Light-emitting diodes (Item No.: P )
|
|
|
- Job Ray
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Teacher's/Lecturer's Sheet Printed: :0:20 P37800 Light-emitting diodes (Item No.: P37800) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physik Education Level: Klasse 0-3 Topic: Elektrizitätslehre Subtopic: Elektronik Experiment: Die Leuchtdiode Difficulty Preparation Time Execution Time Recommended Group Size Intermediate 0 Minutes 0 Minutes 2 Students Additional Requirements: Experiment Variations: Keywords: Task and equipment Information for teachers Additional information Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) are pn junctions composed of GaAs or GaP. Depending on the desired wavelength of light, the substrates are doped with various elements. When the pn junctions are connected to a current source in the forward direction, electrons and holes flood the barrier layer and recombine there. When they do, the expended energy is released in the form of visible or infra-red light. In the reverse direction, LEDs behave the same as normal diodes. However, the maximum reverse voltage is quite small. For some LED types, it is even less than 0 V. Notes on setup and procedure A voltage divider consisting of R and R 2 is used to make it easier to set the voltage in the forward voltage range, which is about V to 2 V. This makes it possible to vary the voltage on the power supply unit U P from 0 V to 2 V without overloading the LED in the forward direction or exceeding the maximum reverse voltage. LEDs may only be operated with a multiplier. The resistor limits the forward current to the admissible value, which is I F, max = 20 ma for the diode type used in this experiment. It can be calculated by using the following formula: R V = (U N U D ) I D,max. Remarks The determination of the type and polarity of a source of current can only be achieved in the way described, when the voltage is at least high enough to light up the diode, but does not exceed the permissible reverse voltage of the diode. When the voltage is too high, it can be adjusted to a voltage which is safe for the diode by using a voltage divider. Robert-Bosch-Breite 0 Tel: info@phywe.de D Göttingen Fax:
2 Printed: :0:20 P37800 Light-emitting diodes (Item No.: P37800) Task and equipment Task What are the characteristics of light-emitting diodes and what are they used for?. Investigate the relationship between current and voltage for a light-emitting diode in forward and reverse direction as well as the electrical power received by the diode. 2. Test the suitability of light-emitting diodes for determining the type of current and the polarity of the current source. Robert-Bosch-Breite 0 Tel: info@phywe.de D Göttingen Fax:
3 Printed: :0:20 P37800 Equipment Position No. Material Order No. Puantity Straight connector module, SB Angled connector module, SB T-shaped connector module, SB Interrupted connector module, SB Straight connector module with socket, SB Angled connector module with socket, SB Resistor module 50 Ohm, SB Resistor module 00 Ohm, SB Light emitting diode module red, SB Connecting cord, 32 A, 250 mm, red Connecting cord, 32 A, 250 mm, blue Connecting cord, 32 A, 500 mm, red Connecting cord, 32 A, 500 mm, blue Multi-range meter, analogue PHYWE power supply DC: V, 2 A / AC: 6 V, 2 V, 5 A Robert-Bosch-Breite 0 Tel: info@phywe.de D Göttingen Fax:
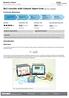
4 Printed: :0:20 P37800 Set-up and procedure Set-up First experiment Set up the experiment according to the schematic diagram as shown in Fig. and Fig. 2. Set the measurement ranges to 0 V- and 30 ma-. Fig. Fig. 2 Second experiment Set up the experiment according to the schematic diagram 2 as shown in Fig. 3 and Fig. 4. Fig. 3 Fig. 4 Robert-Bosch-Breite 0 Tel: info@phywe.de D Göttingen Fax:
5 Printed: :0:20 P37800 Procedure First experiment Switch on the power supply unit and gradually increase the direct voltage up to 2 V, starting at 0 V. Enter the measurements for current and diode voltage in Table in the report. Switch off the power supply unit. Plug the LED into the circuit with reverse polarity, as shown in Fig. 5 and Fig. 6. Switch on the power supply unit and determine measurements for current and voltage as before. Since you inverted the LED polarity, enter the voltage values that you are measuring in the first 2 slots in Table in the report as negative values. Switch off the power supply unit. Fig. 5 Fig. 6 Second experiment Set the power supply to 6 V (direct voltage) and switch it on. Observe the light-emitting diode. Then, switch off the power supply and turn the light-emitting diode through 80 (Fig. 7, Fig. 8). Switch on the power supply and again observe the diode; note your observations in both cases under Result - Observations in the report. Switch off the power supply and switch the connection cord on the power supply unit from direct voltage over to 6 V alternating voltage. Carry out the same observations and replugging of the light-emitting diode as with direct voltage; note your observations under Result - Observations 2. Switch off the power supply unit. Fig. 7 Fig. 8 Robert-Bosch-Breite 0 Tel: info@phywe.de D Göttingen Fax:
6 Printed: :0:20 P37800 Robert-Bosch-Breite 0 Tel: info@phywe.de D Göttingen Fax:
7 Printed: :0:20 P37800 Report: Light-emitting diodes Result - Table (26 Punkte) Record yout measured values in the table. Note the reverse direction voltage in the first 2 slots of the "Voltage at the LED" column. Do the same for the current. Set voltage of power supply unit U P in V Voltage at the LED U F in V Current I F in ma Robert-Bosch-Breite 0 Tel: info@phywe.de D Göttingen Fax:
8 Printed: :0:20 P37800 Number I F in ma U F in V Result - Observations (0 Punkte) Note your observations. Robert-Bosch-Breite 0 Tel: info@phywe.de D Göttingen Fax:
9 Printed: :0:20 P37800 Result - Observations 2 (0 Punkte) Note your observations. Evaluation - Question (0 Punkte) Describe the characteristic curve in the chart of Table in general and in relation to the lighting up of the LED. Compare this characteristic curve with that of a normal silicone diode. Note: The left arm of the graph represents the voltage U R. The minus signs for this arm are just for the technical realisation of displaying the graph. Robert-Bosch-Breite 0 Tel: info@phywe.de D Göttingen Fax:
10 Printed: :0:20 P37800 Evaluation - Question 2 (0 Punkte) How high is the maximum electrical power received by the LED? Draw a comparison between this value and the electrical power of a filament lamp for small voltages. Evaluation - Question 3 (0 Punkte) Explain the behaviour of the LED when connected to direct voltage (Observations ). Robert-Bosch-Breite 0 Tel: info@phywe.de D Göttingen Fax:
11 Printed: :0:20 P37800 Evaluation - Question 4 (0 Punkte) How do you explain Observations 2? Evaluation - Question 5 (0 Punkte) How must one proceed, to use a light-emitting diode in order to recognise the type of voltage and in the case of direct voltage to additionally determine its polarity? Robert-Bosch-Breite 0 Tel: info@phywe.de D Göttingen Fax:
