SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
|
|
|
- Samantha Clemence Burns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
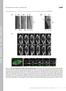
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S1 Examples of spindles assembled on small chromatin bead structures. (a) Spindle assembled on a short string of aligned chromatinbeads. (b-d) Spindles assembled on chromatin-bead clusters of various sizes. Fixed after 70 minutes of spindle assembly. Tubulin, red; chromatinbeads, green. Scale bars, 10 µm. Figure S2 Analysis of chromatin-bead structure bending during spindle assembly. (a, b) Two images from a time-lapse recording of fluorescent tubulin during spindle assembly on a single chromatin-bead string. Bending of a chromatin-bead structure can be seen over time. Beads outline drawn in yellow. Timestamps, min:sec. Scale bars, 10 µm. (c, d) Higher magnification images of the region of chromatin structure bending from the time-lapse recording shown in a and b. (e) Schematic illustration of bending of chromatin linkages between adjacent beads. 1
2 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Figure S3 Incorporation of non-chromatin ( dud ) beads into strings of chromatin beads to perturb the chromatin signal. Fluorophore-labeled dud beads (green) were mixed with DNA-coated beads (blue) before alignment in the magnetic field. (a, b) Many short strings were observed that had nonchromatin beads at one end, suggesting that these shorter strings result from breakage of longer strings at sites of incorporated dud beads. (c, d) In samples in which spindles were assembled on arrays containing both dud and chromatin-beads, dud beads were found predominantly at ends of chromatin-bead structures and sites of bead structure kinks. Tubulin, red. Scale bars, 10 µm. Supplemental Movie Movie corresponding to data shown in Fig. 5. Dynamic microtubules explore the region around the entire chromatin-bead structure. Fluorescent EB1 was imaged in fields surrounding bipolar spindles assembled on a chromatin-bead string by spinning-disc confocal microscopy. 2
3 Supplementary Information Estimation of the force required to bend chromatin-bead strings The stiffness and flexibility of the chromatin beads alignment comes from the contribution of each chromatin polymer, assembled during the interphase, that take part in the cross-linking of adjacent beads (Supplementary Figure S2). We assume for simplicity that the linkers of two adjacent beads, made of chromatin, have a rod-like shape (length L and cross section S). We estimate the surface of contact S to be ~ 1 µm 2 (fluorescent microscopy observations and electron microscopy of chromatin beads 1 ). During spindle pole formation the stress is applied on a few beads (Supplementary Figure S2). The bending modulus B of chromatin linkers is estimated by two ways: a. Estimation of B is obtained by assuming that the chromatin linkers form a continuous rod-like shape having a Young modulus Y (measured for the chromatin to be Pa 2 and chosen to be 500 Pa), and of radius r (~ 0.5 µm) 2. Linear elasticity allows us to calculate the bending modulus B of a continuous rod shape of radius r and Young modulus Y: B = YI = π 4 Yr4 ~ Nm 2 (I is the moment of inertia of a cylinder) 3. b. Estimation of B from the individual contributions of chromatin-molecules grafted on the beads. These polymers contribute equally to the stiffness between beads. Each chromatin polymer has a cross-section area of ~ 200 nm 2 (assumed to be ~ Rg 2 (where Rg is the radius of gyration of the DNA polymer)). We estimate the chromatin polymers number forming the crosslinker to be The chromatin linker bending rigidity is chosen to be the one measured for a single chromatid fiber assembled in vitro, in single chromatin stretching experiments 4. This
4 bending rigidity is b ~ Nm 2. Each linker contribute to the total bending rigidity B, thus B ~ b ~ Nm 2. Both calculations give results of the same order of magnitude. We choose B ~ Nm 2. The force required to bend a rod shape of length L is F = α YI L 2 = π2 B L 2 We find F ~ 2 nn, for a length L ~ 0.3 µm.
5 Methods Reagents Cytostatic factor-arrested Xenopus laevis egg extracts were prepared as described, and driven into interphase by the addition of 0.3 mm CaCl 5 2. Tubulins labeled with fluorophores 6, monastrol 7, p50/dynamitin 8, and p150-cc1 9 were prepared as previously described. DNAcoated beads were prepared as described 10, except that 2-3 pg DNA was bound to each bead. Only mono-disperse preparations of DNA-coated beads with uniform DNA loading (by Hoechst (Sigma-Aldrich) staining) were used. To make labeled dud beads (not coated with DNA), streptavidin Dynabeads (Dynal) were labeled with Oregon Green-succinimidyl ester (Molecular Probes). EB1 labeled with Alexa-594 (Molecular Probes) was prepared and used as previously described 11. Imaging and Data analysis Fluorescence imaging of spindles for quantitation was done using an Axioplan 2 (Carl Zeiss MicroImaging, Inc.) and a 20X (Plan Neo, NA 0.5) or 40x (Plan Neo, NA 0.75) objective, equipped with an Axiocam MRm camera (Carl Zeiss MicroImaging, Inc.). For high-resolution imaging of microtubule organization and EB1 dynamics, images were acquired using an Axiovert 200M (Carl Zeiss MicroImaging, Inc.) and a 100X (Plan Apo, NA 1.4) objective, equipped with a piezo z-motor (Applied Scientific Instrumentation), an Orca ER CCD camera (Hamamatsu), a spinning-disk confocal head, 488- and 568-nm excitation filters, and krypton and argon ion lasers (Solamere Inc., Utah). For microtubule organization, z-sections (separated by 1.0 µm) were acquired, and maximal intensity projections of entire Z-stacks are displayed.
6 For EB1 imaging, single confocal sections were acquired every 2 seconds. X-Rhodamine or Alexa-488-conjugated tubulin was used at ~300 nm for imaging microtubule distribution. Chromatin-beads were imaged by autofluorescence of the paramagnetic beads. Data analysis was performed using Metamorph software (Universal Imaging Corp.) and Axiovision software (Carl Zeiss MicroImaging, Inc.). For purposes of quantitation, counting was limited to structures containing greater than 6, but fewer than 50 beads, and structures were considered strings if they possessed no more than one defect in the linearity of the structure (Fig. 2e, f; 6c; 7c). DNA-Bead Alignment and Spindle Assembly Chambers for DNA-bead alignment and spindle assembly were constructed by sealing two rubber o-rings (9 mm I.D./12 mm O.D., and 20 mm I.D./27 mm O.D., respectively) in an approximately concentric arrangement to a #1.5 coverglass (Fisher Scientific) using VALAP (1:1:1 mixture of Vaseline, lanolin and paraffin). To regulate temperature and humidity in the chambers, distilled water was added to the space between the two o-rings, and each chamber was placed on a homemade metal block, water-cooled to 16 C using a refrigerated water bath circulator (RTE7, Neslab). A solenoid electromagnet (EM or EM , AZeer Enterprises, Inc.) operating at 6V DC was positioned ~2 mm from the edge of each chamber, such that the chamber was near the center of the magnetic field. 60µl fresh egg extract containing 0.3 mm CaCl 2 was gently added to each chamber, and 5 µl DNA-coated beads (at ~6x10 8 beads/ml in 10mM Hepes (ph 7.7), 1 mm MgCl 2, 100 mm KCl, 150 mm sucrose) were gently dispersed through the extract in the chamber using an 130 µm bore beveled-tip syringe (#701, Hamilton Company). The top of the chamber was then
7 sealed with a second coverglass and silicon grease (Beckman). The sealed chambers containing extract and DNA-beads were incubated for two hours at 16 C to assemble chromatin on the beads. 50 µl fresh cytostatic factor-arrested egg extract was then gently mixed into each sample using a large-bore pipette. The chambers were re-sealed and incubated at 16 C for an additional 30 min to allow the extract to enter mitosis. Chambers were then removed from the magnetic field and cooled on ice for at least 15 min to disassemble microtubule structures, and warmed to 16 C to initiate spindle assembly. Indistinguishable results were obtained with or without depolymerization of microtubules by cold treatment. For fixed timepoint analysis, small sample volumes were removed and fixed as described 5. For real-time observations of spindle assembly, µl samples were removed from chambers on ice, and placed in ~75 µm thick flow cells consisting of two thin strips of doublestick tape separating a coverslip and microscope slide. Each flow cell was sealed with VALAP, and imaged in a temperature-controlled room at ~18 C, as described 5.
