Integrators, differentiators, and simple filters
|
|
|
- Stephany Harmon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BEE 233 Laboratory-4 Integrators, differentiators, and simple filters 1. Objectives Analyze and measure characteristics of circuits built with opamps. Design and test circuits with opamps. Plot gain vs. frequency to understand circuit operations. Use SPICE to verify circuit designs. 2. Reference The opamp characteristics and circuits are covered in the textbook. Make sure you know how to analyze circuits using the simple ideal opamp model. Review the usage of the programmable power supply that can set two supply values (e.g. +12 V and 12 V). The convention is to use VCC to denote the positive supply and VEE to denote the negative supply. The only knowledge required for this experiment is: time-domain analysis, basic opamp circuit analysis, and impedance of components. The technique to plot gain as function of frequency is described in the Discussion section below. No knowledge of filters is required. 3. Circuits You will analyze, design, and simulate the circuits below in various parts of this laboratory. Figure 1. Inverting amplifier
2 Figure 2. Simple integrator. Figure 3. Simple differentiator. Figure 4. Integrator with shunt resistor
3 4. Components and specifications Figure 5. A low-pass filter. Quantity Description Comments 3 MC 4741C opamp or equivalent 3 1KΩ resistor 3 10KΩ resistor 1 20KΩ resistor μf capacitor μf capacitor Opamp specifications are available from the laboratory web site of this course or manufacturers web sites. Check your component and download the appropriate specifications. 5. Discussion In many circuits whose signals are sine or cosine, the gain (ratio of output amplitude versus input amplitude) varies as function of the signal frequency, e.g. as shown in table 1 below. Figure 6 shows a plot of the gain versus frequency from this table, using the linear scales on both axes. Since the frequency varies over a very wide range, the plot crunches the frequency axis and does not show much about the circuit gain characteristics above the frequency Hz. Table 1. Gain versus frequency data. Frequency Vo amplitude Vi amplitude G= Vo / Vi (Hz) (V) (V) (ratio) - 3 -
4 Gain Frequency, Hz Figure 6. Linear plot of gain versus frequency
5 Another way to plot is to use logarithmic scale. First, the gain values are converted to db (decibel) using the formula: G (db) = 20 log G As an example, a gain G=100 is converted to G(dB)=40 db; a gain G=0.1 is converted to G(dB)=- 20 db. Table 2 is produced from table 1 using this conversion technique. Table 2. Gain (db) versus frequency data. Frequency G G (Hz) (ratio) (db) Next, a semilog plot is constructed. The horizontal axis is the frequency, in logarithmic scale. The vertical axis is the gain in db, in linear scale. The semilog plot of the data in table 2 is shown in figure 7. Once the raw data of gain versus frequency (e.g. as in table 1) is available from measurements or computations, the db conversion and the semilog plot can be produced using software tools such as Matlab, Excel, etc
6 Figure 7. Semilog plot of db gain versus frequency. Figure 7 shows better these characteristics of the circuit: the db gain is relatively fixed at low frequencies, the db gain drops off linearly at high frequencies, and there is a corner in the gain plot between these two frequency ranges. This type of plots is regularly used to study circuit characteristics as functions of frequencies. 6. Pre-lab 6.1 Designs of simple amplifiers For the circuit in figure 1 with power supplies VCC = 12.0 V, VEE = V, and assuming the opamp is ideal, answer the following questions: 1. Design an inverting amplifier using one opamp and two or more resistors. Design it such that it has a gain of -10 (this gain is negative). Pick resistor values that you have in the lab kit. Include a schematic of this circuit with the component values labeled with your completed pre-lab assignment. 2. Simulate this inverting amplifier circuit with SPICE to make sure the circuit works as designed. Look up the textbook to find a non-inverting amplifier circuit using one opamp and two or more resistors. Then assuming the opamp is ideal, answer the following questions: - 6 -
7 3. Design a non-inverting amplifier such that it has a gain of +11 (this gain is positive). Pickresistor values that you have in the lab kit. Include a schematic of this circuit with the component values labeled with your completed pre-lab assignment. 4. Simulate this non-inverting amplifier circuit with SPICE to make sure the circuit works as designed. 6.2 Analysis of integrators and differentiators For the circuit in Figure 2 with power supplies VCC = 12.0 V, VEE = V, and assuming the opamp is ideal, answer the following question: 1. Derive the time-domain equation for V o (t) in terms of V i (t). Show that the circuit performs the function of an integrator. For the circuit in Figure 3 with power supplies VCC = 12.0 V, VEE = V, and assuming the opamp is ideal, answer the following question: 2. Derive the time-domain equation for V o (t) in terms of V i (t). Show that the circuit performs the function of a differentiator. For the circuit in Figure 4 with power supplies VCC = 12.0 V, VEE = V, and assuming the opamp is ideal, answer the following questions: 3. What is the low-frequency gain of this circuit? 4. For frequencies ω>> 1/ (R b C), show that the circuit performs the function of an integrator. 5. Use SPICE transient analysis to simulate this circuit in the time domain using a sine wave input with amplitude 300 mv and frequency 300 Hz. From the SPICE output plot of the input and output waveforms, confirm that this circuit is an integrator. 6. Try to explain the function of the resistor Rb in this circuit. 6.3 Analysis and simulation of an active low-pass filter For the circuit in Figure 5 with power supplies VCC = 12.0 V, VEE = V, assume the opamp is ideal. The input signal is: where the input amplitude A is small to avoid slew-rate limitations. The output signal for the amplitude of v o (t) in terms of the input amplitude A, input frequency ω, and circuit components R and C is - 7 -
8 The ratio of the output amplitude over the input amplitude is called the gain of the circuit. From above, the circuit gain in terms of input frequency ω and circuit components R and C is 1. Use the numerical values of R and C in the gain equation in item 2. Plot the circuit gain (in db values) as function of frequency (from 1 Hz to 100 KHz), using the technique described in the Discussion section. 2. Use SPICE AC analysis to simulate this circuit and generate the gain plot. Compare the SPICE gain plot with your plot in item 1 above. Explain any differences. 3. If the input signal has low frequency, what is the expected gain from these plots in items 1 and 2 above? If the input signal has high frequency, what is the expected gain from these plots? Based on these gain values, explain why the circuit is named low-pass filter. 4. Note that this circuit is topologically similar to the integrator circuit. Try to explain why these two types of circuits are similar. 7. Experimental procedures 7.1 Instruments needed for this experiment The instruments needed for this experiment are: a power supply, a multimeter, a function generator and an oscilloscope. 7.2 Inverting amplifiers Build the circuit in Figure 1 using power supplies V, V and the resistor values from your design in the Pre-lab, section 6.1 item Use a sine wave input with small amplitude so that the output is not affected by the slew rate in this part. Set ch1 to 1X probe gain and DC coupling. From the starting input frequency of 20 Hz and varying it using sequence up to 1 MHz (i.e. set input frequency to 10 Hz, 20 Hz, 50 Hz, 100 Hz, 200 Hz, up to 1 MHz), measure the experimental values of the gain of this circuit at each frequency. Record them in a table for later data analysis. 2. Save a screenshot from the scope display with both waveforms at the frequency 100 KHz. Turn this screenshot in as part of your lab report
