NAPREDNI FIZIČKI PRAKTIKUM 2 SMJER: ISTRAŽIVAČKI SMJER KAOTIČNE OSCILACIJE U ELEKTRIČNOM TITRAJNOM KRUGU
|
|
|
- Rolf Lyons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NAPREDNI FIZIČKI PRAKTIKUM 2 SMJER: ISTRAŽIVAČKI SMJER KAOTIČNE OSCILACIJE U ELEKTRIČNOM TITRAJNOM KRUGU
2 ISTRAŽIVAČKI SMJER NFP2 1 ZADACI 1. Objasnite pojavu kaotičnog ponašanja u nelinearnim sustavima, npr. u logističkoj mapi. Možete koristiti SAGE za proučavanje logističke jednadžbe: 2. Spojite izlaz generatora signala Hewlett Packard na osciloskop i namjestite da vrijednost DC offseta signala bude nula. Nakon što ste to namjestili nemojte više dirati potenciometar DC offset. Potom sastavite sklop za kaotične oscilacije, koristeći generator signala Hewlett Packard i programski modul Frequency Analysis na računalu. Namjestite frekvenciju na 35 khz, te proučite kako se Fourierov spektar mijenja s promjenom amplitude. Snimite spektre s karakterističnim ponašanjem. 3. Sastavite sklop za kaotične oscilacije, koristeći Cobra3 generator signala i programski modul Universal Writer na računalu. Namjestite frekvenciju na 20 khz, te proučite kako se Fourierov spektar mijenja s promjenom amplitude. Snimite spektre s karakterističnim ponašanjem. 4. Spojite sklop za akustičnu reprodukciju oscilacija, koristeći generator signala Hewlett Packard i zvučnike. Namjestite frekvenciju u rasponu od 10 khz do svojeg praga čujnosti, te proučite što se dogada s promjenom amplitude. S ovom sklopom na tim frekvencijama nećete moći doći do kaotičnog režima, ali možete doći do prve bifurkacije. Pomoću programskog modula Frequency Analysis proučite Fourierov spektar oscilacija i objasnite kakve zvukove čujete. Napomena: diodu treba spojiti u obrnutom smjeru od načina prikazanog u Phywe pripremi.
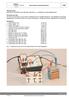
3 Forced oscillations of a non-linear electrical series TEP Related Topics oscillating circuit, forced oscillation, diode, period multiples, Fourier spectrum, chaotic oscillation Principle A sinusoidal voltage is applied to a non-linear circuit with a silicon diode functioning as voltageindependent capacity. The oscillating circuit, i.e. the occurrence of chaotic oscillatory behavior with increasing amplitude is studied. Material 1 Cobra3 Basic Unit, USB Cobra3 power supply Data cable USB Software Cobra3, Frequency Analysis Digital function generator Oscilloscope, 30 MHz, 2 channels Connection box Coil, 1200 turns Diode BY Clamping holder Connecting plug Connector, T type, BNC Adapter, BNC socket, 4 mm socket pair Adapter, BNC socket, 4 mm plug pair Connecting cord, blue, l = 100 mm Connecting cord, red, l = 250 mm Connecting cord, red, l = 500 mm Connecting cord, blue, l = 500 mm Screened cable, BNC, l = 250 mm Screened cable, BNC, l = 750 mm PC, Windows 95 or higher Fig. 1: Experimental set-up P PHYWE Systeme GmbH & Co. KG All rights reserved 1
4 TEP Forced oscillations of a non-linear electrical series Tasks Study the oscillatory behavior of the non-linear circuit for an exciting signal with amplitudes between 0.1 and 15 V at frequency of 35 khz. Investigate the oscillatory image and the Fourier spectrum as functions of the excitation amplitude. Show that period multiples and regions of chaotic oscillatory amplitude occur with increasing amplitude. Set-up Set up the series circuit according to Figs. 1 and 2. The input voltage is tapped off at the diode and fed to the ANALOG IN 2 (+,-) input jacks of the Cobra3 Basic Unit and the oscilloscope channel CH2. Connect the circuit with the power output of the digital function generator. Take care to connect the ground to the diode. Use the T connection to connect the power output with the oscilloscope input jack CH2, too. Procedure Fig. 2: Example circuit. Blue cables are grounding connections. Use a sinusoidal voltage signal as input with an amplitude of 0.1 V. For all measurements use a frequency of 35 khz. Activate the Frequency Analysis program module. Choose the continuous measuring mode and the maximum frequency range. For each measurement set the voltage range to an appropriate value. In the course of this experiment increase the input voltage of the digital function generator progressively from 0.1 to the maximum value in appropriate steps. Observe both signals on the oscilloscope and the PC screen and record both the signal and the Fourier spectrum for each step. For regions of chaos record several spectra for the same amplitude in order to verify that the occurring fundamental frequencies vary in number and value. Fig. 3: schematic circuit Theory As a first approximation, the characteristic of a diode behaves quadratic with amplitude of the input signal. The diode s barrier layer, which is responsible for its capacitance, changes as a function of the applied voltage and the voltage s sign. Due to the quadratic characteristic line, the behaviour becomes nonlinear. This is responsible for the onset of chaos. This behaviour can be described by a bifurcation diagram, which is based on a quadratic function. In Fig. 4 such a diagram is shown which describes the path to chaos for this experiment. The x-axis shows the increasing voltage of the input signal, the y-axis denotes the frequencies. For an increased voltage an increasing quantity of frequencies may be observed. After exceeding a certain threshold the behaviour of the oscillating circuit can no longer be predicted it behaves chaotically. Fig. 4: Logarithmic bifurcation diagram 2 PHYWE Systeme GmbH & Co. KG All rights reserved P
5 Forced oscillations of a non-linear electrical series TEP The theory clearly predicts islands of order in chaos, i.e. for certain input amplitudes the system suddenly oscillates in a non-chaotic manner (see Fig. 4). Generally, however, all of such systems ultimately drift permanently into chaos when the excitation amplitude has increased sufficiently. Spectral analysis is extremely appropriate for the analysis of the occurring oscillation modi. Note: The fundamental theoretical framework for chaos theory can naturally not be presented here. However, it has been exhaustively explained in many publications: P.S. Lindsay, Period doubling and chaotic behaviour in a driven harmonic oscillator, Phys. Rev. Lett. 47 (1981), p W. Lauterborn, W. Meyer-Ilse, Chaos, Physik in unserer Zeit 17 (1986), p. 177 M. Massoth, R. Mettin: Untersuchungen am nichtlinearen RLC-Schwingkreis, Junge Wissenschaft 2 (1987), p. 26 A. May, Anwendungen der Spektrumanalyse zur Auswertung von physikalischen Schulexperimenten Praxis der Naturwissenschaften Physik, 36 (1987), p. 15 Evaluation and results In the following the evaluation of the obtained values is described with the help of example values. Your results may vary from those presented here. At very low voltages the diode does not show its rectifying effect and functions as a pure capacitance. Accordingly, the circuit oscillates like the generator, namely sinusoidal as shown in Fig. 5. Only a single line appears in the Fourier spectrum at the frequency of 35.2 khz which corresponds to the natural frequency of the oscillating circuit. With further increased amplitude of the exciting signal the diode only allows a single half-wave of the alternating signal to pass (Fig. 6). According to the theory of Fourier analysis, this means a spectrum with discrete harmonic lines whose lowest frequency is the fundamental oscillation. These conditions of the oscillatory circuit are far to the left in the bifurcation diagram in Fig. 4. Fig. 5: Voltage tapped off the diode at U SS = 0. 