Lecture 15: Introduction to Mixers
|
|
|
- Jesse Gordon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EECS 142 Lecture 15: Introduction to Mixers Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 15 p. 1/22
2 Mixers IF RF RF IF LO LO An ideal mixer is usually drawn with a multiplier symbol A real mixer cannot be driven by arbitrary inputs. Instead one port, the LO port, is driven by an local oscillator with a fixed amplitude sinusoid. In a down-conversion mixer, the other input port is driven by the RF signal, and the output is at a lower IF intermediate frequency In an up-coversion mixer, the other input is the IF signal and the output is the RF signal A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 15 p. 2/22
3 Frequency Translation down-conversion IF IF RF LO As shown above, an ideal mixer translates the modulation around one carrier to another. In a receiver, this is usually from a higher RF frequency to a lower IF frequency. In a transmitter, it s the inverse. We know that an LTI circuit cannot perform frequency translation. Mixers can be realized with either time-varying circuits or non-linear circuits A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 15 p. 3/22
4 Ideal Multiplier Suppose that the input of the mixer is the RF and LO signal v RF = A(t) cos (ω 0 t + φ(t)) v LO = A LO cos (ω L0 t) Recall the trigonometric identity cos(a + B) = cosacos B sin A sin B Applying the identity, we have v out = v RF v LO = A(t)A LO {cos φ (cos(ω LO + ω 0 )t + cos(ω LO ω 0 )t) 2 sin φ (sin(ω LO + ω 0 )t + sin(ω LO ω 0 )t)} A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 15 p. 4/22
5 Ideal Multiplier (cont) Grouping terms we have v out = A(t)A LO 2 {cos ((ω LO + ω 0 )t + φ(t)) + cos ((ω LO ω 0 )t + φ(t))} We see that the modulation is indeed translated to two new frequencies, LO + RF and LO RF. We usually select either the upper or lower sideband by filtering the output of the mixer high-pass or low-pass RF IF LO A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 15 p. 5/22
6 Mixer + Filter LO-RF RF LO LO+RF Note that the LO can be below the RF (lower side injection) or above the RF (high side injection) Also note that for a given LO, energy at LO ± IF is converted to the same IF frequency. This is a potential problem! A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 15 p. 6/22
7 Upper/Lower Injection and Image Example: Downconversion Mixer RF = 1GHz = 1000MHz IF = 100MHz Let s say we choose a low-side injection: LO = 900MHz That means that any signals or noise at 800MHz will also be downconverted to the same IF A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 15 p. 7/22
8 Receiver Application RF+IMAGE IF LNA LO The image frequency is the second frequency that also down-converts to the same IF. This is undesirable becuase the noise and interferance at the image frequency can potentially overwhelm the receiver. One solution is to filter the image band. This places a restriction on the selection of the IF frequency due to the required filter Q A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 15 p. 8/22
9 Image Rejection IMAGE REJECT RF+IMAGE IF LNA LO Suppose that RF = 1000MHz, and IF = 1MHz. Then the required filter bandwidth is much smaller than 2MHz to knock down the image. In general, the filter Q is given by Q = ω 0 BW = RF BW A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 15 p. 9/22
10 Image Reject Filter In our example, RF = 1000MHz, and IF = 1MHz. The Imagine is on 2IF = 2MHz away. Let s design a filter with f 0 = 1000MHz and f 1 = 1001MHz. A fifth-order Chebyshev filter with 0.2 db ripple is down about 80 db at the IF frequency. But the Q for such a filter is Q = 103 MHz 1MHz = 103 Such a filter requires components with Q > 10 3! A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 15 p. 10/22
11 RF Filtering IF 1 IF 2 LNA LO 1 LO 2 The fact that the required filter Q is so high is related to the problem of filtering interferers. The very reason we choose the superheterodyne architecture is to simplify the filtering problem. It s much easier to filter a fixed IF than filter a variable RF. The image filtering problem can be relaxed by using multi-if stages. Instead of moving to such a low IF where the image filtering is difficult (or expensive and bulky), we down-convert twice, using successively lower IF frequencies. A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 15 p. 11/22
12 Direct Conversion Receiver RF LO leakage IF=DC LNA LO=RF A mixer will frequency translate two frequencies, LO ± IF Why not simply down-convert directly to DC? Another words, why not pick a zero IF? This is the basis of the direct conversion architecture. There are some potential problems... A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 15 p. 12/22
13 Direction Conversion First, note that we must down-convert the desired signal and all the interfering signals. In other words, the LNA and mixer must be extremely linear. Since IF is at DC, all even order distortion now plagues the system, because the distortion at DC can easily swamp the desired signal. Furthermore, CMOS circuits produce a lot of flicker noise. Before we ignored this source of noise becuase it occurs at low frequency. Now it also competes with our signal. Another issue is with LO leakage. If any of the LO leaks into the RF path, then it will self-mix and produce a DC offset. The DC offset can rail the IF amplifier stages. A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 15 p. 13/22
14 Direct Conversion (cont) Example: If the IF amplifier has 80 db of gain, and the mixer has 10 db of gain, estimate the allowed LO leakage. Assume the ADC uses a 1V reference. To rail the output, we require a DC offset less than 10 4 V. If the LO power is 0 dbm (316mV), we require an input leakage voltage < 10 5 V, or an isolation better than 90 db! A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 15 p. 14/22
15 Phase of LO In a direction conversion system, the LO frequency is equal to the RF frequency. Consider an input voltage v(t) = A(t) cos(ω 0 t). Since the LO is generated locally, it s phase is random relative to the RF input: v LO = A LO cos(ω 0 t + φ 0 ) If we are so unlucky that φ 0 = 90, then the output of the mixer will be zero A(t)A LO sin(ω 0 t) cos(ω 0 t)dt T A(t)A LO T sin(ω 0 t) cos(ω 0 t)dt = 0 A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 15 p. 15/22