9 Turn in: a table of gain vs frequency and a screenshot 7.3 Integrators 1. Build the circuit in Figure 4 with power supplies V, V. Apply a sine wave input signal with amplitude 600 mv, DC offset 0V and frequency 1200 Hz. Display the input signal on channel 1 of the oscilloscope. 2. Display V o on Channel 2 and adjust the timebase to display 2 to 3 complete cycles of the signals. Set both ch-1 and ch-2 to 1X probe gain and DC coupling. 3. Save a screenshot from the scope display with both waveforms to confirm that the circuit is an integrator. Turn this screenshot in as part of your lab report. 4. Change the input signal to a square wave with the same 600 mv amplitude, DC offset 0V, and frequency 1200 Hz. Save a screenshot from the scope display with both waveforms to confirm that the circuit is still an integrator. Turn this screenshot in as part of your lab report. 5. Repeat item 4 above using a triangular input signal with same amplitude and frequency. Turn this screenshot in as part of your lab report. 6. Now change the input back to a sine wave as in item 1. Remove the resistor R b while running the function generator and Data capture. Align two waveforms so that is will be easier to see the output. What happens to the output signal? Explain the phenomenon you observe on the oscilloscope. Re-insert the resistor R b and verify that the circuit functions as designed. Turn in: screenshots and answer #6 7.4 Low-pass filters 1. Build the circuit in Figure 5 with power supplies V, V. Use a sine wave of amplitude 200 mv as an input signal (see item 2 below for frequency) and display both the input and output signals on the oscilloscope (2 to 3 complete cycles). Set probe gain 1X and DC coupling. 2. Vary the input signal frequency in sequence from 20 Hz to 100 KHz. At each frequency, measure the gain of the circuit, using the data from the oscilloscope display. Keep this data in a table for later plotting. Turn in: a table of gain vs frequency 8. Data analysis 8.1 Inverting amplifiers - 9 -
10 1. Compare the experimental gain measured in section 7.2 item 1 with the calculated gain in the pre-lab and with the gain as simulated by SPICE. Explain any difference between these values. 2. From the table of data in section 7.2 item 1, plot the gain of this circuit as db versus frequency, using the technique described in the Discussion section. 8.2 Integrators 1. Explain any difference between the SPICE output in section 6.2 item 5 and the experimental data in section 7.3 item With the experimental observation in section 7.3 item 6, explain the function of the resistor R b. 8.3 Low-pass filters 1. From the data in section 7.4 item 2, plot the gain (in db) of the circuit as function of frequency(using the technique described in the Discussion section) and compare it with the plots in section6.3 item 3 and in section 6.3 item 4 (SPICE plot). Explain any differences between these 3 plots
Transmit filter designs for ADSL modems
 EE 233 Laboratory-4 1. Objectives Transmit filter designs for ADSL modems Design a filter from a given topology and specifications. Analyze the characteristics of the designed filter. Use SPICE to verify
EE 233 Laboratory-4 1. Objectives Transmit filter designs for ADSL modems Design a filter from a given topology and specifications. Analyze the characteristics of the designed filter. Use SPICE to verify
Transmit filter designs for ADSL modems
 Transmit filter designs for ADSL modems 1. OBJECTIVES... 2 2. REFERENCE... 2 3. CIRCUITS... 2 4. COMPONENTS AND SPECIFICATIONS... 3 5. DISCUSSION... 3 6. PRE-LAB... 4 6.1 RECORDING SPECIFIED OPAMP PARAMETERS
Transmit filter designs for ADSL modems 1. OBJECTIVES... 2 2. REFERENCE... 2 3. CIRCUITS... 2 4. COMPONENTS AND SPECIFICATIONS... 3 5. DISCUSSION... 3 6. PRE-LAB... 4 6.1 RECORDING SPECIFIED OPAMP PARAMETERS
EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response
 EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of active signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Active Filters, Op-Amp Filters, Bode plots Suggested
EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of active signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Active Filters, Op-Amp Filters, Bode plots Suggested
University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2009 LAB 2 NON IDEAL OPAMPS
 University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2009 LAB 2 NON IDEAL OPAMPS Issued 10/5/2008 Pre Lab Completed 10/12/2008 Lab Due in Lecture 10/21/2008 Introduction In this lab you will characterize
University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2009 LAB 2 NON IDEAL OPAMPS Issued 10/5/2008 Pre Lab Completed 10/12/2008 Lab Due in Lecture 10/21/2008 Introduction In this lab you will characterize
Step Response of RC Circuits
 EE 233 Laboratory-1 Step Response of RC Circuits 1 Objectives Measure the internal resistance of a signal source (eg an arbitrary waveform generator) Measure the output waveform of simple RC circuits excited
EE 233 Laboratory-1 Step Response of RC Circuits 1 Objectives Measure the internal resistance of a signal source (eg an arbitrary waveform generator) Measure the output waveform of simple RC circuits excited
Experiment 1.A. Working with Lab Equipment. ECEN 2270 Electronics Design Laboratory 1
 .A Working with Lab Equipment Electronics Design Laboratory 1 1.A.0 1.A.1 3 1.A.4 Procedures Turn in your Pre Lab before doing anything else Setup the lab waveform generator to output desired test waveforms,
.A Working with Lab Equipment Electronics Design Laboratory 1 1.A.0 1.A.1 3 1.A.4 Procedures Turn in your Pre Lab before doing anything else Setup the lab waveform generator to output desired test waveforms,
ECE 2201 PRELAB 6 BJT COMMON EMITTER (CE) AMPLIFIER
 ECE 2201 PRELAB 6 BJT COMMON EMITTER (CE) AMPLIFIER Hand Analysis P1. Determine the DC bias for the BJT Common Emitter Amplifier circuit of Figure 61 (in this lab) including the voltages V B, V C and V
ECE 2201 PRELAB 6 BJT COMMON EMITTER (CE) AMPLIFIER Hand Analysis P1. Determine the DC bias for the BJT Common Emitter Amplifier circuit of Figure 61 (in this lab) including the voltages V B, V C and V
EE 368 Electronics Lab. Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2)
 EE 368 Electronics Lab Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) 1 Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) Objectives To gain experience with Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp). To
EE 368 Electronics Lab Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) 1 Experiment 10 Operational Amplifier Applications (2) Objectives To gain experience with Operational Amplifier (Op-Amp). To