Transparent and opaque materials (Item No.: P )
 Teacher's/Lecturer's Sheet Printed: 30.03.207 6::47 P063300 Transparent and opaque materials (Item No.: P063300) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physik Education Level: Klasse 7-0 Topic: Optik
Teacher's/Lecturer's Sheet Printed: 30.03.207 6::47 P063300 Transparent and opaque materials (Item No.: P063300) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physik Education Level: Klasse 7-0 Topic: Optik
The solar cell as a diode
 The solar cell as a diode ENT Keywords Solar energy, photovoltaics, solar cell, diode, and dark characteristic Principle A solar cell consists of a p-doped layer and of an n-doped layer. Under the influence
The solar cell as a diode ENT Keywords Solar energy, photovoltaics, solar cell, diode, and dark characteristic Principle A solar cell consists of a p-doped layer and of an n-doped layer. Under the influence
RLC-circuits with Cobra4 Xpert-Link
 Student's Sheet RLC-circuits with Cobra4 Xpert-Link (Item No.: P2440664) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Subtopic: Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, AC Circuits Topic: Electricity
Student's Sheet RLC-circuits with Cobra4 Xpert-Link (Item No.: P2440664) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Subtopic: Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, AC Circuits Topic: Electricity
Light Emitting Diodes
 Light Emitting Diodes Topics covered in this presentation: LED operation LED Characteristics Display devices Protection and limiting 1 of 9 Light Emitting Diode - LED A special type of diode is the Light
Light Emitting Diodes Topics covered in this presentation: LED operation LED Characteristics Display devices Protection and limiting 1 of 9 Light Emitting Diode - LED A special type of diode is the Light
Lecture 7:PN Junction. Structure, Depletion region, Different bias Conditions, IV characteristics, Examples
 Lecture 7:PN Junction Structure, Depletion region, Different bias Conditions, IV characteristics, Examples PN Junction The diode (pn junction) is formed by dopping a piece of intrinsic silicon, such that
Lecture 7:PN Junction Structure, Depletion region, Different bias Conditions, IV characteristics, Examples PN Junction The diode (pn junction) is formed by dopping a piece of intrinsic silicon, such that
Functioning of the human eye (normal vision)
 Teacher's/Lecturer's Sheet Functioning of the human eye (normal vision) (Item No.: P1066700) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physik Education Level: Klasse 7-10 Topic: Optik Subtopic: Das Auge
Teacher's/Lecturer's Sheet Functioning of the human eye (normal vision) (Item No.: P1066700) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physik Education Level: Klasse 7-10 Topic: Optik Subtopic: Das Auge
ECE 440 Lecture 29 : Introduction to the BJT-I Class Outline:
 ECE 440 Lecture 29 : Introduction to the BJT-I Class Outline: Narrow-Base Diode BJT Fundamentals BJT Amplification Things you should know when you leave Key Questions How does the narrow-base diode multiply
ECE 440 Lecture 29 : Introduction to the BJT-I Class Outline: Narrow-Base Diode BJT Fundamentals BJT Amplification Things you should know when you leave Key Questions How does the narrow-base diode multiply
Colour dispersion with a prism (Item No.: P )
 Teacher's/Lecturer's Sheet Colour dispersion with a prism (Item No.: P1066100) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physik Education Level: Klasse 7-10 Topic: Optik Subtopic: Farbenlehre Experiment:
Teacher's/Lecturer's Sheet Colour dispersion with a prism (Item No.: P1066100) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physik Education Level: Klasse 7-10 Topic: Optik Subtopic: Farbenlehre Experiment:
Complementary colours (Item No.: P )
 Teacher's/Lecturer's Sheet Complementary colours (Item No.: P1066300) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physik Education Level: Klasse 7-10 Topic: Optik Subtopic: Farbenlehre Experiment: Komplementärfarben
Teacher's/Lecturer's Sheet Complementary colours (Item No.: P1066300) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physik Education Level: Klasse 7-10 Topic: Optik Subtopic: Farbenlehre Experiment: Komplementärfarben
Diode Limiters or Clipper Circuits
 Diode Limiters or Clipper Circuits Circuits which are used to clip off portions of signal voltages above or below certain levels are called limiters or clippers. Types of Clippers Positive Clipper Negative
Diode Limiters or Clipper Circuits Circuits which are used to clip off portions of signal voltages above or below certain levels are called limiters or clippers. Types of Clippers Positive Clipper Negative
Long-sightedness and its correction (Item No.: P )
 Teacher's/Lecturer's Sheet Long-sightedness and its correction (Item No.: P1066900) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physik Education Level: Klasse 7-10 Topic: Optik Subtopic: Das Auge Experiment:
Teacher's/Lecturer's Sheet Long-sightedness and its correction (Item No.: P1066900) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physik Education Level: Klasse 7-10 Topic: Optik Subtopic: Das Auge Experiment:
Kirchhoff s laws, induction law, Maxwell equations, current, voltage, resistance, parallel connection, series connection, potentiometer
 Kirchhoff s laws with Cobra4 TEP Related Topics Kirchhoff s laws, induction law, Maxwell equations, current, voltage, resistance, parallel connection, series connection, potentiometer Principle First Kirchhoff
Kirchhoff s laws with Cobra4 TEP Related Topics Kirchhoff s laws, induction law, Maxwell equations, current, voltage, resistance, parallel connection, series connection, potentiometer Principle First Kirchhoff
Diodes. Analog Electronics Lesson 4. Objectives and Overview:
 Analog Electronics Lesson 4 Diodes Objectives and Overview: This lesson will introduce p- and n-type material, how they form a junction that rectifies current, and familiarize you with basic p-n junction
Analog Electronics Lesson 4 Diodes Objectives and Overview: This lesson will introduce p- and n-type material, how they form a junction that rectifies current, and familiarize you with basic p-n junction
Analogue Demo Multimeter ADM
 Analogue Demo Multimeter ADM 2 3820-0 PHYWE Systeme GmbH & Co. KG Robert-Bosch-Breite 0 D-37079 Göttingen Telefon +49 (0) 55 604-0 Fax +49 (0) 55 604-07 E-mail info@phywe.de Operating instructions The
Analogue Demo Multimeter ADM 2 3820-0 PHYWE Systeme GmbH & Co. KG Robert-Bosch-Breite 0 D-37079 Göttingen Telefon +49 (0) 55 604-0 Fax +49 (0) 55 604-07 E-mail info@phywe.de Operating instructions The
TO INVESTIGATE THE VARIATION OF CURRENT (I) WITH P.D. (V) FOR (a) A METALLIC CONDUCTOR
 FOR (a) A METALLIC CONDUCTOR Low voltage power supply, rheostat, voltmeter, ammeter, length of nichrome wire. 6 A - Nichrome wire 1. Set up the circuit as shown and set the voltage supply at 6 d.c. 2.
FOR (a) A METALLIC CONDUCTOR Low voltage power supply, rheostat, voltmeter, ammeter, length of nichrome wire. 6 A - Nichrome wire 1. Set up the circuit as shown and set the voltage supply at 6 d.c. 2.
