Inductance of solenoids
|
|
|
- May Patrick
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Inductance of solenoids LEP -01 Related topics Law of inductance, Lenz s law, self-inductance, solenoids, transformer, oscillatory circuit, resonance, damped oscillation, logarithmic decrement, Q factor. Principle A square wave voltage of low frequency is applied to oscillatory circuits comprising coils and capacitors to produce free, damped oscillations. The values of inductance are calculated from the natural frequencies measured, the capacitance being known. Equipment Induction coil, 300 turns, d = 40 mm Induction coil, 300 turns, d = 3 mm Induction coil, 300 turns, d = 5 mm Induction coil, 00 turns, d = 40 mm Induction coil, 100 turns, d = 40 mm Induction coil, 150 turns, d = 5 mm Induction coil, 75 turns, d = 5 mm Coil, 100 turns Oscilloscope, 30 MHz, channels Function generator Capacitor /case 1/ 470 nf Adapter, BNC-plug/socket 4 mm Connection box Connecting cord, l = 50 mm, red Connecting cord, l = 500 mm, red Connecting cord, l = 50 mm, blue Connecting cord, l = 500 mm, blue Tasks To connect coils of different dimensions (length, radius, number of turns) with a known capacitance C to form an oscillatory circuit. From the measurements of the natural frequencies, to calculate the inductances of the coils and determine the relationships between 1. inductance and number of turns. inductance and length 3. inductance and radius. Set-up and procedure Set up the experiment as shown in Fig A square wave voltage of low frequency (f 500 Hz) is applied to the excitation coil L. The sudden change in the magnetic field induces a voltage in coil L1 and creates a free damped oscillation in the L1C oscillatory circuit, the frequency f o of which is measured with the oscilloscope. Coils of different lengths l, diameters r and number of turns N are available (Tab. 1). The diameters and lengths are measured with the vernier caliper and the measuring tape, and the numbers of turns are given. Fig. 1: Experimental set-up. PHYWE series of publications Laboratory Experiments Physics PHYWE SYSTEME GMBH & Co. KG D Göttingen
2 LEP -01 Inductance of solenoids Fig. : Set-up for inductance measurement. The following coils provide the relationships between inductance and radius, length and number of turns that we are investigating: 1.) 3, 6, 7 L = f(n).) 1, 4, 5 L/N = f(l) 3.) 1,, 3 L = f(r) As a difference in length also means a difference in the number of turns, the relationship between inductance and number of turns found in Task 1 must also be used to solve Task. Tab. 1: Table of coil data Coil No. N r l mm mm Cat. No Fig. 3 shows an measurement example and the oscilloscope settings: - Input: CH1 - Volts/div 10 mv - Time/div <0.1 ms - Trigger source CH1 - Trigger mode Norm The oscilloscope shows the rectangular signal and the damped oscillation behind each peak. Determine the frequency f 0 of this damped oszillation. f 0 1 T where T is the oscillation period. Fig. 3: Oscilloscope settings PHYWE series of publications Laboratory Experiments Physics PHYWE SYSTEME GMBH & Co. KG D Göttingen
3 Inductance of solenoids LEP -01 Fig. 4: Inductances of the coils as a function of the number of turns, at constant length and constant radius. Double logarithmic plotting. Fig. 6: Inductance of the coils as a function of the radius, at constant length and number of turns. Double logarithmic plotting. Notes The distance between L1 and L should be as large as possible so that the effect of the excitation coil on the resonant frequency can be disregarded. There should be no iron components in the immediate vicinity of the coils. The tolerance of the oscilloscope time-base is given as 4%. If a higher degree of accuracy is required, the time-base can be calibrated for all measuring ranges with the function generator and a frequency counter prior to these experiments. The magnetic flux through the coil is given by = m o m H A () where m o is the magnetic field constant and m the absolute permeability of the surrounding medium. When this flux changes, it induces a voltage between the ends of the coil, U ind. N Theory and evaluation If a current of strength I flows through a cylindrical coil (solenoid) of length l, cross sectional area A = p r, and number of turns N, a magnetic field is set up in the coil. When l >> r the magnetic field is uniform and the field strength H is easy to calculate: H I N l (1) where N m 0 m A N l I L I L m 0 m p N r l (3) (4) is the coefficient of self-induction (inductance) of the coil. Inductivity Equation (4) for the inductance applies only to very long coils l >> r, with a uniform magnetic field in accordance with (1). In practice, the inductance of coils with l > r can be calculated with greater accuracy by an approximation formula L N r a r l b 3>4 for 0 6 r (5) l 6 1 Fig. 5: Inductance per turn as a function of the length of coil, at constant radius. Double logarithmic plotting. In the experiment, the inductance of various coils is calculated from the natural frequency of an oscillating circuit. v 0 1 LC tot. C tot. is the sum of the capacitance the known capacitor and the input capacitance C i of the oscilloscope. (6) PHYWE series of publications Laboratory Experiments Physics PHYWE SYSTEME GMBH & Co. KG D Göttingen
4 LEP -01 Inductance of solenoids The internal resistance R i of the oscilloscope exercises a damping effect on the oscillatory circuit and causes a negligible shift (approx. 1%) in the resonance frequency. The inductance is therefore represented by 1 L 4p f 0 C tot. where C tot. = C + C i and The table shows the theoretical inductance values of the used coils calculated according to eq. 5. Table f 0 v 0 p Coil No. N r/m l/m L theo /µh The table 3 shows the measured values of the oscillation periods and the corresponding inductance values of the used coils calculated according to eq. 7. These L exp values are plotted in Figs. 4, 5 and 6. (7) L = A N B to the regression line from the measured values in Fig. 4 gives B = 1.95±0.04 ; B theo = (see Eq. 5) Now that we know that L ~ N, we can demonstrate the relationship between inductance and the length of the coil. L A lc N to the regression line from the measured values in Fig. 5 gives C = 0.8 ± ; C theo = L A rd N to the regression line from the measured values in Fig. 6 gives D = 1.86 ± ; D theo = 1.75 The Equation (5) is thus verified within the limits of error. Table 3 Coil No. T exp./µs L exp /µh PHYWE series of publications Laboratory Experiments Physics PHYWE SYSTEME GMBH & Co. KG D Göttingen