Lab 6 Prelab Grading Sheet
 Lab 6 Prelab Grading Sheet NAME: Read through the Background section of this lab and print the prelab and in-lab grading sheets. Then complete the steps below and fill in the Prelab 6 Grading Sheet. You
Lab 6 Prelab Grading Sheet NAME: Read through the Background section of this lab and print the prelab and in-lab grading sheets. Then complete the steps below and fill in the Prelab 6 Grading Sheet. You
ECEN 325 Lab 5: Operational Amplifiers Part III
 ECEN Lab : Operational Amplifiers Part III Objectives The purpose of the lab is to study some of the opamp configurations commonly found in practical applications and also investigate the non-idealities
ECEN Lab : Operational Amplifiers Part III Objectives The purpose of the lab is to study some of the opamp configurations commonly found in practical applications and also investigate the non-idealities
ECEN Network Analysis Section 3. Laboratory Manual
 ECEN 3714----Network Analysis Section 3 Laboratory Manual LAB 07: Active Low Pass Filter Oklahoma State University School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Section 3 Laboratory manual - 1 - Spring
ECEN 3714----Network Analysis Section 3 Laboratory Manual LAB 07: Active Low Pass Filter Oklahoma State University School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Section 3 Laboratory manual - 1 - Spring
EE 233 Circuit Theory Lab 3: First-Order Filters
 EE 233 Circuit Theory Lab 3: First-Order Filters Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Precautions... 1 3 Prelab Exercises... 2 3.1 Inverting Amplifier... 3 3.2 Non-Inverting Amplifier... 4 3.3 Integrating
EE 233 Circuit Theory Lab 3: First-Order Filters Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Precautions... 1 3 Prelab Exercises... 2 3.1 Inverting Amplifier... 3 3.2 Non-Inverting Amplifier... 4 3.3 Integrating
PHYSICS 330 LAB Operational Amplifier Frequency Response
 PHYSICS 330 LAB Operational Amplifier Frequency Response Objectives: To measure and plot the frequency response of an operational amplifier circuit. History: Operational amplifiers are among the most widely
PHYSICS 330 LAB Operational Amplifier Frequency Response Objectives: To measure and plot the frequency response of an operational amplifier circuit. History: Operational amplifiers are among the most widely
BME 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters
 BME 35 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of passive filters. Laboratory Equipment: Agilent Oscilloscope Model 546A Agilent Function Generator
BME 35 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of passive filters. Laboratory Equipment: Agilent Oscilloscope Model 546A Agilent Function Generator
EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response
 EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of passive signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Passive filters, Frequency domain, Bode plots
EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of passive signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Passive filters, Frequency domain, Bode plots
LABORATORY 4. Palomar College ENGR210 Spring 2017 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17
 LABORATORY 4 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17 OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this lab is to evaluate the transient and steady-state circuit response of first order and second order circuits. MINIMUM EQUIPMENT LIST: You will
LABORATORY 4 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17 OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this lab is to evaluate the transient and steady-state circuit response of first order and second order circuits. MINIMUM EQUIPMENT LIST: You will
Operational Amplifiers: Part II
 1. Introduction Operational Amplifiers: Part II The name "operational amplifier" comes from this amplifier's ability to perform mathematical operations. Three good examples of this are the summing amplifier,
1. Introduction Operational Amplifiers: Part II The name "operational amplifier" comes from this amplifier's ability to perform mathematical operations. Three good examples of this are the summing amplifier,
Operational Amplifier Circuits
 ECE VIII. Basic 5 Operational Amplifier Circuits Lab 8 In this lab we will verify the operation of inverting and noninverting amplifiers constructed using Operational Amplifiers. We will also observe the
ECE VIII. Basic 5 Operational Amplifier Circuits Lab 8 In this lab we will verify the operation of inverting and noninverting amplifiers constructed using Operational Amplifiers. We will also observe the
ECE4902 C Lab 7
 ECE902 C2012 - Lab MOSFET Differential Amplifier Resistive Load Active Load PURPOSE: The primary purpose of this lab is to measure the performance of the differential amplifier. This is an important topology
ECE902 C2012 - Lab MOSFET Differential Amplifier Resistive Load Active Load PURPOSE: The primary purpose of this lab is to measure the performance of the differential amplifier. This is an important topology
University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2008 LAB 4 SINGLE STAGE AMPLIFIER
 University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2008 LAB 4 SINGLE STAGE AMPLIFIER Issued 10/27/2008 Report due in Lecture 11/10/2008 Introduction In this lab you will characterize a 2N3904 NPN
University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2008 LAB 4 SINGLE STAGE AMPLIFIER Issued 10/27/2008 Report due in Lecture 11/10/2008 Introduction In this lab you will characterize a 2N3904 NPN
Experiment #7: Designing and Measuring a Common-Emitter Amplifier
 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #7: Designing and Measuring a Common-Emitter Amplifier
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #7: Designing and Measuring a Common-Emitter Amplifier
CHARACTERIZATION OF OP-AMP
 EXPERIMENT 4 CHARACTERIZATION OF OP-AMP OBJECTIVES 1. To sketch and briefly explain an operational amplifier circuit symbol and identify all terminals. 2. To list the amplifier stages in a typical op-amp
EXPERIMENT 4 CHARACTERIZATION OF OP-AMP OBJECTIVES 1. To sketch and briefly explain an operational amplifier circuit symbol and identify all terminals. 2. To list the amplifier stages in a typical op-amp
Experiment #8: Designing and Measuring a Common-Collector Amplifier
 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #8: Designing and Measuring a Common-Collector Amplifier
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #8: Designing and Measuring a Common-Collector Amplifier
1. Hand Calculations (in a manner suitable for submission) For the circuit in Fig. 1 with f = 7.2 khz and a source vin () t 1.
 Objectives The purpose of this laboratory project is to introduce to equipment, measurement techniques, and simulations commonly used in AC circuit analysis. In this laboratory session, each student will:
Objectives The purpose of this laboratory project is to introduce to equipment, measurement techniques, and simulations commonly used in AC circuit analysis. In this laboratory session, each student will:
R 1 R 2. (3) Suppose you have two ac signals, which we ll call signals A and B, which have peak-to-peak amplitudes of 30 mv and 600 mv, respectively.
