FREQUENCY MODULATION. K. P. Luke R. J. McLaughlin R. E. Mortensen G. J. Rubissow
|
|
|
- Maude Jenkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VI. FREQUENCY MODULTION Prof. E. J. Baghdady Prof. J. B. Wiesner J. W. Conley K. P. Luke R. J. McLaughlin R. E. Mortensen G. J. Rubissow F. I. Sheftman R. H. Small D. D. Weiner. CPTURE OF THE WEKER SIGNL: FEEDFORWRD TECHNIQUE In the Quarterly Progress Report of October 15, 1957, page 52, we pointed out that we had devised a feedforward-across-the-limiter technique that could be arranged to suppress whichever of two cochannel FM signals is undesired. simple experimental model of this system was built and tested (1). Before summarizing the experimental results, we shall present a resume of the appropriate theoretical predictions. The simplest realization of a feedforward system is shown in the block diagram of Fig. VI- la. The limiter and amplifier in the lower signal path are, in effect, equivalent to one idealized narrow-band limiter. The upper signal path contains two narrow-band limiters. Each idealized limiter filter is assumed to have one i-f bandwidth. Limiters are inserted in each of the two signal paths in order to ensure that the properties of the output signal will be independent of the input signal level, as long as the resultant input signal amplitude exceeds a certain threshold value. system that is identical in its effect with the one shown in Fig. VI- la, but which requires one less limiter, is shown in Fig. VI-lb. The arrangement in Fig. VI- lb is the more desirable for practical realization. It is easy to show that if the first limiter in Fig. VI-1b is not narrow-band, the combination of the second-limiter and amplifier outputs in phase opposition cannot effect the type of cancellation that is necessary for achieving beneficial changes in the interference conditions at the output. Fig. VI- 1. (a) Simple feedforward system. (b) Simplified form of the system of (a).
2 In the analysis of the equivalent feedforward systems of Fig. VI-la and b we note that for a given weaker-to-stronger signal-amplitude ratio a at the input, the conditions of interference that arise with the frequency differences r = 0 and r = (BW)if are of special interest. The importance of these two limiting conditions stems from the fact that the amount of reduction in the equivalent weaker-to-stronger signal-amplitude ratio that will be effected by a chain of narrow-band limiters decreases with a decrease in the value of the frequency difference, r, between the two signals, relative to the limiter bandwidth. The effect of narrow-band limiting upon the FM disturbance caused by two-signal interference will increase with an increase in the degree of frequency-band limitation suffered by the amplitude-limited resultant of the two signals when they go through the limiter filter. For r = 0, the amplitude-limited resultant of the two input signals will experience no frequency-band limitation in going through the limiter filters, while the greatest possible band limitation will be experienced with r = (BW)if. When the frequency difference r lies between r = 0 and r = (BW) if, the effect of passing the resultant signal through the system will be intermediate between the extremes indicated for r = 0 and r = (BW)if. Thus, for frequency differences that exceed one-half of the i-f bandwidth, the spectrum at the output of the idealized narrow-band limiter will consist of only two components that have the frequencies of the two input sinusoids. If the two signal paths are assumed to have identical phase characteristics, an additive combination of the path outputs results in two signals with new relative amplitudes 1 and aout. family of curves for aout versus a is shown in Fig. VI-2, with K as a running parameter (K is the ratio of the output of the lower signal path to the output of the upper signal path when the input excitation is a single unmodulated carrier). Negative values of K can be interpreted as indicating the condition in which the phase characteristics of the two paths differ by a constant value of 7r (or by an odd multiple of it) but are otherwise identical functions of frequency. The parameter K depends only on certain design constants of which the gain of the amplifier is an easily controllable factor. Evidently, K would not be a constant that is subject to a priori adjustment for all usable signal levels at the input if the lower signal path did not contain the limiter that is shown. It will become evident presently that a constant value of K that is substantially independent of the input signal levels is an important requirement for achieving inferferencesuppression performance that is independent of the input signal level. The curves of Fig. VI-Z reveal some interesting possibilities in relation to the capture of the weaker or stronger of the two input signals under the conditions of this analysis. For example, for values of K that lie in the range < K < 0, the system will depress the ratio of weaker-to-stronger signal amplitude to a value that is smaller than 0. 4 for all input values of this ratio that are below This represents substantial enhancement of the predominance of the originally stronger signal. The curve for
3 0o -02 Fig. VI-2. Plots of the ratio of weaker-to-stronger signal amplitude, aout' at the output of the system of Fig. VI- la as a function of the input ratio a, when the frequency difference exceeds one-half the i-f bandwidth. K = shows that a is less than for all a less than Values of aout > 1 correspond to the situation in which the combination of the signalpath outputs enables the originally weaker signal to emerge as the stronger of the two. Thus, for K = -1.05, aout is greater than 1 for all a in the range < a < 1. This potentiality for capturing the weaker signal is even more clearly brought out by the curves of 1/aou t versus a shown in Fig. VI-3. It is evident that as -K approaches 1 from the right, the range of a values in which the originally weaker signal will emerge as the stronger widens and its lower limit approaches a = 0. But values of K that are centered about -1 indicate signal cancellation that becomes more and more complete as K approaches -1. It is clear, therefore, that a limit on how closely K can approach -1 is placed by considerations that relate, first, to the random noise level at the output of the system, and, second, to the signal-level requirements and sensitivity of the stages driven by it. Consider, next, the situation in which r approaches 0. less than 1-a r = a (BW) min 1 + a if For values of r that are where p z 0. 2 for an ideal filter, the signal at the output of each limiter filter will approach the amplitude-limited resultant of the two input signals more and more closely Consequently, the signal at the output of the system shown in Fig. VI-3a will approach
4 eout(t) = k 2 (l+k) cos[pt + 0(t)] where 0(t) = tan-1 a sin rt 1 + a cos rt and p is the frequency of the stronger signal (in rad/sec). It is evident that for values of r that make up a small fraction of the limiter-filter bandwidths, the average frequency of the output signal will always equal the frequency of the stronger input signal. means that if the chosen value of K enables the system to deliver an output signal whose average frequency equals the frequency of the weaker signal when r is equal to one i-f bandwidth, this condition for the capture of the weaker signal will not subsist as r takes on values that are small fractions of the i-f bandwidth. This Consequently, with a given value of input weaker-to-stronger signal-amplitude ratio, the capture at the output of the system will shift from the weaker to the stronger signal as r is decreased, and back to the weaker signal as r is increased again. The transition in the capture will take place within a frequency-difference range centered about a value of r that is intermediate between zero and (BW)if/2. While r is going through this range of r values, the reception at the output of the succeeding FM demodulator will be marred by the severe distortion that is usually experienced with conventional FM receivers when a approaches 1. Evidently, if either of the systems of Fig. VI-la and b is used to facilitate the capture of the weaker signal, it should be followed by an FM demodulator of high stronger-signal 06-07L Fig. VI-3. Plots of 1/aou t versus a.
