Index. band bending 317 bandwidth limitation 176, 182, 190, 195, 196 BBO
|
|
|
- Annice Wilson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Index β-bab 2O 4 (BBO) 85, 202 β-barium borate see β-bab 2O 4 (BBO) β (BEDT-TTF) 2PF π-conjugated polymer 304 III-V compound semiconductor 363 III-V-N compound semiconductor f chirp compensator 213, 214, 220 configuration 199 phase compensator 202, 207, 226, 228, 237 pulse shaper 106, 109, 180, 196, 254, 280, 281 system 171, 172, 233, 244, 245, 257, 259 acoustic noise 297 active phase compensator 201 adaptive chirp compensation 200 AOM 226 atomic hydrogen exposure 364 attosecond x-ray generation 379 autoconvolution 170, 174 autocorrelation , 166, 167, 170, 189 azobenzen 286 band bending 317 bandwidth limitation 176, 182, 190, 195, 196 BBO see β-bab 2O 4 (BBO) Bessel function 254 bi-directional propagation 15, 16, 44 C carbon nanotube 300 carrier frequency 239 carrier generation rate 318 carrier recombination rate 318 carrier-envelope phase 57, 212 CDW see charge density wave charge density wave 300 chirp VII, 84, 103 coefficient 244 compensation XI, 103, 104, 107, 112, 350 compensator 78, 105, 106 circuit response 295 closed-loop phase control 199 complex electric field 177, 238, 251, 252, 254, 255 compression 54 computer-controlled feedback system 213 constant height mode 290 constant value mode 291 contact potential difference 321 core dispersion 15, 19, 21, 45, 47 CPD 321 creep of piezo element 297 cross-phase modulation 8 cyclodextrin 305 CyD molecule 305 decay slope 374 deformable mirror 106, 226 delta-function 253, 263, 269 diffraction 173, 193 formula 112 dispersion length 22, 49, 225 displacement current 351, 368 double lock-in technique 358 down-chirp 103 energy diagram of STM 293 external vibration 291
2 386 Index feedback compensation 186, 199, 202 control 200 phase compensation 106, 202, 227 pulse compression 201 Spectral-Phase Control Technique 201 system 219 technique 234 femtosecond-ångstrom technology 349 femtosecond-time resolved STM (FTR-STM) X, XII few-to-mono cycle photonics VII, XI, 67, 379 field enhancement effect 315 finite-difference frequency-domain method 10 time-domain method 10 flip-flop motion 302 four-wave mixing 12, 91, 92 Fourier direct method 14 plane 174, 260, 264, 281 transform 167, 168, 177, 178, 182, 188, 238, , 255, 266, 268, 271 -transform-limited pulse 103, 173, 183, 201, 209, 227, 236, 237, 240, 244, 245, 254, 255, 281 fourth-order dispersion 116, 173 FRAC , 172, 173, , , 217, 236 frequency marginal 169, 170, , 196 FROG (frequency-resolved optical gating) 85, 96, 125, 155, , 181, 183, algorithm error 169, 174 FTR-STM see femtosecond-time resolved STM fused-silica fiber 68, 71 FWM see four-wave mixing GaNAs 363 GDD see group delay dispersion grating 172, 173, , 193, 256, 257, 259, 260, 265 group delay 81, 97, 173, 182, 208, 211, 240, 379 dispersion (GDD) 81, 92, 96, 97, 116, 144, 173, 181, 187, 188, 190, 213, 232, 244 group velocity 83, 86 difference 74 dispersion 6, 71 mismatch 71, 208 GVD see group velocity dispersion hollow fiber 68, 82, 85, 86, 119, 123, 224, 226 impulse response 375 induced phase modulation 8, 68, 74, 76, 77, 79, 81, 83 88, 98, 99, 205, 240, 259, 264 pulse compression 207 induced polarization 15 inelastic tunneling 306 instantaneous frequency 239 interference effect 361 IPM see induced phase modulation junction mixing STM 351 Kelvin probe 321 Kondo effect 300 LDOS 294 lens 181, 187, 188, 192, 256, 257, 259, 260 light-modulated scanning tunneling spectroscopy 327 linear chirp 74 LM-STS 327 local density of states see LDOS lock-in amplifier 352, 358 lock-in time constant 367, 372 low dimensional organic conductor 299 low pass filter 374 M-SPIDER 172, 185, 187, 192, 196, , 207, 212, 214, 215, 221, 222, , 244, 245 manipulation by STM 305
3 Index 387 manipulator of optical electric-field wavepackets 247 metal-insulator-semiconductor 321 MIS 321 junction 329 modified spectral-phase interferometer for direct electric-field reconstruction see M-SPIDER SPIDER see M-SPIDER molecular necklace 305 monocycle pulse VII, 195, 196, 224, 379 regime 228 -like pulse 185, 190, 196, 201, 238, 240, 246 multicolor pulse shaping 256, 257, 259, 281, 282 multiple photon absorption 368 excitation 356 NA 308, 350 nearfield optical scanning microscopy 350 wave 350 nonlinear dispersion 19, 21, 47 length 22, 49, 225 refractive index 71, 224 Schrödinger equation 9, 14, 22, 70 NSOM 350 numeric aperture see NA OHD-RIKES 275 one-octave bandwidth XI, 98, 200 exceeding bandwidth 246 optical chopper 358 function generator 247 scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) VII, IX, XI, 379 STM see optical scanning tunneling microscopy wave musical instrument 247 oscillatory structure 89, 90 over-one-octave bandwidth 192, 196, 226, 238, 240, 244, 245 ultrabroadband pulses 224 parametric four-ware mixing 91 passive chirp compensator 213, 226 PCF 31, 68, 91, 92, 95, 213, 214, 217 phase compensation VII, 54, 174, 186, 191, 196, 199, 232, 233, 240, 244, 245 compensator 202, 235 dispersion 103 modulation , 257, photoconductively gated STM 350 photoelectron 368 emission 356 photoisomerization 286 photonic crystal fiber see PCF photonic crystal glass fiber see PCF piezo effect 297 polyrotaxane 305 propagation constant 19 pulse compression 107, 120, 233 pulse train 251, 254, 255, , , 280, 282 pulse-pair-excited STM 353 pump (a pulse pair) and probe techniques XI pump probe technique X quantum-state control 379 Raman induced Kerr effect 275 Raman response 3, 16, 19, 21, 45 Raman scattering 264, 266, 269, 271, 273, 274 Raman spectroscopy 275 real electric field 167, 238, 251, 252 reflective objective 75, 93, 132, 202, 214 regenerative amplifier 356 repetition rate 350, 356 rotaxane 305 S/N ratio 358 SAM 286, 300 sampling theorem 181 scanning electron microscopy 314 nearfield optical microscopy see SNOM, NSOM probe microscopy 289 probe spectroscopy 291
