ECE212H1F University of Toronto 2017 EXPERIMENT #4 FIRST AND SECOND ORDER CIRCUITS ECE212H1F
|
|
|
- Warren Kelley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ECE212H1F University of Toronto 2017 EXPERIMENT #4 FIRST AND SECOND ORDER CIRCUITS ECE212H1F OBJECTIVES: To study the voltage-current relationship for a capacitor. To study the step responses of a series RC circuit. To estimate the resistance and inductance of a coil, using time domain measurements. To study the step response of a series RLC circuit. GENERAL COMMENTS: For the use of the oscilloscope refer to instructions for experiment #3, the lab guidelines and the Laboratory Equipment Instruction Manual. Instead of a step function input for first and second order circuits, a square wave will be used. The period of the square wave has to be set to a value that is large compared to the time constant of the circuit. This is taken into account by the choice of frequencies given in the instructions. Since currents cannot be measured directly, in sections 4.1 and 4.2 the voltage across the 100Ω resistor is measured. Make sure it is connected as shown in Fig. 4 and Fig. 5, i.e. that one of its terminals is connected to ground. TABLE OF CONTENTS: Page REQUIRED READING Exp. 4-3 IINTRODUCTION (A) Circuit Elements Exp. 4-3 (B) First Order Circuits Exp. 4-3 (C) Second-Order Circuits Exp. 4-4 PRE-LAB ASSIGNMENT (A) Voltage-Current Characteristic of a Capacitor Exp. 4-7 (B) Step Response of a Series RC Circuit Exp. 4-7 (C) Parameter Estimation Exp. 4-8 (D) Step Response of a Series RLC Circuit Exp EQUIPMENT Exp Exp. 4-1
2 EXPERIMENT 4.1 Voltage-Current Characteristics of a Capacitor Exp Step Response of a Series RC Circuit Exp Parameter Estimation Exp Step Response of a Series RLC Circuit Exp Underdamped Response Exp Critically Damped and Overdamped Responses Exp REQUIRED READING: J. David Irwin and R. Mark Nelms, Basic Engineering Circuit Analysis, 11 th ed., Chapters 6 and 7. INTRODUCTION: (A) CIRCUIT ELEMENTS The basic elements of electric circuits are the linear time-invariant resistance, inductance, and capacitance, for which the following temporal relations hold: v R = Ri R, dil vl = L dt, dvc ic = C. dt For example, if an ideal capacitor were connected to a triangular voltage source, the current would be a square wave. In the case of an inductor, if the current is forced to be a triangular wave, an ideal inductance develops a square wave voltage. A real inductor, however, has a triangular wave superimposed on the square wave due to its resistance (B) FIRST ORDER CIRCUITS For a series RC circuit, the capacitor voltage response to a step input of V S volts, assuming no initial charge, is: v C ( t) = V S t / RC ( 1 e ) This is shown in Fig. 1. Two parameters define this response: the final value V s and the timeconstant (τ=rc). Another parameter shown in Fig. 1 is the 10%-90% rise time T r (2.20τ). This is a useful alternative parameter, from which the time constant can be derived. Exp. 4-2
3 Fig. 1 (C) SECOND ORDER CIRCUITS The techniques that are used to study second order circuits are very similar to the ones used to study first order circuits. However, the form of the responses of a second order circuit is more complicated than that of first order circuits, therefore more parameters are required to define them. Time-domain response of a second order circuit consists of two parts natural response and forced response. The forced response for a step function input is the step function itself, while the natural response depends only on the circuit elements and decays for time t. The natural response of a second-order circuit, like the series RLC circuit in this experiment, can be underdamped, overdamped, or critically damped. The type of natural response is described by the damping factor ζ, which for the series RLC circuit is: R ς = C L. 2 When ζ < 1, the circuit is underdamped, when ζ > 1 the circuit is overdamped, and when ζ = 1 it is critically damped. In case of an underdamped circuit the natural response is a damped sine wave, in case of an overdamped circuit it is of the form: natural C α1t α t ( t) K e K e v 2 =, 1 2 and in case of a critically damped circuit it is: v natural C αt αt ( t) K e K te = 1 2 In an underdamped series RLC circuit, the complete response can be described by the following expression: v C ( t) = V S V S 1 ς 2 e αt sin ( ω t φ) d Exp. 4-3
4 where: 2 α = ςω 0, ω = ω 0 1 ς d, 0 = 1 ω, and ( ) 2 LC sin φ = 1 ς. The constant ω 0 is the natural, undamped angular frequency of the circuit. Fig. 2 shows the step response of an underdamped circuit. Some of the parameters that can be measured to define this type of response are: final value V S 10%-90% rise time T r period of the oscillation T d time constant (1/α) of the exponential decay envelope V p VS % overshoot: 100 Vs settling time T S, the time required for the response to converge toward the final value within some specified percentage, for example 5% as in Fig. 2. Fig. 2 Exp. 4-4
5 Fig. 3 shows normalized step response curves of a linear second order system for different damping factor values illustrating the transition from an underdamped, through a critically damped, to an overdamped response for increasing values of ζ. Fig. 3 Exp. 4-5
6 PRE-LAB ASSIGNMENT (Preparation) Except for the graph in Fig. C-2 (which can be cut and pasted from the instruction sheet), all graphs must be drawn directly into your lab book. (A) Voltage-Current Characteristic of a Capacitor i C C = 0.1 µf v C v RC R C = 100Ω Fig. A-1 (Identical to Fig. 4) The voltage across a 0.1 µf capacitor is a triangular wave of 6 V peak-to-peak at a frequency of 100Hz. Derive and sketch an expression for the capacitor current i C (t). Ignore the effect of R c on the circuit and consider the capacitor as ideal. Repeat the previous step for a 6 V peak-to-peak sine wave at 100 Hz. (B) Step-Response of a RC circuit Consider the circuit in Fig. B-1 and disregard the current monitoring resistor R C (R C << R) in all your calculations. The signal (t) is a 6V positive step function and initially no charge is stored in the capacitor. R = 10kΩ i C v R v C v RC C = 0.01 µf R C = 100Ω Fig. B-1 (identical to Fig. 5) Exp. 4-6
7 Find the initial and final conditions and determine the time constant τ. Derive an expression for the capacitor voltage v C (t) and current i C (t). Determine the 10%-90% rise time T r. (C) Parameter Estimation i L R = 10kΩ v R Inductor Coil v RL v L R L L d Fig. C-1 (identical to Fig. 6) In the circuit in Fig. C-1, a real (i.e., non-ideal) inductor coil is modeled by the series combination of an ideal inductor L in series with a small resistance R L. Assume R L = 25 Ω and L = 25 mh. The input signal is a 6 V peak-to-peak triangular wave at a frequency of 500 Hz. The inductor current,!!, can be approximated by assuming that the voltage across the inductor coil,!!"#, is small so that the input signal,!!", appears almost entirely across the resistor R, i.e. il vin R. Use this approximation to find the voltage across the real inductor, d, and sketch it for a time of two periods. Fig. C-2 shows the input voltage (t) and the voltage d (t) across a different real inductor. Use the two graphs to estimate its inductance and resistance, L and R L. Exp. 4-7