1 V. The circuit oscillates sinusoidally as the diode is functioning as pure capacitance. Fig. 6: Voltage tapped off the diode at U SS = 1. 0 V. The diode now shows its rectifying effect. In Fig. 7 the oscillating circuit exhibits the behavior occuring in the bifurcation diagram at the first fork. On the oscilloscope screen one signal of higher amplitude and one of lower amplitude are alternately displayed (depending on the trigger settings). This corresponds to a period doubling: the 17.6 khz line appears in the spectrum as the fundamental frequency. Fig. 7: Voltage tapped off the diode at U SS = 3. 0 V. The first period doubling appears. The fundamental frequency is halved. P PHYWE Systeme GmbH & Co. KG All rights reserved 3
6 TEP Forced oscillations of a non-linear electrical series In Fig. 8 an additional period doubling occurs. The fundamental frequency of the spectrum is now at 8.8 khz. On the oscilloscope screen a continually increasing ramification of the periodicity is observed with every additional increase of signal amplitude. In the bifurcation diagram the second splitting has been reached. In Fig. 9 the chaotic status has been achieved. Due to the rectifying effect of the diode, harmonic lines still appear in the Fourier spectrum, but in contrast to the cases above frequencies between these lines appear continuously with changing partial amplitudes. The shape of the Fourier spectrum changes continuously and no two identical measurements for the same signal amplitude can be taken. The circuit oscillates with all the displayed frequencies thus chaotically. The chaotic character of the oscillations also becomes clear when regarding the amplitudes of the recorded signal. Quite obviously, there is no periodicity at all in the sequence of the signal heights. In Fig. 10 the oscillator has left the chaotic state for U SS = V. These islands of order are also predicted by the bifurcation diagram. Only the first fundamental and its higher harmonics show in the spectrum. The amplitudes of the signal are periodic. With further increase of the input signal the oscillator will slip back into chaos. Fig. 8: Voltage tapped off the diode at U SS = 7. 0 V. The second period doubling (period quadrupling) appears. The fundamental frequency is a quarter of the natural frequency. Fig. 9: Voltage tapped off the diode at U SS = 9. 0 V. The circuit is now oscillating chaotically. Remarks on experimental procedure If the circuit in Fig. 3 is expanded according to the circuit diagram in Fig. 11, it is possible to hear the signals of the oscillators over a loudspeaker. To achieve this, the signal is tapped between the coil and the diode over a 1 kω resistor ( ) and led to a LF amplifier ( ). From the amplifier the signal passes to the loudspeaker ( ). A frequency between 8 and 9 khz should be chosen for this experiment. At this frequency, the experiment does not follow the bifurcation diagram as at a frequency of 35 khz. However, with the loudspeaker it is possible to make the period doubling (or frequency bisection) phenomenon audible. The oscillator described here was experimentally investigated for the first time by Lindsay in 1981 (theory section and the given literature therein). Fig. 10: Voltage tapped off the diode at U SS = V. The circuit is in an island of order. Fig. 11: Circuit diagram for acoustic reproduction of the occurring oscillations. 4 PHYWE Systeme GmbH & Co. KG All rights reserved P
Coil in the AC circuit
 Coil in the AC circuit LEP Related topics Inductance, Kirchhoff s laws, parallel connection, series connection, a. c. impedance, phase displacement, vector diagram Principle The impedance and phase displacement
Coil in the AC circuit LEP Related topics Inductance, Kirchhoff s laws, parallel connection, series connection, a. c. impedance, phase displacement, vector diagram Principle The impedance and phase displacement
Acoustic Doppler Effect
 Acoustic Doppler Effect TEP Related Topics Wave propagation, Doppler shift of frequency Principle If an emitter of sound or a detector is set into motion relative to the medium of propagation, the frequency
Acoustic Doppler Effect TEP Related Topics Wave propagation, Doppler shift of frequency Principle If an emitter of sound or a detector is set into motion relative to the medium of propagation, the frequency
Inductance of solenoids with Cobra3
 Inductance of solenoids with Cobra3 TEP Related topics Law of inductance, Lenz s law, self-inductance, solenoids, transformer, oscillatory circuit, resonance, damped oscillation, logarithmic decrement,
Inductance of solenoids with Cobra3 TEP Related topics Law of inductance, Lenz s law, self-inductance, solenoids, transformer, oscillatory circuit, resonance, damped oscillation, logarithmic decrement,
Kirchhoff s laws, induction law, Maxwell equations, current, voltage, resistance, parallel connection, series connection, potentiometer
 Kirchhoff s laws with Cobra4 TEP Related Topics Kirchhoff s laws, induction law, Maxwell equations, current, voltage, resistance, parallel connection, series connection, potentiometer Principle First Kirchhoff
Kirchhoff s laws with Cobra4 TEP Related Topics Kirchhoff s laws, induction law, Maxwell equations, current, voltage, resistance, parallel connection, series connection, potentiometer Principle First Kirchhoff
Inductance of solenoids
 Inductance of solenoids LEP -01 Related topics Law of inductance, Lenz s law, self-inductance, solenoids, transformer, oscillatory circuit, resonance, damped oscillation, logarithmic decrement, Q factor.
Inductance of solenoids LEP -01 Related topics Law of inductance, Lenz s law, self-inductance, solenoids, transformer, oscillatory circuit, resonance, damped oscillation, logarithmic decrement, Q factor.
TEP. RLC Circuit with Cobra3
 RLC Circuit with Cobra3 TEP Related topics Tuned circuit, series-tuned circuit, parallel-tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, capacitor, coil, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width,impedance,
RLC Circuit with Cobra3 TEP Related topics Tuned circuit, series-tuned circuit, parallel-tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, capacitor, coil, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width,impedance,
RLC-circuits TEP. f res. = 1 2 π L C.