Electro - Principles I
 The PN Junction Diode Introduction to the PN Junction Diode Note: In this chapter we consider conventional current flow. Page 11-1 The schematic symbol for the pn junction diode the shown in Figure 1.
The PN Junction Diode Introduction to the PN Junction Diode Note: In this chapter we consider conventional current flow. Page 11-1 The schematic symbol for the pn junction diode the shown in Figure 1.
Application of diodes
 Application of diodes Instructions for the practical exercises of subject AE4B34EM 1 Objective measurements 2 The purpose of this measure is the introduction to the features and applications of semiconductor
Application of diodes Instructions for the practical exercises of subject AE4B34EM 1 Objective measurements 2 The purpose of this measure is the introduction to the features and applications of semiconductor
Electronic devices-i. Difference between conductors, insulators and semiconductors
 Electronic devices-i Semiconductor Devices is one of the important and easy units in class XII CBSE Physics syllabus. It is easy to understand and learn. Generally the questions asked are simple. The unit
Electronic devices-i Semiconductor Devices is one of the important and easy units in class XII CBSE Physics syllabus. It is easy to understand and learn. Generally the questions asked are simple. The unit
Physics 281 EXPERIMENT 7 I-V Curves of Non linear Device
 Physics 281 EXPERIMENT 7 I-V Curves of Non linear Device Print this page to start your lab report (1 copy) Bring a diskette to save your data. OBJECT: To study the method of obtaining the characteristics
Physics 281 EXPERIMENT 7 I-V Curves of Non linear Device Print this page to start your lab report (1 copy) Bring a diskette to save your data. OBJECT: To study the method of obtaining the characteristics
Laboratory No. 01: Small & Large Signal Diode Circuits. Electrical Enginnering Departement. By: Dr. Awad Al-Zaben. Instructor: Eng.
 Laboratory No. 01: Small & Large Signal Diode Circuits Electrical Enginnering Departement By: Dr. Awad Al-Zaben Instructor: Eng. Tamer Shahta Electronics Laboratory EE 3191 February 23, 2014 I. OBJECTIVES
Laboratory No. 01: Small & Large Signal Diode Circuits Electrical Enginnering Departement By: Dr. Awad Al-Zaben Instructor: Eng. Tamer Shahta Electronics Laboratory EE 3191 February 23, 2014 I. OBJECTIVES
Wheatstone bridge (Item No.: P )
 Wheatstone bridge (Item No.: P2410200) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Education Level: University Topic: Electricity and Magnetism Subtopic: Electric Current and Resistance Experiment:
Wheatstone bridge (Item No.: P2410200) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Education Level: University Topic: Electricity and Magnetism Subtopic: Electric Current and Resistance Experiment:
Unijunction Transistor (Volt-Ampere Characteristics)
 Page 1 of 5 Unijunction Transistor (Volt-Ampere Characteristics) Aim :- To draw the volt-ampere characteristics of the unijunction transistor and to find the UJT pameters. Apparatus :- UJT, two variable
Page 1 of 5 Unijunction Transistor (Volt-Ampere Characteristics) Aim :- To draw the volt-ampere characteristics of the unijunction transistor and to find the UJT pameters. Apparatus :- UJT, two variable
Lec (03) Diodes and Applications
 Lec (03) Diodes and Applications Diode Models 1 Diodes and Applications Diode Operation V-I Characteristics of a Diode Diode Models Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectifiers Power Supply Filters and Regulators
Lec (03) Diodes and Applications Diode Models 1 Diodes and Applications Diode Operation V-I Characteristics of a Diode Diode Models Half-Wave and Full-Wave Rectifiers Power Supply Filters and Regulators
Chapter 5: Diodes. I. Theory. Chapter 5: Diodes
 Chapter 5: Diodes This week we will explore another new passive circuit element, the diode. We will also explore some diode applications including conversion of an AC signal into a signal that never changes
Chapter 5: Diodes This week we will explore another new passive circuit element, the diode. We will also explore some diode applications including conversion of an AC signal into a signal that never changes
LAB V. LIGHT EMITTING DIODES
 LAB V. LIGHT EMITTING DIODES 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab you are to measure I-V characteristics of Infrared (IR), Red and Blue light emitting diodes (LEDs). The emission intensity as a function of the diode
LAB V. LIGHT EMITTING DIODES 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab you are to measure I-V characteristics of Infrared (IR), Red and Blue light emitting diodes (LEDs). The emission intensity as a function of the diode
Acoustic Doppler Effect
 Acoustic Doppler Effect TEP Related Topics Wave propagation, Doppler shift of frequency Principle If an emitter of sound or a detector is set into motion relative to the medium of propagation, the frequency
Acoustic Doppler Effect TEP Related Topics Wave propagation, Doppler shift of frequency Principle If an emitter of sound or a detector is set into motion relative to the medium of propagation, the frequency
Lesson 08. Name and affiliation of the author: Professor L B D R P Wijesundera Department of Physics, University of Kelaniya.
 Lesson 08 Title of the Experiment: Identification of active components in electronic circuits and characteristics of a Diode, Zener diode and LED (Activity number of the GCE Advanced Level practical Guide
Lesson 08 Title of the Experiment: Identification of active components in electronic circuits and characteristics of a Diode, Zener diode and LED (Activity number of the GCE Advanced Level practical Guide
KOM2751 Analog Electronics :: Dr. Muharrem Mercimek :: YTU - Control and Automation Dept. 1 1 (CONT D) DIODES
 KOM2751 Analog Electronics :: Dr. Muharrem Mercimek :: YTU - Control and Automation Dept. 1 1 (CONT D) DIODES Most of the content is from the textbook: Electronic devices and circuit theory, Robert L.
KOM2751 Analog Electronics :: Dr. Muharrem Mercimek :: YTU - Control and Automation Dept. 1 1 (CONT D) DIODES Most of the content is from the textbook: Electronic devices and circuit theory, Robert L.
UNIT IX ELECTRONIC DEVICES
 UNT X ELECTRONC DECES Weightage Marks : 07 Semiconductors Semiconductors diode-- characteristics in forward and reverse bias, diode as rectifier. - characteristics of LED, Photodiodes, solarcell and Zener
UNT X ELECTRONC DECES Weightage Marks : 07 Semiconductors Semiconductors diode-- characteristics in forward and reverse bias, diode as rectifier. - characteristics of LED, Photodiodes, solarcell and Zener
Q2. Figure 1 shows the oscilloscope trace an alternating current (a.c.) electricity supply produces.
 SERIES AND PARALEL CIRCUITS Q1. A student set up the electrical circuit shown in the figure below. (a) The ammeter displays a reading of 0.10 A. Calculate the potential difference across the 45 Ω resistor.
SERIES AND PARALEL CIRCUITS Q1. A student set up the electrical circuit shown in the figure below. (a) The ammeter displays a reading of 0.10 A. Calculate the potential difference across the 45 Ω resistor.