5 Inductance of solenoids with Cobra3 LEP -11 Related topics Law of inductance, Lenz s law, self-inductance, solenoids, transformer, oscillatory circuit, resonance, damped oscillation, logarithmic decrement, Q factor. Principle A square wave voltage of low frequency is applied to oscillatory circuits comprising coils and capacitors to produce free, damped oscillations. The values of inductance are calculated from the natural frequencies measured, the capacitance being known. Equipment Cobra3 Basic Unit Power supply, 1 V RS 3 data cable Cobra3 Universal writer software Cobra3 Function generator module Induction coil, 300 turns, dia. 40 mm Induction coil, 300 turns, dia. 3 mm Induction coil, 300 turns, dia. 5 mm Induction coil, 00 turns, dia. 40 mm Induction coil, 100 turns, dia. 40 mm Induction coil, 150 turns, dia. 5 mm Induction coil, 75 turns, dia. 5 mm Coil, 100 turns PEK capacitor /case 1/ 470 nf/50 V Connection box Connecting cord, 50 mm, red Connecting cord, 50 mm, blue Connecting cord, 500 mm, red Connecting cord, 500 mm, blue PC, Windows 95 or higher Tasks To connect coils of different dimensions (length, radius, number of turns) with a known capacitance C to form an oscillatory circuit. From the measurements of the natural frequencies, to calculate the inductances of the coils and determine the relationships between 1. inductance and number of turns. inductance and length 3. inductance and radius. Set-up and procedure Set up the experiment as shown in Fig A square wave voltage of low frequency (f 500 Hz) is applied to the excitation coil L. The sudden change in the magnetic field induces a voltage in coil L1 and creates a free damped oscillation in the L1C oscillatory circuit, the frequency f o of which is measured with the Cobra3 interface. Coils of different lengths l, diameters r and number of turns N are available (Tab. 1). The diameters and lengths are measured with the vernier caliper and the measuring tape, and the numbers of turns are given. Fig. 1: Experimental set-up. PHYWE series of publications Laboratory Experiments Physics PHYWE SYSTEME GMBH & Co. KG D Göttingen
6 LEP -11 Inductance of solenoids with Cobra3 Fig. : Set-up for inductance measurement. Fig. 3: Measuring parameters. Tab. 1: Table of coil data r l Coil No. N Cat. No. mm mm The following coils provide the relationships between inductance and radius, length and number of turns that we are investigating: 1.) 3, 6, 7 L = f(n).) 1, 4, 5 L/N = f(l) 3.) 1,, 3 L = f(r) As a difference in length also means a difference in the number of turns, the relationship between inductance and number of turns found in Task 1 must also be used to solve Task. Notes The distance between L1 and L should be as large as possible so that the effect of the excitation coil on the resonant frequency can be disregarded. There should be no iron components in the immediate vicinity of the coils. Connect the Cobra3 Basic Unit to the computer port COM1, COM or to USB port (for USB computer port use USB to RS3 Converter ). Start the measure program and select Cobra3 Universal Writer Gauge. Begin the measurement using the parameters given in Fig. 3. For the measurement of the oscillation period the Survey Function of the Measure Software is used (see Fig. 4). Fig. 4: Measurement of the oscillation period with the Survey Function PHYWE series of publications Laboratory Experiments Physics PHYWE SYSTEME GMBH & Co. KG D Göttingen
7 Inductance of solenoids with Cobra3 LEP -11 Fig. 4 shows the rectangular signal and the damped oscillation behind each peak. Determine the frequency f 0 of this damped oszillation, The inductance is therefore represented by 1 L 4p f 0 C tot. (7) where T is the oscillation period. Theory and evaluation If a current of strength I flows through a cylindrical coil (solenoid) of length l, cross sectional area A = p r, and number of turns N, a magnetic field is set up in the coil. When l >> r the magnetic field is uniform and the field strength H is easy to calculate: The magnetic flux through the coil is given by (1) = m o m H A () where m o is the magnetic field constant and m the absolute permeability of the surrounding medium. When this flux changes, it induces a voltage between the ends of the coil, where f 0 1 T H I N l U ind. N N m 0 m A N l I L I L m 0 m p N r is the coefficient of self-induction (inductance) of the coil. Inductivity Equation (4) for the inductance applies only to very long coils l >> r, with a uniform magnetic field in accordance with (1). In practice, the inductance of coils with l > r can be calculated with greater accuracy by an approximation formula L N r a r l b 3>4 l (3) (4) where C tot. = C + C i and The table shows the theoretical inductance values of the used coils calculated according to eq. 5. Table The table 3 shows the measured values of the oscillation periods and the corresponding inductance values of the used coils calculated according to eq. 7. These L exp values are plotted in Figs. 5, 6 and 7. Table 3 f 0 v 0 p Coil No. N r/m l/m L theo /µh Coil No. T exp. /µs L exp /µh Fig. 5: Inductances of the coils as a function of the number of turns, at constant length and constant radius. Double logarithmic plotting for 0 6 r (5) l 6 1 In the experiment, the inductance of various coils is calculated from the natural frequency of an oscillating circuit. v 0 1 LC tot. C tot. is the sum of the capacitance the known capacitor and the input capacitance C i of the Cobra3 input. The internal resistance R i of the Cobra3 input exercises a damping effect on the oscillatory circuit and causes a negligible shift (approx. 1%) in the resonance frequency. (6) PHYWE series of publications Laboratory Experiments Physics PHYWE SYSTEME GMBH & Co. KG D Göttingen
8 LEP -11 Inductance of solenoids with Cobra3 Fig. 6: Inductance per turn as a function of the length of coil, at constant radius. Double logarithmic plotting Fig. 7: Inductance of the coils as a function of the radius, at constant length and number of turns. Double logarithmic plotting L = A N B to the regression line from the measured values in Fig. 5 gives B = 1.95±0.04 ; B theo = (see Eq. 5) Now that we know that L ~ N, we can demonstrate the relationship between inductance and the length of the coil. L A lc N to the regression line from the measured values in Fig. 6 gives C = -0.8±0.04 ; C theo = L A rd N to the regression line from the measured values in Fig. 7 gives D = 1.86 ± ; D theo = 1.75 The Equation (5) is thus verified within the limits of error PHYWE series of publications Laboratory Experiments Physics PHYWE SYSTEME GMBH & Co. KG D Göttingen
Inductance of solenoids with Cobra3
 Inductance of solenoids with Cobra3 TEP Related topics Law of inductance, Lenz s law, self-inductance, solenoids, transformer, oscillatory circuit, resonance, damped oscillation, logarithmic decrement,
Inductance of solenoids with Cobra3 TEP Related topics Law of inductance, Lenz s law, self-inductance, solenoids, transformer, oscillatory circuit, resonance, damped oscillation, logarithmic decrement,
Inductance of solenoids
 Inductance of solenoids TEP Related Topics Law of inductance, Lenz s law, self-inductance, solenoids, transformer, coupled oscillatory circuit, resonance, damped oscillation, logarithmic decrement Principle
Inductance of solenoids TEP Related Topics Law of inductance, Lenz s law, self-inductance, solenoids, transformer, coupled oscillatory circuit, resonance, damped oscillation, logarithmic decrement Principle
Electricity. Coil in the AC circuit /11. Electrodynamics. What you need:
 Electrodynamics Electricity Coil in the AC circuit -01/11 What you can learn about Inductance Kirchhoff s laws Maxwell s equations AC impedance Phase displacement Principle: The coil is connected in a
Electrodynamics Electricity Coil in the AC circuit -01/11 What you can learn about Inductance Kirchhoff s laws Maxwell s equations AC impedance Phase displacement Principle: The coil is connected in a
Coil in the AC circuit with Cobra3
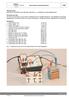 Coil in the AC circuit with Cobra3 TEP Related topics Inductance, Kirchhoff s laws, Maxwell s equations, a.c. impedance, phase displacement. Principle and task The coil is connected in a circuit with a
Coil in the AC circuit with Cobra3 TEP Related topics Inductance, Kirchhoff s laws, Maxwell s equations, a.c. impedance, phase displacement. Principle and task The coil is connected in a circuit with a
Magnetic induction with Cobra3