5 2 0 10O0-CYCLE /400-CYCLE COMPONENT H-i,wa HZ 0 LL ( LLJ wo 00 - LLj 0 T _ WZ H FEEDFORW...- RECEIVER FEEDFORV SIGNL : MODULTION FREQUENCY,1000 CPS 4/ FREQUENCY DEVITION,t75KC SIGNL 8: MODULTION FREQUENCY, 400 CPS FREQUENCY DEVITION, * 75KC CENTER- FREQUENCY SEPRTION,ZERO a Fig. VI-4. Stronger-signal capture characteristics of experimental receiver with and without feedforward. c Z 0oa S50I- Hg SIGNL MODULTION FREQUENCY,IKC DEVITION,75 KC SIGNL B: MODULTION FREQUENCY, 400 CPS, DEVITION,75 KC CENTER -FREQUENCY I I I I I I I I I_ I SEPRTION, ZERO I Z _ D LLL)b OI- OHi- Z 100 LL 0 Uj a, SIGNL : MODULTION FREQUENCY,IKC DEVITION 35KC SIGNL B: MODULTION FREQUENCY, 400CPS, DEVITION 35KC _j ' CENTER-FREQUENCY SEPRTION,ZERO 18I I II I Fig. VI-5. Weaker-signal capture characteristics of the feedforward receiver: cochannel signals. capture capability, in order to minimize the duration of the severe distortion that accompanies the capture transition from one signal to the other. If the system is used to suppress the weaker signal, no capture transitions will arise in the course of a modulation cycle. Hence the system should perform better as a weaker-signal suppressor when the frequency difference between the two input sinusoids goes to zero during every modulation cycle. The capture-transition distortion, which appears whenever the two signals pass through a condition of zero frequency difference, constitutes a performance limitation on the simpler (and more practical) forms of the feedforward technique in applications
6 z w 100r 0 0(2 o -z 0Q < 0 LO z== 5 0 -J 0 EL J ' LL I BB SIGNL : MODULTION FREQUENCY,IKC DEVITION,35KC SIGNL B: MODULTION FREQUENCY, 400 CPS DEVITION, 35 KG CENTER- FREQUENCY SEPRTION,75 KC I.- OZ LLO 0 0. Z)aý5 _j (L n U B/ SIGNL : MODULTION FREQUENCY, IKC DE VITION, 10 KC SIGNL B: MODULTION FREQUENCY, 400 CPS DEViTION, IOKC CENTER -FREQUENCY SEP~RTION,75 KC 0 -~ I Fig. VI- 6. Weaker-signal capture characteristics of the feedforward receiver: optimum performance with half-channel signals. that require close reproduction of the weaker-signal message. If the two signals are cochannel, they may often pass through zero frequency difference, with consequent severe distortion in the weaker-signal reception at the receiver output. However, if the center frequencies of the signals are separated so that their instantaneous frequencies seldom, or never, coincide, the distortion will not be present. In a way, the feedforward scheme of Fig. VI- lb is an extremely simple realization of a simulated ideal bandpass filter with extremely sharp cutoff characteristics for FM signals. n experimental feedforward system based on the block diagram of Fig. VI-lb was built (1). The measured capture performance of this system is illustrated by the plots of Figs. VI-4, VI-5, and VI-6. The signals used in the measurements are described (a) (b) Fig. VI-7. Capture performance of experimental feedforward receiver when the signals have the same center frequency. (a) Weaker-signal modulation (400 cps). (b) Detected weaker- signal modulation with capture- transition distortion from unmodulated stronger signal. (c) Detected weaker-signal modulation with capture-transition distortion from a stronger signal with 1000-cps tone modulation.
7 in the figures. The oscillograms of Fig. VI-7 illustrate the quality of weaker-signal reception when the signals are cochannel and the weaker-to-stronger signal-amplitude ratio is E. J. Baghdady References 1. R. H. Small, Single-channel, two-carrier FM multiplex system, S. M. Thesis, Department of Electrical Engineering, M. I. T., June B. FM RECEIVER DESIGN study was made of the practical requirements in the design of FM receivers for suppressing cochannel interference through the use of cascaded narrow-band limiters and regenerative feedback limiters (1). The amplitude disturbances caused by the interference before and after a stage of idealized narrow-band limiting were computed. Limiting threshold requirements that are sufficient to ensure continuous operation of the limiters were determined. detailed study was made of the potentialities of the 6BN6 gated-beam limiter tube. Fifty 6BN6 tubes were used in this investigation for determining the quality of the limiting characteristic; the optimum values of bias and supply voltages; the limiting threshold; the amplitude of the plate-current fundamental component; and the sensitivity to power-supply and bias-voltage drifts. The extent of the nonlinear loading caused by limiter-input current and the design requirements that prevent nonlinear loading in a cascade of 6BN6 limiters were determined. From the study of the properties of the 6BN6 tube, the capture ratio of a receiver that utilizes a cascade of 6BN6 narrow-band limiters was found to have a determinable upper bound. Practical receiver design criteria were postulated and applied to the construction of an experimental FM receiver. The validity of some of the idealized theoretical models was checked by laboratory tests of the receiver. R. J. McLaughlin References 1. R. J. McLaughlin, study of FM capture effects, S. M. Thesis, Department of Electrical Engineering, M.I.T., June 1, 1958.
MODULATION THEORY AND SYSTEMS XI.
 XI. MODULATION THEORY AND SYSTEMS Prof. E. J. Baghdady J. M. Gutwein R. B. C. Martins Prof. J. B. Wiesner A. L. Helgesson C. Metzadour J. T. Boatwright, Jr. B. H. Hutchinson, Jr. D. D. Weiner A. ADDITIVE
XI. MODULATION THEORY AND SYSTEMS Prof. E. J. Baghdady J. M. Gutwein R. B. C. Martins Prof. J. B. Wiesner A. L. Helgesson C. Metzadour J. T. Boatwright, Jr. B. H. Hutchinson, Jr. D. D. Weiner A. ADDITIVE
Fig. VII-1. Block diagram of experimental i-f discriminator unit. VII. FREQUENCY MODULATION
 VII. FREQUENCY MODULATION Prof. E. J. Baghdady M. Barash D. D. Weiner Prof. J. B. Wiesner R. J. McLaughlin L. D. Shapiro A. REGENERATIVE FEEDBACK AROUND THE LIMITER An experimental study is being conducted
VII. FREQUENCY MODULATION Prof. E. J. Baghdady M. Barash D. D. Weiner Prof. J. B. Wiesner R. J. McLaughlin L. D. Shapiro A. REGENERATIVE FEEDBACK AROUND THE LIMITER An experimental study is being conducted
 UNIT I FUNDAMENTALS OF ANALOG COMMUNICATION Introduction In the Microbroadcasting services, a reliable radio communication system is of vital importance. The swiftly moving operations of modern communities
UNIT I FUNDAMENTALS OF ANALOG COMMUNICATION Introduction In the Microbroadcasting services, a reliable radio communication system is of vital importance. The swiftly moving operations of modern communities
FM WEAKER-SIGNAL SUPPRESSION WITH NARROW-BAND LIMITERS
 tp~//2y~ DOCUMENT ROOM, BOOK 36_4 RESEARCH LABrA: CF E CTRONCS MASSACHUSET'1 NSTTUTE OF TECHNOLO(. ' CAMBRDGE 39, MASSACHUSETTS, U S.A, FM WEAKER-SGNAL SUPPRESSON WTH NARROW-BAND LMTERS ROBERT J. McLAUGHLN
tp~//2y~ DOCUMENT ROOM, BOOK 36_4 RESEARCH LABrA: CF E CTRONCS MASSACHUSET'1 NSTTUTE OF TECHNOLO(. ' CAMBRDGE 39, MASSACHUSETTS, U S.A, FM WEAKER-SGNAL SUPPRESSON WTH NARROW-BAND LMTERS ROBERT J. McLAUGHLN
HF Receivers, Part 2
 HF Receivers, Part 2 Superhet building blocks: AM, SSB/CW, FM receivers Adam Farson VA7OJ View an excellent tutorial on receivers NSARC HF Operators HF Receivers 2 1 The RF Amplifier (Preamp)! Typical
HF Receivers, Part 2 Superhet building blocks: AM, SSB/CW, FM receivers Adam Farson VA7OJ View an excellent tutorial on receivers NSARC HF Operators HF Receivers 2 1 The RF Amplifier (Preamp)! Typical
RECOMMENDATION ITU-R SM.1268*
 Rec. ITU-R SM.1268 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R SM.1268* METHOD OF MEASURING THE MAXIMUM FREQUENCY DEVIATION OF FM BROADCAST EMISSIONS AT MONITORING STATIONS (Question ITU-R 67/1) Rec. ITU-R SM.1268 (1997) The
Rec. ITU-R SM.1268 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R SM.1268* METHOD OF MEASURING THE MAXIMUM FREQUENCY DEVIATION OF FM BROADCAST EMISSIONS AT MONITORING STATIONS (Question ITU-R 67/1) Rec. ITU-R SM.1268 (1997) The
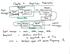 Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
Modulations Analog Modulations Amplitude modulation (AM) Linear modulation Frequency modulation (FM) Phase modulation (PM) cos Angle modulation FM PM Digital Modulations ASK FSK PSK MSK MFSK QAM PAM Etc.