4 388 Index tunneling microscopy (STM) IX, XI, 289, 349 tunneling spectroscopy (STS) 294 Schottky contact 320 second-harmonic generation frequencyresolved optical gating (SHG FROG) 27 selective excitation , , 279, 282 self-assembled monolayer 300 self-phase modulation (SPM) 6, 67, 76, 77, 81 84, 86 88, 91, 92, 95, 96, 99, 103, 201, 225, 256, 259, 261, 264, 289 self-steepening (SST) 6, 19, 21, 47, 91 Sellmeier equation 12, 18 SEM 314 SH interferogram 215, 231, 234 shadowing effect 313 shaken-pulse-pair-excited STM 359 shaker method 358 SHG 153, , 176, 192, 195 shock length 49 Si nonoparticle 304 Si(100) 301 Si(111) sinc-function 253 SLM see spatial light modulator slowly-evolving wave approximation (SEWA) 1 slowly-varying-envelope approximation (SVEA) VII, 1, 22 SNOM 350 soliton effect 98 formation 91 spatial chirp 67, 170 spatial light modulator (SLM) 105, 106, 112, 201, 202, 208, 215, 218, 220, 226, 240, 244, 245 technique XI phase modulator , 180, 196, 252, , 281, 282 spatially resolved SPV 318 spectral filtering effect 169, 170 phase XI, 67, 76, 97, 98, 167, 168, , 182, 184, 186, 203, 204, 208, 213, 222, 227, 237 phase characterization 199 phase difference 178, 179 shear , 181, 186, 190, 207, 227, 232 slicing 259, 260, 281 -phase characterization and compensation XI, 201 -phase compensation 202 -phase feedback technique 205 spectrally-resolved intensity-autocorrelation 78 SPIDER 155, 172, 176, 177, , , 200, 225 interferogram 217 signal , 207, 208, 217, 222, 231, 232, 234 split-step Fourier method 10, 14 SPM see self-phase modulation SPPX-STM 359 SPV 317, 352 SR-SPV 318 SRS see stimulated Raman Scattering SST see self-steepening (SST) steepening see self-steepening (SST) stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS) 91, 92 STM see scanning tunneling microscopy stray capacitance 368, 368 STS see scanning tunneling spectroscopy sum-frequency generation 181, 184, 186, 187, 195 surface photovoltage 317, 352 tapered fiber (TF) 68, 94 96, 218, 219 Taylor expansion 173 tetrachloroethylene 271, 272 TF see tapered fiber thermal drift 297 expansion/shrinking of STM tip 358 fluctuation 291 noise level 295, 296 emission current 320
5 Index 389 third-order dispersion (TOD) 71, 97, 116, 144, 173, 213 nonlinear polarization 71 phase dispersion see third-order dispersion (TOD) Ti:sapphire laser 67, 72 time constant 374 smearing 170, 174, 176, 195, 196 window 113, 255, 281 -dependent phase 67 TIVI 153 TL pulse see Fourier-transform-limited pulse TOD see third-order dispersion transform-limited pulse see Fourier-transform-limited pulse tunnel effect 292 junction 292, 311 transmission coefficient 293 two-spring oscillator model 297 UHV 306 ultrabroadband 169, 171, 176, 180, , 190, 196, 254, 280 pulse generation 69 ultrahigh vacuum (UHV) see UHV unidirectional propagation 22, 44 up-chirp 103 up-chirped pulse 220 vibration isolation 297 vibrationally-synchronized pumping 263, 264, 266, 270, 271, 274 walk-off length 74, 75, 78 Wigner distribution function , 244, 245 WKB approximation 293 zero group-delay dispersion 68 zero-dispersion wavelength (ZDW) 91, 93, 95, 98, 220
How to build an Er:fiber femtosecond laser
 How to build an Er:fiber femtosecond laser Daniele Brida 17.02.2016 Konstanz Ultrafast laser Time domain : pulse train Frequency domain: comb 3 26.03.2016 Frequency comb laser Time domain : pulse train
How to build an Er:fiber femtosecond laser Daniele Brida 17.02.2016 Konstanz Ultrafast laser Time domain : pulse train Frequency domain: comb 3 26.03.2016 Frequency comb laser Time domain : pulse train
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Information Real-space imaging of transient carrier dynamics by nanoscale pump-probe microscopy Yasuhiko Terada, Shoji Yoshida, Osamu Takeuchi, and Hidemi Shigekawa*
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Information Real-space imaging of transient carrier dynamics by nanoscale pump-probe microscopy Yasuhiko Terada, Shoji Yoshida, Osamu Takeuchi, and Hidemi Shigekawa*
taccor Optional features Overview Turn-key GHz femtosecond laser
 taccor Turn-key GHz femtosecond laser Self-locking and maintaining Stable and robust True hands off turn-key system Wavelength tunable Integrated pump laser Overview The taccor is a unique turn-key femtosecond
taccor Turn-key GHz femtosecond laser Self-locking and maintaining Stable and robust True hands off turn-key system Wavelength tunable Integrated pump laser Overview The taccor is a unique turn-key femtosecond
Fiber-Optic Communication Systems
 Fiber-Optic Communication Systems Second Edition GOVIND P. AGRAWAL The Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY A WILEY-iNTERSCIENCE PUBLICATION JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. NEW YORK / CHICHESTER
Fiber-Optic Communication Systems Second Edition GOVIND P. AGRAWAL The Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY A WILEY-iNTERSCIENCE PUBLICATION JOHN WILEY & SONS, INC. NEW YORK / CHICHESTER
Optical Fibers p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Step-Index Fibers p. 2 Graded-Index Fibers p. 4 Design and Fabrication p. 6 Silica Fibers p.
 Preface p. xiii Optical Fibers p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Step-Index Fibers p. 2 Graded-Index Fibers p. 4 Design and Fabrication p. 6 Silica Fibers p. 6 Plastic Optical Fibers p. 9 Microstructure Optical
Preface p. xiii Optical Fibers p. 1 Basic Concepts p. 1 Step-Index Fibers p. 2 Graded-Index Fibers p. 4 Design and Fabrication p. 6 Silica Fibers p. 6 Plastic Optical Fibers p. 9 Microstructure Optical
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy
 Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
Characteristics of point-focus Simultaneous Spatial and temporal Focusing (SSTF) as a two-photon excited fluorescence microscopy Qiyuan Song (M2) and Aoi Nakamura (B4) Abstracts: We theoretically and experimentally
Spectral phase shaping for high resolution CARS spectroscopy around 3000 cm 1
 Spectral phase shaping for high resolution CARS spectroscopy around 3 cm A.C.W. van Rhijn, S. Postma, J.P. Korterik, J.L. Herek, and H.L. Offerhaus Mesa + Research Institute for Nanotechnology, University
Spectral phase shaping for high resolution CARS spectroscopy around 3 cm A.C.W. van Rhijn, S. Postma, J.P. Korterik, J.L. Herek, and H.L. Offerhaus Mesa + Research Institute for Nanotechnology, University
A new picosecond Laser pulse generation method.