Image construction for a convex mirror (Item No.: P )
 Teacher's/Lecturer's Sheet Image construction for a convex mirror (Item No.: P1064200) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physik Education Level: Klasse 7-10 Topic: Optik Subtopic: Reflebion und Brechung
Teacher's/Lecturer's Sheet Image construction for a convex mirror (Item No.: P1064200) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physik Education Level: Klasse 7-10 Topic: Optik Subtopic: Reflebion und Brechung
THERMIONIC AND GASEOUS STATE DIODES
 THERMIONIC AND GASEOUS STATE DIODES Thermionic and gaseous state (vacuum tube) diodes Thermionic diodes are thermionic-valve devices (also known as vacuum tubes, tubes, or valves), which are arrangements
THERMIONIC AND GASEOUS STATE DIODES Thermionic and gaseous state (vacuum tube) diodes Thermionic diodes are thermionic-valve devices (also known as vacuum tubes, tubes, or valves), which are arrangements
UNIT 3: FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS
 FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR: UNIT 3: FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS The field effect transistor is a semiconductor device, which depends for its operation on the control of current by an electric field. There are
FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTOR: UNIT 3: FIELD EFFECT TRANSISTORS The field effect transistor is a semiconductor device, which depends for its operation on the control of current by an electric field. There are
Chapter 1: Semiconductor Diodes
 Chapter 1: Semiconductor Diodes Diodes The diode is a 2-terminal device. A diode ideally conducts in only one direction. 2 Diode Characteristics Conduction Region Non-Conduction Region The voltage across
Chapter 1: Semiconductor Diodes Diodes The diode is a 2-terminal device. A diode ideally conducts in only one direction. 2 Diode Characteristics Conduction Region Non-Conduction Region The voltage across
Lecture 3: Transistors
 Lecture 3: Transistors Now that we know about diodes, let s put two of them together, as follows: collector base emitter n p n moderately doped lightly doped, and very thin heavily doped At first glance,
Lecture 3: Transistors Now that we know about diodes, let s put two of them together, as follows: collector base emitter n p n moderately doped lightly doped, and very thin heavily doped At first glance,
The answer is R= 471 ohms. So we can use a 470 ohm or the next higher one, a 560 ohm.
 Introducing Resistors & LED s P a g e 1 Resistors are used to adjust the voltage and current in a circuit. The higher the resistance value, the more electrons it blocks. Thus, higher resistance will lower
Introducing Resistors & LED s P a g e 1 Resistors are used to adjust the voltage and current in a circuit. The higher the resistance value, the more electrons it blocks. Thus, higher resistance will lower
LAB IV. SILICON DIODE CHARACTERISTICS
 LAB IV. SILICON DIODE CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab you will measure the I-V characteristics of the rectifier and Zener diodes, in both forward and reverse-bias mode, as well as learn what mechanisms
LAB IV. SILICON DIODE CHARACTERISTICS 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab you will measure the I-V characteristics of the rectifier and Zener diodes, in both forward and reverse-bias mode, as well as learn what mechanisms
The equation which links current, potential difference and resistance is:
 Q1.An electrical circuit is shown in the figure below. (a) The current in the circuit is direct current. What is meant by direct current? Tick one box. Current that continuously changes direction. Current
Q1.An electrical circuit is shown in the figure below. (a) The current in the circuit is direct current. What is meant by direct current? Tick one box. Current that continuously changes direction. Current
Franck-Hertz Control Unit
 R Franck-Hertz Control Unit 09105.99 PHYWE Systeme GmbH & Co. KG Robert-Bosch-Breite 10 D-37079 Göttingen Phone +49 (0) 551 604-0 Fax +49 (0) 551 604-107 E-mail info@phywe.de Internet www.phywe.de The
R Franck-Hertz Control Unit 09105.99 PHYWE Systeme GmbH & Co. KG Robert-Bosch-Breite 10 D-37079 Göttingen Phone +49 (0) 551 604-0 Fax +49 (0) 551 604-107 E-mail info@phywe.de Internet www.phywe.de The
EXPERIMENT 5 CURRENT AND VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS OF BJT
 EXPERIMENT 5 CURRENT AND VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS OF BJT 1. OBJECTIVES 1.1 To practice how to test NPN and PNP transistors using multimeter. 1.2 To demonstrate the relationship between collector current
EXPERIMENT 5 CURRENT AND VOLTAGE CHARACTERISTICS OF BJT 1. OBJECTIVES 1.1 To practice how to test NPN and PNP transistors using multimeter. 1.2 To demonstrate the relationship between collector current
EC6202- ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS UNIT TEST-1 EXPECTED QUESTIONS
 EC6202- ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS UNIT TEST-1 EXPECTED QUESTIONS 1. List the PN diode parameters. 1. Bulk Resistance. 2. Static Resistance/Junction Resistance (or) DC Forward Resistance 3. Dynamic
EC6202- ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS UNIT TEST-1 EXPECTED QUESTIONS 1. List the PN diode parameters. 1. Bulk Resistance. 2. Static Resistance/Junction Resistance (or) DC Forward Resistance 3. Dynamic
Solar Cell Parameters and Equivalent Circuit
 9 Solar Cell Parameters and Equivalent Circuit 9.1 External solar cell parameters The main parameters that are used to characterise the performance of solar cells are the peak power P max, the short-circuit
9 Solar Cell Parameters and Equivalent Circuit 9.1 External solar cell parameters The main parameters that are used to characterise the performance of solar cells are the peak power P max, the short-circuit
Diodes. Introduction. Silicon p-n junction diodes. Structure
 Diodes ntroduction A diode is a two terminal circuit element that allows current flow in one direction only. Diodes are thus non-linear circuit elements because the current through them is not proportional
Diodes ntroduction A diode is a two terminal circuit element that allows current flow in one direction only. Diodes are thus non-linear circuit elements because the current through them is not proportional
Circuit Components Lesson 4 From: Emergency Management Ontario
 4.1 Amplifier Fundamentals The role of a amplifier is to produce an output which is an enlarged reproduction of the features of the signal fed into the input. The increase in signal by an amplifier is
4.1 Amplifier Fundamentals The role of a amplifier is to produce an output which is an enlarged reproduction of the features of the signal fed into the input. The increase in signal by an amplifier is
Digital Function Generator
 Digital Function Generator 13654-99 PHYWE Systeme GmbH & Co. KG Robert-Bosch-Breite 10 37079 Göttingen Germany Tel. +49 (0) 551 604-0 Fax +49 (0) 551 604-107 E-mail info@phywe.de Operating Instructions
Digital Function Generator 13654-99 PHYWE Systeme GmbH & Co. KG Robert-Bosch-Breite 10 37079 Göttingen Germany Tel. +49 (0) 551 604-0 Fax +49 (0) 551 604-107 E-mail info@phywe.de Operating Instructions
Objective Type Questions 1. Why pure semiconductors are insulators at 0 o K? 2. What is effect of temperature on barrier voltage? 3.