CHAPTER 2! AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM)
 CHAPTER 2 AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM) Topics 2-1 : AM Concepts 2-2 : Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 2-3 : Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 2-4 : Single-Sideband Modulation 2-5 : AM Power
CHAPTER 2 AMPLITUDE MODULATION (AM) Topics 2-1 : AM Concepts 2-2 : Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 2-3 : Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 2-4 : Single-Sideband Modulation 2-5 : AM Power
Introduction to Receivers
 Introduction to Receivers Purpose: translate RF signals to baseband Shift frequency Amplify Filter Demodulate Why is this a challenge? Interference Large dynamic range required Many receivers must be capable
Introduction to Receivers Purpose: translate RF signals to baseband Shift frequency Amplify Filter Demodulate Why is this a challenge? Interference Large dynamic range required Many receivers must be capable
Outline. Communications Engineering 1
 Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
Outline Introduction Signal, random variable, random process and spectra Analog modulation Analog to digital conversion Digital transmission through baseband channels Signal space representation Optimal
ERC Recommendation 54-01
 ERC Recommendation 54-01 Method of measuring the maximum frequency deviation of FM broadcast emissions in the band 87.5 to 108 MHz at monitoring stations Approved May 1998 Amended 13 February 2015 Amended
ERC Recommendation 54-01 Method of measuring the maximum frequency deviation of FM broadcast emissions in the band 87.5 to 108 MHz at monitoring stations Approved May 1998 Amended 13 February 2015 Amended
X. MODULATION THEORY AND SYSTEMS
 X. MODULATION THEORY AND SYSTEMS Prof. E. J. Baghdady A. L. Helgesson R. B. C. Martins Prof. J. B. Wiesner B. H. Hutchinson, Jr. C. Metzadour J. T. Boatwright, Jr. D. D. Weiner A. SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIOS
X. MODULATION THEORY AND SYSTEMS Prof. E. J. Baghdady A. L. Helgesson R. B. C. Martins Prof. J. B. Wiesner B. H. Hutchinson, Jr. C. Metzadour J. T. Boatwright, Jr. D. D. Weiner A. SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIOS
Method of measuring the maximum frequency deviation of FM broadcast emissions at monitoring stations
 Recommendation ITU-R SM.1268-2 (02/2011) Method of measuring the maximum frequency deviation of FM broadcast emissions at monitoring stations SM Series Spectrum management ii Rec. ITU-R SM.1268-2 Foreword
Recommendation ITU-R SM.1268-2 (02/2011) Method of measuring the maximum frequency deviation of FM broadcast emissions at monitoring stations SM Series Spectrum management ii Rec. ITU-R SM.1268-2 Foreword
Problem Sheet for Amplitude Modulation
 Problem heet for Amplitude Modulation Q1: For the sinusoidaly modulated DB/LC waveform shown in Fig. below. a Find the modulation index. b ketch a line spectrum. c Calculated the ratio of average power
Problem heet for Amplitude Modulation Q1: For the sinusoidaly modulated DB/LC waveform shown in Fig. below. a Find the modulation index. b ketch a line spectrum. c Calculated the ratio of average power
Difference between BJTs and FETs. Junction Field Effect Transistors (JFET)
 Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
Difference between BJTs and FETs Transistors can be categorized according to their structure, and two of the more commonly known transistor structures, are the BJT and FET. The comparison between BJTs
Amplitude Modulated Systems
 Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
Amplitude Modulated Systems Communication is process of establishing connection between two points for information exchange. Channel refers to medium through which message travels e.g. wires, links, or
FM THRESHOLD AND METHODS OF LIMITING ITS EFFECT ON PERFORMANCE
 FM THESHOLD AND METHODS OF LIMITING ITS EFFET ON PEFOMANE AHANEKU, M. A. Lecturer in the Department of Electronic Engineering, UNN ABSTAT This paper presents the outcome of the investigative study carried
FM THESHOLD AND METHODS OF LIMITING ITS EFFET ON PEFOMANE AHANEKU, M. A. Lecturer in the Department of Electronic Engineering, UNN ABSTAT This paper presents the outcome of the investigative study carried
Radio Receiver Architectures and Analysis
 Radio Receiver Architectures and Analysis Robert Wilson December 6, 01 Abstract This article discusses some common receiver architectures and analyzes some of the impairments that apply to each. 1 Contents
Radio Receiver Architectures and Analysis Robert Wilson December 6, 01 Abstract This article discusses some common receiver architectures and analyzes some of the impairments that apply to each. 1 Contents
Part A: Question & Answers UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION
 PANDIAN SARASWATHI YADAV ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATON ENGG. Branch: ECE EC6402 COMMUNICATION THEORY Semester: IV Part A: Question & Answers UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION 1.
PANDIAN SARASWATHI YADAV ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATON ENGG. Branch: ECE EC6402 COMMUNICATION THEORY Semester: IV Part A: Question & Answers UNIT I AMPLITUDE MODULATION 1.
