Vestigial Sideband Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #11, April 7, Prof. Young-Chai Ko
|
|
|
- Jasper Allison
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vestigial Sideband Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #11, April 7, 2011 Prof. Young-Chai Ko
2 Summary Vestigial sideband modulation Baseband representation of modulated wave Baseband representation of pass-band filter Frequency division multiplexing Introduction to Angle Modulation
3 Generation of LSB SSB Using Wideband Low-Pass Filter DSB Spectrum H L (f) SSB Spectrum H L (f) sgn(f ) sgn(f + )
4 Generation of USB SSB Using High-Pass (or Passband) Filter DSB Spectrum H HP (f) SSB Spectrum H HP (f) = sgn(f + ) + sgn(f + ) sgn(f + ) sgn(f )
5 SSB Modulated Wave Lower Sideband SSB s LSB (t) = 1 2 m(t) cos(2 t)+ 1 2 ˆm(t)sin(2 t) Upper sideband SSB s USB (t) = 1 2 m(t) cos(2 t) 1 2 ˆm(t)sin(2 t)
6 Applications of SSB and Difficulties in Implementing SSB Two difficulties of SSB modulations Designing and implementing the sharp Low-pass (or High-pass/pass-band) filter is not easy for circuit designer. Hence, the message signal which does not contain the significant energy in the DC area is often modulated by the SSB such as the speech signal. Spectrum of Speech Signal (Example) 0 [Hz] However, the SSB cannot be applicable for the message signal which contains the significant energy around zero frequency such as video signal, computer data, and etc.
7 Vestigial Sideband (VSB) Modulation VSB Modulation Modulation to overcome the two difficulties of the SSB modulations. Allow a small amount, or vestige, of the unwanted sideband to appear at the output of an SSB modulator The design of the sideband filter is simplified since the need for sharp cutoff at the carrier frequency is eliminated. In addition, a VSB system has improved low-frequency response and can even have dc response.
8 Idea of VSB Modulator Pass-band (or High-pass) filter for USB-SSB modulation 1 H U (f) The filter below is much easier to design and implement 1 1 f 1 + f 1
9 Consider the two-tone message signal given as m(t) =A cos(2 f 1 t)+b cos(2 f 2 t) Message signal multiplied by the carrier wave, that is, DSB signal e DSB (t) = (A cos(2 f 1 t)+bcos(2 f 2 t)) cos(2 t) = 1 2 A cos(2 ( + f 1 )t)+ 1 2 A cos(2 ( f 1 )t) B sin(2 ( + f 1 )t)+ 1 2 B sin(2 ( f 1 )t)
10 Spectrum of DSB signal 1 2 B A 1 2 A 2 B Frequency response of the VSB filter f 2 f 1 f + f 1 + f 2 c 1 1 Output response f 2 f 1 + f 1 + f 2 s(t) = 1 2 A cos(2 ( f 1 )t) A(1 ) cos(2 ( + f 1 )t) B cos(2 ( + f 2 )t) 1 2 A 1 [A(1 )] B f 1 + f 1 + f 2
11 Demodulation of VSB Signal (Coherent method) Downconvert (by Multiplying 4 cos(2 t) ) and low pass filtering Downconvert d(t) = s(t) 4 cos(2 t) = 1 2 A cos(2 ( f 1 )t) 4 cos(2 t) A(1 ) cos(2 ( + f 1 )t) 4 cos(2 t) B cos(2 ( + f 2 )t) 4 cos(2 t) cos(2 ( + f 1 )t) cos(2 t)= 1 apple cos(2 (2 + f 1 )t) + cos(2 f 1 t) 2 Low-Pass Filtering 1 2 cos(2 f 1t)
12 Signal after Low-pass filtering (t) = A cos(2 f 1 t)+a(1 ) cos(2 f 1 t)+b cos(2 f 2 t) = A cos(2 f 1 t)+b cos(2 f 2 t)
13 Television Signals [Ref: Haykin & Moher, Textbook]
14 Baseband Representation of Modulated Waves DSB modulated wave signal s DSB (t) =Am(t) cos(2 t) SSB modulated wave signal s SSB (t) = 1 2 Am(t) cos(2 t) ± 1 2 A ˆm(t)sin(2 t) In general, we can write the linear modulated wave as s(t) =s I (t) cos(2 t) s Q (t)sin(2 t) Carrier wave with frequency quadrature-phase version of the carrier c(t) = cos(2 t) ĉ(t) =sin(2 t) Orthogonal each other
15 We can rewrite the modulated wave as s(t) =s I (t)c(t) s Q (t)ĉ(t) in-phase component of s(t) quadrature(-phase) component of s(t) Introduce the complex envelop of the modulated wave s(t) s(t) =s I (t)+js Q (t) Define the complex carrier wave c(t) =c I (t) jc Q (t)
16 Consider the following s(t) exp(j2 t) = apple s I (t)+js Q (t) apple cos(2 t)+jsin(2 t) Real term apple s(t) exp(j2 t) = s I (t) cos(2 t) s Q (t) sin(2 t) Imaginary term apple s(t) exp(j2 t) = s I (t)sin(2 t)+s Q (t) cos(2 t) s(t) X apple s(t) exp(j2 t)
17 Now consider s(t) =s I (t)+js Q (t) =a(t)e j (t) where a(t) = q s 2 I (t)+js2 Q (t), (t) = tan 1 s Q(t) s I (t) Then we can represent the modulated wave as apple s(t) = < apple = < s(t)e j2 t a(t)e j[2 t+ (t)] = a(t) cos[2 t + (t)] apple = < a(t)e j (t) e j2 t
18 Three different representation of modulated wave using its equivalent baseband signal s(t) = s I (t) cos(2 t) s Q (t)sin(2 t) apple = < s(t)e j2 t = a(t) cos[2 t + (t)]
19 Superheterodyne Receiver [Ref: Haykin & Moher, Textbook]
20 Communication Chipset Architecture LNA Receiver PLL 2 ABB Section 90 0 PLL antenna switch ABB Digital Baseband IC Power Amplifier Switchplexer Transmitter module PA Ctrl 26MHz Osc. LDO s
21 Frequency-Division Multiplexing To transmit a number oommunication signals over the same channel, the signals must be kept apart so that they do not interfere with each other, and thus they can be separated at the receiving end. FDM (Frequency division multiplexing) TDM (Time division multiplexing) SDM (Space division multiplexing) CDM (Code division multiplexing)
22 Block Diagram of FDM
23 Angle Modulation Basic Definition of Angle Modulation s(t) =A c cos[ i (t)] = A c cos[2 t + c ] Phase modulation (PM) if i(t) =2 t + k p m(t) Frequency modulation (FM) if Z t i(t) =2 t +2 k f m( ) d 0
Angle Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #12, April 14, Prof. Young-Chai Ko
 Angle Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #12, April 14, 2011 Prof. Young-Chai Ko koyc@korea.ac.kr Summary Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) Angle Modulation Frequency-Division Multiplexing
Angle Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #12, April 14, 2011 Prof. Young-Chai Ko koyc@korea.ac.kr Summary Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) Angle Modulation Frequency-Division Multiplexing
Frequency Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #15, April 28, Prof. Young-Chai Ko
 Frequency Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #15, April 28, 2011 Prof. Young-Chai Ko koyc@korea.ac.kr Summary Angle Modulation Properties of Angle Modulation Narrowband Frequency Modulation
Frequency Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #15, April 28, 2011 Prof. Young-Chai Ko koyc@korea.ac.kr Summary Angle Modulation Properties of Angle Modulation Narrowband Frequency Modulation
