Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3)
|
|
|
- Damon Black
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive equipment. Partial list of equipment needed: Digital oscilloscope Function generator ELVIS board Scope probes Resistors: 200 Ω and 1 kω (not critical) Capacitor: 100 nf (not critical, substitute as needed) Inductor: 3.9 mh (not critical, substitute as needed) Introduction to the Elvis board The National Instruments Elvis board is a powerful platform for circuit development. One of its many functions is measurement of complex impedance, including the pure reactance of capacitors and inductors. Acquire a capacitor with a value around 100 nf and an inductor in the range of 3 5 mh. Turn on the main Elvis board power with the switch located behind it. Turn on the 2nd power switch at upper right. Insert the desired component (capacitor or inductor) in the DMM/Impedance analyzer using pins OUT+ and OUT. Start the NI ELVISmx Instrument Launcher program on the adjacent PC (found under the National Instruments menu). Select the DMM; an I/O device should be identified (this can take several seconds). Select the appropriate circuit diagram element for capacitor or inductor and push the run button to measure the capacitance or inductance. Record both values. Resistors are measured with the V Ω and COM connections located on the far left side of the Elvis board. Frequency response and complex impedance The following measurements will explore the frequency response of an R C and L R circuit. They will show the frequency dependent behavior of a circuit element (capacitor or inductor) and the importance of phase shift on AC signals. This behavior can be conveniently modeled using complex impedance. For example, assuming a steady state periodic input such as a sinusoidal wave Vosin(wt), the impedance of a capacitor (C) in the same circuit can be written: Z C = 1/jwC, where j = 1. You will be building a voltage divider network as in the previous experiments, but one of the resistors is replaced by a capacitor or inductor. First, test your scope probes on CH 1 and CH 2 to make sure they are operating properly. Consult the previous lab instructions if needed. Setup the function generator to produce
2 a 1 Volt p p sine wave at 1 khz. Note 1: The oscilloscope amplitude may differ from the function generator setting by a factor of 2. This is because the output impedance of the function generator is set to 50 Ω. Change it to high impedance (High Z) using the Utility menu. Using the same guidelines as in the previous experiments, build the following circuit on the breadboard using the resistor and capacitor measured above (nominally R = 200 Ω and C = 0.1 µf): Vin is supplied by the function generator and Vout is the voltage across the capacitor. Measure Vin on CH 1 of the scope. You can use a scope probe connected to R; clip the reference lead to ground. The less cluttered option is to use a BNC T connector to route the function generator signal directly to the CH 1 input (i.e. scope probe not needed) and to the circuit with a BNC/EZ hook cable. Connect a scope probe to CH 2 and clip it across C to measure Vout. Measurement of the signal waveforms Measure the amplitude and phase of Vout relative to the Vin as a function of frequency. The amplitude response is simply the ratio of peak to peak voltage for the two channels. A frequency range between 1 and 30 khz should provide enough data to map out the response, depending on the choice of R and C. The absolute frequency start and end points are not critical; take enough data (8 10 points is adequate, more is better) to show the drop off in signal with increasing frequency. Increase the frequency high enough to make Vout/Vin less than 0.1. The frequency dependent voltage amplitude change at Vout is a straightforward measurement, but determining the voltage phase difference is more challenging. You are displaying two waveforms and can use the adjustable cursors to measure the time delay between key points. This time delay can be directly converted to a phase difference because the period of the waveforms is known. In addition, many modern digital scopes can measure the phase difference directly, displaying the result in degrees of phase. This can be accessed in the measurement menu. If your scope has this capability, perform both measurements and confirm they agree.
3 Note 2: When measuring phase, it is critical to keep track of what is being measured relative to what. For example, the phase difference φ = 45 o could be interpreted as φ = +315 o depending on the perspective. Just as with voltage, phase is always a relative measurement. It has a point of reference and it must be correctly accounted for in your analysis. Note 3: The R C circuit is one of the most important concepts in electronic instrumentation. An experimentalist must be constantly aware of it because there is always stray capacitance present, i.e. unintentional capacitance that can affect the integrity of a measurement. The cutoff frequency of an R C circuit is defined as f c = w c /2π = 1/2πRC. The circuit shown above is a low pass filter because the output signal is reduced as the frequency increases in the neighborhood of f c. If the resistor and capacitor are exchanged, the circuit becomes a high pass filter. If you look at the input connection of any oscilloscope, the input impedance associated with it will be labeled. A typical scope may have a 1 MΩ input resistance in parallel with 20 pf of stray (unintentional but unavoidable) capacitance. This means the scope may act as a low pass filter with a cutoff frequency of around 8 khz. The cutoff can be increased to nearly 160 MHz by using a 50 Ω BNC terminator, which will be in parallel with the internal 1 MΩ resistance. This value is chosen because it is comparable with the characteristic impedance of coaxial cable. When a 50 Ω terminator is used, however, the measured voltage levels will drop accordingly. Low pass filter with inductor The low pass filter can also be implemented with an inductor and resistor arranged as follows: Build this circuit with the second resistor having a value of around 1000 Ω and the inductor measured previously (in the range 3 5 mh) to produce a cutoff frequency near 40 khz (not critical) according to the formula f c = w c /2π = R/2πL. Perform the same set of measurements as with the R C filter, but adjust your data range to account for the higher cutoff frequency. The goal is to show the frequency response rolloff with data points
4 above and below the cutoff frequency. Get data for both amplitude and phase. Note 4: The L R circuit is rarely a concern in electronic design except at radio frequencies (rf) and higher. This is because stray inductance is usually negligible. If the inductor and resistor are exchanged, the circuit becomes a high pass filter. Analysis and writeup The voltage measured at the output of the R C circuit is given by: and for the L R circuit: To model the experimental response, you will need to put the right hand side of the above equations in the form a + jb, where a and b are the real and imaginary parts of the complex number. The frequency dependent amplitude response is then: and the phase response is: Don't forget that the function generator frequency display (Hz) is related to the angular frequency (radians/sec) by the following equation: f = ω / 2π. The lab writeup requires the following: 1) Plot Vout/Vin for the R C circuit. Because this is a complex response, you will need to plot the amplitude and phase data on separate graphs. The amplitude response is a voltage ratio and is dimensionless on the y axis. Display the phase data in degrees (not radians). The x axis of both plots should be frequency (f) in units of Hz or khz. 2) Repeat the analysis described in 1) for the R L circuit.
