Wheatstone bridge (Item No.: P )
|
|
|
- Anne Oliver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
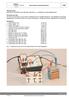
1 Wheatstone bridge (Item No.: P ) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Education Level: University Topic: Electricity and Magnetism Subtopic: Electric Current and Resistance Experiment: Wheatstone bridge Difficulty Preparation Time Execution Time Recommended Group Size Intermediate 1 Hour 2 Hours 2 Students Additional Requirements: Experiment Variations: Adhesive tape, opaque With the resistance board (item no ), another task to determine the conductivity of thin wires can be performed Keywords: Kirchhoff's law, Conductor, Circuit, Voltage, Resistance, Resistivity, Parallel connection, Series connection Overview Short description Principle The Wheatstone bridge is used to determine an unknown resistance with high accuracy by adjusting a connected combination of known resistors. Fig. 1: Experimental set-up of the Wheatstone bridge.
2 Equipment Position No. Material Order No. Quantity 1 PHYWE power supply, 230 V, DC: 0 12 V, 2 A / AC: 6 V, 12 V, 5 A Digital multimeter Slide wire meas. bridge, simple Connection box Resistor 1 Ohm 2%, 2W, G Resistor 2 Ohm 2%, 2W, G Resistor 5 Ohm 5%, 2W, G Resistor 10 Ohm, 1W, G Resistor 47 Ohm, 1W, G Resistor 100 Ohm, 1W, G Resistor 150 Ohm, 1W, G Resistor 220 Ohm, 1W, G Resistor 330 Ohm, 1W, G Resistor 680 Ohm, 1W, G Connecting cord, 32 A, 1000 mm, red Connecting cord, 32 A, 500 mm, red Connecting cord, 32 A, 1000 mm, yellow Connecting cord, 32 A, 1000 mm, blue Connecting cord, 32 A, 500 mm, blue Additional materials Adhesive tape, opaque Optional equipment for task 4 to determine small resistances of thin wires (NOT included in the supply): Tasks Position No. Material Order No. Quantity Resistance board, metal Connecting cord, 32 A, 1000 mm, red Connecting cord, 32 A, 500 mm, yellow Determination of unknown resistors with the Wheatstone bridge. 2. Determination of the total resistance of resistors in series. 3. Determination of the total resistance of resistors in parallel. 4. Optional (see required equipment): Measurement of low resistance and determination of the electrical resistivity of CuNi (Constantan).
3 Set-up and procedure Theory The Wheatstone bridge consists of four resistors that are connected as shown in Fig. 2. A voltage source is connected to the junctions a and c, whilst the ammeter G measures the current flow between the junctions b and d. Fig. 2: Wheatstone bridge, basic circuit diagram. Kirchhoff's second law implies that the application of a certain voltage between a and c causes an equal potential drop across the legs a b c and a d c. Both legs serve as a particular voltage divider. The potentials at the junctions b and d depend on the proportions of the resistors along the respective legs and. (1) If the resistor proportions are adjusted in a way so that the potentials and equalize, the current flow through the ammeter vanishes. The detection of zero current is very easy and could also be carried out with a simple galvanometer. This state is called the point of balance of the Wheatstone bridge. In that case, Eq. 1 can be combined: (2) (3) If three resistors are known and the fourth one, e.g. point of balance, should be identified, it can be calculated after setting the bridge to the. (4) In the present experiment, the resistance in the lower leg is replaced by a slide wire potentiometer as shown in Fig. 3, where a slider contact can be moved along the length of a wire to divide its total resistance in two distinct parts. The wire is made of a homogenous material with a uniform diameter, therefore, its resistance can be specified by (5) where denotes the electrical resistivity of the wire material, is the length of the wire, and is its cross-section. Hence, the resistance of the wire depends on geometrical as well as material-specific properties. Uniform resistivity and cross-section given, the resistance increases proportionally with the length. This implies that the slide wire resistance ratio can be expressed by its lengths proportion.
4 Set-up In advance, up to five randomly selected resistors must be prepared for the measurement. To hide the resistance information, the printed values and optionally the transparent case of the chosen resistors have to be covered with adhesive tape. For separation during the measurement and verification afterwards, the resistors should be labeled with. In the following measuring examples, the used designation is: 220 Ω 2 Ω 47 Ω 5 Ω 680 Ω Fig. 3: Wheatstone bridge circuit diagram. The experimental set-up is shown in Fig. 1. According to Fig. 4, the first unknown resistance and a known resistor (e.g. 100 Ω) are placed on the connection box. The short red cord connects with the red connector of the DC output, while the long red cord connects this junction with the left connector of the slide wire measuring bridge. Likewise, the blue cords are connected with the comparison resistor, the blue connector of the DC output, and the right connector of the slide wire. In between, the yellow cords connect the ammeter G (ma scale, DC mode) with the junction between and as well as the slider of the measuring bridge. The circuit diagram is illustrated in Fig. 3. Fig. 4: Set-up of the upper leg of the Wheatstone bridge with an unknown resistance. Procedure 1. Determination of unknown resistors To obtain the unknown resistance displays zero current., the slider of the measure bridge has to be moved in a position so that the ammeter Depending on the chosen resistors, it is possible that you will detect a remaining current in every slider position. In that case, you have to replace the comparison resistor with a different one. The same procedure is advised if the slider position is close to the wire ends, because the measurement precision will otherwise decrease. Determine the slider position on the ruler and the associated position = 100 cm. Replace and repeat the procedure until all five unknown resistors are determined.
5 Note: The power supply provides a current of up to 2 A at a voltage of 12 V. If the current should exceed that threshold due to e.g. a small resistance in the circuit, the device will reduce the voltage to prevent damage. This is indicated by the glowing of the red LED above the current selector. Nevertheless, the measurement and the results will not be affected by that short-circuit protection. 2. Determination of the total resistance of resistors in series. To determine the resistance of two or three unknown resistors connected in series, the upper leg of the Wheatstone bridge has to be altered according to Fig 5 or Fig. 6, respectively. Resistance is replaced by different combinations of the unknown resistors, while one of the known resistors remains as. Perform the measurements just as you did in task 1 for at least two combinations of two, and two combinations of three resistors. Determine the corresponding slider positions (as well as ). Fig. 5: Set-up for two unknown resistors connected in series. Fig. 6: Set-up for three unknown resistors connected in series. 3. Determination of the total resistance of resistors in parallel. To study the effect of two resistors connected in parallel, the set-up has to be adjusted as shown in Fig. 7. Resistance substituted by two unknown resistors in a parallel circuit, while one of the known resistors serves as. is Repeat the steps of task 1 for at least three different combinations of resistors and determine the corresponding slider positions (as well as ), again. Fig. 7: Set-up of the upper leg of the Wheatstone bridge with two unknown resistors connected in parallel. 4. Optional: Determination of the electrical resistivity of CuNi. Note: For this experimental part, additional equipment is needed. One of the benefits of the Wheatstone bridge is the possibility to precisely determine a low resistance. For demonstration,
6 the resistance of several Constantan wires with varying diameters (and identical length Thereof, the electrical resistivity of Constantan can be obtained. = 100 cm) should be measured. For this purpose, should be replaced by a resistor of approximately 1 Ω, and the CuNi44 wire No. 1 of the resistance board has to be connected as (see Fig. 8 and 9). Again, the measurement has to be carried out like before until the bridge is balanced. Register the slider position (as well as ) and repeat the measurement for the remaining CuNi44 wires No. 2, 3 and 5. Fig. 8: Experimental set-up using the resistance board. Fig. 9: Set-up of the connection box for use of the resistance board with the Wheatstone bridge. Evaluation Kirchhoff's first law implies that the sum over all currents directed towards or away from a junction has to be zero. At the point of balance, with no current flowing through the ammeter, the current flow must remain conserved along both legs of the Wheatstone bridge. Thus Eq. 4 and 5 give the unknown resistance. (6) 1. Determination of unknown resistors Calculate the resistance of the unknown resistors using Eq. 6 and the measured lengths on the slide wire. Reveal the indicated values of the used resistors and compare them to the calculated results (see example in Tab. 1). You will notice that the deviation increases for values measured close to the wire ends. Nevertheless, the absolute values of measured and actual resistance are in good agreement. In order to reduce tolerance, exchange the comparison resistor with a resistor of comparable magnitude to.