16 IQ-Mixer cos(ω LO t) I RF Q sin(ω LO t) To avoid this situation, we can phase lock the LO to the RF by transmitting a pilot tone. Alternatively, we can use two mixers As we shall see, there are other benefits to such a mixer. A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 15 p. 16/22
17 AM Modulation We can see that an upconversion mixer is a natural amplitude modulator If the input to the mixer is a baseband signal A(t), then the output is an AM carrier v o (t) = A(t) cos(ω LO t) How do we modulate the phase? A PLL is one way to do it. The IQ mixer is another way. Let s expand a sinusoid that has AM and PM v o (t) = A(t) cos(ω 0 t + φ(t)) = A(t) cosω 0 t cos φ(t) + A(t) sin ω 0 t sin φ(t) = I(t) cosω 0 t + Q(t) sin ω 0 t A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 15 p. 17/22
18 I-Q Plane Q φ I I(t) = A(t) cos φ(t) Q(t) = A(t) sin φ(t) We can draw a trajectory of points on the I-Q plane to represent different modulation schemes. The amplitude modulation is given by I 2 (t) + Q 2 (t) = A 2 (t)(cos 2 φ(t) + sin 2 φ(t)) = A 2 (t) A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 15 p. 18/22
19 General Modulator The phase modulation is given by Q(t) I(t) = sin φ(t) cosφ(t) = tanφ(t) or 1 Q(t) φ(t) = tan I(t) The IQ modulator is a universal digital modulator. We can draw a set of points in the IQ plane that represent symbols to transmit. For instance, if we transmit I = 0/A and Q = 0, then we have a simple ASK system (amplitude shift keying). A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 15 p. 19/22
20 Digital Modulation: BPSK/QPSK Q Q I I 11 For instance, if we transmit I(t) = ±1, this represents one bit transmission per cycle. But since the I and Q are orthogonal signals, we can improve the efficiency of transmission by also transmitting symbols on the Q axis. If we select four points on a circle to represent 2 bits of information, then we have a constant envelope modulation scheme. A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 15 p. 20/22
21 Modulation Waveforms The data wave form (left) is modulated onto a carrier (below). The first plot shows a simple on/off keying. The second plot shows binary phase shift keying on one channel (I) A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 15 p. 21/22
22 More Bits Per Cycle Q Q I I Eventually, the constellation points get very close together. Because of noise and distortion, the received spectrum will not lie exactly on the constellation points, but instead they will form a cluster around such points. If the clusters run into each other, errors will occur in the transmission. We can increase the radius but that requires more power. A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 15 p. 22/22
Real and Complex Modulation
 Real and Complex Modulation TIPL 4708 Presented by Matt Guibord Prepared by Matt Guibord 1 What is modulation? Modulation is the act of changing a carrier signal s properties (amplitude, phase, frequency)
Real and Complex Modulation TIPL 4708 Presented by Matt Guibord Prepared by Matt Guibord 1 What is modulation? Modulation is the act of changing a carrier signal s properties (amplitude, phase, frequency)
RF/IF Terminology and Specs
 RF/IF Terminology and Specs Contributors: Brad Brannon John Greichen Leo McHugh Eamon Nash Eberhard Brunner 1 Terminology LNA - Low-Noise Amplifier. A specialized amplifier to boost the very small received
RF/IF Terminology and Specs Contributors: Brad Brannon John Greichen Leo McHugh Eamon Nash Eberhard Brunner 1 Terminology LNA - Low-Noise Amplifier. A specialized amplifier to boost the very small received
Radio Receiver Architectures and Analysis
 Radio Receiver Architectures and Analysis Robert Wilson December 6, 01 Abstract This article discusses some common receiver architectures and analyzes some of the impairments that apply to each. 1 Contents
Radio Receiver Architectures and Analysis Robert Wilson December 6, 01 Abstract This article discusses some common receiver architectures and analyzes some of the impairments that apply to each. 1 Contents
Session 3. CMOS RF IC Design Principles
 Session 3 CMOS RF IC Design Principles Session Delivered by: D. Varun 1 Session Topics Standards RF wireless communications Multi standard RF transceivers RF front end architectures Frequency down conversion
Session 3 CMOS RF IC Design Principles Session Delivered by: D. Varun 1 Session Topics Standards RF wireless communications Multi standard RF transceivers RF front end architectures Frequency down conversion
Receiver Architecture
 Receiver Architecture Receiver basics Channel selection why not at RF? BPF first or LNA first? Direct digitization of RF signal Receiver architectures Sub-sampling receiver noise problem Heterodyne receiver
Receiver Architecture Receiver basics Channel selection why not at RF? BPF first or LNA first? Direct digitization of RF signal Receiver architectures Sub-sampling receiver noise problem Heterodyne receiver
Transceiver Architectures (III)
 Image-Reject Receivers Transceiver Architectures (III) Since the image and the signal lie on the two sides of the LO frequency, it is possible to architect the RX so that it can distinguish between the
Image-Reject Receivers Transceiver Architectures (III) Since the image and the signal lie on the two sides of the LO frequency, it is possible to architect the RX so that it can distinguish between the
INTRODUCTION TO TRANSCEIVER DESIGN ECE3103 ADVANCED TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 INTRODUCTION TO TRANSCEIVER DESIGN ECE3103 ADVANCED TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS FUNCTIONS OF A TRANSMITTER The basic functions of a transmitter are: a) up-conversion: move signal to desired RF carrier frequency.
INTRODUCTION TO TRANSCEIVER DESIGN ECE3103 ADVANCED TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS FUNCTIONS OF A TRANSMITTER The basic functions of a transmitter are: a) up-conversion: move signal to desired RF carrier frequency.
Lecture 20: Passive Mixers
 EECS 142 Lecture 20: Passive Mixers Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 20 p.
EECS 142 Lecture 20: Passive Mixers Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture 20 p.