AM Limitations. Amplitude Modulation II. DSB-SC Modulation. AM Modifications
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
Amplitude Modulation II
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
 Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
Outline. Communications Engineering 1
 Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the
 Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
AM and FM MODULATION Lecture 5&6
 AM and FM MODULATION Lecture 5&6 Ir. Muhamad Asvial, MEng., PhD Center for Information and Communication Engineering Research Electrical Engineering Department University of Indonesia Kampus UI Depok,
AM and FM MODULATION Lecture 5&6 Ir. Muhamad Asvial, MEng., PhD Center for Information and Communication Engineering Research Electrical Engineering Department University of Indonesia Kampus UI Depok,
Chapter 3: Analog Modulation Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved.
 Contemporary Communication Systems using MATLAB Chapter 3: Analog Modulation 2013 Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved. 3.1 Preview In this chapter we study analog modulation & demodulation,
Contemporary Communication Systems using MATLAB Chapter 3: Analog Modulation 2013 Cengage Learning Engineering. All Rights Reserved. 3.1 Preview In this chapter we study analog modulation & demodulation,
4- Single Side Band (SSB)
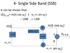 4- Single Side Band (SSB) It can be shown that: s(t) S.S.B = m(t) cos ω c t ± m h (t) sin ω c t -: USB ; +: LSB m(t) X m(t) cos ω c t -π/ cos ω c t -π/ + s S.S.B m h (t) X m h (t) ± sin ω c t 1 Tone Modulation:
4- Single Side Band (SSB) It can be shown that: s(t) S.S.B = m(t) cos ω c t ± m h (t) sin ω c t -: USB ; +: LSB m(t) X m(t) cos ω c t -π/ cos ω c t -π/ + s S.S.B m h (t) X m h (t) ± sin ω c t 1 Tone Modulation:
Amplitude Modulation, II
 Amplitude Modulation, II Single sideband modulation (SSB) Vestigial sideband modulation (VSB) VSB spectrum Modulator and demodulator NTSC TV signsals Quadrature modulation Spectral efficiency Modulator
Amplitude Modulation, II Single sideband modulation (SSB) Vestigial sideband modulation (VSB) VSB spectrum Modulator and demodulator NTSC TV signsals Quadrature modulation Spectral efficiency Modulator
COMM 601: Modulation I
 Prof. Ahmed El-Mahdy, Communications Department The German University in Cairo Text Books [1] Couch, Digital and Analog Communication Systems, 7 th edition, Prentice Hall, 2007. [2] Simon Haykin, Communication
Prof. Ahmed El-Mahdy, Communications Department The German University in Cairo Text Books [1] Couch, Digital and Analog Communication Systems, 7 th edition, Prentice Hall, 2007. [2] Simon Haykin, Communication
B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering)
 Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
Code: 13A04404 R13 B.Tech II Year II Semester (R13) Supplementary Examinations May/June 2017 ANALOG COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS (Electronics and Communication Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 70 PART A
Communication Channels
 Communication Channels wires (PCB trace or conductor on IC) optical fiber (attenuation 4dB/km) broadcast TV (50 kw transmit) voice telephone line (under -9 dbm or 110 µw) walkie-talkie: 500 mw, 467 MHz
Communication Channels wires (PCB trace or conductor on IC) optical fiber (attenuation 4dB/km) broadcast TV (50 kw transmit) voice telephone line (under -9 dbm or 110 µw) walkie-talkie: 500 mw, 467 MHz
Amplitude Modulated Systems
 Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
Master Degree in Electronic Engineering
 Master Degree in Electronic Engineering Analog and telecommunication electronic course (ATLCE-01NWM) Miniproject: Baseband signal transmission techniques Name: LI. XINRUI E-mail: s219989@studenti.polito.it
Master Degree in Electronic Engineering Analog and telecommunication electronic course (ATLCE-01NWM) Miniproject: Baseband signal transmission techniques Name: LI. XINRUI E-mail: s219989@studenti.polito.it
Amplitude Modulation. Ahmad Bilal
 Amplitude Modulation Ahmad Bilal 5-2 ANALOG AND DIGITAL Analog-to-analog conversion is the representation of analog information by an analog signal. Topics discussed in this section: Amplitude Modulation
Amplitude Modulation Ahmad Bilal 5-2 ANALOG AND DIGITAL Analog-to-analog conversion is the representation of analog information by an analog signal. Topics discussed in this section: Amplitude Modulation
UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers)
 UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers) 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier Signal is varied in accordance with the
UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers) 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier Signal is varied in accordance with the
UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION
 UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION Prepared by: S.NANDHINI, Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering, Sriperumbudur, Tamilnadu. CONTENTS Introduction to communication systems
UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION Prepared by: S.NANDHINI, Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering, Sriperumbudur, Tamilnadu. CONTENTS Introduction to communication systems
Problems from the 3 rd edition
 (2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
(2.1-1) Find the energies of the signals: a) sin t, 0 t π b) sin t, 0 t π c) 2 sin t, 0 t π d) sin (t-2π), 2π t 4π Problems from the 3 rd edition Comment on the effect on energy of sign change, time shifting
3.1 Introduction to Modulation
 Haberlesme Sistemlerine Giris (ELE 361) 9 Eylul 2017 TOBB Ekonomi ve Teknoloji Universitesi, Guz 2017-18 Dr. A. Melda Yuksel Turgut & Tolga Girici Lecture Notes Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Speech, music,
Haberlesme Sistemlerine Giris (ELE 361) 9 Eylul 2017 TOBB Ekonomi ve Teknoloji Universitesi, Guz 2017-18 Dr. A. Melda Yuksel Turgut & Tolga Girici Lecture Notes Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Speech, music,
Amplitude Modulation Chapter 2. Modulation process
 Question 1 Modulation process Modulation is the process of translation the baseband message signal to bandpass (modulated carrier) signal at frequencies that are very high compared to the baseband frequencies.
