuit before performing this experiment. Introduction Ohm s law, a well known
Analog Circuits and Systems
 Analog Circuits and Systems Prof. K Radhakrishna Rao Lecture 31: Waveform Generation 1 Review Phase Locked Loop (self tuned filter) 2 nd order High Q low-pass output phase compared with the input 90 phase
Analog Circuits and Systems Prof. K Radhakrishna Rao Lecture 31: Waveform Generation 1 Review Phase Locked Loop (self tuned filter) 2 nd order High Q low-pass output phase compared with the input 90 phase
Lecture 6. Angle Modulation and Demodulation
 Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
Development of Electrocardiograph Monitoring System
 Development of Electrocardiograph Monitoring System Khairul Affendi Rosli 1*, Mohd. Hafizi Omar 1, Ahmad Fariz Hasan 1, Khairil Syahmi Musa 1, Mohd Fairuz Muhamad Fadzil 1, and Shu Hwei Neu 1 1 Department
Development of Electrocardiograph Monitoring System Khairul Affendi Rosli 1*, Mohd. Hafizi Omar 1, Ahmad Fariz Hasan 1, Khairil Syahmi Musa 1, Mohd Fairuz Muhamad Fadzil 1, and Shu Hwei Neu 1 1 Department
Introduction. sig. ref. sig
 Introduction A lock-in amplifier, in common with most AC indicating instruments, provides a DC output proportional to the AC signal under investigation. The special rectifier, called a phase-sensitive
Introduction A lock-in amplifier, in common with most AC indicating instruments, provides a DC output proportional to the AC signal under investigation. The special rectifier, called a phase-sensitive
Exercise 1: RF Stage, Mixer, and IF Filter
 SSB Reception Analog Communications Exercise 1: RF Stage, Mixer, and IF Filter EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION On the circuit board, you will set up the SSB transmitter to transmit a 1000 khz SSB signal
SSB Reception Analog Communications Exercise 1: RF Stage, Mixer, and IF Filter EXERCISE OBJECTIVE DISCUSSION On the circuit board, you will set up the SSB transmitter to transmit a 1000 khz SSB signal
Simple Heartbeat Monitor for Analog Enthusiasts
 Abigail C Rice, Jelimo B Maswan 6.101: Project Proposal Date: 18/4/2014 Introduction Simple Heartbeat Monitor for Analog Enthusiasts An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a simple, non-invasive way of measuring
Abigail C Rice, Jelimo B Maswan 6.101: Project Proposal Date: 18/4/2014 Introduction Simple Heartbeat Monitor for Analog Enthusiasts An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a simple, non-invasive way of measuring
EXPERIMENT 5 Bioelectric Measurements
 Objectives EXPERIMENT 5 Bioelectric Measurements 1) Generate periodic signals with a Signal Generator and display on an Oscilloscope. 2) Investigate a Differential Amplifier to see small signals in a noisy
Objectives EXPERIMENT 5 Bioelectric Measurements 1) Generate periodic signals with a Signal Generator and display on an Oscilloscope. 2) Investigate a Differential Amplifier to see small signals in a noisy
Problems from the 3 rd edition
 (2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
(2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
Lab: Using filters to build an electrocardiograph (ECG or EKG)
 Page 1 /6 Lab: Using filters to build an electrocardiograph (ECG or EKG) Goal: Use filters and amplifiers to build a circuit that will sense and measure a heartbeat. You and your heartbeat Did you know
Page 1 /6 Lab: Using filters to build an electrocardiograph (ECG or EKG) Goal: Use filters and amplifiers to build a circuit that will sense and measure a heartbeat. You and your heartbeat Did you know
BME 405 BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING SENIOR DESIGN 1 Fall 2005 BME Design Mini-Project Project Title
 BME 405 BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING SENIOR DESIGN 1 Fall 2005 BME Design Mini-Project Project Title Basic system for Electrocardiography Customer/Clinical need A recent health care analysis have demonstrated
BME 405 BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING SENIOR DESIGN 1 Fall 2005 BME Design Mini-Project Project Title Basic system for Electrocardiography Customer/Clinical need A recent health care analysis have demonstrated
Non-linear circuits and sensors
 ELEC3106, Electronics Non-linear circuits and sensors 1 ELEC3106 Electronics: lecture 10 summary Non-linear circuits and sensors Torsten Lehmann School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommunication The
ELEC3106, Electronics Non-linear circuits and sensors 1 ELEC3106 Electronics: lecture 10 summary Non-linear circuits and sensors Torsten Lehmann School of Electrical Engineering and Telecommunication The
Measurements on Wireless transmission of ECG signals
 Measurements on Wireless transmission of ECG signals A. Gabrielli a,b, I. Lax a a) INFN Bologna b) Physics Department, University of Bologna, Italy E-mail: alessandro.gabrielli@bo.infn.it IPRD 3-6 October