7 Table 1: Evaluation of unknown resistors with the Wheatstone bridge. Labelling in Ω in mm in mm in Ω actual in Ω deviation in % Determination of the total resistance of resistors in series. Calculate the total resistance of the unknown resistors in the series circuit using Eq. 6 and the measured lengths on the slide wire. Reveal the indicated values of the used resistors and compare them to the calculated results (see example in Tab. 2). Table 2: Evaluation of resistors in a series circuit. Used resistors in Ω in mm in mm in Ω actual in Ω * deviation in %, = , = ,, = ,, = * calculation according to Eq. 7 According to Kirchhoff's second law, the voltage drop across each leg of the Wheatstone bridge sums up to the total applied voltage at the point of balance. Because of the constant current flow along each leg, Ohm's law gives a total resistance that is equal to the sum of each individual resistance value in a series circuit. (7) 3. Determination of the total resistance of resistors in parallel. Calculate the total resistance of the unknown resistors in the parallel circuit using Eq. 6 and the measured lengths on the slide wire. Reveal the indicated values of the used resistors and compare them to the calculated results (see example in Tab. 3). Table 3: Evaluation of resistors in a parallel circuit. Used resistors in Ω in mm in mm in Ω actual in Ω ** deviation in %, and , and , and
8 ** calculation according to Eq. 8 According to Kirchhoff's first law, the total current in a parallel circuit of resistors equals the sum over the currents in each individual branch whereas the voltage is the same for each component. Thus the total resistance of a parallel circuit can be determined using Ohm's law and adding up the reciprocal values of each components' resistance:. (8) Adding a parallel branch to the circuit increases the current flow because the present resistance can be bypassed along the extra branch. Therefore, the total resistance of a parallel circuit is always lower than the resistance value of the smallest particular resistor (see Tab. 3). 4. Optional: Determination of the electrical resistivity of CuNi. Calculate the total resistance example in Tab. 4). of the wires in the parallel circuit using Eq. 6 and the measured lengths on the slide wire (see Table 4: Resistance of various Constantan wires with length l = 1 m. diameter in mm in mm in mm in Ω Corresponding to Eq. 5, the electrical resistivity is an intrinsic property that can be calculated from the measured resistance of the wire and its geometry. (9) Given that the resistance has been obtained for several wires made of the same material, the electrical resistivity of CuNi can be determined with increased accuracy by plotting the resistance against. The proportionality factor corresponds to the slope of the linear fit (as shown in Fig. 10). (10) The slope of the fit in Fig. 10 gives an electrical resistivity of (11) that is in very good agreement with the literature value for Constantan of approximately Ω m.
9 Fig. 10: Resistance of a conductor wire as a function of its geometry /. Remark In this experiment, the resistance values of the four resistors have been taken into account, only. Actually, the resistance of the used cords, the connections as well as the ammeter could not be avoided and have been neglected as there is only a minor influence on the results. It is possible to determine very small resistances with the Wheatstone bridge gaining a high accuracy. Yet, the results lose precision when moving the slider to the far end positions of the potentiometer. For best results, the slider should remain close to the central position, and instead, the comparison resistor should be replaced until its magnitude matches that of the unknown resistor.
Kirchhoff s laws, induction law, Maxwell equations, current, voltage, resistance, parallel connection, series connection, potentiometer
 Kirchhoff s laws with Cobra4 TEP Related Topics Kirchhoff s laws, induction law, Maxwell equations, current, voltage, resistance, parallel connection, series connection, potentiometer Principle First Kirchhoff
Kirchhoff s laws with Cobra4 TEP Related Topics Kirchhoff s laws, induction law, Maxwell equations, current, voltage, resistance, parallel connection, series connection, potentiometer Principle First Kirchhoff
Practical 2.2 EXTENSION OF THE RANGES OF ELECTRICAL MEASURING DEVICES
 Practical. EXTENSION OF THE RANGES OF ELECTRICAL MEASURING DEVICES September 8, 07 Introduction An important characteristic of the electrical instrument is its internal resistance R instr. During the measurements
Practical. EXTENSION OF THE RANGES OF ELECTRICAL MEASURING DEVICES September 8, 07 Introduction An important characteristic of the electrical instrument is its internal resistance R instr. During the measurements
CHAPTER 3: ELECTRIC CURRENT AND DIRECT CURRENT CIRCUIT
 CHAPTER 3: ELECTRIC CURRENT AND DIRECT CURRENT CIRCUIT PSPM II 2005/2006 NO. 3 3. (a) Write Kirchhoff s law for the conservation of energy. FIGURE 2 (b) A circuit of two batteries and two resistors is
CHAPTER 3: ELECTRIC CURRENT AND DIRECT CURRENT CIRCUIT PSPM II 2005/2006 NO. 3 3. (a) Write Kirchhoff s law for the conservation of energy. FIGURE 2 (b) A circuit of two batteries and two resistors is
WHEATSTONE BRIDGE. Objectives
 WHEATSTONE BRIDGE Objectives The Wheatstone bridge is a circuit designed to measure an unknown resistance by comparison with other known resistances. A slide-wire form of the Wheatstone bridge will be
WHEATSTONE BRIDGE Objectives The Wheatstone bridge is a circuit designed to measure an unknown resistance by comparison with other known resistances. A slide-wire form of the Wheatstone bridge will be
PH213 Chapter 26 solutions
 PH213 Chapter 26 solutions 26.6. IDENTIFY: The potential drop is the same across the resistors in parallel, and the current into the parallel combination is the same as the current through the 45.0-Ω resistor.
PH213 Chapter 26 solutions 26.6. IDENTIFY: The potential drop is the same across the resistors in parallel, and the current into the parallel combination is the same as the current through the 45.0-Ω resistor.