5 3) The four data sets generated in 1) and 2) have corresponding theoretical curves. These continuous curves are obtained with the equations described above and using your measured values for R, L, and C. Add the theory curves to the four plots from 1) and 2) (i.e. you should produce two amplitude curves and two phase curves). List the measured component values. Include your equation formulas on each plot. There is no additional writing or explanation required. Your assignment is to generate four graphs (2 amplitude graphs, 2 phase graphs with your data compared to theory) corresponding to the two circuits. The report is due before the next class. E mail your 4 graphs as a single electronic file (.pdf preferred) to the instructor.
Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5)
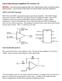 Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy
Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy
EE2210 Laboratory Project 1 Fall 2013 Function Generator and Oscilloscope
 EE2210 Laboratory Project 1 Fall 2013 Function Generator and Oscilloscope For students to become more familiar with oscilloscopes and function generators. Pre laboratory Work Read the TDS 210 Oscilloscope
EE2210 Laboratory Project 1 Fall 2013 Function Generator and Oscilloscope For students to become more familiar with oscilloscopes and function generators. Pre laboratory Work Read the TDS 210 Oscilloscope
ECE 2274 Lab 2 (Network Theorems)
 ECE 2274 Lab 2 (Network Theorems) Forward (DO NOT TURN IN) You are expected to use engineering exponents for all answers (p,n,µ,m, N/A, k, M, G) and to give each with a precision between one and three
ECE 2274 Lab 2 (Network Theorems) Forward (DO NOT TURN IN) You are expected to use engineering exponents for all answers (p,n,µ,m, N/A, k, M, G) and to give each with a precision between one and three
ECE 2274 Lab 2. Your calculator will have a setting that will automatically generate the correct format.
 ECE 2274 Lab 2 Forward (DO NOT TURN IN) You are expected to use engineering exponents for all answers (p,n,µ,m, N/A, k, M, G) and to give each with a precision between one and three leading digits and
ECE 2274 Lab 2 Forward (DO NOT TURN IN) You are expected to use engineering exponents for all answers (p,n,µ,m, N/A, k, M, G) and to give each with a precision between one and three leading digits and
PHASES IN A SERIES LRC CIRCUIT
 PHASES IN A SERIES LRC CIRCUIT Introduction: In this lab, we will use a computer interface to analyze a series circuit consisting of an inductor (L), a resistor (R), a capacitor (C), and an AC power supply.
PHASES IN A SERIES LRC CIRCUIT Introduction: In this lab, we will use a computer interface to analyze a series circuit consisting of an inductor (L), a resistor (R), a capacitor (C), and an AC power supply.
Lab 10: Oscillators (version 1.1)
 Lab 10: Oscillators (version 1.1) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive equipment.
Lab 10: Oscillators (version 1.1) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive equipment.
BME 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters
 BME 35 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of passive filters. Laboratory Equipment: Agilent Oscilloscope Model 546A Agilent Function Generator
BME 35 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of passive filters. Laboratory Equipment: Agilent Oscilloscope Model 546A Agilent Function Generator
Experiment 8: An AC Circuit
 Experiment 8: An AC Circuit PART ONE: AC Voltages. Set up this circuit. Use R = 500 Ω, L = 5.0 mh and C =.01 μf. A signal generator built into the interface provides the emf to run the circuit from Output
Experiment 8: An AC Circuit PART ONE: AC Voltages. Set up this circuit. Use R = 500 Ω, L = 5.0 mh and C =.01 μf. A signal generator built into the interface provides the emf to run the circuit from Output
Experiment 9 AC Circuits
 Experiment 9 AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits
Experiment 9 AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits
LABORATORY 4. Palomar College ENGR210 Spring 2017 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17
 LABORATORY 4 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17 OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this lab is to evaluate the transient and steady-state circuit response of first order and second order circuits. MINIMUM EQUIPMENT LIST: You will
LABORATORY 4 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17 OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this lab is to evaluate the transient and steady-state circuit response of first order and second order circuits. MINIMUM EQUIPMENT LIST: You will
AC Magnitude and Phase
 AC Magnitude and Phase Objectives: oday's experiment provides practical experience with the meaning of magnitude and phase in a linear circuits and the use of phasor algebra to predict the response of
AC Magnitude and Phase Objectives: oday's experiment provides practical experience with the meaning of magnitude and phase in a linear circuits and the use of phasor algebra to predict the response of
AC CURRENTS, VOLTAGES, FILTERS, and RESONANCE
 July 22, 2008 AC Currents, Voltages, Filters, Resonance 1 Name Date Partners AC CURRENTS, VOLTAGES, FILTERS, and RESONANCE V(volts) t(s) OBJECTIVES To understand the meanings of amplitude, frequency, phase,
July 22, 2008 AC Currents, Voltages, Filters, Resonance 1 Name Date Partners AC CURRENTS, VOLTAGES, FILTERS, and RESONANCE V(volts) t(s) OBJECTIVES To understand the meanings of amplitude, frequency, phase,
Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization (8/28/06)
 Electrical Measurement Issues Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization (8/28/06) Electrical measurements are only as meaningful as the quality of the measurement techniques and the instrumentation applied
Electrical Measurement Issues Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization (8/28/06) Electrical measurements are only as meaningful as the quality of the measurement techniques and the instrumentation applied
Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks
 OPTI 380B Intermediate Optics Laboratory Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks Objectives: Lean how to use: Function of an oscilloscope probe. Characterization of capacitors and inductors
OPTI 380B Intermediate Optics Laboratory Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks Objectives: Lean how to use: Function of an oscilloscope probe. Characterization of capacitors and inductors
Frequency Response and Filters
 Frequency Response and Filters Objectives: This experiment provides practical experiences with frequency responses of analog filters. Filters will be constructed and graphs of gain magnitude and phase
Frequency Response and Filters Objectives: This experiment provides practical experiences with frequency responses of analog filters. Filters will be constructed and graphs of gain magnitude and phase