Question 1 Modulation process Modulation is the process of translation the baseband message signal to bandpass (modulated carrier) signal at frequencies that are very high compared to the baseband frequencies.
Introduction to Amplitude Modulation
 1 Introduction to Amplitude Modulation Introduction to project management. Problem definition. Design principles and practices. Implementation techniques including circuit design, software design, solid
1 Introduction to Amplitude Modulation Introduction to project management. Problem definition. Design principles and practices. Implementation techniques including circuit design, software design, solid
(b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3]
![(b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3] (b) What are the differences between FM and PM? (c) What are the differences between NBFM and WBFM? [9+4+3]](/thumbs/85/91561193.jpg) Code No: RR220401 Set No. 1 1. (a) The antenna current of an AM Broadcast transmitter is 10A, if modulated to a depth of 50% by an audio sine wave. It increases to 12A as a result of simultaneous modulation
Code No: RR220401 Set No. 1 1. (a) The antenna current of an AM Broadcast transmitter is 10A, if modulated to a depth of 50% by an audio sine wave. It increases to 12A as a result of simultaneous modulation
! Amplitude of carrier wave varies a mean value in step with the baseband signal m(t)
 page 7.1 CHAPTER 7 AMPLITUDE MODULATION Transmit information-bearing (message) or baseband signal (voice-music) through a Communications Channel Baseband = band of frequencies representing the original
page 7.1 CHAPTER 7 AMPLITUDE MODULATION Transmit information-bearing (message) or baseband signal (voice-music) through a Communications Channel Baseband = band of frequencies representing the original
Code No: R Set No. 1
 Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
Code No: R05220405 Set No. 1 II B.Tech II Semester Regular Examinations, Apr/May 2007 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering and Electronics & Telematics) Time: 3 hours
Introduction. Amplitude Modulation System Angle Modulation System
 Introduction Amplitude Modulation System Angle Modulation System Frequency Modulation Phase Modulation Digital Communication Elements of Information Theory Advanced Communication Techniques 1 Tools for
Introduction Amplitude Modulation System Angle Modulation System Frequency Modulation Phase Modulation Digital Communication Elements of Information Theory Advanced Communication Techniques 1 Tools for
ENSC327 Communications Systems 14: Multiplexing. School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University
 ENSC327 Communications Systems 14: Multiplexing School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University 1 Outline Required background (Recall various modulation schemes) Different Multiplexing strategies:
ENSC327 Communications Systems 14: Multiplexing School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University 1 Outline Required background (Recall various modulation schemes) Different Multiplexing strategies:
Chapter 5. Amplitude Modulation
 Chapter 5 Amplitude Modulation So far we have developed basic signal and system representation techniques which we will now apply to the analysis of various analog communication systems. In particular,
Chapter 5 Amplitude Modulation So far we have developed basic signal and system representation techniques which we will now apply to the analysis of various analog communication systems. In particular,
Communications and Signals Processing
 Communications and Signals Processing Department of Communications An Najah National University 2012/2013 1 3.1 Amplitude Modulation 3.2 Virtues, Limitations, and Modifications of Amplitude Modulation
Communications and Signals Processing Department of Communications An Najah National University 2012/2013 1 3.1 Amplitude Modulation 3.2 Virtues, Limitations, and Modifications of Amplitude Modulation
ENSC327 Communications Systems 14: Multiplexing. Jie Liang School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University
 ENSC327 Communications Systems 14: Multiplexing Jie Liang School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University 1 Outline Multiplexing allows signals to share channels Many different strategies are possible
ENSC327 Communications Systems 14: Multiplexing Jie Liang School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University 1 Outline Multiplexing allows signals to share channels Many different strategies are possible
1B Paper 6: Communications Handout 2: Analogue Modulation
 1B Paper 6: Communications Handout : Analogue Modulation Ramji Venkataramanan Signal Processing and Communications Lab Department of Engineering ramji.v@eng.cam.ac.uk Lent Term 16 1 / 3 Modulation Modulation
1B Paper 6: Communications Handout : Analogue Modulation Ramji Venkataramanan Signal Processing and Communications Lab Department of Engineering ramji.v@eng.cam.ac.uk Lent Term 16 1 / 3 Modulation Modulation
S.E. (Electronics/Electronics and Telecommunication Engg.) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2014 COMMUNICATION THEORY (2008 PATTERN)
 Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4657]-49 S.E. (Electronics/Electronics and Telecommunication Engg.) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2014 COMMUNICATION THEORY (2008 PATTERN)
Total No. of Questions 12] [Total No. of Printed Pages 7 Seat No. [4657]-49 S.E. (Electronics/Electronics and Telecommunication Engg.) (Second Semester) EXAMINATION, 2014 COMMUNICATION THEORY (2008 PATTERN)
Lecture 6. Angle Modulation and Demodulation
 Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
EC2252: COMMUNICATION THEORY SEM / YEAR: II year DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING
