BIOE 123 Module 3. Electronics 2: Time Varying Circuits. Lecture (30 min) Date. Learning Goals
|
|
|
- Clementine Garrett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BIOE 123 Module 3 Electronics 2: Time Varying Circuits Lecture (30 min) Date Learning Goals Learn about the behavior of capacitors and inductors Learn how to analyze time-varying circuits to quantify parameters See the effects of first-order RC filters Learn how to use capacitors and resistors to tune to a particular time constant Learn how to use the oscilloscope to measure signals, particularly the auto-measuring capabilities and the cursors Use the function generator for the first time SUMMARY OF TOPICS (actual lecture notes attached as separate document) Capacitors o Symbol, physical understanding, units, capacitance equations Impedance and voltage across capacitor Time constants o Solving the RC Circuit for charging and discharging Complex signals o AC, sinusoidal waves, Fourier series, square waves o RC circuit effect on square wave Filters o Bode plot o Corner frequency o Low-pass, high-pass, band-pass, notch Inductors o Symbol, physical understanding, units, inductor equations o Inductors in filters o RLC circuit Lab Intro (~15 min) Date SUMMARY OF TOPICS Basic equipment o Oscilloscope
2 o Function generator o Demo of RC charge/discharge and emphasize cursor use Reminder about filters Bode plot more detail, and how to make
3 Electronics 2: Time Varying Circuits Problem Set 3 Due: Date at the end of lab. Text: Practical Electronics for Inventors, Scherz Estimated reading time: 1 hr for Core reading, additional 30 min for optional reading Learning Goals Learn about the behavior of capacitors and inductors Learn how to analyze time-varying circuits and quantify basic parameters See the effects of first-order RC filters Learn how to use capacitors and resistors to tune to a particular time constant CORE READING 2.20: AC circuits 3.6: Capacitors (up through 3.6.4, plus 3.6.9) 3.7: Inductors (up to 3.7.4) 8.1: Things to Know Before You Start Designing Filters 8.2: Basic Filters 8.3: Passive Low-Pass Filter Design 8.4: A Note on Filter Types Download the program and build the following two circuits. Pay careful attention to the direction of the electron flow and accumulation upon connecting components.
4 PROBLEMS Reasonable values for C: uf Reasonable values for R: 1k-100k Ohms 1) Design and draw the circuit for a passive RC high-pass filter with corner frequency of 159 Hz. (Be sure to specify Vin and Vout and select reasonable values for R and C) Draw the frequency response plot. (be sure to properly label axis and indicate corner frequency) 2) Design and draw the circuit for a passive RC low-pass filter with corner frequency of 1590 Hz. (Be sure to specify Vin and Vout and select reasonable values for R and C) Draw the frequency response plot. (be sure to properly label axis and indicate corner frequency) 3) A student connects the two circuits from 1) and 2) such that Vout of 1) is connected directly to Vin of 2) in an attempt to create a bandpass filter. Draw this circuit. The frequency response doesn t seem to match what he predicted based on the two independent circuits. Why might this be the case? 4) How long did the reading take? How long did the homework take? Any additional feedback on these materials? Ex: book readings were clear, or not, HW was too easy or hard?
5 Electronics 2: Time Varying Circuits Laboratory Instructions Date Location: Personal ( collaborators ): Work in pairs. Supervision by instructor and TAs. Objective Learn how to use the function generator Learn how to use the oscilloscope to measure signals, particularly the auto-measuring capabilities and the cursors Learn about the behavior of capacitors See the effects of first-order RC filters Learn how to use capacitors and resistors to tune to a particular time constant Learn how to analyze a simple RC circuit (Note: The other typical major component of time varying circuits is the inductor, but we will not be working with that today.) Background In today s lab you will get used to using capacitors in circuits, as they are an important tool to use when a signal changes with time (which will be most signals of interest). You will examine how a circuit's time constant affects its output, as well as how a filter's R and C values will change signals of various frequencies. The capacitors we are working with aren t polarized, but be aware that polarized capacitors exist. The first section of the lab introduces you the equipment and electric components. As your proficiency increases, you should find that you can rapidly build these circuits and take measurements using the tools. As always, please ask a member of the teaching staff if you are stuck or have questions. *Note: in order to focus on learning to use equipment and filters, a full error analysis section will not be required for today s lab. Parts List/Materials Breadboard (Jameco Electronics) Oscilloscope (Tektronix TDS 1012C-EDU) Function generator (GW Instek GFG-8020H) Jumper wire (Jameco Electronics) Various resistors and capacitors (Jameco Electronics )
6 Planning phase (15 min) The goal of today s unit is for you to learn skills and tools, rather than making a scientific measurement. Therefore you can keep note keeping to a minimum; no error analysis needed if not explicitly required Read the complete experiment instructions Prepare your notebook (again keep to the essential minimum in large you can refer to these instructions) Check that all tools and materials are ready Make a time plan (we already did that for you) and add into your notebook Are there any safety concerns? Experiments/Tasks (execution phase) (130 min) 1. Familiarization with the function generator and oscilloscope? (30 min) *For questions about how to use the function generator, refer to the manual, the First time operations instructions section starting on page 10 may be beneficial. Set the function generator to deliver a 1 khz sine wave with peak-to-peak voltage of 1 V. Measure the peak to peak voltage and the frequency using the oscilloscope. Measure peak-to-peak (p-p) voltage using the cursors Measure p-p voltage using the automatic measure function of the oscilloscope. How would you report error for the p-p voltage? For the frequency? Play around with generating various frequencies, amplitudes, wave forms, and offsets with the function generator and observing and measuring various quantities with the oscilloscope. (free play time!) Show a member of the teaching staff you know how to use this equipment TA Check 2. For today's first experiment, you will receive a capacitor and build a circuit to determine its capacitance. (40 min) Build a high-pass filter using a 10 kω resistor and the mystery capacitor. Draw this circuit
7 Supply this circuit with a Sine wave from the function generator. Record peak-to-peak voltage vs. frequency. Use these values to make a Bode plot and show the frequency response of this circuit. (Using a computer with spreadsheet/plotting capabilities here is helpful, and these plots can be very quick to make). Use at least 10 frequency values to fully capture the response. Report the corner frequency Determine the mystery capacitance (Check with a member of the teaching staff when you have a guess) Bonus: What is your uncertainty / error on this capacitance? TA Check Based on your reading, think about another way to measure this capacitance. *Leave this circuit on the breadboard; it will be used in part For the next experiment, you will build a low-pass filter. Design a filter with corner frequency of 1590 Hz, using a uf capacitor. (20 min) Draw this circuit. Create another Bode plot as in 2) to show the frequency response of this circuit. Report and compare the corner frequency with the targeted value. Discuss whether any discrepancy is likely due to resistor error, capacitor error, or error in measurement. *Leave this circuit on the breadboard; it will be used in part 4.