DC Circuits and Ohm s Law
 DC Circuits and Ohm s Law INTRODUCTION During the nineteenth century so many advances were made in understanding the electrical nature of matter that it has been called the age of electricity. One such
DC Circuits and Ohm s Law INTRODUCTION During the nineteenth century so many advances were made in understanding the electrical nature of matter that it has been called the age of electricity. One such
DC Circuits and Ohm s Law
 DC Circuits and Ohm s Law INTRODUCTION During the nineteenth century so many advances were made in understanding the electrical nature of matter that it has been called the age of electricity. One such
DC Circuits and Ohm s Law INTRODUCTION During the nineteenth century so many advances were made in understanding the electrical nature of matter that it has been called the age of electricity. One such
Physics 201 Laboratory: Analog and Digital Electronics. I-0. Introductory Notes
 Physics 201 Laboratory: Analog and Digital Electronics -0. ntroductory Notes Definitions of circuit and current. Current is the flow of charge. We may think of electrons flowing through a wire as a current
Physics 201 Laboratory: Analog and Digital Electronics -0. ntroductory Notes Definitions of circuit and current. Current is the flow of charge. We may think of electrons flowing through a wire as a current
Basic Circuits. PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics II. 1 Objectives. 2 Equipment List. 3 Theory
 PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics II Basic Circuits 1 Objectives Investigate the relationship among three variables (resistance, current and voltage) in direct current circuits. Investigate the behaviours
PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics II Basic Circuits 1 Objectives Investigate the relationship among three variables (resistance, current and voltage) in direct current circuits. Investigate the behaviours
PHYS 1402 General Physics II Experiment 5: Ohm s Law
 PHYS 1402 General Physics II Experiment 5: Ohm s Law Student Name Objective: To investigate the relationship between current and resistance for ordinary conductors known as ohmic conductors. Theory: For
PHYS 1402 General Physics II Experiment 5: Ohm s Law Student Name Objective: To investigate the relationship between current and resistance for ordinary conductors known as ohmic conductors. Theory: For
ECE215 Lecture 7 Date:
 Lecture 7 Date: 29.08.2016 AC Circuits: Impedance and Admittance, Kirchoff s Laws, Phase Shifter, AC bridge Impedance and Admittance we know: we express Ohm s law in phasor form: where Z is a frequency-dependent
Lecture 7 Date: 29.08.2016 AC Circuits: Impedance and Admittance, Kirchoff s Laws, Phase Shifter, AC bridge Impedance and Admittance we know: we express Ohm s law in phasor form: where Z is a frequency-dependent
Lab 3 DC CIRCUITS AND OHM'S LAW
 43 Name Date Partners Lab 3 DC CIRCUITS AND OHM'S LAW AMPS + - VOLTS OBJECTIVES To learn to apply the concept of potential difference (voltage) to explain the action of a battery in a circuit. To understand
43 Name Date Partners Lab 3 DC CIRCUITS AND OHM'S LAW AMPS + - VOLTS OBJECTIVES To learn to apply the concept of potential difference (voltage) to explain the action of a battery in a circuit. To understand
Lab 11: Circuits. Figure 1: A hydroelectric dam system.
 Description Lab 11: Circuits In this lab, you will study voltage, current, and resistance. You will learn the basics of designing circuits and you will explore how to find the total resistance of a circuit
Description Lab 11: Circuits In this lab, you will study voltage, current, and resistance. You will learn the basics of designing circuits and you will explore how to find the total resistance of a circuit
UNIT-2 CURRENT ELECTRICITY
 UNIT-2 CURRENT ELECTRICITY 1 Marks Question 1. A wire of resistance R is cut into n equal parts.these parts are then connected in parallel with each other. The equivalent resistance of the combination
UNIT-2 CURRENT ELECTRICITY 1 Marks Question 1. A wire of resistance R is cut into n equal parts.these parts are then connected in parallel with each other. The equivalent resistance of the combination
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE. Experiment PA41A ELECTRIC CIRCUITS
 VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE Experiment PA41A ELECTRIC CIRCUITS Equipment (see Appendices) 12V DC power supply (battery): multimeter (and/or milliammeter and voltmeter); electrical leads; alligator clips; fixed
VISUAL PHYSICS ONLINE Experiment PA41A ELECTRIC CIRCUITS Equipment (see Appendices) 12V DC power supply (battery): multimeter (and/or milliammeter and voltmeter); electrical leads; alligator clips; fixed
SF026: PAST YEAR UPS QUESTIONS
 CHAPTER 3: ELECTRIC CURRENT AND DIRECT-CURRENT CIRCUITS UPS SEMESTER 2 2011/2012 1. (a) (i) What is meant by electrical resistivity? (ii) Calculate the resistance of an iron wire of uniform diameter 0.8
CHAPTER 3: ELECTRIC CURRENT AND DIRECT-CURRENT CIRCUITS UPS SEMESTER 2 2011/2012 1. (a) (i) What is meant by electrical resistivity? (ii) Calculate the resistance of an iron wire of uniform diameter 0.8
Unit 8 Combination Circuits
 Unit 8 Combination Circuits Objectives: Define a combination circuit. List the rules for parallel circuits. List the rules for series circuits. Solve for combination circuit values. Characteristics There
Unit 8 Combination Circuits Objectives: Define a combination circuit. List the rules for parallel circuits. List the rules for series circuits. Solve for combination circuit values. Characteristics There
2008 D AI Prove that the current density of a metallic conductor is directly proportional to the drift speed of electrons.
 2008 D 1. Prove that the current density of a metallic conductor is directly proportional to the drift speed of electrons. 2. A number of identical cells, n, each of emf E, internal resistance r connected
2008 D 1. Prove that the current density of a metallic conductor is directly proportional to the drift speed of electrons. 2. A number of identical cells, n, each of emf E, internal resistance r connected
DC CIRCUITS AND OHM'S LAW
 July 15, 2008 DC Circuits and Ohm s Law 1 Name Date Partners DC CIRCUITS AND OHM'S LAW AMPS - VOLTS OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW To learn to apply the concept of potential difference (voltage) to explain the action
July 15, 2008 DC Circuits and Ohm s Law 1 Name Date Partners DC CIRCUITS AND OHM'S LAW AMPS - VOLTS OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW To learn to apply the concept of potential difference (voltage) to explain the action
Lab 4 OHM S LAW AND KIRCHHOFF S CIRCUIT RULES
 57 Name Date Partners Lab 4 OHM S LAW AND KIRCHHOFF S CIRCUIT RULES AMPS - VOLTS OBJECTIVES To learn to apply the concept of potential difference (voltage) to explain the action of a battery in a circuit.
57 Name Date Partners Lab 4 OHM S LAW AND KIRCHHOFF S CIRCUIT RULES AMPS - VOLTS OBJECTIVES To learn to apply the concept of potential difference (voltage) to explain the action of a battery in a circuit.
Kirchhoff s laws. Objectives. Assessment. Assessment. Assessment. Assessment 5/27/14. Apply Kirchhoff s first and second laws.
 Kirchhoff s laws Objectives Apply Kirchhoff s first and second laws. Calculate the current and voltage for resistor circuits connected in parallel. Calculate the current and voltage for resistor circuits
Kirchhoff s laws Objectives Apply Kirchhoff s first and second laws. Calculate the current and voltage for resistor circuits connected in parallel. Calculate the current and voltage for resistor circuits
Ohm s Law. 1 Object. 2 Apparatus. 3 Theory. To study resistors, Ohm s law, linear behavior, and non-linear behavior.