 Objective Type Questions 1. Why pure semiconductors are insulators at 0 o K? 2. What is effect of temperature on barrier voltage? 3. What is difference between electron and hole? 4. Why electrons have
Objective Type Questions 1. Why pure semiconductors are insulators at 0 o K? 2. What is effect of temperature on barrier voltage? 3. What is difference between electron and hole? 4. Why electrons have
International Journal of Research in Advent Technology Available Online at:
 MODELLING LIGHT EMITTING DIODE USING SPICE Dattaprasad Madur 1, Najib Ghatte 2, init Pereira 3, Tushar Surwadkar 4 1 2 3 4 Department of Electronics Fr. Conceicao Rodrigues College of Engineering Fr. Agnel
MODELLING LIGHT EMITTING DIODE USING SPICE Dattaprasad Madur 1, Najib Ghatte 2, init Pereira 3, Tushar Surwadkar 4 1 2 3 4 Department of Electronics Fr. Conceicao Rodrigues College of Engineering Fr. Agnel
LAB V. LIGHT EMITTING DIODES
 LAB V. LIGHT EMITTING DIODES 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab you will measure the I-V characteristics of Infrared (IR), Red and Blue light emitting diodes (LEDs). Using a photodetector, the emission intensity
LAB V. LIGHT EMITTING DIODES 1. OBJECTIVE In this lab you will measure the I-V characteristics of Infrared (IR), Red and Blue light emitting diodes (LEDs). Using a photodetector, the emission intensity
These are samples of learning materials and may not necessarily be exactly the same as those in the actual course. Contents 1.
 Contents These are samples of learning materials and may not necessarily be exactly the same as those in the actual course. Contents 1 Introduction 2 Ohm s law relationships 3 The Ohm s law equation 4
Contents These are samples of learning materials and may not necessarily be exactly the same as those in the actual course. Contents 1 Introduction 2 Ohm s law relationships 3 The Ohm s law equation 4
Using Voltage Dividers to Design a Photo-Sensitive LED Circuit. ( Doug Oliver & Jackie Kane. May be reproduced for non-profit classroom use.
 Using Voltage Dividers to Design a Photo-Sensitive LED Circuit ( 2009 - Doug Oliver & Jackie Kane. May be reproduced for non-profit classroom use.) Purpose: After completing the module students will: 1.
Using Voltage Dividers to Design a Photo-Sensitive LED Circuit ( 2009 - Doug Oliver & Jackie Kane. May be reproduced for non-profit classroom use.) Purpose: After completing the module students will: 1.
Intro to Electricity. Introduction to Transistors. Example Circuit Diagrams. Water Analogy
 Introduction to Transistors Transistors form the basic building blocks of all computer hardware. Invented by William Shockley, John Bardeen and Walter Brattain in 1947, replacing previous vaccuumtube technology
Introduction to Transistors Transistors form the basic building blocks of all computer hardware. Invented by William Shockley, John Bardeen and Walter Brattain in 1947, replacing previous vaccuumtube technology
Wallace Hall Academy. CfE Higher Physics. Unit 3 - Electricity Notes Name
 Wallace Hall Academy CfE Higher Physics Unit 3 - Electricity Notes Name 1 Electrons and Energy Alternating current and direct current Alternating current electrons flow back and forth several times per
Wallace Hall Academy CfE Higher Physics Unit 3 - Electricity Notes Name 1 Electrons and Energy Alternating current and direct current Alternating current electrons flow back and forth several times per
Coil in the AC circuit
 Coil in the AC circuit LEP Related topics Inductance, Kirchhoff s laws, parallel connection, series connection, a. c. impedance, phase displacement, vector diagram Principle The impedance and phase displacement
Coil in the AC circuit LEP Related topics Inductance, Kirchhoff s laws, parallel connection, series connection, a. c. impedance, phase displacement, vector diagram Principle The impedance and phase displacement
Chapter 3 SPECIAL PURPOSE DIODE
 Chapter 3 SPECIAL PURPOSE DIODE 1 Inventor of Zener Diode Clarence Melvin Zener was a professor at Carnegie Mellon University in the department of Physics. He developed the Zener Diode in 1950 and employed
Chapter 3 SPECIAL PURPOSE DIODE 1 Inventor of Zener Diode Clarence Melvin Zener was a professor at Carnegie Mellon University in the department of Physics. He developed the Zener Diode in 1950 and employed
EEE118: Electronic Devices and Circuits
 EEE118: Electronic Devices and Circuits Lecture IIII James E Green Department of Electronic Engineering University of Sheffield j.e.green@sheffield.ac.uk Last Lecture: Review 1 Defined some terminology
EEE118: Electronic Devices and Circuits Lecture IIII James E Green Department of Electronic Engineering University of Sheffield j.e.green@sheffield.ac.uk Last Lecture: Review 1 Defined some terminology
ANSWERS AND MARK SCHEMES. (a) 3 A / 2 1 = 1.5 A 1. (b) 6 V 1. (c) resistance = V / I 1 = 6 / (b) I = V / R 1 = 3 / 15 1 = 0.
 QUESTIONSHEET (a) 3 A / 2 =.5 A (b) 6 V (c) resistance = V / I = 6 /.5 = 4 Ω QUESTIONSHEET 2 TOTAL / 6 (a) 5 Ω + 0 Ω = 5 Ω (b) I = V / R = 3 / 5 = 0.2 A Units are essential in calculations. Sometimes eamination
QUESTIONSHEET (a) 3 A / 2 =.5 A (b) 6 V (c) resistance = V / I = 6 /.5 = 4 Ω QUESTIONSHEET 2 TOTAL / 6 (a) 5 Ω + 0 Ω = 5 Ω (b) I = V / R = 3 / 5 = 0.2 A Units are essential in calculations. Sometimes eamination
Circuits. What is Ohm s law? Section 1: Ohm s Law. Suggested Film. Extension Questions. Q1. What is current? Q2. What is voltage?
 Circuits PHYSICS ELECTRICITY AND CIRCUITS CIRCUITS Section 1: Ohm s Law What is Ohm s law? Ohm s law gives the relation between current, resistance and voltage. It states that the current which fl ows
Circuits PHYSICS ELECTRICITY AND CIRCUITS CIRCUITS Section 1: Ohm s Law What is Ohm s law? Ohm s law gives the relation between current, resistance and voltage. It states that the current which fl ows
AIM:-To observe and draw the Forward bias V-I Characteristics of a P-N Junction diode and study of L.E.D characteristics.
 KARNAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & MANAGEMENT KUNJPURA, KARNAL LAB MANUAL OF ------- SUBJECT CODE DATE OF ISSUE: SEMESTER: BRANCH: REV NO EXPERIMENT NO 1 P-N JUNCTION DIODE CHARACTERISTICS AIM:-To observe
KARNAL INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY & MANAGEMENT KUNJPURA, KARNAL LAB MANUAL OF ------- SUBJECT CODE DATE OF ISSUE: SEMESTER: BRANCH: REV NO EXPERIMENT NO 1 P-N JUNCTION DIODE CHARACTERISTICS AIM:-To observe
Field - Effect Transistor
 Page 1 of 6 Field - Effect Transistor Aim :- To draw and study the out put and transfer characteristics of the given FET and to determine its parameters. Apparatus :- FET, two variable power supplies,
Page 1 of 6 Field - Effect Transistor Aim :- To draw and study the out put and transfer characteristics of the given FET and to determine its parameters. Apparatus :- FET, two variable power supplies,
Università degli Studi di Roma Tor Vergata Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettronica. Analogue Electronics. Paolo Colantonio A.A.
 Università degli Studi di Roma Tor Vergata Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettronica Analogue Electronics Paolo Colantonio A.A. 2015-16 Introduction: materials Conductors e.g. copper or aluminum have a cloud
Università degli Studi di Roma Tor Vergata Dipartimento di Ingegneria Elettronica Analogue Electronics Paolo Colantonio A.A. 2015-16 Introduction: materials Conductors e.g. copper or aluminum have a cloud
Chapter 2. Diodes & Applications
 Chapter 2 Diodes & Applications The Diode A diode is made from a small piece of semiconductor material, usually silicon, in which half is doped as a p region and half is doped as an n region with a pn
Chapter 2 Diodes & Applications The Diode A diode is made from a small piece of semiconductor material, usually silicon, in which half is doped as a p region and half is doped as an n region with a pn
DISCUSSION The best way to test a transistor is to connect it in a circuit that uses the transistor.
 Exercise 1: EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to test a transistor by forward biasing and reverse biasing the junctions. You will verify your results with an ohmmeter.
Exercise 1: EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be able to test a transistor by forward biasing and reverse biasing the junctions. You will verify your results with an ohmmeter.
Physics 160 Lecture 5. R. Johnson April 13, 2015
 Physics 160 Lecture 5 R. Johnson April 13, 2015 Half Wave Diode Rectifiers Full Wave April 13, 2015 Physics 160 2 Note that there is no ground connection on this side of the rectifier! Output Smoothing
Physics 160 Lecture 5 R. Johnson April 13, 2015 Half Wave Diode Rectifiers Full Wave April 13, 2015 Physics 160 2 Note that there is no ground connection on this side of the rectifier! Output Smoothing
Electron Devices and Circuits (EC 8353)
 Electron Devices and Circuits (EC 8353) Prepared by Ms.S.KARKUZHALI, A.P/EEE Diodes The diode is a 2-terminal device. A diode ideally conducts in only one direction. Diode Characteristics Conduction Region
Electron Devices and Circuits (EC 8353) Prepared by Ms.S.KARKUZHALI, A.P/EEE Diodes The diode is a 2-terminal device. A diode ideally conducts in only one direction. Diode Characteristics Conduction Region
I D = I so e I. where: = constant T = junction temperature [K] I so = inverse saturating current I = photovoltaic current
![I D = I so e I. where: = constant T = junction temperature [K] I so = inverse saturating current I = photovoltaic current I D = I so e I. where: = constant T = junction temperature [K] I so = inverse saturating current I = photovoltaic current](/thumbs/83/87981810.jpg) H7. Photovoltaics: Solar Power I. INTRODUCTION The sun is practically an endless source of energy. Most of the energy used in the history of mankind originated from the sun (coal, petroleum, etc.). The
H7. Photovoltaics: Solar Power I. INTRODUCTION The sun is practically an endless source of energy. Most of the energy used in the history of mankind originated from the sun (coal, petroleum, etc.). The
Table of Contents. iii
 Table of Contents Subject Page Experiment 1: Diode Characteristics... 1 Experiment 2: Rectifier Circuits... 7 Experiment 3: Clipping and Clamping Circuits 17 Experiment 4: The Zener Diode 25 Experiment
Table of Contents Subject Page Experiment 1: Diode Characteristics... 1 Experiment 2: Rectifier Circuits... 7 Experiment 3: Clipping and Clamping Circuits 17 Experiment 4: The Zener Diode 25 Experiment
Multichannel Analyser, Extended Version
 Multichannel Analyser, Extended Version 13727-99 PHYWE Systeme GmbH & Co. KG Robert-Bosch-Breite 10 D-37079 Göttingen Phone +49 (0) 551 604-0 Fax +49 (0) 551 604-107 E-mail info@phywe.de Internet www.phywe.de
Multichannel Analyser, Extended Version 13727-99 PHYWE Systeme GmbH & Co. KG Robert-Bosch-Breite 10 D-37079 Göttingen Phone +49 (0) 551 604-0 Fax +49 (0) 551 604-107 E-mail info@phywe.de Internet www.phywe.de
ZT-30 ZeroTEM TRANSMITTER MANUAL
 ZT-30 ZeroTEM TRANSMITTER MANUAL 06 September, 2000 Zonge Engineering and Research Organization, Inc. 3322 East Fort Lowell Road, Tucson, AZ 85716 USA Tel:(520)327-5501 Fax:(520)325-1588 Email:zonge@zonge.com
ZT-30 ZeroTEM TRANSMITTER MANUAL 06 September, 2000 Zonge Engineering and Research Organization, Inc. 3322 East Fort Lowell Road, Tucson, AZ 85716 USA Tel:(520)327-5501 Fax:(520)325-1588 Email:zonge@zonge.com
L MOSFETS, IDENTIFICATION, CURVES. PAGE 1. I. Review of JFET (DRAW symbol for n-channel type, with grounded source)
 L.107.4 MOSFETS, IDENTIFICATION, CURVES. PAGE 1 I. Review of JFET (DRAW symbol for n-channel type, with grounded source) 1. "normally on" device A. current from source to drain when V G = 0 no need to
L.107.4 MOSFETS, IDENTIFICATION, CURVES. PAGE 1 I. Review of JFET (DRAW symbol for n-channel type, with grounded source) 1. "normally on" device A. current from source to drain when V G = 0 no need to
Figure 2.1: Energy Band gap Block Diagram
 Figure 2.1: Energy Band gap Block Diagram Figure 2.2: Log Is Vs 10 3 /T Figure 2.3: Schematic Representation of a p-n Junction Diode Department of Physical Sciences, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology,
Figure 2.1: Energy Band gap Block Diagram Figure 2.2: Log Is Vs 10 3 /T Figure 2.3: Schematic Representation of a p-n Junction Diode Department of Physical Sciences, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology,
 Energy band diagrams Metals: 9. ELECTRONIC DEVICES GIST ρ= 10-2 to 10-8 Ω m Insulators: ρ> 10 8 Ω m Semiconductors ρ= 1 to 10 5 Ω m 109 A. Intrinsic semiconductors At T=0k it acts as insulator At room
Energy band diagrams Metals: 9. ELECTRONIC DEVICES GIST ρ= 10-2 to 10-8 Ω m Insulators: ρ> 10 8 Ω m Semiconductors ρ= 1 to 10 5 Ω m 109 A. Intrinsic semiconductors At T=0k it acts as insulator At room
Student Experiments ELECTRONICS. Manual P9160-4F.