8 4. Now you will combine the circuits from 2) and 3) to make a band-pass filter. To do this, connect the output from the high-pass filter to the input for the low-pass filter and measure the output in the same position you did for the low-pass filter. (20 min) Create another Bode plot as in 2) and 3) to show the frequency response of this circuit. Describe in words the frequency response. What is the least attenuated amplitude (largest V p-p output/v p-p input)? What is the bandwidth of this circuit? For your report, include the Bode plots from each filter from 2) and 3) superimposed on the band-pass filter s Bode plot *Note: Leave this circuit on your breadboard; you ll modify it in the next section. 5. In the circuit from 4) now replace the low-pass filter with a low pass filter with the same corner frequency, but using a 1000 kω resistor instead. (20 min) Make a Bode plot and describe any differences between this frequency response and that from section 4). In your plot, include the Bode plots from each filter from 2) and 3) superimposed on the new band-pass filter s Bode plot What is the least attenuated amplitude (largest V p-p output/v p-p input)? Assuming the new low-pass filter behaves identically to the old one in isolation, what likely caused the change?
9 Be sure to include diagrams for each circuit and all Bode plots in your report. Summary results / error analysis: (0 min) Not necessary for this module. Discussion: (15 min) For your discussion include one bioengineering application for each type of filter you built today (low-pass, high-pass, and band-pass). Report how long each section took. Give one thing you especially liked from this lab, and one change that would improve the material.
BME 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters
 BME 35 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of passive filters. Laboratory Equipment: Agilent Oscilloscope Model 546A Agilent Function Generator
BME 35 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of passive filters. Laboratory Equipment: Agilent Oscilloscope Model 546A Agilent Function Generator
Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Technology. EET 3086C Circuit Analysis Laboratory Experiments. Masood Ejaz
 Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Technology EET 3086C Circuit Analysis Laboratory Experiments Masood Ejaz Experiment # 1 DC Measurements of a Resistive Circuit and Proof of Thevenin Theorem
Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering Technology EET 3086C Circuit Analysis Laboratory Experiments Masood Ejaz Experiment # 1 DC Measurements of a Resistive Circuit and Proof of Thevenin Theorem
LABORATORY 4. Palomar College ENGR210 Spring 2017 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17
 LABORATORY 4 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17 OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this lab is to evaluate the transient and steady-state circuit response of first order and second order circuits. MINIMUM EQUIPMENT LIST: You will
LABORATORY 4 ASSIGNED: 3/21/17 OBJECTIVE: The purpose of this lab is to evaluate the transient and steady-state circuit response of first order and second order circuits. MINIMUM EQUIPMENT LIST: You will
EE2210 Laboratory Project 1 Fall 2013 Function Generator and Oscilloscope
 EE2210 Laboratory Project 1 Fall 2013 Function Generator and Oscilloscope For students to become more familiar with oscilloscopes and function generators. Pre laboratory Work Read the TDS 210 Oscilloscope
EE2210 Laboratory Project 1 Fall 2013 Function Generator and Oscilloscope For students to become more familiar with oscilloscopes and function generators. Pre laboratory Work Read the TDS 210 Oscilloscope
Pre-Lab. Introduction
 Pre-Lab Read through this entire lab. Perform all of your calculations (calculated values) prior to making the required circuit measurements. You may need to measure circuit component values to obtain
Pre-Lab Read through this entire lab. Perform all of your calculations (calculated values) prior to making the required circuit measurements. You may need to measure circuit component values to obtain
Lab 10: Single Supply Amplifier
 Overview This lab assignment implements an inverting voltage amplifier circuit with a single power supply. The amplifier output contains a bias point which is removed by AC coupling the output signal.
Overview This lab assignment implements an inverting voltage amplifier circuit with a single power supply. The amplifier output contains a bias point which is removed by AC coupling the output signal.
ENG 100 Lab #2 Passive First-Order Filter Circuits
 ENG 100 Lab #2 Passive First-Order Filter Circuits In Lab #2, you will construct simple 1 st -order RL and RC filter circuits and investigate their frequency responses (amplitude and phase responses).
ENG 100 Lab #2 Passive First-Order Filter Circuits In Lab #2, you will construct simple 1 st -order RL and RC filter circuits and investigate their frequency responses (amplitude and phase responses).
Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 11: Lab Projects
 Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 11: Lab Projects 11.2.1: Signals with Multiple Frequency Components Overview: In this lab project, we will calculate the magnitude response of an electrical circuit and
Real Analog - Circuits 1 Chapter 11: Lab Projects 11.2.1: Signals with Multiple Frequency Components Overview: In this lab project, we will calculate the magnitude response of an electrical circuit and
ECE 2201 PRELAB 6 BJT COMMON EMITTER (CE) AMPLIFIER
 ECE 2201 PRELAB 6 BJT COMMON EMITTER (CE) AMPLIFIER Hand Analysis P1. Determine the DC bias for the BJT Common Emitter Amplifier circuit of Figure 61 (in this lab) including the voltages V B, V C and V
ECE 2201 PRELAB 6 BJT COMMON EMITTER (CE) AMPLIFIER Hand Analysis P1. Determine the DC bias for the BJT Common Emitter Amplifier circuit of Figure 61 (in this lab) including the voltages V B, V C and V
EECS40 RLC Lab guide
 EECS40 RLC Lab guide Introduction Second-Order Circuits Second order circuits have both inductor and capacitor components, which produce one or more resonant frequencies, ω0. In general, a differential
EECS40 RLC Lab guide Introduction Second-Order Circuits Second order circuits have both inductor and capacitor components, which produce one or more resonant frequencies, ω0. In general, a differential
EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response
 EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of active signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Active Filters, Op-Amp Filters, Bode plots Suggested
EK307 Active Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of active signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Active Filters, Op-Amp Filters, Bode plots Suggested
EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response
 EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of passive signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Passive filters, Frequency domain, Bode plots
EK307 Passive Filters and Steady State Frequency Response Laboratory Goal: To explore the properties of passive signal-processing filters Learning Objectives: Passive filters, Frequency domain, Bode plots
ECE3204 D2015 Lab 1. See suggested breadboard configuration on following page!