 RLC-circuits TEP Keywords Damped and forced oscillations, Kirchhoff s laws, series and parallel tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, reactance, impedance, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width
RLC-circuits TEP Keywords Damped and forced oscillations, Kirchhoff s laws, series and parallel tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, reactance, impedance, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width
Coil in the AC circuit with Cobra3
 Coil in the AC circuit with Cobra3 TEP Related topics Inductance, Kirchhoff s laws, Maxwell s equations, a.c. impedance, phase displacement. Principle and task The coil is connected in a circuit with a
Coil in the AC circuit with Cobra3 TEP Related topics Inductance, Kirchhoff s laws, Maxwell s equations, a.c. impedance, phase displacement. Principle and task The coil is connected in a circuit with a
LEP RLC Circuit
 RLC Circuit LEP Related topics Kirchhoff s laws, series and parallel tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width, loss resistance, damping Principle The
RLC Circuit LEP Related topics Kirchhoff s laws, series and parallel tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width, loss resistance, damping Principle The
Electricity. Coil in the AC circuit /11. Electrodynamics. What you need:
 Electrodynamics Electricity Coil in the AC circuit -01/11 What you can learn about Inductance Kirchhoff s laws Maxwell s equations AC impedance Phase displacement Principle: The coil is connected in a
Electrodynamics Electricity Coil in the AC circuit -01/11 What you can learn about Inductance Kirchhoff s laws Maxwell s equations AC impedance Phase displacement Principle: The coil is connected in a
The solar cell as a diode
 The solar cell as a diode ENT Keywords Solar energy, photovoltaics, solar cell, diode, and dark characteristic Principle A solar cell consists of a p-doped layer and of an n-doped layer. Under the influence
The solar cell as a diode ENT Keywords Solar energy, photovoltaics, solar cell, diode, and dark characteristic Principle A solar cell consists of a p-doped layer and of an n-doped layer. Under the influence
RLC-circuits with Cobra4 Xpert-Link TEP. 1 2 π L C. f res=
 Related topics Damped and forced oscillations, Kirchhoff s laws, series and parallel tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, reactance, impedance, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width Principle
Related topics Damped and forced oscillations, Kirchhoff s laws, series and parallel tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, reactance, impedance, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width Principle
NAPREDNI FIZIČKI PRAKTIKUM 1 SMJER: ISTRAŽIVAČKI STUDIJ FIZIKE ELEKTRIČNI TITRAJNI KRUG
 NAPREDNI FIZIČKI PRAKTIKUM 1 SMJER: ISTRAŽIVAČKI STUDIJ FIZIKE ELEKTRIČNI TITRAJNI KRUG ISTRAŽIVAČKI STUDIJ FIZIKE NFP1 1 ZADACI 1. Odredite ovisnost impedancije o frekvenciji za serijski RLC krug, za
NAPREDNI FIZIČKI PRAKTIKUM 1 SMJER: ISTRAŽIVAČKI STUDIJ FIZIKE ELEKTRIČNI TITRAJNI KRUG ISTRAŽIVAČKI STUDIJ FIZIKE NFP1 1 ZADACI 1. Odredite ovisnost impedancije o frekvenciji za serijski RLC krug, za
Rich Variety of Bifurcation and Chaos in a Simple Non-Source Free Electronic Circuit with a Diode
 International Journal of Pure and Applied Physics ISSN 0973-1776 Volume 6, Number 1 (2010), pp. 63 69 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijpap.htm Rich Variety of Bifurcation and
International Journal of Pure and Applied Physics ISSN 0973-1776 Volume 6, Number 1 (2010), pp. 63 69 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com/ijpap.htm Rich Variety of Bifurcation and
RLC-circuits with Cobra4 Xpert-Link
 Student's Sheet RLC-circuits with Cobra4 Xpert-Link (Item No.: P2440664) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Subtopic: Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, AC Circuits Topic: Electricity
Student's Sheet RLC-circuits with Cobra4 Xpert-Link (Item No.: P2440664) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Subtopic: Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, AC Circuits Topic: Electricity
LABORATORY 4. Palomar College ENGR210 Spring 2017 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17
 LABORATORY 4 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17 OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this lab is to evaluate the transient and steady-state circuit response of first order and second order circuits. MINIMUM EQUIPMENT LIST: You will
LABORATORY 4 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17 OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this lab is to evaluate the transient and steady-state circuit response of first order and second order circuits. MINIMUM EQUIPMENT LIST: You will
Electricity. Interference of microwaves Electromagnetic Oscillations and Waves. What you need:
 Electromagnetic Oscillations and Waves Electricity What you can learn about Wavelength Standing wave Reflection Transmission Michelson interferometer Principle: A microwave beam, after reflection from
Electromagnetic Oscillations and Waves Electricity What you can learn about Wavelength Standing wave Reflection Transmission Michelson interferometer Principle: A microwave beam, after reflection from
Simultaneous amplitude and frequency noise analysis in Chua s circuit
 Typeset using jjap.cls Simultaneous amplitude and frequency noise analysis in Chua s circuit J.-M. Friedt 1, D. Gillet 2, M. Planat 2 1 : IMEC, MCP/BIO, Kapeldreef 75, 3001 Leuven, Belgium
Typeset using jjap.cls Simultaneous amplitude and frequency noise analysis in Chua s circuit J.-M. Friedt 1, D. Gillet 2, M. Planat 2 1 : IMEC, MCP/BIO, Kapeldreef 75, 3001 Leuven, Belgium
Magnetic induction with Cobra3
 Magnetic induction with Cobra3 LEP Related Topics Maxwell s equations, electrical eddy field, magnetic field of coils, coil, magnetic flux, induced voltage. Principle A magnetic field of variable frequency
Magnetic induction with Cobra3 LEP Related Topics Maxwell s equations, electrical eddy field, magnetic field of coils, coil, magnetic flux, induced voltage. Principle A magnetic field of variable frequency
LAB #7: Digital Signal Processing
 LAB #7: Digital Signal Processing Equipment: Pentium PC with NI PCI-MIO-16E-4 data-acquisition board NI BNC 2120 Accessory Box VirtualBench Instrument Library version 2.6 Function Generator (Tektronix
LAB #7: Digital Signal Processing Equipment: Pentium PC with NI PCI-MIO-16E-4 data-acquisition board NI BNC 2120 Accessory Box VirtualBench Instrument Library version 2.6 Function Generator (Tektronix
RLC Circuit with Cobra3
 RLC Circuit with Cobra3 LEP Related topics Tuned circuit, series-tuned circuit, parallel-tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, capacitor, coil, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width,impedance,
RLC Circuit with Cobra3 LEP Related topics Tuned circuit, series-tuned circuit, parallel-tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, capacitor, coil, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width,impedance,
Pre-Lab. Introduction
 Pre-Lab Read through this entire lab. Perform all of your calculations (calculated values) prior to making the required circuit measurements. You may need to measure circuit component values to obtain
Pre-Lab Read through this entire lab. Perform all of your calculations (calculated values) prior to making the required circuit measurements. You may need to measure circuit component values to obtain
Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance
 E5.1 Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance Note: It is strongly recommended that you complete lab E4: Capacitors and the RC Circuit before performing this experiment. Introduction Ohm s law, a well known
E5.1 Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance Note: It is strongly recommended that you complete lab E4: Capacitors and the RC Circuit before performing this experiment. Introduction Ohm s law, a well known