 PULSE GATING : A new picosecond Laser pulse generation method. Picosecond lasers can be found in many fields of applications from research to industry. These lasers are very common in bio-photonics, non-linear
PULSE GATING : A new picosecond Laser pulse generation method. Picosecond lasers can be found in many fields of applications from research to industry. These lasers are very common in bio-photonics, non-linear
Propagation, Dispersion and Measurement of sub-10 fs Pulses
 Propagation, Dispersion and Measurement of sub-10 fs Pulses Table of Contents 1. Theory 2. Pulse propagation through various materials o Calculating the index of refraction Glass materials Air Index of
Propagation, Dispersion and Measurement of sub-10 fs Pulses Table of Contents 1. Theory 2. Pulse propagation through various materials o Calculating the index of refraction Glass materials Air Index of
Dr. Rüdiger Paschotta RP Photonics Consulting GmbH. Competence Area: Fiber Devices
 Dr. Rüdiger Paschotta RP Photonics Consulting GmbH Competence Area: Fiber Devices Topics in this Area Fiber lasers, including exotic types Fiber amplifiers, including telecom-type devices and high power
Dr. Rüdiger Paschotta RP Photonics Consulting GmbH Competence Area: Fiber Devices Topics in this Area Fiber lasers, including exotic types Fiber amplifiers, including telecom-type devices and high power
Fiber Amplifiers. Fiber Lasers. 1*5 World Scientific. Niloy K nulla. University ofconnecticut, USA HONG KONG NEW JERSEY LONDON
 LONDON Fiber Amplifiers Fiber Lasers Niloy K nulla University ofconnecticut, USA 1*5 World Scientific NEW JERSEY SINGAPORE BEIJING SHANGHAI HONG KONG TAIPEI CHENNAI Contents Preface v 1. Introduction 1
LONDON Fiber Amplifiers Fiber Lasers Niloy K nulla University ofconnecticut, USA 1*5 World Scientific NEW JERSEY SINGAPORE BEIJING SHANGHAI HONG KONG TAIPEI CHENNAI Contents Preface v 1. Introduction 1
Optical Communications and Networking 朱祖勍. Sept. 25, 2017
 Optical Communications and Networking Sept. 25, 2017 Lecture 4: Signal Propagation in Fiber 1 Nonlinear Effects The assumption of linearity may not always be valid. Nonlinear effects are all related to
Optical Communications and Networking Sept. 25, 2017 Lecture 4: Signal Propagation in Fiber 1 Nonlinear Effects The assumption of linearity may not always be valid. Nonlinear effects are all related to
Continuum White Light Generation. WhiteLase: High Power Ultrabroadband
 Continuum White Light Generation WhiteLase: High Power Ultrabroadband Light Sources Technology Ultrafast Pulses + Fiber Laser + Non-linear PCF = Spectral broadening from 400nm to 2500nm Ultrafast Fiber
Continuum White Light Generation WhiteLase: High Power Ultrabroadband Light Sources Technology Ultrafast Pulses + Fiber Laser + Non-linear PCF = Spectral broadening from 400nm to 2500nm Ultrafast Fiber
Spider Pulse Characterization
 Spider Pulse Characterization Spectral and Temporal Characterization of Ultrashort Laser Pulses The Spider series by APE is an all-purpose and frequently used solution for complete characterization of
Spider Pulse Characterization Spectral and Temporal Characterization of Ultrashort Laser Pulses The Spider series by APE is an all-purpose and frequently used solution for complete characterization of
Nonlinear Optics (WiSe 2015/16) Lecture 9: December 11, 2015
 Nonlinear Optics (WiSe 2015/16) Lecture 9: December 11, 2015 Chapter 9: Optical Parametric Amplifiers and Oscillators 9.8 Noncollinear optical parametric amplifier (NOPA) 9.9 Optical parametric chirped-pulse
Nonlinear Optics (WiSe 2015/16) Lecture 9: December 11, 2015 Chapter 9: Optical Parametric Amplifiers and Oscillators 9.8 Noncollinear optical parametric amplifier (NOPA) 9.9 Optical parametric chirped-pulse
Characterization of Chirped volume bragg grating (CVBG)
 Characterization of Chirped volume bragg grating (CVBG) Sobhy Kholaif September 7, 017 1 Laser pulses Ultrashort laser pulses have extremely short pulse duration. When the pulse duration is less than picoseconds
Characterization of Chirped volume bragg grating (CVBG) Sobhy Kholaif September 7, 017 1 Laser pulses Ultrashort laser pulses have extremely short pulse duration. When the pulse duration is less than picoseconds
Chad A. Husko 1,, Sylvain Combrié 2, Pierre Colman 2, Jiangjun Zheng 1, Alfredo De Rossi 2, Chee Wei Wong 1,
 SOLITON DYNAMICS IN THE MULTIPHOTON PLASMA REGIME Chad A. Husko,, Sylvain Combrié, Pierre Colman, Jiangjun Zheng, Alfredo De Rossi, Chee Wei Wong, Optical Nanostructures Laboratory, Columbia University
SOLITON DYNAMICS IN THE MULTIPHOTON PLASMA REGIME Chad A. Husko,, Sylvain Combrié, Pierre Colman, Jiangjun Zheng, Alfredo De Rossi, Chee Wei Wong, Optical Nanostructures Laboratory, Columbia University
; A=4π(2m) 1/2 /h. exp (Fowler Nordheim Eq.) 2 const
 Scanning Tunneling Microscopy (STM) Brief background: In 1981, G. Binnig, H. Rohrer, Ch. Gerber and J. Weibel observed vacuum tunneling of electrons between a sharp tip and a platinum surface. The tunnel
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy (STM) Brief background: In 1981, G. Binnig, H. Rohrer, Ch. Gerber and J. Weibel observed vacuum tunneling of electrons between a sharp tip and a platinum surface. The tunnel
Types of losses in optical fiber cable are: Due to attenuation, the power of light wave decreases exponentially with distance.
 UNIT-II TRANSMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF OPTICAL FIBERS SIGNAL ATTENUATION: Signal attenuation in an optical fiber is defined as the decrease in light power during light propagation along an optical fiber.
UNIT-II TRANSMISSION CHARACTERISTICS OF OPTICAL FIBERS SIGNAL ATTENUATION: Signal attenuation in an optical fiber is defined as the decrease in light power during light propagation along an optical fiber.
Faraday Rotators and Isolators
 Faraday Rotators and I. Introduction The negative effects of optical feedback on laser oscillators and laser diodes have long been known. Problems include frequency instability, relaxation oscillations,
Faraday Rotators and I. Introduction The negative effects of optical feedback on laser oscillators and laser diodes have long been known. Problems include frequency instability, relaxation oscillations,
Modified Spectrum Auto-Interferometric Correlation. (MOSAIC) for Single Shot Pulse Characterization
 To appear in OPTICS LETTERS, October 1, 2007 / Vol. 32, No. 19 Modified Spectrum Auto-Interferometric Correlation (MOSAIC) for Single Shot Pulse Characterization Daniel A. Bender* and Mansoor Sheik-Bahae
To appear in OPTICS LETTERS, October 1, 2007 / Vol. 32, No. 19 Modified Spectrum Auto-Interferometric Correlation (MOSAIC) for Single Shot Pulse Characterization Daniel A. Bender* and Mansoor Sheik-Bahae
Solid-State Laser Engineering
 Walter Koechner Solid-State Laser Engineering Fourth Extensively Revised and Updated Edition With 449 Figures Springer Contents 1. Introduction 1 1.1 Optical Amplification 1 1.2 Interaction of Radiation
Walter Koechner Solid-State Laser Engineering Fourth Extensively Revised and Updated Edition With 449 Figures Springer Contents 1. Introduction 1 1.1 Optical Amplification 1 1.2 Interaction of Radiation
Optics and Lasers. Matt Young. Including Fibers and Optical Waveguides
 Matt Young Optics and Lasers Including Fibers and Optical Waveguides Fourth Revised Edition With 188 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Contents
Matt Young Optics and Lasers Including Fibers and Optical Waveguides Fourth Revised Edition With 188 Figures Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong Barcelona Budapest Contents
Lecture 7 Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 7, Slide 1
 Dispersion management Lecture 7 Dispersion compensating fibers (DCF) Fiber Bragg gratings (FBG) Dispersion-equalizing filters Optical phase conjugation (OPC) Electronic dispersion compensation (EDC) Fiber
Dispersion management Lecture 7 Dispersion compensating fibers (DCF) Fiber Bragg gratings (FBG) Dispersion-equalizing filters Optical phase conjugation (OPC) Electronic dispersion compensation (EDC) Fiber
Elements of Optical Networking
 Bruckner Elements of Optical Networking Basics and practice of optical data communication With 217 Figures, 13 Tables and 93 Exercises Translated by Patricia Joliet VIEWEG+ TEUBNER VII Content Preface
Bruckner Elements of Optical Networking Basics and practice of optical data communication With 217 Figures, 13 Tables and 93 Exercises Translated by Patricia Joliet VIEWEG+ TEUBNER VII Content Preface
Index. Cambridge University Press Silicon Photonics Design Lukas Chrostowski and Michael Hochberg. Index.