 ECE3204 D2015 Lab 1 The Operational Amplifier: Inverting and Non-inverting Gain Configurations Gain-Bandwidth Product Relationship Frequency Response Limitation Transfer Function Measurement DC Errors
ECE3204 D2015 Lab 1 The Operational Amplifier: Inverting and Non-inverting Gain Configurations Gain-Bandwidth Product Relationship Frequency Response Limitation Transfer Function Measurement DC Errors
BME/ISE 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters
 BME/ISE 35 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of passive filters. Supplies and Components: Breadboard 4.7 K Resistor 0.047 F Capacitor
BME/ISE 35 Bioelectronics Laboratory Two - Passive Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of passive filters. Supplies and Components: Breadboard 4.7 K Resistor 0.047 F Capacitor
Low_Pass_Filter_1st_Order -- Overview
 Low_Pass_Filter_1st_Order -- Overview 1 st Order Low Pass Filter Objectives: After performing this lab exercise, learner will be able to: Understand and comprehend working of opamp Comprehend basics of
Low_Pass_Filter_1st_Order -- Overview 1 st Order Low Pass Filter Objectives: After performing this lab exercise, learner will be able to: Understand and comprehend working of opamp Comprehend basics of
ECE212H1F University of Toronto 2017 EXPERIMENT #4 FIRST AND SECOND ORDER CIRCUITS ECE212H1F
 ECE212H1F University of Toronto 2017 EXPERIMENT #4 FIRST AND SECOND ORDER CIRCUITS ECE212H1F OBJECTIVES: To study the voltage-current relationship for a capacitor. To study the step responses of a series
ECE212H1F University of Toronto 2017 EXPERIMENT #4 FIRST AND SECOND ORDER CIRCUITS ECE212H1F OBJECTIVES: To study the voltage-current relationship for a capacitor. To study the step responses of a series
Lab 9 Frequency Domain
 Lab 9 Frequency Domain 1 Components Required Resistors Capacitors Function Generator Multimeter Oscilloscope 2 Filter Design Filters are electric components that allow applying different operations to
Lab 9 Frequency Domain 1 Components Required Resistors Capacitors Function Generator Multimeter Oscilloscope 2 Filter Design Filters are electric components that allow applying different operations to
EE233 Autumn 2016 Electrical Engineering University of Washington. EE233 HW7 Solution. Nov. 16 th. Due Date: Nov. 23 rd
 EE233 HW7 Solution Nov. 16 th Due Date: Nov. 23 rd 1. Use a 500nF capacitor to design a low pass passive filter with a cutoff frequency of 50 krad/s. (a) Specify the cutoff frequency in hertz. fc c 50000
EE233 HW7 Solution Nov. 16 th Due Date: Nov. 23 rd 1. Use a 500nF capacitor to design a low pass passive filter with a cutoff frequency of 50 krad/s. (a) Specify the cutoff frequency in hertz. fc c 50000
STUDY OF RC AND RL CIRCUITS Venue: Microelectronics Laboratory in E2 L2
 EXPERIMENT #1 STUDY OF RC AND RL CIRCUITS Venue: Microelectronics Laboratory in E2 L2 I. INTRODUCTION This laboratory is about verifying the transient behavior of RC and RL circuits. You need to revise
EXPERIMENT #1 STUDY OF RC AND RL CIRCUITS Venue: Microelectronics Laboratory in E2 L2 I. INTRODUCTION This laboratory is about verifying the transient behavior of RC and RL circuits. You need to revise
E84 Lab 3: Transistor
 E84 Lab 3: Transistor Cherie Ho and Siyi Hu April 18, 2016 Transistor Testing 1. Take screenshots of both the input and output characteristic plots observed on the semiconductor curve tracer with the following
E84 Lab 3: Transistor Cherie Ho and Siyi Hu April 18, 2016 Transistor Testing 1. Take screenshots of both the input and output characteristic plots observed on the semiconductor curve tracer with the following
STEP RESPONSE OF 1 ST AND 2 ND ORDER CIRCUITS
 STEP RESPONSE OF 1 ST AND 2 ND ORDER CIRCUITS YOUR NAME GTA S SIGNATURE LAB MEETING TIME Objectives: To observe responses of first and second order circuits - RC, RL and RLC circuits, source-free or with
STEP RESPONSE OF 1 ST AND 2 ND ORDER CIRCUITS YOUR NAME GTA S SIGNATURE LAB MEETING TIME Objectives: To observe responses of first and second order circuits - RC, RL and RLC circuits, source-free or with
Welcome to your second Electronics Laboratory Session. In this session you will learn about how to use resistors, capacitors and inductors to make
 Welcome to your second Electronics Laboratory Session. In this session you will learn about how to use resistors, capacitors and inductors to make simple circuits. You will find out how these circuits
Welcome to your second Electronics Laboratory Session. In this session you will learn about how to use resistors, capacitors and inductors to make simple circuits. You will find out how these circuits
SAMPLE: EXPERIMENT 2 Series RLC Circuit / Bode Plot
 SAMPLE: EXPERIMENT 2 Series RLC Circuit / Bode Plot ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- This experiment is an excerpt from: Electric Experiments
SAMPLE: EXPERIMENT 2 Series RLC Circuit / Bode Plot ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- This experiment is an excerpt from: Electric Experiments
ELEG 205 Analog Circuits Laboratory Manual Fall 2016
 ELEG 205 Analog Circuits Laboratory Manual Fall 2016 University of Delaware Dr. Mark Mirotznik Kaleb Burd Patrick Nicholson Aric Lu Kaeini Ekong 1 Table of Contents Lab 1: Intro 3 Lab 2: Resistive Circuits
ELEG 205 Analog Circuits Laboratory Manual Fall 2016 University of Delaware Dr. Mark Mirotznik Kaleb Burd Patrick Nicholson Aric Lu Kaeini Ekong 1 Table of Contents Lab 1: Intro 3 Lab 2: Resistive Circuits
Class #7: Experiment L & C Circuits: Filters and Energy Revisited
 Class #7: Experiment L & C Circuits: Filters and Energy Revisited In this experiment you will revisit the voltage oscillations of a simple LC circuit. Then you will address circuits made by combining resistors
Class #7: Experiment L & C Circuits: Filters and Energy Revisited In this experiment you will revisit the voltage oscillations of a simple LC circuit. Then you will address circuits made by combining resistors
Laboratory 4: Amplification, Impedance, and Frequency Response
 ES 3: Introduction to Electrical Systems Laboratory 4: Amplification, Impedance, and Frequency Response I. GOALS: In this laboratory, you will build an audio amplifier using an LM386 integrated circuit.
ES 3: Introduction to Electrical Systems Laboratory 4: Amplification, Impedance, and Frequency Response I. GOALS: In this laboratory, you will build an audio amplifier using an LM386 integrated circuit.