Inductance of solenoids
 Inductance of solenoids TEP Related Topics Law of inductance, Lenz s law, self-inductance, solenoids, transformer, coupled oscillatory circuit, resonance, damped oscillation, logarithmic decrement Principle
Inductance of solenoids TEP Related Topics Law of inductance, Lenz s law, self-inductance, solenoids, transformer, coupled oscillatory circuit, resonance, damped oscillation, logarithmic decrement Principle
Demonstration of Chaos
 revised 4/27/01 Demonstration of Chaos Advanced Laboratory, Physics 407 University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin 53706 Abstract A simple resonant inductor-resistor-diode series circuit can be used to
revised 4/27/01 Demonstration of Chaos Advanced Laboratory, Physics 407 University of Wisconsin Madison, Wisconsin 53706 Abstract A simple resonant inductor-resistor-diode series circuit can be used to
Magnetic induction with Cobra3
 Principle A magnetic field of variable frequency and varying strength is produced in a long coil. The voltages induced across thin coils which are pushed into the long coil are determined as a function
Principle A magnetic field of variable frequency and varying strength is produced in a long coil. The voltages induced across thin coils which are pushed into the long coil are determined as a function
EE3079 Experiment: Chaos in nonlinear systems
 EE3079 Experiment: Chaos in nonlinear systems Background: November 2, 2016 Revision The theory of nonlinear dynamical systems and Chaos is an intriguing area of mathematics that has received considerable
EE3079 Experiment: Chaos in nonlinear systems Background: November 2, 2016 Revision The theory of nonlinear dynamical systems and Chaos is an intriguing area of mathematics that has received considerable
Sampling and Reconstruction
 Experiment 10 Sampling and Reconstruction In this experiment we shall learn how an analog signal can be sampled in the time domain and then how the same samples can be used to reconstruct the original
Experiment 10 Sampling and Reconstruction In this experiment we shall learn how an analog signal can be sampled in the time domain and then how the same samples can be used to reconstruct the original
Chaotic Circuits and Encryption
 Chaotic Circuits and Encryption Brad Aimone Stephen Larson June 16, 2006 Neurophysics Lab Introduction Chaotic dynamics are a behavior exhibited by some nonlinear dynamical systems. Despite an appearance
Chaotic Circuits and Encryption Brad Aimone Stephen Larson June 16, 2006 Neurophysics Lab Introduction Chaotic dynamics are a behavior exhibited by some nonlinear dynamical systems. Despite an appearance
Experiment 2: Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits
 Experiment 2: Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits Will Chemelewski Partner: Brian Enders TA: Nielsen See laboratory book #1 pages 5-7, data taken September 1, 2009 September 7, 2009 Abstract Transient
Experiment 2: Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits Will Chemelewski Partner: Brian Enders TA: Nielsen See laboratory book #1 pages 5-7, data taken September 1, 2009 September 7, 2009 Abstract Transient
Experiment No. 2 Pre-Lab Signal Mixing and Amplitude Modulation
 Experiment No. 2 Pre-Lab Signal Mixing and Amplitude Modulation Read the information presented in this pre-lab and answer the questions given. Submit the answers to your lab instructor before the experimental
Experiment No. 2 Pre-Lab Signal Mixing and Amplitude Modulation Read the information presented in this pre-lab and answer the questions given. Submit the answers to your lab instructor before the experimental
Digital Function Generator
 Digital Function Generator 13654-99 PHYWE Systeme GmbH & Co. KG Robert-Bosch-Breite 10 37079 Göttingen Germany Tel. +49 (0) 551 604-0 Fax +49 (0) 551 604-107 E-mail info@phywe.de Operating Instructions
Digital Function Generator 13654-99 PHYWE Systeme GmbH & Co. KG Robert-Bosch-Breite 10 37079 Göttingen Germany Tel. +49 (0) 551 604-0 Fax +49 (0) 551 604-107 E-mail info@phywe.de Operating Instructions
DC and AC Circuits. Objective. Theory. 1. Direct Current (DC) R-C Circuit
 [International Campus Lab] Objective Determine the behavior of resistors, capacitors, and inductors in DC and AC circuits. Theory ----------------------------- Reference -------------------------- Young
[International Campus Lab] Objective Determine the behavior of resistors, capacitors, and inductors in DC and AC circuits. Theory ----------------------------- Reference -------------------------- Young
Nonlinear Damping of the LC Circuit using Anti-parallel Diodes. Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of North Carolina at Greensboro,
 Nonlinear Damping of the LC Circuit using Anti-parallel Diodes Edward H. Hellen a) and Matthew J. Lanctot b) Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of North Carolina at Greensboro, Greensboro,
Nonlinear Damping of the LC Circuit using Anti-parallel Diodes Edward H. Hellen a) and Matthew J. Lanctot b) Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of North Carolina at Greensboro, Greensboro,
Magnetic field inside a conductor
 Magnetic field inside a conductor TEP Principle A current is passed through an electrolyte producing a magnetic field. This magnetic field inside the conductor is measured as function of position and current
Magnetic field inside a conductor TEP Principle A current is passed through an electrolyte producing a magnetic field. This magnetic field inside the conductor is measured as function of position and current
Light-emitting diodes (Item No.: P )
 Teacher's/Lecturer's Sheet Printed: 30.03.207 7:0:20 P37800 Light-emitting diodes (Item No.: P37800) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physik Education Level: Klasse 0-3 Topic: Elektrizitätslehre
Teacher's/Lecturer's Sheet Printed: 30.03.207 7:0:20 P37800 Light-emitting diodes (Item No.: P37800) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physik Education Level: Klasse 0-3 Topic: Elektrizitätslehre
Spectrum Analysis - Elektronikpraktikum
 Spectrum Analysis Introduction Why measure a spectra? In electrical engineering we are most often interested how a signal develops over time. For this time-domain measurement we use the Oscilloscope. Like
Spectrum Analysis Introduction Why measure a spectra? In electrical engineering we are most often interested how a signal develops over time. For this time-domain measurement we use the Oscilloscope. Like
Integrators, differentiators, and simple filters
 BEE 233 Laboratory-4 Integrators, differentiators, and simple filters 1. Objectives Analyze and measure characteristics of circuits built with opamps. Design and test circuits with opamps. Plot gain vs.
BEE 233 Laboratory-4 Integrators, differentiators, and simple filters 1. Objectives Analyze and measure characteristics of circuits built with opamps. Design and test circuits with opamps. Plot gain vs.
The oscilloscope and RC filters
 (ta initials) first name (print) last name (print) brock id (ab17cd) (lab date) Experiment 4 The oscilloscope and C filters The objective of this experiment is to familiarize the student with the workstation
(ta initials) first name (print) last name (print) brock id (ab17cd) (lab date) Experiment 4 The oscilloscope and C filters The objective of this experiment is to familiarize the student with the workstation
ECE 6416 Low-Noise Electronics Orientation Experiment
 ECE 6416 Low-Noise Electronics Orientation Experiment Object The object of this experiment is to become familiar with the instruments used in the low noise laboratory. Parts The following parts are required
ECE 6416 Low-Noise Electronics Orientation Experiment Object The object of this experiment is to become familiar with the instruments used in the low noise laboratory. Parts The following parts are required
P a g e 1 ST985. TDR Cable Analyzer Instruction Manual. Analog Arts Inc.