 29:128 Homework Problems 29:128 Homework 0 reference: Chapter 1 of Horowitz and Hill (1) In the circuit shown below, V in = 9 V, R 1 = 1.5 kω, R 2 = 5.6 kω, (a) Calculate V out (b) Calculate the power
29:128 Homework Problems 29:128 Homework 0 reference: Chapter 1 of Horowitz and Hill (1) In the circuit shown below, V in = 9 V, R 1 = 1.5 kω, R 2 = 5.6 kω, (a) Calculate V out (b) Calculate the power
ECE 3155 Experiment I AC Circuits and Bode Plots Rev. lpt jan 2013
 Signature Name (print, please) Lab section # Lab partner s name (if any) Date(s) lab was performed ECE 3155 Experiment I AC Circuits and Bode Plots Rev. lpt jan 2013 In this lab we will demonstrate basic
Signature Name (print, please) Lab section # Lab partner s name (if any) Date(s) lab was performed ECE 3155 Experiment I AC Circuits and Bode Plots Rev. lpt jan 2013 In this lab we will demonstrate basic
FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF COMMON COLLECTOR AMPLIFIER
 Exp. No #5 FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF COMMON COLLECTOR AMPLIFIER Date: OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to analyze and plot the frequency response of a common collector amplifier. EQUIPMENT AND COMPONENTS
Exp. No #5 FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF COMMON COLLECTOR AMPLIFIER Date: OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to analyze and plot the frequency response of a common collector amplifier. EQUIPMENT AND COMPONENTS
ECE Lab #4 OpAmp Circuits with Negative Feedback and Positive Feedback
 ECE 214 Lab #4 OpAmp Circuits with Negative Feedback and Positive Feedback 20 February 2018 Introduction: The TL082 Operational Amplifier (OpAmp) and the Texas Instruments Analog System Lab Kit Pro evaluation
ECE 214 Lab #4 OpAmp Circuits with Negative Feedback and Positive Feedback 20 February 2018 Introduction: The TL082 Operational Amplifier (OpAmp) and the Texas Instruments Analog System Lab Kit Pro evaluation
ELEG 205 Analog Circuits Laboratory Manual Fall 2016
 ELEG 205 Analog Circuits Laboratory Manual Fall 2016 University of Delaware Dr. Mark Mirotznik Kaleb Burd Patrick Nicholson Aric Lu Kaeini Ekong 1 Table of Contents Lab 1: Intro 3 Lab 2: Resistive Circuits
ELEG 205 Analog Circuits Laboratory Manual Fall 2016 University of Delaware Dr. Mark Mirotznik Kaleb Burd Patrick Nicholson Aric Lu Kaeini Ekong 1 Table of Contents Lab 1: Intro 3 Lab 2: Resistive Circuits
Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 11: Lab Projects
 Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 11: Lab Projects 11.2.1: Signals with Multiple Frequency Components Overview: In this lab project, we will calculate the magnitude response of an electrical circuit and
Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 11: Lab Projects 11.2.1: Signals with Multiple Frequency Components Overview: In this lab project, we will calculate the magnitude response of an electrical circuit and
EE 2274 RC and Op Amp Circuit Completed Prior to Coming to Lab. Prelab Part I: RC Circuit
 EE 2274 RC and Op Amp Circuit Completed Prior to Coming to Lab Prelab Part I: RC Circuit 1. Design a high pass filter (Fig. 1) which has a break point f b = 1 khz at 3dB below the midband level (the -3dB
EE 2274 RC and Op Amp Circuit Completed Prior to Coming to Lab Prelab Part I: RC Circuit 1. Design a high pass filter (Fig. 1) which has a break point f b = 1 khz at 3dB below the midband level (the -3dB
EE4902 C Lab 7
 EE4902 C2007 - Lab 7 MOSFET Differential Amplifier Resistive Load Active Load PURPOSE: The primary purpose of this lab is to measure the performance of the differential amplifier. This is an important
EE4902 C2007 - Lab 7 MOSFET Differential Amplifier Resistive Load Active Load PURPOSE: The primary purpose of this lab is to measure the performance of the differential amplifier. This is an important
EE 233 Circuit Theory Lab 2: Amplifiers
 EE 233 Circuit Theory Lab 2: Amplifiers Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Precautions... 1 3 Prelab Exercises... 2 3.1 LM348N Op-amp Parameters... 2 3.2 Voltage Follower Circuit Analysis... 2 3.2.1
EE 233 Circuit Theory Lab 2: Amplifiers Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Precautions... 1 3 Prelab Exercises... 2 3.1 LM348N Op-amp Parameters... 2 3.2 Voltage Follower Circuit Analysis... 2 3.2.1
Digital Applications of the Operational Amplifier
 Lab Procedure 1. Objective This project will show the versatile operation of an operational amplifier in a voltage comparator (Schmitt Trigger) circuit and a sample and hold circuit. 2. Components Qty
Lab Procedure 1. Objective This project will show the versatile operation of an operational amplifier in a voltage comparator (Schmitt Trigger) circuit and a sample and hold circuit. 2. Components Qty
LABORATORY 5 v3 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
 University of California Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 100, Professor Bernhard Boser LABORATORY 5 v3 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER Integrated operational amplifiers opamps
University of California Berkeley Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences EECS 100, Professor Bernhard Boser LABORATORY 5 v3 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER Integrated operational amplifiers opamps
LAB 4 : FET AMPLIFIERS
 LEARNING OUTCOME: LAB 4 : FET AMPLIFIERS In this lab, students design and implement single-stage FET amplifiers and explore the frequency response of the real amplifiers. Breadboard and the Analog Discovery
LEARNING OUTCOME: LAB 4 : FET AMPLIFIERS In this lab, students design and implement single-stage FET amplifiers and explore the frequency response of the real amplifiers. Breadboard and the Analog Discovery
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 02139
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 019.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Laboratory No. READING ASSIGNMENT
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 019.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Laboratory No. READING ASSIGNMENT
Laboratory 6. Lab 6. Operational Amplifier Circuits. Required Components: op amp 2 1k resistor 4 10k resistors 1 100k resistor 1 0.
 Laboratory 6 Operational Amplifier Circuits Required Components: 1 741 op amp 2 1k resistor 4 10k resistors 1 100k resistor 1 0.1 F capacitor 6.1 Objectives The operational amplifier is one of the most
Laboratory 6 Operational Amplifier Circuits Required Components: 1 741 op amp 2 1k resistor 4 10k resistors 1 100k resistor 1 0.1 F capacitor 6.1 Objectives The operational amplifier is one of the most
BME/ISE 3511 Laboratory One - Laboratory Equipment for Measurement. Introduction to biomedical electronic laboratory instrumentation and measurements.