NI ELVIS II+ Tips and Tricks
 NI ELVIS II+ Tips and Tricks For MECH 307 Laboratory Exercises Luke Walker Department of Mechanical Engineering Colorado State University 2017 Edition This is not Copyrighted material. You are free to
NI ELVIS II+ Tips and Tricks For MECH 307 Laboratory Exercises Luke Walker Department of Mechanical Engineering Colorado State University 2017 Edition This is not Copyrighted material. You are free to
EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response
 EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of active signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Active Filters, Op-Amp Filters, Bode plots Suggested
EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of active signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Active Filters, Op-Amp Filters, Bode plots Suggested
EE 210: CIRCUITS AND DEVICES
 EE 210: CIRCUITS AND DEVICES LAB #3: VOLTAGE AND CURRENT MEASUREMENTS This lab features a tutorial on the instrumentation that you will be using throughout the semester. More specifically, you will see
EE 210: CIRCUITS AND DEVICES LAB #3: VOLTAGE AND CURRENT MEASUREMENTS This lab features a tutorial on the instrumentation that you will be using throughout the semester. More specifically, you will see
LRC Circuit PHYS 296 Your name Lab section
 LRC Circuit PHYS 296 Your name Lab section PRE-LAB QUIZZES 1. What will we investigate in this lab? 2. Figure 1 on the following page shows an LRC circuit with the resistor of 1 Ω, the capacitor of 33
LRC Circuit PHYS 296 Your name Lab section PRE-LAB QUIZZES 1. What will we investigate in this lab? 2. Figure 1 on the following page shows an LRC circuit with the resistor of 1 Ω, the capacitor of 33
Lab: Operational Amplifiers
 Page 1 of 6 Laboratory Goals Familiarize students with Integrated Circuit (IC) construction on a breadboard Introduce the LM 741 Op-amp and its applications Design and construct an inverting amplifier
Page 1 of 6 Laboratory Goals Familiarize students with Integrated Circuit (IC) construction on a breadboard Introduce the LM 741 Op-amp and its applications Design and construct an inverting amplifier
Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters
 Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters Goal: In circuits with a time-varying voltage, the relationship between current and voltage is more complicated
Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters Goal: In circuits with a time-varying voltage, the relationship between current and voltage is more complicated
BME/ISE 3511 Laboratory One - Laboratory Equipment for Measurement. Introduction to biomedical electronic laboratory instrumentation and measurements.
 BME/ISE 3511 Laboratory One - Laboratory Equipment for Measurement Learning Objectives: Introduction to biomedical electronic laboratory instrumentation and measurements. Supplies and Components: Breadboard
BME/ISE 3511 Laboratory One - Laboratory Equipment for Measurement Learning Objectives: Introduction to biomedical electronic laboratory instrumentation and measurements. Supplies and Components: Breadboard
PHY203: General Physics III Lab page 1 of 5 PCC-Cascade. Lab: AC Circuits
 PHY203: General Physics III Lab page 1 of 5 Lab: AC Circuits OBJECTIVES: EQUIPMENT: Universal Breadboard (Archer 276-169) 2 Simpson Digital Multimeters (464) Function Generator (Global Specialties 2001)*
PHY203: General Physics III Lab page 1 of 5 Lab: AC Circuits OBJECTIVES: EQUIPMENT: Universal Breadboard (Archer 276-169) 2 Simpson Digital Multimeters (464) Function Generator (Global Specialties 2001)*
PHYS 3322 Modern Laboratory Methods I AC R, RC, and RL Circuits
 Purpose PHYS 3322 Modern Laboratory Methods I AC, C, and L Circuits For a given frequency, doubling of the applied voltage to resistors, capacitors, and inductors doubles the current. Hence, each of these
Purpose PHYS 3322 Modern Laboratory Methods I AC, C, and L Circuits For a given frequency, doubling of the applied voltage to resistors, capacitors, and inductors doubles the current. Hence, each of these
AC Circuits. "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert ( )
 AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits use varying
AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits use varying
Lab #5 Steady State Power Analysis
 Lab #5 Steady State Power Analysis Steady state power analysis refers to the power analysis of circuits that have one or more sinusoid stimuli. This lab covers the concepts of RMS voltage, maximum power
Lab #5 Steady State Power Analysis Steady state power analysis refers to the power analysis of circuits that have one or more sinusoid stimuli. This lab covers the concepts of RMS voltage, maximum power
ECE 201 LAB 8 TRANSFORMERS & SINUSOIDAL STEADY STATE ANALYSIS
 Version 1.1 1 of 8 ECE 201 LAB 8 TRANSFORMERS & SINUSOIDAL STEADY STATE ANALYSIS BEFORE YOU BEGIN PREREQUISITE LABS Introduction to MATLAB Introduction to Lab Equipment Introduction to Oscilloscope Capacitors,
Version 1.1 1 of 8 ECE 201 LAB 8 TRANSFORMERS & SINUSOIDAL STEADY STATE ANALYSIS BEFORE YOU BEGIN PREREQUISITE LABS Introduction to MATLAB Introduction to Lab Equipment Introduction to Oscilloscope Capacitors,
Lab 3: RC Circuits. Construct circuit 2 in EveryCircuit. Set values for the capacitor and resistor to match those in figure 2 and set the frequency to
 Lab 3: RC Circuits Prelab Deriving equations for the output voltage of the voltage dividers you constructed in lab 2 was fairly simple. Now we want to derive an equation for the output voltage of a circuit
Lab 3: RC Circuits Prelab Deriving equations for the output voltage of the voltage dividers you constructed in lab 2 was fairly simple. Now we want to derive an equation for the output voltage of a circuit
Physics 310 Lab 2 Circuit Transients and Oscilloscopes
 Physics 310 Lab 2 Circuit Transients and Oscilloscopes Equipment: function generator, oscilloscope, two BNC cables, BNC T connector, BNC banana adapter, breadboards, wire packs, some banana cables, three
Physics 310 Lab 2 Circuit Transients and Oscilloscopes Equipment: function generator, oscilloscope, two BNC cables, BNC T connector, BNC banana adapter, breadboards, wire packs, some banana cables, three
ECE 2274 Lab 1 (Intro)
 ECE 2274 Lab 1 (Intro) Richard Dumene: Spring 2018 Revised: Richard Cooper: Spring 2018 Forward (DO NOT TURN IN) The purpose of this lab course is to familiarize you with high-end lab equipment, and train
ECE 2274 Lab 1 (Intro) Richard Dumene: Spring 2018 Revised: Richard Cooper: Spring 2018 Forward (DO NOT TURN IN) The purpose of this lab course is to familiarize you with high-end lab equipment, and train
ENG 100 Lab #2 Passive First-Order Filter Circuits
 ENG 100 Lab #2 Passive First-Order Filter Circuits In Lab #2, you will construct simple 1 st -order RL and RC filter circuits and investigate their frequency responses (amplitude and phase responses).