 P a g e 1 ST985 TDR Cable Analyzer Instruction Manual Analog Arts Inc. www.analogarts.com P a g e 2 Contents Software Installation... 4 Specifications... 4 Handling Precautions... 4 Operation Instruction...
P a g e 1 ST985 TDR Cable Analyzer Instruction Manual Analog Arts Inc. www.analogarts.com P a g e 2 Contents Software Installation... 4 Specifications... 4 Handling Precautions... 4 Operation Instruction...
C-7: Nonlinear Oscillator
 C-7: Nonlinear Oscillator The purpose of this experiment is to discover the properties of a nonlinear circuit which closely approximates a driven pendulum. The references are: 1) "Chaotic States and Routes
C-7: Nonlinear Oscillator The purpose of this experiment is to discover the properties of a nonlinear circuit which closely approximates a driven pendulum. The references are: 1) "Chaotic States and Routes
Chaos and Analog Signal Encryption
 Course: PHY42 Instructor: Dr. Ken Kiers Date: 0/2/202 Chaos and Analog Signal Encryption Talbot Knighton Abstract This paper looks at a method for using chaotic circuits to encrypt analog signals. Two
Course: PHY42 Instructor: Dr. Ken Kiers Date: 0/2/202 Chaos and Analog Signal Encryption Talbot Knighton Abstract This paper looks at a method for using chaotic circuits to encrypt analog signals. Two
USER. manual. Falco Systems WMA-100. High Voltage Amplifier DC - 500kHz
 USER manual Falco Systems WMA-100 High Voltage Amplifier DC - 500kHz Falco Systems WMA-100, High Voltage Amplifier DC - 500kHz High voltage: 20x amplification up to +175V and -175V output voltage with
USER manual Falco Systems WMA-100 High Voltage Amplifier DC - 500kHz Falco Systems WMA-100, High Voltage Amplifier DC - 500kHz High voltage: 20x amplification up to +175V and -175V output voltage with
DELTA MODULATION. PREPARATION principle of operation slope overload and granularity...124
 DELTA MODULATION PREPARATION...122 principle of operation...122 block diagram...122 step size calculation...124 slope overload and granularity...124 slope overload...124 granular noise...125 noise and
DELTA MODULATION PREPARATION...122 principle of operation...122 block diagram...122 step size calculation...124 slope overload and granularity...124 slope overload...124 granular noise...125 noise and
ADC and DAC converters. Laboratory Instruction
 ADC and DAC converters Laboratory Instruction Prepared by: Łukasz Buczek 05.2015 Rev. 2018 1. Aim of exercise The aim of exercise is to learn the basics of the analog-to-digital (ADC) and digital-to-analog
ADC and DAC converters Laboratory Instruction Prepared by: Łukasz Buczek 05.2015 Rev. 2018 1. Aim of exercise The aim of exercise is to learn the basics of the analog-to-digital (ADC) and digital-to-analog
Experiment Five: The Noisy Channel Model
 Experiment Five: The Noisy Channel Model Modified from original TIMS Manual experiment by Mr. Faisel Tubbal. Objectives 1) Study and understand the use of marco CHANNEL MODEL module to generate and add
Experiment Five: The Noisy Channel Model Modified from original TIMS Manual experiment by Mr. Faisel Tubbal. Objectives 1) Study and understand the use of marco CHANNEL MODEL module to generate and add
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF IMPULSIVE SYNCHRONIZATION OF CHAOTIC AND HYPERCHAOTIC CIRCUITS
 International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, Vol. 9, No. 7 (1999) 1393 1424 c World Scientific Publishing Company EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF IMPULSIVE SYNCHRONIZATION OF CHAOTIC AND HYPERCHAOTIC CIRCUITS
International Journal of Bifurcation and Chaos, Vol. 9, No. 7 (1999) 1393 1424 c World Scientific Publishing Company EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF IMPULSIVE SYNCHRONIZATION OF CHAOTIC AND HYPERCHAOTIC CIRCUITS
Definitions. Spectrum Analyzer
 SIGNAL ANALYZERS Spectrum Analyzer Definitions A spectrum analyzer measures the magnitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument. The primary use is to measure
SIGNAL ANALYZERS Spectrum Analyzer Definitions A spectrum analyzer measures the magnitude of an input signal versus frequency within the full frequency range of the instrument. The primary use is to measure
ModBox - Spectral Broadening Unit
 ModBox - Spectral Broadening Unit The ModBox Family The ModBox systems are a family of turnkey optical transmitters and external modulation benchtop units for digital and analog transmission, pulsed and
ModBox - Spectral Broadening Unit The ModBox Family The ModBox systems are a family of turnkey optical transmitters and external modulation benchtop units for digital and analog transmission, pulsed and
Physics 310 Lab 2 Circuit Transients and Oscilloscopes
 Physics 310 Lab 2 Circuit Transients and Oscilloscopes Equipment: function generator, oscilloscope, two BNC cables, BNC T connector, BNC banana adapter, breadboards, wire packs, some banana cables, three
Physics 310 Lab 2 Circuit Transients and Oscilloscopes Equipment: function generator, oscilloscope, two BNC cables, BNC T connector, BNC banana adapter, breadboards, wire packs, some banana cables, three
Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks
 OPTI 380B Intermediate Optics Laboratory Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks Objectives: Lean how to use: Function of an oscilloscope probe. Characterization of capacitors and inductors
OPTI 380B Intermediate Optics Laboratory Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks Objectives: Lean how to use: Function of an oscilloscope probe. Characterization of capacitors and inductors
UCE-DSO210 DIGITAL OSCILLOSCOPE USER MANUAL. FATIH GENÇ UCORE ELECTRONICS REV1
 UCE-DSO210 DIGITAL OSCILLOSCOPE USER MANUAL FATIH GENÇ UCORE ELECTRONICS www.ucore-electronics.com 2017 - REV1 Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Turn on or turn off... 3 3. Oscilloscope Mode... 3 3.1. Display
UCE-DSO210 DIGITAL OSCILLOSCOPE USER MANUAL FATIH GENÇ UCORE ELECTRONICS www.ucore-electronics.com 2017 - REV1 Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Turn on or turn off... 3 3. Oscilloscope Mode... 3 3.1. Display
Wireless Communication
 Equipment and Instruments Wireless Communication An oscilloscope, a signal generator, an LCR-meter, electronic components (see the table below), a container for components, and a Scotch tape. Component
Equipment and Instruments Wireless Communication An oscilloscope, a signal generator, an LCR-meter, electronic components (see the table below), a container for components, and a Scotch tape. Component
Surge Generator for MIL-STD 1275
 Surge Generator for MIL-STD 1275 This generator PG1275 is specially designed for the test of the susceptibility to surges and spikes of military 28 Vdc electric circuits. The equipment allows performing
Surge Generator for MIL-STD 1275 This generator PG1275 is specially designed for the test of the susceptibility to surges and spikes of military 28 Vdc electric circuits. The equipment allows performing