8 Fig. C-2 Exp. 4-8
9 (D) Step Response of a Series RLC Circuit Underdamped Response For the circuit in Fig. D-1, set the variable resistor R to 1 kω and assume that the input voltage is a 6 V positive step function. Initially there is no current in the inductor and the capacitor is uncharged. R v R d L = 50 mh v C C = 0.01 µf Fig. D-1 (identical to Fig. 7) Determine the initial and final values of v C. Find the solution for the capacitor voltage v C (t) and plot it versus time. Make use of the normalized step response curves shown in Fig. 3. Determine the damping factor ζ, the natural angular frequency ω 0, the period of the oscillation T d, and estimate the percentage overshoot from the normalized step response in Fig. 3. Determine the value of the resistor for a critically damped response. Determine the value of the resistor for an overdamped response, where ζ = 2. EQUIPMENT GW Function generator Model GFG-813 TEKTRONIX TDS 210 oscilloscope Protoboard Components: 100 Ω, 1 kω, and 10 kω resistors, 0.01 µf and 0.1 µf capacitors, 50 mh inductor Decade resistor box GenRad RLC Digibridge Model 1657/Instek RLC Meter Model 815 Exp. 4-9
10 EXPERIMENT 4.1 Voltage-Current Characteristic of a Capacitor i C C = 0.1 µf v C v RC R C = 100Ω Fig. 4 Preparation: Part (A) of your pre-lab assignment Experiment: Connect the output of the function generator (labeled MAIN) to one of the BNC connectors on the protoboard. Set the waveform to a triangular wave form at 100Hz. Complete the circuit in Fig. 4. Make sure one of the resistor terminals is connected to ground Connect Channel 1 of the oscilloscope to measure the input voltage and adjust it to 6 V peak-topeak. Connect Channel 2 of the oscilloscope to measure v RC across R C and display both wave forms simultaneously. Copy both wave forms into your lab book and label all axes. Repeat your measurements for a 6 V peak-to-peak sine wave at the same frequency. Compare your results with the preparation. Exp. 4-10
11 4.2 Step Response of a Series RC Circuit i C R = 10kΩ v R v C C = 0.01 µf v RC R C = 100Ω Fig. 5 Preparation: Part (B) of your pre-lab assignment Experiment: Convert the RC circuit on your protoboard to that in Fig. 5. Set the function generator to a 6 V positive voltage square wave at 500 Hz. To achieve this, first set the function generator to a 6 V peak-to-peak square wave at 500 Hz. Then pull out the OFFSET knob on the function generator and adjust the DC level until the oscilloscope displays a positive square wave from 0 to 6 V. Connect the oscilloscope probes to simultaneously display v RC and v C v RC (v RC << v C, so v C v RC v C ). Copy both wave forms into your lab book and label all axes. Measure the time constant τ and the rise time T r using the cursors on the oscilloscope. What is the ratio T r /τ? Compare your results to the preparation. Exp. 4-11
12 4.3 Parameter Estimation i L R = 10kΩ v R Inductor Coil v RL v L R L L d Preparation: Part (C) of your pre-lab assignment. Fig. 6 Experiment: Set up the circuit in Fig. 6 and set the function generator to a 6 V peak-to-peak triangular wave at a frequency of 500 Hz. Make sure the DC offset is reset and the OFFSET knob on the function generator is pushed in. Connect the oscilloscope probes such as to measure the input voltage and the inductor voltage simultaneously. In your lab book, plot the measured waveforms!!"! and!!"# (!) From these plots, determine the actual values of the resistance R L and the inductance L, using the same method as in part (C) of your pre-lab assignment. Exp. 4-12
13 4.4 Step-Response for the Series RLC circuit R v R d L = 50 mh v C C = 0.01 µf Fig Underdamped Response Preparation: The first three steps of part (D) of your pre-lab assignment. Experiment: Set up the circuit in Fig. 7, with R = 1kΩ. Set the function generator to a 6 V positive square wave of frequency 500 Hz by (see section 3.2). Display the capacitor voltage v C (t) on the oscilloscope. Use the oscilloscope cursors to measure the initial and final value of v C, the rise time T r, the percentage overshoot, the period of the oscillation T d, and the settling time T S, based on the 5% of final value criterion. Copy the wave form from the oscilloscope into your lab book and label all axes. Compare your results to the preparation. Exp. 4-13
14 4.4.2 Critically Damped and Overdamped Responses Preparation: The last two steps of part (D) of your pre-lab assignment. Experiment: Continue using the circuit in Fig. 7 and display the capacitor voltage v C (t) on the oscilloscope. Slowly increase the resistance from 1 kω while observing the waveform on the oscilloscope until it becomes that of a critically damped response. Record this value of R and compare it to the one obtained in the preparation. Is there is a discrepancy, and if so, what could be a reason for it? Copy the wave form from the oscilloscope into your lab book and label all axes. Further increase the resistance to that with ζ=2 obtained in the preparation and confirm that the waveform on the oscilloscope is overdamped. Copy the wave form into your lab book and label all axes. Exp. 4-14
EECS40 RLC Lab guide
 EECS40 RLC Lab guide Introduction Second-Order Circuits Second order circuits have both inductor and capacitor components, which produce one or more resonant frequencies, ω0. In general, a differential
EECS40 RLC Lab guide Introduction Second-Order Circuits Second order circuits have both inductor and capacitor components, which produce one or more resonant frequencies, ω0. In general, a differential
University of Portland EE 271 Electrical Circuits Laboratory. Experiment: Inductors
 University of Portland EE 271 Electrical Circuits Laboratory Experiment: Inductors I. Objective The objective of this experiment is to verify the relationship between voltage and current in an inductor,
University of Portland EE 271 Electrical Circuits Laboratory Experiment: Inductors I. Objective The objective of this experiment is to verify the relationship between voltage and current in an inductor,
LABORATORY 3: Transient circuits, RC, RL step responses, 2 nd Order Circuits
 LABORATORY 3: Transient circuits, RC, RL step responses, nd Order Circuits Note: If your partner is no longer in the class, please talk to the instructor. Material covered: RC circuits Integrators Differentiators
LABORATORY 3: Transient circuits, RC, RL step responses, nd Order Circuits Note: If your partner is no longer in the class, please talk to the instructor. Material covered: RC circuits Integrators Differentiators
Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Technology. EET 3086C Circuit Analysis Laboratory Experiments. Masood Ejaz
 Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Technology EET 3086C Circuit Analysis Laboratory Experiments Masood Ejaz Experiment # 1 DC Measurements of a Resistive Circuit and Proof of Thevenin Theorem
Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Technology EET 3086C Circuit Analysis Laboratory Experiments Masood Ejaz Experiment # 1 DC Measurements of a Resistive Circuit and Proof of Thevenin Theorem
Electric Circuit Fall 2017 Lab10. LABORATORY 10 RLC Circuits. Guide. Figure 1: Voltage and current in an AC circuit.