Measurements on Wireless transmission of ECG signals A. Gabrielli a,b, I. Lax a a) INFN Bologna b) Physics Department, University of Bologna, Italy E-mail: alessandro.gabrielli@bo.infn.it IPRD 3-6 October
Receiver Design. Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 2011/2/21
 Receiver Design Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 2011/2/21 MW & RF Design / Prof. T. -L. Wu 1 The receiver mush be very sensitive to -110dBm
Receiver Design Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 2011/2/21 MW & RF Design / Prof. T. -L. Wu 1 The receiver mush be very sensitive to -110dBm
( ) ( ) ( p ) ( ) ( ) ( )
 4400 341: Introduction to Communication Systems Spring 2017 Solution to Homework Assignment #5: 1 For a message signal m t = 2 cos 1000t + 9 cos 2000πt 1-a Write expressions (do not sketch for φ /0 t and
4400 341: Introduction to Communication Systems Spring 2017 Solution to Homework Assignment #5: 1 For a message signal m t = 2 cos 1000t + 9 cos 2000πt 1-a Write expressions (do not sketch for φ /0 t and
Communication Channels
 Communication Channels wires (PCB trace or conductor on IC) optical fiber (attenuation 4dB/km) broadcast TV (50 kw transmit) voice telephone line (under -9 dbm or 110 µw) walkie-talkie: 500 mw, 467 MHz
Communication Channels wires (PCB trace or conductor on IC) optical fiber (attenuation 4dB/km) broadcast TV (50 kw transmit) voice telephone line (under -9 dbm or 110 µw) walkie-talkie: 500 mw, 467 MHz
Lecture 4 Biopotential Amplifiers
 Bioinstrument Sahand University of Technology Lecture 4 Biopotential Amplifiers Dr. Shamekhi Summer 2016 OpAmp and Rules 1- A = (gain is infinity) 2- Vo = 0, when v1 = v2 (no offset voltage) 3- Rd = (input
Bioinstrument Sahand University of Technology Lecture 4 Biopotential Amplifiers Dr. Shamekhi Summer 2016 OpAmp and Rules 1- A = (gain is infinity) 2- Vo = 0, when v1 = v2 (no offset voltage) 3- Rd = (input
Analog Circuits and Systems
 Analog Circuits and Systems Prof. K Radhakrishna Rao Lecture 10: Electronic Devices for Analog Circuits 1 Multipliers Multipliers provide multiplication of two input voltages or currents Multipliers can
Analog Circuits and Systems Prof. K Radhakrishna Rao Lecture 10: Electronic Devices for Analog Circuits 1 Multipliers Multipliers provide multiplication of two input voltages or currents Multipliers can
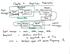 Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
RADIO RECEIVERS ECE 3103 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 RADIO RECEIVERS ECE 3103 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS FUNCTIONS OF A RADIO RECEIVER The main functions of a radio receiver are: 1. To intercept the RF signal by using the receiver antenna 2. Select the
RADIO RECEIVERS ECE 3103 WIRELESS COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS FUNCTIONS OF A RADIO RECEIVER The main functions of a radio receiver are: 1. To intercept the RF signal by using the receiver antenna 2. Select the
Kanchan S. Shrikhande. Department of Instrumentation Engineering, Vivekanand Education Society s Institute of.
 ISOLATED ECG AMPLIFIER WITH RIGHT LEG DRIVE Kanchan S. Shrikhande Department of Instrumentation Engineering, Vivekanand Education Society s Institute of Technology(VESIT),kanchans90@gmail.com Abstract
ISOLATED ECG AMPLIFIER WITH RIGHT LEG DRIVE Kanchan S. Shrikhande Department of Instrumentation Engineering, Vivekanand Education Society s Institute of Technology(VESIT),kanchans90@gmail.com Abstract
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the
 Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
Analog Circuits and Systems
 Analog Circuits and Systems Prof. K Radhakrishna Rao Lecture 4 Analog Signal Processing One-Port Networks 1 Analog Signal Processing Functions ASP Amplification Filtering Oscillation Mixing, Modulation,
Analog Circuits and Systems Prof. K Radhakrishna Rao Lecture 4 Analog Signal Processing One-Port Networks 1 Analog Signal Processing Functions ASP Amplification Filtering Oscillation Mixing, Modulation,
Florida Atlantic University Biomedical Signal Processing Lab Experiment 2 Signal Transduction: Building an analog Electrocardiogram (ECG)
 Florida Atlantic University Biomedical Signal Processing Lab Experiment 2 Signal Transduction: Building an analog Electrocardiogram (ECG) 1. Introduction: The Electrocardiogram (ECG) is a technique of
Florida Atlantic University Biomedical Signal Processing Lab Experiment 2 Signal Transduction: Building an analog Electrocardiogram (ECG) 1. Introduction: The Electrocardiogram (ECG) is a technique of
Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier
 Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier and the first channel. The modulation of the main carrier
Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier and the first channel. The modulation of the main carrier