EE 330 Laboratory 8 Discrete Semiconductor Amplifiers
 EE 330 Laboratory 8 Discrete Semiconductor Amplifiers Fall 2018 Contents Objective:...2 Discussion:...2 Components Needed:...2 Part 1 Voltage Controlled Amplifier...2 Part 2 A Nonlinear Application...3
EE 330 Laboratory 8 Discrete Semiconductor Amplifiers Fall 2018 Contents Objective:...2 Discussion:...2 Components Needed:...2 Part 1 Voltage Controlled Amplifier...2 Part 2 A Nonlinear Application...3
LABORATORY 3 v3 CIRCUIT ELEMENTS
 University of California Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 100, Professor Leon Chua LABORATORY 3 v3 CIRCUIT ELEMENTS The purpose of this laboratory is to familiarize
University of California Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 100, Professor Leon Chua LABORATORY 3 v3 CIRCUIT ELEMENTS The purpose of this laboratory is to familiarize
NON-AMPLIFIED PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE
 NON-AMPLIFIED PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE Thank you for purchasing your Non-amplified Photodetector. This user s guide will help answer any questions you may have regarding the safe use and optimal operation
NON-AMPLIFIED PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE Thank you for purchasing your Non-amplified Photodetector. This user s guide will help answer any questions you may have regarding the safe use and optimal operation
Analogue Demo Multimeter ADM
 Analogue Demo Multimeter ADM 2 3820-0 PHYWE Systeme GmbH & Co. KG Robert-Bosch-Breite 0 D-37079 Göttingen Telefon +49 (0) 55 604-0 Fax +49 (0) 55 604-07 E-mail info@phywe.de Operating instructions The
Analogue Demo Multimeter ADM 2 3820-0 PHYWE Systeme GmbH & Co. KG Robert-Bosch-Breite 0 D-37079 Göttingen Telefon +49 (0) 55 604-0 Fax +49 (0) 55 604-07 E-mail info@phywe.de Operating instructions The
3D Intermodulation Distortion Measurement AN 8
 3D Intermodulation Distortion Measurement AN 8 Application Note to the R&D SYSTEM The modulation of a high frequency tone f (voice tone and a low frequency tone f (bass tone is measured by using the 3D
3D Intermodulation Distortion Measurement AN 8 Application Note to the R&D SYSTEM The modulation of a high frequency tone f (voice tone and a low frequency tone f (bass tone is measured by using the 3D
PCS-150 / PCI-200 High Speed Boxcar Modules
 Becker & Hickl GmbH Kolonnenstr. 29 10829 Berlin Tel. 030 / 787 56 32 Fax. 030 / 787 57 34 email: info@becker-hickl.de http://www.becker-hickl.de PCSAPP.DOC PCS-150 / PCI-200 High Speed Boxcar Modules
Becker & Hickl GmbH Kolonnenstr. 29 10829 Berlin Tel. 030 / 787 56 32 Fax. 030 / 787 57 34 email: info@becker-hickl.de http://www.becker-hickl.de PCSAPP.DOC PCS-150 / PCI-200 High Speed Boxcar Modules
Optical Modulation and Frequency of Operation
 Optical Modulation and Frequency of Operation Developers AB Overby Objectives Preparation Background The objectives of this experiment are to describe and illustrate the differences between frequency of
Optical Modulation and Frequency of Operation Developers AB Overby Objectives Preparation Background The objectives of this experiment are to describe and illustrate the differences between frequency of
Experiment 7: Frequency Modulation and Phase Locked Loops
 Experiment 7: Frequency Modulation and Phase Locked Loops Frequency Modulation Background Normally, we consider a voltage wave form with a fixed frequency of the form v(t) = V sin( ct + ), (1) where c
Experiment 7: Frequency Modulation and Phase Locked Loops Frequency Modulation Background Normally, we consider a voltage wave form with a fixed frequency of the form v(t) = V sin( ct + ), (1) where c
The Oscilloscope. Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. J. Swift ( ) OBJECTIVE To learn to operate a digital oscilloscope.
 The Oscilloscope Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. J. Swift (1667-1745) OBJECTIVE To learn to operate a digital oscilloscope. THEORY The oscilloscope, or scope for short, is a device for drawing
The Oscilloscope Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. J. Swift (1667-1745) OBJECTIVE To learn to operate a digital oscilloscope. THEORY The oscilloscope, or scope for short, is a device for drawing
Standing waves in the microwave range
 Related topics Microwaves, electromagnetic waves, reflection, inverse square law Principle If electromagnetic waves are reflected to and fro between two reflectors, a standing wave results. The wavelength
Related topics Microwaves, electromagnetic waves, reflection, inverse square law Principle If electromagnetic waves are reflected to and fro between two reflectors, a standing wave results. The wavelength
SECOND HARMONIC GENERATION AND Q-SWITCHING
 SECOND HARMONIC GENERATION AND Q-SWITCHING INTRODUCTION In this experiment, the following learning subjects will be worked out: 1) Characteristics of a semiconductor diode laser. 2) Optical pumping on
SECOND HARMONIC GENERATION AND Q-SWITCHING INTRODUCTION In this experiment, the following learning subjects will be worked out: 1) Characteristics of a semiconductor diode laser. 2) Optical pumping on
UCE-DSO212 DIGITAL OSCILLOSCOPE USER MANUAL. UCORE ELECTRONICS
 UCE-DSO212 DIGITAL OSCILLOSCOPE USER MANUAL UCORE ELECTRONICS www.ucore-electronics.com 2017 Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Turn on or turn off... 3 3. Oscilloscope Mode... 4 3.1. Display Description...
UCE-DSO212 DIGITAL OSCILLOSCOPE USER MANUAL UCORE ELECTRONICS www.ucore-electronics.com 2017 Contents 1. Introduction... 2 2. Turn on or turn off... 3 3. Oscilloscope Mode... 4 3.1. Display Description...
Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3)
 Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive
Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive
Laboratory Exercise 6 THE OSCILLOSCOPE
 Introduction Laboratory Exercise 6 THE OSCILLOSCOPE The aim of this exercise is to introduce you to the oscilloscope (often just called a scope), the most versatile and ubiquitous laboratory measuring
Introduction Laboratory Exercise 6 THE OSCILLOSCOPE The aim of this exercise is to introduce you to the oscilloscope (often just called a scope), the most versatile and ubiquitous laboratory measuring
Diode Applications Half-Wave Rectifying
 Lab 5 Diode Applications Half-Wave ectifying Objectives: Study the half-wave rectifying and smoothing with a capacitor for a simple diode circuit. Study the use of a Zener diode in a circuit with an AC
Lab 5 Diode Applications Half-Wave ectifying Objectives: Study the half-wave rectifying and smoothing with a capacitor for a simple diode circuit. Study the use of a Zener diode in a circuit with an AC
EE 330 Laboratory 8 Discrete Semiconductor Amplifiers
 EE 330 Laboratory 8 Discrete Semiconductor Amplifiers Fall 2017 Contents Objective:... 2 Discussion:... 2 Components Needed:... 2 Part 1 Voltage Controlled Amplifier... 2 Part 2 Common Source Amplifier...