8 Supplemental References 1. Reinsch, S. & Karsenti, E. Movement of nuclei along microtubules in Xenopus egg extracts. Curr Biol 7, (1997). 2. Poirier, M. G., Eroglu, S. & Marko, J. F. The bending rigidity of mitotic chromosomes. Mol Biol Cell 13, (2002). 3. Kosevich, A. M., Lifshitz, E. M., Landau, L. D. & Pitaevskii, L. P. Theory of Elasticity (ed. 3) (Butterworth-Heinemann, 1986). 4. Houchmandzadeh, B., Marko, J. F., Chatenay, D. & Libchaber, A. Elasticity and structure of eukaryote chromosomes studied by micromanipulation and micropipette aspiration. J Cell Biol 139, 1-12 (1997). 5. Desai, A., Murray, A., Mitchison, T. J. & Walczak, C. E. The use of Xenopus egg extracts to study mitotic spindle assembly and function in vitro. Methods Cell Biol 61, (1999). 6. Hyman, A. A. Preparation of marked microtubules for the assay of the polarity of microtubule-based motors by fluorescence. J Cell Sci Suppl 14, (1991). 7. Mayer, T. U. et al. Small molecule inhibitor of mitotic spindle bipolarity identified in a phenotype-based screen. Science 286, (1999). 8. Wittmann, T. & Hyman, T. Recombinant p50/dynamitin as a tool to examine the role of dynactin in intracellular processes. Methods Cell Biol 61, (1999). 9. Gaetz, J. & Kapoor, T. M. Dynein/dynactin regulate metaphase spindle length by targeting depolymerizing activities to spindle poles. J Cell Biol 166, (2004). 10. Heald, R. et al. in Cell Biology: A Laboratory Handbook (ed. Celis, J.) (Academic Press, San Diego, CA, 1998). 11. Tirnauer, J. S., Grego, S., Salmon, E. D. & Mitchison, T. J. EB1-microtubule interactions in Xenopus egg extracts: role of EB1 in microtubule stabilization and mechanisms of targeting to microtubules. Mol Biol Cell 13, (2002).
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Sikirzhytski et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201401090/dc1 Figure S1. Behavior and organization of K-fibers in PtK 2
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Sikirzhytski et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201401090/dc1 Figure S1. Behavior and organization of K-fibers in PtK 2
Supplementary Information. Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy Imaging of Microtubule Arrays in Intact Arabidopsis thaliana Seedling Roots
 Supplementary Information Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy Imaging of Microtubule Arrays in Intact Arabidopsis thaliana Seedling Roots Bin Dong 1,, Xiaochen Yang 2,, Shaobin Zhu 1, Diane C.
Supplementary Information Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy Imaging of Microtubule Arrays in Intact Arabidopsis thaliana Seedling Roots Bin Dong 1,, Xiaochen Yang 2,, Shaobin Zhu 1, Diane C.
We attempted to separate the two dyes by acquiring images using a single excitation wavelength and just two emission wavelengths.
 TN437: Spectral Separation of monochrome images using Volocity 4.0 Introduction Spectral Separation is a technique that allows the user to separate images containing data from more than one fluorochrome
TN437: Spectral Separation of monochrome images using Volocity 4.0 Introduction Spectral Separation is a technique that allows the user to separate images containing data from more than one fluorochrome
Supplementary Material (ESI) for Lab on a Chip This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2011
 Supplemental Figure 1: A. Injection of oil (side channel) and cell extract (central channel) in a FFD sealed with a hydrophilic slide (clean glass surface): due to wetting of the cell extract with the
Supplemental Figure 1: A. Injection of oil (side channel) and cell extract (central channel) in a FFD sealed with a hydrophilic slide (clean glass surface): due to wetting of the cell extract with the
3. are adherent cells (ie. cells in suspension are too far away from the coverslip)
 Before you begin, make sure your sample... 1. is seeded on #1.5 coverglass (thickness = 0.17) 2. is an aqueous solution (ie. fixed samples mounted on a slide will not work - not enough difference in refractive
Before you begin, make sure your sample... 1. is seeded on #1.5 coverglass (thickness = 0.17) 2. is an aqueous solution (ie. fixed samples mounted on a slide will not work - not enough difference in refractive
ImageXpress Micro XLS Widefield High Content Screening System. Imaging with a vision.