 Ohm s Law Object To study resistors, Ohm s law, linear behavior, and non-linear behavior. pparatus esistors, power supply, meters, wires, and alligator clips. Theory resistor is a circuit element which
Ohm s Law Object To study resistors, Ohm s law, linear behavior, and non-linear behavior. pparatus esistors, power supply, meters, wires, and alligator clips. Theory resistor is a circuit element which
Ohm's Law and the Measurement of Resistance
 Ohm's Law and the Measurement of Resistance I. INTRODUCTION An electric current flows through a conductor when a potential difference is placed across its ends. The potential difference is generally in
Ohm's Law and the Measurement of Resistance I. INTRODUCTION An electric current flows through a conductor when a potential difference is placed across its ends. The potential difference is generally in
Fig [5]
![Fig [5] Fig [5]](/thumbs/82/85456687.jpg) 1 (a) Fig. 4.1 shows the I-V characteristic of a light-emitting diode (LED). 40 I / 10 3 A 30 20 10 0 1.0 1.5 2.0 V / V Fig. 4.1 (i) In Describe the significant features of the graph in terms of current,
1 (a) Fig. 4.1 shows the I-V characteristic of a light-emitting diode (LED). 40 I / 10 3 A 30 20 10 0 1.0 1.5 2.0 V / V Fig. 4.1 (i) In Describe the significant features of the graph in terms of current,
XII PHYSICS INSTRUMENTS] CHAPTER NO. 15 [ELECTRICAL MEASURING MUHAMMAD AFFAN KHAN LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K
![XII PHYSICS INSTRUMENTS] CHAPTER NO. 15 [ELECTRICAL MEASURING MUHAMMAD AFFAN KHAN LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K XII PHYSICS INSTRUMENTS] CHAPTER NO. 15 [ELECTRICAL MEASURING MUHAMMAD AFFAN KHAN LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K](/thumbs/80/81415743.jpg) XII PHYSICS MUHAMMAD AFFAN KHAN LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K affan_414@live.com https://promotephysics.wordpress.com [ELECTRICAL MEASURING INSTRUMENTS] CHAPTER NO. 15 MOVING COIL GALVANOMETER An electrical
XII PHYSICS MUHAMMAD AFFAN KHAN LECTURER PHYSICS, AKHSS, K affan_414@live.com https://promotephysics.wordpress.com [ELECTRICAL MEASURING INSTRUMENTS] CHAPTER NO. 15 MOVING COIL GALVANOMETER An electrical
Magnetic induction with Cobra3
 Principle A magnetic field of variable frequency and varying strength is produced in a long coil. The voltages induced across thin coils which are pushed into the long coil are determined as a function
Principle A magnetic field of variable frequency and varying strength is produced in a long coil. The voltages induced across thin coils which are pushed into the long coil are determined as a function
Ohm s Law and Electrical Circuits
 Ohm s Law and Electrical Circuits INTRODUCTION In this experiment, you will measure the current-voltage characteristics of a resistor and check to see if the resistor satisfies Ohm s law. In the process
Ohm s Law and Electrical Circuits INTRODUCTION In this experiment, you will measure the current-voltage characteristics of a resistor and check to see if the resistor satisfies Ohm s law. In the process
Downloaded from
 Question 1: What does an electric circuit mean? An electric circuit consists of electric devices, switching devices, source of electricity, etc. that are connected by conducting wires. Question 2: Define
Question 1: What does an electric circuit mean? An electric circuit consists of electric devices, switching devices, source of electricity, etc. that are connected by conducting wires. Question 2: Define
13.Current Electricity Marks :03/04
 13.Current Electricity Marks :03/04 Q. State and explain kirchhoff s laws for an electric network. Ans:- Kirchhoff s law for an electric network :- In 1842 Kirchhoff s stated two laws to determine currents
13.Current Electricity Marks :03/04 Q. State and explain kirchhoff s laws for an electric network. Ans:- Kirchhoff s law for an electric network :- In 1842 Kirchhoff s stated two laws to determine currents
Tangent Galvanometer Investigating the Relationship Between Current and Magnetic Field
 Investigating the Relationship Between Current and Magnetic Field The tangent galvanometer is a device that allows you to measure the strength of the magnetic field at the center of a coil of wire as a
Investigating the Relationship Between Current and Magnetic Field The tangent galvanometer is a device that allows you to measure the strength of the magnetic field at the center of a coil of wire as a
V (in volts) = voltage applied to the circuit, I (in amperes) = current flowing in the circuit, R (in ohms) = resistance of the circuit.
 OHM S LW OBJECTIES: PRT : 1) Become familiar with the use of ammeters and voltmeters to measure DC voltage and current. 2) Learn to use wires and a breadboard to build circuits from a circuit diagram.
OHM S LW OBJECTIES: PRT : 1) Become familiar with the use of ammeters and voltmeters to measure DC voltage and current. 2) Learn to use wires and a breadboard to build circuits from a circuit diagram.
Experiment 3. Ohm s Law. Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current.
 Experiment 3 Ohm s Law 3.1 Objectives Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current. Construct a circuit using resistors, wires and a breadboard
Experiment 3 Ohm s Law 3.1 Objectives Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current. Construct a circuit using resistors, wires and a breadboard
TO INVESTIGATE THE VARIATION OF CURRENT (I) WITH P.D. (V) FOR (a) A METALLIC CONDUCTOR
 FOR (a) A METALLIC CONDUCTOR Low voltage power supply, rheostat, voltmeter, ammeter, length of nichrome wire. 6 A - Nichrome wire 1. Set up the circuit as shown and set the voltage supply at 6 d.c. 2.
FOR (a) A METALLIC CONDUCTOR Low voltage power supply, rheostat, voltmeter, ammeter, length of nichrome wire. 6 A - Nichrome wire 1. Set up the circuit as shown and set the voltage supply at 6 d.c. 2.
Chapter 23 Circuits. Chapter Goal: To understand the fundamental physical principles that govern electric circuits. Slide 23-1
 Chapter 23 Circuits Chapter Goal: To understand the fundamental physical principles that govern electric circuits. Slide 23-1 Chapter 23 Preview Looking Ahead: Analyzing Circuits Practical circuits consist
Chapter 23 Circuits Chapter Goal: To understand the fundamental physical principles that govern electric circuits. Slide 23-1 Chapter 23 Preview Looking Ahead: Analyzing Circuits Practical circuits consist
Experiment 2. Ohm s Law. Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current.
 Experiment 2 Ohm s Law 2.1 Objectives Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current. Construct a circuit using resistors, wires and a breadboard
Experiment 2 Ohm s Law 2.1 Objectives Become familiar with the use of a digital voltmeter and a digital ammeter to measure DC voltage and current. Construct a circuit using resistors, wires and a breadboard
Ohm s Law. 1 Object. 2 Apparatus. 3 Theory. To study resistors, Ohm s law, linear behavior, and non-linear behavior.