EE 330 Laboratory 8 Discrete Semiconductor Amplifiers Fall 2017 Contents Objective:... 2 Discussion:... 2 Components Needed:... 2 Part 1 Voltage Controlled Amplifier... 2 Part 2 Common Source Amplifier...
3D Distortion Measurement (DIS)
 3D Distortion Measurement (DIS) Module of the R&D SYSTEM S4 FEATURES Voltage and frequency sweep Steady-state measurement Single-tone or two-tone excitation signal DC-component, magnitude and phase of
3D Distortion Measurement (DIS) Module of the R&D SYSTEM S4 FEATURES Voltage and frequency sweep Steady-state measurement Single-tone or two-tone excitation signal DC-component, magnitude and phase of
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS AND SYSTEM DESCRIPTION FOR THE. ISO-STIM 01D STIMULUS ISOLATION UNIT ±100 V / ±10 ma, bipolar output
 OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS AND SYSTEM DESCRIPTION FOR THE ISO-STIM 01D STIMULUS ISOLATION UNIT ±100 V / ±10 ma, bipolar output VERSION 4.0 npi 2014 npi electronic GmbH, Bauhofring 16, D-71732 Tamm, Germany
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS AND SYSTEM DESCRIPTION FOR THE ISO-STIM 01D STIMULUS ISOLATION UNIT ±100 V / ±10 ma, bipolar output VERSION 4.0 npi 2014 npi electronic GmbH, Bauhofring 16, D-71732 Tamm, Germany
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Bifurcation-based acoustic switching and rectification N. Boechler, G. Theocharis, and C. Daraio Engineering and Applied Science, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125, USA Supplementary
Bifurcation-based acoustic switching and rectification N. Boechler, G. Theocharis, and C. Daraio Engineering and Applied Science, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125, USA Supplementary
User s Manual ISL71218MEVAL1Z. User s Manual: Evaluation Board. High Reliability Space
 User s Manual ISL71218MEVAL1Z User s Manual: Evaluation Board High Reliability Space Rev. Aug 217 USER S MANUAL ISL71218MEVAL1Z Evaluation Board UG139 Rev.. 1. Overview The ISL71218MEVAL1Z evaluation platform
User s Manual ISL71218MEVAL1Z User s Manual: Evaluation Board High Reliability Space Rev. Aug 217 USER S MANUAL ISL71218MEVAL1Z Evaluation Board UG139 Rev.. 1. Overview The ISL71218MEVAL1Z evaluation platform
10: AMPLIFIERS. Circuit Connections in the Laboratory. Op-Amp. I. Introduction
 10: AMPLIFIERS Circuit Connections in the Laboratory From now on you will construct electrical circuits and test them. The usual way of constructing circuits would be to solder each electrical connection
10: AMPLIFIERS Circuit Connections in the Laboratory From now on you will construct electrical circuits and test them. The usual way of constructing circuits would be to solder each electrical connection
EE 368 Electronics Lab. Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2)
 EE 368 Electronics Lab Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) 1 Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) Objectives To gain experience with Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp). To
EE 368 Electronics Lab Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) 1 Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) Objectives To gain experience with Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp). To
Energy Transfer and Message Filtering in Chaos Communications Using Injection locked Laser Diodes
 181 Energy Transfer and Message Filtering in Chaos Communications Using Injection locked Laser Diodes Atsushi Murakami* and K. Alan Shore School of Informatics, University of Wales, Bangor, Dean Street,
181 Energy Transfer and Message Filtering in Chaos Communications Using Injection locked Laser Diodes Atsushi Murakami* and K. Alan Shore School of Informatics, University of Wales, Bangor, Dean Street,
Physics 309 Lab 3 Bipolar junction transistor
 Physics 39 Lab 3 Bipolar junction transistor The purpose of this third lab is to learn the principles of operation of a bipolar junction transistor, how to characterize its performances, and how to use
Physics 39 Lab 3 Bipolar junction transistor The purpose of this third lab is to learn the principles of operation of a bipolar junction transistor, how to characterize its performances, and how to use
GFT1504 4/8/10 channel Delay Generator
 Features 4 independent Delay Channels (10 in option) 100 ps resolution (1ps in option) 25 ps RMS jitter (channel to channel) 10 second range Channel Output pulse 6 V/50 Ω, 3 ns rise time Independent control
Features 4 independent Delay Channels (10 in option) 100 ps resolution (1ps in option) 25 ps RMS jitter (channel to channel) 10 second range Channel Output pulse 6 V/50 Ω, 3 ns rise time Independent control
Class Room Experiments on Laser Physics. Alika Khare
 Ref ETOP : ETOP004 Class Room Experiments on Laser Physics Alika Khare Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati, Guwahati, 781039, India email: alika@iitg.ernet.in Abstract Lasers
Ref ETOP : ETOP004 Class Room Experiments on Laser Physics Alika Khare Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati, Guwahati, 781039, India email: alika@iitg.ernet.in Abstract Lasers
GFT Channel Digital Delay Generator
 Features 20 independent delay Channels 100 ps resolution 25 ps rms jitter 10 second range Output pulse up to 6 V/50 Ω Independent trigger for every channel Four triggers Three are repetitive from three
Features 20 independent delay Channels 100 ps resolution 25 ps rms jitter 10 second range Output pulse up to 6 V/50 Ω Independent trigger for every channel Four triggers Three are repetitive from three
Student Experiments ELECTRONICS. Manual P9160-4F.
