Re-configurable Electronics Characterization Under Extreme Thermal Environment
|
|
|
- Belinda Francis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Re-configurable Electronics Characterization Under Extreme Thermal Environment Adrian, Veronica Lacayo, Rajeshuni Ramesham, Didier Keymeulen, Ricardo Zebulum, Joe Neff *, Gary Burke, and Taher Daud Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology Pasadena, CA * SPAWAR Systems Center, San Diego, CA 1 MAPLD 2005/P232
2 Outline Objective Compensation of degradation in extreme environments Evolvable hardware, reconfigurability, & potential solution. DSP extreme temperature testing, results, conclusions FPGA extreme temperature testing, results, conclusions Reconfigurable Analog Array (RAA) Development, tests in extreme temperatures, results, and conclusions Acknowledgements: The work described in this paper was performed at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology and was sponsored by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
3 Objective: Surviving longer missions (10+ years) and harsher environments Dramatic changes in hardware/environment, e.g. in case of faults or need for new functions, may require in-situ synthesis of a totally new hardware configuration. Survivability: Maintain functionality coping with changes in HW characteristics Radiation impacts Temperature variations Aging Malfunctions, etc. EHW Versatility: Create new functionality required by changes in requirements or environment New functions required for new mission phase or opportunity Develop space HW that can evolve 2 MAPLD 2005/P232
4 Compensation of Degradations in Extreme Environments (EE) degradation Microelectronics failure Packaging Less Extreme Environment degradation failure More Extreme Environment Compensation by reconfigurable electronics: - of degradations in electronics keep same function for electronics - or degradations at another subsystem/ or system level adapt electronics functionality to maintain same function at system level Many times failure is due to packaging, but before that point degradations could possibly still be compensated. 3 MAPLD 2005/P232
5 I D (ma) 25 C Effects of EE on electronics Circuits are designed to exploit device characteristics within a certain Temperature/Radiation range; when that is exceeded, the circuit function gradually degrades nmos SI MOSFETs C offset voltage, current leakage... Temperature changes device characteristics; device is still operational. V DS (V) V DS (V) Influence may be different between various areas/circuits/components on same chip. It can also change with function. Changes cause degradation in circuit response of a commercial Op Amp. Output, Gain =1 Input sine wave, f = 100kHz If a circuit design is changed to take in consideration the modified device characteristic the response may be corrected. We can map a new circuit design in a reconfigurable chip 4 MAPLD 2005/P232
6 Hardening-By-Reconfiguration Idea of Hardening-By-Reconfiguration (HBR): mitigate drifts, degradation, or damage on electronic devices in EE by using reconfigurable devices and an adaptive self-reconfiguration of circuit topology. related to HBD - in-situ (re) design benefits from HBD for the resources available on the reconfigurable chips. work well with HBP, - extra layer of protection, for expansion of limits of operation in EE: HBP provides survivability to keep devices operational at higher EE limits, while HBR provides adaptation to changes in device characteristics needed for precise functions, specially for analog. Degenerated HBR: multiplexed/switched in fixed circuits, each optimally designed for a temp range Simple HBR: circuit configuration predetermined and memorized for access when needed, HBR configurations are determined in-situ 5 MAPLD 2005/P232
7 Evolvable Hardware Solutions Evolvable hardware (i.e. hardware that self-configures under control of adaptation/ evolutionary algorithms) can preserve/ recover system functionality by reconfiguration/ morphing. If device characteristics change with radiation/temperature, one can preserve the function by finding a different circuit solution, which exploits the altered/modified characteristics Degraded components can be salvaged Completely damaged components can be bypassed MAPLD 2005/P232 6
8 Reconfiguration Mechanisms Most popular searches: population based, use generate and test strategies. Evolutionary/Genetic algorithms are most used technique. Sketch of a simple Evolutionary/Genetic Algorithm A chromosome may simply encode the control of switches eg Initialize a population of candidate solutions Crossover Evaluate population Create a new population based on old one Select the best Acceptable solution found? No Yes Mutation Output solution Crossover and mutation are two common genetic operators used in creating a new population. 7 MAPLD 2005/P232
9 Evolutionary adaptation of field programmable devices Evolutionary Algorithm Genetic search on a population of chromosomes select the best designs from a population reproduce them with some variation iterate until the performance goal is reached. Chromosomes Conversion to a circuit description Control bitstrings Target response Evaluate individual responses and assess their fitness Circuit response Intrinsic evolution Reconfigurable hardware Potential electronic designs/implementations compete; the best ones are slightly modified to search for even more suitable solutions MAPLD 2005/P232 8
10 A Stand-Alone Board-Level Evolvable System (SABLES) DAC Stimulation FPTA-2 DSP GA runs here FPGA ADC Response Analog Array Digital Interface clk DSP + FPTA Fast download for evaluation of individuals Good architecture for moving to a self-reconfigurable system-on-a-chip DSP board; Fits in a box 8 x 8 x 3. TMS320C6701processor 16 analog inputs and outputs at 100 ksamples; 32 Digital I/O at 7.5MHz 9 MAPLD 2005/P232
11 Recovery of temperature-degraded circuits Controllable Oscillator In Out Evolved at room temperature Deteriorated at o C Recovered at o C Out In 10 MAPLD 2005/P232
12 Summary of Evolvable Hardware HBR (hardening-by-reconfiguration), based on evolvable hardware is a technique that extends the range of usability of electronics in extreme environments. The capability of adaptive selfconfiguration was demonstrated for low and high temperatures. The challenge of conventional design is replaced with that of designing a recovery (e.g. evolutionary) process that automatically performs the (re)design in our place. This may be harder than doing the design directly, but makes autonomy and adaptation possible. MAPLD 2005/P232 11
13 Testing of DSP (TI) under Extreme Temperatures Objective Assess the electrical behavior of the Innovative Integration board containing a Digital Signal Processor (DSP) with its JTAG (Blackhawk) connector at extreme low temperatures to develop Self-Reconfigurable Electronics for Extreme Environments (SRE- EE). The objective of the experiment is to determine the lowest temperature at which the DSP component can operate. DSP chip DSP was tested by running a simple Genetic Algorithm (GA) whose target was the maximization of the number of 1 s in the chromosomes JTAG Connector Problem is solved in less than 1 minute, after 464 generations MAPLD 2005/P232 12
14 Test profile 1 DSP Failure +20 o C 8 min Measurement s made Temperature, C Temp. ramp rate: 5 0 C/min -120 o C Time Failed Test was repeated again for 90 o C, 100 o C, 110 o C and 120 o C to narrow the temperature range. Failure was observed during the testing in a temperature range of 110 o C to 120 o C. Failure occured when PC is downloading GA into the DSP (JTAG communication error); The PC-DSP communication failure prevents the read-out of the DSP status/outputs. DSP Board works down to -110 o C but failed for lower temperatures 13 MAPLD 2005/P232
15 Xilinx Virtex-II Pro FPGA Objective: The purpose of testing this board at extreme temperatures is to initially find out whether the evaluation board and the Virtex-II Pro FPGA would survive and continue operating at different temperature ranges down to 180 o C and up to 120 o C. The Virtex-II PP Board was tested at different temperatures. The temperature range covered in this experiment was from o C to 120 o C. The board was powered using 3 power supplies. They were set up at the following voltages: 3.3V DC (to electronics in the board) 2.5V DC ( to I/O s, banks, Rocket I/O Transceivers) 1.5V DC (supplied to the FPGA Core) Surge current (in rush current) was measured on the 1.5V supply. The test FPGA circuit runs self-checking firmware on 2 embedded processors, monitored via RS232 port 14 MAPLD 2005/P232
16 Extreme Temperature Test for the Virtex-II PP Board Reset switch to reset the logic Program switch to load the program PROMS to FPGA configuration Hello World program used to monitor the performance of FPGA The board was never shut down as the temperature was decreased in steps. Once it reached -180ºC, the temperature was brought back up. At intervals, we power cycle the board and measure the in rush current. It was found as temperature ramped up that the board always powered on using reset program switches. 15 MAPLD 2005P232