 LABORATORY 10 RLC Circuits Guide Introduction RLC circuit When an AC signal is input to a RLC circuit, voltage across each element varies as a function of time. The voltage will oscillate with a frequency
LABORATORY 10 RLC Circuits Guide Introduction RLC circuit When an AC signal is input to a RLC circuit, voltage across each element varies as a function of time. The voltage will oscillate with a frequency
#8A RLC Circuits: Free Oscillations
 #8A RL ircuits: Free Oscillations Goals In this lab we investigate the properties of a series RL circuit. Such circuits are interesting, not only for there widespread application in electrical devices,
#8A RL ircuits: Free Oscillations Goals In this lab we investigate the properties of a series RL circuit. Such circuits are interesting, not only for there widespread application in electrical devices,
EXPERIMENT 8: LRC CIRCUITS
 EXPERIMENT 8: LRC CIRCUITS Equipment List S 1 BK Precision 4011 or 4011A 5 MHz Function Generator OS BK 2120B Dual Channel Oscilloscope V 1 BK 388B Multimeter L 1 Leeds & Northrup #1532 100 mh Inductor
EXPERIMENT 8: LRC CIRCUITS Equipment List S 1 BK Precision 4011 or 4011A 5 MHz Function Generator OS BK 2120B Dual Channel Oscilloscope V 1 BK 388B Multimeter L 1 Leeds & Northrup #1532 100 mh Inductor
Experiment 2: Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits
 Experiment 2: Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits Will Chemelewski Partner: Brian Enders TA: Nielsen See laboratory book #1 pages 5-7, data taken September 1, 2009 September 7, 2009 Abstract Transient
Experiment 2: Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits Will Chemelewski Partner: Brian Enders TA: Nielsen See laboratory book #1 pages 5-7, data taken September 1, 2009 September 7, 2009 Abstract Transient
Lab 5 Second Order Transient Response of Circuits
 Lab 5 Second Order Transient Response of Circuits Lab Performed on November 5, 2008 by Nicole Kato, Ryan Carmichael, and Ti Wu Report by Ryan Carmichael and Nicole Kato E11 Laboratory Report Submitted
Lab 5 Second Order Transient Response of Circuits Lab Performed on November 5, 2008 by Nicole Kato, Ryan Carmichael, and Ti Wu Report by Ryan Carmichael and Nicole Kato E11 Laboratory Report Submitted
Experiment 1 LRC Transients
 Physics 263 Experiment 1 LRC Transients 1 Introduction In this experiment we will study the damped oscillations and other transient waveforms produced in a circuit containing an inductor, a capacitor,
Physics 263 Experiment 1 LRC Transients 1 Introduction In this experiment we will study the damped oscillations and other transient waveforms produced in a circuit containing an inductor, a capacitor,
 RC_Circuits RC Circuits Lab Q1 Open the Logger Pro program RC_RL_Circuits via the Logger Launcher icon on your desktop. RC Circuits Lab Part1 Part 1: Measuring Voltage and Current in an RC Circuit 1. 2.
RC_Circuits RC Circuits Lab Q1 Open the Logger Pro program RC_RL_Circuits via the Logger Launcher icon on your desktop. RC Circuits Lab Part1 Part 1: Measuring Voltage and Current in an RC Circuit 1. 2.
Physics 132 Quiz # 23
 Name (please (please print) print) Physics 132 Quiz # 23 I. I. The The current in in an an ac ac circuit is is represented by by a phasor.the value of of the the current at at some time time t t is is
Name (please (please print) print) Physics 132 Quiz # 23 I. I. The The current in in an an ac ac circuit is is represented by by a phasor.the value of of the the current at at some time time t t is is
Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters
 Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters Goal: In circuits with a time-varying voltage, the relationship between current and voltage is more complicated
Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters Goal: In circuits with a time-varying voltage, the relationship between current and voltage is more complicated
Study of Inductive and Capacitive Reactance and RLC Resonance
 Objective Study of Inductive and Capacitive Reactance and RLC Resonance To understand how the reactance of inductors and capacitors change with frequency, and how the two can cancel each other to leave
Objective Study of Inductive and Capacitive Reactance and RLC Resonance To understand how the reactance of inductors and capacitors change with frequency, and how the two can cancel each other to leave
Lab 1: Basic RL and RC DC Circuits
 Name- Surname: ID: Department: Lab 1: Basic RL and RC DC Circuits Objective In this exercise, the DC steady state response of simple RL and RC circuits is examined. The transient behavior of RC circuits
Name- Surname: ID: Department: Lab 1: Basic RL and RC DC Circuits Objective In this exercise, the DC steady state response of simple RL and RC circuits is examined. The transient behavior of RC circuits
Uncovering a Hidden RCL Series Circuit
 Purpose Uncovering a Hidden RCL Series Circuit a. To use the equipment and techniques developed in the previous experiment to uncover a hidden series RCL circuit in a box and b. To measure the values of
Purpose Uncovering a Hidden RCL Series Circuit a. To use the equipment and techniques developed in the previous experiment to uncover a hidden series RCL circuit in a box and b. To measure the values of
Physics 310 Lab 2 Circuit Transients and Oscilloscopes
 Physics 310 Lab 2 Circuit Transients and Oscilloscopes Equipment: function generator, oscilloscope, two BNC cables, BNC T connector, BNC banana adapter, breadboards, wire packs, some banana cables, three
Physics 310 Lab 2 Circuit Transients and Oscilloscopes Equipment: function generator, oscilloscope, two BNC cables, BNC T connector, BNC banana adapter, breadboards, wire packs, some banana cables, three
PHYSICS 221 LAB #6: CAPACITORS AND AC CIRCUITS
 Name: Partners: PHYSICS 221 LAB #6: CAPACITORS AND AC CIRCUITS The electricity produced for use in homes and industry is made by rotating coils of wire in a magnetic field, which results in alternating
Name: Partners: PHYSICS 221 LAB #6: CAPACITORS AND AC CIRCUITS The electricity produced for use in homes and industry is made by rotating coils of wire in a magnetic field, which results in alternating
EE 442. Lab Experiment No. 6. Step Response of a Series RLC Circuit
 EE 44 Laboratory Experiment 6 EE 44 Lab Experiment No. 6 0/0/007 1 I. INTRODUCTION EE 44 Laboratory Experiment 6 The purpose of this experiment is to measure the response of a series RLC circuit to a step
EE 44 Laboratory Experiment 6 EE 44 Lab Experiment No. 6 0/0/007 1 I. INTRODUCTION EE 44 Laboratory Experiment 6 The purpose of this experiment is to measure the response of a series RLC circuit to a step
STUDY OF RC AND RL CIRCUITS Venue: Microelectronics Laboratory in E2 L2
 EXPERIMENT #1 STUDY OF RC AND RL CIRCUITS Venue: Microelectronics Laboratory in E2 L2 I. INTRODUCTION This laboratory is about verifying the transient behavior of RC and RL circuits. You need to revise
EXPERIMENT #1 STUDY OF RC AND RL CIRCUITS Venue: Microelectronics Laboratory in E2 L2 I. INTRODUCTION This laboratory is about verifying the transient behavior of RC and RL circuits. You need to revise
AC CURRENTS, VOLTAGES, FILTERS, and RESONANCE
 July 22, 2008 AC Currents, Voltages, Filters, Resonance 1 Name Date Partners AC CURRENTS, VOLTAGES, FILTERS, and RESONANCE V(volts) t(s) OBJECTIVES To understand the meanings of amplitude, frequency, phase,
July 22, 2008 AC Currents, Voltages, Filters, Resonance 1 Name Date Partners AC CURRENTS, VOLTAGES, FILTERS, and RESONANCE V(volts) t(s) OBJECTIVES To understand the meanings of amplitude, frequency, phase,
University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department. EE 219 Electrical Circuits Lab
 University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 219 Electrical Circuits Lab EXPERIMENT 4 TRANSIENT ANALYSIS Prepared by: Dr. Mohammed Hawa EXPERIMENT 4 TRANSIENT ANALYSIS
University of Jordan School of Engineering Electrical Engineering Department EE 219 Electrical Circuits Lab EXPERIMENT 4 TRANSIENT ANALYSIS Prepared by: Dr. Mohammed Hawa EXPERIMENT 4 TRANSIENT ANALYSIS
EE 241 Experiment #7: NETWORK THEOREMS, LINEARITY, AND THE RESPONSE OF 1 ST ORDER RC CIRCUITS 1
 EE 241 Experiment #7: NETWORK THEOREMS, LINEARITY, AND THE RESPONSE OF 1 ST ORDER RC CIRCUITS 1 PURPOSE: To verify the validity of Thevenin and maximum power transfer theorems. To demonstrate the linear
EE 241 Experiment #7: NETWORK THEOREMS, LINEARITY, AND THE RESPONSE OF 1 ST ORDER RC CIRCUITS 1 PURPOSE: To verify the validity of Thevenin and maximum power transfer theorems. To demonstrate the linear
Physics 481 Experiment 1
 Physics 481 Experiment 1 LAST Name (print) FIRST Name (print) LINEAR CIRCUITS 1 Experiment 1 - Linear Circuits This experiment is designed for getting a hands-on experience with simple linear circuits.