 BME/ISE 3511 Laboratory One - Laboratory Equipment for Measurement Learning Objectives: Introduction to biomedical electronic laboratory instrumentation and measurements. Supplies and Components: Breadboard
BME/ISE 3511 Laboratory One - Laboratory Equipment for Measurement Learning Objectives: Introduction to biomedical electronic laboratory instrumentation and measurements. Supplies and Components: Breadboard
CHARACTERISTICS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS - I
 CHARACTERISTICS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS - I OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to examine non-ideal characteristics of an operational amplifier. The characteristics that are investigated include
CHARACTERISTICS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS - I OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to examine non-ideal characteristics of an operational amplifier. The characteristics that are investigated include
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 5 GAIN-BANDWIDTH PRODUCT AND SLEW RATE OBJECTIVES In this experiment the student will explore two
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EXPERIMENT 5 GAIN-BANDWIDTH PRODUCT AND SLEW RATE OBJECTIVES In this experiment the student will explore two
Assignment 11. 1) Using the LM741 op-amp IC a circuit is designed as shown, then find the output waveform for an input of 5kHz
 Assignment 11 1) Using the LM741 op-amp IC a circuit is designed as shown, then find the output waveform for an input of 5kHz Vo = 1 x R1Cf 0 Vin t dt, voltage output for the op amp integrator 0.1 m 1
Assignment 11 1) Using the LM741 op-amp IC a circuit is designed as shown, then find the output waveform for an input of 5kHz Vo = 1 x R1Cf 0 Vin t dt, voltage output for the op amp integrator 0.1 m 1
BME 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Six - Active Filters
 BME 5 Bioelectronics Laboratory Six - Active Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of active filters. Describe the differences between active and passive filters. Laboratory Equipment:
BME 5 Bioelectronics Laboratory Six - Active Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of active filters. Describe the differences between active and passive filters. Laboratory Equipment:
Introduction to basic laboratory instruments
 BEE 233 Laboratory-1 Introduction to basic laboratory instruments 1. Objectives To learn safety procedures in the laboratory. To learn how to use basic laboratory instruments: power supply, function generator,
BEE 233 Laboratory-1 Introduction to basic laboratory instruments 1. Objectives To learn safety procedures in the laboratory. To learn how to use basic laboratory instruments: power supply, function generator,
ECE4902 C Lab 5 MOSFET Common Source Amplifier with Active Load Bandwidth of MOSFET Common Source Amplifier: Resistive Load / Active Load
 ECE4902 C2012 - Lab 5 MOSFET Common Source Amplifier with Active Load Bandwidth of MOSFET Common Source Amplifier: Resistive Load / Active Load PURPOSE: The primary purpose of this lab is to measure the
ECE4902 C2012 - Lab 5 MOSFET Common Source Amplifier with Active Load Bandwidth of MOSFET Common Source Amplifier: Resistive Load / Active Load PURPOSE: The primary purpose of this lab is to measure the
EE431 Lab 1 Operational Amplifiers
 Feb. 10, 2015 Report all measured data and show all calculations Introduction The purpose of this laboratory exercise is for the student to gain experience with measuring and observing the effects of common
Feb. 10, 2015 Report all measured data and show all calculations Introduction The purpose of this laboratory exercise is for the student to gain experience with measuring and observing the effects of common
ECE ECE285. Electric Circuit Analysis I. Spring Nathalia Peixoto. Rev.2.0: Rev Electric Circuits I
 ECE285 Electric Circuit Analysis I Spring 2014 Nathalia Peixoto Rev.2.0: 140124. Rev 2.1. 140813 1 Lab reports Background: these 9 experiments are designed as simple building blocks (like Legos) and students
ECE285 Electric Circuit Analysis I Spring 2014 Nathalia Peixoto Rev.2.0: 140124. Rev 2.1. 140813 1 Lab reports Background: these 9 experiments are designed as simple building blocks (like Legos) and students
University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2008 LAB 2 ACTIVE FILTERS
 University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2008 LAB 2 ACTIVE FILTERS Issued 9/22/2008 Pre Lab Completed 9/29/2008 Lab Due in Lecture 10/6/2008 Introduction In this lab you will design a
University of Michigan EECS 311: Electronic Circuits Fall 2008 LAB 2 ACTIVE FILTERS Issued 9/22/2008 Pre Lab Completed 9/29/2008 Lab Due in Lecture 10/6/2008 Introduction In this lab you will design a
Experiment 8 Frequency Response
 Experiment 8 Frequency Response W.T. Yeung, R.A. Cortina, and R.T. Howe UC Berkeley EE 105 Spring 2005 1.0 Objective This lab will introduce the student to frequency response of circuits. The student will
Experiment 8 Frequency Response W.T. Yeung, R.A. Cortina, and R.T. Howe UC Berkeley EE 105 Spring 2005 1.0 Objective This lab will introduce the student to frequency response of circuits. The student will
Laboratory Project 1: AC Circuit Measurements and Simulation
 Objectives The purpose of this laboratory project is to introduce to equipment, measurement techniques, and simulations commonly used in C circuit analysis. In this laboratory session, each student will:
Objectives The purpose of this laboratory project is to introduce to equipment, measurement techniques, and simulations commonly used in C circuit analysis. In this laboratory session, each student will:
Lab 9 Frequency Domain
 Lab 9 Frequency Domain 1 Components Required Resistors Capacitors Function Generator Multimeter Oscilloscope 2 Filter Design Filters are electric components that allow applying different operations to
Lab 9 Frequency Domain 1 Components Required Resistors Capacitors Function Generator Multimeter Oscilloscope 2 Filter Design Filters are electric components that allow applying different operations to
Assignment 8 Analyzing Operational Amplifiers in MATLAB and PSpice
 ECEL 301 ECE Laboratory I Dr. A. Fontecchio Assignment 8 Analyzing Operational Amplifiers in MATLAB and PSpice Goal Characterize critical parameters of the inverting or non-inverting opampbased amplifiers.
ECEL 301 ECE Laboratory I Dr. A. Fontecchio Assignment 8 Analyzing Operational Amplifiers in MATLAB and PSpice Goal Characterize critical parameters of the inverting or non-inverting opampbased amplifiers.