 Ohm s Law Object To study resistors, Ohm s law, linear behavior, and non-linear behavior. pparatus esistors, power supply, meters, wires, and alligator clips. Theory resistor is a circuit element which
Ohm s Law Object To study resistors, Ohm s law, linear behavior, and non-linear behavior. pparatus esistors, power supply, meters, wires, and alligator clips. Theory resistor is a circuit element which
Experiment 2 Electric Circuit Fundamentals
 Experiment 2 Electric Circuit Fundamentals Introduction This experiment has two parts. Each part will have to be carried out using the Multisim Electronics Workbench software. The experiment will then
Experiment 2 Electric Circuit Fundamentals Introduction This experiment has two parts. Each part will have to be carried out using the Multisim Electronics Workbench software. The experiment will then
Physics 3330 Experiment #2 Fall DC techniques, dividers, and bridges
 Physics 3330 Experiment #2 Fall 2002 DC techniques, dividers, and bridges Purpose You will gain a familiarity with the circuit board and work with a variety of DC techniques, including voltage dividers,
Physics 3330 Experiment #2 Fall 2002 DC techniques, dividers, and bridges Purpose You will gain a familiarity with the circuit board and work with a variety of DC techniques, including voltage dividers,
Unit 12 - Electric Circuits. By: Albert Hall
 Unit 12 - Electric Circuits By: Albert Hall Unit 12 - Electric Circuits By: Albert Hall Online: < http://cnx.org/content/col12001/1.1/ > OpenStax-CNX This selection and arrangement of content as a collection
Unit 12 - Electric Circuits By: Albert Hall Unit 12 - Electric Circuits By: Albert Hall Online: < http://cnx.org/content/col12001/1.1/ > OpenStax-CNX This selection and arrangement of content as a collection
Table of Contents...2. About the Tutorial...6. Audience...6. Prerequisites...6. Copyright & Disclaimer EMI INTRODUCTION Voltmeter...
 1 Table of Contents Table of Contents...2 About the Tutorial...6 Audience...6 Prerequisites...6 Copyright & Disclaimer...6 1. EMI INTRODUCTION... 7 Voltmeter...7 Ammeter...8 Ohmmeter...8 Multimeter...9
1 Table of Contents Table of Contents...2 About the Tutorial...6 Audience...6 Prerequisites...6 Copyright & Disclaimer...6 1. EMI INTRODUCTION... 7 Voltmeter...7 Ammeter...8 Ohmmeter...8 Multimeter...9
Unit 7 Parallel Circuits
 Unit 7 Parallel Circuits Objectives: Unit 7 Parallel Circuits Discuss the characteristics of parallel circuits. State the three rules for solving electrical values of resistance for parallel circuits.
Unit 7 Parallel Circuits Objectives: Unit 7 Parallel Circuits Discuss the characteristics of parallel circuits. State the three rules for solving electrical values of resistance for parallel circuits.
Pre-Lab for Batteries and Bulbs
 Pre-Lab for Batteries and Bulbs Complex circuits composed of resistors can be simplified by using the concept of equivalent resistors. For example if resistors R 1, R 2, and R 3 are connected in series,
Pre-Lab for Batteries and Bulbs Complex circuits composed of resistors can be simplified by using the concept of equivalent resistors. For example if resistors R 1, R 2, and R 3 are connected in series,
OHM'S LAW AND RESISTANCE NETWORKS OBJECT
 17 E7 E7.1 OHM'S LAW AND RESISTANCE NETWORKS OBJECT The objects of this experiment are to determine the voltage-current relationship for a resistor and to verify the series and parallel resistance formulae.
17 E7 E7.1 OHM'S LAW AND RESISTANCE NETWORKS OBJECT The objects of this experiment are to determine the voltage-current relationship for a resistor and to verify the series and parallel resistance formulae.
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LABORATORY MANUAL (II SEMESTER)
 ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LABORATORY MANUAL (II SEMESTER) LIST OF EXPERIMENTS. Verification of Ohm s laws and Kirchhoff s laws. 2. Verification of Thevenin s and Norton s Theorem. 3. Verification of Superposition
ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS LABORATORY MANUAL (II SEMESTER) LIST OF EXPERIMENTS. Verification of Ohm s laws and Kirchhoff s laws. 2. Verification of Thevenin s and Norton s Theorem. 3. Verification of Superposition
total j = BA, [1] = j [2] total
![total j = BA, [1] = j [2] total total j = BA, [1] = j [2] total](/thumbs/85/91692343.jpg) Name: S.N.: Experiment 2 INDUCTANCE AND LR CIRCUITS SECTION: PARTNER: DATE: Objectives Estimate the inductance of the solenoid used for this experiment from the formula for a very long, thin, tightly wound
Name: S.N.: Experiment 2 INDUCTANCE AND LR CIRCUITS SECTION: PARTNER: DATE: Objectives Estimate the inductance of the solenoid used for this experiment from the formula for a very long, thin, tightly wound
II. Experimental Procedure
 Ph 122 July 27, 2006 Ohm's Law http://www.physics.sfsu.edu/~manuals/ph122/ I. Theory In this lab we will make detailed measurements on one resistor to see if it obeys Ohm's law. We will also verify the
Ph 122 July 27, 2006 Ohm's Law http://www.physics.sfsu.edu/~manuals/ph122/ I. Theory In this lab we will make detailed measurements on one resistor to see if it obeys Ohm's law. We will also verify the
Chapter 20 Electric Circuits
 Chapter 20 Electric Circuits 1 20.1 Electromotive Force and Current In an electric circuit, an energy source and an energy consuming device are connected by conducting wires through which electric charges
Chapter 20 Electric Circuits 1 20.1 Electromotive Force and Current In an electric circuit, an energy source and an energy consuming device are connected by conducting wires through which electric charges
The sum of the currents entering a circuit junction is equal to the sum of the currents leaving the junction.
 By substituting the definition for resistance into the formula for conductance, the reciprocal formula for resistance in parallel circuits is obtained: In parallel circuits, there are junctions where two
By substituting the definition for resistance into the formula for conductance, the reciprocal formula for resistance in parallel circuits is obtained: In parallel circuits, there are junctions where two
Magnetic induction with Cobra3
 Magnetic induction with Cobra3 LEP Related Topics Maxwell s equations, electrical eddy field, magnetic field of coils, coil, magnetic flux, induced voltage. Principle A magnetic field of variable frequency
Magnetic induction with Cobra3 LEP Related Topics Maxwell s equations, electrical eddy field, magnetic field of coils, coil, magnetic flux, induced voltage. Principle A magnetic field of variable frequency
Resistance and Resistivity
 Resistance and Resistivity Lab Section (circle): Day: Monday Tuesday Time: 8:00 9:30 1:10 2:40 Name: Partners: Pre-Lab You are required to finish this section before coming to the lab it will be checked
Resistance and Resistivity Lab Section (circle): Day: Monday Tuesday Time: 8:00 9:30 1:10 2:40 Name: Partners: Pre-Lab You are required to finish this section before coming to the lab it will be checked
Lab. 1: Simple Linear Circuit Analysis
 Lab. 1: Simple Linear Circuit Analysis Philippe Piot (February 9th, 27) 1. Ohm's Law The circuit shown in Figure 1 was built with resistance R=1 and then 1 kω. For these two values of the resistance, the
Lab. 1: Simple Linear Circuit Analysis Philippe Piot (February 9th, 27) 1. Ohm's Law The circuit shown in Figure 1 was built with resistance R=1 and then 1 kω. For these two values of the resistance, the
electronics fundamentals
 electronics fundamentals circuits, devices, and applications THOMAS L. FLOYD DAVID M. BUCHLA chapter 6 Identifying series-parallel relationships Most practical circuits have combinations of series and