Physics 481 Experiment 1 LAST Name (print) FIRST Name (print) LINEAR CIRCUITS 1 Experiment 1 - Linear Circuits This experiment is designed for getting a hands-on experience with simple linear circuits.
Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance
 E5.1 Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance Note: It is strongly recommended that you complete lab E4: Capacitors and the RC Circuit before performing this experiment. Introduction Ohm s law, a well known
E5.1 Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance Note: It is strongly recommended that you complete lab E4: Capacitors and the RC Circuit before performing this experiment. Introduction Ohm s law, a well known
Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3)
 Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive
Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive
Experiment #2 Half Wave Rectifier
 PURPOSE: ELECTRONICS 224 ETR620S Experiment #2 Half Wave Rectifier This laboratory session acquaints you with the operation of a diode power supply. You will study the operation of half-wave and the effect
PURPOSE: ELECTRONICS 224 ETR620S Experiment #2 Half Wave Rectifier This laboratory session acquaints you with the operation of a diode power supply. You will study the operation of half-wave and the effect
Laboratory Exercise 6 THE OSCILLOSCOPE
 Introduction Laboratory Exercise 6 THE OSCILLOSCOPE The aim of this exercise is to introduce you to the oscilloscope (often just called a scope), the most versatile and ubiquitous laboratory measuring
Introduction Laboratory Exercise 6 THE OSCILLOSCOPE The aim of this exercise is to introduce you to the oscilloscope (often just called a scope), the most versatile and ubiquitous laboratory measuring
ECE159H1S University of Toronto 2014 EXPERIMENT #2 OP AMP CIRCUITS AND WAVEFORMS ECE159H1S
 ECE159H1S University of Toronto 2014 EXPERIMENT #2 OP AMP CIRCUITS AND WAVEFORMS ECE159H1S OBJECTIVES: To study the performance and limitations of basic op-amp circuits: the inverting and noninverting
ECE159H1S University of Toronto 2014 EXPERIMENT #2 OP AMP CIRCUITS AND WAVEFORMS ECE159H1S OBJECTIVES: To study the performance and limitations of basic op-amp circuits: the inverting and noninverting
AC Circuits. "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert ( )
 AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits use varying
AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits use varying
CHAPTER 7. Response of First-Order RL and RC Circuits
 CHAPTER 7 Response of First-Order RL and RC Circuits RL and RC Circuits RL (resistor inductor) and RC (resistor-capacitor) circuits. Figure 7.1 The two forms of the circuits for natural response. (a) RL
CHAPTER 7 Response of First-Order RL and RC Circuits RL and RC Circuits RL (resistor inductor) and RC (resistor-capacitor) circuits. Figure 7.1 The two forms of the circuits for natural response. (a) RL
LABORATORY 4. Palomar College ENGR210 Spring 2017 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17
 LABORATORY 4 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17 OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this lab is to evaluate the transient and steady-state circuit response of first order and second order circuits. MINIMUM EQUIPMENT LIST: You will
LABORATORY 4 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17 OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this lab is to evaluate the transient and steady-state circuit response of first order and second order circuits. MINIMUM EQUIPMENT LIST: You will
Operational Amplifiers: Part II
 1. Introduction Operational Amplifiers: Part II The name "operational amplifier" comes from this amplifier's ability to perform mathematical operations. Three good examples of this are the summing amplifier,
1. Introduction Operational Amplifiers: Part II The name "operational amplifier" comes from this amplifier's ability to perform mathematical operations. Three good examples of this are the summing amplifier,
SINUSOIDS February 4, ELEC-281 Network Theory II Wentworth Institute of Technology. Bradford Powers Ryan Ferguson Richard Lupa Benjamin Wolf
 SINUSOIDS February 4, 28 ELEC-281 Network Theory II Wentworth Institute of Technology Bradford Powers Ryan Ferguson Richard Lupa Benjamin Wolf Abstract: Sinusoidal waveforms are studied in three circuits:
SINUSOIDS February 4, 28 ELEC-281 Network Theory II Wentworth Institute of Technology Bradford Powers Ryan Ferguson Richard Lupa Benjamin Wolf Abstract: Sinusoidal waveforms are studied in three circuits:
BIOE 123 Module 3. Electronics 2: Time Varying Circuits. Lecture (30 min) Date. Learning Goals
 BIOE 123 Module 3 Electronics 2: Time Varying Circuits Lecture (30 min) Date Learning Goals Learn about the behavior of capacitors and inductors Learn how to analyze time-varying circuits to quantify parameters
BIOE 123 Module 3 Electronics 2: Time Varying Circuits Lecture (30 min) Date Learning Goals Learn about the behavior of capacitors and inductors Learn how to analyze time-varying circuits to quantify parameters
EE 368 Electronics Lab. Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2)
 EE 368 Electronics Lab Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) 1 Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) Objectives To gain experience with Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp). To
EE 368 Electronics Lab Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) 1 Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) Objectives To gain experience with Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp). To
CHAPTER 6: ALTERNATING CURRENT
 CHAPTER 6: ALTERNATING CURRENT PSPM II 2005/2006 NO. 12(C) 12. (c) An ac generator with rms voltage 240 V is connected to a RC circuit. The rms current in the circuit is 1.5 A and leads the voltage by
CHAPTER 6: ALTERNATING CURRENT PSPM II 2005/2006 NO. 12(C) 12. (c) An ac generator with rms voltage 240 V is connected to a RC circuit. The rms current in the circuit is 1.5 A and leads the voltage by
Non-ideal Behavior of Electronic Components at High Frequencies and Associated Measurement Problems
 Nonideal Behavior of Electronic Components at High Frequencies and Associated Measurement Problems Matthew Beckler beck0778@umn.edu EE30 Lab Section 008 October 27, 2006 Abstract In the world of electronics,
Nonideal Behavior of Electronic Components at High Frequencies and Associated Measurement Problems Matthew Beckler beck0778@umn.edu EE30 Lab Section 008 October 27, 2006 Abstract In the world of electronics,
Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters
 Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters Goal: In circuits with a time-varying voltage, the relationship between current and voltage is more complicated
Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters Goal: In circuits with a time-varying voltage, the relationship between current and voltage is more complicated
EE2210 Laboratory Project 1 Fall 2013 Function Generator and Oscilloscope
 EE2210 Laboratory Project 1 Fall 2013 Function Generator and Oscilloscope For students to become more familiar with oscilloscopes and function generators. Pre laboratory Work Read the TDS 210 Oscilloscope
EE2210 Laboratory Project 1 Fall 2013 Function Generator and Oscilloscope For students to become more familiar with oscilloscopes and function generators. Pre laboratory Work Read the TDS 210 Oscilloscope
ENG 100 Lab #2 Passive First-Order Filter Circuits
 ENG 100 Lab #2 Passive First-Order Filter Circuits In Lab #2, you will construct simple 1 st -order RL and RC filter circuits and investigate their frequency responses (amplitude and phase responses).