ENG 100 Lab #2 Passive First-Order Filter Circuits In Lab #2, you will construct simple 1 st -order RL and RC filter circuits and investigate their frequency responses (amplitude and phase responses).
The Series RLC Circuit and Resonance
 Purpose Theory The Series RLC Circuit and Resonance a. To study the behavior of a series RLC circuit in an AC current. b. To measure the values of the L and C using the impedance method. c. To study the
Purpose Theory The Series RLC Circuit and Resonance a. To study the behavior of a series RLC circuit in an AC current. b. To measure the values of the L and C using the impedance method. c. To study the
PHY 132 Summer 2000 LAB 9: LRC Circuit (Phases) 1
 PHY 132 Summer 2000 LAB 9: LRC Circuit (Phases) 1 Introduction In this lab we will measure the phases (voltage vs current) for each component in a series LRC circuit. Theory L C V_in R Fig. 1 Generic series
PHY 132 Summer 2000 LAB 9: LRC Circuit (Phases) 1 Introduction In this lab we will measure the phases (voltage vs current) for each component in a series LRC circuit. Theory L C V_in R Fig. 1 Generic series
EE 2274 RC and Op Amp Circuit Completed Prior to Coming to Lab. Prelab Part I: RC Circuit
 EE 2274 RC and Op Amp Circuit Completed Prior to Coming to Lab Prelab Part I: RC Circuit 1. Design a high pass filter (Fig. 1) which has a break point f b = 1 khz at 3dB below the midband level (the -3dB
EE 2274 RC and Op Amp Circuit Completed Prior to Coming to Lab Prelab Part I: RC Circuit 1. Design a high pass filter (Fig. 1) which has a break point f b = 1 khz at 3dB below the midband level (the -3dB
Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization
 Electrical Measurement Issues Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization Electrical measurements are only as meaningful as the quality of the measurement techniques and the instrumentation applied to the
Electrical Measurement Issues Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization Electrical measurements are only as meaningful as the quality of the measurement techniques and the instrumentation applied to the
Lab 9 - INTRODUCTION TO AC CURRENTS AND VOLTAGES
 145 Name Date Partners Lab 9 INTRODUCTION TO AC CURRENTS AND VOLTAGES V(volts) t(s) OBJECTIVES To learn the meanings of peak voltage and frequency for AC signals. To observe the behavior of resistors in
145 Name Date Partners Lab 9 INTRODUCTION TO AC CURRENTS AND VOLTAGES V(volts) t(s) OBJECTIVES To learn the meanings of peak voltage and frequency for AC signals. To observe the behavior of resistors in
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering. ESE 206: Electrical Circuits and Systems II - Lab
 University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE 206: Electrical Circuits and Systems II - Lab AC POWER ANALYSIS AND DESIGN I. Purpose and Equipment: Provide experimental
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE 206: Electrical Circuits and Systems II - Lab AC POWER ANALYSIS AND DESIGN I. Purpose and Equipment: Provide experimental
PHYSICS 221 LAB #6: CAPACITORS AND AC CIRCUITS
 Name: Partners: PHYSICS 221 LAB #6: CAPACITORS AND AC CIRCUITS The electricity produced for use in homes and industry is made by rotating coils of wire in a magnetic field, which results in alternating
Name: Partners: PHYSICS 221 LAB #6: CAPACITORS AND AC CIRCUITS The electricity produced for use in homes and industry is made by rotating coils of wire in a magnetic field, which results in alternating
ET1210: Module 5 Inductance and Resonance
 Part 1 Inductors Theory: When current flows through a coil of wire, a magnetic field is created around the wire. This electromagnetic field accompanies any moving electric charge and is proportional to
Part 1 Inductors Theory: When current flows through a coil of wire, a magnetic field is created around the wire. This electromagnetic field accompanies any moving electric charge and is proportional to
Lab Reference Manual. ECEN 326 Electronic Circuits. Texas A&M University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 Lab Reference Manual ECEN 326 Electronic Circuits Texas A&M University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Contents 1. Circuit Analysis in PSpice 3 1.1 Transient and DC Analysis 3 1.2 Measuring
Lab Reference Manual ECEN 326 Electronic Circuits Texas A&M University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Contents 1. Circuit Analysis in PSpice 3 1.1 Transient and DC Analysis 3 1.2 Measuring
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 1 FAMILIARIZATION WITH COMMONLY USED INSTRUMENTATION
 Objectives: ME 365 EXPERIMENT 1 FAMILIARIZATION WITH COMMONLY USED INSTRUMENTATION The primary goal of this laboratory is to study the operation and limitations of several commonly used pieces of instrumentation:
Objectives: ME 365 EXPERIMENT 1 FAMILIARIZATION WITH COMMONLY USED INSTRUMENTATION The primary goal of this laboratory is to study the operation and limitations of several commonly used pieces of instrumentation:
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS) II
 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS) II LAB 5 INTRO: INTRODUCTION TO INVERTING AMPLIFIERS AND OTHER OP-AMP CIRCUITS GOALS In this lab, you will characterize the gain and frequency dependence of inverting op-amp
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS) II LAB 5 INTRO: INTRODUCTION TO INVERTING AMPLIFIERS AND OTHER OP-AMP CIRCUITS GOALS In this lab, you will characterize the gain and frequency dependence of inverting op-amp
Name: First-Order Response: RC Networks Objective: To gain experience with first-order response of RC circuits
 First-Order Response: RC Networks Objective: To gain experience with first-order response of RC circuits Table of Contents: Pre-Lab Assignment 2 Background 2 National Instruments MyDAQ 2 Resistors 3 Capacitors