Name Kyla Jackson, Todd Germeroth, Jake Spooler Date May 5, 2010 Lab 3E Group 3 Experiment Title Project Deliverable 3
 Name Kyla Jackson, Todd Germeroth, Jake Spooler Date May 5, 2010 Lab 3E Group 3 Experiment Title Project Deliverable 3 Objective The objective of this project was to design and construct an ECG measurement
Name Kyla Jackson, Todd Germeroth, Jake Spooler Date May 5, 2010 Lab 3E Group 3 Experiment Title Project Deliverable 3 Objective The objective of this project was to design and construct an ECG measurement
4- Single Side Band (SSB)
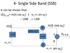 4- Single Side Band (SSB) It can be shown that: s(t) S.S.B = m(t) cos ω c t ± m h (t) sin ω c t -: USB ; +: LSB m(t) X m(t) cos ω c t -π/ cos ω c t -π/ + s S.S.B m h (t) X m h (t) ± sin ω c t 1 Tone Modulation:
4- Single Side Band (SSB) It can be shown that: s(t) S.S.B = m(t) cos ω c t ± m h (t) sin ω c t -: USB ; +: LSB m(t) X m(t) cos ω c t -π/ cos ω c t -π/ + s S.S.B m h (t) X m h (t) ± sin ω c t 1 Tone Modulation:
P08050 Testing Strategy Document
 P85 Testing Strategy Document IFCN standards 1 for digital recording of clinical EEG Verification 2 3 Square-Wave Calibration Test Summary: Square-wave signals must be recorded at the beginning, using
P85 Testing Strategy Document IFCN standards 1 for digital recording of clinical EEG Verification 2 3 Square-Wave Calibration Test Summary: Square-wave signals must be recorded at the beginning, using
Part I - Amplitude Modulation
 EE/CME 392 Laboratory 1-1 Part I - Amplitude Modulation Safety: In this lab, voltages are less than 15 volts and this is not normally dangerous to humans. However, you should assemble or modify a circuit
EE/CME 392 Laboratory 1-1 Part I - Amplitude Modulation Safety: In this lab, voltages are less than 15 volts and this is not normally dangerous to humans. However, you should assemble or modify a circuit
EXPERIMENT 7 The Amplifier
 Objectives EXPERIMENT 7 The Amplifier 1) Understand the operation of the differential amplifier. 2) Determine the gain of each side of the differential amplifier. 3) Determine the gain of the differential
Objectives EXPERIMENT 7 The Amplifier 1) Understand the operation of the differential amplifier. 2) Determine the gain of each side of the differential amplifier. 3) Determine the gain of the differential
Residual Phase Noise Measurement Extracts DUT Noise from External Noise Sources By David Brandon and John Cavey
 Residual Phase Noise easurement xtracts DUT Noise from xternal Noise Sources By David Brandon [david.brandon@analog.com and John Cavey [john.cavey@analog.com Residual phase noise measurement cancels the
Residual Phase Noise easurement xtracts DUT Noise from xternal Noise Sources By David Brandon [david.brandon@analog.com and John Cavey [john.cavey@analog.com Residual phase noise measurement cancels the
Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits. Module 7
 Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits Module 7 Radio Block Diagrams Radio Circuits can be shown as functional blocks connected together. Knowing the description of common
Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits Module 7 Radio Block Diagrams Radio Circuits can be shown as functional blocks connected together. Knowing the description of common
Vestigial Sideband Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #11, April 7, Prof. Young-Chai Ko
 Vestigial Sideband Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #11, April 7, 2011 Prof. Young-Chai Ko koyc@korea.ac.kr Summary Vestigial sideband modulation Baseband representation of modulated wave
Vestigial Sideband Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #11, April 7, 2011 Prof. Young-Chai Ko koyc@korea.ac.kr Summary Vestigial sideband modulation Baseband representation of modulated wave
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II
 EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
ANALOG COMMUNICATION
 ANALOG COMMUNICATION TRAINING LAB Analog Communication Training Lab consists of six kits, one each for Modulation (ACL-01), Demodulation (ACL-02), Modulation (ACL-03), Demodulation (ACL-04), Noise power
ANALOG COMMUNICATION TRAINING LAB Analog Communication Training Lab consists of six kits, one each for Modulation (ACL-01), Demodulation (ACL-02), Modulation (ACL-03), Demodulation (ACL-04), Noise power
Radio Receiver Architectures and Analysis
 Radio Receiver Architectures and Analysis Robert Wilson December 6, 01 Abstract This article discusses some common receiver architectures and analyzes some of the impairments that apply to each. 1 Contents
Radio Receiver Architectures and Analysis Robert Wilson December 6, 01 Abstract This article discusses some common receiver architectures and analyzes some of the impairments that apply to each. 1 Contents
ECE 480 Design Team 6 Electrocardiography and Design