ENG 100 Lab #2 Passive First-Order Filter Circuits In Lab #2, you will construct simple 1 st -order RL and RC filter circuits and investigate their frequency responses (amplitude and phase responses).
INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING AND LABORATORY EXPERIENCE Spring, 2015
 INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING AND LABORATORY EXPERIENCE Spring, 2015 Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Jack Ou, Ph.D. Engineering Science Sonoma State University A SONOMA STATE UNIVERSITY PUBLICATION CONTENTS 1 Electronic
INTRODUCTION TO ENGINEERING AND LABORATORY EXPERIENCE Spring, 2015 Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Jack Ou, Ph.D. Engineering Science Sonoma State University A SONOMA STATE UNIVERSITY PUBLICATION CONTENTS 1 Electronic
Exp. #2-6 : Measurement of the Characteristics of,, and Circuits by Using an Oscilloscope
 PAGE 1/14 Exp. #2-6 : Measurement of the Characteristics of,, and Circuits by Using an Oscilloscope Student ID Major Name Team No. Experiment Lecturer Student's Mentioned Items Experiment Class Date Submission
PAGE 1/14 Exp. #2-6 : Measurement of the Characteristics of,, and Circuits by Using an Oscilloscope Student ID Major Name Team No. Experiment Lecturer Student's Mentioned Items Experiment Class Date Submission
Experiment 8: An AC Circuit
 Experiment 8: An AC Circuit PART ONE: AC Voltages. Set up this circuit. Use R = 500 Ω, L = 5.0 mh and C =.01 μf. A signal generator built into the interface provides the emf to run the circuit from Output
Experiment 8: An AC Circuit PART ONE: AC Voltages. Set up this circuit. Use R = 500 Ω, L = 5.0 mh and C =.01 μf. A signal generator built into the interface provides the emf to run the circuit from Output
INTRODUCTION TO AC FILTERS AND RESONANCE
 AC Filters & Resonance 167 Name Date Partners INTRODUCTION TO AC FILTERS AND RESONANCE OBJECTIVES To understand the design of capacitive and inductive filters To understand resonance in circuits driven
AC Filters & Resonance 167 Name Date Partners INTRODUCTION TO AC FILTERS AND RESONANCE OBJECTIVES To understand the design of capacitive and inductive filters To understand resonance in circuits driven
EXPERIMENT 5 : DIODES AND RECTIFICATION
 EXPERIMENT 5 : DIODES AND RECTIFICATION Component List Resistors, one of each o 2 1010W o 1 1k o 1 10k 4 1N4004 (Imax = 1A, PIV = 400V) Diodes Center tap transformer (35.6Vpp, 12.6 VRMS) 100 F Electrolytic
EXPERIMENT 5 : DIODES AND RECTIFICATION Component List Resistors, one of each o 2 1010W o 1 1k o 1 10k 4 1N4004 (Imax = 1A, PIV = 400V) Diodes Center tap transformer (35.6Vpp, 12.6 VRMS) 100 F Electrolytic
Lab 7 PSpice: Time Domain Analysis
 Lab 7 PSpice: Time Domain Analysis OBJECTIVES 1. Use PSpice Circuit Simulator to simulate circuits containing capacitors and inductors in the time domain. 2. Practice using a switch, and a Pulse & Sinusoidal
Lab 7 PSpice: Time Domain Analysis OBJECTIVES 1. Use PSpice Circuit Simulator to simulate circuits containing capacitors and inductors in the time domain. 2. Practice using a switch, and a Pulse & Sinusoidal
Experiment Number 2. Revised: Summer 2013 PLECS RC, RL, and RLC Simulations
 Preface: Experiment Number 2 Revised: Summer 2013 PLECS RC, RL, and RLC Simulations Preliminary exercises are to be done and submitted individually Laboratory simulation exercises are to be done individually
Preface: Experiment Number 2 Revised: Summer 2013 PLECS RC, RL, and RLC Simulations Preliminary exercises are to be done and submitted individually Laboratory simulation exercises are to be done individually
Experiment Number 2. Revised: Fall 2018 PLECS RC, RL, and RLC Simulations
 Experiment Number 2 Revised: Fall 2018 PLECS RC, RL, and RLC Simulations Preface: Experiment number 2 will be held in CLC room 105, 106, or 107. Your TA will let you know Preliminary exercises are to be
Experiment Number 2 Revised: Fall 2018 PLECS RC, RL, and RLC Simulations Preface: Experiment number 2 will be held in CLC room 105, 106, or 107. Your TA will let you know Preliminary exercises are to be
Lab 3 Transient Response of RC & RL Circuits
 Lab 3 Transient Response of RC & RL Circuits Last Name: First Name: Student Number: Lab Section: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday TA Signature: Note: The Pre-Lab section must be completed prior
Lab 3 Transient Response of RC & RL Circuits Last Name: First Name: Student Number: Lab Section: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday TA Signature: Note: The Pre-Lab section must be completed prior
ASSIGNMENT 3.1 RESISTANCE IN ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
 Unit 2: Engineering Science Unit code: L/601/1404 QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 15 ASSIGNMENT 3.1 RESISTANCE IN ELECTRIC CIRCUITS NAME: Date Issued I agree to the assessment as contained in this assignment.
Unit 2: Engineering Science Unit code: L/601/1404 QCF Level: 4 Credit value: 15 ASSIGNMENT 3.1 RESISTANCE IN ELECTRIC CIRCUITS NAME: Date Issued I agree to the assessment as contained in this assignment.
EE 42/100: Lecture 8. 1 st -Order RC Transient Example, Introduction to 2 nd -Order Transients. EE 42/100 Summer 2012, UC Berkeley T.
 EE 42/100: Lecture 8 1 st -Order RC Transient Example, Introduction to 2 nd -Order Transients Circuits with non-dc Sources Recall that the solution to our ODEs is Particular solution is constant for DC
EE 42/100: Lecture 8 1 st -Order RC Transient Example, Introduction to 2 nd -Order Transients Circuits with non-dc Sources Recall that the solution to our ODEs is Particular solution is constant for DC
1. Hand Calculations (in a manner suitable for submission) For the circuit in Fig. 1 with f = 7.2 khz and a source vin () t 1.