4- Single Side Band (SSB)
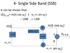 4- Single Side Band (SSB) It can be shown that: s(t) S.S.B = m(t) cos ω c t ± m h (t) sin ω c t -: USB ; +: LSB m(t) X m(t) cos ω c t -π/ cos ω c t -π/ + s S.S.B m h (t) X m h (t) ± sin ω c t 1 Tone Modulation:
4- Single Side Band (SSB) It can be shown that: s(t) S.S.B = m(t) cos ω c t ± m h (t) sin ω c t -: USB ; +: LSB m(t) X m(t) cos ω c t -π/ cos ω c t -π/ + s S.S.B m h (t) X m h (t) ± sin ω c t 1 Tone Modulation:
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal
 Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
Introduction to Amplitude Modulation
 1 Introduction to Amplitude Modulation Introduction to project management. Problem definition. Design principles and practices. Implementation techniques including circuit design, software design, solid
1 Introduction to Amplitude Modulation Introduction to project management. Problem definition. Design principles and practices. Implementation techniques including circuit design, software design, solid
Recap of Last 2 Classes
 Recap of Last 2 Classes Transmission Media Analog versus Digital Signals Bandwidth Considerations Attentuation, Delay Distortion and Noise Nyquist and Shannon Analog Modulation Digital Modulation What
Recap of Last 2 Classes Transmission Media Analog versus Digital Signals Bandwidth Considerations Attentuation, Delay Distortion and Noise Nyquist and Shannon Analog Modulation Digital Modulation What
Introduction to Receivers
 Introduction to Receivers Purpose: translate RF signals to baseband Shift frequency Amplify Filter Demodulate Why is this a challenge? Interference Large dynamic range required Many receivers must be capable
Introduction to Receivers Purpose: translate RF signals to baseband Shift frequency Amplify Filter Demodulate Why is this a challenge? Interference Large dynamic range required Many receivers must be capable
Receiver Architectures
 83080RA/1 Receiver Architectures Markku Renfors Tampere University of Technology Digital Media Institute/Telecommunications 83080RA/2 Topics 1. Main analog components for receivers - amplifiers - filters
83080RA/1 Receiver Architectures Markku Renfors Tampere University of Technology Digital Media Institute/Telecommunications 83080RA/2 Topics 1. Main analog components for receivers - amplifiers - filters
Radio Technology and Architectures. 1 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless L#1
 Radio Technology and Architectures 1 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless L#1 Radio (Architectures) Spectrum plan and legal issues Radio Architectures and components 2 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless
Radio Technology and Architectures 1 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless L#1 Radio (Architectures) Spectrum plan and legal issues Radio Architectures and components 2 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless
Radio Research Directions. Behzad Razavi Communication Circuits Laboratory Electrical Engineering Department University of California, Los Angeles
 Radio Research Directions Behzad Razavi Communication Circuits Laboratory Electrical Engineering Department University of California, Los Angeles Outline Introduction Millimeter-Wave Transceivers - Applications
Radio Research Directions Behzad Razavi Communication Circuits Laboratory Electrical Engineering Department University of California, Los Angeles Outline Introduction Millimeter-Wave Transceivers - Applications
C. Mixers. frequencies? limit? specifications? Perhaps the most important component of any receiver is the mixer a non-linear microwave device.
 9/13/2007 Mixers notes 1/1 C. Mixers Perhaps the most important component of any receiver is the mixer a non-linear microwave device. HO: Mixers Q: How efficient is a typical mixer at creating signals
9/13/2007 Mixers notes 1/1 C. Mixers Perhaps the most important component of any receiver is the mixer a non-linear microwave device. HO: Mixers Q: How efficient is a typical mixer at creating signals
6.976 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 20 Performance Measures of Wireless Communication
 6.976 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 20 Performance Measures of Wireless Communication Michael Perrott Massachusetts Institute of Technology Copyright 2003 by Michael H. Perrott
6.976 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Lecture 20 Performance Measures of Wireless Communication Michael Perrott Massachusetts Institute of Technology Copyright 2003 by Michael H. Perrott
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II
 EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
Efficiently simulating a direct-conversion I-Q modulator
 Efficiently simulating a direct-conversion I-Q modulator Andy Howard Applications Engineer Agilent Eesof EDA Overview An I-Q or vector modulator is a commonly used integrated circuit in communication systems.
Efficiently simulating a direct-conversion I-Q modulator Andy Howard Applications Engineer Agilent Eesof EDA Overview An I-Q or vector modulator is a commonly used integrated circuit in communication systems.
EECS 242: Receiver Architectures
 : Receiver Architectures Outline Complex baseband equivalent of a bandpass signal Double-conversion single-quadrature (Superheterodyne) Direct-conversion (Single-conversion single-quad, homodyne, zero-)
: Receiver Architectures Outline Complex baseband equivalent of a bandpass signal Double-conversion single-quadrature (Superheterodyne) Direct-conversion (Single-conversion single-quad, homodyne, zero-)
Transceiver Architectures
 + Transceiver Architectures Outline Heterodyne Receivers! Problem of Image! Mixing Spurs! Sliding-IF RX Direct-Conversion Receivers! LO Leakage and Offsets! Even-Order Nonlinearity! I/Q Mismatch Image-Reject
+ Transceiver Architectures Outline Heterodyne Receivers! Problem of Image! Mixing Spurs! Sliding-IF RX Direct-Conversion Receivers! LO Leakage and Offsets! Even-Order Nonlinearity! I/Q Mismatch Image-Reject
Problems from the 3 rd edition
 (2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
(2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
Direct-Conversion I-Q Modulator Simulation by Andy Howard, Applications Engineer Agilent EEsof EDA
 Direct-Conversion I-Q Modulator Simulation by Andy Howard, Applications Engineer Agilent EEsof EDA Introduction This article covers an Agilent EEsof ADS example that shows the simulation of a directconversion,
Direct-Conversion I-Q Modulator Simulation by Andy Howard, Applications Engineer Agilent EEsof EDA Introduction This article covers an Agilent EEsof ADS example that shows the simulation of a directconversion,
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation. Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY RX Nonlinearity Issues: 2.2, 2.4 Demodulation: not in the book 2 RX nonlinearities System Nonlinearity
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY RX Nonlinearity Issues: 2.2, 2.4 Demodulation: not in the book 2 RX nonlinearities System Nonlinearity
Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier
 Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier and the first channel. The modulation of the main carrier
Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier and the first channel. The modulation of the main carrier
Modulation (7): Constellation Diagrams
 Modulation (7): Constellation Diagrams Luiz DaSilva Professor of Telecommunications dasilval@tcd.ie +353-1-8963660 Adapted from material by Dr Nicola Marchetti Geometric representation of modulation signal
Modulation (7): Constellation Diagrams Luiz DaSilva Professor of Telecommunications dasilval@tcd.ie +353-1-8963660 Adapted from material by Dr Nicola Marchetti Geometric representation of modulation signal
Berkeley. Mixers: An Overview. Prof. Ali M. Niknejad. U.C. Berkeley Copyright c 2014 by Ali M. Niknejad
 Berkeley Mixers: An Overview Prof. Ali M. U.C. Berkeley Copyright c 2014 by Ali M. Mixers Information PSD Mixer f c The Mixer is a critical component in communication circuits. It translates information
Berkeley Mixers: An Overview Prof. Ali M. U.C. Berkeley Copyright c 2014 by Ali M. Mixers Information PSD Mixer f c The Mixer is a critical component in communication circuits. It translates information
Making Noise in RF Receivers Simulate Real-World Signals with Signal Generators
 Making Noise in RF Receivers Simulate Real-World Signals with Signal Generators Noise is an unwanted signal. In communication systems, noise affects both transmitter and receiver performance. It degrades
Making Noise in RF Receivers Simulate Real-World Signals with Signal Generators Noise is an unwanted signal. In communication systems, noise affects both transmitter and receiver performance. It degrades
Lecture 17: BJT/FET Mixers/Mixer Noise
 EECS 142 Lecture 17: BJT/FET Mixers/Mixer Noise Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture
EECS 142 Lecture 17: BJT/FET Mixers/Mixer Noise Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture
Superheterodyne Receiver Tutorial
 1 of 6 Superheterodyne Receiver Tutorial J P Silver E-mail: john@rfic.co.uk 1 ABSTRACT This paper discusses the basic design concepts of the Superheterodyne receiver in both single and double conversion
1 of 6 Superheterodyne Receiver Tutorial J P Silver E-mail: john@rfic.co.uk 1 ABSTRACT This paper discusses the basic design concepts of the Superheterodyne receiver in both single and double conversion
QUICK START GUIDE FOR DEMONSTRATION CIRCUIT 678A 40MHZ TO 900MHZ DIRECT CONVERSION QUADRATURE DEMODULATOR
 DESCRIPTION QUICK START GUIDE FOR DEMONSTRATION CIRCUIT 678A LT5517 Demonstration circuit 678A is a 40MHz to 900MHz Direct Conversion Quadrature Demodulator featuring the LT5517. The LT 5517 is a direct
DESCRIPTION QUICK START GUIDE FOR DEMONSTRATION CIRCUIT 678A LT5517 Demonstration circuit 678A is a 40MHz to 900MHz Direct Conversion Quadrature Demodulator featuring the LT5517. The LT 5517 is a direct
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation. Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY 2 RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation RX nonlinearities (parts of 2.2) System Nonlinearity Sensitivity
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 8: RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY 2 RX Nonlinearity Issues, Demodulation RX nonlinearities (parts of 2.2) System Nonlinearity Sensitivity
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
Wideband Receiver for Communications Receiver or Spectrum Analysis Usage: A Comparison of Superheterodyne to Quadrature Down Conversion
 A Comparison of Superheterodyne to Quadrature Down Conversion Tony Manicone, Vanteon Corporation There are many different system architectures which can be used in the design of High Frequency wideband
A Comparison of Superheterodyne to Quadrature Down Conversion Tony Manicone, Vanteon Corporation There are many different system architectures which can be used in the design of High Frequency wideband
RFID Systems: Radio Architecture
 RFID Systems: Radio Architecture 1 A discussion of radio architecture and RFID. What are the critical pieces? Familiarity with how radio and especially RFID radios are designed will allow you to make correct
RFID Systems: Radio Architecture 1 A discussion of radio architecture and RFID. What are the critical pieces? Familiarity with how radio and especially RFID radios are designed will allow you to make correct
HY448 Sample Problems
 HY448 Sample Problems 10 November 2014 These sample problems include the material in the lectures and the guided lab exercises. 1 Part 1 1.1 Combining logarithmic quantities A carrier signal with power
HY448 Sample Problems 10 November 2014 These sample problems include the material in the lectures and the guided lab exercises. 1 Part 1 1.1 Combining logarithmic quantities A carrier signal with power
Gain Lab. Image interference during downconversion. Images in Downconversion. Course ECE 684: Microwave Metrology. Lecture Gain and TRL labs
 Gain Lab Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Massachusetts, Amherst Course ECE 684: Microwave Metrology Lecture Gain and TRL labs In lab we will be constructing a downconverter.
Gain Lab Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Massachusetts, Amherst Course ECE 684: Microwave Metrology Lecture Gain and TRL labs In lab we will be constructing a downconverter.
TSEK38 Radio Frequency Transceiver Design: Project work B
 TSEK38 Project Work: Task specification A 1(15) TSEK38 Radio Frequency Transceiver Design: Project work B Course home page: Course responsible: http://www.isy.liu.se/en/edu/kurs/tsek38/ Ted Johansson (ted.johansson@liu.se)
TSEK38 Project Work: Task specification A 1(15) TSEK38 Radio Frequency Transceiver Design: Project work B Course home page: Course responsible: http://www.isy.liu.se/en/edu/kurs/tsek38/ Ted Johansson (ted.johansson@liu.se)
SSB0260A Single Sideband Mixer GHz
 Single Sideband Mixer.2 6. GHz FEATURES LO/RF Frequency: Input IP3: Sideband Suppression: LO Leakage: LO Power: DC Power:.2 6. GHz +32 dbm -45 dbc (Typical) -5 dbm (Typical) -1 to +1 dbm +5V @ 5 ma DESCRIPTION
Single Sideband Mixer.2 6. GHz FEATURES LO/RF Frequency: Input IP3: Sideband Suppression: LO Leakage: LO Power: DC Power:.2 6. GHz +32 dbm -45 dbc (Typical) -5 dbm (Typical) -1 to +1 dbm +5V @ 5 ma DESCRIPTION
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the
 Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering)
 Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
Lab course Analog Part of a State-of-the-Art Mobile Radio Receiver
 Communication Technology Laboratory Wireless Communications Group Prof. Dr. A. Wittneben ETH Zurich, ETF, Sternwartstrasse 7, 8092 Zurich Tel 41 44 632 36 11 Fax 41 44 632 12 09 Lab course Analog Part
Communication Technology Laboratory Wireless Communications Group Prof. Dr. A. Wittneben ETH Zurich, ETF, Sternwartstrasse 7, 8092 Zurich Tel 41 44 632 36 11 Fax 41 44 632 12 09 Lab course Analog Part
EE133 - Prelab 1 Amplitude Modulation and Demodulation
 Prelab 1 - AM Modulation - Prof. Dutton - EE133 Winter 2004 1 EE133 - Prelab 1 Amplitude Modulation and Demodulation 1 Introduction This week we will be taking a look at the amplitude modulation (AM) scheme.