 ECE 480 Design Team 6 Electrocardiography and Design Alex Volinski November 16 th, 2012 Executive Summary Recently there has been a large increase in consumer demand for a new and functional ECG (Electrocardiograph)
ECE 480 Design Team 6 Electrocardiography and Design Alex Volinski November 16 th, 2012 Executive Summary Recently there has been a large increase in consumer demand for a new and functional ECG (Electrocardiograph)
Massachusetts Institute of Technology MIT
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology MIT Real Time Wireless Electrocardiogram (ECG) Monitoring System Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Guilherme K. Kolotelo, Rogers G. Reichert Cambridge, MA
Massachusetts Institute of Technology MIT Real Time Wireless Electrocardiogram (ECG) Monitoring System Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Guilherme K. Kolotelo, Rogers G. Reichert Cambridge, MA
cosω t Y AD 532 Analog Multiplier Board EE18.xx Fig. 1 Amplitude modulation of a sine wave message signal
 University of Saskatchewan EE 9 Electrical Engineering Laboratory III Amplitude and Frequency Modulation Objectives: To observe the time domain waveforms and spectra of amplitude modulated (AM) waveforms
University of Saskatchewan EE 9 Electrical Engineering Laboratory III Amplitude and Frequency Modulation Objectives: To observe the time domain waveforms and spectra of amplitude modulated (AM) waveforms
ECE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications
 ECE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Advanced Digital Communications, Spring-2015, Week-8 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation Any bandpass
ECE5713 : Advanced Digital Communications Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Advanced Digital Communications, Spring-2015, Week-8 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation Any bandpass
Outline. Communications Engineering 1
 Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Implementation of wireless ECG measurement system in ubiquitous health-care environment
 Implementation of wireless ECG measurement system in ubiquitous health-care environment M. C. KIM 1, J. Y. YOO 1, S. Y. YE 2, D. K. JUNG 3, J. H. RO 4, G. R. JEON 4 1 Department of Interdisciplinary Program
Implementation of wireless ECG measurement system in ubiquitous health-care environment M. C. KIM 1, J. Y. YOO 1, S. Y. YE 2, D. K. JUNG 3, J. H. RO 4, G. R. JEON 4 1 Department of Interdisciplinary Program
BIOMEDICAL INSTRUMENTATION PROBLEM SHEET 1
 BIOMEDICAL INSTRUMENTATION PROBLEM SHEET 1 Dr. Gari Clifford Hilary Term 2013 1. (Exemplar Finals Question) a) List the five vital signs which are most commonly recorded from patient monitors in high-risk
BIOMEDICAL INSTRUMENTATION PROBLEM SHEET 1 Dr. Gari Clifford Hilary Term 2013 1. (Exemplar Finals Question) a) List the five vital signs which are most commonly recorded from patient monitors in high-risk
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
 Vectors and ECG s Vectors and ECG s 2 Electrocardiogram (ECG) Depolarization wave passes through the heart and the electrical currents pass into surrounding tissues. Small part of the extracellular current
Vectors and ECG s Vectors and ECG s 2 Electrocardiogram (ECG) Depolarization wave passes through the heart and the electrical currents pass into surrounding tissues. Small part of the extracellular current
Special-Purpose Operational Amplifier Circuits
 Special-Purpose Operational Amplifier Circuits Instrumentation Amplifier An instrumentation amplifier (IA) is a differential voltagegain device that amplifies the difference between the voltages existing
Special-Purpose Operational Amplifier Circuits Instrumentation Amplifier An instrumentation amplifier (IA) is a differential voltagegain device that amplifies the difference between the voltages existing
Technician License Course Chapter 3. Lesson Plan Module 7 Types of Radio Circuits
 Technician License Course Chapter 3 Lesson Plan Module 7 Types of Radio Circuits The Basic Transceiver Combination of transmitter and receiver Abbreviated XCVR (X = trans) Antenna switched between transmitter
Technician License Course Chapter 3 Lesson Plan Module 7 Types of Radio Circuits The Basic Transceiver Combination of transmitter and receiver Abbreviated XCVR (X = trans) Antenna switched between transmitter
Lecture Topics. Doppler CW Radar System, FM-CW Radar System, Moving Target Indication Radar System, and Pulsed Doppler Radar System
 Lecture Topics Doppler CW Radar System, FM-CW Radar System, Moving Target Indication Radar System, and Pulsed Doppler Radar System 1 Remember that: An EM wave is a function of both space and time e.g.
Lecture Topics Doppler CW Radar System, FM-CW Radar System, Moving Target Indication Radar System, and Pulsed Doppler Radar System 1 Remember that: An EM wave is a function of both space and time e.g.