 Objectives The purpose of this laboratory project is to introduce to equipment, measurement techniques, and simulations commonly used in AC circuit analysis. In this laboratory session, each student will:
Objectives The purpose of this laboratory project is to introduce to equipment, measurement techniques, and simulations commonly used in AC circuit analysis. In this laboratory session, each student will:
Class #7: Experiment L & C Circuits: Filters and Energy Revisited
 Class #7: Experiment L & C Circuits: Filters and Energy Revisited In this experiment you will revisit the voltage oscillations of a simple LC circuit. Then you will address circuits made by combining resistors
Class #7: Experiment L & C Circuits: Filters and Energy Revisited In this experiment you will revisit the voltage oscillations of a simple LC circuit. Then you will address circuits made by combining resistors
Integrators, differentiators, and simple filters
 BEE 233 Laboratory-4 Integrators, differentiators, and simple filters 1. Objectives Analyze and measure characteristics of circuits built with opamps. Design and test circuits with opamps. Plot gain vs.
BEE 233 Laboratory-4 Integrators, differentiators, and simple filters 1. Objectives Analyze and measure characteristics of circuits built with opamps. Design and test circuits with opamps. Plot gain vs.
Filters And Waveform Shaping
 Physics 3330 Experiment #3 Fall 2001 Purpose Filters And Waveform Shaping The aim of this experiment is to study the frequency filtering properties of passive (R, C, and L) circuits for sine waves, and
Physics 3330 Experiment #3 Fall 2001 Purpose Filters And Waveform Shaping The aim of this experiment is to study the frequency filtering properties of passive (R, C, and L) circuits for sine waves, and
PHASES IN A SERIES LRC CIRCUIT
 PHASES IN A SERIES LRC CIRCUIT Introduction: In this lab, we will use a computer interface to analyze a series circuit consisting of an inductor (L), a resistor (R), a capacitor (C), and an AC power supply.
PHASES IN A SERIES LRC CIRCUIT Introduction: In this lab, we will use a computer interface to analyze a series circuit consisting of an inductor (L), a resistor (R), a capacitor (C), and an AC power supply.
ELECTRIC CIRCUITS CMPE 253 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING LABORATORY MANUAL ISHIK UNIVERSITY
 ELECTRIC CIRCUITS CMPE 253 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING LABORATORY MANUAL ISHIK UNIVERSITY 2017-2018 1 WEEK EXPERIMENT TITLE NUMBER OF EXPERIMENT No Meeting Instructional Objective 2 Tutorial 1 3
ELECTRIC CIRCUITS CMPE 253 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING LABORATORY MANUAL ISHIK UNIVERSITY 2017-2018 1 WEEK EXPERIMENT TITLE NUMBER OF EXPERIMENT No Meeting Instructional Objective 2 Tutorial 1 3
RC and RL Circuits. Figure 1: Capacitor charging circuit.
 RC and RL Circuits Page 1 RC and RL Circuits RC Circuits In this lab we study a simple circuit with a resistor and a capacitor from two points of view, one in time and the other in frequency. The viewpoint
RC and RL Circuits Page 1 RC and RL Circuits RC Circuits In this lab we study a simple circuit with a resistor and a capacitor from two points of view, one in time and the other in frequency. The viewpoint
The Series RLC Circuit and Resonance
 Purpose Theory The Series RLC Circuit and Resonance a. To study the behavior of a series RLC circuit in an AC current. b. To measure the values of the L and C using the impedance method. c. To study the
Purpose Theory The Series RLC Circuit and Resonance a. To study the behavior of a series RLC circuit in an AC current. b. To measure the values of the L and C using the impedance method. c. To study the
LRC Circuit PHYS 296 Your name Lab section
 LRC Circuit PHYS 296 Your name Lab section PRE-LAB QUIZZES 1. What will we investigate in this lab? 2. Figure 1 on the following page shows an LRC circuit with the resistor of 1 Ω, the capacitor of 33
LRC Circuit PHYS 296 Your name Lab section PRE-LAB QUIZZES 1. What will we investigate in this lab? 2. Figure 1 on the following page shows an LRC circuit with the resistor of 1 Ω, the capacitor of 33
Experiment VI: The LRC Circuit and Resonance
 Experiment VI: The ircuit and esonance I. eferences Halliday, esnick and Krane, Physics, Vol., 4th Ed., hapters 38,39 Purcell, Electricity and Magnetism, hapter 7,8 II. Equipment Digital Oscilloscope Digital
Experiment VI: The ircuit and esonance I. eferences Halliday, esnick and Krane, Physics, Vol., 4th Ed., hapters 38,39 Purcell, Electricity and Magnetism, hapter 7,8 II. Equipment Digital Oscilloscope Digital
The Tuned Circuit. Aim of the experiment. Circuit. Equipment and components. Display of a decaying oscillation. Dependence of L, C and R.
 The Tuned Circuit Aim of the experiment Display of a decaying oscillation. Dependence of L, C and R. Circuit Equipment and components 1 Rastered socket panel 1 Resistor R 1 = 10 Ω, 1 Resistor R 2 = 1 kω
The Tuned Circuit Aim of the experiment Display of a decaying oscillation. Dependence of L, C and R. Circuit Equipment and components 1 Rastered socket panel 1 Resistor R 1 = 10 Ω, 1 Resistor R 2 = 1 kω
Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks
 OPTI 380B Intermediate Optics Laboratory Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks Objectives: Lean how to use: Function of an oscilloscope probe. Characterization of capacitors and inductors
OPTI 380B Intermediate Optics Laboratory Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks Objectives: Lean how to use: Function of an oscilloscope probe. Characterization of capacitors and inductors
Lecture 16 Date: Frequency Response (Contd.)