Frequency Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #15, April 28, Prof. Young-Chai Ko
 Frequency Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #15, April 28, 2011 Prof. Young-Chai Ko koyc@korea.ac.kr Summary Angle Modulation Properties of Angle Modulation Narrowband Frequency Modulation
Frequency Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #15, April 28, 2011 Prof. Young-Chai Ko koyc@korea.ac.kr Summary Angle Modulation Properties of Angle Modulation Narrowband Frequency Modulation
A CRYSTAL LIMITER FOR USE IN AN FM RECEIVER IN THE PRESENCE OF IMPULSE INTERFERENCE
 . A CRYSTAL LIMITER FOR USE IN AN FM RECEIVER IN THE PRESENCE OF IMPULSE INTERFERENCE T. P. CHEATHAM - TECHNICAL REPORT NO. 36 APRIL 24, 1947 RESEARCH LABORATORY OF ELECTRONICS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE
. A CRYSTAL LIMITER FOR USE IN AN FM RECEIVER IN THE PRESENCE OF IMPULSE INTERFERENCE T. P. CHEATHAM - TECHNICAL REPORT NO. 36 APRIL 24, 1947 RESEARCH LABORATORY OF ELECTRONICS MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE
Lecture 6. Angle Modulation and Demodulation
 Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
Lecture 6 and Demodulation Agenda Introduction to and Demodulation Frequency and Phase Modulation Angle Demodulation FM Applications Introduction The other two parameters (frequency and phase) of the carrier
Chapter 3. Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals
 Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals Topics Covered 3-1: AM Concepts 3-2: Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 3-3: Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 3-4: AM Power 3-5: Single-Sideband
Chapter 3 Amplitude Modulation Fundamentals Topics Covered 3-1: AM Concepts 3-2: Modulation Index and Percentage of Modulation 3-3: Sidebands and the Frequency Domain 3-4: AM Power 3-5: Single-Sideband
Application of a Telemetry System using DSB-AM Sub-Carriers
 Application of a Telemetry System using DSB-AM Sub-Carriers Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Roche, A. O. Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal International Telemetering Conference
Application of a Telemetry System using DSB-AM Sub-Carriers Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Roche, A. O. Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal International Telemetering Conference
Introduction to Amplitude Modulation
 1 Introduction to Amplitude Modulation Introduction to project management. Problem definition. Design principles and practices. Implementation techniques including circuit design, software design, solid
1 Introduction to Amplitude Modulation Introduction to project management. Problem definition. Design principles and practices. Implementation techniques including circuit design, software design, solid
A 3 TO 30 MHZ HIGH-RESOLUTION SYNTHESIZER CONSISTING OF A DDS, DIVIDE-AND-MIX MODULES, AND A M/N SYNTHESIZER. Richard K. Karlquist
 A 3 TO 30 MHZ HIGH-RESOLUTION SYNTHESIZER CONSISTING OF A DDS, -AND-MIX MODULES, AND A M/N SYNTHESIZER Richard K. Karlquist Hewlett-Packard Laboratories 3500 Deer Creek Rd., MS 26M-3 Palo Alto, CA 94303-1392
A 3 TO 30 MHZ HIGH-RESOLUTION SYNTHESIZER CONSISTING OF A DDS, -AND-MIX MODULES, AND A M/N SYNTHESIZER Richard K. Karlquist Hewlett-Packard Laboratories 3500 Deer Creek Rd., MS 26M-3 Palo Alto, CA 94303-1392
two computers. 2- Providing a channel between them for transmitting and receiving the signals through it.
 1. Introduction: Communication is the process of transmitting the messages that carrying information, where the two computers can be communicated with each other if the two conditions are available: 1-
1. Introduction: Communication is the process of transmitting the messages that carrying information, where the two computers can be communicated with each other if the two conditions are available: 1-
CH85CH2202-0/85/ $1.00
 SYNCHRONIZATION AND TRACKING WITH SYNCHRONOUS OSCILLATORS Vasil Uzunoglu and Marvin H. White Fairchild Industries Germantown, Maryland Lehigh University Bethlehem, Pennsylvania ABSTRACT A Synchronous Oscillator
SYNCHRONIZATION AND TRACKING WITH SYNCHRONOUS OSCILLATORS Vasil Uzunoglu and Marvin H. White Fairchild Industries Germantown, Maryland Lehigh University Bethlehem, Pennsylvania ABSTRACT A Synchronous Oscillator
CHAPTER 9 FEEDBACK. NTUEE Electronics L.H. Lu 9-1
 CHAPTER 9 FEEDBACK Chapter Outline 9.1 The General Feedback Structure 9.2 Some Properties of Negative Feedback 9.3 The Four Basic Feedback Topologies 9.4 The Feedback Voltage Amplifier (Series-Shunt) 9.5
CHAPTER 9 FEEDBACK Chapter Outline 9.1 The General Feedback Structure 9.2 Some Properties of Negative Feedback 9.3 The Four Basic Feedback Topologies 9.4 The Feedback Voltage Amplifier (Series-Shunt) 9.5
Problem Sheet 1 Probability, random processes, and noise
 Problem Sheet 1 Probability, random processes, and noise 1. If F X (x) is the distribution function of a random variable X and x 1 x 2, show that F X (x 1 ) F X (x 2 ). 2. Use the definition of the cumulative
Problem Sheet 1 Probability, random processes, and noise 1. If F X (x) is the distribution function of a random variable X and x 1 x 2, show that F X (x 1 ) F X (x 2 ). 2. Use the definition of the cumulative
Tuesday, March 22nd, 9:15 11:00
 Nonlinearity it and mismatch Tuesday, March 22nd, 9:15 11:00 Snorre Aunet (sa@ifi.uio.no) Nanoelectronics group Department of Informatics University of Oslo Last time and today, Tuesday 22nd of March:
Nonlinearity it and mismatch Tuesday, March 22nd, 9:15 11:00 Snorre Aunet (sa@ifi.uio.no) Nanoelectronics group Department of Informatics University of Oslo Last time and today, Tuesday 22nd of March:
Title: New High Efficiency Intermodulation Cancellation Technique for Single Stage Amplifiers.
 Title: New High Efficiency Intermodulation Cancellation Technique for Single Stage Amplifiers. By: Ray Gutierrez Micronda LLC email: ray@micronda.com February 12, 2008. Introduction: This article provides
Title: New High Efficiency Intermodulation Cancellation Technique for Single Stage Amplifiers. By: Ray Gutierrez Micronda LLC email: ray@micronda.com February 12, 2008. Introduction: This article provides
CEPT/ERC Recommendation ERC E (Funchal 1998)
 Page 1 Distribution: B CEPT/ERC Recommendation ERC 54-01 E (Funchal 1998) METHOD OF MEASURING THE MAXIMUM FREQUENCY DEVIATION OF FM BROADCAST EMISSIONS IN THE BAND 87.5 MHz TO 108 MHz AT MONITORING STATIONS
Page 1 Distribution: B CEPT/ERC Recommendation ERC 54-01 E (Funchal 1998) METHOD OF MEASURING THE MAXIMUM FREQUENCY DEVIATION OF FM BROADCAST EMISSIONS IN THE BAND 87.5 MHz TO 108 MHz AT MONITORING STATIONS
A Seminar Report On PULSE TIME MODULATION TECHNIQUES. Jithin R. J. (Roll No. EC04B081)
 A Seminar Report On PULSE TIME MODULATION TECHNIQUES Submitted in partial fulfillment for the award of the Degree of Bachelor of Technology in Electronics and Communication Engineering by Jithin R. J.
A Seminar Report On PULSE TIME MODULATION TECHNIQUES Submitted in partial fulfillment for the award of the Degree of Bachelor of Technology in Electronics and Communication Engineering by Jithin R. J.