CHARACTERISTICS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS - II
 CHARACTERISTICS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS - II OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to examine non-ideal characteristics of an operational amplifier. The characteristics that are investigated include
CHARACTERISTICS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS - II OBJECTIVE The purpose of the experiment is to examine non-ideal characteristics of an operational amplifier. The characteristics that are investigated include
Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks
 OPTI 380B Intermediate Optics Laboratory Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks Objectives: Lean how to use: Function of an oscilloscope probe. Characterization of capacitors and inductors
OPTI 380B Intermediate Optics Laboratory Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks Objectives: Lean how to use: Function of an oscilloscope probe. Characterization of capacitors and inductors
Filters And Waveform Shaping
 Physics 3330 Experiment #3 Fall 2001 Purpose Filters And Waveform Shaping The aim of this experiment is to study the frequency filtering properties of passive (R, C, and L) circuits for sine waves, and
Physics 3330 Experiment #3 Fall 2001 Purpose Filters And Waveform Shaping The aim of this experiment is to study the frequency filtering properties of passive (R, C, and L) circuits for sine waves, and
Op-Amp Simulation Part II
 Op-Amp Simulation Part II EE/CS 5720/6720 This assignment continues the simulation and characterization of a simple operational amplifier. Turn in a copy of this assignment with answers in the appropriate
Op-Amp Simulation Part II EE/CS 5720/6720 This assignment continues the simulation and characterization of a simple operational amplifier. Turn in a copy of this assignment with answers in the appropriate
E84 Lab 3: Transistor
 E84 Lab 3: Transistor Cherie Ho and Siyi Hu April 18, 2016 Transistor Testing 1. Take screenshots of both the input and output characteristic plots observed on the semiconductor curve tracer with the following
E84 Lab 3: Transistor Cherie Ho and Siyi Hu April 18, 2016 Transistor Testing 1. Take screenshots of both the input and output characteristic plots observed on the semiconductor curve tracer with the following
Welcome to your second Electronics Laboratory Session. In this session you will learn about how to use resistors, capacitors and inductors to make
 Welcome to your second Electronics Laboratory Session. In this session you will learn about how to use resistors, capacitors and inductors to make simple circuits. You will find out how these circuits
Welcome to your second Electronics Laboratory Session. In this session you will learn about how to use resistors, capacitors and inductors to make simple circuits. You will find out how these circuits
Class #16: Experiment Matlab and Data Analysis
 Class #16: Experiment Matlab and Data Analysis Purpose: The objective of this experiment is to add to our Matlab skill set so that data can be easily plotted and analyzed with simple tools. Background:
Class #16: Experiment Matlab and Data Analysis Purpose: The objective of this experiment is to add to our Matlab skill set so that data can be easily plotted and analyzed with simple tools. Background:
EE320L Electronics I. Laboratory. Laboratory Exercise #2. Basic Op-Amp Circuits. Angsuman Roy. Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
 EE320L Electronics I Laboratory Laboratory Exercise #2 Basic Op-Amp Circuits By Angsuman Roy Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, Las Vegas Objective: The purpose of
EE320L Electronics I Laboratory Laboratory Exercise #2 Basic Op-Amp Circuits By Angsuman Roy Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Nevada, Las Vegas Objective: The purpose of
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 7 SIGNAL CONDITIONING AND LOADING
 ME 365 EXPERIMENT 7 SIGNAL CONDITIONING AND LOADING Objectives: To familiarize the student with the concepts of signal conditioning. At the end of the lab, the student should be able to: Understand the
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 7 SIGNAL CONDITIONING AND LOADING Objectives: To familiarize the student with the concepts of signal conditioning. At the end of the lab, the student should be able to: Understand the
ECE3204 D2015 Lab 1. See suggested breadboard configuration on following page!
 ECE3204 D2015 Lab 1 The Operational Amplifier: Inverting and Non-inverting Gain Configurations Gain-Bandwidth Product Relationship Frequency Response Limitation Transfer Function Measurement DC Errors
ECE3204 D2015 Lab 1 The Operational Amplifier: Inverting and Non-inverting Gain Configurations Gain-Bandwidth Product Relationship Frequency Response Limitation Transfer Function Measurement DC Errors
Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5)
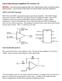 Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy
Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy
Experiment #6: Biasing an NPN BJT Introduction to CE, CC, and CB Amplifiers
 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #6: Biasing an NPN BJT Introduction to CE, CC, and CB
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2115: ENGINEERING ELECTRONICS LABORATORY Experiment #6: Biasing an NPN BJT Introduction to CE, CC, and CB
Operational Amplifiers 2 Active Filters ReadMeFirst
 Operational Amplifiers 2 Active Filters ReadMeFirst Lab Summary In this lab you will build two active filters on a breadboard, using an op-amp, resistors, and capacitors, and take data for the magnitude
Operational Amplifiers 2 Active Filters ReadMeFirst Lab Summary In this lab you will build two active filters on a breadboard, using an op-amp, resistors, and capacitors, and take data for the magnitude
Common-source Amplifiers
 Lab 1: Common-source Amplifiers Introduction The common-source amplifier is one of the basic amplifiers in CMOS analog circuits. Because of its very high input impedance, relatively high gain, low noise,
Lab 1: Common-source Amplifiers Introduction The common-source amplifier is one of the basic amplifiers in CMOS analog circuits. Because of its very high input impedance, relatively high gain, low noise,
Lab 2: Common Emitter Design: Part 2
 Lab 2: Common Emitter Design: Part 2 ELE 344 University of Rhode Island, Kingston, RI 02881-0805, U.S.A. 1 Linearity in High Gain Amplifiers The common emitter amplifier, shown in figure 1, will provide
Lab 2: Common Emitter Design: Part 2 ELE 344 University of Rhode Island, Kingston, RI 02881-0805, U.S.A. 1 Linearity in High Gain Amplifiers The common emitter amplifier, shown in figure 1, will provide
ELEG 205 Analog Circuits Laboratory Manual Fall 2017
 ELEG 205 Analog Circuits Laboratory Manual Fall 2017 University of Delaware Dr. Mark Mirotznik Kaleb Burd Aric Lu Patrick Nicholson Colby Banbury Table of Contents Policies Policy Page 3 Labs Lab 1: Intro
ELEG 205 Analog Circuits Laboratory Manual Fall 2017 University of Delaware Dr. Mark Mirotznik Kaleb Burd Aric Lu Patrick Nicholson Colby Banbury Table of Contents Policies Policy Page 3 Labs Lab 1: Intro
Homework Assignment 03
 Homework Assignment 03 Question 1 (Short Takes), 2 points each unless otherwise noted. 1. Two 0.68 μf capacitors are connected in series across a 10 khz sine wave signal source. The total capacitive reactance
Homework Assignment 03 Question 1 (Short Takes), 2 points each unless otherwise noted. 1. Two 0.68 μf capacitors are connected in series across a 10 khz sine wave signal source. The total capacitive reactance
UNIVERSITY OF UTAH ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT
 UNIVERSITY OF UTAH ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT ECE 3110 LAB EXPERIMENT NO. 4 CLASS AB POWER OUTPUT STAGE Objective: In this laboratory exercise you will build and characterize a class AB power output
UNIVERSITY OF UTAH ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT ECE 3110 LAB EXPERIMENT NO. 4 CLASS AB POWER OUTPUT STAGE Objective: In this laboratory exercise you will build and characterize a class AB power output
Tektronix Courseware. Academic Labs. Sample Labs from Popular Electrical and Electronics Engineering Curriculum
 Tektronix Courseware Academic Labs Sample Labs from Popular Electrical and Electronics Engineering Curriculum March 3, 2014 HalfWaveRectifier -- Overview OBJECTIVES After performing this lab exercise,
Tektronix Courseware Academic Labs Sample Labs from Popular Electrical and Electronics Engineering Curriculum March 3, 2014 HalfWaveRectifier -- Overview OBJECTIVES After performing this lab exercise,
Theory: The idea of this oscillator comes from the idea of positive feedback, which is described by Figure 6.1. Figure 6.1: Positive Feedback
 Name1 Name2 12/2/10 ESE 319 Lab 6: Colpitts Oscillator Introduction: This lab introduced the concept of feedback in combination with bipolar junction transistors. The goal of this lab was to first create
Name1 Name2 12/2/10 ESE 319 Lab 6: Colpitts Oscillator Introduction: This lab introduced the concept of feedback in combination with bipolar junction transistors. The goal of this lab was to first create
Exp. #2-6 : Measurement of the Characteristics of,, and Circuits by Using an Oscilloscope
 PAGE 1/14 Exp. #2-6 : Measurement of the Characteristics of,, and Circuits by Using an Oscilloscope Student ID Major Name Team No. Experiment Lecturer Student's Mentioned Items Experiment Class Date Submission
PAGE 1/14 Exp. #2-6 : Measurement of the Characteristics of,, and Circuits by Using an Oscilloscope Student ID Major Name Team No. Experiment Lecturer Student's Mentioned Items Experiment Class Date Submission
UNIVERSITY OF PENNSYLVANIA EE 206
 UNIVERSITY OF PENNSYLVANIA EE 206 TRANSISTOR BIASING CIRCUITS Introduction: One of the most critical considerations in the design of transistor amplifier stages is the ability of the circuit to maintain
UNIVERSITY OF PENNSYLVANIA EE 206 TRANSISTOR BIASING CIRCUITS Introduction: One of the most critical considerations in the design of transistor amplifier stages is the ability of the circuit to maintain
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 02139
 DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 019 Spring Term 00.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Laboratory No.