 Magnetic induction with Cobra3 LEP Related Topics Maxwell s equations, electrical eddy field, magnetic field of coils, coil, magnetic flux, induced voltage. Principle A magnetic field of variable frequency
Magnetic induction with Cobra3 LEP Related Topics Maxwell s equations, electrical eddy field, magnetic field of coils, coil, magnetic flux, induced voltage. Principle A magnetic field of variable frequency
RLC Circuit with Cobra3
 RLC Circuit with Cobra3 LEP Related topics Tuned circuit, series-tuned circuit, parallel-tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, capacitor, coil, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width,impedance,
RLC Circuit with Cobra3 LEP Related topics Tuned circuit, series-tuned circuit, parallel-tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, capacitor, coil, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width,impedance,
Magnetic induction with Cobra3
 Principle A magnetic field of variable frequency and varying strength is produced in a long coil. The voltages induced across thin coils which are pushed into the long coil are determined as a function
Principle A magnetic field of variable frequency and varying strength is produced in a long coil. The voltages induced across thin coils which are pushed into the long coil are determined as a function
TEP. RLC Circuit with Cobra3
 RLC Circuit with Cobra3 TEP Related topics Tuned circuit, series-tuned circuit, parallel-tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, capacitor, coil, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width,impedance,
RLC Circuit with Cobra3 TEP Related topics Tuned circuit, series-tuned circuit, parallel-tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, capacitor, coil, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width,impedance,
Coil in the AC circuit
 Coil in the AC circuit LEP Related topics Inductance, Kirchhoff s laws, parallel connection, series connection, a. c. impedance, phase displacement, vector diagram Principle The impedance and phase displacement
Coil in the AC circuit LEP Related topics Inductance, Kirchhoff s laws, parallel connection, series connection, a. c. impedance, phase displacement, vector diagram Principle The impedance and phase displacement
RLC-circuits with Cobra4 Xpert-Link TEP. 1 2 π L C. f res=
 Related topics Damped and forced oscillations, Kirchhoff s laws, series and parallel tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, reactance, impedance, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width Principle
Related topics Damped and forced oscillations, Kirchhoff s laws, series and parallel tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, reactance, impedance, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width Principle
LEP RLC Circuit
 RLC Circuit LEP Related topics Kirchhoff s laws, series and parallel tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width, loss resistance, damping Principle The
RLC Circuit LEP Related topics Kirchhoff s laws, series and parallel tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width, loss resistance, damping Principle The
RLC-circuits with Cobra4 Xpert-Link
 Student's Sheet RLC-circuits with Cobra4 Xpert-Link (Item No.: P2440664) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Subtopic: Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, AC Circuits Topic: Electricity
Student's Sheet RLC-circuits with Cobra4 Xpert-Link (Item No.: P2440664) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Subtopic: Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, AC Circuits Topic: Electricity
RLC-circuits TEP. f res. = 1 2 π L C.
 RLC-circuits TEP Keywords Damped and forced oscillations, Kirchhoff s laws, series and parallel tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, reactance, impedance, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width
RLC-circuits TEP Keywords Damped and forced oscillations, Kirchhoff s laws, series and parallel tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, reactance, impedance, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width
ET1210: Module 5 Inductance and Resonance
 Part 1 Inductors Theory: When current flows through a coil of wire, a magnetic field is created around the wire. This electromagnetic field accompanies any moving electric charge and is proportional to
Part 1 Inductors Theory: When current flows through a coil of wire, a magnetic field is created around the wire. This electromagnetic field accompanies any moving electric charge and is proportional to
AP Physics C. Alternating Current. Chapter Problems. Sources of Alternating EMF
 AP Physics C Alternating Current Chapter Problems Sources of Alternating EMF 1. A 10 cm diameter loop of wire is oriented perpendicular to a 2.5 T magnetic field. What is the magnetic flux through the
AP Physics C Alternating Current Chapter Problems Sources of Alternating EMF 1. A 10 cm diameter loop of wire is oriented perpendicular to a 2.5 T magnetic field. What is the magnetic flux through the
15. the power factor of an a.c circuit is.5 what will be the phase difference between voltage and current in this
 1 1. In a series LCR circuit the voltage across inductor, a capacitor and a resistor are 30 V, 30 V and 60 V respectively. What is the phase difference between applied voltage and current in the circuit?
1 1. In a series LCR circuit the voltage across inductor, a capacitor and a resistor are 30 V, 30 V and 60 V respectively. What is the phase difference between applied voltage and current in the circuit?
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENT (Assignment)
 ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENT (Assignment) 1. In an A.C. circuit A ; the current leads the voltage by 30 0 and in circuit B, the current lags behind the voltage by 30 0. What is the
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENT (Assignment) 1. In an A.C. circuit A ; the current leads the voltage by 30 0 and in circuit B, the current lags behind the voltage by 30 0. What is the
Properties of Inductor and Applications
 LABORATORY Experiment 3 Properties of Inductor and Applications 1. Objectives To investigate the properties of inductor for different types of magnetic material To calculate the resonant frequency of a
LABORATORY Experiment 3 Properties of Inductor and Applications 1. Objectives To investigate the properties of inductor for different types of magnetic material To calculate the resonant frequency of a
Magnetic field inside a conductor
 Magnetic field inside a conductor TEP Principle A current is passed through an electrolyte producing a magnetic field. This magnetic field inside the conductor is measured as function of position and current
Magnetic field inside a conductor TEP Principle A current is passed through an electrolyte producing a magnetic field. This magnetic field inside the conductor is measured as function of position and current
Exp. #2-6 : Measurement of the Characteristics of,, and Circuits by Using an Oscilloscope
 PAGE 1/14 Exp. #2-6 : Measurement of the Characteristics of,, and Circuits by Using an Oscilloscope Student ID Major Name Team No. Experiment Lecturer Student's Mentioned Items Experiment Class Date Submission
PAGE 1/14 Exp. #2-6 : Measurement of the Characteristics of,, and Circuits by Using an Oscilloscope Student ID Major Name Team No. Experiment Lecturer Student's Mentioned Items Experiment Class Date Submission
The Tuned Circuit. Aim of the experiment. Circuit. Equipment and components. Display of a decaying oscillation. Dependence of L, C and R.