 Lecture 16 Date: 03.10.2017 Frequency Response (Contd.) Bode Plot (contd.) Bode Plot (contd.) Bode Plot (contd.) not every transfer function has all seven factors. To sketch the Bode plots for a generic
Lecture 16 Date: 03.10.2017 Frequency Response (Contd.) Bode Plot (contd.) Bode Plot (contd.) Bode Plot (contd.) not every transfer function has all seven factors. To sketch the Bode plots for a generic
Laboratory 4. Bandwidth, Filters, and Diodes
 Laboratory 4 Bandwidth, Filters, and Diodes Required Components: k resistor 0. F capacitor N94 small-signal diode LED 4. Objectives In the previous laboratory exercise you examined the effects of input
Laboratory 4 Bandwidth, Filters, and Diodes Required Components: k resistor 0. F capacitor N94 small-signal diode LED 4. Objectives In the previous laboratory exercise you examined the effects of input
Exponential Waveforms
 ENGR 210 Lab 9 Exponential Waveforms Purpose: To measure the step response of circuits containing dynamic elements such as capacitors. Equipment Required: 1 - HP 54xxx Oscilloscope 1 - HP 33120A Function
ENGR 210 Lab 9 Exponential Waveforms Purpose: To measure the step response of circuits containing dynamic elements such as capacitors. Equipment Required: 1 - HP 54xxx Oscilloscope 1 - HP 33120A Function
ECE 231 Laboratory Exercise 6 Frequency / Time Response of RL and RC Circuits
 ECE 231 Laboratory Exercise 6 Frequency / Time Response of RL and RC Circuits Laboratory Group (Names) OBJECTIVES Observe and calculate the response of first-order low pass and high pass filters. Gain
ECE 231 Laboratory Exercise 6 Frequency / Time Response of RL and RC Circuits Laboratory Group (Names) OBJECTIVES Observe and calculate the response of first-order low pass and high pass filters. Gain
EXPERIMENT 5 : THE DIODE
 EXPERIMENT 5 : THE DIODE Component List Resistors, one of each o 1 10 10W o 1 1k o 1 10k 4 1N4004 (Imax = 1A, PIV = 400V) Diodes Center tap transformer (35.6Vpp, 12.6 VRMS) 100 F Electrolytic Capacitor
EXPERIMENT 5 : THE DIODE Component List Resistors, one of each o 1 10 10W o 1 1k o 1 10k 4 1N4004 (Imax = 1A, PIV = 400V) Diodes Center tap transformer (35.6Vpp, 12.6 VRMS) 100 F Electrolytic Capacitor
BME 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters
 BME 35 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of passive filters. Laboratory Equipment: Agilent Oscilloscope Model 546A Agilent Function Generator
BME 35 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of passive filters. Laboratory Equipment: Agilent Oscilloscope Model 546A Agilent Function Generator
EECS 216 Winter 2008 Lab 3: AM Radio Part II: In-Lab & Post-lab Assignment
 EECS 216 Winter 2008 Lab 3: Part II: In-Lab & Post-lab Assignment c Kim Winick 2008 1 Introduction In this laboratory you will assemble and test a working superheterodyne AM radio consisting of a front-end
EECS 216 Winter 2008 Lab 3: Part II: In-Lab & Post-lab Assignment c Kim Winick 2008 1 Introduction In this laboratory you will assemble and test a working superheterodyne AM radio consisting of a front-end
Step Response of RC Circuits
 EE 233 Laboratory-1 Step Response of RC Circuits 1 Objectives Measure the internal resistance of a signal source (eg an arbitrary waveform generator) Measure the output waveform of simple RC circuits excited
EE 233 Laboratory-1 Step Response of RC Circuits 1 Objectives Measure the internal resistance of a signal source (eg an arbitrary waveform generator) Measure the output waveform of simple RC circuits excited
Electronics and Instrumentation ENGR-4300 Spring 2004 Section Experiment 5 Introduction to AC Steady State
 Experiment 5 Introduction to C Steady State Purpose: This experiment addresses combinations of resistors, capacitors and inductors driven by sinusoidal voltage sources. In addition to the usual simulation
Experiment 5 Introduction to C Steady State Purpose: This experiment addresses combinations of resistors, capacitors and inductors driven by sinusoidal voltage sources. In addition to the usual simulation
Boise State University Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 212L Circuit Analysis and Design Lab
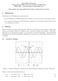 Objecties Boise State Uniersity Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 22L Circuit Analysis and Design Lab Experiment #2: Sinusoidal Steady State and Resonant Circuits The objecties of this
Objecties Boise State Uniersity Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 22L Circuit Analysis and Design Lab Experiment #2: Sinusoidal Steady State and Resonant Circuits The objecties of this
Experiment 7: Undriven & Driven RLC Circuits
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2006 OBJECTIVES Experiment 7: Undriven & Driven RLC Circuits 1. To explore the time dependent behavior of RLC Circuits, both driven
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2006 OBJECTIVES Experiment 7: Undriven & Driven RLC Circuits 1. To explore the time dependent behavior of RLC Circuits, both driven
OBJECTIVE The purpose of this exercise is to design and build a pulse generator.
 ELEC 4 Experiment 8 Pulse Generators OBJECTIVE The purpose of this exercise is to design and build a pulse generator. EQUIPMENT AND PARTS REQUIRED Protoboard LM555 Timer, AR resistors, rated 5%, /4 W,
ELEC 4 Experiment 8 Pulse Generators OBJECTIVE The purpose of this exercise is to design and build a pulse generator. EQUIPMENT AND PARTS REQUIRED Protoboard LM555 Timer, AR resistors, rated 5%, /4 W,
ET1210: Module 5 Inductance and Resonance
 Part 1 Inductors Theory: When current flows through a coil of wire, a magnetic field is created around the wire. This electromagnetic field accompanies any moving electric charge and is proportional to
Part 1 Inductors Theory: When current flows through a coil of wire, a magnetic field is created around the wire. This electromagnetic field accompanies any moving electric charge and is proportional to
Experiment Guide: RC/RLC Filters and LabVIEW
 Description and ackground Experiment Guide: RC/RLC Filters and LabIEW In this lab you will (a) manipulate instruments manually to determine the input-output characteristics of an RC filter, and then (b)
Description and ackground Experiment Guide: RC/RLC Filters and LabIEW In this lab you will (a) manipulate instruments manually to determine the input-output characteristics of an RC filter, and then (b)
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2005 Experiment 10: LR and Undriven LRC Circuits
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.0 Spring 005 Experiment 10: LR and Undriven LRC Circuits OBJECTIVES 1. To determine the inductance L and internal resistance R L of a coil,
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.0 Spring 005 Experiment 10: LR and Undriven LRC Circuits OBJECTIVES 1. To determine the inductance L and internal resistance R L of a coil,
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 1 FAMILIARIZATION WITH COMMONLY USED INSTRUMENTATION
 Objectives: ME 365 EXPERIMENT 1 FAMILIARIZATION WITH COMMONLY USED INSTRUMENTATION The primary goal of this laboratory is to study the operation and limitations of several commonly used pieces of instrumentation:
Objectives: ME 365 EXPERIMENT 1 FAMILIARIZATION WITH COMMONLY USED INSTRUMENTATION The primary goal of this laboratory is to study the operation and limitations of several commonly used pieces of instrumentation:
Laboratory 4: Amplification, Impedance, and Frequency Response
 ES 3: Introduction to Electrical Systems Laboratory 4: Amplification, Impedance, and Frequency Response I. GOALS: In this laboratory, you will build an audio amplifier using an LM386 integrated circuit.
ES 3: Introduction to Electrical Systems Laboratory 4: Amplification, Impedance, and Frequency Response I. GOALS: In this laboratory, you will build an audio amplifier using an LM386 integrated circuit.