AM Limitations. Amplitude Modulation II. DSB-SC Modulation. AM Modifications
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
Review of Lecture 2. Data and Signals - Theoretical Concepts. Review of Lecture 2. Review of Lecture 2. Review of Lecture 2. Review of Lecture 2
 Data and Signals - Theoretical Concepts! What are the major functions of the network access layer? Reference: Chapter 3 - Stallings Chapter 3 - Forouzan Study Guide 3 1 2! What are the major functions
Data and Signals - Theoretical Concepts! What are the major functions of the network access layer? Reference: Chapter 3 - Stallings Chapter 3 - Forouzan Study Guide 3 1 2! What are the major functions
Lecture 6 SIGNAL PROCESSING. Radar Signal Processing Dr. Aamer Iqbal Bhatti. Dr. Aamer Iqbal Bhatti
 Lecture 6 SIGNAL PROCESSING Signal Reception Receiver Bandwidth Pulse Shape Power Relation Beam Width Pulse Repetition Frequency Antenna Gain Radar Cross Section of Target. Signal-to-noise ratio Receiver
Lecture 6 SIGNAL PROCESSING Signal Reception Receiver Bandwidth Pulse Shape Power Relation Beam Width Pulse Repetition Frequency Antenna Gain Radar Cross Section of Target. Signal-to-noise ratio Receiver
THE AMPLIFIER. A-B = C subtractor. INPUTS Figure 1
 OBJECTIVES: THE AMPLIFIER 1) Explain the operation of the differential amplifier. 2) Determine the gain of each side of the differential amplifier. 3) Determine the gain of the differential amplifier as
OBJECTIVES: THE AMPLIFIER 1) Explain the operation of the differential amplifier. 2) Determine the gain of each side of the differential amplifier. 3) Determine the gain of the differential amplifier as
Amplitude Modulation II
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
HY448 Sample Problems
 HY448 Sample Problems 10 November 2014 These sample problems include the material in the lectures and the guided lab exercises. 1 Part 1 1.1 Combining logarithmic quantities A carrier signal with power
HY448 Sample Problems 10 November 2014 These sample problems include the material in the lectures and the guided lab exercises. 1 Part 1 1.1 Combining logarithmic quantities A carrier signal with power
Introduction to Telecommunications and Computer Engineering Unit 3: Communications Systems & Signals
 Introduction to Telecommunications and Computer Engineering Unit 3: Communications Systems & Signals Syedur Rahman Lecturer, CSE Department North South University syedur.rahman@wolfson.oxon.org Acknowledgements
Introduction to Telecommunications and Computer Engineering Unit 3: Communications Systems & Signals Syedur Rahman Lecturer, CSE Department North South University syedur.rahman@wolfson.oxon.org Acknowledgements
Linear electronic. Lecture No. 1
 1 Lecture No. 1 2 3 4 5 Lecture No. 2 6 7 8 9 10 11 Lecture No. 3 12 13 14 Lecture No. 4 Example: find Frequency response analysis for the circuit shown in figure below. Where R S =4kR B1 =8kR B2 =4k R
1 Lecture No. 1 2 3 4 5 Lecture No. 2 6 7 8 9 10 11 Lecture No. 3 12 13 14 Lecture No. 4 Example: find Frequency response analysis for the circuit shown in figure below. Where R S =4kR B1 =8kR B2 =4k R
P08050 Remote EEG Sensing
 P08050 Remote EEG Sensing Team Guide: Dr. Daniel Phillips Customer: Daniel Pontillo Dr. FeiHu Team Members: Dan Pontillo Ankit Bhutani Jonathan Finamore John Frye Zach McGarvey Project goal: Interfacing
P08050 Remote EEG Sensing Team Guide: Dr. Daniel Phillips Customer: Daniel Pontillo Dr. FeiHu Team Members: Dan Pontillo Ankit Bhutani Jonathan Finamore John Frye Zach McGarvey Project goal: Interfacing
Lecture 15: Introduction to Mixers
 EECS 142 Lecture 15: Introduction to Mixers Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture
EECS 142 Lecture 15: Introduction to Mixers Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture
EE3723 : Digital Communications
 EE3723 : Digital Communications Week 8-9: Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad - Digital Communications - EE3723 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation
EE3723 : Digital Communications Week 8-9: Bandpass Modulation MPSK MASK, OOK MFSK 04-May-15 Muhammad Ali Jinnah University, Islamabad - Digital Communications - EE3723 1 In-phase and Quadrature (I&Q) Representation
two computers. 2- Providing a channel between them for transmitting and receiving the signals through it.
 1. Introduction: Communication is the process of transmitting the messages that carrying information, where the two computers can be communicated with each other if the two conditions are available: 1-
1. Introduction: Communication is the process of transmitting the messages that carrying information, where the two computers can be communicated with each other if the two conditions are available: 1-
CME312- LAB Manual DSB-SC Modulation and Demodulation Experiment 6. Experiment 6. Experiment. DSB-SC Modulation and Demodulation
 Experiment 6 Experiment DSB-SC Modulation and Demodulation Objectives : By the end of this experiment, the student should be able to: 1. Demonstrate the modulation and demodulation process of DSB-SC. 2.