Frequency Selective Circuits
 Lab 15 Frequency Selective Circuits Names Objectives in this lab you will Measure the frequency response of a circuit Determine the Q of a resonant circuit Build a filter and apply it to an audio signal
Lab 15 Frequency Selective Circuits Names Objectives in this lab you will Measure the frequency response of a circuit Determine the Q of a resonant circuit Build a filter and apply it to an audio signal
BME 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Six - Active Filters
 BME 5 Bioelectronics Laboratory Six - Active Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of active filters. Describe the differences between active and passive filters. Laboratory Equipment:
BME 5 Bioelectronics Laboratory Six - Active Filters Learning Objectives: Understand the basic principles of active filters. Describe the differences between active and passive filters. Laboratory Equipment:
Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks
 OPTI 380B Intermediate Optics Laboratory Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks Objectives: Lean how to use: Function of an oscilloscope probe. Characterization of capacitors and inductors
OPTI 380B Intermediate Optics Laboratory Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks Objectives: Lean how to use: Function of an oscilloscope probe. Characterization of capacitors and inductors
Lecture Week 7. Quiz 4 - KCL/KVL Capacitors RC Circuits and Phasor Analysis RC filters Workshop
 Lecture Week 7 Quiz 4 - KCL/KVL Capacitors RC Circuits and Phasor Analysis RC filters Workshop Quiz 5 KCL/KVL Please clear desks and turn off phones and put them in back packs You need a pencil, straight
Lecture Week 7 Quiz 4 - KCL/KVL Capacitors RC Circuits and Phasor Analysis RC filters Workshop Quiz 5 KCL/KVL Please clear desks and turn off phones and put them in back packs You need a pencil, straight
LABORATORY #3 QUARTZ CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR DESIGN
 LABORATORY #3 QUARTZ CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR DESIGN OBJECTIVES 1. To design and DC bias the JFET transistor oscillator for a 9.545 MHz sinusoidal signal. 2. To simulate JFET transistor oscillator using MicroCap
LABORATORY #3 QUARTZ CRYSTAL OSCILLATOR DESIGN OBJECTIVES 1. To design and DC bias the JFET transistor oscillator for a 9.545 MHz sinusoidal signal. 2. To simulate JFET transistor oscillator using MicroCap
Lab: Operational Amplifiers
 Page 1 of 6 Laboratory Goals Familiarize students with Integrated Circuit (IC) construction on a breadboard Introduce the LM 741 Op-amp and its applications Design and construct an inverting amplifier
Page 1 of 6 Laboratory Goals Familiarize students with Integrated Circuit (IC) construction on a breadboard Introduce the LM 741 Op-amp and its applications Design and construct an inverting amplifier
ECEN Network Analysis Section 3. Laboratory Manual
 ECEN 3714----Network Analysis Section 3 Laboratory Manual LAB 07: Active Low Pass Filter Oklahoma State University School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Section 3 Laboratory manual - 1 - Spring
ECEN 3714----Network Analysis Section 3 Laboratory Manual LAB 07: Active Low Pass Filter Oklahoma State University School of Electrical and Computer Engineering. Section 3 Laboratory manual - 1 - Spring
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 7 SIGNAL CONDITIONING AND LOADING
 ME 365 EXPERIMENT 7 SIGNAL CONDITIONING AND LOADING Objectives: To familiarize the student with the concepts of signal conditioning. At the end of the lab, the student should be able to: Understand the
ME 365 EXPERIMENT 7 SIGNAL CONDITIONING AND LOADING Objectives: To familiarize the student with the concepts of signal conditioning. At the end of the lab, the student should be able to: Understand the
ECE ECE285. Electric Circuit Analysis I. Spring Nathalia Peixoto. Rev.2.0: Rev Electric Circuits I
 ECE285 Electric Circuit Analysis I Spring 2014 Nathalia Peixoto Rev.2.0: 140124. Rev 2.1. 140813 1 Lab reports Background: these 9 experiments are designed as simple building blocks (like Legos) and students
ECE285 Electric Circuit Analysis I Spring 2014 Nathalia Peixoto Rev.2.0: 140124. Rev 2.1. 140813 1 Lab reports Background: these 9 experiments are designed as simple building blocks (like Legos) and students
PURPOSE: NOTE: Be sure to record ALL results in your laboratory notebook.
 EE4902 Lab 9 CMOS OP-AMP PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to measure the closed-loop performance of an op-amp designed from individual MOSFETs. This op-amp, shown in Fig. 9-1, combines all of the major
EE4902 Lab 9 CMOS OP-AMP PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to measure the closed-loop performance of an op-amp designed from individual MOSFETs. This op-amp, shown in Fig. 9-1, combines all of the major
Experiment 1.A. Working with Lab Equipment. ECEN 2270 Electronics Design Laboratory 1
 .A Working with Lab Equipment Electronics Design Laboratory 1 1.A.0 1.A.1 3 1.A.4 Procedures Turn in your Pre Lab before doing anything else Setup the lab waveform generator to output desired test waveforms,
.A Working with Lab Equipment Electronics Design Laboratory 1 1.A.0 1.A.1 3 1.A.4 Procedures Turn in your Pre Lab before doing anything else Setup the lab waveform generator to output desired test waveforms,
ET 304A Laboratory Tutorial-Circuitmaker For Transient and Frequency Analysis
 ET 304A Laboratory Tutorial-Circuitmaker For Transient and Frequency Analysis All circuit simulation packages that use the Pspice engine allow users to do complex analysis that were once impossible to
ET 304A Laboratory Tutorial-Circuitmaker For Transient and Frequency Analysis All circuit simulation packages that use the Pspice engine allow users to do complex analysis that were once impossible to
University of Portland EE 271 Electrical Circuits Laboratory. Experiment: Inductors
 University of Portland EE 271 Electrical Circuits Laboratory Experiment: Inductors I. Objective The objective of this experiment is to verify the relationship between voltage and current in an inductor,
University of Portland EE 271 Electrical Circuits Laboratory Experiment: Inductors I. Objective The objective of this experiment is to verify the relationship between voltage and current in an inductor,
Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5)
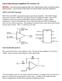 Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy
Lab 9: Operational amplifiers II (version 1.5) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy
Physics 5620 Laboratory 2 DC, RC and Passive Low Pass and High Pass Circuits
 Physics 5620 Laboratory 2 D, and Passie Low Pass and High Pass ircuits Objectie: In this lab you will study D circuits using Kirchoff s laws and Theenin s theorem. You will also study the behaior of circuits