Prelab 1 - AM Modulation - Prof. Dutton - EE133 Winter 2004 1 EE133 - Prelab 1 Amplitude Modulation and Demodulation 1 Introduction This week we will be taking a look at the amplitude modulation (AM) scheme.
Third-Method Narrowband Direct Upconverter for the LF / MF Bands
 Third-Method Narrowband Direct Upconverter for the LF / MF Bands Introduction Andy Talbot G4JNT February 2016 Previous designs for upconverters from audio generated from a soundcard to RF have been published
Third-Method Narrowband Direct Upconverter for the LF / MF Bands Introduction Andy Talbot G4JNT February 2016 Previous designs for upconverters from audio generated from a soundcard to RF have been published
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS-II (In continuation with Part-I)
 MODULATING A SIGNAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS-II (In continuation with Part-I) TRANSMITTING SIGNALS : In order to transmit the original low frequency baseband message efficiently over long distances, the signal
MODULATING A SIGNAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS-II (In continuation with Part-I) TRANSMITTING SIGNALS : In order to transmit the original low frequency baseband message efficiently over long distances, the signal
The Digital Linear Amplifier
 The Digital Linear Amplifier By Timothy P. Hulick, Ph.D. 886 Brandon Lane Schwenksville, PA 19473 e-mail: dxyiwta@aol.com Abstract. This paper is the second of two presenting a modern approach to Digital
The Digital Linear Amplifier By Timothy P. Hulick, Ph.D. 886 Brandon Lane Schwenksville, PA 19473 e-mail: dxyiwta@aol.com Abstract. This paper is the second of two presenting a modern approach to Digital
ADI 2006 RF Seminar. Chapter II RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers
 ADI 2006 RF Seminar Chapter II RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers 1 RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers Fixed Gain and Variable Gain Amplifiers IQ Demodulators Analog-to-Digital
ADI 2006 RF Seminar Chapter II RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers 1 RF/IF Components and Specifications for Receivers Fixed Gain and Variable Gain Amplifiers IQ Demodulators Analog-to-Digital
Transmitters: System Level Specifications
 Berkeley Transmitters: System Level Specifications Prof. Ali M. Niknejad U.C. Berkeley Copyright c 2016 by Ali M. Niknejad 1 / 65 Simple Transmitter Block Diagram DAC PA Transmit Chain Diplexer PLL VCO
Berkeley Transmitters: System Level Specifications Prof. Ali M. Niknejad U.C. Berkeley Copyright c 2016 by Ali M. Niknejad 1 / 65 Simple Transmitter Block Diagram DAC PA Transmit Chain Diplexer PLL VCO
Technical Article A DIRECT QUADRATURE MODULATOR IC FOR 0.9 TO 2.5 GHZ WIRELESS SYSTEMS
 Introduction As wireless system designs have moved from carrier frequencies at approximately 9 MHz to wider bandwidth applications like Personal Communication System (PCS) phones at 1.8 GHz and wireless
Introduction As wireless system designs have moved from carrier frequencies at approximately 9 MHz to wider bandwidth applications like Personal Communication System (PCS) phones at 1.8 GHz and wireless
Digital Signal Analysis
 Digital Signal Analysis Objectives - Provide a digital modulation overview - Review common digital radio impairments Digital Modulation Overview Signal Characteristics to Modify Polar Display / IQ Relationship
Digital Signal Analysis Objectives - Provide a digital modulation overview - Review common digital radio impairments Digital Modulation Overview Signal Characteristics to Modify Polar Display / IQ Relationship
Vestigial Sideband Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #11, April 7, Prof. Young-Chai Ko
 Vestigial Sideband Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #11, April 7, 2011 Prof. Young-Chai Ko koyc@korea.ac.kr Summary Vestigial sideband modulation Baseband representation of modulated wave
Vestigial Sideband Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #11, April 7, 2011 Prof. Young-Chai Ko koyc@korea.ac.kr Summary Vestigial sideband modulation Baseband representation of modulated wave
PTX-0350 RF UPCONVERTER, MHz
 PTX-0350 RF UPCONVERTER, 300 5000 MHz OPERATING MODES I/Q upconverter RF = LO + IF upconverter RF = LO - IF upconverter Synthesizer 10 MHz REFERENCE INPUT/OUTPUT EXTERNAL LOCAL OSCILLATOR INPUT I/Q BASEBAND
PTX-0350 RF UPCONVERTER, 300 5000 MHz OPERATING MODES I/Q upconverter RF = LO + IF upconverter RF = LO - IF upconverter Synthesizer 10 MHz REFERENCE INPUT/OUTPUT EXTERNAL LOCAL OSCILLATOR INPUT I/Q BASEBAND
TSEK03: Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Lecture 5-6: Mixers
 TSEK03: Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Lecture 5-6: Mixers Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY ted.johansson@liu.se Overview 2 Razavi: Chapter 6.1-6.3, pp. 343-398. Lee: Chapter 13. 6.1 Mixers general
TSEK03: Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Lecture 5-6: Mixers Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY ted.johansson@liu.se Overview 2 Razavi: Chapter 6.1-6.3, pp. 343-398. Lee: Chapter 13. 6.1 Mixers general
Low Cost Mixer for the 10.7 to 12.8 GHz Direct Broadcast Satellite Market
 Low Cost Mixer for the.7 to 12.8 GHz Direct Broadcast Satellite Market Application Note 1136 Introduction The wide bandwidth requirement in DBS satellite applications places a big performance demand on
Low Cost Mixer for the.7 to 12.8 GHz Direct Broadcast Satellite Market Application Note 1136 Introduction The wide bandwidth requirement in DBS satellite applications places a big performance demand on
ADI 2006 RF Seminar. Chapter VI A Detailed Look at Wireless Signal Chain Architectures
 DI 2006 R Seminar Chapter VI Detailed Look at Wireless Chain rchitectures 1 Receiver rchitectures Receivers are designed to detect and demodulate the desired signal and remove unwanted blockers Receiver
DI 2006 R Seminar Chapter VI Detailed Look at Wireless Chain rchitectures 1 Receiver rchitectures Receivers are designed to detect and demodulate the desired signal and remove unwanted blockers Receiver
Problem Sheet for Amplitude Modulation
 Problem heet for Amplitude Modulation Q1: For the sinusoidaly modulated DB/LC waveform shown in Fig. below. a Find the modulation index. b ketch a line spectrum. c Calculated the ratio of average power