 The Tuned Circuit Aim of the experiment Display of a decaying oscillation. Dependence of L, C and R. Circuit Equipment and components 1 Rastered socket panel 1 Resistor R 1 = 10 Ω, 1 Resistor R 2 = 1 kω
The Tuned Circuit Aim of the experiment Display of a decaying oscillation. Dependence of L, C and R. Circuit Equipment and components 1 Rastered socket panel 1 Resistor R 1 = 10 Ω, 1 Resistor R 2 = 1 kω
Kirchhoff s laws, induction law, Maxwell equations, current, voltage, resistance, parallel connection, series connection, potentiometer
 Kirchhoff s laws with Cobra4 TEP Related Topics Kirchhoff s laws, induction law, Maxwell equations, current, voltage, resistance, parallel connection, series connection, potentiometer Principle First Kirchhoff
Kirchhoff s laws with Cobra4 TEP Related Topics Kirchhoff s laws, induction law, Maxwell equations, current, voltage, resistance, parallel connection, series connection, potentiometer Principle First Kirchhoff
Surge Generator for MIL-STD 1275
 Surge Generator for MIL-STD 1275 This generator PG1275 is specially designed for the test of the susceptibility to surges and spikes of military 28 Vdc electric circuits. The equipment allows performing
Surge Generator for MIL-STD 1275 This generator PG1275 is specially designed for the test of the susceptibility to surges and spikes of military 28 Vdc electric circuits. The equipment allows performing
Core Technology Group Application Note 1 AN-1
 Measuring the Impedance of Inductors and Transformers. John F. Iannuzzi Introduction In many cases it is necessary to characterize the impedance of inductors and transformers. For instance, power supply
Measuring the Impedance of Inductors and Transformers. John F. Iannuzzi Introduction In many cases it is necessary to characterize the impedance of inductors and transformers. For instance, power supply
An induced emf is the negative of a changing magnetic field. Similarly, a self-induced emf would be found by
 This is a study guide for Exam 4. You are expected to understand and be able to answer mathematical questions on the following topics. Chapter 32 Self-Induction and Induction While a battery creates an
This is a study guide for Exam 4. You are expected to understand and be able to answer mathematical questions on the following topics. Chapter 32 Self-Induction and Induction While a battery creates an
Lab 1. Resonance and Wireless Energy Transfer Physics Enhancement Programme Department of Physics, Hong Kong Baptist University
 Lab 1. Resonance and Wireless Energy Transfer Physics Enhancement Programme Department of Physics, Hong Kong Baptist University 1. OBJECTIVES Introduction to the concept of resonance Observing resonance
Lab 1. Resonance and Wireless Energy Transfer Physics Enhancement Programme Department of Physics, Hong Kong Baptist University 1. OBJECTIVES Introduction to the concept of resonance Observing resonance
Lab E2: B-field of a Solenoid. In the case that the B-field is uniform and perpendicular to the area, (1) reduces to
 E2.1 Lab E2: B-field of a Solenoid In this lab, we will explore the magnetic field created by a solenoid. First, we must review some basic electromagnetic theory. The magnetic flux over some area A is
E2.1 Lab E2: B-field of a Solenoid In this lab, we will explore the magnetic field created by a solenoid. First, we must review some basic electromagnetic theory. The magnetic flux over some area A is
PHYSICS WORKSHEET CLASS : XII. Topic: Alternating current
 PHYSICS WORKSHEET CLASS : XII Topic: Alternating current 1. What is mean by root mean square value of alternating current? 2. Distinguish between the terms effective value and peak value of an alternating
PHYSICS WORKSHEET CLASS : XII Topic: Alternating current 1. What is mean by root mean square value of alternating current? 2. Distinguish between the terms effective value and peak value of an alternating
Experiment 1 Alternating Current with Coil and Ohmic Resistors
 Experiment Alternating Current with Coil and Ohmic esistors - Objects of the experiment - Determining the total impedance and the phase shift in a series connection of a coil and a resistor. - Determining
Experiment Alternating Current with Coil and Ohmic esistors - Objects of the experiment - Determining the total impedance and the phase shift in a series connection of a coil and a resistor. - Determining
Exercise 1: Series Resonant Circuits
 Series Resonance AC 2 Fundamentals Exercise 1: Series Resonant Circuits EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to compute the resonant frequency, total current, and
Series Resonance AC 2 Fundamentals Exercise 1: Series Resonant Circuits EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to compute the resonant frequency, total current, and
Filters And Waveform Shaping
 Physics 3330 Experiment #3 Fall 2001 Purpose Filters And Waveform Shaping The aim of this experiment is to study the frequency filtering properties of passive (R, C, and L) circuits for sine waves, and
Physics 3330 Experiment #3 Fall 2001 Purpose Filters And Waveform Shaping The aim of this experiment is to study the frequency filtering properties of passive (R, C, and L) circuits for sine waves, and
Electron Spin Resonance v2.0
 Electron Spin Resonance v2.0 Background. This experiment measures the dimensionless g-factor (g s ) of an unpaired electron using the technique of Electron Spin Resonance, also known as Electron Paramagnetic
Electron Spin Resonance v2.0 Background. This experiment measures the dimensionless g-factor (g s ) of an unpaired electron using the technique of Electron Spin Resonance, also known as Electron Paramagnetic
Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance
 E5.1 Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance Note: It is strongly recommended that you complete lab E4: Capacitors and the RC Circuit before performing this experiment. Introduction Ohm s law, a well known
E5.1 Lab E5: Filters and Complex Impedance Note: It is strongly recommended that you complete lab E4: Capacitors and the RC Circuit before performing this experiment. Introduction Ohm s law, a well known
Study of Inductive and Capacitive Reactance and RLC Resonance
 Objective Study of Inductive and Capacitive Reactance and RLC Resonance To understand how the reactance of inductors and capacitors change with frequency, and how the two can cancel each other to leave
Objective Study of Inductive and Capacitive Reactance and RLC Resonance To understand how the reactance of inductors and capacitors change with frequency, and how the two can cancel each other to leave
CHAPTER 6: ALTERNATING CURRENT
 CHAPTER 6: ALTERNATING CURRENT PSPM II 2005/2006 NO. 12(C) 12. (c) An ac generator with rms voltage 240 V is connected to a RC circuit. The rms current in the circuit is 1.5 A and leads the voltage by
CHAPTER 6: ALTERNATING CURRENT PSPM II 2005/2006 NO. 12(C) 12. (c) An ac generator with rms voltage 240 V is connected to a RC circuit. The rms current in the circuit is 1.5 A and leads the voltage by
POT/GAL 15 V 10 A and POT/GAL 30 V 2 A. Electrochemical Impedance Potentiostat Galvanostat Test Interface for Alpha-A Analyzer
 POT/GAL 15 V 10 A and POT/GAL 30 V 2 A Electrochemical Impedance Potentiostat Galvanostat Test Interface for Alpha-A Analyzer Issue: 10/2011 Rev. 2.50 by Novocontrol Technologies GmbH & Co. KG Novocontrol
POT/GAL 15 V 10 A and POT/GAL 30 V 2 A Electrochemical Impedance Potentiostat Galvanostat Test Interface for Alpha-A Analyzer Issue: 10/2011 Rev. 2.50 by Novocontrol Technologies GmbH & Co. KG Novocontrol
Electric Stresses on Surge Arrester Insulation under Standard and
 Chapter 5 Electric Stresses on Surge Arrester Insulation under Standard and Non-standard Impulse Voltages 5.1 Introduction Metal oxide surge arresters are used to protect medium and high voltage systems
Chapter 5 Electric Stresses on Surge Arrester Insulation under Standard and Non-standard Impulse Voltages 5.1 Introduction Metal oxide surge arresters are used to protect medium and high voltage systems
Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University
 Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University School of Information, Computer and Communication Technology COURSE : ECS 34 Basic Electrical Engineering Lab INSTRUCTOR : Dr. Prapun
Sirindhorn International Institute of Technology Thammasat University School of Information, Computer and Communication Technology COURSE : ECS 34 Basic Electrical Engineering Lab INSTRUCTOR : Dr. Prapun
Resonance in Circuits
 Resonance in Circuits Purpose: To map out the analogy between mechanical and electronic resonant systems To discover how relative phase depends on driving frequency To gain experience setting up circuits
Resonance in Circuits Purpose: To map out the analogy between mechanical and electronic resonant systems To discover how relative phase depends on driving frequency To gain experience setting up circuits
Experiment 2: Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits
 Experiment 2: Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits Will Chemelewski Partner: Brian Enders TA: Nielsen See laboratory book #1 pages 5-7, data taken September 1, 2009 September 7, 2009 Abstract Transient
Experiment 2: Transients and Oscillations in RLC Circuits Will Chemelewski Partner: Brian Enders TA: Nielsen See laboratory book #1 pages 5-7, data taken September 1, 2009 September 7, 2009 Abstract Transient
CHAPTER 5 Test B Lsn 5-6 to 5-8 TEST REVIEW
 IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 5 Test B Lsn 5-6 to 5-8 TEST REVIEW 1. This question is about electric circuits. (a) (b) Define (i) (ii) electromotive force
IB PHYSICS Name: Period: Date: DEVIL PHYSICS BADDEST CLASS ON CAMPUS CHAPTER 5 Test B Lsn 5-6 to 5-8 TEST REVIEW 1. This question is about electric circuits. (a) (b) Define (i) (ii) electromotive force
DC and AC Circuits. Objective. Theory. 1. Direct Current (DC) R-C Circuit
 [International Campus Lab] Objective Determine the behavior of resistors, capacitors, and inductors in DC and AC circuits. Theory ----------------------------- Reference -------------------------- Young
[International Campus Lab] Objective Determine the behavior of resistors, capacitors, and inductors in DC and AC circuits. Theory ----------------------------- Reference -------------------------- Young
AC CIRCUITS. Part 1: Inductance of a Coil. THEORY: If the current in a resistor R, a capacitor C, and/or an inductor L is given by:
 AC CIRCUITS OBJECTIVE: To study the effect of alternating currents on various electrical quantities in circuits containing resistors, capacitors and inductors. Part 1: Inductance of a Coil THEORY: If the
AC CIRCUITS OBJECTIVE: To study the effect of alternating currents on various electrical quantities in circuits containing resistors, capacitors and inductors. Part 1: Inductance of a Coil THEORY: If the
Magnetism and Induction
 Magnetism and Induction Before the Lab Read the following sections of Giancoli to prepare for this lab: 27-2: Electric Currents Produce Magnetism 28-6: Biot-Savart Law EXAMPLE 28-10: Current Loop 29-1:
Magnetism and Induction Before the Lab Read the following sections of Giancoli to prepare for this lab: 27-2: Electric Currents Produce Magnetism 28-6: Biot-Savart Law EXAMPLE 28-10: Current Loop 29-1:
SUGAR CAPACITY EXPERIMENT
 SUGAR CAPACITY EXPERIMENT A PRACTICAL INTRODUCTION TO AC THEORY P R E A M B L E Sugar Capacity is a PBL Experimental Group Research Project to be undertaken by small groups of (approximately 4) first year
SUGAR CAPACITY EXPERIMENT A PRACTICAL INTRODUCTION TO AC THEORY P R E A M B L E Sugar Capacity is a PBL Experimental Group Research Project to be undertaken by small groups of (approximately 4) first year
U2270B Antenna Design Hints
 U227B Antenna Design Hints General Information The reader antenna is a series resonance circuit consisting of an inductor, a capacitor and a resistor (see figure ). Driver C R R R L R Overall resistance
U227B Antenna Design Hints General Information The reader antenna is a series resonance circuit consisting of an inductor, a capacitor and a resistor (see figure ). Driver C R R R L R Overall resistance
Attenuation and velocity of ultrasound in solid state materials (transmission)
 Attenuation and velocity of ultrasound in solid 5.1.6.08 Related Topics Propagation of ultrasonic waves, time of flight, sound velocity, damping of ultrasonic waves (scattering, reflection, absorption),
Attenuation and velocity of ultrasound in solid 5.1.6.08 Related Topics Propagation of ultrasonic waves, time of flight, sound velocity, damping of ultrasonic waves (scattering, reflection, absorption),
Electronic Instrumentation
 10/15/01 1 Electronic Instrumentation Experiment 3 Part A: Making an Inductor Part B: Measurement of Inductance Part C: imulation of a Transformer Part D: Making a Transformer Review RC and Resonance How
10/15/01 1 Electronic Instrumentation Experiment 3 Part A: Making an Inductor Part B: Measurement of Inductance Part C: imulation of a Transformer Part D: Making a Transformer Review RC and Resonance How
total j = BA, [1] = j [2] total
![total j = BA, [1] = j [2] total total j = BA, [1] = j [2] total](/thumbs/85/91692343.jpg) Name: S.N.: Experiment 2 INDUCTANCE AND LR CIRCUITS SECTION: PARTNER: DATE: Objectives Estimate the inductance of the solenoid used for this experiment from the formula for a very long, thin, tightly wound
Name: S.N.: Experiment 2 INDUCTANCE AND LR CIRCUITS SECTION: PARTNER: DATE: Objectives Estimate the inductance of the solenoid used for this experiment from the formula for a very long, thin, tightly wound
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.02 Spring 2005 Experiment 10: LR and Undriven LRC Circuits
 MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.0 Spring 005 Experiment 10: LR and Undriven LRC Circuits OBJECTIVES 1. To determine the inductance L and internal resistance R L of a coil,
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Physics 8.0 Spring 005 Experiment 10: LR and Undriven LRC Circuits OBJECTIVES 1. To determine the inductance L and internal resistance R L of a coil,
Name: First-Order Response: RC Networks Objective: To gain experience with first-order response of RC circuits
 First-Order Response: RC Networks Objective: To gain experience with first-order response of RC circuits Table of Contents: Pre-Lab Assignment 2 Background 2 National Instruments MyDAQ 2 Resistors 3 Capacitors
First-Order Response: RC Networks Objective: To gain experience with first-order response of RC circuits Table of Contents: Pre-Lab Assignment 2 Background 2 National Instruments MyDAQ 2 Resistors 3 Capacitors
CH 1. Large coil. Small coil. red. Function generator GND CH 2. black GND
 Experiment 6 Electromagnetic Induction "Concepts without factual content are empty; sense data without concepts are blind... The understanding cannot see. The senses cannot think. By their union only can
Experiment 6 Electromagnetic Induction "Concepts without factual content are empty; sense data without concepts are blind... The understanding cannot see. The senses cannot think. By their union only can
The SI unit of inductance is the henry, defined as:
 Inductors A coil of wire, or solenoid, can be used in a circuit to store energy in the magnetic field. We define the inductance of a solenoid having N turns, length l and cross-section area A as: The SI
Inductors A coil of wire, or solenoid, can be used in a circuit to store energy in the magnetic field. We define the inductance of a solenoid having N turns, length l and cross-section area A as: The SI
1. If the flux associated with a coil varies at the rate of 1 weber/min,the induced emf is
 1. f the flux associated with a coil varies at the rate of 1 weber/min,the induced emf is 1 1. 1V 2. V 60 3. 60V 4. Zero 2. Lenz s law is the consequence of the law of conservation of 1. Charge 2. Mass
1. f the flux associated with a coil varies at the rate of 1 weber/min,the induced emf is 1 1. 1V 2. V 60 3. 60V 4. Zero 2. Lenz s law is the consequence of the law of conservation of 1. Charge 2. Mass
Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks
 OPTI 380B Intermediate Optics Laboratory Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks Objectives: Lean how to use: Function of an oscilloscope probe. Characterization of capacitors and inductors
OPTI 380B Intermediate Optics Laboratory Lab 2: Linear and Nonlinear Circuit Elements and Networks Objectives: Lean how to use: Function of an oscilloscope probe. Characterization of capacitors and inductors
Experiment 1 LRC Transients
 Physics 263 Experiment 1 LRC Transients 1 Introduction In this experiment we will study the damped oscillations and other transient waveforms produced in a circuit containing an inductor, a capacitor,
Physics 263 Experiment 1 LRC Transients 1 Introduction In this experiment we will study the damped oscillations and other transient waveforms produced in a circuit containing an inductor, a capacitor,
sin(wt) y(t) Exciter Vibrating armature ENME599 1
 ENME599 1 LAB #3: Kinematic Excitation (Forced Vibration) of a SDOF system Students must read the laboratory instruction manual prior to the lab session. The lab report must be submitted in the beginning
ENME599 1 LAB #3: Kinematic Excitation (Forced Vibration) of a SDOF system Students must read the laboratory instruction manual prior to the lab session. The lab report must be submitted in the beginning
Class XII Chapter 7 Alternating Current Physics
 Question 7.1: A 100 Ω resistor is connected to a 220 V, 50 Hz ac supply. (a) What is the rms value of current in the circuit? (b) What is the net power consumed over a full cycle? Resistance of the resistor,
Question 7.1: A 100 Ω resistor is connected to a 220 V, 50 Hz ac supply. (a) What is the rms value of current in the circuit? (b) What is the net power consumed over a full cycle? Resistance of the resistor,
Figure 4.1 Vector representation of magnetic field.