 ImageXpress Micro XLS Widefield High Content Screening System Imaging with a vision www.moleculardevices.com The ImageXpress Micro Widefield High Content Screening System is the ultimate combination of
ImageXpress Micro XLS Widefield High Content Screening System Imaging with a vision www.moleculardevices.com The ImageXpress Micro Widefield High Content Screening System is the ultimate combination of
Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev. Microscopy course, Michmoret Dec 2005
 Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Why use confocal microscopy? Principles of the laser scanning confocal microscope. Image resolution. Manipulating the
Why and How? Daniel Gitler Dept. of Physiology Ben-Gurion University of the Negev Why use confocal microscopy? Principles of the laser scanning confocal microscope. Image resolution. Manipulating the
Development of a High-speed Super-resolution Confocal Scanner
 Development of a High-speed Super-resolution Confocal Scanner Takuya Azuma *1 Takayuki Kei *1 Super-resolution microscopy techniques that overcome the spatial resolution limit of conventional light microscopy
Development of a High-speed Super-resolution Confocal Scanner Takuya Azuma *1 Takayuki Kei *1 Super-resolution microscopy techniques that overcome the spatial resolution limit of conventional light microscopy
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS. PIN2-Dendra2 transgenic line creation
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS PIN2-Dendra2 transgenic line creation The PIN2-Dendra2 construct was described previously (Jásik et al., 2013). Shortly, for generation of the expressing vector encompassing the PIN2-Dendra2
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS PIN2-Dendra2 transgenic line creation The PIN2-Dendra2 construct was described previously (Jásik et al., 2013). Shortly, for generation of the expressing vector encompassing the PIN2-Dendra2
Formaldehyde Cross-linking of Chromatin from Drosophila
 2 Formaldehyde Cross-linking of Chromatin from Drosophila Protocol from modencode IGSB University of Chicago originally written by Alex Crofts and Sasha Ostapenko and updated by Matt Kirkey. 1. Set centrifuge
2 Formaldehyde Cross-linking of Chromatin from Drosophila Protocol from modencode IGSB University of Chicago originally written by Alex Crofts and Sasha Ostapenko and updated by Matt Kirkey. 1. Set centrifuge
Practical work no. 3: Confocal Live Cell Microscopy
 Practical work no. 3: Confocal Live Cell Microscopy Course Instructor: Mikko Liljeström (MIU) 1 Background Confocal microscopy: The main idea behind confocality is that it suppresses the signal outside
Practical work no. 3: Confocal Live Cell Microscopy Course Instructor: Mikko Liljeström (MIU) 1 Background Confocal microscopy: The main idea behind confocality is that it suppresses the signal outside
ProLong Glass Antifade Mountant
 USER GUIDE ProLong Glass Antifade Mountant Catalog No. P36980, P36981, P36982, P36983, P36984, P36985 Pub. No. MAN0017262 Rev. A.0 Product information ProLong Glass Antifade Mountant is a glycerol-based,
USER GUIDE ProLong Glass Antifade Mountant Catalog No. P36980, P36981, P36982, P36983, P36984, P36985 Pub. No. MAN0017262 Rev. A.0 Product information ProLong Glass Antifade Mountant is a glycerol-based,
BoTest Matrix E Botulinum Neurotoxin Detection Kit Protocol
 BoTest Matrix E Botulinum Neurotoxin Detection Kit Protocol 505 S. Rosa Road, Suite 105 Madison, WI 53719 1-608-441-8174 info@biosentinelpharma.com BioSentinel Part No: L1016, Release Date: May 29, 2014
BoTest Matrix E Botulinum Neurotoxin Detection Kit Protocol 505 S. Rosa Road, Suite 105 Madison, WI 53719 1-608-441-8174 info@biosentinelpharma.com BioSentinel Part No: L1016, Release Date: May 29, 2014
Pixel shift in fluorescence microscopy
 Pixel shift in fluorescence microscopy 1. Introduction Multicolor imaging in fluorescence microscopy is typically performed by sequentially acquiring images of different colors. An overlay of these images
Pixel shift in fluorescence microscopy 1. Introduction Multicolor imaging in fluorescence microscopy is typically performed by sequentially acquiring images of different colors. An overlay of these images
Supplementary Figure 2. Schematic of the outer ring and glass base incorporated with glass microfluidics.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Image of compressor mount ~CM! and bottom side of coverslip compressor ~CC!. a: The CC will thread into the CM and will push down on a 25 mm coverslip that is nestled within the
Supplementary Figure 1. Image of compressor mount ~CM! and bottom side of coverslip compressor ~CC!. a: The CC will thread into the CM and will push down on a 25 mm coverslip that is nestled within the
Fast, high-contrast imaging of animal development with scanned light sheet based structured-illumination microscopy
 nature methods Fast, high-contrast imaging of animal development with scanned light sheet based structured-illumination microscopy Philipp J Keller, Annette D Schmidt, Anthony Santella, Khaled Khairy,
nature methods Fast, high-contrast imaging of animal development with scanned light sheet based structured-illumination microscopy Philipp J Keller, Annette D Schmidt, Anthony Santella, Khaled Khairy,
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/323/5914/638/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Stretching Single Talin Rod Molecules Activates Vinculin Binding Armando del Rio, Raul Perez-Jimenez, Ruchuan Liu, Pere
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/323/5914/638/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Stretching Single Talin Rod Molecules Activates Vinculin Binding Armando del Rio, Raul Perez-Jimenez, Ruchuan Liu, Pere
Alon s SCN ChIP Protocol
 Prior to starting your ChIPs and Shearing 1. Turn on sonifiers and cooling system allow system to reach -1 C before shearing 2. Cool bench top centrifuge to 4 C 3. Prepare all of your buffers with protease
Prior to starting your ChIPs and Shearing 1. Turn on sonifiers and cooling system allow system to reach -1 C before shearing 2. Cool bench top centrifuge to 4 C 3. Prepare all of your buffers with protease
Travel to New Dimensions- LSM 880. The Resolution of a Microscope is limited. The Resolution of a Microscope is limited. Image. Image. Object.
 Travel to New Dimensions- LSM 880 LSM 880: The Power of Sensitivity Our Latest Member of the LSM 880 with GaAsP Detectors Sensitivity, and Ease of Use Innovative High-End Laser Scanning Microscopes from
Travel to New Dimensions- LSM 880 LSM 880: The Power of Sensitivity Our Latest Member of the LSM 880 with GaAsP Detectors Sensitivity, and Ease of Use Innovative High-End Laser Scanning Microscopes from
PARP1-Trap_A for Immunoprecipitation of PARP1- Fusion Proteins from cell extract
 PARP1-Trap_A for Immunoprecipitation of PARP1- Fusion Proteins from cell extract Only for research applications, not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. Introduction Specificity Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase
PARP1-Trap_A for Immunoprecipitation of PARP1- Fusion Proteins from cell extract Only for research applications, not for diagnostic or therapeutic use. Introduction Specificity Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase
BIOL110L-Cell Biology Lab Spring Quarter 2012 Module 3-4 Wednesday May 30, 2012
 BIOL110L-Cell Biology Lab Spring Quarter 2012 Module 3-4 Wednesday May 30, 2012 PART I: Isolation of over-expressed GFP-Karyopherins from yeast extracts by affinity capture on nucleoporins Summary: The
BIOL110L-Cell Biology Lab Spring Quarter 2012 Module 3-4 Wednesday May 30, 2012 PART I: Isolation of over-expressed GFP-Karyopherins from yeast extracts by affinity capture on nucleoporins Summary: The
FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY. Matyas Molnar and Dirk Pacholsky
 FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY Matyas Molnar and Dirk Pacholsky 1 The human eye perceives app. 400-700 nm; best at around 500 nm (green) Has a general resolution down to150-300 μm (human hair: 40-250 μm) We need
FLUORESCENCE MICROSCOPY Matyas Molnar and Dirk Pacholsky 1 The human eye perceives app. 400-700 nm; best at around 500 nm (green) Has a general resolution down to150-300 μm (human hair: 40-250 μm) We need
Ratio Imaging. Dividing one image by another to detect changing conditions. Images collected at different times, wavelengths, polarities, etc
 Ratio Imaging Dividing one image by another to detect changing conditions Images collected at different times, wavelengths, polarities, etc Most common use of ratio imaging is to provide a quick spectral
Ratio Imaging Dividing one image by another to detect changing conditions Images collected at different times, wavelengths, polarities, etc Most common use of ratio imaging is to provide a quick spectral
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1126551/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Visualization of Cellulose Synthase Demonstrates Functional Association with Microtubules Alex R. Paredez, Christopher R.
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1126551/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Visualization of Cellulose Synthase Demonstrates Functional Association with Microtubules Alex R. Paredez, Christopher R.
Opterra II Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope. Innovation with Integrity
 Opterra II Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Enabling 4D Live-Cell Fluorescence Imaging through Speed, Sensitivity, Viability and Simplicity Innovation with Integrity Fluorescence Microscopy The
Opterra II Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Enabling 4D Live-Cell Fluorescence Imaging through Speed, Sensitivity, Viability and Simplicity Innovation with Integrity Fluorescence Microscopy The
We want to thank and acknowledge the authors for sharing this protocol and their contributions to the field.