17 ma ma Comparisonof VcoreTransient at different Temperatures C -180C -140C -180C -140C -100C Samples FPGA Core Samples in rush current monitored as a function of temperature ma ma ma Vco re In Rush Current at + 20C Samples ma Sam ples Vcore In Rush Current at +120C +20 o C +120 o C Samples Samples FPGA core in rush current monitored as a function of high temperature 16 MAPLD 2005/P232
18 Summary: Extreme Temperature Test for the Virtex-II PP Board The Virtex II Pro functioned correctly at temperatures down to 180 o C and up to 120 o C. The Virtex II Pro FPGA did not show a large in rush current at 180 o C and also at 120 o C. All temperatures, voltages, and current registered normal as well as power (on/off) cycling. Over all the high temperature in rush current transient have sharper current and last less than the cold temperature. (~25-30 msec) MAPLD 2005/P232 17
19 Objectives: Reconfigurable Analog Array (RAA) Development Assess the behavior of G m -C filters building blocks at extreme temperatures (from -180 o C to 120 o C); Perform preliminary tests on the functionality recovery through changes in the voltage bias; Components tested (Designed by SPAWAR using TSMC 0.35µm technology): Operational Transconductance Amplifier (OTA); Wide Range OTA (WRTA); Differential pairs. Simulate and test single-ended first order G m -C filter. 18 MAPLD 2005/P232
20 OTA Sweep Down (23 o C to -180 o C) Iout (A) Date: 28 April 2005 Substrate: FPAA C 0C -30C -60C -90C -120C -150C -180C V2 (V) V1 Vbias Iout V2 Vdd: 3.1V Vbias: 0.8V V1: 1.5V V2: 0-3.0V V(Iout): 2V Current lower and upper limits reduce as the temperature reduces. MAPLD 2005/P232 19
21 OTA Bias Sweep at -180 o C C -180C Vb: 1.0V Vb: 0.95V Iout (A) Date: 28 April 2005 Substrate: FPAA V1 Vbias Iout V2 22C, Vb: 0.8V Vb: 0.9V Vb: 0.85V Vb: 0.8V Vb: V V2 (V) Vdd: 3.1V V1: 1.5V V2: 0-3.0V V(Iout): 2V Device function can be recovered by increasing Vb from 0.8V to 0.85V. MAPLD 2005/P232 20
22 WRTA Sweep Up (-180 o C to 22 o C) Iout (A) Date: 28 April 2005 Substrate: FPAA-01 22C -30C -60C -90C -120C -150C V2 (V) V2 Vbias V1 Iout Vdd: 3.1V Vbias: 0.8V V1: 1.5V V2: 0-3.0V V(Iout): 2V Current lower and upper limits reduce as the temperature reduces. MAPLD 2005/P232 21
23 WRTA Bias Sweep at -180 o C C -180C Vb: 0.9V Iout (A) Date: 28 April 2005 Substrate: FPAA-01 22C, Vb: 0.8V Vb: 0.85V Vb: 0.8V Vb: 0.75V Vb: V V2 (V) V2 Vbias V1 Iout Vdd: 3.1V V1: 1.5V V2: 0-3.0V V(Iout): 2V Device function can be recovered by increasing Vb from 0.8V to 0.85V. MAPLD 2005/P232 22
24 OTA Sweep Up (25 o C to 125 o C) 2.00E E E C 120C 100C 80C 60C 40C 25C V1 Iout V2 Iout(A) 5.00E-05 Vbias 0.00E E E E E E E E E+00 Iout(A) -5.00E-05 V2 (V) -1.00E E E-04 V2(V) Vdd: 3.1V V1: 1.5V V2: 0-3.0V V(Iout): 2V Negative and positive saturation voltages increase as the temperature gets higher. 23 MAPLD 2005/P232
25 OTA Bias Sweep at 120 o C 4.00E E V 0.90V Iout(A) 0.85V 2.00E V Room temperature (0.8V) 0.75V 1.00E V 0.5V-0.65V 0.00E+00 V1 0.00E E E E E E E E+00 Iout V2-1.00E-04 Vbias -2.00E E-04 V2 (V) Device function can be recovered by decreasing Vb from 0.8V to around 0.75V. Vdd: 3.1V V1: 1.5V V2: 0-3.0V V(Iout): 2V 24 MAPLD 2005/P232
26 Objectives: First Order GmC Low Pass Filter Test the recovery through V bias in a filter circuit; Built at the board level using two chips (two OTAs); Characterize filter behavior at extreme temperatures and test recovery through adjustment of bias voltage; C x = 10pF G m V V in + - V out - C a = 10pF Vb2 1.5V Vb1 G m1 Capacitors outside the temperature chamber 25 MAPLD 2005/P232
27 Low Temperature Tests Frequency Response 20 T= 0 o C T= 25 o C 15 T= -120 o C T= -30 o C T= -60 o C Gain (db) Frequency(Hz) -10 T= -150 o C,-180 o C -15 Vb1 = 0.9V, Vb2 = 0.7V Filter transfer response deteriorates below -120 o C. 26 MAPLD 2005/P232
28 20 Function Recovery at 180 o C Room Temperature (Vb1 = 0.9V; Vb2 = 0.7V) Recovered at-180 o C (Vb1 = 0.8V; Vb2 = 0.7V) Gain(dB) Output (db) T= -180 o C (Vb1 = 0.9V; Vb2 = 0.7V) -15 Frequency 1(Hz) MAPLD 2005/P232
29 LowTemperature Response in the Time Domain ( f = 10kHz) Out In T = 25 o C Vb1 = 0.9V Vb2 = 0.7V Vout = 1.8Vp-p T = -180 o C Vb1 = 0.9V Vb2 = 0.7V Vout = 0.1Vp-p T = -180 o C Vb1 = 0.8V Vb2 = 0.7V Vout = 1.4Vp-p Filter Recovery at 180 o C 1. Partial functionality recovery accomplished using manual local search over Vb1 and Vb2; 2. There is possibly one or more pair of values Vb1/Vb2 that produce a better recovery at 180oC Sweep Vb1 and Vb2 using finer steps and/or implement non-local and more systematic search. 28 MAPLD 2005/P232
30 Filter Recovery at High Temperature Series1 Series2 Series3 20 T=25 o C Recovered at T=120 o C 15 T=120 o C Gain (db) Frequency(Hz) -5 Vb1 = 0.9V, Vb2 = 0.7V Filter transfer response slightly deteriorates at 120 o C. 29 MAPLD 2005/P232
31 High Temperature Response in the Time Domain (f = 100kHz) T = 25 o C T = 120 o C T = 120 o C (Recovered) Out In T = 25 o C Vb1 = 0.9V Vb2 = 0.7V Vout = 1.3Vp-p T = 120 o C Vb1 = 0.9V Vb2 = 0.7V Vout = 0.9Vp-p T = 120 o C Vb1 = 1.1V Vb2 = 0.6V Vout = 1.3Vp-p MAPLD 2005/P232 30
32 Conclusions Results indicate that bias voltage control adjustment is an efficient mechanism for circuit recovery at extreme temperatures. Small changes in the bias voltage are sufficient to promote functionality recovery of the OTA and WRTA devices tested at low and high temperatures; Low Pass filter recovery was also possible through changes in the bias voltages more systematic search methods and/or algorithms needed to further improve recovered function. MAPLD 2005/P232 31
Re-configurable Electronics Behavior Under Extreme Thermal Environment
 Re-configurable Electronics Behavior Under Extreme Thermal Environment Adrian Stoica, Veronica Lacayo, Ramesham Rajeshuni, Didier Keymeulen, Ricardo Zebulum, Joe Neff *, Gary Burke, and Taher Daud Jet
Re-configurable Electronics Behavior Under Extreme Thermal Environment Adrian Stoica, Veronica Lacayo, Ramesham Rajeshuni, Didier Keymeulen, Ricardo Zebulum, Joe Neff *, Gary Burke, and Taher Daud Jet
High Temperature Experiments for Circuit Self-Recovery
 High Temperature Experiments for Circuit Self-Recovery Didier Keymeulen, Ricardo Zebulum, Vu Duong, Xin Guo *, Ian Ferguson, and Adrian Stoica Jet Propulsion Laboratory 4800 Oak Grove Drive, Pasadena,
High Temperature Experiments for Circuit Self-Recovery Didier Keymeulen, Ricardo Zebulum, Vu Duong, Xin Guo *, Ian Ferguson, and Adrian Stoica Jet Propulsion Laboratory 4800 Oak Grove Drive, Pasadena,
Transistor-Level Circuit Experiments Using Evolvable Hardware
 Transistor-Level Circuit Experiments Using Evolvable Hardware A. Stoica, R.S. Zebulum, D. Keymeulen, M. I. Ferguson, T. Daud, A. Thakoor Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Itutitute of Technology Abstract
Transistor-Level Circuit Experiments Using Evolvable Hardware A. Stoica, R.S. Zebulum, D. Keymeulen, M. I. Ferguson, T. Daud, A. Thakoor Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Itutitute of Technology Abstract
Evolvable Hardware: From On-Chip Circuit Synthesis to Evolvable Space Systems
 Evolvable Hardware: From On-Chip Circuit Synthesis to Evolvable Space Systems Adrian Stoica Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology 4800 Oak Grove Drive Pasadena, CA 91109 818-354-2190
Evolvable Hardware: From On-Chip Circuit Synthesis to Evolvable Space Systems Adrian Stoica Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology 4800 Oak Grove Drive Pasadena, CA 91109 818-354-2190
A Flexible Model of a CMOS Field Programmable Transistor Array Targeted for Hardware Evolution
 A Flexible Model of a CMOS Field Programmable Transistor Array Targeted for Hardware Evolution Ricardo Salem Zebulum Adrian Stoica Didier Keymeulen Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology
A Flexible Model of a CMOS Field Programmable Transistor Array Targeted for Hardware Evolution Ricardo Salem Zebulum Adrian Stoica Didier Keymeulen Jet Propulsion Laboratory California Institute of Technology
Evolutionary Electronics
 Evolutionary Electronics 1 Introduction Evolutionary Electronics (EE) is defined as the application of evolutionary techniques to the design (synthesis) of electronic circuits Evolutionary algorithm (schematic)
Evolutionary Electronics 1 Introduction Evolutionary Electronics (EE) is defined as the application of evolutionary techniques to the design (synthesis) of electronic circuits Evolutionary algorithm (schematic)
Dynamically Reconfigurable Sensor Electronics Concept, Architecture, First Measurement Results, and Perspective
 Institute of Integrated Sensor Systems Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Information Technology Dynamically Reconfigurable Sensor Electronics Concept, Architecture, First Measurement Results, and Perspective
Institute of Integrated Sensor Systems Dept. of Electrical Engineering and Information Technology Dynamically Reconfigurable Sensor Electronics Concept, Architecture, First Measurement Results, and Perspective
PURPOSE: NOTE: Be sure to record ALL results in your laboratory notebook.