Physics 5620 Laboratory 2 D, and Passie Low Pass and High Pass ircuits Objectie: In this lab you will study D circuits using Kirchoff s laws and Theenin s theorem. You will also study the behaior of circuits
Mechatronics. Analog and Digital Electronics: Studio Exercises 1 & 2
 Mechatronics Analog and Digital Electronics: Studio Exercises 1 & 2 There is an electronics revolution taking place in the industrialized world. Electronics pervades all activities. Perhaps the most important
Mechatronics Analog and Digital Electronics: Studio Exercises 1 & 2 There is an electronics revolution taking place in the industrialized world. Electronics pervades all activities. Perhaps the most important
PHYS 3322 Modern Laboratory Methods I AC R, RC, and RL Circuits
 Purpose PHYS 3322 Modern Laboratory Methods I AC, C, and L Circuits For a given frequency, doubling of the applied voltage to resistors, capacitors, and inductors doubles the current. Hence, each of these
Purpose PHYS 3322 Modern Laboratory Methods I AC, C, and L Circuits For a given frequency, doubling of the applied voltage to resistors, capacitors, and inductors doubles the current. Hence, each of these
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS) II
 OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS) II LAB 5 INTRO: INTRODUCTION TO INVERTING AMPLIFIERS AND OTHER OP-AMP CIRCUITS GOALS In this lab, you will characterize the gain and frequency dependence of inverting op-amp
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS (OP-AMPS) II LAB 5 INTRO: INTRODUCTION TO INVERTING AMPLIFIERS AND OTHER OP-AMP CIRCUITS GOALS In this lab, you will characterize the gain and frequency dependence of inverting op-amp
ECE 6416 Low-Noise Electronics Orientation Experiment
 ECE 6416 Low-Noise Electronics Orientation Experiment Object The object of this experiment is to become familiar with the instruments used in the low noise laboratory. Parts The following parts are required
ECE 6416 Low-Noise Electronics Orientation Experiment Object The object of this experiment is to become familiar with the instruments used in the low noise laboratory. Parts The following parts are required
Laboratory 9. Required Components: Objectives. Optional Components: Operational Amplifier Circuits (modified from lab text by Alciatore)
 Laboratory 9 Operational Amplifier Circuits (modified from lab text by Alciatore) Required Components: 1x 741 op-amp 2x 1k resistors 4x 10k resistors 1x l00k resistor 1x 0.1F capacitor Optional Components:
Laboratory 9 Operational Amplifier Circuits (modified from lab text by Alciatore) Required Components: 1x 741 op-amp 2x 1k resistors 4x 10k resistors 1x l00k resistor 1x 0.1F capacitor Optional Components:
AC Circuits. "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert ( )
 AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits use varying
AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits use varying
ESE 150 Lab 04: The Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)
 LAB 04 In this lab we will do the following: 1. Use Matlab to perform the Fourier Transform on sampled data in the time domain, converting it to the frequency domain 2. Add two sinewaves together of differing
LAB 04 In this lab we will do the following: 1. Use Matlab to perform the Fourier Transform on sampled data in the time domain, converting it to the frequency domain 2. Add two sinewaves together of differing
Uncovering a Hidden RCL Series Circuit
 Purpose Uncovering a Hidden RCL Series Circuit a. To use the equipment and techniques developed in the previous experiment to uncover a hidden series RCL circuit in a box and b. To measure the values of
Purpose Uncovering a Hidden RCL Series Circuit a. To use the equipment and techniques developed in the previous experiment to uncover a hidden series RCL circuit in a box and b. To measure the values of
BME 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Five - Operational Amplifiers
 BME 351 Bioelectronics Laboratory Five - Operational Amplifiers Learning Objectives: Be familiar with the operation of a basic op-amp circuit. Be familiar with the characteristics of both ideal and real
BME 351 Bioelectronics Laboratory Five - Operational Amplifiers Learning Objectives: Be familiar with the operation of a basic op-amp circuit. Be familiar with the characteristics of both ideal and real
Sallen-Key_High_Pass_Filter -- Overview
 Sallen-Key_High_Pass_Filter -- Overview Sallen-Key High Pass Filter Objectives: After performing this lab exercise, learner will be able to: Understand & analyze working of Sallen-Key topology of active
Sallen-Key_High_Pass_Filter -- Overview Sallen-Key High Pass Filter Objectives: After performing this lab exercise, learner will be able to: Understand & analyze working of Sallen-Key topology of active
FREQUENCY RESPONSE AND PASSIVE FILTERS LABORATORY
 FREQUENCY RESPONSE AND PASSIVE FILTERS LABORATORY In this experiment we will analytically determine and measure the frequency response of networks containing resistors, AC source/sources, and energy storage
FREQUENCY RESPONSE AND PASSIVE FILTERS LABORATORY In this experiment we will analytically determine and measure the frequency response of networks containing resistors, AC source/sources, and energy storage
Experiment 9 AC Circuits
 Experiment 9 AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits
Experiment 9 AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits
LABORATORY EXPERIMENT. Infrared Transmitter/Receiver
 LABORATORY EXPERIMENT Infrared Transmitter/Receiver (Note to Teaching Assistant: The week before this experiment is performed, place students into groups of two and assign each group a specific frequency
LABORATORY EXPERIMENT Infrared Transmitter/Receiver (Note to Teaching Assistant: The week before this experiment is performed, place students into groups of two and assign each group a specific frequency
ECE 3155 Experiment I AC Circuits and Bode Plots Rev. lpt jan 2013
 Signature Name (print, please) Lab section # Lab partner s name (if any) Date(s) lab was performed ECE 3155 Experiment I AC Circuits and Bode Plots Rev. lpt jan 2013 In this lab we will demonstrate basic
Signature Name (print, please) Lab section # Lab partner s name (if any) Date(s) lab was performed ECE 3155 Experiment I AC Circuits and Bode Plots Rev. lpt jan 2013 In this lab we will demonstrate basic
Lab 13 AC Circuit Measurements
 Lab 13 AC Circuit Measurements Objectives concepts 1. what is impedance, really? 2. function generator and oscilloscope 3. RMS vs magnitude vs Peak-to-Peak voltage 4. phase between sinusoids skills 1.
Lab 13 AC Circuit Measurements Objectives concepts 1. what is impedance, really? 2. function generator and oscilloscope 3. RMS vs magnitude vs Peak-to-Peak voltage 4. phase between sinusoids skills 1.