 We adopted the protocol described in the Extended Experimental Procedures section I.a.1 of the 2014 Cell paper by Rao and Huntley et. al: A 3D Map of the Human Genome at Kilobase Resolution Reveals Principles
We adopted the protocol described in the Extended Experimental Procedures section I.a.1 of the 2014 Cell paper by Rao and Huntley et. al: A 3D Map of the Human Genome at Kilobase Resolution Reveals Principles
Multicolor 4D Fluorescence Microscopy using Ultrathin Bessel Light sheets
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multicolor 4D Fluorescence Microscopy using Ultrathin Bessel Light sheets Teng Zhao, Sze Cheung Lau, Ying Wang, Yumian Su, Hao Wang, Aifang Cheng, Karl Herrup, Nancy Y. Ip, Shengwang
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Multicolor 4D Fluorescence Microscopy using Ultrathin Bessel Light sheets Teng Zhao, Sze Cheung Lau, Ying Wang, Yumian Su, Hao Wang, Aifang Cheng, Karl Herrup, Nancy Y. Ip, Shengwang
High-resolution, low light-dose lightsheet microscope LATTICE LIGHTSHEET
 LATTICE LIGHTSHEET High-resolution, low light-dose lightsheet microscope First developed by Nobel Laureate Dr. Eric Betzig, the 3i Lattice LightSheet microscope is capable of imaging biological systems
LATTICE LIGHTSHEET High-resolution, low light-dose lightsheet microscope First developed by Nobel Laureate Dr. Eric Betzig, the 3i Lattice LightSheet microscope is capable of imaging biological systems
Chapter 2. Methods. 2.1 Golgi Staining
 29 Chapter 2 Methods This chapter describes in detail the methods employed to gather and analyze data for this thesis. Described are the specific protocol for Golgi staining, which is a method of random
29 Chapter 2 Methods This chapter describes in detail the methods employed to gather and analyze data for this thesis. Described are the specific protocol for Golgi staining, which is a method of random
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Gusnowski and Srayko, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201103128/dc1 Figure S1. EB1-GFP velocities from the centrosomes. (A) Mean
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Gusnowski and Srayko, http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201103128/dc1 Figure S1. EB1-GFP velocities from the centrosomes. (A) Mean
AxioCam MRm Pure Sensitivity
 Microscopy from Carl Zeiss AxioCam MRm Pure Sensitivity The New Standard for Digital Fluorescence Imaging AxioCam MRm from Carl Zeiss More Information at Low Light Intensities More than ever before, modern
Microscopy from Carl Zeiss AxioCam MRm Pure Sensitivity The New Standard for Digital Fluorescence Imaging AxioCam MRm from Carl Zeiss More Information at Low Light Intensities More than ever before, modern
Last updated: May 2014 Y.DeGraaf
 FLINDERS MICROSCOPY BIOMEDICAL SERVICES AVAILABLE MICROSCOPES AND SPECIFICATIONS & INFORMATION REGARDING TRAINING FOR NEW USERS Last updated: May 2014 Y.DeGraaf If you have new staff or students (Honours/Masters
FLINDERS MICROSCOPY BIOMEDICAL SERVICES AVAILABLE MICROSCOPES AND SPECIFICATIONS & INFORMATION REGARDING TRAINING FOR NEW USERS Last updated: May 2014 Y.DeGraaf If you have new staff or students (Honours/Masters
Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
 Name of the Core Facility: Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy CORE Forschungszentrum Immunologie Mainz Welcome to the CSLM Core Facility: The CLSM Core Facility enables working groups to incorporate high
Name of the Core Facility: Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy CORE Forschungszentrum Immunologie Mainz Welcome to the CSLM Core Facility: The CLSM Core Facility enables working groups to incorporate high
Integrated into Nanowire Waveguides
 Supporting Information Widely Tunable Distributed Bragg Reflectors Integrated into Nanowire Waveguides Anthony Fu, 1,3 Hanwei Gao, 1,3,4 Petar Petrov, 1, Peidong Yang 1,2,3* 1 Department of Chemistry,
Supporting Information Widely Tunable Distributed Bragg Reflectors Integrated into Nanowire Waveguides Anthony Fu, 1,3 Hanwei Gao, 1,3,4 Petar Petrov, 1, Peidong Yang 1,2,3* 1 Department of Chemistry,
Opterra. Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope. Innovation with Integrity. Cell-Friendly, High-Speed, High-Resolution Imaging
 Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Cell-Friendly, High-Speed, High-Resolution Imaging Innovation with Integrity Fluorescence Microscopy Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Superior
Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Cell-Friendly, High-Speed, High-Resolution Imaging Innovation with Integrity Fluorescence Microscopy Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal Microscope Superior
Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement
 Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY BioVis Uppsala, 2017 Jeremy Adler Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Widefield & Confocal Microscopy
Boulevard du Temple Daguerrotype (Paris,1838) a busy street? Nyquist sampling for movement CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY BioVis Uppsala, 2017 Jeremy Adler Matyas Molnar Dirk Pacholsky Widefield & Confocal Microscopy
Things to check before start-up.
 Byeong Cha Page 1 11/24/2009 Manual for Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Enter you name, the date, the time, and the account number in the user log book. Things to check before start-up. Make sure that your
Byeong Cha Page 1 11/24/2009 Manual for Leica SP2 Confocal Microscope Enter you name, the date, the time, and the account number in the user log book. Things to check before start-up. Make sure that your
ZEISS LSM510META confocal manual
 ZEISS LSM510META confocal manual Switching on the system 1) Switch on the Remote Control button located on the table to the right of the microscope. This is the main switch for the whole system including
ZEISS LSM510META confocal manual Switching on the system 1) Switch on the Remote Control button located on the table to the right of the microscope. This is the main switch for the whole system including
INTRODUCTION TO OPTICAL MICROSCOPY
 Experimental Biophysics TEK265, FYST23, TNF060, FAF010F Lab Exercise Supervisor: Karl Adolfsson Written by Peter Jönsson and Jason Beech Updated by Henrik Persson, Karl Adolfsson and Zhen Li karl.adolfsson@ftf.lth.se
Experimental Biophysics TEK265, FYST23, TNF060, FAF010F Lab Exercise Supervisor: Karl Adolfsson Written by Peter Jönsson and Jason Beech Updated by Henrik Persson, Karl Adolfsson and Zhen Li karl.adolfsson@ftf.lth.se
Microscopy Live Animal Imaging
 Microscopy Live Animal Imaging A collaborative environment that provides the knowledge, instruments, and expertise needed to visualize life at scales ranging from single molecules to entire animals. Project
Microscopy Live Animal Imaging A collaborative environment that provides the knowledge, instruments, and expertise needed to visualize life at scales ranging from single molecules to entire animals. Project
VivaTome. Discover the Dynamics of Life. The Entry-level System that Captures Dynamic Processes with Outstanding Image Quality.