 absorption, 69 active tuning, 234 alignment, 394 396 apodization, 164 applications, 7 automated optical probe station, 389 397 avalanche detector, 268 back reflection, 164 band structures, 30 bandwidth
absorption, 69 active tuning, 234 alignment, 394 396 apodization, 164 applications, 7 automated optical probe station, 389 397 avalanche detector, 268 back reflection, 164 band structures, 30 bandwidth
Optimization of supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fibers for pulse compression
 Optimization of supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fibers for pulse compression Noah Chang Herbert Winful,Ted Norris Center for Ultrafast Optical Science University of Michigan What is Photonic
Optimization of supercontinuum generation in photonic crystal fibers for pulse compression Noah Chang Herbert Winful,Ted Norris Center for Ultrafast Optical Science University of Michigan What is Photonic
Absorption: in an OF, the loss of Optical power, resulting from conversion of that power into heat.
 Absorption: in an OF, the loss of Optical power, resulting from conversion of that power into heat. Scattering: The changes in direction of light confined within an OF, occurring due to imperfection in
Absorption: in an OF, the loss of Optical power, resulting from conversion of that power into heat. Scattering: The changes in direction of light confined within an OF, occurring due to imperfection in
OPTI510R: Photonics. Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona Meinel building R.626
 OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Photodetectors Introduction Most important characteristics Photodetector
OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Photodetectors Introduction Most important characteristics Photodetector
VELA PHOTOINJECTOR LASER. E.W. Snedden, Lasers and Diagnostics Group
 VELA PHOTOINJECTOR LASER E.W. Snedden, Lasers and Diagnostics Group Contents Introduction PI laser step-by-step: Ti:Sapphire oscillator Regenerative amplifier Single-pass amplifier Frequency mixing Emphasis
VELA PHOTOINJECTOR LASER E.W. Snedden, Lasers and Diagnostics Group Contents Introduction PI laser step-by-step: Ti:Sapphire oscillator Regenerative amplifier Single-pass amplifier Frequency mixing Emphasis
Simultaneous measurement of two different-color ultrashort pulses on a single shot
 Wong et al. Vol. 29, No. 8 / August 2012 / J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1889 Simultaneous measurement of two different-color ultrashort pulses on a single shot Tsz Chun Wong,* Justin Ratner, and Rick Trebino School
Wong et al. Vol. 29, No. 8 / August 2012 / J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 1889 Simultaneous measurement of two different-color ultrashort pulses on a single shot Tsz Chun Wong,* Justin Ratner, and Rick Trebino School
14. Measuring Ultrashort Laser Pulses I: Autocorrelation
 14. Measuring Ultrashort Laser Pulses I: Autocorrelation The dilemma The goal: measuring the intensity and phase vs. time (or frequency) Why? The Spectrometer and Michelson Interferometer Autocorrelation
14. Measuring Ultrashort Laser Pulses I: Autocorrelation The dilemma The goal: measuring the intensity and phase vs. time (or frequency) Why? The Spectrometer and Michelson Interferometer Autocorrelation
Romania and High Power Lasers Towards Extreme Light Infrastructure in Romania
 Romania and High Power Lasers Towards Extreme Light Infrastructure in Romania Razvan Dabu, Daniel Ursescu INFLPR, Magurele, Romania Contents GiWALAS laser facility TEWALAS laser facility CETAL project
Romania and High Power Lasers Towards Extreme Light Infrastructure in Romania Razvan Dabu, Daniel Ursescu INFLPR, Magurele, Romania Contents GiWALAS laser facility TEWALAS laser facility CETAL project
Principles of Optics for Engineers
 Principles of Optics for Engineers Uniting historically different approaches by presenting optical analyses as solutions of Maxwell s equations, this unique book enables students and practicing engineers
Principles of Optics for Engineers Uniting historically different approaches by presenting optical analyses as solutions of Maxwell s equations, this unique book enables students and practicing engineers
Second-harmonic generation frequency-resolved optical gating in the single-cycle regime Baltuška, Andrius; Pshenitchnikov, Maxim; Wiersma, Douwe A.
 University of Groningen Second-harmonic generation frequency-resolved optical gating in the single-cycle regime Baltuška, Andrius; Pshenitchnikov, Maxim; Wiersma, Douwe A. Published in: IEEE Journal of
University of Groningen Second-harmonic generation frequency-resolved optical gating in the single-cycle regime Baltuška, Andrius; Pshenitchnikov, Maxim; Wiersma, Douwe A. Published in: IEEE Journal of
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/2/e1700324/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Photocarrier generation from interlayer charge-transfer transitions in WS2-graphene heterostructures Long Yuan, Ting-Fung
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/4/2/e1700324/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Photocarrier generation from interlayer charge-transfer transitions in WS2-graphene heterostructures Long Yuan, Ting-Fung
High energy femtosecond OPA pumped by 1030 nm Nd:KGW laser.
 High energy femtosecond OPA pumped by 1030 nm Nd:KGW laser. V. Kozich 1, A. Moguilevski, and K. Heyne Institut für Experimentalphysik, Freie Universität Berlin, Arnimallee 14, D-14195 Berlin, Germany Abstract
High energy femtosecond OPA pumped by 1030 nm Nd:KGW laser. V. Kozich 1, A. Moguilevski, and K. Heyne Institut für Experimentalphysik, Freie Universität Berlin, Arnimallee 14, D-14195 Berlin, Germany Abstract
atom physics seminar ultra short laser pulses
 atom physics seminar ultra short laser pulses creation and application ultra short laser pulses overview what? - why? - how? creation and optimisation typical experimental setup properties of existing
atom physics seminar ultra short laser pulses creation and application ultra short laser pulses overview what? - why? - how? creation and optimisation typical experimental setup properties of existing
Optical Signal Processing
 Optical Signal Processing ANTHONY VANDERLUGT North Carolina State University Raleigh, North Carolina A Wiley-Interscience Publication John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York / Chichester / Brisbane / Toronto
Optical Signal Processing ANTHONY VANDERLUGT North Carolina State University Raleigh, North Carolina A Wiley-Interscience Publication John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York / Chichester / Brisbane / Toronto
ANALYSIS OF DISPERSION COMPENSATION IN A SINGLE MODE OPTICAL FIBER COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
 ANAYSIS OF DISPERSION COMPENSATION IN A SINGE MODE OPTICA FIBER COMMUNICATION SYSTEM Sani Abdullahi Mohammed 1, Engr. Yahya Adamu and Engr. Matthew Kwatri uka 3 1,,3 Department of Electrical and Electronics