 Chapter 4 Design of Vector Magnetic Field Sensor System 4.1 3-Dimensional Vector Field Representation The vector magnetic field is represented as a combination of three components along the Cartesian coordinate
Chapter 4 Design of Vector Magnetic Field Sensor System 4.1 3-Dimensional Vector Field Representation The vector magnetic field is represented as a combination of three components along the Cartesian coordinate
Single Device Solution for High Speed Testing and Frequency Sweeping IMPEDANCE ANALYZER IM3570
 IMPEDANCE ANALYZER IM3570 Single Device Solution for High Speed Testing and Frequency Sweeping With this new IM3570 Impedance Analyzer, an LCR meter and an impedance analyzer capable of measurement frequencies
IMPEDANCE ANALYZER IM3570 Single Device Solution for High Speed Testing and Frequency Sweeping With this new IM3570 Impedance Analyzer, an LCR meter and an impedance analyzer capable of measurement frequencies
ANADOLU UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND ARCHITECTURE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
 ANADOLU UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND ARCHITECTURE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EEM 206 ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT#3 RESONANT CIRCUITS 1 RESONANT CIRCUITS
ANADOLU UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ENGINEERING AND ARCHITECTURE DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING EEM 206 ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LABORATORY EXPERIMENT#3 RESONANT CIRCUITS 1 RESONANT CIRCUITS
MEASUREMENT OF THE INTERNAL INDUCTANCE OF IMPULSE VOLTAGE GENERATORS AND THE LIMITS OF LI FRONT TIMES
 The 20 th International Symposium on High Voltage Engineering, Buenos Aires, Argentina, August 27 September 01, 2017 MEASUREMENT OF THE INTERNAL INDUCTANCE OF IMPULSE VOLTAGE GENERATORS AND THE LIMITS
The 20 th International Symposium on High Voltage Engineering, Buenos Aires, Argentina, August 27 September 01, 2017 MEASUREMENT OF THE INTERNAL INDUCTANCE OF IMPULSE VOLTAGE GENERATORS AND THE LIMITS
Equipment for Attenuation and velocity of ultrasound in solid state materials (transmission), experimental set-up
 Attenuation and velocity of ultrasound in solid TEAS Related Topics Propagation of ultrasonic waves, time of flight, sound velocity, damping of ultrasonic waves (scattering, reflection, absorption), transmission
Attenuation and velocity of ultrasound in solid TEAS Related Topics Propagation of ultrasonic waves, time of flight, sound velocity, damping of ultrasonic waves (scattering, reflection, absorption), transmission
Radio Frequency Electronics
 Radio Frequency Electronics Preliminaries II Guglielmo Giovanni Maria Marconi Thought off by many people as the inventor of radio Pioneer in long-distance radio communications Shared Nobel Prize in 1909
Radio Frequency Electronics Preliminaries II Guglielmo Giovanni Maria Marconi Thought off by many people as the inventor of radio Pioneer in long-distance radio communications Shared Nobel Prize in 1909
Chapter Moving Charges and Magnetism
 100 Chapter Moving Charges and Magnetism 1. The power factor of an AC circuit having resistance (R) and inductance (L) connected in series and an angular velocity ω is [2013] 2. [2002] zero RvB vbl/r vbl
100 Chapter Moving Charges and Magnetism 1. The power factor of an AC circuit having resistance (R) and inductance (L) connected in series and an angular velocity ω is [2013] 2. [2002] zero RvB vbl/r vbl
Electromagnetic Oscillations and Currents. March 23, 2014 Chapter 30 1
 Electromagnetic Oscillations and Currents March 23, 2014 Chapter 30 1 Driven LC Circuit! The voltage V can be thought of as the projection of the vertical axis of the phasor V m representing the time-varying
Electromagnetic Oscillations and Currents March 23, 2014 Chapter 30 1 Driven LC Circuit! The voltage V can be thought of as the projection of the vertical axis of the phasor V m representing the time-varying
Electricity. Interference of microwaves Electromagnetic Oscillations and Waves. What you need:
 Electromagnetic Oscillations and Waves Electricity What you can learn about Wavelength Standing wave Reflection Transmission Michelson interferometer Principle: A microwave beam, after reflection from
Electromagnetic Oscillations and Waves Electricity What you can learn about Wavelength Standing wave Reflection Transmission Michelson interferometer Principle: A microwave beam, after reflection from
Units. In the following formulae all lengths are expressed in centimeters. The inductance calculated will be in micro-henries = 10-6 henry.
 INDUCTANCE Units. In the following formulae all lengths are expressed in centimeters. The inductance calculated will be in micro-henries = 10-6 henry. Long straight round wire. If l is the length; d, the
INDUCTANCE Units. In the following formulae all lengths are expressed in centimeters. The inductance calculated will be in micro-henries = 10-6 henry. Long straight round wire. If l is the length; d, the
MPS Electrical Test Laboratory, Larsen & Toubro Limited, Mysore Campus, KIADB Industrial Area, Hebbal Hootagalli, Mysore, Karnataka
 Last Amended on - Page 1 of 6 SOURCE 1. DC VOLTAGE $ 1mV to 10 mv 0.13 % to 0.014% Using Multifunction Calibrator 10 mv to 1 V 0.014% to 0.0016% By Direct Method 1 v to 10 V 0.0016% to 0.0017% 10 V to
Last Amended on - Page 1 of 6 SOURCE 1. DC VOLTAGE $ 1mV to 10 mv 0.13 % to 0.014% Using Multifunction Calibrator 10 mv to 1 V 0.014% to 0.0016% By Direct Method 1 v to 10 V 0.0016% to 0.0017% 10 V to