 Microscopy from Carl Zeiss VivaTome Discover the Dynamics of Life The Entry-level System that Captures Dynamic Processes with Outstanding Image Quality. Innovative Technology Captures Dynamic Processes
Microscopy from Carl Zeiss VivaTome Discover the Dynamics of Life The Entry-level System that Captures Dynamic Processes with Outstanding Image Quality. Innovative Technology Captures Dynamic Processes
pluribead KIT Cell Separation Protocol M-Bead
 pluribead KIT Cell Separation Protocol M-Bead pluriselect@hiss-dx.de 15 14 13 12 11 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 50 40 30 20 2 Contents Contents pluribead Kit Components & Additional Materials 2 Separation Protocol
pluribead KIT Cell Separation Protocol M-Bead pluriselect@hiss-dx.de 15 14 13 12 11 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 50 40 30 20 2 Contents Contents pluribead Kit Components & Additional Materials 2 Separation Protocol
LSM 510 META in Chang Gung University
 Content LSM 510 META in Chang ung University LSM 510 META 路 理 The features and applications of LSM 510 META 01-09 Introduction of the hardware 10-12 Fluorescence observation in conventional microscope
Content LSM 510 META in Chang ung University LSM 510 META 路 理 The features and applications of LSM 510 META 01-09 Introduction of the hardware 10-12 Fluorescence observation in conventional microscope
Micro-manipulated Cryogenic & Vacuum Probe Systems
 Janis micro-manipulated probe stations are designed for non-destructive electrical testing using DC, RF, and fiber-optic probes. They are useful in a variety of fields including semiconductors, MEMS, superconductivity,
Janis micro-manipulated probe stations are designed for non-destructive electrical testing using DC, RF, and fiber-optic probes. They are useful in a variety of fields including semiconductors, MEMS, superconductivity,
HoloMonitor. Phase. For competent and powerful discoveries. Holographic time-lapse imaging cytometry
 HoloMonitor M4 Holographic time-lapse imaging cytometry For competent and powerful discoveries Monitor and quantify living cells in their natural environment with unrivaled temporal resolution Phase Holographic
HoloMonitor M4 Holographic time-lapse imaging cytometry For competent and powerful discoveries Monitor and quantify living cells in their natural environment with unrivaled temporal resolution Phase Holographic
1.The Problem LIGHT-LEVEL LEVEL IMAGING. light-level level Cameras. 3. Solutions. 2. Low-light LOW-LIGHT
 LOW-LIGHT LIGHT-LEVEL LEVEL IMAGING 1.The Problem 2. Low-light light-level level Cameras 3. Solutions How Much Light? I. Illumination system: 75 W Xenon Arc (~1mW/nm in visible) 490/10 nm exciter filter
LOW-LIGHT LIGHT-LEVEL LEVEL IMAGING 1.The Problem 2. Low-light light-level level Cameras 3. Solutions How Much Light? I. Illumination system: 75 W Xenon Arc (~1mW/nm in visible) 490/10 nm exciter filter
Maria Smedh, Centre for Cellular Imaging. Maria Smedh, Centre for Cellular Imaging
 Nonlinear microscopy I: Two-photon fluorescence microscopy Multiphoton Microscopy What is multiphoton imaging? Applications Different imaging modes Advantages/disadvantages Scattering of light in thick
Nonlinear microscopy I: Two-photon fluorescence microscopy Multiphoton Microscopy What is multiphoton imaging? Applications Different imaging modes Advantages/disadvantages Scattering of light in thick
You won t be able to measure the incident power precisely. The readout of the power would be lower than the real incident power.
 1. a) Given the transfer function of a detector (below), label and describe these terms: i. dynamic range ii. linear dynamic range iii. sensitivity iv. responsivity b) Imagine you are using an optical
1. a) Given the transfer function of a detector (below), label and describe these terms: i. dynamic range ii. linear dynamic range iii. sensitivity iv. responsivity b) Imagine you are using an optical
Chapter 2 The Study of Microbial Structure: Microscopy and Specimen Preparation
 Chapter 2 The Study of Microbial Structure: Microscopy and Specimen Preparation 1 Lenses and the Bending of Light light is refracted (bent) when passing from one medium to another refractive index a measure
Chapter 2 The Study of Microbial Structure: Microscopy and Specimen Preparation 1 Lenses and the Bending of Light light is refracted (bent) when passing from one medium to another refractive index a measure
Microscopic Structures
 Microscopic Structures Image Analysis Metal, 3D Image (Red-Green) The microscopic methods range from dark field / bright field microscopy through polarisation- and inverse microscopy to techniques like
Microscopic Structures Image Analysis Metal, 3D Image (Red-Green) The microscopic methods range from dark field / bright field microscopy through polarisation- and inverse microscopy to techniques like
Light Microscopy. Upon completion of this lecture, the student should be able to:
 Light Light microscopy is based on the interaction of light and tissue components and can be used to study tissue features. Upon completion of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1- Explain the
Light Light microscopy is based on the interaction of light and tissue components and can be used to study tissue features. Upon completion of this lecture, the student should be able to: 1- Explain the
Observation of the Inner Structures of Sea-Urchin Eggs by Projection X-Ray Microscopy
 Observation of the Inner Structures of Sea-Urchin Eggs by Projection X-Ray Microscopy K. Yada 1, K. Shinohara 2, Y. Hamaguchi 3 1 Aomori Public College, Aomori 030-01, Japan 2 Faculty of Medicine, The
Observation of the Inner Structures of Sea-Urchin Eggs by Projection X-Ray Microscopy K. Yada 1, K. Shinohara 2, Y. Hamaguchi 3 1 Aomori Public College, Aomori 030-01, Japan 2 Faculty of Medicine, The
TrueBlot Protein G Magnetic Beads PG ml. TrueBlot Protein G Magnetic Beads PG ml. Bead Mean Diameter 0.5 µm. Bead Concentration
 Rockland s TrueBlot Protein G Magnetic Beads are uniform, non-aggregating, super-paramagnetic beads coupled with a biomolecule, such as Protein G. These beads are specifically designed, tested and quality
Rockland s TrueBlot Protein G Magnetic Beads are uniform, non-aggregating, super-paramagnetic beads coupled with a biomolecule, such as Protein G. These beads are specifically designed, tested and quality
Supplementary information. Analog Modeling of Worm-Like Chain Molecules Using Macroscopic Beads-on-a-String
 Supplementary information Analog Modeling of Worm-Like Chain Molecules Using Macroscopic Beads-on-a-String Simon Tricard, a, * Efraim Feinstein, b Robert F. Shepherd, a Meital Reches, a Phillip W. Snyder,
Supplementary information Analog Modeling of Worm-Like Chain Molecules Using Macroscopic Beads-on-a-String Simon Tricard, a, * Efraim Feinstein, b Robert F. Shepherd, a Meital Reches, a Phillip W. Snyder,
Observing Microorganisms through a Microscope LIGHT MICROSCOPY: This type of microscope uses visible light to observe specimens. Compound Light Micros
 PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY JIGAR SHAH INSTITUTE OF PHARMACY NIRMA UNIVERSITY Observing Microorganisms through a Microscope LIGHT MICROSCOPY: This type of microscope uses visible light to observe specimens.
PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY JIGAR SHAH INSTITUTE OF PHARMACY NIRMA UNIVERSITY Observing Microorganisms through a Microscope LIGHT MICROSCOPY: This type of microscope uses visible light to observe specimens.