Universitas Sumatera Utara
 Amplitude Shift Keying & Frequency Shift Keying Aim: To generate and demodulate an amplitude shift keyed (ASK) signal and a binary FSK signal. Intro to Generation of ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK -
Amplitude Shift Keying & Frequency Shift Keying Aim: To generate and demodulate an amplitude shift keyed (ASK) signal and a binary FSK signal. Intro to Generation of ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK -
EE-4022 Experiment 3 Frequency Modulation (FM)
 EE-4022 MILWAUKEE SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING 2015 Page 3-1 Student Objectives: EE-4022 Experiment 3 Frequency Modulation (FM) In this experiment the student will use laboratory modules including a Voltage-Controlled
EE-4022 MILWAUKEE SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING 2015 Page 3-1 Student Objectives: EE-4022 Experiment 3 Frequency Modulation (FM) In this experiment the student will use laboratory modules including a Voltage-Controlled
Television co-channel interference: the effect of the polarity of modulation
 RESEARCH DEPARTMENT Television co-channel interference: the effect of the polarity of modulation REPORT No. T 105 1963/15 THE BRITIS H B.ROADCASTI N G ENGINEERING DIVISION CO RPO RATION RESEARCH DEPARTMENT
RESEARCH DEPARTMENT Television co-channel interference: the effect of the polarity of modulation REPORT No. T 105 1963/15 THE BRITIS H B.ROADCASTI N G ENGINEERING DIVISION CO RPO RATION RESEARCH DEPARTMENT
Communication Channels
 Communication Channels wires (PCB trace or conductor on IC) optical fiber (attenuation 4dB/km) broadcast TV (50 kw transmit) voice telephone line (under -9 dbm or 110 µw) walkie-talkie: 500 mw, 467 MHz
Communication Channels wires (PCB trace or conductor on IC) optical fiber (attenuation 4dB/km) broadcast TV (50 kw transmit) voice telephone line (under -9 dbm or 110 µw) walkie-talkie: 500 mw, 467 MHz
Method of measuring the maximum frequency deviation of FM broadcast emissions at monitoring stations. Recommendation ITU-R SM.
 Recommendation ITU-R SM.1268-4 (11/217) Method of measuring the maximum frequency deviation of FM broadcast emissions at monitoring stations SM Series Spectrum management ii Rec. ITU-R SM.1268-4 Foreword
Recommendation ITU-R SM.1268-4 (11/217) Method of measuring the maximum frequency deviation of FM broadcast emissions at monitoring stations SM Series Spectrum management ii Rec. ITU-R SM.1268-4 Foreword
PULSE CODE MODULATION TELEMETRY Properties of Various Binary Modulation Types
 PULSE CODE MODULATION TELEMETRY Properties of Various Binary Modulation Types Eugene L. Law Telemetry Engineer Code 1171 Pacific Missile Test Center Point Mugu, CA 93042 ABSTRACT This paper discusses the
PULSE CODE MODULATION TELEMETRY Properties of Various Binary Modulation Types Eugene L. Law Telemetry Engineer Code 1171 Pacific Missile Test Center Point Mugu, CA 93042 ABSTRACT This paper discusses the
Laboratory 9. Required Components: Objectives. Optional Components: Operational Amplifier Circuits (modified from lab text by Alciatore)
 Laboratory 9 Operational Amplifier Circuits (modified from lab text by Alciatore) Required Components: 1x 741 op-amp 2x 1k resistors 4x 10k resistors 1x l00k resistor 1x 0.1F capacitor Optional Components:
Laboratory 9 Operational Amplifier Circuits (modified from lab text by Alciatore) Required Components: 1x 741 op-amp 2x 1k resistors 4x 10k resistors 1x l00k resistor 1x 0.1F capacitor Optional Components:
Receiver Architecture
 Receiver Architecture Receiver basics Channel selection why not at RF? BPF first or LNA first? Direct digitization of RF signal Receiver architectures Sub-sampling receiver noise problem Heterodyne receiver
Receiver Architecture Receiver basics Channel selection why not at RF? BPF first or LNA first? Direct digitization of RF signal Receiver architectures Sub-sampling receiver noise problem Heterodyne receiver
Amplitude Modulation II
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Multiplexing Mojtaba Vaezi 6-1 Contents
UNIT-3. Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation
 UNIT-3 1. Draw the Block Schematic of AF Wave analyzer and explain its principle and Working? ANS: The wave analyzer consists of a very narrow pass-band filter section which can Be tuned to a particular
UNIT-3 1. Draw the Block Schematic of AF Wave analyzer and explain its principle and Working? ANS: The wave analyzer consists of a very narrow pass-band filter section which can Be tuned to a particular
Elements of Communication System Channel Fig: 1: Block Diagram of Communication System Terminology in Communication System
 Content:- Fundamentals of Communication Engineering : Elements of a Communication System, Need of modulation, electromagnetic spectrum and typical applications, Unit V (Communication terminologies in communication
Content:- Fundamentals of Communication Engineering : Elements of a Communication System, Need of modulation, electromagnetic spectrum and typical applications, Unit V (Communication terminologies in communication
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-2013 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-03 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: PART - A 0. What does the arrow mark indicate
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION MARCH-03 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 0 Subject: PART - A 0. What does the arrow mark indicate
High Dynamic Range Receiver Parameters
 High Dynamic Range Receiver Parameters The concept of a high-dynamic-range receiver implies more than an ability to detect, with low distortion, desired signals differing, in amplitude by as much as 90
High Dynamic Range Receiver Parameters The concept of a high-dynamic-range receiver implies more than an ability to detect, with low distortion, desired signals differing, in amplitude by as much as 90
RECOMMENDATION ITU-R F *, ** Signal-to-interference protection ratios for various classes of emission in the fixed service below about 30 MHz
 Rec. ITU-R F.240-7 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R F.240-7 *, ** Signal-to-interference protection ratios for various classes of emission in the fixed service below about 30 MHz (Question ITU-R 143/9) (1953-1956-1959-1970-1974-1978-1986-1990-1992-2006)
Rec. ITU-R F.240-7 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R F.240-7 *, ** Signal-to-interference protection ratios for various classes of emission in the fixed service below about 30 MHz (Question ITU-R 143/9) (1953-1956-1959-1970-1974-1978-1986-1990-1992-2006)
ANALOGUE TRANSMISSION OVER FADING CHANNELS
 J.P. Linnartz EECS 290i handouts Spring 1993 ANALOGUE TRANSMISSION OVER FADING CHANNELS Amplitude modulation Various methods exist to transmit a baseband message m(t) using an RF carrier signal c(t) =
J.P. Linnartz EECS 290i handouts Spring 1993 ANALOGUE TRANSMISSION OVER FADING CHANNELS Amplitude modulation Various methods exist to transmit a baseband message m(t) using an RF carrier signal c(t) =
Angle Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #12, April 14, Prof. Young-Chai Ko
 Angle Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #12, April 14, 2011 Prof. Young-Chai Ko koyc@korea.ac.kr Summary Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) Angle Modulation Frequency-Division Multiplexing