First-Order Response: RC Networks Objective: To gain experience with first-order response of RC circuits Table of Contents: Pre-Lab Assignment 2 Background 2 National Instruments MyDAQ 2 Resistors 3 Capacitors
Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance
 E5.1 Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance Note: It is strongly recommended that you complete lab E4: Capacitors and the RC Circuit before performing this experiment. Introduction Ohm s law, a well known
E5.1 Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance Note: It is strongly recommended that you complete lab E4: Capacitors and the RC Circuit before performing this experiment. Introduction Ohm s law, a well known
INTRODUCTION TO AC FILTERS AND RESONANCE
 AC Filters & Resonance 167 Name Date Partners INTRODUCTION TO AC FILTERS AND RESONANCE OBJECTIVES To understand the design of capacitive and inductive filters To understand resonance in circuits driven
AC Filters & Resonance 167 Name Date Partners INTRODUCTION TO AC FILTERS AND RESONANCE OBJECTIVES To understand the design of capacitive and inductive filters To understand resonance in circuits driven
DC and AC Circuits. Objective. Theory. 1. Direct Current (DC) R-C Circuit
 [International Campus Lab] Objective Determine the behavior of resistors, capacitors, and inductors in DC and AC circuits. Theory ----------------------------- Reference -------------------------- Young
[International Campus Lab] Objective Determine the behavior of resistors, capacitors, and inductors in DC and AC circuits. Theory ----------------------------- Reference -------------------------- Young
Lab Session 4 Hardware
 Lab Session 4 Hardware Objectives: Upon completion of this experiment, the student will be able to: -Verifying of Transient response, two port network and Fourier analysis circuits Equipment and Components
Lab Session 4 Hardware Objectives: Upon completion of this experiment, the student will be able to: -Verifying of Transient response, two port network and Fourier analysis circuits Equipment and Components
Experiment #2: Introduction to Lab Equipment: Function Generator, Oscilloscope, and Multisim
 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2110: CIRCUIT THEORY LABORATORY Experiment #2: Introduction to Lab Equipment: Function Generator, Oscilloscope,
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2110: CIRCUIT THEORY LABORATORY Experiment #2: Introduction to Lab Equipment: Function Generator, Oscilloscope,
ECE 2201 PRELAB 6 BJT COMMON EMITTER (CE) AMPLIFIER
 ECE 2201 PRELAB 6 BJT COMMON EMITTER (CE) AMPLIFIER Hand Analysis P1. Determine the DC bias for the BJT Common Emitter Amplifier circuit of Figure 61 (in this lab) including the voltages V B, V C and V
ECE 2201 PRELAB 6 BJT COMMON EMITTER (CE) AMPLIFIER Hand Analysis P1. Determine the DC bias for the BJT Common Emitter Amplifier circuit of Figure 61 (in this lab) including the voltages V B, V C and V
Lab 4: Analysis of the Stereo Amplifier
 ECE 212 Spring 2010 Circuit Analysis II Names: Lab 4: Analysis of the Stereo Amplifier Objectives In this lab exercise you will use the power supply to power the stereo amplifier built in the previous
ECE 212 Spring 2010 Circuit Analysis II Names: Lab 4: Analysis of the Stereo Amplifier Objectives In this lab exercise you will use the power supply to power the stereo amplifier built in the previous
NI Elvis Virtual Instrumentation And Prototyping Board
 NI Elvis Virtual Instrumentation And Prototyping Board Objectives: a) Become familiar with NI Elvis hardware ( breadboard ) and software b) Learn resistor color codes c) Learn how to use Digital Multimeter
NI Elvis Virtual Instrumentation And Prototyping Board Objectives: a) Become familiar with NI Elvis hardware ( breadboard ) and software b) Learn resistor color codes c) Learn how to use Digital Multimeter
Non-ideal Behavior of Electronic Components at High Frequencies and Associated Measurement Problems
 Nonideal Behavior of Electronic Components at High Frequencies and Associated Measurement Problems Matthew Beckler beck0778@umn.edu EE30 Lab Section 008 October 27, 2006 Abstract In the world of electronics,
Nonideal Behavior of Electronic Components at High Frequencies and Associated Measurement Problems Matthew Beckler beck0778@umn.edu EE30 Lab Section 008 October 27, 2006 Abstract In the world of electronics,
Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Technology. EET 3086C Circuit Analysis Laboratory Experiments. Masood Ejaz
 Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Technology EET 3086C Circuit Analysis Laboratory Experiments Masood Ejaz Experiment # 1 DC Measurements of a Resistive Circuit and Proof of Thevenin Theorem
Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Technology EET 3086C Circuit Analysis Laboratory Experiments Masood Ejaz Experiment # 1 DC Measurements of a Resistive Circuit and Proof of Thevenin Theorem
Electronics and Instrumentation ENGR-4300 Spring 2004 Section Experiment 5 Introduction to AC Steady State
 Experiment 5 Introduction to C Steady State Purpose: This experiment addresses combinations of resistors, capacitors and inductors driven by sinusoidal voltage sources. In addition to the usual simulation
Experiment 5 Introduction to C Steady State Purpose: This experiment addresses combinations of resistors, capacitors and inductors driven by sinusoidal voltage sources. In addition to the usual simulation
University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department. EE 204 Electrical Engineering Lab
 University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 204 Electrical Engineering Lab EXPERIMENT 1 MEASUREMENT DEVICES Prepared by: Prof. Mohammed Hawa EXPERIMENT 1 MEASUREMENT
University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 204 Electrical Engineering Lab EXPERIMENT 1 MEASUREMENT DEVICES Prepared by: Prof. Mohammed Hawa EXPERIMENT 1 MEASUREMENT
1. Hand Calculations (in a manner suitable for submission) For the circuit in Fig. 1 with f = 7.2 khz and a source vin () t 1.