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING AND COMPUTER SCIENCE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY CAMBRIDGE, MASSACHUSETTS 019 Spring Term 00.101 Introductory Analog Electronics Laboratory Laboratory No.
Laboratory 9. Required Components: Objectives. Optional Components: Operational Amplifier Circuits (modified from lab text by Alciatore)
 Laboratory 9 Operational Amplifier Circuits (modified from lab text by Alciatore) Required Components: 1x 741 op-amp 2x 1k resistors 4x 10k resistors 1x l00k resistor 1x 0.1F capacitor Optional Components:
Laboratory 9 Operational Amplifier Circuits (modified from lab text by Alciatore) Required Components: 1x 741 op-amp 2x 1k resistors 4x 10k resistors 1x l00k resistor 1x 0.1F capacitor Optional Components:
2. BAND-PASS NOISE MEASUREMENTS
 2. BAND-PASS NOISE MEASUREMENTS 2.1 Object The objectives of this experiment are to use the Dynamic Signal Analyzer or DSA to measure the spectral density of a noise signal, to design a second-order band-pass
2. BAND-PASS NOISE MEASUREMENTS 2.1 Object The objectives of this experiment are to use the Dynamic Signal Analyzer or DSA to measure the spectral density of a noise signal, to design a second-order band-pass
Lab 6: Instrumentation Amplifier
 Lab 6: Instrumentation Amplifier INTRODUCTION: A fundamental building block for electrical measurements of biological signals is an instrumentation amplifier. In this lab, you will explore the operation
Lab 6: Instrumentation Amplifier INTRODUCTION: A fundamental building block for electrical measurements of biological signals is an instrumentation amplifier. In this lab, you will explore the operation
Laboratory 4 Operational Amplifier Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of California, San Diego MAE170
 Laboratory 4 Operational Amplifier Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of California, San Diego MAE170 Megan Ong Diana Wu Wong B01 Tuesday 11am April 28 st, 2015 Abstract: The
Laboratory 4 Operational Amplifier Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering University of California, San Diego MAE170 Megan Ong Diana Wu Wong B01 Tuesday 11am April 28 st, 2015 Abstract: The
ECE 310L : LAB 9. Fall 2012 (Hay)
 ECE 310L : LAB 9 PRELAB ASSIGNMENT: Read the lab assignment in its entirety. 1. For the circuit shown in Figure 3, compute a value for R1 that will result in a 1N5230B zener diode current of approximately
ECE 310L : LAB 9 PRELAB ASSIGNMENT: Read the lab assignment in its entirety. 1. For the circuit shown in Figure 3, compute a value for R1 that will result in a 1N5230B zener diode current of approximately
29:128 Homework Problems
 29:128 Homework Problems Revised 22 Feb 2012 29:128 Homework 1 (15 points) references: Sections 1.6-1.7 & 4.8, Meyer Chapter 1 of Horowitz and Hill, 2nd Edition (1) In the circuit shown below, V in = 9
29:128 Homework Problems Revised 22 Feb 2012 29:128 Homework 1 (15 points) references: Sections 1.6-1.7 & 4.8, Meyer Chapter 1 of Horowitz and Hill, 2nd Edition (1) In the circuit shown below, V in = 9
Low_Pass_Filter_1st_Order -- Overview
 Low_Pass_Filter_1st_Order -- Overview 1 st Order Low Pass Filter Objectives: After performing this lab exercise, learner will be able to: Understand and comprehend working of opamp Comprehend basics of
Low_Pass_Filter_1st_Order -- Overview 1 st Order Low Pass Filter Objectives: After performing this lab exercise, learner will be able to: Understand and comprehend working of opamp Comprehend basics of
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PERLIS
 UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PERLIS ANALOG ELECTRONICS CIRCUIT II EKT 214 Semester II (2012/2013) EXPERIMENT # 3 OP-AMP (DIFFERENTIATOR & INTEGRATOR) Analog Electronics II (EKT214) 2012/2013 EXPERIMENT 3 Op-Amp
UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PERLIS ANALOG ELECTRONICS CIRCUIT II EKT 214 Semester II (2012/2013) EXPERIMENT # 3 OP-AMP (DIFFERENTIATOR & INTEGRATOR) Analog Electronics II (EKT214) 2012/2013 EXPERIMENT 3 Op-Amp
2. SINGLE STAGE BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR (BJT) AMPLIFIERS
 2. SINGLE STAGE BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR (BJT) AMPLIFIERS I. Objectives and Contents The goal of this experiment is to become familiar with BJT as an amplifier and to evaluate the basic configurations
2. SINGLE STAGE BIPOLAR JUNCTION TRANSISTOR (BJT) AMPLIFIERS I. Objectives and Contents The goal of this experiment is to become familiar with BJT as an amplifier and to evaluate the basic configurations
Exercise 3 Operational Amplifiers and feedback circuits
 LAB EXERCISE 3 Page 1 of 19 Exercise 3 Operational Amplifiers and feedback circuits 1. Introduction Goal of the exercise The goals of this exercise are: Analyze the behavior of Op Amp circuits with feedback.
LAB EXERCISE 3 Page 1 of 19 Exercise 3 Operational Amplifiers and feedback circuits 1. Introduction Goal of the exercise The goals of this exercise are: Analyze the behavior of Op Amp circuits with feedback.
THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG. Department of Electrical and Electrical Engineering
 THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG Department of Electrical and Electrical Engineering Experiment EC1 The Common-Emitter Amplifier Location: Part I Laboratory CYC 102 Objective: To study the basic operation and
THE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG Department of Electrical and Electrical Engineering Experiment EC1 The Common-Emitter Amplifier Location: Part I Laboratory CYC 102 Objective: To study the basic operation and
When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to relate the gain and bandwidth of an op amp
 Op Amp Fundamentals When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to relate the gain and bandwidth of an op amp In general, the parameters are interactive. However, in this unit, circuit input
Op Amp Fundamentals When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to relate the gain and bandwidth of an op amp In general, the parameters are interactive. However, in this unit, circuit input
Revised: Summer 2010
 EE 2274 PRE-LAB EXPERIMENT 5 DIODE OR GATE & CLIPPING CIRCUIT COMPLETE PRIOR TO COMING TO LAB Part I: 1. Design a diode, Figure 1 OR gate in which the maximum input current,, Iin is less than 5mA. Show
EE 2274 PRE-LAB EXPERIMENT 5 DIODE OR GATE & CLIPPING CIRCUIT COMPLETE PRIOR TO COMING TO LAB Part I: 1. Design a diode, Figure 1 OR gate in which the maximum input current,, Iin is less than 5mA. Show
EE 210: CIRCUITS AND DEVICES
 EE 210: CIRCUITS AND DEVICES LAB #3: VOLTAGE AND CURRENT MEASUREMENTS This lab features a tutorial on the instrumentation that you will be using throughout the semester. More specifically, you will see
EE 210: CIRCUITS AND DEVICES LAB #3: VOLTAGE AND CURRENT MEASUREMENTS This lab features a tutorial on the instrumentation that you will be using throughout the semester. More specifically, you will see
Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET
 Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET LABORATORY MANUAL EXPERIMENT NO. ISSUE NO. : ISSUE DATE: REV. NO. : REV. DATE : PAGE:
Dev Bhoomi Institute Of Technology Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering PRACTICAL INSTRUCTION SHEET LABORATORY MANUAL EXPERIMENT NO. ISSUE NO. : ISSUE DATE: REV. NO. : REV. DATE : PAGE:
INC 253 Digital and electronics laboratory I
 INC 253 Digital and electronics laboratory I Laboratory 4 Wave Shaping Diode Circuits Author: ID CoAuthors: 1. ID 2. ID 3. ID Experiment Date: Report received Date: Comments For Instructor Full Marks Pre
INC 253 Digital and electronics laboratory I Laboratory 4 Wave Shaping Diode Circuits Author: ID CoAuthors: 1. ID 2. ID 3. ID Experiment Date: Report received Date: Comments For Instructor Full Marks Pre
EE 233 Circuit Theory Lab 4: Second-Order Filters
 EE 233 Circuit Theory Lab 4: Second-Order Filters Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Precautions... 1 3 Prelab Exercises... 2 3.1 Generic Equalizer Filter... 2 3.2 Equalizer Filter for Audio Mixer...
EE 233 Circuit Theory Lab 4: Second-Order Filters Table of Contents 1 Introduction... 1 2 Precautions... 1 3 Prelab Exercises... 2 3.1 Generic Equalizer Filter... 2 3.2 Equalizer Filter for Audio Mixer...
Laboratory 4. Bandwidth, Filters, and Diodes
 Laboratory 4 Bandwidth, Filters, and Diodes Required Components: k resistor 0. F capacitor N94 small-signal diode LED 4. Objectives In the previous laboratory exercise you examined the effects of input
Laboratory 4 Bandwidth, Filters, and Diodes Required Components: k resistor 0. F capacitor N94 small-signal diode LED 4. Objectives In the previous laboratory exercise you examined the effects of input
ENG 100 Lab #2 Passive First-Order Filter Circuits
 ENG 100 Lab #2 Passive First-Order Filter Circuits In Lab #2, you will construct simple 1 st -order RL and RC filter circuits and investigate their frequency responses (amplitude and phase responses).
ENG 100 Lab #2 Passive First-Order Filter Circuits In Lab #2, you will construct simple 1 st -order RL and RC filter circuits and investigate their frequency responses (amplitude and phase responses).
Common-Source Amplifiers
 Lab 2: Common-Source Amplifiers Introduction The common-source stage is the most basic amplifier stage encountered in CMOS analog circuits. Because of its very high input impedance, moderate-to-high gain,
Lab 2: Common-Source Amplifiers Introduction The common-source stage is the most basic amplifier stage encountered in CMOS analog circuits. Because of its very high input impedance, moderate-to-high gain,
Experiment #2: Introduction to Lab Equipment: Function Generator, Oscilloscope, and Multisim
 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2110: CIRCUIT THEORY LABORATORY Experiment #2: Introduction to Lab Equipment: Function Generator, Oscilloscope,
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING AND APPLIED SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND COMPUTER ENGINEERING ECE 2110: CIRCUIT THEORY LABORATORY Experiment #2: Introduction to Lab Equipment: Function Generator, Oscilloscope,
EE-2302 Passive Filters and Frequency Response
 EE2302 Passive Filters and Frequency esponse Objective he student should become acquainted with simple passive filters for performing highpass, lowpass, and bandpass operations. he experimental tasks also
EE2302 Passive Filters and Frequency esponse Objective he student should become acquainted with simple passive filters for performing highpass, lowpass, and bandpass operations. he experimental tasks also
Experiment No. 4 The LM 741 Operational Amplifier
 Experiment No. 4 The LM 741 Operational Amplifier By: Prof. Gabriel M. Rebeiz The University of Michigan EECS Dept. Ann Arbor, Michigan The LM * 741 is the most widely used op-amp in the world due to its
Experiment No. 4 The LM 741 Operational Amplifier By: Prof. Gabriel M. Rebeiz The University of Michigan EECS Dept. Ann Arbor, Michigan The LM * 741 is the most widely used op-amp in the world due to its
ECE 231 Laboratory Exercise 6 Frequency / Time Response of RL and RC Circuits
 ECE 231 Laboratory Exercise 6 Frequency / Time Response of RL and RC Circuits Laboratory Group (Names) OBJECTIVES Observe and calculate the response of first-order low pass and high pass filters. Gain
ECE 231 Laboratory Exercise 6 Frequency / Time Response of RL and RC Circuits Laboratory Group (Names) OBJECTIVES Observe and calculate the response of first-order low pass and high pass filters. Gain
Lab 1: Non-Ideal Operational Amplifier and Op-Amp Circuits
 Lab 1: Non-Ideal Operational Amplifier and Op-Amp Circuits 1. Learning Outcomes In this lab, the students evaluate characteristics of the non-ideal operational amplifiers. Students use a simulation tool
Lab 1: Non-Ideal Operational Amplifier and Op-Amp Circuits 1. Learning Outcomes In this lab, the students evaluate characteristics of the non-ideal operational amplifiers. Students use a simulation tool