 EC2252: COMMUNICATION THEORY SEM / YEAR: II year DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE : EC2252 SEM / YEAR : II year SUBJECT NAME : COMMUNICATION THEORY UNIT
EC2252: COMMUNICATION THEORY SEM / YEAR: II year DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT CODE : EC2252 SEM / YEAR : II year SUBJECT NAME : COMMUNICATION THEORY UNIT
S.R.M. Institute of Science & Technology School of Electronics & Communication Engineering
 S.R.M. Institute of Science & Technology School of Electronics & Communication Engineering QUESTION BANK Subject Code : EC314 Subject Name : Communication Engineering Year & Sem : III Year, 6th Sem (EEE)
S.R.M. Institute of Science & Technology School of Electronics & Communication Engineering QUESTION BANK Subject Code : EC314 Subject Name : Communication Engineering Year & Sem : III Year, 6th Sem (EEE)
Lecture 15: Introduction to Mixers
 EECS 142 Lecture 15: Introduction to Mixers Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture
EECS 142 Lecture 15: Introduction to Mixers Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture
S.R.M Institute of Science and Technology (Deemed University) Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering
 S.R.M Institute of Science and Technology (Deemed University) Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering QUESTION BANK Subject Code : EC211 Subject Name : Communication Engineering Year & Sem
S.R.M Institute of Science and Technology (Deemed University) Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering QUESTION BANK Subject Code : EC211 Subject Name : Communication Engineering Year & Sem
CHAPTER 2! AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM)
 CHAPTER 2 AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM) Topics 2-1 : AM Concepts 2-2 : Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 2-3 : Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 2-4 : Single-Sideband Modulation 2-5 : AM Power
CHAPTER 2 AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM) Topics 2-1 : AM Concepts 2-2 : Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 2-3 : Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 2-4 : Single-Sideband Modulation 2-5 : AM Power
Lecture 12 - Analog Communication (II)
 Lecture 12 - Analog Communication (II) James Barnes (James.Barnes@colostate.edu) Spring 2014 Colorado State University Dept of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE423 1 / 12 Outline QAM: quadrature
Lecture 12 - Analog Communication (II) James Barnes (James.Barnes@colostate.edu) Spring 2014 Colorado State University Dept of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE423 1 / 12 Outline QAM: quadrature
COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS-II (In continuation with Part-I)
 MODULATING A SIGNAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS-II (In continuation with Part-I) TRANSMITTING SIGNALS : In order to transmit the original low frequency baseband message efficiently over long distances, the signal
MODULATING A SIGNAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS-II (In continuation with Part-I) TRANSMITTING SIGNALS : In order to transmit the original low frequency baseband message efficiently over long distances, the signal
Chapter 7. Multiple Division Techniques
 Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques 1 Outline Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) Division Multiple Access (TDMA) Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Comparison of FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA Walsh
Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques 1 Outline Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA) Division Multiple Access (TDMA) Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Comparison of FDMA, TDMA, and CDMA Walsh
Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier
 Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier and the first channel. The modulation of the main carrier
Twelve voice signals, each band-limited to 3 khz, are frequency -multiplexed using 1 khz guard bands between channels and between the main carrier and the first channel. The modulation of the main carrier
Analog Communication.
 Analog Communication Vishnu N V Tele is Greek for at a distance, and Communicare is latin for to make common. Telecommunication is the process of long distance communications. Early telecommunications
Analog Communication Vishnu N V Tele is Greek for at a distance, and Communicare is latin for to make common. Telecommunication is the process of long distance communications. Early telecommunications
Technician License Course Chapter 2. Lesson Plan Module 3 Modulation and Bandwidth
 Technician License Course Chapter 2 Lesson Plan Module 3 Modulation and Bandwidth The Basic Radio Station What Happens During Radio Communication? Transmitting (sending a signal): Information (voice, data,
Technician License Course Chapter 2 Lesson Plan Module 3 Modulation and Bandwidth The Basic Radio Station What Happens During Radio Communication? Transmitting (sending a signal): Information (voice, data,
Charan Langton, Editor
 Charan Langton, Editor SIGNAL PROCESSING & SIMULATION NEWSLETTER Baseband, Passband Signals and Amplitude Modulation The most salient feature of information signals is that they are generally low frequency.
Charan Langton, Editor SIGNAL PROCESSING & SIMULATION NEWSLETTER Baseband, Passband Signals and Amplitude Modulation The most salient feature of information signals is that they are generally low frequency.
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal
 Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
3.1 Introduction 3.2 Amplitude Modulation 3.3 Double Sideband-Suppressed Carrier Modulation 3.4 Quadrature-Carrier Multiplexing 3.
 Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Institute of Communications Engineering g National Sun Yat-sen University Outline 3.1 Introduction 3. Amplitude Modulation 3.3
Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Wireless Information Transmission System Lab. Institute of Communications Engineering g National Sun Yat-sen University Outline 3.1 Introduction 3. Amplitude Modulation 3.3
EE4512 Analog and Digital Communications Chapter 6. Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation
 Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Amplitude Modulation Pages 306-309 309 The analytical signal for double sideband, large carrier amplitude modulation
Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Chapter 6 Analog Modulation and Demodulation Amplitude Modulation Pages 306-309 309 The analytical signal for double sideband, large carrier amplitude modulation
Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 10 Single Sideband Modulation We will discuss, now we will continue
Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 10 Single Sideband Modulation We will discuss, now we will continue
Wireless Communication Fading Modulation
 EC744 Wireless Communication Fall 2008 Mohamed Essam Khedr Department of Electronics and Communications Wireless Communication Fading Modulation Syllabus Tentatively Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5
EC744 Wireless Communication Fall 2008 Mohamed Essam Khedr Department of Electronics and Communications Wireless Communication Fading Modulation Syllabus Tentatively Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5
Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits. Module 7
 Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits Module 7 Radio Block Diagrams Radio Circuits can be shown as functional blocks connected together. Knowing the description of common
Technician License Course Chapter 3 Types of Radios and Radio Circuits Module 7 Radio Block Diagrams Radio Circuits can be shown as functional blocks connected together. Knowing the description of common
Lecture-3 Amplitude Modulation: Single Side Band (SSB) Modulation
 Lecture-3 Amplitude Modulation: Single Side Band (SSB) Modulation 3.0 Introduction. 3.1 Baseband Signal SSB Modulation. 3.1.1 Frequency Domain Description. 3.1. Time Domain Description. 3. Single Tone
Lecture-3 Amplitude Modulation: Single Side Band (SSB) Modulation 3.0 Introduction. 3.1 Baseband Signal SSB Modulation. 3.1.1 Frequency Domain Description. 3.1. Time Domain Description. 3. Single Tone
Chapter 3. Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals
 Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals Topics Covered 3-1: AM Concepts 3-2: Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 3-3: Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 3-4: AM Power 3-5: Single-Sideband
Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals Topics Covered 3-1: AM Concepts 3-2: Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 3-3: Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 3-4: AM Power 3-5: Single-Sideband
Dr. Md. Farhad Hossain Associate Professor Department of EEE, BUET
 EEE 309 Communiation Theory Semester: January 06 Dr. Md. Farhad Hossain Assoiate Proessor Department o EEE, BUET Email: marhadhossain@eee.buet.a.bd Oie: ECE 33, ECE Building Part 03-3 Single-sideband Suppressed
EEE 309 Communiation Theory Semester: January 06 Dr. Md. Farhad Hossain Assoiate Proessor Department o EEE, BUET Email: marhadhossain@eee.buet.a.bd Oie: ECE 33, ECE Building Part 03-3 Single-sideband Suppressed
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II
 EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
EE470 Electronic Communication Theory Exam II Open text, closed notes. For partial credit, you must show all formulas in symbolic form and you must work neatly!!! Date: November 6, 2013 Name: 1. [16%]
Real and Complex Modulation
 Real and Complex Modulation TIPL 4708 Presented by Matt Guibord Prepared by Matt Guibord 1 What is modulation? Modulation is the act of changing a carrier signal s properties (amplitude, phase, frequency)
Real and Complex Modulation TIPL 4708 Presented by Matt Guibord Prepared by Matt Guibord 1 What is modulation? Modulation is the act of changing a carrier signal s properties (amplitude, phase, frequency)
 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER GCE@Bodi_ SCIENCE GCE@Bodi_ AND ENIGNEERING GCE@Bodi_ GCE@Bodi_ GCE@Bodi_ Analog and Digital Communication GCE@Bodi_ DEPARTMENT OF CsE Subject Name: Analog and Digital Communication
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER GCE@Bodi_ SCIENCE GCE@Bodi_ AND ENIGNEERING GCE@Bodi_ GCE@Bodi_ GCE@Bodi_ Analog and Digital Communication GCE@Bodi_ DEPARTMENT OF CsE Subject Name: Analog and Digital Communication
Amplitude Modulation Early Radio EE 442 Spring Semester Lecture 6
 Amplitude Modulation Early Radio EE 442 Spring Semester Lecture 6 f f f LO audio baseband m http://www.technologyuk.net/telecommunications/telecom_principles/amplitude_modulation.shtml AM Modulation --
Amplitude Modulation Early Radio EE 442 Spring Semester Lecture 6 f f f LO audio baseband m http://www.technologyuk.net/telecommunications/telecom_principles/amplitude_modulation.shtml AM Modulation --
DT Filters 2/19. Atousa Hajshirmohammadi, SFU
 1/19 ENSC380 Lecture 23 Objectives: Signals and Systems Fourier Analysis: Discrete Time Filters Analog Communication Systems Double Sideband, Sub-pressed Carrier Modulation (DSBSC) Amplitude Modulation
1/19 ENSC380 Lecture 23 Objectives: Signals and Systems Fourier Analysis: Discrete Time Filters Analog Communication Systems Double Sideband, Sub-pressed Carrier Modulation (DSBSC) Amplitude Modulation
Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques for Traffic Channels
 Introduction to Wireless & Mobile Systems Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques for Traffic Channels Outline Introduction Concepts and Models for Multiple Divisions Frequency Division Multiple Access
Introduction to Wireless & Mobile Systems Chapter 7 Multiple Division Techniques for Traffic Channels Outline Introduction Concepts and Models for Multiple Divisions Frequency Division Multiple Access
Amplitude Modulation
 Amplitude Modulation Ang Man Shun October 30, 01 Reference Hwei P. Hsu Analog and Digital Communication Summary Message Carrier Simple AM DSB-LC DSB-SC SSB / VSB Equation m(t) Large Carrier Unity A m cos