 Objectives The purpose of this laboratory project is to introduce to equipment, measurement techniques, and simulations commonly used in AC circuit analysis. In this laboratory session, each student will:
Objectives The purpose of this laboratory project is to introduce to equipment, measurement techniques, and simulations commonly used in AC circuit analysis. In this laboratory session, each student will:
Lab 1: Basic RL and RC DC Circuits
 Name- Surname: ID: Department: Lab 1: Basic RL and RC DC Circuits Objective In this exercise, the DC steady state response of simple RL and RC circuits is examined. The transient behavior of RC circuits
Name- Surname: ID: Department: Lab 1: Basic RL and RC DC Circuits Objective In this exercise, the DC steady state response of simple RL and RC circuits is examined. The transient behavior of RC circuits
Laboratory Exercise 6 THE OSCILLOSCOPE
 Introduction Laboratory Exercise 6 THE OSCILLOSCOPE The aim of this exercise is to introduce you to the oscilloscope (often just called a scope), the most versatile and ubiquitous laboratory measuring
Introduction Laboratory Exercise 6 THE OSCILLOSCOPE The aim of this exercise is to introduce you to the oscilloscope (often just called a scope), the most versatile and ubiquitous laboratory measuring
LAB 8: Activity P52: LRC Circuit
 LAB 8: Activity P52: LRC Circuit Equipment: Voltage Sensor 1 Multimeter 1 Patch Cords 2 AC/DC Electronics Lab (100 μf capacitor; 10 Ω resistor; Inductor Coil; Iron core; 5 inch wire lead) The purpose of
LAB 8: Activity P52: LRC Circuit Equipment: Voltage Sensor 1 Multimeter 1 Patch Cords 2 AC/DC Electronics Lab (100 μf capacitor; 10 Ω resistor; Inductor Coil; Iron core; 5 inch wire lead) The purpose of
EE 368 Electronics Lab. Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2)
 EE 368 Electronics Lab Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) 1 Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) Objectives To gain experience with Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp). To
EE 368 Electronics Lab Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) 1 Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) Objectives To gain experience with Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp). To
SINUSOIDS February 4, ELEC-281 Network Theory II Wentworth Institute of Technology. Bradford Powers Ryan Ferguson Richard Lupa Benjamin Wolf
 SINUSOIDS February 4, 28 ELEC-281 Network Theory II Wentworth Institute of Technology Bradford Powers Ryan Ferguson Richard Lupa Benjamin Wolf Abstract: Sinusoidal waveforms are studied in three circuits:
SINUSOIDS February 4, 28 ELEC-281 Network Theory II Wentworth Institute of Technology Bradford Powers Ryan Ferguson Richard Lupa Benjamin Wolf Abstract: Sinusoidal waveforms are studied in three circuits:
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE319
 University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE39 Laboratory Experiment Parasitic Capacitance and Oscilloscope Loading This lab is designed to familiarize you with some
University of Pennsylvania Department of Electrical and Systems Engineering ESE39 Laboratory Experiment Parasitic Capacitance and Oscilloscope Loading This lab is designed to familiarize you with some
LAB 1: Familiarity with Laboratory Equipment (_/10)
 LAB 1: Familiarity with Laboratory Equipment (_/10) PURPOSE o gain familiarity with basic laboratory equipment oscilloscope, oscillator, multimeter and electronic components. EQUIPMEN (i) Oscilloscope
LAB 1: Familiarity with Laboratory Equipment (_/10) PURPOSE o gain familiarity with basic laboratory equipment oscilloscope, oscillator, multimeter and electronic components. EQUIPMEN (i) Oscilloscope
Theory: The idea of this oscillator comes from the idea of positive feedback, which is described by Figure 6.1. Figure 6.1: Positive Feedback
 Name1 Name2 12/2/10 ESE 319 Lab 6: Colpitts Oscillator Introduction: This lab introduced the concept of feedback in combination with bipolar junction transistors. The goal of this lab was to first create
Name1 Name2 12/2/10 ESE 319 Lab 6: Colpitts Oscillator Introduction: This lab introduced the concept of feedback in combination with bipolar junction transistors. The goal of this lab was to first create
ECE212H1F University of Toronto 2017 EXPERIMENT #4 FIRST AND SECOND ORDER CIRCUITS ECE212H1F
 ECE212H1F University of Toronto 2017 EXPERIMENT #4 FIRST AND SECOND ORDER CIRCUITS ECE212H1F OBJECTIVES: To study the voltage-current relationship for a capacitor. To study the step responses of a series
ECE212H1F University of Toronto 2017 EXPERIMENT #4 FIRST AND SECOND ORDER CIRCUITS ECE212H1F OBJECTIVES: To study the voltage-current relationship for a capacitor. To study the step responses of a series
Lab 13 AC Circuit Measurements
 Lab 13 AC Circuit Measurements Objectives concepts 1. what is impedance, really? 2. function generator and oscilloscope 3. RMS vs magnitude vs Peak-to-Peak voltage 4. phase between sinusoids skills 1.
Lab 13 AC Circuit Measurements Objectives concepts 1. what is impedance, really? 2. function generator and oscilloscope 3. RMS vs magnitude vs Peak-to-Peak voltage 4. phase between sinusoids skills 1.
Pre-Lab. Introduction
 Pre-Lab Read through this entire lab. Perform all of your calculations (calculated values) prior to making the required circuit measurements. You may need to measure circuit component values to obtain
Pre-Lab Read through this entire lab. Perform all of your calculations (calculated values) prior to making the required circuit measurements. You may need to measure circuit component values to obtain
EE-2302 Passive Filters and Frequency Response
 EE2302 Passive Filters and Frequency esponse Objective he student should become acquainted with simple passive filters for performing highpass, lowpass, and bandpass operations. he experimental tasks also
EE2302 Passive Filters and Frequency esponse Objective he student should become acquainted with simple passive filters for performing highpass, lowpass, and bandpass operations. he experimental tasks also
Resonance in Circuits
 Resonance in Circuits Purpose: To map out the analogy between mechanical and electronic resonant systems To discover how relative phase depends on driving frequency To gain experience setting up circuits
Resonance in Circuits Purpose: To map out the analogy between mechanical and electronic resonant systems To discover how relative phase depends on driving frequency To gain experience setting up circuits
Operational Amplifiers 2 Active Filters ReadMeFirst
 Operational Amplifiers 2 Active Filters ReadMeFirst Lab Summary In this lab you will build two active filters on a breadboard, using an op-amp, resistors, and capacitors, and take data for the magnitude
Operational Amplifiers 2 Active Filters ReadMeFirst Lab Summary In this lab you will build two active filters on a breadboard, using an op-amp, resistors, and capacitors, and take data for the magnitude
Electric Circuit Fall 2017 Lab10. LABORATORY 10 RLC Circuits. Guide. Figure 1: Voltage and current in an AC circuit.