electronics fundamentals circuits, devices, and applications THOMAS L. FLOYD DAVID M. BUCHLA chapter 6 Identifying series-parallel relationships Most practical circuits have combinations of series and
21.1 Resistors in Series and Parallel
 808 Chapter 21 Circuits and DC Instruments Explain why batteries in a flashlight gradually lose power and the light dims over time. Describe what happens to a graph of the voltage across a capacitor over
808 Chapter 21 Circuits and DC Instruments Explain why batteries in a flashlight gradually lose power and the light dims over time. Describe what happens to a graph of the voltage across a capacitor over
Chapter 20. Circuits. q I = t. (a) (b) (c) Energy Charge
 Chapter 0 n an electric circuit, an energy source and an energy consuming device are connected by conducting wires through which electric charges move. Circuits Within a battery, a chemical reaction occurs
Chapter 0 n an electric circuit, an energy source and an energy consuming device are connected by conducting wires through which electric charges move. Circuits Within a battery, a chemical reaction occurs
Bell Ringer: Define to the best of your ability the definition of: Current Voltage Resistance
 Bell Ringer: Define to the best of your ability the definition of: Current Voltage Resistance Explain the behavior of the current and the voltage in a Series Circuit. Explain the behavior of the current
Bell Ringer: Define to the best of your ability the definition of: Current Voltage Resistance Explain the behavior of the current and the voltage in a Series Circuit. Explain the behavior of the current
Coil in the AC circuit with Cobra3
 Coil in the AC circuit with Cobra3 TEP Related topics Inductance, Kirchhoff s laws, Maxwell s equations, a.c. impedance, phase displacement. Principle and task The coil is connected in a circuit with a
Coil in the AC circuit with Cobra3 TEP Related topics Inductance, Kirchhoff s laws, Maxwell s equations, a.c. impedance, phase displacement. Principle and task The coil is connected in a circuit with a
A battery transforms chemical energy into electrical energy. Chemical reactions within the cell create a potential difference between the terminals
 D.C Electricity Volta discovered that electricity could be created if dissimilar metals were connected by a conductive solution called an electrolyte. This is a simple electric cell. The Electric Battery
D.C Electricity Volta discovered that electricity could be created if dissimilar metals were connected by a conductive solution called an electrolyte. This is a simple electric cell. The Electric Battery
Electricity. Coil in the AC circuit /11. Electrodynamics. What you need:
 Electrodynamics Electricity Coil in the AC circuit -01/11 What you can learn about Inductance Kirchhoff s laws Maxwell s equations AC impedance Phase displacement Principle: The coil is connected in a
Electrodynamics Electricity Coil in the AC circuit -01/11 What you can learn about Inductance Kirchhoff s laws Maxwell s equations AC impedance Phase displacement Principle: The coil is connected in a
Physics 1051 Laboratory #4 DC Circuits and Ohm s Law. DC Circuits and Ohm s Law
 DC Circuits and Ohm s Law Contents Part I: Objective Part II: Introduction Part III: Apparatus and Setup Part IV: Measurements Part V: Analysis Part VI: Summary and Conclusions Part I: Objective In this
DC Circuits and Ohm s Law Contents Part I: Objective Part II: Introduction Part III: Apparatus and Setup Part IV: Measurements Part V: Analysis Part VI: Summary and Conclusions Part I: Objective In this
CURRENT ELECTRICITY. 1. The S.I. unit of power is (a) Henry (b) coulomb (c) watt (d) watt-hour Ans: c
 CURRENT ELECTRICITY 1. The S.I. unit of power is (a) Henry (b) coulomb (c) watt (d) watt-hour 2. Electric pressure is also called (a) resistance (b) power (c) voltage (d) energy 3. The substances which
CURRENT ELECTRICITY 1. The S.I. unit of power is (a) Henry (b) coulomb (c) watt (d) watt-hour 2. Electric pressure is also called (a) resistance (b) power (c) voltage (d) energy 3. The substances which
SCRIPT. Voltage Dividers
 SCRIPT Hello friends in our earlier discussion we talked about series resistive circuits, when connected in series, resistors form a "string" in which there is only one path for current. Ohm's law can
SCRIPT Hello friends in our earlier discussion we talked about series resistive circuits, when connected in series, resistors form a "string" in which there is only one path for current. Ohm's law can
18-3 Circuit Analogies, and Kirchoff s Rules
 18-3 Circuit Analogies, and Kirchoff s Rules Analogies can help us to understand circuits, because an analogous system helps us build a model of the system we are interested in. For instance, there are
18-3 Circuit Analogies, and Kirchoff s Rules Analogies can help us to understand circuits, because an analogous system helps us build a model of the system we are interested in. For instance, there are
RLC-circuits with Cobra4 Xpert-Link
 Student's Sheet RLC-circuits with Cobra4 Xpert-Link (Item No.: P2440664) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Subtopic: Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, AC Circuits Topic: Electricity
Student's Sheet RLC-circuits with Cobra4 Xpert-Link (Item No.: P2440664) Curricular Relevance Area of Expertise: Physics Subtopic: Inductance, Electromagnetic Oscillations, AC Circuits Topic: Electricity
Ohm's Law and DC Circuits
 Physics Lab II Ohm s Law Name: Partner: Partner: Partner: Ohm's Law and DC Circuits EQUIPMENT NEEDED: Circuits Experiment Board Two Dcell Batteries Wire leads Multimeter 100, 330, 560, 1k, 10k, 100k, 220k
Physics Lab II Ohm s Law Name: Partner: Partner: Partner: Ohm's Law and DC Circuits EQUIPMENT NEEDED: Circuits Experiment Board Two Dcell Batteries Wire leads Multimeter 100, 330, 560, 1k, 10k, 100k, 220k
EE215 FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
 EE215 FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Tai-Chang Chen University of Washington, Bothell Spring 2010 EE215 1 1 WEEK 2 SIMPLE RESISTIVE CIRCUITS April 9 th, 2010 TC Chen UWB 2010 EE215 2 2 QUESTIONS
EE215 FUNDAMENTALS OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Tai-Chang Chen University of Washington, Bothell Spring 2010 EE215 1 1 WEEK 2 SIMPLE RESISTIVE CIRCUITS April 9 th, 2010 TC Chen UWB 2010 EE215 2 2 QUESTIONS
Direct Current Circuits
 PC1143 Physics III Direct Current Circuits 1 Objectives Apply Kirchhoff s rules to several circuits, solve for the currents in the circuits and compare the theoretical values predicted by Kirchhoff s rule
PC1143 Physics III Direct Current Circuits 1 Objectives Apply Kirchhoff s rules to several circuits, solve for the currents in the circuits and compare the theoretical values predicted by Kirchhoff s rule
Industrial Electricity
 Industrial Electricity Name DUE //7 or //7 (Your next lab day) Prelab: efer to the tables on Page 5. Show work neatly and completely on separate paper for any entry labeled calculated. You do not need
Industrial Electricity Name DUE //7 or //7 (Your next lab day) Prelab: efer to the tables on Page 5. Show work neatly and completely on separate paper for any entry labeled calculated. You do not need
Chapter 26: Direct current circuit
 Chapter 26: Direct current circuit Resistors in circuits Equivalent resistance The nature of the electric potential and current in circuit Kirchhoff s rules (for complicated circuit analysis) Resistors
Chapter 26: Direct current circuit Resistors in circuits Equivalent resistance The nature of the electric potential and current in circuit Kirchhoff s rules (for complicated circuit analysis) Resistors
PHYSICS LABORATORY - II