ANAYSIS OF DISPERSION COMPENSATION IN A SINGE MODE OPTICA FIBER COMMUNICATION SYSTEM Sani Abdullahi Mohammed 1, Engr. Yahya Adamu and Engr. Matthew Kwatri uka 3 1,,3 Department of Electrical and Electronics
LASER DIODE MODULATION AND NOISE
 > 5' O ft I o Vi LASER DIODE MODULATION AND NOISE K. Petermann lnstitutfiir Hochfrequenztechnik, Technische Universitdt Berlin Kluwer Academic Publishers i Dordrecht / Boston / London KTK Scientific Publishers
> 5' O ft I o Vi LASER DIODE MODULATION AND NOISE K. Petermann lnstitutfiir Hochfrequenztechnik, Technische Universitdt Berlin Kluwer Academic Publishers i Dordrecht / Boston / London KTK Scientific Publishers
Yb-doped Mode-locked fiber laser based on NLPR Yan YOU
 Yb-doped Mode-locked fiber laser based on NLPR 20120124 Yan YOU Mode locking method-nlpr Nonlinear polarization rotation(nlpr) : A power-dependent polarization change is converted into a power-dependent
Yb-doped Mode-locked fiber laser based on NLPR 20120124 Yan YOU Mode locking method-nlpr Nonlinear polarization rotation(nlpr) : A power-dependent polarization change is converted into a power-dependent
Supplementary Information for
 Supplementary Information for Vibrational Coherence in the Excited State Dynamics of Cr(acac) 3 : Identifying the Reaction Coordinate for Ultrafast Intersystem Crossing Joel N. Schrauben, Kevin L. Dillman,
Supplementary Information for Vibrational Coherence in the Excited State Dynamics of Cr(acac) 3 : Identifying the Reaction Coordinate for Ultrafast Intersystem Crossing Joel N. Schrauben, Kevin L. Dillman,
Power penalty caused by Stimulated Raman Scattering in WDM Systems
 Paper Power penalty caused by Stimulated Raman Scattering in WDM Systems Sławomir Pietrzyk, Waldemar Szczęsny, and Marian Marciniak Abstract In this paper we present results of an investigation into the
Paper Power penalty caused by Stimulated Raman Scattering in WDM Systems Sławomir Pietrzyk, Waldemar Szczęsny, and Marian Marciniak Abstract In this paper we present results of an investigation into the
Fundamental Optics ULTRAFAST THEORY ( ) = ( ) ( q) FUNDAMENTAL OPTICS. q q = ( A150 Ultrafast Theory
 ULTRAFAST THEORY The distinguishing aspect of femtosecond laser optics design is the need to control the phase characteristic of the optical system over the requisite wide pulse bandwidth. CVI Laser Optics
ULTRAFAST THEORY The distinguishing aspect of femtosecond laser optics design is the need to control the phase characteristic of the optical system over the requisite wide pulse bandwidth. CVI Laser Optics
Coherent pulse synthesis: towards sub-cycle optical waveforms
 Laser Photonics Rev., 1 43 (2014) / DOI 10.1002/lpor.201400181 LASER & PHOTONICS REVIEWS Abstract The generation of sub-optical-cycle, carrier envelope phase-stable light pulses is one of the frontiers
Laser Photonics Rev., 1 43 (2014) / DOI 10.1002/lpor.201400181 LASER & PHOTONICS REVIEWS Abstract The generation of sub-optical-cycle, carrier envelope phase-stable light pulses is one of the frontiers
:... resolution is about 1.4 μm, assumed an excitation wavelength of 633 nm and a numerical aperture of 0.65 at 633 nm.
 PAGE 30 & 2008 2007 PRODUCT CATALOG Confocal Microscopy - CFM fundamentals :... Over the years, confocal microscopy has become the method of choice for obtaining clear, three-dimensional optical images
PAGE 30 & 2008 2007 PRODUCT CATALOG Confocal Microscopy - CFM fundamentals :... Over the years, confocal microscopy has become the method of choice for obtaining clear, three-dimensional optical images
PulsekCompressionkofkShortkWavekInfraredk OpticalkParametrickAmplifiedkPulseskusingkak HollowkCorekCapillary
 PulsekCompressionkofkShortkWavekInfraredk OpticalkParametrickAmplifiedkPulseskusingkak HollowkCorekCapillary NevenkIbrakovic LRAP-504 Master ThesisWsubmittedWforWtheWdegreeWofWWWWMasterWofWScienceW 9 ProjectWduration:WWWW13Wmonths
PulsekCompressionkofkShortkWavekInfraredk OpticalkParametrickAmplifiedkPulseskusingkak HollowkCorekCapillary NevenkIbrakovic LRAP-504 Master ThesisWsubmittedWforWtheWdegreeWofWWWWMasterWofWScienceW 9 ProjectWduration:WWWW13Wmonths
Jungwon Kim, Jonathan A. Cox, Jian J. Chen & Franz X. Kärtner. Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science and Research Laboratory
 1 Supplementary Information Drift-free femtosecond timing synchronization of remote optical and microwave sources with better than 10-19 -level stability Jungwon Kim, Jonathan A. Cox, Jian J. Chen & Franz
1 Supplementary Information Drift-free femtosecond timing synchronization of remote optical and microwave sources with better than 10-19 -level stability Jungwon Kim, Jonathan A. Cox, Jian J. Chen & Franz
All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration
 1/36 All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Introduction Major Nonlinear Effects
1/36 All-Optical Signal Processing and Optical Regeneration Govind P. Agrawal Institute of Optics University of Rochester Rochester, NY 14627 c 2007 G. P. Agrawal Outline Introduction Major Nonlinear Effects
THE GENERATION and characterization of ultrafast
 20 IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 37, NO. 1, JANUARY 2001 Aberrations in Temporal Imaging Corey V. Bennett, Student Member, IEEE, and Brian H. Kolner, Member, IEEE Abstract Recent advances in
20 IEEE JOURNAL OF QUANTUM ELECTRONICS, VOL. 37, NO. 1, JANUARY 2001 Aberrations in Temporal Imaging Corey V. Bennett, Student Member, IEEE, and Brian H. Kolner, Member, IEEE Abstract Recent advances in
Title. Author(s)Yamashita, Mikio; Yamane, Keisaku; Morita, Ryuji. CitationIEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electroni. Issue Date
 Title Quasi-automatic phase-control technique for chirp co of few- to mono-cycle optical pulses Author(s)Yamashita, Mikio; Yamane, Keisaku; Morita, Ryuji CitationIEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum
Title Quasi-automatic phase-control technique for chirp co of few- to mono-cycle optical pulses Author(s)Yamashita, Mikio; Yamane, Keisaku; Morita, Ryuji CitationIEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum
Ultrafast Optical Physics II (SoSe 2017) Lecture 9, June 16
 Ultrafast Optical Physics II (SoSe 2017) Lecture 9, June 16 9 Pulse Characterization 9.1 Intensity Autocorrelation 9.2 Interferometric Autocorrelation (IAC) 9.3 Frequency Resolved Optical Gating (FROG)
Ultrafast Optical Physics II (SoSe 2017) Lecture 9, June 16 9 Pulse Characterization 9.1 Intensity Autocorrelation 9.2 Interferometric Autocorrelation (IAC) 9.3 Frequency Resolved Optical Gating (FROG)
PITZ Laser Systems. Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. Cavity. What is a Laser? General introduction: systems, layouts
 PITZ Laser Systems General introduction: systems, layouts Matthias Groß PITZ Laser Systems Technisches Seminar Zeuthen, 14.11.2017 What is a Laser? > General setup Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission
PITZ Laser Systems General introduction: systems, layouts Matthias Groß PITZ Laser Systems Technisches Seminar Zeuthen, 14.11.2017 What is a Laser? > General setup Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission
Optical pulse compression to 5.0 fs by use of only a spatial light modulator for phase compensation
 1742 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/ Vol. 18, No. 11/ November 2001 Karasawa et al. Optical pulse compression to 5.0 fs by use of only a spatial light modulator for phase compensation Naoki Karasawa Department of
1742 J. Opt. Soc. Am. B/ Vol. 18, No. 11/ November 2001 Karasawa et al. Optical pulse compression to 5.0 fs by use of only a spatial light modulator for phase compensation Naoki Karasawa Department of
CONTENTS. Chapter 1 Wave Nature of Light 19
 CONTENTS Chapter 1 Wave Nature of Light 19 1.1 Light Waves in a Homogeneous Medium 19 A. Plane Electromagnetic Wave 19 B. Maxwell's Wave Equation and Diverging Waves 22 Example 1.1.1 A diverging laser
CONTENTS Chapter 1 Wave Nature of Light 19 1.1 Light Waves in a Homogeneous Medium 19 A. Plane Electromagnetic Wave 19 B. Maxwell's Wave Equation and Diverging Waves 22 Example 1.1.1 A diverging laser
Scanning Tunneling Microscopy
 EMSE-515 02 Scanning Tunneling Microscopy EMSE-515 F. Ernst 1 Scanning Tunneling Microscope: Working Principle 2 Scanning Tunneling Microscope: Construction Principle 1 sample 2 sample holder 3 clamps
EMSE-515 02 Scanning Tunneling Microscopy EMSE-515 F. Ernst 1 Scanning Tunneling Microscope: Working Principle 2 Scanning Tunneling Microscope: Construction Principle 1 sample 2 sample holder 3 clamps
High Power and Energy Femtosecond Lasers
 High Power and Energy Femtosecond Lasers PHAROS is a single-unit integrated femtosecond laser system combining millijoule pulse energies and high average powers. PHAROS features a mechanical and optical
High Power and Energy Femtosecond Lasers PHAROS is a single-unit integrated femtosecond laser system combining millijoule pulse energies and high average powers. PHAROS features a mechanical and optical
Optical coherence tomography
 Optical coherence tomography Peter E. Andersen Optics and Plasma Research Department Risø National Laboratory E-mail peter.andersen@risoe.dk Outline Part I: Introduction to optical coherence tomography
Optical coherence tomography Peter E. Andersen Optics and Plasma Research Department Risø National Laboratory E-mail peter.andersen@risoe.dk Outline Part I: Introduction to optical coherence tomography
CARRIER-ENVELOPE PHASE STABILIZATION OF GRATING-BASED CHIRPED-PULSE AMPLIFIERS ERIC WAYNE MOON. B.S., Baker University, 2003
 CARRIER-ENVELOPE PHASE STABILIZATION OF GRATING-BASED CHIRPED-PULSE AMPLIFIERS by ERIC WAYNE MOON B.S., Baker University, 2003 AN ABSTRACT OF A DISSERTATION submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements
CARRIER-ENVELOPE PHASE STABILIZATION OF GRATING-BASED CHIRPED-PULSE AMPLIFIERS by ERIC WAYNE MOON B.S., Baker University, 2003 AN ABSTRACT OF A DISSERTATION submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements
Pulse Shaping Application Note
 Application Note 8010 Pulse Shaping Application Note Revision 1.0 Boulder Nonlinear Systems, Inc. 450 Courtney Way Lafayette, CO 80026-8878 USA Shaping ultrafast optical pulses with liquid crystal spatial
Application Note 8010 Pulse Shaping Application Note Revision 1.0 Boulder Nonlinear Systems, Inc. 450 Courtney Way Lafayette, CO 80026-8878 USA Shaping ultrafast optical pulses with liquid crystal spatial
Development of femtosecond time-resolved scanning tunneling microscopy for nanoscale science and technology
 Science and Technology of Advanced Materials 6 (2005) 582 588 www.elsevier.com/locate/stam Review Development of femtosecond time-resolved scanning tunneling microscopy for nanoscale science and technology
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials 6 (2005) 582 588 www.elsevier.com/locate/stam Review Development of femtosecond time-resolved scanning tunneling microscopy for nanoscale science and technology
Designing for Femtosecond Pulses
 Designing for Femtosecond Pulses White Paper PN 200-1100-00 Revision 1.1 July 2013 Calmar Laser, Inc www.calmarlaser.com Overview Calmar s femtosecond laser sources are passively mode-locked fiber lasers.
Designing for Femtosecond Pulses White Paper PN 200-1100-00 Revision 1.1 July 2013 Calmar Laser, Inc www.calmarlaser.com Overview Calmar s femtosecond laser sources are passively mode-locked fiber lasers.
GRENOUILLE.
 GRENOUILLE Measuring ultrashort laser pulses the shortest events ever created has always been a challenge. For many years, it was possible to create ultrashort pulses, but not to measure them. Techniques
GRENOUILLE Measuring ultrashort laser pulses the shortest events ever created has always been a challenge. For many years, it was possible to create ultrashort pulses, but not to measure them. Techniques
Theoretical Approach. Why do we need ultra short technology?? INTRODUCTION:
 Theoretical Approach Why do we need ultra short technology?? INTRODUCTION: Generating ultrashort laser pulses that last a few femtoseconds is a highly active area of research that is finding applications
Theoretical Approach Why do we need ultra short technology?? INTRODUCTION: Generating ultrashort laser pulses that last a few femtoseconds is a highly active area of research that is finding applications
OPTI510R: Photonics. Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona Meinel building R.626
 OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Announcements HW #5 is assigned (due April 9) April 9 th class will be in
OPTI510R: Photonics Khanh Kieu College of Optical Sciences, University of Arizona kkieu@optics.arizona.edu Meinel building R.626 Announcements HW #5 is assigned (due April 9) April 9 th class will be in
STUDY OF CHIRPED PULSE COMPRESSION IN OPTICAL FIBER FOR ALL FIBER CPA SYSTEM
 International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IJECE) ISSN(P): 78-991; ISSN(E): 78-991X Vol. 4, Issue 6, Oct - Nov 15, 9-16 IASE SUDY OF CHIRPED PULSE COMPRESSION IN OPICAL FIBER FOR
International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IJECE) ISSN(P): 78-991; ISSN(E): 78-991X Vol. 4, Issue 6, Oct - Nov 15, 9-16 IASE SUDY OF CHIRPED PULSE COMPRESSION IN OPICAL FIBER FOR
Remote characterization and dispersion compensation of amplified shaped femtosecond pulses using MIIPS
 Remote characterization and dispersion compensation of amplified shaped femtosecond pulses using MIIPS I. Pastirk Biophotonic Solutions, Inc. Okemos, MI 48864 pastirk@biophotonicsolutions.com X. Zhu, R.
Remote characterization and dispersion compensation of amplified shaped femtosecond pulses using MIIPS I. Pastirk Biophotonic Solutions, Inc. Okemos, MI 48864 pastirk@biophotonicsolutions.com X. Zhu, R.
attosnom I: Topography and Force Images NANOSCOPY APPLICATION NOTE M06 RELATED PRODUCTS G
 APPLICATION NOTE M06 attosnom I: Topography and Force Images Scanning near-field optical microscopy is the outstanding technique to simultaneously measure the topography and the optical contrast of a sample.
APPLICATION NOTE M06 attosnom I: Topography and Force Images Scanning near-field optical microscopy is the outstanding technique to simultaneously measure the topography and the optical contrast of a sample.