 LABORATORY 10 RLC Circuits Guide Introduction RLC circuit When an AC signal is input to a RLC circuit, voltage across each element varies as a function of time. The voltage will oscillate with a frequency
LABORATORY 10 RLC Circuits Guide Introduction RLC circuit When an AC signal is input to a RLC circuit, voltage across each element varies as a function of time. The voltage will oscillate with a frequency
Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters
 Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters Goal: In circuits with a time-varying voltage, the relationship between current and voltage is more complicated
Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters Goal: In circuits with a time-varying voltage, the relationship between current and voltage is more complicated
University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department. EE 219 Electrical Circuits Lab
 University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 219 Electrical Circuits Lab EXPERIMENT 7 RESONANCE Prepared by: Dr. Mohammed Hawa EXPERIMENT 7 RESONANCE OBJECTIVE This experiment
University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 219 Electrical Circuits Lab EXPERIMENT 7 RESONANCE Prepared by: Dr. Mohammed Hawa EXPERIMENT 7 RESONANCE OBJECTIVE This experiment
AC Measurements with the Agilent 54622D Oscilloscope
 AC Measurements with the Agilent 54622D Oscilloscope Objectives: At the end of this experiment you will be able to do the following: 1. Correctly configure the 54622D for measurement of voltages. 2. Perform
AC Measurements with the Agilent 54622D Oscilloscope Objectives: At the end of this experiment you will be able to do the following: 1. Correctly configure the 54622D for measurement of voltages. 2. Perform
Experiment 2: Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits
 Experiment 2: Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits Will Chemelewski Partner: Brian Enders TA: Nielsen See laboratory book #1 pages 5-7, data taken September 1, 2009 September 7, 2009 Abstract Transient
Experiment 2: Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits Will Chemelewski Partner: Brian Enders TA: Nielsen See laboratory book #1 pages 5-7, data taken September 1, 2009 September 7, 2009 Abstract Transient
ECE 4670 Spring 2014 Lab 1 Linear System Characteristics
 ECE 4670 Spring 2014 Lab 1 Linear System Characteristics 1 Linear System Characteristics The first part of this experiment will serve as an introduction to the use of the spectrum analyzer in making absolute
ECE 4670 Spring 2014 Lab 1 Linear System Characteristics 1 Linear System Characteristics The first part of this experiment will serve as an introduction to the use of the spectrum analyzer in making absolute
Lab 10 - INTRODUCTION TO AC FILTERS AND RESONANCE
 159 Name Date Partners Lab 10 - INTRODUCTION TO AC FILTERS AND RESONANCE OBJECTIVES To understand the design of capacitive and inductive filters To understand resonance in circuits driven by AC signals
159 Name Date Partners Lab 10 - INTRODUCTION TO AC FILTERS AND RESONANCE OBJECTIVES To understand the design of capacitive and inductive filters To understand resonance in circuits driven by AC signals
E84 Lab 3: Transistor
 E84 Lab 3: Transistor Cherie Ho and Siyi Hu April 18, 2016 Transistor Testing 1. Take screenshots of both the input and output characteristic plots observed on the semiconductor curve tracer with the following
E84 Lab 3: Transistor Cherie Ho and Siyi Hu April 18, 2016 Transistor Testing 1. Take screenshots of both the input and output characteristic plots observed on the semiconductor curve tracer with the following
Lab Exercise # 9 Operational Amplifier Circuits
 Objectives: THEORY Lab Exercise # 9 Operational Amplifier Circuits 1. To understand how to use multiple power supplies in a circuit. 2. To understand the distinction between signals and power. 3. To understand
Objectives: THEORY Lab Exercise # 9 Operational Amplifier Circuits 1. To understand how to use multiple power supplies in a circuit. 2. To understand the distinction between signals and power. 3. To understand
RLC Frequency Response
 1. Introduction RLC Frequency Response The student will analyze the frequency response of an RLC circuit excited by a sinusoid. Amplitude and phase shift of circuit components will be analyzed at different
1. Introduction RLC Frequency Response The student will analyze the frequency response of an RLC circuit excited by a sinusoid. Amplitude and phase shift of circuit components will be analyzed at different
Integrators, differentiators, and simple filters
 BEE 233 Laboratory-4 Integrators, differentiators, and simple filters 1. Objectives Analyze and measure characteristics of circuits built with opamps. Design and test circuits with opamps. Plot gain vs.
BEE 233 Laboratory-4 Integrators, differentiators, and simple filters 1. Objectives Analyze and measure characteristics of circuits built with opamps. Design and test circuits with opamps. Plot gain vs.
UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, BERKELEY. EE40: Introduction to Microelectronic Circuits Lab 1. Introduction to Circuits and Instruments Guide
 UNERSTY OF CALFORNA, BERKELEY EE40: ntroduction to Microelectronic Circuits Lab 1 ntroduction to Circuits and nstruments Guide 1. Objectives The electronic circuit is the basis for all branches of electrical
UNERSTY OF CALFORNA, BERKELEY EE40: ntroduction to Microelectronic Circuits Lab 1 ntroduction to Circuits and nstruments Guide 1. Objectives The electronic circuit is the basis for all branches of electrical
ET 304A Laboratory Tutorial-Circuitmaker For Transient and Frequency Analysis
 ET 304A Laboratory Tutorial-Circuitmaker For Transient and Frequency Analysis All circuit simulation packages that use the Pspice engine allow users to do complex analysis that were once impossible to
ET 304A Laboratory Tutorial-Circuitmaker For Transient and Frequency Analysis All circuit simulation packages that use the Pspice engine allow users to do complex analysis that were once impossible to
The University of Jordan Mechatronics Engineering Department Electronics Lab.( ) Experiment 1: Lab Equipment Familiarization
 The University of Jordan Mechatronics Engineering Department Electronics Lab.(0908322) Experiment 1: Lab Equipment Familiarization Objectives To be familiar with the main blocks of the oscilloscope and
The University of Jordan Mechatronics Engineering Department Electronics Lab.(0908322) Experiment 1: Lab Equipment Familiarization Objectives To be familiar with the main blocks of the oscilloscope and
ECE3204 D2015 Lab 1. See suggested breadboard configuration on following page!