Amplitude Modulation Ang Man Shun October 30, 01 Reference Hwei P. Hsu Analog and Digital Communication Summary Message Carrier Simple AM DSB-LC DSB-SC SSB / VSB Equation m(t) Large Carrier Unity A m cos
Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals
 3 chapter Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals In the modulation process, the baseband voice, video, or digital signal modifies another, higher-frequency signal called the carrier, which is usually a sine
3 chapter Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals In the modulation process, the baseband voice, video, or digital signal modifies another, higher-frequency signal called the carrier, which is usually a sine
page 7.51 Chapter 7, sections , pp Angle Modulation No Modulation (t) =2f c t + c Instantaneous Frequency 2 dt dt No Modulation
 page 7.51 Chapter 7, sections 7.1-7.14, pp. 322-368 Angle Modulation s(t) =A c cos[(t)] No Modulation (t) =2f c t + c s(t) =A c cos[2f c t + c ] Instantaneous Frequency f i (t) = 1 d(t) 2 dt or w i (t)
page 7.51 Chapter 7, sections 7.1-7.14, pp. 322-368 Angle Modulation s(t) =A c cos[(t)] No Modulation (t) =2f c t + c s(t) =A c cos[2f c t + c ] Instantaneous Frequency f i (t) = 1 d(t) 2 dt or w i (t)
ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I. Review. ELEC 350 Fall
 ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I Review ELEC 350 Fall 007 1 Final Examination Saturday, December 15-3 hours Two pages of notes allowed Calculator Tables provided Fourier transforms Table.1
ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I Review ELEC 350 Fall 007 1 Final Examination Saturday, December 15-3 hours Two pages of notes allowed Calculator Tables provided Fourier transforms Table.1
ANALOGUE TRANSMISSION OVER FADING CHANNELS
 J.P. Linnartz EECS 290i handouts Spring 1993 ANALOGUE TRANSMISSION OVER FADING CHANNELS Amplitude modulation Various methods exist to transmit a baseband message m(t) using an RF carrier signal c(t) =
J.P. Linnartz EECS 290i handouts Spring 1993 ANALOGUE TRANSMISSION OVER FADING CHANNELS Amplitude modulation Various methods exist to transmit a baseband message m(t) using an RF carrier signal c(t) =
CS311: Data Communication. Transmission of Analog Signal - I
 CS311: Data Communication Transmission of Analog Signal - I by Dr. Manas Khatua Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE IIT Jodhpur E-mail: manaskhatua@iitj.ac.in Web: http://home.iitj.ac.in/~manaskhatua http://manaskhatua.github.io/
CS311: Data Communication Transmission of Analog Signal - I by Dr. Manas Khatua Assistant Professor Dept. of CSE IIT Jodhpur E-mail: manaskhatua@iitj.ac.in Web: http://home.iitj.ac.in/~manaskhatua http://manaskhatua.github.io/
Chapter 7 Single-Sideband Modulation (SSB) and Frequency Translation
 Chapter 7 Single-Sideband Modulation (SSB) and Frequency Translation Contents Slide 1 Single-Sideband Modulation Slide 2 SSB by DSBSC-AM and Filtering Slide 3 SSB by DSBSC-AM and Filtering (cont.) Slide
Chapter 7 Single-Sideband Modulation (SSB) and Frequency Translation Contents Slide 1 Single-Sideband Modulation Slide 2 SSB by DSBSC-AM and Filtering Slide 3 SSB by DSBSC-AM and Filtering (cont.) Slide
4.1 REPRESENTATION OF FM AND PM SIGNALS An angle-modulated signal generally can be written as
 1 In frequency-modulation (FM) systems, the frequency of the carrier f c is changed by the message signal; in phase modulation (PM) systems, the phase of the carrier is changed according to the variations
1 In frequency-modulation (FM) systems, the frequency of the carrier f c is changed by the message signal; in phase modulation (PM) systems, the phase of the carrier is changed according to the variations
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK
 KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUB.NAME : COMMUNICATION THEORY SUB.CODE: EC1252 YEAR : II SEMESTER : IV UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION SYSTEMS
KINGS COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUB.NAME : COMMUNICATION THEORY SUB.CODE: EC1252 YEAR : II SEMESTER : IV UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION SYSTEMS
ANALOG COMMUNICATION
 ANALOG COMMUNICATION TRAINING LAB Analog Communication Training Lab consists of six kits, one each for Modulation (ACL-01), Demodulation (ACL-02), Modulation (ACL-03), Demodulation (ACL-04), Noise power
ANALOG COMMUNICATION TRAINING LAB Analog Communication Training Lab consists of six kits, one each for Modulation (ACL-01), Demodulation (ACL-02), Modulation (ACL-03), Demodulation (ACL-04), Noise power
ENSC327 Communications Systems 4. Double Sideband Modulation. Jie Liang School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University
 ENSC327 Communiations Systems 4. Double Sideband Modulation Jie Liang Shool of Engineering Siene Simon Fraser University 1 Outline DSB: Modulator Spetrum Coherent Demodulator: Three methods Quadrature-arrier
ENSC327 Communiations Systems 4. Double Sideband Modulation Jie Liang Shool of Engineering Siene Simon Fraser University 1 Outline DSB: Modulator Spetrum Coherent Demodulator: Three methods Quadrature-arrier
ELEC 350 Communications Theory and Systems: I. Analog Signal Transmission and Reception. ELEC 350 Fall
 ELEC 350 Communiations Theory and Systems: I Analog Signal Transmission and Reeption ELEC 350 Fall 2007 1 ELEC 350 Fall 2007 2 Analog Modulation A large number o signals are analog speeh musi video These
ELEC 350 Communiations Theory and Systems: I Analog Signal Transmission and Reeption ELEC 350 Fall 2007 1 ELEC 350 Fall 2007 2 Analog Modulation A large number o signals are analog speeh musi video These
Angle Modulated Systems
 Angle Modulated Systems Angle of carrier signal is changed in accordance with instantaneous amplitude of modulating signal. Two types Frequency Modulation (FM) Phase Modulation (PM) Use Commercial radio
Angle Modulated Systems Angle of carrier signal is changed in accordance with instantaneous amplitude of modulating signal. Two types Frequency Modulation (FM) Phase Modulation (PM) Use Commercial radio
Elements of Communication System Channel Fig: 1: Block Diagram of Communication System Terminology in Communication System
 Content:- Fundamentals of Communication Engineering : Elements of a Communication System, Need of modulation, electromagnetic spectrum and typical applications, Unit V (Communication terminologies in communication