 EE4902 Lab 9 CMOS OP-AMP PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to measure the closed-loop performance of an op-amp designed from individual MOSFETs. This op-amp, shown in Fig. 9-1, combines all of the major
EE4902 Lab 9 CMOS OP-AMP PURPOSE: The purpose of this lab is to measure the closed-loop performance of an op-amp designed from individual MOSFETs. This op-amp, shown in Fig. 9-1, combines all of the major
Intrinsic Evolution of Analog Circuits on a Programmable Analog Multiplexer Array
 Intrinsic Evolution of Analog Circuits on a Programmable Analog Multiplexer Array José Franco M. Amaral 1, Jorge Luís M. Amaral 1, Cristina C. Santini 2, Marco A.C. Pacheco 2, Ricardo Tanscheit 2, and
Intrinsic Evolution of Analog Circuits on a Programmable Analog Multiplexer Array José Franco M. Amaral 1, Jorge Luís M. Amaral 1, Cristina C. Santini 2, Marco A.C. Pacheco 2, Ricardo Tanscheit 2, and
PowerAmp Design. PowerAmp Design PAD117A RAIL TO RAIL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
 PowerAmp Design RAIL TO RAIL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER Rev J KEY FEATURES LOW COST RAIL TO RAIL INPUT & OUTPUT SINGLE SUPPLY OPERATION HIGH VOLTAGE 100 VOLTS HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT 15A 250 WATT OUTPUT CAPABILITY
PowerAmp Design RAIL TO RAIL OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER Rev J KEY FEATURES LOW COST RAIL TO RAIL INPUT & OUTPUT SINGLE SUPPLY OPERATION HIGH VOLTAGE 100 VOLTS HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT 15A 250 WATT OUTPUT CAPABILITY
Yet, many signal processing systems require both digital and analog circuits. To enable
 Introduction Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) have been a superb solution for rapid and reliable prototyping of digital logic systems at low cost for more than twenty years. Yet, many signal processing
Introduction Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) have been a superb solution for rapid and reliable prototyping of digital logic systems at low cost for more than twenty years. Yet, many signal processing
+2.7V to +5.5V, Low-Power, Triple, Parallel 8-Bit DAC with Rail-to-Rail Voltage Outputs
 19-1560; Rev 1; 7/05 +2.7V to +5.5V, Low-Power, Triple, Parallel General Description The parallel-input, voltage-output, triple 8-bit digital-to-analog converter (DAC) operates from a single +2.7V to +5.5V
19-1560; Rev 1; 7/05 +2.7V to +5.5V, Low-Power, Triple, Parallel General Description The parallel-input, voltage-output, triple 8-bit digital-to-analog converter (DAC) operates from a single +2.7V to +5.5V
PowerAmp Design. PowerAmp Design PAD112 HIGH VOLTAGE OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
 PowerAmp Design Rev C KEY FEATURES LOW COST HIGH VOLTAGE 150 VOLTS HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT 5 AMPS 50 WATT DISSIPATION CAPABILITY 100 WATT OUTPUT CAPABILITY INTEGRATED HEAT SINK AND FAN COMPATIBLE WITH PAD123
PowerAmp Design Rev C KEY FEATURES LOW COST HIGH VOLTAGE 150 VOLTS HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT 5 AMPS 50 WATT DISSIPATION CAPABILITY 100 WATT OUTPUT CAPABILITY INTEGRATED HEAT SINK AND FAN COMPATIBLE WITH PAD123
PowerAmp Design. PowerAmp Design PAD20 COMPACT HIGH VOLTAGE OP AMP
 PowerAmp Design Rev C KEY FEATURES LOW COST HIGH VOLTAGE 150 VOLTS HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT 5A 40 WATT DISSIPATION CAPABILITY 80 WATT OUTPUT CAPABILITY INTEGRATED HEAT SINK AND FAN SMALL SIZE 40mm SQUARE RoHS
PowerAmp Design Rev C KEY FEATURES LOW COST HIGH VOLTAGE 150 VOLTS HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT 5A 40 WATT DISSIPATION CAPABILITY 80 WATT OUTPUT CAPABILITY INTEGRATED HEAT SINK AND FAN SMALL SIZE 40mm SQUARE RoHS
8-Bit, high-speed, µp-compatible A/D converter with track/hold function ADC0820
 8-Bit, high-speed, µp-compatible A/D converter with DESCRIPTION By using a half-flash conversion technique, the 8-bit CMOS A/D offers a 1.5µs conversion time while dissipating a maximum 75mW of power.
8-Bit, high-speed, µp-compatible A/D converter with DESCRIPTION By using a half-flash conversion technique, the 8-bit CMOS A/D offers a 1.5µs conversion time while dissipating a maximum 75mW of power.