ELEG 205 Analog Circuits Laboratory Manual Fall 2017
 ELEG 205 Analog Circuits Laboratory Manual Fall 2017 University of Delaware Dr. Mark Mirotznik Kaleb Burd Aric Lu Patrick Nicholson Colby Banbury Table of Contents Policies Policy Page 3 Labs Lab 1: Intro
ELEG 205 Analog Circuits Laboratory Manual Fall 2017 University of Delaware Dr. Mark Mirotznik Kaleb Burd Aric Lu Patrick Nicholson Colby Banbury Table of Contents Policies Policy Page 3 Labs Lab 1: Intro
ENGR4300 Test 3A Fall 2002
 1. 555 Timer (20 points) Figure 1: 555 Timer Circuit For the 555 timer circuit in Figure 1, find the following values for R1 = 1K, R2 = 2K, C1 = 0.1uF. Show all work. a) (4 points) T1: b) (4 points) T2:
1. 555 Timer (20 points) Figure 1: 555 Timer Circuit For the 555 timer circuit in Figure 1, find the following values for R1 = 1K, R2 = 2K, C1 = 0.1uF. Show all work. a) (4 points) T1: b) (4 points) T2:
Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3)
 Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive
Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive
Group: Names: (1) In this step you will examine the effects of AC coupling of an oscilloscope.
 3.5 Laboratory Procedure / Summary Sheet Group: Names: (1) In this step you will examine the effects of AC coupling of an oscilloscope. Set the function generator to produce a 5 V pp 1kHz sinusoidal output.
3.5 Laboratory Procedure / Summary Sheet Group: Names: (1) In this step you will examine the effects of AC coupling of an oscilloscope. Set the function generator to produce a 5 V pp 1kHz sinusoidal output.
The object of this experiment is to become familiar with the instruments used in the low noise laboratory.
 0. ORIENTATION 0.1 Object The object of this experiment is to become familiar with the instruments used in the low noise laboratory. 0.2 Parts The following parts are required for this experiment: 1. A
0. ORIENTATION 0.1 Object The object of this experiment is to become familiar with the instruments used in the low noise laboratory. 0.2 Parts The following parts are required for this experiment: 1. A
Filters And Waveform Shaping
 Physics 3330 Experiment #3 Fall 2001 Purpose Filters And Waveform Shaping The aim of this experiment is to study the frequency filtering properties of passive (R, C, and L) circuits for sine waves, and
Physics 3330 Experiment #3 Fall 2001 Purpose Filters And Waveform Shaping The aim of this experiment is to study the frequency filtering properties of passive (R, C, and L) circuits for sine waves, and
INTRODUCTION TO FILTER CIRCUITS
 INTRODUCTION TO FILTER CIRCUITS 1 2 Background: Filters may be classified as either digital or analog. Digital filters are implemented using a digital computer or special purpose digital hardware. Analog
INTRODUCTION TO FILTER CIRCUITS 1 2 Background: Filters may be classified as either digital or analog. Digital filters are implemented using a digital computer or special purpose digital hardware. Analog
LAB II. INTRODUCTION TO LAB EQUIPMENT
 1. OBJECTIVE LAB II. INTRODUCTION TO LAB EQUIPMENT In this lab you will learn how to properly operate the oscilloscope Keysight DSOX1102A, the Keithley Source Measure Unit (SMU) 2430, the function generator
1. OBJECTIVE LAB II. INTRODUCTION TO LAB EQUIPMENT In this lab you will learn how to properly operate the oscilloscope Keysight DSOX1102A, the Keithley Source Measure Unit (SMU) 2430, the function generator
ESE 150 Lab 04: The Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT)
 LAB 04 In this lab we will do the following: 1. Use Matlab to perform the Fourier Transform on sampled data in the time domain, converting it to the frequency domain 2. Add two sinewaves together of differing
LAB 04 In this lab we will do the following: 1. Use Matlab to perform the Fourier Transform on sampled data in the time domain, converting it to the frequency domain 2. Add two sinewaves together of differing
Operational Amplifiers: Part II
 1. Introduction Operational Amplifiers: Part II The name "operational amplifier" comes from this amplifier's ability to perform mathematical operations. Three good examples of this are the summing amplifier,
1. Introduction Operational Amplifiers: Part II The name "operational amplifier" comes from this amplifier's ability to perform mathematical operations. Three good examples of this are the summing amplifier,
RC Filters and Basic Timer Functionality
 RC-1 Learning Objectives: RC Filters and Basic Timer Functionality The student who successfully completes this lab will be able to: Build circuits using passive components (resistors and capacitors) from
RC-1 Learning Objectives: RC Filters and Basic Timer Functionality The student who successfully completes this lab will be able to: Build circuits using passive components (resistors and capacitors) from
Integrators, differentiators, and simple filters
 BEE 233 Laboratory-4 Integrators, differentiators, and simple filters 1. Objectives Analyze and measure characteristics of circuits built with opamps. Design and test circuits with opamps. Plot gain vs.
BEE 233 Laboratory-4 Integrators, differentiators, and simple filters 1. Objectives Analyze and measure characteristics of circuits built with opamps. Design and test circuits with opamps. Plot gain vs.
B. Equipment. Advanced Lab
 Advanced Lab Measuring Periodic Signals Using a Digital Oscilloscope A. Introduction and Background We will use a digital oscilloscope to characterize several different periodic voltage signals. We will
Advanced Lab Measuring Periodic Signals Using a Digital Oscilloscope A. Introduction and Background We will use a digital oscilloscope to characterize several different periodic voltage signals. We will
BME/ISE 3512 Bioelectronics. Laboratory Five - Operational Amplifiers
 BME/ISE 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Five - Operational Amplifiers Learning Objectives: Be familiar with the operation of a basic op-amp circuit. Be familiar with the characteristics of both ideal and
BME/ISE 3512 Bioelectronics Laboratory Five - Operational Amplifiers Learning Objectives: Be familiar with the operation of a basic op-amp circuit. Be familiar with the characteristics of both ideal and
Laboratory 3 (drawn from lab text by Alciatore)
 Laboratory 3 (drawn from lab text by Alciatore) The Oscilloscope Required Components: 1 10 resistor 2 100 resistors 2 lk resistors 1 2k resistor 2 4.7M resistors 1 0.F capacitor 1 0.1 F capacitor 1 1.0uF
Laboratory 3 (drawn from lab text by Alciatore) The Oscilloscope Required Components: 1 10 resistor 2 100 resistors 2 lk resistors 1 2k resistor 2 4.7M resistors 1 0.F capacitor 1 0.1 F capacitor 1 1.0uF
EXPERIMENT NUMBER 8 Introduction to Active Filters
 EXPERIMENT NUMBER 8 Introduction to Active Filters i-1 Preface: Preliminary exercises are to be done and submitted individually. Laboratory hardware exercises are to be done in groups. This laboratory
EXPERIMENT NUMBER 8 Introduction to Active Filters i-1 Preface: Preliminary exercises are to be done and submitted individually. Laboratory hardware exercises are to be done in groups. This laboratory
BME/ISE 3511 Laboratory One - Laboratory Equipment for Measurement. Introduction to biomedical electronic laboratory instrumentation and measurements.