 T.C. MARMARA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ARTS AND SCIENCES PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHYSICS LABORATORY - II DEPARTMENT: NAME: SURNAME: NUMBER: 2 T.C.MARMARA UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHYSICS LABORATORY I I MANUAL
T.C. MARMARA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF ARTS AND SCIENCES PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHYSICS LABORATORY - II DEPARTMENT: NAME: SURNAME: NUMBER: 2 T.C.MARMARA UNIVERSITY PHYSICS DEPARTMENT PHYSICS LABORATORY I I MANUAL
Combined Series and Parallel Circuits
 Combined Series and Parallel Circuits Objectives: 1. Calculate the equivalent resistance, current, and voltage of series and parallel circuits. 2. Calculate the equivalent resistance of circuits combining
Combined Series and Parallel Circuits Objectives: 1. Calculate the equivalent resistance, current, and voltage of series and parallel circuits. 2. Calculate the equivalent resistance of circuits combining
Series and Parallel Resistors
 Series and Parallel Resistors Today you will investigate how connecting resistors in series and in parallel affects the properties of a circuit. You will assemble several circuits and measure the voltage
Series and Parallel Resistors Today you will investigate how connecting resistors in series and in parallel affects the properties of a circuit. You will assemble several circuits and measure the voltage
An electric circuit consists of electric devices, switching devices, source of electricity, etc. that are
 Class:X Page 200»Question» What does an electric circuit mean? An electric circuit consists of electric devices, switching devices, source of electricity, etc. that are connected by conducting wires. Define
Class:X Page 200»Question» What does an electric circuit mean? An electric circuit consists of electric devices, switching devices, source of electricity, etc. that are connected by conducting wires. Define
DC Circuits, Ohm's Law and Multimeters Physics 246
 DC Circuits, Ohm's Law and Multimeters Physics 246 Theory: In this lab we will learn the use of multimeters, verify Ohm s law, and study series and parallel combinations of resistors and capacitors. For
DC Circuits, Ohm's Law and Multimeters Physics 246 Theory: In this lab we will learn the use of multimeters, verify Ohm s law, and study series and parallel combinations of resistors and capacitors. For
Important questions of Current Electricity
 Important questions of urrent Electricity 1. In a metre bridge, the null point is found at a distance of 40 cm from. If a resistance of 12 Ω is connected in parallel with, the null point occurs at 50.0
Important questions of urrent Electricity 1. In a metre bridge, the null point is found at a distance of 40 cm from. If a resistance of 12 Ω is connected in parallel with, the null point occurs at 50.0
Lab E2: B-field of a Solenoid. In the case that the B-field is uniform and perpendicular to the area, (1) reduces to
 E2.1 Lab E2: B-field of a Solenoid In this lab, we will explore the magnetic field created by a solenoid. First, we must review some basic electromagnetic theory. The magnetic flux over some area A is
E2.1 Lab E2: B-field of a Solenoid In this lab, we will explore the magnetic field created by a solenoid. First, we must review some basic electromagnetic theory. The magnetic flux over some area A is
Practical 2.1 BASIC ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS AND DATA PROCESSING
 Practical 2.1 BASIC ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS AND DATA PROCESSING September 6, 2017 1 Introduction To measure electrical quantities one uses electrical measuring instruments. There are three main quantities
Practical 2.1 BASIC ELECTRICAL MEASUREMENTS AND DATA PROCESSING September 6, 2017 1 Introduction To measure electrical quantities one uses electrical measuring instruments. There are three main quantities
RLC-circuits TEP. f res. = 1 2 π L C.
 RLC-circuits TEP Keywords Damped and forced oscillations, Kirchhoff s laws, series and parallel tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, reactance, impedance, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width
RLC-circuits TEP Keywords Damped and forced oscillations, Kirchhoff s laws, series and parallel tuned circuit, resistance, capacitance, inductance, reactance, impedance, phase displacement, Q-factor, band-width
PHY 132 Summer 2000 LAB 4: Electric Power DC Circuits 1
 PHY 132 Summer 2 LAB 4: Electric Power DC Circuits 1 Introduction In the first part of this lab we look at electric power dissipated in a load resistor in a circuit with a real power source (finite internal
PHY 132 Summer 2 LAB 4: Electric Power DC Circuits 1 Introduction In the first part of this lab we look at electric power dissipated in a load resistor in a circuit with a real power source (finite internal
Aim: To learn the resistor color codes and building a circuit on a BreadBoard. Equipment required: Resistances, millimeter, power supply
 Understanding the different components Aim: To learn the resistor color codes and building a circuit on a BreadBoard Equipment required: Resistances, millimeter, power supply Resistors are color coded
Understanding the different components Aim: To learn the resistor color codes and building a circuit on a BreadBoard Equipment required: Resistances, millimeter, power supply Resistors are color coded
Lightbulbs and Dimmer Switches: DC Circuits
 Introduction It is truly amazing how much we rely on electricity, and especially on devices operated off of DC current. Your PDA, cell phone, laptop computer and calculator are all examples of DC electronics.
Introduction It is truly amazing how much we rely on electricity, and especially on devices operated off of DC current. Your PDA, cell phone, laptop computer and calculator are all examples of DC electronics.
ENGINEERING COUNCIL CERTIFICATE LEVEL ENGINEERING SCIENCE C103
 ENGINEERING COUNCIL CERTIFICATE LEVEL ENGINEERING SCIENCE C03 TUTORIAL 4 ELECTRICAL RESISTANCE On completion of this tutorial you should be able to do the following. Explain resistance and resistors. Explain
ENGINEERING COUNCIL CERTIFICATE LEVEL ENGINEERING SCIENCE C03 TUTORIAL 4 ELECTRICAL RESISTANCE On completion of this tutorial you should be able to do the following. Explain resistance and resistors. Explain
Branch Current Method
 Script Hello friends. In this series of lectures we have been discussing the various types of circuits, the voltage and current laws and their application to circuits. Today in this lecture we shall be
Script Hello friends. In this series of lectures we have been discussing the various types of circuits, the voltage and current laws and their application to circuits. Today in this lecture we shall be
Resistance Apparatus EM-8812
 Instruction Manual with Experiment Guide and Teachers Notes 012-09573A Resistance Apparatus EM-8812 Resistance Apparatus Table of Contents Contents Introduction...........................................................
Instruction Manual with Experiment Guide and Teachers Notes 012-09573A Resistance Apparatus EM-8812 Resistance Apparatus Table of Contents Contents Introduction...........................................................
Closed circuit complete path for electrons follow. Open circuit no charge flow and no current.
 Section 1 Schematic Diagrams and Circuits Electric Circuits, continued Closed circuit complete path for electrons follow. Open circuit no charge flow and no current. short circuit closed circuit, no load.
Section 1 Schematic Diagrams and Circuits Electric Circuits, continued Closed circuit complete path for electrons follow. Open circuit no charge flow and no current. short circuit closed circuit, no load.