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Methods Cell Biol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2014 July 15.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Methods Cell Biol. 1998 ; 56: 185 215. A High-Resolution Multimode Digital Microscope System E. D. Salmon, Sidney L. Shaw, Jennifer
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Methods Cell Biol. 1998 ; 56: 185 215. A High-Resolution Multimode Digital Microscope System E. D. Salmon, Sidney L. Shaw, Jennifer
TouchBright Ver. 7.51
 TouchBright Ver. 7.51 High-Performance LED Excitation System Efficient Use Long Lifetime Brightest LEDs Compact Design High-Performance Live Cell Instrument Co., LTD www.touchbrightled.com TouchBright
TouchBright Ver. 7.51 High-Performance LED Excitation System Efficient Use Long Lifetime Brightest LEDs Compact Design High-Performance Live Cell Instrument Co., LTD www.touchbrightled.com TouchBright
Working Simultaneously. The Next Level of TIRF Microscopy. cell^tirf Illuminator Motorized Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence
 cell^tirf Illuminator Motorized Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence Four individually aligned illumination beams for simultaneous multi-color TIRF imaging Working Simultaneously The Next Level of TIRF
cell^tirf Illuminator Motorized Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence Four individually aligned illumination beams for simultaneous multi-color TIRF imaging Working Simultaneously The Next Level of TIRF
Internal Medicine Imaging Core Emory University Department of Medicine
 Internal Medicine Imaging Core Emory University Department of Medicine 1 OPERATION OF THE ZEISS LSM 510 META YOU MUST SIGN UP TO USE THE MICROSCOPE OR COMPUTER EVERY TIME NO EXCEPTIONS Before attempting
Internal Medicine Imaging Core Emory University Department of Medicine 1 OPERATION OF THE ZEISS LSM 510 META YOU MUST SIGN UP TO USE THE MICROSCOPE OR COMPUTER EVERY TIME NO EXCEPTIONS Before attempting
Resolution. Diffraction from apertures limits resolution. Rayleigh criterion θ Rayleigh = 1.22 λ/d 1 peak at 2 nd minimum. θ f D
 Microscopy Outline 1. Resolution and Simple Optical Microscope 2. Contrast enhancement: Dark field, Fluorescence (Chelsea & Peter), Phase Contrast, DIC 3. Newer Methods: Scanning Tunneling microscopy (STM),
Microscopy Outline 1. Resolution and Simple Optical Microscope 2. Contrast enhancement: Dark field, Fluorescence (Chelsea & Peter), Phase Contrast, DIC 3. Newer Methods: Scanning Tunneling microscopy (STM),
Accuracy and precision in quantitative fluorescence microscopy
 Published Online: 29 June, 2009 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200903097 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on May 15, 2018 JCB: FEATURE Accuracy and precision in quantitative fluorescence microscopy
Published Online: 29 June, 2009 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200903097 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on May 15, 2018 JCB: FEATURE Accuracy and precision in quantitative fluorescence microscopy
Final Exam, 150 points PMB 185: Techniques in Light Microscopy
 Final Exam, 150 points Name PMB 185: Techniques in Light Microscopy Point value is in parentheses at the end of each question. Note: GFP = green fluorescent protein ; CFP = cyan fluorescent protein ; YFP
Final Exam, 150 points Name PMB 185: Techniques in Light Microscopy Point value is in parentheses at the end of each question. Note: GFP = green fluorescent protein ; CFP = cyan fluorescent protein ; YFP
Zeiss LSM880 Operating Instructions. UTMB Optical Microscopy Core Jan. 16, 2018
 Zeiss LSM880 Operating Instructions UTMB Optical Microscopy Core Jan. 16, 2018 1 1. Power up the microscope Sing the LOGBOOK Steps below will provide power to the computer and all of the microscope components.
Zeiss LSM880 Operating Instructions UTMB Optical Microscopy Core Jan. 16, 2018 1 1. Power up the microscope Sing the LOGBOOK Steps below will provide power to the computer and all of the microscope components.
Using the Nikon TE2000 Inverted Microscope
 Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics Molecular Cytogenetics and Microscopy Core Using the Nikon TE2000 Inverted Microscope Fluorescence image acquisition using Scanalytic s IPLab software and the B&W
Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics Molecular Cytogenetics and Microscopy Core Using the Nikon TE2000 Inverted Microscope Fluorescence image acquisition using Scanalytic s IPLab software and the B&W
QwikCheck Beads Precision and Linearity Kit Instructions QwikCheck GOLD Analyzer
 Medical Electronic Systems www.mes-global.com service@mes-llc.com QwikCheck Beads Precision and Linearity Kit Instructions QwikCheck GOLD Analyzer OVERVIEW The QwikCheck Beads Precision and Linearity Kit
Medical Electronic Systems www.mes-global.com service@mes-llc.com QwikCheck Beads Precision and Linearity Kit Instructions QwikCheck GOLD Analyzer OVERVIEW The QwikCheck Beads Precision and Linearity Kit
Operating Instructions for Zeiss LSM 510
 Operating Instructions for Zeiss LSM 510 Location: GNL 6.312q (BSL3) Questions? Contact: Maxim Ivannikov, maivanni@utmb.edu 1 Attend A Complementary Training Before Using The Microscope All future users
Operating Instructions for Zeiss LSM 510 Location: GNL 6.312q (BSL3) Questions? Contact: Maxim Ivannikov, maivanni@utmb.edu 1 Attend A Complementary Training Before Using The Microscope All future users
Spectral Imaging with the Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal
 Spectral Imaging with the Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal Outline Opterra design overview Scan Modes Light Path Spectral Imaging with Opterra Drosophila larva heart. Opterra Design Overview Supravideo
Spectral Imaging with the Opterra Multipoint Scanning Confocal Outline Opterra design overview Scan Modes Light Path Spectral Imaging with Opterra Drosophila larva heart. Opterra Design Overview Supravideo
EUV microscopy - a user s perspective Dimitri Scholz EUV,
 EUV microscopy - a user s perspective Dimitri Scholz EUV, 09.11.2011 Imaging technologies: available at UCD now and in the next future Begin ab ovo - Simple approaches direct to the goal - Standard methods
EUV microscopy - a user s perspective Dimitri Scholz EUV, 09.11.2011 Imaging technologies: available at UCD now and in the next future Begin ab ovo - Simple approaches direct to the goal - Standard methods
Scanning Ion Conductance Microscope ICnano
 Sperm Cell Epithelial Cells I nner Ear Hair Cells I nner Ear Hair Cell Neurons E- Coli Bac teria Scanning Ion Conductance Microscope ICnano About ionscope About ionscope The ionscope scanning ion conductance
Sperm Cell Epithelial Cells I nner Ear Hair Cells I nner Ear Hair Cell Neurons E- Coli Bac teria Scanning Ion Conductance Microscope ICnano About ionscope About ionscope The ionscope scanning ion conductance
Monitoring of Galvanic Replacement Reaction. between Silver Nanowires and HAuCl 4 by In-Situ. Transmission X-Ray Microscopy
 Supporting Information Monitoring of Galvanic Replacement Reaction between Silver Nanowires and HAuCl 4 by In-Situ Transmission X-Ray Microscopy Yugang Sun *, and Yuxin Wang Center for Nanoscale Materials
Supporting Information Monitoring of Galvanic Replacement Reaction between Silver Nanowires and HAuCl 4 by In-Situ Transmission X-Ray Microscopy Yugang Sun *, and Yuxin Wang Center for Nanoscale Materials
Confocal Microscopy. (Increasing contrast and resolu6on using op6cal sec6oning) Lecture 7. November 2017
 Confocal Microscopy (Increasing contrast and resolu6on using op6cal sec6oning) Lecture 7 November 2017 3 Flavours of Microscope Confocal Laser Scanning Problem: Out of Focus Light Spinning disc 2-Photon
Confocal Microscopy (Increasing contrast and resolu6on using op6cal sec6oning) Lecture 7 November 2017 3 Flavours of Microscope Confocal Laser Scanning Problem: Out of Focus Light Spinning disc 2-Photon
Basics of confocal imaging (part I)
 Basics of confocal imaging (part I) Swiss Institute of Technology (EPFL) Faculty of Life Sciences Head of BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS BIOP arne.seitz@epfl.ch Lateral resolution BioImaging &Optics Platform Light
Basics of confocal imaging (part I) Swiss Institute of Technology (EPFL) Faculty of Life Sciences Head of BIOIMAGING AND OPTICS BIOP arne.seitz@epfl.ch Lateral resolution BioImaging &Optics Platform Light
IC 2 S High Performance Objectives
 M i c r o s c o p y f r o m C a r l Z e i s s IC 2 S igh Performance Objectives for Biomedical Applications with Laser Based Imaging Systems LSM,, ConfoCor, TIRF and ELYRA Carl Zeiss offers a large range
M i c r o s c o p y f r o m C a r l Z e i s s IC 2 S igh Performance Objectives for Biomedical Applications with Laser Based Imaging Systems LSM,, ConfoCor, TIRF and ELYRA Carl Zeiss offers a large range
Procedure & Checklist cdna Capture Using IDT xgen Lockdown Probes
 Procedure & Checklist cdna Capture Using IDT xgen Lockdown Probes Before You Begin This document describes the process for capturing cdna prepared with the SMARTer PCR cdna Synthesis Kit (Clontech) and
Procedure & Checklist cdna Capture Using IDT xgen Lockdown Probes Before You Begin This document describes the process for capturing cdna prepared with the SMARTer PCR cdna Synthesis Kit (Clontech) and
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup.