Problem heet for Amplitude Modulation Q1: For the sinusoidaly modulated DB/LC waveform shown in Fig. below. a Find the modulation index. b ketch a line spectrum. c Calculated the ratio of average power
ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory Amplitude Modulation (AM)
 ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory 1 ---- Amplitude Modulation (AM) 1. Objectives 1.1 Through this the laboratory experiment, you will investigate demodulation of an amplitude modulated (AM)
ELEC3242 Communications Engineering Laboratory 1 ---- Amplitude Modulation (AM) 1. Objectives 1.1 Through this the laboratory experiment, you will investigate demodulation of an amplitude modulated (AM)
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY 2 Basic Definitions Time and Frequency db conversion Power and dbm Filter Basics 3 Filter Filter is a component with frequency
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY 2 Basic Definitions Time and Frequency db conversion Power and dbm Filter Basics 3 Filter Filter is a component with frequency
1 Local oscillator requirements
 978-0-51-86315-5 - Integrated Frequency Synthesizers for Wireless Systems 1 Local oscillator requirements 1 Personal ireless communications have represented, for the microelectronic industry, the market
978-0-51-86315-5 - Integrated Frequency Synthesizers for Wireless Systems 1 Local oscillator requirements 1 Personal ireless communications have represented, for the microelectronic industry, the market
Radio-Frequency Conversion and Synthesis (for a 115mW GPS Receiver)
 Radio-Frequency Conversion and Synthesis (for a 115mW GPS Receiver) Arvin Shahani Stanford University Overview GPS Overview Frequency Conversion Frequency Synthesis Conclusion GPS Overview: Signal Structure
Radio-Frequency Conversion and Synthesis (for a 115mW GPS Receiver) Arvin Shahani Stanford University Overview GPS Overview Frequency Conversion Frequency Synthesis Conclusion GPS Overview: Signal Structure
TECH BRIEF Addressing Phase Noise Challenges in Radar and Communication Systems
 Addressing Phase Noise Challenges in Radar and Communication Systems Phase noise is rapidly becoming the most critical factor addressed in sophisticated radar and communication systems. This is because
Addressing Phase Noise Challenges in Radar and Communication Systems Phase noise is rapidly becoming the most critical factor addressed in sophisticated radar and communication systems. This is because
Other Effects in PLLs. Behzad Razavi Electrical Engineering Department University of California, Los Angeles
 Other Effects in PLLs Behzad Razavi Electrical Engineering Department University of California, Los Angeles Example of Up and Down Skew and Width Mismatch Approximating the pulses on the control line by
Other Effects in PLLs Behzad Razavi Electrical Engineering Department University of California, Los Angeles Example of Up and Down Skew and Width Mismatch Approximating the pulses on the control line by
Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits. Module 7
 Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits Module 7 Radio Block Diagrams Radio Circuits can be shown as functional blocks connected together. Knowing the description of common
Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits Module 7 Radio Block Diagrams Radio Circuits can be shown as functional blocks connected together. Knowing the description of common
Revision of Lecture 2
 Revision of Lecture 2 Pulse shaping Tx/Rx filter pair Design of Tx/Rx filters (pulse shaping): to achieve zero ISI and to maximise received signal to noise ratio Combined Tx/Rx filters: Nyquist system
Revision of Lecture 2 Pulse shaping Tx/Rx filter pair Design of Tx/Rx filters (pulse shaping): to achieve zero ISI and to maximise received signal to noise ratio Combined Tx/Rx filters: Nyquist system
Understanding IP2 and IP3 Issues in Direct Conversion Receivers for WCDMA Wide Area Basestations
 L DESIGN FEATURES Understanding I and I3 Issues in Direct Conversion Receivers for Wide Area Basestations Introduction A direct conversion receiver architecture offers several advantages over the traditional
L DESIGN FEATURES Understanding I and I3 Issues in Direct Conversion Receivers for Wide Area Basestations Introduction A direct conversion receiver architecture offers several advantages over the traditional
ECE513 RF Design for Wireless
 1 ECE513 RF Design for Wireless MODULE 1 RF Systems LECTURE 1 Modulation Techniques Chapter 1, Sections 1.1 1.3 Professor Michael Steer http://www4.ncsu.edu/~mbs 2 Module 1: RF Systems Amplifiers, Mixers
1 ECE513 RF Design for Wireless MODULE 1 RF Systems LECTURE 1 Modulation Techniques Chapter 1, Sections 1.1 1.3 Professor Michael Steer http://www4.ncsu.edu/~mbs 2 Module 1: RF Systems Amplifiers, Mixers
ELT Receiver Architectures and Signal Processing Exam Requirements and Model Questions 2018
 TUT/ICE 1 ELT-44006 Receiver Architectures and Signal Processing Exam Requirements and Model Questions 2018 General idea of these Model Questions is to highlight the central knowledge expected to be known
TUT/ICE 1 ELT-44006 Receiver Architectures and Signal Processing Exam Requirements and Model Questions 2018 General idea of these Model Questions is to highlight the central knowledge expected to be known
Outline. Communications Engineering 1
 Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Lecture 6. Angle Modulation and Demodulation
 Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
I-Q transmission. Lecture 17
 I-Q Transmission Lecture 7 I-Q transmission i Sending Digital Data Binary Phase Shift Keying (BPSK): sending binary data over a single frequency band Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK): sending twice
I-Q Transmission Lecture 7 I-Q transmission i Sending Digital Data Binary Phase Shift Keying (BPSK): sending binary data over a single frequency band Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (QPSK): sending twice
6.101 Project Proposal April 9, 2014 Kayla Esquivel and Jason Yang. General Outline
 6.101 Project Proposal April 9, 2014 Kayla Esquivel and Jason Yang General Outline We will build a superheterodyne AM Radio Receiver circuit that will have a bandwidth of the entire AM spectrum, and whose
6.101 Project Proposal April 9, 2014 Kayla Esquivel and Jason Yang General Outline We will build a superheterodyne AM Radio Receiver circuit that will have a bandwidth of the entire AM spectrum, and whose