 Question 3.1: The storage battery of a car has an emf of 12 V. If the internal resistance of the battery is 0.4Ω, what is the maximum current that can be drawn from the battery? Emf of the battery, E =
Question 3.1: The storage battery of a car has an emf of 12 V. If the internal resistance of the battery is 0.4Ω, what is the maximum current that can be drawn from the battery? Emf of the battery, E =
Chapter 28. Direct Current Circuits
 Chapter 28 Direct Current Circuits Outline 28.1 Electromotive Force 28.2 Resistors in Series and Parallel 28.3 Kirchhoff s Rules 28.1 Electromotive Force (emf) Because the potential difference at the battery
Chapter 28 Direct Current Circuits Outline 28.1 Electromotive Force 28.2 Resistors in Series and Parallel 28.3 Kirchhoff s Rules 28.1 Electromotive Force (emf) Because the potential difference at the battery
1. A battery of internal resistance 2 Ω is connected to an external resistance of 10 Ω. The current is 0.5 A. D. 24.
 1. A battery of internal resistance 2 Ω is connected to an external resistance of 10 Ω. The current is 0.5 A. What is the emf of the battery? A. 1.0 V B. 5.0 V C. 6.0 V D. 24.0 V (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank
1. A battery of internal resistance 2 Ω is connected to an external resistance of 10 Ω. The current is 0.5 A. What is the emf of the battery? A. 1.0 V B. 5.0 V C. 6.0 V D. 24.0 V (Total 1 mark) IB Questionbank
Electronics Review 1 Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics II Week 1
 Electronics Review 1 Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics II Week 1 Administration: o Prayer o Welcome back o Review Quiz 1 Review: o Reading meters: When a current or voltage value is unknown,
Electronics Review 1 Cornerstone Electronics Technology and Robotics II Week 1 Administration: o Prayer o Welcome back o Review Quiz 1 Review: o Reading meters: When a current or voltage value is unknown,
Brown University PHYS 0060 Physics Department LAB B Circuits with Resistors and Diodes
 References: Circuits with Resistors and Diodes Edward M. Purcell, Electricity and Magnetism 2 nd ed, Ch. 4, (McGraw Hill, 1985) R.P. Feynman, Lectures on Physics, Vol. 2, Ch. 22, (Addison Wesley, 1963).
References: Circuits with Resistors and Diodes Edward M. Purcell, Electricity and Magnetism 2 nd ed, Ch. 4, (McGraw Hill, 1985) R.P. Feynman, Lectures on Physics, Vol. 2, Ch. 22, (Addison Wesley, 1963).
Combined Series and Parallel Circuits
 Combined Series and Parallel Circuits Objectives: 1. Calculate the equivalent resistance, current, and voltage of series and parallel l circuits. it 2. Calculate the equivalent resistance of circuits combining
Combined Series and Parallel Circuits Objectives: 1. Calculate the equivalent resistance, current, and voltage of series and parallel l circuits. it 2. Calculate the equivalent resistance of circuits combining
DC Circuits. Date: Introduction
 Group # Date: Names: DC Circuits Introduction In this experiment you will examine how to make simple DC measurements that involve current, voltage, and resistance. The current I through a resistor R with
Group # Date: Names: DC Circuits Introduction In this experiment you will examine how to make simple DC measurements that involve current, voltage, and resistance. The current I through a resistor R with
ANALOG AND DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS
 ANALOG AND DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS Digital Voltmeter (DVM) Used to measure the ac and dc voltages and displays the result in digital form. Types: Ramp type DVM Integrating type DVM Potentiometric type DVM
ANALOG AND DIGITAL INSTRUMENTS Digital Voltmeter (DVM) Used to measure the ac and dc voltages and displays the result in digital form. Types: Ramp type DVM Integrating type DVM Potentiometric type DVM
Lab 1: Basic Lab Equipment and Measurements
 Abstract: Lab 1: Basic Lab Equipment and Measurements This lab exercise introduces the basic measurement instruments that will be used throughout the course. These instruments include multimeters, oscilloscopes,
Abstract: Lab 1: Basic Lab Equipment and Measurements This lab exercise introduces the basic measurement instruments that will be used throughout the course. These instruments include multimeters, oscilloscopes,
AP Physics - Problem Drill 14: Electric Circuits
 AP Physics - Problem Drill 14: Electric Circuits No. 1 of 10 1. Identify the four electric circuit symbols. (A) 1. AC power 2. Battery 3. Light Bulb 4. Resistor (B) 1. Ammeter 2. Resistor 3. AC Power 4.
AP Physics - Problem Drill 14: Electric Circuits No. 1 of 10 1. Identify the four electric circuit symbols. (A) 1. AC power 2. Battery 3. Light Bulb 4. Resistor (B) 1. Ammeter 2. Resistor 3. AC Power 4.
Real Analog Chapter 2: Circuit Reduction. 2 Introduction and Chapter Objectives. After Completing this Chapter, You Should be Able to:
 1300 Henley Court Pullman, WA 99163 509.334.6306 www.store. digilent.com 2 Introduction and Chapter Objectives In Chapter 1, we presented Kirchhoff's laws (which govern the interaction between circuit
1300 Henley Court Pullman, WA 99163 509.334.6306 www.store. digilent.com 2 Introduction and Chapter Objectives In Chapter 1, we presented Kirchhoff's laws (which govern the interaction between circuit
ELECTRIC CIRCUIT PROBLEMS 12 AUGUST 2014
 ELECTRIC CIRCUIT PROBLEMS 12 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Discuss the application of Ohm s Law Explain the series and parallel connection of resistors Discuss the effect of internal
ELECTRIC CIRCUIT PROBLEMS 12 AUGUST 2014 In this lesson we: Lesson Description Discuss the application of Ohm s Law Explain the series and parallel connection of resistors Discuss the effect of internal
Exp. 1 USE OF BASIC ELECTRONIC MEASURING INSTRUMENTS, PART I
 Exp. 1 USE OF BASIC ELECTRONIC MEASURING INSTRUMENTS, PART I PURPOSE: To become familiar with some of the instruments used in this and subsequent labs. To develop proper laboratory procedures relative
Exp. 1 USE OF BASIC ELECTRONIC MEASURING INSTRUMENTS, PART I PURPOSE: To become familiar with some of the instruments used in this and subsequent labs. To develop proper laboratory procedures relative
CK-12 Physics Concepts - Intermediate Answer Key
 Chapter 19: Electrical Circuits 19.1 Series Circuits CK-12 Physics Concepts - Intermediate Answer Key 1. There are three 20.0 Ohm resistors connected in series across a 120 V generator. a. What is the
Chapter 19: Electrical Circuits 19.1 Series Circuits CK-12 Physics Concepts - Intermediate Answer Key 1. There are three 20.0 Ohm resistors connected in series across a 120 V generator. a. What is the
Wave Measurement & Ohm s Law
 Wave Measurement & Ohm s Law Marking scheme : Methods & diagrams : 2 Graph plotting : 1 Tables & analysis : 2 Questions & discussion : 3 Performance : 2 Aim: Various types of instruments are used by engineers
Wave Measurement & Ohm s Law Marking scheme : Methods & diagrams : 2 Graph plotting : 1 Tables & analysis : 2 Questions & discussion : 3 Performance : 2 Aim: Various types of instruments are used by engineers
A battery of emf 10 V and internal resistance 3 Ω is connected to a resistor. If the current
 Question 3.1: The storage battery of a car has an emf of 12 V. If the internal resistance of the battery is 0.4Ω, what is the maximum current that can be drawn from the battery? Emf of the battery, E =
Question 3.1: The storage battery of a car has an emf of 12 V. If the internal resistance of the battery is 0.4Ω, what is the maximum current that can be drawn from the battery? Emf of the battery, E =