CHAPTER 6 IMPLEMENTATION OF FPGA BASED CASCADED MULTILEVEL INVERTER
 8 CHAPTER 6 IMPLEMENTATION OF FPGA BASED CASCADED MULTILEVEL INVERTER 6.1 INTRODUCTION In this part of research, a proto type model of FPGA based nine level cascaded inverter has been fabricated to improve
8 CHAPTER 6 IMPLEMENTATION OF FPGA BASED CASCADED MULTILEVEL INVERTER 6.1 INTRODUCTION In this part of research, a proto type model of FPGA based nine level cascaded inverter has been fabricated to improve
Intelligent Systems Group Department of Electronics. An Evolvable, Field-Programmable Full Custom Analogue Transistor Array (FPTA)
 Department of Electronics n Evolvable, Field-Programmable Full Custom nalogue Transistor rray (FPT) Outline What`s Behind nalog? Evolution Substrate custom made configurable transistor array (FPT) Ways
Department of Electronics n Evolvable, Field-Programmable Full Custom nalogue Transistor rray (FPT) Outline What`s Behind nalog? Evolution Substrate custom made configurable transistor array (FPT) Ways
Fault-Tolerant Evolvable Hardware Using Field-Programmable Transistor Arrays
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON RELIABILITY, VOL. 49, NO. 3, SEPTEMBER 2000 305 Fault-Tolerant Evolvable Hardware Using Field-Programmable Transistor Arrays Didier Keymeulen, Member, IEEE, Ricardo Salem Zebulum,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON RELIABILITY, VOL. 49, NO. 3, SEPTEMBER 2000 305 Fault-Tolerant Evolvable Hardware Using Field-Programmable Transistor Arrays Didier Keymeulen, Member, IEEE, Ricardo Salem Zebulum,
Receiver Architecture
 Receiver Architecture Receiver basics Channel selection why not at RF? BPF first or LNA first? Direct digitization of RF signal Receiver architectures Sub-sampling receiver noise problem Heterodyne receiver
Receiver Architecture Receiver basics Channel selection why not at RF? BPF first or LNA first? Direct digitization of RF signal Receiver architectures Sub-sampling receiver noise problem Heterodyne receiver
ENEE307 Lab 7 MOS Transistors 2: Small Signal Amplifiers and Digital Circuits
 ENEE307 Lab 7 MOS Transistors 2: Small Signal Amplifiers and Digital Circuits In this lab, we will be looking at ac signals with MOSFET circuits and digital electronics. The experiments will be performed
ENEE307 Lab 7 MOS Transistors 2: Small Signal Amplifiers and Digital Circuits In this lab, we will be looking at ac signals with MOSFET circuits and digital electronics. The experiments will be performed
High-Efficiency Step-Up Converters for White LED Main and Subdisplay Backlighting MAX1582/MAX1582Y
 19-2783; Rev 2; 8/05 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE High-Efficiency Step-Up Converters General Description The drive up to six white LEDs in series with a constant current to provide display backlighting for
19-2783; Rev 2; 8/05 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE High-Efficiency Step-Up Converters General Description The drive up to six white LEDs in series with a constant current to provide display backlighting for
Copyright 2007 Year IEEE. Reprinted from ISCAS 2007 International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, May This material is posted here
 Copyright 2007 Year IEEE. Reprinted from ISCAS 2007 International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 27-30 May 2007. This material is posted here with permission of the IEEE. Such permission of the IEEE
Copyright 2007 Year IEEE. Reprinted from ISCAS 2007 International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 27-30 May 2007. This material is posted here with permission of the IEEE. Such permission of the IEEE
DS H01 DIGITAL SYNTHESIZER MODULE SYSTEM SOLUTIONS. Features Applications 174 x 131 x 54 mm. Technical Description
 DS H01 The DS H01 is a high performance dual digital synthesizer with wide output bandwidth specially designed for Defense applications where generation of wideband ultra-low noise signals along with very
DS H01 The DS H01 is a high performance dual digital synthesizer with wide output bandwidth specially designed for Defense applications where generation of wideband ultra-low noise signals along with very
AXYS IndustryAmp PB-800
 AXYS IndustryAmp PB-800 Datasheet by Geert de Vries IndustryAmp PB-800 datasheet User s Notice: No part of this document including the software described in it may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed,
AXYS IndustryAmp PB-800 Datasheet by Geert de Vries IndustryAmp PB-800 datasheet User s Notice: No part of this document including the software described in it may be reproduced, transmitted, transcribed,
Low-Cost, Precision, High-Side Current-Sense Amplifier MAX4172. Features
 19-1184; Rev 0; 12/96 Low-Cost, Precision, High-Side General Description The is a low-cost, precision, high-side currentsense amplifier for portable PCs, telephones, and other systems where battery/dc
19-1184; Rev 0; 12/96 Low-Cost, Precision, High-Side General Description The is a low-cost, precision, high-side currentsense amplifier for portable PCs, telephones, and other systems where battery/dc
HART Modem DS8500. Features
 Rev 1; 2/09 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE General Description The is a single-chip modem with Highway Addressable Remote Transducer (HART) capabilities and satisfies the HART physical layer requirements. The
Rev 1; 2/09 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE General Description The is a single-chip modem with Highway Addressable Remote Transducer (HART) capabilities and satisfies the HART physical layer requirements. The
ECE 363 FINAL (F16) 6 problems for 100 pts Problem #1: Fuel Pump Controller (18 pts)
 ECE 363 FINAL (F16) NAME: 6 problems for 100 pts Problem #1: Fuel Pump Controller (18 pts) You are asked to design a high-side switch for a remotely operated fuel pump. You decide to use the IRF9520 power
ECE 363 FINAL (F16) NAME: 6 problems for 100 pts Problem #1: Fuel Pump Controller (18 pts) You are asked to design a high-side switch for a remotely operated fuel pump. You decide to use the IRF9520 power
Thermocouple Conditioner and Setpoint Controller AD596*/AD597*
 a FEATURES Low Cost Operates with Type J (AD596) or Type K (AD597) Thermocouples Built-In Ice Point Compensation Temperature Proportional Operation 10 mv/ C Temperature Setpoint Operation ON/OFF Programmable
a FEATURES Low Cost Operates with Type J (AD596) or Type K (AD597) Thermocouples Built-In Ice Point Compensation Temperature Proportional Operation 10 mv/ C Temperature Setpoint Operation ON/OFF Programmable
2. Simulated Based Evolutionary Heuristic Methodology
 XXVII SIM - South Symposium on Microelectronics 1 Simulation-Based Evolutionary Heuristic to Sizing Analog Integrated Circuits Lucas Compassi Severo, Alessandro Girardi {lucassevero, alessandro.girardi}@unipampa.edu.br
XXVII SIM - South Symposium on Microelectronics 1 Simulation-Based Evolutionary Heuristic to Sizing Analog Integrated Circuits Lucas Compassi Severo, Alessandro Girardi {lucassevero, alessandro.girardi}@unipampa.edu.br
Analog front-end electronics in beam instrumentation
 Analog front-end electronics in beam instrumentation Basic instrumentation structure Silicon state of art Sampling state of art Instrumentation trend Comments and example on BPM Future Beam Position Instrumentation
Analog front-end electronics in beam instrumentation Basic instrumentation structure Silicon state of art Sampling state of art Instrumentation trend Comments and example on BPM Future Beam Position Instrumentation
Lecture 300 Low Voltage Op Amps (3/28/10) Page 300-1
 Lecture 300 Low Voltage Op Amps (3/28/10) Page 300-1 LECTURE 300 LOW VOLTAGE OP AMPS LECTURE ORGANIZATION Outline Introduction Low voltage input stages Low voltage gain stages Low voltage bias circuits
Lecture 300 Low Voltage Op Amps (3/28/10) Page 300-1 LECTURE 300 LOW VOLTAGE OP AMPS LECTURE ORGANIZATION Outline Introduction Low voltage input stages Low voltage gain stages Low voltage bias circuits
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 54, NO. 3, MARCH
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 54, NO. 3, MARCH 2007 481 Programmable Filters Using Floating-Gate Operational Transconductance Amplifiers Ravi Chawla, Member, IEEE, Farhan