SmartSpice RF Harmonic Balance Based and Shooting Method Based RF Simulation
 SmartSpice RF Harmonic Balance Based and Shooting Method Based RF Simulation Silvaco Overview SSRF Attributes Harmonic balance approach to solve system of equations in frequency domain Well suited for
SmartSpice RF Harmonic Balance Based and Shooting Method Based RF Simulation Silvaco Overview SSRF Attributes Harmonic balance approach to solve system of equations in frequency domain Well suited for
Lecture 12. Carrier Phase Synchronization. EE4900/EE6720 Digital Communications
 EE49/EE6720: Digital Communications 1 Lecture 12 Carrier Phase Synchronization Block Diagrams of Communication System Digital Communication System 2 Informatio n (sound, video, text, data, ) Transducer
EE49/EE6720: Digital Communications 1 Lecture 12 Carrier Phase Synchronization Block Diagrams of Communication System Digital Communication System 2 Informatio n (sound, video, text, data, ) Transducer
Termination Insensitive Mixers By Howard Hausman President/CEO, MITEQ, Inc. 100 Davids Drive Hauppauge, NY
 Termination Insensitive Mixers By Howard Hausman President/CEO, MITEQ, Inc. 100 Davids Drive Hauppauge, NY 11788 hhausman@miteq.com Abstract Microwave mixers are non-linear devices that are used to translate
Termination Insensitive Mixers By Howard Hausman President/CEO, MITEQ, Inc. 100 Davids Drive Hauppauge, NY 11788 hhausman@miteq.com Abstract Microwave mixers are non-linear devices that are used to translate
A 900MHz / 1.8GHz CMOS Receiver for Dual Band Applications*
 FA 8.2: S. Wu, B. Razavi A 900MHz / 1.8GHz CMOS Receiver for Dual Band Applications* University of California, Los Angeles, CA This dual-band CMOS receiver for GSM and DCS1800 applications incorporates
FA 8.2: S. Wu, B. Razavi A 900MHz / 1.8GHz CMOS Receiver for Dual Band Applications* University of California, Los Angeles, CA This dual-band CMOS receiver for GSM and DCS1800 applications incorporates
Designing a 960 MHz CMOS LNA and Mixer using ADS. EE 5390 RFIC Design Michelle Montoya Alfredo Perez. April 15, 2004
 Designing a 960 MHz CMOS LNA and Mixer using ADS EE 5390 RFIC Design Michelle Montoya Alfredo Perez April 15, 2004 The University of Texas at El Paso Dr Tim S. Yao ABSTRACT Two circuits satisfying the
Designing a 960 MHz CMOS LNA and Mixer using ADS EE 5390 RFIC Design Michelle Montoya Alfredo Perez April 15, 2004 The University of Texas at El Paso Dr Tim S. Yao ABSTRACT Two circuits satisfying the
AM Limitations. Amplitude Modulation II. DSB-SC Modulation. AM Modifications
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
TestData Summary of 5.2GHz WLAN Direct Conversion RF Transceiver Board
 Page 1 of 16 ========================================================================================= TestData Summary of 5.2GHz WLAN Direct Conversion RF Transceiver Board =========================================================================================
Page 1 of 16 ========================================================================================= TestData Summary of 5.2GHz WLAN Direct Conversion RF Transceiver Board =========================================================================================
1 MHz 6 GHz RF Mixer with built in PLL Synthesizer
 Windfreak Technologies Preliminary Data Sheet v0.1a MixNV Active Mixer v1.4a $499.00US 1 MHz 6 GHz RF Mixer with built in PLL Synthesizer Features Open source Labveiw GUI software control via USB Run hardware
Windfreak Technologies Preliminary Data Sheet v0.1a MixNV Active Mixer v1.4a $499.00US 1 MHz 6 GHz RF Mixer with built in PLL Synthesizer Features Open source Labveiw GUI software control via USB Run hardware
Quadrature Upconverter for Optical Comms subcarrier generation
 Quadrature Upconverter for Optical Comms subcarrier generation Andy Talbot G4JNT 2011-07-27 Basic Design Overview This source is designed for upconverting a baseband I/Q source such as from SDR transmitter
Quadrature Upconverter for Optical Comms subcarrier generation Andy Talbot G4JNT 2011-07-27 Basic Design Overview This source is designed for upconverting a baseband I/Q source such as from SDR transmitter
Self Calibrated Image Reject Mixer
 Self Calibrated Image Reject Mixer Project name: Self Calibrated Image Reject Mixer. Design number: 6313. Design password: Student names: Mostafa Elmala. Area: mm X mm. Technology: Technology is SCN4ME_SUBM,
Self Calibrated Image Reject Mixer Project name: Self Calibrated Image Reject Mixer. Design number: 6313. Design password: Student names: Mostafa Elmala. Area: mm X mm. Technology: Technology is SCN4ME_SUBM,
Microwave Metrology -ECE 684 Spring Lab Exercise I&Q.v3: I&Q Time and Frequency Domain Measurements
 Lab Exercise I&Q.v3: I&Q Time and Frequency Domain Measurements In this lab exercise you will perform measurements both in time and in frequency to establish the relationship between these two dimension
Lab Exercise I&Q.v3: I&Q Time and Frequency Domain Measurements In this lab exercise you will perform measurements both in time and in frequency to establish the relationship between these two dimension
Amplitude Modulation II
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
General configuration
 Transmitter General configuration In some cases the modulator operates directly at the transmission frequency (no up conversion required) In digital transmitters, the information is represented by the
Transmitter General configuration In some cases the modulator operates directly at the transmission frequency (no up conversion required) In digital transmitters, the information is represented by the
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.976 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Spring 2003 Homework #4: Narrowband LNA s and Mixers
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.976 High Speed Communication Circuits and Systems Spring 2003 Homework #4: Narrowband LNA s and Mixers
Implementation of Digital Signal Processing: Some Background on GFSK Modulation
 Implementation of Digital Signal Processing: Some Background on GFSK Modulation Sabih H. Gerez University of Twente, Department of Electrical Engineering s.h.gerez@utwente.nl Version 5 (March 9, 2016)
Implementation of Digital Signal Processing: Some Background on GFSK Modulation Sabih H. Gerez University of Twente, Department of Electrical Engineering s.h.gerez@utwente.nl Version 5 (March 9, 2016)