Angle Modulation KEEE343 Communication Theory Lecture #12, April 14, 2011 Prof. Young-Chai Ko koyc@korea.ac.kr Summary Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) Angle Modulation Frequency-Division Multiplexing
UNIT 1 QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS
 UNIT 1 QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier signal is varied in accordance with the instantaneous value of the modulating
UNIT 1 QUESTIONS WITH ANSWERS 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier signal is varied in accordance with the instantaneous value of the modulating
Chapter 4: Differential Amplifiers
 Chapter 4: Differential Amplifiers 4.1 Single-Ended and Differential Operation 4.2 Basic Differential Pair 4.3 Common-Mode Response 4.4 Differential Pair with MOS Loads 4.5 Gilbert Cell Single-Ended and
Chapter 4: Differential Amplifiers 4.1 Single-Ended and Differential Operation 4.2 Basic Differential Pair 4.3 Common-Mode Response 4.4 Differential Pair with MOS Loads 4.5 Gilbert Cell Single-Ended and
Receiver Design. Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 2011/2/21
 Receiver Design Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 2011/2/21 MW & RF Design / Prof. T. -L. Wu 1 The receiver mush be very sensitive to -110dBm
Receiver Design Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 2011/2/21 MW & RF Design / Prof. T. -L. Wu 1 The receiver mush be very sensitive to -110dBm
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE-TRICHY QUESTION BANK UNIT IV PART-A
 MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE-TRICHY QUESTION BANK SATELLITE COMMUNICATION DEPT./SEM.:ECE/VIII UNIT IV PART-A 1. What are the advantages of the super heterodyne receiver over TRF receiver? (AUC MAY 2004)
MAHALAKSHMI ENGINEERING COLLEGE-TRICHY QUESTION BANK SATELLITE COMMUNICATION DEPT./SEM.:ECE/VIII UNIT IV PART-A 1. What are the advantages of the super heterodyne receiver over TRF receiver? (AUC MAY 2004)
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler
 EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler Note Set #16 C-T Signals: Using FT Properties 1/12 Recall that FT Properties can be used for: 1. Expanding use of the FT table 2. Understanding real-world concepts
EECE 301 Signals & Systems Prof. Mark Fowler Note Set #16 C-T Signals: Using FT Properties 1/12 Recall that FT Properties can be used for: 1. Expanding use of the FT table 2. Understanding real-world concepts
Rec. ITU-R F RECOMMENDATION ITU-R F *,**
 Rec. ITU-R F.240-6 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R F.240-6 *,** SIGNAL-TO-INTERFERENCE PROTECTION RATIOS FOR VARIOUS CLASSES OF EMISSION IN THE FIXED SERVICE BELOW ABOUT 30 MHz (Question 143/9) Rec. ITU-R F.240-6
Rec. ITU-R F.240-6 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R F.240-6 *,** SIGNAL-TO-INTERFERENCE PROTECTION RATIOS FOR VARIOUS CLASSES OF EMISSION IN THE FIXED SERVICE BELOW ABOUT 30 MHz (Question 143/9) Rec. ITU-R F.240-6
Angle Modulated Systems
 Angle Modulated Systems Angle of carrier signal is changed in accordance with instantaneous amplitude of modulating signal. Two types Frequency Modulation (FM) Phase Modulation (PM) Use Commercial radio
Angle Modulated Systems Angle of carrier signal is changed in accordance with instantaneous amplitude of modulating signal. Two types Frequency Modulation (FM) Phase Modulation (PM) Use Commercial radio
This place covers: Demodulation or transference of signals modulated on a sinusoidal carrier or on electromagnetic waves.
 CPC - H03D - 2017.08 H03D DEMODULATION OR TRANSFERENCE OF MODULATION FROM ONE CARRIER TO ANOTHER (masers, lasers H01S; circuits capable of acting both as modulator and demodulator H03C; details applicable
CPC - H03D - 2017.08 H03D DEMODULATION OR TRANSFERENCE OF MODULATION FROM ONE CARRIER TO ANOTHER (masers, lasers H01S; circuits capable of acting both as modulator and demodulator H03C; details applicable
Lecture 15: Introduction to Mixers
 EECS 142 Lecture 15: Introduction to Mixers Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture
EECS 142 Lecture 15: Introduction to Mixers Prof. Ali M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley Copyright c 2005 by Ali M. Niknejad A. M. Niknejad University of California, Berkeley EECS 142 Lecture
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the
 Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
Speech, music, images, and video are examples of analog signals. Each of these signals is characterized by its bandwidth, dynamic range, and the nature of the signal. For instance, in the case of audio
EE 460L University of Nevada, Las Vegas ECE Department
 EE 460L PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in the context of digital communications is a modulation process which imparts to a sinusoid two or more discrete amplitude levels. These are related
EE 460L PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in the context of digital communications is a modulation process which imparts to a sinusoid two or more discrete amplitude levels. These are related
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-2012 SCHEME OF VALUATION
 GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 40 Subject: PART - A 0. Which region of the transistor
GOVERNMENT OF KARNATAKA KARNATAKA STATE PRE-UNIVERSITY EDUCATION EXAMINATION BOARD II YEAR PUC EXAMINATION JULY-0 SCHEME OF VALUATION Subject Code: 40 Subject: PART - A 0. Which region of the transistor
Local Oscillator Phase Noise and its effect on Receiver Performance C. John Grebenkemper
 Watkins-Johnson Company Tech-notes Copyright 1981 Watkins-Johnson Company Vol. 8 No. 6 November/December 1981 Local Oscillator Phase Noise and its effect on Receiver Performance C. John Grebenkemper All
Watkins-Johnson Company Tech-notes Copyright 1981 Watkins-Johnson Company Vol. 8 No. 6 November/December 1981 Local Oscillator Phase Noise and its effect on Receiver Performance C. John Grebenkemper All
AM Limitations. Amplitude Modulation II. DSB-SC Modulation. AM Modifications
 Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
Lecture 6: Amplitude Modulation II EE 3770: Communication Systems AM Limitations AM Limitations DSB-SC Modulation SSB Modulation VSB Modulation Lecture 6 Amplitude Modulation II Amplitude modulation is
CHAPTER 6 INTRODUCTION TO SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION
 CHAPTER 6 INTRODUCTION TO SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION Broadly speaking, system identification is the art and science of using measurements obtained from a system to characterize the system. The characterization
CHAPTER 6 INTRODUCTION TO SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION Broadly speaking, system identification is the art and science of using measurements obtained from a system to characterize the system. The characterization
Linearity Improvement Techniques for Wireless Transmitters: Part 1
 From May 009 High Frequency Electronics Copyright 009 Summit Technical Media, LLC Linearity Improvement Techniques for Wireless Transmitters: art 1 By Andrei Grebennikov Bell Labs Ireland In modern telecommunication
From May 009 High Frequency Electronics Copyright 009 Summit Technical Media, LLC Linearity Improvement Techniques for Wireless Transmitters: art 1 By Andrei Grebennikov Bell Labs Ireland In modern telecommunication
Let us consider the following block diagram of a feedback amplifier with input voltage feedback fraction,, be positive i.e. in phase.