Content:- Fundamentals of Communication Engineering : Elements of a Communication System, Need of modulation, electromagnetic spectrum and typical applications, Unit V (Communication terminologies in communication
Radio Technology and Architectures. 1 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless L#1
 Radio Technology and Architectures 1 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless L#1 Radio (Architectures) Spectrum plan and legal issues Radio Architectures and components 2 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless
Radio Technology and Architectures 1 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless L#1 Radio (Architectures) Spectrum plan and legal issues Radio Architectures and components 2 ENGN4521/ENGN6521: Embedded Wireless
Emona Telecoms-Trainer ETT-101
 EXPERIMENTS IN MODERN COMMUNICATIONS Emona Telecoms-Trainer ETT-101 Multi-Experiment Single Board Telecommunications Trainer for Technical College and Technical High School Students EMONA INSTRUMENTS www.ett101.com
EXPERIMENTS IN MODERN COMMUNICATIONS Emona Telecoms-Trainer ETT-101 Multi-Experiment Single Board Telecommunications Trainer for Technical College and Technical High School Students EMONA INSTRUMENTS www.ett101.com
PHASE DIVISION MULTIPLEX
 PHASE DIVISION MULTIPLEX PREPARATION... 70 the transmitter... 70 the receiver... 71 EXPERIMENT... 72 a single-channel receiver... 72 a two-channel receiver... 73 TUTORIAL QUESTIONS... 74 Vol A2, ch 8,
PHASE DIVISION MULTIPLEX PREPARATION... 70 the transmitter... 70 the receiver... 71 EXPERIMENT... 72 a single-channel receiver... 72 a two-channel receiver... 73 TUTORIAL QUESTIONS... 74 Vol A2, ch 8,
EECS 307: Lab Handout 2 (FALL 2012)
 EECS 307: Lab Handout 2 (FALL 2012) I- Audio Transmission of a Single Tone In this part you will modulate a low-frequency audio tone via AM, and transmit it with a carrier also in the audio range. The
EECS 307: Lab Handout 2 (FALL 2012) I- Audio Transmission of a Single Tone In this part you will modulate a low-frequency audio tone via AM, and transmit it with a carrier also in the audio range. The
DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS. MSc in Electronic Technologies and Communications
 DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS MSc in Electronic Technologies and Communications Bandpass binary signalling The common techniques of bandpass binary signalling are: - On-off keying (OOK), also known as
DIGITAL COMMUNICATIONS SYSTEMS MSc in Electronic Technologies and Communications Bandpass binary signalling The common techniques of bandpass binary signalling are: - On-off keying (OOK), also known as
Chapter-15. Communication systems -1 mark Questions
 Chapter-15 Communication systems -1 mark Questions 1) What are the three main units of a Communication System? 2) What is meant by Bandwidth of transmission? 3) What is a transducer? Give an example. 4)
Chapter-15 Communication systems -1 mark Questions 1) What are the three main units of a Communication System? 2) What is meant by Bandwidth of transmission? 3) What is a transducer? Give an example. 4)
INTRODUCTION TO TRANSCEIVER DESIGN ECE3103 ADVANCED TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
 INTRODUCTION TO TRANSCEIVER DESIGN ECE3103 ADVANCED TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS FUNCTIONS OF A TRANSMITTER The basic functions of a transmitter are: a) up-conversion: move signal to desired RF carrier frequency.
INTRODUCTION TO TRANSCEIVER DESIGN ECE3103 ADVANCED TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS FUNCTIONS OF A TRANSMITTER The basic functions of a transmitter are: a) up-conversion: move signal to desired RF carrier frequency.
Amplitude Modulation. Amplitude Modulation. Amplitude Modulation. Amplitude Modulation. A. Introduction. A. Introduction
 1. In AM modulation we impart the information of a message signal m(t) on to a sinusoidal carrier c(t). This results in the translation of the message signal to a new frequency range. The motivation for
1. In AM modulation we impart the information of a message signal m(t) on to a sinusoidal carrier c(t). This results in the translation of the message signal to a new frequency range. The motivation for
The Communications Channel (Ch.11):
 ECE-5 Phil Schniter February 5, 8 The Communications Channel (Ch.): The eects o signal propagation are usually modeled as: ECE-5 Phil Schniter February 5, 8 Filtering due to Multipath Propagation: The
ECE-5 Phil Schniter February 5, 8 The Communications Channel (Ch.): The eects o signal propagation are usually modeled as: ECE-5 Phil Schniter February 5, 8 Filtering due to Multipath Propagation: The
M(f) = 0. Linear modulation: linear relationship between the modulated signal and the message signal (ex: AM, DSB-SC, SSB, VSB).
 4 Analog modulation 4.1 Modulation formats The message waveform is represented by a low-pass real signal mt) such that Mf) = 0 f W where W is the message bandwidth. mt) is called the modulating signal.
4 Analog modulation 4.1 Modulation formats The message waveform is represented by a low-pass real signal mt) such that Mf) = 0 f W where W is the message bandwidth. mt) is called the modulating signal.
6. Modulation and Multiplexing Techniques
 6. Modulation and Multiplexing Techniques The quality of analog transmission is S/N (signal to noise ratio). signal power S/N = ---------------------------- baseband noise power S/N can be greater than
6. Modulation and Multiplexing Techniques The quality of analog transmission is S/N (signal to noise ratio). signal power S/N = ---------------------------- baseband noise power S/N can be greater than
AN INTRODUCTION OF ANALOG AND DIGITAL MODULATION TECHNIQUES IN COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
 AN INTRODUCTION OF ANALOG AND DIGITAL MODULATION TECHNIQUES IN COMMUNICATION SYSTEM Rashmi Pandey Vedica Institute of Technology, Bhopal Department of Electronics & Communication rashmipandey07@rediffmail.com
AN INTRODUCTION OF ANALOG AND DIGITAL MODULATION TECHNIQUES IN COMMUNICATION SYSTEM Rashmi Pandey Vedica Institute of Technology, Bhopal Department of Electronics & Communication rashmipandey07@rediffmail.com
Keywords Internet, LabVIEW, Smart Classroom-cum-Laboratory, Teaching and Learning process of communication.