Master Degree in Electronic Engineering
 Master Degree in Electronic Engineering Analog and telecommunication electronic course (ATLCE-01NWM) Miniproject: Baseband signal transmission techniques Name: LI. XINRUI E-mail: s219989@studenti.polito.it
Master Degree in Electronic Engineering Analog and telecommunication electronic course (ATLCE-01NWM) Miniproject: Baseband signal transmission techniques Name: LI. XINRUI E-mail: s219989@studenti.polito.it
Chapter 4. Part 2(a) Digital Modulation Techniques
 Chapter 4 Part 2(a) Digital Modulation Techniques Overview Digital Modulation techniques Bandpass data transmission Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) Phase Shift Keying (PSK) Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) Quadrature
Chapter 4 Part 2(a) Digital Modulation Techniques Overview Digital Modulation techniques Bandpass data transmission Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) Phase Shift Keying (PSK) Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) Quadrature
Analog Devices Welcomes Hittite Microwave Corporation NO CONTENT ON THE ATTACHED DOCUMENT HAS CHANGED
 Analog Devices Welcomes Hittite Microwave Corporation NO CONTENT ON THE ATTACHED DOCUMENT HAS CHANGED www.analog.com www.hittite.com THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK v01.05.00 HMC141/142 MIXER OPERATION
Analog Devices Welcomes Hittite Microwave Corporation NO CONTENT ON THE ATTACHED DOCUMENT HAS CHANGED www.analog.com www.hittite.com THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK v01.05.00 HMC141/142 MIXER OPERATION
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY An Overview of Modulation Techniques: chapter 3.1 3.3.1 2 Introduction (3.1) Analog Modulation Amplitude Modulation Phase and
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY An Overview of Modulation Techniques: chapter 3.1 3.3.1 2 Introduction (3.1) Analog Modulation Amplitude Modulation Phase and
Design of S-Band Double-Conversion Superheterodyne Receiver Front-End for RADAR Systems
 Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Electronics and Radar Technology 2015, Volume 1, Issue 1, pp. 32-37, Article ID Tech-425 Short Communication Open Access Design of S-Band Double-Conversion
Cloud Publications International Journal of Advanced Electronics and Radar Technology 2015, Volume 1, Issue 1, pp. 32-37, Article ID Tech-425 Short Communication Open Access Design of S-Band Double-Conversion
ELEN 701 RF & Microwave Systems Engineering. Lecture 2 September 27, 2006 Dr. Michael Thorburn Santa Clara University
 ELEN 701 RF & Microwave Systems Engineering Lecture 2 September 27, 2006 Dr. Michael Thorburn Santa Clara University Lecture 2 Radio Architecture and Design Considerations, Part I Architecture Superheterodyne
ELEN 701 RF & Microwave Systems Engineering Lecture 2 September 27, 2006 Dr. Michael Thorburn Santa Clara University Lecture 2 Radio Architecture and Design Considerations, Part I Architecture Superheterodyne
Chapter 1: Introduction. EET-223: RF Communication Circuits Walter Lara
 Chapter 1: Introduction EET-223: RF Communication Circuits Walter Lara Introduction Electronic communication involves transmission over medium from source to destination Information can contain voice,
Chapter 1: Introduction EET-223: RF Communication Circuits Walter Lara Introduction Electronic communication involves transmission over medium from source to destination Information can contain voice,
Reflection EVM Impairments in Wideband 60GHz and E band designs
 Reflection EVM Impairments in Wideband 60GHz and E band designs Dror Regev About Presto Engineering Leader in Integrated Test & Product Engineering and Back-end Production services Service hubs in USA,
Reflection EVM Impairments in Wideband 60GHz and E band designs Dror Regev About Presto Engineering Leader in Integrated Test & Product Engineering and Back-end Production services Service hubs in USA,
TSEK38: Radio Frequency Transceiver Design Lecture 3: Superheterodyne TRX design
 TSEK38: Radio Frequency Transceiver Design Lecture 3: Superheterodyne TRX design Ted Johansson, ISY ted.johansson@liu.se 2 Outline of lecture 3 Introduction RF TRX architectures (3) Superheterodyne architecture
TSEK38: Radio Frequency Transceiver Design Lecture 3: Superheterodyne TRX design Ted Johansson, ISY ted.johansson@liu.se 2 Outline of lecture 3 Introduction RF TRX architectures (3) Superheterodyne architecture
Understanding Low Phase Noise Signals. Presented by: Riadh Said Agilent Technologies, Inc.
 Understanding Low Phase Noise Signals Presented by: Riadh Said Agilent Technologies, Inc. Introduction Instabilities in the frequency or phase of a signal are caused by a number of different effects. Each
Understanding Low Phase Noise Signals Presented by: Riadh Said Agilent Technologies, Inc. Introduction Instabilities in the frequency or phase of a signal are caused by a number of different effects. Each
SmartSpice RF Harmonic Balance Based RF Simulator. Advanced RF Circuit Simulation
 SmartSpice RF Harmonic Balance Based RF Simulator Advanced RF Circuit Simulation SmartSpice RF Overview Uses harmonic balance approach to solve system equations in frequency domain Well suited for RF and
SmartSpice RF Harmonic Balance Based RF Simulator Advanced RF Circuit Simulation SmartSpice RF Overview Uses harmonic balance approach to solve system equations in frequency domain Well suited for RF and
Digital Low Level RF for SESAME
 Technical Sector Synchrotron-light for Experimental Science And Applications in the Middle East Subject : RF More specified area: Digital Low Level RF Date: 6/23/2010 Total Number of Pages: 11 Document
Technical Sector Synchrotron-light for Experimental Science And Applications in the Middle East Subject : RF More specified area: Digital Low Level RF Date: 6/23/2010 Total Number of Pages: 11 Document
Local Oscillator Phase Noise and its effect on Receiver Performance C. John Grebenkemper
 Watkins-Johnson Company Tech-notes Copyright 1981 Watkins-Johnson Company Vol. 8 No. 6 November/December 1981 Local Oscillator Phase Noise and its effect on Receiver Performance C. John Grebenkemper All
Watkins-Johnson Company Tech-notes Copyright 1981 Watkins-Johnson Company Vol. 8 No. 6 November/December 1981 Local Oscillator Phase Noise and its effect on Receiver Performance C. John Grebenkemper All