Experiment 6 Experiment DSB-SC Modulation and Demodulation Objectives : By the end of this experiment, the student should be able to: 1. Demonstrate the modulation and demodulation process of DSB-SC. 2.
EECE Circuits and Signals: Biomedical Applications. Lab ECG I The Instrumentation Amplifier
 EECE 150 - Circuits and Signals: Biomedical Applications Lab ECG I The Instrumentation Amplifier Introduction: As discussed in class, instrumentation amplifiers are often used to reject common-mode signals
EECE 150 - Circuits and Signals: Biomedical Applications Lab ECG I The Instrumentation Amplifier Introduction: As discussed in class, instrumentation amplifiers are often used to reject common-mode signals
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-2012 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 40 Subject: PART - A 0. Which region of the transistor
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 40 Subject: PART - A 0. Which region of the transistor
Medlab GmbH EG04000 User Manual. medlab. Four Lead ECG OEM board EG Technical Manual. Copyright Medlab Version Version 1.
 Medlab GmbH EG04000 User Manual medlab Four Lead ECG OEM board EG04000 Technical Manual Copyright Medlab 2014 1 Medlab GmbH EG04000 User Manual Medlab medizinische Diagnosegeräte GmbH Helmholtzstrasse
Medlab GmbH EG04000 User Manual medlab Four Lead ECG OEM board EG04000 Technical Manual Copyright Medlab 2014 1 Medlab GmbH EG04000 User Manual Medlab medizinische Diagnosegeräte GmbH Helmholtzstrasse
Elements of Communication System Channel Fig: 1: Block Diagram of Communication System Terminology in Communication System
 Content:- Fundamentals of Communication Engineering : Elements of a Communication System, Need of modulation, electromagnetic spectrum and typical applications, Unit V (Communication terminologies in communication
Content:- Fundamentals of Communication Engineering : Elements of a Communication System, Need of modulation, electromagnetic spectrum and typical applications, Unit V (Communication terminologies in communication
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation. Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY RX Nonlinearity Issues: 2.2, 2.4 Demodulation: not in the book 2 RX nonlinearities System Nonlinearity
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY RX Nonlinearity Issues: 2.2, 2.4 Demodulation: not in the book 2 RX nonlinearities System Nonlinearity
Cable Testing TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING
 Cable Testing TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING Analog Signals 2 Digital Signals Square waves, like sine waves, are periodic. However, square wave graphs do not continuously vary with time. The wave holds
Cable Testing TELECOMMUNICATIONS AND NETWORKING Analog Signals 2 Digital Signals Square waves, like sine waves, are periodic. However, square wave graphs do not continuously vary with time. The wave holds
Wireless systems. includes issues of
 Wireless systems includes issues of hardware processors, storage, peripherals, networks,... representation of information, analog vs. digital, bits & bytes software applications, operating system organization
Wireless systems includes issues of hardware processors, storage, peripherals, networks,... representation of information, analog vs. digital, bits & bytes software applications, operating system organization
Introduction to Amplitude Modulation
 1 Introduction to Amplitude Modulation Introduction to project management. Problem definition. Design principles and practices. Implementation techniques including circuit design, software design, solid
1 Introduction to Amplitude Modulation Introduction to project management. Problem definition. Design principles and practices. Implementation techniques including circuit design, software design, solid
ADI 2006 RF Seminar. Chapter II RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers
 ADI 2006 RF Seminar Chapter II RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers 1 RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers Fixed Gain and Variable Gain Amplifiers IQ Demodulators Analog-to-Digital
ADI 2006 RF Seminar Chapter II RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers 1 RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers Fixed Gain and Variable Gain Amplifiers IQ Demodulators Analog-to-Digital
8.5 Modulation of Signals
 8.5 Modulation of Signals basic idea and goals measuring atomic absorption without modulation measuring atomic absorption with modulation the tuned amplifier, diode rectifier and low pass the lock-in amplifier
8.5 Modulation of Signals basic idea and goals measuring atomic absorption without modulation measuring atomic absorption with modulation the tuned amplifier, diode rectifier and low pass the lock-in amplifier
Module 8 Theory. dbs AM Detector Ring Modulator Receiver Chain. Functional Blocks Parameters. IRTS Region 4
 Module 8 Theory dbs AM Detector Ring Modulator Receiver Chain Functional Blocks Parameters Decibel (db) The term db or decibel is a relative unit of measurement used frequently in electronic communications
Module 8 Theory dbs AM Detector Ring Modulator Receiver Chain Functional Blocks Parameters Decibel (db) The term db or decibel is a relative unit of measurement used frequently in electronic communications
CHAPTER -15. Communication Systems
 CHAPTER -15 Communication Systems COMMUNICATION Communication is the act of transmission and reception of information. COMMUNICATION SYSTEM: A system comprises of transmitter, communication channel and
CHAPTER -15 Communication Systems COMMUNICATION Communication is the act of transmission and reception of information. COMMUNICATION SYSTEM: A system comprises of transmitter, communication channel and
LINEAR IC APPLICATIONS
 1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
1 B.Tech III Year I Semester (R09) Regular & Supplementary Examinations December/January 2013/14 1 (a) Why is R e in an emitter-coupled differential amplifier replaced by a constant current source? (b)
A low-if 2.4 GHz Integrated RF Receiver for Bluetooth Applications Lai Jiang a, Shaohua Liu b, Hang Yu c and Yan Li d
 Applied Mechanics and Materials Online: 2013-06-27 ISSN: 1662-7482, Vol. 329, pp 416-420 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.329.416 2013 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland A low-if 2.4 GHz Integrated
Applied Mechanics and Materials Online: 2013-06-27 ISSN: 1662-7482, Vol. 329, pp 416-420 doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/amm.329.416 2013 Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland A low-if 2.4 GHz Integrated
Deepali Shukla 1 (Asst.Professor), Vandana Pandya 2 (Asst.Professor) Medicaps Institute of Technology & Management, Indore (M.P.