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 54, NO. 3, MARCH 2007 481 Programmable Filters Using Floating-Gate Operational Transconductance Amplifiers Ravi Chawla, Member, IEEE, Farhan
60V High-Speed Precision Current-Sense Amplifier
 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE MAX9643 General Description The MAX9643 is a high-speed 6V precision unidirectional current-sense amplifier ideal for a wide variety of power-supply control applications. Its high
EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE MAX9643 General Description The MAX9643 is a high-speed 6V precision unidirectional current-sense amplifier ideal for a wide variety of power-supply control applications. Its high
Digital Power: Consider The Possibilities
 Power: Consider The Possibilities Joseph G Renauer Michael G. Amaro David Figoli Texas Instruments 1 The Promise of Power Accuracy and precision No drift Unit to unit uniformity Programmable performance
Power: Consider The Possibilities Joseph G Renauer Michael G. Amaro David Figoli Texas Instruments 1 The Promise of Power Accuracy and precision No drift Unit to unit uniformity Programmable performance
Experiment 1: Amplifier Characterization Spring 2019
 Experiment 1: Amplifier Characterization Spring 2019 Objective: The objective of this experiment is to develop methods for characterizing key properties of operational amplifiers Note: We will be using
Experiment 1: Amplifier Characterization Spring 2019 Objective: The objective of this experiment is to develop methods for characterizing key properties of operational amplifiers Note: We will be using
TRAC020LH TOTALLY RE-CONFIGURABLE ANALOG CIRCUIT - TRAC. Issue 2 - MARCH 1999
 TOTALLY RE-CONFIGURABLE ANALOG CIRCUIT - TRAC Issue 2 - MARCH 1999 TRAC2LH DEVICE DESCRIPTION The TRAC2LH is a Micro-Power version of the existing TRAC products. It also offers significant improvements
TOTALLY RE-CONFIGURABLE ANALOG CIRCUIT - TRAC Issue 2 - MARCH 1999 TRAC2LH DEVICE DESCRIPTION The TRAC2LH is a Micro-Power version of the existing TRAC products. It also offers significant improvements
Current Mode PWM Controller
 application INFO available UC1842/3/4/5 Current Mode PWM Controller FEATURES Optimized For Off-line And DC To DC Converters Low Start Up Current (
application INFO available UC1842/3/4/5 Current Mode PWM Controller FEATURES Optimized For Off-line And DC To DC Converters Low Start Up Current (
A Self-Contained Large-Scale FPAA Development Platform
 A SelfContained LargeScale FPAA Development Platform Christopher M. Twigg, Paul E. Hasler, Faik Baskaya School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, Georgia 303320250
A SelfContained LargeScale FPAA Development Platform Christopher M. Twigg, Paul E. Hasler, Faik Baskaya School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Georgia Institute of Technology, Atlanta, Georgia 303320250
350MHz, Ultra-Low-Noise Op Amps
 9-442; Rev ; /95 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 35MHz, Ultra-Low-Noise Op Amps General Description The / op amps combine high-speed performance with ultra-low-noise performance. The is compensated for closed-loop
9-442; Rev ; /95 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE 35MHz, Ultra-Low-Noise Op Amps General Description The / op amps combine high-speed performance with ultra-low-noise performance. The is compensated for closed-loop
NOVEMBER 29, 2017 COURSE PROJECT: CMOS TRANSIMPEDANCE AMPLIFIER ECG 720 ADVANCED ANALOG IC DESIGN ERIC MONAHAN
 NOVEMBER 29, 2017 COURSE PROJECT: CMOS TRANSIMPEDANCE AMPLIFIER ECG 720 ADVANCED ANALOG IC DESIGN ERIC MONAHAN 1.Introduction: CMOS Transimpedance Amplifier Avalanche photodiodes (APDs) are highly sensitive,
NOVEMBER 29, 2017 COURSE PROJECT: CMOS TRANSIMPEDANCE AMPLIFIER ECG 720 ADVANCED ANALOG IC DESIGN ERIC MONAHAN 1.Introduction: CMOS Transimpedance Amplifier Avalanche photodiodes (APDs) are highly sensitive,
MAX1002/MAX1003 Evaluation Kits
 9-50; Rev 0; 6/97 MAX00/MAX00 Evaluation Kits General Description The MAX00/MAX00 evaluation kits (EV kits) simplify evaluation of the 60Msps MAX00 and 90Msps MAX00 dual, 6-bit analog-to-digital converters
9-50; Rev 0; 6/97 MAX00/MAX00 Evaluation Kits General Description The MAX00/MAX00 evaluation kits (EV kits) simplify evaluation of the 60Msps MAX00 and 90Msps MAX00 dual, 6-bit analog-to-digital converters
A DSP IMPLEMENTED DIGITAL FM MULTIPLEXING SYSTEM
 A DSP IMPLEMENTED DIGITAL FM MULTIPLEXING SYSTEM Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Rosenthal, Glenn K. Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal International Telemetering Conference
A DSP IMPLEMENTED DIGITAL FM MULTIPLEXING SYSTEM Item Type text; Proceedings Authors Rosenthal, Glenn K. Publisher International Foundation for Telemetering Journal International Telemetering Conference
STRS COMPLIANT FPGA WAVEFORM DEVELOPMENT
 STRS COMPLIANT FPGA WAVEFORM DEVELOPMENT Jennifer Nappier (Jennifer.M.Nappier@nasa.gov); Joseph Downey (Joseph.A.Downey@nasa.gov); NASA Glenn Research Center, Cleveland, Ohio, United States Dale Mortensen
STRS COMPLIANT FPGA WAVEFORM DEVELOPMENT Jennifer Nappier (Jennifer.M.Nappier@nasa.gov); Joseph Downey (Joseph.A.Downey@nasa.gov); NASA Glenn Research Center, Cleveland, Ohio, United States Dale Mortensen
A Modular Framework for the Evolution of Circuits on Configurable Transistor Array Architectures.
 A Modular Framework for the Evolution of Circuits on Configurable Transistor Array Architectures. Martin Trefzer, Jörg Langeheine, Karlheinz Meier, Johannes Schemmel Ruprecht-Karls-University of Heidelberg
A Modular Framework for the Evolution of Circuits on Configurable Transistor Array Architectures. Martin Trefzer, Jörg Langeheine, Karlheinz Meier, Johannes Schemmel Ruprecht-Karls-University of Heidelberg
Current-mode PWM controller
 DESCRIPTION The is available in an 8-Pin mini-dip the necessary features to implement off-line, fixed-frequency current-mode control schemes with a minimal external parts count. This technique results
DESCRIPTION The is available in an 8-Pin mini-dip the necessary features to implement off-line, fixed-frequency current-mode control schemes with a minimal external parts count. This technique results
Signal Forge. Signal Forge 1000 TM Synthesized Signal Generator. Digital and RF Tester with 1 GHz Range. Key Features
 Signal Forge TM Signal Forge 1000 TM Synthesized Signal Generator L 8.5 W 5.4 H 1.5 Digital and RF Tester with 1 GHz Range The Signal Forge 1000 combines a 1 GHz frequency range with three dedicated outputs
Signal Forge TM Signal Forge 1000 TM Synthesized Signal Generator L 8.5 W 5.4 H 1.5 Digital and RF Tester with 1 GHz Range The Signal Forge 1000 combines a 1 GHz frequency range with three dedicated outputs
10.1: A 4 GSample/s 8b ADC in 0.35-um CMOS
 10.1: A 4 GSample/s 8b ADC in 0.35-um CMOS Ken Poulton, Robert Neff, Art Muto, Wei Liu*, Andy Burstein**, Mehrdad Heshami*** Agilent Technologies, Palo Alto, CA *Agilent Technologies, Colorado Springs,
10.1: A 4 GSample/s 8b ADC in 0.35-um CMOS Ken Poulton, Robert Neff, Art Muto, Wei Liu*, Andy Burstein**, Mehrdad Heshami*** Agilent Technologies, Palo Alto, CA *Agilent Technologies, Colorado Springs,
Four-Channel Sample-and-Hold Amplifier AD684
 a FEATURES Four Matched Sample-and-Hold Amplifiers Independent Inputs, Outputs and Control Pins 500 ns Hold Mode Settling 1 s Maximum Acquisition Time to 0.01% Low Droop Rate: 0.01 V/ s Internal Hold Capacitors
a FEATURES Four Matched Sample-and-Hold Amplifiers Independent Inputs, Outputs and Control Pins 500 ns Hold Mode Settling 1 s Maximum Acquisition Time to 0.01% Low Droop Rate: 0.01 V/ s Internal Hold Capacitors
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS. AN109 Microprocessor-compatible DACs Dec
 INTEGRATED CIRCUITS 1988 Dec DAC products are designed to convert a digital code to an analog signal. Since a common source of digital signals is the data bus of a microprocessor, DAC circuits that are
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS 1988 Dec DAC products are designed to convert a digital code to an analog signal. Since a common source of digital signals is the data bus of a microprocessor, DAC circuits that are