11. AC-resistances of capacitor and inductors: Reactances.
 11. AC-resistances of capacitor and inductors: Reactances. Purpose: To study the behavior of the AC voltage signals across elements in a simple series connection of a resistor with an inductor and with
11. AC-resistances of capacitor and inductors: Reactances. Purpose: To study the behavior of the AC voltage signals across elements in a simple series connection of a resistor with an inductor and with
Chapter 2. Inductor Design for RFIC Applications
 Chapter 2 Inductor Design for RFIC Applications 2.1 Introduction A current carrying conductor generates magnetic field and a changing current generates changing magnetic field. According to Faraday s laws
Chapter 2 Inductor Design for RFIC Applications 2.1 Introduction A current carrying conductor generates magnetic field and a changing current generates changing magnetic field. According to Faraday s laws
LCR METER Series. A New Series of LCR Meters to Meet Your Applications. From Production Lines to Research and Development
 LCR METER Series Component measuring instruments From Production Lines to Research and Development A New Series of LCR Meters to Meet Your Applications New LCR METER Models IM3523, IM3533, and IM3533-01
LCR METER Series Component measuring instruments From Production Lines to Research and Development A New Series of LCR Meters to Meet Your Applications New LCR METER Models IM3523, IM3533, and IM3533-01
A New Series of LCR Meters to Meet Your Applications
 Series A New Series of LCR Meters to Meet Your Applications From Production Lines to Research and Development 2 LCR Meter Series Full Product Lineup Model IM3536 IM3533 IM3523 LCR HiTESTER 3511-50 IM3533
Series A New Series of LCR Meters to Meet Your Applications From Production Lines to Research and Development 2 LCR Meter Series Full Product Lineup Model IM3536 IM3533 IM3523 LCR HiTESTER 3511-50 IM3533
Wireless Communication
 Equipment and Instruments Wireless Communication An oscilloscope, a signal generator, an LCR-meter, electronic components (see the table below), a container for components, and a Scotch tape. Component
Equipment and Instruments Wireless Communication An oscilloscope, a signal generator, an LCR-meter, electronic components (see the table below), a container for components, and a Scotch tape. Component
resistor box inductor 3 BNC to banana + V L
 Physics ab II Inductance and Circuit Page 1/5 Name: Partner: Partner: Purpose: To investigate how the voltage across an inductor changes in response to changing currents. To measure the inductance by measuring
Physics ab II Inductance and Circuit Page 1/5 Name: Partner: Partner: Purpose: To investigate how the voltage across an inductor changes in response to changing currents. To measure the inductance by measuring
Series and Parallel Resonance
 School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 33:4 Principles of Electrical Engineering II aboratory Experiment 1 Series and Parallel esonance 1 Introduction Objectives To introduce
School of Engineering Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering 33:4 Principles of Electrical Engineering II aboratory Experiment 1 Series and Parallel esonance 1 Introduction Objectives To introduce
Electromagnetic Induction - A
 Electromagnetic Induction - A APPARATUS 1. Two 225-turn coils 2. Table Galvanometer 3. Rheostat 4. Iron and aluminum rods 5. Large circular loop mounted on board 6. AC ammeter 7. Variac 8. Search coil
Electromagnetic Induction - A APPARATUS 1. Two 225-turn coils 2. Table Galvanometer 3. Rheostat 4. Iron and aluminum rods 5. Large circular loop mounted on board 6. AC ammeter 7. Variac 8. Search coil
Exercise 2: Q and Bandwidth of a Series RLC Circuit
 Series Resonance AC 2 Fundamentals Exercise 2: Q and Bandwidth of a Series RLC Circuit EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to calculate the bandwidth and Q of a series
Series Resonance AC 2 Fundamentals Exercise 2: Q and Bandwidth of a Series RLC Circuit EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to calculate the bandwidth and Q of a series
Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization (8/28/06)
 Electrical Measurement Issues Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization (8/28/06) Electrical measurements are only as meaningful as the quality of the measurement techniques and the instrumentation applied
Electrical Measurement Issues Experiment 1: Instrument Familiarization (8/28/06) Electrical measurements are only as meaningful as the quality of the measurement techniques and the instrumentation applied
Experiment 9 AC Circuits
 Experiment 9 AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits
Experiment 9 AC Circuits "Look for knowledge not in books but in things themselves." W. Gilbert (1540-1603) OBJECTIVES To study some circuit elements and a simple AC circuit. THEORY All useful circuits
Experiment 3 Topic: Dynamic System Response Week A Procedure
 Experiment 3 Topic: Dynamic System Response Week A Procedure Laboratory Assistant: Email: Office Hours: LEX-3 Website: Brock Hedlund bhedlund@nd.edu 11/05 11/08 5 pm to 6 pm in B14 http://www.nd.edu/~jott/measurements/measurements_lab/e3
Experiment 3 Topic: Dynamic System Response Week A Procedure Laboratory Assistant: Email: Office Hours: LEX-3 Website: Brock Hedlund bhedlund@nd.edu 11/05 11/08 5 pm to 6 pm in B14 http://www.nd.edu/~jott/measurements/measurements_lab/e3
a) Basic unit of an ideal transmission line b) an ideal transmission line
 Pulses in cables eferences: H.J. Pain: The Physics of ibrations and Waves, 5 th ed., Wiley, Chapter 7 (Waves in Transmission lines) T.. Kuphaldt: Lessons in Electric Circuits, olume AC, Chapter 4 (Transmission
Pulses in cables eferences: H.J. Pain: The Physics of ibrations and Waves, 5 th ed., Wiley, Chapter 7 (Waves in Transmission lines) T.. Kuphaldt: Lessons in Electric Circuits, olume AC, Chapter 4 (Transmission
Design of Integrated LC Filter Using Multilayer Flexible Ferrite Sheets S. Coulibaly 1, G. Loum 1, K.A. Diby 2
 IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 232-3331, Volume 1, Issue 6 Ver. I (Nov Dec. 215), PP 35-43 www.iosrjournals.org Design of Integrated LC Filter
IOSR Journal of Electrical and Electronics Engineering (IOSR-JEEE) e-issn: 2278-1676,p-ISSN: 232-3331, Volume 1, Issue 6 Ver. I (Nov Dec. 215), PP 35-43 www.iosrjournals.org Design of Integrated LC Filter
10 Electromagnetic Interactions
 Lab 10 Electromagnetic Interactions What You Need To Know: The Physics Electricity and magnetism are intrinsically linked and not separate phenomena. A changing magnetic field can create an electric field
Lab 10 Electromagnetic Interactions What You Need To Know: The Physics Electricity and magnetism are intrinsically linked and not separate phenomena. A changing magnetic field can create an electric field
3.2 Measurement of high voltages
 DEPT OF HIGH VOLTAGE AND INSULATION ENG, HONGQING UNIVERSITY Part I- hapter 3: Insulation test techniques 3. Measurement of high voltages Instructor: Dr. Jian Li Lecture 7- DEPT OF HIGH VOLTAGE AND INSULATION
DEPT OF HIGH VOLTAGE AND INSULATION ENG, HONGQING UNIVERSITY Part I- hapter 3: Insulation test techniques 3. Measurement of high voltages Instructor: Dr. Jian Li Lecture 7- DEPT OF HIGH VOLTAGE AND INSULATION
#8A RLC Circuits: Free Oscillations
 #8A RL ircuits: Free Oscillations Goals In this lab we investigate the properties of a series RL circuit. Such circuits are interesting, not only for there widespread application in electrical devices,
#8A RL ircuits: Free Oscillations Goals In this lab we investigate the properties of a series RL circuit. Such circuits are interesting, not only for there widespread application in electrical devices,
Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2 2 = 1 LC. Review ( ) Review (2) Review (3) e! Rt. cos "t + # ( ) q = q max. Spring Semester 2005 Lecture 30 U E
 Review hysics for Scientists & Engineers Spring Semester 005 Lecture 30! If we have a single loop RLC circuit, the charge in the circuit as a function of time is given by! Where q = q max e! Rt L cos "t
Review hysics for Scientists & Engineers Spring Semester 005 Lecture 30! If we have a single loop RLC circuit, the charge in the circuit as a function of time is given by! Where q = q max e! Rt L cos "t
y 2irfCj Resonance in AC Circuits Summary v v The rms current in an LRC series circuit is given by (see Eqs , 21-15, 21-llb, and 21-12b):
 -* Resonance in AC Circuits The rms current in an LRC series circuit is given by (see Eqs. 21-14, 21-15, 21-llb, and 21-12b): -'rms v v
-* Resonance in AC Circuits The rms current in an LRC series circuit is given by (see Eqs. 21-14, 21-15, 21-llb, and 21-12b): -'rms v v
SAMPLE: EXPERIMENT 2 Series RLC Circuit / Bode Plot
 SAMPLE: EXPERIMENT 2 Series RLC Circuit / Bode Plot ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- This experiment is an excerpt from: Electric Experiments
SAMPLE: EXPERIMENT 2 Series RLC Circuit / Bode Plot ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- This experiment is an excerpt from: Electric Experiments
Exercises of resistors 1. Calculate the resistance of a 10 m long Copper wire with diameter d = 1.0 mm.