 P a g e 2 Contents 1) Oscillators 3 Sinusoidal Oscillators Phase Shift Oscillators 4 Wien Bridge Oscillators 4 Square Wave Generator 5 Triangular Wave Generator Using Square Wave Generator 6 Using Comparator
P a g e 2 Contents 1) Oscillators 3 Sinusoidal Oscillators Phase Shift Oscillators 4 Wien Bridge Oscillators 4 Square Wave Generator 5 Triangular Wave Generator Using Square Wave Generator 6 Using Comparator
RECOMMENDATION ITU-R S *
 Rec. ITU-R S.446-4 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R S.446-4 * Carrier energy dispersal for systems employing angle modulation by analogue signals or digital modulation in the fixed-satellite service (1966-1974-1978-1992-1993)
Rec. ITU-R S.446-4 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R S.446-4 * Carrier energy dispersal for systems employing angle modulation by analogue signals or digital modulation in the fixed-satellite service (1966-1974-1978-1992-1993)
UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers)
 UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers) 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier Signal is varied in accordance with the
UNIT-I AMPLITUDE MODULATION (2 Marks Questions and Answers) 1. Define modulation? Modulation is a process by which some characteristics of high frequency carrier Signal is varied in accordance with the
Rec. ITU-R SM RECOMMENDATION ITU-R SM SPECTRA AND BANDWIDTH OF EMISSIONS. (Question ITU-R 76/1)
 Rec. ITU-R SM.38-1 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R SM.38-1 SPECTRA AND BANDWIDTH OF EMISSIONS (Question ITU-R 76/1) (1948-1951-1953-1956-1959-1963-1966-197-1974-1978-198-1986-199-1994-1999) Rec. ITU-R SM.38-1 The
Rec. ITU-R SM.38-1 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R SM.38-1 SPECTRA AND BANDWIDTH OF EMISSIONS (Question ITU-R 76/1) (1948-1951-1953-1956-1959-1963-1966-197-1974-1978-198-1986-199-1994-1999) Rec. ITU-R SM.38-1 The
Modifying Bragg Grating Interrogation System and Studying Corresponding Problems
 Modifying Bragg Grating Interrogation System and Studying Corresponding Problems 1998 Abstract An improved fiber Bragg grating (FBG) interrogation system is described. The system utilises time domain multiplexing
Modifying Bragg Grating Interrogation System and Studying Corresponding Problems 1998 Abstract An improved fiber Bragg grating (FBG) interrogation system is described. The system utilises time domain multiplexing
Noise and Distortion in Microwave System
 Noise and Distortion in Microwave System Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 1 Introduction Noise is a random process from many sources: thermal,
Noise and Distortion in Microwave System Prof. Tzong-Lin Wu EMC Laboratory Department of Electrical Engineering National Taiwan University 1 Introduction Noise is a random process from many sources: thermal,
Effects of Intensity and Position Modulation On Switched Electrode Electronics Beam Position Monitor Systems at Jefferson Lab*
 JLAB-ACT--9 Effects of Intensity and Position Modulation On Switched Electrode Electronics Beam Position Monitor Systems at Jefferson Lab* Tom Powers Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility Newport
JLAB-ACT--9 Effects of Intensity and Position Modulation On Switched Electrode Electronics Beam Position Monitor Systems at Jefferson Lab* Tom Powers Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility Newport
RECOMMENDATION ITU-R BS
 Rec. ITU-R BS.1194-1 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R BS.1194-1 SYSTEM FOR MULTIPLEXING FREQUENCY MODULATION (FM) SOUND BROADCASTS WITH A SUB-CARRIER DATA CHANNEL HAVING A RELATIVELY LARGE TRANSMISSION CAPACITY
Rec. ITU-R BS.1194-1 1 RECOMMENDATION ITU-R BS.1194-1 SYSTEM FOR MULTIPLEXING FREQUENCY MODULATION (FM) SOUND BROADCASTS WITH A SUB-CARRIER DATA CHANNEL HAVING A RELATIVELY LARGE TRANSMISSION CAPACITY
Differential Amplifiers/Demo
 Differential Amplifiers/Demo Motivation and Introduction The differential amplifier is among the most important circuit inventions, dating back to the vacuum tube era. Offering many useful properties,
Differential Amplifiers/Demo Motivation and Introduction The differential amplifier is among the most important circuit inventions, dating back to the vacuum tube era. Offering many useful properties,
Receiver Architectures
 Receiver Architectures Modules: VCO (2), Quadrature Utilities (2), Utilities, Adder, Multiplier, Phase Shifter (2), Tuneable LPF (2), 100-kHz Channel Filters, Audio Oscillator, Noise Generator, Speech,
Receiver Architectures Modules: VCO (2), Quadrature Utilities (2), Utilities, Adder, Multiplier, Phase Shifter (2), Tuneable LPF (2), 100-kHz Channel Filters, Audio Oscillator, Noise Generator, Speech,
CLOCK AND DATA RECOVERY (CDR) circuits incorporating
 IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 39, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2004 1571 Brief Papers Analysis and Modeling of Bang-Bang Clock and Data Recovery Circuits Jri Lee, Member, IEEE, Kenneth S. Kundert, and
IEEE JOURNAL OF SOLID-STATE CIRCUITS, VOL. 39, NO. 9, SEPTEMBER 2004 1571 Brief Papers Analysis and Modeling of Bang-Bang Clock and Data Recovery Circuits Jri Lee, Member, IEEE, Kenneth S. Kundert, and
4.1 REPRESENTATION OF FM AND PM SIGNALS An angle-modulated signal generally can be written as
 1 In frequency-modulation (FM) systems, the frequency of the carrier f c is changed by the message signal; in phase modulation (PM) systems, the phase of the carrier is changed according to the variations
1 In frequency-modulation (FM) systems, the frequency of the carrier f c is changed by the message signal; in phase modulation (PM) systems, the phase of the carrier is changed according to the variations
Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 23 The Phase Locked Loop (Contd.) We will now continue our discussion
Communication Engineering Prof. Surendra Prasad Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 23 The Phase Locked Loop (Contd.) We will now continue our discussion
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal
 Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
Modulation is the process of impressing a low-frequency information signal (baseband signal) onto a higher frequency carrier signal Modulation is a process of mixing a signal with a sinusoid to produce
Restoration Performance Report
 Restoration Performance Report Report Date: July 15, 2015 Manufacturer: Fisher Model: 500-C Receiver Special Notes: Full Gold Level Restoration service completed. Chassis ultrasonically cleaned. All coupling
Restoration Performance Report Report Date: July 15, 2015 Manufacturer: Fisher Model: 500-C Receiver Special Notes: Full Gold Level Restoration service completed. Chassis ultrasonically cleaned. All coupling
note application Measurement of Frequency Stability and Phase Noise by David Owen
 application Measurement of Frequency Stability and Phase Noise note by David Owen The stability of an RF source is often a critical parameter for many applications. Performance varies considerably with
application Measurement of Frequency Stability and Phase Noise note by David Owen The stability of an RF source is often a critical parameter for many applications. Performance varies considerably with
The Digital Linear Amplifier
 The Digital Linear Amplifier By Timothy P. Hulick, Ph.D. 886 Brandon Lane Schwenksville, PA 19473 e-mail: dxyiwta@aol.com Abstract. This paper is the second of two presenting a modern approach to Digital
The Digital Linear Amplifier By Timothy P. Hulick, Ph.D. 886 Brandon Lane Schwenksville, PA 19473 e-mail: dxyiwta@aol.com Abstract. This paper is the second of two presenting a modern approach to Digital
DOUBLE SIDEBAND SUPPRESSED CARRIER TELEMETRY SYSTEM 1