 BME/ISE 3511 Laboratory One - Laboratory Equipment for Measurement Learning Objectives: Introduction to biomedical electronic laboratory instrumentation and measurements. Supplies and Components: Breadboard
BME/ISE 3511 Laboratory One - Laboratory Equipment for Measurement Learning Objectives: Introduction to biomedical electronic laboratory instrumentation and measurements. Supplies and Components: Breadboard
FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF R, L AND C ELEMENTS
 FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF R, L AND C ELEMENTS Marking scheme : Methods & diagrams : 3 Graph plotting : - Tables & analysis : 2 Questions & discussion : 3 Performance : 2 Aim: This experiment will investigate
FREQUENCY RESPONSE OF R, L AND C ELEMENTS Marking scheme : Methods & diagrams : 3 Graph plotting : - Tables & analysis : 2 Questions & discussion : 3 Performance : 2 Aim: This experiment will investigate
EE431 Lab 1 Operational Amplifiers
 Feb. 10, 2015 Report all measured data and show all calculations Introduction The purpose of this laboratory exercise is for the student to gain experience with measuring and observing the effects of common
Feb. 10, 2015 Report all measured data and show all calculations Introduction The purpose of this laboratory exercise is for the student to gain experience with measuring and observing the effects of common
Assist Lecturer: Marwa Maki. Active Filters
 Active Filters In past lecture we noticed that the main disadvantage of Passive Filters is that the amplitude of the output signals is less than that of the input signals, i.e., the gain is never greater
Active Filters In past lecture we noticed that the main disadvantage of Passive Filters is that the amplitude of the output signals is less than that of the input signals, i.e., the gain is never greater
10: AMPLIFIERS. Circuit Connections in the Laboratory. Op-Amp. I. Introduction
 10: AMPLIFIERS Circuit Connections in the Laboratory From now on you will construct electrical circuits and test them. The usual way of constructing circuits would be to solder each electrical connection
10: AMPLIFIERS Circuit Connections in the Laboratory From now on you will construct electrical circuits and test them. The usual way of constructing circuits would be to solder each electrical connection
Lab #2 First Order RC Circuits Week of 27 January 2015
 ECE214: Electrical Circuits Laboratory Lab #2 First Order RC Circuits Week of 27 January 2015 1 Introduction In this lab you will investigate the magnitude and phase shift that occurs in an RC circuit
ECE214: Electrical Circuits Laboratory Lab #2 First Order RC Circuits Week of 27 January 2015 1 Introduction In this lab you will investigate the magnitude and phase shift that occurs in an RC circuit
Lab 4: Analysis of the Stereo Amplifier
 ECE 212 Spring 2010 Circuit Analysis II Names: Lab 4: Analysis of the Stereo Amplifier Objectives In this lab exercise you will use the power supply to power the stereo amplifier built in the previous
ECE 212 Spring 2010 Circuit Analysis II Names: Lab 4: Analysis of the Stereo Amplifier Objectives In this lab exercise you will use the power supply to power the stereo amplifier built in the previous
ECE 4670 Spring 2014 Lab 1 Linear System Characteristics
 ECE 4670 Spring 2014 Lab 1 Linear System Characteristics 1 Linear System Characteristics The first part of this experiment will serve as an introduction to the use of the spectrum analyzer in making absolute
ECE 4670 Spring 2014 Lab 1 Linear System Characteristics 1 Linear System Characteristics The first part of this experiment will serve as an introduction to the use of the spectrum analyzer in making absolute
Exercise 1: Series RLC Circuits
 RLC Circuits AC 2 Fundamentals Exercise 1: Series RLC Circuits EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to analyze series RLC circuits by using calculations and measurements.
RLC Circuits AC 2 Fundamentals Exercise 1: Series RLC Circuits EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to analyze series RLC circuits by using calculations and measurements.
Laboratory 6. Lab 6. Operational Amplifier Circuits. Required Components: op amp 2 1k resistor 4 10k resistors 1 100k resistor 1 0.
 Laboratory 6 Operational Amplifier Circuits Required Components: 1 741 op amp 2 1k resistor 4 10k resistors 1 100k resistor 1 0.1 F capacitor 6.1 Objectives The operational amplifier is one of the most
Laboratory 6 Operational Amplifier Circuits Required Components: 1 741 op amp 2 1k resistor 4 10k resistors 1 100k resistor 1 0.1 F capacitor 6.1 Objectives The operational amplifier is one of the most
Laboratory Project 4: Frequency Response and Filters
 2240 Laboratory Project 4: Frequency Response and Filters K. Durney and N. E. Cotter Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of Utah Salt Lake City, UT 84112 Abstract-You will build a
2240 Laboratory Project 4: Frequency Response and Filters K. Durney and N. E. Cotter Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of Utah Salt Lake City, UT 84112 Abstract-You will build a
Instructions for the final examination:
 School of Information, Computer and Communication Technology Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University Practice Problems for the Final Examination COURSE : ECS304 Basic Electrical
School of Information, Computer and Communication Technology Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University Practice Problems for the Final Examination COURSE : ECS304 Basic Electrical
ECE 231 Laboratory Exercise 6 Frequency / Time Response of RL and RC Circuits
 ECE 231 Laboratory Exercise 6 Frequency / Time Response of RL and RC Circuits Laboratory Group (Names) OBJECTIVES Observe and calculate the response of first-order low pass and high pass filters. Gain
ECE 231 Laboratory Exercise 6 Frequency / Time Response of RL and RC Circuits Laboratory Group (Names) OBJECTIVES Observe and calculate the response of first-order low pass and high pass filters. Gain
Lab #7: Transient Response of a 1 st Order RC Circuit
 Lab #7: Transient Response of a 1 st Order RC Circuit Theory & Introduction Goals for Lab #7 The goal of this lab is to explore the transient response of a 1 st Order circuit. In order to explore the 1
Lab #7: Transient Response of a 1 st Order RC Circuit Theory & Introduction Goals for Lab #7 The goal of this lab is to explore the transient response of a 1 st Order circuit. In order to explore the 1
Precalculations Individual Portion Filter Lab: Building and Testing Electrical Filters