EUP3452A. 2A,30V,300KHz Step-Down Converter DESCRIPTION FEATURES APPLICATIONS. Typical Application Circuit
 2A,30V,300KHz Step-Down Converter DESCRIPTION The is current mode, step-down switching regulator capable of driving 2A continuous load with excellent line and load regulation. The can operate with an input
2A,30V,300KHz Step-Down Converter DESCRIPTION The is current mode, step-down switching regulator capable of driving 2A continuous load with excellent line and load regulation. The can operate with an input
ADS9850 Signal Generator Module
 1. Introduction ADS9850 Signal Generator Module This module described here is based on ADS9850, a CMOS, 125MHz, and Complete DDS Synthesizer. The AD9850 is a highly integrated device that uses advanced
1. Introduction ADS9850 Signal Generator Module This module described here is based on ADS9850, a CMOS, 125MHz, and Complete DDS Synthesizer. The AD9850 is a highly integrated device that uses advanced
IF Digitally Controlled Variable-Gain Amplifier
 19-2601; Rev 1; 2/04 IF Digitally Controlled Variable-Gain Amplifier General Description The high-performance, digitally controlled variable-gain amplifier is designed for use from 0MHz to 400MHz. The
19-2601; Rev 1; 2/04 IF Digitally Controlled Variable-Gain Amplifier General Description The high-performance, digitally controlled variable-gain amplifier is designed for use from 0MHz to 400MHz. The
SGM V Step-Up LED Driver
 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The SGM3725 is a versatile constant current LED driver with a high efficiency step-up converter architecture. Unique technology and high 1.35A current limit allow SGM3725 to drive up
GENERAL DESCRIPTION The SGM3725 is a versatile constant current LED driver with a high efficiency step-up converter architecture. Unique technology and high 1.35A current limit allow SGM3725 to drive up
PowerAmp Design. PowerAmp Design PAD541 COMPACT POWER OP AMP
 PowerAmp Design COMPACT POWER OP AMP Rev E KEY FEATURES LOW COST HIGH VOLTAGE 00 VOLTS HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT 5 AMPS 50 WATT DISSIPATION CAPABILITY 00 WATT OUTPUT CAPABILITY 0.63 HEIGHT SIP DESIGN APPLICATIONS
PowerAmp Design COMPACT POWER OP AMP Rev E KEY FEATURES LOW COST HIGH VOLTAGE 00 VOLTS HIGH OUTPUT CURRENT 5 AMPS 50 WATT DISSIPATION CAPABILITY 00 WATT OUTPUT CAPABILITY 0.63 HEIGHT SIP DESIGN APPLICATIONS
High-Efficiency, 26V Step-Up Converters for Two to Six White LEDs
 19-2731; Rev 1; 10/03 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE High-Efficiency, 26V Step-Up Converters General Description The step-up converters drive up to six white LEDs with a constant current to provide backlight
19-2731; Rev 1; 10/03 EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE High-Efficiency, 26V Step-Up Converters General Description The step-up converters drive up to six white LEDs with a constant current to provide backlight
An Evolutionary Approach to the Synthesis of Combinational Circuits
 An Evolutionary Approach to the Synthesis of Combinational Circuits Cecília Reis Institute of Engineering of Porto Polytechnic Institute of Porto Rua Dr. António Bernardino de Almeida, 4200-072 Porto Portugal
An Evolutionary Approach to the Synthesis of Combinational Circuits Cecília Reis Institute of Engineering of Porto Polytechnic Institute of Porto Rua Dr. António Bernardino de Almeida, 4200-072 Porto Portugal
A Current-Measurement Front-End with 160dB Dynamic Range and 7ppm INL
 A Current-Measurement Front-End with 160dB Dynamic Range and 7ppm INL Chung-Lun Hsu and Drew A. Hall University of California, San Diego, La Jolla, CA, USA International Solid-State Circuits Conference
A Current-Measurement Front-End with 160dB Dynamic Range and 7ppm INL Chung-Lun Hsu and Drew A. Hall University of California, San Diego, La Jolla, CA, USA International Solid-State Circuits Conference
Design and FPGA Implementation of an Adaptive Demodulator. Design and FPGA Implementation of an Adaptive Demodulator
 Design and FPGA Implementation of an Adaptive Demodulator Sandeep Mukthavaram August 23, 1999 Thesis Defense for the Degree of Master of Science in Electrical Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering
Design and FPGA Implementation of an Adaptive Demodulator Sandeep Mukthavaram August 23, 1999 Thesis Defense for the Degree of Master of Science in Electrical Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering
HM3410D Low Noise, Fast Transient 1A Step-Down Converter
 General Description The HM3410D is a 1.4MHz step-down converter with an input voltage range of 2.3V to 6.0V and output voltage as low as 0.6V. It is optimized to react quickly to a load variation. The
General Description The HM3410D is a 1.4MHz step-down converter with an input voltage range of 2.3V to 6.0V and output voltage as low as 0.6V. It is optimized to react quickly to a load variation. The
AM Stabilized RF Amplifier Driver
 LIGO T00074 AM Stabilized RF Amplifier Driver SURF Project Final Report August 00 Jing Luo Mentor: Daniel Sigg Co Mentor: Paul Schwinberg Abstract: The AOM/EOM driver is a high power RF amplifier used
LIGO T00074 AM Stabilized RF Amplifier Driver SURF Project Final Report August 00 Jing Luo Mentor: Daniel Sigg Co Mentor: Paul Schwinberg Abstract: The AOM/EOM driver is a high power RF amplifier used
Simultaneous Co-Test of High Performance DAC-ADC Pairs May 13-28
 Simultaneous Co-Test of High Performance DAC-ADC Pairs Adviser & Client Members Luke Goetzke Ben Magstadt Tao Chen Aug, 2012 May, 2013 1 Agenda Project Description Project Design Test and Debug Results
Simultaneous Co-Test of High Performance DAC-ADC Pairs Adviser & Client Members Luke Goetzke Ben Magstadt Tao Chen Aug, 2012 May, 2013 1 Agenda Project Description Project Design Test and Debug Results
PB63 PB63A. Dual Power Booster Amplifier PB63
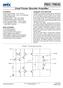 Dual Power Booster Amplifier A FEATURES Wide Supply Range ± V to ±75 V High Output Current Up to 2 A Continuous Programmable Gain High Slew Rate 1 V/µs Typical Programmable Output Current Limit High Power
Dual Power Booster Amplifier A FEATURES Wide Supply Range ± V to ±75 V High Output Current Up to 2 A Continuous Programmable Gain High Slew Rate 1 V/µs Typical Programmable Output Current Limit High Power
An Optimized Performance Amplifier
 Electrical and Electronic Engineering 217, 7(3): 85-89 DOI: 1.5923/j.eee.21773.3 An Optimized Performance Amplifier Amir Ashtari Gargari *, Neginsadat Tabatabaei, Ghazal Mirzaei School of Electrical and
Electrical and Electronic Engineering 217, 7(3): 85-89 DOI: 1.5923/j.eee.21773.3 An Optimized Performance Amplifier Amir Ashtari Gargari *, Neginsadat Tabatabaei, Ghazal Mirzaei School of Electrical and
FlexDDS-NG DUAL. Dual-Channel 400 MHz Agile Waveform Generator
 FlexDDS-NG DUAL Dual-Channel 400 MHz Agile Waveform Generator Excellent signal quality Rapid parameter changes Phase-continuous sweeps High speed analog modulation Wieserlabs UG www.wieserlabs.com FlexDDS-NG
FlexDDS-NG DUAL Dual-Channel 400 MHz Agile Waveform Generator Excellent signal quality Rapid parameter changes Phase-continuous sweeps High speed analog modulation Wieserlabs UG www.wieserlabs.com FlexDDS-NG
ECE 415/515 ANALOG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT DESIGN
 ECE 415/515 ANALOG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT DESIGN OPAMP DESIGN AND SIMULATION Vishal Saxena OPAMP DESIGN PROJECT R 2 v out v in /2 R 1 C L v in v out V CM R L V CM C L V CM -v in /2 R 1 C L (a) (b) R 2 ECE415/EO
ECE 415/515 ANALOG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT DESIGN OPAMP DESIGN AND SIMULATION Vishal Saxena OPAMP DESIGN PROJECT R 2 v out v in /2 R 1 C L v in v out V CM R L V CM C L V CM -v in /2 R 1 C L (a) (b) R 2 ECE415/EO
Development of a sampling ASIC for fast detector signals
 Development of a sampling ASIC for fast detector signals Hervé Grabas Work done in collaboration with Henry Frisch, Jean-François Genat, Eric Oberla, Gary Varner, Eric Delagnes, Dominique Breton. Signal
Development of a sampling ASIC for fast detector signals Hervé Grabas Work done in collaboration with Henry Frisch, Jean-François Genat, Eric Oberla, Gary Varner, Eric Delagnes, Dominique Breton. Signal