 DOUBLE SIDEBAND SUPPRESSED CARRIER TELEMETRY SYSTEM 1 F. J. SCHMITT Lockheed Electronics Company White Sands Missile Range, New Mexico. Summary Vibration, shock, and acoustic data constitute one of the
DOUBLE SIDEBAND SUPPRESSED CARRIER TELEMETRY SYSTEM 1 F. J. SCHMITT Lockheed Electronics Company White Sands Missile Range, New Mexico. Summary Vibration, shock, and acoustic data constitute one of the
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY An Overview of Modulation Techniques: chapter 3.1 3.3.1 2 Introduction (3.1) Analog Modulation Amplitude Modulation Phase and
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY An Overview of Modulation Techniques: chapter 3.1 3.3.1 2 Introduction (3.1) Analog Modulation Amplitude Modulation Phase and
EE390 Final Exam Fall Term 2002 Friday, December 13, 2002
 Name Page 1 of 11 EE390 Final Exam Fall Term 2002 Friday, December 13, 2002 Notes 1. This is a 2 hour exam, starting at 9:00 am and ending at 11:00 am. The exam is worth a total of 50 marks, broken down
Name Page 1 of 11 EE390 Final Exam Fall Term 2002 Friday, December 13, 2002 Notes 1. This is a 2 hour exam, starting at 9:00 am and ending at 11:00 am. The exam is worth a total of 50 marks, broken down
INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA
 COMM.ENG INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA 9/9/2017 LECTURES 1 Objectives To give a background on Communication system components and channels (media) A distinction between analogue
COMM.ENG INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS AND TRANSMISSION MEDIA 9/9/2017 LECTURES 1 Objectives To give a background on Communication system components and channels (media) A distinction between analogue
REPORT ITU-R M Adaptability of real zero single sideband technology to HF data communications
 Rep. ITU-R M.2026 1 REPORT ITU-R M.2026 Adaptability of real zero single sideband technology to HF data communications (2001) 1 Introduction Automated HF communications brought a number of innovative solutions
Rep. ITU-R M.2026 1 REPORT ITU-R M.2026 Adaptability of real zero single sideband technology to HF data communications (2001) 1 Introduction Automated HF communications brought a number of innovative solutions
An Introduction to Spectrum Analyzer. An Introduction to Spectrum Analyzer
 1 An Introduction to Spectrum Analyzer 2 Chapter 1. Introduction As a result of rapidly advancement in communication technology, all the mobile technology of applications has significantly and profoundly
1 An Introduction to Spectrum Analyzer 2 Chapter 1. Introduction As a result of rapidly advancement in communication technology, all the mobile technology of applications has significantly and profoundly
Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay
 Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 27 EDFA In the last lecture, we talked about wavelength
Advanced Optical Communications Prof. R. K. Shevgaonkar Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Lecture No. # 27 EDFA In the last lecture, we talked about wavelength
Chaotic Communications With Correlator Receivers: Theory and Performance Limits
 Chaotic Communications With Correlator Receivers: Theory and Performance Limits GÉZA KOLUMBÁN, SENIOR MEMBER, IEEE, MICHAEL PETER KENNEDY, FELLOW, IEEE, ZOLTÁN JÁKÓ, AND GÁBOR KIS Invited Paper This paper
Chaotic Communications With Correlator Receivers: Theory and Performance Limits GÉZA KOLUMBÁN, SENIOR MEMBER, IEEE, MICHAEL PETER KENNEDY, FELLOW, IEEE, ZOLTÁN JÁKÓ, AND GÁBOR KIS Invited Paper This paper
SPEECH ANALYSIS* Prof. M. Halle G. W. Hughes A. R. Adolph
 XII. SPEECH ANALYSIS* Prof. M. Halle G. W. Hughes A. R. Adolph A. STUDIES OF PITCH PERIODICITY In the past a number of devices have been built to extract pitch-period information from speech. These efforts
XII. SPEECH ANALYSIS* Prof. M. Halle G. W. Hughes A. R. Adolph A. STUDIES OF PITCH PERIODICITY In the past a number of devices have been built to extract pitch-period information from speech. These efforts
Chapter VII. MIXERS and DETECTORS
 Class Notes, 31415 RF-Communication Circuits Chapter VII MIXERS and DETECTORS Jens Vidkjær NB235 ii Contents VII Mixers and Detectors... 1 VII-1 Mixer Basics... 2 A Prototype FET Mixer... 2 Example VII-1-1
Class Notes, 31415 RF-Communication Circuits Chapter VII MIXERS and DETECTORS Jens Vidkjær NB235 ii Contents VII Mixers and Detectors... 1 VII-1 Mixer Basics... 2 A Prototype FET Mixer... 2 Example VII-1-1
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY
 TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY 2 Basic Definitions Time and Frequency db conversion Power and dbm Filter Basics 3 Filter Filter is a component with frequency
TSEK02: Radio Electronics Lecture 2: Modulation (I) Ted Johansson, EKS, ISY 2 Basic Definitions Time and Frequency db conversion Power and dbm Filter Basics 3 Filter Filter is a component with frequency
Analog and Telecommunication Electronics
 Politecnico di Torino Electronic Eng. Master Degree Analog and Telecommunication Electronics C5 - Synchronous demodulation» AM and FM demodulation» Coherent demodulation» Tone decoders AY 2015-16 19/03/2016-1
Politecnico di Torino Electronic Eng. Master Degree Analog and Telecommunication Electronics C5 - Synchronous demodulation» AM and FM demodulation» Coherent demodulation» Tone decoders AY 2015-16 19/03/2016-1
Nonlinearities in Power Amplifier and its Remedies
 International Journal of Electronics Engineering Research. ISSN 0975-6450 Volume 9, Number 6 (2017) pp. 883-887 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Nonlinearities in Power Amplifier
International Journal of Electronics Engineering Research. ISSN 0975-6450 Volume 9, Number 6 (2017) pp. 883-887 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com Nonlinearities in Power Amplifier
Investigation on Multiple Antenna Transmission Techniques in Evolved UTRA. OFDM-Based Radio Access in Downlink. Features of Evolved UTRA and UTRAN
 Evolved UTRA and UTRAN Investigation on Multiple Antenna Transmission Techniques in Evolved UTRA Evolved UTRA (E-UTRA) and UTRAN represent long-term evolution (LTE) of technology to maintain continuous
Evolved UTRA and UTRAN Investigation on Multiple Antenna Transmission Techniques in Evolved UTRA Evolved UTRA (E-UTRA) and UTRAN represent long-term evolution (LTE) of technology to maintain continuous
EE303: Communication Systems
 EE303: Communication Systems Professor A. Manikas Chair of Communications and Array Processing Imperial College London An Overview of Fundamentals: Channels, Criteria and Limits Prof. A. Manikas (Imperial
EE303: Communication Systems Professor A. Manikas Chair of Communications and Array Processing Imperial College London An Overview of Fundamentals: Channels, Criteria and Limits Prof. A. Manikas (Imperial
EE 400L Communications. Laboratory Exercise #7 Digital Modulation
 EE 400L Communications Laboratory Exercise #7 Digital Modulation Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, at Las Vegas PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in
EE 400L Communications Laboratory Exercise #7 Digital Modulation Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, at Las Vegas PREPARATION 1- ASK Amplitude shift keying - ASK - in
Time division multiplexing The block diagram for TDM is illustrated as shown in the figure
 CHAPTER 2 Syllabus: 1) Pulse amplitude modulation 2) TDM 3) Wave form coding techniques 4) PCM 5) Quantization noise and SNR 6) Robust quantization Pulse amplitude modulation In pulse amplitude modulation,
CHAPTER 2 Syllabus: 1) Pulse amplitude modulation 2) TDM 3) Wave form coding techniques 4) PCM 5) Quantization noise and SNR 6) Robust quantization Pulse amplitude modulation In pulse amplitude modulation,