 Exercises of resistors 1. Calculate the resistance of a 10 m long Copper wire with diameter d = 1.0 mm. 2. Calculate the resistances of following equipment: using 220V AC a) a 1000 W electric heater b)
Exercises of resistors 1. Calculate the resistance of a 10 m long Copper wire with diameter d = 1.0 mm. 2. Calculate the resistances of following equipment: using 220V AC a) a 1000 W electric heater b)
LCR METER Series. A New Series of LCR Meters to Meet Your Applications. From Production Lines to Research and Development
 LCR METER Series Component measuring instruments From Production Lines to Research and Development A New Series of LCR Meters to Meet Your Applications New LCR METER Models IM3523, IM3533, and IM3533-01
LCR METER Series Component measuring instruments From Production Lines to Research and Development A New Series of LCR Meters to Meet Your Applications New LCR METER Models IM3523, IM3533, and IM3533-01
Project: Electromagnetic Ring Launcher
 Project: Electromagnetic Ring Launcher Introduction: In science museums and physics-classrooms an experiment is very commonly demonstrated called the Jumping Ring or Electromagnetic Ring Launcher. The
Project: Electromagnetic Ring Launcher Introduction: In science museums and physics-classrooms an experiment is very commonly demonstrated called the Jumping Ring or Electromagnetic Ring Launcher. The
VE7CNF - 630m Antenna Matching Measurements Using an Oscilloscope
 VE7CNF - 630m Antenna Matching Measurements Using an Oscilloscope Toby Haynes October, 2016 1 Contents VE7CNF - 630m Antenna Matching Measurements Using an Oscilloscope... 1 Introduction... 1 References...
VE7CNF - 630m Antenna Matching Measurements Using an Oscilloscope Toby Haynes October, 2016 1 Contents VE7CNF - 630m Antenna Matching Measurements Using an Oscilloscope... 1 Introduction... 1 References...
Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3)
 Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive
Lab 3: AC Low pass filters (version 1.3) WARNING: Use electrical test equipment with care! Always double-check connections before applying power. Look for short circuits, which can quickly destroy expensive
University of Pittsburgh
 University of Pittsburgh Experiment #11 Lab Report Inductance/Transformers Submission Date: 12/04/2017 Instructors: Dr. Minhee Yun John Erickson Yanhao Du Submitted By: Nick Haver & Alex Williams Station
University of Pittsburgh Experiment #11 Lab Report Inductance/Transformers Submission Date: 12/04/2017 Instructors: Dr. Minhee Yun John Erickson Yanhao Du Submitted By: Nick Haver & Alex Williams Station
Simple electrical circuit to light up a gas discharge lamp
 TECHNICS AND INFORMATICS IN EDUCATION 6 th International Conference, Faculty of Technical Sciences, Čačak, Serbia, 8 9th May 016 TEHNIKA I INFORMATIKA U OBRAZOVANJU 6. međunarodna konferencija, Fakultet
TECHNICS AND INFORMATICS IN EDUCATION 6 th International Conference, Faculty of Technical Sciences, Čačak, Serbia, 8 9th May 016 TEHNIKA I INFORMATIKA U OBRAZOVANJU 6. međunarodna konferencija, Fakultet
SENSOR AND MEASUREMENT EXPERIMENTS
 SENSOR AND MEASUREMENT EXPERIMENTS Page: 1 Contents 1. Capacitive sensors 2. Temperature measurements 3. Signal processing and data analysis using LabVIEW 4. Load measurements 5. Noise and noise reduction
SENSOR AND MEASUREMENT EXPERIMENTS Page: 1 Contents 1. Capacitive sensors 2. Temperature measurements 3. Signal processing and data analysis using LabVIEW 4. Load measurements 5. Noise and noise reduction
LCR CIRCUITS Institute of Lifelong Learning, University of Delhi
 L UTS nstitute of Lifelong Learning, University of Delhi L UTS PHYSS (LAB MANUAL) nstitute of Lifelong Learning, University of Delhi PHYSS (LAB MANUAL) L UTS ntroduction ircuits containing an inductor
L UTS nstitute of Lifelong Learning, University of Delhi L UTS PHYSS (LAB MANUAL) nstitute of Lifelong Learning, University of Delhi PHYSS (LAB MANUAL) L UTS ntroduction ircuits containing an inductor
PHY152 Experiment 4: Oscillations in the RC-Circuits (Measurements with an oscilloscope)
 PHY152 Experiment 4: Oscillations in the RC-Circuits (Measurements with an oscilloscope) If you have not used an oscilloscope before, the web site http://www.upscale.utoronto.ca/generalinterest/harrison/oscilloscope/oscilloscope.html
PHY152 Experiment 4: Oscillations in the RC-Circuits (Measurements with an oscilloscope) If you have not used an oscilloscope before, the web site http://www.upscale.utoronto.ca/generalinterest/harrison/oscilloscope/oscilloscope.html
LAB 8: Activity P52: LRC Circuit
 LAB 8: Activity P52: LRC Circuit Equipment: Voltage Sensor 1 Multimeter 1 Patch Cords 2 AC/DC Electronics Lab (100 μf capacitor; 10 Ω resistor; Inductor Coil; Iron core; 5 inch wire lead) The purpose of
LAB 8: Activity P52: LRC Circuit Equipment: Voltage Sensor 1 Multimeter 1 Patch Cords 2 AC/DC Electronics Lab (100 μf capacitor; 10 Ω resistor; Inductor Coil; Iron core; 5 inch wire lead) The purpose of