PGx11 series. Transform Limited Broadly Tunable Picosecond OPA APPLICATIONS. Available models
 PGx1 PGx3 PGx11 PT2 Transform Limited Broadly Tunable Picosecond OPA optical parametric devices employ advanced design concepts in order to produce broadly tunable picosecond pulses with nearly Fourier-transform
PGx1 PGx3 PGx11 PT2 Transform Limited Broadly Tunable Picosecond OPA optical parametric devices employ advanced design concepts in order to produce broadly tunable picosecond pulses with nearly Fourier-transform
Fast Raman Spectral Imaging Using Chirped Femtosecond Lasers
 Fast Raman Spectral Imaging Using Chirped Femtosecond Lasers Dan Fu 1, Gary Holtom 1, Christian Freudiger 1, Xu Zhang 2, Xiaoliang Sunney Xie 1 1. Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Harvard
Fast Raman Spectral Imaging Using Chirped Femtosecond Lasers Dan Fu 1, Gary Holtom 1, Christian Freudiger 1, Xu Zhang 2, Xiaoliang Sunney Xie 1 1. Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Harvard
Fiber Laser Chirped Pulse Amplifier
 Fiber Laser Chirped Pulse Amplifier White Paper PN 200-0200-00 Revision 1.2 January 2009 Calmar Laser, Inc www.calmarlaser.com Overview Fiber lasers offer advantages in maintaining stable operation over
Fiber Laser Chirped Pulse Amplifier White Paper PN 200-0200-00 Revision 1.2 January 2009 Calmar Laser, Inc www.calmarlaser.com Overview Fiber lasers offer advantages in maintaining stable operation over
Outline. Motivation Experimental Set-Up Theory behind the set-up Results Acknowledgements
 Outline Motivation Experimental Set-Up Theory behind the set-up Results Acknowledgements Motivation Attosecond pulses could be used to study time-dependence of atomic dynamics. Greater control of pulse
Outline Motivation Experimental Set-Up Theory behind the set-up Results Acknowledgements Motivation Attosecond pulses could be used to study time-dependence of atomic dynamics. Greater control of pulse
Testing with Femtosecond Pulses
 Testing with Femtosecond Pulses White Paper PN 200-0200-00 Revision 1.3 January 2009 Calmar Laser, Inc www.calmarlaser.com Overview Calmar s femtosecond laser sources are passively mode-locked fiber lasers.
Testing with Femtosecond Pulses White Paper PN 200-0200-00 Revision 1.3 January 2009 Calmar Laser, Inc www.calmarlaser.com Overview Calmar s femtosecond laser sources are passively mode-locked fiber lasers.
dnx/dt = -9.3x10-6 / C dny/dt = -13.6x10-6 / C dnz/dt = ( λ)x10-6 / C
 Lithium Triborate Crystal LBO Lithium triborate (LiB3O5 or LBO) is an excellent nonlinear optical crystal for many applications. It is grown by an improved flux method. AOTK s LBO is Featured by High damage
Lithium Triborate Crystal LBO Lithium triborate (LiB3O5 or LBO) is an excellent nonlinear optical crystal for many applications. It is grown by an improved flux method. AOTK s LBO is Featured by High damage
Fiberoptic Communication Systems By Dr. M H Zaidi. Optical Amplifiers
 Optical Amplifiers Optical Amplifiers Optical signal propagating in fiber suffers attenuation Optical power level of a signal must be periodically conditioned Optical amplifiers are a key component in
Optical Amplifiers Optical Amplifiers Optical signal propagating in fiber suffers attenuation Optical power level of a signal must be periodically conditioned Optical amplifiers are a key component in
Gerhard K. Ackermann and Jurgen Eichler. Holography. A Practical Approach BICENTENNIAL. WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA
 Gerhard K. Ackermann and Jurgen Eichler Holography A Practical Approach BICENTENNIAL BICENTENNIAL WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Contents Preface XVII Part 1 Fundamentals of Holography 1 1 Introduction
Gerhard K. Ackermann and Jurgen Eichler Holography A Practical Approach BICENTENNIAL BICENTENNIAL WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA Contents Preface XVII Part 1 Fundamentals of Holography 1 1 Introduction
Figure1. To construct a light pulse, the electric component of the plane wave should be multiplied with a bell shaped function.
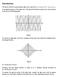 Introduction The Electric field of a monochromatic plane wave is given by is the angular frequency of the plane wave. The plot of this function is given by a cosine function as shown in the following graph.
Introduction The Electric field of a monochromatic plane wave is given by is the angular frequency of the plane wave. The plot of this function is given by a cosine function as shown in the following graph.
레이저의주파수안정화방법및그응용 박상언 ( 한국표준과학연구원, 길이시간센터 )
 레이저의주파수안정화방법및그응용 박상언 ( 한국표준과학연구원, 길이시간센터 ) Contents Frequency references Frequency locking methods Basic principle of loop filter Example of lock box circuits Quantifying frequency stability Applications
레이저의주파수안정화방법및그응용 박상언 ( 한국표준과학연구원, 길이시간센터 ) Contents Frequency references Frequency locking methods Basic principle of loop filter Example of lock box circuits Quantifying frequency stability Applications
Optical Information Processing. Adolf W. Lohmann. Edited by Stefan Sinzinger. Ch>
 Optical Information Processing Adolf W. Lohmann Edited by Stefan Sinzinger Ch> Universitätsverlag Ilmenau 2006 Contents Preface to the 2006 edition 13 Preface to the third edition 15 Preface volume 1 17
Optical Information Processing Adolf W. Lohmann Edited by Stefan Sinzinger Ch> Universitätsverlag Ilmenau 2006 Contents Preface to the 2006 edition 13 Preface to the third edition 15 Preface volume 1 17
Microscopic Structures
 Microscopic Structures Image Analysis Metal, 3D Image (Red-Green) The microscopic methods range from dark field / bright field microscopy through polarisation- and inverse microscopy to techniques like
Microscopic Structures Image Analysis Metal, 3D Image (Red-Green) The microscopic methods range from dark field / bright field microscopy through polarisation- and inverse microscopy to techniques like
A Coherent Technical Note August 29, Propagation, Dispersion and Measurement of sub-10 fs Pulses. Table of Contents
 Propagation, Dispersion and Measurement of sub-10 fs Pulses Table of Contents 1. Theory 2. Pulse propagation through various materials o Calculating the index of refraction Glass materials Air Index of
Propagation, Dispersion and Measurement of sub-10 fs Pulses Table of Contents 1. Theory 2. Pulse propagation through various materials o Calculating the index of refraction Glass materials Air Index of
TIGER Femtosecond and Picosecond Ti:Sapphire Lasers. Customized systems with SESAM technology*
 TIGER Femtosecond and Picosecond Ti:Sapphire Lasers Customized systems with SESAM technology* www.lumentum.com Data Sheet The TIGER femtosecond and picosecond lasers combine soliton mode-locking, a balance
TIGER Femtosecond and Picosecond Ti:Sapphire Lasers Customized systems with SESAM technology* www.lumentum.com Data Sheet The TIGER femtosecond and picosecond lasers combine soliton mode-locking, a balance
REVIEW ON COMPARATIVE STUDY OF KERR EFFECT ON OPTICAL WDM NETWORK
 REVIEW ON COMPARATIVE STUDY OF KERR EFFECT ON OPTICAL WDM NETWORK Abhineet Kaur 1, Atul Mahajan 2 1 M.Tech Scholar Electronics and Communication & Engineering Department, Amritsar College of Engineering
REVIEW ON COMPARATIVE STUDY OF KERR EFFECT ON OPTICAL WDM NETWORK Abhineet Kaur 1, Atul Mahajan 2 1 M.Tech Scholar Electronics and Communication & Engineering Department, Amritsar College of Engineering
RECENTLY, using near-field scanning optical