 ECE3204 D2015 Lab 1 The Operational Amplifier: Inverting and Non-inverting Gain Configurations Gain-Bandwidth Product Relationship Frequency Response Limitation Transfer Function Measurement DC Errors
ECE3204 D2015 Lab 1 The Operational Amplifier: Inverting and Non-inverting Gain Configurations Gain-Bandwidth Product Relationship Frequency Response Limitation Transfer Function Measurement DC Errors
EE 1210 Op Amps, Gain, and Signal Integrity Laboratory Project 6
 Objective Information The purposes of this laboratory project are for the student to observe an inverting operational amplifier circuit, to demonstrate how the resistors in an operational amplifier circuit
Objective Information The purposes of this laboratory project are for the student to observe an inverting operational amplifier circuit, to demonstrate how the resistors in an operational amplifier circuit
Study of Inductive and Capacitive Reactance and RLC Resonance
 Objective Study of Inductive and Capacitive Reactance and RLC Resonance To understand how the reactance of inductors and capacitors change with frequency, and how the two can cancel each other to leave
Objective Study of Inductive and Capacitive Reactance and RLC Resonance To understand how the reactance of inductors and capacitors change with frequency, and how the two can cancel each other to leave
Instructions for the final examination:
 School of Information, Computer and Communication Technology Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University Practice Problems for the Final Examination COURSE : ECS304 Basic Electrical
School of Information, Computer and Communication Technology Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University Practice Problems for the Final Examination COURSE : ECS304 Basic Electrical
Laboratory Project 1: AC Circuit Measurements and Simulation
 Objectives The purpose of this laboratory project is to introduce to equipment, measurement techniques, and simulations commonly used in C circuit analysis. In this laboratory session, each student will:
Objectives The purpose of this laboratory project is to introduce to equipment, measurement techniques, and simulations commonly used in C circuit analysis. In this laboratory session, each student will:
EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response
 EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of passive signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Passive filters, Frequency domain, Bode plots
EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of passive signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Passive filters, Frequency domain, Bode plots
Lab E2: B-field of a Solenoid. In the case that the B-field is uniform and perpendicular to the area, (1) reduces to
 E2.1 Lab E2: B-field of a Solenoid In this lab, we will explore the magnetic field created by a solenoid. First, we must review some basic electromagnetic theory. The magnetic flux over some area A is
E2.1 Lab E2: B-field of a Solenoid In this lab, we will explore the magnetic field created by a solenoid. First, we must review some basic electromagnetic theory. The magnetic flux over some area A is
Week 4: Experiment 24. Using Nodal or Mesh Analysis to Solve AC Circuits with an addition of Equivalent Impedance
 Week 4: Experiment 24 Using Nodal or Mesh Analysis to Solve AC Circuits with an addition of Equivalent Impedance Lab Lectures You have two weeks to complete Experiment 27: Complex Power 2/27/2012 (Pre-Lab
Week 4: Experiment 24 Using Nodal or Mesh Analysis to Solve AC Circuits with an addition of Equivalent Impedance Lab Lectures You have two weeks to complete Experiment 27: Complex Power 2/27/2012 (Pre-Lab
Sept 13 Pre-lab due Sept 12; Lab memo due Sept 19 at the START of lab time, 1:10pm
 Sept 13 Pre-lab due Sept 12; Lab memo due Sept 19 at the START of lab time, 1:10pm EGR 220: Engineering Circuit Theory Lab 1: Introduction to Laboratory Equipment Pre-lab Read through the entire lab handout
Sept 13 Pre-lab due Sept 12; Lab memo due Sept 19 at the START of lab time, 1:10pm EGR 220: Engineering Circuit Theory Lab 1: Introduction to Laboratory Equipment Pre-lab Read through the entire lab handout
Physics 364, Fall 2014, reading due your answers to by 11pm on Sunday
 Physics 364, Fall 204, reading due 202-09-07. Email your answers to ashmansk@hep.upenn.edu by pm on Sunday Course materials and schedule are at http://positron.hep.upenn.edu/p364 Assignment: (a) First
Physics 364, Fall 204, reading due 202-09-07. Email your answers to ashmansk@hep.upenn.edu by pm on Sunday Course materials and schedule are at http://positron.hep.upenn.edu/p364 Assignment: (a) First
AC Circuits INTRODUCTION DISCUSSION OF PRINCIPLES. Resistance in an AC Circuit
 AC Circuits INTRODUCTION The study of alternating current 1 (AC) in physics is very important as it has practical applications in our daily lives. As the name implies, the current and voltage change directions
AC Circuits INTRODUCTION The study of alternating current 1 (AC) in physics is very important as it has practical applications in our daily lives. As the name implies, the current and voltage change directions
Resonant Frequency of the LRC Circuit (Power Output, Voltage Sensor)
 72 Resonant Frequency of the LRC Circuit (Power Output, Voltage Sensor) Equipment List Qty Items Part Numbers 1 PASCO 750 Interface 1 Voltage Sensor CI-6503 1 AC/DC Electronics Laboratory EM-8656 2 Banana
72 Resonant Frequency of the LRC Circuit (Power Output, Voltage Sensor) Equipment List Qty Items Part Numbers 1 PASCO 750 Interface 1 Voltage Sensor CI-6503 1 AC/DC Electronics Laboratory EM-8656 2 Banana
Series and Parallel Resonance
 School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 33:4 Principles of Electrical Engineering II aboratory Experiment 1 Series and Parallel esonance 1 Introduction Objectives To introduce
School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 33:4 Principles of Electrical Engineering II aboratory Experiment 1 Series and Parallel esonance 1 Introduction Objectives To introduce
Exercise 1: Inductors
 Exercise 1: Inductors EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to describe the effect an inductor has on dc and ac circuits by using measured values. You will verify your
Exercise 1: Inductors EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to describe the effect an inductor has on dc and ac circuits by using measured values. You will verify your
1.0 Introduction to VirtualBench
 Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction to VirtualBench... 3 1. 1 VirtualBench in the Laboratory... 3 1.2 VirtualBench Specifications... 4 1.3 Introduction to VirtualBench Getting Started Guide Lab Exercises...
Table of Contents 1.0 Introduction to VirtualBench... 3 1. 1 VirtualBench in the Laboratory... 3 1.2 VirtualBench Specifications... 4 1.3 Introduction to VirtualBench Getting Started Guide Lab Exercises...
Lab 2: Capacitors. Integrator and Differentiator Circuits
 Lab 2: Capacitors Topics: Differentiator Integrator Low-Pass Filter High-Pass Filter Band-Pass Filter Integrator and Differentiator Circuits The simple RC circuits that you built in a previous section
Lab 2: Capacitors Topics: Differentiator Integrator Low-Pass Filter High-Pass Filter Band-Pass Filter Integrator and Differentiator Circuits The simple RC circuits that you built in a previous section