ML4818 Phase Modulation/Soft Switching Controller
 Phase Modulation/Soft Switching Controller www.fairchildsemi.com Features Full bridge phase modulation zero voltage switching circuit with programmable ZV transition times Constant frequency operation
Phase Modulation/Soft Switching Controller www.fairchildsemi.com Features Full bridge phase modulation zero voltage switching circuit with programmable ZV transition times Constant frequency operation
DAT175: Topics in Electronic System Design
 DAT175: Topics in Electronic System Design Analog Readout Circuitry for Hearing Aid in STM90nm 21 February 2010 Remzi Yagiz Mungan v1.10 1. Introduction In this project, the aim is to design an adjustable
DAT175: Topics in Electronic System Design Analog Readout Circuitry for Hearing Aid in STM90nm 21 February 2010 Remzi Yagiz Mungan v1.10 1. Introduction In this project, the aim is to design an adjustable
781/ /
 781/329-47 781/461-3113 SPECIFICATIONS DC SPECIFICATIONS J Parameter Min Typ Max Units SAMPLING CHARACTERISTICS Acquisition Time 5 V Step to.1% 25 375 ns 5 V Step to.1% 2 35 ns Small Signal Bandwidth 15
781/329-47 781/461-3113 SPECIFICATIONS DC SPECIFICATIONS J Parameter Min Typ Max Units SAMPLING CHARACTERISTICS Acquisition Time 5 V Step to.1% 25 375 ns 5 V Step to.1% 2 35 ns Small Signal Bandwidth 15
LM2900 LM3900 LM3301 Quad Amplifiers
 LM2900 LM3900 LM3301 Quad Amplifiers General Description The LM2900 series consists of four independent dual input internally compensated amplifiers which were designed specifically to operate off of a
LM2900 LM3900 LM3301 Quad Amplifiers General Description The LM2900 series consists of four independent dual input internally compensated amplifiers which were designed specifically to operate off of a
Hot Topics and Cool Ideas in Scaled CMOS Analog Design
 Engineering Insights 2006 Hot Topics and Cool Ideas in Scaled CMOS Analog Design C. Patrick Yue ECE, UCSB October 27, 2006 Slide 1 Our Research Focus High-speed analog and RF circuits Device modeling,
Engineering Insights 2006 Hot Topics and Cool Ideas in Scaled CMOS Analog Design C. Patrick Yue ECE, UCSB October 27, 2006 Slide 1 Our Research Focus High-speed analog and RF circuits Device modeling,
Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators
 Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators FEATURES Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for Single-ended or Push-pull Applications Low Standby Current 8mA Typical Interchangeable with
Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators FEATURES Complete PWM Power Control Circuitry Uncommitted Outputs for Single-ended or Push-pull Applications Low Standby Current 8mA Typical Interchangeable with
SGM3736 PWM Dimming, 38V Step-Up LED Driver
 GENERAL DESCRIPTION The SGM3736 is a versatile constant current LED driver with a high efficiency step-up converter architecture. The low-side power MOSFET is integrated in the device, significantly shrinking
GENERAL DESCRIPTION The SGM3736 is a versatile constant current LED driver with a high efficiency step-up converter architecture. The low-side power MOSFET is integrated in the device, significantly shrinking
Data Converters Performance at Extreme Temperatures
 Data Converters Performance at Extreme Temperatures Rarnesham Rejeshuni Nikil Kumar James Mao Didier Keymeulen Ricardo S. Zebulum Adrian Stoica Jet Propulsion Laboratory California nstitute of Technology
Data Converters Performance at Extreme Temperatures Rarnesham Rejeshuni Nikil Kumar James Mao Didier Keymeulen Ricardo S. Zebulum Adrian Stoica Jet Propulsion Laboratory California nstitute of Technology
-40 C to +85 C. AABN -40 C to +85 C 8 SO -40 C to +85 C 6 SOT23-6 AABP
 19-1434; Rev 1; 5/99 Low-Cost, SOT23, Voltage-Output, General Description The MAX4173 low-cost, precision, high-side currentsense amplifier is available in a tiny SOT23-6 package. It features a voltage
19-1434; Rev 1; 5/99 Low-Cost, SOT23, Voltage-Output, General Description The MAX4173 low-cost, precision, high-side currentsense amplifier is available in a tiny SOT23-6 package. It features a voltage
ADA485-/ADA485- TABLE OF CONTENTS Features... Applications... Pin Configurations... General Description... Revision History... Specifications... 3 Spe
 NC NC NC NC 5 6 7 8 6 NC 4 PD 3 PD FEATURES Ultralow power-down current: 5 na/amplifier maximum Low quiescent current:.4 ma/amplifier High speed 75 MHz, 3 db bandwidth V/μs slew rate 85 ns settling time
NC NC NC NC 5 6 7 8 6 NC 4 PD 3 PD FEATURES Ultralow power-down current: 5 na/amplifier maximum Low quiescent current:.4 ma/amplifier High speed 75 MHz, 3 db bandwidth V/μs slew rate 85 ns settling time
Using the Peak Detector Voltage to Compensate Output Voltage Change over Temperature
 Using the Peak Detector Voltage to Compensate Output Voltage Change over Temperature This document explains how to use the driver amplifier s peak detector to compensate the amplifier s output voltage
Using the Peak Detector Voltage to Compensate Output Voltage Change over Temperature This document explains how to use the driver amplifier s peak detector to compensate the amplifier s output voltage
High-speed and High-precision Motion Controller
 High-speed and High-precision Motion Controller - KSMC - Definition High-Speed Axes move fast Execute the controller ( position/velocity loop, current loop ) at high frequency High-Precision High positioning
High-speed and High-precision Motion Controller - KSMC - Definition High-Speed Axes move fast Execute the controller ( position/velocity loop, current loop ) at high frequency High-Precision High positioning
A Digitally Enhanced 1.8-V 15-b 40- Msample/s CMOS Pipelined ADC
 A Digitally Enhanced.8-V 5-b 4- Msample/s CMOS d ADC Eric Siragusa and Ian Galton University of California San Diego Now with Analog Devices San Diego California Outline Conventional PADC Example Digitally
A Digitally Enhanced.8-V 5-b 4- Msample/s CMOS d ADC Eric Siragusa and Ian Galton University of California San Diego Now with Analog Devices San Diego California Outline Conventional PADC Example Digitally
AD596/AD597 SPECIFICATIONS +60 C and V S = 10 V, Type J (AD596), Type K (AD597) Thermocouple,
 AD597 SPECIFICATIONS (@ +60 C and V S = 10 V, Type J (AD596), Type K (AD597) Thermocouple, unless otherwise noted) Model AD596AH AD597AH AD597AR Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Units ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM
AD597 SPECIFICATIONS (@ +60 C and V S = 10 V, Type J (AD596), Type K (AD597) Thermocouple, unless otherwise noted) Model AD596AH AD597AH AD597AR Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Units ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM
Block Diagram. i_in. q_in (optional) clk. 0 < seed < use both ports i_in and q_in
 Key Design Features Block Diagram Synthesizable, technology independent VHDL IP Core -bit signed input samples gain seed 32 dithering use_complex Accepts either complex (I/Q) or real input samples Programmable
Key Design Features Block Diagram Synthesizable, technology independent VHDL IP Core -bit signed input samples gain seed 32 dithering use_complex Accepts either complex (I/Q) or real input samples Programmable
Overview. Figure 2. Figure 1. Doc: page 1 of 5. Revision: July 24, Henley Court Pullman, WA (509) Voice and Fax
 Programming Cable for Xilinx FPGAs Revision: July 24, 2012 1300 Henley Court Pullman, WA 99163 (509) 334 6306 Voice and Fax Overview The Joint Test Action Group (JTAG)-HS2 programming cable is a high-speed
Programming Cable for Xilinx FPGAs Revision: July 24, 2012 1300 Henley Court Pullman, WA 99163 (509) 334 6306 Voice and Fax Overview The Joint Test Action Group (JTAG)-HS2 programming cable is a high-speed
Co-evolution for Communication: An EHW Approach
 Journal of Universal Computer Science, vol. 13, no. 9 (2007), 1300-1308 submitted: 12/6/06, accepted: 24/10/06, appeared: 28/9/07 J.UCS Co-evolution for Communication: An EHW Approach Yasser Baleghi Damavandi,
Journal of Universal Computer Science, vol. 13, no. 9 (2007), 1300-1308 submitted: 12/6/06, accepted: 24/10/06, appeared: 28/9/07 J.UCS Co-evolution for Communication: An EHW Approach Yasser Baleghi Damavandi,