 1 2 1 2 Theoretical and Experimental Study of Near-Field Beam Properties of High Power Laser Diodes W. D. Herzog, G. Ulu, B. B. Goldberg, and G. H. Vander Rhodes, M. S. Ünlü L. Brovelli, C. Harder Abstract
1 2 1 2 Theoretical and Experimental Study of Near-Field Beam Properties of High Power Laser Diodes W. D. Herzog, G. Ulu, B. B. Goldberg, and G. H. Vander Rhodes, M. S. Ünlü L. Brovelli, C. Harder Abstract
High Energy Non - Collinear OPA
 High Energy Non - Collinear OPA Basics of Operation FEATURES Pulse Duration less than 10 fs possible High Energy (> 80 microjoule) Visible Output Wavelength Tuning Computer Controlled Tuning Range 250-375,
High Energy Non - Collinear OPA Basics of Operation FEATURES Pulse Duration less than 10 fs possible High Energy (> 80 microjoule) Visible Output Wavelength Tuning Computer Controlled Tuning Range 250-375,
Notes on Optical Amplifiers
 Notes on Optical Amplifiers Optical amplifiers typically use energy transitions such as those in atomic media or electron/hole recombination in semiconductors. In optical amplifiers that use semiconductor
Notes on Optical Amplifiers Optical amplifiers typically use energy transitions such as those in atomic media or electron/hole recombination in semiconductors. In optical amplifiers that use semiconductor
WDM Concept and Components. EE 8114 Course Notes
 WDM Concept and Components EE 8114 Course Notes Part 1: WDM Concept Evolution of the Technology Why WDM? Capacity upgrade of existing fiber networks (without adding fibers) Transparency:Each optical channel
WDM Concept and Components EE 8114 Course Notes Part 1: WDM Concept Evolution of the Technology Why WDM? Capacity upgrade of existing fiber networks (without adding fibers) Transparency:Each optical channel
Analytical analysis of modulated signal in apertureless scanning near-field optical microscopy C. H. Chuang and Y. L. Lo *
 Research Express@NCKU Volume 5 Issue 10 - October 3, 2008 [ http://research.ncku.edu.tw/re/articles/e/20081003/2.html ] Analytical analysis of modulated signal in apertureless scanning near-field optical
Research Express@NCKU Volume 5 Issue 10 - October 3, 2008 [ http://research.ncku.edu.tw/re/articles/e/20081003/2.html ] Analytical analysis of modulated signal in apertureless scanning near-field optical
Basic Components of Spectroscopic. Instrumentation
 Basic Components of Spectroscopic Ahmad Aqel Ifseisi Assistant Professor of Analytical Chemistry College of Science, Department of Chemistry King Saud University P.O. Box 2455 Riyadh 11451 Saudi Arabia
Basic Components of Spectroscopic Ahmad Aqel Ifseisi Assistant Professor of Analytical Chemistry College of Science, Department of Chemistry King Saud University P.O. Box 2455 Riyadh 11451 Saudi Arabia
Semiconductor Detector Systems
 Semiconductor Detector Systems Helmuth Spieler Physics Division, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS ix CONTENTS 1 Detector systems overview 1 1.1 Sensor 2 1.2 Preamplifier 3
Semiconductor Detector Systems Helmuth Spieler Physics Division, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS ix CONTENTS 1 Detector systems overview 1 1.1 Sensor 2 1.2 Preamplifier 3
Controllable harmonic mode locking and multiple pulsing in a Ti:sapphire laser
 Controllable harmonic mode locking and multiple pulsing in a Ti:sapphire laser Xiaohong Han, Jian Wu, and Heping Zeng* State Key Laboratory of Precision Spectroscopy, and Department of Physics, East China
Controllable harmonic mode locking and multiple pulsing in a Ti:sapphire laser Xiaohong Han, Jian Wu, and Heping Zeng* State Key Laboratory of Precision Spectroscopy, and Department of Physics, East China
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE of TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161/6637 Practice Quiz 2 Issued X:XXpm 4/XX/2004 Spring Term, 2004 Due X:XX+1:30pm 4/XX/2004 Please utilize
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE of TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.161/6637 Practice Quiz 2 Issued X:XXpm 4/XX/2004 Spring Term, 2004 Due X:XX+1:30pm 4/XX/2004 Please utilize
FIBER OPTICS. Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar. Department of Electrical Engineering. Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay. Lecture: 35. Self-Phase-Modulation
 FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 35 Self-Phase-Modulation (SPM) Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of Electrical
FIBER OPTICS Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture: 35 Self-Phase-Modulation (SPM) Fiber Optics, Prof. R.K. Shevgaonkar, Dept. of Electrical
Lecture 3 Fiber Optical Communication Lecture 3, Slide 1
 Lecture 3 Dispersion in single-mode fibers Material dispersion Waveguide dispersion Limitations from dispersion Propagation equations Gaussian pulse broadening Bit-rate limitations Fiber losses Fiber Optical
Lecture 3 Dispersion in single-mode fibers Material dispersion Waveguide dispersion Limitations from dispersion Propagation equations Gaussian pulse broadening Bit-rate limitations Fiber losses Fiber Optical
Bragg and fiber gratings. Mikko Saarinen
 Bragg and fiber gratings Mikko Saarinen 27.10.2009 Bragg grating - Bragg gratings are periodic perturbations in the propagating medium, usually periodic variation of the refractive index - like diffraction
Bragg and fiber gratings Mikko Saarinen 27.10.2009 Bragg grating - Bragg gratings are periodic perturbations in the propagating medium, usually periodic variation of the refractive index - like diffraction
Lecture 19 Optical Characterization 1
 Lecture 19 Optical Characterization 1 1/60 Announcements Homework 5/6: Is online now. Due Wednesday May 30th at 10:00am. I will return it the following Wednesday (6 th June). Homework 6/6: Will be online
Lecture 19 Optical Characterization 1 1/60 Announcements Homework 5/6: Is online now. Due Wednesday May 30th at 10:00am. I will return it the following Wednesday (6 th June). Homework 6/6: Will be online
Optical Fiber Technology. Photonic Network By Dr. M H Zaidi
 Optical Fiber Technology Numerical Aperture (NA) What is numerical aperture (NA)? Numerical aperture is the measure of the light gathering ability of optical fiber The higher the NA, the larger the core
Optical Fiber Technology Numerical Aperture (NA) What is numerical aperture (NA)? Numerical aperture is the measure of the light gathering ability of optical fiber The higher the NA, the larger the core
COMPONENTS OF OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS. Chapter 7 UV, Visible and IR Instruments
 COMPONENTS OF OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS Chapter 7 UV, Visible and IR Instruments 1 Topics A. GENERAL DESIGNS B. SOURCES C. WAVELENGTH SELECTORS D. SAMPLE CONTAINERS E. RADIATION TRANSDUCERS F. SIGNAL PROCESSORS
COMPONENTS OF OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS Chapter 7 UV, Visible and IR Instruments 1 Topics A. GENERAL DESIGNS B. SOURCES C. WAVELENGTH SELECTORS D. SAMPLE CONTAINERS E. RADIATION TRANSDUCERS F. SIGNAL PROCESSORS
COMPONENTS OF OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS. Topics
 COMPONENTS OF OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS Chapter 7 UV, Visible and IR Instruments Topics A. GENERAL DESIGNS B. SOURCES C. WAVELENGTH SELECTORS D. SAMPLE CONTAINERS E. RADIATION TRANSDUCERS F. SIGNAL PROCESSORS
COMPONENTS OF OPTICAL INSTRUMENTS Chapter 7 UV, Visible and IR Instruments Topics A. GENERAL DESIGNS B. SOURCES C. WAVELENGTH SELECTORS D. SAMPLE CONTAINERS E. RADIATION TRANSDUCERS F. SIGNAL PROCESSORS