 Student Experiments Manual ELECTRONICS P9160-4F www.ntl.at INDEX 1. SEMICONDUCTORS EOS 1.1 PTC-resistor EOS 1.2 NTC-resistor EOS 1.3 Light dependent resistor (LDR) EOS 1.4 Measuring the luminous intensity
Student Experiments Manual ELECTRONICS P9160-4F www.ntl.at INDEX 1. SEMICONDUCTORS EOS 1.1 PTC-resistor EOS 1.2 NTC-resistor EOS 1.3 Light dependent resistor (LDR) EOS 1.4 Measuring the luminous intensity
An important note about your Charged Up Exploration Kit.
 ChargedUp Hands On Exploration Kit First An important note about your. DO NOT ASSUME that you will see something at the tournament because it was in this kit. This supplemental study material IS NOT part
ChargedUp Hands On Exploration Kit First An important note about your. DO NOT ASSUME that you will see something at the tournament because it was in this kit. This supplemental study material IS NOT part
INTRODUCTION TO MOS TECHNOLOGY
 INTRODUCTION TO MOS TECHNOLOGY 1. The MOS transistor The most basic element in the design of a large scale integrated circuit is the transistor. For the processes we will discuss, the type of transistor
INTRODUCTION TO MOS TECHNOLOGY 1. The MOS transistor The most basic element in the design of a large scale integrated circuit is the transistor. For the processes we will discuss, the type of transistor
1) A silicon diode measures a low value of resistance with the meter leads in both positions. The trouble, if any, is
 1) A silicon diode measures a low value of resistance with the meter leads in both positions. The trouble, if any, is A [ ]) the diode is open. B [ ]) the diode is shorted to ground. C [v]) the diode is
1) A silicon diode measures a low value of resistance with the meter leads in both positions. The trouble, if any, is A [ ]) the diode is open. B [ ]) the diode is shorted to ground. C [v]) the diode is
Superbright LED JOSEF HUBEŇÁK. Physics teachers inventions fair 11
 Superbright LED JOSEF HUBEŇÁK The first light emitting diodes made in the Czech Republic occurred in the TESLA catalogue in 1980s. The first in the series was LQ 100. It shone with red light. In the catalogue
Superbright LED JOSEF HUBEŇÁK The first light emitting diodes made in the Czech Republic occurred in the TESLA catalogue in 1980s. The first in the series was LQ 100. It shone with red light. In the catalogue
Learning Objectives:
 Topic 5.4 Instrumentation Systems Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you will be able to; describe the use of the following analogue sensors: thermistors and strain gauges; describe the use
Topic 5.4 Instrumentation Systems Learning Objectives: At the end of this topic you will be able to; describe the use of the following analogue sensors: thermistors and strain gauges; describe the use
Basic Electronics Learning by doing Prof. T.S. Natarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras
 Basic Electronics Learning by doing Prof. T.S. Natarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 38 Unit junction Transistor (UJT) (Characteristics, UJT Relaxation oscillator,
Basic Electronics Learning by doing Prof. T.S. Natarajan Department of Physics Indian Institute of Technology, Madras Lecture 38 Unit junction Transistor (UJT) (Characteristics, UJT Relaxation oscillator,
Physics 4C Chabot College Scott Hildreth
 Physics 4C Chabot College Scott Hildreth The Inverse Square Law for Light Intensity vs. Distance Using Microwaves Experiment Goals: Experimentally test the inverse square law for light using Microwaves.
Physics 4C Chabot College Scott Hildreth The Inverse Square Law for Light Intensity vs. Distance Using Microwaves Experiment Goals: Experimentally test the inverse square law for light using Microwaves.
SEMICONDUCTOR ELECTRONICS: MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS. Class XII : PHYSICS WORKSHEET
 SEMICONDUCT ELECTRONICS: MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS Class XII : PHYSICS WKSHEET 1. How is a n-p-n transistor represented symbolically? (1) 2. How does conductivity of a semiconductor change
SEMICONDUCT ELECTRONICS: MATERIALS, DEVICES AND SIMPLE CIRCUITS Class XII : PHYSICS WKSHEET 1. How is a n-p-n transistor represented symbolically? (1) 2. How does conductivity of a semiconductor change
Standing waves in the microwave range
 Related topics Microwaves, electromagnetic waves, reflection, inverse square law Principle If electromagnetic waves are reflected to and fro between two reflectors, a standing wave results. The wavelength
Related topics Microwaves, electromagnetic waves, reflection, inverse square law Principle If electromagnetic waves are reflected to and fro between two reflectors, a standing wave results. The wavelength
Federal Urdu University of Arts, Science & Technology Islamabad Pakistan SECOND SEMESTER ELECTRONICS - I
 SECOND SEMESTER ELECTRONICS - I BASIC ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS LAB DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Prepared By: Checked By: Approved By: Engr. Yousaf Hameed Engr. M.Nasim Khan Dr.Noman Jafri Lecturer
SECOND SEMESTER ELECTRONICS - I BASIC ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS LAB DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Prepared By: Checked By: Approved By: Engr. Yousaf Hameed Engr. M.Nasim Khan Dr.Noman Jafri Lecturer
UNIT 3 Transistors JFET
 UNIT 3 Transistors JFET Mosfet Definition of BJT A bipolar junction transistor is a three terminal semiconductor device consisting of two p-n junctions which is able to amplify or magnify a signal. It
UNIT 3 Transistors JFET Mosfet Definition of BJT A bipolar junction transistor is a three terminal semiconductor device consisting of two p-n junctions which is able to amplify or magnify a signal. It
Resistance and Ohm s Law R V I. 1 ohm = 1 volt ampere
 Resistance and Ohm s Law If you maintain an electric potential difference, or voltage V, across any conductor, an electric current occurs. In general, the magnitude of the current depends on the potential
Resistance and Ohm s Law If you maintain an electric potential difference, or voltage V, across any conductor, an electric current occurs. In general, the magnitude of the current depends on the potential
The Discussion of this exercise covers the following points:
 Exercise 1 The Diode EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the operation of a diode. DISCUSSION OUTLINE The Discussion of this exercise covers the following
Exercise 1 The Diode EXERCISE OBJECTIVE When you have completed this exercise, you will be familiar with the operation of a diode. DISCUSSION OUTLINE The Discussion of this exercise covers the following
10/27/2009 Reading: Chapter 10 of Hambley Basic Device Physics Handout (optional)
 EE40 Lec 17 PN Junctions Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/27/2009 Reading: Chapter 10 of Hambley Basic Device Physics Handout (optional) Slide 1 PN Junctions Semiconductor Physics of pn junctions (for reference
EE40 Lec 17 PN Junctions Prof. Nathan Cheung 10/27/2009 Reading: Chapter 10 of Hambley Basic Device Physics Handout (optional) Slide 1 PN Junctions Semiconductor Physics of pn junctions (for reference
EECE251 Circuit Analysis I Set 6: Diodes
 EECE251 Circuit Analysis I Set 6: Diodes Shahriar Mirabbasi Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of British Columbia shahriar@ece.ubc.ca Thanks to Dr. Linares and Dr. Yan for sharing
EECE251 Circuit Analysis I Set 6: Diodes Shahriar Mirabbasi Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of British Columbia shahriar@ece.ubc.ca Thanks to Dr. Linares and Dr. Yan for sharing
Class XII - Physics Semiconductor Electronics. Chapter-wise Problems
 lass X - Physics Semiconductor Electronics Materials, Device and Simple ircuit hapter-wise Problems Multiple hoice Question :- 14.1 The conductivity of a semiconductor increases with increase in temperature
lass X - Physics Semiconductor Electronics Materials, Device and Simple ircuit hapter-wise Problems Multiple hoice Question :- 14.1 The conductivity of a semiconductor increases with increase in temperature
RLC-circuits TEP. f res. = 1 2 π L C.