RF Integrated Circuits
 Introduction and Motivation RF Integrated Circuits The recent explosion in the radio frequency (RF) and wireless market has caught the semiconductor industry by surprise. The increasing demand for affordable
Introduction and Motivation RF Integrated Circuits The recent explosion in the radio frequency (RF) and wireless market has caught the semiconductor industry by surprise. The increasing demand for affordable
The counterpart to a DAC is the ADC, which is generally a more complicated circuit. One of the most popular ADC circuit is the successive
 1 The counterpart to a DAC is the ADC, which is generally a more complicated circuit. One of the most popular ADC circuit is the successive approximation converter. 2 3 The idea of sampling is fully covered
1 The counterpart to a DAC is the ADC, which is generally a more complicated circuit. One of the most popular ADC circuit is the successive approximation converter. 2 3 The idea of sampling is fully covered
Embedded System Hardware - Reconfigurable Hardware -
 2 Embedded System Hardware - Reconfigurable Hardware - Peter Marwedel Informatik 2 TU Dortmund Germany GOPs/J Courtesy: Philips Hugo De Man, IMEC, 27 Energy Efficiency of FPGAs 2, 28-2- Reconfigurable
2 Embedded System Hardware - Reconfigurable Hardware - Peter Marwedel Informatik 2 TU Dortmund Germany GOPs/J Courtesy: Philips Hugo De Man, IMEC, 27 Energy Efficiency of FPGAs 2, 28-2- Reconfigurable
Industrial PSU with universal input voltage range ( VAC line to line) and configurable output voltage. North America
 World-Wide 3-phase Input Voltage Range (nom. 200 Vrms to 480 Vrms), PF > 0.94 High Power Density 16 W/in 3 94% Typical Efficiency Parallel Operation up to 16 Units (50.4 kw) Cold-Plate Cooling System -25
World-Wide 3-phase Input Voltage Range (nom. 200 Vrms to 480 Vrms), PF > 0.94 High Power Density 16 W/in 3 94% Typical Efficiency Parallel Operation up to 16 Units (50.4 kw) Cold-Plate Cooling System -25
A 12-bit Interpolated Pipeline ADC using Body Voltage Controlled Amplifier
 A 12-bit Interpolated Pipeline ADC using Body Voltage Controlled Amplifier Hyunui Lee, Masaya Miyahara, and Akira Matsuzawa Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan Outline Background Body voltage controlled
A 12-bit Interpolated Pipeline ADC using Body Voltage Controlled Amplifier Hyunui Lee, Masaya Miyahara, and Akira Matsuzawa Tokyo Institute of Technology, Japan Outline Background Body voltage controlled
TDA 4700 TDA Control IC for Single-Ended and Push-Pull Switched-Mode Power Supplies (SMPS)
 Control IC for Single-Ended and Push-Pull Switched-Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) TDA 4700 Features Feed-forward control (line hum suppression) Symmetry inputs for push-pull converter (TDA 4700) Push-pull
Control IC for Single-Ended and Push-Pull Switched-Mode Power Supplies (SMPS) TDA 4700 Features Feed-forward control (line hum suppression) Symmetry inputs for push-pull converter (TDA 4700) Push-pull
MP1527 2A, 1.3MHz Step-Up Converter
 General Description The is a 2A, fixed frequency step-up converter in a tiny 16 lead QFN package. The high 1.3MHz switching frequency allows for smaller external components producing a compact solution
General Description The is a 2A, fixed frequency step-up converter in a tiny 16 lead QFN package. The high 1.3MHz switching frequency allows for smaller external components producing a compact solution
Hot Swap Controller Enables Standard Power Supplies to Share Load
 L DESIGN FEATURES Hot Swap Controller Enables Standard Power Supplies to Share Load Introduction The LTC435 Hot Swap and load share controller is a powerful tool for developing high availability redundant
L DESIGN FEATURES Hot Swap Controller Enables Standard Power Supplies to Share Load Introduction The LTC435 Hot Swap and load share controller is a powerful tool for developing high availability redundant
Programmable, Off-Line, PWM Controller
 Programmable, Off-Line, PWM Controller FEATURES All Control, Driving, Monitoring, and Protection Functions Included Low-Current Off Line Start Circuit Voltage Feed Forward or Current Mode Control High
Programmable, Off-Line, PWM Controller FEATURES All Control, Driving, Monitoring, and Protection Functions Included Low-Current Off Line Start Circuit Voltage Feed Forward or Current Mode Control High
Solid State Devices & Circuits. 18. Advanced Techniques
 ECE 442 Solid State Devices & Circuits 18. Advanced Techniques Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical l&c Computer Engineering i University of Illinois jschutt@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 Darlington Configuration - Popular
ECE 442 Solid State Devices & Circuits 18. Advanced Techniques Jose E. Schutt-Aine Electrical l&c Computer Engineering i University of Illinois jschutt@emlab.uiuc.edu 1 Darlington Configuration - Popular
Low Cost, High Speed, Rail-to-Rail, Output Op Amps ADA4851-1/ADA4851-2/ADA4851-4
 Low Cost, High Speed, Rail-to-Rail, Output Op Amps ADA485-/ADA485-/ADA485-4 FEATURES High speed 3 MHz, 3 db bandwidth 375 V/μs slew rate 55 ns settling time to.% Excellent video specifications. db flatness:
Low Cost, High Speed, Rail-to-Rail, Output Op Amps ADA485-/ADA485-/ADA485-4 FEATURES High speed 3 MHz, 3 db bandwidth 375 V/μs slew rate 55 ns settling time to.% Excellent video specifications. db flatness:
Wideband Spectral Measurement Using Time-Gated Acquisition Implemented on a User-Programmable FPGA
 Wideband Spectral Measurement Using Time-Gated Acquisition Implemented on a User-Programmable FPGA By Raajit Lall, Abhishek Rao, Sandeep Hari, and Vinay Kumar Spectral measurements for some of the Multiple
Wideband Spectral Measurement Using Time-Gated Acquisition Implemented on a User-Programmable FPGA By Raajit Lall, Abhishek Rao, Sandeep Hari, and Vinay Kumar Spectral measurements for some of the Multiple
Chapter IX Using Calibration and Temperature Compensation to improve RF Power Detector Accuracy By Carlos Calvo and Anthony Mazzei
 Chapter IX Using Calibration and Temperature Compensation to improve RF Power Detector Accuracy By Carlos Calvo and Anthony Mazzei Introduction Accurate RF power management is a critical issue in modern
Chapter IX Using Calibration and Temperature Compensation to improve RF Power Detector Accuracy By Carlos Calvo and Anthony Mazzei Introduction Accurate RF power management is a critical issue in modern
Lecture 240 Cascode Op Amps (3/28/10) Page 240-1
 Lecture 240 Cascode Op Amps (3/28/10) Page 2401 LECTURE 240 CASCODE OP AMPS LECTURE ORGANIZATION Outline Lecture Organization Single Stage Cascode Op Amps Two Stage Cascode Op Amps Summary CMOS Analog
Lecture 240 Cascode Op Amps (3/28/10) Page 2401 LECTURE 240 CASCODE OP AMPS LECTURE ORGANIZATION Outline Lecture Organization Single Stage Cascode Op Amps Two Stage Cascode Op Amps Summary CMOS Analog
Part No. Package Marking Material Packing SD42530 HSOP SD42530 Pb free Tube SD42530TR HSOP SD42530 Pb free Tape&Reel
 4-CHANNEL 1A HIGH POWER LED DRIVER WITH 6~48V INPUT DESCRIPTION The SD4253 is a step-down PWM control LED driver with a builtin power MOSFET. It achieves 1A continuous output current in 6~48V input voltage
4-CHANNEL 1A HIGH POWER LED DRIVER WITH 6~48V INPUT DESCRIPTION The SD4253 is a step-down PWM control LED driver with a builtin power MOSFET. It achieves 1A continuous output current in 6~48V input voltage
Current Mode PWM Controller
 Current Mode PWM Controller UC1842/3/4/5 FEATURES Optimized For Off-line And DC To DC Converters Low Start Up Current (
Current Mode PWM Controller UC1842/3/4/5 FEATURES Optimized For Off-line And DC To DC Converters Low Start Up Current (
Signal Forge. Signal Forge 1000 TM Synthesized Signal Generator. Flexible Design Enables Testing of RF and Clock-driven Systems.
 Signal Forge TM Signal Forge 1000 TM Synthesized Signal Generator L 8.5 W 5.4 H 1.5 Flexible Design Enables Testing of RF and Clock-driven Systems The Signal Forge 1000 combines a 1 GHz frequency range
Signal Forge TM Signal Forge 1000 TM Synthesized Signal Generator L 8.5 W 5.4 H 1.5 Flexible Design Enables Testing of RF and Clock-driven Systems The Signal Forge 1000 combines a 1 GHz frequency range