 Open Hardware Platform For Reconstruction Of ECG Signal Deepali Shukla 1 (Asst.Professor), Vandana Pandya 2 (Asst.Professor) Medicaps Institute of Technology & Management, Indore (M.P.), India Abstract
Open Hardware Platform For Reconstruction Of ECG Signal Deepali Shukla 1 (Asst.Professor), Vandana Pandya 2 (Asst.Professor) Medicaps Institute of Technology & Management, Indore (M.P.), India Abstract
B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering)
 Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
Lecture 12. Carrier Phase Synchronization. EE4900/EE6720 Digital Communications
 EE49/EE6720: Digital Communications 1 Lecture 12 Carrier Phase Synchronization Block Diagrams of Communication System Digital Communication System 2 Informatio n (sound, video, text, data, ) Transducer
EE49/EE6720: Digital Communications 1 Lecture 12 Carrier Phase Synchronization Block Diagrams of Communication System Digital Communication System 2 Informatio n (sound, video, text, data, ) Transducer
Changing the sampling rate
 Noise Lecture 3 Finally you should be aware of the Nyquist rate when you re designing systems. First of all you must know your system and the limitations, e.g. decreasing sampling rate in the speech transfer
Noise Lecture 3 Finally you should be aware of the Nyquist rate when you re designing systems. First of all you must know your system and the limitations, e.g. decreasing sampling rate in the speech transfer
6.976 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 20 Performance Measures of Wireless Communication
 6.976 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 20 Performance Measures of Wireless Communication Michael Perrott Massachusetts Institute of Technology Copyright 2003 by Michael H. Perrott
6.976 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 20 Performance Measures of Wireless Communication Michael Perrott Massachusetts Institute of Technology Copyright 2003 by Michael H. Perrott
5 TIPS FOR GETTING THE MOST OUT OF Your Function Generator
 5 TIPS FOR GETTING THE MOST OUT OF Your Function Generator Introduction Modern function/waveform generators are extremely versatile, going well beyond the basic sine, square, and ramp waveforms. Function
5 TIPS FOR GETTING THE MOST OUT OF Your Function Generator Introduction Modern function/waveform generators are extremely versatile, going well beyond the basic sine, square, and ramp waveforms. Function
ENGR 4323/5323 Digital and Analog Communication
 ENGR 4323/5323 Digital and Analog Communication Chapter 1 Introduction Engineering and Physics University of Central Oklahoma Dr. Mohamed Bingabr Course Materials Textbook: Modern Digital and Analog Communication,
ENGR 4323/5323 Digital and Analog Communication Chapter 1 Introduction Engineering and Physics University of Central Oklahoma Dr. Mohamed Bingabr Course Materials Textbook: Modern Digital and Analog Communication,
Outline / Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 3: Physical Layer Signals, Modulation, Multiplexing. Cartoon View 1 A Wave of Energy
 Outline 18-452/18-750 Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 3: Physical Layer Signals, Modulation, Multiplexing Peter Steenkiste Carnegie Mellon University Spring Semester 2017 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wirelesss17/
Outline 18-452/18-750 Wireless Networks and Applications Lecture 3: Physical Layer Signals, Modulation, Multiplexing Peter Steenkiste Carnegie Mellon University Spring Semester 2017 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wirelesss17/
EXPERIMENT 3 - Part I: DSB-SC Amplitude Modulation
 OBJECTIVE To generate DSB-SC amplitude modulated signal. EXPERIMENT 3 - Part I: DSB-SC Amplitude Modulation PRELIMINARY DISCUSSION In the modulation process, the message signal (the baseband voice, video,
OBJECTIVE To generate DSB-SC amplitude modulated signal. EXPERIMENT 3 - Part I: DSB-SC Amplitude Modulation PRELIMINARY DISCUSSION In the modulation process, the message signal (the baseband voice, video,
Chapter 5 AM Receivers
 Chapter 5 AM Receivers Prepared by Prof.V.K.Jain 1 Lecture outcome After studying this lecture, you should be able to: Describe the basic superheterodyne system Choose suitable intermediate frequencies
Chapter 5 AM Receivers Prepared by Prof.V.K.Jain 1 Lecture outcome After studying this lecture, you should be able to: Describe the basic superheterodyne system Choose suitable intermediate frequencies
Ques on (2): [18 Marks] a) Draw the atrial synchronous Pacemaker block diagram and explain its operation. Benha University June 2013
![Ques on (2): [18 Marks] a) Draw the atrial synchronous Pacemaker block diagram and explain its operation. Benha University June 2013 Ques on (2): [18 Marks] a) Draw the atrial synchronous Pacemaker block diagram and explain its operation. Benha University June 2013](/thumbs/87/96832478.jpg) Benha University June 2013 Benha Faculty of Engineering Electrical Department Hospital Instrumentations (E472) 4 Th year (control) Dr.Waleed Abdel Aziz Salem Time: 3 Hrs Answer the following questions.