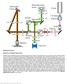 Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup. Excitation from a femtosecond laser is passed through intensity control and shuttering optics (1/2 λ wave plate, polarizing beam splitting
Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic of 2P-ISIM AO optical setup. Excitation from a femtosecond laser is passed through intensity control and shuttering optics (1/2 λ wave plate, polarizing beam splitting
Introduction. INSTRUCTION MANUAL CAT XL, 6500-XLCORE, 6500-FL Evos-XL, Evos-XL/Core, Evos-FL
 1 INSTRUCTION MANUAL CAT. 6500-XL, 6500-XLCORE, 6500-FL Evos-XL, Evos-XL/Core, Evos-FL Introduction Experience faster results and easier cell imaging with an EVOS imaging system! An EVOS system is the
1 INSTRUCTION MANUAL CAT. 6500-XL, 6500-XLCORE, 6500-FL Evos-XL, Evos-XL/Core, Evos-FL Introduction Experience faster results and easier cell imaging with an EVOS imaging system! An EVOS system is the
Procedure & Checklist - cdna Capture Using SeqCap EZ Libraries
 Procedure & Checklist - cdna Capture Using SeqCap EZ Libraries Before You Begin This document describes the process for capturing cdna prepared with the SMARTer PCR cdna Synthesis Kit (Clontech) and pulled-down
Procedure & Checklist - cdna Capture Using SeqCap EZ Libraries Before You Begin This document describes the process for capturing cdna prepared with the SMARTer PCR cdna Synthesis Kit (Clontech) and pulled-down
Immunomagnetic Cell Separation
 Immunomagnetic Cell Separation 17 2 Immunomagnetic Cell Separation Catherine Clarke and Susan Davies 1. Introduction In metastasis research, it may sometimes be necessary to separate populations of tumor
Immunomagnetic Cell Separation 17 2 Immunomagnetic Cell Separation Catherine Clarke and Susan Davies 1. Introduction In metastasis research, it may sometimes be necessary to separate populations of tumor
Release characteristics of the chemoattractant-loaded microparticles
 nature methods Cell stimulation with optically manipulated microsources Holger Kress, Jin-Gyu Park, Cecile O Mejean, Jason D Forster, Jason Park, Spencer S Walse, Yong Zhang, Dianqing Wu, Orion D Weiner,
nature methods Cell stimulation with optically manipulated microsources Holger Kress, Jin-Gyu Park, Cecile O Mejean, Jason D Forster, Jason Park, Spencer S Walse, Yong Zhang, Dianqing Wu, Orion D Weiner,
CeMM- ChIPmentation protocol v1.1 (2015/10/14)
 CeMM- ChIPmentation protocol v1.1 (2015/10/14) Authors: Christian Schmidl (cschmidl@cemm.oeaw.ac.at) and Christoph Bock (cbock@cemm.oeaw.ac.at). Paper website: http://chipmentation.computational-epigenetics.org
CeMM- ChIPmentation protocol v1.1 (2015/10/14) Authors: Christian Schmidl (cschmidl@cemm.oeaw.ac.at) and Christoph Bock (cbock@cemm.oeaw.ac.at). Paper website: http://chipmentation.computational-epigenetics.org
Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter
 Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter Michal Balberg +, George Barbastathis*, Sergio Fantini % and David J. Brady University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana,
Confocal Imaging Through Scattering Media with a Volume Holographic Filter Michal Balberg +, George Barbastathis*, Sergio Fantini % and David J. Brady University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana,
Structural, optical, and electrical properties of phasecontrolled cesium lead iodide nanowires
 Electronic Supplementary Material Structural, optical, and electrical properties of phasecontrolled cesium lead iodide nanowires Minliang Lai 1, Qiao Kong 1, Connor G. Bischak 1, Yi Yu 1,2, Letian Dou
Electronic Supplementary Material Structural, optical, and electrical properties of phasecontrolled cesium lead iodide nanowires Minliang Lai 1, Qiao Kong 1, Connor G. Bischak 1, Yi Yu 1,2, Letian Dou
Light Guide Overview
 Light Guide Overview 2 Fiber-Optic Basics Light guides are an important component in optimizing an optical system as they connect the various functional units such as the light source to a probe or a probe
Light Guide Overview 2 Fiber-Optic Basics Light guides are an important component in optimizing an optical system as they connect the various functional units such as the light source to a probe or a probe
CONFOCAL MICROSCOPE (Zeiss LSM 510 META v4.2)
 Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics Molecular Cytogenetics and Microscopy Core CONFOCAL MICROSCOPE (Zeiss LSM 510 META v4.2) 1) STARTING THE SYSTEM Abridged INSTRUCTIONS Switch on the mercury bulb
Wellcome Trust Centre for Human Genetics Molecular Cytogenetics and Microscopy Core CONFOCAL MICROSCOPE (Zeiss LSM 510 META v4.2) 1) STARTING THE SYSTEM Abridged INSTRUCTIONS Switch on the mercury bulb
Imaging Retreat - UMASS Customized real-time confocal and 2-photon imaging
 Imaging Retreat - UMASS 2012 Customized real-time confocal and 2-photon imaging Mike Sanderson Department of Microbiology and Physiological Systems University of Massachusetts Medical School Thanks for
Imaging Retreat - UMASS 2012 Customized real-time confocal and 2-photon imaging Mike Sanderson Department of Microbiology and Physiological Systems University of Massachusetts Medical School Thanks for
HoloMonitor M4. For powerful discoveries in your incubator
 HoloMonitor M4 For powerful discoveries in your incubator HoloMonitor offers unique imaging capabilities that greatly enhance our understanding of cell behavior, previously unachievable by other technologies
HoloMonitor M4 For powerful discoveries in your incubator HoloMonitor offers unique imaging capabilities that greatly enhance our understanding of cell behavior, previously unachievable by other technologies
Probing the Mechanics of doublestranded DNA using Magnetic Tweezers
 Probing the Mechanics of doublestranded DNA using Magnetic Tweezers Praktikum: g5b July 30, 2015 Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich Department of Physics Supervisors: Franziska Kriegel, Philipp Walker,
Probing the Mechanics of doublestranded DNA using Magnetic Tweezers Praktikum: g5b July 30, 2015 Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich Department of Physics Supervisors: Franziska Kriegel, Philipp Walker,
III III 0 IIOI DID IIO 1101 I II 0II II 100 III IID II DI II
 (19) United States III III 0 IIOI DID IIO 1101 I0 1101 0II 0II II 100 III IID II DI II US 200902 19549A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0219549 Al Nishizaka et al. (43) Pub.