Introduction. Transients in RLC Circuits
 Introduction In this experiment, we will study the behavior of simple electronic circuits whose response varies as a function of the driving frequency. One key feature of these circuits is that they exhibit
Introduction In this experiment, we will study the behavior of simple electronic circuits whose response varies as a function of the driving frequency. One key feature of these circuits is that they exhibit
Experiment 18: Driven RLC Circuit
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8. Spring 3 Experiment 8: Driven LC Circuit OBJECTIVES To measure the resonance frequency and the quality factor of a driven LC circuit INTODUCTION
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8. Spring 3 Experiment 8: Driven LC Circuit OBJECTIVES To measure the resonance frequency and the quality factor of a driven LC circuit INTODUCTION
Series and Parallel Resonant Circuits
 Series and Parallel Resonant Circuits Aim: To obtain the characteristics of series and parallel resonant circuits. Apparatus required: Decade resistance box, Decade inductance box, Decade capacitance box
Series and Parallel Resonant Circuits Aim: To obtain the characteristics of series and parallel resonant circuits. Apparatus required: Decade resistance box, Decade inductance box, Decade capacitance box
MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND. Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science. Laboratory Manual for. Eng Circuit Analysis (2013)
 MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Laboratory Manual for Eng. 3821 Circuit Analysis (2013) Instructor: E. W. Gill PREFACE The laboratory exercises in this manual
MEMORIAL UNIVERSITY OF NEWFOUNDLAND Faculty of Engineering and Applied Science Laboratory Manual for Eng. 3821 Circuit Analysis (2013) Instructor: E. W. Gill PREFACE The laboratory exercises in this manual
Experiment 9 AC Circuits
 Experiment 9 AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits
Experiment 9 AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits
11. AC-resistances of capacitor and inductors: Reactances.
 11. AC-resistances of capacitor and inductors: Reactances. Purpose: To study the behavior of the AC voltage signals across elements in a simple series connection of a resistor with an inductor and with
11. AC-resistances of capacitor and inductors: Reactances. Purpose: To study the behavior of the AC voltage signals across elements in a simple series connection of a resistor with an inductor and with
Power Electronics Laboratory-2 Uncontrolled Rectifiers
 Roll. No: Checked By: Date: Grade: Power Electronics Laboratory-2 and Uncontrolled Rectifiers Objectives: 1. To analyze the working and performance of a and half wave uncontrolled rectifier. 2. To analyze
Roll. No: Checked By: Date: Grade: Power Electronics Laboratory-2 and Uncontrolled Rectifiers Objectives: 1. To analyze the working and performance of a and half wave uncontrolled rectifier. 2. To analyze
LAB 1: Familiarity with Laboratory Equipment (_/10)
 LAB 1: Familiarity with Laboratory Equipment (_/10) PURPOSE o gain familiarity with basic laboratory equipment oscilloscope, oscillator, multimeter and electronic components. EQUIPMEN (i) Oscilloscope
LAB 1: Familiarity with Laboratory Equipment (_/10) PURPOSE o gain familiarity with basic laboratory equipment oscilloscope, oscillator, multimeter and electronic components. EQUIPMEN (i) Oscilloscope
Chapter 30 Inductance, Electromagnetic. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 30 Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, and AC Circuits 30-7 AC Circuits with AC Source Resistors, capacitors, and inductors have different phase relationships between current and voltage
Chapter 30 Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, and AC Circuits 30-7 AC Circuits with AC Source Resistors, capacitors, and inductors have different phase relationships between current and voltage
The Oscilloscope. Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. J. Swift ( ) OBJECTIVE To learn to operate a digital oscilloscope.
 The Oscilloscope Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. J. Swift (1667-1745) OBJECTIVE To learn to operate a digital oscilloscope. THEORY The oscilloscope, or scope for short, is a device for drawing
The Oscilloscope Vision is the art of seeing things invisible. J. Swift (1667-1745) OBJECTIVE To learn to operate a digital oscilloscope. THEORY The oscilloscope, or scope for short, is a device for drawing
Network Analysis I Laboratory EECS 70LA
 Network Analysis I Laboratory EECS 70LA Spring 2018 Edition Written by: Franco De Flaviis, P. Burke Table of Contents Page no. Foreword...3 Summary...4 Report Guidelines and Grading Policy...5 Introduction
Network Analysis I Laboratory EECS 70LA Spring 2018 Edition Written by: Franco De Flaviis, P. Burke Table of Contents Page no. Foreword...3 Summary...4 Report Guidelines and Grading Policy...5 Introduction
Lab 11. Speed Control of a D.C. motor. Motor Characterization
 Lab 11. Speed Control of a D.C. motor Motor Characterization Motor Speed Control Project 1. Generate PWM waveform 2. Amplify the waveform to drive the motor 3. Measure motor speed 4. Estimate motor parameters
Lab 11. Speed Control of a D.C. motor Motor Characterization Motor Speed Control Project 1. Generate PWM waveform 2. Amplify the waveform to drive the motor 3. Measure motor speed 4. Estimate motor parameters
Worksheet for Exploration 31.1: Amplitude, Frequency and Phase Shift
 Worksheet for Exploration 31.1: Amplitude, Frequency and Phase Shift We characterize the voltage (or current) in AC circuits in terms of the amplitude, frequency (period) and phase. The sinusoidal voltage
Worksheet for Exploration 31.1: Amplitude, Frequency and Phase Shift We characterize the voltage (or current) in AC circuits in terms of the amplitude, frequency (period) and phase. The sinusoidal voltage
EENG-201 Experiment # 4: Function Generator, Oscilloscope
 EENG-201 Experiment # 4: Function Generator, Oscilloscope I. Objectives Upon completion of this experiment, the student should be able to 1. To become familiar with the use of a function generator. 2.
EENG-201 Experiment # 4: Function Generator, Oscilloscope I. Objectives Upon completion of this experiment, the student should be able to 1. To become familiar with the use of a function generator. 2.
EC-3: Capacitors and RC-Decay
 Your TA will use this sheet to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. You must use complete sentences and clearly explain your reasoning to receive full credit. EC-3, Part I: Do not do
Your TA will use this sheet to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. You must use complete sentences and clearly explain your reasoning to receive full credit. EC-3, Part I: Do not do
Sonoma State University Department of Engineering Science Spring 2017
 EE 110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Lab 4 Introduction to AC Measurements (I) AC signals, Function Generators and Oscilloscopes Function Generator (AC) Battery
EE 110 Introduction to Engineering & Laboratory Experience Saeid Rahimi, Ph.D. Lab 4 Introduction to AC Measurements (I) AC signals, Function Generators and Oscilloscopes Function Generator (AC) Battery
Lab 9 AC FILTERS AND RESONANCE
 151 Name Date Partners ab 9 A FITES AND ESONANE OBJETIES OEIEW To understand the design of capacitive and inductive filters To understand resonance in circuits driven by A signals In a previous lab, you
151 Name Date Partners ab 9 A FITES AND ESONANE OBJETIES OEIEW To understand the design of capacitive and inductive filters To understand resonance in circuits driven by A signals In a previous lab, you
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring Experiment 11: Driven RLC Circuit
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.2 Spring 24 Experiment 11: Driven LC Circuit OBJECTIVES 1. To measure the resonance frequency and the quality factor of a driven LC circuit.
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.2 Spring 24 Experiment 11: Driven LC Circuit OBJECTIVES 1. To measure the resonance frequency and the quality factor of a driven LC circuit.
Lab 8 - INTRODUCTION TO AC CURRENTS AND VOLTAGES
 08-1 Name Date Partners ab 8 - INTRODUCTION TO AC CURRENTS AND VOTAGES OBJECTIVES To understand the meanings of amplitude, frequency, phase, reactance, and impedance in AC circuits. To observe the behavior
08-1 Name Date Partners ab 8 - INTRODUCTION TO AC CURRENTS AND VOTAGES OBJECTIVES To understand the meanings of amplitude, frequency, phase, reactance, and impedance in AC circuits. To observe the behavior