 Volume 4, Issue 10, October 2014 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Smart Classroom-cum-Laboratory
Volume 4, Issue 10, October 2014 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Smart Classroom-cum-Laboratory
ENSC327 Communications Systems 4. Double Sideband Modulation. School of Engineering Science Simon Fraser University
 ENSC327 Communiations Systems 4. Double Sideband Modulation Shool of Engineering Siene Simon Fraser University 1 Outline Required Bakground DSB: Modulator Spetrum Coherent Demodulator: Three methods Quadrature-arrier
ENSC327 Communiations Systems 4. Double Sideband Modulation Shool of Engineering Siene Simon Fraser University 1 Outline Required Bakground DSB: Modulator Spetrum Coherent Demodulator: Three methods Quadrature-arrier
V. CHANDRA SEKAR Professor and Head Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering SASTRA University, Kumbakonam
 V. CHANDRA SEKAR Professor and Head Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering SASTRA University, Kumbakonam 1 Contents Preface v 1. Introduction 1 1.1 What is Communication? 1 1.2 Modulation
V. CHANDRA SEKAR Professor and Head Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering SASTRA University, Kumbakonam 1 Contents Preface v 1. Introduction 1 1.1 What is Communication? 1 1.2 Modulation
ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS. BY P.Swetha, Assistant Professor (Units 1, 2 & 5) K.D.K.Ajay, Assistant Professor (Units 3 & 4)
 ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS BY P.Swetha, Assistant Professor (Units 1, 2 & 5) K.D.K.Ajay, Assistant Professor (Units 3 & 4) (R15A0409) ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS Course Objectives: Objective of the course is to:
ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS BY P.Swetha, Assistant Professor (Units 1, 2 & 5) K.D.K.Ajay, Assistant Professor (Units 3 & 4) (R15A0409) ANALOG COMMUNICATIONS Course Objectives: Objective of the course is to:
Superheterodyne Receiver Tutorial
 1 of 6 Superheterodyne Receiver Tutorial J P Silver E-mail: john@rfic.co.uk 1 ABSTRACT This paper discusses the basic design concepts of the Superheterodyne receiver in both single and double conversion
1 of 6 Superheterodyne Receiver Tutorial J P Silver E-mail: john@rfic.co.uk 1 ABSTRACT This paper discusses the basic design concepts of the Superheterodyne receiver in both single and double conversion
two computers. 2- Providing a channel between them for transmitting and receiving the signals through it.
 1. Introduction: Communication is the process of transmitting the messages that carrying information, where the two computers can be communicated with each other if the two conditions are available: 1-
1. Introduction: Communication is the process of transmitting the messages that carrying information, where the two computers can be communicated with each other if the two conditions are available: 1-
Objectives. Presentation Outline. Digital Modulation Lecture 01
 Digital Modulation Lecture 01 Review of Analogue Modulation Introduction to Digital Modulation Techniques Richard Harris Objectives You will be able to: Classify the various approaches to Analogue Modulation
Digital Modulation Lecture 01 Review of Analogue Modulation Introduction to Digital Modulation Techniques Richard Harris Objectives You will be able to: Classify the various approaches to Analogue Modulation
Digital Modulation Lecture 01. Review of Analogue Modulation Introduction to Digital Modulation Techniques Richard Harris
 Digital Modulation Lecture 01 Review of Analogue Modulation Introduction to Digital Modulation Techniques Richard Harris Objectives You will be able to: Classify the various approaches to Analogue Modulation
Digital Modulation Lecture 01 Review of Analogue Modulation Introduction to Digital Modulation Techniques Richard Harris Objectives You will be able to: Classify the various approaches to Analogue Modulation
A Complete Set of Experiments for Communication Classes
 A Complete Set of Experiments for Communication Classes Firas Hassan Ohio Northern University, Ada, OH 45810 f-hassan@onu.edu Abstract In this paper, a set of module based hands-on experiments that cover
A Complete Set of Experiments for Communication Classes Firas Hassan Ohio Northern University, Ada, OH 45810 f-hassan@onu.edu Abstract In this paper, a set of module based hands-on experiments that cover
Amplitude Modulation
 Amplitude Modulation Manasvi Grover Electronics and Communications Department Northern India Engineering College, New Delhi, India Maninder Bir Singh Gulshan Electronics and Communications Department Northern
Amplitude Modulation Manasvi Grover Electronics and Communications Department Northern India Engineering College, New Delhi, India Maninder Bir Singh Gulshan Electronics and Communications Department Northern
SOME FEATURES OF SIGNAL DEMODULATION RESULTING FROM THE PRACTICAL IMPLEMENTATION OF A DIRECT CONVERSION RADIO RECEIVER
 Philips J. Res. 41, 219-231, 1986 R1l27 SOME FEATURES OF SIGNAL DEMODULATION RESULTING FROM THE PRACTICAL IMPLEMENTATION OF A DIRECT CONVERSION RADIO RECEIVER by R. A. BROWN, R. J. DEWEY and C. J. COLLIER
Philips J. Res. 41, 219-231, 1986 R1l27 SOME FEATURES OF SIGNAL DEMODULATION RESULTING FROM THE PRACTICAL IMPLEMENTATION OF A DIRECT CONVERSION RADIO RECEIVER by R. A. BROWN, R. J. DEWEY and C. J. COLLIER
UNIT 1 QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS
 UNIT 1 QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier signal is varied in accordance with the instantaneous value of the modulating
UNIT 1 QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier signal is varied in accordance with the instantaneous value of the modulating
Introduction to Receivers
 Introduction to Receivers Purpose: translate RF signals to baseband Shift frequency Amplify Filter Demodulate Why is this a challenge? Interference Large dynamic range required Many receivers must be capable
Introduction to Receivers Purpose: translate RF signals to baseband Shift frequency Amplify Filter Demodulate Why is this a challenge? Interference Large dynamic range required Many receivers must be capable