 Student Experiments Manual ELECTRONICS P9160-4F www.ntl.at INDEX 1. SEMICONDUCTORS EOS 1.1 PTC-resistor EOS 1.2 NTC-resistor EOS 1.3 Light dependent resistor (LDR) EOS 1.4 Measuring the luminous intensity
Student Experiments Manual ELECTRONICS P9160-4F www.ntl.at INDEX 1. SEMICONDUCTORS EOS 1.1 PTC-resistor EOS 1.2 NTC-resistor EOS 1.3 Light dependent resistor (LDR) EOS 1.4 Measuring the luminous intensity
Using Circuits, Signals and Instruments
 Using Circuits, Signals and Instruments To be ignorant of one s ignorance is the malady of the ignorant. A. B. Alcott (1799-1888) Some knowledge of electrical and electronic technology is essential for
Using Circuits, Signals and Instruments To be ignorant of one s ignorance is the malady of the ignorant. A. B. Alcott (1799-1888) Some knowledge of electrical and electronic technology is essential for
Systematical measurement errors
 Systematical measurement errors Along the lines of the rule formulated by Schrödinger that a system can influenced even by observing, an EUT can be influenced by a normal measurements. If the measurement
Systematical measurement errors Along the lines of the rule formulated by Schrödinger that a system can influenced even by observing, an EUT can be influenced by a normal measurements. If the measurement
Description of options, upgrades and accessories for the laser beam stabilization system Compact
 Description of options, upgrades and accessories for the laser beam stabilization system Compact The basic configuration of the Compact laser beam stabilization system is fully equipped for stabilization
Description of options, upgrades and accessories for the laser beam stabilization system Compact The basic configuration of the Compact laser beam stabilization system is fully equipped for stabilization
UNIT-3. Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation
 UNIT-3 1. Draw the Block Schematic of AF Wave analyzer and explain its principle and Working? ANS: The wave analyzer consists of a very narrow pass-band filter section which can Be tuned to a particular
UNIT-3 1. Draw the Block Schematic of AF Wave analyzer and explain its principle and Working? ANS: The wave analyzer consists of a very narrow pass-band filter section which can Be tuned to a particular
NON-AMPLIFIED HIGH SPEED PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE
 NON-AMPLIFIED HIGH SPEED PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE Thank you for purchasing your Non-amplified High Speed Photodetector. This user s guide will help answer any questions you may have regarding the safe
NON-AMPLIFIED HIGH SPEED PHOTODETECTOR USER S GUIDE Thank you for purchasing your Non-amplified High Speed Photodetector. This user s guide will help answer any questions you may have regarding the safe
ECE 4670 Spring 2014 Lab 1 Linear System Characteristics
 ECE 4670 Spring 2014 Lab 1 Linear System Characteristics 1 Linear System Characteristics The first part of this experiment will serve as an introduction to the use of the spectrum analyzer in making absolute
ECE 4670 Spring 2014 Lab 1 Linear System Characteristics 1 Linear System Characteristics The first part of this experiment will serve as an introduction to the use of the spectrum analyzer in making absolute
Timing Noise Measurement of High-Repetition-Rate Optical Pulses
 564 Timing Noise Measurement of High-Repetition-Rate Optical Pulses Hidemi Tsuchida National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology 1-1-1 Umezono, Tsukuba, 305-8568 JAPAN Tel: 81-29-861-5342;
564 Timing Noise Measurement of High-Repetition-Rate Optical Pulses Hidemi Tsuchida National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology 1-1-1 Umezono, Tsukuba, 305-8568 JAPAN Tel: 81-29-861-5342;
ArbStudio Arbitrary Waveform Generators
 ArbStudio Arbitrary Waveform Generators Key Features Outstanding performance with 16-bit, 1 GS/s sample rate and 2 Mpts/Ch 2 and 4 channel models Digital pattern generator PWM mode Sweep and burst modes
ArbStudio Arbitrary Waveform Generators Key Features Outstanding performance with 16-bit, 1 GS/s sample rate and 2 Mpts/Ch 2 and 4 channel models Digital pattern generator PWM mode Sweep and burst modes
Group: Names: (1) In this step you will examine the effects of AC coupling of an oscilloscope.
 3.5 Laboratory Procedure / Summary Sheet Group: Names: (1) In this step you will examine the effects of AC coupling of an oscilloscope. Set the function generator to produce a 5 V pp 1kHz sinusoidal output.
3.5 Laboratory Procedure / Summary Sheet Group: Names: (1) In this step you will examine the effects of AC coupling of an oscilloscope. Set the function generator to produce a 5 V pp 1kHz sinusoidal output.
Chapter 5: Diodes. I. Theory. Chapter 5: Diodes
 Chapter 5: Diodes This week we will explore another new passive circuit element, the diode. We will also explore some diode applications including conversion of an AC signal into a signal that never changes
Chapter 5: Diodes This week we will explore another new passive circuit element, the diode. We will also explore some diode applications including conversion of an AC signal into a signal that never changes
OPVibr Ultrasonic vibration measurement system Ultrasonic vibrometer INSTRUCTION MANUAL
 Przedsiębiorstwo Badawczo-Produkcyjne OPTEL Sp. z o.o. ul. Morelowskiego 30 PL-52-429 Wrocław tel.: +48 (071) 329 68 54 fax.: +48 (071) 329 68 52 e-mail: optel@optel.pl http://www.optel.pl Wrocław, 2015.11.04
Przedsiębiorstwo Badawczo-Produkcyjne OPTEL Sp. z o.o. ul. Morelowskiego 30 PL-52-429 Wrocław tel.: +48 (071) 329 68 54 fax.: +48 (071) 329 68 52 e-mail: optel@optel.pl http://www.optel.pl Wrocław, 2015.11.04
Computer-Based Project on VLSI Design Co 3/8
 Computer-Based Project on VLSI Design Co 3/8 This pamphlet describes a laboratory activity based on a former third year EIST experiment. Its purpose is the measurement of the switching speed of some CMOS
Computer-Based Project on VLSI Design Co 3/8 This pamphlet describes a laboratory activity based on a former third year EIST experiment. Its purpose is the measurement of the switching speed of some CMOS
cosω t Y AD 532 Analog Multiplier Board EE18.xx Fig. 1 Amplitude modulation of a sine wave message signal
 University of Saskatchewan EE 9 Electrical Engineering Laboratory III Amplitude and Frequency Modulation Objectives: To observe the time domain waveforms and spectra of amplitude modulated (AM) waveforms
University of Saskatchewan EE 9 Electrical Engineering Laboratory III Amplitude and Frequency Modulation Objectives: To observe the time domain waveforms and spectra of amplitude modulated (AM) waveforms
Precalculations Individual Portion Introductory Lab: Basic Operation of Common Laboratory Instruments
 Name: Date of lab: Section number: M E 345. Lab 1 Precalculations Individual Portion Introductory Lab: Basic Operation of Common Laboratory Instruments Precalculations Score (for instructor or TA use only):
Name: Date of lab: Section number: M E 345. Lab 1 Precalculations Individual Portion Introductory Lab: Basic Operation of Common Laboratory Instruments Precalculations Score (for instructor or TA use only):
1. Hand Calculations (in a manner suitable for submission) For the circuit in Fig. 1 with f = 7.2 khz and a source vin () t 1.
 Objectives The purpose of this laboratory project is to introduce to equipment, measurement techniques, and simulations commonly used in AC circuit analysis. In this laboratory session, each student will:
Objectives The purpose of this laboratory project is to introduce to equipment, measurement techniques, and simulations commonly used in AC circuit analysis. In this laboratory session, each student will:
PHYSICS 107 LAB #9: AMPLIFIERS
 Section: Monday / Tuesday (circle one) Name: Partners: PHYSICS 107 LAB #9: AMPLIFIERS Equipment: headphones, 4 BNC cables with clips at one end, 3 BNC T connectors, banana BNC (Male- Male), banana-bnc
Section: Monday / Tuesday (circle one) Name: Partners: PHYSICS 107 LAB #9: AMPLIFIERS Equipment: headphones, 4 BNC cables with clips at one end, 3 BNC T connectors, banana BNC (Male- Male), banana-bnc
System Inputs, Physical Modeling, and Time & Frequency Domains
 System Inputs, Physical Modeling, and Time & Frequency Domains There are three topics that require more discussion at this point of our study. They are: Classification of System Inputs, Physical Modeling,
System Inputs, Physical Modeling, and Time & Frequency Domains There are three topics that require more discussion at this point of our study. They are: Classification of System Inputs, Physical Modeling,