Benha University June 2013 Benha Faculty of Engineering Electrical Department Hospital Instrumentations (E472) 4 Th year (control) Dr.Waleed Abdel Aziz Salem Time: 3 Hrs Answer the following questions.
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler Note Set #16 C-T Signals: Using FT Properties 1/12 Recall that FT Properties can be used for: 1. Expanding use of the FT table 2. Understanding real-world concepts
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler Note Set #16 C-T Signals: Using FT Properties 1/12 Recall that FT Properties can be used for: 1. Expanding use of the FT table 2. Understanding real-world concepts
ECEN620: Network Theory Broadband Circuit Design Fall 2014
 ECEN60: Network Theory Broadband Circuit Design Fall 014 Lecture 13: Frequency Synthesizer Examples Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Agenda Frequency Synthesizer Examples Design
ECEN60: Network Theory Broadband Circuit Design Fall 014 Lecture 13: Frequency Synthesizer Examples Sam Palermo Analog & Mixed-Signal Center Texas A&M University Agenda Frequency Synthesizer Examples Design
DESIGN OF OTA-C FILTER FOR BIOMEDICAL APPLICATIONS
 DESIGN OF OTA-C FILTER FOR BIOMEDICAL APPLICATIONS Sreedhar Bongani 1, Dvija Mounika Chirumamilla 2 1 (ECE, MCIS, MANIPAL UNIVERSITY, INDIA) 2 (ECE, K L University, INDIA) ABSTRACT-This paper presents
DESIGN OF OTA-C FILTER FOR BIOMEDICAL APPLICATIONS Sreedhar Bongani 1, Dvija Mounika Chirumamilla 2 1 (ECE, MCIS, MANIPAL UNIVERSITY, INDIA) 2 (ECE, K L University, INDIA) ABSTRACT-This paper presents
ELEN 701 RF & Microwave Systems Engineering. Lecture 2 September 27, 2006 Dr. Michael Thorburn Santa Clara University
 ELEN 701 RF & Microwave Systems Engineering Lecture 2 September 27, 2006 Dr. Michael Thorburn Santa Clara University Lecture 2 Radio Architecture and Design Considerations, Part I Architecture Superheterodyne
ELEN 701 RF & Microwave Systems Engineering Lecture 2 September 27, 2006 Dr. Michael Thorburn Santa Clara University Lecture 2 Radio Architecture and Design Considerations, Part I Architecture Superheterodyne
Medlab GmbH EG05000 User Manual. medlab. Five Lead ECG OEM board EG Technical Manual. Copyright Medlab Version Version 1.
 Medlab GmbH EG05000 User Manual medlab Five Lead ECG OEM board EG05000 Technical Manual Copyright Medlab 2016 1 Medlab GmbH EG05000 User Manual Medlab GmbH support@medlab.eu www.medlab.eu 2 Medlab GmbH
Medlab GmbH EG05000 User Manual medlab Five Lead ECG OEM board EG05000 Technical Manual Copyright Medlab 2016 1 Medlab GmbH EG05000 User Manual Medlab GmbH support@medlab.eu www.medlab.eu 2 Medlab GmbH
APPLICATION NOTE 3942 Optimize the Buffer Amplifier/ADC Connection
 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Communications Circuits > APP 3942 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > High-Speed Interconnect > APP 3942
Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > Communications Circuits > APP 3942 Maxim > Design Support > Technical Documents > Application Notes > High-Speed Interconnect > APP 3942