(19) United States III III 0 IIOI DID IIO 1101 I0 1101 0II 0II II 100 III IID II DI II US 200902 19549A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0219549 Al Nishizaka et al. (43) Pub.
In-Vivo IMAGING SYSTEMS. A complete line of high resolution optical & X-ray systems for pre-clinical imaging
 In-Vivo IMAGING SYSTEMS A complete line of high resolution optical & X-ray systems for pre-clinical imaging In-Vivo Imaging Systems Carestream is a strong, successful, multi-billion dollar, international
In-Vivo IMAGING SYSTEMS A complete line of high resolution optical & X-ray systems for pre-clinical imaging In-Vivo Imaging Systems Carestream is a strong, successful, multi-billion dollar, international
INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY. Urs Ziegler THE PROBLEM
 INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch THE PROBLEM 1 ORGANISMS ARE LARGE LIGHT AND ELECTRONS: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES v = Wavelength ( ) Speed (v) Frequency ( ) Amplitude (A) Propagation
INTRODUCTION TO MICROSCOPY Urs Ziegler ziegler@zmb.uzh.ch THE PROBLEM 1 ORGANISMS ARE LARGE LIGHT AND ELECTRONS: ELECTROMAGNETIC WAVES v = Wavelength ( ) Speed (v) Frequency ( ) Amplitude (A) Propagation
Zeiss Axiovert 135 Fluorescence Microscope Quick Guide / Operations Manual (v. 1.0 February 09)
 University of Chicago Integrated Light Microscopy Core Dr. Vytas Bindokas, Director http://digital.bsd.uchicago.edu By: Christine Labno, Assistant Director Room: AB-129 Phone: 4-9040 Zeiss Axiovert 135
University of Chicago Integrated Light Microscopy Core Dr. Vytas Bindokas, Director http://digital.bsd.uchicago.edu By: Christine Labno, Assistant Director Room: AB-129 Phone: 4-9040 Zeiss Axiovert 135
LETTERS. Force production by disassembling microtubules
 Vol 438 17 November 2005 doi:10.1038/nature04132 Force production by disassembling microtubules Ekaterina L. Grishchuk 1,2, Maxim I. Molodtsov 1,3, Fazly I. Ataullakhanov 3,4,5 & J. Richard McIntosh 1
Vol 438 17 November 2005 doi:10.1038/nature04132 Force production by disassembling microtubules Ekaterina L. Grishchuk 1,2, Maxim I. Molodtsov 1,3, Fazly I. Ataullakhanov 3,4,5 & J. Richard McIntosh 1
DIC Imaging using Laser Scanning Microscopes (LSM) on Inverted Stands
 DIC Imaging using Laser Scanning Microscopes (LSM) on Inverted Stands Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) imaging is a technique used to increase contrast in brightfield images. In confocal systems,
DIC Imaging using Laser Scanning Microscopes (LSM) on Inverted Stands Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) imaging is a technique used to increase contrast in brightfield images. In confocal systems,
Advanced Optical Microscopy lecture. 03. December 2012 Kai Wicker
 Advanced Optical Microscopy lecture 03. December 2012 Kai Wicker Today: Optical transfer functions (OTF) and point spread functions (PSF) in incoherent imaging. 1. Quick revision: the incoherent wide-field
Advanced Optical Microscopy lecture 03. December 2012 Kai Wicker Today: Optical transfer functions (OTF) and point spread functions (PSF) in incoherent imaging. 1. Quick revision: the incoherent wide-field
Lecture 16. OMX - Structured Illumination Microscopy Ian Dobbie x Microscopy Course Lecture 16 1
 Lecture 16 OMX - Structured Illumination Microscopy Ian Dobbie x13323 Microscopy Course 2014 - Lecture 16 1 Super-resolution fluorescence microscopy Specificity Sensitivity Non-invasive (in situ & in vivo)
Lecture 16 OMX - Structured Illumination Microscopy Ian Dobbie x13323 Microscopy Course 2014 - Lecture 16 1 Super-resolution fluorescence microscopy Specificity Sensitivity Non-invasive (in situ & in vivo)
Life Science Instrumentation. New Generation. Light Sheet Fluorescence Microscope. Alph
 Life Science Instrumentation Light Sheet Fluorescence Microscope New Generation Alph Modular Light Sheet Microscope Alpha 3 is a new generation of light sheet fluorescence microscope addressing the needs
Life Science Instrumentation Light Sheet Fluorescence Microscope New Generation Alph Modular Light Sheet Microscope Alpha 3 is a new generation of light sheet fluorescence microscope addressing the needs
IN Cell Analyzer 6500HS
 GE Healthcare IN Cell Analyzer 6500HS IN Cell Analyzer 6500HS is a fully-automated confocal cell imaging system from GE Healthcare. Building on the capabilities of earlier IN Cell Analyzer systems, it
GE Healthcare IN Cell Analyzer 6500HS IN Cell Analyzer 6500HS is a fully-automated confocal cell imaging system from GE Healthcare. Building on the capabilities of earlier IN Cell Analyzer systems, it
Enriching Beads Oligo (dt) Magnetic Beads for mrna Purification
 Enriching Beads Oligo (dt) Magnetic Beads for mrna Purification Isolate the mrna transcriptome in 15 minutes User Guidance Enriching Biotechnology Rev. 1.0 October 25th. 2018 Why choose Enriching Beads
Enriching Beads Oligo (dt) Magnetic Beads for mrna Purification Isolate the mrna transcriptome in 15 minutes User Guidance Enriching Biotechnology Rev. 1.0 October 25th. 2018 Why choose Enriching Beads
Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) Verses Dark Field and Phase Contrast Microscopy. E. D. Salmon University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
 Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) Verses Dark Field and Phase Contrast Microscopy E. D. Salmon University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill How Does Contrast in DIC Differ from Phase and Pol? n e
Differential Interference Contrast (DIC) Verses Dark Field and Phase Contrast Microscopy E. D. Salmon University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill How Does Contrast in DIC Differ from Phase and Pol? n e
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
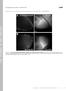 Supplemental material Parton et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201103160/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. MTs in the oocyte lack posttranslational modifications
Supplemental material Parton et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201103160/dc1 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Figure S1. MTs in the oocyte lack posttranslational modifications