 Name: Date of lab: Section number: M E 345. Lab 6 Precalculations Individual Portion Filter Lab: Building and Testing Electrical Filters Precalculations Score (for instructor or TA use only): / 20 1. (4)
Name: Date of lab: Section number: M E 345. Lab 6 Precalculations Individual Portion Filter Lab: Building and Testing Electrical Filters Precalculations Score (for instructor or TA use only): / 20 1. (4)
EC-3: Capacitors and RC-Decay
 Your TA will use this sheet to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. You must use complete sentences and clearly explain your reasoning to receive full credit. EC-3, Part I: Do not do
Your TA will use this sheet to score your lab. It is to be turned in at the end of lab. You must use complete sentences and clearly explain your reasoning to receive full credit. EC-3, Part I: Do not do
ECE 201 LAB 8 TRANSFORMERS & SINUSOIDAL STEADY STATE ANALYSIS
 Version 1.1 1 of 8 ECE 201 LAB 8 TRANSFORMERS & SINUSOIDAL STEADY STATE ANALYSIS BEFORE YOU BEGIN PREREQUISITE LABS Introduction to MATLAB Introduction to Lab Equipment Introduction to Oscilloscope Capacitors,
Version 1.1 1 of 8 ECE 201 LAB 8 TRANSFORMERS & SINUSOIDAL STEADY STATE ANALYSIS BEFORE YOU BEGIN PREREQUISITE LABS Introduction to MATLAB Introduction to Lab Equipment Introduction to Oscilloscope Capacitors,
CHAPTER 14. Introduction to Frequency Selective Circuits
 CHAPTER 14 Introduction to Frequency Selective Circuits Frequency-selective circuits Varying source frequency on circuit voltages and currents. The result of this analysis is the frequency response of
CHAPTER 14 Introduction to Frequency Selective Circuits Frequency-selective circuits Varying source frequency on circuit voltages and currents. The result of this analysis is the frequency response of
Name: Date: Score: / (75)
 Name: Date: Score: / (75) This lab MUST be done in your normal lab time NO LATE LABS Bring Textbook to Lab. You don t need to use your lab notebook, just fill in the blanks, you ll be graded when you re
Name: Date: Score: / (75) This lab MUST be done in your normal lab time NO LATE LABS Bring Textbook to Lab. You don t need to use your lab notebook, just fill in the blanks, you ll be graded when you re
Designing Information Devices and Systems II Fall 2017 Miki Lustig and Michel Maharbiz Homework 3
 EECS 16B Designing Information Devices and Systems II Fall 2017 Miki Lustig and Michel Maharbiz Homework 3 This homework is due September 19, 2017, at Noon. Please use radians for all angles in phasor
EECS 16B Designing Information Devices and Systems II Fall 2017 Miki Lustig and Michel Maharbiz Homework 3 This homework is due September 19, 2017, at Noon. Please use radians for all angles in phasor
EE 210: CIRCUITS AND DEVICES
 EE 210: CIRCUITS AND DEVICES OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS PART II This is the second of two laboratory sessions that provide an introduction to the op amp. In this session you will study three amplifiers designs:
EE 210: CIRCUITS AND DEVICES OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS PART II This is the second of two laboratory sessions that provide an introduction to the op amp. In this session you will study three amplifiers designs:
1. Hand Calculations (in a manner suitable for submission) For the circuit in Fig. 1 with f = 7.2 khz and a source vin () t 1.
 Objectives The purpose of this laboratory project is to introduce to equipment, measurement techniques, and simulations commonly used in AC circuit analysis. In this laboratory session, each student will:
Objectives The purpose of this laboratory project is to introduce to equipment, measurement techniques, and simulations commonly used in AC circuit analysis. In this laboratory session, each student will:
Physics 303 Fall Module 4: The Operational Amplifier
 Module 4: The Operational Amplifier Operational Amplifiers: General Introduction In the laboratory, analog signals (that is to say continuously variable, not discrete signals) often require amplification.
Module 4: The Operational Amplifier Operational Amplifiers: General Introduction In the laboratory, analog signals (that is to say continuously variable, not discrete signals) often require amplification.
Purpose: 1) to investigate the electrical properties of a diode; and 2) to use a diode to construct an AC to DC converter.
 Name: Partner: Partner: Partner: Purpose: 1) to investigate the electrical properties of a diode; and 2) to use a diode to construct an AC to DC converter. The Diode A diode is an electrical device which
Name: Partner: Partner: Partner: Purpose: 1) to investigate the electrical properties of a diode; and 2) to use a diode to construct an AC to DC converter. The Diode A diode is an electrical device which
EXPERIMENT 10: SINGLE-TRANSISTOR AMPLIFIERS 11/11/10
 EXPERIMENT 10: SINGLE-TRANSISTOR AMPLIFIERS 11/11/10 In this experiment we will measure the characteristics of the standard common emitter amplifier. We will use the 2N3904 npn transistor. If you have
EXPERIMENT 10: SINGLE-TRANSISTOR AMPLIFIERS 11/11/10 In this experiment we will measure the characteristics of the standard common emitter amplifier. We will use the 2N3904 npn transistor. If you have
Introduction to oscilloscope. and time dependent circuits
 Physics 9 Intro to oscilloscope, v.1.0 p. 1 NAME: SECTION DAY/TIME: TA: LAB PARTNER: Introduction to oscilloscope and time dependent circuits Introduction In this lab, you ll learn the basics of how to
Physics 9 Intro to oscilloscope, v.1.0 p. 1 NAME: SECTION DAY/TIME: TA: LAB PARTNER: Introduction to oscilloscope and time dependent circuits Introduction In this lab, you ll learn the basics of how to
Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters
 Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters Goal: In circuits with a time-varying voltage, the relationship between current and voltage is more complicated
Lab #2: Electrical Measurements II AC Circuits and Capacitors, Inductors, Oscillators and Filters Goal: In circuits with a time-varying voltage, the relationship between current and voltage is more complicated
ECE4902 C Lab 5 MOSFET Common Source Amplifier with Active Load Bandwidth of MOSFET Common Source Amplifier: Resistive Load / Active Load
 ECE4902 C2012 - Lab 5 MOSFET Common Source Amplifier with Active Load Bandwidth of MOSFET Common Source Amplifier: Resistive Load / Active Load PURPOSE: The primary purpose of this lab is to measure the
ECE4902 C2012 - Lab 5 MOSFET Common Source Amplifier with Active Load Bandwidth of MOSFET Common Source Amplifier: Resistive Load / Active Load PURPOSE: The primary purpose of this lab is to measure the