 RLC-circuits TEP Keywords Damped and forced oscillations, Kirchhoff s laws, series and parallel tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, reactance, impedance, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width
RLC-circuits TEP Keywords Damped and forced oscillations, Kirchhoff s laws, series and parallel tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, reactance, impedance, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width
BME/ISE 3512 Laboratory - Three Diode (1N4001)
 BME/ISE 3512 Laboratory Three Diode (1N4001) Learning Objectives: Understand the concept of PN junction diodes, their application as rectifiers, the nature and application of halfwave and fullwave rectifiers,
BME/ISE 3512 Laboratory Three Diode (1N4001) Learning Objectives: Understand the concept of PN junction diodes, their application as rectifiers, the nature and application of halfwave and fullwave rectifiers,
Diode Characteristics and Applications
 Diode Characteristics and Applications Topics covered in this presentation: Diode Characteristics Diode Clamp Protecting Against Back-EMF Half-Wave Rectifier The Zener Diode 1 of 18 Diode Characteristics
Diode Characteristics and Applications Topics covered in this presentation: Diode Characteristics Diode Clamp Protecting Against Back-EMF Half-Wave Rectifier The Zener Diode 1 of 18 Diode Characteristics
EK 307 Lab: Light-Emitting Diodes. In-lab Assignment (Complete Level 1 and additionally level 2 if you choose to):
 EK 307 Lab: Light-Emitting Diodes Laboratory Goal: To explore the characteristics of the light emitting diode. Learning Objectives: Voltage, Current, Power, and Instrumentation. Suggested Tools: Voltage
EK 307 Lab: Light-Emitting Diodes Laboratory Goal: To explore the characteristics of the light emitting diode. Learning Objectives: Voltage, Current, Power, and Instrumentation. Suggested Tools: Voltage
Electronic Principles Eighth Edition
 Part 1 Electronic Principles Eighth Edition Chapter 1 Introduction SELF-TEST 1. a 7. b 13. c 19. b 2. c 8. c 14. d 20. c 3. a 9. b 15. b 21. b 4. b 10. a 16. b 22. b 5. d 11. a 17. a 23. c 6. d 12. a 18.
Part 1 Electronic Principles Eighth Edition Chapter 1 Introduction SELF-TEST 1. a 7. b 13. c 19. b 2. c 8. c 14. d 20. c 3. a 9. b 15. b 21. b 4. b 10. a 16. b 22. b 5. d 11. a 17. a 23. c 6. d 12. a 18.
Analog Electronic Circuits
 Analog Electronic Circuits Chapter 1: Semiconductor Diodes Objectives: To become familiar with the working principles of semiconductor diode To become familiar with the design and analysis of diode circuits
Analog Electronic Circuits Chapter 1: Semiconductor Diodes Objectives: To become familiar with the working principles of semiconductor diode To become familiar with the design and analysis of diode circuits
LEP Optical pumping
 Related topics Spontaeous emission, induced emission, mean lifetime of a metastable state, relaxation, inversion, diode laser. Principle and task The visible light of a semiconductor diode laser is used
Related topics Spontaeous emission, induced emission, mean lifetime of a metastable state, relaxation, inversion, diode laser. Principle and task The visible light of a semiconductor diode laser is used
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject PHYSICS 9792/02 Paper 2 Part A Written Paper October/November 2013 INSERT The question
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge International Level 3 Pre-U Certificate Principal Subject PHYSICS 9792/02 Paper 2 Part A Written Paper October/November 2013 INSERT The question
MY-HITE ADJUSTABLE TABLE
 081717 MY-HITE ADJUSTABLE TABLE Model Number : FSQAHTB FRIANT & ASSOC. 4901 E.12 STREET OAKLAND, CA 94601 T:510.535.5113 FAX:510.535.5237 www.friant.com/systems/my-hite Please Read Instructions Before
081717 MY-HITE ADJUSTABLE TABLE Model Number : FSQAHTB FRIANT & ASSOC. 4901 E.12 STREET OAKLAND, CA 94601 T:510.535.5113 FAX:510.535.5237 www.friant.com/systems/my-hite Please Read Instructions Before
MY-HITE CORNER ADJUSTABLE TABLE
 081717 MY-HITE CORNER ADJUSTABLE TABLE C-LEG OPTION Model Number : FCNAHBC FRIANT & ASSOC. 4901 E.12 STREET OAKLAND, CA 94601 T:510.535.5113 FAX:510.535.5237 www.friant.com/systems/my-hite Please Read
081717 MY-HITE CORNER ADJUSTABLE TABLE C-LEG OPTION Model Number : FCNAHBC FRIANT & ASSOC. 4901 E.12 STREET OAKLAND, CA 94601 T:510.535.5113 FAX:510.535.5237 www.friant.com/systems/my-hite Please Read
IP1 Datasheet PWM OUTPUT WITH SINGLE CHANNEL ADC MODULE FEATURES DESCRIPTION CONNECTOR DETAILS
 PWM OUTPUT WITH SINGLE CHANNEL ADC MODULE FEATURES 1 PWM Output (3.3V) 0 Hz 1 khz Single Channel 3.3V 12-bit ADC input for voltage sensing Optional automated PWM adjustment based on input voltage for standalone
PWM OUTPUT WITH SINGLE CHANNEL ADC MODULE FEATURES 1 PWM Output (3.3V) 0 Hz 1 khz Single Channel 3.3V 12-bit ADC input for voltage sensing Optional automated PWM adjustment based on input voltage for standalone
Semiconductor Lasers Semiconductors were originally pumped by lasers or e-beams First diode types developed in 1962: Create a pn junction in
 Semiconductor Lasers Semiconductors were originally pumped by lasers or e-beams First diode types developed in 1962: Create a pn junction in semiconductor material Pumped now with high current density
Semiconductor Lasers Semiconductors were originally pumped by lasers or e-beams First diode types developed in 1962: Create a pn junction in semiconductor material Pumped now with high current density
